Names: ESS 315 Lab # 1 Seismic Hazards along the Cascadia Subduction Zone
|
|
|
- Melvyn Black
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
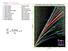
1 Names: ESS 315 Lab # 1 Seismic Hazards along the Cascadia Subduction Zone 1 Seismographs located throughout the Pacific Northwest record thousands of earthquakes each year in Washington and Oregon. Between one and two dozen of these earthquakes cause enough ground shaking to be felt by residents, though few cause any damage. However, based on the history of past damaging earthquakes and our understanding of the geologic history of the Pacific Northwest and of the interaction between the Juan de Fuca (oceanic) and North American (continental) plates, it is inevitable that damaging earthquakes (magnitude 6 or greater) will recur in our region. To date, we have no way to predict whether this event will occur today or many years in the future. Earthquakes are driven by geologic processes that produce stress in the earth. In the Pacific Northwest, the ocean floor is being subducted beneath the North American continent along a major plate boundary parallel to the coast of Washington and Oregon. The boundary, called the Cascadia Subduction Zone lies about 50 miles offshore and extends from the middle of Vancouver Island in British Columbia past Washington and Oregon to northern California. Damaging earthquakes occur in the continental crust and deep in the subducted oceanic plate as well as along the subduction zone (Fig. 1-1). Figure 1-1: Earthquakes along the Cascadia Subduction Zone
2 2 Deep earthquakes in the subducted oceanic plate: The three most recent damaging earthquakes in Washington, 2001 (M 6.8, near Olympia) 1965 (M 6.5, located between Seattle and Tacoma) and 1949 (M 7.1, near Olympia), were approximately miles deep, within the oceanic plate where it lies beneath the continent. These earthquakes caused serious damage, and were felt as far away as Montana. Other sizable events that were probably deep occurred in 1882, 1909, and Shallow earthquakes in the continental crust: The largest historic earthquake in Washington or Oregon occurred in 1872 in the North Cascades. This earthquake had an estimated magnitude 7.4 and was followed by many aftershocks. It was probably at a depth of 10 miles or less within the continental crust. In 1993, crustal earthquakes in Oregon caused over $30 million in damages, and in January 1995 a magnitude 5.0 crustal earthquake was widely felt and did minor damage in the Puget Lowland. There are many crustal faults in Washington and Oregon that could produce damaging earthquakes. Geologic evidence indicates that a large shallow earthquake took place within the central Puget Basin 1,100 years ago along what is now called the Seattle Fault, causing massive block landslides into Lake Washington, a tsunami in Puget Sound which left sand deposits at West Point in Seattle and at Cultus Bay on Whidbey Island, and large rock avalanches on the southeastern Olympic Peninsula. Subduction Zone megathrust earthquakes: Although no large earthquakes have happened along the offshore Cascadia Subduction Zone since our historic records began in 1790, similar subduction zones worldwide do produce great earthquakes - magnitude 8 or larger. These occur because the oceanic crust sticks as it is being pushed beneath the continent, rather than sliding smoothly. Over hundreds of years, large stresses build which are released suddenly in great earthquakes. Such earthquakes typically have a minute or more of strong ground shaking, and are quickly followed by damaging tsunamis and numerous large aftershocks. The M 9.2 Alaskan earthquake of 1964 was a great subduction zone earthquake (as was the recent M 9.0 earthquake in Indonesia). Geological evidence shows that the Cascadia Subduction Zone has also generated great earthquakes, and the most recent one was about 300 years ago. Large earthquakes also occur at the southern end of the Cascadia Subduction Zone (near the Oregon-California border) where it meets the San Andreas Fault system: including a magnitude 7.1 earthquake in 1992, and a magnitude 6.8 (estimated) earthquake in Seismic Waves There are three main types of seismic wave energy generated by earthquakes, and each travels through the earth a different velocities. P- (compressional) and S- (shear) waves are both body waves, which will travel outward from the point of origin (e.g., like light or sound waves) and will propagate through the earth. Compressional waves deform rock through a change in volume while shear wave deform material through a change in shape. P waves are the fastest seismic waves, traveling at about 6.0 km/sec through the Earth s crust. S-waves travel at about 3.5 km/sec through the Earth s crust. Surface waves (analogous to ocean waves), the slowest seismic waves, are restricted to the Earth s surface and are associated with the greatest ground shaking. Because P-waves travel faster than S-waves, they arrive sooner at any given distance from the origin of the earthquake. The greater the distance from the origin, the greater the lag time between the arrivals of the P- and S-waves. This fact is important to locating the epicenter of an earthquake--that point on the Earth s surface which lies directly above the focus of seismic energy release.
3 Locating earthquake epicenters 3 If a seismic event has been recorded by at least three or more seismographs, its epicenter can be determined using simple calculations. In today s lab you will determine the location of the epicenter using seismic data from one of two earthquake seismograms shown below (Fig. 1-2). Figure 1-2 (above): Seismograms for two earthquakes in North America.
4 Tables 1-1A and 1-1B 4 Earthquake 1 (1-A) STATION Time of P arrival (min) A Time of S arrival (min) P-S lag time (min) Distance from epicenter (km) B C Earthquake 2 (1-1B) STATION Time of P arrival (min) A Time of S arrival (min) P-S lag time (min) Distance from epicenter (km) B C 1. Determine the distance between the seismograph and epicenter. This is accomplished by comparing the arrival times of the P- and S- waves (See Fig. 1-3) using average traveltime curves for each respective wave. The greater the difference between arrival times, the greater the corresponding distance from the seismic station and epicenter. Record this information for each of the three seismic stations in the Tables 1-1A and 1-1B. Convert the lag times to distances from the epicenter using the lowermost curve in Fig Figure Using a compass and pencil draw three circles (or arcs) on the North American map (Fig. 1-4) centered on the seismic stations with radii equal to the distance from the epicenter.
5 5 Golden Pasadena Mephis Figure 1-4: Seismic hazard map of the United States showing three seismic stations (Pasadena, CA, Golden, CO, Mephis, TN), shown by circles on map. 3. Is the epicenter of your earthquake near a plate boundary? If so, what type of plate boundary? Assigning Earthquake Magnitudes The magnitude of an earthquake is the quantitative description of the energy it releases. The Richter scale is the most common magnitude scale and is based on the height, or amplitude, of the first P-wave arrival recorded on a seismogram, adjusted for distance to the epicenter. Wave amplitude is directly related to the total area of rupture (slip) on a fault, which is a major factor governing the energy released during an earthquake. Because the energy released during earthquakes can vary greatly, the Richter scale is logarithmic. Each unit increase on the Richter scale corresponds to a ten-fold increase in P-wave amplitude and rupture area, and a thirty-fold increase in seismic energy release. If a Richter magnitude 1 earthquake is assigned an energy value of 1, then the relationship between earthquake magnitude (M) and energy (E) is: E=30 M-1 Using the above mathematical equation, make a plot of earthquake energy release (E, vertical axis) vs. magnitude from 1 to 9 (M, horizontal axis) on the semi-logarithmic graph paper provided.
