Status and Phenomenology of the Standard Model
|
|
|
- Emory Bishop
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Status and Phenomenology of the Standard Model The new standard model Experimental tests, unique features, anomalies, hints of new physics Precision tests Higgs Heavy quarks Neutrinos FCNC and EDMs Astrophysics and cosmology Theoretical problems Perspective
2 The New Standard Model Standard model, Majorana): supplemented with neutrino mass (Dirac or SU(3) SU(2) U(1) classical relativity }{{} focus of talk Mathematically consistent field theory of strong, weak, electromagnetic interactions Correct to first approximation down to cm Complicated, free parameters, fine tunings must be new physics
3 Many special features usually not maintained in BSM m ν = 0 in old standard model (need to add singlet fermion and/or triplet Higgs and/or higher dimensional operator (HDO)) Yukawa coupling h gm/m W flavor conserving and small for light fermions (partially maintained in MSSM and simple 2HDM) No FCNC at tree level (Z or h); suppressed at loop level (SUSY loops; Z from strings, DSB) Suppressed off-diagonal CP ; highly suppressed diagonal (EDMs) (SUSY loops, soft parameters, exotics) B, L conserved perturbatively (B L non-perturbatively) (GUT (string) interactions, R p ) New TeV scale interactions suggested by top-down (Z, exotics, extended Higgs)
4 The Weak Charged Current Fermi Theory incorporated in SM and made renormalizable CKM matrix for F = 3 involves 3 angles and 1 CP -violating phase (after removing unobservable q L phases) (new interations involving q R could make observable) V = V ud V us V ub V cd V cs V cb V td V td V td Extensive studies, especially in B decays, to test unitarity of V as probe of new physics and test origin of CP violation Need additional source of CP breaking for baryogenesis
5 Overconstrain unitarity triangle as test of SM η Babar, Belle: sin 2β = ± from Bd 0(t) J/ψK S (little theory error) R u (ρ,η) α R t α, γ harder Anomalies in electroweak penguins? γ (0,0) (1,0) β
6 1.5 excluded area has CL < sin 2β m d η ε K γ α β B ρρ m s & m d V ub /V cb -0.5 ε K -1 C K M f i t t e r Winter 2004 B ρρ ρ
7 The Weak Neutral Current Prediction of SU(2) U(1) WNC discovered 1973: Gargamelle at CERN, HPW at FNAL Tested in many processes: νe νe, νn νn, νn νx; e D ex; atomic parity violation; e + e, Z-pole reactions WNC, W, and Z are primary test/prediction of electroweak model
8 The LEP/SLC Era Z Pole: e + e Z l + l, q q, ν ν LEP (CERN), Z s, unpolarized (ALEPH, DELPHI, L3, OPAL); SLC (SLAC), , P e 75 % (SLD) Z pole observables lineshape: M Z, Γ Z, σ branching ratios e + e, µ + µ, τ + τ q q, c c, b b, s s ν ν N ν = ± if m ν < M Z /2 asymmetries: FB, polarization, P τ, mixed lepton family universality
9
10 LEP averages of leptonic widths Γ e ± 0.12 MeV Γ µ ± 0.18 MeV Γ τ ± 0.22 MeV Γ l ± 0.09 MeV m H [GeV] m Z = ± 2 MeV m t = ± 5.1 GeV [MeV] Γ l
11 Winter 2004 Measurement Fit O meas O fit /σ meas α (5) had (m Z ) ± m Z [GeV] ± Γ Z [GeV] ± σ 0 had [nb] ± R l ± A 0,l fb ± A l (P τ ) ± R b ± R c ± A 0,b fb ± A 0,c fb ± A b ± A c ± A l (SLD) ± sin 2 θ lept eff (Q fb ) ± m W [GeV] ± Γ W [GeV] ± m t [GeV] ±
12 Gauge Self-Interactions Three and four-point interactions predicted by gauge invariance Indirectly verified by radiative corrections, α s running in QCD, etc. Strong cancellations in high energy amplitudes would be upset by anomalous couplings Tree-level diagrams contributing to e + e W + W
13
14 The Precision Program WNC, Z, Z-pole, W, m t Implications SM correct and unique to zeroth approx. (gauge principle, group, representations) SM correct at loop level (renorm gauge theory; m t, α s, M H ) TeV physics severely constrained (unification vs compositeness) Precise gauge couplings (gauge unification)
15 Problems with the Standard Model Lagrangian after symmetry breaking: ( ψ i i m i m ih ν L = L gauge + L Higgs + i g ( ) 2 J µ W 2 W µ + J µ W W + µ ej µ Q A µ ) ψ i g 2 cos θ W J µ Z Z µ Standard model: SU(2) U(1) (extended to include ν masses) + QCD + general relativity Mathematically consistent, renormalizable theory Correct to cm
16 However, too much arbitrariness and fine-tuning: O(27) parameters (+ 2 for Majorana ν), and electric charges Gauge Problem complicated gauge group with 3 couplings charge quantization ( q e = q p ) unexplained Possible solutions: strings; grand unification; magnetic monopoles (partial); anomaly constraints (partial) Fermion problem Fermion masses, mixings, families unexplained Neutrino masses, nature? CP violation inadequate to explain baryon asymmetry Possible solutions: strings; brane worlds; family symmetries; compositeness; radiative hierarchies. New sources of CP violation.
17 Higgs/hierarchy problem Expect M 2 H = O(M 2 W ) higher order corrections: δm 2 H /M 2 W 1034 Possible solutions: supersymmetry; dynamical symmetry breaking; large extra dimensions; Little Higgs Strong CP problem Can add θ 32π 2 g 2 s F F to QCD (breaks, P, T, CP) d N θ < 10 9 but δθ weak 10 3 Possible solutions: spontaneously broken global U(1) (Peccei- Quinn) axion; unbroken global U(1) (massless u quark); spontaneously broken CP + other symmetries
18 Graviton problem gravity not unified quantum gravity not renormalizable cosmological constant: Λ SSB = 8πG N V > Λ obs ( for GUTs, strings) Possible solutions: supergravity and Kaluza Klein unify strings yield finite gravity. Λ?
19 (Nearly) Unique Features of the old Standard Model m ν = 0 in old standard model (need to add singlet fermion and/or triplet Higgs and/or higher dimensional operator (HDO)) Oscillation experiments confirm non-zero masses, LMA, SSM (also helioseismology) Excluded sterile, RSPF, new interactions as dominant Oscillation dip observed (further constrains/excludes alternatives)
20 3 ν Patterns Solar: LMA (SNO, Kamland) m ev 2 for LMA Atmospheric: m 2 Atm ev 2, nearmaximal mixing Reactor: U e3 small
21 2 ) (ev 2 m ) 2 (ev 2 m Solar 95% C.L. 99% C.L % C.L. solar best fit tan 2 θ KamLAND 95% C.L. 99% C.L % C.L. KamLAND best fit tan 2 θ KamLAND+Solar fluxes 95% C.L. 99% C.L % C.L. global best fit
22 Data/Prediction (null osc.) L/E (km/gev)
23 Mixings: let ν ± 1 2 (ν µ ± ν τ ): ν 3 ν + ν 2 cos θ ν sin θ ν e ν 1 sin θ ν + cos θ ν e Hierarchical pattern Analogous to quarks, charged leptons ββ 0ν rate very small Inverted quasi-degenerate pattern ββ 0ν if Majorana May be radiative unstable
24 Outstanding issues Dirac or Majorana Distinguish by ββ 0ν, at least for inverted, degenerate. Observation? Dirac Mass Connects distinct Weyl spinors (usually active to sterile): (m D ν L N R + h.c.) 4 components, L = 0 I = 1 Higgs doublet 2 Why small? LED? HDO? ν L h N R v = φ m D = hv
25 Majorana Mass Connects Weyl spinor with itself: 1 2 (m T ν L νr c + h.c.) (active); 1 2 (m S N L cn R + h.c.) (sterile) 2 components, L = ±2 Active: I = 1 triplet or seesaw Sterile: I = 0 singlet or bare mass ν L ν c R ν L ν L
26 Scale of neutrino masses: 0.05 ev < m ν < O(0.3 ev). Probe by β decay (KATRIN), cosmology, ββ 0ν Type of hierarchy: ββ 0ν U e3, leptonic CP LSND? Additional (sterile) neutrino(s) which mix with ordinary. MiniBooNE. Leptogenesis?
