QUAD/DUAL N-CHANNEL ENHANCEMENT MODE EPAD PRECISION MATCHED PAIR MOSFET ARRAY
|
|
|
- Alexia Austin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 TM DVNCD INR DVICS, INC. QUD/DU N-CHNN NHNCMNT MOD PD PRCISION MTCHD PIR MOSFT RRY PD D8/D9 N B D VGS(th)= +.V GNR DSCRIPTION D8/D9 ar high prcision monolithic quad/dual nhancmnt mod N-Channl MOSFTS matchd at th factory using D s provn PD CMOS tchnology. Ths dvics ar intndd for low voltag, small signal applications. Th D8/D9 MOSFTS ar dsignd and uilt for xcptional dvic lctrical charactristics matching. Sinc ths dvics ar on th sam monolithic chip, thy also xhiit xcllnt tmpco tracking charactristics. Thy ar vrsatil circuit lmnts usful as dsign componnts for a road rang of analog applications, such as asic uilding locks for currnt sourcs, diffrntial amplifir input stags, transmission gats, and multiplxr applications. For most applications, connct th V+ pin to th most positiv voltag and th V- and IC pins to th most ngativ voltag in th systm. ll othr pins must hav voltags within ths voltag limits at all tims. Th D8/D9 dvics ar uilt for minimum offst voltag and diffrntial thrmal rspons, and thy ar suitd for switching and amplifying applications in <+.V to +V systms whr low input ias currnt, low input capacitanc and fast switching spd ar dsird, as ths dvics xhiit wll controlld turn-off and su-thrshold charactristics and can iasd and opratd in th su-thrshold rgion. Sinc ths ar MOSFT dvics, thy fatur vry larg (almost infinit) currnt gain in a low frquncy, or nar DC, oprating nvironmnt. Th D8/D9 ar suital for us in vry low oprating voltag or vry low powr (nanowatt), prcision applications which rquir vry high currnt gain, ta, such as currnt mirrors and currnt sourcs. Th high input impdanc and th high DC currnt gain of th Fild ffct Transistors rsult from xtrmly low currnt loss through th control gat. Th DC currnt gain is limitd y th gat input lakag currnt, which is spcifid at 3p at room tmpratur. For xampl, DC ta of th dvic at a drain currnt of 3m, input lakag currnt of 3p, and 5 C is 3m/3p =,,. FTURS nhancmnt-mod (normally off) Prcision Gat Thrshold Voltag of +.V Matchd MOSFT-to-MOSFT charactristics Tight lot-to-lot paramtric control ow input capacitanc V GS(th) match (V OS ) to mv High input impdanc Ω typical Positiv, zro, and ngativ V GS(th) tmpratur cofficint DC currnt gain > 8 ow input and output lakag currnts ORDRING INFORMTION ( suffix dnots lad-fr (RoHS)) Oprating Tmpratur Rang* C to +7 C C to +7 C 6-Pin 6-Pin 8-Pin 8-Pin SOIC Plastic Dip SOIC Plastic Dip Packag Packag Packag Packag D8SC D8PC D9S D9P PPICTIONS Ultra low powr (nanowatt) analog and digital circuits Ultra low oprating voltag (<.V) circuits Su-thrshold iasd and opratd circuits Prcision currnt mirrors and currnt sourcs Nano-mp currnt sourcs High impdanc rsistor simulators Capacitiv pros and snsor intrfacs Diffrntial amplifir input stags Discrt Voltag comparators and lvl shiftrs Voltag ias circuits Sampl and Hold circuits nalog and digital invrtrs Charg dtctors and charg intgrators Sourc followrs and High Impdanc uffrs Currnt multiplirs Discrt nalog switchs / multiplxrs PIN CONFIGURTION IC* D8 SC, PC PCKGS D9 S, P PCKGS *IC pins ar intrnally connctd. Connct to V- 6 G N D N 3 M M 5 S V + 3 V - 5 V - D N 6 M M 3 G N 7 IC* 8 V - V - 9 IC* G N D N S V - V- V - V- 7 3 M M 6 V- 5 8 IC* G N D N V + S 3 D N3 G N3 IC* IC* G N D N V- * Contact factory for industrial tmp. rang or usr-spcifid thrshold voltag valus. 6 dvancd inar Dvics, Inc., Vrs..3 of
2 BSOUT MXIMUM RTINGS Drain-Sourc voltag, VDS.6V Gat-Sourc voltag, VGS.6V Powr dissipation 5 mw Oprating tmpratur rang SC, PC, S, P C to +7 C Storag tmpratur rang -65 C to +5 C ad tmpratur, sconds +6 C CUTION: SD Snsitiv Dvic. Us static control procdurs in SD controlld nvironmnt. OPRTING CTRIC CHRCTRISTICS V+ = +5V V- = GND T = 5 C unlss othrwis spcifid D8/D9 Paramtr Symol Min Typ Max Unit Tst Conditions Gat Thrshold Voltag VGS(th).8.. V IDS = µ, VDS =.V Offst Voltag VOS mv VGS(th)-VGS(th) Offst VoltagTmpco TCVOS 5 µv/ C VDS = VDS Gat Thrshold Voltag TCVGS(th) -.7 mv/ C IDS = µ, VDS =.V Tmpco. IDS = µ, VDS =.V +.6 IDS = µ, VDS =.V Drain Sourc On Currnt IDS(ON). m VGS = +9.7V, VDS = +5V 3. VGS = +.V, VDS = +5V Forward Transconductanc GFS. mmho VGS = +.V VDS = +9.V Transconductanc Mismatch GFS.8 % Output Conductanc GOS 68 µmho VGS = +.V VDS = +9.V Drain Sourc On Rsistanc RDS(ON) 5 Ω VGS = +.V VDS = +.V Drain Sourc On Rsistanc RDS(ON).5 % Mismatch Drain Sourc Brakdown BVDSX V V- = VGS = -.8V Voltag IDS =.µ Drain Sourc akag Currnt IDS(OFF) p VGS = -.8V, VDS =+5V V- = -5V n T = 5 C Gat akag Currnt IGSS 3 p VGS = +5V, VDS = V n T =5 C Input Capacitanc CISS.5 pf Transfr Rvrs Capacitanc CRSS. pf Turn-on Dlay Tim ton ns V+ = 5V, R= 5KΩ Turn-off Dlay Tim toff ns V+ = 5V, R= 5KΩ Crosstalk 6 db f = KHz Nots: Consists of junction lakag currnts D8/D9, Vrs..3 dvancd inar Dvics of
3 PRFORMNC CHRCTRISTICS OF PD PRCISION MTCHD PIR MOSFT FMIY D8xx/D9xx/D8xx/D9xx ar monolithic quad/dual N-Channl MOSFTs matchd at th factory using D s provn PD CMOS tchnology. Ths dvics ar intndd for low voltag, small signal applications. D s lctrically Programmal nalog Dvic (PD) tchnology provids a family of matchd transistors with a rang of prcision thrshold valus. ll mmrs of this family ar dsignd and activly programmd for xcptional matching of dvic lctrical charactristics. Thrshold valus rang from -3.5V Dpltion to +3.5V nhancmnt dvics, including standard products spcifid at -3.5V, -.3V, -.V, +.V, +.V, +.V, +.8V, +.V, and +3.3V. D can also provid any customr dsird valu twn -3.5V and +3.5V. For all ths dvics, vn th dpltion and zro thrshold transistors, D PD tchnology nals th sam wll controlld turn-off, suthrshold, and low lakag charactristics as standard nhancmnt mod MOSFTs. With th dsign and activ programming, vn units from diffrnt atchs and diffrnt dats of manufactur hav wll matchd charactristics. s ths dvics ar on th sam monolithic chip, thy also xhiit xcllnt tmpco tracking. This PD MOSFT rray product family (PD MOSFT) is availal in th thr sparat catgoris, ach providing a distinctly diffrnt st of lctrical spcifications and charactristics. Th first catgory is th D8/D9 Zro-Thrshold mod PD MOSFTs. Th scond catgory is th D8xx/ D9xx nhancmnt mod PD MOSFTs. Th third catgory is th D8xx/D9xx dpltion mod PD MOSFTs. (Th suffix xx dnots thrshold voltag in.v stps, for xampl, xx = 8 dnots.8v). Th D8/D9 (quad/dual) ar PD MOSFTs in which th individual thrshold voltag of ach MOSFT is fixd at zro. Th thrshold voltag is dfind as I DS = V DS =.V whn th gat voltag V GS =.V. Zro thrshold dvics oprat in th nhancmnt rgion whn opratd aov thrshold voltag and currnt lvl (V GS >.V and I DS > µ) and suthrshold rgion whn opratd at or low thrshold voltag and currnt lvl (V GS <=.V and I DS < µ). This dvic, along with othr vry low thrshold voltag mmrs of th product family, constitut a class of PD MOSFTs that nal ultra low supply voltag opration and nanopowr typ of circuit dsigns, applical in ithr analog or digital circuits. Th D8xx/D9xx (quad/dual) product family faturs prcision matchd nhancmnt mod PD MOSFT dvics, which rquir a positiv ias voltag to turn on. Prcision thrshold valus such as +.V, +.8V, +.V ar offrd. No conductiv channl xists twn th sourc and drain at zro applid gat voltag for ths dvics, xcpt that th +.V vrsion has a suthrshold currnt at aout n. Th D8xx/D9xx (quad/dual) faturs dpltion mod PD MOSFTs, which ar normally-on dvics whn th gat ias voltag is at zro volts. Th dpltion mod thrshold voltag is at a ngativ voltag lvl at which th PD MOSFT turns off. Without a supply voltag and/or with V