6 6 Figure 1-5 shows seismograms from 5 earthquake events, all recorded at a distance of 100 km from the epicenter. Determine the magnitudes of the earthquakes represented by comparing the amplitude of their first P-wave arrival with the P-wave amplitude on the record for the devastating 1988 magnitude 7 earthquake in Armenia. Remember that 10- fold increase in P-wave amplitude (A) corresponds to a 1 unit increase in magnitude, so if a magnitude 7 earthquake registers a P-wave amplitude of 1 mm, then: A=10 M-7 (where A is amplitude in mm) Solving for M, this equation becomes M=log(A, in mm)+7 Figure 1-5: Seismograms from 5 earthquake events (100 km from epicenter). Enter the P-wave amplitudes and magnitudes in Table 1-2 below then plot these earthquakes on your magnitude vs. energy release graph on the following page. Table 1-2 EVENT MAXIMUM AMPLITUDE MAGNITUDE 1988: Armenia 1.00 mm : Loma Prieta, CA 1976: Tangshan, China 1964: Southern Alaska 1 Megaton Nuclear Explosion
7 7 Earthquake magnitude vs. energy 1E+12 1E+11 1E+10 1E+09 1E+08 energy 1E+07 1E magnitude Earthquake Damage and Intensity Earthquake damage can result from both primary effects, that cause damage directly (i.e., ground shaking and fault rupture) and secondary effects, that cause damage indirectly through processes that result from the earthquake event (i.e., fire, landslides, tsunamis, liquefaction, flooding). The amount of damage (intensity) that results from a given earthquake is related to several factors: 1) magnitude of the earthquake, 2) distance to the earthquake focus, 3) type of faulting, and 4) type of geologic substrate. Earthquake intensity has been quantified using the modified Mercalli intensity scale that is based on the amount of vibration people feel during low-magnitude earthquakes and the extent of damage to buildings during high-magnitude quakes (see the Mercalli scale in Table 1-3 at the back of this handout).
8 8 Most earthquake damage is caused by ground shaking. The wide variety of effects caused by earthquake ground shaking results partly from differences in the way geologic substrates transmit seismic waves. Unconsolidated sediments will tend to amplify seismic waves, particularly soft sediments like artificial fill and fine-grained muds or clays (See Fig. 1-6 below). Fig. 1-6: Seismograms recorded for a magnitude 4.1 aftershock to the Loma Prieta earthquake (taken from Murck et al., 1996), on bedrock in the Oakland Hills (S4), on unconsolidated material (i.e., sand and gravel) near an uncollapsed portion of the freeway (S3), and on mud near the collapsed Nimitz Freeway (S1). All three seismograms are plotted on the same scale. We have provided seismograms of the magnitude 3.5 Beacon Hill Earthquake for various regions of downtown Seattle (Figure 1-7). Based on your knowledge about the relationship between substrate and seismic wave amplification, determine which three Seismograms represent locations overlying artificial fill,, and. One of the locations overlies Tertiary bedrock. Which seismogram do you thing represents a bedrock location?. Find this location on the geologic map of Seattle (provided in lab). What geologic substrate underlies this seismogram?. Use the geologic map (provided in lab) of Seattle to determine the substrate that Seattle University, University of Washington the Space Needle overlie..
9 Mag 3.5 Bea con Hill Ea rthq uake, Feb 10 th, 1997 (S-wave ground velocity recorded by 2 Hz north-south seismometers) 9 Harbor Island Kingdome (Seahawk Stadium) Warehouse District Beacon Hill West Seattle South Warehouse District Yesler Terrace Space Needle Franklin HS Seward Park Seconds Figure 1-7: Seattle seismograms recording S-wave ground velocities.
10 10 We have copied a portion of the surficial geologic map of Seattle (Figure 1-8). We would like you to develop a seismic risk map for this part of Seattle. We would like you to subdivide your risk map into three different risk-levels (III-high, II-moderate, and I-low), based mainly on substrate conditions and potential for seismic-induced landslides. Use a red pencil crayon to color in all of your high-risk areas, orange pencil crayon for moderate risk areas and yellow for lower risk areas. Figure 1-8: Surfical geology map of South Seattle (see map provided in laboratory for geologic unit description).
11 11 Which of Seattle s famous landmarks are located in high-risk locations? What is the earthquake risk for the location where you live (Use the surficial geologic map (provided in laboratory)? TABLE MODIFIED MERCALLI INTENSITY SCALE MMI Summary Full description value description I Not felt Not felt. Marginal and long period effects of large earthquakes. II Felt by persons at rest, on upper floors, or favorably placed III Felt indoors. Hanging objects swing. Vibration like passing of light trucks. Duration estimated. May not be recognized as an earthquake IV Hanging objects swing. Vibration like passing of heavy trucks; or sensation of a jolt like a heavy ball striking the walls. Standing motor cars rock. Windows, dishes, doors rattle Glasses clink. Crockery clashes. In the upper range of IV, wooden walls and frame creak. V Pictures move Felt outdoors; direction estimated. Sleepers wakened. Liquids disturbed, some spilled. Small unstable objects displaced or upset. Doors swing, close, open. Shutters, pictures move Pendulum clocks stop, start, change rate. VI Objects fall Felt by all. Many frightened and run outdoors. Persons walk unsteadily. Windows, dishes, glassware broken. Knickknacks, books, etc., off shelves. Pictures off walls. Furniture moved or overturned. Weak plaster and masonry D* cracked. Small bells ring (church, school). Trees, bushes shaken VII VIII Nonstructural damage Moderate damage (visibly, or heard to rustle). Difficult to stand. Noticed by drivers of motor cars. Hanging objects quiver. Furniture broken. Damage to masonry D, including cracks. Weak chimneys broken at roof line. Fall of plaster, loose bricks, stones, tiles, cornices (also unbraced parapets and architectural ornaments). Some cracks in masonry C. Waves on ponds; water turbid with mud. Small slides caving in along sand or gravel banks. Large bells ring. Concrete irrigation ditches damaged Steering of motor cars affected. Damage to masonry C; partial collapse. Some damage to masonry B; none to masonry A. Fall of stucco and some masonry walls. Twisting, fall of chimneys, factory stacks, monuments, towers, elevated tanks. Frame houses moved on foundations if not bolted down; loose panel walls thrown out. Decayed piling broken off. Branches broken from trees. Changes in flow or temperature of springs and wells. Cracks in wet ground and on steep slopes. IX Heavy damage General panic. Masonry D destroyed; masonry C heavily damaged, sometimes with complete collapse; masonry B seriously damaged (General damage to foundations.) Frame structures, if not bolted, shifted off foundations. Frames racked. Serious to reservoirs. Underground pipes broken. Conspicuous cracks in reservoirs. Underground pipes broken. Conspicuous cracks in fountains, sand craters. X Extreme damage Most masonry and frame structures destroyed with their foundations. Some well-built wooden structures and bridges destroyed. Serious damage to dams, dikes, embankments. Large landslides. Water thrown on banks of canals, rivers, lakes, etc. Sand and mud shifted horizontally on beaches and flat land. Rails bent slightly. XI XII Rails bent greatly. Underground pipelines completely out of service. Damage nearly total. Large rock masses displaced. Lines of sight and level distorted. Objects thrown into the air. *Masonry A: Good workmanship, mortar, and design; reinforced, especially laterally, and bound together by using steel, concrete, etc.; designed to resist lateral forces. Masonry B: Good workmanship and mortar; reinforced, but not designed in detail to resist lateral forces. Masonry C: Ordinary workmanship and mortar; no extreme weaknesses like failing to tie in at corners, but neither reinforced nor designed against horizontal forces. Masonry D: Weak materials, such as adobe; poor mortar; low standards of workmanship; weak horizontally. Full descriptions are from: Richter, C.F., Elementary Seismology. W.H. Freeman and Company, San Francisco, pp ;
earthquakes 1. Earthquakes occur when plates grind against one another along cracks called faults.
