Experiment #9 BJT Dynamic Circuits
|
|
|
- Ethan Carroll
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exprimnt #9 BJT Dynamic Circuits Jonathan Rodrick Hakan Durmus Scott Kilpatrick Burgss Introduction: In th last la, w larnd th point of iasing an analog circuit corrctly is so th activ dvics within th circuit oprat in a dsiral fashion (linarly) on signals that ntr th circuit. Ths signals ar prturations aout th ias point (or quiscnt point, a.k.a. Q-point); for instanc, you might ias your input port at 2, and thn add a 100 m pak-to-pak sin wav to this ias voltag. Idally, you would lik amplifirs to prfct linar dvics, maning th output signal is som multipl of th input signal, indpndnt of th input amplitud. Transistors ar normally non-linar dvics (rcall thir I- charactristics), so th output amplitud dos dpnd upon th input amplitud. Howvr, y suitaly rstricting th amplitud of th input swing (using a small signal ) and corrctly iasing th circuit (Q point), th rsultant output will show vry littl curvatur, maning that th non-linar circuit acts approximatly linar for small-signal dviations aout th ias point. In this la, dynamic circuits using BJTs will introducd. Onc a BJT is iasd in such a way that it oprats in a linar rgion, thn th small-signal BJT modl may usd for analysis and dsign of circuits that contain th transistor. This modl forms th asis for undrstanding th dynamic prformanc of svral commonly ncountrd circuits. Thory: Small-Signal Modl for th Bipolar Transistor Th small-signal modl for an NPN ipolar transistor is shown in figur 9.1. For th purposs of this la, th modls and thory prsntd will focus on th NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor. Th following modls also apply for th PNP transistor with th slight modification of: rvrsing th dirction of all controlld currnt sourcs and ranch currnts, and a rvrsal in polarity of all port and ranch voltags. r c µ r c c π + v _ i rπ βig m v r o r Figur 9.1 Small-signal modl for th ipolar transistor. 1
2 Not: Th small signal modl is just a tool that is usd to hlp circuit dsignrs analyz circuits utilizing BJTs. This tool is only valid if th transistor is oprating in its linar rang. Thrfor it should undrstood that whn using th small signal modl, that significant ffort has n mad to nsur that th signal ing procssd in th amplifir is not too larg, thus validating th small signal modl accuracy. A larg nough signal may caus th transistor to lav its linar opration if its signal chang has a magnitud larg nough to offst th st Q (iasing) point, thus causing signal distortion. Th ky lmnt in th small signal modl is th controlld currnt sourc, which can shown as dpnding on th intrnal as currnt i (or th intrnal as-mittr voltag v ). Th quantity g m is dfind as g m i v c 1 signifying how rsponsiv th collctor currnt is to changs in th driving voltag v. Th small signal modl accounts th various intrnal rsistancs associatd with ach trminal. Rsistor r is th small rsistanc associatd with th highly dopd mittr. Rsistor r is a distriutd, non-linar rsistanc, and thus hard to charactriz with a singl valu, ut it corrsponds to th rsistanc twn th as contact and that rgion of th as matrial lying undrnath th mittr. Likwis, rsistor r c is hard to charactriz with a singl valu, ut rprsnts th nt rsistanc twn th collctor contact and th ottom portion of th as matrial. Rsistor r π, known as th mittr-as junction diffusion rsistanc, is not a physical rsistanc (it is a mathmatical modl concivd from a Taylor sris xpansion of th as-mittr currnt, I BE, aout th Q-point) lik th prcding thr, ut rathr a dynamic quantity dfind as (9.1) r π i v 1 (9.2) It rprsnts how rsistant th input as currnt is to changs in th intrnal as-mittr voltag (i.., th voltag not including th voltag drop across r, rprsntd as v in th small signal modl). Th controlld sourc indicats how much th collctor currnt changs for a chang in as currnt (or quivalntly, as-mittr voltag). Lik r π, rsistor r o is a dynamic rsistanc and it is know as th forward Early rsistanc. It rprsnts th influnc of changs in collctor-mittr voltag on collctor currnt, and thus is calculatd y r o c 1 i v c (9.3) For high Early voltags, A E, this rsistanc is ngligil, and thus th collctor voltag has a ngligil impact on th currnt flowing out of th collctor contact. Th intrnal rsistanc dos hav profound ffcts on ovrall circuit prformanc. Larg as, collctor, and mittr rsistancs rduc circuit gain, diminish gain-andwidth product, and incras lctrical nois. Howvr, r, r, and r c ar invrsly proportional to th mittr-as junction injction ara and a pric is paid for incrasing th ara to lowr rsistancs. Incrasing th ara of th dvic rsults in largr parasitic capacitancs, so incrasing th siz of th transistor to rduc intrnal rsistanc rducs th circuit rspons spd. Powr consumption is also a trad-off. All intrnal rsistanc, particularly r, dcras monotonically with incrasing th as and collctor ias currnts, I B and I C rspctivly. In th world of wirlss and moil lctronics, w want th attris in our cll phon to last longr, so larg powr consumption in wirlss lctronics is avoidd. Wlcom to th wondrful world of circuit dsign, whr hindring constraints ar invrsly proportional to ach othr. Your jo as a circuit dsignr is to find a happy mdian that allows you to mt all th spcifications for your dsign. 2
3 Th small signal modl also accounts for intrnal parasitic capacitancs found with in th BJT. C µ rprsnts th dpltion capacitanc of th as-collctor junction. C π is composd of two parts: 1) a diffusion capacitanc givn y C π q v i c τ F τ F v and 2) a dpltion capacitanc, which is usually ngligil compard to th diffusion capacitanc whn th as-mittr junction is forward-iasd. To dvlop numrical valus for th symols in th small-signals modl, th dfining drivativs must valuatd symolically, thn valuatd aout th Q-point. With th ias quantitis spcifid, numrical valus may assignd to ach small-signal paramtr. Th small signal modl dos giv a circuit dsignr a good fl on how parasitic capacitanc affcts th prformanc of th circuit. A maturd circuit dsignr can y inspction s th limitations of any topology. For instanc, if andwidth is ing considrd a good circuit dsignr would avoid xposing any larg parasitic capacitanc to any larg impdancs (Rmmr th tim constant, in trms of frquncy, is invrsly proportional to RC). Canonic Clls of Linar BJT Tchnology. Th BJT Transistor has four asic topologis that ar uilding locks for mor complicatd circuit architctur. A singl BJT transistor may connctd in a diod, common mittr, common collctor, or common as configuration. A quick and simpl way to dtrmin th diffrnc twn th common as, collctor, or mittr is: First, dtrmin what trminals whr th input and output ar connctd. Thn, th particular canonic cll rcivs its nam from th trminal that is lftovr. For xampl, if you ar looking at th ac BJT configuration in figur 9.2, you will notic that th input is at th as, whil th output is locatd at th collctor. Hnc, th lftovr trminal is th mittr and this canonic cll is dmd a common mittr amplifir. g m (9.4) R l o R in R out R s s R Figur 9.2 An AC schmatic diagram of a common mittr amplifir. 3
4 Diod -Connctd Transistor. Th simplst canonic cll for th BJT is th diod-connctd transistor. Th collctor is tid to th as of th transistor, so it xhiits I- havior of a convntional PN junction diod. Figur 9.3 dpicts a transistor connctd this way and its small-signal quivalnt circuit. This modl assums th transistor is iasd in th linar rgion and lavs out th Q-point currnts. Th diod-connctd transistor rducs th numr of trminals of a typical BJT to two (th as and collctor ar now th sam trminal). This two trminal dvic may modld as a two trminal rsistor sn in figur 9.3. Using th low-frquncy small-signal modl of BJT (nglcting all capacitanc), th quivalnt rsistanc of th diod-connctd can found to qual R d. R d ( ro + rc ) ( r + rπ ) r + ro β 1+ r + r + r + r o c π (9.5) If r o >>r c +r +r π, thn quation 9.5 rducs to R d r r + r + 1+ β π (9.9) Figur 9.3(a) Diod-Connctd BJT and () its small-signal low frquncy quivalnt modl. Common Emittr Canonic Cll. Th common mittr amplifir was shown in figur 9.2. Rplacing th schmatic symol of a BJT in figur 9.2 with th small signal modl, on can calculat th gain, input impdanc and th output 4
