Selective Convexity in Extended GDEA Model
|
|
|
- Joy Warren
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vl. 5, 20, n. 78, Selectve nvet n Etended GDEA Mdel Sevan Shaee a and Fahad Hssenadeh Ltf b a. Depatment f Mathematcs, ehan Nth Banch, Islamc Aad Unvest, ehan, Ian b. Depatment f Mathematcs, Scence and Reseach Banch, Islamc Aad Unvest, ehan, Ian Abstact In ths pape, an etensn f the genealed data envelpment analss (GDEA mdel has been ntduced. In ths genealatn dffeent cases f pductn pssblt set (PPS f the etended genealed data envelpment analss (EGDEA mdel ae nvestgated. he ppsed EGDEA mdel s used t evaluate decsn s makng unts (DMUs ethe wth full cnvet assumptn mpsed n nputs and utputs (R and B mdels wthut cnsdeng cnvet assumptn f each nput and utput (FDH mdel. We have ppsed a mdel n the EGDEA, whch can teat each nput and utput ndvduall wth espect t the cnvet assumptn. Kewds: Genealed Data Envelpment Analss; Selectve nvet. Intductn GDEA mdel was suggested b Yun et al. [6] s a methd, whch can teat the basc DEA [,2] mdels, specfcall, the R mdel, the B mdel and the FDH mdel n a unfed wa. hee ae theetcal ppetes n elatnshps amng the GDEA mdel and thse DEA mdels. he GDEA mdel makes t pssble t calculate the effcenc f DMUs ncpatng vaus pefeence stuctues f decsn makes. In de t fnd a bette appmatn f evaluatn f DMUs, the GDEA mdel has been develped t etended GDEA (EGDEA mdel. hs develpment has been pefmed b the ntepetatn f dual f the GDEA mdel. Als, ths mpvement leads us t defne the defntn f the PPS f the EGDEA mdel. he defntn f the PPS f the EGDEA espndng auth. Shaee@ah.cm (Sevan Shaee P.O.B: 455/775 and 455/4933, Pst de:
2 3862 S. Shaee and F. Hssenadeh Ltf mdel defned n ths pape has specal stuctue: unde sme specal cndtns ethe the full cnvet assumptn f the PPS nn-cnvet assumptn can be btaned b ts defntn. But ths defntn causes sme pblems t the analst. Snce, he she has t accept ethe the full cnvet assumptn f the PPS f the EGDEA (R and B mdels negate the full cnvet assumptn at all (FDH mdel. In ethe case sme shtcmngs and msleadng estmates ae undestandable. In de t vecme the dlemma, a new defntn f the PPS f the EGDEA has been pesented that allws each nput and utput can be udged ndvduall wth espect t the cnvet assumptn. We have used the cncept f selectve cnvet n DEA [5] n de t ppse the abve mentned PPS. hs fleblt f the defntn n the ppsed PPS f the EGDEA mdel slves the shtcmngs f the pevus defntn. he abve assumptn f selectve cnvet leads t the develpment f a ange f new EGDEA mdel, f whch the FDH and B mdels ae tw specal cases. Als the eact defntn f PPS f the EGDEA mdel has been pesented n de t mpse the selectve cnvet assumptn n t. In the defntn f the PPS f the EGDEA mdel dffeent cases f PPS has been cnsdeed f whch the PPS f the R, the B and the FDH mdels ae specal cases f the mentned defntn. he pape s gven n 7 Sectns. In Sectn 2, we have nvestgated basc GDEA and etended GDEA mdels. he mtvatn f etended mdels has been descbed n sectn 3. he dffeent ppetes f PPS have been cnsdeed n Sectn 4. he defntn f new ange f etended GDEA mdels that allw selectve cnvet n the fmulatn has been ntduced n Sectn 5. A numecal eample s gven n Sectn 6. Sectn 7 nvestgates a mdel t fnd the full effcent DMUs n the ppsed mdel. 2. Basc GDEA and etended GDEA mdels In the fllwng dscussn, we assume that thee est n DMUs t be evaluated. Each DMU cnsumes vang amunts f m dffeent nputs t pduce p dffeent utputs. Specfcall, DMU cnsumes amunts = f nputs (=,,m and pduces amunts = f utputs (k=,,p. f these cnstants, whch geneall take the ( fm f bseved data, we assume > 0 f each (=,,m and > 0 f each k=,,p. Futhe, we assume that thee ae n duplcated n bseved data. he p n utput mat f the n DMUs s dented b Y, and the m n nput mat f the n DMUs dented b X. =,..., and =,..., ae amunts f nputs and ( m ( ( p utputs f DMU, whch s evaluated. In addtn, ε s a small pstve numbe (nn- Achmedean and =(,, s a unt vect. he fmulatn f GDEA mdel s n the fllwng manne Yun [6]:
3 Selectve cnvet n etended GDEA mdel 3863 Mame Δ S. t. Δ,μ k,ν ~ Δ d p p = = μ m v m = = μ + + α( p μ ( v = = =, = 0, + μ, ν ε, =,..., p, =,..., m m ν ( +, =,..., n, ( Nw we can fnd the dual f the mdel ( as fllws: Mnme w, κ, λ, s S. t. ω ε { α( Z λ 0, s 0. n whch an utput-nput vect DMUs espectvel, dented b Y =, =,..., n and Z = X λ =, s Z + D } λ w + s + κ = 0, (2 f a DMU, =,,n, and utput-nput mat Z f all In addtn, we dente a ( p + m n mat Z b Z = (,,..., and w = ( ω,..., ω and α s a gven pstve numbe. A ( p + m n mat D = ( d,..., d n s a mat ( Z Z eplaced b 0, ecept f the mamal cmpnent (f thee est plual mamal cmpnents, nl ne s chsen fm amng them n each clumn. he mdel (2 fstl tes t pect DMU unde the dectn =(,, whch s a ( p + m unt vect. If the pectn s n the weakl effcent fnte the mdel (2 tes t pect the DMU 0 n the stngl effcent fnte b usng the cncept f nn- Achmedean wth slack vaables vect s whch s a ( p + m -vect. In de t use me genealed mdel we etend the GDEA mdel n whch the ppsed mdel can pect a DMU unde evaluatn alng an feasble dectn such as δ δ = 0, δ 0. heefe we ppse the etended GDEA mdel n the fllwng δ manne:
4 3864 S. Shaee and F. Hssenadeh Ltf Mame S. t. Δ,μ,ν k Δ ~ Δ d p m μ δ + = = p μ = = + α( m p μ ( v δ v = = =, = 0, + μ, ν ε, =,..., p, =,..., m m ν ( +, =,..., n, (3 and the dual f mdel (3: Mnme w, κ, λ, s S. t. ω ε { α( Z s λ =, δ Z + D } λ ω + s δ + κ = 0, λ 0, s 0. In mdel (4 we fstl mve t each t effcent fnte alng the dectn δ δ = 0, δ 0 and secndl, t t vansh slack vaables n de t fnd stngl δ effcent unts. We defne the pductn pssblt set (PPS f etended GDEA technlg n the fllwng manne: (4 PPS EGDEA { ˆ ˆ = ( ˆ, ˆ ( α( Z Z + D λ + κˆ 0, λ =, 0} (5 = λ heem. We have the fllwng stuctues: a If α s suffcentl small pstve numbe and κ s fed at e then (5 wll be the PPS f FDH technlg. b If α s suffcentl lage pstve numbe and κ s fed at e then (5 wll be the PPS f B technlg. c If α s suffcentl lage pstve numbe then (5 wll be the PPS f R technlg. Pf: We knw that the PPS f R, B and FDH mdels ae espectvel as fllws:
5 Selectve cnvet n etended GDEA mdel 3865 PPS PPS PPS R B FDH = {ˆ = ( ˆ, ˆ = {ˆ = ( ˆ, ˆ = {ˆ = ( ˆ, ˆ Zλ ˆ, λ 0}, Zλ ˆ, λ =, λ 0}, Zλ ˆ, λ =, λ {0,}, =,.., n} a If α s suffcentl small pstve numbe and κ s fed at e then fm (5 we wll have D ˆ λ 0. Fm the defntn f D ˆ the fllwng nequaltes wll be satsfed wth λ, = 0 : = λ k ˆ and ˆ, =,..., n. heefe, we wll have Zλ ˆ f λ = that s the eact defntn f PPS f FDH technlg. and λ {0, } b If α s suffcentl lage pstve numbe and κ s fed at e then fm (5 we wll have α ( Zˆ Z λ 0 but then ( Zˆ Z λ 0 and ths mples that Zλ Zˆ λ and als because λ =, we wll have Zλ ˆ and ths s the eact defntn f PPS f B technlg. c If α s suffcentl lage pstve numbe then fm (5, It s bvus that n n ˆ α α ( Z Z λ + κˆ 0 and t s elevant that X Xˆ α λ and λ Y Yˆ but = α + κ = α + κ n α then f we set λ = λ, =,..., n, t wll be btaned that λ X Xˆ and α + κ n = λ Y Yˆ whch ae the eact defntn f PPS f R technlg. = 3. Mtvatn f mdfcatn In GDEA mdel, the cncept f adal effcenc s cmpehensble b ntng the stuctue f GDEA mdel. It s undestandable the DMU unde evaluatn appaches effcent fnte alng the dectn (,, that s a (m+p-vect. Appachng effcent fnte nl alng the abve mentned dectn causes sme shtcmngs and msleadng estmates, because smetmes the DMU t be evaluated has t appach effcent fnte alng a cetan and specfc dectn. F eample, f mantanng sme specal cndtns the DMU unde evaluatn s nt able t ncease decease sme specal utputs nputs espectvel. heefe we need t make sme changes n the fmulatn f GDEA mdel t vecme shtcmngs and weaknesses. In ppsed EGDEA mdel the DMU t be evaluated appaches effcent fnte alng an abta dectn. hs fleblt f fundatn f EGDEA mdel nt nl has me genealed
6 3866 S. Shaee and F. Hssenadeh Ltf stuctue but als pvdes bette appmatn. B the wa EGDEA mdel slves the weaknesses and dsadvantages f GDEA mdel. he stuctue f PPS f EGDEA mdel s based n paametc dmnatn stuctue. he PPS f dffeent technlges such as B and FDH technlg can be acheved b changng paamete α fm suffcentl lage pstve numbe t suffcentl small pstve numbe espectvel. On ne hand sme ambguus pnts ae appaent n the chce f paamete, f eample, f paameteα s nethe suffcentl lage pstve numbe n suffcentl small pstve numbe, what s the pductn technlg? Is t FDH technlg B technlg a mtue f FDH and B technlg? On the the hand almst all the tmes, ethe the full cnvet assumptn f B technlg elaatn f the cnvet assumptn f FDH technlg mght be pblematc. F eample, cnsde a stuatn that a specal nput f DMUs s the numbe f emplee. It s bvus that the abve mentned nput ften s nt a pat f cnvet assumptn because the cmpste unt f DMUs ma be nfeasble. Als lts f dffeent eamples ma be addessed n dffeent felds [5] wth pevus stuctue. heefe the use f selectve cnvet t vecme the dffcultes caused b EGDEA mdel s unavdable. Based n the abve dscussn, we need t mdf the defntn f the PPS f EGDEA technlg n a wa that allws each nput and utput t be evaluated ndvduall wth espect t cnvet assumptn that cause the cncept f selectve cnvet. he pblem f selectve cnvet s gven n emaned sectns. 4. Ppetes f the PPS f EGDEA mdel In de t pesent a sutable defntn t the PPS f the EGDEA mdel that can teat wth each nput and utput ndvduall wth espect t the cnvet assumptn, we need t defne sme ppetes f the PPS f EGDEA mdel. Als we need t pesent a ppet that can develp the teatment f PPS unde the cnsdeatn f abta cnvet assumptn f each nput and utput. Wth cnsdeng last assumptn, t s pssble t defne a PPS based n the mentned ppetes that can behave wth each nput and utput ndvduall wth espect t ts cmplance wth the cnvet assumptn. hs assumptn s called Selectve cnvet and has been defned b Pdnvsk [5]. We use the cncept f selectve cnvet n de t mpve the defntn f the PPS f EGDEA mdel that can cnsde the cnvet assumptn t abta nput and utput. Wth the defntn f the PPS f EGDEA based n the stated ppetes, a new mdel can be btaned that B and FDH mdels ae specal cases f ppsed mdel. We pstulate the fllwng ppetes f P (the pductn pssblt set: (A Nn-empt assumptn. DMU = (, P, =,..., n. (A2 Pssblt assumptn. = (, P, 0 and mples = (, P.