 earthquakes BEGIN 1 earthquakes 1. Earthquakes occur when plates grind against one another along cracks called faults. 2 earthquakes 1. Earthquakes occur when plates grind against one another along cracks
earthquakes BEGIN 1 earthquakes 1. Earthquakes occur when plates grind against one another along cracks called faults. 2 earthquakes 1. Earthquakes occur when plates grind against one another along cracks
Released Science Inquiry Task Location Grade 11
 Date: Your Name: Released Science Inquiry Task Location 2009 Grade 11 Science Directions: You will be completing an extended-response inquiry task called Location. Explain the reasons for all of your answers.
Date: Your Name: Released Science Inquiry Task Location 2009 Grade 11 Science Directions: You will be completing an extended-response inquiry task called Location. Explain the reasons for all of your answers.
1. Why do earthquakes happen? 3. What type of mechanical waves are Primary or P waves? 4. What type of mechanical waves are Secondary or S waves?
 Name Period Earthquake Activity Background Information Earthquakes occur because of a sudden release of stored energy. This energy has built up over long periods of time as a result of tectonic forces
Name Period Earthquake Activity Background Information Earthquakes occur because of a sudden release of stored energy. This energy has built up over long periods of time as a result of tectonic forces
Earthquakes. Dr. Mark van der Meijde INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND EARTH OBSERVATION
 Earthquakes Dr. Mark van der Meijde vandermeijde@itc.nl INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND EARTH OBSERVATION Topics to handle Theory of earthquakes Mechanism Strength Measurements
Earthquakes Dr. Mark van der Meijde vandermeijde@itc.nl INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND EARTH OBSERVATION Topics to handle Theory of earthquakes Mechanism Strength Measurements
Earthquake. earthquake, epicenters in the U.S. Kobe, Japan deaths
 Kobe, Japan 1995 5000 deaths Earthquakes It is estimated that there are 500,000 detectable earthquakes in the world each year. 100,000 of those can be felt, and 100 of them cause damage. The world's deadliest
Kobe, Japan 1995 5000 deaths Earthquakes It is estimated that there are 500,000 detectable earthquakes in the world each year. 100,000 of those can be felt, and 100 of them cause damage. The world's deadliest
An earthquake can cause:
 Earthquakes An earthquake is a sudden rapid shaking of the earth. They are caused by the breaking and shifting of the rock beneath the earth s surface. Often found in conjunction with Plate tectonic boundaries.
Earthquakes An earthquake is a sudden rapid shaking of the earth. They are caused by the breaking and shifting of the rock beneath the earth s surface. Often found in conjunction with Plate tectonic boundaries.
dt r = 0 sin i 0 = P d Δ V 0
 dt dδ = r 0 sin i 0 V 0 = P sin i toa Me Always someone needs to reorder and make difficult to check Me One that agrees with me many don t though many agree with each other science begins Locating Local
dt dδ = r 0 sin i 0 V 0 = P sin i toa Me Always someone needs to reorder and make difficult to check Me One that agrees with me many don t though many agree with each other science begins Locating Local
EPS 20: Earthquakes. Laboratory Exercise 1. Intensity
 Name GSI Name EPS 20: Earthquakes Laboratory Exercise 1 Intensity Purpose: To investigate seismic intensity and how it is used to describe the effects of earthquakes Background: Several hundred years ago,
Name GSI Name EPS 20: Earthquakes Laboratory Exercise 1 Intensity Purpose: To investigate seismic intensity and how it is used to describe the effects of earthquakes Background: Several hundred years ago,
Mw 7.8, Southwest of Sumatra, Indonesia Wed, 2 March 2016 at 12:49:48 UTC M /03/03
 Earthquake overview AFGHANISTA N PAKISTA N INDIA A moment magnitude (Mw) 7.8 earthquake struck in South West, Indonesia. The epicentre was centered about 800 km West South West of Padang, Sumatra province,
Earthquake overview AFGHANISTA N PAKISTA N INDIA A moment magnitude (Mw) 7.8 earthquake struck in South West, Indonesia. The epicentre was centered about 800 km West South West of Padang, Sumatra province,
Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy.
 Earthquake Machine Stick-slip: Elastic Rebound Theory Jerky motions on faults produce EQs Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy. Three
Earthquake Machine Stick-slip: Elastic Rebound Theory Jerky motions on faults produce EQs Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy. Three
FOURTH GRADE HAZARDS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE HAZARDS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types of volcanoes.
FOURTH GRADE HAZARDS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types of volcanoes.
