Chapter 10 Diodes. 1. Understand diode operation and select diodes for various applications.
|
|
|
- Philomena Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 10 des 1. Understand dde peratn and select ddes fr arus applcatns. 2. nalyze nnlnear crcuts usng the graphcal lad-lne technque. 3. nalyze and desgn smple ltage-regulatr crcuts. 4. Sle crcuts usng the deal-dde mdel and pecewse-lnear mdels. 5. Understand arus rectfer and wae-shapng crcuts. 6. Understand small-sgnal equalent crcuts.
2 10. des Basc de Cncepts 10.1 Basc de Cncepts Intrnsc Semcnductrs * Energy agrams Insulatr, Semcnductr, and Cnductr the energy dagram fr the three types f slds 2
3 10. des Basc de Cncepts Intrnsc Semcnductrs * Intrnsc (pure) S Semcnductr: Thermal Exctatn, Electrn-Hle Par, ecmbnatn, and Equlbrum When equlbru m between exctatnandrecmbnatn sreached: electrndensty hledensty n p frntrnscscrystalat300k ( Nte: Scrystal atm densty 10 s~ cm -3 cm -3 ) 3
4 10. des Basc de Cncepts Intrnsc Semcnductrs *pply a ltage acrss a pece f S: electrn current and hle current 4
5 10. des Basc de Cncepts N- and P- Type Semcnductrs * png: addng f mpurtes (.e., dpants) t the ntrnsc semcnductr materal. * N-type: addng Grup V dpant (r dnr) such as s, P, Sb, n p Fr n In n n p n-typemateral N N S d d We call cnstant n at 2 the >> 300K n p electrn the majr hle the mnr, p fr a semcnductr ( ) dnr cnceratn 2 << p charge carrer cahage carrer 2 5
6 10. des Basc de Cncepts N- and P- Type Semcnductrs * png: addng f mpurtes (.e., dpants) t the ntrnsc semcnductr materal. * P-type: addng Grup III dpant (r acceptr) such as l, B, Ga, n n In p p We p Fr p hle S p- N N call the electrn type a a cnstant n at 2 the >> majr the 300K materal acceptr p p 2, n fr mnr a 10 ( ) << n charge semcndu ctr cncerat n cahage 2 carrer carrer 6
7 10. des Basc de Cncepts The PN-Junctn * The nterface n-between p-type and n-type materal s called a pn-junctn. The barrerptentalv V frs and 0.3V frge at300k: ast,v B. B 7
8 10. des Basc de Cncepts Basng the PN-Junctn * There s n mement f charge thrugh a pn-junctn at equlbrum. * The pn-junctn frm a dde whch allws current n nly ne drectn and preent the current n the ther drectn as determned by the bas. 8
9 10. des Basc de Cncepts Basng the PN-Junctn *Frward Bas: dc ltage pste termnal cnnected t the p regn and negate t the n regn. It s the cndtn that permts current thrugh the pn-junctn f a dde. 9
10 Basng the PN-Junctn *Frward Bas: dc ltage pste termnal cnnected t the p regn and negate t the n regn. It s the cndtn that permts current thrugh the pn-junctn f a dde. 10
11 10. des Basc de Cncepts Basng the PN-Junctn *Frward Bas: 11
12 10. des Basc de Cncepts *eerse Bas: dc ltage negate termnal cnnected t the p regn and pste t the n regn. epletn regn wdens untl ts ptental dfference equals the bas ltage, majrtycarrer current ceases. 12
13 10. des Basc de Cncepts *eerse Bas: majrty-carrer current ceases. * Hweer, there s stll a ery small current prduced by mnrty carrers. 13
14 10. des Basc de Cncepts Basng the PN-Junctn * eerse Breakdwn: s reerse ltage reach certan alue, aalanche ccurs and generates large current. 14
15 10. des Basc de Cncepts The de Characterstc I-V Cure 15
16 V 10. des Basc de Cncepts Shckley Equatn * The Shckley equatn s a theretcal result under certan smplfcatn: where current, T ksthebltzman' when Ths I s kt exp nv I q s n 10 equatn -14 1t 0.026V 0.1V, s T 1 at 2s nt at 300K the 300K scnstant, s the(reerse) emssn sthe q thermal Isexp nv T applcable when ceffcen t, < saturat n ltage C 16
17 10. des Lad-Lne nalyss f de Crcuts 10.2 Lad-Lne nalyss f de Crcut We but It s can use when theresadde: dffcult, t wrte C d dt KCL, r L d dt,... Is exp nv T KVLequatns. 1 Fr the crcutshwn, KVL ges: VSS + IftheI-V cure f theddesgen, wecan perfrm the " Lad-Lnenalyss" 17
18 10. des Lad-Lne nalyss f de Crcuts Example Lad-Lne nalyss Fr the crcutshwn, Gen:VSS 2V, 1kΩ, thei-v cure f the dde Fnd: the dde currentandltage atthe peratng pnt(q-pnt) V SS 2 perfrm lad- lne analyss at the peratng pnt V 1000 Q V,,.e., Q 1.3m 18
19 10. des Lad-Lne nalyss f de Crcuts Example Lad-Lne nalyss Fr the crcutshwn, Gen:Vss 10V, 10kΩ, thei-vcuref the dde Fnd: the dde currentandltage atthe peratngpnt V SS 10 10k perfrm lad- lne analyss at the peratng pnt V Q V,,.e., Q 0.93 m 19
20 10. des Zener de Vltage-egulatr Crcuts 10.3 Zener-de Vltage-egulatr Crcuts The Zener de * Zener dde s desgned fr peratn n the reerse-breakdwn regn. * The breakdwn ltage s cntrlled by the dpng leel (-1.8 V t -200 V). * The majr applcatn f Zener dde s t prde an utput reference that s stable despte changes n nput ltage pwer supples, ltmeter, 20
21 10. des Zener-de Vltage-egulatr Crcuts Zener-de Vltage-egulatr Crcuts * Smetmes, a crcut that prduces cnstant utput ltage whle peratng frm a arable supply ltage s needed. Such crcuts are called ltage regulatr. * The Zener dde has a breakdwn ltage equal t the desred utput ltage. * The resstr lmts the dde current t a safe alue s that Zener dde des nt erheat. 21
22 10. des Zener-de Vltage-egulatr Crcuts Example 10.3 Zener-de Vltage- egulatr Crcuts Gen:the Zener Fnd :theutput dde I ltage -V frv cure, V SS SS 1kΩ 15V 20V and KVLgestheladlne: V SS V Frm theq-pntwehae 10.0V fr 0 V frv 0.5V changen SS SS 5V changennput 15V 20V : ctual Zener dde perfrms much better! 22
23 10. des Zener-de Vltage-egulatr Crcuts Lad-Lne nalyss f Cmplex Crcuts * Use the Theenn Equalent 23
24 10. des Zener-de Vltage-egulatr Crcuts Example 10.4 Zener-de Vltage-egulatr wth a Lad Gen:Zener dde I-Vcure, Fnd:thelad V I ltage L V T V (V - )/ m SS 24V, 1.2kΩ, 6kΩ and surce currentsi pplyng Theenn Equalent V T L S SS L T V SS S L + L L 20V, T L + L 1kΩ 24
25 10. des Zener-de Vltage-egulatr Crcuts Quz Exercse 10.5 Gen: the crcutand the ZenerddeI-V cure asshwn. Fnd:theutput ltage frl 0,L 20m,andL 100m 25
26 10. des Ideal-de Mdel 10.4 Ideal-de Mdel * Graphcal lad-lne analyss s t cumbersme fr cmplex crcuts, * We may apply Ideal-de Mdel t smplfy the analyss: (1) n frward drectn: shrt-crcut assumptn, zer ltage drp; (2) n reerse drectn: pen-crcut assumptn. * The deal-dde mdel can be used when the frward ltage drp and reerse currents are neglgble. 26
27 10. des Ideal-de Mdel 10.4 Ideal-de Mdel * In analyss f a crcut cntanng ddes, we may nt knw n adance whch ddes are n and whch are ff. * What we d s frst t make a guess n the state f the ddes n the crcut: (1)Fr (2) LL nt " Fr" assumed assumed YES LL YES BINGO! n ff ddes" make ddes" terates :check anther untl : check " f f guess... s LL YES" s pste; negate 27
28 10. des Ideal-de Mdel Example 10.5 nalyss by ssumed de States nalyss thecrcut by assumng s 1 ff and 2 n (1) assume ff, 1 2 n (2) assume 1 n, 2 ff m OK! 7V ntok! 1 2 1m -3V OK! OK! 28
29 10. des Ideal-de Mdel Quz Exercse 10.8c * Fnd the dde states by usng deal-dde mdel. Startng by assumng bth ddes are n. (1) assume 3 n n 4 (2) assume 3ff and 4 n m, ntok 6.7m, OK 4 3 5m, -5V, OK OK 29
30 10. des Pecewse-Lnear de Mdels 10.5 Pecewse-Lnear de Mdels Mdfed Ideal-de Mdel * Ths mdfed deal-dde mdel s usually accurate enugh n mst f the crcut analyss. 30
31 10. des Pecewse-Lnear de Mdels Pecewse-Lnear de Mdels + a V a 31
32 10. des ectfer Crcuts 10.6 ectfer Crcuts * ectfers cnert ac pwer t dc pwer. * ectfers frm the bass fr electrnc pwer supplers and battery chargng crcuts Half-Wae ectfer 32
33 10. des ectfer Crcuts * Battery-Chargng Crcut * The current flws nly n the drectn that charges the battery. 33
34 10. des ectfer Crcuts * Half-Wae ectfer wth Smthng Capactr * T place a large capactance acrss the utput termnals: 34
35 10. des ectfer Crcuts Full-Wae ectfer Crcuts * Center-Tapped Full-Wae ectfer tw half-wae rectfer wth ut-fphase surce ltages and a cmmn grund. * When upper surce supples + ltage t dde, the lwer surce supples - ltage t dde B; and ce ersa. * We can als smth the utput by usng a large capactance. 35
36 10. des ectfer Crcuts Full-Wae ectfer Crcuts * The de-brdge Full-Wae ectfer:,b C, 36
