GPS measurements of present-day uplift in the Southern Tibet
|
|
|
- Elfreda Baldwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 52, , 2000 GPS measurements of present-day uplift in the Southern Tibet Caijun Xu, Jingnan Liu, Chenghua Song, Weiping Jiang, and Chuang Shi School of Geoscience and Surveying Engineering, Wuhan Technical University of Surveying and Mapping (WTUSM), 129 Luyou Road, Wuhan , P. R. China (Received December 31, 1999; Revised May 17, 2000; Accepted May 19, 2000) Wuhan Technical University Surveying and Mapping (WTUSM) carried out three GPS campaigns in the Tibetan Plateau since To improve the vertical component precision of GPS measurement, we estimated the remaining tropospheric refraction using the piecewise linear method after the SAASTAMOINEN model and corrected the tropospheric refraction by selecting one parameter for every two hours model to consider the variation of tropospheric refraction. Using the IGS combined ephemeris and corresponding EOP Series for 1995 and 1997 GPS campaigns, all baseline vectors were processed by GAMIT (Ver. 9.71) software, and network adjustment was carried out in ITRF97 frame by PowerAdj software (Ver. 3.3) which was developed by WTUSM considering the baseline vectors full covariance matrix. The resulting vertical velocity field determined from GPS campaigns in 1995 and 1997 shows that the average uplift rate in ITRF 97 frame is about 7.8 ± 7.6 mm/yr for all 14 repeated surveying stations in Tibet, and the average uplift rate is 16.2 ± 7.9 mm/yr in southern Tibet, which are compared with the results from the gravity measurements, leveling data and fission-track dating (FT). 1. Introduction The high elevation of the Himalayas and Tibet is resulted from the continuing collision between India and Asia, which started more than million years ago (Ma et al., 1998). Leveling data with very sparse spatial sampling in southern Tibet between 1959 and 1981 suggest that the Himalayan divide may be rising at a rate of 7.5 ± 5.6 mm/yr relative to central Tibet (Jackson and Bilham, 1994a, b). First-order precise leveling data in Tibet from Geolmud to Lhasa, and from Shiqianhe to Lhasa between 1959 to 1961 and 1979 to 1981 suggest that Tibet vises at rate of 5.8 mm/yr relative to Xining (Zhang, 1991). Leveling data also suggest the southern Tibet rising at rate more than 10 mm/yr (Zhang, 1987; Jiang, 1989; Zhang, 1991; Ma, 1989; Wang et al., 1993; Chen, 1996). FT (Fission-track dating) result shows an average uplift rate between 10 mm/yr to 30 mm/yr in Himalayas since 1 Ma (Zhong and Ding, 1996). Although the vertical component uncertainty in GPS measurements is longer than 5 mm, vertical movements can be measured in areas where the uplift rate is high. Three GPS campaigns were carried out in the Tibetan plateau by WTUSM in 1993, 1995 and Since there was no IGS combined ephemeris and corresponding EOP Series for 1993 GPS campaign, we studied the uplift rate in southern Tibet using GPS measurements in 1995 and 1997 in this paper. 2. GPS Campaigns A sketch of GPS monitoring sites in the Qinghai-Tibet plateau is shown in Fig. 1. The GPS Monitoring sites are mainly deployed in the Tibet block, Himalayan block, and Copy right c The Society of Geomagnetism and Earth, Planetary and Space Sciences (SGEPSS); The Seismological Society of Japan; The Volcanological Society of Japan; The Geodetic Society of Japan; The Japanese Society for Planetary Sciences. Qaidam block. The GPS-chain network crosses the Honxil- Bayan Har, Jinsha Jiang, Nujiang-Lancang Jiang and Yarlung Zangbo Jiang rift systems. The shortest baseline and longest baseline in the network are 62 km and 1185 km respectively, the mean length of baselines is 364 km. The first GPS campaign took place from July 18 to August 24, 1993, the second one took place from June 5 to July 5, 1995, and the third one carried out from June 5 to June 25, There were two observation sessions at every site in each campaign, one was in daytime, the other was at night, and every observation session lasted 9 hours. The details of the GPS campaigns are listed in Table GPS Data Processing We used the GAMIT software (King and Bock, 1995) to estimate daily station positions simultaneously with orbital and atmospheric parameters using dual-frequency, doubly differenced GPS phase observations at sites in Tibet and Lhasa IGS station. We use the GLOBK software (Herring, 1995) to combine the daily solutions of each survey. Both orbital and station parameters are estimated, allowing orbital parameters to vary stochastically according to the level of unmodeled accelerations of the satellites and the strength of the global tracking data. The final solution file contains (loosely constrained) estimates of station positions for each (few-day to several-week) survey, with orbital parameters suppressed. We use the PowerAdj software Ver. 3.3, which is developed by WTUSM, to combine the solution files ( quasiobservations ) from all of the surveys in order to estimate station positions and their velocities. 3.1 Fiducial station and GPS precise ephemeris The Fiducial point technique has been used in data processing. Lhasa station was chosen as the fiducial station. Using its ITRF97 coordinates and velocity, the station coordinate 735
2 736 C. XU et al.: PRESENT-DAY UPLIFT IN SOUTHERN TIBET Fig. 1. Sketch of GPS monitoring sites in the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Table 1. Statistics for GPS campaigns in Tibet plateau. Camp. Monitoring Synchronous observation Receiver period stations total 2 sites 3 sites 4 sites 5 sites type number Rogue SNR Rogue SNR Rogue SNR was reduced to the observation instantaneous epoch corresponding to the ephemeris. In each solution the coordinates were assigned a priori constraint of 5 mm for horizontal and 10 mm for vertical. We used the IGS combined ephemeris and corresponding EOP Series for 1995 and 1997 GPS campaigns. The satellite coordinates were constrained within a priori uncertainty of ppm. 3.2 Tropospheric correction The tropospheric refraction is the main limiting factor in GPS positioning, especially there is exquiste variation of weather in Tibetan Plateau. The RMS of vertical component will be improved if the influence of tropospheric refraction is reduced. In data processing we estimated the remaining tropospheric refraction using the piecewise linear method after the SAASTAMOINEN model corrected the tropospheric refraction. Choosing tropospheric delay bias parameters are critical for fitting the tropospheric refraction and getting good results. RMS of GPS site coordinates is shown in Table 2(a) for 5 kinds of testing situation. Situation c is the best method for improving the daily solution considering synthetically the results (repeatability of baseline components) in Table 2(a), so we select one parameter every two hours after the SAAS- TAMOINEN model for tropospheric correcting. 3.3 Repeatability of baseline Repeatability of baseline s component can express the precision of solution, and is one of the most important quality indexes of GPS positioning. Repeatability (daily to daily solution over the weighted mean square error) σ can be expressed with fixed error and scale error. It may be described as follows: σ = a + bl. Here a is fixed error and b is scale error, l is length of each component repeatability of baseline component is listed in Table 2(b). Table 2(b) shows that repeatability of vertical component is better than 6.4 mm l. 3.4 Adjustment of each campaigns in an uniform datum PowerADJ Ver. 3.3 developed by WTUSM is used to process the baseline vectors including their full covariance ma-
3 C. XU et al.: PRESENT-DAY UPLIFT IN SOUTHERN TIBET 737 Table 2(a). Comparison of Repeatability of baseline component. N-S E-W UP L a + b 10 8 l a + b 10 8 l a + b 10 8 l a + b 10 8 l a 0.3 mm l 2.5 mm l 5.5 mm l 0.6 mm l b 0.6 mm l 2.1 mm l 5.0 mm l 0.8 mm l c 0.4 mm l 1.3 mm l 5.4 mm l 0.3 mm l d 0.6 mm l 2.2 mm l 6.9 mm l 0.5 mm l e 0.4 mm l 2.2 mm l 6.1 mm l 0.7 mm l a one parameter every half hour for modeling the variation of the tropospheric refraction, b one parameter every one hour for modeling the variation of the tropospheric refraction, c one parameter every two hours for modeling the variation of the tropospheric refraction, d one parameter every four hours for modeling the variation of the tropospheric refraction, e one parameter for modeling the variation of the tropospheric refraction. Table 2(b). Comparison of Repeatability of baseline component. N-S E-W UP L a + b 10 8 l a + b 10 8 l a + b 10 8 l a + b 10 8 l mm l 5.8 mm l 6.2 mm l 4.2 mm l mm l 2.4 mm l 6.4 mm l 2.0 mm l Table 3. Data information of GPS campaigns in adjustment. Datum of daily solution Adjustment datum for GPS campaigns Precise ephemeris Reference frame of ephemeris Observation Reference frame of Epoch and EOP and fiducial station instantaneous epoch fiducial stations IGS ITRF ITRF IGS ITRF ITRF Fig. 2(a). Statistics for precision of GPS baselines (RMS ratio to baseline length). Fig. 2(b). Statistics for precision of GPS site coordinates (RMS). trix. The data information of GPS campaigns in the adjustment is listed in Table 3. Statistics for RMS ratio to baseline length and RMS of GPS site coordinates are shown in Fig. 2(a) and (b), respectively. 4. Uplifting Rate in Tibet The following characteristics of vertical deformation in Tibet are derived from our solutions listed in Table 4 and Fig. 3.
