Electroweak Theory: 3
|
|
|
- Willa Wilkerson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electroweak Theory: 3 Introduction QED The Fermi theory The standard model Precision tests CP violation; K and B systems Higgs physics Prospectus STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 55
2 References Slides at pgl/talks/ subject to revision P. Langacker, The Standard Model and Beyond, CRC Press, 2010 especially chapters 6, 7 P. Langacker, Introduction to the Standard Model and Electroweak Physics, [arxiv: [hep-ph]] TASI 2008 E.D. Commins and P.H. Bucksbaum, Weak Interactions of Leptons and Quarks, Cambridge, 1983 P. Renton, Electroweak Interactions, Cambridge, 1990 Precision Tests of the Standard Electroweak Model, ed. P. Langacker World, 1995 especially Fetscher and Gerber; Herczog; Deutsch and Quin K. Nakamura et al. [Particle Data Group], J. Phys. G 37, electroweak and other reviews STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 56
3 Previous Lecture The Weak Interactions of Hadrons Semi-Leptonic Processes in the Fermi Theory π and K Decays, and the Strong Interactions β Decay and Related Processes Charm c Quark and Third Family CKM Universality STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 57
4 This Lecture The Standard Electroweak Model Beyond the Fermi Theory Gauge Theories and the Standard Model The Standard Electroweak Model Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking and the Higgs Mechanism The Lagrangian after Symmetry Breaking STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 58
5 Beyond the Fermi Theory Fermi theory successfully describes large number of WCC processes However, not renormalizable Radiative corrections divergent but needed Unitarity violated at high energy E CM 1 TeV Loop processes such as K 0 K 0 mixing meaningless/incorrect More complete theory needed e e ν e ν e e e ν e ν e ν e ν e e e s d J µ J µ J µ J µ J µ J µ J µ J e ν e µ e ν e u u ν e ν e e e ν e ν e e e d s e e ν e ν e e e ν e ν e STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 59
6 Gauge Theories Standard Model is remarkably successful gauge theory of the microscopic interactions Gauge symmetry apparently massless spin-1 vector, gauge bosons Interactions group, representations, gauge coupling Like QED U1, but gauge self interactions for non-abelian Application to strong short range confinement Application to weak short range spontaneous symmetry breaking Higgs or dynamical Unique renormalizable field theory for spin-1 STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 60
7 Non-Abelian n non-interacting fermions of same mass m: iγ µ x m ψ µ a = 0, a = 1 n, invariant under global SUn group, ψ 1. ψ n expi N β i L i ψ 1. ψ n i=1. L i are n n generator matrices N = n 2 1; β i are real parameters [L i, L j ] = ic ijk L k c ijk are structure constants STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 61
8 Gauge local transformation: β i β i x iγ µ N x µδ ab g γ µ A i µ Li ab mδ ab ψ b = 0 i=1 Invariant under Φ ψ 1. ψ n Φ UΦ A µ L A µ L U A µ LU 1 + i g µu U 1 U e i β L 1 STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 62
9 Gauge invariance implies: N apparently massless gauge bosons A i µ Specified interactions up to gauge coupling g, group, representations, including self interactions A i µ ψ a igl i ab γµ ψ b g g 2 Generalize to other groups, representations, chiral L R Chiral Projections: ψ LR 1 Typeset by FoilTEX 2 1 γ 5ψ independent fields Chirality = helicity up to Om/E STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 63
10 The Standard Model Gauge group SU3 SU2 U1; gauge couplings g s, g, g u d L u d L u d L νe e u R u R u R ν er? d R d R d R e R L = left-handed, R = right-handed L SU3: u u u, d d d 8 gluons SU2: u L d L, ν el e L W ± ; phases W 0 U1: phases B Heavy families c, s, ν µ, µ, t, b, ν τ, τ STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 64
11 The Standard Electroweak Model Gauge part Field strength tensors L SU2 U1 = L gauge + L φ + L f + L Yukawa L gauge = 1 4 F i µν F µνi 1 4 B µνb µν B µν = µ B ν ν B µ F i µν = µ W i ν νw i µ gɛ ijkw j µ W k ν, i = 1 3 gg is SU2 U1 gauge coupling; ɛ ijk is totally antisymmetric symbol Three and four-point self-interactions for the W i g g 2 B and W 3 mix to form γ, Z STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 65
12 U1: Φ j expig y j βφ j, y j = q j t 3 j = weak hypercharge Scalar part where φ = φ + φ 0 Gauge covariant derivative: L φ = D µ φ D µ φ V φ is the complex Higgs doublet with y φ = 1/2 D µ φ = µ + ig τ i 2 W i µ + ig 2 B µ φ where τ i are the Pauli matrices Three and four-point interactions between gauge and scalar fields g g 2 STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 66
13 Higgs potential V φ = +µ 2 φ φ + λφ φ 2 φ φ = φ }{{} φ + φ + + φ 0 φ 0 Allowed by renormalizability and gauge invariance Spontaneous symmetry breaking for µ 2 < 0 Vacuum stability: λ > 0 Quartic self-interactions φ 0 φ + λ φ 0 φ STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 67
14 Fermion part L f = F m=1 q 0 ml i Dq0 ml + l 0 ml i Dl0 ml + ū 0 mr i Du0 mr + d 0 mr i Dd0 mr + ē0 mr i De0 mr + ν0 mr i Dν0 mr L-doublets R-singlets u q 0 ml = 0 m d 0 m L l 0 ml = ν 0 m e 0 m u 0 mr, d0 mr, e 0 mr, ν0 mr? L F 3 families; m = 1 F = family index; 0 = weak eigenstates definite SU2 rep., mixtures of mass eigenstates flavors; quark color indices α = r, g, b suppressed e.g., u 0 mαl. Can add gauge singlet ν 0 mr for Dirac neutrino mass term STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 68
15 Different chiral L and R representations lead to parity and charge conjugation violation maximal for SU2 Fermion mass terms forbidden by chiral symmetry Triangle anomalies absent for chosen hypercharges and 3 colors includes quark-lepton cancellations exercize j i k STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 69
16 Gauge covariant derivatives D µ q 0 ml = µ + ig 2 τ i W i µ + ig 6 B µ q 0 ml D µ l 0 ml = µ + ig 2 τ i W i µ ig 2 B µ D µ u 0 mr = µ + i 2 3 g B µ u 0 mr D µ d 0 mr = µ i g 3 B µ d 0 mr D µ e 0 mr = µ ig B µ e 0 mr D µ ν 0 mr = µ ν 0 mr l 0 ml Read off W and B couplings to fermions W i µ i g 2 τ i 1 γ5 γ µ 2 B µ ig 1 γ5 yγ µ 2 STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 70
17 Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking Higgs mechanism Gauge invariance implies massless gauge bosons and fermions Weak interactions short ranged spontaneous symmetry breaking for mass; also for fermions Allow classical ground state expectation value for Higgs field v = 0 φ 0 = constant, φ = φ + φ 0 µ v 0 increases energy, but important for monopoles, strings, domain walls, phase transitions e.g., EWPT, baryogenesis Minimize V v to find v and quantize φ = φ v STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 71
18 SU2 U1: introduce Hermitian basis φ = φ + φ 0 = 2 1 φ 1 + iφ φ 3 + iφ 4 where φ i = φ i. 2 V φ = 1 2 µ2 4 i=1 φ 2 i λ 4 i=1 φ 2 i is O4 invariant. w.l.o.g. choose 0 φ i 0 = 0, i = 1, 2, 4 and 0 φ 3 0 = ν V φ V v = 1 2 µ2 ν λν4 STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 72
19 For µ 2 < 0, minimum at V ν = νµ 2 + λν 2 = 0 ν = µ 2 /λ 1/2 SSB for µ 2 = 0 also; must consider loop corrections φ ν v the generators L 1, L 2, and L 3 Y spontaneously broken, L 1 v 0, etc L i = τ i 2, Y = 1 2 I 1 0 Qv = L 3 + Y v = 0 0 SU2 U1 Y U1 Q v = 0 U1 Q unbroken STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 73
20 Rewrite Lagrangian in New Vacuum Physical Higgs scalar oscillations around minimum: M H = 2λν Higgs covariant kinetic energy terms: D µ φ D µ φ = ν [ g 2 τ i W i µ + g 2 B µ]2 0 ν + H terms M 2 W W +µ W µ + M 2 Z 2 Zµ Z µ + H kinetic energy and gauge interaction terms W e L W e L ν ν g 2 M W = gν h ν e g 2 2 h e ν W ν e R m e = h eν W 2 ν e R STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 74
21 Mass eigenstate bosons: W, Z, and A photon W ± = 1 2 W 1 iw 2 Z = sin θ W B + cos θ W W 3 A = cos θ W B + sin θ W W 3 Weak angle: tan θ W g /g Masses: M W = gν 2, M Z = g 2 + g 2 ν 2 = M W cos θ W, M A = 0 Goldstone scalars eaten longitudinal components of W ±, Z STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 75
