Mw 7.8, Southwest of Sumatra, Indonesia Wed, 2 March 2016 at 12:49:48 UTC M /03/03
|
|
|
- Joshua Gray
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Earthquake overview AFGHANISTA N PAKISTA N INDIA A moment magnitude (Mw) 7.8 earthquake struck in South West, Indonesia. The epicentre was centered about 800 km West South West of Padang, Sumatra province, Indonesia. M /03/03 Pakistan The depth has been estimated to be about 24 km (~15 miles). No fatalities or damaged to population centres have been reported. Image courtesy of Google Earth.
2 Earthquake hazard map Moderate (IV) shaking was felt in some of the Sumatran coastal regions closest to the epicenter. Otherwise Slight (III) shaking was felt in the rest of the surrounding region. Shaking Intensity Modified Mercalli Intensity Scale (MMI) I. Instrument al Not felt by many people unless in favourable conditions. II. Weak Felt only by a few people at best, especially on the upper floors of buildings. Delicately suspended objects may swing. III. Slight Felt quite noticeably by people indoors, especially on the upper floors of buildings. Many to do not recognise it as an earthquake. Standing motor cars may rock slightly. Vibration similar to the passing of a truck. Duration estimated. IV. Moderate Felt indoors by many people, outdoors by a few people during the day. At night, some awakened. V. Rather Strong Felt outside by most, may not be felt by some people in non-favourable conditions. Dishes and windows may break and large bells will ring. Vibrations like train passing close to house. VI. Strong Felt by all; many frightened and run outdoors, walk unsteadily. Windows, dishes, glassware broken; books fall off shelves; some heavy furniture moved or overturned; a few instances of fallen plaster. Damage slight. VII. Very Strong Difficult to stand; furniture broken; damage negligible in building of good design and construction; slight to moderate in well-built ordinary structures; considerable damage in poorly built or badly designed structures; some chimneys broken. Noticed by people driving motor cars. VIII. Destructive Damage slight in specially designed structures; considerable in ordinary substantial buildings with partial collapse. Damage great in poorly built structures. Fall of chimneys, factory stacks, columns, monuments, walls. Heavy furniture moved. IX. Violent General panic; damage considerable in poorly designed structures, well designed frame structures thrown out of plumb. Damage great in substantial buildings, with partial collapse. Buildings shifted off foundations. X. Intense Some well build wooden structures destroyed; most masonry and frame structures destroyed with foundation. Rails bent. XI. Extreme Few, if any masonry structures remain standing. Bridges destroyed. Rails bent greatly. XII. Cataclysmi c Total destruction everything is destroyed. Lines of sight and level distorted. Objects thrown into the air. The ground moves in waves or ripples. Large amounts of rock move position. Landscape altered, or leveled by several meters. In some cases, even the routes of rivers are changed. Image courtesy of US Geological Survey
3 Earthquake hazard map Green alert for shaking-related fatalities and economic losses There is a low likelihood of casualties and damage USGS PAGER Map with MMI contour overlay Images courtesy of the US Geological Survey
4 Earthquake slip model N/S transform faults Left: Graph displaying the total energy release over time for the rupture. The most energy release occurred approximately 15 seconds after the start of the earthquake. Right: Cross section of the preliminary slip model generated by the USGS from seismic data Images courtesy of US Geological Survey
5 Historical seismicity M /04/11 Large strike-slip earthquakes are not uncommon in the boundary region between the India and Australia plates. M /04/11 One such event occurred in 2000; a M7.9 earthquake was generated as a strike slip ruptured to the south east of the March 3, 2016 earthquake. In 2012, two earthquakes M8+ occurred in the same day due to a series of ruptures to the north. M /06/18 M /03/03 Image courtesy of Google Earth Despite their marine location, the strike slip nature of these earthquakes tends to NOT generate large tsunamis.
6 Earthquake focal mechanism The depth of this earthquake is 24 km, which is known as a crustal earthquake. The focal mechanism shows that this earthquake has a strike slip mechanism. ra at u bd Su n io ct n Zo e The rupture fault plane is orientated N-S, showing left lateral strike slip motion m Su The earthquake occurred in the Wharton basin transform faults which can be easily seen from the bathymetry. N/S transform faults Above: Corresponding focal mechanism for Indonesian earthquake (obtained from USGS) Left: Rupture of a strike slip fault showing left lateral displacement indicated by arrows, fault plane is indicated by thin black arrows Below: Location of the earthquake (yellow star). Transform faults trending North-South give information on ruptured fault plane
7 Tectonic setting The 2016 Mw 7.8 earthquake occurred nearly 600 km to the southwest of the Sumatra subduction zone, where the India and Australia plates subduct to the north-northeast beneath the Sunda plate. In the diffuse plate boundary region separating the India and Australia plates, southwest of the major subduction zone, there are also other strike slip earthquakes occurred before. All these events are caused by north striking fault or right lateral slip on an approximately west striking fault. Map showing the location of the plate boundary, subduction zone and the The relative plate motion rate between the Indo-Australia and Sunda plates is rapid. At southern tip of Sumatra is roughly 63 mm/yr northeast and then decreasing and counterclockwise rotating to 44 mm/yr northwest at Andaman Islands.
8 Seismic waves recorded in the UK P-waves S-waves Even though the earthquake occurred more that 10,900 km (~6700 miles) from the UK, the seismic waves emitted by this earthquake can still be measured. The plot above shows the vertical component of the seismic waves measured at seismic stations across the UK. The colour of the line corresponds to the station at which it was recorded, shown on the map on the right hand side of the slide.
