University of Groningen. Electrodialytic recovery of acids and bases Visser, Cornelis
|
|
|
- Darrell Watson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unversty of Gronngen Eletrodlyt reovery of ds nd bses Vsser, Cornels IMPORTANT NOTE: You re dvsed to onsult the publsher's verson (publsher's PDF) f you wsh to te from t. Plese hek the doument verson below. Doument Verson Publsher's PDF, lso known s Verson of reord Publton dte: 2001 Lnk to publton n Unversty of Gronngen/UMCG reserh dtbse Ctton for publshed verson (APA): Vsser, C. (2001). Eletrodlyt reovery of ds nd bses: Multomponent mss trnsfer desrpton [Gronngen]: Unversty of Gronngen Copyrght Other thn for strtly personl use, t s not permtted to downlod or to forwrd/dstrbute the tet or prt of t wthout the onsent of the uthor(s) nd/or opyrght holder(s), unless the work s under n open ontent lense (lke Cretve Commons). Tke-down poly If you beleve tht ths doument brehes opyrght plese ontt us provdng detls, nd we wll remove ess to the work mmedtely nd nvestgte your lm. Downloded from the Unversty of Gronngen/UMCG reserh dtbse (Pure): For tehnl resons the number of uthors shown on ths over pge s lmted to 10 mmum. Downlod dte:
2 3 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes Introduton In ths hpter the mss trnsfer equtons re ntrodued, whh re used to model the movement of ons nd wter n multomponent eletrolytes nd eletrolytemembrne systems. The hgh on onentrtons present n both the eletrolyte solutons nd nsde the membrne led to strong non-deltes n the heml potentl grdents nd to sgnfnt on-on frton ntertons. To nlude these effets nto the mss trnsfer model, the Mwell-Stefn equtons were hosen. The drwbk of usng these equtons rther thn the more smple Nernst-Plnk equtons, s tht for the omple multomponent eletrolyte-membrne systems under nvestgton, lot of trnsport prmeters re ntrodued. For onentrted eletrolytes, these prmeters re known [1]. In seton t s shown tht from lterture some lmted estmtes of the dffuson oeffents n eletrodlyss membrnes n be mde, but tht rgorous mesurements re neessry to obtn the requred ury. Ths leds to lrge mount of dffuson eperments, desrbed n seton 3.2, from whh the prmeters were obtned. The resultng dffuson oeffents found for the dfferent ED membrnes re dsussed n seton The Mwell Stefn desrpton of mss trnsfer The Mwell-Stefn equtons re most esly understood s fore blne on the seprte spees n mture: drvng fore on spees frton fores wth other spees In the systems onsdered here, there re three ontrbutons to ths grdent. The frst s due to the grdent of the tvty (whh s relted to onentrton). The seond s the effet of the eletrl grdent; ths only pples to ons. The thrd s the effet of pressure grdent. Ths term s mportnt n severl eperments wth pressure dfferene ross membrne. As formul: F RT ln z F φ V p (3.1) A omplete dervton of the thermodynm drvng fore for homogeneous membrne phse s gven n [2, p.177]. Here, s the tvty of. F s the Frdy onstnt, z the hrge number of nd V the prtl molr volume of. 37
3 Chpter 3 The rght sde of the equtons ontns terms for the frton between spees nd eh of the other spees. Ths frton s tken to be proportonl to the lol mount of (gven by ts mole frton ) nd to the dfferene n velotes ( u u ). Epressed s fores per mole of ths beomes: n ( u u ) F ζ (3.2) 1 Here, ζ s frton oeffent; there s one suh oeffent for eh pr of spees. The omplete equton beomes: RT ln n ( u u ) z F φ V p ζ (3.3) 1 For every omponent, equton 3.3 s defned. However, these equtons only ontn ( n 1) veloty dfferenes, so one of them s superfluous. For prtl purposes, equton 3.3 s modfed n severl wys: The frton oeffents re repled by dffusvtes: ζ RT The velotes re repled by flues: u N t The whole equton s multpled by ( 1) nd by to obtn fores per mole of mture: ln zf RT V φ RT p n ( N N ) 1 t (3.4) Wth some smplftons ppled to equton 3.4, t n be shown tht the Mwell-Stefn redues nto the Nernst-Plnk equton, whh s ommonly used n eletrohemstry. Consder equton 3.5: 38
4 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes 39 ( ) n RT z 1 t N N φ F (3.5) The drvng fores were obtned by gnorng: non-deltes (ths s vld only n dlute solutons) the pressure grdent, whh re mostly neglgble nsde eletrolytes. In dlute solutons, on-on ntertons n be gnored. The remnng frtons re the on-wter ntertons. If we further ssume N w 0, equton 3.5 beomes: w t w RT z N φ F wth (for dlute solutons): D w Ths n be wrtten s the Nernst-Plnk equton: φ RT z D F N (3.6) Mss trnsfer n multomponent eletrolytes In Mwell-Stefn equton for multomponent eletrolyte solutons, the pressure term from equton 3.4 n be gnored. Development of the tvty term (epressed for the z-dreton) of the drvng fores leds to: dz d ln d z f d ) ln( d z f d f f d z d f ) ( ) ( 1 1 n d z d f f d z d d z d f d z d f f n n ln δ δ
5 Chpter 3 n 1 Γ 1 d d z For multomponent mtures, the omplete equton beomes: n Γ 1 d dz zf RT dφ dz n ( N N ) 1 t (3.7) (3.8) From severl vlble multomponent models [4], the grdents of the sngle spees tvty oeffents n be obtned whh re needed n the lulton of the thermodynm orreton ftor mtr, Γ. In sngle eletrolyte, the thermodynm orreton ftor redues nto: d ln f ± Γ± ± d± 1 (3.9) From (more smple) sngle eletrolyte models [4], the men eletrolyte tvty oeffents, needed n equton 3.9 n be lulted Mss trnsfer n eletrodlyss membrnes When mss trnsfer n membrnes s onsdered, two pprohes n be followed: strutured model nd homogeneous model. A strutured model s pproprte when pore szes re lrge nd vsous flow beomes onsderble, for emple n ultrfltrton membrnes [7]. Eletrodlyss membrnes n be onsdered homogeneous, when the pore sze s onsdered. The o-on sorpton mesurements, desrbed n Chpter 2, show tht the hrge dstrbuton n eletrodlyss membrnes s less homogeneous thn mght be epeted. The sorpton behvour suggests regons wth hgh onentrtons of fed hrges, provdng Donnn (oon) eluson, nd regons whh hve omposton omprble to the eternl eletrolytes. By usng homogeneous mss trnsfer model, these onentrton vrtons re verged. The mss trnsfer equtons re obtned by nludng the membrne phse s subsequent omponent, hvng zero flu. Due to the dffulty of fndng (sngle spees) tvty oeffents for the membrne phse (Chpter 2), the tvty term smplfed nto the mole frton grdents. We then obtn: 40
6 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes z F RT φ V RT p n ( N N ) 1 t t m m N (3.10) In equton 3.10, the number of omponents n nludes ll ons nd wter, but not the membrne phse; t s nluded by the etr term on the rght-hnd sde. For omplete desrpton of the system, 1 to n equtons re needed Membrne dffusvtes: lterture dt Multomponent mss trnsfer dt for eletrolyte-membrne systems s srely found n lterture, espelly mesurements t hgh eletrolyte onentrtons. For the Nfon membrne, dffusvty dt s reported for NCl [9,11] nd NOH [12] systems. In [11] nd [12], Nfon 120 membrne s nvestgted n NCl nd NOH up to 4 M, t 298, 313 nd 333 K. The onverson of the orgnlly reported phenomenologl oeffents nto multomponent dffuson oeffent, ws tken from [13]. For N/Cl, negtve vlues re reported for onentrtons between 1 nd 4 M. Cl /m s negtve bove 2 M. The hgh vlue of OH /m t 2 M lso drops below zero bove 3.5 M. In [9], Nfon 110 (non-renfored) s mesured n NCl up to 5 M t 298 K. The results from the two soures, nd those from ths work re shown fgure 3.1 nd 3.2. Eept for the vlue of N/Cl t 1.5 M, -7E-09 m 2 s 1, the dffuson oeffents t 1.5 M eternl onentrton re shown, for omprson wth the oeffents reported n ths hpter (seton 3.3.2). The ppled urrent denstes n eletro-osmoss or ED eperments, were low: 55 [9] nd 23 [11] (A m 2 ), whh my queston the pplblty of the dt to hgh-urrent ED. It n be epeted [8], tht the membrne-phse dffuson oeffents wll be omprble to ther lqud-phse equvlents, orreted wth some sort of tortuosty ftor, τ. Ths ftor, n turn, n be obtned from the vod frton, ε : 0 τ wth: 1.5 τ ε (3.11) In equton 3.11, the supersrpt 0 denotes the free soluton dffusvty. It s shown [8] tht the equton n be used to predt the ntertons wth wter (, w,,w nd w, m ) from the eletrolyte vlues. The predtons show generlly lower dffusvtes thn the ones found n the Nfon membrne, both n the referenes nd n ths work. 41
7 Chpter 3 / m 2 s 1 1e-8 1e-9 1e-10 Nrebsk [11] Pnturo [9] Ths work 1e-11 N /Cl N /H 2 O Cl /H 2 O N /m Cl /m H 2 O/m Fgure 3.1: Multomponent dffuson oeffents from lterture t 1.5 M nd ths work for the system Nfon-NCl. 1e-8 Nrebsk [12] Ths work / m 2 s 1 1e-9 1e-10 1e-11 N /OH N /H 2 O N /m OH /H 2 O OH /m H 2 O/m Fgure 3.2: Multomponent dffuson oeffents from lterture t 1.5 M nd ths work for the system Nfon-NOH. 42
8 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes 3.2 Estmton of membrne dffuson oeffents by modellng sets of eperments Ths seton desrbes the method wth whh membrne dffusvty oeffents were lulted. Per eletrolyte-membrne system, s dffusvtes nvolve (t lest) s dfferent epermentl mesurements. In the net setons, the seleted dffuson eperments re desrbed, ombned wth the mthemtl models needed for the optmston lultons Choe of the eperments Sttergood nd Lghtfoot [5] reported the determnton of dffusvtes of sulfonted polystyrene groups on polyethylene-type ton-ehnge membrne. The mesurements were mde n 0.1 N AgNO 3 nd NCl. The low eternl onentrtons enbled (three) o-on ntertons to be gnored. Four nterton prmeters were determned, nludng the sotope self-dffuson oeffent, wth four eperments: eletro-osmot wter trnsport, eletrl ondutvty, hydrodynm permeblty, nd ounter-on self-dffuson. In smlr nvestgton, Pnturo nd Bennon [9] report the equlbrum nd trnsport prmeters of NCl n Nfon 110 membrne, t fve onentrton levels up to 5.0 M. The hosen eperments were: dlyss, eletrodlyss * nd reverse osmoss. In eh eperment, both onentrton nd volume hnges were mesured, resultng n s epermentl dt ponts, from whh the s dffusvtes were lulted by n optmston method. Nrebsk et l mesured dffuson oeffents for the system Nfon 120-NCl [11], nd Nfon 120-NOH [12], t three tempertures nd t dfferent onentrton levels, up to 4 M. The s dffuson eperments, desrbed n [10] were: membrne resstne, eletro-osmot volume flow, ell emf nd pressure-drven volume flow. In dlyss eperment, osmot volume flow nd slt dffuson were mesured. Due to the hgh eletrolyte onentrtons whh re present n the eletrodlyss eperments, t n be epeted tht ll s ntertons, nludng o-on ntertons, present n sngle eletrolyte-membrne system hve to be tken nto ount. Thus (mnmum) set of s mesurements hs to be performed. By hoosng set of eperments tht ontns (ll) three dfferent drvng fores, nd n whh ounter- nd o-on nd wter flues re mesured, t s epeted tht ll s dffusvtes n be lulted. * The eletrodlyss eperments derbed n the pper re (n terms of eletrodes, urrent denstes nd sze) more omprble to our eletro-osmoss eperment rther thn the eletrodlyss eperments desrbed n ths thess. 43
9 Chpter 3 Intlly, four eperments yeldng s prmeters were rred out: Dlyss (resultng n slt dffuson flu nd n osmot wter flu), eletro-osmoss (volume flu nd eletrolyte onentrton hnge), membrne resstne nd pressure-drven volume flow. The drwbk of ths set ws, tht t only works for systems wth ether HCl or NCl, beuse the Ag/AgCl eletrodes n eletro-osmoss only work n hlorde-ontnng eletrolytes. It lso turned out tht the onentrton hnge n eletro-osmoss ws too smll to yeld reproduble nformton on o-on lekge, due to the short eperment tmes nd low urrent densty. To fll n the lkng mesurements, the onentrton-dependent on nd wter flues, mesured n the ED eperments (desrbed n Chpter 4), were nluded n the dt set. Another dvntge of nludng the hgh-urrent densty eperments nto the dt set s tht possble dependeny of the membrne dffusvtes on the urrent densty s tken nto ount. The set of eperments s gven n tble 3.1. The hosen eletrolytes re those wth whh the spef membrne s ontted durng the ED eperment seres (Chpter 4). Tble 3.1: The set of dffuson eperments. System Dffuson dlyss Eletroosmoss Resstne Pressure Eletrodlyss ARA - HCl ARA - H 2 SO 4 - AW - HCl AW - H 2 SO 4 - Nfon - HCl Nfon - H 2 SO Nfon - NCl - Nfon - NOH - Nfon - N 2 SO Dffuson Dlyss In ths prtl eperment dffusonl flues re mesured of sngle eletrolytes nd wter. At the strt, onentrted eletrolyte s present t one sde of the membrne, pure wter s present t the other sde. Due to onentrton-dependent o-on sorpton, o-on onentrton grdent wll be present nsde the membrne. As the onentrton of fed hrges s ssumed to be onstnt, the ounter-ons wll hve the sme onentrton grdent. The dfferent mobltes of the ons wll led to (smll) eletrl potentl grdent, usng the ons to move wth the sme flu. Wter, hvng n opposte onentrton grdent over the membrne, s 44
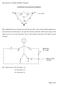