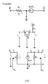
7 Selectve cnvet n etended GDEA mdel 3867 Ou thd ppet takes n t accunt the stuatns whee nl sme f the nputs and utputs ae suppsed t satsf the cnvet pncple, whle the thes ae nt. state ths ppet fmall, cnsde the fllwng pattn f the nput and utput sets I and O: N N I = I I, O = O O N N whee the subsets I and I, as well as O and O, ae mutuall dsnt. he fllwng ppet states that a cnve cmbnatn f an tw feasble DMUs = (, and = (, s feasble pvded the nputs and utputs f these tw N N DMUs fm the sets I and O ae dentcal. (A3 Selectve cnvet assumptn. = (, P and = (, P. N N Assume that = f all I and = f all O. hen, f an λ [0,], the unt λ + ( λ P. he cncept f the ppet (A3, s llustated b Pdnvsk [5]. Me genealed nfmatn can be fund n Pdnvsk [5]. We llustate the selectve cnvet assumptn n the fllwng eample. Eample. In de t llustate the cncept f the assumptn f selectve cnvet, cnsde the DMUs A and B n able 2. able 2. he data set f Eample 2 Output Input Input 2 Input 3 DMU A DMU B We have llustated n Fgue, the PPS f mdfed EGDEA technlg f tw DMUs n the thee dmensnal space, wth egad t the selectve cnvet assumptn. he unn f tw tanspted unbunded cnes epesents the FDH technlg btaned b the tw unts. akng n t accunt the selectve cnvet assumptn wth egad t set I = {,3 }, the unbunded psm BDqt s added t the FDH technlg acheved b the tw DMUs. In patcula, because f cnsdeatn (A3, cnve cmbnatn f feasble unts ae feasble pvded the nput 2 s dentcal. F me llustatn f nput 2 s equal t 4, the applcatn f the assumptn f selectve cnvet leads t the tangle BD beng egaded as feasble.
8 3868 S. Shaee and F. Hssenadeh Ltf Input 3 Input 2 Input Fg..he pductn pssblt set n Eample. As we can see n the assumptn f selectve cnvet (A3, t s an cnceptual assumptn and we can nt use t n pactcal pblems and we need t make sme mdfcatn n (A3. ths end, we utle the genealatn f selectve cnvet assumptn as eplaned n Pdnvsk [5]. We use the genealatn f selectve cnvet assumptn n the fllwng manne: ( A 3 Genealed selectve cnvet asumptn. nsde an K DMUs k = ( k, k P, k =,..., K. F an vect the unt as fllws: K λk, λ k = k = ma{ k k =,..., K}, f I f I N (6 K λ R + such that K k = λ = defne K λk k, f O λ = k = (7 N ma{ k k =,..., K}, f O λ λ λ hen = (, P. It s clea that the assumptn ( A3 mples (A3. In the pesence f pssblt assumptn (A2, the cnvese s als tue. Me nfmatn can be fund n Pdnvsk [5]. heefe the set f assumptns (A, (A2 and (A3 s equvalent t the set (A, (A2 and ( A 3. k
9 Selectve cnvet n etended GDEA mdel 3869 We have used the cncepts f selectve cnvet, n de t ppse a slutn and fnd a sutable defntn t the PPS f etended GDEA technlg. In the fllwng sectn the defntn f the PPS f etended GDEA technlg has been pesented. 4. he PPS f EGDEA wth egad t selectve cnvet assumptn Based n the ppetes eplaned n the pevus sectn, we epesent a mdfed defntn f the PPS f EGDEA that nt nl satsfes the nn-empt assumptn and pssblt assumptn but als the selectve cnvet assumptn. Wthut lse f genealt we can assume that the set I cntans the fst,..., m N nputs whle the set I cntans the m +,..., m nputs and als the set O cntans the N fst,..., whle the set O s the set +,...,. Wth these ntatn an vect f nputs can be epesented n the fm N = [, ] and als N = [, ] whee and ae the fst m and cmpnents f nputs and utput vects espectvel. he same ntatn etends t the, Z and Z matces whee s the fst cmpnents f utputs and fst m cmpnents f nputs, Z s the fst ws f Z and ws + untl + m and Z smla t Z althugh wth these ntatn we wll have N, Z N N and Z the emaned pats f the mentned vect and matces espectvel. hee fe, the fllwng heem s epesented based n the pncples (A, (A2 and (A3. heem 2. he mnmal PPS f etended GDEA technlg P, whch satsfes the ams (A-(A3, s the set f all pas ˆ = ( ˆ, ˆ such that ˆ 0 and ˆ 0 and thee n ests a vect λ R f whch the fllwng elatns ae tue (because we use the FDH and B technlg κ s fed at e: ˆ ( α ( Z Z + Dˆ λ 0 (8 D N ˆ λ 0 (9 λ = and λ 0 (0 Pf. nsde = (, that s an bseved DMU. It s bvus that ( α( Z Z + D λ 0, D N λ 0 f λ =, λ k = 0 and theefe (A s satsfed. see (A2, cnsde ˆ = ( ˆ, ˆ P, ˆ 0and ˆ. Because, ˆ = ( ˆ, ˆ P, thee est a vect λˆ that satsfes the cndtns (8-(0, theefe ˆ ( α ( Z Z + Dˆ λ 0, D N ˆ λ 0. B the defntn f mat D and u assumptn t s tval that ˆ ˆ ( λ ( ˆ Z Z Z Z λ and ˆ λ ˆ N D ˆ D λ and ˆ N D λ ˆ ˆ D λ, theefe = (, P and the pncple (A2 s satsfed.
10 3870 S. Shaee and F. Hssenadeh Ltf In de t see that P satsfes (A3, cnsde an tw unts = (, P and N N = (, P such that = f I and = f O. hen these tw unts satsf (8-(0 wth sme vects λ and λ espectvel. F an β [0,] β β β cnsde = (, = β (, + ( β (, and defne λ β = βλ + ( β λ. hen β β β β the cndtns (8-(0 ae bvusl satsfed b the unt = (, and λ = λ. heefe (A3 s satsfed. pve that P s the mnmal set, assume that anthe set P als satsfes (A-(A3. We need t shw that, f (, = P, then = (, P. nsde epesentatn (8-(0 f the unt = (, P. F the vect λ fm ths λ λ λ epesentatn, defne = (, accdng t (6 and (7, whee K shuld be taken equal t n, the numbe f bseved DMUs. Snce P satsfes ( A 3 the unt λ λ λ = (, P. Snce ths unt dmnates = (, n the Paet sense, accdng t (A2, = (, P. heem 2 shws that the PPS defned b the elatns (8-(0 s a subset f an the set P whch satsfes the pncples (A, (A2 and (A3. heefe the PPS P s the mnmal set based n the abve thee pncples. 5. he etended GDEA mdel based n selectve cnvet assumptn Accdng t heem 2, mdel (4 wthut usng slack vaables and κ fed at e, we ppse the EGDEA mdel based n selectve cnvet assumptn n the fllwng manne: Mnme ω w,λ S. t. δ = δ { α( Z D N λ =, λ 0 Z δ λ ω δ + D N N N N whch ( δ δ δ 0, δ } λ ω 0, δ ( s the decmpstn f vect δ t the acceptance f cnve and nn-cnve paametes. heefe, we use mdel ( n de t slve sme pblems that allw cnve and nn-cnve data.