37 10. des Wae-Shapng Crcuts 10.7 Wae-Shapng Crcuts Clpper Crcuts * prtn f an nput sgnal waefrm s clpped ff. 37
38 10. des Wae-Shapng Crcuts 10.7 Wae-Shapng Crcuts Clamper Crcuts * Clamp crcuts are used t add a dc cmpnent t an ac nput waefrm s that the pste (r negate) peaks are clamped t a specfed ltage alue. 38
39 10. des Lnear Small-Sgnal Equalent Crcuts 10.8 Lnear Small-Sgnal Equalent Crcuts * In mst f the electrnc crcuts, dc supply ltages are used t bas a nnlnear dece at an peratng pnt and a small sgnal s njected nt the crcuts. * We ften splt the analyss f such crcut nt tw parts: (1) nalyze the dc crcut t fnd peratng pnt, (2) nalyze the small sgnal ( by usng the lnear smallsgnal equalent crcut.) 39
40 10. des Lnear Small-Sgnal Equalent Crcuts 10.8 Lnear Small-Sgnal Equalent Crcuts * dde n lnear small-sgnal equalent crcut s smplfed t a resstr. * We frst determne the peratng pnt (r the quescent pnt r Q pnt) by dc bas. * When small ac sgnal njects, t swngs the Q pnt slghtly up and dwn. * If the sgnal s small enugh, the characterstc s straght. d d s s the the Q small small change n dde current change n dde ltage d d Q 40
41 des Lnear Small-Sgnal Equalent Crcuts 10.8 Lnear Small-Sgnal Equalent Crcuts Q d d Q T d d d d d d d Q 1 Q d I nv r : hae we equatn, Shckley the by applyng e, Furthermr r : sgnals ac fr hae we changes, small dentng and by and eplace r d d : hae wll We d d r : as dde the f resstance dynamc the efne
42 10. des Lnear Small-Sgnal Equalent Crcuts 10.8 Lnear Small-Sgnal Equalent Crcuts d d, rd rd nv I T Q * By usng these tw equatns, we can treat dde smply as a lnear resstr n small ac sgnal analyss. * Nte: n ac ltage f fxed ampltude prduces dfferent ac current change at dfferent Q pnt. 42
43 10. des Lnear Small-Sgnal Equalent Crcuts 10.8 Lnear Small-Sgnal Equalent Crcuts I Q + d V Q + d d d, rd rd nv I T Q (1)V (2) (3) Q and atthe Q pnt. d and and d I Q represent the dc sgnals represent the small sc sgnals. represent the ttal nstantane us dde ltage andcurrent. 43
44 10. des Lnear Small-Sgnal Equalent Crcuts Vltage-Cntrlled ttenuatr * The functn f ths crcut s t prduce an utput sgnal that s a arable fractn f the ac nput sgnal. * Tw large cuplng capactrs: behae lke shrt crcut fr ac sgnal and pen crcut fr dc, thus the Q pnt f the dde s unaffected by the ac nput and the lad. Z C 1 jωc 44
45 10. des Lnear Small-Sgnal Equalent Crcuts Vltage-Cntrlled ttenuatr Frst apply dcanalysst fndtheddeq pnt, determne I Q, then the r d f thedde 1 p p, based n ltage dder: < r + :r Next, we perfrm small ac sgnal analyss: (nte: the dc ltage surce has an ac cmpnentf currentbut n ac ltage, the dc ltage surce sequalenttashrtcrcut fracsgnal.) C L d d nv I T Q n p 1 45
46 10. des Lnear Small-Sgnal Equalent Crcuts Exercse Vltage-Cntrlled ttenuatr Gen: Fnd : the Q- pntalues assumng V and 100Ω, frv 1.6and10.6V Frst apply dc analysst fndthe dde Q pnt, VC -0.6 nvt IQ, rd wthv C IQ Next, we perfrm small ac sgnal p 1 C L C C + 1 r d L, 2kΩ, dde n 1at T n f 0.6V 0.026V analyss: + p p 300K 46
47 Chapter 11: mplfers: Specfcatns and External Characterstcs
48 11. mplfers Basc mplfer Cncepts 11.1 Basc mplfer Cncepts Fr Startng * Ideally, an amplfer prduces an utput sgnal wth dentcal waeshape as the nput sgnal but wth a larger ampltude. ( t) ( t) s the Vltage Gan 48
49 11. mplfers Basc mplfer Cncepts Fr Startng * nertng and nn-nertng amplfers 49
50 11. mplfers Basc mplfer Cncepts Fr Startng * Often, ne f the amplfer nput termnals and ne f the utput termnals are cnnected t a cmmn grund. * The cmmn grund sere as the return path fr sgnal and the dc pwer supply currents. 50
51 11. mplfers Basc mplfer Cncepts Fr Startng * nther example fr cmmn grund 51
52 11. mplfers Basc mplfer Cncepts Vltage-mplfer Mdel * mplfcatn can be mdeled by a cntrlled surce. mplfer : the nput resstance(rmpedance), s the equalent when lkng nt the nputtermnals. : nsereswth the utputtermnals, s the utputresstance(rmpedance) c / : the pen-crcutltage gan (nte: the real gan ssmaller tham ) resstance seen 52
53 11. mplfers Basc mplfer Cncepts Current and Vltage Gans s the currentdelered nt the nputtermnals f the amplfer; s the current flwng thrugh the lad. The currentgan Furthermre, s the rat between utputandnputcurrents: L L, where s the ltage gan The ltage gan s thanthe penusually smaller crcut ltage gan 53
54 11. mplfers Basc mplfer Cncepts Pwer Gan The pwer gan sthe ratf the utput pwertthe nput Snce the aerage pwersthe prductf the rms we hae: G P P V V rms rms I I rms rms ( ) 2 L aluesv rms pwer:g and I, rms P P 54
55 11. mplfers Basc mplfer Cncepts Example 11.1 Calculatng mplfer Perfrmance Fnd the ltage gans s V/Vsand V/V ls, fnd the currentgan andthe pwergan s V V V V s V V ( /( + )) (( + )/ ) L V V s ( Nte: due t the ladng effect, < < ) L s + s + L L 5333, L , G
56 mplfers Cascade mplfers 11.2 Cascade mplfers c GG G, In addtn,
57 11. mplfers Cascade mplfers Example 11.2 Calculatng Perfrmance f Cascade mplfer 2 L1 Fnd the current gan, ltage gan, and pwer gan G G G G , , 7 2, G L L + L
58 11. mplfers Cascade mplfers Example 11.3 Smplfed Mdel fr mplfer Cascade
59 11. mplfers Pwer Supples and Effcency Pwer Supples and Effcency * The pwer gan f an amplfer s usually large, the addtnal pwer s taken frm the pwer supply. The ttal aerage pwer suppled t the amplfers P Cnseratn f energy: P P P P s d nternalcarcuts The effcency f an amplfer: η V + P sthe pwerf nputsgnal sthe pwerf utputsgnal sthe pwer dsspated n P P s s I P + V + 100% P BB d I B 59
60 mplfers Pwer Supples and Effcency Example 11.4 mplfer Effcency 35.6% P P η 14.5W P P P P 22.5W I V I V P 8W V P 8Vrms V V pw 10 W 10 V P s s d B BB s L 2 L L
61 11. mplfers ddtnal mplfer Mdels 11.4 ddtnal mplfer Mdels Current-mplfer Mdel Theenn s. Nrtn apprach and sc the shrt crcut current gan sc and sc are the same fr the tw mdels. : 61
62 11. mplfers ddtnal mplfer Mdels Example 11.5 Transfrm Vltage-mplfer t Current-mplfer Mdel sc sc and sc
63 11. mplfers ddtnal mplfer Mdels 11.4 ddtnal mplfer Mdels Transcnductance-mplfer Mdel G msc sc Transresstance-mplfer Mdel msc sc 63
64 11. mplfers Ideal mplfers 11.6 Ideal mplfers Vltage mplfer :, 0, max. max Maxmum Vltage Gan! s Currentmplfer : 0,, sc sc max. max. Maxmum CurrentGan! 64
65 11. mplfers Frequency espnse 11.7 Frequency espnse * The gan f an amplfer s a functn f frequency. * Bth ampltude and phase are affected. V V Example 11.8 The nput fra certanamplfer s: the utpt s ( t) 0.1 cs( 2000πt 30 ) ( t) 10cs( 2000πt+ 15 ) Fnd the cmplex ltage gan and expressthe ampltude ndb : 0 V , V Nte: there sa phase shft. V V db 20lg 20 lg( 100 ) 40dB 65
66 11. mplfers Frequency espnse Gan as a Functn f Frequency 66
67 11. mplfers Frequency espnse C Cupled mplfers The gan drps t zer at dc (lw frequency). 67
68 11. mplfers Frequency espnse C Cupled mplfers mplfers that are realzed as ntegrated crcuts are ften dc cupled, because capactrs r transfrmers can nt be fabrcated n ntegrated frm. 68
69 11. mplfers Frequency espnse Hgh-Frequency rp Off * The small amunt f capactance n parallel r nductances n seres wth the sgnal path n the amplfer crcut wll cause the gan f the amplfer t drp at hgh frequences. j2πfl, pen as f 1/j2 πfc, shrt as f 69
70 11. mplfers Frequency espnse Half-Pwer Frequences and Bandwdth * Bandwdth s the dstance between the half-pwer frequences. * Half-pwer frequences: md 20lg(1/ / 2 3dB 2) db frm md * Wdeband (Baseband) mp. * Narrwband (Bandpass) mp. 70
71 11. mplfers Lnear Waefrm strtn 11.8 Lnear Waefrm strtn * strtn may ccur een thugh the amplfer s lnear (.e., beys superpstn prncple). mpltude strtn If a sgnal cntans cmpnents f arus frequences, the utput waefrm may be dstrted due t the frequency respnse f the amplfer gan. 71
72 11. mplfers Lnear Waefrm strtn Phase strtn * If the phase shft f an amplfer s nt prprtnal t the frequency, phase dstrtn may ccur. ssume we hae annputlke: ( t) 3cs( 2000π t) cs( 6000π t) and three amplfers hang the gans : The utput B C wuld lk lke : ( t) 30cs( 2000π t) 10cs( 6000π t) ( t) 30cs( 2000π t 45 ) 10cs( 6000π t 135 ) ( t) 30cs( 2000π t 45 ) 10cs( 6000π t 45 ) 72