9 Find more BGS (British Geological Survey) seismology and earthquakes frequently asked questions GO! IRIS (Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology) learning about earthquakes GO! UK School Seismology Project classroom activities, videos and support documents GO! USGS (United States Geological Survey) FAQs, glossary, posters, animations GO! USGS summary of the earthquake GO! 9
10 @seismologyuol
Magnitude 6.3, NORTH OF MOROCCO
 Earthquake location & overview A magnitude 6.3 earthquake struck in Alboran Sea, orth of Morocco; the epicentre was centered about 54 km ( 34 miles) E of Al Hoceima. The depth has been estimated to be
Earthquake location & overview A magnitude 6.3 earthquake struck in Alboran Sea, orth of Morocco; the epicentre was centered about 54 km ( 34 miles) E of Al Hoceima. The depth has been estimated to be
earthquakes 1. Earthquakes occur when plates grind against one another along cracks called faults.
 earthquakes BEGIN 1 earthquakes 1. Earthquakes occur when plates grind against one another along cracks called faults. 2 earthquakes 1. Earthquakes occur when plates grind against one another along cracks
earthquakes BEGIN 1 earthquakes 1. Earthquakes occur when plates grind against one another along cracks called faults. 2 earthquakes 1. Earthquakes occur when plates grind against one another along cracks
1. Why do earthquakes happen? 3. What type of mechanical waves are Primary or P waves? 4. What type of mechanical waves are Secondary or S waves?
 Name Period Earthquake Activity Background Information Earthquakes occur because of a sudden release of stored energy. This energy has built up over long periods of time as a result of tectonic forces
Name Period Earthquake Activity Background Information Earthquakes occur because of a sudden release of stored energy. This energy has built up over long periods of time as a result of tectonic forces
Earthquake. earthquake, epicenters in the U.S. Kobe, Japan deaths
 Kobe, Japan 1995 5000 deaths Earthquakes It is estimated that there are 500,000 detectable earthquakes in the world each year. 100,000 of those can be felt, and 100 of them cause damage. The world's deadliest
Kobe, Japan 1995 5000 deaths Earthquakes It is estimated that there are 500,000 detectable earthquakes in the world each year. 100,000 of those can be felt, and 100 of them cause damage. The world's deadliest
EPS 20: Earthquakes. Laboratory Exercise 1. Intensity
 Name GSI Name EPS 20: Earthquakes Laboratory Exercise 1 Intensity Purpose: To investigate seismic intensity and how it is used to describe the effects of earthquakes Background: Several hundred years ago,
Name GSI Name EPS 20: Earthquakes Laboratory Exercise 1 Intensity Purpose: To investigate seismic intensity and how it is used to describe the effects of earthquakes Background: Several hundred years ago,
An earthquake can cause:
 Earthquakes An earthquake is a sudden rapid shaking of the earth. They are caused by the breaking and shifting of the rock beneath the earth s surface. Often found in conjunction with Plate tectonic boundaries.
Earthquakes An earthquake is a sudden rapid shaking of the earth. They are caused by the breaking and shifting of the rock beneath the earth s surface. Often found in conjunction with Plate tectonic boundaries.
Earthquakes. Dr. Mark van der Meijde INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND EARTH OBSERVATION
 Earthquakes Dr. Mark van der Meijde vandermeijde@itc.nl INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND EARTH OBSERVATION Topics to handle Theory of earthquakes Mechanism Strength Measurements
Earthquakes Dr. Mark van der Meijde vandermeijde@itc.nl INTERNATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR GEO-INFORMATION SCIENCE AND EARTH OBSERVATION Topics to handle Theory of earthquakes Mechanism Strength Measurements
Released Science Inquiry Task Location Grade 11
 Date: Your Name: Released Science Inquiry Task Location 2009 Grade 11 Science Directions: You will be completing an extended-response inquiry task called Location. Explain the reasons for all of your answers.
Date: Your Name: Released Science Inquiry Task Location 2009 Grade 11 Science Directions: You will be completing an extended-response inquiry task called Location. Explain the reasons for all of your answers.
Magnitude 7.0 PAPUA, INDONESIA
 A 7.0 magnitude earthquake struck eastern Indonesia's mountainous West Papua province on Saturday but there were no immediate reports of casualties or damage. The region is sparsely populated. According
A 7.0 magnitude earthquake struck eastern Indonesia's mountainous West Papua province on Saturday but there were no immediate reports of casualties or damage. The region is sparsely populated. According
FOURTH GRADE HAZARDS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES
 FOURTH GRADE HAZARDS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types of volcanoes.
FOURTH GRADE HAZARDS 1 WEEK LESSON PLANS AND ACTIVITIES PLATE TECTONIC CYCLE OVERVIEW OF FOURTH GRADE VOLCANOES WEEK 1. PRE: Comparing different structures of volcanoes. LAB: Modeling three types of volcanoes.
Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy.
 Earthquake Machine Stick-slip: Elastic Rebound Theory Jerky motions on faults produce EQs Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy. Three
Earthquake Machine Stick-slip: Elastic Rebound Theory Jerky motions on faults produce EQs Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy. Three
Satellite Image. False-color IR satellite view of basins and ranges north of Snake River Plain Lost River Rangelower. Lemhi Range-upper.
