55:041 Electronic Circuits
|
|
|
- Jeffry Porter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 55:04 Electrnc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectns f Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty
2 Cnfguratn f Feedback mplfer S S S S fb Negate feedback S S S fb S S S S S β s the feedback transfer functn Implct ssumptns Made T s the lp gan f T Input sgnal s transmtted thrugh amplfer and nt thrugh β netwrk Output sgnal s transmtted thrugh β netwrk nly There are n ladng effects β netwrk des nt lad amplfer mplfer (wth/wthut β netwrk) des nt lad surce S S. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 2
3 β s the feedback transfer functn T s the lp gan = β f Prfund result: Clsed-lp gan s ndependent frm pen-lp gan, and we can cntrl the clsedlp gan wth the amunt f feedback. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 3
4 Example Hw gd s the /β apprxmatn? ssume pen-lp gan s = 0 5, and the clsed-lp gan s f = 50. Then f f / ssume pen-lp gan s =0 6, wth the same β f Practcally the same clsed-lp gan. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 4
5 Gan Senstty f d f d d f d Ddng bth sdes wth clsed-lp gan yelds d f f d 2 d d f f d Ths shws that the % change n clsed-lp gan s smaller, by a factr +β, than the % change n pen-lp gan.. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 5
6 Gan Senstty n engneer desgned a feedback amplfer β = , and = 0 5. By hw much des the clsed-lp gan change when the same feedback netwrk s used, but an amplfer wth pen-lp gan = 0 6 s used? d f f d % In ther wrds, the pen-lp gan changed by a factr 0, whle the clsed lp gan changed abut 0.5%.. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 6
7 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 7 Gan Versus Frequency ssume we can characterze the frequency respnse f an amplfer wth a sngle ple (ths s true fr many p-amps) H s s ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( s s s f H f s s. ) ( We assume the feedback netwrk s ndependent frm frequency The clsed-lp gan s smaller than the pen-lp gan by a factr (+β) The 3 db bandwdth s larger by a factr (+β)
8 Gan-Bandwdth Prduct Gan-bandwdth prduct f a feedback amplfer s cnstant We can ncrease bandwdth at the expense f gan. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 8
9 Nse Senstty n S N S N 00 0 n n S N S 0 N Cnclusns. Negate feedback can reduce nternallygenerated addte amplfer nse Same clsed-lp gan as preus amplfers 2 2 n S (mpre S/N) 2 2 N 2. Negate feedback per 00se wll 0. nt reduce S/N wth respect t external nse n n S N S N 000 S N. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 9
10 eductn f Nnlnear Dstrtn Open-Lp Gan Nn-lnear because the gan depends n the sgnal f Clsed-lp gan, β = Kruger Feedback & Stablty 0
11 dantages f Negate Feedback. Gan Senstty aratns n gan s reduced 2. Bandwdth Extensn larger than that f basc amplfer 3. Nse Senstty may ncrease S/N rat 4. eductn f Nnlnear Dstrtn 5. Cntrl f Impedance Leels nput and utput mpedances can be ncreased r decreased Dsadantages f Negate Feedback. Crcut Gan reduced cmpared t that f basc amplfer 2. Stablty pssblty that feedback crcut wll becme unstable and scllate at hgh frequences. Kruger Feedback & Stablty
12 Ideal Basc Feedback Cnfguratns Vltage mplfer Very Cmmn Current mplfer Transcnductance mplfer (ltage n-current ut) Cnerts current t ltage Transresstance mplfer (current n-ltage ut) Cnerts ltage t current. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 2
13 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 3
14 ecap: Cnfguratn f Feedback mplfer Negate feedback β s the feedback transfer functn Implct ssumptns Made T s the lp gan f T Input sgnal s transmtted thrugh amplfer and nt thrugh β netwrk Output sgnal s transmtted thrugh β netwrk nly There are n ladng effects β netwrk des nt lad amplfer mplfer (wth/wthut β netwrk) des nt lad surce. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 4
15 ecap-ideal Basc Feedback Cnfguratns Vltage mplfer Current mplfer Transcnductance mplfer (ltage n-current ut) Cnerts current t ltage Transresstance mplfer (current n-ltage ut) Cnerts ltage t current. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 5
16 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 6 Ideal Seres-Shunt Feedback f Vltage mplfer V I x Sample utput ltage and feed t back t nput Ideal: assume feedback netwrk des nt lad utput/nput 0 x x V I V x x I I x I x x f I V KVL: V x
17 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 7 Seres-Shunt Feedback Output esstance Hw d we determne utput resstance?. Turn ff ndependent surces 2. dd test ltage V x 3. See what test current I x flws 4. Determne V x /I x V V x x x V V I x x V V x V x x f I V KCL Fast
18 Equalent Crcut: Seres-Shunt Feedback Crcut f f f Useful t thnk f ths as the mprement factr BW f BW. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 8
19 Ideal Basc Feedback Cnfguratns Vltage mplfer Current mplfer Transcnductance mplfer (ltage n-current ut) Cnerts current t ltage Transresstance mplfer (current n-ltage ut) Cnerts ltage t current. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 9
20 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 20 Ideal Shunt-Seres Feedback f Current mplfer Sample utput current and feed t back t nput Ideal: assume feedback netwrk des nt lad utput, s that I s unaffected e I I I I I I I V I I f I V Feedback = Subtract, educe, Steal Frm Fast
21 Ideal Shunt-Seres Feedback Hw d we determne utput resstance?. Turn ff ndependent surces 2. dd test current I x utput 3. See what test current V x results 4. Determne V x /I x I I x V x I I x x x I I I x f V I x x Fast. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 2
22 Equalent Crcut: Shunt-Seres Feedback Crcut Current mplfer f Useful t thnk f ths as the mprement factr f f V I x x. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 22
23 ecap - Ideal Basc Feedback Cnfguratns Vltage mplfer Current mplfer Transcnductance mplfer (ltage n-current ut) Cnerts current t ltage Transresstance mplfer (current n-ltage ut) Cnerts ltage t current. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 23
24 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 24 Ideal Seres-Shunt Feedback f Vltage mplfer V I x Sample utput ltage and feed t back t nput Ideal: assume feedback netwrk des nt lad utput/nput x V I V x x x I I x I x x f I V Fast
25 Ideal Seres-Seres Feedback Crcut Sample utput current and feed t back t nput as a ltage Ideal: assume feedback netwrk des nt lad utput, s that I s unaffected Transcnductance mplfer (ltage n-current ut) gf g z g Unts f β Z? V/ Fast f? (neglect S ) I I I f I z z gv z I g I z g Cnerts utput current t a ltage. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 25
26 Ideal Seres-Seres Feedback Crcut I x V x Fast I I x I I x x f V x V x V V I z gv g x I x I z z x x g f? (neglect S ). Kruger Feedback & Stablty 26
27 Equalent Crcut: Seres-Seres Feedback Crcut Transcnductance mplfer (ltage n-current ut) f z g gf f z g Useful t thnk f ths as the mprement factr g z g. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 27
28 ecap-ideal Basc Feedback Cnfguratns Vltage mplfer Current mplfer Transcnductance mplfer (ltage n-current ut) Cnerts current t ltage Transresstance mplfer (current n-ltage ut) Cnerts ltage t current. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 28
29 Ideal Shunt-Shunt Feedback Crcut Sample utput ltage and feed t back t nput as a current Ideal: assume feedback netwrk des nt lad utput, s that V s unaffected Transresstance mplfer (current n-ltage ut) zf z g z f f g g z z Cnerts utput ltage t a current. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 29
30 Equalent Crcut: Shunt-Shunt Feedback Crcut Transresstance mplfer (current n-ltage ut) Useful t thnk f ths as the mprement factr f f g z z g. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 30 g z zf z
31 Summary f Feedback mplfer Functns. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 3
32 Ntes n Unts and Subscrpts Transresstance mplfer (current n-ltage ut) z V I Unts f resstance/mpedance (Z) I fb g I V fb Unts f cnductance (g) Cnerts utput ltage t current f z zf f g z g z g z Prduct shuld be dmensnless. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 32
33 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 33 Op-mp Seres-Shunt Feedback Crcut Seres-shunt feedback Input mpedance wll ncrease Output mpedance wll decrease Bandwdth wll ncrease Seres-shunt feedback Take sme f the utput ltage Feed t back n seres wth nput ssume ery large fb V V V f f 2 2 f 2 f
34 Op-mp Seres-Seres Feedback Transcnductance amplfer (ltage n, current ut) Feedback: ltage n seres wth nput ltage Feedback ltage s a functn f utput current E cnerts current t ltage Ideal p-amp, neglect base current: gf I V Seres-Seres Feedback E Z E. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 34
35 Op-mp Shunt-Seres Feedback f F /. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 35
36 Op-mp Shunt-Shunt Feedback Current-n, ltage-ut Transresstance Z Output ltage and 2 generate a feedback current that reduces current flwng nt p-amp Ideal p-amp, neglect nput current: g 2 Feedback reduces nput mpedance Shunt-Shunt Feedback. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 36
37 Dscrete Shunt-Seres Transstr Crcut. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 37
38 Dscrete Transstr Crcut Vltage ut Current n Nte that C2 E 2 E 2 s that ths crcut s really samplng the utput ltage Output ltage and F generate a feedback current that reduces current flwng nt amplfer Shunt-Seres Feedback. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 38