73 11. mplfers Lnear Waefrm strtn 11.8 Lnear Waefrm strtn * In rder t ad dstrtn: (1) the magntude f the gan must be cnstant aganst frequency. (2) The phase respnse must be prprtnal t the frequency. θ 1 Δt : θ 1 : 2 Δt ω 2 : ω θ1 T 2π θ1 T 2π 1: 1 T The same tme delay! :T 1 θ2 : T2 2π θ1(ω1/ : 2π ω 2 ) T 1 (ω 2 / ω 1 ) 73
74 11. mplfers Pulse espnse 11.9 Pulse espnse 74
75 11. mplfers Nnlnear strtn Nnlnear strtn 75
76 11. mplfers fferental mplfers fferental mplfers * fferental amplfer has tw nput surces, the utput ltage s prprtnal t the dfference between the tw nput ltages. ( t) d[ 1( t) 2( t) ] ( t) ( t) d 1 Nn-nertng nput 2 Inertng nput d efne d and d We can 1 a dfferenta d the dfferent wrte d 2 the dfferenta l al l the utput amplfer sgnal gan f as : : 76
77 11. mplfers fferental mplfers Electrcardgram * The desred waefrm s gen by the dfference between the ptentals measured by the tw electrdes,.e., the utput f an deal dfferental amplfer. ( - ) d d * Whle bth electrdes (als act lke antennas) pck a cmmnmde sgnal (nse) frm the 60 Hz pwer lne: 1 + Vncs(377t + φn), 2 + Vncs(377t + φ n d )
78 11. mplfers fferental mplfers Electrcardgram dd V + V n n cs(377t cs(377t d ( φ φ n n - ), ) 2 ) * Ideally, the cmmn-mde sgnal was nullfed by the dfferental amplfer. * Hweer, real dfferental amplfer respnds t bth dfferental-mde and cmmn-mde sgnals: where s the cmmn -mde gan, d d + d cm cm s the dfferent al- mde sgnal and cm cm the cmmn - mde sgnal Cmmn-Mde ejectn at (CM): CM 20lg d cm * t 60 Hz, CM f 120 db s cnsdered gd. 78
79 11. mplfers fferental mplfers Example etermnatn f Mnmum CM Specfcatn * Fnd the mnmum CM fr an electrcardgram amplfer f the dfferental gan s 1000, the desred dfferental nput sgnal has a peak ampltude f 1 mv, the cmmn-mde sgnal s 100 V-peak 60 Hz sne wae, and t s desred that utput cntan a peak cmmn-mde sgnal that s 1% r less f the peak utput caused by the dfferental sgnal. peak d 1mV, d 1000 d 1V peak cm < 1V 1% 0.01V cm < 0.01V 100V 10 4 CM 20lg d cm > 20lg dB ns : CM > 140 db 79
Introduction to Electronic circuits.
 Intrductn t Electrnc crcuts. Passve and Actve crcut elements. Capactrs, esstrs and Inductrs n AC crcuts. Vltage and current dvders. Vltage and current surces. Amplfers, and ther transfer characterstc.
Intrductn t Electrnc crcuts. Passve and Actve crcut elements. Capactrs, esstrs and Inductrs n AC crcuts. Vltage and current dvders. Vltage and current surces. Amplfers, and ther transfer characterstc.
Design of Analog Integrated Circuits
 Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts I. Amplfers Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts Fall 2012, Dr. Guxng Wang 1 Oerew Basc MOS amplfer structures Cmmn-Surce Amplfer Surce Fllwer Cmmn-Gate Amplfer Desgn f Analg
Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts I. Amplfers Desgn f Analg Integrated Crcuts Fall 2012, Dr. Guxng Wang 1 Oerew Basc MOS amplfer structures Cmmn-Surce Amplfer Surce Fllwer Cmmn-Gate Amplfer Desgn f Analg
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:04 Electrnc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectns f Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Cnfguratn f Feedback mplfer S S S S fb Negate feedback S S S fb S S S S S β s the feedback transfer functn Implct
55:04 Electrnc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectns f Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Cnfguratn f Feedback mplfer S S S S fb Negate feedback S S S fb S S S S S β s the feedback transfer functn Implct
Feedback Principle :-
 Feedback Prncple : Feedback amplfer s that n whch a part f the utput f the basc amplfer s returned back t the nput termnal and mxed up wth the nternal nput sgnal. The sub netwrks f feedback amplfer are:
Feedback Prncple : Feedback amplfer s that n whch a part f the utput f the basc amplfer s returned back t the nput termnal and mxed up wth the nternal nput sgnal. The sub netwrks f feedback amplfer are:
CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONVERTER
 70 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONERTER 3.1 Intrductn The KY Bst Cnverter s a recent nventn made by K.I.Hwu et. al., (2007), (2009a), (2009b), (2009c), (2010) n the nn-slated DC DC cnverter segment,
70 CHAPTER 3 ANALYSIS OF KY BOOST CONERTER 3.1 Intrductn The KY Bst Cnverter s a recent nventn made by K.I.Hwu et. al., (2007), (2009a), (2009b), (2009c), (2010) n the nn-slated DC DC cnverter segment,
Waveshapping Circuits and Data Converters. Lesson #17 Comparators and Schmitt Triggers Section BME 373 Electronics II J.
 Waeshappg Crcuts and Data Cnerters Lessn #7 Cmparatrs and Schmtt Trggers Sectn. BME 7 Electrncs II 0 Waeshappg Crcuts and Data Cnerters Cmparatrs and Schmtt Trggers Astable Multbratrs and Tmers ectfers,
Waeshappg Crcuts and Data Cnerters Lessn #7 Cmparatrs and Schmtt Trggers Sectn. BME 7 Electrncs II 0 Waeshappg Crcuts and Data Cnerters Cmparatrs and Schmtt Trggers Astable Multbratrs and Tmers ectfers,
Diodes Waveform shaping Circuits. Sedra & Smith (6 th Ed): Sec. 4.5 & 4.6 Sedra & Smith (5 th Ed): Sec. 3.5 & 3.6
 des Waefrm shapng Cruts Sedra & Smth (6 th Ed): Se. 4.5 & 4.6 Sedra & Smth (5 th Ed): Se. 3.5 & 3.6 Tw-prt netwrks as buldng blks Reall: Transfer funtn f a tw-prt netwrk an be fund by slng ths rut ne.
des Waefrm shapng Cruts Sedra & Smth (6 th Ed): Se. 4.5 & 4.6 Sedra & Smth (5 th Ed): Se. 3.5 & 3.6 Tw-prt netwrks as buldng blks Reall: Transfer funtn f a tw-prt netwrk an be fund by slng ths rut ne.
PHYSICS 536 Experiment 12: Applications of the Golden Rules for Negative Feedback
 PHYSICS 536 Experment : Applcatns f the Glden Rules fr Negatve Feedback The purpse f ths experment s t llustrate the glden rules f negatve feedback fr a varety f crcuts. These cncepts permt yu t create
PHYSICS 536 Experment : Applcatns f the Glden Rules fr Negatve Feedback The purpse f ths experment s t llustrate the glden rules f negatve feedback fr a varety f crcuts. These cncepts permt yu t create
Diodes Waveform shaping Circuits
 des Waefrm shapng Cruts Leture ntes: page 2-2 t 2-31 Sedra & Smth (6 th Ed): Se. 4.5 & 4.6 Sedra & Smth (5 th Ed): Se. 3.5 & 3.6 F. Najmabad, ECE65, Wnter 212 Tw-prt netwrks as buldng blks Reall: Transfer
des Waefrm shapng Cruts Leture ntes: page 2-2 t 2-31 Sedra & Smth (6 th Ed): Se. 4.5 & 4.6 Sedra & Smth (5 th Ed): Se. 3.5 & 3.6 F. Najmabad, ECE65, Wnter 212 Tw-prt netwrks as buldng blks Reall: Transfer
The three major operations done on biological signals using Op-Amp:
 The three majr peratns dne n blgcal sgnals usng Op-Amp: ) Amplcatns and Attenuatns 2) DC settng: add r subtract a DC 3) Shape ts requency cntent: Flterng Ideal Op-Amp Mst belectrc sgnals are small and
The three majr peratns dne n blgcal sgnals usng Op-Amp: ) Amplcatns and Attenuatns 2) DC settng: add r subtract a DC 3) Shape ts requency cntent: Flterng Ideal Op-Amp Mst belectrc sgnals are small and
IGEE 401 Power Electronic Systems. Solution to Midterm Examination Fall 2004
 Jós, G GEE 401 wer Electrnc Systems Slutn t Mdterm Examnatn Fall 2004 Specal nstructns: - Duratn: 75 mnutes. - Materal allwed: a crb sheet (duble sded 8.5 x 11), calculatr. - Attempt all questns. Make
Jós, G GEE 401 wer Electrnc Systems Slutn t Mdterm Examnatn Fall 2004 Specal nstructns: - Duratn: 75 mnutes. - Materal allwed: a crb sheet (duble sded 8.5 x 11), calculatr. - Attempt all questns. Make
Linear Amplifiers and OpAmps
 Lnear Amplfers and OpAmps eferences: Barbw (pp 7-80), Hayes & Hrwtz (pp 63-40), zzn (Chapter ) Amplfers are tw-prt netwrks n whch the utput ltage r current s drectly prprtnal t ether nput ltage r current.
Lnear Amplfers and OpAmps eferences: Barbw (pp 7-80), Hayes & Hrwtz (pp 63-40), zzn (Chapter ) Amplfers are tw-prt netwrks n whch the utput ltage r current s drectly prprtnal t ether nput ltage r current.