GS =.V th PD MOSFT dvic is alrady turnd on and xhiits a dfind and controlld on-rsistanc twn th sourc and drain trminals. Th D8xx/D9xx dpltion mod PD MOSFTs ar diffrnt from most othr typs of dpltion mod MOSFTs and crtain typs of JFTs in that thy do not xhiit high gat lakag currnts and channl/junction lakag currnts. Whn ngativ signal voltags ar applid to th gat trminal, th dsignr/usr can dpnd on th PD MOSFT dvic to controlld, modulatd and turnd off prcisly. Th dvic can modulatd and turnd-off undr th control of th gat voltag in th sam mannr as th nhancmnt mod PD MOSFT and th sam dvic quations apply. PD MOSFTs ar idal for minimum offst voltag and diffrntial thrmal rspons, and thy ar usd for switching and amplifying applications in low voltag (V to V or +/-.5V to +/-5V) or ultra low voltag (lss than V or +/-.5V) systms. Thy fatur low input ias currnt (lss than 3p max.), ultra low powr (microwatt) or Nanopowr (powr masurd in nanowatt) opration, low input capacitanc and fast switching spd. Ths dvics can usd whr a comination of ths charactristics ar dsird. KY PPICTION NVIRONMNT PD MOSFT rray products ar for circuit applications in on or mor of th following oprating nvironmnts: * ow voltag: V to V or +/-.5V to +/-5V * Ultra low voltag: lss than V or +/-.5V * ow powr: voltag x currnt = powr masurd in microwatt * Nanopowr: voltag x currnt = powr masurd in nanowatt * Prcision matching and tracking of two or mor MOSFTs CTRIC CHRCTRISTICS Th turn-on and turn-off lctrical charactristics of th PD MOSFT products ar shown in th Drain-Sourc On Currnt vs Drain-Sourc On Voltag and Drain-Sourc On Currnt vs Gat- Sourc Voltag graphs. ach graph shows th Drain-Sourc On Currnt vrsus Drain-Sourc On Voltag charactristics as a function of Gat-Sourc voltag in a diffrnt oprating rgion undr diffrnt ias conditions. s th thrshold voltag is tightly spcifid, th Drain-Sourc On Currnt at a givn gat input voltag is ttr controlld and mor prdictal whn compard to many othr typs of MOSFTs. PD MOSFTs hav similarly to a standard MOSFT, thrfor classic quations for a n-channl MOSFT applis to PD MOSFT as wll. Th Drain currnt in th linar rgion (V DS < V GS - V GS(th) ) is givn y: I DS = u. C OX. W/. [V GS - V GS(th) - V DS /]. V DS whr: u = Moility C OX = Capacitanc / unit ara of Gat lctrod V GS = Gat to Sourc voltag V GS(th) = Turn-on thrshold voltag V DS = Drain to Sourc voltag W = Channl width = Channl lngth In this rgion of opration th I DS valu is proportional to V DS valu and th dvic can usd as a gat-voltag controlld rsistor. For highr valus of V DS whr V DS >= V GS - V GS(th), th saturation currnt I DS is now givn y (approx.): I DS = u. C OX. W/. [V GS - V GS(th) ] D8/D9, Vrs..3 dvancd inar Dvics 3 of
4 SUB-THRSHOD RGION OF OPRTION PRFORMNC CHRCTRISTICS OF PD PRCISION MTCHD PIR MOSFT FMIY (cont.) ZRO TMPRTUR COFFICINT (ZTC) OPRTION ow voltag systms, namly thos oprating at 5V, 3.3V or lss, typically rquir MOSFTs that hav thrshold voltag of V or lss. Th thrshold, or turn-on, voltag of th MOSFT is a voltag low which th MOSFT conduction channl rapidly turns off. For analog dsigns, this thrshold voltag dirctly affcts th oprating signal voltag rang and th oprating ias currnt lvls. t or low thrshold voltag, an PD MOSFT xhiits a turnoff charactristic in an oprating rgion calld th suthrshold rgion. This is whn th PD MOSFT conduction channl rapidly turns off as a function of dcrasing applid gat voltag. Th conduction channl inducd y th gat voltag on th gat lctrod dcrass xponntially and causs th drain currnt to dcras xponntially. Howvr, th conduction channl dos not shut off aruptly with dcrasing gat voltag. Rathr, it dcrass at a fixd rat of approximatly 6mV pr dcad of drain currnt dcras. Thus, if th thrshold voltag is +.V, for xampl, th drain currnt is µ at V GS = +.V. t V GS = +.9V, th drain currnt would dcras to.µ. xtrapolating from this, th drain currnt is.µ (n) at V GS = -.3V, n at V GS = -.V, and so forth. This suthrshold charactristic xtnds all th way down to currnt lvls low n and is limitd y othr currnts such as junction lakag currnts. t a drain currnt to dclard zro currnt y th usr, th V GS voltag at that zro currnt can now stimatd. Not that using th aov xampl, with V GS(th) = +.V, th drain currnt still hovrs around n whn th gat is at zro volts, or ground. OW POWR ND NNOPOWR Whn supply voltags dcras, th powr consumption of a givn load rsistor dcrass as th squar of th supply voltag. So on of th nfits in rducing supply voltag is to rduc powr consumption. Whil dcrasing powr supply voltags and powr consumption go hand-in-hand with dcrasing usful C andwidth and at th sam tim incrass nois ffcts in th circuit, a circuit dsignr can mak th ncssary tradoffs and adjustmnts in any givn circuit dsign and ias th circuit accordingly. With PD MOSFTs, a circuit that prforms a spcific function can dsignd so that powr consumption can minimizd. In som cass, ths circuits oprat in low powr mod whr th powr consumd is masur in micro-watts. In othr cass, powr dissipation can rducd to th nano-watt rgion and still provid a usful and controlld circuit function opration. For an PD MOSFT in this product family, thr xist oprating points whr th various factors that caus th currnt to incras as a function of tmpratur alanc out thos that caus th currnt to dcras, thry cancling ach othr, and rsulting in nt tmpratur cofficint of nar zro. On of ths tmpratur stal oprating points is otaind y a ZTC voltag ias condition, which is.55v aov a thrshold voltag whn V GS = V DS, rsulting in a tmpratur stal currnt lvl of aout 68µ. For othr ZTC oprating points, s ZTC charactristics. PRFORMNC CHRCTRISTICS Prformanc charactristics of th PD MOSFT product family ar shown in th following graphs. In gnral, th thrshold voltag shift for ach mmr of th product family causs othr affctd lctrical charactristics to shift with an quivalnt linar shift in V GS(th) ias voltag. This linar shift in V GS causs th suthrshold I-V curvs to shift linarly as wll. ccordingly, th suthrshold oprating currnt can dtrmind y calculating th gat voltag drop rlativ to its thrshold voltag, V GS(th). R DS(ON) T V GS = GROUND Svral of th PD MOSFTs produc a fixd rsistanc whn thir gat is groundd. For D8, th drain currnt is µ at V DS =.V and V GS =.V. Thus, just y grounding th gat of th D8, a rsistor with R DS(ON) = ~KΩ is producd. Whn an D8 gat is groundd, th drain currnt I DS = V DS =.V, producing R DS(ON) = 5.KΩ. Similarly, D83 and D835 produc drain currnts of 77µ and 85µ, rspctivly, at V GS =.V, and R DS(ON) valus of.3kω and 5Ω, rspctivly. MTCHING CHRCTRISTICS ky nfit of using a matchd pair PD MOSFT is to maintain tmpratur tracking. In gnral, for PD MOSFT matchd pair dvics, on dvic of th matchd pair has gat lakag currnts, junction tmpratur ffcts, and drain currnt tmpratur cofficint as a function of ias voltag that cancl out similar ffcts of th othr dvic, rsulting in a tmpratur stal circuit. s mntiond arlir, this tmpratur staility can furthr nhancd y iasing th matchd-pairs at Zro Tmpco (ZTC) point, vn though that could rquir spcial circuit configuration and powr consumption dsign considration. D8/D9, Vrs..3 dvancd inar Dvics of
5 TYPIC PRFORMNC CHRCTRISTICS (m) 5 3 OUTPUT CHRCTRISTICS T = +5 C VGS - VGS(th) = +5V VGS - VGS(th) = +V VGS - VGS(th) = +3V VGS - VGS(th) = +V VGS - VGS(th) = +V DRIN-SOURC ON RSISTNC (Ω) DRIN-SOURC ON RSISTNC vs. T = +5 C VGS = VGS(th) + V VGS = VGS(th) + 6V 6 8 DRIN-SOURC ON VOTG (V) (µ) (m) 5 5 FORWRD TRNSFR CHRCTRISTICS T = +5 C V DS = +V V GS(th) = -.V V GS(th) =.V V GS(th) = +.V V GS(th) = -.3V V GS(th) = -3.5V V GS(th) = +.8V V GS(th) = +.V TRNSCONDUCTNC (m/v) TRNSCONDUCTNC vs. MBINT TMPRTUR GT-SOURC VOTG (V) MBINT TMPRTUR ( C) (n).. SUBTHRSHOD FORWRD TRNSFR CHRCTRISTICS - V GS(th) = -3.5V -3 T = +5 C V DS = +.V - V GS(th) = -.3V V GS(th) = -.V - V GS(th) =.V V GS(th) = +.V V GS(th) = +.8V V GS(th) = +.V (n).. SUBTHRSHOD FORWRD TRNSFR CHRCTRISTICS V DS = +.V Slop = ~ mv/dcad V GS(th) -.5 V GS(th) -. V GS(th) -.3 V GS(th) -. V GS(th) -. V GS(th) GT-SOURC VOTG (V) GT-SOURC VOTG (V) D8/D9, Vrs..3 dvancd inar Dvics 5 of