4 738 C. XU et al.: PRESENT-DAY UPLIFT IN SOUTHERN TIBET Table 4. Vertical motion rate in Tibet by GPS campaigns in 1995 and 1997 in ITRF97 frame. Site Longitude Latitude Uplifting rate RMS remark East ( ) North ( ) mm/yr mm/yr Geolmud (GL) (0001) Budongqua (BD) (0002) Erdaogou (ED) (0003) Yanshiping (YS) (0004) Wenquan (WQ) (0005) Amdo (AD) (0006) Suoxian (SX) (0014) Naque (NQ) (0007) Lhasa (LS) (0008) Saga (SG) (0012) Xigaze (XG) in Southern Tibet (0013) Lhaze (LZ) in Southern Tibet (0010) Gyangze (GZ) in Southern Tibet (0009) Nyalam (NL) in Southern Tibet (0011) (1) In southern Tibet (NL, GZ, LZ, XG), the vertical motion rate is between 6.6 ± 6.6 mm/yr to 22.1 ± 7.4 mm/yr, and the average vertical motion rate is 16.2±7.9 mm/yr in ITRF97 frame. (2) The average vertical motion rate is 7.8 ± 7.6 mm/yr for the 14 repeated surveying stations in Tibet by GPS campaigns 95 and 97 in ITRF97 frame. The uplifting rates in Southern Tibet obtained by GPS measurements are agree with 7.5 ± 5.6 mm/yr relative to central Tibet from regional leveling data (Jackson and Bilham, 1994a, b) and more than 10 mm/yr in Southern Tibet estimated from leveling data relative to Huanghai mean sea level (Zhang, 1987; Zhang, 1991). They are also consistent with uplifting rate of mm/yr relative to ChengDu, Sichuan province, calculated from gravity measurements (Zhang, 1996) and rates between 10 mm/yr to 30 mm/yr in Himalayan terrain since 1 Ma inferred fission-track dating (FT) and its sampling heights of rocks (Zhong and Ding, 1996). 5. Discussions and Conclusions The average uplift rate is about 16.2 ± 7.9 mm/yr in the Southern Tibet estimated by GPS95 and GPS97 measurements in ITRF97 frame, which agree with the rates obtained from leveling data, gravity data and Fission-track dating (FT). The agreement of present-day GPS providing rate and geological mean rate from FT shows that the Cenozoic tectonic activity is still very active in the Southern Tibet and its surrounding regions. It is possible to determine vertical motion rate by GPS measurements in the Southern Tibet. The precision of vertical component of GPS measurements can be improved by adopting a proper model of tropospheric refraction. However, the uncertainties of the uplift rate are mostly larger than 5 mm/yr, and are larger than the uplift rates themselves at some sites in Tibet Plateau. It is important to survey continuously for a longer time and to survey
5 C. XU et al.: PRESENT-DAY UPLIFT IN SOUTHERN TIBET 739 Fig. 3. Vertical velocity of GPS monitoring stations in Tibet Plateau (97 95), here NL, GZ, LZ and XG are deployed in the Southern Tibet. repeated in a longer interval. Wenquan s uplift rate of about 10.4±7.9 mm/yr is difficult in interpreting. It seems much more likely that the site at Wenquan is unstable, or that it is affected by localized subsidence due to groundwater withdrawal, or that there was a blunder in one of the antenna height measurements. More repeat GPS surveys in Tibet (including the Southern Tibet) and more monitoring sites are especially desirable to determine the mechanics of the uplift. Acknowledgments. We thank Dr. Kosuke Heki, Dr. Jeff Freymueller and Dr. Makoto OMURA for their comments improving the manuscript greatly. This research was funded by National Nature Science Foundation of China grant , and References Chen, J. Y. and J. Zhang, On the crustal movement in Qumolongma feng and its adjacent area, ACTA Geophysica Sinica, 39, 67 78, Herring, T. A., GLOBK: Global kalman filter VLBI and GPS analysis program, version 4.0, Mass. Inst. Technol., Cambridge, Jackson, M. and R. Bilham, GPS Measurements across the Nepal Himalaya, Geophys. Res. Lett., 21, , 1994a. Jackson, M. and R. Bilham, Constraints on Himalayan deformation inferred from vertical velocity fields in Nepal and Tibet, J. Geophys. Res., 99(b7), , 1994b. Jiang, F. Z., C. J. Zhang, Z. H. Ni, and Y. P. Liu, Isostatic field Nontidal gravity measurement in Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, ACTA Geophysica Sinica, 32, , King, R. W. and Y. Bock, Documentation for the MIT GPS analysis software: GAMIT, version 9.3, Mass. Inst. Technol., Cambridge, Ma, X. Y, Lithospheric dynamics atlas of China, China Cartographic Publishing House, Beijing China, 18, Ma, Z. J., J. S. Zhang, and Y. P. Wang, The 3-d deformational movement episodes and neotectonic domains in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, ACTA Geologica Sinica, 72(3), , Wang, W. Y. and Z. Q. Yang, Application of the GPS technology in the survey of plate tectonic motion and vertical crustal displacement in the Himalayan area, J. Xi an coll. Geol., 15, 1 8, Zhang, C. J., Study on the Qinghai-Xizang crust and its movements via the temporal and spatial gravity distribution, Seismology and Geology, 18(3), , Zhang, Q. S., The problem of uplift rate of the Tibetan Plateau, Chinese Science Bulletin, , 1991 (in Chinese). Zhang, Z., The map of the recent vertical crustal deformation rate in China, Chinese National Report on Geodesy presented to the 19th general assembly of IUGG, Vancouver, Zhong, D. Q. and L. Ding, Science in China (series D), vol. 26, , C. Xu ( cjxu@hpb1.wtusm.edu.cn), J. Liu, C. Song, W. Jiang, and C. Shi
Specific gravity field and deep crustal structure of the Himalayas east structural knot
 49 4 2006 7 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 49, No. 4 Jul., 2006,,.., 2006, 49 (4) :1045 1052 Teng J W, Wang Q S, Wang GJ, et al. Specific gravity field and deep crustal structure of the Himalayas east
49 4 2006 7 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 49, No. 4 Jul., 2006,,.., 2006, 49 (4) :1045 1052 Teng J W, Wang Q S, Wang GJ, et al. Specific gravity field and deep crustal structure of the Himalayas east
Study on the feature of surface rupture zone of the west of Kunlunshan pass earthquake ( M S 811) with high spatial resolution satellite images
 48 2 2005 3 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 48, No. 2 Mar., 2005,,. M S 811.,2005,48 (2) :321 326 Shan X J, Li J H, Ma C. Study on the feature of surface rupture zone of the West of Kunlunshan Pass
48 2 2005 3 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 48, No. 2 Mar., 2005,,. M S 811.,2005,48 (2) :321 326 Shan X J, Li J H, Ma C. Study on the feature of surface rupture zone of the West of Kunlunshan Pass
Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data
 Johannes Böhm, Arthur Niell, Paul Tregoning, and Harald Schuh Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data Geophysical Research Letters Vol. 33,
Johannes Böhm, Arthur Niell, Paul Tregoning, and Harald Schuh Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data Geophysical Research Letters Vol. 33,
DEFORMATION KINEMATICS OF TIBETAN PLATEAU DETERMINED FROM GPS OBSERVATIONS
 DEFORMATION KINEMATICS OF TIBETAN PLATEAU DETERMINED FROM GPS OBSERVATIONS Jinwei Ren Institute of Geology, China Seismological Bureau, Beijing 100029 China Tel: (10)62009095; Fax: (10)62009003; email:
DEFORMATION KINEMATICS OF TIBETAN PLATEAU DETERMINED FROM GPS OBSERVATIONS Jinwei Ren Institute of Geology, China Seismological Bureau, Beijing 100029 China Tel: (10)62009095; Fax: (10)62009003; email:
Determination of Current Velocity Field (Rate) of North Anatolian Fault in Izmit-Sapanca Segment
 Determination of Current Velocity Field (Rate) of North Anatolian Fault in Izmit-Sapanca Segment Cetin MEKIK, Bulent TURGUT, Haluk OZENER, Turkish Republic INTRODUCTION Turkey is geologically the part
Determination of Current Velocity Field (Rate) of North Anatolian Fault in Izmit-Sapanca Segment Cetin MEKIK, Bulent TURGUT, Haluk OZENER, Turkish Republic INTRODUCTION Turkey is geologically the part
The Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data
 The Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data J. Boehm, A. Niell, P. Tregoning, H. Schuh Troposphere mapping functions are used in the analyses
The Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data J. Boehm, A. Niell, P. Tregoning, H. Schuh Troposphere mapping functions are used in the analyses
STRUCTURE OF THE CRUST AND UPPER MANTLE PATTERN AND VELOCITY DISTRIBUTIONAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE NORTHERN HIMALAYAN MOUNTAIN REGION
 J. Phys. Earth, 33, 157-171, 1985 STRUCTURE OF THE CRUST AND UPPER MANTLE PATTERN AND VELOCITY DISTRIBUTIONAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE NORTHERN HIMALAYAN MOUNTAIN REGION Ji-wen TENG,* Shao-bai XIONG,* Zhou-xun
J. Phys. Earth, 33, 157-171, 1985 STRUCTURE OF THE CRUST AND UPPER MANTLE PATTERN AND VELOCITY DISTRIBUTIONAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE NORTHERN HIMALAYAN MOUNTAIN REGION Ji-wen TENG,* Shao-bai XIONG,* Zhou-xun
ESTIMATES OF HORIZONTAL DISPLACEMENTS ASSOCIATED WITH THE 1999 TAIWAN EARTHQUAKE
 ESTIMATES OF HORIZONTAL DISPLACEMENTS ASSOCIATED WITH THE 1999 TAIWAN EARTHQUAKE C. C. Chang Department of Surveying and Mapping Engineering Chung Cheng Institute of Technology, Taiwan, ROC ABSTRACT A
ESTIMATES OF HORIZONTAL DISPLACEMENTS ASSOCIATED WITH THE 1999 TAIWAN EARTHQUAKE C. C. Chang Department of Surveying and Mapping Engineering Chung Cheng Institute of Technology, Taiwan, ROC ABSTRACT A
SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences. Preseismic deformation in the seismogenic zone of the Lushan M S 7.0 earthquake detected by GPS observations
 SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences RESEARCH PAPER September 2015 Vol.58 No.9: 1592 1601 doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5128-0 Preseismic deformation in the seismogenic zone of the Lushan M S 7.0 earthquake detected
SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences RESEARCH PAPER September 2015 Vol.58 No.9: 1592 1601 doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5128-0 Preseismic deformation in the seismogenic zone of the Lushan M S 7.0 earthquake detected
ESTIMATING THE RESIDUAL TROPOSPHERIC DELAY FOR AIRBORNE DIFFERENTIAL GPS POSITIONING (A SUMMARY)
 ESTIMATING THE RESIDUAL TROPOSPHERIC DELAY FOR AIRBORNE DIFFERENTIAL GPS POSITIONING (A SUMMARY) J. Paul Collins and Richard B. Langley Geodetic Research Laboratory Department of Geodesy and Geomatics
ESTIMATING THE RESIDUAL TROPOSPHERIC DELAY FOR AIRBORNE DIFFERENTIAL GPS POSITIONING (A SUMMARY) J. Paul Collins and Richard B. Langley Geodetic Research Laboratory Department of Geodesy and Geomatics
Impact of a priori zenith hydrostatic delay errors on GPS estimates of station heights and zenith total delays
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L23303, doi:10.1029/2006gl027706, 2006 Impact of a priori zenith hydrostatic delay errors on GPS estimates of station heights and zenith
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L23303, doi:10.1029/2006gl027706, 2006 Impact of a priori zenith hydrostatic delay errors on GPS estimates of station heights and zenith
Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Mathematical models in GPS" Mathematical models used in GPS"
 12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Prof. Thomas Herring" Room 54-820A; 253-5941" tah@mit.edu" http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 " Mathematical models in GPS" Review assignment
12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Prof. Thomas Herring" Room 54-820A; 253-5941" tah@mit.edu" http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 " Mathematical models in GPS" Review assignment
The Application of GNSS to Monitoring Fault Deformation
 The Application of GNSS to Monitoring Fault Deformation Shengtao FENG, Wanju BO, Jianfeng SU, Haitao ZHOU, Xuesong DU, Wenni WAN, Tianhai LIU, China Key words: GNSS, fault deformation, baseline, crustal
The Application of GNSS to Monitoring Fault Deformation Shengtao FENG, Wanju BO, Jianfeng SU, Haitao ZHOU, Xuesong DU, Wenni WAN, Tianhai LIU, China Key words: GNSS, fault deformation, baseline, crustal
Is the deformation rate of the Longmenshan fault zone really small? Insight from seismic data at the two-decade time scale
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 62, 887 891, 2010 Is the deformation rate of the Longmenshan fault zone really small? Insight from seismic data at the two-decade time scale Yizhe Zhao 1, Zhongliang Wu 1,2,
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 62, 887 891, 2010 Is the deformation rate of the Longmenshan fault zone really small? Insight from seismic data at the two-decade time scale Yizhe Zhao 1, Zhongliang Wu 1,2,
A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin, F. Perosanz, F. Mercier and J. Marty. AVENUE project. June, 20
 Efficient QR Sequential Least Square algorithm for high frequency GNSS Precise Point Positioning A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin, F. Perosanz, F. Mercier and J. Marty AVENUE project June, 20 A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin,
Efficient QR Sequential Least Square algorithm for high frequency GNSS Precise Point Positioning A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin, F. Perosanz, F. Mercier and J. Marty AVENUE project June, 20 A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin,
Introduction to geodetic VLBI
 Introduction to geodetic VLBI David Mayer Andreas Hellerschmied Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
Introduction to geodetic VLBI David Mayer Andreas Hellerschmied Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
Establishment of the three-dimensional kinematic reference frame by space geodetic measurements
 LETTER Earth Planets Space, 52, 959 963, 2000 Establishment of the three-dimensional kinematic reference frame by space geodetic measurements M. D. Gerasimenko 1 and Teruyuki Kato 2 1 Institute of Applied
LETTER Earth Planets Space, 52, 959 963, 2000 Establishment of the three-dimensional kinematic reference frame by space geodetic measurements M. D. Gerasimenko 1 and Teruyuki Kato 2 1 Institute of Applied
E. Calais Purdue University - EAS Department Civil 3273
 E. Calais urdue University - EAS Department Civil 3273 ecalais@purdue.edu Need for a Reference Frame 1. ositions and velocities from geodetic measurements: Are not direct observations, but estimated quantities
E. Calais urdue University - EAS Department Civil 3273 ecalais@purdue.edu Need for a Reference Frame 1. ositions and velocities from geodetic measurements: Are not direct observations, but estimated quantities
Actual Continuous Kinematic Model (ACKIM) of the Earth s Crust based on ITRF2014