5 impdanc. Figur 9.4 shows a common mittr amplifir utilizing th small signal modl. Assuming that r c is ngligil and ignoring th arly ffct (r o ) th gain, input rsistanc (R in ) and output rsistanc (R out ) may calculatd. r out r s r i r c o s rin r π βi r o r L R r x r Figur 9.4 A low frquncy common mittr canonic cll using th small signal modl. r r + r + β + 1)( r + r ) in ( x π (9.7) whr r x is th rsistanc sn y mittr. r out (9.8) and A v o s βrl rs + r + r + ( β + 1)( r + rx ) π (9.9) assuming β is larg, thn th gain rducs to A v o s rl r x (9.10) Th common mittr canonic cll is usd to achiv an invrting gain that is indpndnt of th transistor β. R in dpnds on what th valu of r x, ut sinc it is multiplid y β it is assumd not to too small. R out is vry larg. With a R in that can mad fairly larg and a R out is vry larg, th common mittr is not a vry idal voltag amplifir. Additional transistors can usd to nhanc prformanc, so that th common-mittr canonic can usd as a good voltag amplifir. 5
6 Common Collctor Canonic Cll. A common collctor canonic cll is shown in figur 9.5. Notic, th input nor th output of th canonic cll is connctd to th collctor of th transistor. R l r y R s s r x o R Figur 9.5 An ac schmatic of a common-collctor (a.k.a. an mittr followr) BJT canonic cll. Using th Small signal modl it can shown that th gain, input rsistanc and th output rsistanc ar th following A o s ( β + 1) r r + r + r + ( β + 1)( r s + r ) π x (9.11) In this xampl, choosing a small R th gain will rduc to A o s 1 (9.12) with r r + r + β + 1)( r + r ) in ( x π (9.13) and 6
7 r out r r + + r π + r ( β +1) y (9.14) Sinc th gain can dsignd narly qual on, r in can mad fairly larg, whil r out is small (du to it ing invrsly proportional to β) th common collctor canonic cll can dsignd to a dcnt voltag uffr. Sinc th common collctor is usually usd as a voltag uffr, it is somtims rfrrd to as a mittr followr du to th mittr following (or matching) th voltag that is connctd to th as. Common Bas Canonic Cll. Th common as canonic cll is shown in figur 9.9. Th input is a currnt sourc at th mittr, whil th output is takn at th collctor. Hnc, this is a common as configuration of a BJT. R l R 1 r y r out r in I s Figur 9.9 An AC common as BJT canonic cll. Using th small-signal modl it can shown that th currnt gain (A i ), r in, and r out ar th following. A i Io β α 1 I β + 1 s (9.15) r out (9.19) 7
8 r in r r + + r π + r ( β +1) y (9.17) Th common as has a currnt gain of aout on, a larg output rsistanc and a small input rsistanc. Thrfor, it is commonly usd as a currnt uffr. Common Emittr Amplifir Exampl In th prvious la, th common-mittr amplifir was iasd, ut no mntion was mad of why it is calld an amplifir. To answr this, w analyz th circuit in th prvious la, with a fw modifications. First, w nd to fd our input signal into th as, without th DC ias of th signal sourc and th commonmittr amplifir intrfring with ach othr. This is accomplishd y adding an AC coupling capacitor (C in ) to th input port, larg nough so that it will act lik an AC short at th frquncis at which w oprat, thus liminating any transfr of DC offsts. Scond, th amplifir nds to driv a rsistiv load which w don t want to upst our ias point, so w appnd anothr AC coupling capacitor (C out ) to th output port. Third, w rplac th transistor symol usd in th prvious la with th small-signal modl, lading to th following circuit: C in r c µ r c C out out i s R 1 R 2 r π c π βi r o R c R load r + R Figur 9.7 An AC common-mittr amplifir with rsistiv load for AC analysis (from xprimnt #5 figur 5.5) Assuming that w ar at low-nough frquncis that th parasitic capacitancs of th BJT don t affct our rsults, ut a high nough frquncy whr th coupling capacitors ar acting lik shorts, and furthr nglcting th Early, sourc, and intrnal mittr rsistancs, analysis of our modl lads to: v A v ( ) out β Rload Rc vs r + rπ + ( β + 1) R (9.18) With larg ta, this rducs to R R R A v load c (9.19) 8
9 ( ) a rathr simpl xprssion indpndnt of transistor paramtrs. As long as R load Rc > R, th transfr function has a magnitud gratr than 1, xplaining why th common-mittr is calld an amplifir. For th valus drivd in th prvious la, this rquirs that R load at last 375Ω for gain. Notic: th sourc rsistanc in this xampl was ignord, which is only valid in an idal world. This assumption causs th voltag division ffcts, which would normally caus y th iasing transistors R 1 and R 2, to ignord. Howvr, if on was to uild this circuit, any sourc rsistanc would caus ths two iasing rsistors to diminish th gain and thus would nd to accountd for during dsign. Conclusion: Th dynamic us of th BJT transistor was xplord in this xprimnt. Thr wr four fundamntal configurations covrd that ar known as th BJT canonical clls. Each canonic cll has diffrnt uniqu nficial charactristics as wll as limitations. Exprimnt #10 will dal with comining canonic clls to ovrcom th limitations inhrnt of a singl cll topology. It is vry crucial that th canonic clls ar wll undrstood as thy will giv a circuit dsignr th aility to rakdown and valuat complicatd circuit topologis virtually y inspction. 9
10 Rfrnc rading 1) John Choma, Jr. EE348 lctur nots. Univrsity of Southrn California. Spring ) David Johns & Kn Martin. Analog intgratd Circuit Dsign. John Wily & Sons, Inc., Nw York, ) Paul R. Gray & Rort G. Myr. Analysis and Dsign of Analog Intgratd Circuits. John Wily & Sons, Inc., Nw York,
11 Pr-la Exrciss 1) Givn th dfinitions of th small-signal paramtrs for th ipolar transistor, xprss r π, g m, and r o in trms of ias paramtrs (.g., collctor currnt, c, tc.). For a 1mA currnt and c of 3.2 as wll as an Early voltag of 200 and a Bta of 100, what ar th valus of r π, g m and r o? 2) Using figur 9.2, dsign an amplifir with a small signal gain magnitud of 7. Your jo is to choos th corrct rsistor valus that dtrmin th iasing point and corrct gain magnitud. Assum you ar using a 10kHz sin wav input with a magnitud of 50m (100m pak-to-pak). B sur that your signal dosn t driv th transistor out of th linar rgion. Your dsign must us a ground to 5 powr supply and not draw mor than 5mA through any givn ranch. rify your dsign using Spic. Is it possil to mt th rquird spcifications? If, not why not? 3) Nglcting any iasing issus, if th rsistors you us in th prvious prolm hav a tolranc of ±5%, what is th maximum rror th gain can xprinc du xclusivly to th tolrancs of th rsistors? 4) Driv th xprssions givn for th voltag gain, input rsistanc and output rsistanc for th common collctor circuit in figur ) Driv th xprssions givn for th currnt gain, input rsistanc and output rsistanc for th common as circuit in figur ) Driv th xprssions for th gain, input rsistanc, and output rsistanc for th low-frquncy common-mittr amplifir in figur ) Building upon th common-mittr iasing xampl picturd in figur 5.5 from xprimnt #5, what is th maximum gain that can achivd if th collctor currnt is fixd at 1mA and th as voltag is fixd at 1? Assum s is a 10kHz sin wav with a magnitud 50m (100m pak-to-pak) Can a gain of 50 achivd? Why or why not? Whil nsuring that th transistor nvr lavs linar opration, what is th maximum gain that can otaind? What R C valu givs you th maximum gain? Us SPICE to vrify your dsign and your suspnsions aout th maximum amount of gain that you can otain. Us th.op command to vrify th ias currnts and voltags for your circuit, and an.ac or.tran analysis to osrv th voltag gain. 8) Plac a larg (.g., 0.1 uf) capacitor across rsistor R in th prvious prolm. By inspction can you thoriz what happns to th gain and why? Do a SPICE simulation to confirm your rspons. 9) Exprss th output currnt of th Wilson currnt, figur 8.7, sourc in trms of th rfrnc currnt. Do not nglct as currnts in your analysis, and assum ach transistor has th sam β. Your final answr should in trms of th rfrnc currnt and β. (Hint: your final answr I I ( rror) should look lik out rf 1 2, whr th rror dpnds invrsly on β.) Do a small signal analysis to dtrmin a symolic xprssion for th output rsistanc of th Wilson currnt sourc. Assum vry transistor has idntical small-signal paramtrs. Assum you dsir you an output currnt of 1 ma, and your supply, cc, is 5. What is th approximat siz of th rquird rfrnc rsistor, R? 11