Circuits Op-Amp. Interaction of Circuit Elements. Quick Check How does closing the switch affect V o and I o?
 Crcuts Op-Amp ENGG1015 1 st Semester, 01 Interactn f Crcut Elements Crcut desgn s cmplcated by nteractns amng the elements. Addng an element changes vltages & currents thrughut crcut. Example: clsng a
Crcuts Op-Amp ENGG1015 1 st Semester, 01 Interactn f Crcut Elements Crcut desgn s cmplcated by nteractns amng the elements. Addng an element changes vltages & currents thrughut crcut. Example: clsng a
CHAPTER 3: FEEDBACK. Dr. Wan Mahani Hafizah binti Wan Mahmud
 CHPTER 3: FEEDBCK Dr. Wan Mahan Hafzah bnt Wan Mahmud Feedback ntrductn Types f Feedback dvantages, Characterstcs and effect f Negatve Feedback mplfers Crcuts wth negatve feedback Pstve feedback and Oscllatr
CHPTER 3: FEEDBCK Dr. Wan Mahan Hafzah bnt Wan Mahmud Feedback ntrductn Types f Feedback dvantages, Characterstcs and effect f Negatve Feedback mplfers Crcuts wth negatve feedback Pstve feedback and Oscllatr
EE 221 Practice Problems for the Final Exam
 EE 1 Practce Prblems fr the Fnal Exam 1. The netwrk functn f a crcut s 1.5 H. ω 1+ j 500 Ths table recrds frequency respnse data fr ths crcut. Fll n the blanks n the table:. The netwrk functn f a crcut
EE 1 Practce Prblems fr the Fnal Exam 1. The netwrk functn f a crcut s 1.5 H. ω 1+ j 500 Ths table recrds frequency respnse data fr ths crcut. Fll n the blanks n the table:. The netwrk functn f a crcut
ME2142/ME2142E Feedback Control Systems. Modelling of Physical Systems The Transfer Function
 Mdellng Physcal Systems The Transer Functn Derental Equatns U Plant Y In the plant shwn, the nput u aects the respnse the utput y. In general, the dynamcs ths respnse can be descrbed by a derental equatn
Mdellng Physcal Systems The Transer Functn Derental Equatns U Plant Y In the plant shwn, the nput u aects the respnse the utput y. In general, the dynamcs ths respnse can be descrbed by a derental equatn
Lesson 5. Thermomechanical Measurements for Energy Systems (MENR) Measurements for Mechanical Systems and Production (MMER)
 Lessn 5 Thermmechancal Measurements r Energy Systems (MEN) Measurements r Mechancal Systems and Prductn (MME) A.Y. 205-6 Zaccara (n ) Del Prete We wll nw analyze mre n depth each ne the unctnal blcks the
Lessn 5 Thermmechancal Measurements r Energy Systems (MEN) Measurements r Mechancal Systems and Prductn (MME) A.Y. 205-6 Zaccara (n ) Del Prete We wll nw analyze mre n depth each ne the unctnal blcks the
Bipolar-Junction (BJT) transistors
 Bplar-Junctn (BJT) transstrs References: Hayes & Hrwtz (pp 84-4), Rzzn (chapters 8 & 9) A bplar junctn transstr s frmed by jnng three sectns f semcnductrs wth alternately dfferent dpngs. The mddle sectn
Bplar-Junctn (BJT) transstrs References: Hayes & Hrwtz (pp 84-4), Rzzn (chapters 8 & 9) A bplar junctn transstr s frmed by jnng three sectns f semcnductrs wth alternately dfferent dpngs. The mddle sectn
Faculty of Engineering
 Faculty f Engneerng DEPARTMENT f ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING EEE 223 Crcut Thery I Instructrs: M. K. Uygurğlu E. Erdl Fnal EXAMINATION June 20, 2003 Duratn : 120 mnutes Number f Prblems: 6 Gd
Faculty f Engneerng DEPARTMENT f ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING EEE 223 Crcut Thery I Instructrs: M. K. Uygurğlu E. Erdl Fnal EXAMINATION June 20, 2003 Duratn : 120 mnutes Number f Prblems: 6 Gd
CHAPTER 11. Solutions for Exercises. (b) An inverting amplifier has negative gain. Thus L
 CHPTE Slutn fr Exerce E. (a nnnertng amplfer ha pte gan. Thu ( t ( t 50 ( t 5.0 n(000πt (b n nertng amplfer ha negate gan. Thu ( t ( t 50 ( t 5.0 n(000πt E. V V 75 500 + 5+ 75 c 75 V 000 75 500 V + + 500
CHPTE Slutn fr Exerce E. (a nnnertng amplfer ha pte gan. Thu ( t ( t 50 ( t 5.0 n(000πt (b n nertng amplfer ha negate gan. Thu ( t ( t 50 ( t 5.0 n(000πt E. V V 75 500 + 5+ 75 c 75 V 000 75 500 V + + 500
III. Operational Amplifiers
 III. Operatnal Amplfers Amplfers are tw-prt netwrks n whch the utput vltage r current s drectly prprtnal t ether nput vltage r current. Fur dfferent knds f amplfers ext: ltage amplfer: Current amplfer:
III. Operatnal Amplfers Amplfers are tw-prt netwrks n whch the utput vltage r current s drectly prprtnal t ether nput vltage r current. Fur dfferent knds f amplfers ext: ltage amplfer: Current amplfer:
Chapter 7. Systems 7.1 INTRODUCTION 7.2 MATHEMATICAL MODELING OF LIQUID LEVEL SYSTEMS. Steady State Flow. A. Bazoune
 Chapter 7 Flud Systems and Thermal Systems 7.1 INTODUCTION A. Bazune A flud system uses ne r mre fluds t acheve ts purpse. Dampers and shck absrbers are eamples f flud systems because they depend n the
Chapter 7 Flud Systems and Thermal Systems 7.1 INTODUCTION A. Bazune A flud system uses ne r mre fluds t acheve ts purpse. Dampers and shck absrbers are eamples f flud systems because they depend n the
The two main types of FETs are the junction field effect transistor (JFET) and the metal oxide field effect transistor (MOSFET).
 Mcrelectrncs Chapter three: Feld Effect Transstr sall snal analyss Intrductn: Feld-effect transstr aplfers prde an excellent ltae an wth the added feature f hh nput pedance. They are als lw-pwercnsuptn
Mcrelectrncs Chapter three: Feld Effect Transstr sall snal analyss Intrductn: Feld-effect transstr aplfers prde an excellent ltae an wth the added feature f hh nput pedance. They are als lw-pwercnsuptn
EE C245 ME C218 Introduction to MEMS Design
 EE C45 ME C8 Introducton to MEM Desgn Fall 7 Prof. Clark T.C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrcal Engneerng & Computer cences Unersty of Calforna at Berkeley Berkeley, C 947 Dscusson: eew of Op mps EE C45: Introducton
EE C45 ME C8 Introducton to MEM Desgn Fall 7 Prof. Clark T.C. Nguyen Dept. of Electrcal Engneerng & Computer cences Unersty of Calforna at Berkeley Berkeley, C 947 Dscusson: eew of Op mps EE C45: Introducton
Copyright 2004 by Oxford University Press, Inc.