6 TYPIC PRFORMNC CHRCTRISTICS (cont.) (m) 5 3, BIS CURRNT vs. MBINT TMPRTUR -55 C -5 C C +7 C +5 C (µ) 5, BIS CURRNT vs. MBINT TMPRTUR Zro Tmpratur Cofficint (ZTC) +5 C -5 C VGS(th)- VGS(th) VGS(th)+ VGS(th)+ VGS(th)+3 VGS(th)+ V GS(th) V GS(th) +. V GS(th) +. V GS(th) +.6 V GS(th) +.8 V GS(th) +. GT- ND DRIN-SOURC VOTG (V GS = V DS ) (V) GT- ND DRIN-SOURC VOTG (V GS = V DS ) (V) (µ).. vs. DRIN-SOURC ON RSISTNC T = +5 C V GS = -.V to +5.V VDS = +.V VDS = +5V VDS = +V. VDS = +V DRIN-SOURC ON RSISTNC (KΩ) GT-SOURC VOTG (V) V GS(th) + V GS(th) +3 V GS(th) + V GS(th) + V GS(th) V GS(th) - GT-SOURC VOTG vs. V DS = R ON I DS(ON) D VGS S VDS IDS(ON) VDS = +.5V T = +5 C VDS = +.5V T = +5 C VDS = +5V T = +5 C VDS = +5V T = +5 C. (µ) 5 vs. OUTPUT VOTG OFFST VOTG vs. MBINT TMPRTUR (m) 3 T = +5 C VDS = +V VDS = +5V VDS = +V OFFST VOTG (mv) RPRSNTTIV UNITS V GS(th) V GS(th) + V GS(th) + V GS(th) +3 V GS(th) + V GS(th) OUTPUT VOTG (V) MBINT TMPRTUR ( C) D8/D9, Vrs..3 dvancd inar Dvics 6 of
7 TYPIC PRFORMNC CHRCTRISTICS (cont.) GT KG CURRNT vs. MBINT TMPRTUR GT SOURC VOTG vs. DRIN-SOURC ON RSISTNC GT KG CURRNT (p). IGSS GT-SOURC VOTG (V) VGS(th)+ VGS(th)+3 VGS(th)+ VGS(th)+ VGS(th) +5 C +5 C.V V DS 5.V VGS 6 D S VDS IDS(ON) 8 MBINT TMPRTUR ( C) DRIN-SOURC ON RSISTNC (KΩ) DRIN-GT DIOD CONNCTD VOTG TMPCO (mv/ C) DRIN-GT DIOD CONNCTD VOTG TMPCO vs C T +5 C (µ) TRNSCONDUCTNC (mω - ) TRNSFR CHRCTRISTICS T = +5 C V DS = +V V GS(th) = -.V GT-SOURC VOTG (V) V GS(th) = -3.5V V GS(th) = -.3V V GS(th) =.V V GS(th) = +.V V GS(th) = +.8V V GS(th) = +.V ZRO TMPRTUR COFFICINT CHRCTRISTICS SUBTHRSHOD CHRCTRISTICS GT-SOURC VOTG (V) V GS(th) = -3.5V V GS(th) = -.3V, -.V,.V, +.V, +.8V, +.V..5.. DRIN-SOURC ON VOTG (V) 5. GT-SOURC VOTG (V) VGS(th) = +.V T = +5 C VGS(th) = +.V T = +55 C. VGS(th) = +.V T = +5 C VGS(th) = +.V -.5 T = +55 C. (n) D8/D9, Vrs..3 dvancd inar Dvics 7 of
8 TYPIC PRFORMNC CHRCTRISTICS (cont.) TRNCONDUCTNC (mω - ) TRNCONDUCTNC vs. T = +5 C V DS = +V THRSHOD VOTG (V) V t =.V THRSHOD VOTG vs. MBINT TMPRTUR I DS = +µ V DS = +.V V t = +.V V t = +.V V t = +.8V V t = +.V (m) MBINT TMPRTUR ( C).3 NORMIZD SUBTHRSHOD CHRCTRISTICS RTIV TO GT THRSHOD VOTG. SUBTHRSHOD FORWRD TRNSFR CHRCTRISTICS GT-SOURC VOTG VGS - VGS(th) (V) C V DS = +.V +5 C THRSHOD VOTG (V) I DS = +µ V DS = +.V VGS(th) =.V VGS(th) = -.V VGS(th) = -.3V VGS(th) = -3.5V -.. (n) MBINT TMPRTUR ( C) D8/D9, Vrs..3 dvancd inar Dvics 8 of
9 SOIC-6 PCKG DRWING 6 Pin Plastic SOIC Packag Millimtrs Inchs Dim Min Max Min Max S (5 ) C D D BSC.5 BSC H S S (5 ) H C D8/D9, Vrs..3 dvancd inar Dvics 9 of
10 PDIP-6 PCKG DRWING 6 Pin Plastic DIP Packag Millimtrs Inchs Dim Min Max Min Max S D c D S c D8/D9, Vrs..3 dvancd inar Dvics of
11 SOIC-8 PCKG DRWING 8 Pin Plastic SOIC Packag Millimtrs Inchs S (5 ) D Dim C D-8 Min Max Min Max BSC.5 BSC H S S (5 ) H C D8/D9, Vrs..3 dvancd inar Dvics of
12 PDIP-8 PCKG DRWING 8 Pin Plastic DIP Packag Millimtrs Inchs Dim Min Max Min Max S D c D S c D8/D9, Vrs..3 dvancd inar Dvics of
DUAL P-CHANNEL MATCHED MOSFET PAIR
 DVNCD INR DVICS, INC. D1102/D1102B D1102 DU P-CHNN MTCHD MOSFT PIR GNR DSCRIPTION Th D1102 is a monolithic dual P-channl matchd transistor pair intndd for a road rang of analog applications. Ths nhancmntmod
DVNCD INR DVICS, INC. D1102/D1102B D1102 DU P-CHNN MTCHD MOSFT PIR GNR DSCRIPTION Th D1102 is a monolithic dual P-channl matchd transistor pair intndd for a road rang of analog applications. Ths nhancmntmod
QUAD/DUAL ELECTRICALLY PROGRAMMABLE ANALOG DEVICE (EPAD )
 TM VN INR VI, IN. P 8/ N B QU/U TRIY PROGRMMB NOG VI (P ) GNR RIPTION 8/ ar monolithic quad/dual P (lctrically Programmal nalog vic) N-channl MOFTs with lctrically adjustal thrshold (turn-on) voltag. Th
TM VN INR VI, IN. P 8/ N B QU/U TRIY PROGRMMB NOG VI (P ) GNR RIPTION 8/ ar monolithic quad/dual P (lctrically Programmal nalog vic) N-channl MOFTs with lctrically adjustal thrshold (turn-on) voltag. Th
G D S. Drain-Source Voltage 60 V Gate-Source Voltage + 20 V. at T =100 C Continuous Drain Current 3. Linear Derating Factor 0.
 N-channl Enhancmnt-mod Powr MOSFET Simpl Driv Rquirmnt D Fast Switching Charactristics Low On-rsistanc R DS(ON) 36mΩ G RoHS-compliant, halogn-fr I D 25A S BV DSS 6V Dscription Advancd Powr MOSFETs from
N-channl Enhancmnt-mod Powr MOSFET Simpl Driv Rquirmnt D Fast Switching Charactristics Low On-rsistanc R DS(ON) 36mΩ G RoHS-compliant, halogn-fr I D 25A S BV DSS 6V Dscription Advancd Powr MOSFETs from
G D S. Drain-Source Voltage 30 V Gate-Source Voltage. at T =100 C Continuous Drain Current 3
 N-channl Enhancmnt-mod Powr MOSFET Simpl Driv Rquirmnt D Fast Switching Charactristics Low Gat Charg R DS(ON) 25mΩ G RoHS-compliant, halogn-fr I D 28A S BV DSS 30V Dscription Advancd Powr MOSFETs from
N-channl Enhancmnt-mod Powr MOSFET Simpl Driv Rquirmnt D Fast Switching Charactristics Low Gat Charg R DS(ON) 25mΩ G RoHS-compliant, halogn-fr I D 28A S BV DSS 30V Dscription Advancd Powr MOSFETs from
Design Guidelines for Quartz Crystal Oscillators. R 1 Motional Resistance L 1 Motional Inductance C 1 Motional Capacitance C 0 Shunt Capacitance
 TECHNICAL NTE 30 Dsign Guidlins for Quartz Crystal scillators Introduction A CMS Pirc oscillator circuit is wll known and is widly usd for its xcllnt frquncy stability and th wid rang of frquncis ovr which
TECHNICAL NTE 30 Dsign Guidlins for Quartz Crystal scillators Introduction A CMS Pirc oscillator circuit is wll known and is widly usd for its xcllnt frquncy stability and th wid rang of frquncis ovr which
SP490/SP491. Full Duplex RS-485 Transceivers. Now Available in Lead Free Packaging
 SP490/SP491 Full uplx RS-485 Transcivrs FTURS +5V Only Low Powr icmos rivr/rcivr nal (SP491) RS-485 and RS-422 rivrs/rcivrs Pin Compatil with LTC490 and SN75179 (SP490) Pin Compatil with LTC491 and SN75180
SP490/SP491 Full uplx RS-485 Transcivrs FTURS +5V Only Low Powr icmos rivr/rcivr nal (SP491) RS-485 and RS-422 rivrs/rcivrs Pin Compatil with LTC490 and SN75179 (SP490) Pin Compatil with LTC491 and SN75180
Precision Micropower 2.5V ShuntVoltage Reference
 SPX4040 Prcision Micropowr.5V ShuntVoltag Rfrnc FETURES Trimmd Bandgap to 0.5% and % Wid Oprating Currnt 0µ to 5m Extndd Tmpratur Rang: -40 C to 85 C Low Tmpratur Cofficint 00 ppm/ C Rplacmnt in for LM4040
SPX4040 Prcision Micropowr.5V ShuntVoltag Rfrnc FETURES Trimmd Bandgap to 0.5% and % Wid Oprating Currnt 0µ to 5m Extndd Tmpratur Rang: -40 C to 85 C Low Tmpratur Cofficint 00 ppm/ C Rplacmnt in for LM4040
Voltage, Current, Power, Series Resistance, Parallel Resistance, and Diodes
 Lctur 1. oltag, Currnt, Powr, Sris sistanc, Paralll sistanc, and Diods Whn you start to dal with lctronics thr ar thr main concpts to start with: Nam Symbol Unit oltag volt Currnt ampr Powr W watt oltag
Lctur 1. oltag, Currnt, Powr, Sris sistanc, Paralll sistanc, and Diods Whn you start to dal with lctronics thr ar thr main concpts to start with: Nam Symbol Unit oltag volt Currnt ampr Powr W watt oltag
The pn junction: 2 Current vs Voltage (IV) characteristics
 Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Exam 1. It is important that you clearly show your work and mark the final answer clearly, closed book, closed notes, no calculator.
 Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
IXBT22N300HV IXBH22N300HV
 High Voltag, High Gain BIMOSFT TM Monolithic Bipolar MOS Transistor Advanc Tchnical Information IXBTNHV IXBHNHV V CS = V = A V C(sat). TO-6HV (IXBT) Symbol Tst Conditions Maximum Ratings V CS = 5 C to
High Voltag, High Gain BIMOSFT TM Monolithic Bipolar MOS Transistor Advanc Tchnical Information IXBTNHV IXBHNHV V CS = V = A V C(sat). TO-6HV (IXBT) Symbol Tst Conditions Maximum Ratings V CS = 5 C to
NTHU ESS5850 Micro System Design F. G. Tseng Fall/2016, 7-2, p1. Lecture 7-2 MOSIS/SCNA Design Example- Piezoresistive type Accelerometer II
 F. G. Tsng Fall/016, 7-, p1 ctur 7- MOSIS/SCNA Dsign Exampl-!! Pizorsistivity Pizorsistiv typ Acclromtr II a Considr a conductiv lock of dimnsion a as shown in th figur. If a currnt is passd through th
F. G. Tsng Fall/016, 7-, p1 ctur 7- MOSIS/SCNA Dsign Exampl-!! Pizorsistivity Pizorsistiv typ Acclromtr II a Considr a conductiv lock of dimnsion a as shown in th figur. If a currnt is passd through th
SP1001 Series - 8pF 15kV Unidirectional TVS Array
 Sris - 8pF kv Unidirctional TVS Array RoHS Pb GRN scription Znr diods fabricatd in a propritary silicon avalanch tchnology protct ach I/O pin to provid a high lvl of protction for lctronic quipmnt that
Sris - 8pF kv Unidirctional TVS Array RoHS Pb GRN scription Znr diods fabricatd in a propritary silicon avalanch tchnology protct ach I/O pin to provid a high lvl of protction for lctronic quipmnt that
Status of LAr TPC R&D (2) 2014/Dec./23 Neutrino frontier workshop 2014 Ryosuke Sasaki (Iwate U.)
 Status of LAr TPC R&D (2) 214/Dc./23 Nutrino frontir workshop 214 Ryosuk Sasaki (Iwat U.) Tabl of Contnts Dvlopmnt of gnrating lctric fild in LAr TPC Introduction - Gnrating strong lctric fild is on of
Status of LAr TPC R&D (2) 214/Dc./23 Nutrino frontir workshop 214 Ryosuk Sasaki (Iwat U.) Tabl of Contnts Dvlopmnt of gnrating lctric fild in LAr TPC Introduction - Gnrating strong lctric fild is on of
2/12/2013. Overview. 12-Power Transmission Text: Conservation of Complex Power. Introduction. Power Transmission-Short Line
 //03 Ovrviw -owr Transmission Txt: 4.6-4.0 ECEGR 45 owr ystms Consrvation of Complx owr hort in owr Transmission owr Transmission isualization Radial in Mdium and ong in owr Transmission oltag Collaps
//03 Ovrviw -owr Transmission Txt: 4.6-4.0 ECEGR 45 owr ystms Consrvation of Complx owr hort in owr Transmission owr Transmission isualization Radial in Mdium and ong in owr Transmission oltag Collaps
General Notes About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidelines
 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Gnral Nots About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidlins 1. Th solutions contain th most common mthod of solving th fr-rspons qustions and th allocation
AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Gnral Nots About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidlins 1. Th solutions contain th most common mthod of solving th fr-rspons qustions and th allocation
IXTT3N200P3HV IXTH3N200P3HV
 Advanc Tchnical Information High Voltag Powr MOSFET S I R S(on) = V = A N-Channl Enhancmnt Mod TO-HV (IXTT) G S (Tab) Symbol Tst Conditions Maximum Ratings S = C to C V V GR = C to C, R GS = M V S Continuous
Advanc Tchnical Information High Voltag Powr MOSFET S I R S(on) = V = A N-Channl Enhancmnt Mod TO-HV (IXTT) G S (Tab) Symbol Tst Conditions Maximum Ratings S = C to C V V GR = C to C, R GS = M V S Continuous
General Purpose ESD Protection - SP1001 Series. Description. Features. Applications
 TVS iod Arrays (SPA iods) Gnral Purpos ES Protction - SP00 Sris SP00 Sris - 8pF kv Unidirctional TVS Array RoHS Pb GREEN scription Znr diods fabricatd in a propritary silicon avalanch tchnology protct
TVS iod Arrays (SPA iods) Gnral Purpos ES Protction - SP00 Sris SP00 Sris - 8pF kv Unidirctional TVS Array RoHS Pb GREEN scription Znr diods fabricatd in a propritary silicon avalanch tchnology protct
Electronic Circuits. BJT Amplifiers. Manar Mohaisen Office: F208 Department of EECE
 Elctronic Circuits BJT mplifirs Manar Mohaisn Offic: F208 Email: manar.subhi@kut.ac.kr Dpartmnt of EECE viw of th Prcdnt Lctur Explain th DC Oprating Point Explain th Voltag-dividr Bias Othr Bias Mthods
Elctronic Circuits BJT mplifirs Manar Mohaisn Offic: F208 Email: manar.subhi@kut.ac.kr Dpartmnt of EECE viw of th Prcdnt Lctur Explain th DC Oprating Point Explain th Voltag-dividr Bias Othr Bias Mthods
KTC4080 SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA HIGH FREQUENCY LOW NOISE AMPLIFIER APPLICATION. VHF BAND AMPLIFIER APPLICATION. FEATURES. MAXIMUM RATING (Ta=25 )
 SMICONDUCTOR TCHNICAL DATA KTC48 PITAXIAL PLANAR NPN TRANSISTOR HIGH FRQUNCY LOW NOIS AMPLIFIR APPLICATION. VHF BAND AMPLIFIR APPLICATION. FATURS Small Reverse Transr Capacitance : C =.7pF(Tp.) Low Noise
SMICONDUCTOR TCHNICAL DATA KTC48 PITAXIAL PLANAR NPN TRANSISTOR HIGH FRQUNCY LOW NOIS AMPLIFIR APPLICATION. VHF BAND AMPLIFIR APPLICATION. FATURS Small Reverse Transr Capacitance : C =.7pF(Tp.) Low Noise
Extraction of Doping Density Distributions from C-V Curves
 Extraction of Doping Dnsity Distributions from C-V Curvs Hartmut F.-W. Sadrozinski SCIPP, Univ. California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 9564 USA 1. Connction btwn C, N, V Start with Poisson quation d V =
Extraction of Doping Dnsity Distributions from C-V Curvs Hartmut F.-W. Sadrozinski SCIPP, Univ. California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 9564 USA 1. Connction btwn C, N, V Start with Poisson quation d V =
ECE 344 Microwave Fundamentals
 ECE 44 Microwav Fundamntals Lctur 08: Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Part Prpard By Dr. hrif Hkal 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Powr dividrs, combinrs and dirctional
ECE 44 Microwav Fundamntals Lctur 08: Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Part Prpard By Dr. hrif Hkal 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Powr dividrs, combinrs and dirctional
Principles of Humidity Dalton s law
 Principls of Humidity Dalton s law Air is a mixtur of diffrnt gass. Th main gas componnts ar: Gas componnt volum [%] wight [%] Nitrogn N 2 78,03 75,47 Oxygn O 2 20,99 23,20 Argon Ar 0,93 1,28 Carbon dioxid
Principls of Humidity Dalton s law Air is a mixtur of diffrnt gass. Th main gas componnts ar: Gas componnt volum [%] wight [%] Nitrogn N 2 78,03 75,47 Oxygn O 2 20,99 23,20 Argon Ar 0,93 1,28 Carbon dioxid
Experiment #9 BJT Dynamic Circuits
 Exprimnt #9 BJT Dynamic Circuits Jonathan Rodrick Hakan Durmus Scott Kilpatrick Burgss Introduction: In th last la, w larnd th point of iasing an analog circuit corrctly is so th activ dvics within th
Exprimnt #9 BJT Dynamic Circuits Jonathan Rodrick Hakan Durmus Scott Kilpatrick Burgss Introduction: In th last la, w larnd th point of iasing an analog circuit corrctly is so th activ dvics within th
Ch. 24 Molecular Reaction Dynamics 1. Collision Theory
 Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Low Capacitance ESD Protection - SP3003 Series. Description. Features. Applications. LCD/ PDP TVs DVD Players Desktops MP3/ PMP Digital Cameras
 TVS iod Arrays (SPA iods) SP3003 Sris 0.65pF iod Array RoHS Pb GREEN scription Th SP3003 has ultra low capacitanc rail-to-rail diods with an additional znr diod fabricatd in a propritary silicon avalanch
TVS iod Arrays (SPA iods) SP3003 Sris 0.65pF iod Array RoHS Pb GREEN scription Th SP3003 has ultra low capacitanc rail-to-rail diods with an additional znr diod fabricatd in a propritary silicon avalanch
Lecture #15. Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs)
 ctur #5 OUTN Th iolar Junction Transistor Fundamntals dal Transistor Analysis Rading: hatr 0,. 30 ctur 5, Slid iolar Junction Transistors (JTs Ovr th ast 3 ads, th highr layout dnsity and low-owr advantag
ctur #5 OUTN Th iolar Junction Transistor Fundamntals dal Transistor Analysis Rading: hatr 0,. 30 ctur 5, Slid iolar Junction Transistors (JTs Ovr th ast 3 ads, th highr layout dnsity and low-owr advantag
A Propagating Wave Packet Group Velocity Dispersion
 Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
Seebeck and Peltier Effects
 Sbck and Pltir Effcts Introduction Thrmal nrgy is usually a byproduct of othr forms of nrgy such as chmical nrgy, mchanical nrgy, and lctrical nrgy. Th procss in which lctrical nrgy is transformd into
Sbck and Pltir Effcts Introduction Thrmal nrgy is usually a byproduct of othr forms of nrgy such as chmical nrgy, mchanical nrgy, and lctrical nrgy. Th procss in which lctrical nrgy is transformd into
EXST Regression Techniques Page 1
 EXST704 - Rgrssion Tchniqus Pag 1 Masurmnt rrors in X W hav assumd that all variation is in Y. Masurmnt rror in this variabl will not ffct th rsults, as long as thy ar uncorrlatd and unbiasd, sinc thy
EXST704 - Rgrssion Tchniqus Pag 1 Masurmnt rrors in X W hav assumd that all variation is in Y. Masurmnt rror in this variabl will not ffct th rsults, as long as thy ar uncorrlatd and unbiasd, sinc thy
Part 7: Capacitance And Capacitors
 Part 7: apacitanc And apacitors 7. Elctric harg And Elctric Filds onsidr a pair of flat, conducting plats, arrangd paralll to ach othr (as in figur 7.) and sparatd by an insulator, which may simply b air.