10 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes epeted to move n the other dreton. The wter flu n be mesured from volume hnges, or n be obtned from mole blnes. The enounter of the wter flu wth the eletrolyte flu s epeted to be governed by wter-on nd wtermembrne ntertons. Epermentl Before eh dffusonl prtl eperment, the membrnes re equlbrted n severl steps. If neessry, ons from dfferent eletrolytes re removed frst, nd repled by the rght ounter-on. The membrne n now be equlbrted n the eletrolyte wth the sme omposton s n the dffuson eperment. In dffuson dlyss, membrnes re pled n n eletrolyte hvng hlf the onentrton of the eletrolyte used n the onentrted omprtment, beuse n the eperment t s ontted wth pure wter s well. The followng method s used, n whh the durton of eh step s t lest one hour: 1. 2 (Mllpore) Mll-Q wter to remove o-ons from the membrne M eletrolyte to obtn the rght ounter-on form 3. gn 1 Mll-Q wter to remove (eess) o-ons 4. 2 the eletrolyte wth the sme onentrton used n the eperment, eept n dffuson dlyss, s stted bove. The epermentl setup s shown n fgure 3.3. The ell used s the sme s n the eletrodlyss eperments (Chpter 4), n ths se onsstng of two omprtments seprted by one ED-membrne. The membrne re s 0.01 m 2. No eletrl urrent s ppled. From the strred vessels, n eletrolyte s pumped through one omprtment, pure wter s pumped through the other. The pure wter hs Mll-Q qulty. 45
11 Chpter 3 Fgure 3.3: Epermentl setup for dffuson dlyss mesurements. The strtng volumes re 2.0 dm 3 for both fluds. The flow rte s the sme s n ED eperments, resultng n the sme flud flm thkness. The temperture of the fluds s kept t 25 ± 0.5 C by mens of wter bth. In both flows the temperture nd the ondutvty re mesured, nd dt re stored n omputer. As the proess took ple rther slowly, the durton of the eperments ws etended to 72 hours. After 15 mnutes nd fter 72 hours, smples were tken from both flows. By mens of ttrton (d, bse or hlorde) nd ondutvty mesurements (N 2 SO 4 ), strt nd fnl onentrtons were determned. After ompletely emptyng the setup, the fnl flud volumes were mesured. The eperments re lsted n tble 3.2. Tble 3.2: Mesured systems n dffuson dlyss System duplo s (mol m 3 ) Nfon - HCl Nfon - H 2 SO Nfon - NCl Nfon - NOH Nfon - N 2 SO ARA - HCl ARA - H 2 SO AW - HCl AW - H 2 SO
12 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes Results The lulton of men eperment flues, nd olleted epermentl dt n be found n Append I.1. The results for eletrolyte nd wter flues re shown n fgure 3.4 nd 3.5 (dt from tble I.3). N slt / mol m 2 s 1 5.0e-5 4.0e-5 3.0e-5 2.0e-5 1.0e-5 b d e 0.0 Nfon ARA Fgure 3.4: Mesured eletrolyte flues through Nfon, ARA nd AW membrnes. The eletrolytes represented by the brs re: HCl (), H 2 SO 4 (b), NCl (), NOH (d), N 2 SO 4 (e). AW 8.0e-3 b N w / mol m 2 s 1 6.0e-3 4.0e-3 2.0e-3 d e 0.0 Nfon ARA Fgure 3.5: Mesured wter flues through Nfon, ARA nd AW membrnes. Legend: the sme s n fgure 3.4. AW 47
13 Chpter 3 Modellng The model nvolves the lulton of the men flues of ons nd wter through n eletrodlyss membrne. The sme model used for ED smultons, outlned n seton 4.3, n be ppled here. Ths model onssts of membrne lyer wth flud flms on ether sde. The (boundry) ondtons n the se of dffuson dlyss re: 1. No urrent s ppled nd eqully mny negtve nd postve ons re trnsported. 2. The men onentrtons grdents, sne the flues to be lulted re men flues. 3. The thkness of the flud flms s ssumed to be the sme s n ED modellng, beuse the sme flow rte ws used. 4. The men eperment tempertures Eletro-osmoss In the eletro-osmoss eperment, the volume flu through n eletrodlyss membrne s nvestgted. An eletrl urrent drves ons through the membrne. In ton-ehnge membrne, tons wll rry lmost ll of the urrent, n n non-ehnge membrne the nons. Wth the movng ons, wter s moved through the membrne, resultng n mesurble volume hnge of both omprtments. Reversble Ag/AgCl eletrodes re used. The ell potentl s kept low to prevent gs-evoluton retons to nfluene the volume hnges. The volume hnge n be red from pllres mounted on top of the ell. Epermentl A shemt pture of the setup s shown n fgure 3.6. The membrne, wth dmeter d m 3.19 m, s pled between two omprtments of ml eh (l b h m). An Ag/AgCl eletrode s pled n both omprtments. The eletrodes onsst of slver wre (d 1 mm) wth n AgCl lyer, obtned from thod otng n 1 M NCl. Two pllres (d 1.44 mm) re pled upon the omprtments, whh re strred by two Teflon mgnet strrers (d s 2.0 m). A PT- 100 probe s pled n the node omprtment for temperture regstrton. Before eh eperment, the membrnes were equlbrted s eplned n seton After fttng the membrne, the omprtments were flled wth the pproprte eletrolyte, nd were losed rtght. The pllres were pled, flled wth eletrolyte. In ll eperments (lsted n tble 3.4) onstnt urrent of I A ( 76.3 A m 2 ) ws ppled. The volume hnges, whh were red from the pllres, nd the temperture were reorded for 2 hours. For eh eletrolyte- 48
14 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes membrne system, two membrne smples were mesured twe, resultng n n verge flu lulted from four eperments. PT 100 pllry CEM Fgure 3.6: Cell used for eletro-osmoss mesurements. At both slver hlorde eletrodes, the followng hlf reton tkes ple: Ag(s) Cl (q) AgCl(s) e (1) E (V) Possble sde retons re: 2 H 2 O(l) 4 H (q) O 2 (g) 4 e (2) E (V) 2 H 2 O(l) 2 e 2 OH (q) 2 H 2 (g) (3) E (V) As the sde retons nvolve gs evoluton whh results n volume hnges, the potentl dfferene should not eeed the theoretl vlue t whh they strt to our. The Nernst equton ws used to lulte these eletrode potentls for the dfferent eletrolytes. The results re lsted n tble 3.3. Tble 3.3: Atvtes nd Nernst potentls for the three possble retons, from whh V m ws lulted System Cl H OH E 1 (V) E 2 (V) E 3 (V) V m (V) 0.5 M NCl E E M NCl E E M NCl E E M HCl E
15 Chpter 3 Other ontrbutons to the overll ell potentls re lqud flm nd membrne resstne nd overpotentls, resultng n hgher epermentl potentls. Results For the system Nfon-0.5 M NCl, the pllry volumes from the 4 eperments re plotted, s ontnuous lnes, n fgure mesurements T effet V / ml t / s Fgure 3.7: Result of eletro-osmoss mesurement (for Nfon-0.5 M NCl). The lnes show the four mesurements. The upper hlf represents volume nrese (from wter nflu) n the thode omprtment, the lower hlf shows volume derese n the thode omprtment. The dotted lnes show the effet of temperture rse on the verged mesurements. The lnes ndte good reprodublty (< 5 % error). As n be seen n fgure 3.7 nd n tble 3.4, the mesured volume nrese n one omprtment eeeds the volume derese n the other. Ths n be eplned by: 1. The eletrl resstnes use temperture rse of bout 1 C durng eh eperment, resultng n slght epnson of both eletrolytes. From the reorded tempertures, ths effet s tken nto ount n the lulton of the verge flues by usng temperture-dependent wter densty. 2. Ar (smll but unknown quntty) present n the omprtments epnds even more durng temperture rse. Ths effet nreses the mesured flu n the pllry of the omprtment where the wter s flowng nto, nd dereses the mesured flu n the other. Ths observed effet ould not be nluded n the lultons, but the dfferene n the flues nels n the model. By tkng ount of the epnson (though less thn tht of wter) of the PMMA ell. 50
16 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes Tble 3.4: Averge volume flues (J) n eletro-osmoss n thode nd node omprtment nludng temperture-hnge orreton, wth stndrd devtons nd men eperment temperture. Eletrolyte J thode (ml hr 1 ) σ J node (ml hr 1 ) σ T vg ( C) Nfon ( C) 0.5 M NCl M NCl M NCl M HCl ARA 1.0 M HCl AW 1.0 M HCl Modellng The prmeter to be modelled n eletro-osmoss s the volume-hnge whh results from membrne flues. Agn we use the ED smulton model, outlned n seton 4.3. For eletro-osmoss, the boundry ondtons for the model re: strt, I A, A m 7.99E 04 m 2, T T vg. The thkness of the flud flms ws obtned from survey of mss trnsfer desrptons n (ylndrl) strred ells, desrbed n [15, p.44-47]. The Sherwood number s lulted from: p Sh ARe S (3.12) The prmeters A nd p re tken from [14], nvolvng mss trnsfer mesurements n the lmnr regon. The Reynolds number nd the Shmdt number re lulted from: Wth: ρ bnd Re η b 2 s ηb S ` (3.13) ρ b D ρ b eletrolyte densty kg m 3 η b eletrolyte vsosty P s n strrer speed (4.5 s 1 ) s 1 d s strrer dmeter (2.0 m) m 51
17 Chpter 3 D Fk dffusvty oeffent m 2 s 1 The flm thkness s obtned from: d d flm (3.14) Sh n whh d s the ell dmeter; n ths ell d 5.54 m. The resultng flm thkness s summed n tble 3.5. Tble 3.5: Clulted flm thkness, used n the eletro-osmoss model. Eletrolyte d flm (m) 0.5 M NCl 1.22E M NCl 1.23E M NCl 1.26E M HCl 1.62E 04 For the Nfon systems, the ontrbuton of the flm-lyer resstne to the overll mss-trnsfer resstne rnges from 11% n 2 M NCl to 30 % n 0.5 M NCl. In 1 M HCl ths ontrbuton s 19 %. The mole flues, resultng from the (ED) model, re onverted nto volume flues, usng prtl molr volumes of the nvolved spees. Vlues for V re gven n tble 4.3. The eletrode retons, the onverson of AgCl nto Ag nd Cl, or ve vers, uses smll volume hnge, whh s tken nto ount. The molr volume of sold AgCl 2.58e 05 (m 3 mol 1 ) nd the molr volume of queous AgCl 2.25e 05 (m 3 mol 1 ) Resstne In ths eperment we mesure the AC resstne of n ED membrne n sngle eletrolyte-membrne system. The resstne of n on-ehnge membrne s determned by the onentrtons of the ons nsde the membrne. At low eternl onentrtons, the o-on onentrton n the membrne s low, whh leves the ounter-ons to determne the membrne resstne. As the eletrolyte onentrton nreses, o-ons wll enter the membrne resultng n deresed membrne resstne. At hgh eletrolyte onentrtons, on-on ntertons n the membrne beome ppreble, whh my result n n nresed the resstne. It s therefore ler tht o-ons must be nluded n the mss trnsfer model. 52
18 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes Epermentl Three types of membrnes re mesured n up to 5 eletrolytes. Eh membrneeletrolyte ombnton ws mesured t 4 or 5 onentrtons. The epermentl setup onssts of resstne ell, entrfugl pump, n utomt Phlps PM 6303A RCL meter, PT-100 temperture sensor. The eletrolyte s rulted through the ell by pump. The temperture s kept onstnt t 25.0 C by usng wter bth, whh ools the het produed by the pump. In fgure 3.8 the setup s dsplyed. RCL meter Wter bth Resstne ell pump PT 100 Fgure 3.8: Epermentl setup of the resstne mesurements. The resstne ell ontns hmber, wth dmeter of 8.03 mm, wth pltnum (blk) eletrodes on ether sdes. The eletrolyte flow runs prllel to membrne smple whh n be lmped between the two hlves of the ell. As the mesured resstne onssts of the sum of eletrolyte nd membrne resstne, the eletrolyte resstne s mesured seprtely wth the membrne removed from the ell. Due to the smll re of the membrne whh s mesured, up to 10 smples of eh membrne were mesured, from whh n verge resstne ws lulted. The equlbrton of the smples n the eletrolyte nvolved the sme proedure s 53
19 Chpter 3 eplned n seton Wth eh new eletrolyte or dfferent onentrton, the whole setup ws refreshed (t lest 3 tmes) untl onstnt soluton resstne ws obtned t 25.0 C. After set of three membrnes were mesured, the soluton ws mesured gn to ensure the resstne hd remned onstnt. The verge resstnes of ll membrne-eletrolyte systems re gven n tble 3.6. The mesurement errors, epressed n perentges, re gven n tble 3.7. Tble 3.6: Epermentl membrne resstnes (R m ), gven n ohm (Ω). System (M) 0.25 (M) 0.50 (M) 0.75 (M) 1.0 (M) 1.25 (M) 2.0 (M) 4.0 Nfon - HCl Nfon - H 2 SO Nfon - NCl Nfon - NOH Nfon - N 2 SO ARA - HCl ARA - H 2 SO AW - HCl AW - H 2 SO Tble 3.7: Men error perentges of eh membrne-eletrolyte resstne mesurement. Eletrolyte 3Nfon % ARA % AW % HCl H 2 SO NCl 3.0 NOH 1.5 N 2 SO The results of Nfon n NCl n be ompred to Nfon 120 ondutvtes, reported n [11]. As tble 3.8 shows, the ondutvty of Nfon 450 n NCl s hgher over the mesured onentrton rnge. 54
20 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes Tble 3.8: Comprson of Nfon 450 ondutvty n NCl wth Nfon 120 [11] t T 298K. NCl (mol m 3 ) K Nfon 120 (S m 1 ) K Nfon 450 (S m 1 ) Modellng As the resstnes to be modelled re pure membrne resstnes, mesured usng very smll AC urrents, the flud flms (whh re smll nywy beuse of turbulene n the ell) n be left out of the model. The sme flud s pumped through the two ell hmbers, onsequently the onentrton grdents n be left out of the model equtons. We need three equtons () to desrbe the four omponent (n1; n3) membrne system: zf RT n dφ dz ( N N ) 1 t t m m N In these equtons, the eletrl potentl grdent n be wrtten s: (3.15) dφ V wth: V I R m F A m ( z N z N ) R m (3.16) dz d m In equton 3.16, d m s the membrne thkness nd A m s the membrne re. By usng ths substtuton for V n the Mwell-Stefn equtons, R m n be lulted s funton of physl onstnts, membrne sze nd membrne dffusvtes by elmnton of the flues. The result of the dervton s: Rm wth the onstnts: 1 4b2 2b4 1b4 2b3 4b1 3b2 (3.17) z zf RTd m 2 A m z zf b3 RTd m 2 A m 55
21 Chpter 3 56 m m RTd A z F m m RTd A z b F w w t w 1 wm m w w t 2 w w t w 1 wm m w w t 4 b 2 w t w 1 wm m w w m t m w t w t 4 2 w t w 1 wm m w w m t m w t w t 2 b In these equtons, ll s membrne dffuson oeffents tke prt n the model. The gven equtons n be used for both ton-ehnge membrnes nd nonehnge membrnes Pressure-drven permeton In ths prtl eperment, eletrolyte nd wter volume flues through pressursed membrne re mesured. Intlly, eletrolyte or wter s present t both sdes of the membrne. On one sde the flud pressure s nresed n three steps, up to 8 br. On the other sde, permeton s mesured usng pllry. The mount of flud tht psses through the membrne durng the eperment, s very smll. As result hnges n the ompostons of the fluds on the two sdes re neglgble. Three types of membrnes were mesured, n eletrolytes wth dfferent onentrtons. The Nfon membrne ws ddtonlly mesured n H - nd N -form wth pure wter.