22 Will show: Fermi constant G F / 2 g 2 /8M 2 W G F = GeV 2 from muon lifetime Electroweak scale: ν = 2M W /g 2G F 1/2 246 GeV Will show: g = e/ sin θ W α = e 2 /4π 1/ M W = M Z cos θ W = gν 2 πα/ 2G F 1/2 sin θ W Weak neutral current: sin 2 θ W 0.23 M W 78 GeV, and M Z 89 GeV increased by 2 GeV by loop corrections Discovered at CERN: UA1 and UA2, 1983 STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 76
23 Fermion Masses and Mixings Yukawa Higgs-fermion interaction + analogous u, e, ν terms L Y uk = = F Γ d mn q 0 ml φd0 nr + h.c. m,n=1 F m,n=1 Γ d mn [ū0 ml φ+ d 0 nr + d 0 ml φ0 dnr] 0 + h.c. u 0 ml d 0 ml φ + iγ d mn φ 0 iγ d mn d 0 nr d 0 nr STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 77
24 For φ 1 2 L Y uk = i 0 ν + H F M d d 0 mn ml d0 nr m,n=1 unitary gauge m i dil d ir 1 + H ν 1 + H ν + h.c. + h.c. = i m i di d i 1 + H ν with M d Γ d ν/ 2 d i = d il + d ir are mass eigenstates of mass m i For F = 3 A d L M d A d R = m d m s m b, d s b L,R = A d L,R }{{} unitary d0 1 d 0 2 d 0 3 L,R Higgs H couplings to fermions are diagonal in flavor and mass STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 78
25 The Weak Charged Current Fermi Theory incorporated in SM and made renormalizable W -fermion interaction L = g 2 2 J µ W W µ + J µ W W + µ Charge-raising current ignoring ν masses J µ W = F m=1 0 [ ν m γµ 1 γ 5 e 0 m + ] ū0 m γµ 1 γ 5 d 0 m = ν e ν µ ν τ γ µ 1 γ 5 e µ τ + ū c tγ µ 1 γ 5 V d s b STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 79
26 Ignore ν masses for now Pure V A maximal P and C violation; CP conserved except for phases in V V = A u L Ad L is F F unitary Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa CKM matrix from mismatch between weak and Yukawa interactions Cabibbo matrix for F = 2 V = cos θc sin θ c sin θ c cos θ c sin θ c 0.23 Cabibbo angle Good zeroth-order description since third family almost decouples General unitary 2 2: 1 angle and 3 unobservable q L phases STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 80
27 CKM matrix for F = 3 involves 3 angles and 1 CP -violating phase after removing unobservable q L phases new interations involving q R could make observable V = V ud V us V ub V cd V cs V cb V td V td V td Extensive studies, especially in B decays, to test unitarity of V as probe of new physics and test origin of CP violation Need additional source of CP breaking for baryogenesis STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 81
28 Effective zero- range 4-fermi interaction Fermi theory For Q M W, neglect Q 2 in W propagator L cc eff = g J µ W gµν Q 2 M 2 W J ν W g2 8M 2 W J µ W J W µ Fermi constant: G F 2 g2 8M 2 W = 1 2ν 2 Muon lifetime: τ 1 = G2 F m5 µ 192π 3 G F = GeV 2 Weak scale: ν = 2 0 φ GeV Excellent description of β, K, hyperon, heavy quark, µ, and τ decays, ν µ e µ ν e, ν µ n µ p, ν µ N µ X STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 82
29 Full theory probed: e ± p ν e X at high energy HERA Electroweak radiative corrections loop level Very important. Only calculable in full theory. M KS M KL, kaon CP violation, B B mixing loop level 1.5 excluded area has CL > 0.95 excluded at CL > 0.95 " $m d sin 2! $m s & $m d CKMFITTER group: ' 0 % K V ub /V cb " #! # # sol. w/ cos 2! < 0 excl. at CL > 0.95 % K C K M f i t t e r EPS 2005 " & STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 83
30 Quantum Electrodynamics QED Incorporated into standard model Lagrangian: L = gg µ g2 + g 2J Q cos θ W B µ + sin θ W W 3 µ Photon field: A µ = cos θ W B µ + sin θ W W 3 µ Positron electric charge: e = g sin θ W, where tan θ W g /g STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 84
31 Electromagnetic current: F J µ Q = [ 2 m=1 F = m=1 3ū0 m γµ u 0 m 1 3 [ 2 µ u m 1 3ūmγ 3 d 0 m γµ d 0 m ē0 m γµ e 0 m ] d m γ µ d m ē m γ µ e m ] Electric charge: Q = T 3 + Y, where Y = weak hypercharge coefficient of ig B µ in covariant derivatives Flavor diagonal: Same form in weak and mass bases because fields which mix have same charge Purely vector parity conserving: L and R fields have same charge q i = t 3 i + y i is the same for L and R fields, even though t 3 i and y i are not STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 85
32 Prediction of SU2 U1 The Weak Neutral Current g2 + g 2 L = J µ Z sin θ W B µ + cos θ W W 3 µ 2 g = J µ Z 2 cos θ Z µ W Neutral current process and effective 4-fermi interaction for Q M Z STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 86
33 Neutral current: J µ Z = [ū0 ml γµ u 0 ml d 0 ml γµ d 0 ml + ν0 ml γµ ν 0 ml ] ē0 ml γµ e 0 ml m = m 2 sin 2 θ W J µ Q [ūml γ µ u ml d ml γ µ d ml + ν ml γ µ ν ml ē ml γ µ ] e ml 2 sin 2 θ W J µ Q Flavor diagonal: Same form in weak and mass bases because fields which mix have same charge GIM mechanism: c quark predicted so that s L could be in doublet to avoid unwanted flavor changing neutral currents FCNC at tree and loop level Parity and charge conjugation violated but not maximally: first term is pure V A, second is V STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 87
34 Effective 4-fermi interaction for Q 2 M 2 Z : L NC eff = G F 2 J µ Z J Zµ Coefficient same as WCC because G F 2 = g2 8M 2 W = g2 + g 2 8M 2 Z STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 88
35 Cross-section pb Z e + e hadrons 10 2 CESR DORIS PEP W + W - 10 KEKB PEP-II PETRA TRISTAN SLC LEP I LEP II Centre-of-mass energy GeV 10. Electroweak model and constraints on new physics 15!"$!"$'%!"$'!"$''!"$'$ " WW pb LEP PRELIMINARY 17/02/2005 *+, $ θ ' µ!"$'!"$&%!"$&!"$&'!"$&$!"$&!"$$% -. / /43 CD556E -F4<G 4@AB8 ν*+,- 5617# 859 :4;<=>?,!"!!!#!"!!#!"!#!"# # #! #!! #!!! #!!!! µ!"#$%& 10 0 YFSWW/RacoonWW no ZWW vertex Gentle only # e exchange Gentle !s GeV STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 89
36 The Z, the W, and the Weak Neutral Current Primary prediction and test of electroweak unification WNC discovered 1973 Gargamelle at CERN, HPW at FNAL 70 s, 80 s: weak neutral current experiments few % Pure weak: νn, νe scattering Weak-elm interference in ed, e + e, atomic parity violation Model independent analyses νe, νq, eq SU2 U1 group/representations; t and ν τ exist; m t limit; hint for SUSY unification; limits on TeV scale physics W, Z discovered directly 1983 UA1, UA2 STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 90
37 90 s: Z pole LEP, SLD, 0.1%; lineshape, modes, asymmetries LEP 2: M W, Higgs search, gauge self-interactions Tevatron: m t, M W, Higgs search 4th generation weak neutral current experiments atomic parity Boulder; νe; νn NuTeV; polarized Møller asymmetry SLAC STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 91
38 SM correct and unique to zeroth approx. gauge principle, group, representations SM correct at loop level renorm gauge theory; m t, α s, M H TeV physics severely constrained unification vs compositeness Consistent with light elementary Higgs Precise gauge couplings SUSY gauge unification Measurement Fit O meas O fit /σ meas α 5 had m Z ± m Z [GeV] ± Γ Z [GeV] ± σ 0 had [nb] ± R l ± A 0,l fb ± A l P τ ± R b ± R c ± A 0,b fb ± A 0,c fb ± A b ± A c ± A l SLD ± sin 2 θ lept eff Q fb ± m W [GeV] ± Γ W [GeV] ± m t [GeV] ± August STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 92
Electroweak Theory, SSB, and the Higgs: Lecture 2
 1 Electroweak Theory, SSB, and the iggs: Lecture Spontaneous symmetry breaking (iggs mechanism) - Gauge invariance implies massless gauge bosons and fermions - Weak interactions short ranged spontaneous
1 Electroweak Theory, SSB, and the iggs: Lecture Spontaneous symmetry breaking (iggs mechanism) - Gauge invariance implies massless gauge bosons and fermions - Weak interactions short ranged spontaneous
Introduction to the Standard Model
 Introduction to the Standard Model Origins of the Electroweak Theory Gauge Theories The Standard Model References: 2008 TASI lectures: arxiv:0901.0241 [hep-ph] and The Standard Model and Beyond, CRC Press
