UNIT 1: WATER SYSTEMS ON EARTH CHAPTER 2: OCEANS CONTROL THE WATER CYCLE
|
|
|
- Osborne Owens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIT 1: WATER SYSTEMS ON EARTH CHAPTER 2: OCEANS CONTROL THE WATER CYCLE
2 ORIGINS OF OCEAN WATER OCEANS HAVE FILLED OVER HUNDREDS OF MILLIONS OF YEARS SCIENTISTS BELIEVE THE OCEANS ARE MORE THAN 3 BILLION YEARS OLD. WATER MAY HAVE ORIGINALLY BEEN RELEASED FROM VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS WHEN THE VAPOUR FROM THE ERUPTIONS COOLED AND CONDENSED. SOME BELIEVE THE WATER CAME FROM ICE COMETS.
3 EARTH'S OCEANS - PAGE 38 ***Oceans Assignment***
4 OCEAN BASINS: THERE ARE FOUR PROCESSES THAT LEAD TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF OCEAN BASINS: 1.PLATE TECTONICS 2.VOLCANIC ACTIONS 3.EROSIONS 4.GLACIATION
5 1. PLATE TECTONICS PIECES OF THE LAND MOVE OVER THE EARTH'S SURFACE CHANGES POSITION OF THE CONTINENTS INFLUENCED WHERE OCEAN BASINS ARE LOCATED Video Clip 1 Video Clip 2
6 2. VOLCANIC ACTION UNDERWATER VOLCANOES ARE GENERALLY FOUND AT THE EDGES OF TECTONIC PLATES WHEN VOLCANOES ERUPT UNDERWATER, NEW OCEANIC CRUST (OCEAN FLOOR) IS FORMED BY THE HOT MOLTEN ROCK SLOWLY COOLING AND SOLIDIFYING VOLCANOES HAVE BUILT OCEAN FLOOR ALONG MID-OCEAN RIDGES IN AREAS WHERE PLATES SEPARATE VOLCANOES HAVE HELPED BUILD CONTINENTAL DIVIDES IN AREAS WHERE PLATES HAVE COLLIDED AND MOUNTAIN BUILDING OCCURS
7 3. EROSION THE PROCESS BY WHICH THE SURFACE OF THE EARTH IS WORN AWAY BY THE ACTION OF WATER, GLACIERS, WINDS, WAVES, ETC. EROSION HAS FURTHER DEVELOPED CONTINENTAL DRAINAGE SYSTEMS AS MATERIAL IS REMOVED AND DEPOSITED INTO THE OCEAN BASINS.
8 4. GLACIATION A FORCE OF EROSION IN THE DEVELOPMENT OF CONTINENTAL DRAINAGE SYSTEMS. WHEN GLACIERS MELT, THE WATER THAT THEY RELEASE WEARS AWAY THE EARTH AS IT FLOWS DOWN TO THE OCEANS AND OTHER DRAINAGE BASINS.
9 THE OCEAN BASINS - PAGE THE CONTINENTAL SHELF: FROM THE EDGE OF THE WATER TO THE "DROP- OFF" ZONE. 2. THE CONTINENTAL SLOPE: THE "DROP-OFF" (FROM THE PELAGIC ZONE TO THE BENTHIC ZONE) 3. THE ABYSSAL PLAIN: THE WIDE, FLAT AREAS OF THE OCEAN FLOOR, THEY ARE MADE UP OF SEDIMENT FROM EARTHQUAKES THAT CAUSE UNDERWATER LANDSLIDES, OR SIMPLY BY GRAVITY. 4. MID-OCEAN RIDGE: OCEAN RIDGES ARE FORMED WHEN TWO TECTONIC PLATES ARE PUSHED APART. MAGMA OOZES UP THROUGH THE GAP AND FORMS A MOUNTAIN CHAIN (LIKE A SCAB). THE LARGEST IS THE MID- ATLANTIC RIDGE.
10
11 EXAMPLES OF CANADIAN INSTITUTIONS THAT DO RESEARCH INVOLVING OCEANS: ENVIRONMENT CANADA FEDERAL FISHERIES OCEAN SCIENCE CENTRE FOR COLD OCEAN RESEARCH MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY ***Ocean Floor Assignment***
12 TECHNOLOGIES USED TO RESEARCH THE OCEAN FLOOR: 1. SONAR 2. SATELLITES 3. UNDERWATER PHOTOGRAPHY/VIDEOGRAPHY 4. SUBMERSIBLES 5. DIVING
13 1. SONAR: SOUND WAVES ARE SENT DOWN FROM A SHIP CAN BE USED TO MAP UNDERWATER MOUNTAINS, VALLEYS, AND CANYONS ON THE OCEAN FLOOR. Video clip
14 2. SATELLITES: ORBIT THE EARTH, USE RADAR, INFRARED LIGHT, OR OTHER TECHNOLOGIES TO MEASURE FEATURES ON THE OCEAN FLOOR. SURVEYS LARGE AREAS OF OCEANS IN A SHORT PERIOD OF TIME. GATHERS INFORMATION FROM BUOYS ABOUT WATER AND AIR TEMPERATURE FOR WEATHER STATIONS. Video Clip
15 3. UNDERWATER PHOTOGRAPHY/VIDEOGRAPHY: CAMERAS TAKE HIGH RESOLUTION (CLEAR) UNDERWATER PHOTOS AND VIDEOS. CAN GO UP TO 6000M BENEATH THE SURFACE.
16 4. SUBMERSIBLES (SUBMARINES): SMALL BUT EXTREMELY STRONG VEHICLES (BECAUSE OF THE HIGH PRESSURE UNDERWATER) THAT ARE CAPABLE OF TRAVELLING TO GREAT DEPTHS. 2 TYPES: 1. REMOTELY-OPERATED VEHICLES (ROV): PEOPLE CONTROL IT FROM A SHIP ADVANTAGE: CAN STAY DOWN FOR LONG PERIODS OF TIME AND GO TO FURTHER DEPTHS THAN MANNED SUBMERSIBLES Video Clip 1 Video Clip 2
17 2. MANNED SUBMERSIBLES: CARRY PEOPLE INSIDE ADVANTAGE: PEOPLE CAN MAKE THEIR OWN OBSERVATIONS OF THE DEEP SEA. Video Clip
18 5. DIVING: NEW TECHNOLOGY ALLOWS PEOPLE TO DIVE DEEPER THAN EVER BEFORE, BUT THEY STILL CANNOT GO AS DEEP AS OTHER TECHNOLOGIES. ADVANTAGE: PEOPLE CAN MAKE THEIR OWN OBSERVATIONS. NOTE: Although all of these technologies help our understanding, NO single data collection method provides a complete picture of the ocean floor. STSE: Undersea Adventure
19 PAGE 43: #'S 1-4 PAGE 51: #'S 1-8, 11 TECHNOLOGY PROJECT PRACTICE
20 OCEAN CURRENTS A LARGE AMOUNT OF OCEAN WATER THAT MOVES IN A PARTICULAR AND UNCHANGING DIRECTION. Video Clip Grand Bank, NL
21 THERE ARE MORE THAN 20 MAJOR CURRENTS IN THE WORLD LARGEST: ANTARCTIC CIRCUMPOLAR CURRENT See Page 52
22 LOCAL OCEAN CURRENTS: 1. LABRADOR CURRENT: COLD WATER FROM NEAR GREENLAND. 2. GULF STREAM: WARM WATER FROM THE TROPICS. THESE CURRENTS RUN BY THE COAST OF NEWFOUNDLAND AND LABRADOR THROUGH THE ATLANTIC OCEAN.
