The elastic crustal response to seasonal water mass changes in the Amazon basin
|
|
|
- Job Woods
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Escola Politécnica da Universidade de São Paulo The elastic crustal response to seasonal water mass changes in the Amazon basin Prof. Dr. Denizar Blitzkow (1) Sônia Maria Alves Costa (2) Dra. Ana Cristina Oliveira Cancoro de Matos (1) (1)Laboratory of Topography and Geodesy Department of Transportation Engineering University of São Paulo (2)Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics Coordination of Geodesy Geociences Division IVth Scientific Meeting of the ORE-HYBAM, Lima (Peru), 6-96 September 2011
2 Motivation Improvement in the understanding of water cycle in Amazon region and its relation with vertical component variation; Application of two different space geodetic measurement techniques GPS and GRACE in order to analyze the water cycle and its connection with the vertical displacement of the lithosphere; Crust response of the GPS due to water loading; GRACE Equivalent Water Height and the relationship with water storage; In-situ data from ANA (Agência Nacional de Águas) gauge stations are available for the validation of GRACE models/grids; Selection of Gauge stations for this study within a radius of 100 km around GPS stations; Possibility for the estimation of the correlation coefficient between in-situ data and GRACE, anti-correlation of GPS and in-situ data, as well as phase differences between in-situ data and GRACE; Use of Wavelet Power Spectrum (WPS) in order to visualize phase evaluations between ANA and GRACE time series.
3 Data sets Period of study: 2007 to 2010 In-situ water level measurements provided by ANA from 84 gauge stations in Amazon, Tocantins and Paraná Basins. Informations and data available at: 10-day GRACE data geoid solutions computed by (Bruinsma et al., 2010; Lemoine et al., 2007): 145 files ( until ) expressed in Stokes coefficients up to degree 50 (i.e., ~450 km spatial resolution) corrected for atmospheric (ECMWF) and ocean tides (MOG-2D). Informations and data available at: Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) data from 24 continuous monitoring stations of Instituto Brasileiro de Geografía e Estatística (IBGE), Low-Latitude Ionospheric Sensor Network (LISN), Serviço Geológico Brasileiro and International GNSS Service (IGS). Informations and data available at: ftp://geoftp.ibge.gov.br (RBMC) (LISN) ftp://igscb.jpl.nasa.gov (IGS)
4 Region of Study with Basins/Sub-basins and Station's distribution
5 GNSS Network A total of 1461 days between years 2007 to 2010 (GPS weeks 1408 to 1616) from 35 stations located in South and Central America, with a densification in Amazon basin, were processed. Software used: Bernese, version 5.0, Bernese Processing Engine (BPE) Processing Strategy (parameters and models) Processing Strategy (parameters and models) Double Difference (DD) solutions using the ionosphere-free linear combination; Phase center corrections of antennas (receptor and satellites) were applied using IGS absolute calibration values, model IGS05; Satellite orbits, EOPs from final combined solution IGS; New ambiguity resolution schedule was implemented applying 4 different strategies in a baseline-by-baseline mode performing the following steps: (1) Melbourne-Wuebbena approach (< 6000 km) (2) Quasi-Ionosphere-Free (QIF) approach (< 2000 km) (3) Phase-based widelane/narrowlane method (< 200 km) (4) Direct L1/L2 method (< 20 km) The ocean loading model used is the FES2004; Solid earth tidal displacement was corrected using the tide model TIDE2000 (IERS 2000). Ocean tides was corrected using OT CSR30 model (IERS 2003 ); Atmospheric parameters: the hydrostatic component of the zenith tropospheric delay was estimated each 2h applying the Niell mapping function.
6 GNSS Network Configuration
7 GNSS Data Analysis Position time series The position time series of stations were obtained from the daily double difference solutions. Each daily solution was aligned to the weekly IGS05 solutions applying minimum constraint strategy. The IGS05 stations used for the reference frame definition were: AREQ, BRFT, CHPI, CRO1, KOUR, LPGS, MANA, RIOP, SCUB and UNSA. Daily position evaluation The time series transformation parameters between daily and IGS05 weekly solutions were estimated in order to check the external fit of daily results. The RMS for the north (N), east (E) and up (U) components to be 1.4, 1.5 and 5.6 mm. Statistics of transformation parameters between daily solutions and IGS05 weekly solutions Mean StdDev TX(mm) TY(mm) TZ(mm) ROT_X(") ROT_Y(") ROT_Z(") SCALE(ppm)
8 Time series of transformation parameters between daily and IGS05 solutions
9 Peak to peak variation of vertical component Seasonal Amplitudes in the GPS stations Anual variation in vertical compoment (mm) GPS Stations The highest values occur between October and November when the ebb period of the river is finishing and rivers have the lowest water level. The lowest values of vertical component occur between April and May when the rain season is finishing and rivers are full of water (flood period).