20.1 Earthquakes. Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES. Earthquakes and plate boundaries 500 UNIT 6 EARTH S STRUCTURE
 Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES 20.1 Earthquakes In Chapter 19, you read about the San Andreas Fault, which lies along the California coast (Figure 20.1). This fault passes right through San Francisco
Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES 20.1 Earthquakes In Chapter 19, you read about the San Andreas Fault, which lies along the California coast (Figure 20.1). This fault passes right through San Francisco
Earthquakes and Earth s Chapter. Interior
 Earthquakes and Earth s Chapter Interior 8.1 What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Focus and Epicenter Focus is the point within Earth
Earthquakes and Earth s Chapter Interior 8.1 What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Focus and Epicenter Focus is the point within Earth
ENVI.2030L - Earthquakes
 ENVI.2030L - Earthquakes Name I. Introduction The crust of the earth behaves in a brittle manner. Stress is the force applied to a brittle substance and strain represents the build-up of energy in the
ENVI.2030L - Earthquakes Name I. Introduction The crust of the earth behaves in a brittle manner. Stress is the force applied to a brittle substance and strain represents the build-up of energy in the
ESS 202. Landslide. Earthquake effects. ! Natural Hazards. More quake effects. ! Man-aided hazards. Stanford library in 1906
 ESS 202 Today: The Size of an Earthquake! Intensity! Magnitude! Moment House after tsunami, Brumbaugh 8-18 Earthquake effects! Natural Hazards " Ground shaking # Structural collapse # Falling objects "
ESS 202 Today: The Size of an Earthquake! Intensity! Magnitude! Moment House after tsunami, Brumbaugh 8-18 Earthquake effects! Natural Hazards " Ground shaking # Structural collapse # Falling objects "
Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating.
 CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
Figure Diagram of earth movements produced by (a) P-waves and (b) S-waves.
 Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 10: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the focus or
Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 10: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the focus or
Forces in Earth s Crust
 Name Date Class Earthquakes Section Summary Forces in Earth s Crust Guide for Reading How does stress in the crust change Earth s surface? Where are faults usually found, and why do they form? What land
Name Date Class Earthquakes Section Summary Forces in Earth s Crust Guide for Reading How does stress in the crust change Earth s surface? Where are faults usually found, and why do they form? What land
C2.2 The physics of Earthquakes
 C2.2 The physics of Earthquakes C2.2.1 Stress axes and faults Most earthquakes occur because of the mechanical failure on brittle faults. The type of faulting is a consequence of the stress pattern causing
C2.2 The physics of Earthquakes C2.2.1 Stress axes and faults Most earthquakes occur because of the mechanical failure on brittle faults. The type of faulting is a consequence of the stress pattern causing
An entire branch of Earth science, called, is devoted to the study of earthquakes.
 Lesson One Essential Question Where do earthquakes take place? What causes earthquakes? What are three different types of faults that occur at plate boundaries? How does energy from earthquakes travels
Lesson One Essential Question Where do earthquakes take place? What causes earthquakes? What are three different types of faults that occur at plate boundaries? How does energy from earthquakes travels
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 3 Understanding Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information:
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 3 Understanding Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information:
Magnitude 6.3, NORTH OF MOROCCO
 Earthquake location & overview A magnitude 6.3 earthquake struck in Alboran Sea, orth of Morocco; the epicentre was centered about 54 km ( 34 miles) E of Al Hoceima. The depth has been estimated to be
Earthquake location & overview A magnitude 6.3 earthquake struck in Alboran Sea, orth of Morocco; the epicentre was centered about 54 km ( 34 miles) E of Al Hoceima. The depth has been estimated to be
Earthquake Damage Scenario
 Chapter 2. Earthquake Damage Scenario CHAPTER 2. EARTHQUAKE DAMAGE SCENARIO 2.1 Earthquake Scenario Setting and Ground Motion 2.1.1 Fault in the Philippines The Philippines is located in latitude 5 to
Chapter 2. Earthquake Damage Scenario CHAPTER 2. EARTHQUAKE DAMAGE SCENARIO 2.1 Earthquake Scenario Setting and Ground Motion 2.1.1 Fault in the Philippines The Philippines is located in latitude 5 to
Earthquakes. Building Earth s Surface, Part 2. Science 330 Summer What is an earthquake?
 Earthquakes Building Earth s Surface, Part 2 Science 330 Summer 2005 What is an earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all
Earthquakes Building Earth s Surface, Part 2 Science 330 Summer 2005 What is an earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all
Earthquakes & Volcanoes
 Earthquakes & Volcanoes Geology - the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change geo = Earth; ology = study of Earth s Layers Plate Tectonics - the
Earthquakes & Volcanoes Geology - the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change geo = Earth; ology = study of Earth s Layers Plate Tectonics - the
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Satellite Image. False-color IR satellite view of basins and ranges north of Snake River Plain Lost River Rangelower. Lemhi Range-upper.
 Satellite Image False-color IR satellite view of basins and ranges north of Snake River Plain Lost River Rangelower center Lemhi Range-upper center Challis, Idaho is left of center Epicenter of 1983, magnitude
Satellite Image False-color IR satellite view of basins and ranges north of Snake River Plain Lost River Rangelower center Lemhi Range-upper center Challis, Idaho is left of center Epicenter of 1983, magnitude
BUREAU OF MINERAL RESOURCES GEOLOGY AND GEOPHYSICS
 681// (3) COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA DEPARTMENT OF NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT BUREAU OF MINERAL RESOURCES GEOLOGY AND GEOPHYSICS RECORDS: %ICIER RECORD NO. 1968/11 IBRARY ra 1 7J UN 1968 ref: SEISMICITY OF BOUGAINVILLE,
681// (3) COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA DEPARTMENT OF NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT BUREAU OF MINERAL RESOURCES GEOLOGY AND GEOPHYSICS RECORDS: %ICIER RECORD NO. 1968/11 IBRARY ra 1 7J UN 1968 ref: SEISMICITY OF BOUGAINVILLE,
UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES
 UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE An earthquake is a sudden motion or trembling of the Earth caused by the abrupt release of energy that is stored in rocks. Modern geologists know that most earthquakes
UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE An earthquake is a sudden motion or trembling of the Earth caused by the abrupt release of energy that is stored in rocks. Modern geologists know that most earthquakes
Chapter 13 Earthquakes and Earth s Interior
 Chapter 13 Earthquakes and Earth s Interior The crust of the Earth is made up of floating tectonic plates- huge continent-sized chunks of solid rock floating on molten rock. Rock masses along the boundaries
Chapter 13 Earthquakes and Earth s Interior The crust of the Earth is made up of floating tectonic plates- huge continent-sized chunks of solid rock floating on molten rock. Rock masses along the boundaries
Section Forces Within Earth. 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes
 Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Goals In this activity you will:
 Activity 3 How Big Was It? Goals In this activity you will: Rank the effects of earthquakes. Map the intensity of earthquakes. Interpret a map of earthquake intensity to infer the general location of the
Activity 3 How Big Was It? Goals In this activity you will: Rank the effects of earthquakes. Map the intensity of earthquakes. Interpret a map of earthquake intensity to infer the general location of the
Earthquakes and Earth s Interior
 - What are Earthquakes? Earthquakes and Earth s Interior - The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy - Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks - Continuing adjustment
- What are Earthquakes? Earthquakes and Earth s Interior - The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy - Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks - Continuing adjustment
I. What are Earthquakes?
 I. What are Earthquakes? A. There is more to earthquakes than just the shaking of the ground. An entire branch of Earth science, called seismology, is devoted to the study of earthquakes. B. Earthquakes
I. What are Earthquakes? A. There is more to earthquakes than just the shaking of the ground. An entire branch of Earth science, called seismology, is devoted to the study of earthquakes. B. Earthquakes
Dynamic Crust Regents Review
 Name Dynamic Crust Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the table below, which lists the location of some earthquakes, their Richter magnitude, and their year of occurrence. Data
Name Dynamic Crust Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the table below, which lists the location of some earthquakes, their Richter magnitude, and their year of occurrence. Data
What is an Earthquake?