Part 7: apacitanc And apacitors 7. Elctric harg And Elctric Filds onsidr a pair of flat, conducting plats, arrangd paralll to ach othr (as in figur 7.) and sparatd by an insulator, which may simply b air.
A crash-course in transistor circuits
 A crash-cours in transistor circuits Patrick R. LClair July 19, 2011 Contnts 1 Transistors 1 1.1 Basic charactristics.................................... 1 1.2 Notation...........................................
A crash-cours in transistor circuits Patrick R. LClair July 19, 2011 Contnts 1 Transistors 1 1.1 Basic charactristics.................................... 1 1.2 Notation...........................................
NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 1 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSIS HEMISTRY MTHEMTIS
![NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 1 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSIS HEMISTRY MTHEMTIS NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 1 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSIS HEMISTRY MTHEMTIS](/thumbs/79/79886930.jpg) . (D). (A). (D). (D) 5. (B) 6. (A) 7. (A) 8. (A) 9. (B). (A). (D). (B). (B). (C) 5. (D) NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y C o m m o n P r a c t i c T s t 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Dat: 8.8.6 ANSWER PHYSIS
. (D). (A). (D). (D) 5. (B) 6. (A) 7. (A) 8. (A) 9. (B). (A). (D). (B). (B). (C) 5. (D) NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y C o m m o n P r a c t i c T s t 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Dat: 8.8.6 ANSWER PHYSIS
20-V N-Channel 1.8-V (G-S) MOSFET
 -V N-Channl.8-V (G-) MOFET PROUCT UMMARY V (V) R (on) (Ω) I (A).37 at V G = 4. V 7.3.39 at V G =. V 7..43 at V G =.8 V 6.8 FEATURE TrnchFET Powr MOFET MICRO FOOT Chipscal Packaging Rducs Footprint Ara
-V N-Channl.8-V (G-) MOFET PROUCT UMMARY V (V) R (on) (Ω) I (A).37 at V G = 4. V 7.3.39 at V G =. V 7..43 at V G =.8 V 6.8 FEATURE TrnchFET Powr MOFET MICRO FOOT Chipscal Packaging Rducs Footprint Ara
PHYS ,Fall 05, Term Exam #1, Oct., 12, 2005
 PHYS1444-,Fall 5, Trm Exam #1, Oct., 1, 5 Nam: Kys 1. circular ring of charg of raius an a total charg Q lis in th x-y plan with its cntr at th origin. small positiv tst charg q is plac at th origin. What
PHYS1444-,Fall 5, Trm Exam #1, Oct., 1, 5 Nam: Kys 1. circular ring of charg of raius an a total charg Q lis in th x-y plan with its cntr at th origin. small positiv tst charg q is plac at th origin. What
2008 AP Calculus BC Multiple Choice Exam
 008 AP Multipl Choic Eam Nam 008 AP Calculus BC Multipl Choic Eam Sction No Calculator Activ AP Calculus 008 BC Multipl Choic. At tim t 0, a particl moving in th -plan is th acclration vctor of th particl
008 AP Multipl Choic Eam Nam 008 AP Calculus BC Multipl Choic Eam Sction No Calculator Activ AP Calculus 008 BC Multipl Choic. At tim t 0, a particl moving in th -plan is th acclration vctor of th particl
The Transmission Line Wave Equation
 1//5 Th Transmission Lin Wav Equation.doc 1/6 Th Transmission Lin Wav Equation Q: So, what functions I (z) and V (z) do satisfy both tlgraphr s quations?? A: To mak this asir, w will combin th tlgraphr
1//5 Th Transmission Lin Wav Equation.doc 1/6 Th Transmission Lin Wav Equation Q: So, what functions I (z) and V (z) do satisfy both tlgraphr s quations?? A: To mak this asir, w will combin th tlgraphr
22/ Breakdown of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. Selection rules for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branches.
 Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
ECE602 Exam 1 April 5, You must show ALL of your work for full credit.
 ECE62 Exam April 5, 27 Nam: Solution Scor: / This xam is closd-book. You must show ALL of your work for full crdit. Plas rad th qustions carfully. Plas chck your answrs carfully. Calculators may NOT b
ECE62 Exam April 5, 27 Nam: Solution Scor: / This xam is closd-book. You must show ALL of your work for full crdit. Plas rad th qustions carfully. Plas chck your answrs carfully. Calculators may NOT b
Impedance Transformation and Parameter Relations
 8/1/18 Cours nstructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Offic: A 337 Phon: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utp.du EE 4347 Applid Elctromagntics Topic 4 mpdanc Transformation and Paramtr Rlations mpdanc Ths Transformation
8/1/18 Cours nstructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Offic: A 337 Phon: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utp.du EE 4347 Applid Elctromagntics Topic 4 mpdanc Transformation and Paramtr Rlations mpdanc Ths Transformation
MEASURING HEAT FLUX FROM A COMPONENT ON A PCB
 MEASURING HEAT FLUX FROM A COMPONENT ON A PCB INTRODUCTION Elctronic circuit boards consist of componnts which gnrats substantial amounts of hat during thir opration. A clar knowldg of th lvl of hat dissipation
MEASURING HEAT FLUX FROM A COMPONENT ON A PCB INTRODUCTION Elctronic circuit boards consist of componnts which gnrats substantial amounts of hat during thir opration. A clar knowldg of th lvl of hat dissipation
Electromagnetism Physics 15b
 lctromagntism Physics 15b Lctur #8 lctric Currnts Purcll 4.1 4.3 Today s Goals Dfin lctric currnt I Rat of lctric charg flow Also dfin lctric currnt dnsity J Charg consrvation in a formula Ohm s Law vryon
lctromagntism Physics 15b Lctur #8 lctric Currnts Purcll 4.1 4.3 Today s Goals Dfin lctric currnt I Rat of lctric charg flow Also dfin lctric currnt dnsity J Charg consrvation in a formula Ohm s Law vryon
2SA2029 / 2SA1774EB / 2SA1774 / 2SA1576UB / 2SA1576A / 2SA1037AK. Outline. Base UMT3. Base. Package size (mm) Taping code
 2S2029 / 2S1774B / 2S1774 / 2S1576UB / 2S1576 / 2S1037K PNP 50m -50V Gnral Purpos Transistors Datasht Outlin Paramtr V CO I C Valu 50V 150m VMT3 MT3F Collctor Bas Bas mittr mittr Collctor Faturs 1) Gnral
2S2029 / 2S1774B / 2S1774 / 2S1576UB / 2S1576 / 2S1037K PNP 50m -50V Gnral Purpos Transistors Datasht Outlin Paramtr V CO I C Valu 50V 150m VMT3 MT3F Collctor Bas Bas mittr mittr Collctor Faturs 1) Gnral
SER/BER in a Fading Channel
 SER/BER in a Fading Channl Major points for a fading channl: * SNR is a R.V. or R.P. * SER(BER) dpnds on th SNR conditional SER(BER). * Two prformanc masurs: outag probability and avrag SER(BER). * Ovrall,
SER/BER in a Fading Channl Major points for a fading channl: * SNR is a R.V. or R.P. * SER(BER) dpnds on th SNR conditional SER(BER). * Two prformanc masurs: outag probability and avrag SER(BER). * Ovrall,
5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics
 MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
P. Bruschi - Notes on Mixed Signal Design
 Chaptr 1. Concpts and dfinitions about Data Acquisition Systms Elctronic systms An lctronic systms is a complx lctronic ntwor, which intracts with th physical world through snsors (input dvics) and actuators
Chaptr 1. Concpts and dfinitions about Data Acquisition Systms Elctronic systms An lctronic systms is a complx lctronic ntwor, which intracts with th physical world through snsors (input dvics) and actuators
Bifurcation Theory. , a stationary point, depends on the value of α. At certain values
 Dnamic Macroconomic Thor Prof. Thomas Lux Bifurcation Thor Bifurcation: qualitativ chang in th natur of th solution occurs if a paramtr passs through a critical point bifurcation or branch valu. Local
Dnamic Macroconomic Thor Prof. Thomas Lux Bifurcation Thor Bifurcation: qualitativ chang in th natur of th solution occurs if a paramtr passs through a critical point bifurcation or branch valu. Local
Physics 178/278 - David Kleinfeld - Fall checked Winter 2014
 Physics 178/278 - David Klinfld - Fall 2005 - chckd Wintr 2014 1 Elctrodiffusion W prviously discussd how th motion of frly dissolvd ions and macromolculs is govrnd by diffusion, th random motion of molculs
Physics 178/278 - David Klinfld - Fall 2005 - chckd Wintr 2014 1 Elctrodiffusion W prviously discussd how th motion of frly dissolvd ions and macromolculs is govrnd by diffusion, th random motion of molculs
Numbering Systems Basic Building Blocks Scaling and Round-off Noise. Number Representation. Floating vs. Fixed point. DSP Design.