23 THE WARM GULF STREAM CURRENT MIXES WITH THE COLD LABRADOR CURRENT AND MAKES HEAVY FOG. Video Clip
24 UPWELLING STRONG WINDS BLOW OFFSHORE AND PUSH SURFACE WATER AWAY FROM THE LAND. COLD, DEEP WATER THEN RISES FROM BELOW TO REPLACE THE SURFACE WATER THAT HAS BEEN MOVED OUT TO SEA. UPWELLING WATER CONTAINS LOTS OF NUTRIENTS. EXAMPLE: THE GRAND BANKS Video Clip
25 WAVES: LARGE RIPPLES SET IN MOTION BY STEADY WINDS. WAVES ON THE SURFACE OF WATER ARE THE RESULT OF A TRANSFER OF ENERGY FROM MOVING AIR TO THE WATER.
26 CREST: THE HIGHEST PART OF A WAVE. TROUGH: THE LOWEST PART OF A WAVE. WAVELENGTH: DISTANCE FROM CREST TO CREST OR TROUGH TO TROUGH. I.E LENGTH OF A WAVE BEFORE IT REPEATS ITSELF. WAVE HEIGHT: THE DISTANCE FROM TROUGH TO CREST OF A WAVE. Bill Nye Waves Video
27 TSUNAMIS: GIANT WAVES THAT CAN BE SENT IN MOTION BY EARTHQUAKES ON THE OCEAN FLOOR, LANDSLIDES OR VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS NEAR THE SHORELINE. Newfoundland had a tsunami in 1929 Video Clip 1 Video Clip 2 ***Waves Assignment***
28 EROSION & DEPOSITION WEATHERED: THE BREAKDOWN OF ROCKS INTO SMALLER PARTICLES. EROSION: THE MOVING OF SEDIMENT (WEATHERED PARTICLES). DEPOSITION: WHEN ERODED MATERIAL IS DROPPED OR LEFT BEHIND. EROSION AND DEPOSITION HAVE A HUGE IMPACT ON OUR SHORELINES. Video Clip
29 HOW WAVES INTERACT WITH SHORELINES 1. THE SHAPE OF THE SHORELINE. WAVE ENERGY IS CONCENTRATED ON HEADLANDS AND SPREADS OUT AS IT REACHES BAYS. HEADLANDS ARE THE PARTS OF THE SHORE THAT STICK OUT FURTHEST IN THE WATER. BAYS ARE THE PARTS THAT STICK IN THE MOST.
30 2. THE SLOPE OF THE SHORELINE AS ROCKS RUB AGAINST EACH OTHER IN THE WAVE WATER, FRAGMENTS OF ROCKS ARE SMOOTHED OUT AND GROUND DOWN TO SMALLER PIECES (PEBBLES/SAND). IF THE SHORELINE HAS A STEEP SLOPE, THE FRAGMENTS WILL GET WASHED OUT TO SEA, LEAVING A VERY ROCKY SHORELINE. IF THE SHORELINE HAS A MORE GRADUAL SLOPE, THE ROCK FRAGMENTS WILL BUILD UP, CREATING A SANDY BEACH.
31 3. THE TYPE OF ROCK MATERIAL DEPENDING ON THE TYPE OF ROCK THAT THE SHORELINE IS MADE OF, THE WAVES CAN ERODE THE SHORELINE MORE QUICKLY. SOFTER ROCK, LIKE SANDSTONE, WILL ERODE AT A FASTER RATE THAN MORE RESISTANT TYPES, SUCH A SHALE. EX: THE RED ROCKS FOUND IN ST. GEORGE'S ERODE FASTER THAN THE CLIFFS OF BELL ISLAND IN CONCEPTION BAY. IF A SHORELINE IS MADE OF BOTH TYPES OF ROCK, YOU WILL SEE UNEVEN EROSION. THIS IS HOW HEADLANDS AND BAYS ARE FORMED. HEADLANDS ARE ALWAYS MADE OF A HARDER MATERIAL THAN BAYS ARE. Simulation
32 4. THE WAVE ENERGY: HIGHER WAVE ENERGY WILL ERODE A SHORELINE MORE QUICKLY THAN LOWER WAVE ENERGY WILL. PLACES THAT HAVE MORE WIND WILL HAVE STRONGER WAVES WITH MORE ENERGY.
33 BEACHES HOW EROSION AND DEPOSITION AFFECT... SAND AND SEDIMENT ARE ALWAYS BEING REMOVED (ERODED) AND DEPOSITED BY WAVES. SEDIMENTS ARE DEPOSITED BY SIZE. SHOALS & SAND BARS DEPOSITION OF SEDIMENTS RESULTING IN LOCALIZED SHALLOWING OF THE WATER. SEA CAVES HEADLANDS ARE ERODED PART WAY THROUGH THE HEADLAND. SEA ARCHES OCCURS WHEN A SEA CAVE IS ERODED ALL THE WAY THROUGH THE HEADLAND. SEA STACKS OCCURS WHEN THE TOP OF A SEA ARCH BECOMES WEAK AND CAVES IN (EROSION). HEADLAND SEA CAVE SEA ARCH SEA STACK
34
35 PRACTICE PAGE 69 #'S 1-5 PAGE 77 #'S 1-2, 4-5, 9 EROSION AND LANDFORM ASSIGNMENT
36 TIDES THE SLOW RISE AND FALL OF THE WATER LEVEL OF THE OCEAN. THE UPPER AND LOWER EDGES OF A BEACH ARE DETERMINED BY THE HIGH- AND-LOW TIDE MARK. CONNECTED TO THE MOTION OF THE MOON AND SPINNING OF THE EARTH MOON EXERTS A GREATER FORCE OF PULL THAN SUN SINCE IT IS CLOSER TO THE EARTH. TIDAL RANGE: THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN HIGH AND LOW TIDES
37 1. SPRING TIDE TYPES OF TIDES: OCCURS TWICE A MONTH WHEN EARTH, SUN AND MOON ARE IN A LINE. TIDAL RANGE IS GREATEST. CAUSES EXTRA HIGH AND LOW TIDES. EXTRA PULL MEANS EXTRA TIDAL DIFFERENCE 2. NEAP TIDE OCCURS TWICE A MONTH WHEN SUN AND MOON ARE AT RIGHT ANGLES TO ONE ANOTHER. WATER IS GETTING PULLED IN TWO DIRECTIONS, WHICH CANCELS OUT THE OVERALL EFFECT. TIDAL RANGE IS SMALLEST. VIDEO
38 TECHNOLOGIES DESIGNED TO CONTAIN DAMAGE DUE TO WAVES: 1. BREAKWATERS: A BARRIER THAT PROTECTS A HARBOR OR SHORE FROM THE FULL IMPACT OF WAVES. 2. JETTIES/WHARVES: A STRUCTURE (PIER), THAT PROJECTS INTO A BODY OF WATER TO INFLUENCE THE CURRENT OR TIDE OR TO PROTECT A HARBOR OR SHORELINE FROM STORMS AND EROSION.