11 Selectve cnvet n etended GDEA mdel Numecal eample llustate the utcmes f the ppsed mdel, we used the mdfed mdel ( f the data set n able 2. he esults f u mdel ae pesented amng the clumns f able 3. able 3 shws the effcenc f each f DMUs btaned b slvng mdel (4 wthut 0 slack vaables,κ fed at e, 3 δ = and ne tme f α = 0 suffcentl lage that causes the B effcenc and the the tme f α = that causes the FDH effcenc. Als dffeent cases slved b mdel ( wth ncpatng selectve cnvet pncple based n dffeent chce f the sets I and O. We knw that n mdel (4 wthut slack vaables and (, f ω = 0 then the DMU unde evaluatn s effcent (but nt necessal full effcent the wse s nt effcent. We can see that the me mdel ( eaches t the B technlg amng the clumns f able 3, the less the DMUs ae effcent and t s bvus b the defntn f PPS f B and FDH technlg. able 2. he data set f numecal eample Input Input 2 Output Output 2 Output 3 DMU DMU DMU DMU DMU able 3. he effcenc f DMUs n dffeent mdels DMU FDH Mdel (, Mdel (, Mdel (, B α = 3 α = 0 3 α = 0 3 α = 0 3 α = 0 I = { }, O = {} I = {}, I = {}, O = {,2} O = {,2,3}
12 3872 S. Shaee and F. Hssenadeh Ltf 6. Fndng full effcent DMUs In ths sectn we use a new mdel n de t vef whethe the taget DMU = (, f DMU s effcent n Paet sense. F eample n mdel (4 the taget f DMU n the case when α s suffcentl lage s n the fllwng manne: α + κ = ωδ (2 α α We ntduce the unt ( + s, + s wth espect t taget DMU = (, btaned fm (2, whee s and s ae nn-negatve vects f dmensn p and m, espectvel. Mdel (3 has been suggested t fnd the full effcent (effcent n Paet sense DMUs. he sum f vects s and s s mamed n mdel (3, whle the cnstants ensue that the esultng unt ( + s, + s s feasble n technlg P, as defned n heem 2. Mdel (3 can be slved wth espect t the vaable vects N λ, s and s. Ntatns s, s, s and s ae defned as pevus sectns. Mame s S. t. { α( Z D N λ + s λ =, λ 0, s Z N 0. + D 0 } λ + κ N + s = 0, (3 N s s n whch = N s and s =. s N s Suppse that λ and s s an ptmal slutn t mdel (3. hen t s eas t see that the DMU ( + s, + s s effcent n Paet sense and can be cnsdeed as the full effcent taget f DMU. In patcula, f the ptmal slutn n mdel ( s equal t e and s = 0 n the ptmal slutn f mdel (3, then DMU s tself effcent n Paet sense. 7. nclusn In ths pape, an etensn f GDEA mdel based n paametc dmnatn stuctue has been suggested. In addtn, we defned the PPS f EGDEA technlg. We used the
13 Selectve cnvet n etended GDEA mdel 3873 cncept f selectve cnvet assumptn n DEA t ppse a ange f new EGDEA mdel that allws each nput and utput can be udged ndvduall wth espect t cnvet assumptn. F fndng the abve mdel, we ntduced a new stuctue f PPS f EGDEA mdel unde cnsdeatn f selectve cnvet assumptn. Als, the ppsed methd has been utled n a numecal eample and we encunteed wth the epected esults. Futheme, we nvestgated the pblem f fndng full effcent DMUs wth a mdel btaned b the secnd ptmatn stage n DEA. Refeences [] Allen, R., Athanasspuls, A., Dsn, R.G., hanassuls, E., Weghts estctns and value udgements n data envelpment analss: Evlutn, develpment and futue dectns. Annals f Opeatns Reseach 997; 73, [2] Banke, R.D., hanes, A., pe, W.W., sme mdels f estmatng techncal and scale neffcences n data envelpment analss. Management Scence 984; 30, [3] Pdnvsk, V.V., Pductn tade-ffs and weght estctns n data envelpment analss. Junal f peatnal Reseach Scet 2004; 55, [4] Pdnvsk, V.V., he eplct le f weght bunds n mdels f data envelpment analss. Junal f Opeatnal Reseach Scet2005; 56, [5] Pdnvsk, V.V., Selectve cnvet n DEA mdels. Eupean Junal f Opeatnal Reseach 2005; [6] Yun, Y.B., Nakaama, H., ann,., A genealed mdel f data envelpment analss. Eupean Junal f Opeatnal Reseach 2004; Receved: August, 20
Cost, revenue and profit efficiency measurement in DEA: A directional distance function approach
 Cst, evenue and pft effcency measuement n DEA: A dectnal dstance functn appach Besh K. Sah a, Mahmd Mehdlzad b, Kau Tne c a Xave Insttute f Management, Bhubaneswa 75 03, Inda b Depatment f Mathematcs,
Cst, evenue and pft effcency measuement n DEA: A dectnal dstance functn appach Besh K. Sah a, Mahmd Mehdlzad b, Kau Tne c a Xave Insttute f Management, Bhubaneswa 75 03, Inda b Depatment f Mathematcs,
LEAP FROG TECHNIQUE. Operational Simulation of LC Ladder Filters ECEN 622 (ESS) TAMU-AMSC
 LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP
LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP
Introduction of Two Port Network Negative Feedback (Uni lateral Case) Feedback Topology Analysis of feedback applications
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w Pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83h 3 Feedback w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w Pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83h 3 Feedback w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Electric potential energy Electrostatic force does work on a particle : Potential energy (: i initial state f : final state):
 Electc ptental enegy Electstatc fce des wk n a patcle : v v v v W = F s = E s. Ptental enegy (: ntal state f : fnal state): Δ U = U U = W. f ΔU Electc ptental : Δ : ptental enegy pe unt chag e. J ( Jule)
Electc ptental enegy Electstatc fce des wk n a patcle : v v v v W = F s = E s. Ptental enegy (: ntal state f : fnal state): Δ U = U U = W. f ΔU Electc ptental : Δ : ptental enegy pe unt chag e. J ( Jule)
Lecture 2 Feedback Amplifier
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
A New Method for Solving Integer Linear. Programming Problems with Fuzzy Variables
 Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vl. 4, 00, n. 0, 997-004 A New Methd fr Slvng Integer Lnear Prgrammng Prblems wth Fuzzy Varables P. Pandan and M. Jayalakshm Department f Mathematcs, Schl f Advanced Scences,
Appled Mathematcal Scences, Vl. 4, 00, n. 0, 997-004 A New Methd fr Slvng Integer Lnear Prgrammng Prblems wth Fuzzy Varables P. Pandan and M. Jayalakshm Department f Mathematcs, Schl f Advanced Scences,
is needed and this can be established by multiplying A, obtained in step 3, by, resulting V = A x y =. = x, located in 1 st quadrant rotated about 2
 Ct Cllege f New Yk MATH (Calculus Ntes) Page 1 f 1 Essental Calculus, nd edtn (Stewat) Chapte 7 Sectn, and 6 auth: M. Pak Chapte 7 sectn : Vlume Suface f evlutn (Dsc methd) 1) Estalsh the tatn as and the
Ct Cllege f New Yk MATH (Calculus Ntes) Page 1 f 1 Essental Calculus, nd edtn (Stewat) Chapte 7 Sectn, and 6 auth: M. Pak Chapte 7 sectn : Vlume Suface f evlutn (Dsc methd) 1) Estalsh the tatn as and the
Multistage Median Ranked Set Sampling for Estimating the Population Median
 Jounal of Mathematcs and Statstcs 3 (: 58-64 007 ISSN 549-3644 007 Scence Publcatons Multstage Medan Ranked Set Samplng fo Estmatng the Populaton Medan Abdul Azz Jeman Ame Al-Oma and Kamaulzaman Ibahm
Jounal of Mathematcs and Statstcs 3 (: 58-64 007 ISSN 549-3644 007 Scence Publcatons Multstage Medan Ranked Set Samplng fo Estmatng the Populaton Medan Abdul Azz Jeman Ame Al-Oma and Kamaulzaman Ibahm
Data envelopment analysis (DEA) Thirty years on
 Avalable nlne at www.scencedect.cm Eupean Junal f Opeatnal Reseach 19 (009) 1 17 Invted Revew Data envelpment analyss (DEA) Thty yeas n Wade D. Ck a, *, Lay M. Sefd b a Depatment f Opeatns Management and
Avalable nlne at www.scencedect.cm Eupean Junal f Opeatnal Reseach 19 (009) 1 17 Invted Revew Data envelpment analyss (DEA) Thty yeas n Wade D. Ck a, *, Lay M. Sefd b a Depatment f Opeatns Management and
Summary of DLT method for stereo camera calibration, 3D reconstruction and robot-camera integration
 tes n T Smma f T meth f stee camea calbatn, ecnstctn an bt-camea ntegatn. amea calbatn Statng pnt: pespecte eqatns f a camea These eqatns map the cnates f a genec pnt n space,, nt the cespnng cnates n
tes n T Smma f T meth f stee camea calbatn, ecnstctn an bt-camea ntegatn. amea calbatn Statng pnt: pespecte eqatns f a camea These eqatns map the cnates f a genec pnt n space,, nt the cespnng cnates n
Feedback Principle :-
 Feedback Prncple : Feedback amplfer s that n whch a part f the utput f the basc amplfer s returned back t the nput termnal and mxed up wth the nternal nput sgnal. The sub netwrks f feedback amplfer are:
Feedback Prncple : Feedback amplfer s that n whch a part f the utput f the basc amplfer s returned back t the nput termnal and mxed up wth the nternal nput sgnal. The sub netwrks f feedback amplfer are:
Optimization of the Electron Gun with a Permanent Ion Trap
 4.3.-178 Optmzatn f the Electn Gun wth a Pemanent In Tap We Le Xabng Zhang Jn Dng Fe Dpla Technlg R&D CenteSutheat Unvet Nangjng Chna Danel den Engelen Pduct and Pce Develpment(PPD)LG.Phlp Dpla 5600 MD
4.3.-178 Optmzatn f the Electn Gun wth a Pemanent In Tap We Le Xabng Zhang Jn Dng Fe Dpla Technlg R&D CenteSutheat Unvet Nangjng Chna Danel den Engelen Pduct and Pce Develpment(PPD)LG.Phlp Dpla 5600 MD
Scalars and Vectors Scalar
 Scalas and ectos Scala A phscal quantt that s completel chaacteed b a eal numbe (o b ts numecal value) s called a scala. In othe wods a scala possesses onl a magntude. Mass denst volume tempeatue tme eneg
Scalas and ectos Scala A phscal quantt that s completel chaacteed b a eal numbe (o b ts numecal value) s called a scala. In othe wods a scala possesses onl a magntude. Mass denst volume tempeatue tme eneg
T-model: - + v o. v i. i o. v e. R i
 T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
Work, Energy, and Power. AP Physics C
 k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
Linear Plus Linear Fractional Capacitated Transportation Problem with Restricted Flow
 Amercan urnal f Operatns Research,,, 58-588 Publshed Onlne Nvember (http://www.scrp.rg/urnal/ar) http://dx.d.rg/.46/ar..655 Lnear Plus Lnear Fractnal Capactated Transprtatn Prblem wth Restrcted Flw Kavta
Amercan urnal f Operatns Research,,, 58-588 Publshed Onlne Nvember (http://www.scrp.rg/urnal/ar) http://dx.d.rg/.46/ar..655 Lnear Plus Lnear Fractnal Capactated Transprtatn Prblem wth Restrcted Flw Kavta
A Note on Equivalences in Measuring Returns to Scale
 Internatnal Jurnal f Busness and Ecnmcs, 2013, Vl. 12, N. 1, 85-89 A Nte n Equvalences n Measurng Returns t Scale Valentn Zelenuk Schl f Ecnmcs and Centre fr Effcenc and Prductvt Analss, The Unverst f
Internatnal Jurnal f Busness and Ecnmcs, 2013, Vl. 12, N. 1, 85-89 A Nte n Equvalences n Measurng Returns t Scale Valentn Zelenuk Schl f Ecnmcs and Centre fr Effcenc and Prductvt Analss, The Unverst f
element k Using FEM to Solve Truss Problems
 sng EM t Slve Truss Prblems A truss s an engneerng structure cmpsed straght members, a certan materal, that are tpcall pn-ned at ther ends. Such members are als called tw-rce members snce the can nl transmt
sng EM t Slve Truss Prblems A truss s an engneerng structure cmpsed straght members, a certan materal, that are tpcall pn-ned at ther ends. Such members are als called tw-rce members snce the can nl transmt
(5) Furthermore, the third constraint implies the following equation: (6)
 T-Element Refactng System f Gaussan and Annula-Gaussan Beams Tansfmatn Abdallah K. Che *, Nabl I. Khachab, Mahmud K. Habb Electcal Engneeng Depatment, Cllege f Engneeng and Petleum, Kuat Unvesty, P. O.