27 Flavor Changing Neutral Currents In SM: Yukawa coupling h gm/m W flavor conserving and small for light fermions (partially maintained in MSSM and simple 2HDM) In SM: no FCNC at tree level (Z or h); suppressed at loop level Violated in almost all extensions, including SUSY loops; Z from strings, DSB Hard to give precise expectations, but critical to search Third family transitions (rare B, τ ) often largest, but small induced effects in first two families (µ, K decays) may be more sensitive (MEG at PSI, MECO at BNL, PRIME at JHF)
28 History of Lepton Flavor Violation Searches " - N # e - N " + # e + $ " + # e + e + e K 0% #" + e - K +% #& + " + e - SINDRUMII MECO Goal! P. Souder, Syracuse From Zero to... 5/13/04 8
29 What might we expect? Supersymmetry Predictions at ~ ~ l µ - j l j e - q ~ χ 0 i q µ - q e - q Compositeness!! 3000 TeV C Heavy Neutrinos ( 2 % 13 " N en! # U U 8 10 N µ - W e - q q e - µ - e - H t t t q q Second Higgs g =10 g -4 H" e # H"" M L Leptoquarks! 3000 ) ) TeV/c " d ed 2 µ - d L d e - µ - e - γ,z,z q q After W. Marciano Heavy Z, Anomalous Z coupling M Z$! 3000 TeV/c B(Z & " e) ' 10 % 17 2 P. Souder, Syracuse From Zero to... 5/13/04 10
30 CP Violation SM: suppressed off-diagonal CP ; highly suppressed diagonal (EDMs) Larger in SUSY (loops, soft parameters) unless tuning or cancellations Larger in other extensions, e.g., singlet scalars in Z models (but may be hidden) B decays, leptonic CP, EDMs Need additional CP for baryogenesis
31
32 Baryon and Lepton Number Violation SM: B, L conserved perturbatively (B L non-perturbatively) Violated in BSM, e.g., by GUT (string) interactions or R p Proton decay expected at some level in many extensions, especially Planck scale L needed for Majorana neutrino masses ββ 0ν New B and/or L invoked in some baryogenesis schemes
33 mode exposure εb m observed B.G. (ktï yr) (%) event p e + + π p µ + + π p e + + η p µ + + η n ν + η p e + + ρ p e + + ω p e + + γ p µ + + γ p ν + K K + νµ + (spectrum) prompt γ + µ K + π + π n ν + K K 0 π 0 π K 0 π + π p e + K K 0 π 0 π K 0 π + π - 2-ring ring p µ + K K 0 π 0 π K 0 π + π - 2-ring ring p e + π 0 e + η e + ω e + ρ 0 e + K 0 µ + π 0 µ + η µ + ω µ + ρ 0 µ + K 0 + ν π ν ρ + + ν K n e + π - e + ρ - µ + π - µ + ρ - ν π 0 ν η ν ω ν ρ 0 0 ν K SK IMB3 KAM Soudan lifetime limit (years)
34 TeV Physics New TeV scale interactions suggested by top-down Z or other new interactions Implications for highly non-standard Higgs, FCNC, CDM, baryogenesis Exotics Extra Higgs doublets and singlets Exotic quarks and leptons Fractional charges Quasi-hidden sectors
35 Hints and Anomalies Gauge unification in supersymmetric extension If not accident or compensation, severely limits new TeV scale physics Precision data suggests light Higgs
36 Precision data suggests light Higgs M H = GeV (< 246 GeV at 95% including indirect) Consistent with SUSY (but does not prove) χ Theory uncertainty α (5) α had = ± ± incl. low Q 2 data Has increased due to new D0 m t value and lower M W A b F B pulls up, A l down 1 0 Excluded m H [GeV] Preliminary
37
38 Atomic parity violation? Now in agreement after complete radiative corrections. NuTeV? Unresolved. Likely QCD or structure function issue. Electroweak penguins in B φk S, Kπ? b V qb W + V qd d Experimental situation uncertain SUSY loops for large tan β or tree effects, e.g. FCNC Z d q = u c t u u d
39 Anomalous magnetic moment of muon Hadronic vacuum polarization (e + e vs τ decay); light by light If real, then SUSY with large tan β and low masses is possibility
40
41 Cross section [cm 2 ] (normalised to nucleon) WIMP Mass [GeV] Dark Matter 30% matter, mainly dark No SM candidates; SUSY LSP if R P conserved (MSSM tightly constrained); axions 70% dark energy Higgs VeV, QCD vacuum energy in SM, but too large by ; new fields? quintessence? JDEM (SNAP)
42
43 Baryogenesis Baryon asymmetry n B /n γ Possible mechanisms GUT baryogenesis (wiped out by sphalerons for B L=0) Leptogenesis (for heavy right-handed Majorana neutrino in seesaw) Electroweak baryogenesis
44 EB requires strong first order transition, v(t c )/T c > and adequate CP violation in expanding bubble wall q broken phase φ = 0 v Wall unbroken phase q Absent in SM q CP becomes our world Sph Γ B + L _~ 0 CP q Narrow parameter range in MSSM _ q _ q Sph Γ B + L >> H _ q _ q Possible in Z (W. Bernreuther, hep-ph/ )
45 Conclusions Standard Model is spectacularly successful, but has many parameters, tunings, and unexplained features Must be new physics Theoretical ideas Strings Grand Unification (canonical or modified) Supersymmetry Top-down remnants (Z, exotics) Large extra dimensions, deconstruction Dynamical symmetry breaking, compositeness, Little Higgs
46 Experimental probes Hadron colliders: Tevatron, LHC Linear collider/clic FCNC, EDM, heavy quark, precision, neutrino, p decay Cosmology/astrophysics Tremendous opportunities in particle physics, to develop standard theory valid to the Planck scale
Supersymmetry, Dark Matter, and Neutrinos
 Supersymmetry, Dark Matter, and Neutrinos The Standard Model and Supersymmetry Dark Matter Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics The Physics of Supersymmetry Gauge Theories Gauge symmetry requires existence
Supersymmetry, Dark Matter, and Neutrinos The Standard Model and Supersymmetry Dark Matter Neutrino Physics and Astrophysics The Physics of Supersymmetry Gauge Theories Gauge symmetry requires existence
Beyond the Standard Model
 Beyond the Standard Model The Standard Model Problems with the Standard Model New Physics Supersymmetry Extended Electroweak Symmetry Grand Unification References: 2008 TASI lectures: arxiv:0901.0241 [hep-ph]
Beyond the Standard Model The Standard Model Problems with the Standard Model New Physics Supersymmetry Extended Electroweak Symmetry Grand Unification References: 2008 TASI lectures: arxiv:0901.0241 [hep-ph]
Weak Interactions and Neutrinos in the LHC Era
 Weak Interactions and Neutrinos in the LHC Era The standard model Testing the standard model Problems Beyond the standard model Where are we going? The New Standard Model Standard model, Majorana): supplemented
Weak Interactions and Neutrinos in the LHC Era The standard model Testing the standard model Problems Beyond the standard model Where are we going? The New Standard Model Standard model, Majorana): supplemented
Electroweak Physics. Precision Experiments: Historical Perspective. LEP/SLC Physics. Probing the Standard Model. Beyond the Standard Model
 Electroweak Physics Precision Experiments: Historical Perspective LEP/SLC Physics Probing the Standard Model Beyond the Standard Model The Z, the W, and the Weak Neutral Current Primary prediction and
Electroweak Physics Precision Experiments: Historical Perspective LEP/SLC Physics Probing the Standard Model Beyond the Standard Model The Z, the W, and the Weak Neutral Current Primary prediction and
Introduction to the Standard Model
 Introduction to the Standard Model Origins of the Electroweak Theory Gauge Theories The Standard Model Lagrangian Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking The Gauge Interactions Problems With the Standard Model (
Introduction to the Standard Model Origins of the Electroweak Theory Gauge Theories The Standard Model Lagrangian Spontaneous Symmetry Breaking The Gauge Interactions Problems With the Standard Model (
Neutrinos: status, models, string theory expectations
 Neutrinos: status, models, string theory expectations Introduction Neutrino preliminaries and status Models String embeddings Intersecting brane The Z 3 heterotic orbifold Embedding the Higgs triplet Outlook
Neutrinos: status, models, string theory expectations Introduction Neutrino preliminaries and status Models String embeddings Intersecting brane The Z 3 heterotic orbifold Embedding the Higgs triplet Outlook
Neutrino masses respecting string constraints
 Neutrino masses respecting string constraints Introduction Neutrino preliminaries The GUT seesaw Neutrinos in string constructions The triplet model (Work in progress, in collaboration with J. Giedt, G.