 Actual Continuous Kinematic Model (ACKIM) of the Earth s Crust based on ITRF2014 Hermann Drewes Technische Universität München Joint Scientific Assembly of the International Association of Geodesy and
Actual Continuous Kinematic Model (ACKIM) of the Earth s Crust based on ITRF2014 Hermann Drewes Technische Universität München Joint Scientific Assembly of the International Association of Geodesy and
Distribution and magnetic features of igneous rocks in the Gaize-Nima area of Tibet plateau based on magnetic data
 Bulgarian Chemical Communications, Special Edition H, (pp. 14 18) 2017 14 Distribution and magnetic features of igneous rocks in the Gaize-Nima area of Tibet plateau based on magnetic data C.G. Zhang 1
Bulgarian Chemical Communications, Special Edition H, (pp. 14 18) 2017 14 Distribution and magnetic features of igneous rocks in the Gaize-Nima area of Tibet plateau based on magnetic data C.G. Zhang 1
Tomographic imaging of P wave velocity structure beneath the region around Beijing
 403 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0403-9 Tomographic imaging of P wave velocity structure beneath the region around Beijing Zhifeng Ding Xiaofeng Zhou Yan Wu Guiyin Li and Hong Zhang Institute of Geophysics,
403 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0403-9 Tomographic imaging of P wave velocity structure beneath the region around Beijing Zhifeng Ding Xiaofeng Zhou Yan Wu Guiyin Li and Hong Zhang Institute of Geophysics,
New Progress of SinoProbe:
 New Progress of SinoProbe: Deep Exploration in China, 2008-2012 Shuwen DONG, Tingdong LI, et al. Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences Beijing 100037 China Background of Deep Exploration in World USA
New Progress of SinoProbe: Deep Exploration in China, 2008-2012 Shuwen DONG, Tingdong LI, et al. Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences Beijing 100037 China Background of Deep Exploration in World USA
The effect and correction of non-tectonic crustal deformation for continuous GPS position time series
 The effect and correction of non-tectonic crustal deformation for continuous GPS position time series WANG Min 1,2) SHEN Zheng-Kang 1,3) DONG Da-Nan 4) 1) State Key Laboratory of Earthquake Dynamics, Institute
The effect and correction of non-tectonic crustal deformation for continuous GPS position time series WANG Min 1,2) SHEN Zheng-Kang 1,3) DONG Da-Nan 4) 1) State Key Laboratory of Earthquake Dynamics, Institute
Background information
 First Announcement and Call for Abstract Submission 2 nd International Workshop on Multi-observations and Interpretations of Tibet, Xinjiang and Siberia (TibXS) (IWGS) 2 nd TibXS Workshop, July 22-26,
First Announcement and Call for Abstract Submission 2 nd International Workshop on Multi-observations and Interpretations of Tibet, Xinjiang and Siberia (TibXS) (IWGS) 2 nd TibXS Workshop, July 22-26,
Advantages of GNSS in Monitoring Crustal Deformation for Detection of Precursors to Strong Earthquakes
 Positioning, 2013, 4, 11-19 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/pos.2013.41003 Published Online February 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/pos) 11 Advantages of GNSS in Monitoring Crustal Deformation for Detection
Positioning, 2013, 4, 11-19 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/pos.2013.41003 Published Online February 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/pos) 11 Advantages of GNSS in Monitoring Crustal Deformation for Detection
Lecture 2 Measurement Systems. GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy
 Lecture 2 Measurement Systems GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy VLBI and SLR VLBI Very Long Baseline Interferometry SLR Satellite Laser Ranging Very Long Baseline Interferometry VLBI Geometric Delay δg S Baseline
Lecture 2 Measurement Systems GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy VLBI and SLR VLBI Very Long Baseline Interferometry SLR Satellite Laser Ranging Very Long Baseline Interferometry VLBI Geometric Delay δg S Baseline
A BROADBAND SEISMIC EXPERIMENT IN YUNNAN, SOUTHWEST CHINA. Sponsored by Defense Threat Reduction Agency. Contract No.
 A BROADBAND SEISMIC EXPERIMENT IN YUNNAN, SOUTHWEST CHINA Wenjie Jiao, 1 Winston Chan, 1 and Chunyong Wang 2 Multimax Inc., 1 Institute of Geophysics, China Seismological Bureau 2 Sponsored by Defense
A BROADBAND SEISMIC EXPERIMENT IN YUNNAN, SOUTHWEST CHINA Wenjie Jiao, 1 Winston Chan, 1 and Chunyong Wang 2 Multimax Inc., 1 Institute of Geophysics, China Seismological Bureau 2 Sponsored by Defense
Case Study of Japan: Crustal deformation monitoring with GNSS and InSAR
 Technical Seminar Reference Frame in Practice, Case Study of Japan: Crustal deformation monitoring with GNSS and InSAR Basara Miyahara miyahara-b96ip@milt.go.jp Geospatial Information Authority of Japan
Technical Seminar Reference Frame in Practice, Case Study of Japan: Crustal deformation monitoring with GNSS and InSAR Basara Miyahara miyahara-b96ip@milt.go.jp Geospatial Information Authority of Japan
Humidity 3D field comparisons between GNSS tomography, IASI satellite observations and ALARO model. Belgian Institute for Space Aeronomy BIRA 3
 Oral Presentation, EGU0-85 Humidity D field comparisons between, H. Brenot, C. Champollion, A. Deckmyn, R. van Malderen, N. Kumps, R. Warnant, E. Goudenhoofdt, L. Delobbe and M. De Mazière contact: Belgian
Oral Presentation, EGU0-85 Humidity D field comparisons between, H. Brenot, C. Champollion, A. Deckmyn, R. van Malderen, N. Kumps, R. Warnant, E. Goudenhoofdt, L. Delobbe and M. De Mazière contact: Belgian
S-wave velocity structure beneath Changbaishan volcano inferred from receiver function
 Earthq Sci (2009)22: 409 416 409 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0409-3 S-wave velocity structure beneath Changbaishan volcano inferred from receiver function Jianping Wu Yuehong Ming Lihua Fang Weilai Wang Institute
Earthq Sci (2009)22: 409 416 409 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0409-3 S-wave velocity structure beneath Changbaishan volcano inferred from receiver function Jianping Wu Yuehong Ming Lihua Fang Weilai Wang Institute
v Hypothesis: The uplift of the Tibetan Plateau is an active driver for global cooling of the Cenozoic period By Roslyn Gober 11 February 2015
 Objective Uplift of Tibetan Plateau as Active Driver for Cenozoic Climate Change v Use Paleoarchives from the Tibetan Plateau to support the uplift weathering hypothesis for global cooling over the last
Objective Uplift of Tibetan Plateau as Active Driver for Cenozoic Climate Change v Use Paleoarchives from the Tibetan Plateau to support the uplift weathering hypothesis for global cooling over the last
A study on crustal structures of Changbaishan2Jingpohu volcanic area using receiver functions
 48 2 2005 3 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 48, No. 2 Mar., 2005,,..,2005,48 (2) :352 358 Duan Y H, Zhang X K, Liu Z,et al. A study on crustal structures of Changbaishan2Jingpohu volcanic area using
48 2 2005 3 CHINESE JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICS Vol. 48, No. 2 Mar., 2005,,..,2005,48 (2) :352 358 Duan Y H, Zhang X K, Liu Z,et al. A study on crustal structures of Changbaishan2Jingpohu volcanic area using