39 3. VEGETATION: PLANTS ALONG THE SHORELINE CAN KEEP EROSION FROM AFFECTING SHORELINE. 4. SEA WALLS: PROTECTIVE STRUCTURES OF STONE OR CONCRETE. EXTEND FROM SHORE INTO WATER TO PREVENT BEACH FROM WASHING AWAY.
40 PRACTICE TIDES AND TECHNOLOGY ASSIGNMENT SEE YOUR NOTES AND TEXT BOOK TO ANSWER THESE QUESTIONS: PAGE 77: #'S 1, 3, 4, 5, 8, 10, 11 PAGE 78: #'S 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17, 21, 22, 24
Section 2.1 Ocean Basins. - Has helped determine where ocean basins are located. - Tectonic plates move changing the position of the continents.
 Science 8 Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2: Oceans Control the Water Cycle Section 2.1 Ocean Basins Oceans are important because: 1. Primary water source for the water cycle 2. Control weather
Science 8 Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2: Oceans Control the Water Cycle Section 2.1 Ocean Basins Oceans are important because: 1. Primary water source for the water cycle 2. Control weather
Grade 8 Science. Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2
 Grade 8 Science Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2 Oceans are important... 1. Primary water source for the water cycle 2. Control weather 3. Support diverse life 4. Provides humans with food, minerals,
Grade 8 Science Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2 Oceans are important... 1. Primary water source for the water cycle 2. Control weather 3. Support diverse life 4. Provides humans with food, minerals,
Science 8 - Water Systems Test - Chapters 1-2
 Science 8 - Water Systems Test - Chapters 1-2 Multiple Choice (30 marks) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What percentage represents the amount of fresh
Science 8 - Water Systems Test - Chapters 1-2 Multiple Choice (30 marks) Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What percentage represents the amount of fresh
Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2
 Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2 Create a mind map with the driving question, Why are Oceans Important? Remember: Why are oceans so important? Why are oceans so important? Primary water source
Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2 Create a mind map with the driving question, Why are Oceans Important? Remember: Why are oceans so important? Why are oceans so important? Primary water source
The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are
 11.1 Ocean Basins The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are w the Pacific w the Atlantic w the Indian w the Southern w the Arctic The
11.1 Ocean Basins The surface of the ocean floor is as varied as the land. The five major oceans, from largest to smallest, are w the Pacific w the Atlantic w the Indian w the Southern w the Arctic The
Science 8 Chapter 2 Section 1
 Science 8 Chapter 2 Section 1 Ocean Basins (pp. 38-51) The World s Oceans The five major oceans, in order from largest to smallest, are the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic The Southern
Science 8 Chapter 2 Section 1 Ocean Basins (pp. 38-51) The World s Oceans The five major oceans, in order from largest to smallest, are the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic The Southern
A physical feature of the Earth s surface
 Earth s Landforms A physical feature of the Earth s surface A physical feature of the Earth s surface LANDFORM Highest of Earth s physical features Highest of Earth s physical features MOUNTAIN Low area
Earth s Landforms A physical feature of the Earth s surface A physical feature of the Earth s surface LANDFORM Highest of Earth s physical features Highest of Earth s physical features MOUNTAIN Low area
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write or. 1.
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write or. 1.
The Marine Environment
 The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
The Marine Environment SECTION 16.1 Shoreline Features In your textbook, read about erosional landforms, beaches, estuaries, longshore currents, and rip currents. For each statement below, write true or
4. In areas where tectonic plates collide, the seafloor has deep. 5. In areas where tectonic plates separate, the seafloor has mid- ocean
 Name Date Hour Table Chapter 14 Lesson One- General Directions: Use the word bank below to complete each statement. NOT all terms are used. abyssal plains brackish water condensation energy freshwater
Name Date Hour Table Chapter 14 Lesson One- General Directions: Use the word bank below to complete each statement. NOT all terms are used. abyssal plains brackish water condensation energy freshwater
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE!
 ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
ARE YOU READY TO THINK? Look at the first slide THINK PAIR SHARE! WHAT PROMINENT FEATURE CAN YOU IDENTIFY IN THIS PICTURE? What do you think the different colors represent? Who might find such a picture
Oceanography. Oceanography is the study of the deep sea and shallow coastal oceans.
 Oceanography Oceanography is the study of the deep sea and shallow coastal oceans. Studying the Ocean Floor To determine the shape and composition of the ocean floor, scientists use techniques such as
Oceanography Oceanography is the study of the deep sea and shallow coastal oceans. Studying the Ocean Floor To determine the shape and composition of the ocean floor, scientists use techniques such as
water erosion lithosphere Describe the process of erosion and deposition. chemical weathering Dissolving limestone is an example of.
 At one time, there was one large island off the coast of Mississippi and now it is two separate islands. What caused the island to be split into two? water erosion The crust and the top part of the upper
At one time, there was one large island off the coast of Mississippi and now it is two separate islands. What caused the island to be split into two? water erosion The crust and the top part of the upper
Read Across America. Listen as I read for facts about Volcanoes. In the Shadow of the Volcano
 Read Across America Listen as I read for facts about Volcanoes. In the Shadow of the Volcano Constructive & Destructive Processes Earth s surface is always changing. Blowing wind and flowing water causes
Read Across America Listen as I read for facts about Volcanoes. In the Shadow of the Volcano Constructive & Destructive Processes Earth s surface is always changing. Blowing wind and flowing water causes
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 10, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 10, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Beaches are created by the actions of waves, tides,
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 10, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Beaches are created by the actions of waves, tides,
Ocean and Coastal Processes. Ocean Basins. Chapter 20. Ocean Basins and Plates. Ocean Terms. Sea Arch Bay-mouth Bar Spit Tombolo Coast.