Neutrino masses respecting string constraints Introduction Neutrino preliminaries The GUT seesaw Neutrinos in string constructions The triplet model (Work in progress, in collaboration with J. Giedt, G.
The Physics of Heavy Z-prime Gauge Bosons
 The Physics of Heavy Z-prime Gauge Bosons Tevatron LHC LHC LC LC 15fb -1 100fb -1 14TeV 1ab -1 14TeV 0.5TeV 1ab -1 P - =0.8 P + =0.6 0.8TeV 1ab -1 P - =0.8 P + =0.6 χ ψ η LR SSM 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 2σ m Z'
The Physics of Heavy Z-prime Gauge Bosons Tevatron LHC LHC LC LC 15fb -1 100fb -1 14TeV 1ab -1 14TeV 0.5TeV 1ab -1 P - =0.8 P + =0.6 0.8TeV 1ab -1 P - =0.8 P + =0.6 χ ψ η LR SSM 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 2σ m Z'
Neutrino Basics. m 2 [ev 2 ] tan 2 θ. Reference: The Standard Model and Beyond, CRC Press. Paul Langacker (IAS) LSND 90/99% SuperK 90/99% MINOS K2K
![Neutrino Basics. m 2 [ev 2 ] tan 2 θ. Reference: The Standard Model and Beyond, CRC Press. Paul Langacker (IAS) LSND 90/99% SuperK 90/99% MINOS K2K Neutrino Basics. m 2 [ev 2 ] tan 2 θ. Reference: The Standard Model and Beyond, CRC Press. Paul Langacker (IAS) LSND 90/99% SuperK 90/99% MINOS K2K](/thumbs/93/112869275.jpg) Neutrino Basics CDHSW m 2 [ev 2 ] 10 0 10 3 10 6 10 9 KARMEN2 Cl 95% NOMAD MiniBooNE Ga 95% Bugey CHOOZ ν X ν µ ν τ ν τ NOMAD all solar 95% SNO 95% CHORUS NOMAD CHORUS LSND 90/99% SuperK 90/99% MINOS K2K
Neutrino Basics CDHSW m 2 [ev 2 ] 10 0 10 3 10 6 10 9 KARMEN2 Cl 95% NOMAD MiniBooNE Ga 95% Bugey CHOOZ ν X ν µ ν τ ν τ NOMAD all solar 95% SNO 95% CHORUS NOMAD CHORUS LSND 90/99% SuperK 90/99% MINOS K2K
Electroweak Theory, SSB, and the Higgs: Lecture 2
 1 Electroweak Theory, SSB, and the iggs: Lecture Spontaneous symmetry breaking (iggs mechanism) - Gauge invariance implies massless gauge bosons and fermions - Weak interactions short ranged spontaneous
1 Electroweak Theory, SSB, and the iggs: Lecture Spontaneous symmetry breaking (iggs mechanism) - Gauge invariance implies massless gauge bosons and fermions - Weak interactions short ranged spontaneous
Beyond Standard Model Effects in Flavour Physics: p.1
 Beyond Standard Model Effects in Flavour Physics: Alakabha Datta University of Mississippi Feb 13, 2006 Beyond Standard Model Effects in Flavour Physics: p.1 OUTLINE Standard Model (SM) and its Problems.
Beyond Standard Model Effects in Flavour Physics: Alakabha Datta University of Mississippi Feb 13, 2006 Beyond Standard Model Effects in Flavour Physics: p.1 OUTLINE Standard Model (SM) and its Problems.
Implications of a Heavy Z Gauge Boson
 Implications of a Heavy Z Gauge Boson Motivations A (string-motivated) model Non-standard Higgs sector, CDM, g µ 2 Electroweak baryogenesis FCNC and B s B s mixing References T. Han, B. McElrath, PL, hep-ph/0402064
Implications of a Heavy Z Gauge Boson Motivations A (string-motivated) model Non-standard Higgs sector, CDM, g µ 2 Electroweak baryogenesis FCNC and B s B s mixing References T. Han, B. McElrath, PL, hep-ph/0402064
Lecture 18 - Beyond the Standard Model
 Lecture 18 - Beyond the Standard Model Why is the Standard Model incomplete? Grand Unification Baryon and Lepton Number Violation More Higgs Bosons? Supersymmetry (SUSY) Experimental signatures for SUSY
Lecture 18 - Beyond the Standard Model Why is the Standard Model incomplete? Grand Unification Baryon and Lepton Number Violation More Higgs Bosons? Supersymmetry (SUSY) Experimental signatures for SUSY
The Matter-Antimatter Asymmetry and New Interactions
 The Matter-Antimatter Asymmetry and New Interactions The baryon (matter) asymmetry The Sakharov conditions Possible mechanisms A new very weak interaction Recent Reviews M. Trodden, Electroweak baryogenesis,
The Matter-Antimatter Asymmetry and New Interactions The baryon (matter) asymmetry The Sakharov conditions Possible mechanisms A new very weak interaction Recent Reviews M. Trodden, Electroweak baryogenesis,
Neutrinos and Fundamental Symmetries: L, CP, and CP T
 Neutrinos and Fundamental Symmetries: L, CP, and CP T Outstanding issues Lepton number (L) CP violation CP T violation Outstanding issues in neutrino intrinsic properties Scale of underlying physics? (string,
Neutrinos and Fundamental Symmetries: L, CP, and CP T Outstanding issues Lepton number (L) CP violation CP T violation Outstanding issues in neutrino intrinsic properties Scale of underlying physics? (string,
Implications of an extra U(1) gauge symmetry
 Implications of an extra U(1) gauge symmetry Motivations 400 LEP2 (209 GeV) Higgsstrahlung Cross Section A (string-motivated) model σ(e + e - -> ZH) (fb) 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 H 1 H 2 Standard Model
Implications of an extra U(1) gauge symmetry Motivations 400 LEP2 (209 GeV) Higgsstrahlung Cross Section A (string-motivated) model σ(e + e - -> ZH) (fb) 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 H 1 H 2 Standard Model
Neutrinos as a Unique Probe: cm
 Neutrinos as a Unique Probe: 10 33 10 +28 cm Particle Physics νn, µn, en scattering: existence/properties of quarks, QCD Weak decays (n pe ν e, µ e ν µ ν e ): Fermi theory, parity violation, quark mixing
Neutrinos as a Unique Probe: 10 33 10 +28 cm Particle Physics νn, µn, en scattering: existence/properties of quarks, QCD Weak decays (n pe ν e, µ e ν µ ν e ): Fermi theory, parity violation, quark mixing
Foundations of Physics III Quantum and Particle Physics Lecture 13
 Foundations of Physics III Quantum and Particle Physics Lecture 13 Frank Krauss February 27, 2012 1 Construction of the Standard Model 2 The Standard Model: Tests and status 3 Beyond the Standard Model?
Foundations of Physics III Quantum and Particle Physics Lecture 13 Frank Krauss February 27, 2012 1 Construction of the Standard Model 2 The Standard Model: Tests and status 3 Beyond the Standard Model?