12 La Exrcis 1) Build th dsign you can up for qustion #2 in th prla. Masur th gain and th currnt through ach ranch and compar it to your spic rsults. Ar your rsults within 5% of spcifications givn in th prla? Prform any ncssary changs or twaking of rsistor valus to gt within 5% of spcs. Nxt, Chang th input signal lvl y ±9-dB. Dos th circuit still hav linarly? Why or why not? 2) Build th dsign which givs you th maximum achival gain that you dtrmind is possil from th common mittr amplifir in prolm #7 of th prla. rify it opration y comparing th magnitud of th input signal to th magnitud of th output signal. 3) Kp th circuit from th prvious prolm, ut rplac R C with a potntiomtr. ary th pot until you rach th maximum achival gain whil still maintaining a as-collctor rvrs ias to nsur linarity. Masur th valu of th potntiomtr that givs you th maximum possil gain. Dos this valu agr with what you drivd in qustion #7 of th prla? Why or why not? 4) Plac a larg (.g., 0.1 uf) capacitor across rsistor R of th last prolm. Using a function gnrator, swt th frquncy from 1kHz to 35kHz taking a masurmnt of th magnitud vry 1kHz. What dos adding th capacitor do to th gain? Dos this agr with your prdiction for qustion #8 in th prla? 5) Dsign th mittr followr in figur 9.5. Choos th DC voltag of th sourc, s, and th rsistor valus that ias th transistor with 1mA. Givn: cc 5, and s is a 10kHz sin wav input with a magnitud of 50m (100m pak-to-pak). Masur th gain of your circuit? Now slct rsistor valus that maximiz th output swing (ac signal magnitud). Did this affct th gain of your circuit? If so, y how much? 6) Add a 300Ω and th capacitor C D to th mittr followr, as sn in figur 9.8. Th capacitor, C D, should vry larg. What is th purpos of this capacitor? Estimat th gain and thn masur it. Dos driving this small rsistanc affct th ac gain of you circuit? Why is this nficial? Could you driv th sam small rsistanc with a common-mittr? Why or why not? cc R cc C D out s R R L Figur 9.8 7) Dsign th common mittr circuit with th mittr dgnration rsistor R. Using what you drivd in th pr-la, what ffct dos R hav on th prformanc of th circuit? Using a sourc dc offst of 1, us what you larnd in xprimnt #5 to ias this circuit so that it has an mittr currnt of 1mA. Choos a valu for R l, so that th output has maximum swing capaility: For 12
13 linarity purposs, don t lt th collctor-mittr voltag ( CE ) drop low 0.7 (It should larg than SAT 0.2, ut to saf, kp it aov BE. Masur th gain of this circuit. Can you otain a gain of 50 givn th sam supply voltag and currnt limitations? 8) Add a 300Ω and th capacitor C D to th common mittr, as sn in figur 9.9. Estimat th gain using what you drivd in th pr-la. Masur th gain. Is th gain th sam as masur in part (a)? Basd on your rsults, what is a asic limitation of th common mittr amplifir? 9) Build th common-mittr amplifir of Figur 9.2. Dtrmin an appropriat input signal lvl so that th output signal is larg nough to masur, ut small nough so that th transistor acts linarly. Dtrmin th low-frquncy gain at 10 khz. Dos it match rasonaly wll with your hand rsults? Chang Plac a 0.1µF capacitor across R and r-masur th AC gain (you may nd to adjust your input signal amplitud onc mor to nsur linar havior). 13
Voltage, Current, Power, Series Resistance, Parallel Resistance, and Diodes
 Lctur 1. oltag, Currnt, Powr, Sris sistanc, Paralll sistanc, and Diods Whn you start to dal with lctronics thr ar thr main concpts to start with: Nam Symbol Unit oltag volt Currnt ampr Powr W watt oltag
Lctur 1. oltag, Currnt, Powr, Sris sistanc, Paralll sistanc, and Diods Whn you start to dal with lctronics thr ar thr main concpts to start with: Nam Symbol Unit oltag volt Currnt ampr Powr W watt oltag
Design Guidelines for Quartz Crystal Oscillators. R 1 Motional Resistance L 1 Motional Inductance C 1 Motional Capacitance C 0 Shunt Capacitance
 TECHNICAL NTE 30 Dsign Guidlins for Quartz Crystal scillators Introduction A CMS Pirc oscillator circuit is wll known and is widly usd for its xcllnt frquncy stability and th wid rang of frquncis ovr which
TECHNICAL NTE 30 Dsign Guidlins for Quartz Crystal scillators Introduction A CMS Pirc oscillator circuit is wll known and is widly usd for its xcllnt frquncy stability and th wid rang of frquncis ovr which
Electronic Circuits. BJT Amplifiers. Manar Mohaisen Office: F208 Department of EECE
 Elctronic Circuits BJT mplifirs Manar Mohaisn Offic: F208 Email: manar.subhi@kut.ac.kr Dpartmnt of EECE viw of th Prcdnt Lctur Explain th DC Oprating Point Explain th Voltag-dividr Bias Othr Bias Mthods
Elctronic Circuits BJT mplifirs Manar Mohaisn Offic: F208 Email: manar.subhi@kut.ac.kr Dpartmnt of EECE viw of th Prcdnt Lctur Explain th DC Oprating Point Explain th Voltag-dividr Bias Othr Bias Mthods
Exam 1. It is important that you clearly show your work and mark the final answer clearly, closed book, closed notes, no calculator.
 Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
The pn junction: 2 Current vs Voltage (IV) characteristics
 Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
A Propagating Wave Packet Group Velocity Dispersion
 Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
General Notes About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidelines
 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Gnral Nots About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidlins 1. Th solutions contain th most common mthod of solving th fr-rspons qustions and th allocation
AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Gnral Nots About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidlins 1. Th solutions contain th most common mthod of solving th fr-rspons qustions and th allocation
ECE 344 Microwave Fundamentals
 ECE 44 Microwav Fundamntals Lctur 08: Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Part Prpard By Dr. hrif Hkal 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Powr dividrs, combinrs and dirctional
ECE 44 Microwav Fundamntals Lctur 08: Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Part Prpard By Dr. hrif Hkal 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Powr dividrs, combinrs and dirctional
Engineering 1620: High Frequency Effects in BJT Circuits an Introduction Especially for the Friday before Spring Break
 nginring 162: High Frquncy ffcts in BJT Circuits an Inoduction spcially for th Friday bfor Spring Brak I hav prpard ths nots bcaus on th day bfor a major vacation brak som popl find it ncssary to lav arly
nginring 162: High Frquncy ffcts in BJT Circuits an Inoduction spcially for th Friday bfor Spring Brak I hav prpard ths nots bcaus on th day bfor a major vacation brak som popl find it ncssary to lav arly
Extraction of Doping Density Distributions from C-V Curves
 Extraction of Doping Dnsity Distributions from C-V Curvs Hartmut F.-W. Sadrozinski SCIPP, Univ. California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 9564 USA 1. Connction btwn C, N, V Start with Poisson quation d V =
Extraction of Doping Dnsity Distributions from C-V Curvs Hartmut F.-W. Sadrozinski SCIPP, Univ. California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 9564 USA 1. Connction btwn C, N, V Start with Poisson quation d V =
A crash-course in transistor circuits
 A crash-cours in transistor circuits Patrick R. LClair July 19, 2011 Contnts 1 Transistors 1 1.1 Basic charactristics.................................... 1 1.2 Notation...........................................
A crash-cours in transistor circuits Patrick R. LClair July 19, 2011 Contnts 1 Transistors 1 1.1 Basic charactristics.................................... 1 1.2 Notation...........................................
ECE602 Exam 1 April 5, You must show ALL of your work for full credit.
 ECE62 Exam April 5, 27 Nam: Solution Scor: / This xam is closd-book. You must show ALL of your work for full crdit. Plas rad th qustions carfully. Plas chck your answrs carfully. Calculators may NOT b
ECE62 Exam April 5, 27 Nam: Solution Scor: / This xam is closd-book. You must show ALL of your work for full crdit. Plas rad th qustions carfully. Plas chck your answrs carfully. Calculators may NOT b
Lecture #15. Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs)
 ctur #5 OUTN Th iolar Junction Transistor Fundamntals dal Transistor Analysis Rading: hatr 0,. 30 ctur 5, Slid iolar Junction Transistors (JTs Ovr th ast 3 ads, th highr layout dnsity and low-owr advantag
ctur #5 OUTN Th iolar Junction Transistor Fundamntals dal Transistor Analysis Rading: hatr 0,. 30 ctur 5, Slid iolar Junction Transistors (JTs Ovr th ast 3 ads, th highr layout dnsity and low-owr advantag
22/ Breakdown of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. Selection rules for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branches.
 Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Title: Vibrational structure of electronic transition
 Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
What are those βs anyway? Understanding Design Matrix & Odds ratios
 Ral paramtr stimat WILD 750 - Wildlif Population Analysis of 6 What ar thos βs anyway? Undrsting Dsign Matrix & Odds ratios Rfrncs Hosmr D.W.. Lmshow. 000. Applid logistic rgrssion. John Wily & ons Inc.