 Chapter 20 Ocean Basins and Plates Ocean and Coastal Processes Tide Wave Height Length Period Base Refraction Tsunami Beach Sea stack Ocean Terms Sea Arch Bay-mouth Bar Spit Tombolo Coast Emergent Submergent
Chapter 20 Ocean Basins and Plates Ocean and Coastal Processes Tide Wave Height Length Period Base Refraction Tsunami Beach Sea stack Ocean Terms Sea Arch Bay-mouth Bar Spit Tombolo Coast Emergent Submergent
Earth Science S5E1b (EarthScienceS5E1b)
 Name: Date: 1. The flattest part of the ocean floor is the A. trench. B. abyssal plain. C. continental shelf. D. mid-ocean rift valley. 2. Which causes some parts of the ocean to be saltier than other
Name: Date: 1. The flattest part of the ocean floor is the A. trench. B. abyssal plain. C. continental shelf. D. mid-ocean rift valley. 2. Which causes some parts of the ocean to be saltier than other
Social Studies. Chapter 2 Canada s Physical Landscape
 Social Studies Chapter 2 Canada s Physical Landscape Introduction Canada s geography its landforms and climate - has a great impact on Canadians sense of identity. Planet Earth The earth is divided into
Social Studies Chapter 2 Canada s Physical Landscape Introduction Canada s geography its landforms and climate - has a great impact on Canadians sense of identity. Planet Earth The earth is divided into
Chapter 17. Ocean and Coastal Processes
 Chapter 17 Ocean and Coastal Processes Ocean Basins and Plates Ocean Basins Ocean Basins are profoundly different from the continents. Ocean crust is thin and dense and young. New ocean crust is generated
Chapter 17 Ocean and Coastal Processes Ocean Basins and Plates Ocean Basins Ocean Basins are profoundly different from the continents. Ocean crust is thin and dense and young. New ocean crust is generated
OCEANOGRAPHY II NOTES
 TIDES OCEANOGRAPHY II NOTES MRS. BURKEY EARTH SPACE SCIENCE CY CREEK HS THE RISE AND FALL IN SEA LEVEL IS CALLED A TIDE. CAUSED BY A GIANT WAVE. AVERAGE LOW-TIDE/HIGH-TIDE CYCLE TAKES ABOUT 12 HRS AND
TIDES OCEANOGRAPHY II NOTES MRS. BURKEY EARTH SPACE SCIENCE CY CREEK HS THE RISE AND FALL IN SEA LEVEL IS CALLED A TIDE. CAUSED BY A GIANT WAVE. AVERAGE LOW-TIDE/HIGH-TIDE CYCLE TAKES ABOUT 12 HRS AND
I. Earth s Layers a. Crust: Earth s outside layer. Made of mostly rock. i. Continental: er; made of mostly granite, forms the continents and shallow
 I. Earth s Layers a. Crust: Earth s outside layer. Made of mostly rock. i. Continental: er; made of mostly granite, forms the continents and shallow sea beds, floats! ii. Oceanic: er; dense rock such as
I. Earth s Layers a. Crust: Earth s outside layer. Made of mostly rock. i. Continental: er; made of mostly granite, forms the continents and shallow sea beds, floats! ii. Oceanic: er; dense rock such as
Social Studies 9 UNIT 2 GEOGRAPHIC INFLUENCES ON IDENTITY: PLACE AND PEOPLE
 Social Studies 9 UNIT 2 GEOGRAPHIC INFLUENCES ON IDENTITY: PLACE AND PEOPLE The Structure of the Earth To understand the forces that create Canada's physical landscape we must understand the structure
Social Studies 9 UNIT 2 GEOGRAPHIC INFLUENCES ON IDENTITY: PLACE AND PEOPLE The Structure of the Earth To understand the forces that create Canada's physical landscape we must understand the structure
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA
 UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
UNIT 3 GEOLOGY VOCABULARY FLASHCARDS THESE KEY VOCABULARY WORDS AND PHRASES APPEAR ON THE UNIT 3 CBA A map that shows Earth s Topographic Map surface topography, which is Earth s shape and features Contour
Changes to Land 5.7B. landforms: features on the surface of Earth such as mountains, hills, dunes, oceans and rivers
 All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut away land
All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut away land
Chemistry 8 Chapter 7 Review Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. Define Mass The amount of matter in a substance or object.
 Chemistry 8 Chapter 7 Review Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. Define Mass The amount of matter in a substance or object. 2. Define Volume The amount of space taken up by a substance or object. 3. What are the
Chemistry 8 Chapter 7 Review Kinetic Molecular Theory 1. Define Mass The amount of matter in a substance or object. 2. Define Volume The amount of space taken up by a substance or object. 3. What are the
Think about the landforms where you live. How do you think they have changed over time? How do you think they will change in the future?
 reflect All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut
reflect All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut
Chapter 2 Geography. Getting to know Earth
 Chapter 2 Geography Getting to know Earth Our Solar System Sun is at the center of our solar system Contains a lot of Mass» Mass gives the Sun gravitational pull» This keeps the planets in our solar system
Chapter 2 Geography Getting to know Earth Our Solar System Sun is at the center of our solar system Contains a lot of Mass» Mass gives the Sun gravitational pull» This keeps the planets in our solar system
Unit 8 Test Review -- Oceanography
 Unit 8 Test Review -- Oceanography Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. D 1. A large body of saline water that may be surrounded by land is a(n)
Unit 8 Test Review -- Oceanography Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. D 1. A large body of saline water that may be surrounded by land is a(n)
What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using
 7 th Grade Lesson What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using the sentence frame. You have 4 minutes. Weathering is. This changes the Earth s surface because. 1
7 th Grade Lesson What is weathering and how does it change Earth s surface? Answer the question using the sentence frame. You have 4 minutes. Weathering is. This changes the Earth s surface because. 1
Objectives: Describe the structure of the ocean floor. Describe light intensity and temperature characteristics at different ocean depths.
 Ocean Structure Virtual Lab What are some characteristics of the ocean and the ocean floor? Earths highest mountains, deepest valleys, and flattest plains are found not on land but under the ocean. Beyond
Ocean Structure Virtual Lab What are some characteristics of the ocean and the ocean floor? Earths highest mountains, deepest valleys, and flattest plains are found not on land but under the ocean. Beyond
How does erosion happen?