New Physics from the String Vacuum
 New Physics from the String Vacuum The string vacuum Extended MSSM quivers String remnants Small neutrino masses Quivers: Cvetič, Halverson, PL, JHEP 1111,058 (1108.5187) Z : Rev.Mod.Phys.81,1199 (0801.145)
New Physics from the String Vacuum The string vacuum Extended MSSM quivers String remnants Small neutrino masses Quivers: Cvetič, Halverson, PL, JHEP 1111,058 (1108.5187) Z : Rev.Mod.Phys.81,1199 (0801.145)
Overview of cosmological constraints on neutrino mass, number, and types
 Overview of cosmological constraints on neutrino mass, number, and types Preliminaries Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Large Scale Structure and CMB Brief Comments Supernovae Magnetic Moments Decays Ultra High
Overview of cosmological constraints on neutrino mass, number, and types Preliminaries Big Bang Nucleosynthesis Large Scale Structure and CMB Brief Comments Supernovae Magnetic Moments Decays Ultra High
The Standard Model and Beyond
 The Standard Model and Beyond Nobuchika Okada Department of Physics and Astronomy The University of Alabama 2011 BCVSPIN ADVANCED STUDY INSTITUTE IN PARTICLE PHYSICS AND COSMOLOGY Huê, Vietnam, 25-30,
The Standard Model and Beyond Nobuchika Okada Department of Physics and Astronomy The University of Alabama 2011 BCVSPIN ADVANCED STUDY INSTITUTE IN PARTICLE PHYSICS AND COSMOLOGY Huê, Vietnam, 25-30,
Electroweak Theory: 3
 Electroweak Theory: 3 Introduction QED The Fermi theory The standard model Precision tests CP violation; K and B systems Higgs physics Prospectus STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 55 References Slides
Electroweak Theory: 3 Introduction QED The Fermi theory The standard model Precision tests CP violation; K and B systems Higgs physics Prospectus STIAS January, 2011 Paul Langacker IAS 55 References Slides
Introduction to particle physics Lecture 13: The Standard Model
 Introduction to particle physics Lecture 13: The Standard Model Frank Krauss IPPP Durham U Durham, Epiphany term 2010 1 / 23 Outline 1 The Standard Model: Construction 2 The Standard Model: Tests and status
Introduction to particle physics Lecture 13: The Standard Model Frank Krauss IPPP Durham U Durham, Epiphany term 2010 1 / 23 Outline 1 The Standard Model: Construction 2 The Standard Model: Tests and status
The Standard Model of particle physics and beyond
 The Standard Model of particle physics and beyond - Lecture 3: Beyond the Standard Model Avelino Vicente IFIC CSIC / U. Valencia Physics and astrophysics of cosmic rays in space Milano September 2016 1
The Standard Model of particle physics and beyond - Lecture 3: Beyond the Standard Model Avelino Vicente IFIC CSIC / U. Valencia Physics and astrophysics of cosmic rays in space Milano September 2016 1
Elements of Grand Unification
 Elements of Grand Unification Problems with the Standard Model The Two Paths Grand Unification The Georgi-Glashow SU(5) Model Beyond SU(5) arger Groups Supersymmetry Extra Dimensions Additional Implications
Elements of Grand Unification Problems with the Standard Model The Two Paths Grand Unification The Georgi-Glashow SU(5) Model Beyond SU(5) arger Groups Supersymmetry Extra Dimensions Additional Implications
The Standard Model and Beyond
 Paul Langacker The Standard Model and Beyond CRC PRESS Boca Raton Ann Arbor London Tokyo Contents Preface xi 1 Notation and Conventions 1 1.1 Problems............................. 5 2 Review of Perturbative
Paul Langacker The Standard Model and Beyond CRC PRESS Boca Raton Ann Arbor London Tokyo Contents Preface xi 1 Notation and Conventions 1 1.1 Problems............................. 5 2 Review of Perturbative
A model of the basic interactions between elementary particles is defined by the following three ingredients:
 I. THE STANDARD MODEL A model of the basic interactions between elementary particles is defined by the following three ingredients:. The symmetries of the Lagrangian; 2. The representations of fermions
I. THE STANDARD MODEL A model of the basic interactions between elementary particles is defined by the following three ingredients:. The symmetries of the Lagrangian; 2. The representations of fermions
Grand Unification. Strong, weak, electromagnetic unified at Q M X M Z Simple group SU(3) SU(2) U(1) Gravity not included
 Pati-Salam, 73; Georgi-Glashow, 74 Grand Unification Strong, weak, electromagnetic unified at Q M X M Z Simple group G M X SU(3) SU() U(1) Gravity not included (perhaps not ambitious enough) α(q ) α 3
Pati-Salam, 73; Georgi-Glashow, 74 Grand Unification Strong, weak, electromagnetic unified at Q M X M Z Simple group G M X SU(3) SU() U(1) Gravity not included (perhaps not ambitious enough) α(q ) α 3
FLAVOR PHYSICS BEYOND THE STANDARD MODEL
 SFB Colloquium DESY Hamburg, July 3rd, 2008 FLAVOR PHYSICS BEYOND THE STANDARD MODEL Gudrun Hiller, Dortmund University of Technology Standard Model of Particle Physics renormalizable quantum field theory
SFB Colloquium DESY Hamburg, July 3rd, 2008 FLAVOR PHYSICS BEYOND THE STANDARD MODEL Gudrun Hiller, Dortmund University of Technology Standard Model of Particle Physics renormalizable quantum field theory
Low Energy Precision Tests of Supersymmetry
 Low Energy Precision Tests of Supersymmetry M.J. Ramsey-Musolf Caltech Wisconsin-Madison M.R-M & S. Su, hep-ph/0612057 J. Erler & M.R-M, PPNP 54, 351 (2005) Outline I. Motivation: Why New Symmetries? Why
Low Energy Precision Tests of Supersymmetry M.J. Ramsey-Musolf Caltech Wisconsin-Madison M.R-M & S. Su, hep-ph/0612057 J. Erler & M.R-M, PPNP 54, 351 (2005) Outline I. Motivation: Why New Symmetries? Why
Supersymmetry Breaking
 Supersymmetry Breaking LHC Search of SUSY: Part II Kai Wang Phenomenology Institute Department of Physics University of Wisconsin Madison Collider Phemonology Gauge Hierarchy and Low Energy SUSY Gauge
Supersymmetry Breaking LHC Search of SUSY: Part II Kai Wang Phenomenology Institute Department of Physics University of Wisconsin Madison Collider Phemonology Gauge Hierarchy and Low Energy SUSY Gauge
W + W - The Z pole. e + e hadrons SLC. Cross-section (pb) Centre-of-mass energy (GeV) P529 Spring,
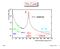 The Z pole Cross-section (pb) 10 5 10 4 Z e + e hadrons 10 3 10 2 CESR DORIS PEP W + W - 10 KEKB PEP-II PETRA TRISTAN SLC LEP I LEP II 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 Centre-of-mass energy (GeV)
The Z pole Cross-section (pb) 10 5 10 4 Z e + e hadrons 10 3 10 2 CESR DORIS PEP W + W - 10 KEKB PEP-II PETRA TRISTAN SLC LEP I LEP II 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220 Centre-of-mass energy (GeV)
Physics 662. Particle Physics Phenomenology. February 21, Physics 662, lecture 13 1
 Physics 662 Particle Physics Phenomenology February 21, 2002 Physics 662, lecture 13 1 Physics Beyond the Standard Model Supersymmetry Grand Unified Theories: the SU(5) GUT Unification energy and weak
Physics 662 Particle Physics Phenomenology February 21, 2002 Physics 662, lecture 13 1 Physics Beyond the Standard Model Supersymmetry Grand Unified Theories: the SU(5) GUT Unification energy and weak
Neutrino Mass in Strings
 Neutrino Mass in Strings Introduction Neutrino preliminaries Models String embeddings Intersecting brane The Z 3 heterotic orbifold Embedding the Higgs triplet Outlook Neutrino mass Nonzero mass may be
Neutrino Mass in Strings Introduction Neutrino preliminaries Models String embeddings Intersecting brane The Z 3 heterotic orbifold Embedding the Higgs triplet Outlook Neutrino mass Nonzero mass may be
Electroweak Theory: 5
 Electroweak Theory: 5 Introduction QED The Fermi theory The standard model Precision tests CP violation; K and B systems Higgs physics Prospectus STIAS (January, 2011) Paul Langacker (IAS) 162 References
Electroweak Theory: 5 Introduction QED The Fermi theory The standard model Precision tests CP violation; K and B systems Higgs physics Prospectus STIAS (January, 2011) Paul Langacker (IAS) 162 References