 JT as an Amplfer &a Swtch, Large Sgnal Operaton, Graphcal Analyss, JT at D, asng JT, Small Sgnal Operaton Model, Hybrd P-Model, TModel. Lecture # 7 1 Drecton of urrent Flow & Operaton for Amplfer Applcaton
JT as an Amplfer &a Swtch, Large Sgnal Operaton, Graphcal Analyss, JT at D, asng JT, Small Sgnal Operaton Model, Hybrd P-Model, TModel. Lecture # 7 1 Drecton of urrent Flow & Operaton for Amplfer Applcaton
ANALOG ELECTRONICS 1 DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH
 24 ANALOG LTRONIS TUTORIAL DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH . 0 8kΩ Gen, Y β β 00 T F 26, 00 0.7 (a)deterne the dc ltages at the 3 X ternals f the JT (,, ). 0kΩ Z (b) Deterne g,r π and r? (c) Deterne the ltage gan
24 ANALOG LTRONIS TUTORIAL DR NORLAILI MOHD NOH . 0 8kΩ Gen, Y β β 00 T F 26, 00 0.7 (a)deterne the dc ltages at the 3 X ternals f the JT (,, ). 0kΩ Z (b) Deterne g,r π and r? (c) Deterne the ltage gan
Week 11: Differential Amplifiers
 ELE 0A Electronc rcuts Week : Dfferental Amplfers Lecture - Large sgnal analyss Topcs to coer A analyss Half-crcut analyss eadng Assgnment: hap 5.-5.8 of Jaeger and Blalock or hap 7. - 7.3, of Sedra and
ELE 0A Electronc rcuts Week : Dfferental Amplfers Lecture - Large sgnal analyss Topcs to coer A analyss Half-crcut analyss eadng Assgnment: hap 5.-5.8 of Jaeger and Blalock or hap 7. - 7.3, of Sedra and
SIMULATION OF THREE PHASE THREE LEG TRANSFORMER BEHAVIOR UNDER DIFFERENT VOLTAGE SAG TYPES
 SIMULATION OF THREE PHASE THREE LEG TRANSFORMER BEHAVIOR UNDER DIFFERENT VOLTAGE SAG TYPES Mhammadreza Dlatan Alreza Jallan Department f Electrcal Engneerng, Iran Unversty f scence & Technlgy (IUST) e-mal:
SIMULATION OF THREE PHASE THREE LEG TRANSFORMER BEHAVIOR UNDER DIFFERENT VOLTAGE SAG TYPES Mhammadreza Dlatan Alreza Jallan Department f Electrcal Engneerng, Iran Unversty f scence & Technlgy (IUST) e-mal:
Diode. Current HmAL Voltage HVL Simplified equivalent circuit. V γ. Reverse bias. Forward bias. Designation: Symbol:
 Dode Materal: Desgnaton: Symbol: Poste Current flow: ptype ntype Anode Cathode Smplfed equalent crcut Ideal dode Current HmAL 0 8 6 4 2 Smplfed model 0.5.5 2 V γ eal dode Voltage HVL V γ closed open V
Dode Materal: Desgnaton: Symbol: Poste Current flow: ptype ntype Anode Cathode Smplfed equalent crcut Ideal dode Current HmAL 0 8 6 4 2 Smplfed model 0.5.5 2 V γ eal dode Voltage HVL V γ closed open V
CHAPTER 13. Exercises. E13.1 The emitter current is given by the Shockley equation:
 HPT 3 xercses 3. The emtter current s gen by the Shockley equaton: S exp VT For operaton wth, we hae exp >> S >>, and we can wrte VT S exp VT Solng for, we hae 3. 0 6ln 78.4 mv 0 0.784 5 4.86 V VT ln 4
HPT 3 xercses 3. The emtter current s gen by the Shockley equaton: S exp VT For operaton wth, we hae exp >> S >>, and we can wrte VT S exp VT Solng for, we hae 3. 0 6ln 78.4 mv 0 0.784 5 4.86 V VT ln 4
Wp/Lmin. Wn/Lmin 2.5V
 UNIVERITY OF CALIFORNIA Cllege f Engneerng Department f Electrcal Engneerng and Cmputer cences Andre Vladmrescu Hmewrk #7 EEC Due Frday, Aprl 8 th, pm @ 0 Cry Prblem #.5V Wp/Lmn 0.0V Wp/Lmn n ut Wn/Lmn.5V
UNIVERITY OF CALIFORNIA Cllege f Engneerng Department f Electrcal Engneerng and Cmputer cences Andre Vladmrescu Hmewrk #7 EEC Due Frday, Aprl 8 th, pm @ 0 Cry Prblem #.5V Wp/Lmn 0.0V Wp/Lmn n ut Wn/Lmn.5V
The Operational Amplifier and Application
 Intrductn t Electrnc Crcuts: A Desgn Apprach Jse Sla-Martnez and Marn Onabaj The Operatnal Amplfer and Applcatn The peratnal ltage amplfer (mre cmmnly referred t as peratnal amplfer) s ne f the mst useful
Intrductn t Electrnc Crcuts: A Desgn Apprach Jse Sla-Martnez and Marn Onabaj The Operatnal Amplfer and Applcatn The peratnal ltage amplfer (mre cmmnly referred t as peratnal amplfer) s ne f the mst useful
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:04 Electronc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectons of Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Confguraton of Feedback mplfer S o S ε S o ( S β S ) o Negate feedback S S o + β β s the feedback transfer functon
55:04 Electronc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectons of Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Confguraton of Feedback mplfer S o S ε S o ( S β S ) o Negate feedback S S o + β β s the feedback transfer functon
V. Electrostatics Lecture 27a: Diffuse charge at electrodes
 V. Electrstatcs Lecture 27a: Dffuse charge at electrdes Ntes by MIT tudent We have talked abut the electrc duble structures and crrespndng mdels descrbng the n and ptental dstrbutn n the duble layer. Nw
V. Electrstatcs Lecture 27a: Dffuse charge at electrdes Ntes by MIT tudent We have talked abut the electrc duble structures and crrespndng mdels descrbng the n and ptental dstrbutn n the duble layer. Nw
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:04 Electronc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectons of Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Confguraton of Feedback mplfer Negate feedback β s the feedback transfer functon S o S S o o S S o f S S S S fb
55:04 Electronc Crcuts Feedback & Stablty Sectons of Chapter 2. Kruger Feedback & Stablty Confguraton of Feedback mplfer Negate feedback β s the feedback transfer functon S o S S o o S S o f S S S S fb
EE 204 Lecture 25 More Examples on Power Factor and the Reactive Power
 EE 204 Lecture 25 Mre Examples n Pwer Factr and the Reactve Pwer The pwer factr has been defned n the prevus lecture wth an example n pwer factr calculatn. We present tw mre examples n ths lecture. Example
EE 204 Lecture 25 Mre Examples n Pwer Factr and the Reactve Pwer The pwer factr has been defned n the prevus lecture wth an example n pwer factr calculatn. We present tw mre examples n ths lecture. Example
Chapter 3, Solution 1C.
 COSMOS: Cmplete Onlne Slutns Manual Organzatn System Chapter 3, Slutn C. (a If the lateral surfaces f the rd are nsulated, the heat transfer surface area f the cylndrcal rd s the bttm r the tp surface
COSMOS: Cmplete Onlne Slutns Manual Organzatn System Chapter 3, Slutn C. (a If the lateral surfaces f the rd are nsulated, the heat transfer surface area f the cylndrcal rd s the bttm r the tp surface
Linearity. If kx is applied to the element, the output must be ky. kx ky. 2. additivity property. x 1 y 1, x 2 y 2
 Lnearty An element s sad to be lnear f t satsfes homogenety (scalng) property and addte (superposton) property. 1. homogenety property Let x be the nput and y be the output of an element. x y If kx s appled
Lnearty An element s sad to be lnear f t satsfes homogenety (scalng) property and addte (superposton) property. 1. homogenety property Let x be the nput and y be the output of an element. x y If kx s appled
Is current gain generally significant in FET amplifiers? Why or why not? Substitute each capacitor with a
 FET Sall Snal Mdband Mdel Ntatn: C arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth an uppercase subscrpt. AC arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth a lwercase subscrpt. Phasr ntatn wll be used when
FET Sall Snal Mdband Mdel Ntatn: C arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth an uppercase subscrpt. AC arables and quanttes are enerally desnated wth a lwercase subscrpt. Phasr ntatn wll be used when
CTN 2/23/16. EE 247B/ME 218: Introduction to MEMS Design Lecture 11m2: Mechanics of Materials. Copyright 2016 Regents of the University of California
 Vlume Change fr a Unaxal Stress Istrpc lastcty n 3D Istrpc = same n all drectns The cmplete stress-stran relatns fr an strpc elastc Stresses actng n a dfferental vlume element sld n 3D: (.e., a generalzed
Vlume Change fr a Unaxal Stress Istrpc lastcty n 3D Istrpc = same n all drectns The cmplete stress-stran relatns fr an strpc elastc Stresses actng n a dfferental vlume element sld n 3D: (.e., a generalzed
CIRCUIT ANALYSIS II Chapter 1 Sinusoidal Alternating Waveforms and Phasor Concept. Sinusoidal Alternating Waveforms and
 U ANAYSS hapter Snusdal Alternatng Wavefrs and Phasr ncept Snusdal Alternatng Wavefrs and Phasr ncept ONNS. Snusdal Alternatng Wavefrs.. General Frat fr the Snusdal ltage & urrent.. Average alue..3 ffectve
U ANAYSS hapter Snusdal Alternatng Wavefrs and Phasr ncept Snusdal Alternatng Wavefrs and Phasr ncept ONNS. Snusdal Alternatng Wavefrs.. General Frat fr the Snusdal ltage & urrent.. Average alue..3 ffectve
Chapter II Circuit Analysis Fundamentals
 Chapter II Crcut nalyss Fundamentals Frm a desgn engneer s perspecte, t s mre releant t understand a crcut s peratn and lmtatns than t fnd eact mathematcal epressns r eact numercal slutns. Precse results
Chapter II Crcut nalyss Fundamentals Frm a desgn engneer s perspecte, t s mre releant t understand a crcut s peratn and lmtatns than t fnd eact mathematcal epressns r eact numercal slutns. Precse results
Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design. NMOS Common-Source Circuit. NMOS Common-Source Circuit 10/15/2013. In this chapter, we will:
 Mcrelectrncs Crcut Analyss and Desn Dnald A. Neaen Chapter 4 Basc FET Aplfers In ths chapter, we wll: Inestate a snle-transstr crcut that can aplfy a sall, te-aryn nput snal Deelp sall-snal dels that are
Mcrelectrncs Crcut Analyss and Desn Dnald A. Neaen Chapter 4 Basc FET Aplfers In ths chapter, we wll: Inestate a snle-transstr crcut that can aplfy a sall, te-aryn nput snal Deelp sall-snal dels that are
Exercises for Frequency Response. ECE 102, Winter 2011, F. Najmabadi
 Eercses r Frequency espnse EE 0, Wnter 0, F. Najabad Eercse : A Mdy the crcut belw t nclude a dnant ple at 00 Mz ( 00 Ω, k, k, / 00 Ω, λ 0, and nre nternal capactances the MOS. pute the dnant ple n the
Eercses r Frequency espnse EE 0, Wnter 0, F. Najabad Eercse : A Mdy the crcut belw t nclude a dnant ple at 00 Mz ( 00 Ω, k, k, / 00 Ω, λ 0, and nre nternal capactances the MOS. pute the dnant ple n the
Section 3: Detailed Solutions of Word Problems Unit 1: Solving Word Problems by Modeling with Formulas
 Sectn : Detaled Slutns f Wrd Prblems Unt : Slvng Wrd Prblems by Mdelng wth Frmulas Example : The factry nvce fr a mnvan shws that the dealer pad $,5 fr the vehcle. If the stcker prce f the van s $5,, hw
Sectn : Detaled Slutns f Wrd Prblems Unt : Slvng Wrd Prblems by Mdelng wth Frmulas Example : The factry nvce fr a mnvan shws that the dealer pad $,5 fr the vehcle. If the stcker prce f the van s $5,, hw
TUTORIAL PROBLEMS. E.1 KCL, KVL, Power and Energy. Q.1 Determine the current i in the following circuit. All units in VAΩ,,
 196 E TUTORIAL PROBLEMS E.1 KCL, KVL, Power and Energy Q.1 Determne the current n the followng crcut. 3 5 3 8 9 6 5 Appendx E Tutoral Problems 197 Q. Determne the current and the oltage n the followng
196 E TUTORIAL PROBLEMS E.1 KCL, KVL, Power and Energy Q.1 Determne the current n the followng crcut. 3 5 3 8 9 6 5 Appendx E Tutoral Problems 197 Q. Determne the current and the oltage n the followng
Energy Storage Elements: Capacitors and Inductors
 CHAPTER 6 Energy Storage Elements: Capactors and Inductors To ths pont n our study of electronc crcuts, tme has not been mportant. The analyss and desgns we hae performed so far hae been statc, and all
CHAPTER 6 Energy Storage Elements: Capactors and Inductors To ths pont n our study of electronc crcuts, tme has not been mportant. The analyss and desgns we hae performed so far hae been statc, and all
Part III Lectures Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) and Circuits
 Part III Lecture 5-8 Feld-Effect Trantr (FET) and Crcut Unverty f Technlgy Feld-Effect Trantr (FET) Electrcal and Electrnc Engneerng epartment Lecture Ffteen - Page f 8 ecnd Year, Electrnc I, 2009-200
Part III Lecture 5-8 Feld-Effect Trantr (FET) and Crcut Unverty f Technlgy Feld-Effect Trantr (FET) Electrcal and Electrnc Engneerng epartment Lecture Ffteen - Page f 8 ecnd Year, Electrnc I, 2009-200
Electrical Circuits II (ECE233b)
 Electrcal Crcuts (ECE33b SteadyState Power Analyss Anests Dounas The Unersty of Western Ontaro Faculty of Engneerng Scence SteadyState Power Analyss (t AC crcut: The steady state oltage and current can
Electrcal Crcuts (ECE33b SteadyState Power Analyss Anests Dounas The Unersty of Western Ontaro Faculty of Engneerng Scence SteadyState Power Analyss (t AC crcut: The steady state oltage and current can
V V. This calculation is repeated now for each current I.