 How does erosion happen? By National Geographic, adapted by Newsela staff on 10.03.17 Word Count 682 Level 830L These rock formations, in Bryce Canyon National Park, Utah, are called hoodoos. Although
How does erosion happen? By National Geographic, adapted by Newsela staff on 10.03.17 Word Count 682 Level 830L These rock formations, in Bryce Canyon National Park, Utah, are called hoodoos. Although
Oceanography II Notes
 Oceanography II Notes Tides The rise and fall in sea level is called a tide. Caused by a giant wave and the gravitational pull of the moon and sun on the ocean One low-tide/high-tide cycle takes about
Oceanography II Notes Tides The rise and fall in sea level is called a tide. Caused by a giant wave and the gravitational pull of the moon and sun on the ocean One low-tide/high-tide cycle takes about
1 Earth s Oceans. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify What are the five main oceans?
 CHAPTER 13 1 Earth s Oceans SECTION Exploring the Oceans BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What affects the salinity of ocean water? What affects
CHAPTER 13 1 Earth s Oceans SECTION Exploring the Oceans BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What affects the salinity of ocean water? What affects
Unit 4 - Water. Earth s Interior. Earth s Interior. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Continental Drift. Crust. Mantle. Core.
 Unit 4 - Water How did the oceans form? What special adaptations do saltwater organisms have? Where does our water come from? How do humans affect the Earth s water? Crust Rigid outer shell of Earth Oceanic
Unit 4 - Water How did the oceans form? What special adaptations do saltwater organisms have? Where does our water come from? How do humans affect the Earth s water? Crust Rigid outer shell of Earth Oceanic
Physical Geography A Living Planet
 Physical Geography A Living Planet The geography and structure of the earth are continually being changed by internal forces, like plate tectonics, and external forces, like the weather. Iguaçu Falls at
Physical Geography A Living Planet The geography and structure of the earth are continually being changed by internal forces, like plate tectonics, and external forces, like the weather. Iguaçu Falls at
Chapter 1 Section 2. Land, Water, and Climate
 Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
Essential Question: How are the geological features that exist on land similar to the geological features on the ocean floor?
 Essential Question: How are the geological features that exist on land similar to the geological features on the ocean floor? Geography of the Oceans The world ocean can be divided into four main ocean
Essential Question: How are the geological features that exist on land similar to the geological features on the ocean floor? Geography of the Oceans The world ocean can be divided into four main ocean
Seas. A sea is a part of an ocean that is nearly surrounded by water. The Mediterranean, Arctic and Black Sea are really part of the Atlantic Ocean.
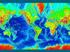 Exploring the Ocean Since ancient times people have studied the ocean such as waters and ocean floor It provides food and services, and serves as a route for trade and travel The World s Oceans 71% of
Exploring the Ocean Since ancient times people have studied the ocean such as waters and ocean floor It provides food and services, and serves as a route for trade and travel The World s Oceans 71% of
What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley
 1 What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley Alfred Wegener s theory of continental drift was 2 not accepted by scientists when the theory was first proposed.
1 What type of land feature is located at Point A? A Cliff B Delta C Mountain D Valley Alfred Wegener s theory of continental drift was 2 not accepted by scientists when the theory was first proposed.
Bathymetry Measures the vertical distance from the ocean surface to mountains, valleys, plains, and other sea floor features
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools.
Objectives. Vocabulary
 Shoreline Features Objectives Explain how shoreline features are formed and modified by marine processes. Describe the major erosional and depositional shoreline features. Vocabulary wave refraction beach
Shoreline Features Objectives Explain how shoreline features are formed and modified by marine processes. Describe the major erosional and depositional shoreline features. Vocabulary wave refraction beach
Chapter 2 Planet Earth
 Chapter 2 Planet Earth Section Notes Earth and the Sun s Energy Water on Earth The Land Close-up The Water Cycle World Almanac Major Eruptions in the Ring of Fire Quick Facts Chapter 2 Visual Summary Video
Chapter 2 Planet Earth Section Notes Earth and the Sun s Energy Water on Earth The Land Close-up The Water Cycle World Almanac Major Eruptions in the Ring of Fire Quick Facts Chapter 2 Visual Summary Video
Chapter Overview. Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry
 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
deep within the planet. They are also shaped by conditions on the planet s surface. In
 Chapter 4 Landforms, Water, and Natural Resources Earth is home to many different types of landforms. These landforms are shaped by forces deep within the planet. They are also shaped by conditions on
Chapter 4 Landforms, Water, and Natural Resources Earth is home to many different types of landforms. These landforms are shaped by forces deep within the planet. They are also shaped by conditions on
Chapter 2: Physical Geography
 Chapter 2: Physical Geography Pg. 39-68 Learning Goals for Chp2: q q q q q Explain how the Earth moves in space and why seasons change. Outline the factors that influence climate and recognize different
Chapter 2: Physical Geography Pg. 39-68 Learning Goals for Chp2: q q q q q Explain how the Earth moves in space and why seasons change. Outline the factors that influence climate and recognize different
Geol 117 Lecture 18 Beaches & Coastlines. I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition:
 I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
4 Tides. What causes tides? How do tides vary?
 CHAPTER 14 4 Tides SECTION The Movement of Ocean Water BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What causes tides? How do tides vary? National Science
CHAPTER 14 4 Tides SECTION The Movement of Ocean Water BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What causes tides? How do tides vary? National Science
Science 8 Unit 1 Test Review Analyze factors that affect productivity and species distribution in marine and fresh water environments.
 Science 8 Unit 1 Test Review How does water shape our world? 1. Define a water system in your own words 2. What is water important for? (3 things at least) 3. What is water made of? Water in our world
Science 8 Unit 1 Test Review How does water shape our world? 1. Define a water system in your own words 2. What is water important for? (3 things at least) 3. What is water made of? Water in our world
Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor
 Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 3 Marine Provinces 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 3 Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean
Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 3 Marine Provinces 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 3 Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean
Slow and Steady By ReadWorks
 By ReadWorks How did all the amazing things on our planet form? How did magnificent mountain ranges rise up in one place and beautiful beaches form elsewhere? Why do some places experience earthquakes
By ReadWorks How did all the amazing things on our planet form? How did magnificent mountain ranges rise up in one place and beautiful beaches form elsewhere? Why do some places experience earthquakes
Exploring Geography. Chapter 1
 Exploring Geography Chapter 1 The Study of Geography Geography is the study of where people, places, and things are located and how they relate to each other. Greek meaning writing about or describing
Exploring Geography Chapter 1 The Study of Geography Geography is the study of where people, places, and things are located and how they relate to each other. Greek meaning writing about or describing
WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE
 UNIT 8 WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH... 2 2 THE FORMATION OF THE RELIEF: INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FORCES.... 2 2.1 Internal forces:
UNIT 8 WHAT IS THE EARTH MADE OF? LITHOSPHERE AND HYDROSPHERE TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH... 2 2 THE FORMATION OF THE RELIEF: INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FORCES.... 2 2.1 Internal forces:
Physical Oceanography
 Physical Oceanography SECTION 15.1 The Oceans In your textbook, read about modern oceanography. For each item in Column A, write the letter of the matching item in Column B. e b c d a Column A 1. German
Physical Oceanography SECTION 15.1 The Oceans In your textbook, read about modern oceanography. For each item in Column A, write the letter of the matching item in Column B. e b c d a Column A 1. German
STAAR 2013 #20; RC3; Readiness 1. Glaciers are masses of ice that move slowly on land. Which of these features was most likely formed by a glacier?