Introduction to the Standard Model Origins of the Electroweak Theory Gauge Theories The Standard Model References: 2008 TASI lectures: arxiv:0901.0241 [hep-ph] and The Standard Model and Beyond, CRC Press
Electroweak Theory: 2
 Electroweak Theory: 2 Introduction QED The Fermi theory The standard model Precision tests CP violation; K and B systems Higgs physics Prospectus STIAS (January, 2011) Paul Langacker (IAS) 31 References
Electroweak Theory: 2 Introduction QED The Fermi theory The standard model Precision tests CP violation; K and B systems Higgs physics Prospectus STIAS (January, 2011) Paul Langacker (IAS) 31 References
Beyond the Standard Model
 Beyond the Standard Model The Standard Model Problems with the Standard Model New Physics Supersymmetry Extended Electroweak Symmetry Grand Unification References: 2008 TASI lectures: arxiv:0901.0241 [hep-ph]
Beyond the Standard Model The Standard Model Problems with the Standard Model New Physics Supersymmetry Extended Electroweak Symmetry Grand Unification References: 2008 TASI lectures: arxiv:0901.0241 [hep-ph]
Introduction to the Standard Model
 Introduction to the Standard Model Origins of the Electroweak Theory Gauge Theories The Standard Model Lagrangian Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking The Gauge Interactions Problems With the Standard Model (
Introduction to the Standard Model Origins of the Electroweak Theory Gauge Theories The Standard Model Lagrangian Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking The Gauge Interactions Problems With the Standard Model (
Introduction to the Standard Model
 Introduction to the Standard Model Origins of the Electroweak Theory Gauge Theories The Standard Model Lagrangian Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking The Gauge Interactions Problems With the Standard Model (
Introduction to the Standard Model Origins of the Electroweak Theory Gauge Theories The Standard Model Lagrangian Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking The Gauge Interactions Problems With the Standard Model (
Electroweak Theory: 5
 Electroweak Theory: 5 Introduction QED The Fermi theory The standard model Precision tests CP violation; K and B systems Higgs physics Prospectus STIAS (January, 2011) Paul Langacker (IAS) 162 References
Electroweak Theory: 5 Introduction QED The Fermi theory The standard model Precision tests CP violation; K and B systems Higgs physics Prospectus STIAS (January, 2011) Paul Langacker (IAS) 162 References
Supersymmetry, Dark Matter, and Neutrinos
 Supersymmetry, Dark Matter, and Neutrinos The Standard Model and Supersymmetry Dark Matter Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics The Physics of Supersymmetry Gauge Theories Gauge symmetry requires existence
Supersymmetry, Dark Matter, and Neutrinos The Standard Model and Supersymmetry Dark Matter Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics The Physics of Supersymmetry Gauge Theories Gauge symmetry requires existence
Electroweak Physics. Precision Experiments: Historical Perspective. LEP/SLC Physics. Probing the Standard Model. Beyond the Standard Model
 Electroweak Physics Precision Experiments: Historical Perspective LEP/SLC Physics Probing the Standard Model Beyond the Standard Model The Z, the W, and the Weak Neutral Current Primary prediction and
Electroweak Physics Precision Experiments: Historical Perspective LEP/SLC Physics Probing the Standard Model Beyond the Standard Model The Z, the W, and the Weak Neutral Current Primary prediction and
W + W - The Z pole. e + e hadrons SLC. Cross-section (pb) Centre-of-mass energy (GeV) P529 Spring,
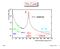 The Z pole Cross-section (pb) 10 5 10 4 Z e + e hadrons 10 3 10 2 CESR DORIS PEP W + W - 10 KEKB PEP-II PETRA TRISTAN SLC LEP I LEP II 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 Centre-of-mass energy (GeV)
The Z pole Cross-section (pb) 10 5 10 4 Z e + e hadrons 10 3 10 2 CESR DORIS PEP W + W - 10 KEKB PEP-II PETRA TRISTAN SLC LEP I LEP II 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 Centre-of-mass energy (GeV)
The Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa (CKM) matrix
 The Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa (CKM) matrix Charge-raising current J µ W = ( ν e ν µ ν τ )γ µ (1 γ 5 ) V = A u L Ad L e µ τ + (ū c t)γ µ (1 γ 5 )V Mismatch between weak and quark masses, and between A u,d
The Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa (CKM) matrix Charge-raising current J µ W = ( ν e ν µ ν τ )γ µ (1 γ 5 ) V = A u L Ad L e µ τ + (ū c t)γ µ (1 γ 5 )V Mismatch between weak and quark masses, and between A u,d
Introduction to the Standard Model New Horizons in Lattice Field Theory IIP Natal, March 2013
 Introduction to the Standard Model New Horizons in Lattice Field Theory IIP Natal, March 2013 Rogerio Rosenfeld IFT-UNESP Lecture 1: Motivation/QFT/Gauge Symmetries/QED/QCD Lecture 2: QCD tests/electroweak
Introduction to the Standard Model New Horizons in Lattice Field Theory IIP Natal, March 2013 Rogerio Rosenfeld IFT-UNESP Lecture 1: Motivation/QFT/Gauge Symmetries/QED/QCD Lecture 2: QCD tests/electroweak
Standard Model & Beyond
 XI SERC School on Experimental High-Energy Physics National Institute of Science Education and Research 13 th November 2017 Standard Model & Beyond Lecture III Sreerup Raychaudhuri TIFR, Mumbai 2 Fermions
XI SERC School on Experimental High-Energy Physics National Institute of Science Education and Research 13 th November 2017 Standard Model & Beyond Lecture III Sreerup Raychaudhuri TIFR, Mumbai 2 Fermions
Fundamental Symmetries - 2
 HUGS 2018 Jefferson Lab, Newport News, VA May 29- June 15 2018 Fundamental Symmetries - 2 Vincenzo Cirigliano Los Alamos National Laboratory Plan of the lectures Review symmetry and symmetry breaking Introduce
HUGS 2018 Jefferson Lab, Newport News, VA May 29- June 15 2018 Fundamental Symmetries - 2 Vincenzo Cirigliano Los Alamos National Laboratory Plan of the lectures Review symmetry and symmetry breaking Introduce
Tests of the Electroweak Theory
 Tests of the Electroweak Theory History/introduction Weak charged current QED Weak neutral current Precision tests Rare processes CP violation and B decays Neutrino mass FNAL (December 6, 2005) Paul Langacker
Tests of the Electroweak Theory History/introduction Weak charged current QED Weak neutral current Precision tests Rare processes CP violation and B decays Neutrino mass FNAL (December 6, 2005) Paul Langacker
IX. Electroweak unification
 IX. Electroweak unification The problem of divergence A theory of weak interactions only by means of W ± bosons leads to infinities e + e - γ W - W + e + W + ν e ν µ e - W - µ + µ Divergent integrals Figure
IX. Electroweak unification The problem of divergence A theory of weak interactions only by means of W ± bosons leads to infinities e + e - γ W - W + e + W + ν e ν µ e - W - µ + µ Divergent integrals Figure
Abdelhak DJOUADI ( LPT Orsay)
 Physics at the LHC bdelhak DJOUDI ( LPT Orsay) Standard Physics at the LHC 1 The Standard Model QCD at the LHC 3 Tests of the SM at the LHC The SM Higgs at the LHC SUSY and SUSY Higgs at the LHC Physics
Physics at the LHC bdelhak DJOUDI ( LPT Orsay) Standard Physics at the LHC 1 The Standard Model QCD at the LHC 3 Tests of the SM at the LHC The SM Higgs at the LHC SUSY and SUSY Higgs at the LHC Physics
Status and Phenomenology of the Standard Model
 Status and Phenomenology of the Standard Model The new standard model Experimental tests, unique features, anomalies, hints of new physics Precision tests Higgs Heavy quarks Neutrinos FCNC and EDMs Astrophysics
Status and Phenomenology of the Standard Model The new standard model Experimental tests, unique features, anomalies, hints of new physics Precision tests Higgs Heavy quarks Neutrinos FCNC and EDMs Astrophysics
Beyond Standard Model Effects in Flavour Physics: p.1
 Beyond Standard Model Effects in Flavour Physics: Alakabha Datta University of Mississippi Feb 13, 2006 Beyond Standard Model Effects in Flavour Physics: p.1 OUTLINE Standard Model (SM) and its Problems.