 Earthquakes What is an Earthquake? Earthquake - sometimes violent shaking of ground caused by movement of Earth s tectonic plates; creates seismic waves Often followed by smaller earthquakes (aftershocks);
Earthquakes What is an Earthquake? Earthquake - sometimes violent shaking of ground caused by movement of Earth s tectonic plates; creates seismic waves Often followed by smaller earthquakes (aftershocks);
Earthquake Notes. Earthquakes occur all the time all over the world, both along plate edges and along faults.
 Earthquake Notes Name: Date: Where Do Earthquakes Happen? Earthquakes occur all the time all over the world, both along plate edges and along faults. Most earthquakes occur along the edge of the oceanic
Earthquake Notes Name: Date: Where Do Earthquakes Happen? Earthquakes occur all the time all over the world, both along plate edges and along faults. Most earthquakes occur along the edge of the oceanic
Measuring the Size of an Earthquake
 Earthquake Hazard Information Hazard, Risk, Magnitude, Intensity, Earthquake Statistics Part 1 (Information for interpreting the results of building contest and shake table testing; L. Braile, 03/12/03)
Earthquake Hazard Information Hazard, Risk, Magnitude, Intensity, Earthquake Statistics Part 1 (Information for interpreting the results of building contest and shake table testing; L. Braile, 03/12/03)
Earthquakes.
 Earthquakes http://thismodernworld.com/comic-archive Elastic rebound http://projects.crustal.ucsb.edu/understanding/elastic/rebound.html Elastic rebound Rocks store energy elastically When stored stress
Earthquakes http://thismodernworld.com/comic-archive Elastic rebound http://projects.crustal.ucsb.edu/understanding/elastic/rebound.html Elastic rebound Rocks store energy elastically When stored stress
Earthquakes An introduction to earthquake monitoring techniques
 Earthquakes An introduction to earthquake monitoring techniques TEACHER S COPY Aims To understand what an earthquake is and where they occur To gain an insight into how earthquakes are recorded and how
Earthquakes An introduction to earthquake monitoring techniques TEACHER S COPY Aims To understand what an earthquake is and where they occur To gain an insight into how earthquakes are recorded and how
Figure Diagram of earth movements produced by (a) P-waves and (b) S-waves.
 Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 11: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the focus or
Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 11: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the focus or
Earthquakes Chapter 19
 Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Chapt pt 15 er EARTHQUAKES! BFRB P 215 ages -226
 Chapter 15 EARTHQUAKES! BFRB Pages 215-226226 Earthquake causes An earthquake is the shaking of the Earth s crust caused by a release of energy The movement of the Earth s plates causes most earthquakes
Chapter 15 EARTHQUAKES! BFRB Pages 215-226226 Earthquake causes An earthquake is the shaking of the Earth s crust caused by a release of energy The movement of the Earth s plates causes most earthquakes
Earthquakes Earth, 9th edition, Chapter 11 Key Concepts What is an earthquake? Earthquake focus and epicenter What is an earthquake?
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Earthquakes Earth, 9 th edition, Chapter 11 Key Concepts Earthquake basics. "" and locating earthquakes.. Destruction resulting from earthquakes. Predicting earthquakes. Earthquakes
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Earthquakes Earth, 9 th edition, Chapter 11 Key Concepts Earthquake basics. "" and locating earthquakes.. Destruction resulting from earthquakes. Predicting earthquakes. Earthquakes
Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p ) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by:
 Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p. 65-85) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by: --sedimentary horizontal rock layers (strata) are found
Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p. 65-85) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by: --sedimentary horizontal rock layers (strata) are found
11/30/16 EARTHQUAKES ELASTIC LIMIT FAULT FORCE AND PLATES WHAT DO YOU NOTICE?
 ELASTIC LIMIT EARTHQUAKES Bend sitck but do not break it. What do you notice? No bend until it breaks. Describe the energy and forces at work. (Kinetic, potential etc) 8 TH GRADE FAULT FORCE AND PLATES
ELASTIC LIMIT EARTHQUAKES Bend sitck but do not break it. What do you notice? No bend until it breaks. Describe the energy and forces at work. (Kinetic, potential etc) 8 TH GRADE FAULT FORCE AND PLATES
Science Starter. Describe in your own words what an Earthquake is and what causes it. Answer The MSL
 Science Starter Describe in your own words what an Earthquake is and what causes it. Answer The MSL WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE AND HOW DO WE MEASURE THEM? Chapter 8, Section 8.1 & 8.2 Looking Back Deserts Wind-shaped
Science Starter Describe in your own words what an Earthquake is and what causes it. Answer The MSL WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE AND HOW DO WE MEASURE THEM? Chapter 8, Section 8.1 & 8.2 Looking Back Deserts Wind-shaped
Earthquakes.
 Earthquakes http://quake.usgs.gov/recenteqs/latestfault.htm An earthquake is a sudden motion or shaking of the Earth's crust, caused by the abrupt release of stored energy in the rocks beneath the surface.
Earthquakes http://quake.usgs.gov/recenteqs/latestfault.htm An earthquake is a sudden motion or shaking of the Earth's crust, caused by the abrupt release of stored energy in the rocks beneath the surface.
A Violent Pulse: Earthquakes. Lecture #2
 A Violent Pulse: Earthquakes Lecture #2 Earthquakes Are Always Happening ~ 1,000,000 / yr Most are small o Detected only by instruments Large EQ ~ 20 / yr cause extensive damage ~ 1 catastrophic EQ / year
A Violent Pulse: Earthquakes Lecture #2 Earthquakes Are Always Happening ~ 1,000,000 / yr Most are small o Detected only by instruments Large EQ ~ 20 / yr cause extensive damage ~ 1 catastrophic EQ / year
How to Use This Presentation
 How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
Earthquakes. Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics. Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics. Chapter 6 Modern Earth Science. Modern Earth Science. Section 6.