 Earth oot amp #1 5.7 Recognize how landforms such as deltas, canyons, and sand dunes are the result of changes to Earth s surface by wind, water, and ice. STR 2013 #20; R3; Readiness 1. Glaciers are masses
Earth oot amp #1 5.7 Recognize how landforms such as deltas, canyons, and sand dunes are the result of changes to Earth s surface by wind, water, and ice. STR 2013 #20; R3; Readiness 1. Glaciers are masses
SCIENCE TEST1 (VWILLIAMSSCIENCETEST1)
 Name: Date: 1. In which of the following areas would soil erosion MOST LIKELY occur if they received the same amount of rainfall? A. a forest B. flat agricultural lands C. agricultural lands on steep slopes
Name: Date: 1. In which of the following areas would soil erosion MOST LIKELY occur if they received the same amount of rainfall? A. a forest B. flat agricultural lands C. agricultural lands on steep slopes
In 1990, 50% of the U.S. population lived within 75 km of a coast. By 2010, 75% of the U.S. population will live within 75 km of a coast.
 In 1990, 50% of the U.S. population lived within 75 km of a coast. By 2010, 75% of the U.S. population will live within 75 km of a coast. High Tech Methods for Surveying the Deep Sea Floor Fig. 20.18 1
In 1990, 50% of the U.S. population lived within 75 km of a coast. By 2010, 75% of the U.S. population will live within 75 km of a coast. High Tech Methods for Surveying the Deep Sea Floor Fig. 20.18 1
1. Erosion by Running Water Most powerful cause of erosion
 I. Destructive Forces Notes: Destructive force: a process in which land is destroyed or changed such as weathering and erosion. All landforms are a result of a combination of constructive and destructive
I. Destructive Forces Notes: Destructive force: a process in which land is destroyed or changed such as weathering and erosion. All landforms are a result of a combination of constructive and destructive
Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition. The Big Question:
 Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition The Big Question: 1 Design a way to represent and describe the 4 types of mass movement. You may use pictures, diagrams, list, web, chart, etc 2 Chapter 3: Erosion and
Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition The Big Question: 1 Design a way to represent and describe the 4 types of mass movement. You may use pictures, diagrams, list, web, chart, etc 2 Chapter 3: Erosion and
Plate Tectonics. Chapter 17. Great Idea: The entire Earth is still changing, due to the slow convection of soft, hot rocks deep within the planet.
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 17 Great Idea: The entire Earth is still changing, due to the slow convection of soft, hot rocks deep within the planet. 1 Chapter Outline The Dynamic Earth Plate Tectonics: A Unifying
Plate Tectonics Chapter 17 Great Idea: The entire Earth is still changing, due to the slow convection of soft, hot rocks deep within the planet. 1 Chapter Outline The Dynamic Earth Plate Tectonics: A Unifying
8 th Grade Science Plate Tectonics and Topography Review
 8 th Grade Science Plate Tectonics and Topography Review #1 Scientists believe that the land masses of Earth were once joined together as one supercontinent called. A: Australia B: Wegner C: Pangaea D:
8 th Grade Science Plate Tectonics and Topography Review #1 Scientists believe that the land masses of Earth were once joined together as one supercontinent called. A: Australia B: Wegner C: Pangaea D:
Constructive & Destructive Forces
 Constructive & Destructive Forces Intro: Constructive Forces Processes that create landforms. Destructive Forces Processes that destroy landforms. Intro: Constructive Forces Volcanoes Deposition Landslides
Constructive & Destructive Forces Intro: Constructive Forces Processes that create landforms. Destructive Forces Processes that destroy landforms. Intro: Constructive Forces Volcanoes Deposition Landslides
Directed Reading. Section: The Water Planet. surface is called the a. Earth s ocean. b. Pacific Ocean. c. salt-water ocean. d. global ocean.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Water Planet 1. The body of salt water covering nearly three-quarters of the Earth s surface is called the a. Earth s ocean. b. Pacific Ocean. c. salt-water
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Water Planet 1. The body of salt water covering nearly three-quarters of the Earth s surface is called the a. Earth s ocean. b. Pacific Ocean. c. salt-water
Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface
 Oceanography Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface An ocean must be large and have features which set it apart from other oceans (currents, water
Oceanography Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface An ocean must be large and have features which set it apart from other oceans (currents, water
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY
 MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Bathymetry BATHYMETRY BATHYMETRY THE UNDERWATER EQUIVALENT TO TOPOGRAPHY THE STUDY OF WATER DEPTH A BATHYMETRIC MAP SHOWS FLOOR RELIEF OR TERRAIN AS CONTOUR LINES Bathymetry
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Bathymetry BATHYMETRY BATHYMETRY THE UNDERWATER EQUIVALENT TO TOPOGRAPHY THE STUDY OF WATER DEPTH A BATHYMETRIC MAP SHOWS FLOOR RELIEF OR TERRAIN AS CONTOUR LINES Bathymetry
Earth s Dynamic Surface
 Earth s Dynamic Surface Key Concepts What is the difference between physical and chemical weathering? How do water, ice, and wind change Earth s surface? Changing Earth s Surface What do you think? Read
Earth s Dynamic Surface Key Concepts What is the difference between physical and chemical weathering? How do water, ice, and wind change Earth s surface? Changing Earth s Surface What do you think? Read
6th Grade Science Sample Assessment Items S6E3c.
 Composition 6th Grade Science Sample Assessment Items Ocean water differs from freshwater in that it has. A. a lower temperature B. a higher temperature C. a higher concentration of silicon dioxide D.
Composition 6th Grade Science Sample Assessment Items Ocean water differs from freshwater in that it has. A. a lower temperature B. a higher temperature C. a higher concentration of silicon dioxide D.
Chapter 2 Earth s Interlocking Systems pg The Earth and Its Forces pg
 Chapter 2 Earth s Interlocking Systems pg. 24 55 2 1 The Earth and Its Forces pg. 27 33 Connecting to Your World and Internal Forces Shaping the Earth The Earth is unique in the solar system because it
Chapter 2 Earth s Interlocking Systems pg. 24 55 2 1 The Earth and Its Forces pg. 27 33 Connecting to Your World and Internal Forces Shaping the Earth The Earth is unique in the solar system because it
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Grade 9 Social Studies Canadian Identity. Chapter 2 Review Canada s Physical Landscape
 Grade 9 Social Studies Canadian Identity Chapter 2 Review Canada s Physical Landscape Name: Unit 1: Empowerment Terms (notes or textbook) 1. Core 2. Crust 3. Mantle 4. Magma 5. Continental drift 6. Plate
Grade 9 Social Studies Canadian Identity Chapter 2 Review Canada s Physical Landscape Name: Unit 1: Empowerment Terms (notes or textbook) 1. Core 2. Crust 3. Mantle 4. Magma 5. Continental drift 6. Plate
Section 1: The Geosphere
 Section 1: The Geosphere Preview Classroom Catalyst Objectives The Earth as a System Discovering Earth s Interior The Composition of the Earth The Structure of the Earth Plate Tectonics Section 1: The
Section 1: The Geosphere Preview Classroom Catalyst Objectives The Earth as a System Discovering Earth s Interior The Composition of the Earth The Structure of the Earth Plate Tectonics Section 1: The
Name Date Class. How have geologists learned about Earth s inner structure? What are the characteristics of Earth s crust, mantle, and core?