 Satellite Image False-color IR satellite view of basins and ranges north of Snake River Plain Lost River Rangelower center Lemhi Range-upper center Challis, Idaho is left of center Epicenter of 1983, magnitude
Satellite Image False-color IR satellite view of basins and ranges north of Snake River Plain Lost River Rangelower center Lemhi Range-upper center Challis, Idaho is left of center Epicenter of 1983, magnitude
Measuring the Size of an Earthquake
 Earthquake Hazard Information Hazard, Risk, Magnitude, Intensity, Earthquake Statistics Part 1 (Information for interpreting the results of building contest and shake table testing; L. Braile, 03/12/03)
Earthquake Hazard Information Hazard, Risk, Magnitude, Intensity, Earthquake Statistics Part 1 (Information for interpreting the results of building contest and shake table testing; L. Braile, 03/12/03)
ENVI.2030L - Earthquakes
 ENVI.2030L - Earthquakes Name I. Introduction The crust of the earth behaves in a brittle manner. Stress is the force applied to a brittle substance and strain represents the build-up of energy in the
ENVI.2030L - Earthquakes Name I. Introduction The crust of the earth behaves in a brittle manner. Stress is the force applied to a brittle substance and strain represents the build-up of energy in the
II Seismic waves: Nearly- pure elasic waves
 MAGNITUDE AND INTENSITY (10) I Main Topics A Seismic waves B Magnitude C Intensity D Evernden s equaion for intensity decay 2/9/15 GG303 1 A Seismic waves 1 Cause damage 2 Provide quanitaive informaion
MAGNITUDE AND INTENSITY (10) I Main Topics A Seismic waves B Magnitude C Intensity D Evernden s equaion for intensity decay 2/9/15 GG303 1 A Seismic waves 1 Cause damage 2 Provide quanitaive informaion
Magnitude 6.9 GULF OF CALIFORNIA
 A pair of strong earthquakes struck off the coast of Mexico early Thursday only minutes apart. The magnitude 6.9 and 6.2 were centered about 85 miles northeast of Guerrero Negro in the Mexican state of
A pair of strong earthquakes struck off the coast of Mexico early Thursday only minutes apart. The magnitude 6.9 and 6.2 were centered about 85 miles northeast of Guerrero Negro in the Mexican state of
Earthquake Damage Scenario
 Chapter 2. Earthquake Damage Scenario CHAPTER 2. EARTHQUAKE DAMAGE SCENARIO 2.1 Earthquake Scenario Setting and Ground Motion 2.1.1 Fault in the Philippines The Philippines is located in latitude 5 to
Chapter 2. Earthquake Damage Scenario CHAPTER 2. EARTHQUAKE DAMAGE SCENARIO 2.1 Earthquake Scenario Setting and Ground Motion 2.1.1 Fault in the Philippines The Philippines is located in latitude 5 to
Magnitude 7.1 NEAR THE EAST COAST OF HONSHU, JAPAN
 Japan was rattled by a strong aftershock and tsunami warning Thursday night nearly a month after a devastating earthquake and tsunami flattened the northeastern coast. This earthquake can be considered
Japan was rattled by a strong aftershock and tsunami warning Thursday night nearly a month after a devastating earthquake and tsunami flattened the northeastern coast. This earthquake can be considered
Magnitude 7.7 QUEEN CHARLOTTE ISLANDS REGION
 A major 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck at 8:04 PM local time in western British Columbia, Canada. The epicenter is located on Moresby Island, the southern large island in the Queen Charlotte Islands region.
A major 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck at 8:04 PM local time in western British Columbia, Canada. The epicenter is located on Moresby Island, the southern large island in the Queen Charlotte Islands region.
Magnitude 7.0 VANUATU
 A major earthquake struck in the southwest Pacific Ocean at a depth of 27 km beneath the island of Melampa in the Vanuatu island chain. There are no reports of damage. The Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI)
A major earthquake struck in the southwest Pacific Ocean at a depth of 27 km beneath the island of Melampa in the Vanuatu island chain. There are no reports of damage. The Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI)
Earthquakes and Earth s Chapter. Interior
 Earthquakes and Earth s Chapter Interior 8.1 What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Focus and Epicenter Focus is the point within Earth
Earthquakes and Earth s Chapter Interior 8.1 What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Focus and Epicenter Focus is the point within Earth
Magnitude 7.5 PAPUA NEW GUINEA
 A magnitude 7.5 earthquake occurred 33 kilometers (20 miles) southwest of Tari, Papua New Guinea, at a depth of 35 km (22 miles). Papua New Guinea is located on the eastern half of the island of New Guinea,
A magnitude 7.5 earthquake occurred 33 kilometers (20 miles) southwest of Tari, Papua New Guinea, at a depth of 35 km (22 miles). Papua New Guinea is located on the eastern half of the island of New Guinea,
Magnitude 7.0 N of ANCHORAGE, ALASKA
 A magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred just before 8:30 am local time 8 miles north of Anchorage at a depth of 40.9 km (25.4 miles). There are reports of major infrastructure damage and damage to many homes
A magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred just before 8:30 am local time 8 miles north of Anchorage at a depth of 40.9 km (25.4 miles). There are reports of major infrastructure damage and damage to many homes
Magnitude 8.2 NORTHWEST OF IQUIQUE, CHILE
 An 8.2-magnitude earthquake struck off the coast of northern Chile, generating a local tsunami. The USGS reported the earthquake was centered 95 km (59 miles) northwest of Iquique at a depth of 20.1km
An 8.2-magnitude earthquake struck off the coast of northern Chile, generating a local tsunami. The USGS reported the earthquake was centered 95 km (59 miles) northwest of Iquique at a depth of 20.1km
Magnitude 7.8 SCOTIA SEA
 A magnitude 7.8 earthquake has occurred in the South Orkney Island region in the Scotia Sea. According to the USGS, this earthquake is the latest in a series of moderate-tolarge earthquakes to strike this
A magnitude 7.8 earthquake has occurred in the South Orkney Island region in the Scotia Sea. According to the USGS, this earthquake is the latest in a series of moderate-tolarge earthquakes to strike this
Magnitude 7.6 HONDURAS
 A magnitude 7.6 earthquake has occurred in the Caribbean between Honduras and the Cayman Islands approximately 125 miles (202 km) north-northeast of Barra Patuca, Honduras, and 188 miles (303 km) southwest
A magnitude 7.6 earthquake has occurred in the Caribbean between Honduras and the Cayman Islands approximately 125 miles (202 km) north-northeast of Barra Patuca, Honduras, and 188 miles (303 km) southwest
Magnitude 6.3 SOUTH ISLAND OF NEW ZEALAND
 A magnitude 6.3 earthquake shook the southern New Zealand city of Christchurch. At least 100 people are reported dead, and there are reports of collapsed buildings, cracked streets and flooding due to
A magnitude 6.3 earthquake shook the southern New Zealand city of Christchurch. At least 100 people are reported dead, and there are reports of collapsed buildings, cracked streets and flooding due to
20.1 Earthquakes. Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES. Earthquakes and plate boundaries 500 UNIT 6 EARTH S STRUCTURE
 Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES 20.1 Earthquakes In Chapter 19, you read about the San Andreas Fault, which lies along the California coast (Figure 20.1). This fault passes right through San Francisco
Chapter 20 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES 20.1 Earthquakes In Chapter 19, you read about the San Andreas Fault, which lies along the California coast (Figure 20.1). This fault passes right through San Francisco
Magnitude 7.0 NEW CALEDONIA
 A magnitude 7.0 earthquake has occurred 82km ENE of Maré Island, the secondlargest of the Loyalty Islands in the archipelago of New Caledonia. The initial report of the magnitude and shallow 10km depth
A magnitude 7.0 earthquake has occurred 82km ENE of Maré Island, the secondlargest of the Loyalty Islands in the archipelago of New Caledonia. The initial report of the magnitude and shallow 10km depth
Monday 11 May 2015 Morning
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Monday 11 May 2015 Morning AS GCE GEOLOGY F791/01 Global Tectonics *5003095113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Monday 11 May 2015 Morning AS GCE GEOLOGY F791/01 Global Tectonics *5003095113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
Magnitude 8.2 FIJI. A magnitude 8.2 earthquake occurred km (226.7 mi) E of Suva, Fiji at a depth of km (350 miles).