39 Dscrete Transstr Crcut Current-n, ltage-ut Transresstance Z Output ltage and F generate a feedback current that reduces current flwng nt transstr base Feedback reduces nput mpedance Shunt-Shunt Feedback g F. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 39
40 Multstage Feedback Crcut I fb I Output ltage and F generate a feedback current that reduces current flwng nt transstr base Feedback reduces nput mpedance Skp Shunt-Shunt Feedback. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 40
41 ecap-cnfguratn f Feedback mplfer Negate feedback β s the feedback transfer functn Implct ssumptns Made T s the lp gan f T Input sgnal s transmtted thrugh amplfer and nt thrugh β netwrk Output sgnal s transmtted thrugh β netwrk nly There are n ladng effects β netwrk des nt lad amplfer mplfer (wth/wthut β netwrk) des nt lad surce. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 4
42 Stablty ecall defntn f lp gan: T = β We assume β s nt a functn f frequency Hweer, the amplfer gan,, s a functn f frequency = (s), and we nrmally set s = jω, s = (jω). Thus T(jω) = β(jω). Clsed-lp gan: If T(jω) = -, then f f ( j) ( j) ( j) T( j) ( j) Instablty We can wrte T( j) T( j) Equalent cndtns fr stablty T( j) r less than 80 Gan margn: when the amplfer phase shft s80, hw much headrm/margn befre the gan s and the amplfer becmes unstable? Phase margn: when the amplfer gan s, hw much mre headrm/margn befre the phase shft s80 amplfer becmes unstable?. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 42
43 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 43 ja T 2 a ja T ja T 2 a ja T tan a a a tan tan jb ja K T 2 2 b a K jb ja K T ) ( tan ) ( tan tan tan b a b a Cmplex Number eew
44 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 44? ), ( tan 80 b b M 2 0 ) ( f j K f T 2 0 ) ( f j K f T?, 0 0 ) ( f f K f j K f T M b 80 tan f K
45 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty ) ( f j f j K f T ) ( f f K f T?, 0 0 ) ( f f f K f T Numercal slutn, tral-and-errr
46 (jω). Kruger Feedback & Stablty 46
47 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 47
48 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 48
49 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 49
50 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 50
51 Bde Plt: Phase and Gan Margns Lp Gan T(jω) = β ( jω) = 0 db gan margn 0 T( f ) 80 db f f 80 phase margn 80 ( f). Kruger Feedback & Stablty 5
52 Bde Plt: Phase and Gan Margns Stable r unstable?. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 52
53 Plttng Lp Gan If β s ndependent f frequency, then the lp gan T(jω) = β(jω) s smply a scaled ersn f the pen-lp gan.. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 53
54 Plttng Lp Gan If β s ndependent f frequency, then the lp gan T(jω) = β (jω)s smply a scaled ersn f the pen-lp gan. T( j) 20lg 20lg 20lg db 20lg 20lg We can determne the lp gan by graphcally subtractng a plt f 20lg(/β ) frm the pen lp Bde plt. pwerful aratn f the graphcal subtractn technque s the fllwng. Often 20lg s aalable n graphcal frm. It s ery cnenent t plt 20lg(/β ) n ths graph, and cnsder ths the new frequency axs.. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 54
55 Graphcal Subtractn n amplfer has pen-lp gan shwn belw. The amplfer s used n a feedback cnfguratn and the clsed-lp gan s 4,000. What are the phase- and gan margns? Ths s where lp gan s (0 db) 0 db New axs clsedlp 32 db clsedlp 4,000 20lg 72 db Gan margn s 32 db 87 Phase margn s 87 mplfer s stable. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 55
56 Graphcal Subtractn n amplfer has pen-lp gan shwn belw. The amplfer s used n a feedback cnfguratn and the clsed-lp gan s,000. What s the phase margn? clsedlp clsedlp,000 20lg 60 db Phase margn s 90. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 56
57 n amplfer has pen-lp gan shwn left. The amplfer s used n a feedback cnfguratn and the clsed-lp gan s 00. What are the phase- and gan margns? What s the clsed-lp bandwdth? 45 db clsedlp clsedlp 00 20lg 40 db 90 Phase margn s 90 Gan margn s 45 Bandwdth ~ MHz. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 57
58 Nyqust Stablty Crtern (Sectn 2.9.3) Nt Cered. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 58
59 eew: Lp Gan/Stablty N frequency dependence f ( s) ( s ) ( s) ( s) ( s) f ( s) ( s) T( s) Gan depends n frequency Gan and feedback depend n frequency T( s) T( j) T(jω) s a cmplex functn T( j) T( j) s j f ( j) ( j) T( j) If T(jω) = and the phase s 80 then T(jω) = - f ( j) ( j) Instablty. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 59
60 Lp Gan The term (+β) s used frequently n feedback amplfer analyss Lp gan T = β s mprtant n determnng stablty Step : Break the feedback lp Step 2: Termnate s that prts see same mpedances Step 3: Insert a test current/ltage and measure respnse: T = -V r /V t Can be used as an analyss technque, n SPICE, as well as n sme actual crcuts. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 60
61 V T V r t. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 6
62 p n Lp gan? t t 0. t n t n 20 p 3 n 60 t p 60, p n 3,000 t T t 00. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 62
63 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 63
64 mplfer has an pen-lp gan 5 0 f j 3 0 f j 0 5 Is amplfer stable f used s that clsed-lp gan - 00? clsed lp 00, 0.0 Lp gan T s T ( f ) (0.0) T( f ) 3 0 f j 3 0 f j 0 5 Stable? examne phase- and gan margns T ( f ) f tan tan f Sle fr f 62 Hw? f = 30 khz 8 phase margn => amplfer s stable. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 64
65 Bde Plt: Phase and Gan Margns Lp Gan T(jω) = β ( jω) = 0 db gan margn 0 T( f ) 80 db f f 80 phase margn 80 ( f). Kruger Feedback & Stablty 65
66 Bde Plt: Phase and Gan Margns Stable r unstable?. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 66
67 Plttng Lp Gan If β s ndependent f frequency, then the lp gan T(jω) = β s smply a scaled ersn f the pen-lp gan.. Kruger Feedback & Stablty 67
68 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 68
69 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 69
70 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 70
71 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 7
72 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 72
73 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 73
74 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 74
75 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 75
76 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 76
77 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 77
78 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 78
79 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 79
80 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 80
81 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 8
82 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 82
83 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 83
84 . Kruger Feedback & Stablty 84
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:04 Electronc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectons of Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Confguraton of Feedback mplfer Negate feedback β s the feedback transfer functon S o S S o o S S o f S S S S fb
55:04 Electronc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectons of Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Confguraton of Feedback mplfer Negate feedback β s the feedback transfer functon S o S S o o S S o f S S S S fb
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:04 Electronc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectons of Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Confguraton of Feedback mplfer S o S ε S o ( S β S ) o Negate feedback S S o + β β s the feedback transfer functon
55:04 Electronc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectons of Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Confguraton of Feedback mplfer S o S ε S o ( S β S ) o Negate feedback S S o + β β s the feedback transfer functon
Design of Analog Integrated Circuits
 Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts I. Amplfers Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts Fall 2012, Dr. Guxng Wang 1 Oerew Basc MOS amplfer structures Cmmn-Surce Amplfer Surce Fllwer Cmmn-Gate Amplfer Desgn f Analg
Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts I. Amplfers Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts Fall 2012, Dr. Guxng Wang 1 Oerew Basc MOS amplfer structures Cmmn-Surce Amplfer Surce Fllwer Cmmn-Gate Amplfer Desgn f Analg
Feedback Principle :-
 Feedback Prncple : Feedback amplfer s that n whch a part f the utput f the basc amplfer s returned back t the nput termnal and mxed up wth the nternal nput sgnal. The sub netwrks f feedback amplfer are:
Feedback Prncple : Feedback amplfer s that n whch a part f the utput f the basc amplfer s returned back t the nput termnal and mxed up wth the nternal nput sgnal. The sub netwrks f feedback amplfer are:
Introduction to Electronic circuits.
 Intrductn t Electrnc crcuts. Passve and Actve crcut elements. Capactrs, esstrs and Inductrs n AC crcuts. Vltage and current dvders. Vltage and current surces. Amplfers, and ther transfer characterstc.
Intrductn t Electrnc crcuts. Passve and Actve crcut elements. Capactrs, esstrs and Inductrs n AC crcuts. Vltage and current dvders. Vltage and current surces. Amplfers, and ther transfer characterstc.