 Chapter 4 Plate Tectonics Section 1 Summary Earth s Interior How have geologists learned about Earth s inner structure? What are the characteristics of Earth s crust, mantle, and core? Earth s surface
Chapter 4 Plate Tectonics Section 1 Summary Earth s Interior How have geologists learned about Earth s inner structure? What are the characteristics of Earth s crust, mantle, and core? Earth s surface
TEACHER BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE. Surface Processes: Weathering and Erosion
 TEACHER BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE Surface Processes: Weathering and Erosion Core Concepts Precipitation (caused by the water cycle) and wind cause rocks to be broken into smaller pieces in the process called
TEACHER BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE Surface Processes: Weathering and Erosion Core Concepts Precipitation (caused by the water cycle) and wind cause rocks to be broken into smaller pieces in the process called
Do Now: Vocabulary: Objectives. Vocabulary: 1/5/2016. Wegener? (Can they move?) the idea that continents have moved over time?
 Do Now: 1. Who was Alfred Wegener? 2. What was Pangaea? 3. Are continents fixed? (Can they move?) 4. What evidence supports the idea that continents have moved over time? Objectives What evidence suggests
Do Now: 1. Who was Alfred Wegener? 2. What was Pangaea? 3. Are continents fixed? (Can they move?) 4. What evidence supports the idea that continents have moved over time? Objectives What evidence suggests
Vocabulary Words. theory continental drift fault magma lava. weathering glacier erosion deposition delta
 Earth s Landforms Vocabulary Words theory continental drift fault magma lava weathering glacier erosion deposition delta Theory: A possible explanation. Continental drift: The continuing movement of the
Earth s Landforms Vocabulary Words theory continental drift fault magma lava weathering glacier erosion deposition delta Theory: A possible explanation. Continental drift: The continuing movement of the
PLATE TECTONICS. SECTION 17.1 Drifting Continents
 Date Period Name PLATE TECTONICS SECTION.1 Drifting Continents In your textbook, read about continental drift. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes each statement. 1. Early mapmakers thought
Date Period Name PLATE TECTONICS SECTION.1 Drifting Continents In your textbook, read about continental drift. Circle the letter of the choice that best completes each statement. 1. Early mapmakers thought
Almost of Earth is covered by water. On a map, the continents appear as huge islands surrounded by a vast global ocean.
 Earth s Oceans & Ocean Floor Date: Feelin Blue What are Earth s five main oceans? Almost of Earth is covered by water. On a map, the continents appear as huge islands surrounded by a vast global ocean.
Earth s Oceans & Ocean Floor Date: Feelin Blue What are Earth s five main oceans? Almost of Earth is covered by water. On a map, the continents appear as huge islands surrounded by a vast global ocean.
Erosion and Deposition
 Erosion and Deposition The Erosion-Deposition Process What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Erosion and Deposition The Erosion-Deposition Process What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Erosion and Deposition
 Erosion and Deposition Erosion Sediment natural forces move rock/soil from one place to another. gravity, water, wind, glaciers, waves are causes material moved by erosion Deposition when erosion lays
Erosion and Deposition Erosion Sediment natural forces move rock/soil from one place to another. gravity, water, wind, glaciers, waves are causes material moved by erosion Deposition when erosion lays
4. An object vibrating faster will have a higher frequency and a higher: 5. Sound is a wave.
 Name : Put a check in the box each time you answer the question correctly Science Review checklist Part Two Cover the right column with a piece of paper or your hand. Answer the question and check your
Name : Put a check in the box each time you answer the question correctly Science Review checklist Part Two Cover the right column with a piece of paper or your hand. Answer the question and check your
Question: What is the primary reason for the great abundance of fish along the Peruvian coast?
 Buzzer Question # 1 Question Type: toss-up Question Format: Multiple Choice Category: Biology What is the primary reason for the great abundance of fish along the Peruvian coast? Answer W: upwelling Answer
Buzzer Question # 1 Question Type: toss-up Question Format: Multiple Choice Category: Biology What is the primary reason for the great abundance of fish along the Peruvian coast? Answer W: upwelling Answer
Weathering of Rocks. Weathering - Breakdown of rocks into pieces (sediment) 2 main types of weathering to rocks
 Weathering of Rocks Weathering - Breakdown of rocks into pieces (sediment) 2 main types of weathering to rocks Mechanical weathering requires physical forces to break rocks into smaller pieces. Chemical
Weathering of Rocks Weathering - Breakdown of rocks into pieces (sediment) 2 main types of weathering to rocks Mechanical weathering requires physical forces to break rocks into smaller pieces. Chemical
Tips for Success on a Test
 Number of Incorrect: Final Grade: Parent Signature: Top Tips for Success on a Test 1. Read the following statements at least two times. 2. Circle the key words in each question/ or statement. (*Remember
Number of Incorrect: Final Grade: Parent Signature: Top Tips for Success on a Test 1. Read the following statements at least two times. 2. Circle the key words in each question/ or statement. (*Remember
The Dynamic Earth Section 1. Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 1: The Geosphere DAY 1
 Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 1: The Geosphere DAY 1 The Earth as a System The Earth is an integrated system that consists of rock, air, water, and living things that all interact with each other.
Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 1: The Geosphere DAY 1 The Earth as a System The Earth is an integrated system that consists of rock, air, water, and living things that all interact with each other.
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY
 MARINE GEOLOGY MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Marine Geology 4 LAYERS OF THE EARTH CRUST THICKNESS: VARIES BETWEEN OCEAN & CONTINENTS 5-40 KM STATE: SOLID ELEMENTS: SILICON, ALUMINUM, CALCIUM, SODIUM, POTASSIUM
MARINE GEOLOGY MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Marine Geology 4 LAYERS OF THE EARTH CRUST THICKNESS: VARIES BETWEEN OCEAN & CONTINENTS 5-40 KM STATE: SOLID ELEMENTS: SILICON, ALUMINUM, CALCIUM, SODIUM, POTASSIUM
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Chapter 18, Seafloor Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Abyssal fans are made
Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Chapter 18, Seafloor Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Abyssal fans are made
Earth Boot Camp. 3.7B: Investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes and landslides.
