Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots
|
|
|
- Dominick Logan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots Name: Date: Engage Think about the ocean and the seafloor. 1. Draw a sketch of what you picture when you think about the seafloor.
2 Explore 2. When your teacher projects the Pacific Ocean map, observe it carefully. Describe what you see. Read the following: The ocean is Earth s final frontier. According to NOAA, the ocean s average depth is 4.3 kilometers, which is 2.65 miles. This means that on average there are 4,300 meters, or over 14,000 feet, of water above the seafloor. This deep and flat area of the ocean is called the abyssal plain. Some areas, such as those along coastlines, are much shallower. There also are underwater mountains that stretch up from the abyssal plain towards the ocean surface. These features are called seamounts. The tops of seamounts can reach very close to the sea surface. Other areas are much deeper. The deepest spot in the ocean is the Mariana Trench, with a water depth of 6.8 miles or 10,924 meters, or over 35,566 feet. Many organisms live in the ocean s deepest areas and on its surface, but scientists are still learning about them all. The description of the ocean s depth and seafloor features is called bathymetry. 2 Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots
3 3. In the chart below, name, sketch, and describe each feature from the slides shared by your teacher. Feature Name Sketch Description Depth Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots 3
4 Use the Albatross Tracking and Bathymetry Maps provided by your teacher to answer the following questions. 4. What seafloor features can you observe on your map? 5. The dots on the map indicate noon locations of tracked Black-footed Albatross. Follow the directions for each step below, and record your findings in the data table. a. Count the total number of dots on each map. b. Count the number of dots located in shallow water when the birds were either over ocean shaded or shaded These shallow areas include continental shelf, continental slope, seamounts, and banks. c. Count the number of dots located in the deep water. These are areas with depths over 2000m, on the abyssal plain. 6. Find the percentage of the total time that the albatross spent in both shallow vs deep water. Record each percentage in the data table. d. To calculate the time spent in shallow water: e. To calculate the time spent in deep water: 4 Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots
5 Total Location Counts Number of Dots Percentage of Time Spent 100% (the total amount of time) Shallow Water Deep Water 7. Did the albatross spend more time in shallow water or deep water? Use your data to support your answer. 8. Write your data in the class data table on the board. 9. In the North Pacific, 87% of the ocean is deep and 13% is shallow. According to the class data, are these birds spending about 87% of their time in deep water? How do you know? Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots 5
6 10. Scientists compare habitat use with habitat availability to measure preference and identify hotspots. For instance, when you are at a restaurant, all the food on a menu is availability, and what people order is preference. On your maps, circle any hotspots for your albatross. Hotspots are areas where an albatross spent a lot of time (multiple days) or that an albatross repeatedly visited. A coldspot is an area they traveled through in route to another destination but did not stay long. 11. How can you explain your findings? Why do you think albatross select or prefer certain areas 12. Seamount habitats make up approximately 5% of the sea floor. Explore the Seamount track and count the number of locations over the Kammut Guyot feature. Does the albatross spend more than 5% of its time on top of this seamount? If so, why? 6 Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots
7 Explain Ocean Productivity and Food You are now very familiar with seafloor features, such as seamounts and continental shelves and slopes. You have also identified areas that albatross visit over and over again. Seafloor features can affect how much food is available in different areas. Albatross take advantage of this. Diatoms are one of the most common types of phytoplankton. Food provides both energy and nutrients. Imagine you are eating a cheeseburger with lettuce and tomato on a bun. In each bite, you are getting protein, carbohydrates, fat, vitamins (like Vitamins A and C) and minerals (like calcium and potassium). The food gives you the energy you need to do your life activities, like walking, breathing, and pumping your blood. The nutrients are used for life activities and to build body structures, including muscles and bones. Both energy and nutrients can be hard to get in the ocean. Almost all of the energy available to ocean organisms comes from the sun. Tiny plant-like organisms called phytoplankton capture the sun s energy. They use the sun s energy to create sugar in a process called photosynthesis. Phytoplankton make fats and oils. These compounds store the sugar, or chemical energy. Ocean grazers eat the sugars and fats, just like cows or grasshoppers eat plants on land. The grazers are then eaten by other predators, like squid and small fish, which receive the energy and nutrients. But, the sun only lights the top layer of the ocean (photic zone). Therefore, organisms living in deep water must travel to the surface to eat or get energy from the organisms living in the sunlit areas above them. Luckily for them, dead organisms and other waste (poop, skeletons) sink down. Deep ocean organisms eat these materials for their energy. Like you, phytoplankton need nutrients for their life activities, including photosynthesis. Land plants, which also do photosynthesis, get their nutrients from the soil. Soil is made up of pieces of rock and broken-down plant material. The remains of living organisms are broken down by decomposition. Decomposition makes the nutrients in the dead organisms available in the soil. In the ocean, when organisms die, they sink deeper into the water. Decomposition happens in the deep water. That means that the nutrients become available where there is no sunlight. Remember, though, that phytoplankton live near the ocean s surface because they need sunlight. Therefore, the nutrients from decomposition are not available to them. In certain areas of the ocean, however, deep water containing lots of nutrients is brought up to the surface, where phytoplankton live. This process is called upwelling. Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots 7
8 Credit: NOAA Upwelling can happen for several reasons. Some upwelling is caused by the makani, the wind. When wind consistently blows parallel to a coastline, it pushes water away from the coast. This movement pulls up nutrient-rich water from down below (about m deep) to replace the water at the surface. This type of upwelling occurs along the West Coast of the U.S. and many other coastlines. Water moves up the continental slope and onto the continental shelf. Upwelling can also happen in the open ocean, when deep-water currents encounter a seamount. Water flowing around a large obstacle, like an underwater mountain, will be pushed upwards and mix the nutrients into the surface waters. These are the two reasons why upwelling often happens near continental slopes and near seamounts. Upwelling gives lots of nutrients to phytoplankton. These tiny organisms photosynthesize and reproduce very quickly. Phytoplankton are eaten by other organisms, which also get eaten by larger predators. Energy and nutrients are passed to organisms higher up the food chain, including mōlī (Laysan albatross), koholā (whales), and honu (sea turtles). Lots of phytoplankton means that lots of energy and nutrients are available to the ecosystem. 13. How might areas of upwelling affect albatross? 8 Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots
9 14. Were the hotspots that you identified areas in which you would expect upwelling? How do you know? Elaborate Protecting Ocean Habitats United States National Marine Sanctuaries and Marine Monuments are often compared with National Parks because they protect underwater treasures. These treasures include marine animal habitats and important cultural areas like shipwrecks. National Marine Sanctuaries and Monuments are marine protected areas (MPAs). Creating MPAs is one of the ways in which we can care for, mālama, our ocean, kai. In our studies of albatross, we will focus on some of the sanctuaries and monuments in the Pacific Ocean. 15. Read the following passage, which introduces some of the Marine Protected Areas in the Pacific Ocean. In the data table, take notes about each. Marine Protected Areas Description of Location Important Facts / Ideas Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots 9
10 U.S. National Marine Sanctuaries (NMS) and Marine Monument near the West Coast and Hawai i Along the coast of Washington State is the Olympic Coast NMS, which protects lush kelp forests, deep water corals, and over 150 shipwrecks. The sanctuary covers over 3,000 square miles of ocean, and includes productive waters important for marine mammals such as sea otters and orcas, and seabirds including albatross and gulls. The Cordell Bank NMS is named for a rocky habitat, or bank, that sticks up above the sandy seafloor. This bank is home to cold-water corals, algae, fish, and many other organisms. Marine mammals and seabirds, such as whales, seals and sea lions, murres, albatross and shearwaters, frequent this sanctuary to feed themselves and their young. The sanctuary protects 529 square miles of waters northwest of San Francisco. Located near Cordell Bank and just beyond the city of San Francisco is the Gulf of Farallones NMS, named for its location near the Farallon Islands. The sanctuary protects several different ecosystems including wetlands, the open ocean and reefs, within it s nearly 1,300 square miles of waters. Like Cordell Bank, the Gulf of the Farallones NMS is located in very productive waters that provide food for many seabirds and marine mammals. Monterey Bay NMS covers over 6,000 square miles of ocean and is home to numerous marine mammals, seabirds, fish, plants, and invertebrates such as sea stars, anemones, and corals. It includes one of the largest kelp forests and near-shore underwater canyons in the United States. Also, it protects the Davidson Seamount, the only seamount inside a NMS. It is located off the Central Coast of California. In Southern California, one finds the Channel Islands NMS. This sanctuary protects the Santa Barbara Channel and areas surrounding the Channel Islands. Protected ecosystems include rocky intertidal, kelp forests, rocky reefs, sandy bottom and open ocean. Species include over 60 types of seabirds, many invertebrates, fish, and marine mammals. Channel Islands NMS protects 1,500 square miles of ocean. The Hawaiian Humpback Whale NMS is found in the warm waters near the main Hawaiian Islands. It protects an important breeding ground for humpback whales, which are affected by human activities including collisions with boats, entanglement in fishing gear, noise pollution, and water quality issues. North of the main Hawaiian Islands lies the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands, or, ancestral islands, of the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument (pronounced Pa-pa-hah-now-mo-koo-ah-keh-ah). This Monument protects 140,000 square miles of the Pacific Ocean. Habitats protected include coral reefs, open ocean, and sandy beaches. Over 7,000 marine species make their homes within the Monument. U.S. National Marine Sanctuaries protect ocean areas by limiting pollution, damage to coral and rocky seabeds, and some extractive activities such as oil drilling. The National Marine Monument can also restrict fishing and recreational boating. Papahānaumokuākea also protects important cultural areas for Native Hawaiians. 10 Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots
11 16. Answer the following questions based on the information above and your data table: a. Which is the largest national marine sanctuary or monument? b. Which national marine sanctuary or monument is most interesting to you? Why? Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots 11
12 Albatross are very vulnerable to human activities. These seabirds are often accidentally snared on fish hooks. They can also be tangled in fishing line. Other pollutants, including plastic trash and oil spills, can affect their nutrition and health. 17. Based on the albatross hotspots you identified, draw an area in which you would recommend creating a protected area specifically to protect albatross. 12 Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots
13 18. Why would creating a national marine sanctuary to protect albatross be a challenge? What human activities might conflict with an area like this? Why? Evaluate Return to your sketch in Question What do you think about this sketch now? Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots 13
14 2. Draw a new sketch of the seafloor, including features that you are now more familiar with. Label these features. 3. Which features might result in upwelling? 14 Lesson 3: Protecting Ocean Hotspots
Name Class Date. The ocean floor has varied and distinct surfaces much like those found on land.
 6 Explore the Seafloor BigIdeas The ocean floor has varied and distinct surfaces much like those found on land. Satellites orbiting Earth, as well as sonar technology, are used to map the seafloor. The
6 Explore the Seafloor BigIdeas The ocean floor has varied and distinct surfaces much like those found on land. Satellites orbiting Earth, as well as sonar technology, are used to map the seafloor. The
Ocean Zones How are the intertidal, neritic, and oceanic zones different?
 Ocean Zones How are the intertidal, neritic, and oceanic zones different? How deep does sunlight travel into the ocean and how does that affect plants and animals? What technology is used to explore the
Ocean Zones How are the intertidal, neritic, and oceanic zones different? How deep does sunlight travel into the ocean and how does that affect plants and animals? What technology is used to explore the
Organisms in the Ocean
 Oceans Objective 8.E.1.2 Summarize evidence that Earth's oceans are a reservoir of nutrients, minerals, dissolved gases, and life forms: estuaries, marine ecosystems, upwelling, and behavior of gases in
Oceans Objective 8.E.1.2 Summarize evidence that Earth's oceans are a reservoir of nutrients, minerals, dissolved gases, and life forms: estuaries, marine ecosystems, upwelling, and behavior of gases in
Bell Ringer. water cycle? gaseous water (water vapor)? How do you know? 1. What are the five components of the
 Bell Ringer 1. What are the five components of the water cycle? 2. Are clouds composed of liquid water or gaseous water (water vapor)? How do you know? 3. How are glaciers formed? Salt Water - Oceans Characteristics
Bell Ringer 1. What are the five components of the water cycle? 2. Are clouds composed of liquid water or gaseous water (water vapor)? How do you know? 3. How are glaciers formed? Salt Water - Oceans Characteristics
4. In areas where tectonic plates collide, the seafloor has deep. 5. In areas where tectonic plates separate, the seafloor has mid- ocean
 Name Date Hour Table Chapter 14 Lesson One- General Directions: Use the word bank below to complete each statement. NOT all terms are used. abyssal plains brackish water condensation energy freshwater
Name Date Hour Table Chapter 14 Lesson One- General Directions: Use the word bank below to complete each statement. NOT all terms are used. abyssal plains brackish water condensation energy freshwater
Ocean facts continued
 Ocean Facts A dynamic system in which many chemical and physical changes take place Formed over millions of years as precipitation filled low areas on Earth called basins and now covers 70% of the Earth
Ocean Facts A dynamic system in which many chemical and physical changes take place Formed over millions of years as precipitation filled low areas on Earth called basins and now covers 70% of the Earth
Almost of Earth is covered by water. On a map, the continents appear as huge islands surrounded by a vast global ocean.