10 Hydrological in-situ data collection and organization ANA in-situ data were collected from HIDROWED data base - Sistema de Informações Hidrológicas (HIDRO). The following parameters were used for data selection: Stations in a radius of 100 km from GNSS stations; Stations with data available for the period between 2007 to 2010; Stations installed in the main rivers of basins on the water stream ; From the daily data it was computed the Weighed Moving Average for intervals of 10 days and after that the hydrological station's time series were created using the GRACE Reference Dates (RD). OBS: The same procedure was applied for the GPS geometric heights after GNSS data processing.
11 GRACE data collection and organization The Equivalent Water Height (EWH) grids, second release (RL02), deduced from GRACE gravity field models (10-day models), computed by Centre National d Etudes Spatiales/Groupe de Recherches de Géodésie Spatiale (CNES/GRGS). For each 10-day GRACE geoids, the Stokes coefficients are converted into EWH coefficients, and then 1 x1 global grids of water thickness (in mm) are calculated, from degree 2 to 50. For the period between 2007 to 2010, there are 146 grids. The horizontal coordinates of the hydrological stations were interpolated by applying a bi-linear algorithm to the EWH grids and producing the EWH time series. The EWH grids and the hydrological in-situ data time series were used for the analysis of correlation coefficients, phase and amplitude.
12 Methodology For each 10-day geoid, the Stokes coefficients were converted into equivalent water height coefficients (Ramillien et al., 2005), and then 1 x1 global grid of water thickness (in mm) was calculated. From the ground-base station positions, GRACE-based water heights were interpolated by applying a bilinear algorithm to the gridded data. Thus, for the same position, satellite and ground-based data were compared. The reference date (RD) of each grid was taken as the day of the mid-10-day interval. The RD was used to compare GRACE water thickness (EWH) with daily in-situ water level data and GNSS, specifically on the same mean period of 10-day. A linear equation was assumed and fitted by least-square linear inversion: Y(t) = a X(t) + b (model), (Equation 1) where: GRACE X ANA ANA X GPS X(t): GRACE X(t): in situ data (ANA) Y(t): in situ data (ANA) Y(t): GPS a: transfer function slope coefficient b: Y-axis intersection value
13 RESULTS COEFFICIENT OF DETERMINATION (R²)( ) EVALUATION IN-SITU HYDROLOGICAL DATA X GRACE EWH Considerations about the climate (precipitation) and hydrogeology were taken into account when the coefficient of determination R² was analyzed. A good correlation (R² 0,7) is evident in 70% of hydrological stations ( on the water stream ) and the highest values are located between the end of Solimões and beginning of Amazon rivers, as well as in Madeira river and its tributaries, mainly in areas close to Colombia (Tabatinga) and Peru (Guajara-mirim). The low correlation (R² < 0,7) is found in Tocantins and Paraná basins, mainly close to Palmas, Imperatriz and Cuiabá. The same was observed in the north part of Amazon basin, close to São Gabriel da Cachoeira and Boa Vista. It was observed in these areas as well as in regions close to Amazonas mouth a delay between seasonal cycles of hydrological stations and Grace EWH. This is observed in the phase difference results from both observations. IN-SITU HYDROLOGICAL DATA X GPS Considering the GNSS and ANA data strong anti-correlations are found in Manaus, Urukuritiba, Porto Velho, Santarém, Altamira, Guajara-mirim, Marabá and Tefé areas in sedimentary and cenozoic domains; low anti-correlation is found in the neighbour basins (Tocantins and Paraná) and close to Amazonas mouth.
14 Coefficient of Determination between GRACE EWH and Hydrological Stations (ANA) The high coefficient of determination(r²>0.7) is found at the southern edge of the Amazon river and it indicates the strong relation between ANA and GRACE results.