22 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes Epermentl The setup s shown n fgure 3.9. The eletrolyte s present n 500 ml vessel, whh s pressursed from ntrogen ylnder. The pressure s mesured nd dusted f neessry. Pressure red-out pllry N 2 ylnder Membrne ell Fgure 3.9: Epermentl setup of the pressure permeton mesurements. The equlbrted membrne ws pled n stnless steel Mllpore XX flter holder (fgure 3.10), equpped wth Vton O-rng. The effetve membrne dmeter s 47 mm. On the tmospher sde, the module ws flled wth eletrolyte or wter nd 0.1 ml pllry ws ftted for volume-flu mesurement. Fgure 3.10: Mllpore 47 mm membrne flter holder. 57
23 Chpter 3 Eh membrne-eletrolyte system ws mesured t three pressure dfferenes. At eh pressure, the mesurement lsted t lest 40 mnutes. The mesured systems n be found n tble I.4 nd I.5 n Append I nd n tble 3.9. For eh system, the verge flu of up to 4 dfferent membrne smples ws tken. For the system Nfon-NOH, the mesured flues re shown n fgure 3.11, s funton of pressure dfferene. The lnes represent the slopes of the mesurements, whh re tbulted n tble 3.9. Gong from pure wter to 2.0 M NOH, derese of the flu n be observed. The deresed membrne swellng s epeted to be usng ths effet N form 0.5 M 1.0 M M J V / ml hr P / 10 5 P Fgure 3.11: Volume flues mesured wth the Nfon-NOH system t dfferent eternl onentrtons. Symbols: see legend; the lnes represent lner fts. The vlue of dj V /dp ws obtned by fttng the mesured vlues (gven n ppend tble I.4 nd I.5) to strght lne gong through the orgn, by tkng nto ount the stndrd devtons. The numbers were lulted for 1 m 2 membrne. The results, gven n tble 3.9, ndte n verge mesurement-error of 5%. Ths nludes H 2 SO 4 mesurements, whh show errors of up to 15%. 58
24 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes Tble 3.9: Conentrton dependeny of dj V /dp, epressed per m 2 membrne. System (mol m 3 ) dj V /dp (m 3 P 1 s 1 ) Nfon H form E E 16 HCl E E E E 16 H 2 SO E E E E 15 N form E E 17 NCl E E 16 NOH E E E E E E 17 N 2 SO E E 18 ARA HCl E E 17 H 2 SO E E 16 AW HCl E E 17 H 2 SO E E E E 16 The results for Nfon from tble 3.9 re shown grphlly n fgure It s ler tht (wter) flues re hgher n H -form membrne thn n N -form membrne. Ths result s n greement wth: 1. The eletro-osmoss eperments (see fgure 3.13) show hgher flues n N - form Nfon ompred to the H -form. Ths mens hgher drg of wter moleules by N ons. The other wy round, when wter s moved due to pressure grdent, t wll sense more resstne from N thn from H ons. The resultng membrne dffuson oeffents H/H2O nd N/H2O (see tble 3.15) reflet the effets. 2. Wth the sme onentrton dependeny of the nternl wter onentrton on H nd N eletrolytes (seton 2.3.1), the derese of the mesured flu s epeted to be hgher for H-eletrolytes beuse of the hgher vlues t low onentrtons. The model desrpton of these eperments s shown n fgure σ 59
25 Chpter 3 dj V /dp / m 3 P 1 s 1 4.0e e e e-14 HCl H 2 SO 4 NCl NOH N 2 SO / mol m 3 Fgure 3.12: Deresng volume flues wth onentrton n Nfon membrnes wth dfferent eletrolytes. 0 represents the H nd N form, mesured wth pure wter. The results n be ompred to pressure-drven flow eperments desrbed n [11] rred out wth Nfon 120 membrne. Mesurements t 25 C, show the derese from 3E 14 to 1.5E 14 n the vlue of dj V /dp, when the eternl NCl mollty nreses from 0.1 to 4 mol kg 1. Modellng The mesured volume flu n be lulted from modelled membrne mole flues usng: n J V V N (3.18) 1 For the lulton of these flues we n use the ED membrne smulton model, outlned n seton 4.3. In the membrne-phse Mwell-Stefn equtons, pressure grdent s dded to the LHS: zf RT V φ p RT n 1 ( N N ) k, m k, N m k, m m d grd t (3.19) 60
26 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes The followng ssumptons nd boundry ondtons re used: 1. A flud flm s present on the pressursed sde, hvng the thkness of the Vton rng (2.5 mm). On the tmospher sde, the thkness of the membrne-support (1 mm) s tken s flud flm thkness. 2. b (bulk) onentrton present t both sdes of the membrne. 3. No-urrent ondton. 4. No pressure grdent s present n the flud flms Eletrodlyss flues In seton 4.2.1, method s shown n whh eperment-verged on nd wter flues re lulted from volume nd onentrton hnges, nd the eletrl urrent. In Chpter 4 the results re used to desrbe the ED eperments n terms of membrne effeny nd energy onsumpton. In ths seton, these flues re used to etend the set of dt neessry to lulte the membrne-phse dffuson oeffents. In tble 3.10 to 3.13, these flues re gven for the hosen membrneeletrolyte systems. Tble 3.10: ED flues: Nfon H 2 SO 4 -HCl. In tbles 3.10 up to 3.13 the flues N re epressed n (mol m 2 s 1 ). (mol m 3 ) Ep. N H σ N Cl σ N H2O σ , 2, 9, E E E E E E , 13, E E E E E E 03 Tble 3.11: ED flues: Nfon NCl-NOH. (mol m 3 ) Ep. N N σ N OH σ N H2O σ , 2, 9, E E E E E E , 13, E E E E E E 03 Tble 3.12: ED flues: AEM HCl-NCl. (mol m 3 ) Ep. N H σ N Cl σ N H2O σ ARA: E E E E E E 03 AW: , 2, 9, E E E E E E 03 AW: , 13, E E E E E E 03 61
27 Chpter 3 Tble 3.13: ED flues: AEM H 2 SO 4 -N 2 SO 4. (mol m 3 ) Ep. N H σ N SO42 σ N H2O σ ARA: , 11, E E E E E E 03 ARA: , 15, E E E E E E 03 AW: E E E E E E 03 The flues re verge vlues, tken over number of eperments n whh the eletrolyte-membrne systems ours t the gven onentrton. The stndrd devton ndtes the reprodublty of the found flues. In systems where only one eperment s used for the flu lulton, the stndrd devton found n the ft results s gven. Modellng The model for the verge membrne flues s strghtforwrd nd uses the sme lulton s dsussed n 4.3. The followng ondtons re used: 1. As the flues re verge vlues of severl eperments, the onentrtons of the eletrolytes on both sdes of the membrne re verged s well. 2. Smlrly, n verge urrent s lulted. 3.3 Modellng results In ths seton, the method to lulte membrne dffusvtes from the prtl eperments s desrbed. The results re gven n terms of the membrne dffusvtes, nd for eh membrne, the epermentl results re ompred grphlly to the models. In eletrolytes, some Mwell Stefn dffuson oeffents show strong onentrton dependeny. The resstne, pressure nd the eletrodlyss eperments were performed t dfferent onentrtons. However, the eletro-osmoss nd dffuson dlyss eperments were performed t one onentrton level or onentrton dfferene. It ws therefore not possble to ft the membrne dffuson oeffents s funton of onentrton The optmston method For every membrne, the omplete set of prtl eperments s ftted n one go, by optmsng the whole set of hosen dffusvtes. Fttng per membrne-eletrolyte system s not possble method, beuse ertn ntertons, for emple N /H 2 O, our not only n systems wth NCl, but lso n those ontnng NOH or N 2 SO 4. Obvously sngle vlue for suh nterton, vld n ny multomponent system, 62
28 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes s desred. Not every dffusvty n be found by fttng. For emple, some on-on ntertons hve only lmted mportne (resultng n lrge error n the orrespondng ft prmeter), or ny vlue they my hve worsens the model. Durng fttng, these prmeters mostly end up s the mmum llowed vlue, or wth n error of severl orders of mgntude. As upper llowne for the dffuson oeffent, the eletrolyte vlue s used, the lowest llowne typlly les ftor of 100 below. The ppled numerl optmston uses the Mrqurdt-Levenberg method [16], n whh the dfferene (epressed s sum of the h-squres) between model nd mesured ponts s mnmsed by dustment of the ft prmeter mtr (). The sum of squres s defned s: n 2 y mesured ymodel ( ) χ( ) (3.20) σ 1 In equton 3.20, σ ndtes the stndrd devton of the mesurement. Its vlue determnes the mportne of the spef epermentl pont. If we wnt set of m ponts (for emple onentrton-dependent resstnes) to hve the sme weght s sngle pont eperment, thn the vlue of σ for the set of ponts s nresed by: 2 σ m (3.21) new σ old Dffuson oeffents n Nfon In the ED setup, the Nfon membrne s pled between dfferent eletrolytes. These re HCl, H 2 SO 4, NCl, NOH nd N 2 SO 4, therefore ntrodung fve dfferent ons nto the system. Combned wth wter nd the fed-hrges, ths mounts up to seven spees. The totl number of bnry nterton prmeters from n omponents s lulted from: n ( n 1) / 2 (3.22) Ths yelds 21 dffusvtes. The totl number of prtl eperments wth dfferent eletrolyte-nfon systems whh hve been mesured s 26. Some prtl eperments ontn mesurements t dfferent onentrtons (osmoss, resstne, pressure nd ED). The totl number of dt ponts, obtned from the prtl eperments, s 92. In tble 3.14 n overvew of the dt set, wth verge It s ssumed, throughout ths thess, tht H2 SO 4 dssolves ompletely nto H nd ons, therefore vodng the ntroduton of one more spees (HSO 4 ). 2 SO 4 63
29 Chpter 3 epermentl errors s shown, wth the model stndrd devton (epressed n %), obtned from the optmston lulton. Tble 3.14: The dt set used for fttng the dffuson oeffents of the Nfon 450 membrne. Prtl eperment number of dt ponts number of systems vg. eperment error (%) model error (%) Osmoss Dlyss slt flu Dlyss wter flu Resstne Pressure ED o-on flu ED wter flu The resultng set of multomponent membrne-phse dffuson oeffents, wth the stndrd devton, s gven n tble Two oeffents, H/Cl nd N/OH, ended up wth the mmum llowed vlues. Two non-wter dffusvtes, Cl /H2O nd OH /H2O, were set fed to n estmte, lulted from the emprl equton The dffuson oeffents (for NCl nd NOH systems) re ompred wth lterture dt n fgure 3.1 nd 3.2 n seton For Nfon-NCl, the results show most greement wth the work presented by [9], eept for the low vlue tht ws found for Cl /m n ths work. In [11], lso low (nd negtve) vlues re reported for ths oeffent. When the work n [12] s ompred to the results presented here wth respet to the system Nfon-NOH, generlly hgher dffusvtes re obtned n ths work. The eepton s OH /m, but n [12] ths oeffent beomes negtve t onentrtons bove 3.5 M. 64
30 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes Tble 3.15: The set of ftted dffuson oeffents, wth stndrd devtons, for Nfon 450 membrne. prmeter: σ ( ) (m 2 s 1 ) H /Cl 1.00E E 08 N /Cl 5.80E E 11 N /OH 1.00E E 07 H / 2 SO E E 09 N / 2 SO E E 08 H /H 2 O 4.11E E 10 N /H 2 O 5.14E E 11 Cl /H 2 O 6.23E 10 OH /H 2 O 1.62E 09 2 SO 4 /H 2 O 1.62E E 10 H /m 1.45E E 10 N /m 2.26E E 11 Cl /m 1.69E E 12 OH /m 1.58E E 11 2 SO 4 /m 7.41E E 12 H 2 O/m 7.92E E 11 On pge 66, the results of the optmston proedure re shown for every prtl eperment. The dfferenes between the model nd the sngle eperments tht n be seen n the vrous grphs, re refleted by the verge model errors from tble The eperments tht were desrbed (reltvely) well by the model re resstne, pressure nd eletro-osmoss. In dffuson dlyss, some slt-flues re lulted too hgh, nd the wter flues too smll. ED s desrbed well for the NCl/NOH system (wth slghtly too low wter flues), but wth too low o-on lekge n the HCl/H 2 SO 4 system, whh s of lmted mportne. 65
31 Chpter 3 Results for Nfon 450 membrne: J V / ml hr b N / mol m 2 s 1 5.0e-5 2.5e e-5-5.0e-5 b b d d e e Fgure 3.13: Eletro-osmoss epermentl nd model flues (ross-hthed olumns). The postve nd negtve y-s represent the volume nrese- nd derese speeds n the pllres. Legend: () NCl, (b) HCl. R m / Ω / mol m 3 Fgure 3.14: Eletrl membrne resstne, eperments (symbols) nd model (lnes). Legend: see fgure N / mol m 2 s b b d d Fgure 3.16: Dffuson dlyss flues, epermentl nd model (ross-hthed olumns) flues. Whte olumns: eletrolyte flu; grey olumns: wter flu. Legend: () NCl, (b) NOH, () HCl, (d) H 2 SO 4, (e) N 2 SO 4. dj V /dp / m 3 P 1 s 1 4.0e e / mol m 3 HCl H 2 SO 4 NCl NOH N 2 SO 4 Fgure 3.17: Pressure permeton epermentl (symbols) nd model flues (lnes). Components: see legend. Fgure 3.15: Eletro-dlyss epermentl nd model flues (ross-hthed olumns). Whte olumns: o-on lekge flu; grey olumns: wter flu. Legend: () 2 M NOH, (b) 4 M NOH, () 2 M HCl, (d) 4 M HCl. 66