 Earth s Oceans & Ocean Floor Date: Feelin Blue What are Earth s five main oceans? Almost of Earth is covered by water. On a map, the continents appear as huge islands surrounded by a vast global ocean.
Earth s Oceans & Ocean Floor Date: Feelin Blue What are Earth s five main oceans? Almost of Earth is covered by water. On a map, the continents appear as huge islands surrounded by a vast global ocean.
Seas. A sea is a part of an ocean that is nearly surrounded by water. The Mediterranean, Arctic and Black Sea are really part of the Atlantic Ocean.
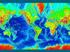 Exploring the Ocean Since ancient times people have studied the ocean such as waters and ocean floor It provides food and services, and serves as a route for trade and travel The World s Oceans 71% of
Exploring the Ocean Since ancient times people have studied the ocean such as waters and ocean floor It provides food and services, and serves as a route for trade and travel The World s Oceans 71% of
What Lives in the Open Ocean and Where Do They Live?
 Open Ocean 2 Concepts What are some of the organisms in the ocean? How do the physical (abiotic) properties of the ocean define what organisms live there? Standards Addressed HCPS 5.1, 5.2, & 5.3 Duration
Open Ocean 2 Concepts What are some of the organisms in the ocean? How do the physical (abiotic) properties of the ocean define what organisms live there? Standards Addressed HCPS 5.1, 5.2, & 5.3 Duration
DIAGRAM 1: Ocean Carbon Cycle DIAGRAM 2: Terrestrial Carbon Cycle
 DIAGRAM 1: Ocean Carbon Cycle DIAGRAM 2: Terrestrial Carbon Cycle DIAGRAM 3: Ocean Monthly CO 2 Flux Molecules of CO 2 enter the ocean by diffusing into the sea surface waters and dissolving a physio-chemical
DIAGRAM 1: Ocean Carbon Cycle DIAGRAM 2: Terrestrial Carbon Cycle DIAGRAM 3: Ocean Monthly CO 2 Flux Molecules of CO 2 enter the ocean by diffusing into the sea surface waters and dissolving a physio-chemical
OCEAN ZONES. 1. Intertidal Zone 2. Near-Shore Zone 3. Open-Ocean Zone
 OCEAN ZONES 1. Intertidal Zone 2. Near-Shore Zone 3. Open-Ocean Zone Where the Ocean Meets the Land (Place) Intertidal Zone The intertidal zone is the area between the high- and low-tide lines. At high
OCEAN ZONES 1. Intertidal Zone 2. Near-Shore Zone 3. Open-Ocean Zone Where the Ocean Meets the Land (Place) Intertidal Zone The intertidal zone is the area between the high- and low-tide lines. At high
OCEAN ZONES. 1. Intertidal Zone 2. Near-Shore Zone 3. Open-Ocean Zone
 OCEAN ZONES 1. Intertidal Zone 2. Near-Shore Zone 3. Open-Ocean Zone Where the Ocean Meets the Land (Place) Intertidal Zone The intertidal zone is the area between the high- and low-tide lines. At high
OCEAN ZONES 1. Intertidal Zone 2. Near-Shore Zone 3. Open-Ocean Zone Where the Ocean Meets the Land (Place) Intertidal Zone The intertidal zone is the area between the high- and low-tide lines. At high
Primary Productivity (Phytoplankton) Lab
 Name: Section: Due Date: Lab 10A-1 Primary Productivity (Phytoplankton) Lab Before Coming to Lab: Read Chapter 13 (387-424) in Thurman & Trujillo, 11 th ed. The purpose of this lab is to familiarize you
Name: Section: Due Date: Lab 10A-1 Primary Productivity (Phytoplankton) Lab Before Coming to Lab: Read Chapter 13 (387-424) in Thurman & Trujillo, 11 th ed. The purpose of this lab is to familiarize you
Unit 4 - Water. Earth s Interior. Earth s Interior. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Crust. Mantle. Core.
 Unit 4 - Water How did the oceans form? What special adaptations do saltwater organisms have? Where does our water come from? How do humans affect the Earth s water? Crust Rigid outer shell of Earth Oceanic
Unit 4 - Water How did the oceans form? What special adaptations do saltwater organisms have? Where does our water come from? How do humans affect the Earth s water? Crust Rigid outer shell of Earth Oceanic
Science 8 - Water Systems Test - Chapters 1-2
 Science 8 - Water Systems Test - Chapters 1-2 Multiple Choice (30 marks) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What percentage represents the amount of fresh
Science 8 - Water Systems Test - Chapters 1-2 Multiple Choice (30 marks) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What percentage represents the amount of fresh
Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface
 Oceanography Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface An ocean must be large and have features which set it apart from other oceans (currents, water
Oceanography Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface An ocean must be large and have features which set it apart from other oceans (currents, water
Marine biologists have identified over 250,000 marine species. This number is constantly increasing as new organisms are discovered.