 A magnitude 8.2 earthquake occurred 364.8 km (226.7 mi) E of Suva, Fiji at a depth of 563.4 km (350 miles). There is no risk of a tsunami from an earthquake at this depth. Images courtesy of Google The
A magnitude 8.2 earthquake occurred 364.8 km (226.7 mi) E of Suva, Fiji at a depth of 563.4 km (350 miles). There is no risk of a tsunami from an earthquake at this depth. Images courtesy of Google The
A magnitude 7.8 earthquake has occurred km (63.3 mi) ESE of Suva, Fiji at a depth of km (378 miles).
 A magnitude 7.8 earthquake has occurred 101.8 km (63.3 mi) ESE of Suva, Fiji at a depth of 608.6 km (378 miles). There is no risk of a tsunami from an earthquake at this depth. Images courtesy of Google
A magnitude 7.8 earthquake has occurred 101.8 km (63.3 mi) ESE of Suva, Fiji at a depth of 608.6 km (378 miles). There is no risk of a tsunami from an earthquake at this depth. Images courtesy of Google
Magnitude 7.9 SE of KODIAK, ALASKA
 A magnitude 7.9 earthquake occurred at 12:31 am local time 181 miles southeast of Kodiak at a depth of 25 km (15.5 miles). There are no immediate reports of damage or fatalities. Light shaking from this
A magnitude 7.9 earthquake occurred at 12:31 am local time 181 miles southeast of Kodiak at a depth of 25 km (15.5 miles). There are no immediate reports of damage or fatalities. Light shaking from this
Magnitude 7.5 NEW BRITAIN REGION, PAPUA NEW GUINEA
 A magnitude 7.5 earthquake struck off the eastern coast of Papua New Guinea on Tuesday, approximately 130 km (81 mi) southsouthwest of Kokopo at a depth of 42 km (26.1 mi). There are reports of some structural
A magnitude 7.5 earthquake struck off the eastern coast of Papua New Guinea on Tuesday, approximately 130 km (81 mi) southsouthwest of Kokopo at a depth of 42 km (26.1 mi). There are reports of some structural
Magnitude 7.1 SOUTH SANDWICH ISLANDS
 A magnitude 7.1 earthquake occurred at a depth of 164.7 km (102 miles) in the South Sandwich Islands, an uninhabited British territory off the coast of Argentina in the southern Atlantic Ocean. Antarctica
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake occurred at a depth of 164.7 km (102 miles) in the South Sandwich Islands, an uninhabited British territory off the coast of Argentina in the southern Atlantic Ocean. Antarctica
Magnitude 7.1 PHILIPPINES
 A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck in the southeastern Philippines just after 8 am local time Tuesday morning killing 82 people and reducing a 17 th century church to rubble. Offices and schools were closed
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck in the southeastern Philippines just after 8 am local time Tuesday morning killing 82 people and reducing a 17 th century church to rubble. Offices and schools were closed
Magnitude 7.1 PERU. There are early reports of homes and roads collapsed leaving one dead and several dozen injured.
 A magnitude 7.1 earthquake has occurred offshore Peru. The earthquake struck just after 4 a.m. local time and was centered near the coast of Peru, 40 km (25 miles) south-southwest of Acari, Peru at a depth
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake has occurred offshore Peru. The earthquake struck just after 4 a.m. local time and was centered near the coast of Peru, 40 km (25 miles) south-southwest of Acari, Peru at a depth
Magnitude 8.3 SEA OF OKHOTSK
 A powerful earthquake in Russia's Far East was felt as far away as Moscow, about 7,000 kilometers (4,400 miles) west of the epicenter, but no casualties or damage were reported. The epicenter was in the
A powerful earthquake in Russia's Far East was felt as far away as Moscow, about 7,000 kilometers (4,400 miles) west of the epicenter, but no casualties or damage were reported. The epicenter was in the
7.1 FIJI 1, :57:22 UTC
 A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck 141 km (88 miles) northeast of Ndoi Island, Fiji, and 313 km (194 mi) west-northwest of Nuku alofa, Tonga according to the US Geological Survey, but there were no reports
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck 141 km (88 miles) northeast of Ndoi Island, Fiji, and 313 km (194 mi) west-northwest of Nuku alofa, Tonga according to the US Geological Survey, but there were no reports
Magnitude 7.3 OFFSHORE EL SALVADOR
 A magnitude 7.3 earthquake struck off the Pacific coast of Central America late Monday night, early reports indicate one death. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 40 km (24.9 miles). Its epicenter was
A magnitude 7.3 earthquake struck off the Pacific coast of Central America late Monday night, early reports indicate one death. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 40 km (24.9 miles). Its epicenter was
Magnitude 7.6 & 7.4 SOLOMON ISLANDS
 A magnitude 7.6 earthquake struck near the Solomon Islands on Sunday morning local time; there were no immediate reports of damage. The earthquake was centered 100 km (60 miles) south of Kira Kira, a town
A magnitude 7.6 earthquake struck near the Solomon Islands on Sunday morning local time; there were no immediate reports of damage. The earthquake was centered 100 km (60 miles) south of Kira Kira, a town
Magnitude 7.5 NEW BRITAIN REGION, PAPUA NEW GUINEA
 A magnitude 7.5 earthquake struck off the eastern coast of Papua New Guinea on Sunday, approximately 54 km (33 miles) southeast of Kokopo. Residents reported strong ground shaking for about five minutes.