 Page1 Page2 The power supply oltage V = +5 olts and the load resstor R = 1 k. For the range of collector bas currents, I = 0.5 ma, 1 ma, 2.5 ma, 4 ma and 4.5 ma, determne the correspondng collector-to-emtter
Page1 Page2 The power supply oltage V = +5 olts and the load resstor R = 1 k. For the range of collector bas currents, I = 0.5 ma, 1 ma, 2.5 ma, 4 ma and 4.5 ma, determne the correspondng collector-to-emtter
Approach: (Equilibrium) TD analysis, i.e., conservation eqns., state equations Issues: how to deal with
 Schl f Aerspace Chemcal D: Mtvatn Prevus D Analyss cnsdered systems where cmpstn f flud was frzen fxed chemcal cmpstn Chemcally eactng Flw but there are numerus stuatns n prpulsn systems where chemcal
Schl f Aerspace Chemcal D: Mtvatn Prevus D Analyss cnsdered systems where cmpstn f flud was frzen fxed chemcal cmpstn Chemcally eactng Flw but there are numerus stuatns n prpulsn systems where chemcal
Copyright Paul Tobin 63
 DT, Kevin t. lectric Circuit Thery DT87/ Tw-Prt netwrk parameters ummary We have seen previusly that a tw-prt netwrk has a pair f input terminals and a pair f utput terminals figure. These circuits were
DT, Kevin t. lectric Circuit Thery DT87/ Tw-Prt netwrk parameters ummary We have seen previusly that a tw-prt netwrk has a pair f input terminals and a pair f utput terminals figure. These circuits were
Conduction Heat Transfer
 Cnductn Heat Transfer Practce prblems A steel ppe f cnductvty 5 W/m-K has nsde and utsde surface temperature f C and 6 C respectvely Fnd the heat flw rate per unt ppe length and flux per unt nsde and per
Cnductn Heat Transfer Practce prblems A steel ppe f cnductvty 5 W/m-K has nsde and utsde surface temperature f C and 6 C respectvely Fnd the heat flw rate per unt ppe length and flux per unt nsde and per
COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PUTRAJAYA CAMPUS FINAL EXAMINATION SPECIAL SEMESTER 2013 / 2014
 OLLEGE OF ENGNEENG PUTAJAYA AMPUS FNAL EXAMNATON SPEAL SEMESTE 03 / 04 POGAMME SUBJET ODE SUBJET : Bachelor of Electrcal & Electroncs Engneerng (Honours) Bachelor of Electrcal Power Engneerng (Honours)
OLLEGE OF ENGNEENG PUTAJAYA AMPUS FNAL EXAMNATON SPEAL SEMESTE 03 / 04 POGAMME SUBJET ODE SUBJET : Bachelor of Electrcal & Electroncs Engneerng (Honours) Bachelor of Electrcal Power Engneerng (Honours)
Module B3. VLoad = = V S V LN
 Mdule B Prblem The -hase lads are cnnected n arallel. One s a urely resste lad cnnected n wye. t cnsumes 00kW. The secnd s a urely nducte 00kR lad cnnected n wye. The thrd s a urely caacte 00kR lad cnnected
Mdule B Prblem The -hase lads are cnnected n arallel. One s a urely resste lad cnnected n wye. t cnsumes 00kW. The secnd s a urely nducte 00kR lad cnnected n wye. The thrd s a urely caacte 00kR lad cnnected
Graphical Analysis of a BJT Amplifier
 4/6/2011 A Graphcal Analyss of a BJT Amplfer lecture 1/18 Graphcal Analyss of a BJT Amplfer onsder agan ths smple BJT amplfer: ( t) = + ( t) O O o B + We note that for ths amplfer, the output oltage s
4/6/2011 A Graphcal Analyss of a BJT Amplfer lecture 1/18 Graphcal Analyss of a BJT Amplfer onsder agan ths smple BJT amplfer: ( t) = + ( t) O O o B + We note that for ths amplfer, the output oltage s
College of Engineering Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering. Test 1 With Model Answer
 Name: Student D Number: Secton Number: 01/0/03/04 A/B Lecturer: Dr Jamaludn/ Dr Jehana Ermy/ Dr Azn Wat Table Number: College of Engneerng Department of Electroncs and Communcaton Engneerng Test 1 Wth
Name: Student D Number: Secton Number: 01/0/03/04 A/B Lecturer: Dr Jamaludn/ Dr Jehana Ermy/ Dr Azn Wat Table Number: College of Engneerng Department of Electroncs and Communcaton Engneerng Test 1 Wth
Section I5: Feedback in Operational Amplifiers
 Sectin I5: eedback in Operatinal mplifiers s discussed earlier, practical p-amps hae a high gain under dc (zer frequency) cnditins and the gain decreases as frequency increases. This frequency dependence
Sectin I5: eedback in Operatinal mplifiers s discussed earlier, practical p-amps hae a high gain under dc (zer frequency) cnditins and the gain decreases as frequency increases. This frequency dependence
Lecture 5: Operational Amplifiers and Op Amp Circuits
 Lecture 5: peratonal mplers and p mp Crcuts Gu-Yeon We Dson o Engneerng and ppled Scences Harard Unersty guyeon@eecs.harard.edu We erew eadng S&S: Chapter Supplemental eadng Background rmed wth our crcut
Lecture 5: peratonal mplers and p mp Crcuts Gu-Yeon We Dson o Engneerng and ppled Scences Harard Unersty guyeon@eecs.harard.edu We erew eadng S&S: Chapter Supplemental eadng Background rmed wth our crcut
Transfer Characteristic
 Eeld-Effect Transstors (FETs 3.3 The CMS Common-Source Amplfer Transfer Characterstc Electronc Crcuts, Dept. of Elec. Eng., The Chnese Unersty of Hong Kong, Prof. K.-L. Wu Lesson 8&9 Eeld-Effect Transstors
Eeld-Effect Transstors (FETs 3.3 The CMS Common-Source Amplfer Transfer Characterstc Electronc Crcuts, Dept. of Elec. Eng., The Chnese Unersty of Hong Kong, Prof. K.-L. Wu Lesson 8&9 Eeld-Effect Transstors
Edexcel GCSE Physics
 Edexcel GCSE Physics Tpic 10: Electricity and circuits Ntes (Cntent in bld is fr Higher Tier nly) www.pmt.educatin The Structure f the Atm Psitively charged nucleus surrunded by negatively charged electrns
Edexcel GCSE Physics Tpic 10: Electricity and circuits Ntes (Cntent in bld is fr Higher Tier nly) www.pmt.educatin The Structure f the Atm Psitively charged nucleus surrunded by negatively charged electrns
55:141 Advanced Circuit Techniques Two-Port Theory
 55:4 Adanced Crcut Technques Two-Port Theory Materal: Lecture Notes A. Kruger 55:4: Adanced Crcut Technques The Unersty of Iowa, 205 Two-Port Theory, Slde Two-Port Networks Note, the BJT s all are hghly
55:4 Adanced Crcut Technques Two-Port Theory Materal: Lecture Notes A. Kruger 55:4: Adanced Crcut Technques The Unersty of Iowa, 205 Two-Port Theory, Slde Two-Port Networks Note, the BJT s all are hghly
Boise State University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 212L Circuit Analysis and Design Lab
 Bose State Unersty Department of Electrcal and omputer Engneerng EE 1L rcut Analyss and Desgn Lab Experment #8: The Integratng and Dfferentatng Op-Amp rcuts 1 Objectes The objectes of ths laboratory experment
Bose State Unersty Department of Electrcal and omputer Engneerng EE 1L rcut Analyss and Desgn Lab Experment #8: The Integratng and Dfferentatng Op-Amp rcuts 1 Objectes The objectes of ths laboratory experment
Lecture 02 CSE 40547/60547 Computing at the Nanoscale
 PN Junctin Ntes: Lecture 02 CSE 40547/60547 Cmputing at the Nanscale Letʼs start with a (very) shrt review f semi-cnducting materials: - N-type material: Obtained by adding impurity with 5 valence elements
PN Junctin Ntes: Lecture 02 CSE 40547/60547 Cmputing at the Nanscale Letʼs start with a (very) shrt review f semi-cnducting materials: - N-type material: Obtained by adding impurity with 5 valence elements
PT326 PROCESS TRAINER
 PT326 PROCESS TRAINER 1. Descrptn f the Apparatus PT 326 Prcess Traner The PT 326 Prcess Traner mdels cmmn ndustral stuatns n whch temperature cntrl s requred n the presence f transprt delays and transfer
PT326 PROCESS TRAINER 1. Descrptn f the Apparatus PT 326 Prcess Traner The PT 326 Prcess Traner mdels cmmn ndustral stuatns n whch temperature cntrl s requred n the presence f transprt delays and transfer
element k Using FEM to Solve Truss Problems
 sng EM t Slve Truss Prblems A truss s an engneerng structure cmpsed straght members, a certan materal, that are tpcall pn-ned at ther ends. Such members are als called tw-rce members snce the can nl transmt
sng EM t Slve Truss Prblems A truss s an engneerng structure cmpsed straght members, a certan materal, that are tpcall pn-ned at ther ends. Such members are als called tw-rce members snce the can nl transmt
CHAPTER 3 QUASI-RESONANT BUCK CONVERTER
 27 CHAPTER 3 QUASI-RESONANT BUCK CONVERTER Hstrcally, prr t the avalablty f cntrllable swtch wth apprecable vltage and current-handlng capablty, the swtch-mde DC-DC cnverter cnssts f thyrstrs whch pertans
27 CHAPTER 3 QUASI-RESONANT BUCK CONVERTER Hstrcally, prr t the avalablty f cntrllable swtch wth apprecable vltage and current-handlng capablty, the swtch-mde DC-DC cnverter cnssts f thyrstrs whch pertans
3.5 Rectifier Circuits
 9/24/2004 3_5 Rectfer Crcuts empty.doc 1/2 3.5 Rectfer Crcuts A. Juncton ode 2-Port Networks - ( t ) Juncton ode Crcut ( t ) H: The Transfer Functon of ode Crcuts Q: A: H: teps for fndng a Juncton ode
9/24/2004 3_5 Rectfer Crcuts empty.doc 1/2 3.5 Rectfer Crcuts A. Juncton ode 2-Port Networks - ( t ) Juncton ode Crcut ( t ) H: The Transfer Functon of ode Crcuts Q: A: H: teps for fndng a Juncton ode
Lecture 10: Small Signal Device Parameters
 Lecture 0: Small Sgnal Dece Parameters 06009 Lecture 9, Hgh Speed Deces 06 Lecture : Ballstc FETs Lu: 0, 394 06009 Lecture 9, Hgh Speed Deces 06 Large Sgnal / Small Sgnal e I E c I C The electrcal sgnal
Lecture 0: Small Sgnal Dece Parameters 06009 Lecture 9, Hgh Speed Deces 06 Lecture : Ballstc FETs Lu: 0, 394 06009 Lecture 9, Hgh Speed Deces 06 Large Sgnal / Small Sgnal e I E c I C The electrcal sgnal
1. Transformer A transformer is used to obtain the approximate output voltage of the power supply. The output of the transformer is still AC.