Beyond Standard Model Effects in Flavour Physics: Alakabha Datta University of Mississippi Feb 13, 2006 Beyond Standard Model Effects in Flavour Physics: p.1 OUTLINE Standard Model (SM) and its Problems.
Interactions... + similar terms for µ and τ Feynman rule: gauge-boson propagator: ig 2 2 γ λ(1 γ 5 ) = i(g µν k µ k ν /M 2 W ) k 2 M 2 W
 Interactions... L W-l = g [ νγµ (1 γ 5 )ew µ + +ēγ µ (1 γ 5 )νwµ ] + similar terms for µ and τ Feynman rule: e λ ig γ λ(1 γ 5 ) ν gauge-boson propagator: W = i(g µν k µ k ν /M W ) k M W. Chris Quigg Electroweak
Interactions... L W-l = g [ νγµ (1 γ 5 )ew µ + +ēγ µ (1 γ 5 )νwµ ] + similar terms for µ and τ Feynman rule: e λ ig γ λ(1 γ 5 ) ν gauge-boson propagator: W = i(g µν k µ k ν /M W ) k M W. Chris Quigg Electroweak
Tests of the Electroweak Theory
 Tests of the Electroweak Theory History/introduction Weak charged current QED Weak neutral current Precision tests Rare processes CP violation and B decays Neutrino mass FNAL (December 13, 2005) Paul Langacker
Tests of the Electroweak Theory History/introduction Weak charged current QED Weak neutral current Precision tests Rare processes CP violation and B decays Neutrino mass FNAL (December 13, 2005) Paul Langacker
The Z, the W, and the Weak Neutral Current
 The Z, the W, and the Weak Neutral Current g L Z = J µ Z 2 cos θ Z µ W J µ Z = r t 3 rl ψ 0 r γµ (1 γ 5 )ψ 0 r 2 sin2 θ W J µ Q t 3 ul = t3 dl = t3 νl = t3 el = 1 2, tan θ W = g /g L NC eff = G F 2 J µ
The Z, the W, and the Weak Neutral Current g L Z = J µ Z 2 cos θ Z µ W J µ Z = r t 3 rl ψ 0 r γµ (1 γ 5 )ψ 0 r 2 sin2 θ W J µ Q t 3 ul = t3 dl = t3 νl = t3 el = 1 2, tan θ W = g /g L NC eff = G F 2 J µ
Grand Unification. Strong, weak, electromagnetic unified at Q M X M Z Simple group SU(3) SU(2) U(1) Gravity not included
 Pati-Salam, 73; Georgi-Glashow, 74 Grand Unification Strong, weak, electromagnetic unified at Q M X M Z Simple group G M X SU(3) SU() U(1) Gravity not included (perhaps not ambitious enough) α(q ) α 3
Pati-Salam, 73; Georgi-Glashow, 74 Grand Unification Strong, weak, electromagnetic unified at Q M X M Z Simple group G M X SU(3) SU() U(1) Gravity not included (perhaps not ambitious enough) α(q ) α 3
Electroweak physics and the LHC an introduction to the Standard Model
 Electroweak physics and the LHC an introduction to the Standard Model Paolo Gambino INFN Torino LHC School Martignano 12-18 June 2006 Outline Prologue on weak interactions Express review of gauge theories
Electroweak physics and the LHC an introduction to the Standard Model Paolo Gambino INFN Torino LHC School Martignano 12-18 June 2006 Outline Prologue on weak interactions Express review of gauge theories
Current knowledge tells us that matter is made of fundamental particle called fermions,
 Chapter 1 Particle Physics 1.1 Fundamental Particles Current knowledge tells us that matter is made of fundamental particle called fermions, which are spin 1 particles. Our world is composed of two kinds
Chapter 1 Particle Physics 1.1 Fundamental Particles Current knowledge tells us that matter is made of fundamental particle called fermions, which are spin 1 particles. Our world is composed of two kinds
Lecture 16 V2. October 24, 2017
 Lecture 16 V2 October 24, 2017 Recap: gamma matrices Recap: pion decay properties Unifying the weak and electromagnetic interactions Ø Recap: QED Lagrangian for U Q (1) gauge symmetry Ø Introduction of
Lecture 16 V2 October 24, 2017 Recap: gamma matrices Recap: pion decay properties Unifying the weak and electromagnetic interactions Ø Recap: QED Lagrangian for U Q (1) gauge symmetry Ø Introduction of
An Introduction to the Standard Model of Particle Physics
 An Introduction to the Standard Model of Particle Physics W. N. COTTINGHAM and D. A. GREENWOOD Ж CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface. page xiii Notation xv 1 The particle physicist's view of Nature
An Introduction to the Standard Model of Particle Physics W. N. COTTINGHAM and D. A. GREENWOOD Ж CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface. page xiii Notation xv 1 The particle physicist's view of Nature
A model of the basic interactions between elementary particles is defined by the following three ingredients:
 I. THE STANDARD MODEL A model of the basic interactions between elementary particles is defined by the following three ingredients:. The symmetries of the Lagrangian; 2. The representations of fermions
I. THE STANDARD MODEL A model of the basic interactions between elementary particles is defined by the following three ingredients:. The symmetries of the Lagrangian; 2. The representations of fermions
The Physics of Heavy Z-prime Gauge Bosons
 The Physics of Heavy Z-prime Gauge Bosons Tevatron LHC LHC LC LC 15fb -1 100fb -1 14TeV 1ab -1 14TeV 0.5TeV 1ab -1 P - =0.8 P + =0.6 0.8TeV 1ab -1 P - =0.8 P + =0.6 χ ψ η LR SSM 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 2σ m Z'
The Physics of Heavy Z-prime Gauge Bosons Tevatron LHC LHC LC LC 15fb -1 100fb -1 14TeV 1ab -1 14TeV 0.5TeV 1ab -1 P - =0.8 P + =0.6 0.8TeV 1ab -1 P - =0.8 P + =0.6 χ ψ η LR SSM 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 2σ m Z'
Lecture 11. Weak interactions
 Lecture 11 Weak interactions 1962-66: Formula/on of a Unified Electroweak Theory (Glashow, Salam, Weinberg) 4 intermediate spin 1 interaction carriers ( bosons ): the photon (γ) responsible for all electromagnetic
Lecture 11 Weak interactions 1962-66: Formula/on of a Unified Electroweak Theory (Glashow, Salam, Weinberg) 4 intermediate spin 1 interaction carriers ( bosons ): the photon (γ) responsible for all electromagnetic
Standard Model of Particle Physics SS 2013
 ecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 013 (Weak) Neutral Currents 1 Contents Theoretical Motivation for Neutral Currents NC Processes Experimental Discovery Measurement of the Weinberg
ecture: Standard Model of Particle Physics Heidelberg SS 013 (Weak) Neutral Currents 1 Contents Theoretical Motivation for Neutral Currents NC Processes Experimental Discovery Measurement of the Weinberg
Flavour Physics Lecture 1
 Flavour Physics Lecture 1 Chris Sachrajda School of Physics and Astronomy University of Southampton Southampton SO17 1BJ UK New Horizons in Lattice Field Theory, Natal, Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil March
Flavour Physics Lecture 1 Chris Sachrajda School of Physics and Astronomy University of Southampton Southampton SO17 1BJ UK New Horizons in Lattice Field Theory, Natal, Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil March
Antonio Pich. IFIC, CSIC Univ. Valencia.