A magnitude 7.5 earthquake struck off the eastern coast of Papua New Guinea on Sunday, approximately 54 km (33 miles) southeast of Kokopo. Residents reported strong ground shaking for about five minutes.
Geologic Conditions. his section of the Background Report describes the existing conditions of the City of Elk Grove relative to Geologic Conditions.
 T his section of the Background Report describes the existing conditions of the City of Elk Grove relative to Geologic Conditions. Setting The Planning Area is located within the Great Valley geomorphic
T his section of the Background Report describes the existing conditions of the City of Elk Grove relative to Geologic Conditions. Setting The Planning Area is located within the Great Valley geomorphic
Magnitude 7.5 PALU, INDONESIA
 A magnitude 7.5 earthquake occurred 80.8 km (50.2 mi) north of Palu, Indonesia at a depth of 10 km (6.2 miles). This earthquake triggered a tsunami with wave heights up to 2 m (6.6 ft) that an official
A magnitude 7.5 earthquake occurred 80.8 km (50.2 mi) north of Palu, Indonesia at a depth of 10 km (6.2 miles). This earthquake triggered a tsunami with wave heights up to 2 m (6.6 ft) that an official
Magnitude 7.4 SOUTH GEORGIA ISLAND REGION
 A magnitude 7.4 earthquake occurred in the South Georgia Island Region. South Georgia Island is a British territory in the South Atlantic Ocean that lies about 800 miles east of the Falkland Islands. It
A magnitude 7.4 earthquake occurred in the South Georgia Island Region. South Georgia Island is a British territory in the South Atlantic Ocean that lies about 800 miles east of the Falkland Islands. It
Basic Seismological Characterization for Goshen County, Wyoming
 Basic Seismological Characterization for Goshen County, Wyoming by James C. Case, Rachel N. Toner, and Robert Kirkwood Wyoming State Geological Survey September 2002 BACKGROUND Seismological characterizations
Basic Seismological Characterization for Goshen County, Wyoming by James C. Case, Rachel N. Toner, and Robert Kirkwood Wyoming State Geological Survey September 2002 BACKGROUND Seismological characterizations
Course Outline (1) 2. Engineering Seismology. #2 Engineering Seismology
 CE3.98N Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering # Engineering Seismology January 15, 3 Fumio Yamazaki yamazaki@ait.ac.th http://www.sce.ait.ac.th/people/faculty/~yamazaki SEC/SCE, AIT. 1 1. Introduction
CE3.98N Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering # Engineering Seismology January 15, 3 Fumio Yamazaki yamazaki@ait.ac.th http://www.sce.ait.ac.th/people/faculty/~yamazaki SEC/SCE, AIT. 1 1. Introduction
Basic Seismological Characterization for Niobrara County, Wyoming
 Basic Seismological Characterization for Niobrara County, Wyoming by James C. Case, Rachel N. Toner, and Robert Kirkwood Wyoming State Geological Survey September 2002 BACKGROUND Seismological characterizations
Basic Seismological Characterization for Niobrara County, Wyoming by James C. Case, Rachel N. Toner, and Robert Kirkwood Wyoming State Geological Survey September 2002 BACKGROUND Seismological characterizations
Earthquakes. These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page.
 Earthquakes These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are not
Earthquakes These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are not
Tsunami waves swept away houses and cars in northern Japan and pushed ships aground.
 Japan was struck by a magnitude 8.9 earthquake off its northeastern coast Friday. This is one of the largest earthquakes that Japan has ever experienced. In downtown Tokyo, large buildings shook violently
Japan was struck by a magnitude 8.9 earthquake off its northeastern coast Friday. This is one of the largest earthquakes that Japan has ever experienced. In downtown Tokyo, large buildings shook violently
Magnitude 7.2 OAXACA, MEXICO
 A magnitude 7.2 earthquake has occurred in Oaxaca, Mexico at a depth of 24.6 km (15 miles). It was felt as far away as Guatemala. There have been no reported deaths directly linked to the earthquake. Emergency
A magnitude 7.2 earthquake has occurred in Oaxaca, Mexico at a depth of 24.6 km (15 miles). It was felt as far away as Guatemala. There have been no reported deaths directly linked to the earthquake. Emergency
Technical Considerations Associated with Risk Management of Induced Seismicity in Waste-Water Disposal & Hydraulic Fracturing Operations
 Technical Considerations Associated with Risk Management of Induced Seismicity in Waste-Water Disposal & Hydraulic Fracturing Operations K. J. (Kris) Nygaard, Sr. Stimulation Consultant ExxonMobil Production
Technical Considerations Associated with Risk Management of Induced Seismicity in Waste-Water Disposal & Hydraulic Fracturing Operations K. J. (Kris) Nygaard, Sr. Stimulation Consultant ExxonMobil Production
Earthquakes An introduction to earthquake monitoring techniques
 Earthquakes An introduction to earthquake monitoring techniques TEACHER S COPY Aims To understand what an earthquake is and where they occur To gain an insight into how earthquakes are recorded and how
Earthquakes An introduction to earthquake monitoring techniques TEACHER S COPY Aims To understand what an earthquake is and where they occur To gain an insight into how earthquakes are recorded and how
Goals In this activity you will:
 Activity 3 How Big Was It? Goals In this activity you will: Rank the effects of earthquakes. Map the intensity of earthquakes. Interpret a map of earthquake intensity to infer the general location of the
Activity 3 How Big Was It? Goals In this activity you will: Rank the effects of earthquakes. Map the intensity of earthquakes. Interpret a map of earthquake intensity to infer the general location of the
C2.2 The physics of Earthquakes
 C2.2 The physics of Earthquakes C2.2.1 Stress axes and faults Most earthquakes occur because of the mechanical failure on brittle faults. The type of faulting is a consequence of the stress pattern causing
C2.2 The physics of Earthquakes C2.2.1 Stress axes and faults Most earthquakes occur because of the mechanical failure on brittle faults. The type of faulting is a consequence of the stress pattern causing
IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS F. GEOLOGY AND SOILS
 IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS F. GEOLOGY AND SOILS INTRODUCTION This section of the DEIR evaluates potential impacts to the project site s geologic environment that may result from implementation of
IV. ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT ANALYSIS F. GEOLOGY AND SOILS INTRODUCTION This section of the DEIR evaluates potential impacts to the project site s geologic environment that may result from implementation of
Dynamic Crust Regents Review
 Name Dynamic Crust Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the table below, which lists the location of some earthquakes, their Richter magnitude, and their year of occurrence. Data
Name Dynamic Crust Regents Review Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the table below, which lists the location of some earthquakes, their Richter magnitude, and their year of occurrence. Data
A magnitude 7.4 earthquake struck 255 km (158 miles) southwest of Tonga, according to the US Geological Survey, but there were no reports of damage.