 Numbring Systms Basic Building Blocks Scaling and Round-off Nois Numbr Rprsntation Viktor Öwall viktor.owall@it.lth.s Floating vs. Fixd point In floating point a valu is rprsntd by mantissa dtrmining th
Numbring Systms Basic Building Blocks Scaling and Round-off Nois Numbr Rprsntation Viktor Öwall viktor.owall@it.lth.s Floating vs. Fixd point In floating point a valu is rprsntd by mantissa dtrmining th
REFLECTIVE OBJECT SENSOR
 QR4 PACKAG DIMNSIONS + + D.6 (6.) D + +.49 (.5). (8.4).97 (5.) 4.4 (8.) SCHMATIC.8 (.).8 (.46) SQ. (4X) 4. (.54).6 (9.) NOTS:. Dimensions for all drawings are in inches.. Tolerance of ±. on all non-nominal
QR4 PACKAG DIMNSIONS + + D.6 (6.) D + +.49 (.5). (8.4).97 (5.) 4.4 (8.) SCHMATIC.8 (.).8 (.46) SQ. (4X) 4. (.54).6 (9.) NOTS:. Dimensions for all drawings are in inches.. Tolerance of ±. on all non-nominal
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING CLASSIFICATION OF SIGNALS
 Slid DIGITAL SIGAL PROCESSIG UIT I DISCRETE TIME SIGALS AD SYSTEM Slid Rviw of discrt-tim signals & systms Signal:- A signal is dfind as any physical quantity that varis with tim, spac or any othr indpndnt
Slid DIGITAL SIGAL PROCESSIG UIT I DISCRETE TIME SIGALS AD SYSTEM Slid Rviw of discrt-tim signals & systms Signal:- A signal is dfind as any physical quantity that varis with tim, spac or any othr indpndnt
Chapter 6 Folding. Folding
 Chaptr 6 Folding Wintr 1 Mokhtar Abolaz Folding Th folding transformation is usd to systmatically dtrmin th control circuits in DSP architctur whr multipl algorithm oprations ar tim-multiplxd to a singl
Chaptr 6 Folding Wintr 1 Mokhtar Abolaz Folding Th folding transformation is usd to systmatically dtrmin th control circuits in DSP architctur whr multipl algorithm oprations ar tim-multiplxd to a singl
SAFE HANDS & IIT-ian's PACE EDT-15 (JEE) SOLUTIONS
 It is not possibl to find flu through biggr loop dirctly So w will find cofficint of mutual inductanc btwn two loops and thn find th flu through biggr loop Also rmmbr M = M ( ) ( ) EDT- (JEE) SOLUTIONS
It is not possibl to find flu through biggr loop dirctly So w will find cofficint of mutual inductanc btwn two loops and thn find th flu through biggr loop Also rmmbr M = M ( ) ( ) EDT- (JEE) SOLUTIONS
NAND R/S - CD4044BMS Q VDD
 DATASHT CD0BMS, CD0BMS CMOS Quad State R/S Latches FN Rev 0.00 December Features High Voltage Types (0V Rating) Quad NOR R/S Latch- CD0BMS Quad NAND R/S Latch - CD0BMS State Outputs with Common Output
DATASHT CD0BMS, CD0BMS CMOS Quad State R/S Latches FN Rev 0.00 December Features High Voltage Types (0V Rating) Quad NOR R/S Latch- CD0BMS Quad NAND R/S Latch - CD0BMS State Outputs with Common Output
ESE (Prelims) - Offline Test Series ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING SUBJECT: Power Electronics & Drives, Power Systems and Signals & Systems SOLUTIONS
 TEST ID: 8 ESE- 9 (Prlims) - Offlin Tst Sris ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Tst-5 SUBJECT: Powr Elctronics & Drivs, Powr Systms and Signals & Systms SOLUTIONS. Ans: (b) Powr diod rcovry dpnds on th charg stord
TEST ID: 8 ESE- 9 (Prlims) - Offlin Tst Sris ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Tst-5 SUBJECT: Powr Elctronics & Drivs, Powr Systms and Signals & Systms SOLUTIONS. Ans: (b) Powr diod rcovry dpnds on th charg stord
2. Laser physics - basics
 . Lasr physics - basics Spontanous and stimulatd procsss Einstin A and B cofficints Rat quation analysis Gain saturation What is a lasr? LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulatd Emission of Radiation "light"
. Lasr physics - basics Spontanous and stimulatd procsss Einstin A and B cofficints Rat quation analysis Gain saturation What is a lasr? LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulatd Emission of Radiation "light"
Construction of asymmetric orthogonal arrays of strength three via a replacement method
 isid/ms/26/2 Fbruary, 26 http://www.isid.ac.in/ statmath/indx.php?modul=prprint Construction of asymmtric orthogonal arrays of strngth thr via a rplacmnt mthod Tian-fang Zhang, Qiaoling Dng and Alok Dy
isid/ms/26/2 Fbruary, 26 http://www.isid.ac.in/ statmath/indx.php?modul=prprint Construction of asymmtric orthogonal arrays of strngth thr via a rplacmnt mthod Tian-fang Zhang, Qiaoling Dng and Alok Dy
Engineering 1620: High Frequency Effects in BJT Circuits an Introduction Especially for the Friday before Spring Break
 nginring 162: High Frquncy ffcts in BJT Circuits an Inoduction spcially for th Friday bfor Spring Brak I hav prpard ths nots bcaus on th day bfor a major vacation brak som popl find it ncssary to lav arly
nginring 162: High Frquncy ffcts in BJT Circuits an Inoduction spcially for th Friday bfor Spring Brak I hav prpard ths nots bcaus on th day bfor a major vacation brak som popl find it ncssary to lav arly
Multiple RS-232 Drivers & Receivers
 Multipl S232 rivrs & ivrs Produt sription Th ar monolithi dvi ontaining 3 indpndnt drivs and 5 rivrs. Ths ar dsignd to intrfa twn dat trminal quipmnt and dat ommuniation quipmnt as dsignd y I232. Faturs
Multipl S232 rivrs & ivrs Produt sription Th ar monolithi dvi ontaining 3 indpndnt drivs and 5 rivrs. Ths ar dsignd to intrfa twn dat trminal quipmnt and dat ommuniation quipmnt as dsignd y I232. Faturs
4.2 Design of Sections for Flexure
 4. Dsign of Sctions for Flxur This sction covrs th following topics Prliminary Dsign Final Dsign for Typ 1 Mmbrs Spcial Cas Calculation of Momnt Dmand For simply supportd prstrssd bams, th maximum momnt
4. Dsign of Sctions for Flxur This sction covrs th following topics Prliminary Dsign Final Dsign for Typ 1 Mmbrs Spcial Cas Calculation of Momnt Dmand For simply supportd prstrssd bams, th maximum momnt
Math 34A. Final Review
 Math A Final Rviw 1) Us th graph of y10 to find approimat valus: a) 50 0. b) y (0.65) solution for part a) first writ an quation: 50 0. now tak th logarithm of both sids: log() log(50 0. ) pand th right
Math A Final Rviw 1) Us th graph of y10 to find approimat valus: a) 50 0. b) y (0.65) solution for part a) first writ an quation: 50 0. now tak th logarithm of both sids: log() log(50 0. ) pand th right
Supplementary Materials
 6 Supplmntary Matrials APPENDIX A PHYSICAL INTERPRETATION OF FUEL-RATE-SPEED FUNCTION A truck running on a road with grad/slop θ positiv if moving up and ngativ if moving down facs thr rsistancs: arodynamic
6 Supplmntary Matrials APPENDIX A PHYSICAL INTERPRETATION OF FUEL-RATE-SPEED FUNCTION A truck running on a road with grad/slop θ positiv if moving up and ngativ if moving down facs thr rsistancs: arodynamic
Characteristics of Gliding Arc Discharge Plasma
 Caractristics of Gliding Arc Discarg Plasma Lin Li( ), Wu Bin(, Yang Ci(, Wu Cngkang ( Institut of Mcanics, Cins Acadmy of Scincs, Bijing 8, Cina E-mail: linli@imc.ac.cn Abstract A gliding arc discarg
Caractristics of Gliding Arc Discarg Plasma Lin Li( ), Wu Bin(, Yang Ci(, Wu Cngkang ( Institut of Mcanics, Cins Acadmy of Scincs, Bijing 8, Cina E-mail: linli@imc.ac.cn Abstract A gliding arc discarg
Chapter 3: Capacitors, Inductors, and Complex Impedance
 haptr 3: apacitors, Inductors, and omplx Impdanc In this chaptr w introduc th concpt of complx rsistanc, or impdanc, by studying two ractiv circuit lmnts, th capacitor and th inductor. W will study capacitors
haptr 3: apacitors, Inductors, and omplx Impdanc In this chaptr w introduc th concpt of complx rsistanc, or impdanc, by studying two ractiv circuit lmnts, th capacitor and th inductor. W will study capacitors
Finite element discretization of Laplace and Poisson equations
 Finit lmnt discrtization of Laplac and Poisson quations Yashwanth Tummala Tutor: Prof S.Mittal 1 Outlin Finit Elmnt Mthod for 1D Introduction to Poisson s and Laplac s Equations Finit Elmnt Mthod for 2D-Discrtization