 Earth Boot Camp 3.7B: Investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes and landslides. Release Questions 2006 #21 (65%) 1. In which of these ways can volcanoes help
Earth Boot Camp 3.7B: Investigate rapid changes in Earth s surface such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes and landslides. Release Questions 2006 #21 (65%) 1. In which of these ways can volcanoes help
core mantle crust the center of the Earth the middle layer of the Earth made up of molten (melted) rock
 core the center of the Earth mantle the middle layer of the Earth made up of molten (melted) rock crust the surface layer of the Earth that includes the continents and oceans 1 continental drift the theory
core the center of the Earth mantle the middle layer of the Earth made up of molten (melted) rock crust the surface layer of the Earth that includes the continents and oceans 1 continental drift the theory
Earth / Environmental Science. Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR
 Earth / Environmental Science Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR The Blue Planet Nearly 70% of the Earth s surface is covered by the global ocean It was not until the 1800s that the ocean became an important focus
Earth / Environmental Science Ch. 14 THE OCEAN FLOOR The Blue Planet Nearly 70% of the Earth s surface is covered by the global ocean It was not until the 1800s that the ocean became an important focus
Physical Oceanography
 Physical Oceanography SECTION 15.1 The Oceans In your textbook, read about modern oceanography. For each item in Column A, write the letter of the matching item in Column B. Column A 1. German research
Physical Oceanography SECTION 15.1 The Oceans In your textbook, read about modern oceanography. For each item in Column A, write the letter of the matching item in Column B. Column A 1. German research
1/6/ th Grade Earth s Surface. Chapter 3: Erosion and Deposition. Lesson 1 (Mass Movement)
 Lesson 1 (Mass Movement) 7 th Grade Earth s Surface Chapter 3: Erosion and Deposition Weathering the chemical and physical processes that break down rock at Earth s surface Mechanical weathering when rock
Lesson 1 (Mass Movement) 7 th Grade Earth s Surface Chapter 3: Erosion and Deposition Weathering the chemical and physical processes that break down rock at Earth s surface Mechanical weathering when rock
Plate Tectonics. Chapter 8
 Plate Tectonics Chapter 8 Vocabulary Crust Mantle Core Lithosphere Continental Drift Plate Tectonics Plate Boundary Fault What Are The Earth s Layers Made Of? Atmosphere: Contains nitrogen, oxygen, carbon
Plate Tectonics Chapter 8 Vocabulary Crust Mantle Core Lithosphere Continental Drift Plate Tectonics Plate Boundary Fault What Are The Earth s Layers Made Of? Atmosphere: Contains nitrogen, oxygen, carbon
Ocean Scavenger Hunt. Materials: pencil study notes timer. Directions:
 Ocean Scavenger Hunt Materials: pencil study notes timer Directions: 1. Each student receives a copy of the scavenger hunt, placed upside down on their desk. 2. Explain to students that they will scavenge
Ocean Scavenger Hunt Materials: pencil study notes timer Directions: 1. Each student receives a copy of the scavenger hunt, placed upside down on their desk. 2. Explain to students that they will scavenge
4 Deforming the Earth s Crust
 CHAPTER 7 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust SECTION Plate Tectonics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What happens when rock is placed under stress?
CHAPTER 7 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust SECTION Plate Tectonics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What happens when rock is placed under stress?
Small area of the ocean that is partially surrounded by land. The Ocean Basins. Three Major Oceans. Three Major Oceans. What is a SEA?
 The Ocean Basins How Deep is the Ocean? 1 2 Three Major Oceans Three Major Oceans Pacific Atlantic the shallowest ocean (3.3km average depth) Indian second shallowest ocean (3.8km average depth) Pacific
The Ocean Basins How Deep is the Ocean? 1 2 Three Major Oceans Three Major Oceans Pacific Atlantic the shallowest ocean (3.3km average depth) Indian second shallowest ocean (3.8km average depth) Pacific
TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID: GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom
 TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID:1542715 GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom Geology part 1 Page 1 of 6 Student: Class: Date: 1. The picture below shows
TEST NAME:Geology part 1 TEST ID:1542715 GRADE:06 - Sixth Grade SUBJECT:Life and Physical Sciences TEST CATEGORY: My Classroom Geology part 1 Page 1 of 6 Student: Class: Date: 1. The picture below shows
1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere
 CHAPTER 15 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is Earth s atmosphere made of? How
CHAPTER 15 1 Characteristics of the Atmosphere SECTION The Atmosphere BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is Earth s atmosphere made of? How
Test on Chapters 7-11 Monday, April 28, 2014 No Calculator Required
 Test on Chapters 7-11 Monday, April 28, 2014 No Calculator Required Chapter Sections: Oceans: 7.1 7.2 7.4 Bathymetry: 8.3 Earth s Interior: 10.1 10.2 10.3 Plate Tectonics: 11.1 11.2 11.3 Study/Review:
Test on Chapters 7-11 Monday, April 28, 2014 No Calculator Required Chapter Sections: Oceans: 7.1 7.2 7.4 Bathymetry: 8.3 Earth s Interior: 10.1 10.2 10.3 Plate Tectonics: 11.1 11.2 11.3 Study/Review:
GRADE 7 SCIENCE UNIT 4: THE EARTH S CRUST. 11/12 Earth s Crust is constantly changing Weathering and Erosion
 GRADE 7 SCIENCE UNIT 4: THE EARTH S CRUST 11/12 Earth s Crust is constantly changing Weathering and Erosion Earth s Structure - Layers of the Earth Draw a labeled Diagram Layers of the Earth Rap s https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q9j1xgaxyzy
GRADE 7 SCIENCE UNIT 4: THE EARTH S CRUST 11/12 Earth s Crust is constantly changing Weathering and Erosion Earth s Structure - Layers of the Earth Draw a labeled Diagram Layers of the Earth Rap s https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q9j1xgaxyzy
Erosion and Deposition
 CHAPTER 3 LESSON 2 Erosion and Deposition Landforms Shaped by Water and Wind Key Concepts What are the stages of stream development? How do water erosion and deposition change Earth s surface? How do wind
CHAPTER 3 LESSON 2 Erosion and Deposition Landforms Shaped by Water and Wind Key Concepts What are the stages of stream development? How do water erosion and deposition change Earth s surface? How do wind
Section 1: Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics Section 2: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 3: Minerals and Rocks Section 4: Weathering and Erosion
 Section 1: Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics Section 2: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 3: Minerals and Rocks Section 4: Weathering and Erosion Key Terms Crust Mantle Core Lithosphere Plate Tectonics
Section 1: Earth s Interior and Plate Tectonics Section 2: Earthquakes and Volcanoes Section 3: Minerals and Rocks Section 4: Weathering and Erosion Key Terms Crust Mantle Core Lithosphere Plate Tectonics