CHAPTER 3: FEEDBACK. Dr. Wan Mahani Hafizah binti Wan Mahmud
 CHPTER 3: FEEDBCK Dr. Wan Mahan Hafzah bnt Wan Mahmud Feedback ntrductn Types f Feedback dvantages, Characterstcs and effect f Negatve Feedback mplfers Crcuts wth negatve feedback Pstve feedback and Oscllatr
CHPTER 3: FEEDBCK Dr. Wan Mahan Hafzah bnt Wan Mahmud Feedback ntrductn Types f Feedback dvantages, Characterstcs and effect f Negatve Feedback mplfers Crcuts wth negatve feedback Pstve feedback and Oscllatr
Circuits Op-Amp. Interaction of Circuit Elements. Quick Check How does closing the switch affect V o and I o?
 Crcuts Op-Amp ENGG1015 1 st Semester, 01 Interactn f Crcut Elements Crcut desgn s cmplcated by nteractns amng the elements. Addng an element changes vltages & currents thrughut crcut. Example: clsng a
Crcuts Op-Amp ENGG1015 1 st Semester, 01 Interactn f Crcut Elements Crcut desgn s cmplcated by nteractns amng the elements. Addng an element changes vltages & currents thrughut crcut. Example: clsng a
Linear Amplifiers and OpAmps
 Lnear Amplfers and OpAmps eferences: Barbw (pp 7-80), Hayes & Hrwtz (pp 63-40), zzn (Chapter ) Amplfers are tw-prt netwrks n whch the utput ltage r current s drectly prprtnal t ether nput ltage r current.
Lnear Amplfers and OpAmps eferences: Barbw (pp 7-80), Hayes & Hrwtz (pp 63-40), zzn (Chapter ) Amplfers are tw-prt netwrks n whch the utput ltage r current s drectly prprtnal t ether nput ltage r current.
The three major operations done on biological signals using Op-Amp:
 The three majr peratns dne n blgcal sgnals usng Op-Amp: ) Amplcatns and Attenuatns 2) DC settng: add r subtract a DC 3) Shape ts requency cntent: Flterng Ideal Op-Amp Mst belectrc sgnals are small and
The three majr peratns dne n blgcal sgnals usng Op-Amp: ) Amplcatns and Attenuatns 2) DC settng: add r subtract a DC 3) Shape ts requency cntent: Flterng Ideal Op-Amp Mst belectrc sgnals are small and
PHYSICS 536 Experiment 12: Applications of the Golden Rules for Negative Feedback
 PHYSICS 536 Experment : Applcatns f the Glden Rules fr Negatve Feedback The purpse f ths experment s t llustrate the glden rules f negatve feedback fr a varety f crcuts. These cncepts permt yu t create
PHYSICS 536 Experment : Applcatns f the Glden Rules fr Negatve Feedback The purpse f ths experment s t llustrate the glden rules f negatve feedback fr a varety f crcuts. These cncepts permt yu t create
EE 221 Practice Problems for the Final Exam
 EE 1 Practce Prblems fr the Fnal Exam 1. The netwrk functn f a crcut s 1.5 H. ω 1+ j 500 Ths table recrds frequency respnse data fr ths crcut. Fll n the blanks n the table:. The netwrk functn f a crcut
EE 1 Practce Prblems fr the Fnal Exam 1. The netwrk functn f a crcut s 1.5 H. ω 1+ j 500 Ths table recrds frequency respnse data fr ths crcut. Fll n the blanks n the table:. The netwrk functn f a crcut
55:141 Advanced Circuit Techniques Two-Port Theory
 55:4 Adanced Crcut Technques Two-Port Theory Materal: Lecture Notes A. Kruger 55:4: Adanced Crcut Technques The Unersty of Iowa, 03 Two-Port Theory, Slde What Are Two-Ports? Basc dea: replace a complex
55:4 Adanced Crcut Technques Two-Port Theory Materal: Lecture Notes A. Kruger 55:4: Adanced Crcut Technques The Unersty of Iowa, 03 Two-Port Theory, Slde What Are Two-Ports? Basc dea: replace a complex
III. Operational Amplifiers
 III. Operatnal Amplfers Amplfers are tw-prt netwrks n whch the utput vltage r current s drectly prprtnal t ether nput vltage r current. Fur dfferent knds f amplfers ext: ltage amplfer: Current amplfer:
III. Operatnal Amplfers Amplfers are tw-prt netwrks n whch the utput vltage r current s drectly prprtnal t ether nput vltage r current. Fur dfferent knds f amplfers ext: ltage amplfer: Current amplfer:
55:141 Advanced Circuit Techniques Two-Port Theory
 55:4 Adanced Crcut Technques Two-Port Theory Materal: Lecture Notes A. Kruger 55:4: Adanced Crcut Technques The Unersty of Iowa, 205 Two-Port Theory, Slde Two-Port Networks Note, the BJT s all are hghly
55:4 Adanced Crcut Technques Two-Port Theory Materal: Lecture Notes A. Kruger 55:4: Adanced Crcut Technques The Unersty of Iowa, 205 Two-Port Theory, Slde Two-Port Networks Note, the BJT s all are hghly
ME2142/ME2142E Feedback Control Systems. Modelling of Physical Systems The Transfer Function
 Mdellng Physcal Systems The Transer Functn Derental Equatns U Plant Y In the plant shwn, the nput u aects the respnse the utput y. In general, the dynamcs ths respnse can be descrbed by a derental equatn
Mdellng Physcal Systems The Transer Functn Derental Equatns U Plant Y In the plant shwn, the nput u aects the respnse the utput y. In general, the dynamcs ths respnse can be descrbed by a derental equatn
Section I5: Feedback in Operational Amplifiers
 Sectin I5: eedback in Operatinal mplifiers s discussed earlier, practical p-amps hae a high gain under dc (zer frequency) cnditins and the gain decreases as frequency increases. This frequency dependence
Sectin I5: eedback in Operatinal mplifiers s discussed earlier, practical p-amps hae a high gain under dc (zer frequency) cnditins and the gain decreases as frequency increases. This frequency dependence
The Operational Amplifier and Application
 Intrductn t Electrnc Crcuts: A Desgn Apprach Jse Sla-Martnez and Marn Onabaj The Operatnal Amplfer and Applcatn The peratnal ltage amplfer (mre cmmnly referred t as peratnal amplfer) s ne f the mst useful
Intrductn t Electrnc Crcuts: A Desgn Apprach Jse Sla-Martnez and Marn Onabaj The Operatnal Amplfer and Applcatn The peratnal ltage amplfer (mre cmmnly referred t as peratnal amplfer) s ne f the mst useful
Is current gain generally significant in FET amplifiers? Why or why not? Substitute each capacitor with a
 FET Sall Snal Mdband Mdel Ntatn: C arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth an uppercase subscrpt. AC arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth a lwercase subscrpt. Phasr ntatn wll be used when
FET Sall Snal Mdband Mdel Ntatn: C arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth an uppercase subscrpt. AC arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth a lwercase subscrpt. Phasr ntatn wll be used when
Diodes Waveform shaping Circuits. Sedra & Smith (6 th Ed): Sec. 4.5 & 4.6 Sedra & Smith (5 th Ed): Sec. 3.5 & 3.6
 des Waefrm shapng Cruts Sedra & Smth (6 th Ed): Se. 4.5 & 4.6 Sedra & Smth (5 th Ed): Se. 3.5 & 3.6 Tw-prt netwrks as buldng blks Reall: Transfer funtn f a tw-prt netwrk an be fund by slng ths rut ne.
des Waefrm shapng Cruts Sedra & Smth (6 th Ed): Se. 4.5 & 4.6 Sedra & Smth (5 th Ed): Se. 3.5 & 3.6 Tw-prt netwrks as buldng blks Reall: Transfer funtn f a tw-prt netwrk an be fund by slng ths rut ne.