 A magnitude 7.4 earthquake struck 255 km (158 miles) southwest of Tonga, according to the US Geological Survey, but there were no reports of damage. The earthquake hit at 5:19 am local time and was centered
A magnitude 7.4 earthquake struck 255 km (158 miles) southwest of Tonga, according to the US Geological Survey, but there were no reports of damage. The earthquake hit at 5:19 am local time and was centered
Magnitude 7.0 PERU. This region of the Andes is a sparsely populated area, there were no immediate reports of injuries or damage.
 A magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred in southeastern Peru on Friday about 27 kilometers northeast of the town of Azángaro, Peru, near the border with Bolivia. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 257.4
A magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred in southeastern Peru on Friday about 27 kilometers northeast of the town of Azángaro, Peru, near the border with Bolivia. The earthquake occurred at a depth of 257.4
ESS 202. Landslide. Earthquake effects. ! Natural Hazards. More quake effects. ! Man-aided hazards. Stanford library in 1906
 ESS 202 Today: The Size of an Earthquake! Intensity! Magnitude! Moment House after tsunami, Brumbaugh 8-18 Earthquake effects! Natural Hazards " Ground shaking # Structural collapse # Falling objects "
ESS 202 Today: The Size of an Earthquake! Intensity! Magnitude! Moment House after tsunami, Brumbaugh 8-18 Earthquake effects! Natural Hazards " Ground shaking # Structural collapse # Falling objects "
Introduction to Engineering Seismology
 Introduction to Engineering Seismology Sudhir K Jain Mythology The Myths 2 The Earth is held up by 4 elephants that stand on the back of a turtle. The turtle is balanced in turn on a cobra. When any of
Introduction to Engineering Seismology Sudhir K Jain Mythology The Myths 2 The Earth is held up by 4 elephants that stand on the back of a turtle. The turtle is balanced in turn on a cobra. When any of
Earthquakes Science & Safety. Ms Joan L. Latchman Seismologist Seismic Research Unit
 Earthquakes Science & Safety Ms Joan L. Latchman Seismologist Seismic Research Unit Summary Trinidad lies in an area of high earthquake activity for the Caribbean. Earthquake safety tips should be practiced
Earthquakes Science & Safety Ms Joan L. Latchman Seismologist Seismic Research Unit Summary Trinidad lies in an area of high earthquake activity for the Caribbean. Earthquake safety tips should be practiced
Magnitude 7.0 SOUTH ISLAND OF NEW ZEALAND
 A powerful 7.0-magnitude earthquake shook much of New Zealand's South Island early Saturday morning local time. USGS A damaged building near Manchester St. New Zealand Herald Photo / Colin Cross A car
A powerful 7.0-magnitude earthquake shook much of New Zealand's South Island early Saturday morning local time. USGS A damaged building near Manchester St. New Zealand Herald Photo / Colin Cross A car
Inquiry: Sumatran earthquakes with GPS Earth Science Education
 Inquiry: Sumatran earthquakes with GPS Earth Science Education www.earthobservatory.sg Preparation: Before doing this investigation, complete two introductory investigations using GPS data from UNAVCO
Inquiry: Sumatran earthquakes with GPS Earth Science Education www.earthobservatory.sg Preparation: Before doing this investigation, complete two introductory investigations using GPS data from UNAVCO
I. What are Earthquakes?
 I. What are Earthquakes? A. There is more to earthquakes than just the shaking of the ground. An entire branch of Earth science, called seismology, is devoted to the study of earthquakes. B. Earthquakes
I. What are Earthquakes? A. There is more to earthquakes than just the shaking of the ground. An entire branch of Earth science, called seismology, is devoted to the study of earthquakes. B. Earthquakes
Magnitude 7.6 & 7.6 PERU
 Two deep 7.6 magnitude earthquakes have shaken a sparsely populated jungle region near the Peru-Brazil border in southeast Peru. There were no immediate reports of injuries or damage. The second M 7.6
Two deep 7.6 magnitude earthquakes have shaken a sparsely populated jungle region near the Peru-Brazil border in southeast Peru. There were no immediate reports of injuries or damage. The second M 7.6
appendix e: geologic and seismic hazards
 appendix e: geologic and seismic hazards CONTENTS: E-2 Fault Rupture E-3 Ground Shaking E-5 Seismic Ground Deformation E-5 Liquification E-6 Seismically Induces Landslide E-6 Landslide Hazard E The following
appendix e: geologic and seismic hazards CONTENTS: E-2 Fault Rupture E-3 Ground Shaking E-5 Seismic Ground Deformation E-5 Liquification E-6 Seismically Induces Landslide E-6 Landslide Hazard E The following
Earthquakes Science & Safety. Dr. Richard Robertson Geologist & Head Seismic Research Unit
 Earthquakes Science & Safety Dr. Richard Robertson Geologist & Head Seismic Research Unit Summary The Eastern Caribbean islands are in a seismically active part of the world. Earthquake safety tips should
Earthquakes Science & Safety Dr. Richard Robertson Geologist & Head Seismic Research Unit Summary The Eastern Caribbean islands are in a seismically active part of the world. Earthquake safety tips should
Identifying the causes and effects of earthquakes
 Science 3 Physical Earth and Space Life LESSON 57 Identifying the causes and effects of earthquakes Lesson Preparation Program Materials Child s Booklet E Exploring the Earth s Structure (pp. 12 13) Optional:
Science 3 Physical Earth and Space Life LESSON 57 Identifying the causes and effects of earthquakes Lesson Preparation Program Materials Child s Booklet E Exploring the Earth s Structure (pp. 12 13) Optional:
Magnitude 7.6 SOUTH OF IQUIQUE, CHILE
 A powerful aftershock struck off northern Chile prompting an evacuation of the coastal area and raising fears of a tsunami. This magnitude 7.6 earthquake is the largest of a series of aftershocks following
A powerful aftershock struck off northern Chile prompting an evacuation of the coastal area and raising fears of a tsunami. This magnitude 7.6 earthquake is the largest of a series of aftershocks following
SECTION 3. Housing. EAppendix E GEOLOGIC AND SEISMIC HAZARDS
 SECTION 3 Housing EAppendix E GEOLOGIC AND SEISMIC HAZARDS E-2 Housing Commission Attachment B Appendix E Geologic and Seismic Hazards The following definitions provide a more comprehensive discussion