Finit lmnt discrtization of Laplac and Poisson quations Yashwanth Tummala Tutor: Prof S.Mittal 1 Outlin Finit Elmnt Mthod for 1D Introduction to Poisson s and Laplac s Equations Finit Elmnt Mthod for 2D-Discrtization
ECE 2210 / 00 Phasor Examples
 EE 0 / 00 Phasor Exampls. Add th sinusoidal voltags v ( t ) 4.5. cos( t 30. and v ( t ) 3.. cos( t 5. v ( t) using phasor notation, draw a phasor diagram of th thr phasors, thn convrt back to tim domain
EE 0 / 00 Phasor Exampls. Add th sinusoidal voltags v ( t ) 4.5. cos( t 30. and v ( t ) 3.. cos( t 5. v ( t) using phasor notation, draw a phasor diagram of th thr phasors, thn convrt back to tim domain
4.4 Design of Sections for Flexure (Part III)
 4.4 Dsign of Sctions for Flxur (Part ) This sction covrs th following topics. Choic of Sctions Dtrmination of Limiting Zon Post-tnsioning in Stags 4.4.1 Choic of Sctions Th typ of sction is slctd asd on
4.4 Dsign of Sctions for Flxur (Part ) This sction covrs th following topics. Choic of Sctions Dtrmination of Limiting Zon Post-tnsioning in Stags 4.4.1 Choic of Sctions Th typ of sction is slctd asd on
NLX2G00. Dual 2-Input NAND Gate
 ual 2-Input NN Gat Th NLX2G00 is an advancd high-spd dual 2-input CMOS NN gat in ultra-small footprint. Th NLX2G00 input structurs provid protction whn voltags up to 7.0 volts ar applid, rgardlss of th
ual 2-Input NN Gat Th NLX2G00 is an advancd high-spd dual 2-input CMOS NN gat in ultra-small footprint. Th NLX2G00 input structurs provid protction whn voltags up to 7.0 volts ar applid, rgardlss of th
TRANSISTOR AND DIODE STUDIES. Prof. H. J. Zimmermann Prof. S. J. Mason C. R. Hurtig Prof. R. B. Adler Dr. W. D. Jackson R. E.
 XI. TANSISTO AND DIODE STUDIES Prof. H. J. Zimmrmann Prof. S. J. Mason C.. Hurti Prof.. B. Adlr Dr. W. D. Jackson. E. Nlson A. DESIGN OF TANSFOMEESS TANSISTO AUDIO AMPIFIES Considrabl ffort by many oranizations
XI. TANSISTO AND DIODE STUDIES Prof. H. J. Zimmrmann Prof. S. J. Mason C.. Hurti Prof.. B. Adlr Dr. W. D. Jackson. E. Nlson A. DESIGN OF TANSFOMEESS TANSISTO AUDIO AMPIFIES Considrabl ffort by many oranizations
Chapter 3: Capacitors, Inductors, and Complex Impedance
 haptr 3: apacitors, Inductors, and omplx Impdanc In this chaptr w introduc th concpt of complx rsistanc, or impdanc, by studying two ractiv circuit lmnts, th capacitor and th inductor. W will study capacitors
haptr 3: apacitors, Inductors, and omplx Impdanc In this chaptr w introduc th concpt of complx rsistanc, or impdanc, by studying two ractiv circuit lmnts, th capacitor and th inductor. W will study capacitors
Outline. Why speech processing? Speech signal processing. Advanced Multimedia Signal Processing #5:Speech Signal Processing 2 -Processing-
 Outlin Advancd Multimdia Signal Procssing #5:Spch Signal Procssing -Procssing- Intllignt Elctronic Systms Group Dpt. of Elctronic Enginring, UEC Basis of Spch Procssing Nois Rmoval Spctral Subtraction
Outlin Advancd Multimdia Signal Procssing #5:Spch Signal Procssing -Procssing- Intllignt Elctronic Systms Group Dpt. of Elctronic Enginring, UEC Basis of Spch Procssing Nois Rmoval Spctral Subtraction
α I I R α N I F I F i C i E R Cx R Ex C Cx i B R Bx
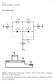 Bipolar transistor, continud - 1 - Ebrs-Moll modl α I I R α N I F E i E i C C R Ex I F I R R Cx C Cx i B R Bx B E B C Figur 1: Dashd lin indicats th "intrinsic" portion of th dvic, xcluding "parasitic"
Bipolar transistor, continud - 1 - Ebrs-Moll modl α I I R α N I F E i E i C C R Ex I F I R R Cx C Cx i B R Bx B E B C Figur 1: Dashd lin indicats th "intrinsic" portion of th dvic, xcluding "parasitic"
4. Money cannot be neutral in the short-run the neutrality of money is exclusively a medium run phenomenon.
 PART I TRUE/FALSE/UNCERTAIN (5 points ach) 1. Lik xpansionary montary policy, xpansionary fiscal policy rturns output in th mdium run to its natural lvl, and incrass prics. Thrfor, fiscal policy is also
PART I TRUE/FALSE/UNCERTAIN (5 points ach) 1. Lik xpansionary montary policy, xpansionary fiscal policy rturns output in th mdium run to its natural lvl, and incrass prics. Thrfor, fiscal policy is also
Hydrogen Atom and One Electron Ions
 Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
DATA SHEET. PDTA124E series PNP resistor-equipped transistors; R1 = 22 kω, R2 = 22 kω DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS
 ISCRT SMICONUCTORS T SHT PT24 sris Suprsds data of 200 pr 4 2004 ug 02 PT24 sris FTURS uilt-in bias rsistors Simplifid circuit dsign Rduction of componnt count Rducd pick and plac costs. PPLICTIONS Gnral
ISCRT SMICONUCTORS T SHT PT24 sris Suprsds data of 200 pr 4 2004 ug 02 PT24 sris FTURS uilt-in bias rsistors Simplifid circuit dsign Rduction of componnt count Rducd pick and plac costs. PPLICTIONS Gnral
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering
 CS 152 Computr Architctur and Enginring Lctur 11 VLSI I 2005-2-22 John Lazzaro (www.cs.brkly.du/~lazzaro) TAs: Td Hong and David Marquardt www-inst.cs.brkly.du/~cs152/ Last Tim: Piplin Hazard Rsolution
CS 152 Computr Architctur and Enginring Lctur 11 VLSI I 2005-2-22 John Lazzaro (www.cs.brkly.du/~lazzaro) TAs: Td Hong and David Marquardt www-inst.cs.brkly.du/~cs152/ Last Tim: Piplin Hazard Rsolution
cycle that does not cross any edges (including its own), then it has at least
 W prov th following thorm: Thorm If a K n is drawn in th plan in such a way that it has a hamiltonian cycl that dos not cross any dgs (including its own, thn it has at last n ( 4 48 π + O(n crossings Th
W prov th following thorm: Thorm If a K n is drawn in th plan in such a way that it has a hamiltonian cycl that dos not cross any dgs (including its own, thn it has at last n ( 4 48 π + O(n crossings Th
Definition1: The ratio of the radiation intensity in a given direction from the antenna to the radiation intensity averaged over all directions.
 Dirctivity or Dirctiv Gain. 1 Dfinition1: Dirctivity Th ratio of th radiation intnsity in a givn dirction from th antnna to th radiation intnsity avragd ovr all dirctions. Dfinition2: Th avg U is obtaind
Dirctivity or Dirctiv Gain. 1 Dfinition1: Dirctivity Th ratio of th radiation intnsity in a givn dirction from th antnna to th radiation intnsity avragd ovr all dirctions. Dfinition2: Th avg U is obtaind
Linear-Phase FIR Transfer Functions. Functions. Functions. Functions. Functions. Functions. Let
 It is impossibl to dsign an IIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas It is always possibl to dsign an FIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas rspons W now dvlop th forms of th linarphas FIR transfr
It is impossibl to dsign an IIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas It is always possibl to dsign an FIR transfr function with an xact linar-phas rspons W now dvlop th forms of th linarphas FIR transfr
32-Tap Digitally Programmable Potentiometer (DPP )
 -Tap Digitally Programmabl Potntiomtr (DPP ) CAT FEATURES -position linar tapr potntiomtr Low powr CMOS tchnology Singl supply opration:.v V Incrmnt up/down srial intrfac Rsistanc valus: 0kΩ, 0kΩ and 00kΩ
-Tap Digitally Programmabl Potntiomtr (DPP ) CAT FEATURES -position linar tapr potntiomtr Low powr CMOS tchnology Singl supply opration:.v V Incrmnt up/down srial intrfac Rsistanc valus: 0kΩ, 0kΩ and 00kΩ
Principles of active remote sensing: Lidars. 1. Optical interactions of relevance to lasers. Lecture 22
 Lctur 22 Principls of activ rmot snsing: Lidars Ojctivs: 1. Optical intractions of rlvanc to lasrs. 2. Gnral principls of lidars. 3. Lidar quation. quird rading: G: 8.4.1, 8.4.2 Additional/advancd rading:.m.