Lecture 2 Feedback Amplifier
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w-pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un-lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse-Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83hkn 3 Feedback mples w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Introduction of Two Port Network Negative Feedback (Uni lateral Case) Feedback Topology Analysis of feedback applications
 Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w Pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83h 3 Feedback w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Lectue Feedback mple ntductn w Pt Netwk Negatve Feedback Un lateal Case Feedback plg nalss eedback applcatns Clse Lp Gan nput/output esstances e:83h 3 Feedback w-pt Netwk z-paametes Open-Ccut mpedance
Diodes Waveform shaping Circuits
 des Waefrm shapng Cruts Leture ntes: page 2-2 t 2-31 Sedra & Smth (6 th Ed): Se. 4.5 & 4.6 Sedra & Smth (5 th Ed): Se. 3.5 & 3.6 F. Najmabad, ECE65, Wnter 212 Tw-prt netwrks as buldng blks Reall: Transfer
des Waefrm shapng Cruts Leture ntes: page 2-2 t 2-31 Sedra & Smth (6 th Ed): Se. 4.5 & 4.6 Sedra & Smth (5 th Ed): Se. 3.5 & 3.6 F. Najmabad, ECE65, Wnter 212 Tw-prt netwrks as buldng blks Reall: Transfer
OP AMP CHARACTERISTICS
 O AM CHAACTESTCS Static p amp limitatins EFEENCE: Chapter 5 textbk (ESS) EOS CAUSED BY THE NUT BAS CUENT AND THE NUT OFFSET CUENT Op Amp t functin shuld have fr the input terminals a DC path thrugh which
O AM CHAACTESTCS Static p amp limitatins EFEENCE: Chapter 5 textbk (ESS) EOS CAUSED BY THE NUT BAS CUENT AND THE NUT OFFSET CUENT Op Amp t functin shuld have fr the input terminals a DC path thrugh which
CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONVERTER
 70 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONERTER 3.1 Intrductn The KY Bst Cnverter s a recent nventn made by K.I.Hwu et. al., (2007), (2009a), (2009b), (2009c), (2010) n the nn-slated DC DC cnverter segment,
70 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONERTER 3.1 Intrductn The KY Bst Cnverter s a recent nventn made by K.I.Hwu et. al., (2007), (2009a), (2009b), (2009c), (2010) n the nn-slated DC DC cnverter segment,
Waveshapping Circuits and Data Converters. Lesson #17 Comparators and Schmitt Triggers Section BME 373 Electronics II J.
 Waeshappg Crcuts and Data Cnerters Lessn #7 Cmparatrs and Schmtt Trggers Sectn. BME 7 Electrncs II 0 Waeshappg Crcuts and Data Cnerters Cmparatrs and Schmtt Trggers Astable Multbratrs and Tmers ectfers,
Waeshappg Crcuts and Data Cnerters Lessn #7 Cmparatrs and Schmtt Trggers Sectn. BME 7 Electrncs II 0 Waeshappg Crcuts and Data Cnerters Cmparatrs and Schmtt Trggers Astable Multbratrs and Tmers ectfers,
EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design
 EE C45 ME C8 Introducton to MEM Desgn Fall 7 Prof. Clark T.C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrcal Engneerng & Computer cences Unersty of Calforna at Berkeley Berkeley, C 947 Dscusson: eew of Op mps EE C45: Introducton
EE C45 ME C8 Introducton to MEM Desgn Fall 7 Prof. Clark T.C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrcal Engneerng & Computer cences Unersty of Calforna at Berkeley Berkeley, C 947 Dscusson: eew of Op mps EE C45: Introducton
Exercises for Frequency Response. ECE 102, Winter 2011, F. Najmabadi
 Eercses r Frequency espnse EE 0, Wnter 0, F. Najabad Eercse : A Mdy the crcut belw t nclude a dnant ple at 00 Mz ( 00 Ω, k, k, / 00 Ω, λ 0, and nre nternal capactances the MOS. pute the dnant ple n the
Eercses r Frequency espnse EE 0, Wnter 0, F. Najabad Eercse : A Mdy the crcut belw t nclude a dnant ple at 00 Mz ( 00 Ω, k, k, / 00 Ω, λ 0, and nre nternal capactances the MOS. pute the dnant ple n the
Bipolar-Junction (BJT) transistors
 Bplar-Junctn (BJT) transstrs References: Hayes & Hrwtz (pp 84-4), Rzzn (chapters 8 & 9) A bplar junctn transstr s frmed by jnng three sectns f semcnductrs wth alternately dfferent dpngs. The mddle sectn
Bplar-Junctn (BJT) transstrs References: Hayes & Hrwtz (pp 84-4), Rzzn (chapters 8 & 9) A bplar junctn transstr s frmed by jnng three sectns f semcnductrs wth alternately dfferent dpngs. The mddle sectn
Chapter 7. Systems 7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF LIQUID LEVEL SYSTEMS. Steady State Flow. A. Bazoune
 Chapter 7 Flud Systems and Thermal Systems 7.1 INTODUCTION A. Bazune A flud system uses ne r mre fluds t acheve ts purpse. Dampers and shck absrbers are eamples f flud systems because they depend n the
Chapter 7 Flud Systems and Thermal Systems 7.1 INTODUCTION A. Bazune A flud system uses ne r mre fluds t acheve ts purpse. Dampers and shck absrbers are eamples f flud systems because they depend n the
Technote 6. Op Amp Definitions. April 1990 Revised 11/22/02. Tim J. Sobering SDE Consulting
 Technte 6 prl 990 Resed /22/02 Op mp Dentns Tm J. Sberng SDE Cnsultng sdecnsultng@pbx.cm 990 Tm J. Sberng. ll rghts resered. Op mp Dentns Pge 2 Op mp Dentns Ths Technte summrzes the bsc pertnl mpler dentns
Technte 6 prl 990 Resed /22/02 Op mp Dentns Tm J. Sberng SDE Cnsultng sdecnsultng@pbx.cm 990 Tm J. Sberng. ll rghts resered. Op mp Dentns Pge 2 Op mp Dentns Ths Technte summrzes the bsc pertnl mpler dentns
Revision: August 19, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 .7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
.7.4: Direct frequency dmain circuit analysis Revisin: August 9, 00 5 E Main Suite D Pullman, WA 9963 (509) 334 6306 ice and Fax Overview n chapter.7., we determined the steadystate respnse f electrical
Lecture 20a. Circuit Topologies and Techniques: Opamps
 Lecture a Circuit Tplgies and Techniques: Opamps In this lecture yu will learn: Sme circuit tplgies and techniques Intrductin t peratinal amplifiers Differential mplifier IBIS1 I BIS M VI1 vi1 Vi vi I
Lecture a Circuit Tplgies and Techniques: Opamps In this lecture yu will learn: Sme circuit tplgies and techniques Intrductin t peratinal amplifiers Differential mplifier IBIS1 I BIS M VI1 vi1 Vi vi I
Chapter II Circuit Analysis Fundamentals
 Chapter II Crcut nalyss Fundamentals Frm a desgn engneer s perspecte, t s mre releant t understand a crcut s peratn and lmtatns than t fnd eact mathematcal epressns r eact numercal slutns. Precse results
Chapter II Crcut nalyss Fundamentals Frm a desgn engneer s perspecte, t s mre releant t understand a crcut s peratn and lmtatns than t fnd eact mathematcal epressns r eact numercal slutns. Precse results
FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERS. v i or v s v 0
 FEEDBCK MPLIFIERS Feedback n mplers FEEDBCK IS THE PROCESS OF FEEDING FRCTION OF OUTPUT ENERGY (VOLTGE OR CURRENT) BCK TO THE INPUT CIRCUIT. THE CIRCUIT EMPLOYED FOR THIS PURPOSE IS CLLED FEEDBCK NETWORK.
FEEDBCK MPLIFIERS Feedback n mplers FEEDBCK IS THE PROCESS OF FEEDING FRCTION OF OUTPUT ENERGY (VOLTGE OR CURRENT) BCK TO THE INPUT CIRCUIT. THE CIRCUIT EMPLOYED FOR THIS PURPOSE IS CLLED FEEDBCK NETWORK.