New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts
 Fourth Swarm science meeting and geodetic missions workshop ESA, 20-24 March 2017, Banff, Alberta, Canada New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts Richard
Fourth Swarm science meeting and geodetic missions workshop ESA, 20-24 March 2017, Banff, Alberta, Canada New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts Richard
CORS Network and Datum Harmonisation in the Asia-Pacific Region. Richard Stanaway and Craig Roberts
 CORS Network and Datum Harmonisation in the Asia-Pacific Region Richard Stanaway and Craig Roberts School of Surveying and Spatial Information Systems University of New South Wales CORS Networks in the
CORS Network and Datum Harmonisation in the Asia-Pacific Region Richard Stanaway and Craig Roberts School of Surveying and Spatial Information Systems University of New South Wales CORS Networks in the
From Earthquakes to Mountains: the Earth s Crust in Motion
 Dean s Freshman Honor Seminar (SCI 110) Eric Calais Associate Professor of Geophysics Purdue University Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences ecalais@purdue.edu http:/www.eas.purdue.edu/~calais
Dean s Freshman Honor Seminar (SCI 110) Eric Calais Associate Professor of Geophysics Purdue University Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences ecalais@purdue.edu http:/www.eas.purdue.edu/~calais
Modeling of co- and post-seismic surface deformation and gravity changes of M W 6.9 Yushu, Qinghai, earthquake
 Earthq Sci (2011)24: 177 183 177 doi:10.1007/s11589-010-0782-y Modeling of co- and post-seismic surface deformation and gravity changes of M W 6.9 Yushu, Qinghai, earthquake Chengli Liu 1,2 Bin Shan 1,2
Earthq Sci (2011)24: 177 183 177 doi:10.1007/s11589-010-0782-y Modeling of co- and post-seismic surface deformation and gravity changes of M W 6.9 Yushu, Qinghai, earthquake Chengli Liu 1,2 Bin Shan 1,2
Variations of snow cover in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers in China between 1960 and 1999
 420 Journal of Glaciology, Vol. 53, No. 182, 2007 Variations of snow cover in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers in China between 1960 and 1999 YANG Jianping, DING Yongjian, LIU Shiyin,
420 Journal of Glaciology, Vol. 53, No. 182, 2007 Variations of snow cover in the source regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers in China between 1960 and 1999 YANG Jianping, DING Yongjian, LIU Shiyin,
Connecting terrestrial to celestial reference frames
 Russian Academy of Sciences Central Astronomical Observatory at Pulkovo IAU XXVIII General Assembly, Joint Discussion 7, Beijing, China, August 28, 2012 Connecting terrestrial to celestial reference frames
Russian Academy of Sciences Central Astronomical Observatory at Pulkovo IAU XXVIII General Assembly, Joint Discussion 7, Beijing, China, August 28, 2012 Connecting terrestrial to celestial reference frames
Case study of Japan: Reference Frames in Practice
 Case study of Japan: Reference Frames in Practice Basara Miyahara and Koji Matsuo Sponsors: 1 Outline Introduction - Geodetic reference frame of Japan - GEONET : continuous GNSS observation system Geometric
Case study of Japan: Reference Frames in Practice Basara Miyahara and Koji Matsuo Sponsors: 1 Outline Introduction - Geodetic reference frame of Japan - GEONET : continuous GNSS observation system Geometric
Indian mantle corner flow at southern Tibet revealed by shear wave splitting measurements
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L02308, doi:10.1029/2007gl031753, 2008 Indian mantle corner flow at southern Tibet revealed by shear wave splitting measurements Yuanyuan
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L02308, doi:10.1029/2007gl031753, 2008 Indian mantle corner flow at southern Tibet revealed by shear wave splitting measurements Yuanyuan
Strain accumulation studies between Antarctica and India through geodetic tying of two continents from continuous GPS measurements
 Indian Journal of Marine Sciences Vol. 37(4), December 2008, pp. 404-411 Strain accumulation studies between Antarctica and India through geodetic tying of two continents from continuous GPS measurements
Indian Journal of Marine Sciences Vol. 37(4), December 2008, pp. 404-411 Strain accumulation studies between Antarctica and India through geodetic tying of two continents from continuous GPS measurements
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES
 USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
Mount Everest and the Gobi Desert
 Mount Everest and the Gobi Desert 1 Mount Everest is part of the mountain chain known as the Himalaya. Adventurers from all over the world come to try to climb it. Mount Everest is the highest mountain
Mount Everest and the Gobi Desert 1 Mount Everest is part of the mountain chain known as the Himalaya. Adventurers from all over the world come to try to climb it. Mount Everest is the highest mountain
A comparative study of the bottomside profile parameters over Wuhan with IRI-2001 for
 Earth Planets Space, 58, 601 605, 2006 A comparative study of the bottomside profile parameters over Wuhan with IRI-2001 for 1999 2004 Huajiao Chen 1,2,3, Libo Liu 1, Weixing Wan 1, Baiqi Ning 1, and Jiuhou
Earth Planets Space, 58, 601 605, 2006 A comparative study of the bottomside profile parameters over Wuhan with IRI-2001 for 1999 2004 Huajiao Chen 1,2,3, Libo Liu 1, Weixing Wan 1, Baiqi Ning 1, and Jiuhou
Modernization of National Geodetic Datum in China *
 UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.102/IP.16 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Nineteenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 29 October 1 November 2012 Item 6(b) of the provisional
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.102/IP.16 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Nineteenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 29 October 1 November 2012 Item 6(b) of the provisional
GPS 10, GPS , GPS. (J PL ) Zumbeger. mm, cm ; ( Global RT K) [3 ]
![GPS 10, GPS , GPS. (J PL ) Zumbeger. mm, cm ; ( Global RT K) [3 ] GPS 10, GPS , GPS. (J PL ) Zumbeger. mm, cm ; ( Global RT K) [3 ]](/thumbs/92/110253734.jpg) 27 3 Vol. 27 No. 3 2002 6 Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University J une 2002 :1000-050X(2002) 03-0234-07 :A GPS 1 2 (1,,430072) (2 GPS,129,430079) : ; IGS IGS,,, 15min, X Y Z 20cm : GPS ;;
27 3 Vol. 27 No. 3 2002 6 Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University J une 2002 :1000-050X(2002) 03-0234-07 :A GPS 1 2 (1,,430072) (2 GPS,129,430079) : ; IGS IGS,,, 15min, X Y Z 20cm : GPS ;;
FORMAT FOR TECHNICAL PAPERS
 TOWARDS A MODERNIZED GEODETIC DATUM FOR NEPAL: OPTIONS FOR DEVELOPING AN ACCURATE TERRESTRIAL REFERENCE FRAME FOLLOWING THE APRIL 25, 2015 MW7.8 GORKHA EARTHQUAKE Chris PEARSON 1, Niraj MANANDHA 2 ABSTRACT
TOWARDS A MODERNIZED GEODETIC DATUM FOR NEPAL: OPTIONS FOR DEVELOPING AN ACCURATE TERRESTRIAL REFERENCE FRAME FOLLOWING THE APRIL 25, 2015 MW7.8 GORKHA EARTHQUAKE Chris PEARSON 1, Niraj MANANDHA 2 ABSTRACT
Application of Atmosphere Precipitation Resources Distribution Remote Sensed by Ground-based GPS in the West of Taiwan Strait.