 Antonio Pich IFIC, CSIC Univ. alencia Antonio.Pich@cern.ch Fermion Masses Fermion Generations Quark Mixing Lepton Mixing Standard Model Parameters CP iolation Quarks Leptons Bosons up down electron neutrino
Antonio Pich IFIC, CSIC Univ. alencia Antonio.Pich@cern.ch Fermion Masses Fermion Generations Quark Mixing Lepton Mixing Standard Model Parameters CP iolation Quarks Leptons Bosons up down electron neutrino
Lepton Flavor Violation
 Lepton Flavor Violation I. The (Extended) Standard Model Flavor Puzzle SSI 2010 : Neutrinos Nature s mysterious messengers SLAC, 9 August 2010 Yossi Nir (Weizmann Institute of Science) LFV 1/39 Lepton
Lepton Flavor Violation I. The (Extended) Standard Model Flavor Puzzle SSI 2010 : Neutrinos Nature s mysterious messengers SLAC, 9 August 2010 Yossi Nir (Weizmann Institute of Science) LFV 1/39 Lepton
Elementary Particles, Flavour Physics and all that...
 Elementary Particles, Flavour Physics and all that... 1 Flavour Physics The term Flavour physics was coined in 1971 by Murray Gell-Mann and his student at the time, Harald Fritzsch, at a Baskin-Robbins
Elementary Particles, Flavour Physics and all that... 1 Flavour Physics The term Flavour physics was coined in 1971 by Murray Gell-Mann and his student at the time, Harald Fritzsch, at a Baskin-Robbins
The Higgs Boson and Electroweak Symmetry Breaking
 The Higgs Boson and Electroweak Symmetry Breaking 1. Minimal Standard Model M. E. Peskin Chiemsee School September 2014 The Higgs boson has an odd position in the Standard Model of particle physics. On
The Higgs Boson and Electroweak Symmetry Breaking 1. Minimal Standard Model M. E. Peskin Chiemsee School September 2014 The Higgs boson has an odd position in the Standard Model of particle physics. On
Lecture 10: Weak Interaction. 1
 Lecture 10: Weak Interaction http://faculty.physics.tamu.edu/kamon/teaching/phys627/ 1 Standard Model Lagrangian http://pdg.lbl.gov/2017/reviews/rpp2017-rev-standard-model.pdf Standard Model Lagrangian
Lecture 10: Weak Interaction http://faculty.physics.tamu.edu/kamon/teaching/phys627/ 1 Standard Model Lagrangian http://pdg.lbl.gov/2017/reviews/rpp2017-rev-standard-model.pdf Standard Model Lagrangian
The Standard Model and Beyond
 Paul Langacker The Standard Model and Beyond CRC PRESS Boca Raton Ann Arbor London Tokyo Contents Preface xi 1 Notation and Conventions 1 1.1 Problems............................. 5 2 Review of Perturbative
Paul Langacker The Standard Model and Beyond CRC PRESS Boca Raton Ann Arbor London Tokyo Contents Preface xi 1 Notation and Conventions 1 1.1 Problems............................. 5 2 Review of Perturbative
The Higgs discovery - a portal to new physics
 The Higgs discovery - a portal to new physics Department of astronomy and theoretical physics, 2012-10-17 1 / 1 The Higgs discovery 2 / 1 July 4th 2012 - a historic day in many ways... 3 / 1 July 4th 2012
The Higgs discovery - a portal to new physics Department of astronomy and theoretical physics, 2012-10-17 1 / 1 The Higgs discovery 2 / 1 July 4th 2012 - a historic day in many ways... 3 / 1 July 4th 2012
Shahram Rahatlou University of Rome
 Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa Matrix and CP Violation in Standard Model Shahram Rahatlou University of Rome Lecture 1 Lezioni di Fisica delle Particelle Elementari Many thanks to Vivek Sharma (UCSD) And Achille
Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa Matrix and CP Violation in Standard Model Shahram Rahatlou University of Rome Lecture 1 Lezioni di Fisica delle Particelle Elementari Many thanks to Vivek Sharma (UCSD) And Achille
Introduction to particle physics Lecture 6
 Introduction to particle physics Lecture 6 Frank Krauss IPPP Durham U Durham, Epiphany term 2009 Outline 1 Fermi s theory, once more 2 From effective to full theory: Weak gauge bosons 3 Massive gauge bosons:
Introduction to particle physics Lecture 6 Frank Krauss IPPP Durham U Durham, Epiphany term 2009 Outline 1 Fermi s theory, once more 2 From effective to full theory: Weak gauge bosons 3 Massive gauge bosons:
Electroweak interactions of quarks. Benoit Clément, Université Joseph Fourier/LPSC Grenoble
 Electroweak interactions of quarks Benoit Clément, Université Joseph Fourier/LPSC Grenoble HASCO School, Göttingen, July 15-27 2012 1 PART 1 : Hadron decay, history of flavour mixing PART 2 : Oscillations
Electroweak interactions of quarks Benoit Clément, Université Joseph Fourier/LPSC Grenoble HASCO School, Göttingen, July 15-27 2012 1 PART 1 : Hadron decay, history of flavour mixing PART 2 : Oscillations
PHYSICS PARTICLE. An Introductory Course of. Palash B. Pal. CRC Press. Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics. Kolkata, India. Taylor &.
 An Introductory Course of PARTICLE PHYSICS Palash B. Pal Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata, India W CRC Press Taylor &. Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the &
An Introductory Course of PARTICLE PHYSICS Palash B. Pal Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics Kolkata, India W CRC Press Taylor &. Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the &
Tales From The Dark Side of Particle Physics (The Dark-Light Connection) William J. Marciano
 Tales From The Dark Side of Particle Physics (The Dark-Light Connection) Based on H. Davoudiasl, H-S Lee &WJM Viewer Discretion Advised Beware the Ides of March! William J. Marciano The Best of Times or
Tales From The Dark Side of Particle Physics (The Dark-Light Connection) Based on H. Davoudiasl, H-S Lee &WJM Viewer Discretion Advised Beware the Ides of March! William J. Marciano The Best of Times or
Problems for SM/Higgs (I)
 Problems for SM/Higgs (I) 1 Draw all possible Feynman diagrams (at the lowest level in perturbation theory) for the processes e + e µ + µ, ν e ν e, γγ, ZZ, W + W. Likewise, draw all possible Feynman diagrams
Problems for SM/Higgs (I) 1 Draw all possible Feynman diagrams (at the lowest level in perturbation theory) for the processes e + e µ + µ, ν e ν e, γγ, ZZ, W + W. Likewise, draw all possible Feynman diagrams
FLAVOR PHYSICS BEYOND THE STANDARD MODEL
 SFB Colloquium DESY Hamburg, July 3rd, 2008 FLAVOR PHYSICS BEYOND THE STANDARD MODEL Gudrun Hiller, Dortmund University of Technology Standard Model of Particle Physics renormalizable quantum field theory
SFB Colloquium DESY Hamburg, July 3rd, 2008 FLAVOR PHYSICS BEYOND THE STANDARD MODEL Gudrun Hiller, Dortmund University of Technology Standard Model of Particle Physics renormalizable quantum field theory
Basics of Higgs Physics
 Basics of iggs Physics Sven einemeyer, IFCA (Santander) Karlsruhe, 07/2007 1. The iggs Boson in the SM 2. The iggs Boson in the MSSM Sven einemeyer Basics of iggs Physics presusy07 (Karlsruhe) 23.07.2007
Basics of iggs Physics Sven einemeyer, IFCA (Santander) Karlsruhe, 07/2007 1. The iggs Boson in the SM 2. The iggs Boson in the MSSM Sven einemeyer Basics of iggs Physics presusy07 (Karlsruhe) 23.07.2007
Leptons and SU(2) U(1)
 Leptons and SU() U(1) Contents I. Defining the Leptonic Standard Model 1 II. L kin and the gauge symmetry 3 III. L mψ = 0 4 IV. L φ and spontaneous symmetry breaking 4 V. Back to L kin (φ): The vector
Leptons and SU() U(1) Contents I. Defining the Leptonic Standard Model 1 II. L kin and the gauge symmetry 3 III. L mψ = 0 4 IV. L φ and spontaneous symmetry breaking 4 V. Back to L kin (φ): The vector
Higgs Physics from the Lattice Lecture 1: Standard Model Higgs Physics
 Higgs Physics from the Lattice Lecture 1: Standard Model Higgs Physics Julius Kuti University of California, San Diego INT Summer School on Lattice QCD and its applications Seattle, August 8-28, 2007 Julius
Higgs Physics from the Lattice Lecture 1: Standard Model Higgs Physics Julius Kuti University of California, San Diego INT Summer School on Lattice QCD and its applications Seattle, August 8-28, 2007 Julius
Quantum Field Theory. and the Standard Model. !H Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS MATTHEW D. SCHWARTZ. Harvard University
 Quantum Field Theory and the Standard Model MATTHEW D. Harvard University SCHWARTZ!H Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS t Contents v Preface page xv Part I Field theory 1 1 Microscopic theory of radiation 3 1.1
Quantum Field Theory and the Standard Model MATTHEW D. Harvard University SCHWARTZ!H Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS t Contents v Preface page xv Part I Field theory 1 1 Microscopic theory of radiation 3 1.1
Adding families: GIM mechanism and CKM matrix
 Particules Élémentaires, Gravitation et Cosmologie Année 2007-08 08 Le Modèle Standard et ses extensions Cours VII: 29 février f 2008 Adding families: GIM mechanism and CKM matrix 29 fevrier 2008 G. Veneziano,
Particules Élémentaires, Gravitation et Cosmologie Année 2007-08 08 Le Modèle Standard et ses extensions Cours VII: 29 février f 2008 Adding families: GIM mechanism and CKM matrix 29 fevrier 2008 G. Veneziano,
OUTLINE. CHARGED LEPTONIC WEAK INTERACTION - Decay of the Muon - Decay of the Neutron - Decay of the Pion
 Weak Interactions OUTLINE CHARGED LEPTONIC WEAK INTERACTION - Decay of the Muon - Decay of the Neutron - Decay of the Pion CHARGED WEAK INTERACTIONS OF QUARKS - Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism - Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
Weak Interactions OUTLINE CHARGED LEPTONIC WEAK INTERACTION - Decay of the Muon - Decay of the Neutron - Decay of the Pion CHARGED WEAK INTERACTIONS OF QUARKS - Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism - Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
From Friday: Neutrino Summary. Three neutrinos in the Standard Model:!e,!µ,!" Only left-handed neutrinos and right-handed antineutrinos are observed.