Section 3: Detailed Solutions of Word Problems Unit 1: Solving Word Problems by Modeling with Formulas
 Sectn : Detaled Slutns f Wrd Prblems Unt : Slvng Wrd Prblems by Mdelng wth Frmulas Example : The factry nvce fr a mnvan shws that the dealer pad $,5 fr the vehcle. If the stcker prce f the van s $5,, hw
Sectn : Detaled Slutns f Wrd Prblems Unt : Slvng Wrd Prblems by Mdelng wth Frmulas Example : The factry nvce fr a mnvan shws that the dealer pad $,5 fr the vehcle. If the stcker prce f the van s $5,, hw
Faculty of Engineering
 Faculty f Engneerng DEPARTMENT f ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING EEE 223 Crcut Thery I Instructrs: M. K. Uygurğlu E. Erdl Fnal EXAMINATION June 20, 2003 Duratn : 120 mnutes Number f Prblems: 6 Gd
Faculty f Engneerng DEPARTMENT f ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING EEE 223 Crcut Thery I Instructrs: M. K. Uygurğlu E. Erdl Fnal EXAMINATION June 20, 2003 Duratn : 120 mnutes Number f Prblems: 6 Gd
ANALOG ELECTRONICS DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH
 24 ANALOG LTRONIS lass 5&6&7&8&9 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH 3.3.3 n-ase cnfguatn V V Rc I π π g g R V /p sgnal appled t. O/p taken f. ted t ac gnd. The hybd-π del pdes an accuate epesentatn f the sall-sgnal
24 ANALOG LTRONIS lass 5&6&7&8&9 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH 3.3.3 n-ase cnfguatn V V Rc I π π g g R V /p sgnal appled t. O/p taken f. ted t ac gnd. The hybd-π del pdes an accuate epesentatn f the sall-sgnal
ANALOG ELECTRONICS 1 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH
 24 ANALOG LTRONIS TUTORIAL DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH . 0 8kΩ Gen, Y β β 00 T F 26, 00 0.7 (a)deterne the dc ltages at the 3 X ternals f the JT (,, ). 0kΩ Z (b) Deterne g,r π and r? (c) Deterne the ltage gan
24 ANALOG LTRONIS TUTORIAL DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH . 0 8kΩ Gen, Y β β 00 T F 26, 00 0.7 (a)deterne the dc ltages at the 3 X ternals f the JT (,, ). 0kΩ Z (b) Deterne g,r π and r? (c) Deterne the ltage gan
IGEE 401 Power Electronic Systems. Solution to Midterm Examination Fall 2004
 Jós, G GEE 401 wer Electrnc Systems Slutn t Mdterm Examnatn Fall 2004 Specal nstructns: - Duratn: 75 mnutes. - Materal allwed: a crb sheet (duble sded 8.5 x 11), calculatr. - Attempt all questns. Make
Jós, G GEE 401 wer Electrnc Systems Slutn t Mdterm Examnatn Fall 2004 Specal nstructns: - Duratn: 75 mnutes. - Materal allwed: a crb sheet (duble sded 8.5 x 11), calculatr. - Attempt all questns. Make
FE REVIEW OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS)( ) 8/25/2010
 FE REVEW OPERATONAL AMPLFERS (OP-AMPS)( ) 1 The Op-amp 2 An op-amp has two nputs and one output. Note the op-amp below. The termnal labeled l wth the (-) sgn s the nvertng nput and the nput labeled wth
FE REVEW OPERATONAL AMPLFERS (OP-AMPS)( ) 1 The Op-amp 2 An op-amp has two nputs and one output. Note the op-amp below. The termnal labeled l wth the (-) sgn s the nvertng nput and the nput labeled wth
CHAPTER 11. Solutions for Exercises. (b) An inverting amplifier has negative gain. Thus L
 CHPTE Slutn fr Exerce E. (a nnnertng amplfer ha pte gan. Thu ( t ( t 50 ( t 5.0 n(000πt (b n nertng amplfer ha negate gan. Thu ( t ( t 50 ( t 5.0 n(000πt E. V V 75 500 + 5+ 75 c 75 V 000 75 500 V + + 500
CHPTE Slutn fr Exerce E. (a nnnertng amplfer ha pte gan. Thu ( t ( t 50 ( t 5.0 n(000πt (b n nertng amplfer ha negate gan. Thu ( t ( t 50 ( t 5.0 n(000πt E. V V 75 500 + 5+ 75 c 75 V 000 75 500 V + + 500
Wp/Lmin. Wn/Lmin 2.5V
 UNIVERITY OF CALIFORNIA Cllege f Engneerng Department f Electrcal Engneerng and Cmputer cences Andre Vladmrescu Hmewrk #7 EEC Due Frday, Aprl 8 th, pm @ 0 Cry Prblem #.5V Wp/Lmn 0.0V Wp/Lmn n ut Wn/Lmn.5V
UNIVERITY OF CALIFORNIA Cllege f Engneerng Department f Electrcal Engneerng and Cmputer cences Andre Vladmrescu Hmewrk #7 EEC Due Frday, Aprl 8 th, pm @ 0 Cry Prblem #.5V Wp/Lmn 0.0V Wp/Lmn n ut Wn/Lmn.5V
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERS
 Department o Electrcal and Computer Engneerng UNIT I EII FEEDBCK MPLIFIES porton the output sgnal s ed back to the nput o the ampler s called Feedback mpler. Feedback Concept: block dagram o an ampler
Department o Electrcal and Computer Engneerng UNIT I EII FEEDBCK MPLIFIES porton the output sgnal s ed back to the nput o the ampler s called Feedback mpler. Feedback Concept: block dagram o an ampler
A New Modeling Method and Controller Design for a DC DC Zeta Converter
 Electrcal Engneerng esearch (EE), Vlume, 5 A New Mdelng Methd and ntrller esgn fr a Zeta nerter Elshan aaran Hagh, Ebrahm Babae *, ela Mhammadan Faculty f Electrcal and mputer Engneerng, Unersty f Tabrz,
Electrcal Engneerng esearch (EE), Vlume, 5 A New Mdelng Methd and ntrller esgn fr a Zeta nerter Elshan aaran Hagh, Ebrahm Babae *, ela Mhammadan Faculty f Electrcal and mputer Engneerng, Unersty f Tabrz,
PT326 PROCESS TRAINER
 PT326 PROCESS TRAINER 1. Descrptn f the Apparatus PT 326 Prcess Traner The PT 326 Prcess Traner mdels cmmn ndustral stuatns n whch temperature cntrl s requred n the presence f transprt delays and transfer
PT326 PROCESS TRAINER 1. Descrptn f the Apparatus PT 326 Prcess Traner The PT 326 Prcess Traner mdels cmmn ndustral stuatns n whch temperature cntrl s requred n the presence f transprt delays and transfer
Copyright Paul Tobin 63
 DT, Kevin t. lectric Circuit Thery DT87/ Tw-Prt netwrk parameters ummary We have seen previusly that a tw-prt netwrk has a pair f input terminals and a pair f utput terminals figure. These circuits were
DT, Kevin t. lectric Circuit Thery DT87/ Tw-Prt netwrk parameters ummary We have seen previusly that a tw-prt netwrk has a pair f input terminals and a pair f utput terminals figure. These circuits were
CURRENT FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERs
 Abstract-The need r hgh speed, wdeband amplers s the drng rce behnd the deelpment the Current Feedback Ampler (CFA). The CFA has sgncant adantages er cnentnal amplers n terms slew rate perrmance and nherently
Abstract-The need r hgh speed, wdeband amplers s the drng rce behnd the deelpment the Current Feedback Ampler (CFA). The CFA has sgncant adantages er cnentnal amplers n terms slew rate perrmance and nherently
Schedule. ECEN 301 Discussion #17 Operational Amplifiers 1. Date Day Class No. Lab Due date. Exam
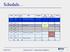 chedule Date Day Class N. Title Chapters HW Due date 29 Oct Wed 17 Operatinal mplifiers 8.1 8.2 Lab Due date Exam 30 Oct Thu 31 Oct ri ecitatin HW 7 1 N at 2 N un 3 N Mn 18 Operatinal mplifiers 8.3 8.4
chedule Date Day Class N. Title Chapters HW Due date 29 Oct Wed 17 Operatinal mplifiers 8.1 8.2 Lab Due date Exam 30 Oct Thu 31 Oct ri ecitatin HW 7 1 N at 2 N un 3 N Mn 18 Operatinal mplifiers 8.3 8.4
Conduction Heat Transfer
 Cnductn Heat Transfer Practce prblems A steel ppe f cnductvty 5 W/m-K has nsde and utsde surface temperature f C and 6 C respectvely Fnd the heat flw rate per unt ppe length and flux per unt nsde and per
Cnductn Heat Transfer Practce prblems A steel ppe f cnductvty 5 W/m-K has nsde and utsde surface temperature f C and 6 C respectvely Fnd the heat flw rate per unt ppe length and flux per unt nsde and per
Module B3. VLoad = = V S V LN
 Mdule B Prblem The -hase lads are cnnected n arallel. One s a urely resste lad cnnected n wye. t cnsumes 00kW. The secnd s a urely nducte 00kR lad cnnected n wye. The thrd s a urely caacte 00kR lad cnnected
Mdule B Prblem The -hase lads are cnnected n arallel. One s a urely resste lad cnnected n wye. t cnsumes 00kW. The secnd s a urely nducte 00kR lad cnnected n wye. The thrd s a urely caacte 00kR lad cnnected
The two main types of FETs are the junction field effect transistor (JFET) and the metal oxide field effect transistor (MOSFET).
 Mcrelectrncs Chapter three: Feld Effect Transstr sall snal analyss Intrductn: Feld-effect transstr aplfers prde an excellent ltae an wth the added feature f hh nput pedance. They are als lw-pwercnsuptn
Mcrelectrncs Chapter three: Feld Effect Transstr sall snal analyss Intrductn: Feld-effect transstr aplfers prde an excellent ltae an wth the added feature f hh nput pedance. They are als lw-pwercnsuptn
Transfer Characteristic
 Eeld-Effect Transstors (FETs 3.3 The CMS Common-Source Amplfer Transfer Characterstc Electronc Crcuts, Dept. of Elec. Eng., The Chnese Unersty of Hong Kong, Prof. K.-L. Wu Lesson 8&9 Eeld-Effect Transstors
Eeld-Effect Transstors (FETs 3.3 The CMS Common-Source Amplfer Transfer Characterstc Electronc Crcuts, Dept. of Elec. Eng., The Chnese Unersty of Hong Kong, Prof. K.-L. Wu Lesson 8&9 Eeld-Effect Transstors
Common Gate Amplifier
 mmn Gate Ampler Fure (a) shs a cmmn ate ampler th deal current surce lad. Fure (b) shs the deal current surce mplemented by PMOS th cnstant ate t surce vltae. DD DD G M G M G M (a) (b) Fure. mmn ate ampler.
mmn Gate Ampler Fure (a) shs a cmmn ate ampler th deal current surce lad. Fure (b) shs the deal current surce mplemented by PMOS th cnstant ate t surce vltae. DD DD G M G M G M (a) (b) Fure. mmn ate ampler.
Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design. NMOS Common-Source Circuit. NMOS Common-Source Circuit 10/15/2013. In this chapter, we will:
 Mcrelectrncs Crcut Analyss and Desn Dnald A. Neaen Chapter 4 Basc FET Aplfers In ths chapter, we wll: Inestate a snle-transstr crcut that can aplfy a sall, te-aryn nput snal Deelp sall-snal dels that are
Mcrelectrncs Crcut Analyss and Desn Dnald A. Neaen Chapter 4 Basc FET Aplfers In ths chapter, we wll: Inestate a snle-transstr crcut that can aplfy a sall, te-aryn nput snal Deelp sall-snal dels that are
Part III Lectures Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) and Circuits
 Part III Lecture 5-8 Feld-Effect Trantr (FET) and Crcut Unverty f Technlgy Feld-Effect Trantr (FET) Electrcal and Electrnc Engneerng epartment Lecture Ffteen - Page f 8 ecnd Year, Electrnc I, 2009-200
Part III Lecture 5-8 Feld-Effect Trantr (FET) and Crcut Unverty f Technlgy Feld-Effect Trantr (FET) Electrcal and Electrnc Engneerng epartment Lecture Ffteen - Page f 8 ecnd Year, Electrnc I, 2009-200
T-model: - + v o. v i. i o. v e. R i
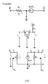 T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
CTN 2/23/16. EE 247B/ME 218: Introduction to MEMS Design Lecture 11m2: Mechanics of Materials. Copyright 2016 Regents of the University of California
 Vlume Change fr a Unaxal Stress Istrpc lastcty n 3D Istrpc = same n all drectns The cmplete stress-stran relatns fr an strpc elastc Stresses actng n a dfferental vlume element sld n 3D: (.e., a generalzed
Vlume Change fr a Unaxal Stress Istrpc lastcty n 3D Istrpc = same n all drectns The cmplete stress-stran relatns fr an strpc elastc Stresses actng n a dfferental vlume element sld n 3D: (.e., a generalzed
Edexcel GCSE Physics
 Edexcel GCSE Physics Tpic 10: Electricity and circuits Ntes (Cntent in bld is fr Higher Tier nly) www.pmt.educatin The Structure f the Atm Psitively charged nucleus surrunded by negatively charged electrns
Edexcel GCSE Physics Tpic 10: Electricity and circuits Ntes (Cntent in bld is fr Higher Tier nly) www.pmt.educatin The Structure f the Atm Psitively charged nucleus surrunded by negatively charged electrns
CIRCUIT ANALYSIS II Chapter 1 Sinusoidal Alternating Waveforms and Phasor Concept. Sinusoidal Alternating Waveforms and
 U ANAYSS hapter Snusdal Alternatng Wavefrs and Phasr ncept Snusdal Alternatng Wavefrs and Phasr ncept ONNS. Snusdal Alternatng Wavefrs.. General Frat fr the Snusdal ltage & urrent.. Average alue..3 ffectve
U ANAYSS hapter Snusdal Alternatng Wavefrs and Phasr ncept Snusdal Alternatng Wavefrs and Phasr ncept ONNS. Snusdal Alternatng Wavefrs.. General Frat fr the Snusdal ltage & urrent.. Average alue..3 ffectve
SIMULATION OF THREE PHASE THREE LEG TRANSFORMER BEHAVIOR UNDER DIFFERENT VOLTAGE SAG TYPES
 SIMULATION OF THREE PHASE THREE LEG TRANSFORMER BEHAVIOR UNDER DIFFERENT VOLTAGE SAG TYPES Mhammadreza Dlatan Alreza Jallan Department f Electrcal Engneerng, Iran Unversty f scence & Technlgy (IUST) e-mal:
SIMULATION OF THREE PHASE THREE LEG TRANSFORMER BEHAVIOR UNDER DIFFERENT VOLTAGE SAG TYPES Mhammadreza Dlatan Alreza Jallan Department f Electrcal Engneerng, Iran Unversty f scence & Technlgy (IUST) e-mal:
EE 204 Lecture 25 More Examples on Power Factor and the Reactive Power
 EE 204 Lecture 25 Mre Examples n Pwer Factr and the Reactve Pwer The pwer factr has been defned n the prevus lecture wth an example n pwer factr calculatn. We present tw mre examples n ths lecture. Example
EE 204 Lecture 25 Mre Examples n Pwer Factr and the Reactve Pwer The pwer factr has been defned n the prevus lecture wth an example n pwer factr calculatn. We present tw mre examples n ths lecture. Example
Two Port Characterizations
 lectronc Crcuts Two Port Characterzatons Contents Input and output resstances Two port networks Models Prof. C.K. Tse: -port networks Impedances and loadng effects Voltage amplfers R s R out smaller the
lectronc Crcuts Two Port Characterzatons Contents Input and output resstances Two port networks Models Prof. C.K. Tse: -port networks Impedances and loadng effects Voltage amplfers R s R out smaller the
Lab 11 LRC Circuits, Damped Forced Harmonic Motion
 Physics 6 ab ab 11 ircuits, Damped Frced Harmnic Mtin What Yu Need T Knw: The Physics OK this is basically a recap f what yu ve dne s far with circuits and circuits. Nw we get t put everything tgether
Physics 6 ab ab 11 ircuits, Damped Frced Harmnic Mtin What Yu Need T Knw: The Physics OK this is basically a recap f what yu ve dne s far with circuits and circuits. Nw we get t put everything tgether
T(s) 1+ T(s) 2. Phase Margin Test for T(s) a. Unconditionally Stable φ m = 90 o for 1 pole T(s) b. Conditionally Stable Case 1.
 Lecture 49 Danger f Instability/Oscillatin When Emplying Feedback In PWM Cnverters A. Guessing Clsed Lp Stability Frm Open Lp Frequency Respnse Data. T(s) versus T(s) + T(s) 2. Phase Margin Test fr T(s)
Lecture 49 Danger f Instability/Oscillatin When Emplying Feedback In PWM Cnverters A. Guessing Clsed Lp Stability Frm Open Lp Frequency Respnse Data. T(s) versus T(s) + T(s) 2. Phase Margin Test fr T(s)
Lecture 12. Heat Exchangers. Heat Exchangers Chee 318 1
 Lecture 2 Heat Exchangers Heat Exchangers Chee 38 Heat Exchangers A heat exchanger s used t exchange heat between tw fluds f dfferent temperatures whch are separated by a sld wall. Heat exchangers are
Lecture 2 Heat Exchangers Heat Exchangers Chee 38 Heat Exchangers A heat exchanger s used t exchange heat between tw fluds f dfferent temperatures whch are separated by a sld wall. Heat exchangers are
Chapter 10 Diodes. 1. Understand diode operation and select diodes for various applications.