 A wide variety of organisms inhabit the marine environment. These organisms range in size from microscopic bacteria and algae to the largest organisms alive today blue whales, which are as long as three
A wide variety of organisms inhabit the marine environment. These organisms range in size from microscopic bacteria and algae to the largest organisms alive today blue whales, which are as long as three
Earth Science 11 Learning Guide Unit Complete the following paragraph about the ocean and ocean water with the following words:
 Earth Science 11 Learning Guide Unit 8 Name: 8-1 Ocean Properties 1. Complete the following paragraph about the ocean and ocean water with the following words: thousand chloride 70% salinity water sodium
Earth Science 11 Learning Guide Unit 8 Name: 8-1 Ocean Properties 1. Complete the following paragraph about the ocean and ocean water with the following words: thousand chloride 70% salinity water sodium
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore
 Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore CO NTINENTAL SHEL F For the complete encyclopedic entry with media
Your web browser (Safari 7) is out of date. For more security, comfort and the best experience on this site: Update your browser Ignore CO NTINENTAL SHEL F For the complete encyclopedic entry with media
How are oceans important to humans? What are the differences between phytoplankton and zooplankton? What is the importance of plankton?
 Study Guide Chapter 1 Main Ideas Describe and identify the zones of the ocean. Oceans benefit humanity in many ways. Plankton is the basis of the entire oceanic food chain. How much of our oxygen does
Study Guide Chapter 1 Main Ideas Describe and identify the zones of the ocean. Oceans benefit humanity in many ways. Plankton is the basis of the entire oceanic food chain. How much of our oxygen does
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write or. 1.
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write or. 1.
How are oceans important to humans? What are the differences between phytoplankton and zooplankton?
 Study Guide Chapter 1 Main Ideas Describe and identify the zones of the ocean. Oceans benefit humanity in many ways. Plankton is the basis of the entire oceanic food chain. How much of our oxygen does
Study Guide Chapter 1 Main Ideas Describe and identify the zones of the ocean. Oceans benefit humanity in many ways. Plankton is the basis of the entire oceanic food chain. How much of our oxygen does
Write To Learn. I know:
 Name: Date: Class: I m learning from: Write To Learn I m learning from: I see: I know: I hear: I notice: I wonder: I connect: I m learning from: I remember: I have learned about: Key points in my own words:
Name: Date: Class: I m learning from: Write To Learn I m learning from: I see: I know: I hear: I notice: I wonder: I connect: I m learning from: I remember: I have learned about: Key points in my own words:
Science 5 - Sawyer Oceans [Exam ID:6030]
![Science 5 - Sawyer Oceans [Exam ID:6030] Science 5 - Sawyer Oceans [Exam ID:6030]](/thumbs/96/126548050.jpg) Science 5 - Sawyer Oceans [Exam I:6030] 1 Koa and Neeve are swimming and jumping in the waves at the beach. On which part of the ocean are they standing? Mountain range ontinental rise byssal plain ontinental
Science 5 - Sawyer Oceans [Exam I:6030] 1 Koa and Neeve are swimming and jumping in the waves at the beach. On which part of the ocean are they standing? Mountain range ontinental rise byssal plain ontinental
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
Two of the main currents in the Arctic region are the North Atlantic Current (in red) and the Transport Current (in blue).
 Have you ever enjoyed playing in the snow or making snowmen in the wintertime? The winter season is our coldest season. However, some of the coldest days we have here in Indiana have the same temperature
Have you ever enjoyed playing in the snow or making snowmen in the wintertime? The winter season is our coldest season. However, some of the coldest days we have here in Indiana have the same temperature
Oceanography. Oceanography is the study of the deep sea and shallow coastal oceans.
 Oceanography Oceanography is the study of the deep sea and shallow coastal oceans. Studying the Ocean Floor To determine the shape and composition of the ocean floor, scientists use techniques such as
Oceanography Oceanography is the study of the deep sea and shallow coastal oceans. Studying the Ocean Floor To determine the shape and composition of the ocean floor, scientists use techniques such as
Write To Learn. I know:
 Name: Date: Class: I m learning from: Write To Learn I m learning from: I see: I know: I hear: I notice: I wonder: I connect: I m learning from: I have learned about: I remember: Key points in my own words:
Name: Date: Class: I m learning from: Write To Learn I m learning from: I see: I know: I hear: I notice: I wonder: I connect: I m learning from: I have learned about: I remember: Key points in my own words:
Objectives: Describe the structure of the ocean floor. Describe light intensity and temperature characteristics at different ocean depths.
 Ocean Structure Virtual Lab What are some characteristics of the ocean and the ocean floor? Earths highest mountains, deepest valleys, and flattest plains are found not on land but under the ocean. Beyond
Ocean Structure Virtual Lab What are some characteristics of the ocean and the ocean floor? Earths highest mountains, deepest valleys, and flattest plains are found not on land but under the ocean. Beyond
200 Meters Down Topic: Ocean Zones (5 th 8 th grade)
 200 Meters Down Topic: Ocean Zones (5 th 8 th grade) by Lodge 200 Meters Down Have you people heard about the plankton? Just tiny algae and it s floating, right What about the nekton like jellyfish? They
200 Meters Down Topic: Ocean Zones (5 th 8 th grade) by Lodge 200 Meters Down Have you people heard about the plankton? Just tiny algae and it s floating, right What about the nekton like jellyfish? They
Earth / Environmental Science. Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR
 Earth / Environmental Science Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR The Blue Planet Nearly 70% of the Earth s surface is covered by the global ocean It was not until the 1800s that the ocean became an important focus
Earth / Environmental Science Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR The Blue Planet Nearly 70% of the Earth s surface is covered by the global ocean It was not until the 1800s that the ocean became an important focus
INTERACTIONS IN AN ENVIRONMENT
 reflect Earth is full of living things. Our planet has many kinds of organisms including bacteria, fungi (like mushrooms), plants, and animals. In some ways, living things are alike. Almost all living
reflect Earth is full of living things. Our planet has many kinds of organisms including bacteria, fungi (like mushrooms), plants, and animals. In some ways, living things are alike. Almost all living
Unit 8 Test Review -- Oceanography
 Unit 8 Test Review -- Oceanography Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. D 1. A large body of saline water that may be surrounded by land is a(n)
Unit 8 Test Review -- Oceanography Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. D 1. A large body of saline water that may be surrounded by land is a(n)
Ocean Floor. Continental Margins. Divided into 3 major regions. Continental Margins. Ocean Basins. Mid-Ocean Ridges. Include:
 Ocean Floor Divided into 3 major regions Continental Margins Ocean Basins Mid-Ocean Ridges Continental Margins Include: Continental Shelves Continental Slopes Continental Rise 1 Continental Shelves Part
Ocean Floor Divided into 3 major regions Continental Margins Ocean Basins Mid-Ocean Ridges Continental Margins Include: Continental Shelves Continental Slopes Continental Rise 1 Continental Shelves Part
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE!
 ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
Changes to Land 5.7B. landforms: features on the surface of Earth such as mountains, hills, dunes, oceans and rivers
 All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut away land
All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut away land
Oceans. PPt. by, Robin D. Seamon
 Oceans PPt. by, Robin D. Seamon Ocean Notes Salt water/ salinity 360 million square miles 3.5 billion years old 100,000 + species 28 degrees to 86 degrees F 7 miles down in some places Mineral composition:
Oceans PPt. by, Robin D. Seamon Ocean Notes Salt water/ salinity 360 million square miles 3.5 billion years old 100,000 + species 28 degrees to 86 degrees F 7 miles down in some places Mineral composition:
Benthic Deep Ocean Zone. By: Amanda, Alyssa, Mason, and Skai
 Benthic Deep Ocean Zone By: Amanda, Alyssa, Mason, and Skai The Benthic Zone The darkest, deepest, and best part of the ocean Benthic Zone Basic Info The Benthic Zone is located at the bottom of the ocean,
Benthic Deep Ocean Zone By: Amanda, Alyssa, Mason, and Skai The Benthic Zone The darkest, deepest, and best part of the ocean Benthic Zone Basic Info The Benthic Zone is located at the bottom of the ocean,
Warm Up 1: Ocean Floors LT I can explain the concept of Pangea. I can describe how Ocean Ridges form and give examples of them.
 Warm Up 1: Ocean Floors 4-18-17 LT I can explain the concept of Pangea. I can describe how Ocean Ridges form and give examples of them. Q1. How do we get a diversity of birds? Q2. How did the breeds of
Warm Up 1: Ocean Floors 4-18-17 LT I can explain the concept of Pangea. I can describe how Ocean Ridges form and give examples of them. Q1. How do we get a diversity of birds? Q2. How did the breeds of
Think about the landforms where you live. How do you think they have changed over time? How do you think they will change in the future?
 reflect All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut
reflect All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut
Project. Aim: How does energy flow in Arctic and Antarctic ecosystems? Explore. The four food webs are:
 Name: Date: Aim: How does energy flow in Arctic and Antarctic ecosystems? Explore The four food webs are: o Antarctic Marine Food Web o Arctic Marine Food Web o Tundra Land Food Web o Tundra Freshwater
Name: Date: Aim: How does energy flow in Arctic and Antarctic ecosystems? Explore The four food webs are: o Antarctic Marine Food Web o Arctic Marine Food Web o Tundra Land Food Web o Tundra Freshwater
General Characteristics
 Polar Seas General Characteristics Seasonal Sea ice can cover up to 13% of Earth s surface Arctic 5% of the world ocean Mostly north of the Arctic Circle Antarctic 10% of the world ocean General Characteristics
Polar Seas General Characteristics Seasonal Sea ice can cover up to 13% of Earth s surface Arctic 5% of the world ocean Mostly north of the Arctic Circle Antarctic 10% of the world ocean General Characteristics
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 9693 MARINE SCIENCE
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 9693 MARINE SCIENCE 9693/01 Paper 1 (AS Structured Questions), maximum
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 9693 MARINE SCIENCE 9693/01 Paper 1 (AS Structured Questions), maximum
Organism Interactions in Ecosystems
 Organism Interactions in Ecosystems Have you ever grown a plant or taken care of a pet? If so, you know they have certain needs such as water or warmth. Plants need sunlight to grow. Animals need food
Organism Interactions in Ecosystems Have you ever grown a plant or taken care of a pet? If so, you know they have certain needs such as water or warmth. Plants need sunlight to grow. Animals need food
Science Grade 4. Unit 1 Healthy Habitats
 Science Grade 4 Unit 1 Healthy Habitats What is a habitat Habitat - The place where an animal or a plant normally lives or grows and that provides them with everything they need to survive. Habitat A habitat
Science Grade 4 Unit 1 Healthy Habitats What is a habitat Habitat - The place where an animal or a plant normally lives or grows and that provides them with everything they need to survive. Habitat A habitat
Biogeographic Approach to Coastal Assessments & Spatial Planning
 NOAA s Biogeographic Approach to Coastal Assessments & Spatial Planning Mark E. Monaco Mark.Monaco@noaa.gov Center for Coastal Monitoring and Assessment http://ccma.nos.noaa.gov/about/biogeography Biogeography
NOAA s Biogeographic Approach to Coastal Assessments & Spatial Planning Mark E. Monaco Mark.Monaco@noaa.gov Center for Coastal Monitoring and Assessment http://ccma.nos.noaa.gov/about/biogeography Biogeography
Organism Species Population Community Ecosystem
 Name: Date: Period: Ecosystems and Their Interactions S8.B.3.1 Getting the idea The environment is everything that surrounds an organism. Organisms cooperate and compete with each other to get everything
Name: Date: Period: Ecosystems and Their Interactions S8.B.3.1 Getting the idea The environment is everything that surrounds an organism. Organisms cooperate and compete with each other to get everything
1. Name at least one place that the mid-atlantic Ridge is exposed above sea level.
 Interpreting Tectonic and Bathymetric Maps. The purpose of this lab is to provide experience interpreting the bathymetry of the seafloor in terms of tectonic and geologic settings and processes. Use the
Interpreting Tectonic and Bathymetric Maps. The purpose of this lab is to provide experience interpreting the bathymetry of the seafloor in terms of tectonic and geologic settings and processes. Use the
The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are
 11.1 Ocean Basins The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are w the Pacific w the Atlantic w the Indian w the Southern w the Arctic The
11.1 Ocean Basins The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are w the Pacific w the Atlantic w the Indian w the Southern w the Arctic The
Lesson Overview 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions
 THINK ABOUT IT If you ask someone where an organism lives, that person might answer on a coral reef or in the desert. Lesson Overview 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions These answers give the environment
THINK ABOUT IT If you ask someone where an organism lives, that person might answer on a coral reef or in the desert. Lesson Overview 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions These answers give the environment
Lesson: Primary Production
 Lesson: Primary Production By Keith Meldahl Corresponding to Chapter 14: Primary Producers Microscopic phytoplankton -- tiny single-celled plants that float at the ocean s surface, are the ultimate food
Lesson: Primary Production By Keith Meldahl Corresponding to Chapter 14: Primary Producers Microscopic phytoplankton -- tiny single-celled plants that float at the ocean s surface, are the ultimate food