15 (1a) (1b) city/station São Gabriel da Cachoeira basin Amazon river NEGRO state Amazonas latitude longitude Hydro-geological Domain Crystalline Distance GPS/ANA (Km) 3.12 ANA WL Phase (degree) ANA WL Ampli. (mm) GRACE EWH Phase (degree) GPS Phase (degree) Phase dif. (ANA GRACE) days GRACE EWH Ampli. (mm) GPS Ampli. (mm) Phase dif. (ANA GPS) days (1c)
16 coerence cross Wavelet Power Spectrum (WPS) São Gabriel da Cachoeira
17 (2a) (2b) city/station Marabá basin Tocantins river TOCANTINS state Pará latitude longitude Hydro-geological Domain Sedimentary Distance GPS/ANA (Km) 2.64 ANA WL Phase (degree) ANA WL Ampli. (mm) GRACE EWH Phase (degree) GRACE EWH Ampli. (mm) GPS Phase (degree) Phase dif. (ANA GRACE) days GPS Ampli. (mm) Phase dif. (ANA GPS) days (2c)
18 coerence cross Wavelet Power Spectrum (WPS) Marabá
19 (3a) (3b) city/station Porto Velho basin Amazon river MADEIRA state Rondonia latitude longitude Hydro-geological Domain Cenozoic Distance GPS/ANA (Km) 4.87 ANA WL Phase (degree) ANA WL Ampli. (mm) GRACE EWH Phase (degree) GRACE EWH Ampli. (mm) GPS Phase (degree) Phase dif. (ANA GRACE) days GPS Ampli. (mm) Phase dif. (ANA GPS) days (3c)
20 Wavelet Power Spectrum (WPS) Porto Velho coerence cross
21 (4a) (4b) city/station Manaus basin Amazon SOLIMÕES river AMAZONAS state Amazonas latitude longitude Hydro-geological Domain Sedimentary Distance GPS/ANA (Km) ANA WL Phase (degree) ANA WL Ampli. (mm) GRACE EWH Phase (degree) GRACE EWH Ampli. (mm) (4c) GPS Phase (degree) GPS Ampli. (mm) Phase dif. (ANA GRACE) days 3.27 Phase dif. (ANA GPS) days
22 coerence cross Wavelet Power Spectrum (WPS) Manaus
23 Phase(ANA X GRACE) Amplitudes comparison Amplitude(ANA between X GRACE) ANA and GRACE EWH Rivers Amp. ANA Amp. GRACE Amplitude (mm) Uraricoera_Boa_V. Tocantins_Palmas Xingú_Altamira Araguaia Tocantins_Impz Cuiabá Tocantins_Marabá Tapajós_Itaituba Teles Pires/Tapajós Jaru/Jiparana Araguari_Macapá Acre/Abuna_Riob Guama_Belém Guaporé/Branco Teles Pires/Tapajós Javari/Itaguai Madeira_Porto_V. Tapajós_Santarém Amaz./Solimões_Pari Amaz./Solimões_Tefé Amaz./Solimões_Letí Amaz./Solimões_Uruk Mamore_Guajara Amaz./Solimões_Nau Negro_Saga Phase Differences ANA X GRACE EWH Rivers Phase (degrees)
24 Phase differences between Hydrological Stations (ANA) and GRACE EWH from year The year 2009 was selected for the evaluation of phase differences due to highest precipitation recorded. It was observed that in most cases phase differences are negative varying between 0 to -10 in the Amazonas and Solimões rivers.
25 (a) Year 2007 (b) Year 2008 Precipitation (c) (c) Year Year2009 br/ (d) Year 2010
26 Hydro-geological Domains nfoid=756&sid=9
27 Phase in S.G. da Cachoeira ID_ANA YEAR AMPL ANA (mm) PHASE (dg) AMPL_EWH (mm) PHASE (dg) PHASE DIF (days) RIVER Negro Curicuriari Negro Curicuriari 2009 MAX MIN AVER Negro Considering the average phase difference between years 2007, 2008 and 2009, in S.G da Cachoeira an unusual behavior of GRACE EWH can be found. Phase is positive only in this part of Negro River, indicating that Grace EWH cycle is around 20 days in advance with respect to insitu data cycle
28 Time Series of water cycle in S.G. da Cachoeira Negative phase Positive phase River Negro Considering the average phase difference between years 2007, 2008 and 2009, in S.G da Cachoeira an unusual behavior of GRACE EWH can be found. Phase is positive only in this part of Negro River, indicating that Grace EWH cycle is around 20 days in advance with respect to in-situ data cycle.