 Earthquakes Chapter 6 Modern Earth Science Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Section 6.1 Modern Earth Science Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Earthquakes are the result of stresses in Earth s s lithosphere.
Earthquakes Chapter 6 Modern Earth Science Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Section 6.1 Modern Earth Science Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Earthquakes are the result of stresses in Earth s s lithosphere.
Lecture Outline Wednesday-Monday April 18 23, 2018
 Lecture Outline Wednesday-Monday April 18 23, 2018 Questions? Lecture Final Exam Lecture Section 1 Friday May 4, 8:00-10:00am Lecture Section 2 Friday May 4, 3:10-5:10 pm Final Exam is 70% new material
Lecture Outline Wednesday-Monday April 18 23, 2018 Questions? Lecture Final Exam Lecture Section 1 Friday May 4, 8:00-10:00am Lecture Section 2 Friday May 4, 3:10-5:10 pm Final Exam is 70% new material
Figure 2-1. Diagram of earth movements produced by (a) P-waves and (b) S-waves.
 Geology 102, Winter 2006 Name(s): Lab 2: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the
Geology 102, Winter 2006 Name(s): Lab 2: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the
Identifying the causes and effects of earthquakes
 Science 3 Physical Earth and Space Life LESSON 57 Identifying the causes and effects of earthquakes Lesson Preparation Program Materials Child s Booklet E Exploring the Earth s Structure (pp. 12 13) Optional:
Science 3 Physical Earth and Space Life LESSON 57 Identifying the causes and effects of earthquakes Lesson Preparation Program Materials Child s Booklet E Exploring the Earth s Structure (pp. 12 13) Optional:
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Earthquakes. Forces Within Eartth. Faults form when the forces acting on rock exceed the rock s strength.
 Earthquakes Vocabulary: Stress Strain Elastic Deformation Plastic Deformation Fault Seismic Wave Primary Wave Secondary Wave Focus Epicenter Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish
Earthquakes Vocabulary: Stress Strain Elastic Deformation Plastic Deformation Fault Seismic Wave Primary Wave Secondary Wave Focus Epicenter Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish
Earthquakes. Photo credit: USGS
 Earthquakes Earthquakes Photo credit: USGS Pancaked Building - 1985 Mexico City Earthquakes don t kill people - buildings do! An earthquake is the motion or trembling of the ground produced by sudden displacement
Earthquakes Earthquakes Photo credit: USGS Pancaked Building - 1985 Mexico City Earthquakes don t kill people - buildings do! An earthquake is the motion or trembling of the ground produced by sudden displacement
Earthquakes. Chapter Test A. Multiple Choice. Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left.
 Earthquakes Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Stress that pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions is called a. shearing. b. tension.
Earthquakes Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Stress that pushes a mass of rock in two opposite directions is called a. shearing. b. tension.
SECTION 3. Housing. EAppendix E GEOLOGIC AND SEISMIC HAZARDS
 SECTION 3 Housing EAppendix E GEOLOGIC AND SEISMIC HAZARDS E-2 Housing Commission Attachment B Appendix E Geologic and Seismic Hazards The following definitions provide a more comprehensive discussion
SECTION 3 Housing EAppendix E GEOLOGIC AND SEISMIC HAZARDS E-2 Housing Commission Attachment B Appendix E Geologic and Seismic Hazards The following definitions provide a more comprehensive discussion
Earthquake Lab Introduction: Purpose: Method: Equipment needed: Fundamental Concepts and Key Terms:
 Earthquake Lab Introduction: Seismology is that branch of the geological sciences which is concerned with the study of earthquakes. Purpose: The purpose of this exercise is to introduce some fundamental
Earthquake Lab Introduction: Seismology is that branch of the geological sciences which is concerned with the study of earthquakes. Purpose: The purpose of this exercise is to introduce some fundamental
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
appendix e: geologic and seismic hazards
 appendix e: geologic and seismic hazards CONTENTS: E-2 Fault Rupture E-3 Ground Shaking E-5 Seismic Ground Deformation E-5 Liquification E-6 Seismically Induces Landslide E-6 Landslide Hazard E The following
appendix e: geologic and seismic hazards CONTENTS: E-2 Fault Rupture E-3 Ground Shaking E-5 Seismic Ground Deformation E-5 Liquification E-6 Seismically Induces Landslide E-6 Landslide Hazard E The following
C) 10:20:40 A) the difference between the arrival times of the P -wave and the S -wave
 1. The arrival time of the first earthquake P-wave at a seismograph station was 10:11:20 (hours:minutes:seconds). If the epicenter of the earthquake is 8000 km away, what was the approximate arrival time
1. The arrival time of the first earthquake P-wave at a seismograph station was 10:11:20 (hours:minutes:seconds). If the epicenter of the earthquake is 8000 km away, what was the approximate arrival time
Important Concepts. Earthquake hazards can be categorized as:
 Lecture 1 Page 1 Important Concepts Monday, August 17, 2009 1:05 PM Earthquake Engineering is a branch of Civil Engineering that requires expertise in geology, seismology, civil engineering and risk assessment.
Lecture 1 Page 1 Important Concepts Monday, August 17, 2009 1:05 PM Earthquake Engineering is a branch of Civil Engineering that requires expertise in geology, seismology, civil engineering and risk assessment.
II Seismic waves: Nearly- pure elasic waves
 MAGNITUDE AND INTENSITY (10) I Main Topics A Seismic waves B Magnitude C Intensity D Evernden s equaion for intensity decay 2/9/15 GG303 1 A Seismic waves 1 Cause damage 2 Provide quanitaive informaion
MAGNITUDE AND INTENSITY (10) I Main Topics A Seismic waves B Magnitude C Intensity D Evernden s equaion for intensity decay 2/9/15 GG303 1 A Seismic waves 1 Cause damage 2 Provide quanitaive informaion
AIM: What are the features of Earthquakes and where are they located? Do Now: What are some words that are associated with earthquakes?
 Notepack # 11 November 8, 201 AIM: What are the features of Earthquakes and where are they located? Do Now: What are some words that are associated with earthquakes? What are Earthquakes? The shaking or
Notepack # 11 November 8, 201 AIM: What are the features of Earthquakes and where are they located? Do Now: What are some words that are associated with earthquakes? What are Earthquakes? The shaking or
Monday 11 May 2015 Morning
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Monday 11 May 2015 Morning AS GCE GEOLOGY F791/01 Global Tectonics *5003095113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Monday 11 May 2015 Morning AS GCE GEOLOGY F791/01 Global Tectonics *5003095113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
A physical feature of the Earth s surface
 Earth s Landforms A physical feature of the Earth s surface A physical feature of the Earth s surface LANDFORM Highest of Earth s physical features Highest of Earth s physical features MOUNTAIN Low area
Earth s Landforms A physical feature of the Earth s surface A physical feature of the Earth s surface LANDFORM Highest of Earth s physical features Highest of Earth s physical features MOUNTAIN Low area
Slide 1. Earth Science. Chapter 5 Earthquakes
 Slide 1 Earth Science Chapter 5 Earthquakes Slide 2 Forces in Earth's Crust A force that acts on rock to change its shape or volume is stress 3 types of stress acting on rock layers Tension pulls on the
Slide 1 Earth Science Chapter 5 Earthquakes Slide 2 Forces in Earth's Crust A force that acts on rock to change its shape or volume is stress 3 types of stress acting on rock layers Tension pulls on the
I. Locations of Earthquakes. Announcements. Earthquakes Ch. 5. video Northridge, California earthquake, lecture on Chapter 5 Earthquakes!