1. What makes plants different than animals?
 1. What makes plants different than animals? tiger lily tiger 1. Plants are producers, which means they make their own food (through photosynthesis). 2. While plants can move certain structures, they cannot
1. What makes plants different than animals? tiger lily tiger 1. Plants are producers, which means they make their own food (through photosynthesis). 2. While plants can move certain structures, they cannot
The Water Planet Ch. 22
 The Water Planet Ch. 22 What is Oceanography? the study of the Earth s oceans using chemistry, biology, geology, and physics. Oceans cover 70% of the Earth s surface Ocean Research 22.1 The use of submarines
The Water Planet Ch. 22 What is Oceanography? the study of the Earth s oceans using chemistry, biology, geology, and physics. Oceans cover 70% of the Earth s surface Ocean Research 22.1 The use of submarines
LOWER PRIMARY SCHOOL WORKBOOK
 CORAL CAY CONSERVATION & JFA EDUCATIONAL AIDS LOWER PRIMARY SCHOOL WORKBOOK ECOLOGY, RELATIONSHIPS & INTERACTIONS - Prepared by - Alexia Tamblyn, Director of Ecology, JFA Craig Turner, Managing Director,
CORAL CAY CONSERVATION & JFA EDUCATIONAL AIDS LOWER PRIMARY SCHOOL WORKBOOK ECOLOGY, RELATIONSHIPS & INTERACTIONS - Prepared by - Alexia Tamblyn, Director of Ecology, JFA Craig Turner, Managing Director,
Brief Intro on Sea Plants
 1 Brief Intro on Sea Plants This website will help you learn about the major varieties of underwater sea plants beneath the vast, deep oceans and seas. You will learn their names, colors, types, how they
1 Brief Intro on Sea Plants This website will help you learn about the major varieties of underwater sea plants beneath the vast, deep oceans and seas. You will learn their names, colors, types, how they
Chapter Niches and Community Interactions
 Chapter 4 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions Key Questions: 1) What is a niche? 2) How does competition shape communities? 3) How do predation and herbivory shape communites? 4) What are three primary
Chapter 4 4.2 Niches and Community Interactions Key Questions: 1) What is a niche? 2) How does competition shape communities? 3) How do predation and herbivory shape communites? 4) What are three primary
Biology Unit 2 Test. True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false.
 Biology Unit 2 Test True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. A climax community is usually the stable result of succession. 2. The colonization of new sites by communities of organisms
Biology Unit 2 Test True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. A climax community is usually the stable result of succession. 2. The colonization of new sites by communities of organisms
Food Chains. energy: what is needed to do work or cause change
 Have you ever seen a picture that shows a little fish about to be eaten by a big fish? Sometimes the big fish has an even bigger fish behind it. This is a simple food chain. A food chain is the path of
Have you ever seen a picture that shows a little fish about to be eaten by a big fish? Sometimes the big fish has an even bigger fish behind it. This is a simple food chain. A food chain is the path of
Small area of the ocean that is partially surrounded by land. The Ocean Basins. Three Major Oceans. Three Major Oceans. What is a SEA?
 The Ocean Basins How Deep is the Ocean? 1 2 Three Major Oceans Three Major Oceans Pacific Atlantic the shallowest ocean (3.3km average depth) Indian second shallowest ocean (3.8km average depth) Pacific
The Ocean Basins How Deep is the Ocean? 1 2 Three Major Oceans Three Major Oceans Pacific Atlantic the shallowest ocean (3.3km average depth) Indian second shallowest ocean (3.8km average depth) Pacific
Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2
 Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2 Create a mind map with the driving question, Why are Oceans Important? Remember: Why are oceans so important? Why are oceans so important? Primary water source
Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2 Create a mind map with the driving question, Why are Oceans Important? Remember: Why are oceans so important? Why are oceans so important? Primary water source
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 13 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 13 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 13 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
BIO 2 GO! Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis 3134,3136
 BIO 2 GO! Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis 3134,3136 Photosynthesis and chemosynthesis are similar in that they both make glucose. Photosynthesis is the process in which green plants use the sun s energy
BIO 2 GO! Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis 3134,3136 Photosynthesis and chemosynthesis are similar in that they both make glucose. Photosynthesis is the process in which green plants use the sun s energy
Unit 7: What is an ecosystem?