T-Element Refactng System f Gaussan and Annula-Gaussan Beams Tansfmatn Abdallah K. Che *, Nabl I. Khachab, Mahmud K. Habb Electcal Engneeng Depatment, Cllege f Engneeng and Petleum, Kuat Unvesty, P. O.
Reference Guide. OnFront. 2 The Professional Tool for Efficiency and Productivity Measurement. Economic Measurement and Quality Corporation
 Reference Gude OnFrnt The Prfessnal Tl fr Effcenc and Prductvt Measurement Ecnmc Measurement and Qualt rpratn Reference Gude t OnFrnt b Rlf Färe Prfessr f Ecnmcs Shawna Grsspf Prfessr f Ecnmcs EMQ AB
Reference Gude OnFrnt The Prfessnal Tl fr Effcenc and Prductvt Measurement Ecnmc Measurement and Qualt rpratn Reference Gude t OnFrnt b Rlf Färe Prfessr f Ecnmcs Shawna Grsspf Prfessr f Ecnmcs EMQ AB
Circuits Op-Amp. Interaction of Circuit Elements. Quick Check How does closing the switch affect V o and I o?
 Crcuts Op-Amp ENGG1015 1 st Semester, 01 Interactn f Crcut Elements Crcut desgn s cmplcated by nteractns amng the elements. Addng an element changes vltages & currents thrughut crcut. Example: clsng a
Crcuts Op-Amp ENGG1015 1 st Semester, 01 Interactn f Crcut Elements Crcut desgn s cmplcated by nteractns amng the elements. Addng an element changes vltages & currents thrughut crcut. Example: clsng a
ICRA: Incremental Cycle Reduction Algorithm for optimizing multi-constrained multicast routing
 ICRA: Incemental Cycle Reductn Algthm f ptmzng mult-cnstaned multcast utng Nauel Ben Al HANA Reseach Gup, ENI, Unvesty f Manuba, Tunsa nauel.benal@ens.nu.tn Mkls Mlna INA, Unvesty f Rennes 1, Fance mlna@sa.f
ICRA: Incemental Cycle Reductn Algthm f ptmzng mult-cnstaned multcast utng Nauel Ben Al HANA Reseach Gup, ENI, Unvesty f Manuba, Tunsa nauel.benal@ens.nu.tn Mkls Mlna INA, Unvesty f Rennes 1, Fance mlna@sa.f
Hotelling s Rule. Therefore arbitrage forces P(t) = P o e rt.
 Htelling s Rule In what fllws I will use the tem pice t dente unit pfit. hat is, the nminal mney pice minus the aveage cst f pductin. We begin with cmpetitin. Suppse that a fim wns a small pa, a, f the
Htelling s Rule In what fllws I will use the tem pice t dente unit pfit. hat is, the nminal mney pice minus the aveage cst f pductin. We begin with cmpetitin. Suppse that a fim wns a small pa, a, f the
Fault detection of batch process based on multi-way Kernel T-PLS
 Avalable nlne www.jcp.cm Junal f Chemcal and Phamaceutcal Reseach, 04, 6(7):338-346 Reseach Atcle SSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Fault detectn f batch pcess based n mult-wa Kenel -PLS Zha aqang*,
Avalable nlne www.jcp.cm Junal f Chemcal and Phamaceutcal Reseach, 04, 6(7):338-346 Reseach Atcle SSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Fault detectn f batch pcess based n mult-wa Kenel -PLS Zha aqang*,
More Effective Optimum Synthesis of Path Generating Four-Bar Mechanisms
 Junal f Multdscplnay Engneeng Scence and Technlgy (JMEST) ISSN: 59- Vl. Issue 5, May - 5 Me Effectve Optmum Synthess f Path Geneatng Fu-Ba Mechansms Wen-Y Ln Depatment f Mechancal Engneeng De Ln Insttute
Junal f Multdscplnay Engneeng Scence and Technlgy (JMEST) ISSN: 59- Vl. Issue 5, May - 5 Me Effectve Optmum Synthess f Path Geneatng Fu-Ba Mechansms Wen-Y Ln Depatment f Mechancal Engneeng De Ln Insttute
hitt Phy2049: Magnetism 6/10/2011 Magnetic Field Units Force Between Two Parallel Currents Force Between Two Anti-Parallel Currents
 6/0/0 Phy049: Magsm Last lectue: t-avat s and Ampee s law: Magc eld due t a staght we Cuent lps (whle bts)and slends Tday: emnde and aaday s law. htt Tw lng staght wes pece the plane f the pape at vetces
6/0/0 Phy049: Magsm Last lectue: t-avat s and Ampee s law: Magc eld due t a staght we Cuent lps (whle bts)and slends Tday: emnde and aaday s law. htt Tw lng staght wes pece the plane f the pape at vetces
8 Baire Category Theorem and Uniform Boundedness
 8 Bae Categoy Theoem and Unfom Boundedness Pncple 8.1 Bae s Categoy Theoem Valdty of many esults n analyss depends on the completeness popety. Ths popety addesses the nadequacy of the system of atonal
8 Bae Categoy Theoem and Unfom Boundedness Pncple 8.1 Bae s Categoy Theoem Valdty of many esults n analyss depends on the completeness popety. Ths popety addesses the nadequacy of the system of atonal
N = N t ; t 0. N is the number of claims paid by the
 Iulan MICEA, Ph Mhaela COVIG, Ph Canddate epatment of Mathematcs The Buchaest Academy of Economc Studes an CECHIN-CISTA Uncedt Tac Bank, Lugoj SOME APPOXIMATIONS USE IN THE ISK POCESS OF INSUANCE COMPANY
Iulan MICEA, Ph Mhaela COVIG, Ph Canddate epatment of Mathematcs The Buchaest Academy of Economc Studes an CECHIN-CISTA Uncedt Tac Bank, Lugoj SOME APPOXIMATIONS USE IN THE ISK POCESS OF INSUANCE COMPANY
Summary chapter 4. Electric field s can distort charge distributions in atoms and molecules by stretching and rotating:
 Summa chapte 4. In chapte 4 dielectics ae discussed. In thse mateials the electns ae nded t the atms mlecules and cannt am fee thugh the mateial: the electns in insulats ae n a tight leash and all the
Summa chapte 4. In chapte 4 dielectics ae discussed. In thse mateials the electns ae nded t the atms mlecules and cannt am fee thugh the mateial: the electns in insulats ae n a tight leash and all the
If there are k binding constraints at x then re-label these constraints so that they are the first k constraints.
 Mathematcal Foundatons -1- Constaned Optmzaton Constaned Optmzaton Ma{ f ( ) X} whee X {, h ( ), 1,, m} Necessay condtons fo to be a soluton to ths mamzaton poblem Mathematcally, f ag Ma{ f ( ) X}, then
Mathematcal Foundatons -1- Constaned Optmzaton Constaned Optmzaton Ma{ f ( ) X} whee X {, h ( ), 1,, m} Necessay condtons fo to be a soluton to ths mamzaton poblem Mathematcally, f ag Ma{ f ( ) X}, then
Set of square-integrable function 2 L : function space F
 Set of squae-ntegable functon L : functon space F Motvaton: In ou pevous dscussons we have seen that fo fee patcles wave equatons (Helmholt o Schödnge) can be expessed n tems of egenvalue equatons. H E,
Set of squae-ntegable functon L : functon space F Motvaton: In ou pevous dscussons we have seen that fo fee patcles wave equatons (Helmholt o Schödnge) can be expessed n tems of egenvalue equatons. H E,
Mining Inexact Spatial Patterns
 Mnng Inexact patal attens engyu Hng Cdnated cence Labaty nvesty f Illns at bana-champagn bana, IL 680 Emal: hng@fp.uuc.edu Abstact Ths k ppses the methdlgy f autmatcally mdelng and mnng nexact spatal pattens.
Mnng Inexact patal attens engyu Hng Cdnated cence Labaty nvesty f Illns at bana-champagn bana, IL 680 Emal: hng@fp.uuc.edu Abstact Ths k ppses the methdlgy f autmatcally mdelng and mnng nexact spatal pattens.