29 RESULTS EVALUATION OF AMPLITUDE AND PHASE (ANA X GRACE EWH) The Year 2010 could not be included in this evaluation because the observations from the hydrological stations are not yet available. The highest amplitudes of GRACE EWH reach 500 mm in Manaus and Urukuritiba areas. The largest inter-annual amplitudes were observed between years 2008 and 2009 in both data. The highest amplitudes observed by in-situ data have a good agreement when compared with GRACE EWH observations, mainly in the biggest rivers in Amazon basin, like Amazonas, Solimões, Tapajós, Xingú and Madeira. In some cases the Grace EWH amplitudes are not proportional to the observed amplitudes by in-situ data. This is the case of Leticia, in the boundary between Brazil and Colombia. The high amplitude values are observed in 2007 in the north part of Amazon basin and in Amazon and Madeira rivers in % of phase differences are between -10 and -50, meaning that GRACE observations have a delay of ~ 10 to 50 days when compared with in-situ data. The wavelet analysis shows the same results. Positive phase between GRACE and in-situ data was found only in S. Gabriel da Cachoeira (Negro River).
30 Final Considerations This study is important for helping the understanding the hydrological cycle in Amazon basin and its connection with vertical component variation. Grace observations have in general a good response in Amazon Basin due to the great water level variation in this region. In the sedimentary areas of Amazon basin GRACE has a better response mainly in the biggest rivers like Amazonas, Solimões, Tapajós, Xingú and Madeira. For the future, it is planned to look after satellite altimetry in regions with poor hydrological in situ observations.
31 Future Work To evalutate GRACE grids of vertical deflection with GPS results, applying the same corrections in both data (atmospheric and ocean loading). To estimate the crust response based in phase differences of local observations and evaluating hydrogeologic domains. Acknowledgements ANA agency for the hydrometric stations data, CNPq for supporting this research, GRGS (Groupe de Recherche en Géodésie Spatiale) for Geopotential Models.
Activities in South America: Gravity and Geoid Projects
 Activities in South America: Gravity and Geoid Projects Segundo Taller de Grupo de Trabajo I SIRGAS Montevideo - Uruguay May 26 a 30, 2008 Maria Cristina Pacino Universidade de Rosário CGED - IBGE Denizar
Activities in South America: Gravity and Geoid Projects Segundo Taller de Grupo de Trabajo I SIRGAS Montevideo - Uruguay May 26 a 30, 2008 Maria Cristina Pacino Universidade de Rosário CGED - IBGE Denizar
EPUSP. ( Escola Politécnica da Universidade de São Paulo
 EPUSP Escola Politécnica da Universidade de São Paulo Present and Future of the gravity surveys and geoid model in South America Denizar Blitzkow Ana Cristina Oliveira Cancoro de Matos Gabriel do Nascimento
EPUSP Escola Politécnica da Universidade de São Paulo Present and Future of the gravity surveys and geoid model in South America Denizar Blitzkow Ana Cristina Oliveira Cancoro de Matos Gabriel do Nascimento
Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations. Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis
 Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis Observatoire de Paris SYRTE, 61 av. de l'observatoire, 7514 Paris Introduction Gravity field
Earth rotation and Earth gravity field from GRACE observations Lucia Seoane, Christian Bizouard, Daniel Gambis Observatoire de Paris SYRTE, 61 av. de l'observatoire, 7514 Paris Introduction Gravity field
SIRGAS: Basis for Geosciences, Geodata, and Navigation in Latin America
 SIRGAS: Basis for Geosciences, Geodata, and Navigation in Latin America Claudio Brunini President of SIRGAS Universidad Nacional de La Plata, Argentina María Virginia Mackern President of SIRGAS/WG-I:
SIRGAS: Basis for Geosciences, Geodata, and Navigation in Latin America Claudio Brunini President of SIRGAS Universidad Nacional de La Plata, Argentina María Virginia Mackern President of SIRGAS/WG-I:
Hydrological Mass Variations due to Extreme Weather Conditions in Central Europe from Regional GRACE 4D Expansions
 Hydrological Mass Variations due to Extreme Weather Conditions in Central Europe from Regional GRACE 4D Expansions Florian Seitz 1, Michael Schmidt 2, C.K. Shum 3, Yiqun Chen 3 1 Earth Oriented Space Science
Hydrological Mass Variations due to Extreme Weather Conditions in Central Europe from Regional GRACE 4D Expansions Florian Seitz 1, Michael Schmidt 2, C.K. Shum 3, Yiqun Chen 3 1 Earth Oriented Space Science
Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data
 Johannes Böhm, Arthur Niell, Paul Tregoning, and Harald Schuh Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data Geophysical Research Letters Vol. 33,
Johannes Böhm, Arthur Niell, Paul Tregoning, and Harald Schuh Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data Geophysical Research Letters Vol. 33,
The Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data
 The Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data J. Boehm, A. Niell, P. Tregoning, H. Schuh Troposphere mapping functions are used in the analyses
The Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data J. Boehm, A. Niell, P. Tregoning, H. Schuh Troposphere mapping functions are used in the analyses
At the moment, an effort is under way to provide altimetric information for the Working Group III (GTIII) of SIRGAS.