 Unit 7: What is an ecosystem? Lesson 20 An ecosystem is an area or habitat that contains living and non-living things. The living and non-living things depend on each other in many different ways. An ecosystem
Unit 7: What is an ecosystem? Lesson 20 An ecosystem is an area or habitat that contains living and non-living things. The living and non-living things depend on each other in many different ways. An ecosystem
Chapter Overview. Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry
 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
10/6/ th Grade Ecology and the Environment. Chapter 2: Ecosystems and Biomes
 7 th Grade Ecology and the Environment Chapter 2: Ecosystems and Biomes Lesson 1 (Energy Flow in Ecosystems) Each organism in an ecosystem fills an energy role. Producer an organism that can make its own
7 th Grade Ecology and the Environment Chapter 2: Ecosystems and Biomes Lesson 1 (Energy Flow in Ecosystems) Each organism in an ecosystem fills an energy role. Producer an organism that can make its own
Ocean Scavenger Hunt. Materials: pencil study notes timer. Directions:
 Ocean Scavenger Hunt Materials: pencil study notes timer Directions: 1. Each student receives a copy of the scavenger hunt, placed upside down on their desk. 2. Explain to students that they will scavenge
Ocean Scavenger Hunt Materials: pencil study notes timer Directions: 1. Each student receives a copy of the scavenger hunt, placed upside down on their desk. 2. Explain to students that they will scavenge
Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor
 Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 3 Marine Provinces 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 3 Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean
Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 3 Marine Provinces 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 3 Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean
Unit 6: The Sea Floor
 Unit 6: The Sea Floor Turn to Page 62 in Introduction to the World s Oceans Study the bathymetric chart What features do you see? How do the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans differ? What do you think accounts
Unit 6: The Sea Floor Turn to Page 62 in Introduction to the World s Oceans Study the bathymetric chart What features do you see? How do the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans differ? What do you think accounts
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Oceans: The Last Frontier Foundations, 6e - Chapter 9 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Oceans: The Last Frontier Foundations, 6e - Chapter 9 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College The vast world ocean Earth is often referred
Evolution and Life in the Ocean
 Characteristics of All Living Things Contain matter in a highly organized state Capture, store and transmit energy; all organisms require energy Capable of reproduction Change through time and adapt to
Characteristics of All Living Things Contain matter in a highly organized state Capture, store and transmit energy; all organisms require energy Capable of reproduction Change through time and adapt to
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Chapter 18, Seafloor Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Abyssal fans are made
Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Chapter 18, Seafloor Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Abyssal fans are made
Tolerance. Tolerance. Tolerance 10/22/2010
 Section 4.2 Mrs. Michaelsen Tolerance Every species has its own range of tolerance: The ability to survive and reproduce under a range of environmental circumstances. Tolerance Stress can result when an
Section 4.2 Mrs. Michaelsen Tolerance Every species has its own range of tolerance: The ability to survive and reproduce under a range of environmental circumstances. Tolerance Stress can result when an
The Sea Floor. Chapter 2
 The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
I. Earth s Layers a. Crust: Earth s outside layer. Made of mostly rock. i. Continental: er; made of mostly granite, forms the continents and shallow
 I. Earth s Layers a. Crust: Earth s outside layer. Made of mostly rock. i. Continental: er; made of mostly granite, forms the continents and shallow sea beds, floats! ii. Oceanic: er; dense rock such as
I. Earth s Layers a. Crust: Earth s outside layer. Made of mostly rock. i. Continental: er; made of mostly granite, forms the continents and shallow sea beds, floats! ii. Oceanic: er; dense rock such as
Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. A Continent of Ice
 Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. A Continent of Ice Imagine a place with bone-chilling temperatures and blizzards so thick you cannot see your hand
Indicate the answer choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. A Continent of Ice Imagine a place with bone-chilling temperatures and blizzards so thick you cannot see your hand
Question: What is the primary reason for the great abundance of fish along the Peruvian coast?
 Buzzer Question # 1 Question Type: toss-up Question Format: Multiple Choice Category: Biology What is the primary reason for the great abundance of fish along the Peruvian coast? Answer W: upwelling Answer
Buzzer Question # 1 Question Type: toss-up Question Format: Multiple Choice Category: Biology What is the primary reason for the great abundance of fish along the Peruvian coast? Answer W: upwelling Answer
Elements of Ocean Engineering Prof. Ashoke Bhar Department of Ocean Engineering and Naval Architecture Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Elements of Ocean Engineering Prof. Ashoke Bhar Department of Ocean Engineering and Naval Architecture Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 4 Physical Oceanography - IV (Refer Slide Time:
Elements of Ocean Engineering Prof. Ashoke Bhar Department of Ocean Engineering and Naval Architecture Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 4 Physical Oceanography - IV (Refer Slide Time:
Carbon Cycling Internal
 Carbon Cycling Internal The 4 subcycles Atmosphere The Earth s Atmosphere The Earth has a radius of some 6400 km. Ninety-nine percent of the earth's atmosphere is contained within a layer approximately
Carbon Cycling Internal The 4 subcycles Atmosphere The Earth s Atmosphere The Earth has a radius of some 6400 km. Ninety-nine percent of the earth's atmosphere is contained within a layer approximately
BUNDLE 9: ENERGY AND ECOLOGY Review
 BUNDLE 9: ENERGY AND ECOLOGY Review 1. Describe Cellular Respiration, what happens, where does it happen, what type of organism does it take place in? What is the equation for respiration? Happens in the
BUNDLE 9: ENERGY AND ECOLOGY Review 1. Describe Cellular Respiration, what happens, where does it happen, what type of organism does it take place in? What is the equation for respiration? Happens in the
Coral bleaching and climate change Featured scientist: Carly Kenkel from The University of Texas at Austin
 Name Coral bleaching and climate change Featured scientist: Carly Kenkel from The University of Texas at Austin Research Background: Corals are animals that build coral reefs. Coral reefs are home to many
Name Coral bleaching and climate change Featured scientist: Carly Kenkel from The University of Texas at Austin Research Background: Corals are animals that build coral reefs. Coral reefs are home to many
Tuesday, September 05, 2017 Planet Earth
 Tuesday, September 05, 2017 Planet Earth Objective: Describe the solar system and Earth s location in it. Identify Earth s shape. Discuss Earth s structure. List Earth s landforms Do Now: What is a compass
Tuesday, September 05, 2017 Planet Earth Objective: Describe the solar system and Earth s location in it. Identify Earth s shape. Discuss Earth s structure. List Earth s landforms Do Now: What is a compass
Bathymetry Measures the vertical distance from the ocean surface to mountains, valleys, plains, and other sea floor features
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools.
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 10, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 10, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Beaches are created by the actions of waves, tides,
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 10, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Beaches are created by the actions of waves, tides,
Introduction to the Seafloor. Follow the steps below while taking notes in your science notebook.
 Procedure Follow the steps below while taking notes in your science notebook. 1. Name and locate all of the continents. 2. Identify linear (straight-line) and arcuate (curved-line) features on the continents.
Procedure Follow the steps below while taking notes in your science notebook. 1. Name and locate all of the continents. 2. Identify linear (straight-line) and arcuate (curved-line) features on the continents.