32 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes Dffuson oeffents of eletrolytes n ARA nd AW The non-ehnge membrnes, ARA nd AW, re pled between HCl nd NCl or between H 2 SO 4 nd N 2 SO 4 durng eletrodlyss. Ths ntrodues four dfferent ons nto the system. Combned wth wter nd the fed-hrges, ths mounts up to s spees tkng prt n the dffuson nlyss. For two resons, N ntertons re left out of the prtl eperments: Frstly t s ler from fgure 4.2 tht N ons ply mnor role n the AEM, s the eletrl feld tends to move them wy from the membrne. Seondly, dffuson eperments of ths type of AEM n ph-neutrl eletrolytes re trvl beuse the fed hrges beome deprotonsed nd thus neutrl. For the sme reson, OH nnot be tken nto ount. The totl number of nterton prmeters resultng from the fve remnng spees, lulted from equton 3.22, beomes 10. The totl number of prtl eperments wth dfferent eletrolyte-aem systems whh hve been mesured s 13 (the sme for ARA nd for AW). The totl number of dt ponts, obtned from the prtl eperments, s 26. The dt set, wth epermentl nd optmston model errors, s shown n tble Tble 3.16: The dt set used for fttng the dffuson oeffents of ARA nd AW membrne. Prtl eperment number of dt ponts number of systems vg. ep. error (%) ARA model error (%) ARA vg. ep. error (%) AW model error (%) AW Osmoss Dlyss slt flu Dlyss wter flu Resstne Pressure ED o-on flu ED wter flu The resultng set of multomponent membrne-phse dffuson oeffents, wth the stndrd devton, s gven n tble As no eperments were rred out wth NOH, the oeffents N/H2O nd OH /H2O were guessed from the lqud dffuson oeffents nd equton The sme ws neessry for H/H2O, whh proved mpossble to obtn from the optmston lulton. The dfferent epermentl behvour of AW ompred to ARA (hgh resstne, smller onlekge nd wter flues) s found bk n the model n the form of smller dffuson 67
33 Chpter 3 oeffents. The low vlue of the AW SO42 /m oeffent, used onvergene problems n the ED optmston nd smulton lultons. Tble 3.17: The set of ftted dffuson oeffents, wth stndrd devtons, for ARA-02 nd AW-09 membrne. prmeter: (m 2 s 1 ) ARA σ ( ) ARA (m 2 s 1 ) AW σ ( ) AW H /H 2 O 5.94E E 10 N /H 2 O 7.98E E 11 Cl /H 2 O 2.39E E E E 11 OH /H 2 O 3.47E E 10 2 SO 4 /H 2 O 4.33E E E E 13 H /m 2.97E E E E 13 Cl /m 2.28E E E E 13 2 SO 4 /m 3.13E E E E 14 H 2 O/m 1.44E E E E 11 The results of the optmston proedure for modellng the prtl eperments wth the AEM s re shown grphlly on the net pge. The verge model errors re gven n tble The eperments tht were desrbed (reltvely) well by the model re resstne nd eletro-osmoss. The model for the pressure eperments works not well for AW-H 2 SO 4. For dffuson dlyss, the (overll) poor ft n be ttrbuted to the hgh epermentl errors, whh ontrbute lttle to the totl sum of squres. The ED model performs well, eept tht t predts too low H lekge flues for the (mportnt) NCl/HCl system, for both ARA nd AW. 68
34 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes Results for AW nd ARA membrnes: J V / ml hr Fgure 3.18: Eletro-osmoss epermentl nd model flues (ross-hthed olumns). The postve nd negtve y-s represent the volume nrese- nd derese speeds n the pllres. Legend: () AW HCl, (b) ARA HCl. b N / mol m 2 s 1 1.0e e-4 b Fgure 3.21: Dffuson dlyss epermentl nd model (ross-hthed olumns) flues. Whte olumns: eletrolyte flu (left y-s); grey olumns: wter flu (rght y-s). Legend: () AW HCl, (b) AW H 2 SO 4, () ARA HCl, (d) ARA H 2 SO 4. d d N / mol m 2 s b b d d e e f f dj V /dp / m 3 P 1 s b b Fgure 3.19: Eletro-dlyss epermentl nd model flues (ross-hthed olumns). Whte olumns: o-on lekge flu (left y-s); grey olumns: wter flu (rght y-s). Legend: () AW 2 M HCl, (b) AW 4 M HCl, () AW 2 M H 2 SO 4 (d) ARA 2 M HCl, (e) ARA 2 M H 2 SO 4 Fgure 3.22: Pressure permeton epermentl nd model (ross-hthed olumns) flues. Whte olumns: AW, grey olumns: ARA. Legend: () 0.1 M HCl, (b) 0.1 M H 2 SO 4, () 0.25 M H 2 SO 4. R m / Ω AW HCl AW H 2 SO 4 ARA HCl ARA H 2 SO / mol m 3 (f) ARA 4 M H 2 SO 4. Fgure 3.20: Eletrl membrne resstne, eperments (symbols) nd model (lnes). Components: see legend. 69
35 Chpter Conluson In ths hpter, the determnton of the membrne dffuson oeffents s desrbed. It ws shown tht lrge mount of multomponent dffuson oeffents follow from the dfferent eletrolyte-membrne systems n the performed ED eperments. Aprt from the equlbrum propertes, desrbed n the preedng hpter, these dffusvtes re mportnt prmeters for the ED mss trnsfer model, tht forms the mn m of ths thess. A set of seprte dffuson eperments ws developed nd performed. By modellng ll eperments, for eh membrne, the prmeters ould be lulted by mens of prmeter optmston method. It proved possble to desrbe the eperments to gret etent nd thus fnd the dffuson oeffents, lthough epermentl error ws pssed on to onsderble stndrd devtons n some oeffents. In both ton nd non membrnes, t proved dffult to ft the o-on/wter dffuson oeffents from eperments. Although gret mount of dt s to be gthered to buld omplete multomponent mss trnsfer model, the method s needed to ount for: ll drvng fores, nludng pressure grdents the flu of wter n ED systems due to drg from (ounter) ons. tvty oeffents nsde membrnes (lthough not nluded n the mss trnsfer model). 3.5 Referenes 1 Chpmn, T.W. The Trnsport Propertes of Conentrted Eletrolyt Solutons. Ph.D. thess, Unversty of Clforn, Berkeley, CA, Lghtfoot, E.N. Trnsport Phenomen nd Lvng Systems, Wley, New York, Tylor, R. nd Krshn, R. Multomponent Mss Trnsfer, John Wley & Sons, New York, Zemts, J.F., Clrk, D.M., Rfl, M., nd Srvner, N.C. Thermodynms of solutons. In: Hndbook of Aqueous Eletrolyte Thermodynms, Anonymous New York: DIPPR, Sttergood, E.M. nd Lghtfoot, E.N. Dffusonl Interton n n Ion- Ehnge Membrne. Trns. Frdy So. 64: , Krshn, R. Dffuson n Multomponent Eletrolyte Systems. Chem. Eng. Journl 35:19-24,
36 Dffuson n Eletrodlyss Membrnes 7 Noordmn, T.R. Hgh Flu Ultrfltrton. Ph.D. thess, Unversty of Gronngen, Wesselngh, J.A., Vonk, P., nd Kreveld, G. Eplorng the Mwell-Stefn Desrpton of Ion Ehnge. The Cheml Engneerng Journl 57:75-89, Pnturo, P.N. nd Bennon, D.N. Mss Trnsport of Eletrolytes n membrnes. 2. Determnton of NCl Equlbrum nd Trnsport Prmeters for Nfon. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundm. 23: , Nrebsk, A., Koter, S., nd Kuwsk, W. Ions nd wter trnsport ross hrged Nfon membrnes. Irreversble thermodynms pproh. Deslnton 51:3-17, Nrebsk, A., Koter, S., nd Kuwsk, W. Irreversble thermodynms of trnsport ross hrged membrnes. Prt I - Mrosop resstne oeffents for system wth Nfon 120 membrne. Journl of membrne Sene 25: , Nrebsk, A., Kuwsk, W., nd Koter, S. Irreversble thermodynms of trnsport ross hrged membrnes. Prt II - Ion-wter ntertons n permeton of lkl. Journl of membrne Sene 30: , Kreveld, G. The Mwell-Stefn Desrpton of Mss Trnsfer n Ion Ehnge nd Eletrodlyss. Ph.D. thess, Unversty of Gronngen, Colton, C.K. nd Smth, K.A. Mss trnsfer to rottng flud. II. Trnsport from the bse of n gtted ylndrl tnk, AIChE J. 18:958, Oers, C.W. vn. Solute Reeton n Multomponent Systems durng Ultrfltrton, Ph.D. thess, Unversty of Endhoven, Press, W.H., Flnnery, B.P., Teukolsky, S.A., Vetterlng, W.T. Numerl Repes n Psl, New York: Cmbrgde Unversty Press
37
Concept of Activity. Concept of Activity. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Constants [ C] [ D] [ A] [ B]
![Concept of Activity. Concept of Activity. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Constants [ C] [ D] [ A] [ B] Concept of Activity. Concept of Activity. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Constants [ C] [ D] [ A] [ B]](/thumbs/80/81967334.jpg) Conept of Atvty Equlbrum onstnt s thermodynm property of n equlbrum system. For heml reton t equlbrum; Conept of Atvty Thermodynm Equlbrum Constnts A + bb = C + dd d [C] [D] [A] [B] b Conentrton equlbrum
Conept of Atvty Equlbrum onstnt s thermodynm property of n equlbrum system. For heml reton t equlbrum; Conept of Atvty Thermodynm Equlbrum Constnts A + bb = C + dd d [C] [D] [A] [B] b Conentrton equlbrum
Mass Transfer as you have learned it. Diffusion with Drift. Classic - in Gases 1. Three Gases (1) Appendix. Mass transfer in
 to ourse mterl for ÅA TF ourse 44 / 8 Mss trnsfer nd seprton tehnology Mssöverf verförng rng oh seprtonsten ( MÖF-ST ) See lso Krshn & Wesselngh Chem. Eng. S. 5(6) 997 86-9 Appendx. Mss trnsfer n mult-omponent
to ourse mterl for ÅA TF ourse 44 / 8 Mss trnsfer nd seprton tehnology Mssöverf verförng rng oh seprtonsten ( MÖF-ST ) See lso Krshn & Wesselngh Chem. Eng. S. 5(6) 997 86-9 Appendx. Mss trnsfer n mult-omponent
" = #N d$ B. Electromagnetic Induction. v ) $ d v % l. Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday s Law. Faraday s Law of Induction
 Eletromgnet Induton nd Frdy s w Eletromgnet Induton Mhel Frdy (1791-1867) dsoered tht hngng mgnet feld ould produe n eletr urrent n ondutor pled n the mgnet feld. uh urrent s lled n ndued urrent. The phenomenon
Eletromgnet Induton nd Frdy s w Eletromgnet Induton Mhel Frdy (1791-1867) dsoered tht hngng mgnet feld ould produe n eletr urrent n ondutor pled n the mgnet feld. uh urrent s lled n ndued urrent. The phenomenon
DCDM BUSINESS SCHOOL NUMERICAL METHODS (COS 233-8) Solutions to Assignment 3. x f(x)
 DCDM BUSINESS SCHOOL NUMEICAL METHODS (COS -8) Solutons to Assgnment Queston Consder the followng dt: 5 f() 8 7 5 () Set up dfference tble through fourth dfferences. (b) Wht s the mnmum degree tht n nterpoltng
DCDM BUSINESS SCHOOL NUMEICAL METHODS (COS -8) Solutons to Assgnment Queston Consder the followng dt: 5 f() 8 7 5 () Set up dfference tble through fourth dfferences. (b) Wht s the mnmum degree tht n nterpoltng
Lecture 7 Circuits Ch. 27
 Leture 7 Cruts Ch. 7 Crtoon -Krhhoff's Lws Tops Dret Current Cruts Krhhoff's Two ules Anlyss of Cruts Exmples Ammeter nd voltmeter C ruts Demos Three uls n rut Power loss n trnsmsson lnes esstvty of penl
Leture 7 Cruts Ch. 7 Crtoon -Krhhoff's Lws Tops Dret Current Cruts Krhhoff's Two ules Anlyss of Cruts Exmples Ammeter nd voltmeter C ruts Demos Three uls n rut Power loss n trnsmsson lnes esstvty of penl
Chapter Newton-Raphson Method of Solving a Nonlinear Equation
 Chpter.4 Newton-Rphson Method of Solvng Nonlner Equton After redng ths chpter, you should be ble to:. derve the Newton-Rphson method formul,. develop the lgorthm of the Newton-Rphson method,. use the Newton-Rphson
Chpter.4 Newton-Rphson Method of Solvng Nonlner Equton After redng ths chpter, you should be ble to:. derve the Newton-Rphson method formul,. develop the lgorthm of the Newton-Rphson method,. use the Newton-Rphson
Abhilasha Classes Class- XII Date: SOLUTION (Chap - 9,10,12) MM 50 Mob no
 hlsh Clsses Clss- XII Dte: 0- - SOLUTION Chp - 9,0, MM 50 Mo no-996 If nd re poston vets of nd B respetvel, fnd the poston vet of pont C n B produed suh tht C B vet r C B = where = hs length nd dreton
hlsh Clsses Clss- XII Dte: 0- - SOLUTION Chp - 9,0, MM 50 Mo no-996 If nd re poston vets of nd B respetvel, fnd the poston vet of pont C n B produed suh tht C B vet r C B = where = hs length nd dreton
Trigonometry. Trigonometry. Solutions. Curriculum Ready ACMMG: 223, 224, 245.