Chapter 7. Systems 7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF LIQUID LEVEL SYSTEMS. Steady State Flow. A. Bazoune
 Chapter 7 Flud Systems and Thermal Systems 7.1 INTODUCTION A. Bazune A flud system uses ne r mre fluds t acheve ts purpse. Dampers and shck absrbers are eamples f flud systems because they depend n the
Chapter 7 Flud Systems and Thermal Systems 7.1 INTODUCTION A. Bazune A flud system uses ne r mre fluds t acheve ts purpse. Dampers and shck absrbers are eamples f flud systems because they depend n the
Energy in Closed Systems
 Enegy n Closed Systems Anamta Palt palt.anamta@gmal.com Abstact The wtng ndcates a beakdown of the classcal laws. We consde consevaton of enegy wth a many body system n elaton to the nvese squae law and
Enegy n Closed Systems Anamta Palt palt.anamta@gmal.com Abstact The wtng ndcates a beakdown of the classcal laws. We consde consevaton of enegy wth a many body system n elaton to the nvese squae law and
Analytical Solution to Diffusion-Advection Equation in Spherical Coordinate Based on the Fundamental Bloch NMR Flow Equations
 Intenatinal Junal f heetical and athematical Phsics 5, 5(5: 4-44 OI:.593/j.ijtmp.555.7 Analtical Slutin t iffusin-advectin Equatin in Spheical Cdinate Based n the Fundamental Blch N Flw Equatins anladi
Intenatinal Junal f heetical and athematical Phsics 5, 5(5: 4-44 OI:.593/j.ijtmp.555.7 Analtical Slutin t iffusin-advectin Equatin in Spheical Cdinate Based n the Fundamental Blch N Flw Equatins anladi
INTRODUCTION. consider the statements : I there exists x X. f x, such that. II there exists y Y. such that g y
 INRODUCION hs dssetaton s the eadng of efeences [1], [] and [3]. Faas lemma s one of the theoems of the altenatve. hese theoems chaacteze the optmalt condtons of seveal mnmzaton poblems. It s nown that
INRODUCION hs dssetaton s the eadng of efeences [1], [] and [3]. Faas lemma s one of the theoems of the altenatve. hese theoems chaacteze the optmalt condtons of seveal mnmzaton poblems. It s nown that
14 The Boole/Stone algebra of sets
 14 The Ble/Stne algebra f sets 14.1. Lattces and Blean algebras. Gven a set A, the subsets f A admt the fllwng smple and famlar peratns n them: (ntersectn), (unn) and - (cmplementatn). If X, Y A, then
14 The Ble/Stne algebra f sets 14.1. Lattces and Blean algebras. Gven a set A, the subsets f A admt the fllwng smple and famlar peratns n them: (ntersectn), (unn) and - (cmplementatn). If X, Y A, then
Chapter 6 : Gibbs Free Energy
 Wnter 01 Chem 54: ntrductry hermdynamcs Chapter 6 : Gbbs Free Energy... 64 Defntn f G, A... 64 Mawell Relatns... 65 Gbbs Free Energy G(,) (ure substances)... 67 Gbbs Free Energy fr Mtures... 68 ΔG f deal
Wnter 01 Chem 54: ntrductry hermdynamcs Chapter 6 : Gbbs Free Energy... 64 Defntn f G, A... 64 Mawell Relatns... 65 Gbbs Free Energy G(,) (ure substances)... 67 Gbbs Free Energy fr Mtures... 68 ΔG f deal
Active Load. Reading S&S (5ed): Sec. 7.2 S&S (6ed): Sec. 8.2
 cte La ean S&S (5e: Sec. 7. S&S (6e: Sec. 8. In nteate ccuts, t s ffcult t fabcate essts. Instea, aplfe cnfuatns typcally use acte las (.e. las ae w acte eces. Ths can be ne usn a cuent suce cnfuatn,.e.
cte La ean S&S (5e: Sec. 7. S&S (6e: Sec. 8. In nteate ccuts, t s ffcult t fabcate essts. Instea, aplfe cnfuatns typcally use acte las (.e. las ae w acte eces. Ths can be ne usn a cuent suce cnfuatn,.e.
Groupoid and Topological Quotient Group
 lobal Jounal of Pue and Appled Mathematcs SSN 0973-768 Volume 3 Numbe 7 07 pp 373-39 Reseach nda Publcatons http://wwwpublcatoncom oupod and Topolocal Quotent oup Mohammad Qasm Manna Depatment of Mathematcs
lobal Jounal of Pue and Appled Mathematcs SSN 0973-768 Volume 3 Numbe 7 07 pp 373-39 Reseach nda Publcatons http://wwwpublcatoncom oupod and Topolocal Quotent oup Mohammad Qasm Manna Depatment of Mathematcs
IGEE 401 Power Electronic Systems. Solution to Midterm Examination Fall 2004
 Jós, G GEE 401 wer Electrnc Systems Slutn t Mdterm Examnatn Fall 2004 Specal nstructns: - Duratn: 75 mnutes. - Materal allwed: a crb sheet (duble sded 8.5 x 11), calculatr. - Attempt all questns. Make
Jós, G GEE 401 wer Electrnc Systems Slutn t Mdterm Examnatn Fall 2004 Specal nstructns: - Duratn: 75 mnutes. - Materal allwed: a crb sheet (duble sded 8.5 x 11), calculatr. - Attempt all questns. Make
Imprecise DEA for Setting Scale Efficient Targets
 Int. Jurnal f Math. Anali, Vl. 3, 2009, n. 6, 747-756 Imprecie DEA fr Setting Scale Efficient Target N. Malekmhammadi a, F. Heinzadeh Ltfi b and Azmi B Jaafar c a Intitute fr Mathematical Reearch, Univeriti
Int. Jurnal f Math. Anali, Vl. 3, 2009, n. 6, 747-756 Imprecie DEA fr Setting Scale Efficient Target N. Malekmhammadi a, F. Heinzadeh Ltfi b and Azmi B Jaafar c a Intitute fr Mathematical Reearch, Univeriti
Phys 331: Ch 9,.6-.7 Noninertial Frames: Centrifugal and Corriolis forces 1. And and
 Phs 331: Ch 9 6-7 Nnnetal Fames: Centfual and Cls fces 1 Mn 1/5 Wed 1/7 Thus F Mn 1/6 96-7 Fctnal Fces: Centfual and Cls 98-9 Fee-Fall Cls Fucault 101- Cente f Mass & Rtatn abut a Fed As 103-4 Rtatn abut
Phs 331: Ch 9 6-7 Nnnetal Fames: Centfual and Cls fces 1 Mn 1/5 Wed 1/7 Thus F Mn 1/6 96-7 Fctnal Fces: Centfual and Cls 98-9 Fee-Fall Cls Fucault 101- Cente f Mass & Rtatn abut a Fed As 103-4 Rtatn abut
Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy Observer for a Switching Bioprocess: Sector Nonlinearity Approach
 Takag-Sugen Fuzzy Obseve f a Swtchng Bpcess: Sect Nnlneaty Appach Enque J. Heea-López, Benadn Castll-Tled, Jesús Ramíez-Códva and Eugén C. Feea Cent de Investgacón y Asstenca en Tecnlgía y Dseñ del Estad
Takag-Sugen Fuzzy Obseve f a Swtchng Bpcess: Sect Nnlneaty Appach Enque J. Heea-López, Benadn Castll-Tled, Jesús Ramíez-Códva and Eugén C. Feea Cent de Investgacón y Asstenca en Tecnlgía y Dseñ del Estad
Physics 107 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #20
 Physcs 107 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #0 Cutnell & Jhnsn, 7 th etn Chapter 6: Prblems 5, 7, 74, 104, 114 *5 Cncept Smulatn 6.4 prves the ptn f explrng the ray agram that apples t ths prblem. The stance between
Physcs 107 HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT #0 Cutnell & Jhnsn, 7 th etn Chapter 6: Prblems 5, 7, 74, 104, 114 *5 Cncept Smulatn 6.4 prves the ptn f explrng the ray agram that apples t ths prblem. The stance between
Exploiting vector space properties for the global optimization of process networks
 Exptng vectr space prpertes fr the gbal ptmzatn f prcess netwrks Juan ab Ruz Ignac Grssmann Enterprse Wde Optmzatn Meetng March 00 Mtvatn - The ptmzatn f prcess netwrks s ne f the mst frequent prblems
Exptng vectr space prpertes fr the gbal ptmzatn f prcess netwrks Juan ab Ruz Ignac Grssmann Enterprse Wde Optmzatn Meetng March 00 Mtvatn - The ptmzatn f prcess netwrks s ne f the mst frequent prblems
Summary 7. ELECTROMAGNETIC JOINT. ROTATING MAGNETIC FIELD. SPACE-PHASOR THEORY... 2
 uay 7. ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT. ROTATIG MAGETIC FIELD. PACE-PHAOR THEORY... 7.1 ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT... 7. UMER OF POLE... 4 7. DITRIUTED WIDIG... 5 7.4 TORQUE EXPREIO... 6 7.5 PACE PHAOR... 7 7.6 THREE-PHAE
uay 7. ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT. ROTATIG MAGETIC FIELD. PACE-PHAOR THEORY... 7.1 ELECTROMAGETIC JOIT... 7. UMER OF POLE... 4 7. DITRIUTED WIDIG... 5 7.4 TORQUE EXPREIO... 6 7.5 PACE PHAOR... 7 7.6 THREE-PHAE
Generating Functions, Weighted and Non-Weighted Sums for Powers of Second-Order Recurrence Sequences
 Geneatng Functons, Weghted and Non-Weghted Sums fo Powes of Second-Ode Recuence Sequences Pantelmon Stăncă Aubun Unvesty Montgomey, Depatment of Mathematcs Montgomey, AL 3614-403, USA e-mal: stanca@studel.aum.edu
Geneatng Functons, Weghted and Non-Weghted Sums fo Powes of Second-Ode Recuence Sequences Pantelmon Stăncă Aubun Unvesty Montgomey, Depatment of Mathematcs Montgomey, AL 3614-403, USA e-mal: stanca@studel.aum.edu
_J _J J J J J J J J _. 7 particles in the blue state; 3 particles in the red state: 720 configurations _J J J _J J J J J J J J _
 Dsrder and Suppse I have 10 partcles that can be n ne f tw states ether the blue state r the red state. Hw many dfferent ways can we arrange thse partcles amng the states? All partcles n the blue state:
Dsrder and Suppse I have 10 partcles that can be n ne f tw states ether the blue state r the red state. Hw many dfferent ways can we arrange thse partcles amng the states? All partcles n the blue state:
Wp/Lmin. Wn/Lmin 2.5V
 UNIVERITY OF CALIFORNIA Cllege f Engneerng Department f Electrcal Engneerng and Cmputer cences Andre Vladmrescu Hmewrk #7 EEC Due Frday, Aprl 8 th, pm @ 0 Cry Prblem #.5V Wp/Lmn 0.0V Wp/Lmn n ut Wn/Lmn.5V
UNIVERITY OF CALIFORNIA Cllege f Engneerng Department f Electrcal Engneerng and Cmputer cences Andre Vladmrescu Hmewrk #7 EEC Due Frday, Aprl 8 th, pm @ 0 Cry Prblem #.5V Wp/Lmn 0.0V Wp/Lmn n ut Wn/Lmn.5V
FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERS. β f
 FEEDBC MPLFES X - X X X * What negatve eedback? ddng the eedback gnal t the nput a t patally cancel the nput gnal t the ample. * What eedback? Takng a ptn the gnal avng at the lad and eedng t back t the
FEEDBC MPLFES X - X X X * What negatve eedback? ddng the eedback gnal t the nput a t patally cancel the nput gnal t the ample. * What eedback? Takng a ptn the gnal avng at the lad and eedng t back t the
EEE2146 Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design. MIC2: Investigation of Amplifier Parameters of a Common-Collector Amplifier
 EEE2146 Mcelectncs Ccut Analyss and Desgn Expement MIC2 MIC2: Inestgatn f Amplfe Paametes f a Cmmn-Cllect Amplfe Ttal Pecentage: 5% (Fm 40% Cusewk Mak) 1. Objecte T nestgate the ltage and cuent gans and
EEE2146 Mcelectncs Ccut Analyss and Desgn Expement MIC2 MIC2: Inestgatn f Amplfe Paametes f a Cmmn-Cllect Amplfe Ttal Pecentage: 5% (Fm 40% Cusewk Mak) 1. Objecte T nestgate the ltage and cuent gans and
Rigid Bodies: Equivalent Systems of Forces
 Engneeng Statcs, ENGR 2301 Chapte 3 Rgd Bodes: Equvalent Sstems of oces Intoducton Teatment of a bod as a sngle patcle s not alwas possble. In geneal, the se of the bod and the specfc ponts of applcaton
Engneeng Statcs, ENGR 2301 Chapte 3 Rgd Bodes: Equvalent Sstems of oces Intoducton Teatment of a bod as a sngle patcle s not alwas possble. In geneal, the se of the bod and the specfc ponts of applcaton
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectional Mathematics 2006 Solution Set
 WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal 006 Slutin Set. Cect answe: e. mph is 76 feet pe minute, and 4 mph is 35 feet pe minute. The tip up the hill takes 600/76, 3.4 minutes, and the tip dwn takes 600/35,.70
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal 006 Slutin Set. Cect answe: e. mph is 76 feet pe minute, and 4 mph is 35 feet pe minute. The tip up the hill takes 600/76, 3.4 minutes, and the tip dwn takes 600/35,.70
P 365. r r r )...(1 365
 SCIENCE WORLD JOURNAL VOL (NO4) 008 www.scecncewoldounal.og ISSN 597-64 SHORT COMMUNICATION ANALYSING THE APPROXIMATION MODEL TO BIRTHDAY PROBLEM *CHOJI, D.N. & DEME, A.C. Depatment of Mathematcs Unvesty
SCIENCE WORLD JOURNAL VOL (NO4) 008 www.scecncewoldounal.og ISSN 597-64 SHORT COMMUNICATION ANALYSING THE APPROXIMATION MODEL TO BIRTHDAY PROBLEM *CHOJI, D.N. & DEME, A.C. Depatment of Mathematcs Unvesty
Example
 hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
Section 10 Regression with Stochastic Regressors
 Sectn 10 Regressn wth Stchastc Regressrs Meanng f randm regressrs Untl nw, we have assumed (aganst all reasn) that the values f x have been cntrlled by the expermenter. Ecnmsts almst never actually cntrl
Sectn 10 Regressn wth Stchastc Regressrs Meanng f randm regressrs Untl nw, we have assumed (aganst all reasn) that the values f x have been cntrlled by the expermenter. Ecnmsts almst never actually cntrl
CONVEX COMBINATIONS OF ANALYTIC FUNCTIONS
 rnat. J. Math. & Math. S. Vl. 6 N. (983) 33534 335 ON THE RADUS OF UNVALENCE OF CONVEX COMBNATONS OF ANALYTC FUNCTONS KHALDA. NOOR, FATMA M. ALOBOUD and NAEELA ALDHAN Mathematcs Department Scence Cllege
rnat. J. Math. & Math. S. Vl. 6 N. (983) 33534 335 ON THE RADUS OF UNVALENCE OF CONVEX COMBNATONS OF ANALYTC FUNCTONS KHALDA. NOOR, FATMA M. ALOBOUD and NAEELA ALDHAN Mathematcs Department Scence Cllege
Regression with Stochastic Regressors
 Sectn 9 Regressn wth Stchastc Regressrs Meanng f randm regressrs Untl nw, we have assumed (aganst all reasn) that the values f x have been cntrlled by the expermenter. Ecnmsts almst never actually cntrl
Sectn 9 Regressn wth Stchastc Regressrs Meanng f randm regressrs Untl nw, we have assumed (aganst all reasn) that the values f x have been cntrlled by the expermenter. Ecnmsts almst never actually cntrl
EPr over F(X} AA+ A+A. For AeF, a generalized inverse. ON POLYNOMIAL EPr MATRICES
 Intenat. J. Hath. & Math. S. VOL. 15 NO. 2 (1992) 261-266 ON POLYNOMIAL EP MATRICES 261 AR. MEENAKSHI and N. ANANOAM Depatment f Mathematics, Annamalai Univeslty, Annamalainaga- 68 2, Tamll Nadu, INDIA.
Intenat. J. Hath. & Math. S. VOL. 15 NO. 2 (1992) 261-266 ON POLYNOMIAL EP MATRICES 261 AR. MEENAKSHI and N. ANANOAM Depatment f Mathematics, Annamalai Univeslty, Annamalainaga- 68 2, Tamll Nadu, INDIA.
PHYSICS 536 Experiment 12: Applications of the Golden Rules for Negative Feedback
 PHYSICS 536 Experment : Applcatns f the Glden Rules fr Negatve Feedback The purpse f ths experment s t llustrate the glden rules f negatve feedback fr a varety f crcuts. These cncepts permt yu t create
PHYSICS 536 Experment : Applcatns f the Glden Rules fr Negatve Feedback The purpse f ths experment s t llustrate the glden rules f negatve feedback fr a varety f crcuts. These cncepts permt yu t create
Strees Analysis in Elastic Half Space Due To a Thermoelastic Strain
 IOSR Junal f Mathematics (IOSRJM) ISSN: 78-578 Vlume, Issue (July-Aug 0), PP 46-54 Stees Analysis in Elastic Half Space Due T a Themelastic Stain Aya Ahmad Depatment f Mathematics NIT Patna Biha India
IOSR Junal f Mathematics (IOSRJM) ISSN: 78-578 Vlume, Issue (July-Aug 0), PP 46-54 Stees Analysis in Elastic Half Space Due T a Themelastic Stain Aya Ahmad Depatment f Mathematics NIT Patna Biha India
The Gradient and Applications This unit is based on Sections 9.5 and 9.6, Chapter 9. All assigned readings and exercises are from the textbook
 The Gadient and Applicatins This unit is based n Sectins 9.5 and 9.6 Chapte 9. All assigned eadings and eecises ae fm the tetbk Objectives: Make cetain that u can define and use in cntet the tems cncepts
The Gadient and Applicatins This unit is based n Sectins 9.5 and 9.6 Chapte 9. All assigned eadings and eecises ae fm the tetbk Objectives: Make cetain that u can define and use in cntet the tems cncepts
Chapter I Matrices, Vectors, & Vector Calculus 1-1, 1-9, 1-10, 1-11, 1-17, 1-18, 1-25, 1-27, 1-36, 1-37, 1-41.
 Chapte I Matces, Vectos, & Vecto Calculus -, -9, -0, -, -7, -8, -5, -7, -36, -37, -4. . Concept of a Scala Consde the aa of patcles shown n the fgue. he mass of the patcle at (,) can be epessed as. M (,
Chapte I Matces, Vectos, & Vecto Calculus -, -9, -0, -, -7, -8, -5, -7, -36, -37, -4. . Concept of a Scala Consde the aa of patcles shown n the fgue. he mass of the patcle at (,) can be epessed as. M (,
State-Space Model Based Generalized Predictive Control for Networked Control Systems
 Prceedngs f the 7th Wrld Cngress he Internatnal Federatn f Autmatc Cntrl State-Space Mdel Based Generalzed Predctve Cntrl fr Netwred Cntrl Systems Bn ang* Gu-Png Lu** We-Hua Gu*** and Ya-Ln Wang**** *Schl
Prceedngs f the 7th Wrld Cngress he Internatnal Federatn f Autmatc Cntrl State-Space Mdel Based Generalzed Predctve Cntrl fr Netwred Cntrl Systems Bn ang* Gu-Png Lu** We-Hua Gu*** and Ya-Ln Wang**** *Schl
Example 11: The man shown in Figure (a) pulls on the cord with a force of 70
 Chapte Tw ce System 35.4 α α 100 Rx cs 0.354 R 69.3 35.4 β β 100 Ry cs 0.354 R 111 Example 11: The man shwn in igue (a) pulls n the cd with a fce f 70 lb. Repesent this fce actin n the suppt A as Catesian
Chapte Tw ce System 35.4 α α 100 Rx cs 0.354 R 69.3 35.4 β β 100 Ry cs 0.354 R 111 Example 11: The man shwn in igue (a) pulls n the cd with a fce f 70 lb. Repesent this fce actin n the suppt A as Catesian
4DVAR, according to the name, is a four-dimensional variational method.