 Particle Physics Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2012 ecture 17: Electroweak Theory! Weak Isospin and Hypercharge! SU(2) and U(1) symmetries! Weak Isospin and Hypercharge currents!w and Z bosons!z
Particle Physics Dr Victoria Martin, Spring Semester 2012 ecture 17: Electroweak Theory! Weak Isospin and Hypercharge! SU(2) and U(1) symmetries! Weak Isospin and Hypercharge currents!w and Z bosons!z
The Standard Model Part. II
 Our Story Thus Far The Standard Model Part. II!!We started with QED (and!)!!we extended this to the Fermi theory of weak interactions! Adding G F!!Today we will extended this to Glashow-Weinberg-Salam
Our Story Thus Far The Standard Model Part. II!!We started with QED (and!)!!we extended this to the Fermi theory of weak interactions! Adding G F!!Today we will extended this to Glashow-Weinberg-Salam
May 7, Physics Beyond the Standard Model. Francesco Fucito. Introduction. Standard. Model- Boson Sector. Standard. Model- Fermion Sector
 - Boson - May 7, 2017 - Boson - The standard model of particle physics is the state of the art in quantum field theory All the knowledge we have developed so far in this field enters in its definition:
- Boson - May 7, 2017 - Boson - The standard model of particle physics is the state of the art in quantum field theory All the knowledge we have developed so far in this field enters in its definition:
HIGGS&AT&LHC. Electroweak&symmetry&breaking&and&Higgs& Shahram&Rahatlou. Fisica&delle&Par,celle&Elementari,&Anno&Accademico&
 IGGS&AT&LC Electroweak&symmetry&breaking&and&iggs& Lecture&9& Shahram&Rahatlou Fisica&delle&Par,celle&Elementari,&Anno&Accademico&2014815 htt://www.roma1.infn.it/eole/rahatlou/articelle/ WO&NEEDS&IGGS?
IGGS&AT&LC Electroweak&symmetry&breaking&and&iggs& Lecture&9& Shahram&Rahatlou Fisica&delle&Par,celle&Elementari,&Anno&Accademico&2014815 htt://www.roma1.infn.it/eole/rahatlou/articelle/ WO&NEEDS&IGGS?
Electroweak unification
 Electroweak unification Electroweak unification τ Experimental facts τ SU(2) L U(1) Y gauge theory τ Charged current interaction τ Neutral current interaction τ Gauge self-interactions III/1 Experimental
Electroweak unification Electroweak unification τ Experimental facts τ SU(2) L U(1) Y gauge theory τ Charged current interaction τ Neutral current interaction τ Gauge self-interactions III/1 Experimental
Outline. Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction. Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks. Neutral Weak Interaction. Electroweak Unification
 Weak Interactions Outline Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction Decay of the Muon Decay of the Neutron Decay of the Pion Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
Weak Interactions Outline Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction Decay of the Muon Decay of the Neutron Decay of the Pion Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
Non-Abelian SU(2) H and Two-Higgs Doublets
 Non-Abelian SU(2) H and Two-Higgs Doublets Technische Universität Dortmund Wei- Chih Huang 25 Sept 2015 Kavli IPMU arxiv:1510.xxxx(?) with Yue-Lin Sming Tsai, Tzu-Chiang Yuan Plea Please do not take any
Non-Abelian SU(2) H and Two-Higgs Doublets Technische Universität Dortmund Wei- Chih Huang 25 Sept 2015 Kavli IPMU arxiv:1510.xxxx(?) with Yue-Lin Sming Tsai, Tzu-Chiang Yuan Plea Please do not take any
Part III The Standard Model
 Part III The Standard Model Theorems Based on lectures by C. E. Thomas Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2017 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
Part III The Standard Model Theorems Based on lectures by C. E. Thomas Notes taken by Dexter Chua Lent 2017 These notes are not endorsed by the lecturers, and I have modified them (often significantly)
Quantum Field Theory 2 nd Edition
 Quantum Field Theory 2 nd Edition FRANZ MANDL and GRAHAM SHAW School of Physics & Astromony, The University of Manchester, Manchester, UK WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd., Publication Contents Preface
Quantum Field Theory 2 nd Edition FRANZ MANDL and GRAHAM SHAW School of Physics & Astromony, The University of Manchester, Manchester, UK WILEY A John Wiley and Sons, Ltd., Publication Contents Preface
Introduction to particle physics Lecture 13: The Standard Model
 Introduction to particle physics Lecture 13: The Standard Model Frank Krauss IPPP Durham U Durham, Epiphany term 2010 1 / 23 Outline 1 The Standard Model: Construction 2 The Standard Model: Tests and status
Introduction to particle physics Lecture 13: The Standard Model Frank Krauss IPPP Durham U Durham, Epiphany term 2010 1 / 23 Outline 1 The Standard Model: Construction 2 The Standard Model: Tests and status
Foundations of Physics III Quantum and Particle Physics Lecture 13
 Foundations of Physics III Quantum and Particle Physics Lecture 13 Frank Krauss February 27, 2012 1 Construction of the Standard Model 2 The Standard Model: Tests and status 3 Beyond the Standard Model?
Foundations of Physics III Quantum and Particle Physics Lecture 13 Frank Krauss February 27, 2012 1 Construction of the Standard Model 2 The Standard Model: Tests and status 3 Beyond the Standard Model?