SECTION 3 Housing EAppendix E GEOLOGIC AND SEISMIC HAZARDS E-2 Housing Commission Attachment B Appendix E Geologic and Seismic Hazards The following definitions provide a more comprehensive discussion
A Violent Pulse: Earthquakes. Lecture #2
 A Violent Pulse: Earthquakes Lecture #2 Earthquakes Are Always Happening ~ 1,000,000 / yr Most are small o Detected only by instruments Large EQ ~ 20 / yr cause extensive damage ~ 1 catastrophic EQ / year
A Violent Pulse: Earthquakes Lecture #2 Earthquakes Are Always Happening ~ 1,000,000 / yr Most are small o Detected only by instruments Large EQ ~ 20 / yr cause extensive damage ~ 1 catastrophic EQ / year
Magnitude 7.3 IRAQ. Early reports indicate that 140 have been killed with over 800 injuries reported. Sunday, November 12, 2017 at 18:18:17 UTC
 A magnitude 7.3 earthquake has occurred in the northern border region of Iran and Iraq centered about 350 kilometers (217 miles) north of Baghdad at a depth of 33.9 km (21 miles). The earthquake was felt
A magnitude 7.3 earthquake has occurred in the northern border region of Iran and Iraq centered about 350 kilometers (217 miles) north of Baghdad at a depth of 33.9 km (21 miles). The earthquake was felt
Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating.
 CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
An entire branch of Earth science, called, is devoted to the study of earthquakes.
 Lesson One Essential Question Where do earthquakes take place? What causes earthquakes? What are three different types of faults that occur at plate boundaries? How does energy from earthquakes travels
Lesson One Essential Question Where do earthquakes take place? What causes earthquakes? What are three different types of faults that occur at plate boundaries? How does energy from earthquakes travels
Names: ESS 315 Lab # 1 Seismic Hazards along the Cascadia Subduction Zone
 Names: ESS 315 Lab # 1 Seismic Hazards along the Cascadia Subduction Zone 1 Seismographs located throughout the Pacific Northwest record thousands of earthquakes each year in Washington and Oregon. Between
Names: ESS 315 Lab # 1 Seismic Hazards along the Cascadia Subduction Zone 1 Seismographs located throughout the Pacific Northwest record thousands of earthquakes each year in Washington and Oregon. Between
Magnitude 7.3 NEPAL. Tuesday, May 12, 2015 at 07:05:19 UTC
 A magnitude 7.3 earthquake has occurred near Mount Everest. Early reports suggest 32 people have been killed and at least 1,000 were injured in the earthquake. The region is still in recovery from a 7.8
A magnitude 7.3 earthquake has occurred near Mount Everest. Early reports suggest 32 people have been killed and at least 1,000 were injured in the earthquake. The region is still in recovery from a 7.8
PADANG EARTHQUAKE, WEST SUMATRA ON MARCH 6, 2007
 PADANG EARTHQUAKE, WEST SUMATRA ON MARCH 6, 2007 EARTHQUAKE DETAILS The U. S. Geological Survey (USGS) informed a strong earthquake struck west Sumatra on Tuesday March 6, 2007 at 10:49 with a magnitude
PADANG EARTHQUAKE, WEST SUMATRA ON MARCH 6, 2007 EARTHQUAKE DETAILS The U. S. Geological Survey (USGS) informed a strong earthquake struck west Sumatra on Tuesday March 6, 2007 at 10:49 with a magnitude
Seismic Waves. 1. Seismic Deformation
 Types of Waves 1. Seismic Deformation Seismic Waves When an earthquake fault ruptures, it causes two types of deformation: static; and dynamic. Static deformation is the permanent displacement of the ground
Types of Waves 1. Seismic Deformation Seismic Waves When an earthquake fault ruptures, it causes two types of deformation: static; and dynamic. Static deformation is the permanent displacement of the ground
THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR
 JURNAL KEJURUTERAAN AWAM (JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING) Vol. 15 No. 2, 2002 THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR Assoc. Prof. Dr. Azlan Adnan Hendriyawan Structural Earthquake
JURNAL KEJURUTERAAN AWAM (JOURNAL OF CIVIL ENGINEERING) Vol. 15 No. 2, 2002 THE EFFECT OF THE LATEST SUMATRA EARTHQUAKE TO MALAYSIAN PENINSULAR Assoc. Prof. Dr. Azlan Adnan Hendriyawan Structural Earthquake
The Size of an Earthquake. Intensity of Shaking (Robert Mallet, 1857) Calculation of Earthquake Magnitude (Charles Richter, 1935)
 The Size of an Earthquake Intensity of Shaking (Robert Mallet, 1857) Calculation of Earthquake Magnitude (Charles Richter, 1935) In 1857, Robert Mallet produced isoseismal lines based on quantified damage
The Size of an Earthquake Intensity of Shaking (Robert Mallet, 1857) Calculation of Earthquake Magnitude (Charles Richter, 1935) In 1857, Robert Mallet produced isoseismal lines based on quantified damage
Earthquakes and Earth s Interior
 - What are Earthquakes? Earthquakes and Earth s Interior - The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy - Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks - Continuing adjustment
- What are Earthquakes? Earthquakes and Earth s Interior - The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy - Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks - Continuing adjustment
Basic Seismological Characterization for Sheridan County, Wyoming
 Basic Seismological Characterization for Sheridan County, Wyoming by James C. Case, Rachel N. Toner, and Robert Kirkwood Wyoming State Geological Survey September 2002 BACKGROUND Seismological characterizations
Basic Seismological Characterization for Sheridan County, Wyoming by James C. Case, Rachel N. Toner, and Robert Kirkwood Wyoming State Geological Survey September 2002 BACKGROUND Seismological characterizations
Section Forces Within Earth. 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes
 Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
dt r = 0 sin i 0 = P d Δ V 0
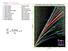 dt dδ = r 0 sin i 0 V 0 = P sin i toa Me Always someone needs to reorder and make difficult to check Me One that agrees with me many don t though many agree with each other science begins Locating Local
dt dδ = r 0 sin i 0 V 0 = P sin i toa Me Always someone needs to reorder and make difficult to check Me One that agrees with me many don t though many agree with each other science begins Locating Local
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Physical Geology Lab. Teacher Check (show your screen to your teacher) Part ONE: Dynamic Earth. Continents Over Time.