 4th International Conference on Mechatronics, Materials, Chemistry and Computer Engineering (ICMMCCE 2015) Application of Atmosphere Precipitation Resources Distribution Remote Sensed by Ground-based GPS
4th International Conference on Mechatronics, Materials, Chemistry and Computer Engineering (ICMMCCE 2015) Application of Atmosphere Precipitation Resources Distribution Remote Sensed by Ground-based GPS
Geodetically observed surface displacements of the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, earthquake
 Earth Planets Space, 52, 403 413, 2000 Geodetically observed surface displacements of the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, earthquake Ming Yang 1, Ruey-Juin Rau 2, Jyh-Yih Yu 1, and Ting-To Yu 2 1 Department of Surveying
Earth Planets Space, 52, 403 413, 2000 Geodetically observed surface displacements of the 1999 Chi-Chi, Taiwan, earthquake Ming Yang 1, Ruey-Juin Rau 2, Jyh-Yih Yu 1, and Ting-To Yu 2 1 Department of Surveying
V r : A new index to represent the variation rate of geomagnetic activity
 Earthq Sci (2010)23: 343 348 343 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0731-9 V r : A new index to represent the variation rate of geomagnetic activity Dongmei Yang 1, Yufei He 1 Chuanhua Chen 2 and Jiadong Qian 3 1
Earthq Sci (2010)23: 343 348 343 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-010-0731-9 V r : A new index to represent the variation rate of geomagnetic activity Dongmei Yang 1, Yufei He 1 Chuanhua Chen 2 and Jiadong Qian 3 1
Mantle anisotropy across the southwestern boundary of the Ordos block, North China
 Earthq Sci (200)23: 549 553 549 Doi: 0.007/s589-00-0754-2 Mantle anisotropy across the southwestern boundary of the Ordos block, North China, Yongcai Tang Yongshun John Chen Yuanyuan V. Fu 2 Haiyang Wang
Earthq Sci (200)23: 549 553 549 Doi: 0.007/s589-00-0754-2 Mantle anisotropy across the southwestern boundary of the Ordos block, North China, Yongcai Tang Yongshun John Chen Yuanyuan V. Fu 2 Haiyang Wang
Cloud type climatology over the Tibetan Plateau: A comparison of ISCCP and MODIS/TERRA measurements with surface observations
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L17716, doi: 10.1029/2006GL026890, 2006 Cloud type climatology over the Tibetan Plateau: A comparison of ISCCP and MODIS/TERRA measurements with surface observations
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L17716, doi: 10.1029/2006GL026890, 2006 Cloud type climatology over the Tibetan Plateau: A comparison of ISCCP and MODIS/TERRA measurements with surface observations
TECTONIC MOVEMENTS MONITORING OF SUDETIC MARGINAL FAULT USING SHORT GPS BASELINES
 POSTER PAPER SESSION TECTONIC MOVEMENTS MONITORING OF SUDETIC MARGINAL FAULT USING SHORT GPS ASELINES ernard Kontny Department of Geodesy and Photogrammetry Agricultural University of Wroclaw, Poland Abstract
POSTER PAPER SESSION TECTONIC MOVEMENTS MONITORING OF SUDETIC MARGINAL FAULT USING SHORT GPS ASELINES ernard Kontny Department of Geodesy and Photogrammetry Agricultural University of Wroclaw, Poland Abstract
The Victorian Seismic Zone 2011 GNSS Campaign Data Analysis
 G E O S C I E N C E A U S T R A L I A The Victorian Seismic Zone 2011 GNSS Campaign Data Analysis G. Hu Record 2012/38 GeoCat # 74005 APPLYING GEOSCIENCE TO AUSTRALIA S MOST IMPORTANT CHALLENGES The Victorian
G E O S C I E N C E A U S T R A L I A The Victorian Seismic Zone 2011 GNSS Campaign Data Analysis G. Hu Record 2012/38 GeoCat # 74005 APPLYING GEOSCIENCE TO AUSTRALIA S MOST IMPORTANT CHALLENGES The Victorian
Frequent epoch reference frames instead of instant station positions and constant velocities
 Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut Technische Universität München (DGFI-TUM) Frequent epoch reference frames instead of instant station positions and constant velocities Hermann Drewes Deutsches
Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut Technische Universität München (DGFI-TUM) Frequent epoch reference frames instead of instant station positions and constant velocities Hermann Drewes Deutsches
Journal of Remote Sensing & GIS ISSN:
 Journal of Remote Sensing & GIS Journal of Remote Sensing & GIS Mhmod et al., J Remote Sensing & GIS 2015, 4:3 DOI: 10.4172/2469-4134.1000146 Research Article Open Access Monitor and Study Horizontal and
Journal of Remote Sensing & GIS Journal of Remote Sensing & GIS Mhmod et al., J Remote Sensing & GIS 2015, 4:3 DOI: 10.4172/2469-4134.1000146 Research Article Open Access Monitor and Study Horizontal and
Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry
 Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
Deformation monitoring and analysis using Victorian regional CORS data
 Journal of Global Positioning Systems (2005) Vol. 4, No. 1-2: 129-138 Deformation monitoring and analysis using Victorian regional CORS data Kefei Zhang 1, Youjian Hu 1,2, Gangjun Liu 1, Falin Wu 1 and
Journal of Global Positioning Systems (2005) Vol. 4, No. 1-2: 129-138 Deformation monitoring and analysis using Victorian regional CORS data Kefei Zhang 1, Youjian Hu 1,2, Gangjun Liu 1, Falin Wu 1 and
Measuring Water Resources Unit 3: Groundwater withdrawal and fluctuations in the height of Earth's surface student exercise
 Measuring Water Resources Unit 3: Groundwater withdrawal and fluctuations in the height of Earth's surface student exercise Eric Small (University of Colorado) and Bruce Douglas (Indiana University) Complete
Measuring Water Resources Unit 3: Groundwater withdrawal and fluctuations in the height of Earth's surface student exercise Eric Small (University of Colorado) and Bruce Douglas (Indiana University) Complete
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37, L02304, doi: /2009gl041835, 2010
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl041835, 2010 Seismic structure of the Longmen Shan region from S wave tomography and its relationship with the Wenchuan
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2009gl041835, 2010 Seismic structure of the Longmen Shan region from S wave tomography and its relationship with the Wenchuan
Chapter 2 Study on the Earth s Volume Change by Using Space Observed Technology
 Chapter 2 Study on the Earth s Volume Change by Using Space Observed Technology Xinhui Zhu, Fuping Sun and Ren Wang Abstract Although plate tectonics already being the studying basis and mainstream of
Chapter 2 Study on the Earth s Volume Change by Using Space Observed Technology Xinhui Zhu, Fuping Sun and Ren Wang Abstract Although plate tectonics already being the studying basis and mainstream of
HIMALAYAN AIRBORNE GRAVITY AND GEOID OF NEPAL
 Mt. Everest HIMALAYAN AIRBORNE GRAVITY AND GEOID OF NEPAL -Niraj Manandhar Head, Geodetic Survey Branch Survey Department, Geodetic Survey Branch Project Background Air Borne Gravity Survey Project was
Mt. Everest HIMALAYAN AIRBORNE GRAVITY AND GEOID OF NEPAL -Niraj Manandhar Head, Geodetic Survey Branch Survey Department, Geodetic Survey Branch Project Background Air Borne Gravity Survey Project was
Electronic supplement for Forearc motion and deformation between El Salvador and Nicaragua: GPS, seismic, structural, and paleomagnetic observations
 DR2011053 Electronic supplement for Forearc motion and deformation between El Salvador and Nicaragua: GPS, seismic, structural, and paleomagnetic observations by D. Alvarado et al., Lithosphere, April,
DR2011053 Electronic supplement for Forearc motion and deformation between El Salvador and Nicaragua: GPS, seismic, structural, and paleomagnetic observations by D. Alvarado et al., Lithosphere, April,
A unified analysis of crustal motion in Southern California, : The SCEC crustal motion map
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008549, 2011 A unified analysis of crustal motion in Southern California, 1970 2004: The SCEC crustal motion map Z. K. Shen, 1,2 R. W. King,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011jb008549, 2011 A unified analysis of crustal motion in Southern California, 1970 2004: The SCEC crustal motion map Z. K. Shen, 1,2 R. W. King,
SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences
 SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences RESEARCH PAPER September 2011 Vol.54 No.9: 1386 1393 doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4177-2 Crustal P-wave velocity structure of the Longmenshan region and its tectonic implications
SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences RESEARCH PAPER September 2011 Vol.54 No.9: 1386 1393 doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4177-2 Crustal P-wave velocity structure of the Longmenshan region and its tectonic implications
The PaTrop Experiment
 Improved estimation of the tropospheric delay component in GNSS and InSAR measurements in the Western Corinth Gulf (Greece), by the use of a highresolution meteorological model: The PaTrop Experiment N.
Improved estimation of the tropospheric delay component in GNSS and InSAR measurements in the Western Corinth Gulf (Greece), by the use of a highresolution meteorological model: The PaTrop Experiment N.
Trends of Tropospheric Ozone over China Based on Satellite Data ( )
 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 2(1): 43 48, 2011 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2011.00043 ARTICLE Trends of Tropospheric Ozone over China Based on Satellite Data (1979 2005) Xiaobin
ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 2(1): 43 48, 2011 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2011.00043 ARTICLE Trends of Tropospheric Ozone over China Based on Satellite Data (1979 2005) Xiaobin
Effects of fault movement and material properties on deformation and stress fields of Tibetan Plateau
 Earthq Sci (2011)24: 185 197 185 doi:10.1007/s11589-011-0783-5 Effects of fault movement and material properties on deformation and stress fields of Tibetan Plateau Yong Zheng 1, Xiong Xiong 1 Yong Chen
Earthq Sci (2011)24: 185 197 185 doi:10.1007/s11589-011-0783-5 Effects of fault movement and material properties on deformation and stress fields of Tibetan Plateau Yong Zheng 1, Xiong Xiong 1 Yong Chen
Challenges and perspectives for CRF and TRF determination
 Challenges and perspectives for CRF and TRF determination J. Böhm, Z. Malkin, S. Lambert, C. Ma with contributions by H. Spicakova, L. Plank, and H. Schuh Consistency TRF EOP CRF ITRF2008 from VLBI/GNSS/SLR/DORIS
Challenges and perspectives for CRF and TRF determination J. Böhm, Z. Malkin, S. Lambert, C. Ma with contributions by H. Spicakova, L. Plank, and H. Schuh Consistency TRF EOP CRF ITRF2008 from VLBI/GNSS/SLR/DORIS
Evolution of Continents Chapter 20
 Evolution of Continents Chapter 20 Does not contain complete lecture notes. Mountain belts Orogenesis the processes that collectively produce a mountain belt Includes folding, thrust faulting, metamorphism,
Evolution of Continents Chapter 20 Does not contain complete lecture notes. Mountain belts Orogenesis the processes that collectively produce a mountain belt Includes folding, thrust faulting, metamorphism,
The International Terrestrial Reference Frame. What is a Terrestrial Reference Frame?