 Trgonometry Trgonometry Solutons Currulum Redy CMMG:, 4, 4 www.mthlets.om Trgonometry Solutons Bss Pge questons. Identfy f the followng trngles re rght ngled or not. Trngles,, d, e re rght ngled ndted
Trgonometry Trgonometry Solutons Currulum Redy CMMG:, 4, 4 www.mthlets.om Trgonometry Solutons Bss Pge questons. Identfy f the followng trngles re rght ngled or not. Trngles,, d, e re rght ngled ndted
VECTORS VECTORS VECTORS VECTORS. 2. Vector Representation. 1. Definition. 3. Types of Vectors. 5. Vector Operations I. 4. Equal and Opposite Vectors
 1. Defnton A vetor s n entt tht m represent phsl quntt tht hs mgntude nd dreton s opposed to slr tht ls dreton.. Vetor Representton A vetor n e represented grphll n rrow. The length of the rrow s the mgntude
1. Defnton A vetor s n entt tht m represent phsl quntt tht hs mgntude nd dreton s opposed to slr tht ls dreton.. Vetor Representton A vetor n e represented grphll n rrow. The length of the rrow s the mgntude
Principle Component Analysis
 Prncple Component Anlyss Jng Go SUNY Bufflo Why Dmensonlty Reducton? We hve too mny dmensons o reson bout or obtn nsghts from o vsulze oo much nose n the dt Need to reduce them to smller set of fctors
Prncple Component Anlyss Jng Go SUNY Bufflo Why Dmensonlty Reducton? We hve too mny dmensons o reson bout or obtn nsghts from o vsulze oo much nose n the dt Need to reduce them to smller set of fctors
Shuai Dong. Using Math and Science to improve your game
 Computtonl phscs Shu Dong Usng Mth nd Sene to mprove our gme Appromton of funtons Lner nterpolton Lgrnge nterpolton Newton nterpolton Lner sstem method Lest-squres ppromton Mllkn eperment Wht s nterpolton?
Computtonl phscs Shu Dong Usng Mth nd Sene to mprove our gme Appromton of funtons Lner nterpolton Lgrnge nterpolton Newton nterpolton Lner sstem method Lest-squres ppromton Mllkn eperment Wht s nterpolton?
6 Random Errors in Chemical Analysis
 6 Rndom Error n Cheml Anl 6A The ture of Rndom Error 6A- Rndom Error Soure? Fg. 6- Three-dmenonl plot howng olute error n Kjeldhl ntrogen determnton for four dfferent nlt. Anlt Pree Aurte 4 Tle 6- Pole
6 Rndom Error n Cheml Anl 6A The ture of Rndom Error 6A- Rndom Error Soure? Fg. 6- Three-dmenonl plot howng olute error n Kjeldhl ntrogen determnton for four dfferent nlt. Anlt Pree Aurte 4 Tle 6- Pole
Physics 121 Sample Common Exam 2 Rev2 NOTE: ANSWERS ARE ON PAGE 7. Instructions:
 Physcs 121 Smple Common Exm 2 Rev2 NOTE: ANSWERS ARE ON PAGE 7 Nme (Prnt): 4 Dgt ID: Secton: Instructons: Answer ll 27 multple choce questons. You my need to do some clculton. Answer ech queston on the
Physcs 121 Smple Common Exm 2 Rev2 NOTE: ANSWERS ARE ON PAGE 7 Nme (Prnt): 4 Dgt ID: Secton: Instructons: Answer ll 27 multple choce questons. You my need to do some clculton. Answer ech queston on the
ME 501A Seminar in Engineering Analysis Page 1
 More oundr-vlue Prolems nd genvlue Prolems n Os ovemer 9, 7 More oundr-vlue Prolems nd genvlue Prolems n Os Lrr retto Menl ngneerng 5 Semnr n ngneerng nlss ovemer 9, 7 Outlne Revew oundr-vlue prolems Soot
More oundr-vlue Prolems nd genvlue Prolems n Os ovemer 9, 7 More oundr-vlue Prolems nd genvlue Prolems n Os Lrr retto Menl ngneerng 5 Semnr n ngneerng nlss ovemer 9, 7 Outlne Revew oundr-vlue prolems Soot
Effectiveness and Efficiency Analysis of Parallel Flow and Counter Flow Heat Exchangers
 Interntonl Journl of Applton or Innovton n Engneerng & Mngement (IJAIEM) Web Ste: www.jem.org Eml: edtor@jem.org Effetveness nd Effeny Anlyss of Prllel Flow nd Counter Flow Het Exngers oopes wr 1, Dr.Govnd
Interntonl Journl of Applton or Innovton n Engneerng & Mngement (IJAIEM) Web Ste: www.jem.org Eml: edtor@jem.org Effetveness nd Effeny Anlyss of Prllel Flow nd Counter Flow Het Exngers oopes wr 1, Dr.Govnd
Chapter Newton-Raphson Method of Solving a Nonlinear Equation
 Chpter 0.04 Newton-Rphson Method o Solvng Nonlner Equton Ater redng ths chpter, you should be ble to:. derve the Newton-Rphson method ormul,. develop the lgorthm o the Newton-Rphson method,. use the Newton-Rphson
Chpter 0.04 Newton-Rphson Method o Solvng Nonlner Equton Ater redng ths chpter, you should be ble to:. derve the Newton-Rphson method ormul,. develop the lgorthm o the Newton-Rphson method,. use the Newton-Rphson
Applied Statistics Qualifier Examination
 Appled Sttstcs Qulfer Exmnton Qul_june_8 Fll 8 Instructons: () The exmnton contns 4 Questons. You re to nswer 3 out of 4 of them. () You my use ny books nd clss notes tht you mght fnd helpful n solvng
Appled Sttstcs Qulfer Exmnton Qul_june_8 Fll 8 Instructons: () The exmnton contns 4 Questons. You re to nswer 3 out of 4 of them. () You my use ny books nd clss notes tht you mght fnd helpful n solvng
Electrochemical Thermodynamics. Interfaces and Energy Conversion
 CHE465/865, 2006-3, Lecture 6, 18 th Sep., 2006 Electrochemcl Thermodynmcs Interfces nd Energy Converson Where does the energy contrbuton F zϕ dn come from? Frst lw of thermodynmcs (conservton of energy):
CHE465/865, 2006-3, Lecture 6, 18 th Sep., 2006 Electrochemcl Thermodynmcs Interfces nd Energy Converson Where does the energy contrbuton F zϕ dn come from? Frst lw of thermodynmcs (conservton of energy):
Definition of Tracking
 Trckng Defnton of Trckng Trckng: Generte some conclusons bout the moton of the scene, objects, or the cmer, gven sequence of mges. Knowng ths moton, predct where thngs re gong to project n the net mge,
Trckng Defnton of Trckng Trckng: Generte some conclusons bout the moton of the scene, objects, or the cmer, gven sequence of mges. Knowng ths moton, predct where thngs re gong to project n the net mge,
Chemical Reaction Engineering
 Lecture 20 hemcl Recton Engneerng (RE) s the feld tht studes the rtes nd mechnsms of chemcl rectons nd the desgn of the rectors n whch they tke plce. Lst Lecture Energy Blnce Fundmentls F 0 E 0 F E Q W
Lecture 20 hemcl Recton Engneerng (RE) s the feld tht studes the rtes nd mechnsms of chemcl rectons nd the desgn of the rectors n whch they tke plce. Lst Lecture Energy Blnce Fundmentls F 0 E 0 F E Q W
Rank One Update And the Google Matrix by Al Bernstein Signal Science, LLC
 Introducton Rnk One Updte And the Google Mtrx y Al Bernsten Sgnl Scence, LLC www.sgnlscence.net here re two dfferent wys to perform mtrx multplctons. he frst uses dot product formulton nd the second uses
Introducton Rnk One Updte And the Google Mtrx y Al Bernsten Sgnl Scence, LLC www.sgnlscence.net here re two dfferent wys to perform mtrx multplctons. he frst uses dot product formulton nd the second uses
Quiz: Experimental Physics Lab-I
 Mxmum Mrks: 18 Totl tme llowed: 35 mn Quz: Expermentl Physcs Lb-I Nme: Roll no: Attempt ll questons. 1. In n experment, bll of mss 100 g s dropped from heght of 65 cm nto the snd contner, the mpct s clled
Mxmum Mrks: 18 Totl tme llowed: 35 mn Quz: Expermentl Physcs Lb-I Nme: Roll no: Attempt ll questons. 1. In n experment, bll of mss 100 g s dropped from heght of 65 cm nto the snd contner, the mpct s clled
UNIVERSITY OF IOANNINA DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS. M.Sc. in Economics MICROECONOMIC THEORY I. Problem Set II
 Mcroeconomc Theory I UNIVERSITY OF IOANNINA DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS MSc n Economcs MICROECONOMIC THEORY I Techng: A Lptns (Note: The number of ndctes exercse s dffculty level) ()True or flse? If V( y )
Mcroeconomc Theory I UNIVERSITY OF IOANNINA DEPARTMENT OF ECONOMICS MSc n Economcs MICROECONOMIC THEORY I Techng: A Lptns (Note: The number of ndctes exercse s dffculty level) ()True or flse? If V( y )
4. Eccentric axial loading, cross-section core
 . Eccentrc xl lodng, cross-secton core Introducton We re strtng to consder more generl cse when the xl force nd bxl bendng ct smultneousl n the cross-secton of the br. B vrtue of Snt-Vennt s prncple we
. Eccentrc xl lodng, cross-secton core Introducton We re strtng to consder more generl cse when the xl force nd bxl bendng ct smultneousl n the cross-secton of the br. B vrtue of Snt-Vennt s prncple we
SECONDAR Y - MRIEĦEL HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2017/2018
 Yer 9 PHYSICAL EDUCATION (OPTION) TIME: 1h 30mn SECONDAR Y - MRIEĦEL HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2017/2018 Nme: Clss: Seton A Seton B Seton C Seton D TOTAL MARK 16 20 32 12 THEORY PAPER (80) 40% THEORY PAPER
Yer 9 PHYSICAL EDUCATION (OPTION) TIME: 1h 30mn SECONDAR Y - MRIEĦEL HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2017/2018 Nme: Clss: Seton A Seton B Seton C Seton D TOTAL MARK 16 20 32 12 THEORY PAPER (80) 40% THEORY PAPER
Name: SID: Discussion Session:
 Nme: SID: Dscusson Sesson: hemcl Engneerng hermodynmcs -- Fll 008 uesdy, Octoer, 008 Merm I - 70 mnutes 00 onts otl losed Book nd Notes (5 ponts). onsder n del gs wth constnt het cpctes. Indcte whether
Nme: SID: Dscusson Sesson: hemcl Engneerng hermodynmcs -- Fll 008 uesdy, Octoer, 008 Merm I - 70 mnutes 00 onts otl losed Book nd Notes (5 ponts). onsder n del gs wth constnt het cpctes. Indcte whether
] dx (3) = [15x] 2 0
![] dx (3) = [15x] 2 0 ] dx (3) = [15x] 2 0](/thumbs/80/81916477.jpg) Leture 6. Double Integrls nd Volume on etngle Welome to Cl IV!!!! These notes re designed to be redble nd desribe the w I will eplin the mteril in lss. Hopefull the re thorough, but it s good ide to hve
Leture 6. Double Integrls nd Volume on etngle Welome to Cl IV!!!! These notes re designed to be redble nd desribe the w I will eplin the mteril in lss. Hopefull the re thorough, but it s good ide to hve
Voltammetry. Bulk electrolysis: relatively large electrodes (on the order of cm 2 ) Voltammetry:
 Voltammetry varety of eletroanalytal methods rely on the applaton of a potental funton to an eletrode wth the measurement of the resultng urrent n the ell. In ontrast wth bul eletrolyss methods, the objetve
Voltammetry varety of eletroanalytal methods rely on the applaton of a potental funton to an eletrode wth the measurement of the resultng urrent n the ell. In ontrast wth bul eletrolyss methods, the objetve
TELCOM 2130 Time Varying Queues. David Tipper Associate Professor Graduate Telecommunications and Networking Program University of Pittsburgh Slides 7
 TELOM 3 Tme Vryng Queues Dvd Tpper Assote Professor Grdute Teleommuntons nd Networkng Progrm Unversty of Pttsburgh ldes 7 Tme Vryng Behvor Teletrff typlly hs lrge tme of dy vrtons Men number of lls per
TELOM 3 Tme Vryng Queues Dvd Tpper Assote Professor Grdute Teleommuntons nd Networkng Progrm Unversty of Pttsburgh ldes 7 Tme Vryng Behvor Teletrff typlly hs lrge tme of dy vrtons Men number of lls per
6 Roots of Equations: Open Methods
 HK Km Slghtly modfed 3//9, /8/6 Frstly wrtten t Mrch 5 6 Roots of Equtons: Open Methods Smple Fed-Pont Iterton Newton-Rphson Secnt Methods MATLAB Functon: fzero Polynomls Cse Study: Ppe Frcton Brcketng
HK Km Slghtly modfed 3//9, /8/6 Frstly wrtten t Mrch 5 6 Roots of Equtons: Open Methods Smple Fed-Pont Iterton Newton-Rphson Secnt Methods MATLAB Functon: fzero Polynomls Cse Study: Ppe Frcton Brcketng