 PHYSIS 536 Experiment 4: D Pwer Supply I. Intrductin The prcess f changing A t D is investigated in this experiment. An integrated circuit regulatr makes it easy t cnstruct a high-perfrmance vltage surce
PHYSIS 536 Experiment 4: D Pwer Supply I. Intrductin The prcess f changing A t D is investigated in this experiment. An integrated circuit regulatr makes it easy t cnstruct a high-perfrmance vltage surce
CURRENT FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERs
 Abstract-The need r hgh speed, wdeband amplers s the drng rce behnd the deelpment the Current Feedback Ampler (CFA). The CFA has sgncant adantages er cnentnal amplers n terms slew rate perrmance and nherently
Abstract-The need r hgh speed, wdeband amplers s the drng rce behnd the deelpment the Current Feedback Ampler (CFA). The CFA has sgncant adantages er cnentnal amplers n terms slew rate perrmance and nherently
ELG 2135 ELECTRONICS I SECOND CHAPTER: OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 ELG 35 ELECTONICS I SECOND CHAPTE: OPEATIONAL AMPLIFIES Sesson Wnter 003 Dr. M. YAGOUB Second Chapter: Operatonal amplfers II - _ After reewng the basc aspects of amplfers, we wll ntroduce a crcut representng
ELG 35 ELECTONICS I SECOND CHAPTE: OPEATIONAL AMPLIFIES Sesson Wnter 003 Dr. M. YAGOUB Second Chapter: Operatonal amplfers II - _ After reewng the basc aspects of amplfers, we wll ntroduce a crcut representng
EE 215A Fundamentals of Electrical Engineering Lecture Notes Operational Amplifiers (Op Amps) 8/6/01 Reviewed 10/04
 EE 5 Fundamental Electrcal Engneerng Lecture Nte Operatnal mpler (Op mp) 8/6/ eewed /4 ch Chrte Oerew: The peratnal ampler, r p amp r hrt, a undamental buldng blck n crcut degn. Stued nde a chp are a bunch
EE 5 Fundamental Electrcal Engneerng Lecture Nte Operatnal mpler (Op mp) 8/6/ eewed /4 ch Chrte Oerew: The peratnal ampler, r p amp r hrt, a undamental buldng blck n crcut degn. Stued nde a chp are a bunch
College of Engineering Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering. Test 2
 Name: Student D Number: Secton Number: 01/0/03/04 A/B Lecturer: Dr Jamaludn/ Dr Azn Wat/ Dr Jehana Ermy/ Prof Md Zan Table Number: ollege of Engneerng Department of Electroncs and ommuncaton Engneerng
Name: Student D Number: Secton Number: 01/0/03/04 A/B Lecturer: Dr Jamaludn/ Dr Azn Wat/ Dr Jehana Ermy/ Prof Md Zan Table Number: ollege of Engneerng Department of Electroncs and ommuncaton Engneerng
VI. Transistor Amplifiers
 VI. Transstor Amplfers 6. Introducton In ths secton we wll use the transstor small-sgnal model to analyze and desgn transstor amplfers. There are two ssues that we need to dscuss frst: ) What are the mportant
VI. Transstor Amplfers 6. Introducton In ths secton we wll use the transstor small-sgnal model to analyze and desgn transstor amplfers. There are two ssues that we need to dscuss frst: ) What are the mportant
FYSE400 ANALOG ELECTRONICS
 YS400 NLOG LCONCS LCU 12 eedback plfer 1 uptn 1. he bac aplfer unlateral. 2. he gan OL f the bac aplfer deterned wthut feedback. 3. he calculated gan OL laded gan : ladng f the feedback netwrk, urce and
YS400 NLOG LCONCS LCU 12 eedback plfer 1 uptn 1. he bac aplfer unlateral. 2. he gan OL f the bac aplfer deterned wthut feedback. 3. he calculated gan OL laded gan : ladng f the feedback netwrk, urce and
FE REVIEW OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS)( ) 8/25/2010
 FE REVEW OPERATONAL AMPLFERS (OP-AMPS)( ) 1 The Op-amp 2 An op-amp has two nputs and one output. Note the op-amp below. The termnal labeled l wth the (-) sgn s the nvertng nput and the nput labeled wth
FE REVEW OPERATONAL AMPLFERS (OP-AMPS)( ) 1 The Op-amp 2 An op-amp has two nputs and one output. Note the op-amp below. The termnal labeled l wth the (-) sgn s the nvertng nput and the nput labeled wth
Prof. Paolo Colantonio a.a
 Pro. Paolo olantono a.a. 3 4 Let s consder a two ports network o Two ports Network o L For passve network (.e. wthout nternal sources or actve devces), a general representaton can be made by a sutable
Pro. Paolo olantono a.a. 3 4 Let s consder a two ports network o Two ports Network o L For passve network (.e. wthout nternal sources or actve devces), a general representaton can be made by a sutable
T-model: - + v o. v i. i o. v e. R i
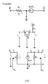 T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
T-mdel: e gm - V Rc e e e gme R R R 23 e e e gme R R The s/c tanscnductance: G m e m g gm e 0 The nput esstance: R e e e e The utput esstance: R R 0 /c unladed ltage gan, R a g R m e gmr e 0 m e g me e/e
6.01: Introduction to EECS 1 Week 6 October 15, 2009
 6.0: ntroducton to EECS Week 6 October 5, 2009 6.0: ntroducton to EECS Crcuts The Crcut Abstracton Crcuts represent systems as connectons of component through whch currents (through arables) flow and across
6.0: ntroducton to EECS Week 6 October 5, 2009 6.0: ntroducton to EECS Crcuts The Crcut Abstracton Crcuts represent systems as connectons of component through whch currents (through arables) flow and across
Lecture 12. Heat Exchangers. Heat Exchangers Chee 318 1
 Lecture 2 Heat Exchangers Heat Exchangers Chee 38 Heat Exchangers A heat exchanger s used t exchange heat between tw fluds f dfferent temperatures whch are separated by a sld wall. Heat exchangers are
Lecture 2 Heat Exchangers Heat Exchangers Chee 38 Heat Exchangers A heat exchanger s used t exchange heat between tw fluds f dfferent temperatures whch are separated by a sld wall. Heat exchangers are
Coupled Inductors and Transformers
 Cupled nductrs and Transfrmers Self-nductance When current i flws thrugh the cil, a magnetic flux is prduced arund it. d d di di v= = = dt di dt dt nductance: = d di This inductance is cmmnly called self-inductance,
Cupled nductrs and Transfrmers Self-nductance When current i flws thrugh the cil, a magnetic flux is prduced arund it. d d di di v= = = dt di dt dt nductance: = d di This inductance is cmmnly called self-inductance,
Chapter 6. Operational Amplifier. inputs can be defined as the average of the sum of the two signals.