Lctur 22 Principls of activ rmot snsing: Lidars Ojctivs: 1. Optical intractions of rlvanc to lasrs. 2. Gnral principls of lidars. 3. Lidar quation. quird rading: G: 8.4.1, 8.4.2 Additional/advancd rading:.m.
Types of Transfer Functions. Types of Transfer Functions. Types of Transfer Functions. Ideal Filters. Ideal Filters
 Typs of Transfr Typs of Transfr x[n] X( LTI h[n] H( y[n] Y( y [ n] h[ k] x[ n k] k Y ( H ( X ( Th tim-domain classification of an LTI digital transfr function is basd on th lngth of its impuls rspons h[n]:
Typs of Transfr Typs of Transfr x[n] X( LTI h[n] H( y[n] Y( y [ n] h[ k] x[ n k] k Y ( H ( X ( Th tim-domain classification of an LTI digital transfr function is basd on th lngth of its impuls rspons h[n]:
u 3 = u 3 (x 1, x 2, x 3 )
 Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
1.2 Faraday s law A changing magnetic field induces an electric field. Their relation is given by:
 Elctromagntic Induction. Lorntz forc on moving charg Point charg moving at vlocity v, F qv B () For a sction of lctric currnt I in a thin wir dl is Idl, th forc is df Idl B () Elctromotiv forc f s any
Elctromagntic Induction. Lorntz forc on moving charg Point charg moving at vlocity v, F qv B () For a sction of lctric currnt I in a thin wir dl is Idl, th forc is df Idl B () Elctromotiv forc f s any
Title: Vibrational structure of electronic transition
 Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
Data Assimilation 1. Alan O Neill National Centre for Earth Observation UK
 Data Assimilation 1 Alan O Nill National Cntr for Earth Obsrvation UK Plan Motivation & basic idas Univariat (scalar) data assimilation Multivariat (vctor) data assimilation 3d-Variational Mthod (& optimal
Data Assimilation 1 Alan O Nill National Cntr for Earth Obsrvation UK Plan Motivation & basic idas Univariat (scalar) data assimilation Multivariat (vctor) data assimilation 3d-Variational Mthod (& optimal
COMPUTER GENERATED HOLOGRAMS Optical Sciences 627 W.J. Dallas (Monday, April 04, 2005, 8:35 AM) PART I: CHAPTER TWO COMB MATH.
 C:\Dallas\0_Courss\03A_OpSci_67\0 Cgh_Book\0_athmaticalPrliminaris\0_0 Combath.doc of 8 COPUTER GENERATED HOLOGRAS Optical Scincs 67 W.J. Dallas (onday, April 04, 005, 8:35 A) PART I: CHAPTER TWO COB ATH
C:\Dallas\0_Courss\03A_OpSci_67\0 Cgh_Book\0_athmaticalPrliminaris\0_0 Combath.doc of 8 COPUTER GENERATED HOLOGRAS Optical Scincs 67 W.J. Dallas (onday, April 04, 005, 8:35 A) PART I: CHAPTER TWO COB ATH
CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS
 CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS Stig Holst ABB Automation Products Swdn Bapuji S Palki ABB Utilitis India This papr rports
CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS Stig Holst ABB Automation Products Swdn Bapuji S Palki ABB Utilitis India This papr rports
Homotopy perturbation technique
 Comput. Mthods Appl. Mch. Engrg. 178 (1999) 257±262 www.lsvir.com/locat/cma Homotopy prturbation tchniqu Ji-Huan H 1 Shanghai Univrsity, Shanghai Institut of Applid Mathmatics and Mchanics, Shanghai 272,
Comput. Mthods Appl. Mch. Engrg. 178 (1999) 257±262 www.lsvir.com/locat/cma Homotopy prturbation tchniqu Ji-Huan H 1 Shanghai Univrsity, Shanghai Institut of Applid Mathmatics and Mchanics, Shanghai 272,
First order differential equation Linear equation; Method of integrating factors
 First orr iffrntial quation Linar quation; Mtho of intgrating factors Exampl 1: Rwrit th lft han si as th rivativ of th prouct of y an som function by prouct rul irctly. Solving th first orr iffrntial
First orr iffrntial quation Linar quation; Mtho of intgrating factors Exampl 1: Rwrit th lft han si as th rivativ of th prouct of y an som function by prouct rul irctly. Solving th first orr iffrntial
First derivative analysis
 Robrto s Nots on Dirntial Calculus Chaptr 8: Graphical analysis Sction First drivativ analysis What you nd to know alrady: How to us drivativs to idntiy th critical valus o a unction and its trm points
Robrto s Nots on Dirntial Calculus Chaptr 8: Graphical analysis Sction First drivativ analysis What you nd to know alrady: How to us drivativs to idntiy th critical valus o a unction and its trm points
TPC8116-H TPC8116-H. High Efficiency DC/DC Converter Applications Notebook PC Applications Portable Equipment Applications CCFL Inverter Applications
 TOSHIBA Field Effect Transistor Silicon P-Channel MOS Type (Ultra-High-Speed U-MOSIII) High Efficiency DC/DC Converter Applications Notebook PC Applications Portable Equipment Applications CCFL Inverter
TOSHIBA Field Effect Transistor Silicon P-Channel MOS Type (Ultra-High-Speed U-MOSIII) High Efficiency DC/DC Converter Applications Notebook PC Applications Portable Equipment Applications CCFL Inverter
Text: WMM, Chapter 5. Sections , ,
 Lcturs 6 - Continuous Probabilit Distributions Tt: WMM, Chaptr 5. Sctions 6.-6.4, 6.6-6.8, 7.-7. In th prvious sction, w introduc som of th common probabilit distribution functions (PDFs) for discrt sampl
Lcturs 6 - Continuous Probabilit Distributions Tt: WMM, Chaptr 5. Sctions 6.-6.4, 6.6-6.8, 7.-7. In th prvious sction, w introduc som of th common probabilit distribution functions (PDFs) for discrt sampl
100-Tap Digitally Programmable Potentiometer (DPP )
 00-Tap Digitally Programmabl Potntiomtr ( ) CAT FEATURES 00-position linar tapr potntiomtr Non-volatil EEPROM wipr storag 0nA ultra-low standby currnt Singl supply opration:.v.0v Incrmnt up/down srial
00-Tap Digitally Programmabl Potntiomtr ( ) CAT FEATURES 00-position linar tapr potntiomtr Non-volatil EEPROM wipr storag 0nA ultra-low standby currnt Singl supply opration:.v.0v Incrmnt up/down srial
E hf. hf c. 2 2 h 2 2 m v f ' f 2f ' f cos c
 EXPERIMENT 9: COMPTON EFFECT Rlatd Topics Intractions of photons with lctrons, consrvation of momntum and nrgy, inlastic and lastic scattring, intraction cross sction, Compton wavlngth. Principl Whn photons
EXPERIMENT 9: COMPTON EFFECT Rlatd Topics Intractions of photons with lctrons, consrvation of momntum and nrgy, inlastic and lastic scattring, intraction cross sction, Compton wavlngth. Principl Whn photons
DIELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
 DILCTRIC AD MAGTIC PROPRTIS OF MATRIALS Dilctric Proprtis: Dilctric matrial Dilctric constant Polarization of dilctric matrials, Typs of Polarization (Polarizability). quation of intrnal filds in liquid
DILCTRIC AD MAGTIC PROPRTIS OF MATRIALS Dilctric Proprtis: Dilctric matrial Dilctric constant Polarization of dilctric matrials, Typs of Polarization (Polarizability). quation of intrnal filds in liquid
Sliding Mode Flow Rate Observer Design
 Sliding Mod Flow Rat Obsrvr Dsign Song Liu and Bin Yao School of Mchanical Enginring, Purdu Univrsity, Wst Lafaytt, IN797, USA liu(byao)@purdudu Abstract Dynamic flow rat information is ndd in a lot of
Sliding Mod Flow Rat Obsrvr Dsign Song Liu and Bin Yao School of Mchanical Enginring, Purdu Univrsity, Wst Lafaytt, IN797, USA liu(byao)@purdudu Abstract Dynamic flow rat information is ndd in a lot of
26-Sep-16. Nuclear energy production. Nuclear energy production. Nuclear energy production. Nuclear energy production
 Aim: valuat nrgy-gnration rat pr unit mass. Sun: (chck L /M, human ) nrgy-gnration rat producd from fusion of two nucli a + A: nrgy rlasd pr raction raction rat pr unit volum (includs cross sction and
Aim: valuat nrgy-gnration rat pr unit mass. Sun: (chck L /M, human ) nrgy-gnration rat producd from fusion of two nucli a + A: nrgy rlasd pr raction raction rat pr unit volum (includs cross sction and
Preliminary Fundamentals
 1.0 Introduction Prliminary Fundamntals In all of our prvious work, w assumd a vry simpl modl of th lctromagntic torqu T (or powr) that is rquird in th swing quation to obtain th acclrating torqu. This
1.0 Introduction Prliminary Fundamntals In all of our prvious work, w assumd a vry simpl modl of th lctromagntic torqu T (or powr) that is rquird in th swing quation to obtain th acclrating torqu. This
100-Tap Digitally Programmable Potentiometer (DPP )
 00-Tap igitally Programmabl Potntiomtr ( ) CT FTURS 00-position linar tapr potntiomtr Non-volatil PROM wipr storag 0n ultra-low standby currnt Singl supply opration:.v.0v Incrmnt up/down srial intrfac
00-Tap igitally Programmabl Potntiomtr ( ) CT FTURS 00-position linar tapr potntiomtr Non-volatil PROM wipr storag 0n ultra-low standby currnt Singl supply opration:.v.0v Incrmnt up/down srial intrfac