 Chapter 10 des 1. Understand dde peratn and select ddes fr arus applcatns. 2. nalyze nnlnear crcuts usng the graphcal lad-lne technque. 3. nalyze and desgn smple ltage-regulatr crcuts. 4. Sle crcuts usng
Chapter 10 des 1. Understand dde peratn and select ddes fr arus applcatns. 2. nalyze nnlnear crcuts usng the graphcal lad-lne technque. 3. nalyze and desgn smple ltage-regulatr crcuts. 4. Sle crcuts usng
Synchronous Motor V-Curves
 Synchrnus Mtr V-Curves 1 Synchrnus Mtr V-Curves Intrductin Synchrnus mtrs are used in applicatins such as textile mills where cnstant speed peratin is critical. Mst small synchrnus mtrs cntain squirrel
Synchrnus Mtr V-Curves 1 Synchrnus Mtr V-Curves Intrductin Synchrnus mtrs are used in applicatins such as textile mills where cnstant speed peratin is critical. Mst small synchrnus mtrs cntain squirrel
Lecture 5: Operational Amplifiers and Op Amp Circuits
 Lecture 5: peratonal mplers and p mp Crcuts Gu-Yeon We Dson o Engneerng and ppled Scences Harard Unersty guyeon@eecs.harard.edu We erew eadng S&S: Chapter Supplemental eadng Background rmed wth our crcut
Lecture 5: peratonal mplers and p mp Crcuts Gu-Yeon We Dson o Engneerng and ppled Scences Harard Unersty guyeon@eecs.harard.edu We erew eadng S&S: Chapter Supplemental eadng Background rmed wth our crcut
Lesson 5. Thermomechanical Measurements for Energy Systems (MENR) Measurements for Mechanical Systems and Production (MMER)
 Lessn 5 Thermmechancal Measurements r Energy Systems (MEN) Measurements r Mechancal Systems and Prductn (MME) A.Y. 205-6 Zaccara (n ) Del Prete We wll nw analyze mre n depth each ne the unctnal blcks the
Lessn 5 Thermmechancal Measurements r Energy Systems (MEN) Measurements r Mechancal Systems and Prductn (MME) A.Y. 205-6 Zaccara (n ) Del Prete We wll nw analyze mre n depth each ne the unctnal blcks the
Bicycle Generator Dump Load Control Circuit: An Op Amp Comparator with Hysteresis
 Bicycle Generatr Dump Lad Cntrl Circuit: An Op Amp Cmparatr with Hysteresis Sustainable Technlgy Educatin Prject University f Waterl http://www.step.uwaterl.ca December 1, 2009 1 Summary This dcument describes
Bicycle Generatr Dump Lad Cntrl Circuit: An Op Amp Cmparatr with Hysteresis Sustainable Technlgy Educatin Prject University f Waterl http://www.step.uwaterl.ca December 1, 2009 1 Summary This dcument describes
BASIC DIRECT-CURRENT MEASUREMENTS
 Brwn University Physics 0040 Intrductin BASIC DIRECT-CURRENT MEASUREMENTS The measurements described here illustrate the peratin f resistrs and capacitrs in electric circuits, and the use f sme standard
Brwn University Physics 0040 Intrductin BASIC DIRECT-CURRENT MEASUREMENTS The measurements described here illustrate the peratin f resistrs and capacitrs in electric circuits, and the use f sme standard
ELG4139: Op Amp-based Active Filters
 ELG439: Op Amp-baed Actve Flter Advantage: educed ze and weght, and therere paratc. Increaed relablty and mprved perrmance. Smpler degn than r pave lter and can realze a wder range unctn a well a prvdng
ELG439: Op Amp-baed Actve Flter Advantage: educed ze and weght, and therere paratc. Increaed relablty and mprved perrmance. Smpler degn than r pave lter and can realze a wder range unctn a well a prvdng
Shell Stiffness for Diffe ent Modes
 Engneerng Mem N 28 February 0 979 SUGGESTONS FOR THE DEFORMABLE SUBREFLECTOR Sebastan vn Herner Observatns wth the present expermental versn (Engneerng Dv nternal Reprt 09 July 978) have shwn that a defrmable
Engneerng Mem N 28 February 0 979 SUGGESTONS FOR THE DEFORMABLE SUBREFLECTOR Sebastan vn Herner Observatns wth the present expermental versn (Engneerng Dv nternal Reprt 09 July 978) have shwn that a defrmable
FE REVIEW OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS)
 FE EIEW OPEATIONAL AMPLIFIES (OPAMPS) 1 The Opamp An opamp has two nputs and one output. Note the opamp below. The termnal labeled wth the () sgn s the nvertng nput and the nput labeled wth the () sgn
FE EIEW OPEATIONAL AMPLIFIES (OPAMPS) 1 The Opamp An opamp has two nputs and one output. Note the opamp below. The termnal labeled wth the () sgn s the nvertng nput and the nput labeled wth the () sgn
Approach: (Equilibrium) TD analysis, i.e., conservation eqns., state equations Issues: how to deal with
 Schl f Aerspace Chemcal D: Mtvatn Prevus D Analyss cnsdered systems where cmpstn f flud was frzen fxed chemcal cmpstn Chemcally eactng Flw but there are numerus stuatns n prpulsn systems where chemcal
Schl f Aerspace Chemcal D: Mtvatn Prevus D Analyss cnsdered systems where cmpstn f flud was frzen fxed chemcal cmpstn Chemcally eactng Flw but there are numerus stuatns n prpulsn systems where chemcal
Chapter 6 : Gibbs Free Energy
 Wnter 01 Chem 54: ntrductry hermdynamcs Chapter 6 : Gbbs Free Energy... 64 Defntn f G, A... 64 Mawell Relatns... 65 Gbbs Free Energy G(,) (ure substances)... 67 Gbbs Free Energy fr Mtures... 68 ΔG f deal
Wnter 01 Chem 54: ntrductry hermdynamcs Chapter 6 : Gbbs Free Energy... 64 Defntn f G, A... 64 Mawell Relatns... 65 Gbbs Free Energy G(,) (ure substances)... 67 Gbbs Free Energy fr Mtures... 68 ΔG f deal
Micro and Smart Systems
 Micr and Smart Systems Lecture 33 OpAmps Circuits and signal cnditining fr micrsystems devices Prf K.N.Bhat, ECE Department, IISc Bangalre email: knbhat@gmail.cm Tpics fr Discussin Amplifiers and Op Amp
Micr and Smart Systems Lecture 33 OpAmps Circuits and signal cnditining fr micrsystems devices Prf K.N.Bhat, ECE Department, IISc Bangalre email: knbhat@gmail.cm Tpics fr Discussin Amplifiers and Op Amp
Part a: Writing the nodal equations and solving for v o gives the magnitude and phase response: tan ( 0.25 )
 + - Hmewrk 0 Slutin ) In the circuit belw: a. Find the magnitude and phase respnse. b. What kind f filter is it? c. At what frequency is the respnse 0.707 if the generatr has a ltage f? d. What is the
+ - Hmewrk 0 Slutin ) In the circuit belw: a. Find the magnitude and phase respnse. b. What kind f filter is it? c. At what frequency is the respnse 0.707 if the generatr has a ltage f? d. What is the
MODULE TITLE : ELECTRONICS TOPIC TITLE : AMPLIFIERS LESSON 1 : FEEDBACK
 MODULE TITLE : ELECTONICS TOPIC TITLE : AMPLIFIES LESSON : FEEDBACK EL - 3 - INTODUCTION This lessn trduces the ideas f negative feedback, which we shw can vercme the disadvantages f wide parameter variat
MODULE TITLE : ELECTONICS TOPIC TITLE : AMPLIFIES LESSON : FEEDBACK EL - 3 - INTODUCTION This lessn trduces the ideas f negative feedback, which we shw can vercme the disadvantages f wide parameter variat
, where. This is a highpass filter. The frequency response is the same as that for P.P.14.1 RC. Thus, the sketches of H and φ are shown below.
 hapter 4, Slutn. H ( H(, where H π H ( φ H ( tan - ( Th a hghpa lter. The requency repne the ame a that r P.P.4. except that. Thu, the ketche H and φ are hwn belw. H.77 / φ 9 45 / hapter 4, Slutn. H(,
hapter 4, Slutn. H ( H(, where H π H ( φ H ( tan - ( Th a hghpa lter. The requency repne the ame a that r P.P.4. except that. Thu, the ketche H and φ are hwn belw. H.77 / φ 9 45 / hapter 4, Slutn. H(,
CHAPTER 5. Solutions for Exercises
 HAPTE 5 Slutins fr Exercises E5. (a We are given v ( t 50 cs(00π t 30. The angular frequency is the cefficient f t s we have ω 00π radian/s. Then f ω / π 00 Hz T / f 0 ms m / 50 / 06. Furthermre, v(t attains
HAPTE 5 Slutins fr Exercises E5. (a We are given v ( t 50 cs(00π t 30. The angular frequency is the cefficient f t s we have ω 00π radian/s. Then f ω / π 00 Hz T / f 0 ms m / 50 / 06. Furthermre, v(t attains
Physics 2010 Motion with Constant Acceleration Experiment 1
 . Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
. Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
General Amplifiers. Analog Electronics Circuits Nagamani A N. Lecturer, PESIT, Bangalore 85. Cascade connection - FET & BJT
 Analg lectrnics Circuits Nagamani A N Lecturer, PST, Bangalre 85 mail nagamani@pes.edu General Amplifiers Cascade cnnectin - FT & BJT Numerical Cascde cnnectin arlingtn cnnectin Packaged arlingtn cnnectin
Analg lectrnics Circuits Nagamani A N Lecturer, PST, Bangalre 85 mail nagamani@pes.edu General Amplifiers Cascade cnnectin - FT & BJT Numerical Cascde cnnectin arlingtn cnnectin Packaged arlingtn cnnectin
ZVS Boost Converter. (a) (b) Fig 6.29 (a) Quasi-resonant boost converter with M-type switch. (b) Equivalent circuit.