UNIT 1: WATER SYSTEMS ON EARTH CHAPTER 2: OCEANS CONTROL THE WATER CYCLE
 UNIT 1: WATER SYSTEMS ON EARTH CHAPTER 2: OCEANS CONTROL THE WATER CYCLE ORIGINS OF OCEAN WATER OCEANS HAVE FILLED OVER HUNDREDS OF MILLIONS OF YEARS SCIENTISTS BELIEVE THE OCEANS ARE MORE THAN 3 BILLION
UNIT 1: WATER SYSTEMS ON EARTH CHAPTER 2: OCEANS CONTROL THE WATER CYCLE ORIGINS OF OCEAN WATER OCEANS HAVE FILLED OVER HUNDREDS OF MILLIONS OF YEARS SCIENTISTS BELIEVE THE OCEANS ARE MORE THAN 3 BILLION
And. Mad Science of Colorado West Grandview Ave. Suite #5 Arvada, CO Name
 And Name Mad Science of Colorado 7100 West Grandview Ave. Suite #5 Arvada, CO 80002 303-403-0432 www.colorado.madscience.org While enjoying Elitch Gardens, spend some time at each of the five Mad Science
And Name Mad Science of Colorado 7100 West Grandview Ave. Suite #5 Arvada, CO 80002 303-403-0432 www.colorado.madscience.org While enjoying Elitch Gardens, spend some time at each of the five Mad Science
narrated by sylvia earle/oceans ove
 Chapter 13 Exploring the Oceans Section 1 Earth's Ocean List the major divisions of the global ocean. Describe the history of Earth's oceans Identify the properties of ocean water. Describe the interactions
Chapter 13 Exploring the Oceans Section 1 Earth's Ocean List the major divisions of the global ocean. Describe the history of Earth's oceans Identify the properties of ocean water. Describe the interactions
Name period date assigned date due date returned. Natural Disasters
 Name period date assigned date due date returned Match the following natural disaster to its description. Write the capital letter of the definition in the blank in front of the natural disaster. 1. tornado
Name period date assigned date due date returned Match the following natural disaster to its description. Write the capital letter of the definition in the blank in front of the natural disaster. 1. tornado
6th Grade. Name. Teacher School. This page intentionally left blank for use after your visit to The Living Planet Aquarium.
 6th Grade Student Research Booklet Name Teacher School This page intentionally left blank for use after your visit to The Living Planet Aquarium. 16 These pages are for you to use back in the classroom
6th Grade Student Research Booklet Name Teacher School This page intentionally left blank for use after your visit to The Living Planet Aquarium. 16 These pages are for you to use back in the classroom
Understanding Oceans, Gulfs & Tides
 SCS-2005-13 Water and Me Series Understanding s, Gulfs & Tides Monty C. Dozier Assistant Professor and Extension Water Resources Specialist The dictionary defines the ocean as the whole body of saltwater
SCS-2005-13 Water and Me Series Understanding s, Gulfs & Tides Monty C. Dozier Assistant Professor and Extension Water Resources Specialist The dictionary defines the ocean as the whole body of saltwater
Ecosystems and Communities
 Ecosystems and Communities Chapter 4 Section Outline Section 4-1 4 1 The Role of Climate A. What Is Climate? 1. Weather is day to day at a particular time and place 2. Climate is year-to-year averages
Ecosystems and Communities Chapter 4 Section Outline Section 4-1 4 1 The Role of Climate A. What Is Climate? 1. Weather is day to day at a particular time and place 2. Climate is year-to-year averages
CLASSIFICATION AND VARIATION
 1 Living organisms Living things are made of tiny units called cells. Cells help living organisms to carry out one or more of the following life processes. Draw lines to match each process to its definition.
1 Living organisms Living things are made of tiny units called cells. Cells help living organisms to carry out one or more of the following life processes. Draw lines to match each process to its definition.
Unit: 4 Plate Tectonics LT 4.1 Earth s Interior: I can draw and interpret models of the interior of the earth.
 Unit: 4 Plate Tectonics LT 4.1 Earth s Interior: I can draw and interpret models of the interior of the earth. 1. Can you draw the 3-layer model and the 5-layer model of the Earth? #1 Yes I can: 2. Can
Unit: 4 Plate Tectonics LT 4.1 Earth s Interior: I can draw and interpret models of the interior of the earth. 1. Can you draw the 3-layer model and the 5-layer model of the Earth? #1 Yes I can: 2. Can
Warm Up Vocabulary Check
 Warm Up Vocabulary Check Surface current Coriolis Effect global winds upwelling Gulf Stream deep current climate El Nino convection current continental deflection 1.The apparent curving of the path of
Warm Up Vocabulary Check Surface current Coriolis Effect global winds upwelling Gulf Stream deep current climate El Nino convection current continental deflection 1.The apparent curving of the path of
Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators
 Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators Table of Contents Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Correlation Chart... 7 Benchmarks Chapter 1 The Practice of Science...................... 11
Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators Table of Contents Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Correlation Chart... 7 Benchmarks Chapter 1 The Practice of Science...................... 11
Vanishing Species 5.1. Before You Read. Read to Learn. Biological Diversity. Section. What do biodiversity studies tell us?
 Vanishing Species Before You Read Dinosaurs are probably the most familiar organisms that are extinct, or no longer exist. Many plants and animals that are alive today are in danger of dying out. Think
Vanishing Species Before You Read Dinosaurs are probably the most familiar organisms that are extinct, or no longer exist. Many plants and animals that are alive today are in danger of dying out. Think
Lesson 2. Antarctic Oceanography: Component I - Ice/Glaciers Component II - Marine Snow
 Lesson 2. Antarctic Oceanography: Component I - Ice/Glaciers Component II - Marine Snow Lesson Objectives: Introduces students to the different kinds of ice found in Antarctica, Students will become familiar
Lesson 2. Antarctic Oceanography: Component I - Ice/Glaciers Component II - Marine Snow Lesson Objectives: Introduces students to the different kinds of ice found in Antarctica, Students will become familiar
Plate Tectonics Unit III: A Few More Details (2 pts)
 T. James Noyes, El Camino College Plate Tectonics Unit III: A Few More Details (Topic 11A-3) page 1 Name: Section: Plate Tectonics Unit III: A Few More Details (2 pts) How do we know what the interior
T. James Noyes, El Camino College Plate Tectonics Unit III: A Few More Details (Topic 11A-3) page 1 Name: Section: Plate Tectonics Unit III: A Few More Details (2 pts) How do we know what the interior
ARCHAEBACTERIA. EUBACTERIA. PROTISTS. FUNGI. PLANTS. ANIMALS
 THE KINGDOMS ARCHAEBACTERIA. EUBACTERIA. PROTISTS. FUNGI. PLANTS. ANIMALS ARCHAEBACTERIA.. Archeabacteria are found in extreme environments, such as hot boiling water, and thermal vents under conditions
THE KINGDOMS ARCHAEBACTERIA. EUBACTERIA. PROTISTS. FUNGI. PLANTS. ANIMALS ARCHAEBACTERIA.. Archeabacteria are found in extreme environments, such as hot boiling water, and thermal vents under conditions