 Physical Geology Lab Name Hour Part ONE: Dynamic Earth Earth s Structure Name the Layer: The only liquid layer Only a few miles thick (under oceans) Mostly solid iron and nickel Made of hot, semi-solid
Physical Geology Lab Name Hour Part ONE: Dynamic Earth Earth s Structure Name the Layer: The only liquid layer Only a few miles thick (under oceans) Mostly solid iron and nickel Made of hot, semi-solid
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 3 Understanding Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information:
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Session 3 Understanding Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Lecturer: Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG Contact Information:
How to Use This Presentation
 How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
How to Use This Presentation To View the presentation as a slideshow with effects select View on the menu bar and click on Slide Show. To advance through the presentation, click the right-arrow key or
News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake
 News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake PASADENA, Calif. - Kerry Sieh, the Robert P. Sharp Professor of Geology at the California Institute of Technology and a member of Caltech's
News Release December 30, 2004 The Science behind the Aceh Earthquake PASADENA, Calif. - Kerry Sieh, the Robert P. Sharp Professor of Geology at the California Institute of Technology and a member of Caltech's
EARTHQUAKES AND EARTHQUAKE-RESISTANT DESIGN OF STRUCTURES. Er. K. S. BHARGAV LECTURER Department of Civil Engineering, GGSGP CHEEKA
 EARTHQUAKES AND EARTHQUAKE-RESISTANT DESIGN OF STRUCTURES by Er. K. S. BHARGAV LECTURER Department of Civil Engineering, GGSGP CHEEKA SCOPE OF PRESENTATION EARTHQUAKE AND ITS CHARACTERIZATION EARTHQUAKE-RESISTANT
EARTHQUAKES AND EARTHQUAKE-RESISTANT DESIGN OF STRUCTURES by Er. K. S. BHARGAV LECTURER Department of Civil Engineering, GGSGP CHEEKA SCOPE OF PRESENTATION EARTHQUAKE AND ITS CHARACTERIZATION EARTHQUAKE-RESISTANT
Seismic risk in Romania
 Seismic risk in Romania Dr.eng. Mihaela Lazarescu National R&D Institute for Environmetal Protection ICIM Bucharest Spl. Independentei 294, cod 060031 Bucharest ROMANIA This is the list of significant
Seismic risk in Romania Dr.eng. Mihaela Lazarescu National R&D Institute for Environmetal Protection ICIM Bucharest Spl. Independentei 294, cod 060031 Bucharest ROMANIA This is the list of significant
Information for this section has been provided by Wyoming State Geological Survey (WSGS).
 Chapter 11: Earthquakes POTENTIAL, AND IMPACTS Information for this section has been provided by Wyoming State Geological Survey (WSGS). Fremont County has experienced damaging earthquakes in the past
Chapter 11: Earthquakes POTENTIAL, AND IMPACTS Information for this section has been provided by Wyoming State Geological Survey (WSGS). Fremont County has experienced damaging earthquakes in the past
Earthquakes. Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics. Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics. Chapter 6 Modern Earth Science. Modern Earth Science. Section 6.
 Earthquakes Chapter 6 Modern Earth Science Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Section 6.1 Modern Earth Science Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Earthquakes are the result of stresses in Earth s s lithosphere.
Earthquakes Chapter 6 Modern Earth Science Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Section 6.1 Modern Earth Science Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Earthquakes are the result of stresses in Earth s s lithosphere.
Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Pearson Education, Inc.
 Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Measuring the Size of Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the size of an earthquake are: 1. Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale
Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Measuring the Size of Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the size of an earthquake are: 1. Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale
UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES
 UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE An earthquake is a sudden motion or trembling of the Earth caused by the abrupt release of energy that is stored in rocks. Modern geologists know that most earthquakes
UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE An earthquake is a sudden motion or trembling of the Earth caused by the abrupt release of energy that is stored in rocks. Modern geologists know that most earthquakes
Module 7: Plate Tectonics and Earth's Structure Topic 4 Content : Earthquakes Presentation Notes. Earthquakes
 Earthquakes 1 Topic 4 Content: Earthquakes Presentation Notes Earthquakes are vibrations within the Earth produced by the rapid release of energy from rocks that break under extreme stress. Earthquakes
Earthquakes 1 Topic 4 Content: Earthquakes Presentation Notes Earthquakes are vibrations within the Earth produced by the rapid release of energy from rocks that break under extreme stress. Earthquakes
FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA
 FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA Myo Thant 1, Hiroshi Kawase 2, Subagyo Pramumijoyo 3, Heru Hendrayana
FOCAL MECHANISMS OF SUBDUCTION ZONE EARTHQUAKES ALONG THE JAVA TRENCH: PRELIMINARY STUDY FOR THE PSHA FOR YOGYAKARTA REGION, INDONESIA Myo Thant 1, Hiroshi Kawase 2, Subagyo Pramumijoyo 3, Heru Hendrayana
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquakes Modified
 Plate Tectonics Earthquakes Modified Recall that the earth s crust is broken into large pieces called. These slowly moving plates each other, each other, or from each other. This causes much on the rocks.
Plate Tectonics Earthquakes Modified Recall that the earth s crust is broken into large pieces called. These slowly moving plates each other, each other, or from each other. This causes much on the rocks.