Ral paramtr stimat WILD 750 - Wildlif Population Analysis of 6 What ar thos βs anyway? Undrsting Dsign Matrix & Odds ratios Rfrncs Hosmr D.W.. Lmshow. 000. Applid logistic rgrssion. John Wily & ons Inc.
Lecture 16: Bipolar Junction Transistors. Large Signal Models.
 Whits, EE 322 Ltur 16 Pag 1 of 8 Ltur 16: Bipolar Juntion Transistors. Larg Signal Modls. Transistors prform ky funtions in most ltroni iruits. This is rtainly tru in RF iruits, inluding th NorCal 40A.
Whits, EE 322 Ltur 16 Pag 1 of 8 Ltur 16: Bipolar Juntion Transistors. Larg Signal Modls. Transistors prform ky funtions in most ltroni iruits. This is rtainly tru in RF iruits, inluding th NorCal 40A.
α I I R α N I F I F i C i E R Cx R Ex C Cx i B R Bx
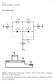 Bipolar transistor, continud - 1 - Ebrs-Moll modl α I I R α N I F E i E i C C R Ex I F I R R Cx C Cx i B R Bx B E B C Figur 1: Dashd lin indicats th "intrinsic" portion of th dvic, xcluding "parasitic"
Bipolar transistor, continud - 1 - Ebrs-Moll modl α I I R α N I F E i E i C C R Ex I F I R R Cx C Cx i B R Bx B E B C Figur 1: Dashd lin indicats th "intrinsic" portion of th dvic, xcluding "parasitic"
10. The Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
 Th Discrt-Tim Fourir Transform (DTFT Dfinition of th discrt-tim Fourir transform Th Fourir rprsntation of signals plays an important rol in both continuous and discrt signal procssing In this sction w
Th Discrt-Tim Fourir Transform (DTFT Dfinition of th discrt-tim Fourir transform Th Fourir rprsntation of signals plays an important rol in both continuous and discrt signal procssing In this sction w
MCB137: Physical Biology of the Cell Spring 2017 Homework 6: Ligand binding and the MWC model of allostery (Due 3/23/17)
 MCB37: Physical Biology of th Cll Spring 207 Homwork 6: Ligand binding and th MWC modl of allostry (Du 3/23/7) Hrnan G. Garcia March 2, 207 Simpl rprssion In class, w drivd a mathmatical modl of how simpl
MCB37: Physical Biology of th Cll Spring 207 Homwork 6: Ligand binding and th MWC modl of allostry (Du 3/23/7) Hrnan G. Garcia March 2, 207 Simpl rprssion In class, w drivd a mathmatical modl of how simpl
The Matrix Exponential
 Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by Dan Klain Vrsion 28928 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix () A A k I + A + k!
Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by Dan Klain Vrsion 28928 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix () A A k I + A + k!
The Matrix Exponential
 Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by D. Klain Vrsion 207.0.05 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom. Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix A A k I + A + k!
Th Matrix Exponntial (with xrciss) by D. Klain Vrsion 207.0.05 Corrctions and commnts ar wlcom. Th Matrix Exponntial For ach n n complx matrix A, dfin th xponntial of A to b th matrix A A k I + A + k!
u x v x dx u x v x v x u x dx d u x v x u x v x dx u x v x dx Integration by Parts Formula
 7. Intgration by Parts Each drivativ formula givs ris to a corrsponding intgral formula, as w v sn many tims. Th drivativ product rul yilds a vry usful intgration tchniqu calld intgration by parts. Starting
7. Intgration by Parts Each drivativ formula givs ris to a corrsponding intgral formula, as w v sn many tims. Th drivativ product rul yilds a vry usful intgration tchniqu calld intgration by parts. Starting
2/12/2013. Overview. 12-Power Transmission Text: Conservation of Complex Power. Introduction. Power Transmission-Short Line
 //03 Ovrviw -owr Transmission Txt: 4.6-4.0 ECEGR 45 owr ystms Consrvation of Complx owr hort in owr Transmission owr Transmission isualization Radial in Mdium and ong in owr Transmission oltag Collaps
//03 Ovrviw -owr Transmission Txt: 4.6-4.0 ECEGR 45 owr ystms Consrvation of Complx owr hort in owr Transmission owr Transmission isualization Radial in Mdium and ong in owr Transmission oltag Collaps
ES 330 Electronics II Homework # 9 (Fall 2017 Due Monday, December 4, 2017)
 Pag1 Na OLUTON E 330 Elctronics Howork # 9 (Fall 017 Du Monday, Dcbr 4, 017) Probl 1 (14 points) Dsign a MO diffrntial aplifir illsuratd in th schatic blow to oprat at O = 0.5 olt with a transconductanc
Pag1 Na OLUTON E 330 Elctronics Howork # 9 (Fall 017 Du Monday, Dcbr 4, 017) Probl 1 (14 points) Dsign a MO diffrntial aplifir illsuratd in th schatic blow to oprat at O = 0.5 olt with a transconductanc
Chapter 3: Capacitors, Inductors, and Complex Impedance
 haptr 3: apacitors, Inductors, and omplx Impdanc In this chaptr w introduc th concpt of complx rsistanc, or impdanc, by studying two ractiv circuit lmnts, th capacitor and th inductor. W will study capacitors
haptr 3: apacitors, Inductors, and omplx Impdanc In this chaptr w introduc th concpt of complx rsistanc, or impdanc, by studying two ractiv circuit lmnts, th capacitor and th inductor. W will study capacitors
CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS
 CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS Stig Holst ABB Automation Products Swdn Bapuji S Palki ABB Utilitis India This papr rports
CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS Stig Holst ABB Automation Products Swdn Bapuji S Palki ABB Utilitis India This papr rports
5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics
 MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
MIT OpnCoursWar http://ocw.mit.du 5.80 Small-Molcul Spctroscopy and Dynamics Fall 008 For information about citing ths matrials or our Trms of Us, visit: http://ocw.mit.du/trms. Lctur # 3 Supplmnt Contnts
Fourier Transforms and the Wave Equation. Key Mathematics: More Fourier transform theory, especially as applied to solving the wave equation.
 Lur 7 Fourir Transforms and th Wav Euation Ovrviw and Motivation: W first discuss a fw faturs of th Fourir transform (FT), and thn w solv th initial-valu problm for th wav uation using th Fourir transform
Lur 7 Fourir Transforms and th Wav Euation Ovrviw and Motivation: W first discuss a fw faturs of th Fourir transform (FT), and thn w solv th initial-valu problm for th wav uation using th Fourir transform
Definition1: The ratio of the radiation intensity in a given direction from the antenna to the radiation intensity averaged over all directions.