The Standar Model of Particle Physics Lecture II
 The Standar Model of Particle Physics Lecture II Radiative corrections, renormalization, and physical observables Laura Reina Maria Laach School, Bautzen, September 2011 Outline of Lectures II Radiative
The Standar Model of Particle Physics Lecture II Radiative corrections, renormalization, and physical observables Laura Reina Maria Laach School, Bautzen, September 2011 Outline of Lectures II Radiative
Outline. Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction. Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks. Neutral Weak Interaction. Electroweak Unification
 Weak Interactions Outline Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction Decay of the Muon Decay of the Neutron Decay of the Pion Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
Weak Interactions Outline Charged Leptonic Weak Interaction Decay of the Muon Decay of the Neutron Decay of the Pion Charged Weak Interactions of Quarks Cabibbo-GIM Mechanism Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa
12 Best Reasons to Like CP Violation
 12 Best Reasons to Like CP Violation SSI 2012 The Electroweak Scale: Unraveling the Mysteries at the LHC SLAC, California 27 July 2012 Yossi Nir (Weizmann Institute of Science) SSI40 1/35 CP Violation
12 Best Reasons to Like CP Violation SSI 2012 The Electroweak Scale: Unraveling the Mysteries at the LHC SLAC, California 27 July 2012 Yossi Nir (Weizmann Institute of Science) SSI40 1/35 CP Violation
Gauge Symmetry in QED
 Gauge Symmetry in QED The Lagrangian density for the free e.m. field is L em = 1 4 F µνf µν where F µν is the field strength tensor F µν = µ A ν ν A µ = Thus L em = 1 (E B ) 0 E x E y E z E x 0 B z B y
Gauge Symmetry in QED The Lagrangian density for the free e.m. field is L em = 1 4 F µνf µν where F µν is the field strength tensor F µν = µ A ν ν A µ = Thus L em = 1 (E B ) 0 E x E y E z E x 0 B z B y
The Higgs Mechanism and the Higgs Particle
 The Higgs Mechanism and the Higgs Particle Heavy-Ion Seminar... or the Anderson-Higgs-Brout-Englert-Guralnik-Hagen-Kibble Mechanism Philip W. Anderson Peter W. Higgs Tom W. B. Gerald Carl R. François Robert
The Higgs Mechanism and the Higgs Particle Heavy-Ion Seminar... or the Anderson-Higgs-Brout-Englert-Guralnik-Hagen-Kibble Mechanism Philip W. Anderson Peter W. Higgs Tom W. B. Gerald Carl R. François Robert
Anomaly. Kenichi KONISHI University of Pisa. College de France, 14 February 2006
 Anomaly Kenichi KONISHI University of Pisa College de France, 14 February 2006 Abstract Symmetry and quantization U A (1) anomaly and π 0 decay Origin of anomalies Chiral and nonabelian anomaly Anomally
Anomaly Kenichi KONISHI University of Pisa College de France, 14 February 2006 Abstract Symmetry and quantization U A (1) anomaly and π 0 decay Origin of anomalies Chiral and nonabelian anomaly Anomally
The Standard Model of Electroweak Physics. Christopher T. Hill Head of Theoretical Physics Fermilab
 The Standard Model of Electroweak Physics Christopher T. Hill Head of Theoretical Physics Fermilab Lecture I: Incarnations of Symmetry Noether s Theorem is as important to us now as the Pythagorean Theorem
The Standard Model of Electroweak Physics Christopher T. Hill Head of Theoretical Physics Fermilab Lecture I: Incarnations of Symmetry Noether s Theorem is as important to us now as the Pythagorean Theorem
Introduction to Elementary Particles
 David Criffiths Introduction to Elementary Particles Second, Revised Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Preface to the First Edition IX Preface to the Second Edition XI Formulas and Constants
David Criffiths Introduction to Elementary Particles Second, Revised Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Preface to the First Edition IX Preface to the Second Edition XI Formulas and Constants
Models of Neutrino Masses
 Models of Neutrino Masses Fernando Romero López 13.05.2016 1 Introduction and Motivation 3 2 Dirac and Majorana Spinors 4 3 SU(2) L U(1) Y Extensions 11 4 Neutrino masses in R-Parity Violating Supersymmetry
Models of Neutrino Masses Fernando Romero López 13.05.2016 1 Introduction and Motivation 3 2 Dirac and Majorana Spinors 4 3 SU(2) L U(1) Y Extensions 11 4 Neutrino masses in R-Parity Violating Supersymmetry
Theory of CP Violation
 Theory of CP Violation IPPP, Durham CP as Natural Symmetry of Gauge Theories P and C alone are not natural symmetries: consider chiral gauge theory: L = 1 4 F µνf µν + ψ L i σdψ L (+ψ R iσ ψ R) p.1 CP
Theory of CP Violation IPPP, Durham CP as Natural Symmetry of Gauge Theories P and C alone are not natural symmetries: consider chiral gauge theory: L = 1 4 F µνf µν + ψ L i σdψ L (+ψ R iσ ψ R) p.1 CP
Lectures on Supersymmetry I
 I Carlos E.M. Wagner HEP Division, Argonne National Laboratory Enrico Fermi Institute, University of Chicago Ecole de Physique de Les Houches, France, August 5, 005. PASI 006, Puerto Vallarta, Mexico,
I Carlos E.M. Wagner HEP Division, Argonne National Laboratory Enrico Fermi Institute, University of Chicago Ecole de Physique de Les Houches, France, August 5, 005. PASI 006, Puerto Vallarta, Mexico,
Introduction to the SM (5)
 Y. Grossman The SM (5) TES-HEP, July 12, 2015 p. 1 Introduction to the SM (5) Yuval Grossman Cornell Y. Grossman The SM (5) TES-HEP, July 12, 2015 p. 2 Yesterday... Yesterday: Symmetries Today SSB the
Y. Grossman The SM (5) TES-HEP, July 12, 2015 p. 1 Introduction to the SM (5) Yuval Grossman Cornell Y. Grossman The SM (5) TES-HEP, July 12, 2015 p. 2 Yesterday... Yesterday: Symmetries Today SSB the
Hidden two-higgs doublet model
 Hidden two-higgs doublet model C, Uppsala and Lund University SUSY10, Bonn, 2010-08-26 1 Two Higgs doublet models () 2 3 4 Phenomenological consequences 5 Two Higgs doublet models () Work together with
Hidden two-higgs doublet model C, Uppsala and Lund University SUSY10, Bonn, 2010-08-26 1 Two Higgs doublet models () 2 3 4 Phenomenological consequences 5 Two Higgs doublet models () Work together with
Higgs Physics and QCD
 Higgs Physics and QCD William Kilgore Brookhaven National Laboratory CTEQ Summer School June, 004 Outline The Standard Model & the Higgs Mechanism Agents of Electro-weak Symmetry Breaking The Higgs Boson
Higgs Physics and QCD William Kilgore Brookhaven National Laboratory CTEQ Summer School June, 004 Outline The Standard Model & the Higgs Mechanism Agents of Electro-weak Symmetry Breaking The Higgs Boson
Weak Interactions: towards the Standard Model of Physics
 Weak Interactions: towards the Standard Model of Physics Weak interactions From β-decay to Neutral currents Weak interactions: are very different world CP-violation: power of logics and audacity Some experimental
Weak Interactions: towards the Standard Model of Physics Weak interactions From β-decay to Neutral currents Weak interactions: are very different world CP-violation: power of logics and audacity Some experimental
The Role and Discovery of the Higgs
 The Role and Discovery of the Higgs David Clarke Abstract This paper summarizes the importance of the Higgs boson in QFT and outlines experiments leading up to the discovery of the Higgs boson. First we
The Role and Discovery of the Higgs David Clarke Abstract This paper summarizes the importance of the Higgs boson in QFT and outlines experiments leading up to the discovery of the Higgs boson. First we
The Standard Model and Beyond
 The Standard Model and Beyond Nobuchika Okada Department of Physics and Astronomy The University of Alabama 2011 BCVSPIN ADVANCED STUDY INSTITUTE IN PARTICLE PHYSICS AND COSMOLOGY Huê, Vietnam, 25-30,
The Standard Model and Beyond Nobuchika Okada Department of Physics and Astronomy The University of Alabama 2011 BCVSPIN ADVANCED STUDY INSTITUTE IN PARTICLE PHYSICS AND COSMOLOGY Huê, Vietnam, 25-30,
Lecture 03. The Standard Model of Particle Physics. Part II The Higgs Boson Properties of the SM
 Lecture 03 The Standard Model of Particle Physics Part II The Higgs Boson Properties of the SM The Standard Model So far we talked about all the particles except the Higgs If we know what the particles
Lecture 03 The Standard Model of Particle Physics Part II The Higgs Boson Properties of the SM The Standard Model So far we talked about all the particles except the Higgs If we know what the particles
Introduction and Theoretical Background
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Theoretical Background The Standard Model of particle physics has been tested by many experiments and has been shown to accurately describe particle interactions at the highest