 51-100-21 Environmental Geology Summer 2006 Tuesday & Thursday 6-9:20 p.m. Dr. Beyer Earthquakes Ch. 5 I. Locations of Earthquakes II. Earthquake Processes III. Effects of Earthquakes IV. Earthquake Risk
51-100-21 Environmental Geology Summer 2006 Tuesday & Thursday 6-9:20 p.m. Dr. Beyer Earthquakes Ch. 5 I. Locations of Earthquakes II. Earthquake Processes III. Effects of Earthquakes IV. Earthquake Risk
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13 Earthquakes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Three different types of seismic waves are recorded by seismographs Key Figure
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 13 Earthquakes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Three different types of seismic waves are recorded by seismographs Key Figure
H. GEOLOGY, SOILS AND SEISMICITY
 This section assesses the geotechnical conditions within the Plan area and its vicinity. Impacts associated with implementation of the Draft Specific Plan are analyzed and mitigation measures are recommended
This section assesses the geotechnical conditions within the Plan area and its vicinity. Impacts associated with implementation of the Draft Specific Plan are analyzed and mitigation measures are recommended
Earthquakes How and Where Earthquakes Occur
 Earthquakes How and Where Earthquakes Occur PPT Modified from Troy HS Is there such thing as earthquake weather? Absolutely NOT!!! Geologists believe that there is no connection between weather and earthquakes.
Earthquakes How and Where Earthquakes Occur PPT Modified from Troy HS Is there such thing as earthquake weather? Absolutely NOT!!! Geologists believe that there is no connection between weather and earthquakes.
Seismic Waves. 1. Seismic Deformation
 Types of Waves 1. Seismic Deformation Seismic Waves When an earthquake fault ruptures, it causes two types of deformation: static; and dynamic. Static deformation is the permanent displacement of the ground
Types of Waves 1. Seismic Deformation Seismic Waves When an earthquake fault ruptures, it causes two types of deformation: static; and dynamic. Static deformation is the permanent displacement of the ground
Name Date Class. radiate in all directions, carrying some of the. of plate boundaries have different usual patterns of.
 Chapter Outline Earthquakes CHAPTER 6 Lesson 1: Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries A. What is an earthquake? 1. A(n) is the rupture and sudden movement of rocks along a fault. A fault is a fracture surface
Chapter Outline Earthquakes CHAPTER 6 Lesson 1: Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries A. What is an earthquake? 1. A(n) is the rupture and sudden movement of rocks along a fault. A fault is a fracture surface
Chapter: Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 Table of Contents Chapter: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 1: Earthquakes Section 2: Volcanoes Section 3: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Plate Tectonics 1 Earthquakes What causes earthquakes? Elastic Rebound
Table of Contents Chapter: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 1: Earthquakes Section 2: Volcanoes Section 3: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Plate Tectonics 1 Earthquakes What causes earthquakes? Elastic Rebound
EQ Monitoring and Hazards NOTES.notebook. January 07, P-wave. S-wave. surface waves. distance
 Earthquake Monitoring and Hazards Reading a Seismogram General guidelines: P-wave First disruption of trace = Second disruption of trace = surface waves Largest disruption of trace = Not the distance to
Earthquake Monitoring and Hazards Reading a Seismogram General guidelines: P-wave First disruption of trace = Second disruption of trace = surface waves Largest disruption of trace = Not the distance to
Unit 7: Dynamic Planet: Earthquakes & Volcanoes
 Unit 7: Dynamic Planet: Earthquakes & Volcanoes Lecture 3 Objectives: E3.4C - Describe the effects of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions on humans. E3.4f - Explain why fences are offset after an earthquake
Unit 7: Dynamic Planet: Earthquakes & Volcanoes Lecture 3 Objectives: E3.4C - Describe the effects of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions on humans. E3.4f - Explain why fences are offset after an earthquake
Magnitude 6.5 OFFSHORE NORTHERN CALIFORNIA
 A powerful offshore earthquake that struck near the Northern California coast left a hodgepodge of debris for communities to sort through Sunday but spared residents any serious injury. After 25,000 people
A powerful offshore earthquake that struck near the Northern California coast left a hodgepodge of debris for communities to sort through Sunday but spared residents any serious injury. After 25,000 people
Physical Geology Lab. Teacher Check (show your screen to your teacher) Part ONE: Dynamic Earth. Continents Over Time.
 Physical Geology Lab Name Hour Part ONE: Dynamic Earth Earth s Structure Name the Layer: The only liquid layer Only a few miles thick (under oceans) Mostly solid iron and nickel Made of hot, semi-solid
Physical Geology Lab Name Hour Part ONE: Dynamic Earth Earth s Structure Name the Layer: The only liquid layer Only a few miles thick (under oceans) Mostly solid iron and nickel Made of hot, semi-solid
Chapter 4 Earthquakes and Tsunamis
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 21 30 March 2004 100 100 100 96 A B C D F Exam Scores 95 94 94 90 85 83 83 83 Mean 72 67 61 59 59 55 54 41 Mean = 78.5 Median = 83 Any Questions? Chapter 4 Earthquakes
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 21 30 March 2004 100 100 100 96 A B C D F Exam Scores 95 94 94 90 85 83 83 83 Mean 72 67 61 59 59 55 54 41 Mean = 78.5 Median = 83 Any Questions? Chapter 4 Earthquakes
Chapter 4 Earthquakes and Tsunamis. Geology of the Hawaiian Islands. Any Questions? Class March Mean = 78.