 Dirctivity or Dirctiv Gain. 1 Dfinition1: Dirctivity Th ratio of th radiation intnsity in a givn dirction from th antnna to th radiation intnsity avragd ovr all dirctions. Dfinition2: Th avg U is obtaind
Dirctivity or Dirctiv Gain. 1 Dfinition1: Dirctivity Th ratio of th radiation intnsity in a givn dirction from th antnna to th radiation intnsity avragd ovr all dirctions. Dfinition2: Th avg U is obtaind
ECE 2210 / 00 Phasor Examples
 EE 0 / 00 Phasor Exampls. Add th sinusoidal voltags v ( t ) 4.5. cos( t 30. and v ( t ) 3.. cos( t 5. v ( t) using phasor notation, draw a phasor diagram of th thr phasors, thn convrt back to tim domain
EE 0 / 00 Phasor Exampls. Add th sinusoidal voltags v ( t ) 4.5. cos( t 30. and v ( t ) 3.. cos( t 5. v ( t) using phasor notation, draw a phasor diagram of th thr phasors, thn convrt back to tim domain
That is, we start with a general matrix: And end with a simpler matrix:
 DIAGON ALIZATION OF THE STR ESS TEN SOR INTRO DUCTIO N By th us of Cauchy s thorm w ar abl to rduc th numbr of strss componnts in th strss tnsor to only nin valus. An additional simplification of th strss
DIAGON ALIZATION OF THE STR ESS TEN SOR INTRO DUCTIO N By th us of Cauchy s thorm w ar abl to rduc th numbr of strss componnts in th strss tnsor to only nin valus. An additional simplification of th strss
Estimation of apparent fraction defective: A mathematical approach
 Availabl onlin at www.plagiarsarchlibrary.com Plagia Rsarch Library Advancs in Applid Scinc Rsarch, 011, (): 84-89 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Estimation of apparnt fraction dfctiv: A mathmatical
Availabl onlin at www.plagiarsarchlibrary.com Plagia Rsarch Library Advancs in Applid Scinc Rsarch, 011, (): 84-89 ISSN: 0976-8610 CODEN (USA): AASRFC Estimation of apparnt fraction dfctiv: A mathmatical
Einstein Equations for Tetrad Fields
 Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Higher order derivatives
 Robrto s Nots on Diffrntial Calculus Chaptr 4: Basic diffrntiation ruls Sction 7 Highr ordr drivativs What you nd to know alrady: Basic diffrntiation ruls. What you can larn hr: How to rpat th procss of
Robrto s Nots on Diffrntial Calculus Chaptr 4: Basic diffrntiation ruls Sction 7 Highr ordr drivativs What you nd to know alrady: Basic diffrntiation ruls. What you can larn hr: How to rpat th procss of
SER/BER in a Fading Channel
 SER/BER in a Fading Channl Major points for a fading channl: * SNR is a R.V. or R.P. * SER(BER) dpnds on th SNR conditional SER(BER). * Two prformanc masurs: outag probability and avrag SER(BER). * Ovrall,
SER/BER in a Fading Channl Major points for a fading channl: * SNR is a R.V. or R.P. * SER(BER) dpnds on th SNR conditional SER(BER). * Two prformanc masurs: outag probability and avrag SER(BER). * Ovrall,
Data Assimilation 1. Alan O Neill National Centre for Earth Observation UK
 Data Assimilation 1 Alan O Nill National Cntr for Earth Obsrvation UK Plan Motivation & basic idas Univariat (scalar) data assimilation Multivariat (vctor) data assimilation 3d-Variational Mthod (& optimal
Data Assimilation 1 Alan O Nill National Cntr for Earth Obsrvation UK Plan Motivation & basic idas Univariat (scalar) data assimilation Multivariat (vctor) data assimilation 3d-Variational Mthod (& optimal
Status of LAr TPC R&D (2) 2014/Dec./23 Neutrino frontier workshop 2014 Ryosuke Sasaki (Iwate U.)
 Status of LAr TPC R&D (2) 214/Dc./23 Nutrino frontir workshop 214 Ryosuk Sasaki (Iwat U.) Tabl of Contnts Dvlopmnt of gnrating lctric fild in LAr TPC Introduction - Gnrating strong lctric fild is on of
Status of LAr TPC R&D (2) 214/Dc./23 Nutrino frontir workshop 214 Ryosuk Sasaki (Iwat U.) Tabl of Contnts Dvlopmnt of gnrating lctric fild in LAr TPC Introduction - Gnrating strong lctric fild is on of
MEASURING HEAT FLUX FROM A COMPONENT ON A PCB
 MEASURING HEAT FLUX FROM A COMPONENT ON A PCB INTRODUCTION Elctronic circuit boards consist of componnts which gnrats substantial amounts of hat during thir opration. A clar knowldg of th lvl of hat dissipation
MEASURING HEAT FLUX FROM A COMPONENT ON A PCB INTRODUCTION Elctronic circuit boards consist of componnts which gnrats substantial amounts of hat during thir opration. A clar knowldg of th lvl of hat dissipation
Chapter 3: Capacitors, Inductors, and Complex Impedance
 haptr 3: apacitors, Inductors, and omplx Impdanc In this chaptr w introduc th concpt of complx rsistanc, or impdanc, by studying two ractiv circuit lmnts, th capacitor and th inductor. W will study capacitors
haptr 3: apacitors, Inductors, and omplx Impdanc In this chaptr w introduc th concpt of complx rsistanc, or impdanc, by studying two ractiv circuit lmnts, th capacitor and th inductor. W will study capacitors
Addition of angular momentum
 Addition of angular momntum April, 07 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat
Addition of angular momntum April, 07 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat
4.2 Design of Sections for Flexure
 4. Dsign of Sctions for Flxur This sction covrs th following topics Prliminary Dsign Final Dsign for Typ 1 Mmbrs Spcial Cas Calculation of Momnt Dmand For simply supportd prstrssd bams, th maximum momnt
4. Dsign of Sctions for Flxur This sction covrs th following topics Prliminary Dsign Final Dsign for Typ 1 Mmbrs Spcial Cas Calculation of Momnt Dmand For simply supportd prstrssd bams, th maximum momnt
There is an arbitrary overall complex phase that could be added to A, but since this makes no difference we set it to zero and choose A real.
 Midtrm #, Physics 37A, Spring 07. Writ your rsponss blow or on xtra pags. Show your work, and tak car to xplain what you ar doing; partial crdit will b givn for incomplt answrs that dmonstrat som concptual
Midtrm #, Physics 37A, Spring 07. Writ your rsponss blow or on xtra pags. Show your work, and tak car to xplain what you ar doing; partial crdit will b givn for incomplt answrs that dmonstrat som concptual
EXST Regression Techniques Page 1
 EXST704 - Rgrssion Tchniqus Pag 1 Masurmnt rrors in X W hav assumd that all variation is in Y. Masurmnt rror in this variabl will not ffct th rsults, as long as thy ar uncorrlatd and unbiasd, sinc thy
EXST704 - Rgrssion Tchniqus Pag 1 Masurmnt rrors in X W hav assumd that all variation is in Y. Masurmnt rror in this variabl will not ffct th rsults, as long as thy ar uncorrlatd and unbiasd, sinc thy
3 Finite Element Parametric Geometry
 3 Finit Elmnt Paramtric Gomtry 3. Introduction Th intgral of a matrix is th matrix containing th intgral of ach and vry on of its original componnts. Practical finit lmnt analysis rquirs intgrating matrics,
3 Finit Elmnt Paramtric Gomtry 3. Introduction Th intgral of a matrix is th matrix containing th intgral of ach and vry on of its original componnts. Practical finit lmnt analysis rquirs intgrating matrics,
Math 34A. Final Review
 Math A Final Rviw 1) Us th graph of y10 to find approimat valus: a) 50 0. b) y (0.65) solution for part a) first writ an quation: 50 0. now tak th logarithm of both sids: log() log(50 0. ) pand th right
Math A Final Rviw 1) Us th graph of y10 to find approimat valus: a) 50 0. b) y (0.65) solution for part a) first writ an quation: 50 0. now tak th logarithm of both sids: log() log(50 0. ) pand th right
Why is a E&M nature of light not sufficient to explain experiments?
 1 Th wird world of photons Why is a E&M natur of light not sufficint to xplain xprimnts? Do photons xist? Som quantum proprtis of photons 2 Black body radiation Stfan s law: Enrgy/ ara/ tim = Win s displacmnt
1 Th wird world of photons Why is a E&M natur of light not sufficint to xplain xprimnts? Do photons xist? Som quantum proprtis of photons 2 Black body radiation Stfan s law: Enrgy/ ara/ tim = Win s displacmnt
Classical Magnetic Dipole
 Lctur 18 1 Classical Magntic Dipol In gnral, a particl of mass m and charg q (not ncssarily a point charg), w hav q g L m whr g is calld th gyromagntic ratio, which accounts for th ffcts of non-point charg
Lctur 18 1 Classical Magntic Dipol In gnral, a particl of mass m and charg q (not ncssarily a point charg), w hav q g L m whr g is calld th gyromagntic ratio, which accounts for th ffcts of non-point charg
Solution of Assignment #2
 olution of Assignmnt #2 Instructor: Alirza imchi Qustion #: For simplicity, assum that th distribution function of T is continuous. Th distribution function of R is: F R ( r = P( R r = P( log ( T r = P(log
olution of Assignmnt #2 Instructor: Alirza imchi Qustion #: For simplicity, assum that th distribution function of T is continuous. Th distribution function of R is: F R ( r = P( R r = P( log ( T r = P(log
EFFECT OF BALL PROPERTIES ON THE BALL-BAT COEFFICIENT OF RESTITUTION
 EFFECT OF BALL PROPERTIES ON THE BALL-BAT COEFFICIENT OF RESTITUTION A. M. NATHAN 1 AND L. V. SMITH 2 1 Univrsity of Illinois, 1110 W. Grn Strt, Urbana, IL 61801, USA, E-mail: a-nathan@illinois.du 2 Washington
EFFECT OF BALL PROPERTIES ON THE BALL-BAT COEFFICIENT OF RESTITUTION A. M. NATHAN 1 AND L. V. SMITH 2 1 Univrsity of Illinois, 1110 W. Grn Strt, Urbana, IL 61801, USA, E-mail: a-nathan@illinois.du 2 Washington
Lecture Outline. Skin Depth Power Flow 8/7/2018. EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics. Topic 3e
 8/7/018 Cours Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Offic: A 337 Phon: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utp.du EE 4347 Applid Elctromagntics Topic 3 Skin Dpth & Powr Flow Skin Dpth Ths & Powr nots Flow may contain
8/7/018 Cours Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Offic: A 337 Phon: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utp.du EE 4347 Applid Elctromagntics Topic 3 Skin Dpth & Powr Flow Skin Dpth Ths & Powr nots Flow may contain
Middle East Technical University Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 413 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis
 Middl East Tchnical Univrsity Dpartmnt of Mchanical Enginring ME 43 Introduction to Finit Elmnt Analysis Chaptr 3 Computr Implmntation of D FEM Ths nots ar prpard by Dr. Cünyt Srt http://www.m.mtu.du.tr/popl/cunyt
Middl East Tchnical Univrsity Dpartmnt of Mchanical Enginring ME 43 Introduction to Finit Elmnt Analysis Chaptr 3 Computr Implmntation of D FEM Ths nots ar prpard by Dr. Cünyt Srt http://www.m.mtu.du.tr/popl/cunyt
Where k is either given or determined from the data and c is an arbitrary constant.