U(1) Gauge Extensions of the Standard Model
 U(1) Gauge Extensions of the Standard Model Ernest Ma Physics and Astronomy Department University of California Riverside, CA 92521, USA U(1) Gauge Extensions of the Standard Model (int08) back to start
U(1) Gauge Extensions of the Standard Model Ernest Ma Physics and Astronomy Department University of California Riverside, CA 92521, USA U(1) Gauge Extensions of the Standard Model (int08) back to start
Gauge coupling unification without leptoquarks Mikhail Shaposhnikov
 Gauge coupling unification without leptoquarks Mikhail Shaposhnikov March 9, 2017 Work with Georgios Karananas, 1703.02964 Heidelberg, March 9, 2017 p. 1 Outline Motivation Gauge coupling unification without
Gauge coupling unification without leptoquarks Mikhail Shaposhnikov March 9, 2017 Work with Georgios Karananas, 1703.02964 Heidelberg, March 9, 2017 p. 1 Outline Motivation Gauge coupling unification without
November 24, Scalar Dark Matter from Grand Unified Theories. T. Daniel Brennan. Standard Model. Dark Matter. GUTs. Babu- Mohapatra Model
 Scalar from November 24, 2014 1 2 3 4 5 What is the? Gauge theory that explains strong weak, and electromagnetic forces SU(3) C SU(2) W U(1) Y Each generation (3) has 2 quark flavors (each comes in one
Scalar from November 24, 2014 1 2 3 4 5 What is the? Gauge theory that explains strong weak, and electromagnetic forces SU(3) C SU(2) W U(1) Y Each generation (3) has 2 quark flavors (each comes in one
The Standard Model and beyond
 The Standard Model and beyond In this chapter we overview the structure of the Standard Model (SM) of particle physics, its shortcomings, and different ideas for physics beyond the Standard Model (BSM)
The Standard Model and beyond In this chapter we overview the structure of the Standard Model (SM) of particle physics, its shortcomings, and different ideas for physics beyond the Standard Model (BSM)
SUSY and Exotics. UK HEP Forum"From the Tevatron to the LHC, Cosener s House, May /05/2009 Steve King, UK HEP Forum '09, Abingdon 1
 SUSY and Exotics Standard Model and the Origin of Mass Puzzles of Standard Model and Cosmology Bottom-up and top-down motivation Extra dimensions Supersymmetry - MSSM -NMSSM -E 6 SSM and its exotics UK
SUSY and Exotics Standard Model and the Origin of Mass Puzzles of Standard Model and Cosmology Bottom-up and top-down motivation Extra dimensions Supersymmetry - MSSM -NMSSM -E 6 SSM and its exotics UK
F. Börkeroth, F. J. de Anda, I. de Medeiros Varzielas, S. F. King. arxiv:
 F. Börkeroth, F. J. de Anda, I. de Medeiros Varzielas, S. F. King S FLASY 2015 arxiv:1503.03306 Standard Model Gauge theory SU(3)C X SU(2)L X U(1)Y Standard Model Gauge theory SU(3)C X SU(2)L X U(1)Y SM:
F. Börkeroth, F. J. de Anda, I. de Medeiros Varzielas, S. F. King S FLASY 2015 arxiv:1503.03306 Standard Model Gauge theory SU(3)C X SU(2)L X U(1)Y Standard Model Gauge theory SU(3)C X SU(2)L X U(1)Y SM:
Who is afraid of quadratic divergences? (Hierarchy problem) & Why is the Higgs mass 125 GeV? (Stability of Higgs potential)
 Who is afraid of quadratic divergences? (Hierarchy problem) & Why is the Higgs mass 125 GeV? (Stability of Higgs potential) Satoshi Iso (KEK, Sokendai) Based on collaborations with H.Aoki (Saga) arxiv:1201.0857
Who is afraid of quadratic divergences? (Hierarchy problem) & Why is the Higgs mass 125 GeV? (Stability of Higgs potential) Satoshi Iso (KEK, Sokendai) Based on collaborations with H.Aoki (Saga) arxiv:1201.0857
Minimal Extension of the Standard Model of Particle Physics. Dmitry Gorbunov
 Minimal Extension of the Standard Model of Particle Physics Dmitry Gorbunov Institute for Nuclear Research, Moscow, Russia 14th Lomonosov Conference on Elementary Paticle Physics, Moscow, MSU, 21.08.2009
Minimal Extension of the Standard Model of Particle Physics Dmitry Gorbunov Institute for Nuclear Research, Moscow, Russia 14th Lomonosov Conference on Elementary Paticle Physics, Moscow, MSU, 21.08.2009
Sterile Neutrinos from the Top Down
 Sterile Neutrinos from the Top Down Active-sterile mixing The landscape Small Dirac/Majorana masses The mini-seesaw Light Sterile Neutrinos: A White Paper (K. Abazajian et al), 1204.5379 Neutrino Masses
Sterile Neutrinos from the Top Down Active-sterile mixing The landscape Small Dirac/Majorana masses The mini-seesaw Light Sterile Neutrinos: A White Paper (K. Abazajian et al), 1204.5379 Neutrino Masses
Neutrinos and Cosmos. Hitoshi Murayama (Berkeley) Texas Conference at Stanford Dec 17, 2004
 Neutrinos and Cosmos Hitoshi Murayama (Berkeley) Texas Conference at Stanford Dec 17, 2004 Outline A Little Historical Perspective Interpretation of Data & Seven Questions Matter Anti-Matter Asymmetry
Neutrinos and Cosmos Hitoshi Murayama (Berkeley) Texas Conference at Stanford Dec 17, 2004 Outline A Little Historical Perspective Interpretation of Data & Seven Questions Matter Anti-Matter Asymmetry
PHYSICS BEYOND SM AND LHC. (Corfu 2010)
 PHYSICS BEYOND SM AND LHC (Corfu 2010) We all expect physics beyond SM Fantastic success of SM (LEP!) But it has its limits reflected by the following questions: What is the origin of electroweak symmetry
PHYSICS BEYOND SM AND LHC (Corfu 2010) We all expect physics beyond SM Fantastic success of SM (LEP!) But it has its limits reflected by the following questions: What is the origin of electroweak symmetry
Introduction to Supersymmetry
 Introduction to Supersymmetry I. Antoniadis Albert Einstein Center - ITP Lecture 5 Grand Unification I. Antoniadis (Supersymmetry) 1 / 22 Grand Unification Standard Model: remnant of a larger gauge symmetry
Introduction to Supersymmetry I. Antoniadis Albert Einstein Center - ITP Lecture 5 Grand Unification I. Antoniadis (Supersymmetry) 1 / 22 Grand Unification Standard Model: remnant of a larger gauge symmetry
Neutrino Masses SU(3) C U(1) EM, (1.2) φ(1, 2) +1/2. (1.3)
 Neutrino Masses Contents I. The renormalizable Standard Model 1 II. The non-renormalizable Standard Model III. The See-Saw Mechanism 4 IV. Vacuum Oscillations 5 V. The MSW effect 7 VI. Experimental results
Neutrino Masses Contents I. The renormalizable Standard Model 1 II. The non-renormalizable Standard Model III. The See-Saw Mechanism 4 IV. Vacuum Oscillations 5 V. The MSW effect 7 VI. Experimental results
Higgs Signals and Implications for MSSM
 Higgs Signals and Implications for MSSM Shaaban Khalil Center for Theoretical Physics Zewail City of Science and Technology SM Higgs at the LHC In the SM there is a single neutral Higgs boson, a weak isospin
Higgs Signals and Implications for MSSM Shaaban Khalil Center for Theoretical Physics Zewail City of Science and Technology SM Higgs at the LHC In the SM there is a single neutral Higgs boson, a weak isospin
Supersymmetry Basics. J. Hewett SSI J. Hewett
 Supersymmetry Basics J. Hewett SSI 2012 J. Hewett Basic SUSY References A Supersymmetry Primer, Steve Martin hep-ph/9709356 Theory and Phenomenology of Sparticles, Manual Drees, Rohini Godbole, Probir
Supersymmetry Basics J. Hewett SSI 2012 J. Hewett Basic SUSY References A Supersymmetry Primer, Steve Martin hep-ph/9709356 Theory and Phenomenology of Sparticles, Manual Drees, Rohini Godbole, Probir
Little Higgs Models Theory & Phenomenology
 Little Higgs Models Theory Phenomenology Wolfgang Kilian (Karlsruhe) Karlsruhe January 2003 How to make a light Higgs (without SUSY) Minimal models The Littlest Higgs and the Minimal Moose Phenomenology
Little Higgs Models Theory Phenomenology Wolfgang Kilian (Karlsruhe) Karlsruhe January 2003 How to make a light Higgs (without SUSY) Minimal models The Littlest Higgs and the Minimal Moose Phenomenology
SUSY PHENOMENOLOGY. A Dissertation BO HU
 SUSY PHENOMENOLOGY A Dissertation by BO HU Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY August 2004
SUSY PHENOMENOLOGY A Dissertation by BO HU Submitted to the Office of Graduate Studies of Texas A&M University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY August 2004