 6 Operatonal mpler Chapter 6 Operatonal mpler CC Symbol: nput nput Output EE () Non-nvertng termnal, () nvertng termnal nput mpedance : Few mega (ery hgh), Output mpedance : Less than (ery low) Derental
6 Operatonal mpler Chapter 6 Operatonal mpler CC Symbol: nput nput Output EE () Non-nvertng termnal, () nvertng termnal nput mpedance : Few mega (ery hgh), Output mpedance : Less than (ery low) Derental
LECTURES 4 AND 5 THREE-PHASE CONNECTIONS (1)
 ECE 330 POWER CIRCUITS AND ELECTROMECHANICS LECTURES 4 AND 5 THREEPHASE CONNECTIONS (1) AcknwledgmentThese handuts and lecture ntes given in class are based n material frm Prf. Peter Sauer s ECE 330 lecture
ECE 330 POWER CIRCUITS AND ELECTROMECHANICS LECTURES 4 AND 5 THREEPHASE CONNECTIONS (1) AcknwledgmentThese handuts and lecture ntes given in class are based n material frm Prf. Peter Sauer s ECE 330 lecture
Transistors. Lesson #10 Chapter 4. BME 372 Electronics I J.Schesser
 Tanssts essn #10 Chapte 4 BM 372 lectncs 154 Hmewk Ps. 4.40, 4.42, 4.43, 4.45, 4.46, 4.51, 4.53, 4.54, 4.56 BM 372 lectncs 155 Hmewk Answes #20 Ps. 4.40 See fgue 4.33 BM 372 lectncs 156 Ps. 4.42 Hmewk
Tanssts essn #10 Chapte 4 BM 372 lectncs 154 Hmewk Ps. 4.40, 4.42, 4.43, 4.45, 4.46, 4.51, 4.53, 4.54, 4.56 BM 372 lectncs 155 Hmewk Answes #20 Ps. 4.40 See fgue 4.33 BM 372 lectncs 156 Ps. 4.42 Hmewk
3.2 Terminal Characteristics of Junction Diodes (pp )
 /9/008 secton3_termnal_characterstcs_of_juncton_odes.doc /6 3. Termnal Characterstcs of Juncton odes (pp.47-53) A Juncton ode I.E., A real dode! Smlar to an deal dode, ts crcut symbol s: HO: The Juncton
/9/008 secton3_termnal_characterstcs_of_juncton_odes.doc /6 3. Termnal Characterstcs of Juncton odes (pp.47-53) A Juncton ode I.E., A real dode! Smlar to an deal dode, ts crcut symbol s: HO: The Juncton
I. INTRODUCTION. There are two other circuit elements that we will use and are special cases of the above elements. They are:
 I. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Crcut Theory Fundamentals In ths course we study crcuts wth non-lnear elements or deces (dodes and transstors). We wll use crcut theory tools to analyze these crcuts. Snce some of tools
I. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Crcut Theory Fundamentals In ths course we study crcuts wth non-lnear elements or deces (dodes and transstors). We wll use crcut theory tools to analyze these crcuts. Snce some of tools
A New Modeling Method and Controller Design for a DC DC Zeta Converter
 Electrcal Engneerng esearch (EE), Vlume, 5 A New Mdelng Methd and ntrller esgn fr a Zeta nerter Elshan aaran Hagh, Ebrahm Babae *, ela Mhammadan Faculty f Electrcal and mputer Engneerng, Unersty f Tabrz,
Electrcal Engneerng esearch (EE), Vlume, 5 A New Mdelng Methd and ntrller esgn fr a Zeta nerter Elshan aaran Hagh, Ebrahm Babae *, ela Mhammadan Faculty f Electrcal and mputer Engneerng, Unersty f Tabrz,
The Decibel and its Usage
 The Decbel and ts Usage Consder a two-stage amlfer system, as shown n Fg.. Each amlfer rodes an ncrease of the sgnal ower. Ths effect s referred to as the ower gan,, of the amlfer. Ths means that the sgnal
The Decbel and ts Usage Consder a two-stage amlfer system, as shown n Fg.. Each amlfer rodes an ncrease of the sgnal ower. Ths effect s referred to as the ower gan,, of the amlfer. Ths means that the sgnal
Boise State University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 212L Circuit Analysis and Design Lab
 Bose State Unersty Department of Electrcal and omputer Engneerng EE 1L rcut Analyss and Desgn Lab Experment #8: The Integratng and Dfferentatng Op-Amp rcuts 1 Objectes The objectes of ths laboratory experment
Bose State Unersty Department of Electrcal and omputer Engneerng EE 1L rcut Analyss and Desgn Lab Experment #8: The Integratng and Dfferentatng Op-Amp rcuts 1 Objectes The objectes of ths laboratory experment
I. INTRODUCTION. 1.1 Circuit Theory Fundamentals
 I. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Crcut Theory Fundamentals Crcut theory s an approxmaton to Maxwell s electromagnetc equatons n order to smplfy analyss of complcated crcuts. A crcut s made of seeral elements (boxes
I. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Crcut Theory Fundamentals Crcut theory s an approxmaton to Maxwell s electromagnetc equatons n order to smplfy analyss of complcated crcuts. A crcut s made of seeral elements (boxes
FEEDBACK AMPLIFIERS. v i or v s v 0
 FEEDBCK MPLIFIERS Feedback n mplers FEEDBCK IS THE PROCESS OF FEEDING FRCTION OF OUTPUT ENERGY (VOLTGE OR CURRENT) BCK TO THE INPUT CIRCUIT. THE CIRCUIT EMPLOYED FOR THIS PURPOSE IS CLLED FEEDBCK NETWORK.
FEEDBCK MPLIFIERS Feedback n mplers FEEDBCK IS THE PROCESS OF FEEDING FRCTION OF OUTPUT ENERGY (VOLTGE OR CURRENT) BCK TO THE INPUT CIRCUIT. THE CIRCUIT EMPLOYED FOR THIS PURPOSE IS CLLED FEEDBCK NETWORK.
1. Ideal OP Amps. +V cc. R o. v 1 v 2. v o. R d 2 1. V cc. Ideal Characteristics A = (gain is infinite) (no offset voltage) R
 . Ideal OP Amps Op amp Hgh-gan d dfferental amplfer ( ) D pwer supples are requred Usually used wth external negate feedbak Assume deal p amp desgn rut hek nn-deal haratersts are mprtant mdfy f neessary
. Ideal OP Amps Op amp Hgh-gan d dfferental amplfer ( ) D pwer supples are requred Usually used wth external negate feedbak Assume deal p amp desgn rut hek nn-deal haratersts are mprtant mdfy f neessary
Technote 6. Op Amp Definitions. April 1990 Revised 11/22/02. Tim J. Sobering SDE Consulting
 Technte 6 prl 990 Resed /22/02 Op mp Dentns Tm J. Sberng SDE Cnsultng sdecnsultng@pbx.cm 990 Tm J. Sberng. ll rghts resered. Op mp Dentns Pge 2 Op mp Dentns Ths Technte summrzes the bsc pertnl mpler dentns
Technte 6 prl 990 Resed /22/02 Op mp Dentns Tm J. Sberng SDE Cnsultng sdecnsultng@pbx.cm 990 Tm J. Sberng. ll rghts resered. Op mp Dentns Pge 2 Op mp Dentns Ths Technte summrzes the bsc pertnl mpler dentns
BME 5742 Biosystems Modeling and Control
 BME 5742 Bsystems Mdeln and Cntrl Cell Electrcal Actvty: In Mvement acrss Cell Membrane and Membrane Ptental Dr. Zv Rth (FAU) 1 References Hppensteadt-Peskn, Ch. 3 Dr. Rbert Farley s lecture ntes Inc Equlbra
BME 5742 Bsystems Mdeln and Cntrl Cell Electrcal Actvty: In Mvement acrss Cell Membrane and Membrane Ptental Dr. Zv Rth (FAU) 1 References Hppensteadt-Peskn, Ch. 3 Dr. Rbert Farley s lecture ntes Inc Equlbra
G = G 1 + G 2 + G 3 G 2 +G 3 G1 G2 G3. Network (a) Network (b) Network (c) Network (d)
 Massachusetts Insttute of Technology Department of Electrcal Engneerng and Computer Scence 6.002 í Electronc Crcuts Homework 2 Soluton Handout F98023 Exercse 21: Determne the conductance of each network
Massachusetts Insttute of Technology Department of Electrcal Engneerng and Computer Scence 6.002 í Electronc Crcuts Homework 2 Soluton Handout F98023 Exercse 21: Determne the conductance of each network
( ) = ( ) + ( 0) ) ( )
 EETOMAGNETI OMPATIBIITY HANDBOOK 1 hapter 9: Transent Behavor n the Tme Doman 9.1 Desgn a crcut usng reasonable values for the components that s capable of provdng a tme delay of 100 ms to a dgtal sgnal.
EETOMAGNETI OMPATIBIITY HANDBOOK 1 hapter 9: Transent Behavor n the Tme Doman 9.1 Desgn a crcut usng reasonable values for the components that s capable of provdng a tme delay of 100 ms to a dgtal sgnal.
Physic 231 Lecture 33
 Physc 231 Lecture 33 Man pnts f tday s lecture: eat and heat capacty: Q cm Phase transtns and latent heat: Q Lm ( ) eat flw Q k 2 1 t L Examples f heat cnductvty, R values fr nsulatrs Cnvectn R L / k Radatn
Physc 231 Lecture 33 Man pnts f tday s lecture: eat and heat capacty: Q cm Phase transtns and latent heat: Q Lm ( ) eat flw Q k 2 1 t L Examples f heat cnductvty, R values fr nsulatrs Cnvectn R L / k Radatn
55:141 Advanced Circuit Techniques Two-Port Theory
 55:4 Adanced Crcut Technques Two-Port Theory Materal: Lecture Notes A. Kruger 55:4: Adanced Crcut Technques The Unersty of Iowa, 03 Two-Port Theory, Slde What Are Two-Ports? Basc dea: replace a complex
55:4 Adanced Crcut Technques Two-Port Theory Materal: Lecture Notes A. Kruger 55:4: Adanced Crcut Technques The Unersty of Iowa, 03 Two-Port Theory, Slde What Are Two-Ports? Basc dea: replace a complex
1.4 Small-signal models of BJT
 1.4 Small-sgnal models of J Analog crcuts often operate wth sgnal levels that are small compared to the bas currents and voltages n the crcut. Under ths condton, ncremental or small-sgnal models can be
1.4 Small-sgnal models of J Analog crcuts often operate wth sgnal levels that are small compared to the bas currents and voltages n the crcut. Under ths condton, ncremental or small-sgnal models can be