7.2 Volume. A cross section is the shape we get when cutting straight through an object.
 7. Volume Let s revew the volume of smple sold, cylnder frst. Cylnder s volume=se re heght. As llustrted n Fgure (). Fgure ( nd (c) re specl cylnders. Fgure () s rght crculr cylnder. Fgure (c) s ox. A
7. Volume Let s revew the volume of smple sold, cylnder frst. Cylnder s volume=se re heght. As llustrted n Fgure (). Fgure ( nd (c) re specl cylnders. Fgure () s rght crculr cylnder. Fgure (c) s ox. A
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundgl, Hyderbd - 5 3 FRESHMAN ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Nme : MATHEMATICS II Code : A6 Clss : II B. Te II Semester Brn : FRESHMAN ENGINEERING Yer : 5 Fulty
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundgl, Hyderbd - 5 3 FRESHMAN ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Nme : MATHEMATICS II Code : A6 Clss : II B. Te II Semester Brn : FRESHMAN ENGINEERING Yer : 5 Fulty
ESCI 342 Atmospheric Dynamics I Lesson 1 Vectors and Vector Calculus
 ESI 34 tmospherc Dnmcs I Lesson 1 Vectors nd Vector lculus Reference: Schum s Outlne Seres: Mthemtcl Hndbook of Formuls nd Tbles Suggested Redng: Mrtn Secton 1 OORDINTE SYSTEMS n orthonorml coordnte sstem
ESI 34 tmospherc Dnmcs I Lesson 1 Vectors nd Vector lculus Reference: Schum s Outlne Seres: Mthemtcl Hndbook of Formuls nd Tbles Suggested Redng: Mrtn Secton 1 OORDINTE SYSTEMS n orthonorml coordnte sstem
Fall 2012 Analysis of Experimental Measurements B. Eisenstein/rev. S. Errede. with respect to λ. 1. χ λ χ λ ( ) λ, and thus:
 More on χ nd errors : uppose tht we re fttng for sngle -prmeter, mnmzng: If we epnd The vlue χ ( ( ( ; ( wth respect to. χ n Tlor seres n the vcnt of ts mnmum vlue χ ( mn χ χ χ χ + + + mn mnmzes χ, nd
More on χ nd errors : uppose tht we re fttng for sngle -prmeter, mnmzng: If we epnd The vlue χ ( ( ( ; ( wth respect to. χ n Tlor seres n the vcnt of ts mnmum vlue χ ( mn χ χ χ χ + + + mn mnmzes χ, nd
CISE 301: Numerical Methods Lecture 5, Topic 4 Least Squares, Curve Fitting
 CISE 3: umercl Methods Lecture 5 Topc 4 Lest Squres Curve Fttng Dr. Amr Khouh Term Red Chpter 7 of the tetoo c Khouh CISE3_Topc4_Lest Squre Motvton Gven set of epermentl dt 3 5. 5.9 6.3 The reltonshp etween
CISE 3: umercl Methods Lecture 5 Topc 4 Lest Squres Curve Fttng Dr. Amr Khouh Term Red Chpter 7 of the tetoo c Khouh CISE3_Topc4_Lest Squre Motvton Gven set of epermentl dt 3 5. 5.9 6.3 The reltonshp etween
Chemical Reaction Engineering
 Lecture 20 hemcl Recton Engneerng (RE) s the feld tht studes the rtes nd mechnsms of chemcl rectons nd the desgn of the rectors n whch they tke plce. Lst Lecture Energy Blnce Fundmentls F E F E + Q! 0
Lecture 20 hemcl Recton Engneerng (RE) s the feld tht studes the rtes nd mechnsms of chemcl rectons nd the desgn of the rectors n whch they tke plce. Lst Lecture Energy Blnce Fundmentls F E F E + Q! 0
Module 3: Element Properties Lecture 5: Solid Elements
 Modue : Eement Propertes eture 5: Sod Eements There re two s fmes of three-dmenson eements smr to two-dmenson se. Etenson of trngur eements w produe tetrhedrons n three dmensons. Smr retngur preeppeds
Modue : Eement Propertes eture 5: Sod Eements There re two s fmes of three-dmenson eements smr to two-dmenson se. Etenson of trngur eements w produe tetrhedrons n three dmensons. Smr retngur preeppeds
Two Coefficients of the Dyson Product
 Two Coeffcents of the Dyson Product rxv:07.460v mth.co 7 Nov 007 Lun Lv, Guoce Xn, nd Yue Zhou 3,,3 Center for Combntorcs, LPMC TJKLC Nnk Unversty, Tnjn 30007, P.R. Chn lvlun@cfc.nnk.edu.cn gn@nnk.edu.cn
Two Coeffcents of the Dyson Product rxv:07.460v mth.co 7 Nov 007 Lun Lv, Guoce Xn, nd Yue Zhou 3,,3 Center for Combntorcs, LPMC TJKLC Nnk Unversty, Tnjn 30007, P.R. Chn lvlun@cfc.nnk.edu.cn gn@nnk.edu.cn
Dennis Bricker, 2001 Dept of Industrial Engineering The University of Iowa. MDP: Taxi page 1
 Denns Brcker, 2001 Dept of Industrl Engneerng The Unversty of Iow MDP: Tx pge 1 A tx serves three djcent towns: A, B, nd C. Ech tme the tx dschrges pssenger, the drver must choose from three possble ctons:
Denns Brcker, 2001 Dept of Industrl Engneerng The Unversty of Iow MDP: Tx pge 1 A tx serves three djcent towns: A, B, nd C. Ech tme the tx dschrges pssenger, the drver must choose from three possble ctons:
INTRODUCTION TO COMPLEX NUMBERS
 INTRODUCTION TO COMPLEX NUMBERS The numers -4, -3, -, -1, 0, 1,, 3, 4 represent the negtve nd postve rel numers termed ntegers. As one frst lerns n mddle school they cn e thought of s unt dstnce spced
INTRODUCTION TO COMPLEX NUMBERS The numers -4, -3, -, -1, 0, 1,, 3, 4 represent the negtve nd postve rel numers termed ntegers. As one frst lerns n mddle school they cn e thought of s unt dstnce spced
1 This diagram represents the energy change that occurs when a d electron in a transition metal ion is excited by visible light.
 1 This igrm represents the energy hnge tht ours when eletron in trnsition metl ion is exite y visile light. Give the eqution tht reltes the energy hnge ΔE to the Plnk onstnt, h, n the frequeny, v, of the
1 This igrm represents the energy hnge tht ours when eletron in trnsition metl ion is exite y visile light. Give the eqution tht reltes the energy hnge ΔE to the Plnk onstnt, h, n the frequeny, v, of the
On Adaptive Control of Simulated Moving Bed Plants. Plants Using Comsol s Simulink Interface. Speaker: Marco Fütterer
 daptve Smulated Movng ed Plants Usng Comsol s Smulnk Interfae Speaker: Maro Fütterer Insttut für utomatserungstehnk Otto-von-Guerke Unverstät Unverstätsplatz, D-39106 Magdeburg Germany e-mal: maro.fuetterer@ovgu.de
daptve Smulated Movng ed Plants Usng Comsol s Smulnk Interfae Speaker: Maro Fütterer Insttut für utomatserungstehnk Otto-von-Guerke Unverstät Unverstätsplatz, D-39106 Magdeburg Germany e-mal: maro.fuetterer@ovgu.de
REGULARIZATION IN QUANTUM GAUGE THEORY OF GRAVITATION WITH DE SITTER INNER SYMMETRY
 THEORETICAL PHYSICS REGULARIZATION IN QUANTUM GAUGE THEORY OF GRAVITATION WITH DE SITTER INNER SYMMETRY V. CHIRIÞOIU 1, G. ZET 1 Poltehn Unversty Tmºor, Tehnl Physs Deprtment, Romn E-ml: vorel.hrtou@et.upt.ro
THEORETICAL PHYSICS REGULARIZATION IN QUANTUM GAUGE THEORY OF GRAVITATION WITH DE SITTER INNER SYMMETRY V. CHIRIÞOIU 1, G. ZET 1 Poltehn Unversty Tmºor, Tehnl Physs Deprtment, Romn E-ml: vorel.hrtou@et.upt.ro
Electromagnetism Notes, NYU Spring 2018
 Eletromgnetism Notes, NYU Spring 208 April 2, 208 Ation formultion of EM. Free field desription Let us first onsider the free EM field, i.e. in the bsene of ny hrges or urrents. To tret this s mehnil system
Eletromgnetism Notes, NYU Spring 208 April 2, 208 Ation formultion of EM. Free field desription Let us first onsider the free EM field, i.e. in the bsene of ny hrges or urrents. To tret this s mehnil system
Variable time amplitude amplification and quantum algorithms for linear algebra. Andris Ambainis University of Latvia
 Vrble tme mpltude mplfcton nd quntum lgorthms for lner lgebr Andrs Ambns Unversty of Ltv Tlk outlne. ew verson of mpltude mplfcton;. Quntum lgorthm for testng f A s sngulr; 3. Quntum lgorthm for solvng
Vrble tme mpltude mplfcton nd quntum lgorthms for lner lgebr Andrs Ambns Unversty of Ltv Tlk outlne. ew verson of mpltude mplfcton;. Quntum lgorthm for testng f A s sngulr; 3. Quntum lgorthm for solvng
Smart Motorways HADECS 3 and what it means for your drivers
 Vehcle Rentl Smrt Motorwys HADECS 3 nd wht t mens for your drvers Vehcle Rentl Smrt Motorwys HADECS 3 nd wht t mens for your drvers You my hve seen some news rtcles bout the ntroducton of Hghwys Englnd
Vehcle Rentl Smrt Motorwys HADECS 3 nd wht t mens for your drvers Vehcle Rentl Smrt Motorwys HADECS 3 nd wht t mens for your drvers You my hve seen some news rtcles bout the ntroducton of Hghwys Englnd
Humidity Profiling with a VHF Wind Profiler and GPS Measurements
 Humdty Proflng wth VHF Wnd Profler nd GPS esurements Vldslv Klus, Joël Vn Belen*, nd Yves Pontn* ( ) entre Ntonl de Reherhes étéorologues (NR), étéo Frne, Toulouse, Frne (*) Lortore de étéorologe Physue
Humdty Proflng wth VHF Wnd Profler nd GPS esurements Vldslv Klus, Joël Vn Belen*, nd Yves Pontn* ( ) entre Ntonl de Reherhes étéorologues (NR), étéo Frne, Toulouse, Frne (*) Lortore de étéorologe Physue
PHYSICS 212 MIDTERM II 19 February 2003
 PHYSICS 1 MIDERM II 19 Feruary 003 Exam s losed ook, losed notes. Use only your formula sheet. Wrte all work and answers n exam ooklets. he aks of pages wll not e graded unless you so request on the front
PHYSICS 1 MIDERM II 19 Feruary 003 Exam s losed ook, losed notes. Use only your formula sheet. Wrte all work and answers n exam ooklets. he aks of pages wll not e graded unless you so request on the front
Remember: Project Proposals are due April 11.