 The International Terrestrial Reference Frame As early as the 15th century, Swedes noticed that rocks in their harbors were slowly rising out of the sea [Ekman, 1991]. These local observations were not
The International Terrestrial Reference Frame As early as the 15th century, Swedes noticed that rocks in their harbors were slowly rising out of the sea [Ekman, 1991]. These local observations were not
Prepared by Dongchen E Chinese Antarctic Center of Surveying and Mapping Chinese representative to SCAR WG-GGI
 SCAR XXVI Tokyo,Japan July, 2000 Report of Current Activities of China for 1998-2000 Prepared by Dongchen E Chinese Antarctic Center of Surveying and Mapping Chinese representative to SCAR WG-GGI Chinese
SCAR XXVI Tokyo,Japan July, 2000 Report of Current Activities of China for 1998-2000 Prepared by Dongchen E Chinese Antarctic Center of Surveying and Mapping Chinese representative to SCAR WG-GGI Chinese
Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry
 VieVS User-Workshop 2017 Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry Johannes Böhm VLBI How does it work? VLBI a flowchart SINEX skd vex2 drudge drudge snp/prc snp/prc NGS Mark4 Mark4
VieVS User-Workshop 2017 Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry Johannes Böhm VLBI How does it work? VLBI a flowchart SINEX skd vex2 drudge drudge snp/prc snp/prc NGS Mark4 Mark4
A viscoelastic model for time-dependent simulating analysis of the Wenchuan earthquake fault Cheng Hua, Jin Cheng and Qi-fu Chen
 Journal of Math-for-Industry, Vol. 4 (2012A-10), pp. 79 83 A viscoelastic model for time-dependent simulating analysis of the Wenchuan earthquake fault Cheng Hua, Jin Cheng and Qi-fu Chen Received on February
Journal of Math-for-Industry, Vol. 4 (2012A-10), pp. 79 83 A viscoelastic model for time-dependent simulating analysis of the Wenchuan earthquake fault Cheng Hua, Jin Cheng and Qi-fu Chen Received on February
GEORED Project: GNSS Geodesy Network for Geodynamics Research in Colombia, South America. Héctor Mora-Páez
 GEORED Project: GNSS Geodesy Network for Geodynamics Research in Colombia, South America. Héctor Mora-Páez Colombian Geological Survey UNAVCO SCIENCE MEETING Feb 27 March 1, 2012 Boulder, CO, TECTONIC
GEORED Project: GNSS Geodesy Network for Geodynamics Research in Colombia, South America. Héctor Mora-Páez Colombian Geological Survey UNAVCO SCIENCE MEETING Feb 27 March 1, 2012 Boulder, CO, TECTONIC
Development of a New Japanese Geoid Model, GSIGEO2000
 53 Hiroyuki NAKAGAWA, Kojin WADA, Tadayuki KIKKAWA, Hisao SHIMO, Hisashi ANDOU, Yuki KUROISHI, Yuki HATANAKA, Hiromi SHIGEMATSU, Kazuyuki TANAKA, Yoichi FUKUDA 1) Abstract GSI developed a new Japanese
53 Hiroyuki NAKAGAWA, Kojin WADA, Tadayuki KIKKAWA, Hisao SHIMO, Hisashi ANDOU, Yuki KUROISHI, Yuki HATANAKA, Hiromi SHIGEMATSU, Kazuyuki TANAKA, Yoichi FUKUDA 1) Abstract GSI developed a new Japanese
Impact of A Priori Gradients on VLBI-Derived Terrestrial Reference Frames
 Impact of A Priori Gradients on VLBI-Derived Terrestrial Reference Frames J. Böhm, H. Spicakova, L. Urquhart, P. Steigenberger, H. Schuh Abstract We compare the influence of two different a priori gradient
Impact of A Priori Gradients on VLBI-Derived Terrestrial Reference Frames J. Böhm, H. Spicakova, L. Urquhart, P. Steigenberger, H. Schuh Abstract We compare the influence of two different a priori gradient
National Seismological Centre: An Overview, Prospects and Challenges
 National Seismological Centre: An Overview, Prospects and Challenges By Soma Nath Sapkota Department of Mines and Geology National Seismological Centre Nepal India Himalaya Tibetan Plateau India continental
National Seismological Centre: An Overview, Prospects and Challenges By Soma Nath Sapkota Department of Mines and Geology National Seismological Centre Nepal India Himalaya Tibetan Plateau India continental
This presentation covers the following areas
 Geodetic Datums and Coordinate Systems for Surveying and Mapping in Hong Kong FIG Working Week 2012 Rome, Italy 6-10 May Simon KWOK Hong Kong, China 1 This presentation covers the following areas Explains
Geodetic Datums and Coordinate Systems for Surveying and Mapping in Hong Kong FIG Working Week 2012 Rome, Italy 6-10 May Simon KWOK Hong Kong, China 1 This presentation covers the following areas Explains
Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points)
 Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points) Here you will work with GPS Time Series data to explore plate motion and deformation in California. This lab modifies an exercise found here: http://www.unavco.org:8080/cws/pbonucleus/draftresources/sanandreas/
Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points) Here you will work with GPS Time Series data to explore plate motion and deformation in California. This lab modifies an exercise found here: http://www.unavco.org:8080/cws/pbonucleus/draftresources/sanandreas/
NTUA, Faculty of Rural and Surveying Engineering, Dionysos Satellite Observatory, Higher Geodesy Laboratory NOA, Institute of Geodynamics 1
 NOA, Institute of Geodynamics 1 Crustal Deformation from GPS measurements at the Ionian Sea : Preliminary Results Anastasiou 1 D., Paradissis 1 D., Ganas 2 A., Marinou 1 A., Papazissi 1 K., Drakatos 2
NOA, Institute of Geodynamics 1 Crustal Deformation from GPS measurements at the Ionian Sea : Preliminary Results Anastasiou 1 D., Paradissis 1 D., Ganas 2 A., Marinou 1 A., Papazissi 1 K., Drakatos 2
Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 91 (2012), REALIZATION OF ETRF2000 AS A NEW TERRESTRIAL REFERENCE FRAME IN REPUBLIC OF SERBIA
 Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 91 (2012), 199-206 Contributed paper REALIZATION OF ETRF2000 AS A NEW TERRESTRIAL REFERENCE FRAME IN REPUBLIC OF SERBIA D. BLAGOJEVIĆ and V. VASILIĆ Faculty of Civil Engineering,
Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 91 (2012), 199-206 Contributed paper REALIZATION OF ETRF2000 AS A NEW TERRESTRIAL REFERENCE FRAME IN REPUBLIC OF SERBIA D. BLAGOJEVIĆ and V. VASILIĆ Faculty of Civil Engineering,
Lower Crustal Flow and Its Relation to the Surface Deformation and Stress Distribution in Western Sichuan Region, China
 Journal of Earth Science, Vol. 5, No. 4, p. 630 637, August 014 ISSN 1674-487X Printed in China DOI: 10.1007/s1583-014-0467-x Lower Crustal Flow and Its Relation to the Surface Deformation and Stress Distribution
Journal of Earth Science, Vol. 5, No. 4, p. 630 637, August 014 ISSN 1674-487X Printed in China DOI: 10.1007/s1583-014-0467-x Lower Crustal Flow and Its Relation to the Surface Deformation and Stress Distribution
Uncertainties in Quantitatively Estimating the Atmospheric Heat Source over the Tibetan Plateau
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2014, VOL. 7, NO. 1, 28 33 Uncertainties in Quantitatively Estimating the Atmospheric Heat Source over the Tibetan Plateau DUAN An-Min 1, 3, WANG Mei-Rong 1, 2,
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2014, VOL. 7, NO. 1, 28 33 Uncertainties in Quantitatively Estimating the Atmospheric Heat Source over the Tibetan Plateau DUAN An-Min 1, 3, WANG Mei-Rong 1, 2,
REGIONAL REFERENCE FRAMES: THE IAG PERSPECTIVE
 REGIONAL REFERENCE FRAMES: THE IAG PERSPECTIVE João Agria Torres SPUIAGG IAG Sub-commission 1.3: Regional Reference Frames jatorres@iol.pt 1. About the IAG CONTENT 2. Objectives and organization of SC
REGIONAL REFERENCE FRAMES: THE IAG PERSPECTIVE João Agria Torres SPUIAGG IAG Sub-commission 1.3: Regional Reference Frames jatorres@iol.pt 1. About the IAG CONTENT 2. Objectives and organization of SC