Moriond QCD La Thuile, March 14 21, Flavour physics in the LHC era. An introduction. Clara Matteuzzi. INFN and Universita Milano-Bicocca
 Moriond QCD La Thuile, March 14 21, 2009 Flavour physics in the LHC era An introduction Clara Matteuzzi INFN and Universita Milano-Bicocca 1 Contents 1. The flavor structure of the Standard Model 2. Tests
Moriond QCD La Thuile, March 14 21, 2009 Flavour physics in the LHC era An introduction Clara Matteuzzi INFN and Universita Milano-Bicocca 1 Contents 1. The flavor structure of the Standard Model 2. Tests
Search for SUperSYmmetry SUSY
 PART 3 Search for SUperSYmmetry SUSY SUPERSYMMETRY Symmetry between fermions (matter) and bosons (forces) for each particle p with spin s, there exists a SUSY partner p~ with spin s-1/2. q ~ g (s=1)
PART 3 Search for SUperSYmmetry SUSY SUPERSYMMETRY Symmetry between fermions (matter) and bosons (forces) for each particle p with spin s, there exists a SUSY partner p~ with spin s-1/2. q ~ g (s=1)
May 7, Physics Beyond the Standard Model. Francesco Fucito. Introduction. Standard. Model- Boson Sector. Standard. Model- Fermion Sector
 - Boson - May 7, 2017 - Boson - The standard model of particle physics is the state of the art in quantum field theory All the knowledge we have developed so far in this field enters in its definition:
- Boson - May 7, 2017 - Boson - The standard model of particle physics is the state of the art in quantum field theory All the knowledge we have developed so far in this field enters in its definition:
E 6 Spectra at the TeV Scale
 E 6 Spectra at the TeV Scale Instituts-Seminar Kerne und Teilchen, TU Dresden Alexander Knochel Uni Freiburg 24.06.2010 Based on: F. Braam, AK, J. Reuter, arxiv:1001.4074 [hep-ph], JHEP06(2010)013 Outline
E 6 Spectra at the TeV Scale Instituts-Seminar Kerne und Teilchen, TU Dresden Alexander Knochel Uni Freiburg 24.06.2010 Based on: F. Braam, AK, J. Reuter, arxiv:1001.4074 [hep-ph], JHEP06(2010)013 Outline
Search for physics beyond the Standard Model at LEP 2
 Search for physics beyond the Standard Model at LEP 2 Theodora D. Papadopoulou NTU Athens DESY Seminar 28/10/03 1 Outline Introduction about LEP Alternatives to the Higgs mechanism Technicolor Contact
Search for physics beyond the Standard Model at LEP 2 Theodora D. Papadopoulou NTU Athens DESY Seminar 28/10/03 1 Outline Introduction about LEP Alternatives to the Higgs mechanism Technicolor Contact
Aspetti della fisica oltre il Modello Standard all LHC
 Aspetti della fisica oltre il Modello Standard all LHC (con enfasi sulla verificabilità sperimentale in gruppo I e II) Andrea Romanino SISSA e INFN TS Giornata di Seminari, INFN TS, 07.07.09 The Standard
Aspetti della fisica oltre il Modello Standard all LHC (con enfasi sulla verificabilità sperimentale in gruppo I e II) Andrea Romanino SISSA e INFN TS Giornata di Seminari, INFN TS, 07.07.09 The Standard
Neutrinos and Astrophysics
 Neutrinos and Astrophysics Astrophysical neutrinos Solar and stellar neutrinos Supernovae High energy neutrinos Cosmology Leptogenesis Big bang nucleosynthesis Large-scale structure and CMB Relic neutrinos
Neutrinos and Astrophysics Astrophysical neutrinos Solar and stellar neutrinos Supernovae High energy neutrinos Cosmology Leptogenesis Big bang nucleosynthesis Large-scale structure and CMB Relic neutrinos
Sterile Neutrinos from the Top Down
 Sterile Neutrinos from the Top Down Active-sterile mixing The landscape Small Dirac or Majorana masses (or both) The mini-seesaw Light Sterile Neutrinos: A White Paper (K. Abazajian et al), 1204.5379 Neutrino
Sterile Neutrinos from the Top Down Active-sterile mixing The landscape Small Dirac or Majorana masses (or both) The mini-seesaw Light Sterile Neutrinos: A White Paper (K. Abazajian et al), 1204.5379 Neutrino
SUPERSYMETRY FOR ASTROPHYSICISTS
 Dark Matter: From the Cosmos to the Laboratory SUPERSYMETRY FOR ASTROPHYSICISTS Jonathan Feng University of California, Irvine 29 Jul 1 Aug 2007 SLAC Summer Institute 30 Jul 1 Aug 07 Feng 1 Graphic: N.
Dark Matter: From the Cosmos to the Laboratory SUPERSYMETRY FOR ASTROPHYSICISTS Jonathan Feng University of California, Irvine 29 Jul 1 Aug 2007 SLAC Summer Institute 30 Jul 1 Aug 07 Feng 1 Graphic: N.
EDMs and flavor violation in SUSY models
 EDMs and flavor violation in SUSY models Junji Hisano Institute for Cosmic Ray Research (ICRR), University of Tokyo The 3rd International Symposium on LEPTON MOMENTS Cape Cod, June 2006 Contents of my
EDMs and flavor violation in SUSY models Junji Hisano Institute for Cosmic Ray Research (ICRR), University of Tokyo The 3rd International Symposium on LEPTON MOMENTS Cape Cod, June 2006 Contents of my
The mass of the Higgs boson
 The mass of the Higgs boson LHC : Higgs particle observation CMS 2011/12 ATLAS 2011/12 a prediction Higgs boson found standard model Higgs boson T.Plehn, M.Rauch Spontaneous symmetry breaking confirmed
The mass of the Higgs boson LHC : Higgs particle observation CMS 2011/12 ATLAS 2011/12 a prediction Higgs boson found standard model Higgs boson T.Plehn, M.Rauch Spontaneous symmetry breaking confirmed
Proton Decay and GUTs. Hitoshi Murayama (Berkeley) Durham July 20, 2005
 Proton Decay and GUTs Hitoshi Murayama (Berkeley) SUSY05 @ Durham July 20, 2005 Why do we pursue proton decay? Minimal SU(5) GUT excluded by IMB Minimal SUSY SU(5) GUT excluded by SuperKamiokande Why do
Proton Decay and GUTs Hitoshi Murayama (Berkeley) SUSY05 @ Durham July 20, 2005 Why do we pursue proton decay? Minimal SU(5) GUT excluded by IMB Minimal SUSY SU(5) GUT excluded by SuperKamiokande Why do
The Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa (CKM) matrix
 The Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa (CKM) matrix Charge-raising current J µ W = ( ν e ν µ ν τ )γ µ (1 γ 5 ) V = A u L Ad L e µ τ + (ū c t)γ µ (1 γ 5 )V Mismatch between weak and quark masses, and between A u,d
The Cabibbo-Kobayashi-Maskawa (CKM) matrix Charge-raising current J µ W = ( ν e ν µ ν τ )γ µ (1 γ 5 ) V = A u L Ad L e µ τ + (ū c t)γ µ (1 γ 5 )V Mismatch between weak and quark masses, and between A u,d
Lecture 03. The Standard Model of Particle Physics. Part III Extensions of the Standard Model
 Lecture 03 The Standard Model of Particle Physics Part III Extensions of the Standard Model Where the SM Works Excellent description of 3 of the 4 fundamental forces Explains nuclear structure, quark confinement,
Lecture 03 The Standard Model of Particle Physics Part III Extensions of the Standard Model Where the SM Works Excellent description of 3 of the 4 fundamental forces Explains nuclear structure, quark confinement,
Status and prospects of neutrino oscillations
 Status and prospects of neutrino oscillations S. Bilenky JINR(Dubna)TRIUMF June 10, 2017 The award of the 2015 Nobel Prize to T. Kajita and A. McDonald for the discovery of neutrino oscillations, which
Status and prospects of neutrino oscillations S. Bilenky JINR(Dubna)TRIUMF June 10, 2017 The award of the 2015 Nobel Prize to T. Kajita and A. McDonald for the discovery of neutrino oscillations, which
THE DREAM OF GRAND UNIFIED THEORIES AND THE LHC. Latsis symposium, Zurich, Graham Ross
 THE DREAM OF GRAND UNIFIED THEORIES AND THE HC atsis symposium, Zurich, 2013 Graham Ross The Standard Model after HC 8 u Symmetries è Dynamics Gauge bosons Chiral Matter Higgs u i d i SU(3) SU(2) U(1)
THE DREAM OF GRAND UNIFIED THEORIES AND THE HC atsis symposium, Zurich, 2013 Graham Ross The Standard Model after HC 8 u Symmetries è Dynamics Gauge bosons Chiral Matter Higgs u i d i SU(3) SU(2) U(1)
Flavor Models with Sterile Neutrinos. NuFact 11 Geneva, Aug, He Zhang
 Flavor Models with Sterile Neutrinos NuFact 11 Geneva, Aug, 2011 Contents: Sterile neutrinos in ν-osc. and 0νββ decays Mechanisms for light sterile neutrino masses Flavor symmetry with sterile neutrinos