 Bonformtcs ecture Notes Announcements Remember: Project Proposls re due Aprl. Clss 22 Aprl 4, 2002 A. Hdden Mrov Models. Defntons Emple - Consder the emple we tled bout n clss lst tme wth the cons. However,
Bonformtcs ecture Notes Announcements Remember: Project Proposls re due Aprl. Clss 22 Aprl 4, 2002 A. Hdden Mrov Models. Defntons Emple - Consder the emple we tled bout n clss lst tme wth the cons. However,
Forces on curved surfaces Buoyant force Stability of floating and submerged bodies
 Stti Surfe ores Stti Surfe ores 8m wter hinge? 4 m ores on plne res ores on urved surfes Buont fore Stbilit of floting nd submerged bodies ores on Plne res Two tpes of problems Horizontl surfes (pressure
Stti Surfe ores Stti Surfe ores 8m wter hinge? 4 m ores on plne res ores on urved surfes Buont fore Stbilit of floting nd submerged bodies ores on Plne res Two tpes of problems Horizontl surfes (pressure
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1. Given a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
 1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
1 PYTHAGORAS THEOREM 1 1 Pythgors Theorem In this setion we will present geometri proof of the fmous theorem of Pythgors. Given right ngled tringle, the squre of the hypotenuse is equl to the sum of the
Chapter Gauss-Seidel Method
 Chpter 04.08 Guss-Sedel Method After redg ths hpter, you should be ble to:. solve set of equtos usg the Guss-Sedel method,. reogze the dvtges d ptflls of the Guss-Sedel method, d. determe uder wht odtos
Chpter 04.08 Guss-Sedel Method After redg ths hpter, you should be ble to:. solve set of equtos usg the Guss-Sedel method,. reogze the dvtges d ptflls of the Guss-Sedel method, d. determe uder wht odtos
Physics 41 Chapter 22 HW Serway 7 th Edition
 yss 41 apter H Serway 7 t Edton oneptual uestons: 1,, 8, 1 roblems: 9, 1, 0,, 7, 9, 48, 54, 55 oneptual uestons: 1,, 8, 1 1 Frst, te effeny of te automoble engne annot exeed te arnot effeny: t s lmted
yss 41 apter H Serway 7 t Edton oneptual uestons: 1,, 8, 1 roblems: 9, 1, 0,, 7, 9, 48, 54, 55 oneptual uestons: 1,, 8, 1 1 Frst, te effeny of te automoble engne annot exeed te arnot effeny: t s lmted
Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Bath. Mathematics ME Problem sheet 11 Least Squares Fitting of data
 Deprtment of Mechncl Engneerng, Unversty of Bth Mthemtcs ME10305 Prolem sheet 11 Lest Squres Fttng of dt NOTE: If you re gettng just lttle t concerned y the length of these questons, then do hve look t
Deprtment of Mechncl Engneerng, Unversty of Bth Mthemtcs ME10305 Prolem sheet 11 Lest Squres Fttng of dt NOTE: If you re gettng just lttle t concerned y the length of these questons, then do hve look t
Dr. Steward s CHM152 Exam #2 Review Spring 2014 (Ch ) KEY
 Dr. Stewrd s CHM152 Em #2 Review Spring 2014 (Ch. 16. 17) KEY 1. Eplin the commonion effect. Wek cid or wek bse s % dissocition will decrese if they re plced in solutions with one of the products of dissocition.
Dr. Stewrd s CHM152 Em #2 Review Spring 2014 (Ch. 16. 17) KEY 1. Eplin the commonion effect. Wek cid or wek bse s % dissocition will decrese if they re plced in solutions with one of the products of dissocition.
Review Topic 14: Relationships between two numerical variables
 Review Topi 14: Reltionships etween two numeril vriles Multiple hoie 1. Whih of the following stterplots est demonstrtes line of est fit? A B C D E 2. The regression line eqution for the following grph
Review Topi 14: Reltionships etween two numeril vriles Multiple hoie 1. Whih of the following stterplots est demonstrtes line of est fit? A B C D E 2. The regression line eqution for the following grph
Example
 Chapter Example.- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sold slab of 5.5 wt% agar gel at 78 o K s.6 mm thk and ontans a unform onentraton of urea of. kmol/m 3.
Chapter Example.- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ sold slab of 5.5 wt% agar gel at 78 o K s.6 mm thk and ontans a unform onentraton of urea of. kmol/m 3.
Physical Chemistry I for Biochemists Chem340. Lecture 38 (4/20/11) Yoshitaka Ishii. Announcement
 Physicl Chemistry I for Biochemists Chem34 Lecture 38 (4//11) Yoshitk Ishii Ch. 9.7 9.1 9.1 Announcement HW1 due dte is 4/7 (Wed) Exm 3 will be returned probbly this Fridy Finl Exm 5/4 (Wed) 1 3 pm Quiz
Physicl Chemistry I for Biochemists Chem34 Lecture 38 (4//11) Yoshitk Ishii Ch. 9.7 9.1 9.1 Announcement HW1 due dte is 4/7 (Wed) Exm 3 will be returned probbly this Fridy Finl Exm 5/4 (Wed) 1 3 pm Quiz
Learning Enhancement Team
 Lernng Enhnement Tem Worsheet: The Cross Produt These re the model nswers for the worsheet tht hs questons on the ross produt etween vetors. The Cross Produt study gude. z x y. Loong t mge, you n see tht
Lernng Enhnement Tem Worsheet: The Cross Produt These re the model nswers for the worsheet tht hs questons on the ross produt etween vetors. The Cross Produt study gude. z x y. Loong t mge, you n see tht
Solubilities and Thermodynamic Properties of SO 2 in Ionic
 Solubltes nd Therodync Propertes of SO n Ionc Lquds Men Jn, Yucu Hou, b Weze Wu, *, Shuhng Ren nd Shdong Tn, L Xo, nd Zhgng Le Stte Key Lbortory of Checl Resource Engneerng, Beng Unversty of Checl Technology,
Solubltes nd Therodync Propertes of SO n Ionc Lquds Men Jn, Yucu Hou, b Weze Wu, *, Shuhng Ren nd Shdong Tn, L Xo, nd Zhgng Le Stte Key Lbortory of Checl Resource Engneerng, Beng Unversty of Checl Technology,
GAUSS ELIMINATION. Consider the following system of algebraic linear equations
 Numercl Anlyss for Engneers Germn Jordnn Unversty GAUSS ELIMINATION Consder the followng system of lgebrc lner equtons To solve the bove system usng clsscl methods, equton () s subtrcted from equton ()
Numercl Anlyss for Engneers Germn Jordnn Unversty GAUSS ELIMINATION Consder the followng system of lgebrc lner equtons To solve the bove system usng clsscl methods, equton () s subtrcted from equton ()
Solution of Tutorial 5 Drive dynamics & control
 ELEC463 Unversty of New South Wles School of Electrcl Engneerng & elecommunctons ELEC463 Electrc Drve Systems Queston Motor Soluton of utorl 5 Drve dynmcs & control 500 rev/mn = 5.3 rd/s 750 rted 4.3 Nm
ELEC463 Unversty of New South Wles School of Electrcl Engneerng & elecommunctons ELEC463 Electrc Drve Systems Queston Motor Soluton of utorl 5 Drve dynmcs & control 500 rev/mn = 5.3 rd/s 750 rted 4.3 Nm
Lecture 36. Finite Element Methods
 CE 60: Numercl Methods Lecture 36 Fnte Element Methods Course Coordntor: Dr. Suresh A. Krth, Assocte Professor, Deprtment of Cvl Engneerng, IIT Guwht. In the lst clss, we dscussed on the ppromte methods
CE 60: Numercl Methods Lecture 36 Fnte Element Methods Course Coordntor: Dr. Suresh A. Krth, Assocte Professor, Deprtment of Cvl Engneerng, IIT Guwht. In the lst clss, we dscussed on the ppromte methods
ragsdale (zdr82) HW6 ditmire (58335) 1 the direction of the current in the figure. Using the lower circuit in the figure, we get
 rgsdle (zdr8) HW6 dtmre (58335) Ths prnt-out should hve 5 questons Multple-choce questons my contnue on the next column or pge fnd ll choces efore nswerng 00 (prt of ) 00 ponts The currents re flowng n
rgsdle (zdr8) HW6 dtmre (58335) Ths prnt-out should hve 5 questons Multple-choce questons my contnue on the next column or pge fnd ll choces efore nswerng 00 (prt of ) 00 ponts The currents re flowng n
Model Fitting and Robust Regression Methods
 Dertment o Comuter Engneerng Unverst o Clorn t Snt Cruz Model Fttng nd Robust Regresson Methods CMPE 64: Imge Anlss nd Comuter Vson H o Fttng lnes nd ellses to mge dt Dertment o Comuter Engneerng Unverst
Dertment o Comuter Engneerng Unverst o Clorn t Snt Cruz Model Fttng nd Robust Regresson Methods CMPE 64: Imge Anlss nd Comuter Vson H o Fttng lnes nd ellses to mge dt Dertment o Comuter Engneerng Unverst
Chem Homework 11 due Monday, Apr. 28, 2014, 2 PM
 Chem 44 - Homework due ondy, pr. 8, 4, P.. . Put this in eq 8.4 terms: E m = m h /m e L for L=d The degenery in the ring system nd the inresed sping per level (4x bigger) mkes the sping between the HOO
Chem 44 - Homework due ondy, pr. 8, 4, P.. . Put this in eq 8.4 terms: E m = m h /m e L for L=d The degenery in the ring system nd the inresed sping per level (4x bigger) mkes the sping between the HOO
ECEN 5807 Lecture 26
 ECEN 5807 eture 6 HW 8 due v D Frdy, rh, 0 S eture 8 on Wed rh 0 wll be leture reorded n 0 he week of rh 5-9 Sprng brek, no le ody: Conlude pled-dt odelng of hghfrequeny ndutor dyn n pek urrentode ontrolled
ECEN 5807 eture 6 HW 8 due v D Frdy, rh, 0 S eture 8 on Wed rh 0 wll be leture reorded n 0 he week of rh 5-9 Sprng brek, no le ody: Conlude pled-dt odelng of hghfrequeny ndutor dyn n pek urrentode ontrolled
Green s Theorem. (2x e y ) da. (2x e y ) dx dy. x 2 xe y. (1 e y ) dy. y=1. = y e y. y=0. = 2 e
 Green s Theorem. Let be the boundry of the unit squre, y, oriented ounterlokwise, nd let F be the vetor field F, y e y +, 2 y. Find F d r. Solution. Let s write P, y e y + nd Q, y 2 y, so tht F P, Q. Let
Green s Theorem. Let be the boundry of the unit squre, y, oriented ounterlokwise, nd let F be the vetor field F, y e y +, 2 y. Find F d r. Solution. Let s write P, y e y + nd Q, y 2 y, so tht F P, Q. Let
CONTINUE ON LEADS PLACEMENT
 Hert Letrure ECG leds, ECE4610, Z. Moussv CONTINUE ON LEADS PLACEMENT A I L LA I II III 0 II F III Three ddtonl leds re unpolr eletrodes euse they onsst of the potentl pperng on one eletrode tken th respet
Hert Letrure ECG leds, ECE4610, Z. Moussv CONTINUE ON LEADS PLACEMENT A I L LA I II III 0 II F III Three ddtonl leds re unpolr eletrodes euse they onsst of the potentl pperng on one eletrode tken th respet
Introduction to Numerical Integration Part II
 Introducton to umercl Integrton Prt II CS 75/Mth 75 Brn T. Smth, UM, CS Dept. Sprng, 998 4/9/998 qud_ Intro to Gussn Qudrture s eore, the generl tretment chnges the ntegrton prolem to ndng the ntegrl w
Introducton to umercl Integrton Prt II CS 75/Mth 75 Brn T. Smth, UM, CS Dept. Sprng, 998 4/9/998 qud_ Intro to Gussn Qudrture s eore, the generl tretment chnges the ntegrton prolem to ndng the ntegrl w
CHAPTER 20: Second Law of Thermodynamics
 CHAER 0: Second Lw of hermodynmics Responses to Questions 3. kg of liquid iron will hve greter entropy, since it is less ordered thn solid iron nd its molecules hve more therml motion. In ddition, het
CHAER 0: Second Lw of hermodynmics Responses to Questions 3. kg of liquid iron will hve greter entropy, since it is less ordered thn solid iron nd its molecules hve more therml motion. In ddition, het
An Adaptive Control Algorithm for Multiple-Input Multiple-Output Systems Using Neural Networks
 An Adptve Control Algorthm for Multple-Input Multple-Output Systems Usng Neurl Networks JOSE NORIEGA Deprtmento de Investgón en Fís Unversdd de Sonor Rosles y Blvd. Lus Enns, Col. Centro, CP, Hllo, Son.
An Adptve Control Algorthm for Multple-Input Multple-Output Systems Usng Neurl Networks JOSE NORIEGA Deprtmento de Investgón en Fís Unversdd de Sonor Rosles y Blvd. Lus Enns, Col. Centro, CP, Hllo, Son.