 Exponntial growth and dcay applications W wish to solv an quation that has a drivativ. dy ky k > dx This quation says that th rat of chang of th function is proportional to th function. Th solution is
Exponntial growth and dcay applications W wish to solv an quation that has a drivativ. dy ky k > dx This quation says that th rat of chang of th function is proportional to th function. Th solution is
INC 693, 481 Dynamics System and Modelling: Linear Graph Modeling II Dr.-Ing. Sudchai Boonto Assistant Professor
 INC 69, 48 Dynamics Systm and Modlling: Linar Graph Modling II Dr.-Ing. Sudchai Boonto Assistant Profssor Dpartmnt of Control Systm and Instrumntation Enginring King Mongkut s Unnivrsity of Tchnology Thonuri
INC 69, 48 Dynamics Systm and Modlling: Linar Graph Modling II Dr.-Ing. Sudchai Boonto Assistant Profssor Dpartmnt of Control Systm and Instrumntation Enginring King Mongkut s Unnivrsity of Tchnology Thonuri
Sliding Mode Flow Rate Observer Design
 Sliding Mod Flow Rat Obsrvr Dsign Song Liu and Bin Yao School of Mchanical Enginring, Purdu Univrsity, Wst Lafaytt, IN797, USA liu(byao)@purdudu Abstract Dynamic flow rat information is ndd in a lot of
Sliding Mod Flow Rat Obsrvr Dsign Song Liu and Bin Yao School of Mchanical Enginring, Purdu Univrsity, Wst Lafaytt, IN797, USA liu(byao)@purdudu Abstract Dynamic flow rat information is ndd in a lot of
IXBT22N300HV IXBH22N300HV
 High Voltag, High Gain BIMOSFT TM Monolithic Bipolar MOS Transistor Advanc Tchnical Information IXBTNHV IXBHNHV V CS = V = A V C(sat). TO-6HV (IXBT) Symbol Tst Conditions Maximum Ratings V CS = 5 C to
High Voltag, High Gain BIMOSFT TM Monolithic Bipolar MOS Transistor Advanc Tchnical Information IXBTNHV IXBHNHV V CS = V = A V C(sat). TO-6HV (IXBT) Symbol Tst Conditions Maximum Ratings V CS = 5 C to
cycle that does not cross any edges (including its own), then it has at least
 W prov th following thorm: Thorm If a K n is drawn in th plan in such a way that it has a hamiltonian cycl that dos not cross any dgs (including its own, thn it has at last n ( 4 48 π + O(n crossings Th
W prov th following thorm: Thorm If a K n is drawn in th plan in such a way that it has a hamiltonian cycl that dos not cross any dgs (including its own, thn it has at last n ( 4 48 π + O(n crossings Th
Problem Set 6 Solutions
 6.04/18.06J Mathmatics for Computr Scinc March 15, 005 Srini Dvadas and Eric Lhman Problm St 6 Solutions Du: Monday, March 8 at 9 PM in Room 3-044 Problm 1. Sammy th Shark is a financial srvic providr
6.04/18.06J Mathmatics for Computr Scinc March 15, 005 Srini Dvadas and Eric Lhman Problm St 6 Solutions Du: Monday, March 8 at 9 PM in Room 3-044 Problm 1. Sammy th Shark is a financial srvic providr
Ch. 24 Molecular Reaction Dynamics 1. Collision Theory
 Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Elements of Statistical Thermodynamics
 24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
Brief Introduction to Statistical Mechanics
 Brif Introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Purpos: Ths nots ar intndd to provid a vry quick introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Th fild is of cours far mor vast than could b containd in ths fw pags.
Brif Introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Purpos: Ths nots ar intndd to provid a vry quick introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Th fild is of cours far mor vast than could b containd in ths fw pags.
Search sequence databases 3 10/25/2016
 Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Part 7: Capacitance And Capacitors
 Part 7: apacitanc And apacitors 7. Elctric harg And Elctric Filds onsidr a pair of flat, conducting plats, arrangd paralll to ach othr (as in figur 7.) and sparatd by an insulator, which may simply b air.
Part 7: apacitanc And apacitors 7. Elctric harg And Elctric Filds onsidr a pair of flat, conducting plats, arrangd paralll to ach othr (as in figur 7.) and sparatd by an insulator, which may simply b air.
First derivative analysis
 Robrto s Nots on Dirntial Calculus Chaptr 8: Graphical analysis Sction First drivativ analysis What you nd to know alrady: How to us drivativs to idntiy th critical valus o a unction and its trm points
Robrto s Nots on Dirntial Calculus Chaptr 8: Graphical analysis Sction First drivativ analysis What you nd to know alrady: How to us drivativs to idntiy th critical valus o a unction and its trm points
NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 1 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSIS HEMISTRY MTHEMTIS
![NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 1 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSIS HEMISTRY MTHEMTIS NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 1 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSIS HEMISTRY MTHEMTIS](/thumbs/79/79886930.jpg) . (D). (A). (D). (D) 5. (B) 6. (A) 7. (A) 8. (A) 9. (B). (A). (D). (B). (B). (C) 5. (D) NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y C o m m o n P r a c t i c T s t 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Dat: 8.8.6 ANSWER PHYSIS
. (D). (A). (D). (D) 5. (B) 6. (A) 7. (A) 8. (A) 9. (B). (A). (D). (B). (B). (C) 5. (D) NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y C o m m o n P r a c t i c T s t 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Dat: 8.8.6 ANSWER PHYSIS
Addition of angular momentum
 Addition of angular momntum April, 0 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat th
Addition of angular momntum April, 0 Oftn w nd to combin diffrnt sourcs of angular momntum to charactriz th total angular momntum of a systm, or to divid th total angular momntum into parts to valuat th
EEO 401 Digital Signal Processing Prof. Mark Fowler
 EEO 401 Digital Signal Procssing Prof. Mark Fowlr Dtails of th ot St #19 Rading Assignmnt: Sct. 7.1.2, 7.1.3, & 7.2 of Proakis & Manolakis Dfinition of th So Givn signal data points x[n] for n = 0,, -1
EEO 401 Digital Signal Procssing Prof. Mark Fowlr Dtails of th ot St #19 Rading Assignmnt: Sct. 7.1.2, 7.1.3, & 7.2 of Proakis & Manolakis Dfinition of th So Givn signal data points x[n] for n = 0,, -1
E hf. hf c. 2 2 h 2 2 m v f ' f 2f ' f cos c
 EXPERIMENT 9: COMPTON EFFECT Rlatd Topics Intractions of photons with lctrons, consrvation of momntum and nrgy, inlastic and lastic scattring, intraction cross sction, Compton wavlngth. Principl Whn photons
EXPERIMENT 9: COMPTON EFFECT Rlatd Topics Intractions of photons with lctrons, consrvation of momntum and nrgy, inlastic and lastic scattring, intraction cross sction, Compton wavlngth. Principl Whn photons
The van der Waals interaction 1 D. E. Soper 2 University of Oregon 20 April 2012
 Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
4.4 Design of Sections for Flexure (Part III)
 4.4 Dsign of Sctions for Flxur (Part ) This sction covrs th following topics. Choic of Sctions Dtrmination of Limiting Zon Post-tnsioning in Stags 4.4.1 Choic of Sctions Th typ of sction is slctd asd on
4.4 Dsign of Sctions for Flxur (Part ) This sction covrs th following topics. Choic of Sctions Dtrmination of Limiting Zon Post-tnsioning in Stags 4.4.1 Choic of Sctions Th typ of sction is slctd asd on
Precision Micropower 2.5V ShuntVoltage Reference
 SPX4040 Prcision Micropowr.5V ShuntVoltag Rfrnc FETURES Trimmd Bandgap to 0.5% and % Wid Oprating Currnt 0µ to 5m Extndd Tmpratur Rang: -40 C to 85 C Low Tmpratur Cofficint 00 ppm/ C Rplacmnt in for LM4040
SPX4040 Prcision Micropowr.5V ShuntVoltag Rfrnc FETURES Trimmd Bandgap to 0.5% and % Wid Oprating Currnt 0µ to 5m Extndd Tmpratur Rang: -40 C to 85 C Low Tmpratur Cofficint 00 ppm/ C Rplacmnt in for LM4040
4037 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Lvl MARK SCHEME for th Octobr/Novmbr 0 sris 40 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 40/ Papr, maimum raw mark 80 This mark schm is publishd as an aid to tachrs and candidats,
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Ordinary Lvl MARK SCHEME for th Octobr/Novmbr 0 sris 40 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS 40/ Papr, maimum raw mark 80 This mark schm is publishd as an aid to tachrs and candidats,
Homotopy perturbation technique
 Comput. Mthods Appl. Mch. Engrg. 178 (1999) 257±262 www.lsvir.com/locat/cma Homotopy prturbation tchniqu Ji-Huan H 1 Shanghai Univrsity, Shanghai Institut of Applid Mathmatics and Mchanics, Shanghai 272,
Comput. Mthods Appl. Mch. Engrg. 178 (1999) 257±262 www.lsvir.com/locat/cma Homotopy prturbation tchniqu Ji-Huan H 1 Shanghai Univrsity, Shanghai Institut of Applid Mathmatics and Mchanics, Shanghai 272,
Answer Homework 5 PHA5127 Fall 1999 Jeff Stark
 Answr omwork 5 PA527 Fall 999 Jff Stark A patint is bing tratd with Drug X in a clinical stting. Upon admiion, an IV bolus dos of 000mg was givn which yildd an initial concntration of 5.56 µg/ml. A fw
Answr omwork 5 PA527 Fall 999 Jff Stark A patint is bing tratd with Drug X in a clinical stting. Upon admiion, an IV bolus dos of 000mg was givn which yildd an initial concntration of 5.56 µg/ml. A fw
SECTION where P (cos θ, sin θ) and Q(cos θ, sin θ) are polynomials in cos θ and sin θ, provided Q is never equal to zero.