Chapter 1 Introduction and Theoretical Background The Standard Model of particle physics has been tested by many experiments and has been shown to accurately describe particle interactions at the highest
Higgs Boson Phenomenology Lecture I
 iggs Boson Phenomenology Lecture I Laura Reina TASI 2011, CU-Boulder, June 2011 Outline of Lecture I Understanding the Electroweak Symmetry Breaking as a first step towards a more fundamental theory of
iggs Boson Phenomenology Lecture I Laura Reina TASI 2011, CU-Boulder, June 2011 Outline of Lecture I Understanding the Electroweak Symmetry Breaking as a first step towards a more fundamental theory of
Lecture 18 - Beyond the Standard Model
 Lecture 18 - Beyond the Standard Model Why is the Standard Model incomplete? Grand Unification Baryon and Lepton Number Violation More Higgs Bosons? Supersymmetry (SUSY) Experimental signatures for SUSY
Lecture 18 - Beyond the Standard Model Why is the Standard Model incomplete? Grand Unification Baryon and Lepton Number Violation More Higgs Bosons? Supersymmetry (SUSY) Experimental signatures for SUSY
Week 3: Renormalizable lagrangians and the Standard model lagrangian 1 Reading material from the books
 Week 3: Renormalizable lagrangians and the Standard model lagrangian 1 Reading material from the books Burgess-Moore, Chapter Weiberg, Chapter 5 Donoghue, Golowich, Holstein Chapter 1, 1 Free field Lagrangians
Week 3: Renormalizable lagrangians and the Standard model lagrangian 1 Reading material from the books Burgess-Moore, Chapter Weiberg, Chapter 5 Donoghue, Golowich, Holstein Chapter 1, 1 Free field Lagrangians
Lecture 12 Weak Decays of Hadrons
 Lecture 12 Weak Decays of Hadrons π + and K + decays Semileptonic decays Hyperon decays Heavy quark decays Rare decays The Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa Matrix 1 Charged Pion Decay π + decay by annihilation
Lecture 12 Weak Decays of Hadrons π + and K + decays Semileptonic decays Hyperon decays Heavy quark decays Rare decays The Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa Matrix 1 Charged Pion Decay π + decay by annihilation
+ µ 2 ) H (m 2 H 2
 I. THE HIGGS POTENTIAL AND THE LIGHT HIGGS BOSON In the previous chapter, it was demonstrated that a negative mass squared in the Higgs potential is generated radiatively for a large range of boundary
I. THE HIGGS POTENTIAL AND THE LIGHT HIGGS BOSON In the previous chapter, it was demonstrated that a negative mass squared in the Higgs potential is generated radiatively for a large range of boundary
Finding the Higgs boson
 Finding the Higgs boson Sally Dawson, BN XIII Mexican School of Particles and Fields ecture 1, Oct, 008 Properties of the Higgs boson Higgs production at the Tevatron and HC Discovery vs spectroscopy Collider
Finding the Higgs boson Sally Dawson, BN XIII Mexican School of Particles and Fields ecture 1, Oct, 008 Properties of the Higgs boson Higgs production at the Tevatron and HC Discovery vs spectroscopy Collider
Lecture III: Higgs Mechanism
 ecture III: Higgs Mechanism Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking The Higgs Mechanism Mass Generation for eptons Quark Masses & Mixing III.1 Symmetry Breaking One example is the infinite ferromagnet the nearest
ecture III: Higgs Mechanism Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking The Higgs Mechanism Mass Generation for eptons Quark Masses & Mixing III.1 Symmetry Breaking One example is the infinite ferromagnet the nearest
The Standard Model and beyond
 The Standard Model and beyond In this chapter we overview the structure of the Standard Model (SM) of particle physics, its shortcomings, and different ideas for physics beyond the Standard Model (BSM)
The Standard Model and beyond In this chapter we overview the structure of the Standard Model (SM) of particle physics, its shortcomings, and different ideas for physics beyond the Standard Model (BSM)
Gauge Theories of the Standard Model
 Gauge Theories of the Standard Model Professors: Domènec Espriu (50%, coordinador) Jorge Casalderrey (25%) Federico Mescia (25%) Time Schedule: Mon, Tue, Wed: 11:50 13:10 According to our current state
Gauge Theories of the Standard Model Professors: Domènec Espriu (50%, coordinador) Jorge Casalderrey (25%) Federico Mescia (25%) Time Schedule: Mon, Tue, Wed: 11:50 13:10 According to our current state
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C4: PARTICLE PHYSICS
 754 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C4: PARTICLE PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 04 Thursday, 9 June,.30 pm 5.45 pm 5 minutes
754 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C4: PARTICLE PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 04 Thursday, 9 June,.30 pm 5.45 pm 5 minutes
Lecture 23. November 16, Developing the SM s electroweak theory. Fermion mass generation using a Higgs weak doublet
 Lecture 23 November 16, 2017 Developing the SM s electroweak theory Research News: Higgs boson properties and use as a dark matter probe Fermion mass generation using a Higgs weak doublet Summary of the
Lecture 23 November 16, 2017 Developing the SM s electroweak theory Research News: Higgs boson properties and use as a dark matter probe Fermion mass generation using a Higgs weak doublet Summary of the
Fermions of the ElectroWeak Theory
 Fermions of the ElectroWeak Theory The Quarks, The eptons, and their Masses. This is my second set of notes on the Glashow Weinberg Salam theory of weak and electromagnetic interactions. The first set
Fermions of the ElectroWeak Theory The Quarks, The eptons, and their Masses. This is my second set of notes on the Glashow Weinberg Salam theory of weak and electromagnetic interactions. The first set
Electroweak Physics. Krishna S. Kumar. University of Massachusetts, Amherst
 Electroweak Physics Krishna S. Kumar University of Massachusetts, Amherst Acknowledgements: M. Grunewald, C. Horowitz, W. Marciano, C. Quigg, M. Ramsey-Musolf, www.particleadventure.org Electroweak Physics
Electroweak Physics Krishna S. Kumar University of Massachusetts, Amherst Acknowledgements: M. Grunewald, C. Horowitz, W. Marciano, C. Quigg, M. Ramsey-Musolf, www.particleadventure.org Electroweak Physics
November 24, Scalar Dark Matter from Grand Unified Theories. T. Daniel Brennan. Standard Model. Dark Matter. GUTs. Babu- Mohapatra Model
 Scalar from November 24, 2014 1 2 3 4 5 What is the? Gauge theory that explains strong weak, and electromagnetic forces SU(3) C SU(2) W U(1) Y Each generation (3) has 2 quark flavors (each comes in one
Scalar from November 24, 2014 1 2 3 4 5 What is the? Gauge theory that explains strong weak, and electromagnetic forces SU(3) C SU(2) W U(1) Y Each generation (3) has 2 quark flavors (each comes in one
PARTICLE PHYSICS Major Option
 PATICE PHYSICS Major Option Michaelmas Term 00 ichard Batley Handout No 8 QED Maxwell s equations are invariant under the gauge transformation A A A χ where A ( φ, A) and χ χ ( t, x) is the 4-vector potential
PATICE PHYSICS Major Option Michaelmas Term 00 ichard Batley Handout No 8 QED Maxwell s equations are invariant under the gauge transformation A A A χ where A ( φ, A) and χ χ ( t, x) is the 4-vector potential
Some fundamental questions
 Some fundamental questions What is the standard model of elementary particles and their interactions? What is the origin of mass and electroweak symmetry breaking? What is the role of anti-matter in Nature?
Some fundamental questions What is the standard model of elementary particles and their interactions? What is the origin of mass and electroweak symmetry breaking? What is the role of anti-matter in Nature?
SM, EWSB & Higgs. MITP Summer School 2017 Joint Challenges for Cosmology and Colliders. Homework & Exercises
 SM, EWSB & Higgs MITP Summer School 017 Joint Challenges for Cosmology and Colliders Homework & Exercises Ch!"ophe Grojean Ch!"ophe Grojean DESY (Hamburg) Humboldt University (Berlin) ( christophe.grojean@desy.de
SM, EWSB & Higgs MITP Summer School 017 Joint Challenges for Cosmology and Colliders Homework & Exercises Ch!"ophe Grojean Ch!"ophe Grojean DESY (Hamburg) Humboldt University (Berlin) ( christophe.grojean@desy.de
A Two Higgs Doublet Model for the Top Quark
 UR 1446 November 1995 A Two Higgs Doublet Model for the Top Quark Ashok Das and Chung Kao 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY 14627, USA Abstract A two Higgs doublet
UR 1446 November 1995 A Two Higgs Doublet Model for the Top Quark Ashok Das and Chung Kao 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester, Rochester, NY 14627, USA Abstract A two Higgs doublet