Mr. Mane S.G. 1, Mr. Powar R.V. 2
 IOSR Journl of Computer Engneerng (IOSR-JCE) ISSN : 2278-066, ISBN : 2278-8727, PP : 5-9 www.osrjournls.org Fndng Attrbute Seleton Mesures by Computng Loss of Informton nd Ambguty for Dt Mr. Mne S.G.,
IOSR Journl of Computer Engneerng (IOSR-JCE) ISSN : 2278-066, ISBN : 2278-8727, PP : 5-9 www.osrjournls.org Fndng Attrbute Seleton Mesures by Computng Loss of Informton nd Ambguty for Dt Mr. Mne S.G.,
Issues in Information Systems Volume 14, Issue 1, pp , 2013
 Issues n Informton Systems Volume 4, Issue, pp.58-65, 0 RITI REVIEW OF POPUR MUTI-RITERI DEISION MKING METHODOGIES Yong. Shn, Frns Mron Unversty, yshn@fmron.edu Seungho. ee, Ulsn ollege, shlee@u. Sun G
Issues n Informton Systems Volume 4, Issue, pp.58-65, 0 RITI REVIEW OF POPUR MUTI-RITERI DEISION MKING METHODOGIES Yong. Shn, Frns Mron Unversty, yshn@fmron.edu Seungho. ee, Ulsn ollege, shlee@u. Sun G
Temperature. Chapter Heat Engine
 Chapter 3 Temperature In prevous chapters of these notes we ntroduced the Prncple of Maxmum ntropy as a technque for estmatng probablty dstrbutons consstent wth constrants. In Chapter 9 we dscussed the
Chapter 3 Temperature In prevous chapters of these notes we ntroduced the Prncple of Maxmum ntropy as a technque for estmatng probablty dstrbutons consstent wth constrants. In Chapter 9 we dscussed the
ECE 6340 Intermediate EM Waves. Fall Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 3
 C 634 Intermedate M Waves Fall 216 Prof. Davd R. akson Dept. of C Notes 3 1 Types of Current ρ v Note: The free-harge densty ρ v refers to those harge arrers (ether postve or negatve) that are free to
C 634 Intermedate M Waves Fall 216 Prof. Davd R. akson Dept. of C Notes 3 1 Types of Current ρ v Note: The free-harge densty ρ v refers to those harge arrers (ether postve or negatve) that are free to
TDDB AT LOW VOLTAGES: AN ELECTROCHEMICAL PERSPECTIVE
 TDDB AT LOW VOLTAGES: AN ELECTROCEMICAL PERSPECTIVE R. Murldhr, T. Shw, F. Chen 2, P. Oldges 3, D. Edelsten, S. Cohen, R. Ahnt 3, G. Bonll nd M. Bznt 4 IBM Thoms J. Wtson Reserh Center, Yorktown eghts,
TDDB AT LOW VOLTAGES: AN ELECTROCEMICAL PERSPECTIVE R. Murldhr, T. Shw, F. Chen 2, P. Oldges 3, D. Edelsten, S. Cohen, R. Ahnt 3, G. Bonll nd M. Bznt 4 IBM Thoms J. Wtson Reserh Center, Yorktown eghts,
Chapter 2. LOGARITHMS
 Chpter. LOGARITHMS Dte: - 009 A. INTRODUCTION At the lst hpter, you hve studied bout Idies d Surds. Now you re omig to Logrithms. Logrithm is ivers of idies form. So Logrithms, Idies, d Surds hve strog
Chpter. LOGARITHMS Dte: - 009 A. INTRODUCTION At the lst hpter, you hve studied bout Idies d Surds. Now you re omig to Logrithms. Logrithm is ivers of idies form. So Logrithms, Idies, d Surds hve strog
Global alignment. Genome Rearrangements Finding preserved genes. Lecture 18
 Computt onl Biology Leture 18 Genome Rerrngements Finding preserved genes We hve seen before how to rerrnge genome to obtin nother one bsed on: Reversls Knowledge of preserved bloks (or genes) Now we re
Computt onl Biology Leture 18 Genome Rerrngements Finding preserved genes We hve seen before how to rerrnge genome to obtin nother one bsed on: Reversls Knowledge of preserved bloks (or genes) Now we re
Generalized Lorentz Transformation Allowing the Relative Velocity of Inertial Reference Systems Greater Than the Light Velocity
 Generlzed Lorentz Trnsformton Allowng the Relte Veloty of Inertl Referene Systems Greter Thn the Lght Veloty Yu-Kun Zheng Memer of the Chnese Soety of Grtton nd Reltst Astrophyss Eml:yzheng@puorgn Astrt:
Generlzed Lorentz Trnsformton Allowng the Relte Veloty of Inertl Referene Systems Greter Thn the Lght Veloty Yu-Kun Zheng Memer of the Chnese Soety of Grtton nd Reltst Astrophyss Eml:yzheng@puorgn Astrt:
New Algorithms: Linear, Nonlinear, and Integer Programming
 New Algorthms: ner, Nonlner, nd Integer Progrmmng Dhnnjy P. ehendle Sr Prshurmhu College, Tl Rod, Pune-400, Ind dhnnjy.p.mehendle@gml.om Astrt In ths pper we propose new lgorthm for lner progrmmng. Ths
New Algorthms: ner, Nonlner, nd Integer Progrmmng Dhnnjy P. ehendle Sr Prshurmhu College, Tl Rod, Pune-400, Ind dhnnjy.p.mehendle@gml.om Astrt In ths pper we propose new lgorthm for lner progrmmng. Ths
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Example Problems on Heat Transfer
 Prncples of Food and Boprocess Engneerng (FS 31) Solutons to Example Problems on Heat Transfer 1. We start wth Fourer s law of heat conducton: Q = k A ( T/ x) Rearrangng, we get: Q/A = k ( T/ x) Here,
Prncples of Food and Boprocess Engneerng (FS 31) Solutons to Example Problems on Heat Transfer 1. We start wth Fourer s law of heat conducton: Q = k A ( T/ x) Rearrangng, we get: Q/A = k ( T/ x) Here,
CALCULATING REACTING QUANTITIES
 MODULE 2 14 WORKSHEET WORKSHEET For multiple-hoie questions 1 5 irle the letter orresponding to the most orret nswer. 1 The lned eqution for the urning of utnol (C 4 H 9 OH) is given elow: C 4 H 9 OH(l)
MODULE 2 14 WORKSHEET WORKSHEET For multiple-hoie questions 1 5 irle the letter orresponding to the most orret nswer. 1 The lned eqution for the urning of utnol (C 4 H 9 OH) is given elow: C 4 H 9 OH(l)
Gravity Drainage Prior to Cake Filtration
 1 Gravty Dranage Pror to ake Fltraton Sott A. Wells and Gregory K. Savage Department of vl Engneerng Portland State Unversty Portland, Oregon 97207-0751 Voe (503) 725-4276 Fax (503) 725-4298 ttp://www.e.pdx.edu/~wellss
1 Gravty Dranage Pror to ake Fltraton Sott A. Wells and Gregory K. Savage Department of vl Engneerng Portland State Unversty Portland, Oregon 97207-0751 Voe (503) 725-4276 Fax (503) 725-4298 ttp://www.e.pdx.edu/~wellss
University of Groningen. Electrodialytic recovery of acids and bases Visser, Cornelis
 Unversty of Gronngen Eletrodalyt reovery of ads and bases Vsser, Cornels IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advsed to onsult the publsher's verson (publsher's PDF) f you wsh to te from t. Please hek the doument verson
Unversty of Gronngen Eletrodalyt reovery of ads and bases Vsser, Cornels IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advsed to onsult the publsher's verson (publsher's PDF) f you wsh to te from t. Please hek the doument verson
( ) 1. 1) Let f( x ) = 10 5x. Find and simplify f( 2) and then state the domain of f(x).
 Mth 15 Fettermn/DeSmet Gustfson/Finl Em Review 1) Let f( ) = 10 5. Find nd simplif f( ) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = +. Find nd simplif f(1) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = 8.
Mth 15 Fettermn/DeSmet Gustfson/Finl Em Review 1) Let f( ) = 10 5. Find nd simplif f( ) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = +. Find nd simplif f(1) nd then stte the domin of f(). ) Let f( ) = 8.
SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE
 SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Indices & Logrithms 2 Contents Indices.2 Frctionl Indices.4 Logrithms 6 Exponentil equtions. Simplifying Surds 13 Opertions on Surds..16 Scientific Nottion..18
SUMMER KNOWHOW STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Indices & Logrithms 2 Contents Indices.2 Frctionl Indices.4 Logrithms 6 Exponentil equtions. Simplifying Surds 13 Opertions on Surds..16 Scientific Nottion..18
Project 6: Minigoals Towards Simplifying and Rewriting Expressions
 MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
MAT 51 Wldis Projet 6: Minigols Towrds Simplifying nd Rewriting Expressions The distriutive property nd like terms You hve proly lerned in previous lsses out dding like terms ut one prolem with the wy
Tutorial Worksheet. 1. Find all solutions to the linear system by following the given steps. x + 2y + 3z = 2 2x + 3y + z = 4.
 Mth 5 Tutoril Week 1 - Jnury 1 1 Nme Setion Tutoril Worksheet 1. Find ll solutions to the liner system by following the given steps x + y + z = x + y + z = 4. y + z = Step 1. Write down the rgumented mtrix
Mth 5 Tutoril Week 1 - Jnury 1 1 Nme Setion Tutoril Worksheet 1. Find ll solutions to the liner system by following the given steps x + y + z = x + y + z = 4. y + z = Step 1. Write down the rgumented mtrix
Table of Content. c 1 / 5
 Tehnil Informtion - t nd t Temperture for Controlger 03-2018 en Tble of Content Introdution....................................................................... 2 Definitions for t nd t..............................................................
Tehnil Informtion - t nd t Temperture for Controlger 03-2018 en Tble of Content Introdution....................................................................... 2 Definitions for t nd t..............................................................
4.4 Areas, Integrals and Antiderivatives
 . res, integrls nd ntiderivtives 333. Ares, Integrls nd Antiderivtives This section explores properties of functions defined s res nd exmines some connections mong res, integrls nd ntiderivtives. In order
. res, integrls nd ntiderivtives 333. Ares, Integrls nd Antiderivtives This section explores properties of functions defined s res nd exmines some connections mong res, integrls nd ntiderivtives. In order
Numbers and indices. 1.1 Fractions. GCSE C Example 1. Handy hint. Key point
 GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
GCSE C Emple 7 Work out 9 Give your nswer in its simplest form Numers n inies Reiprote mens invert or turn upsie own The reiprol of is 9 9 Mke sure you only invert the frtion you re iviing y 7 You multiply
Chapter Gauss Quadrature Rule of Integration
 Chpter 7. Guss Qudrture Rule o Integrtion Ater reding this hpter, you should e le to:. derive the Guss qudrture method or integrtion nd e le to use it to solve prolems, nd. use Guss qudrture method to
Chpter 7. Guss Qudrture Rule o Integrtion Ater reding this hpter, you should e le to:. derive the Guss qudrture method or integrtion nd e le to use it to solve prolems, nd. use Guss qudrture method to
CENTROID (AĞIRLIK MERKEZİ )
 CENTOD (ĞLK MEKEZİ ) centrod s geometrcl concept rsng from prllel forces. Tus, onl prllel forces possess centrod. Centrod s tougt of s te pont were te wole wegt of pscl od or sstem of prtcles s lumped.
CENTOD (ĞLK MEKEZİ ) centrod s geometrcl concept rsng from prllel forces. Tus, onl prllel forces possess centrod. Centrod s tougt of s te pont were te wole wegt of pscl od or sstem of prtcles s lumped.
Exercise 10: Theory of mass transfer coefficient at boundary
 Partle Tehnology Laboratory Prof. Sotrs E. Pratsns Sonneggstrasse, ML F, ETH Zentrum Tel.: +--6 5 http://www.ptl.ethz.h 5-97- U Stoffaustaush HS 7 Exerse : Theory of mass transfer oeffent at boundary Chapter,
Partle Tehnology Laboratory Prof. Sotrs E. Pratsns Sonneggstrasse, ML F, ETH Zentrum Tel.: +--6 5 http://www.ptl.ethz.h 5-97- U Stoffaustaush HS 7 Exerse : Theory of mass transfer oeffent at boundary Chapter,
ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 6 ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Introducton Runge-Kutt Metods Mult-step Metods Sstem o Equtons Boundr Vlue Problems Crcterstc Vlue Problems Cpter 6 Ordnr Derentl Equtons / 6. Introducton In mn engneerng
6 ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Introducton Runge-Kutt Metods Mult-step Metods Sstem o Equtons Boundr Vlue Problems Crcterstc Vlue Problems Cpter 6 Ordnr Derentl Equtons / 6. Introducton In mn engneerng
Reducing the Computational Effort of Stochastic Multi-Period DC Optimal Power Flow with Storage
 Redung the Computtonl Effort of Stohst Mult-Perod DC Optml Power Flow wth Storge Olver Mégel Görn Andersson Power Systems Lbortory ETH Zürh Zürh, Swtzerlnd {megel, ndersson}@eeh.ee.ethz.h Johnn L. Mtheu
Redung the Computtonl Effort of Stohst Mult-Perod DC Optml Power Flow wth Storge Olver Mégel Görn Andersson Power Systems Lbortory ETH Zürh Zürh, Swtzerlnd {megel, ndersson}@eeh.ee.ethz.h Johnn L. Mtheu
CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT. PART IA (First Year) Paper 4 : Mathematical Methods
 Engneerng Prt I 009-0, Pper 4, Mthemtl Methods, Fst Course, J.B.Young CMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING DEPRTMENT PRT I (Frst Yer) 009-00 Pper 4 : Mthemtl Methods Leture ourse : Fst Mths Course, Letures
Engneerng Prt I 009-0, Pper 4, Mthemtl Methods, Fst Course, J.B.Young CMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY ENGINEERING DEPRTMENT PRT I (Frst Yer) 009-00 Pper 4 : Mthemtl Methods Leture ourse : Fst Mths Course, Letures
AP CALCULUS Test #6: Unit #6 Basic Integration and Applications
 AP CALCULUS Test #6: Unit #6 Bsi Integrtion nd Applitions A GRAPHING CALCULATOR IS REQUIRED FOR SOME PROBLEMS OR PARTS OF PROBLEMS IN THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION. () The ext numeril vlue of the orret
AP CALCULUS Test #6: Unit #6 Bsi Integrtion nd Applitions A GRAPHING CALCULATOR IS REQUIRED FOR SOME PROBLEMS OR PARTS OF PROBLEMS IN THIS PART OF THE EXAMINATION. () The ext numeril vlue of the orret
Homogeneous model: Horizontal pipe and horizontal well. Flow loops can't duplicate field conditions. Daniel D. Joseph. April 2001
 Homogeneous model of producton of heavy ol through horzontal ppelnes and wells based on the Naver-Stokes equatons n the ppelne or the well and Darcy's law n the reservor Homogeneous model: Danel D. Joseph
Homogeneous model of producton of heavy ol through horzontal ppelnes and wells based on the Naver-Stokes equatons n the ppelne or the well and Darcy's law n the reservor Homogeneous model: Danel D. Joseph