 4D-Varatnal Data Assmlatn (4D-Var) 4DVAR, accrdng t the name, s a fur-dmensnal varatnal methd. 4D-Var s actually a smple generalzatn f 3D-Var fr bservatns that are dstrbuted n tme. he equatns are the same,
4D-Varatnal Data Assmlatn (4D-Var) 4DVAR, accrdng t the name, s a fur-dmensnal varatnal methd. 4D-Var s actually a smple generalzatn f 3D-Var fr bservatns that are dstrbuted n tme. he equatns are the same,
Engineering Mechanics. Force resultants, Torques, Scalar Products, Equivalent Force systems
 Engneeng echancs oce esultants, Toques, Scala oducts, Equvalent oce sstems Tata cgaw-hll Companes, 008 Resultant of Two oces foce: acton of one bod on anothe; chaacteed b ts pont of applcaton, magntude,
Engneeng echancs oce esultants, Toques, Scala oducts, Equvalent oce sstems Tata cgaw-hll Companes, 008 Resultant of Two oces foce: acton of one bod on anothe; chaacteed b ts pont of applcaton, magntude,
CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONVERTER
 70 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONERTER 3.1 Intrductn The KY Bst Cnverter s a recent nventn made by K.I.Hwu et. al., (2007), (2009a), (2009b), (2009c), (2010) n the nn-slated DC DC cnverter segment,
70 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONERTER 3.1 Intrductn The KY Bst Cnverter s a recent nventn made by K.I.Hwu et. al., (2007), (2009a), (2009b), (2009c), (2010) n the nn-slated DC DC cnverter segment,
Physics 11b Lecture #2. Electric Field Electric Flux Gauss s Law
 Physcs 11b Lectue # Electc Feld Electc Flux Gauss s Law What We Dd Last Tme Electc chage = How object esponds to electc foce Comes n postve and negatve flavos Conseved Electc foce Coulomb s Law F Same
Physcs 11b Lectue # Electc Feld Electc Flux Gauss s Law What We Dd Last Tme Electc chage = How object esponds to electc foce Comes n postve and negatve flavos Conseved Electc foce Coulomb s Law F Same
APPLICATIONS OF SEMIGENERALIZED -CLOSED SETS
 Intenatonal Jounal of Mathematcal Engneeng Scence ISSN : 22776982 Volume Issue 4 (Apl 202) http://www.mes.com/ https://stes.google.com/ste/mesounal/ APPLICATIONS OF SEMIGENERALIZED CLOSED SETS G.SHANMUGAM,
Intenatonal Jounal of Mathematcal Engneeng Scence ISSN : 22776982 Volume Issue 4 (Apl 202) http://www.mes.com/ https://stes.google.com/ste/mesounal/ APPLICATIONS OF SEMIGENERALIZED CLOSED SETS G.SHANMUGAM,
The Role of Open Channels in Overlapping Resonances Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, Vol. 31, No DOI /bkcs
 The Rle f Open Channels n Ovelappng Resnances Bull. Kean Chem. Sc., Vl. 3, N. 3 DOI.5/bkcs..3..3 Rle f Open Channels n Ovelappng Resnances Studed by Multchannel Quantum Defect They n Systems Invlvng Nndegeneate
The Rle f Open Channels n Ovelappng Resnances Bull. Kean Chem. Sc., Vl. 3, N. 3 DOI.5/bkcs..3..3 Rle f Open Channels n Ovelappng Resnances Studed by Multchannel Quantum Defect They n Systems Invlvng Nndegeneate
Consider the simple circuit of Figure 1 in which a load impedance of r is connected to a voltage source. The no load voltage of r
 1 Intductin t Pe Unit Calculatins Cnside the simple cicuit f Figue 1 in which a lad impedance f L 60 + j70 Ω 9. 49 Ω is cnnected t a vltage suce. The n lad vltage f the suce is E 1000 0. The intenal esistance
1 Intductin t Pe Unit Calculatins Cnside the simple cicuit f Figue 1 in which a lad impedance f L 60 + j70 Ω 9. 49 Ω is cnnected t a vltage suce. The n lad vltage f the suce is E 1000 0. The intenal esistance
Exercises for Frequency Response. ECE 102, Fall 2012, F. Najmabadi
 Eecses Fequency espnse EE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Eecse : Fnd the d-band an and the lwe cut- equency the aple belw. µ n (W/ 4 A/, t 0.5, λ 0, 0 µf, and µf Bth capacts ae lw- capacts. F. Najabad, EE0, Fall
Eecses Fequency espnse EE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Eecse : Fnd the d-band an and the lwe cut- equency the aple belw. µ n (W/ 4 A/, t 0.5, λ 0, 0 µf, and µf Bth capacts ae lw- capacts. F. Najabad, EE0, Fall
ME 3600 Control Systems Frequency Domain Analysis
 ME 3600 Cntl Systems Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
ME 3600 Cntl Systems Fequency Dmain Analysis The fequency espnse f a system is defined as the steady-state espnse f the system t a sinusidal (hamnic) input. F linea systems, the esulting utput is itself
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Derivation of Lagrange Equations from D Alembert s Principle
 1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Devaton of Lagange Equatons fom D Alembet s Pncple 2 D Alembet s Pncple Followng a smla agument fo the vtual dsplacement to be consstent wth constants,.e, (no vtual wok fo
1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Devaton of Lagange Equatons fom D Alembet s Pncple 2 D Alembet s Pncple Followng a smla agument fo the vtual dsplacement to be consstent wth constants,.e, (no vtual wok fo
Module 9 Thin and thick cylinders
 Mdule 9 Thn and thck cylndes Vesn 2 ME, IIT Khaagu Lessn 3 Desgn ncles f thck cylndes Vesn 2 ME, IIT Khaagu Instuctnal Objectves: At the end f ths lessn, the students shuld have the knwledge f: Falue thees
Mdule 9 Thn and thck cylndes Vesn 2 ME, IIT Khaagu Lessn 3 Desgn ncles f thck cylndes Vesn 2 ME, IIT Khaagu Instuctnal Objectves: At the end f ths lessn, the students shuld have the knwledge f: Falue thees
A Method of Reliability Target Setting for Electric Power Distribution Systems Using Data Envelopment Analysis
 27 กก ก 9 2-3 2554 ก ก ก A Method of Relablty aget Settng fo Electc Powe Dstbuton Systems Usng Data Envelopment Analyss ก 2 ก ก ก ก ก 0900 2 ก ก ก ก ก 0900 E-mal: penjan262@hotmal.com Penjan Sng-o Psut
27 กก ก 9 2-3 2554 ก ก ก A Method of Relablty aget Settng fo Electc Powe Dstbuton Systems Usng Data Envelopment Analyss ก 2 ก ก ก ก ก 0900 2 ก ก ก ก ก 0900 E-mal: penjan262@hotmal.com Penjan Sng-o Psut
Mathematical Modeling & Analysis of Brake Pad for Wear Characteristics
 Intenatnal Cnfeence n Ideas, Impact and Innvatn n Mechancal Engneeng (ICIIIME 07 ISSN: -869 Vlume: 5 Issue: 6 048 056 Mathematcal Mdelng & Analyss f Bake Pad f Wea Chaactestcs S. R. Kakad, R.M. Me, D.
Intenatnal Cnfeence n Ideas, Impact and Innvatn n Mechancal Engneeng (ICIIIME 07 ISSN: -869 Vlume: 5 Issue: 6 048 056 Mathematcal Mdelng & Analyss f Bake Pad f Wea Chaactestcs S. R. Kakad, R.M. Me, D.
V. Principles of Irreversible Thermodynamics. s = S - S 0 (7.3) s = = - g i, k. "Flux": = da i. "Force": = -Â g a ik k = X i. Â J i X i (7.