Flavor Models with Sterile Neutrinos NuFact 11 Geneva, Aug, 2011 Contents: Sterile neutrinos in ν-osc. and 0νββ decays Mechanisms for light sterile neutrino masses Flavor symmetry with sterile neutrinos
Mirror fermions, electroweak scale right-handed neutrinos and experimental implications
 Mirror fermions, electroweak scale right-handed neutrinos and experimental implications P. Q. Hung University of Virginia Ljubljana 2008 Plan of Talk The question of parity restoration at high energies:
Mirror fermions, electroweak scale right-handed neutrinos and experimental implications P. Q. Hung University of Virginia Ljubljana 2008 Plan of Talk The question of parity restoration at high energies:
Higgs Physics. Yasuhiro Okada (KEK) November 26, 2004, at KEK
 Higgs Physics Yasuhiro Okada (KEK) November 26, 2004, at KEK 1 Higgs mechanism One of two principles of the Standard Model. Gauge invariance and Higgs mechanism Origin of the weak scale. Why is the weak
Higgs Physics Yasuhiro Okada (KEK) November 26, 2004, at KEK 1 Higgs mechanism One of two principles of the Standard Model. Gauge invariance and Higgs mechanism Origin of the weak scale. Why is the weak
Family Replicated Gauge Group Models
 Proceedings of Institute of Mathematics of NAS of Ukraine 2004, Vol. 50, Part 2, 77 74 Family Replicated Gauge Group Models C.D. FROGGATT, L.V. LAPERASHVILI, H.B. NIELSEN and Y. TAKANISHI Department of
Proceedings of Institute of Mathematics of NAS of Ukraine 2004, Vol. 50, Part 2, 77 74 Family Replicated Gauge Group Models C.D. FROGGATT, L.V. LAPERASHVILI, H.B. NIELSEN and Y. TAKANISHI Department of
Theory of CP Violation
 Theory of CP Violation IPPP, Durham CP as Natural Symmetry of Gauge Theories P and C alone are not natural symmetries: consider chiral gauge theory: L = 1 4 F µνf µν + ψ L i σdψ L (+ψ R iσ ψ R) p.1 CP
Theory of CP Violation IPPP, Durham CP as Natural Symmetry of Gauge Theories P and C alone are not natural symmetries: consider chiral gauge theory: L = 1 4 F µνf µν + ψ L i σdψ L (+ψ R iσ ψ R) p.1 CP
Models of Neutrino Masses
 Models of Neutrino Masses Fernando Romero López 13.05.2016 1 Introduction and Motivation 3 2 Dirac and Majorana Spinors 4 3 SU(2) L U(1) Y Extensions 11 4 Neutrino masses in R-Parity Violating Supersymmetry
Models of Neutrino Masses Fernando Romero López 13.05.2016 1 Introduction and Motivation 3 2 Dirac and Majorana Spinors 4 3 SU(2) L U(1) Y Extensions 11 4 Neutrino masses in R-Parity Violating Supersymmetry
How does neutrino confine GUT and Cosmology? July T. Fukuyama Center of Quantum Universe, Okayama-U
 How does neutrino confine GUT and Cosmology? July 11 08 T. Fukuyama (Rits) @ Center of Quantum Universe, Okayama-U 1. Introduction Neutrino oscillation breaks SM. Then is OK? does not predict 1. Gauge
How does neutrino confine GUT and Cosmology? July 11 08 T. Fukuyama (Rits) @ Center of Quantum Universe, Okayama-U 1. Introduction Neutrino oscillation breaks SM. Then is OK? does not predict 1. Gauge
TeV-scale type-i+ii seesaw mechanism and its collider signatures at the LHC
 TeV-scale type-i+ii seesaw mechanism and its collider signatures at the LHC Wei Chao (IHEP) Outline Brief overview of neutrino mass models. Introduction to a TeV-scale type-i+ii seesaw model. EW precision
TeV-scale type-i+ii seesaw mechanism and its collider signatures at the LHC Wei Chao (IHEP) Outline Brief overview of neutrino mass models. Introduction to a TeV-scale type-i+ii seesaw model. EW precision
Two-Higgs-doublet models with Higgs symmetry
 Two-Higgs-doublet models with Higgs symmetry Chaehyun Yu a a School of Physics, KIAS, Seoul 130-722, Korea Abstract We investigate two-higgs-doublet models (2HDMs) with local U(1) H Higgs flavor symmetry
Two-Higgs-doublet models with Higgs symmetry Chaehyun Yu a a School of Physics, KIAS, Seoul 130-722, Korea Abstract We investigate two-higgs-doublet models (2HDMs) with local U(1) H Higgs flavor symmetry
Neutrino Masses and Dark Matter in Gauge Theories for Baryon and Lepton Numbers
 Neutrino Masses and Dark Matter in Gauge Theories for Baryon and Lepton Numbers DPG Frühjahrstagung 014 in Mainz Based on Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 31801 (013), Phys. Rev. D 88, 051701(R) (013), arxiv:1309.3970
Neutrino Masses and Dark Matter in Gauge Theories for Baryon and Lepton Numbers DPG Frühjahrstagung 014 in Mainz Based on Phys. Rev. Lett. 110, 31801 (013), Phys. Rev. D 88, 051701(R) (013), arxiv:1309.3970
Split Supersymmetry A Model Building Approach
 Split Supersymmetry A Model Building Approach Kai Wang Phenomenology Institute Department of Physics the University of Wisconsin Madison UC Riverside HEP Seminar In Collaboration with Ilia Gogoladze (Notre
Split Supersymmetry A Model Building Approach Kai Wang Phenomenology Institute Department of Physics the University of Wisconsin Madison UC Riverside HEP Seminar In Collaboration with Ilia Gogoladze (Notre
IX. Electroweak unification
 IX. Electroweak unification The problem of divergence A theory of weak interactions only by means of W ± bosons leads to infinities e + e - γ W - W + e + W + ν e ν µ e - W - µ + µ Divergent integrals Figure
IX. Electroweak unification The problem of divergence A theory of weak interactions only by means of W ± bosons leads to infinities e + e - γ W - W + e + W + ν e ν µ e - W - µ + µ Divergent integrals Figure
SUSY Phenomenology & Experimental searches
 SUSY Phenomenology & Experimental searches Slides available at: Alex Tapper http://www.hep.ph.ic.ac.uk/~tapper/lecture.html Objectives - Know what Supersymmetry (SUSY) is - Understand qualitatively the
SUSY Phenomenology & Experimental searches Slides available at: Alex Tapper http://www.hep.ph.ic.ac.uk/~tapper/lecture.html Objectives - Know what Supersymmetry (SUSY) is - Understand qualitatively the
SO(10) SUSY GUTs with family symmetries: the test of FCNCs
 SO(10) SUSY GUTs with family symmetries: the test of FCNCs Outline Diego Guadagnoli Technical University Munich The DR Model: an SO(10) SUSY GUT with D 3 family symmetry Top down approach to the MSSM+
SO(10) SUSY GUTs with family symmetries: the test of FCNCs Outline Diego Guadagnoli Technical University Munich The DR Model: an SO(10) SUSY GUT with D 3 family symmetry Top down approach to the MSSM+
The first one second of the early universe and physics beyond the Standard Model
 The first one second of the early universe and physics beyond the Standard Model Koichi Hamaguchi (University of Tokyo) @ Colloquium at Yonsei University, November 9th, 2016. Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/CfA/M.Markevitch
The first one second of the early universe and physics beyond the Standard Model Koichi Hamaguchi (University of Tokyo) @ Colloquium at Yonsei University, November 9th, 2016. Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/CfA/M.Markevitch
CP Violation Beyond the Standard Model
 CP Violation Beyond the Standard Model 5th Recontres du Vietnam Hanoi August 7, 2004 Yossi Nir (Weizmann Institute of Science) Thanks to: Sandrine Laplace, Zoltan Ligeti CPV BSM 1/21 Motivation Why do
CP Violation Beyond the Standard Model 5th Recontres du Vietnam Hanoi August 7, 2004 Yossi Nir (Weizmann Institute of Science) Thanks to: Sandrine Laplace, Zoltan Ligeti CPV BSM 1/21 Motivation Why do
Fundamental Symmetries - 2
 HUGS 2018 Jefferson Lab, Newport News, VA May 29- June 15 2018 Fundamental Symmetries - 2 Vincenzo Cirigliano Los Alamos National Laboratory Plan of the lectures Review symmetry and symmetry breaking Introduce
HUGS 2018 Jefferson Lab, Newport News, VA May 29- June 15 2018 Fundamental Symmetries - 2 Vincenzo Cirigliano Los Alamos National Laboratory Plan of the lectures Review symmetry and symmetry breaking Introduce
Probing the Majorana nature in radiative seesaw models at collider experiments
 Probing the Majorana nature in radiative seesaw models at collider experiments Shinya KANEMURA (U. of Toyama) M. Aoki, SK and O. Seto, PRL 102, 051805 (2009). M. Aoki, SK and O. Seto, PRD80, 033007 (2009).