 EEL6246 Pwer Electrnics II Chapter 6 Lecture 6 Dr. Sam Abdel-Rahman ZVS Bst Cnverter The quasi-resnant bst cnverter by using the M-type switch as shwn in Fig. 6.29(a) with its simplified circuit shwn in
EEL6246 Pwer Electrnics II Chapter 6 Lecture 6 Dr. Sam Abdel-Rahman ZVS Bst Cnverter The quasi-resnant bst cnverter by using the M-type switch as shwn in Fig. 6.29(a) with its simplified circuit shwn in
Lead/Lag Compensator Frequency Domain Properties and Design Methods
 Lectures 6 and 7 Lead/Lag Cmpensatr Frequency Dmain Prperties and Design Methds Definitin Cnsider the cmpensatr (ie cntrller Fr, it is called a lag cmpensatr s K Fr s, it is called a lead cmpensatr Ntatin
Lectures 6 and 7 Lead/Lag Cmpensatr Frequency Dmain Prperties and Design Methds Definitin Cnsider the cmpensatr (ie cntrller Fr, it is called a lag cmpensatr s K Fr s, it is called a lead cmpensatr Ntatin
V. Electrostatics Lecture 27a: Diffuse charge at electrodes
 V. Electrstatcs Lecture 27a: Dffuse charge at electrdes Ntes by MIT tudent We have talked abut the electrc duble structures and crrespndng mdels descrbng the n and ptental dstrbutn n the duble layer. Nw
V. Electrstatcs Lecture 27a: Dffuse charge at electrdes Ntes by MIT tudent We have talked abut the electrc duble structures and crrespndng mdels descrbng the n and ptental dstrbutn n the duble layer. Nw
Lucas Imperfect Information Model
 Lucas Imerfect Infrmatn Mdel 93 Lucas Imerfect Infrmatn Mdel The Lucas mdel was the frst f the mdern, mcrfundatns mdels f aggregate suly and macrecnmcs It bult drectly n the Fredman-Phels analyss f the
Lucas Imerfect Infrmatn Mdel 93 Lucas Imerfect Infrmatn Mdel The Lucas mdel was the frst f the mdern, mcrfundatns mdels f aggregate suly and macrecnmcs It bult drectly n the Fredman-Phels analyss f the
ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Notes
 ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Ntes Lecture #5 Objectives fr lecture #5: 1. Analysis f precisin current reference 2. Appraches fr evaluating tlerances 3. Temperature Cefficients evaluatin technique 4. Fundamentals
ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Ntes Lecture #5 Objectives fr lecture #5: 1. Analysis f precisin current reference 2. Appraches fr evaluating tlerances 3. Temperature Cefficients evaluatin technique 4. Fundamentals
POWER AMPLIFIERS. 1. Explain what are classes A, B, AB and C amplifiers in terms of DC biasing using a MOSFET drain characteristic.
 CTONIC 3 XCI OW AMII. xpla what are classes A, B, AB and C amplifiers terms f DC biasg usg a MOT dra characteristic.. efer t the graphs f page and the table at the tp f page 3 f the thery ntes t answer
CTONIC 3 XCI OW AMII. xpla what are classes A, B, AB and C amplifiers terms f DC biasg usg a MOT dra characteristic.. efer t the graphs f page and the table at the tp f page 3 f the thery ntes t answer
1. Ideal OP Amps. +V cc. R o. v 1 v 2. v o. R d 2 1. V cc. Ideal Characteristics A = (gain is infinite) (no offset voltage) R
 . Ideal OP Amps Op amp Hgh-gan d dfferental amplfer ( ) D pwer supples are requred Usually used wth external negate feedbak Assume deal p amp desgn rut hek nn-deal haratersts are mprtant mdfy f neessary
. Ideal OP Amps Op amp Hgh-gan d dfferental amplfer ( ) D pwer supples are requred Usually used wth external negate feedbak Assume deal p amp desgn rut hek nn-deal haratersts are mprtant mdfy f neessary
Lesson #14. Section BME 373 Electronics II J.Schesser
 Feedback and Oscillatrs Lessn #4 Impedances Sectin 9.35 65 Types f ffeedback Type f ffeedback k(the utput tentity fed dback): Vltage Feedback s. Current Feedback β s. β Hw it is achieed (the means t fed
Feedback and Oscillatrs Lessn #4 Impedances Sectin 9.35 65 Types f ffeedback Type f ffeedback k(the utput tentity fed dback): Vltage Feedback s. Current Feedback β s. β Hw it is achieed (the means t fed
Chapter 30. Inductance
 Chapter 30 nductance 30. Self-nductance Cnsider a lp f wire at rest. f we establish a current arund the lp, it will prduce a magnetic field. Sme f the magnetic field lines pass thrugh the lp. et! be the
Chapter 30 nductance 30. Self-nductance Cnsider a lp f wire at rest. f we establish a current arund the lp, it will prduce a magnetic field. Sme f the magnetic field lines pass thrugh the lp. et! be the
_J _J J J J J J J J _. 7 particles in the blue state; 3 particles in the red state: 720 configurations _J J J _J J J J J J J J _
 Dsrder and Suppse I have 10 partcles that can be n ne f tw states ether the blue state r the red state. Hw many dfferent ways can we arrange thse partcles amng the states? All partcles n the blue state:
Dsrder and Suppse I have 10 partcles that can be n ne f tw states ether the blue state r the red state. Hw many dfferent ways can we arrange thse partcles amng the states? All partcles n the blue state:
Coupled Inductors and Transformers
 Cupled nductrs and Transfrmers Self-nductance When current i flws thrugh the cil, a magnetic flux is prduced arund it. d d di di v= = = dt di dt dt nductance: = d di This inductance is cmmnly called self-inductance,
Cupled nductrs and Transfrmers Self-nductance When current i flws thrugh the cil, a magnetic flux is prduced arund it. d d di di v= = = dt di dt dt nductance: = d di This inductance is cmmnly called self-inductance,
Why working at higher frequencies?
 Advanced course on ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISATION OF NANOSCALE SAMPLES & BIOCHEMICAL INTERFACES: methods and electronc nstrumentaton. MEASURING SMALL CURRENTS When speed comes nto play Why workng at hgher
Advanced course on ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISATION OF NANOSCALE SAMPLES & BIOCHEMICAL INTERFACES: methods and electronc nstrumentaton. MEASURING SMALL CURRENTS When speed comes nto play Why workng at hgher
Fields and Waves I. Lecture 3
 Fields and Waves I ecture 3 Input Impedance n Transmissin ines K. A. Cnnr Electrical, Cmputer, and Systems Engineering Department Rensselaer Plytechnic Institute, Try, NY These Slides Were Prepared by
Fields and Waves I ecture 3 Input Impedance n Transmissin ines K. A. Cnnr Electrical, Cmputer, and Systems Engineering Department Rensselaer Plytechnic Institute, Try, NY These Slides Were Prepared by
LEAP FROG TECHNIQUE. Operational Simulation of LC Ladder Filters ECEN 622 (ESS) TAMU-AMSC
 LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP
LEAP FOG TEHNQUE Opeatnal Smulatn f L Ladde Fltes L pttype lw senstvty One fm f ths technque s called Leapf Technque Fundamental Buldn Blcks ae - nteats - Secnd-de ealzatns Fltes cnsdeed - LP - BP - HP
Chapter 6. Operational Amplifier. inputs can be defined as the average of the sum of the two signals.
 6 Operatonal mpler Chapter 6 Operatonal mpler CC Symbol: nput nput Output EE () Non-nvertng termnal, () nvertng termnal nput mpedance : Few mega (ery hgh), Output mpedance : Less than (ery low) Derental
6 Operatonal mpler Chapter 6 Operatonal mpler CC Symbol: nput nput Output EE () Non-nvertng termnal, () nvertng termnal nput mpedance : Few mega (ery hgh), Output mpedance : Less than (ery low) Derental
FYSE400 ANALOG ELECTRONICS
 YS400 NLOG LCONCS LCU 12 eedback plfer 1 uptn 1. he bac aplfer unlateral. 2. he gan OL f the bac aplfer deterned wthut feedback. 3. he calculated gan OL laded gan : ladng f the feedback netwrk, urce and
YS400 NLOG LCONCS LCU 12 eedback plfer 1 uptn 1. he bac aplfer unlateral. 2. he gan OL f the bac aplfer deterned wthut feedback. 3. he calculated gan OL laded gan : ladng f the feedback netwrk, urce and
ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis
 ECE 00 Circuit Analysis Lessn 6 Chapter 4 Sec 4., 4.5, 4.7 Series LC Circuit C Lw Pass Filter Daniel M. Litynski, Ph.D. http://hmepages.wmich.edu/~dlitynsk/ ECE 00 Circuit Analysis Lessn 5 Chapter 9 &
ECE 00 Circuit Analysis Lessn 6 Chapter 4 Sec 4., 4.5, 4.7 Series LC Circuit C Lw Pass Filter Daniel M. Litynski, Ph.D. http://hmepages.wmich.edu/~dlitynsk/ ECE 00 Circuit Analysis Lessn 5 Chapter 9 &