 SETION 6. 57 6. Evaluation of Dfinit Intgrals Exampl 6.6 W hav usd dfinit intgrals to valuat contour intgrals. It may com as a surpris to larn that contour intgrals and rsidus can b usd to valuat crtain
SETION 6. 57 6. Evaluation of Dfinit Intgrals Exampl 6.6 W hav usd dfinit intgrals to valuat contour intgrals. It may com as a surpris to larn that contour intgrals and rsidus can b usd to valuat crtain
Quasi-Classical States of the Simple Harmonic Oscillator
 Quasi-Classical Stats of th Simpl Harmonic Oscillator (Draft Vrsion) Introduction: Why Look for Eignstats of th Annihilation Oprator? Excpt for th ground stat, th corrspondnc btwn th quantum nrgy ignstats
Quasi-Classical Stats of th Simpl Harmonic Oscillator (Draft Vrsion) Introduction: Why Look for Eignstats of th Annihilation Oprator? Excpt for th ground stat, th corrspondnc btwn th quantum nrgy ignstats
P. Bruschi - Notes on Mixed Signal Design
 Chaptr 1. Concpts and dfinitions about Data Acquisition Systms Elctronic systms An lctronic systms is a complx lctronic ntwor, which intracts with th physical world through snsors (input dvics) and actuators
Chaptr 1. Concpts and dfinitions about Data Acquisition Systms Elctronic systms An lctronic systms is a complx lctronic ntwor, which intracts with th physical world through snsors (input dvics) and actuators
Outline. Thanks to Ian Blockland and Randy Sobie for these slides Lifetimes of Decaying Particles Scattering Cross Sections Fermi s Golden Rule
 Outlin Thanks to Ian Blockland and andy obi for ths slids Liftims of Dcaying Particls cattring Cross ctions Frmi s Goldn ul Physics 424 Lctur 12 Pag 1 Obsrvabls want to rlat xprimntal masurmnts to thortical
Outlin Thanks to Ian Blockland and andy obi for ths slids Liftims of Dcaying Particls cattring Cross ctions Frmi s Goldn ul Physics 424 Lctur 12 Pag 1 Obsrvabls want to rlat xprimntal masurmnts to thortical
Forces. Quantum ElectroDynamics. α = = We have now:
 W hav now: Forcs Considrd th gnral proprtis of forcs mdiatd by xchang (Yukawa potntial); Examind consrvation laws which ar obyd by (som) forcs. W will nxt look at thr forcs in mor dtail: Elctromagntic
W hav now: Forcs Considrd th gnral proprtis of forcs mdiatd by xchang (Yukawa potntial); Examind consrvation laws which ar obyd by (som) forcs. W will nxt look at thr forcs in mor dtail: Elctromagntic
NTHU ESS5850 Micro System Design F. G. Tseng Fall/2016, 7-2, p1. Lecture 7-2 MOSIS/SCNA Design Example- Piezoresistive type Accelerometer II
 F. G. Tsng Fall/016, 7-, p1 ctur 7- MOSIS/SCNA Dsign Exampl-!! Pizorsistivity Pizorsistiv typ Acclromtr II a Considr a conductiv lock of dimnsion a as shown in th figur. If a currnt is passd through th
F. G. Tsng Fall/016, 7-, p1 ctur 7- MOSIS/SCNA Dsign Exampl-!! Pizorsistivity Pizorsistiv typ Acclromtr II a Considr a conductiv lock of dimnsion a as shown in th figur. If a currnt is passd through th
High Energy Physics. Lecture 5 The Passage of Particles through Matter
 High Enrgy Physics Lctur 5 Th Passag of Particls through Mattr 1 Introduction In prvious lcturs w hav sn xampls of tracks lft by chargd particls in passing through mattr. Such tracks provid som of th most
High Enrgy Physics Lctur 5 Th Passag of Particls through Mattr 1 Introduction In prvious lcturs w hav sn xampls of tracks lft by chargd particls in passing through mattr. Such tracks provid som of th most
Chapter 13 GMM for Linear Factor Models in Discount Factor form. GMM on the pricing errors gives a crosssectional
 Chaptr 13 GMM for Linar Factor Modls in Discount Factor form GMM on th pricing rrors givs a crosssctional rgrssion h cas of xcss rturns Hors rac sting for charactristic sting for pricd factors: lambdas
Chaptr 13 GMM for Linar Factor Modls in Discount Factor form GMM on th pricing rrors givs a crosssctional rgrssion h cas of xcss rturns Hors rac sting for charactristic sting for pricd factors: lambdas
Seebeck and Peltier Effects
 Sbck and Pltir Effcts Introduction Thrmal nrgy is usually a byproduct of othr forms of nrgy such as chmical nrgy, mchanical nrgy, and lctrical nrgy. Th procss in which lctrical nrgy is transformd into
Sbck and Pltir Effcts Introduction Thrmal nrgy is usually a byproduct of othr forms of nrgy such as chmical nrgy, mchanical nrgy, and lctrical nrgy. Th procss in which lctrical nrgy is transformd into
2.3 Matrix Formulation
 23 Matrix Formulation 43 A mor complicatd xampl ariss for a nonlinar systm of diffrntial quations Considr th following xampl Exampl 23 x y + x( x 2 y 2 y x + y( x 2 y 2 (233 Transforming to polar coordinats,
23 Matrix Formulation 43 A mor complicatd xampl ariss for a nonlinar systm of diffrntial quations Considr th following xampl Exampl 23 x y + x( x 2 y 2 y x + y( x 2 y 2 (233 Transforming to polar coordinats,
NEW APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA
 NE APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA Mirca I CÎRNU Ph Dp o Mathmatics III Faculty o Applid Scincs Univrsity Polithnica o Bucharst Cirnumirca @yahoocom Abstract In a rcnt papr [] 5 th indinit intgrals
NE APPLICATIONS OF THE ABEL-LIOUVILLE FORMULA Mirca I CÎRNU Ph Dp o Mathmatics III Faculty o Applid Scincs Univrsity Polithnica o Bucharst Cirnumirca @yahoocom Abstract In a rcnt papr [] 5 th indinit intgrals
Impedance Transformation and Parameter Relations
 8/1/18 Cours nstructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Offic: A 337 Phon: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utp.du EE 4347 Applid Elctromagntics Topic 4 mpdanc Transformation and Paramtr Rlations mpdanc Ths Transformation
8/1/18 Cours nstructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Offic: A 337 Phon: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utp.du EE 4347 Applid Elctromagntics Topic 4 mpdanc Transformation and Paramtr Rlations mpdanc Ths Transformation
Background: We have discussed the PIB, HO, and the energy of the RR model. In this chapter, the H-atom, and atomic orbitals.
 Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
4. Money cannot be neutral in the short-run the neutrality of money is exclusively a medium run phenomenon.
 PART I TRUE/FALSE/UNCERTAIN (5 points ach) 1. Lik xpansionary montary policy, xpansionary fiscal policy rturns output in th mdium run to its natural lvl, and incrass prics. Thrfor, fiscal policy is also
PART I TRUE/FALSE/UNCERTAIN (5 points ach) 1. Lik xpansionary montary policy, xpansionary fiscal policy rturns output in th mdium run to its natural lvl, and incrass prics. Thrfor, fiscal policy is also
Last time. Resistors. Circuits. Question. Quick Quiz. Quick Quiz. ( V c. Which bulb is brighter? A. A B. B. C. Both the same
 Last tim Bgin circuits Rsistors Circuits Today Rsistor circuits Start rsistor-capacitor circuits Physical layout Schmatic layout Tu. Oct. 13, 2009 Physics 208 Lctur 12 1 Tu. Oct. 13, 2009 Physics 208 Lctur
Last tim Bgin circuits Rsistors Circuits Today Rsistor circuits Start rsistor-capacitor circuits Physical layout Schmatic layout Tu. Oct. 13, 2009 Physics 208 Lctur 12 1 Tu. Oct. 13, 2009 Physics 208 Lctur
ELECTRON-MUON SCATTERING
 ELECTRON-MUON SCATTERING ABSTRACT Th lctron charg is considrd to b distributd or xtndd in spac. Th diffrntial of th lctron charg is st qual to a function of lctron charg coordinats multiplid by a four-dimnsional
ELECTRON-MUON SCATTERING ABSTRACT Th lctron charg is considrd to b distributd or xtndd in spac. Th diffrntial of th lctron charg is st qual to a function of lctron charg coordinats multiplid by a four-dimnsional
As the matrix of operator B is Hermitian so its eigenvalues must be real. It only remains to diagonalize the minor M 11 of matrix B.
 7636S ADVANCED QUANTUM MECHANICS Solutions Spring. Considr a thr dimnsional kt spac. If a crtain st of orthonormal kts, say, and 3 ar usd as th bas kts, thn th oprators A and B ar rprsntd by a b A a and
7636S ADVANCED QUANTUM MECHANICS Solutions Spring. Considr a thr dimnsional kt spac. If a crtain st of orthonormal kts, say, and 3 ar usd as th bas kts, thn th oprators A and B ar rprsntd by a b A a and
Chapter 13 Aggregate Supply
 Chaptr 13 Aggrgat Supply 0 1 Larning Objctivs thr modls of aggrgat supply in which output dpnds positivly on th pric lvl in th short run th short-run tradoff btwn inflation and unmploymnt known as th Phillips
Chaptr 13 Aggrgat Supply 0 1 Larning Objctivs thr modls of aggrgat supply in which output dpnds positivly on th pric lvl in th short run th short-run tradoff btwn inflation and unmploymnt known as th Phillips
Introduction to Condensed Matter Physics
 Introduction to Condnsd Mattr Physics pcific hat M.P. Vaughan Ovrviw Ovrviw of spcific hat Hat capacity Dulong-Ptit Law Einstin modl Dby modl h Hat Capacity Hat capacity h hat capacity of a systm hld at
Introduction to Condnsd Mattr Physics pcific hat M.P. Vaughan Ovrviw Ovrviw of spcific hat Hat capacity Dulong-Ptit Law Einstin modl Dby modl h Hat Capacity Hat capacity h hat capacity of a systm hld at
4. (5a + b) 7 & x 1 = (3x 1)log 10 4 = log (M1) [4] d = 3 [4] T 2 = 5 + = 16 or or 16.
![4. (5a + b) 7 & x 1 = (3x 1)log 10 4 = log (M1) [4] d = 3 [4] T 2 = 5 + = 16 or or 16. 4. (5a + b) 7 & x 1 = (3x 1)log 10 4 = log (M1) [4] d = 3 [4] T 2 = 5 + = 16 or or 16.](/thumbs/86/93688166.jpg) . 7 7 7... 7 7 (n )0 7 (M) 0(n ) 00 n (A) S ((7) 0(0)) (M) (7 00) 8897 (A). (5a b) 7 7... (5a)... (M) 7 5 5 (a b ) 5 5 a b (M)(A) So th cofficint is 75 (A) (C) [] S (7 7) (M) () 8897 (A) (C) [] 5. x.55
. 7 7 7... 7 7 (n )0 7 (M) 0(n ) 00 n (A) S ((7) 0(0)) (M) (7 00) 8897 (A). (5a b) 7 7... (5a)... (M) 7 5 5 (a b ) 5 5 a b (M)(A) So th cofficint is 75 (A) (C) [] S (7 7) (M) () 8897 (A) (C) [] 5. x.55
PHA 5127 Answers Homework 2 Fall 2001
 PH 5127 nswrs Homwork 2 Fall 2001 OK, bfor you rad th answrs, many of you spnt a lot of tim on this homwork. Plas, nxt tim if you hav qustions plas com talk/ask us. Thr is no nd to suffr (wll a littl suffring
PH 5127 nswrs Homwork 2 Fall 2001 OK, bfor you rad th answrs, many of you spnt a lot of tim on this homwork. Plas, nxt tim if you hav qustions plas com talk/ask us. Thr is no nd to suffr (wll a littl suffring
Introduction to Multicopter Design and Control
 Introduction to Multicoptr Dsign and Control Lsson 05 Coordinat Systm and Attitud Rprsntation Quan Quan, Associat Profssor _uaa@uaa.du.cn BUAA Rlial Flight Control Group, http://rfly.uaa.du.cn/ Bihang
Introduction to Multicoptr Dsign and Control Lsson 05 Coordinat Systm and Attitud Rprsntation Quan Quan, Associat Profssor _uaa@uaa.du.cn BUAA Rlial Flight Control Group, http://rfly.uaa.du.cn/ Bihang
Procdings of IC-IDC0 ( and (, ( ( and (, and (f ( and (, rspctivly. If two input signals ar compltly qual, phas spctra of two signals ar qual. That is
 Procdings of IC-IDC0 EFFECTS OF STOCHASTIC PHASE SPECTRUM DIFFERECES O PHASE-OLY CORRELATIO FUCTIOS PART I: STATISTICALLY COSTAT PHASE SPECTRUM DIFFERECES FOR FREQUECY IDICES Shunsu Yamai, Jun Odagiri,
Procdings of IC-IDC0 EFFECTS OF STOCHASTIC PHASE SPECTRUM DIFFERECES O PHASE-OLY CORRELATIO FUCTIOS PART I: STATISTICALLY COSTAT PHASE SPECTRUM DIFFERECES FOR FREQUECY IDICES Shunsu Yamai, Jun Odagiri,
Calculus II (MAC )
 Calculus II (MAC232-2) Tst 2 (25/6/25) Nam (PRINT): Plas show your work. An answr with no work rcivs no crdit. You may us th back of a pag if you nd mor spac for a problm. You may not us any calculators.
Calculus II (MAC232-2) Tst 2 (25/6/25) Nam (PRINT): Plas show your work. An answr with no work rcivs no crdit. You may us th back of a pag if you nd mor spac for a problm. You may not us any calculators.
On the Hamiltonian of a Multi-Electron Atom
 On th Hamiltonian of a Multi-Elctron Atom Austn Gronr Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA Octobr 29, 2010 1 Introduction In this papr, w will xhibit th procss of achiving th Hamiltonian for an lctron gas. Making
On th Hamiltonian of a Multi-Elctron Atom Austn Gronr Drxl Univrsity Philadlphia, PA Octobr 29, 2010 1 Introduction In this papr, w will xhibit th procss of achiving th Hamiltonian for an lctron gas. Making
Coupled Pendulums. Two normal modes.
 Tim Dpndnt Two Stat Problm Coupld Pndulums Wak spring Two normal mods. No friction. No air rsistanc. Prfct Spring Start Swinging Som tim latr - swings with full amplitud. stationary M +n L M +m Elctron
Tim Dpndnt Two Stat Problm Coupld Pndulums Wak spring Two normal mods. No friction. No air rsistanc. Prfct Spring Start Swinging Som tim latr - swings with full amplitud. stationary M +n L M +m Elctron