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 21 30 March 2004 Any Questions? 100 100 100 96 A B C D F Exam Scores 95 94 94 90 85 83 83 83 Mean 72 67 61 59 59 55 54 41 Mean = 78.5 Median = 83 Chapter 4 Earthquakes
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 21 30 March 2004 Any Questions? 100 100 100 96 A B C D F Exam Scores 95 94 94 90 85 83 83 83 Mean 72 67 61 59 59 55 54 41 Mean = 78.5 Median = 83 Chapter 4 Earthquakes
21. Earthquakes I (p ; 306)
 21. Earthquakes I (p. 296-303; 306) How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the last 4,000 years? How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the past century? What two recent earthquakes
21. Earthquakes I (p. 296-303; 306) How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the last 4,000 years? How many people have been killed by earthquakes in the past century? What two recent earthquakes
Plate Tectonics IDEA THAT EARTH S SURFACE IS BROKEN INTO PLATES THAT MOVE AROUND. Fault = fracture in the crust where the movement has occurred
 Warm-up #14 A mountain range found 100 meters above sea level is measured to be 1,000 meters high from its tallest peak. From the top, the first 500 meters are incredibly steep. After this point, the mountain
Warm-up #14 A mountain range found 100 meters above sea level is measured to be 1,000 meters high from its tallest peak. From the top, the first 500 meters are incredibly steep. After this point, the mountain
Determining the Earthquake Epicenter: Japan
 Practice Name: Hour: Determining the Earthquake Epicenter: Japan Measuring the S-P interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest of the world.
Practice Name: Hour: Determining the Earthquake Epicenter: Japan Measuring the S-P interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest of the world.
Introduction to Engineering Seismology
 Introduction to Engineering Seismology Sudhir K Jain Mythology The Myths 2 The Earth is held up by 4 elephants that stand on the back of a turtle. The turtle is balanced in turn on a cobra. When any of
Introduction to Engineering Seismology Sudhir K Jain Mythology The Myths 2 The Earth is held up by 4 elephants that stand on the back of a turtle. The turtle is balanced in turn on a cobra. When any of
Earthquakes = shaking of Earth because of a rapid release of energy
 There are more than 30,000 earthquakes worldwide each year! Earthquakes = shaking of Earth because of a rapid release of energy usually because of movement of tectonic plates Most earthquakes last for
There are more than 30,000 earthquakes worldwide each year! Earthquakes = shaking of Earth because of a rapid release of energy usually because of movement of tectonic plates Most earthquakes last for
Module 7: Plate Tectonics and Earth's Structure Topic 4 Content : Earthquakes Presentation Notes. Earthquakes
 Earthquakes 1 Topic 4 Content: Earthquakes Presentation Notes Earthquakes are vibrations within the Earth produced by the rapid release of energy from rocks that break under extreme stress. Earthquakes
Earthquakes 1 Topic 4 Content: Earthquakes Presentation Notes Earthquakes are vibrations within the Earth produced by the rapid release of energy from rocks that break under extreme stress. Earthquakes
INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES
 INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES Seismology = Study of earthquakes Seismologists = Scientists who study earthquakes Earthquake = Trembling or shaking of the earth s surface, usually as a result of the movement
INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES Seismology = Study of earthquakes Seismologists = Scientists who study earthquakes Earthquake = Trembling or shaking of the earth s surface, usually as a result of the movement
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model
 Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Magnitude 7.7 QUEEN CHARLOTTE ISLANDS REGION
 A major 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck at 8:04 PM local time in western British Columbia, Canada. The epicenter is located on Moresby Island, the southern large island in the Queen Charlotte Islands region.
A major 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck at 8:04 PM local time in western British Columbia, Canada. The epicenter is located on Moresby Island, the southern large island in the Queen Charlotte Islands region.
Magnitude 6.9 GULF OF CALIFORNIA
 A pair of strong earthquakes struck off the coast of Mexico early Thursday only minutes apart. The magnitude 6.9 and 6.2 were centered about 85 miles northeast of Guerrero Negro in the Mexican state of
A pair of strong earthquakes struck off the coast of Mexico early Thursday only minutes apart. The magnitude 6.9 and 6.2 were centered about 85 miles northeast of Guerrero Negro in the Mexican state of
Earthquake Investigation
 Exploration A Earthquake Investigation 1. Obtain a piece of plastic putty and knead it into a rectangular shape. 2. Push the ends of the putty toward the middle. Draw and describe what it looks like below.
Exploration A Earthquake Investigation 1. Obtain a piece of plastic putty and knead it into a rectangular shape. 2. Push the ends of the putty toward the middle. Draw and describe what it looks like below.
Earthquake. What is it? Can we predict it?
 Earthquake What is it? Can we predict it? What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. Rocks under stress accumulate
Earthquake What is it? Can we predict it? What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. Rocks under stress accumulate
VIDEO The 2011 Japanese Earthquake and Tsunami
 VIDEO The 2011 Japanese Earthquake and Tsunami Why was it so large and devastating? Why so short a warning? Why did tsunami precautions fail? What happened elsewhere? The Loma Prieta Earthquake (1989)
VIDEO The 2011 Japanese Earthquake and Tsunami Why was it so large and devastating? Why so short a warning? Why did tsunami precautions fail? What happened elsewhere? The Loma Prieta Earthquake (1989)
Magnitude 6.3 SOUTH ISLAND OF NEW ZEALAND
 A magnitude 6.3 earthquake shook the southern New Zealand city of Christchurch. At least 100 people are reported dead, and there are reports of collapsed buildings, cracked streets and flooding due to
A magnitude 6.3 earthquake shook the southern New Zealand city of Christchurch. At least 100 people are reported dead, and there are reports of collapsed buildings, cracked streets and flooding due to
Objectives. Vocabulary
 Forces Within Earth Objectives Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish among the three types of faults. Contrast three types of seismic waves. Vocabulary stress strain fault primary
Forces Within Earth Objectives Define stress and strain as they apply to rocks. Distinguish among the three types of faults. Contrast three types of seismic waves. Vocabulary stress strain fault primary
What is an earthquake?
 What is an earthquake? Shaking or vibration of the ground rocks undergoing deformation break suddenly along a fault 1906 San Francisco earthquake Oblique view of the San Andreas fault and San Francisco
What is an earthquake? Shaking or vibration of the ground rocks undergoing deformation break suddenly along a fault 1906 San Francisco earthquake Oblique view of the San Andreas fault and San Francisco
SEISMOLOGY. - The study of earthquakes waves and how they move through the body and around the surface of the earth.
 EARTHQUAKES SEISMOLOGY - The study of earthquakes waves and how they move through the body and around the surface of the earth. Seismic Waves - vibrations generated in the earths interior that carry energy
EARTHQUAKES SEISMOLOGY - The study of earthquakes waves and how they move through the body and around the surface of the earth. Seismic Waves - vibrations generated in the earths interior that carry energy
Lab 7: Earthquakes. Figure 7-1. Diagram of earth movements produced by (a) P-waves and (b) S-waves.
 Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 7: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the focus or hypocenter.
Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 7: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the focus or hypocenter.