Probing the Majorana nature in radiative seesaw models at collider experiments Shinya KANEMURA (U. of Toyama) M. Aoki, SK and O. Seto, PRL 102, 051805 (2009). M. Aoki, SK and O. Seto, PRD80, 033007 (2009).
Kaluza-Klein Theories - basic idea. Fig. from B. Greene, 00
 Kaluza-Klein Theories - basic idea Fig. from B. Greene, 00 Kaluza-Klein Theories - basic idea mued mass spectrum Figure 3.2: (Taken from [46]). The full spectrum of the UED model at the first KK level,
Kaluza-Klein Theories - basic idea Fig. from B. Greene, 00 Kaluza-Klein Theories - basic idea mued mass spectrum Figure 3.2: (Taken from [46]). The full spectrum of the UED model at the first KK level,
Tests of the Electroweak Theory
 Tests of the Electroweak Theory History/introduction Weak charged current QED Weak neutral current Precision tests Rare processes CP violation and B decays Neutrino mass FNAL (December 13, 2005) Paul Langacker
Tests of the Electroweak Theory History/introduction Weak charged current QED Weak neutral current Precision tests Rare processes CP violation and B decays Neutrino mass FNAL (December 13, 2005) Paul Langacker
Is there a new physics between electroweak and Planck scale?
 Is there a new physics between electroweak and Planck scale? Mikhail Shaposhnikov LAUNCH 09 - Heidelberg, MPIK Heidelberg, 12 November 2009 p. 1 Yes proton decay yes (?) new physics at LHC yes (?) searches
Is there a new physics between electroweak and Planck scale? Mikhail Shaposhnikov LAUNCH 09 - Heidelberg, MPIK Heidelberg, 12 November 2009 p. 1 Yes proton decay yes (?) new physics at LHC yes (?) searches
Natural Electroweak Symmetry Breaking in NMSSM and Higgs at 100 GeV
 Natural Electroweak Symmetry Breaking in NMSSM and Higgs at 100 GeV Radovan Dermíšek Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton R.D. and J. F. Gunion, hep-ph/0502105 R.D. and J. F. Gunion, hep-ph/0510322
Natural Electroweak Symmetry Breaking in NMSSM and Higgs at 100 GeV Radovan Dermíšek Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton R.D. and J. F. Gunion, hep-ph/0502105 R.D. and J. F. Gunion, hep-ph/0510322
New Physics below the Fermi Scale. Mikhail Shaposhnikov
 New Physics below the Fermi Scale Mikhail Shaposhnikov September 6, 2016 CERN, September 6, 2016 p. 1 The LHC has discovered something quite unexpected (at least, up to now, ICHEP 2016): The Higgs boson
New Physics below the Fermi Scale Mikhail Shaposhnikov September 6, 2016 CERN, September 6, 2016 p. 1 The LHC has discovered something quite unexpected (at least, up to now, ICHEP 2016): The Higgs boson
Exploring Universal Extra-Dimensions at the LHC
 Exploring Universal Extra-Dimensions at the LHC Southampton University & Rutherford Appleton Laboratory 1 Problems to be addressed by the underlying theory The Nature of Electroweak Symmetry Breaking The
Exploring Universal Extra-Dimensions at the LHC Southampton University & Rutherford Appleton Laboratory 1 Problems to be addressed by the underlying theory The Nature of Electroweak Symmetry Breaking The
SUSY Phenomenology a
 KEK-TH-606 November 1998 SUSY Phenomenology a Yasuhiro Okada KEK, Oho 1-1, Tsukuba, 305-0801 Japan Three topics on phenomenology in supersymmetric models are reviewed, namely, the Higgs sector in the supersymmetric
KEK-TH-606 November 1998 SUSY Phenomenology a Yasuhiro Okada KEK, Oho 1-1, Tsukuba, 305-0801 Japan Three topics on phenomenology in supersymmetric models are reviewed, namely, the Higgs sector in the supersymmetric
Physics at the TeV Scale Discovery Prospects Using the ATLAS Detector at the LHC
 Physics at the TeV Scale Discovery Prospects Using the ATLAS Detector at the LHC Peter Krieger Carleton University Physics Motivations Experimental Theoretical New particles searches Standard Model Higgs
Physics at the TeV Scale Discovery Prospects Using the ATLAS Detector at the LHC Peter Krieger Carleton University Physics Motivations Experimental Theoretical New particles searches Standard Model Higgs
Neutrino Mass Models
 Neutrino Mass Models S Uma Sankar Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Mumbai, India S. Uma Sankar (IITB) IWAAP-17, BARC (Mumbai) 01 December 2017 1 / 15 Neutrino Masses LEP experiments
Neutrino Mass Models S Uma Sankar Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Mumbai, India S. Uma Sankar (IITB) IWAAP-17, BARC (Mumbai) 01 December 2017 1 / 15 Neutrino Masses LEP experiments
Astroparticle Physics and the LC
 Astroparticle Physics and the LC Manuel Drees Bonn University Astroparticle Physics p. 1/32 Contents 1) Introduction: A brief history of the universe Astroparticle Physics p. 2/32 Contents 1) Introduction:
Astroparticle Physics and the LC Manuel Drees Bonn University Astroparticle Physics p. 1/32 Contents 1) Introduction: A brief history of the universe Astroparticle Physics p. 2/32 Contents 1) Introduction:
The Electro-Weak Sector. Precision Experiments before LEP LEP Physics Probing the Standard Model Beyond the Standard Model
 The Electro-Weak Sector Precision Experiments before LEP LEP Physics Probing the Standard Model Beyond the Standard Model P. Langacker CERN, LEP Fest 11 October, 2000 The Z, the W, and the Weak Neutral
The Electro-Weak Sector Precision Experiments before LEP LEP Physics Probing the Standard Model Beyond the Standard Model P. Langacker CERN, LEP Fest 11 October, 2000 The Z, the W, and the Weak Neutral
Beyond the SM, Supersymmetry
 Beyond the SM, 1/ 44 Beyond the SM, A. B. Lahanas University of Athens Nuclear and Particle Physics Section Athens - Greece Beyond the SM, 2/ 44 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Beyond the SM Grand Unified Theories
Beyond the SM, 1/ 44 Beyond the SM, A. B. Lahanas University of Athens Nuclear and Particle Physics Section Athens - Greece Beyond the SM, 2/ 44 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Beyond the SM Grand Unified Theories
EFFECTS OF NEW LEPTONS IN ELECTROWEAK PRECISION DATA
 EFFECTS OF NEW LEPTONS IN ELECTROWEAK PRECISION DATA In collaboration with F. del Águila and M. Pérez-Victoria Phys. Rev. D78: 013010, 2008 Depto. de Física Teórica y del Cosmos Universidad de Granada
EFFECTS OF NEW LEPTONS IN ELECTROWEAK PRECISION DATA In collaboration with F. del Águila and M. Pérez-Victoria Phys. Rev. D78: 013010, 2008 Depto. de Física Teórica y del Cosmos Universidad de Granada
Heavy Sterile Neutrinos at CEPC
 Wei Liao East China University of Science and Technology Based on arxiv:17.09266, in collaboration with X.H. Wu INPAC SJTU, Nov. 17 2017 Outline Review of neutrino mass low energy seesaw model constraint
Wei Liao East China University of Science and Technology Based on arxiv:17.09266, in collaboration with X.H. Wu INPAC SJTU, Nov. 17 2017 Outline Review of neutrino mass low energy seesaw model constraint