 Themodynamcs and Knetcs of Solds 71 V. Pncples of Ievesble Themodynamcs 5. Onsage s Teatment s = S - S 0 = s( a 1, a 2,...) a n = A g - A n (7.6) Equlbum themodynamcs detemnes the paametes of an equlbum
Themodynamcs and Knetcs of Solds 71 V. Pncples of Ievesble Themodynamcs 5. Onsage s Teatment s = S - S 0 = s( a 1, a 2,...) a n = A g - A n (7.6) Equlbum themodynamcs detemnes the paametes of an equlbum
CHAPTER GAUSS'S LAW
 lutins--ch 14 (Gauss's Law CHAPTE 14 -- GAU' LAW 141 This pblem is ticky An electic field line that flws int, then ut f the cap (see Figue I pduces a negative flux when enteing and an equal psitive flux
lutins--ch 14 (Gauss's Law CHAPTE 14 -- GAU' LAW 141 This pblem is ticky An electic field line that flws int, then ut f the cap (see Figue I pduces a negative flux when enteing and an equal psitive flux
THE EQUIVALENCE OF GRAM-SCHMIDT AND QR FACTORIZATION (page 227) Gram-Schmidt provides another way to compute a QR decomposition: n
 HE EQUIVAENCE OF GRA-SCHID AND QR FACORIZAION (page 7 Ga-Schdt podes anothe way to copute a QR decoposton: n gen ectos,, K, R, Ga-Schdt detenes scalas j such that o + + + [ ] [ ] hs s a QR factozaton of
HE EQUIVAENCE OF GRA-SCHID AND QR FACORIZAION (page 7 Ga-Schdt podes anothe way to copute a QR decoposton: n gen ectos,, K, R, Ga-Schdt detenes scalas j such that o + + + [ ] [ ] hs s a QR factozaton of
The International Association for the Properties of Water and Steam
 IAPWS R6-95(016) The Intenatnal Asscatn f the Ppetes f Wate and Steam Desden, Gemany Septeme 016 Revsed Release n the IAPWS Fmulatn 1995 f the Themdynamc Ppetes f Odnay Wate Sustance f Geneal and Scentfc
IAPWS R6-95(016) The Intenatnal Asscatn f the Ppetes f Wate and Steam Desden, Gemany Septeme 016 Revsed Release n the IAPWS Fmulatn 1995 f the Themdynamc Ppetes f Odnay Wate Sustance f Geneal and Scentfc
Asymmetric Capital-Tax Competition, Unemployment and Losses from Capital Market Integration
 Asymmetc Captal-Tax Cmpettn, Unemplyment and Lsses fm Captal Maet Integatn Rüdge Pethg Fede Klleß CESIFO WORKING PAPER NO. 2795 CATEGORY : PUBLIC FINANCE SEPTEMBER 2009 An electnc vesn f the pape may be
Asymmetc Captal-Tax Cmpettn, Unemplyment and Lsses fm Captal Maet Integatn Rüdge Pethg Fede Klleß CESIFO WORKING PAPER NO. 2795 CATEGORY : PUBLIC FINANCE SEPTEMBER 2009 An electnc vesn f the pape may be
CHAPTER 24 GAUSS LAW
 CHAPTR 4 GAUSS LAW LCTRIC FLUX lectic flux is a measue f the numbe f electic filed lines penetating sme suface in a diectin pependicula t that suface. Φ = A = A csθ with θ is the angle between the and
CHAPTR 4 GAUSS LAW LCTRIC FLUX lectic flux is a measue f the numbe f electic filed lines penetating sme suface in a diectin pependicula t that suface. Φ = A = A csθ with θ is the angle between the and
Optimization Methods: Linear Programming- Revised Simplex Method. Module 3 Lecture Notes 5. Revised Simplex Method, Duality and Sensitivity analysis
 Optmzaton Meods: Lnea Pogammng- Revsed Smple Meod Module Lectue Notes Revsed Smple Meod, Dualty and Senstvty analyss Intoducton In e pevous class, e smple meod was dscussed whee e smple tableau at each
Optmzaton Meods: Lnea Pogammng- Revsed Smple Meod Module Lectue Notes Revsed Smple Meod, Dualty and Senstvty analyss Intoducton In e pevous class, e smple meod was dscussed whee e smple tableau at each
Optimization Frequency Design of Eddy Current Testing
 5th WSEAS Int. Cnfeence n Appled Electagnetcs, Weless and Optcal Cuncatns, Tenefe, Span, Decebe 14-16, 2007 127 Optzatn Fequency Desgn f Eddy Cuent Testng NAONG MUNGKUNG 1, KOMKIT CHOMSUWAN 1, NAONG PIMPU
5th WSEAS Int. Cnfeence n Appled Electagnetcs, Weless and Optcal Cuncatns, Tenefe, Span, Decebe 14-16, 2007 127 Optzatn Fequency Desgn f Eddy Cuent Testng NAONG MUNGKUNG 1, KOMKIT CHOMSUWAN 1, NAONG PIMPU
6. Cascode Amplifiers and Cascode Current Mirrors
 6. Cascde plfes and Cascde Cuent Ms Seda & Sth Sec. 7 (MOS ptn (S&S 5 th Ed: Sec. 6 MOS ptn & ne fequency espnse ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Cascde aplfe s a ppula buldn blck f ICs Cascde Cnfuatn CG stae
6. Cascde plfes and Cascde Cuent Ms Seda & Sth Sec. 7 (MOS ptn (S&S 5 th Ed: Sec. 6 MOS ptn & ne fequency espnse ECE 0, Fall 0, F. Najabad Cascde aplfe s a ppula buldn blck f ICs Cascde Cnfuatn CG stae
Chapter 3, Solution 1C.
 COSMOS: Cmplete Onlne Slutns Manual Organzatn System Chapter 3, Slutn C. (a If the lateral surfaces f the rd are nsulated, the heat transfer surface area f the cylndrcal rd s the bttm r the tp surface
COSMOS: Cmplete Onlne Slutns Manual Organzatn System Chapter 3, Slutn C. (a If the lateral surfaces f the rd are nsulated, the heat transfer surface area f the cylndrcal rd s the bttm r the tp surface
Physics 2A Chapter 11 - Universal Gravitation Fall 2017
 Physcs A Chapte - Unvesal Gavtaton Fall 07 hese notes ae ve pages. A quck summay: he text boxes n the notes contan the esults that wll compse the toolbox o Chapte. hee ae thee sectons: the law o gavtaton,
Physcs A Chapte - Unvesal Gavtaton Fall 07 hese notes ae ve pages. A quck summay: he text boxes n the notes contan the esults that wll compse the toolbox o Chapte. hee ae thee sectons: the law o gavtaton,
A Brief Guide to Recognizing and Coping With Failures of the Classical Regression Assumptions
 A Bef Gude to Recognzng and Copng Wth Falues of the Classcal Regesson Assumptons Model: Y 1 k X 1 X fxed n epeated samples IID 0, I. Specfcaton Poblems A. Unnecessay explanatoy vaables 1. OLS s no longe
A Bef Gude to Recognzng and Copng Wth Falues of the Classcal Regesson Assumptons Model: Y 1 k X 1 X fxed n epeated samples IID 0, I. Specfcaton Poblems A. Unnecessay explanatoy vaables 1. OLS s no longe
Contact, information, consultations
 ontact, nfomaton, consultatons hemsty A Bldg; oom 07 phone: 058-347-769 cellula: 664 66 97 E-mal: wojtek_c@pg.gda.pl Offce hous: Fday, 9-0 a.m. A quote of the week (o camel of the week): hee s no expedence
ontact, nfomaton, consultatons hemsty A Bldg; oom 07 phone: 058-347-769 cellula: 664 66 97 E-mal: wojtek_c@pg.gda.pl Offce hous: Fday, 9-0 a.m. A quote of the week (o camel of the week): hee s no expedence
gravity r2,1 r2 r1 by m 2,1
 Gavtaton Many of the foundatons of classcal echancs wee fst dscoveed when phlosophes (ealy scentsts and atheatcans) ted to explan the oton of planets and stas. Newton s ost faous fo unfyng the oton of
Gavtaton Many of the foundatons of classcal echancs wee fst dscoveed when phlosophes (ealy scentsts and atheatcans) ted to explan the oton of planets and stas. Newton s ost faous fo unfyng the oton of
2/24/2014. The point mass. Impulse for a single collision The impulse of a force is a vector. The Center of Mass. System of particles
 /4/04 Chapte 7 Lnea oentu Lnea oentu of a Sngle Patcle Lnea oentu: p υ It s a easue of the patcle s oton It s a vecto, sla to the veloct p υ p υ p υ z z p It also depends on the ass of the object, sla
/4/04 Chapte 7 Lnea oentu Lnea oentu of a Sngle Patcle Lnea oentu: p υ It s a easue of the patcle s oton It s a vecto, sla to the veloct p υ p υ p υ z z p It also depends on the ass of the object, sla
MAXIMIN CLUSTERS FOR NEAR-REPLICATE REGRESSION LACK OF FIT TESTS. BY FORREST R. MILLER, JAMES W. NEILL AND BRIAN W. SHERFEY Kansas State University
 The Annals f Statstcs 1998, Vl. 6, N. 4, 14111433 MAXIMIN CLUSTERS FOR NEAR-REPLICATE REGRESSION LACK OF FIT TESTS BY FORREST R. MILLER, JAMES W. NEILL AND BRIAN W. SHERFEY Kansas State Unversty T assess
The Annals f Statstcs 1998, Vl. 6, N. 4, 14111433 MAXIMIN CLUSTERS FOR NEAR-REPLICATE REGRESSION LACK OF FIT TESTS BY FORREST R. MILLER, JAMES W. NEILL AND BRIAN W. SHERFEY Kansas State Unversty T assess
Application of Net Radiation Transfer Method for Optimization and Calculation of Reduction Heat Transfer, Using Spherical Radiation Shields
 Wld Applied Sciences Junal (4: 457-46, 00 ISSN 88-495 IDOSI Publicatins, 00 Applicatin f Net Radiatin Tansfe Methd f Optimizatin and Calculatin f Reductin Heat Tansfe, Using Spheical Radiatin Shields Seyflah
Wld Applied Sciences Junal (4: 457-46, 00 ISSN 88-495 IDOSI Publicatins, 00 Applicatin f Net Radiatin Tansfe Methd f Optimizatin and Calculatin f Reductin Heat Tansfe, Using Spheical Radiatin Shields Seyflah
ANALOG ELECTRONICS DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH
 24 ANALOG LTRONIS lass 5&6&7&8&9 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH 3.3.3 n-ase cnfguatn V V Rc I π π g g R V /p sgnal appled t. O/p taken f. ted t ac gnd. The hybd-π del pdes an accuate epesentatn f the sall-sgnal
24 ANALOG LTRONIS lass 5&6&7&8&9 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH 3.3.3 n-ase cnfguatn V V Rc I π π g g R V /p sgnal appled t. O/p taken f. ted t ac gnd. The hybd-π del pdes an accuate epesentatn f the sall-sgnal
Shakedown Analysis of a Composite Cylinder with a Cross-hole
 hakedwn nalyss f a Cmpste Cylnde wth a Css-hle Hafeng Chen *, Wehang Chen, Tanba L, James Ue Depatment f Mechancal Engneeng, Unvesty f tathclyde, Glasgw, G XJ, UK bstact: In ths study, bth the lwe and
hakedwn nalyss f a Cmpste Cylnde wth a Css-hle Hafeng Chen *, Wehang Chen, Tanba L, James Ue Depatment f Mechancal Engneeng, Unvesty f tathclyde, Glasgw, G XJ, UK bstact: In ths study, bth the lwe and
OBJECTIVE To investigate the parallel connection of R, L, and C. 1 Electricity & Electronics Constructor EEC470
 Assignment 7 Paallel Resnance OBJECTIVE T investigate the paallel cnnectin f R,, and C. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Qty Appaatus 1 Electicity & Electnics Cnstuct EEC470 1 Basic Electicity and Electnics Kit EEC471-1
Assignment 7 Paallel Resnance OBJECTIVE T investigate the paallel cnnectin f R,, and C. EQUIPMENT REQUIRED Qty Appaatus 1 Electicity & Electnics Cnstuct EEC470 1 Basic Electicity and Electnics Kit EEC471-1
The Minimum Universal Cost Flow in an Infeasible Flow Network
 Journal of Scences, Islamc Republc of Iran 17(2): 175-180 (2006) Unversty of Tehran, ISSN 1016-1104 http://jscencesutacr The Mnmum Unversal Cost Flow n an Infeasble Flow Network H Saleh Fathabad * M Bagheran
Journal of Scences, Islamc Republc of Iran 17(2): 175-180 (2006) Unversty of Tehran, ISSN 1016-1104 http://jscencesutacr The Mnmum Unversal Cost Flow n an Infeasble Flow Network H Saleh Fathabad * M Bagheran