Three-dimensional distribution of water vapor estimated from tropospheric delay of GPS data in a mesoscale precipitation system of the Baiu front
 Earth Planets Space, 52, 927 933, 2000 Three-dimensional distribution of water vapor estimated from tropospheric delay of GPS data in a mesoscale precipitation system of the Baiu front Hiromu Seko 1, Seiichi
Earth Planets Space, 52, 927 933, 2000 Three-dimensional distribution of water vapor estimated from tropospheric delay of GPS data in a mesoscale precipitation system of the Baiu front Hiromu Seko 1, Seiichi
Preliminary Microgravity Measurement Of Paka Geothermal Prospect
 Preliminary Microgravity Measurement Of Paka Geothermal Prospect Presented by: Levi Shako and Calistus Ndongoli Date: 4/November/2016 Venue: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia Introduction Microgravity is a geophysical
Preliminary Microgravity Measurement Of Paka Geothermal Prospect Presented by: Levi Shako and Calistus Ndongoli Date: 4/November/2016 Venue: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia Introduction Microgravity is a geophysical
Slip Rates Estimate of Western North Anatolian Fault System in Turkey
 Slip Rates Estimate of Western North Anatolian Fault System in Turkey Haluk OZENER, Asli DOGRU, Bahadir AKTUG, Semih ERGINTAV, Bulent TURGUT, Onur YILMAZ, Kerem HALICIOGLU, Onur GURKAN, Turkey Keywords:
Slip Rates Estimate of Western North Anatolian Fault System in Turkey Haluk OZENER, Asli DOGRU, Bahadir AKTUG, Semih ERGINTAV, Bulent TURGUT, Onur YILMAZ, Kerem HALICIOGLU, Onur GURKAN, Turkey Keywords:
Towards an improved ILRS TRF contribution
 Towards an improved ILRS TRF contribution Erricos C. Pavlis ILRS Analysis Coordinator JCET/ & NASA Goddard IERS Workshop on Conventions 2007 20-21 Sept. 2007, Sèvres, France Overview The ILRS Network Geometry
Towards an improved ILRS TRF contribution Erricos C. Pavlis ILRS Analysis Coordinator JCET/ & NASA Goddard IERS Workshop on Conventions 2007 20-21 Sept. 2007, Sèvres, France Overview The ILRS Network Geometry
Transient signal detection using GPS measurements: Transient inflation at Akutan volcano, Alaska, during early 2008
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl046904, 2011 Transient signal detection using GPS measurements: Transient inflation at Akutan volcano, Alaska, during early 2008 Kang Hyeun Ji
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2011gl046904, 2011 Transient signal detection using GPS measurements: Transient inflation at Akutan volcano, Alaska, during early 2008 Kang Hyeun Ji
Ground motion attenuation relations of small and moderate earthquakes in Sichuan region
 Earthq Sci (2009)22: 277 282 277 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0277-x Ground motion attenuation relations of small and moderate earthquakes in Sichuan region Lanchi Kang 1, and Xing Jin 1,2 1 Fuzhou University,
Earthq Sci (2009)22: 277 282 277 Doi: 10.1007/s11589-009-0277-x Ground motion attenuation relations of small and moderate earthquakes in Sichuan region Lanchi Kang 1, and Xing Jin 1,2 1 Fuzhou University,
Rapid Determination of Earthquake Magnitude using GPS for Tsunami Warning Systems: An Opportunity for IGS to Make a Difference
 Rapid Determination of Earthquake Magnitude using GPS for Tsunami Warning Systems: An Opportunity for IGS to Make a Difference Geoffrey Blewitt, 1 Corné Kreemer, 1 William C. Hammond, 1 Hans-Peter Plag,
Rapid Determination of Earthquake Magnitude using GPS for Tsunami Warning Systems: An Opportunity for IGS to Make a Difference Geoffrey Blewitt, 1 Corné Kreemer, 1 William C. Hammond, 1 Hans-Peter Plag,
Title: Impact of Regional Reference Frame Definition on Geodynamic Interpretations
 Author manuscript, published in "Journal of Geodynamics 49, 3-4 (2010) 116" DOI : 10.1016/j.jog.2009.10.002 Title: Impact of Regional Reference Frame Definition on Geodynamic Interpretations Authors: J.
Author manuscript, published in "Journal of Geodynamics 49, 3-4 (2010) 116" DOI : 10.1016/j.jog.2009.10.002 Title: Impact of Regional Reference Frame Definition on Geodynamic Interpretations Authors: J.
Middle and upper crust shear-wave velocity structure of the Chinese mainland
 Vol.20 No.4 (359~369) ACTA SEISMOLOGICA SINICA July, 2007 Article ID: 1000-9116(2007)04-0359-11 doi: 10.1007/s11589-007-0359-6 Middle and upper crust shear-wave velocity structure of the Chinese mainland
Vol.20 No.4 (359~369) ACTA SEISMOLOGICA SINICA July, 2007 Article ID: 1000-9116(2007)04-0359-11 doi: 10.1007/s11589-007-0359-6 Middle and upper crust shear-wave velocity structure of the Chinese mainland
Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate
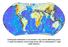 Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate interiors) Tectonic plates and their boundaries today -- continents
Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate interiors) Tectonic plates and their boundaries today -- continents
Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 11
 12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 11 Prof. Thomas Herring http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 Statistical approach to estimation Summary Look at estimation from statistical point
12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 11 Prof. Thomas Herring http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 Statistical approach to estimation Summary Look at estimation from statistical point
Long-term Crustal Deformation in and around Japan, Simulated by a 3-D Plate Subduction Model
 Long-term Crustal Deformation in and around Japan, Simulated by a 3-D Plate Subduction Model Chihiro Hashimoto (1) and Mitsuhiro Matsu ura (2) (1) Institute of Frontier Research for Earth Evolution, Japan
Long-term Crustal Deformation in and around Japan, Simulated by a 3-D Plate Subduction Model Chihiro Hashimoto (1) and Mitsuhiro Matsu ura (2) (1) Institute of Frontier Research for Earth Evolution, Japan
Lithospheric plates. Geology of the Batemans Bay region. Tectonic processes
 1 Lithospheric plates Enormous heat sources in the Earth s deep interior, acquired during the very early history of the planet billions of years ago continue to drive present-day geological at the surface.
1 Lithospheric plates Enormous heat sources in the Earth s deep interior, acquired during the very early history of the planet billions of years ago continue to drive present-day geological at the surface.
The Size and Duration of the Sumatra-Andaman Earthquake from Far-Field Static Offsets
 The Size and Duration of the Sumatra-Andaman Earthquake from Far-Field Static Offsets P. Banerjee, 1 F. F. Pollitz, 2 R. Bürgmann 3 * 1 Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, Dehra Dun, 248001, India. 2
The Size and Duration of the Sumatra-Andaman Earthquake from Far-Field Static Offsets P. Banerjee, 1 F. F. Pollitz, 2 R. Bürgmann 3 * 1 Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology, Dehra Dun, 248001, India. 2
From Global to National Geodetic Reference Frames: how are they connected and why are they needed?
 From Global to National Geodetic Reference Frames: how are they connected and why are they needed? Zuheir ALTAMIMI Institut National de l Information Géographique et Forestière, France Vice-President,
From Global to National Geodetic Reference Frames: how are they connected and why are they needed? Zuheir ALTAMIMI Institut National de l Information Géographique et Forestière, France Vice-President,