 IAG Brazilian National Report National Committee of IUGG Commité IAG - Travaux Period 2003-2007 Prepared by: Denizar Blitzkow IAG National Correspondent Introduction This report intends to cover most of
IAG Brazilian National Report National Committee of IUGG Commité IAG - Travaux Period 2003-2007 Prepared by: Denizar Blitzkow IAG National Correspondent Introduction This report intends to cover most of
Crustal motion geodesy in Bolivia
 Crustal motion geodesy in Bolivia Jacob Heck 1, Michael Bevis 1, Arturo Echalar 2, Dana Caccamise 1, Kevin Ahlgren 1,3, Ben Brooks 4, David Raleigh 1, Jonathan Weiss 4 1 Ohio State University - USA 2 Instituto
Crustal motion geodesy in Bolivia Jacob Heck 1, Michael Bevis 1, Arturo Echalar 2, Dana Caccamise 1, Kevin Ahlgren 1,3, Ben Brooks 4, David Raleigh 1, Jonathan Weiss 4 1 Ohio State University - USA 2 Instituto
Atmospheric Effects in Space Geodesy
 Atmospheric Effects in Space Geodesy Johannes Böhm 18 November 2011 @ UNESP, Presidente Prudente, Brazil The atmosphere.. is not only causing troubles in space geodesy.. but it opens up a wide field of
Atmospheric Effects in Space Geodesy Johannes Böhm 18 November 2011 @ UNESP, Presidente Prudente, Brazil The atmosphere.. is not only causing troubles in space geodesy.. but it opens up a wide field of
Lecture 2 Measurement Systems. GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy
 Lecture 2 Measurement Systems GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy VLBI and SLR VLBI Very Long Baseline Interferometry SLR Satellite Laser Ranging Very Long Baseline Interferometry VLBI Geometric Delay δg S Baseline
Lecture 2 Measurement Systems GEOS 655 Tectonic Geodesy VLBI and SLR VLBI Very Long Baseline Interferometry SLR Satellite Laser Ranging Very Long Baseline Interferometry VLBI Geometric Delay δg S Baseline
New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts
 Fourth Swarm science meeting and geodetic missions workshop ESA, 20-24 March 2017, Banff, Alberta, Canada New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts Richard
Fourth Swarm science meeting and geodetic missions workshop ESA, 20-24 March 2017, Banff, Alberta, Canada New satellite mission for improving the Terrestrial Reference Frame: means and impacts Richard
Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Mathematical models in GPS" Mathematical models used in GPS"
 12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Prof. Thomas Herring" Room 54-820A; 253-5941" tah@mit.edu" http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 " Mathematical models in GPS" Review assignment
12.540 Principles of the Global Positioning System Lecture 18" Prof. Thomas Herring" Room 54-820A; 253-5941" tah@mit.edu" http://geoweb.mit.edu/~tah/12.540 " Mathematical models in GPS" Review assignment
Towards a Consistent Conventional Treatment of Surface-Load Induced Deformations
 Towards a Consistent Conventional Treatment of Surface-Load Induced Deformations Hans-Peter Plag(1), Geoff Blewitt, Tom A. Herring (1) Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology and Seismological Laboratory University
Towards a Consistent Conventional Treatment of Surface-Load Induced Deformations Hans-Peter Plag(1), Geoff Blewitt, Tom A. Herring (1) Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology and Seismological Laboratory University
A Glimpse at Geodetic Activities in Latin America
 UNIVERSIDADE DO ESTADO DO RIO DE JANEIRO CENTRO DE TECNOLOGIA E CIÊNCIAS FACULDADE DE ENGENHARIA DEPARTAMENTO DE ENGENHARIA CARTOGRÁFICA A Glimpse at Geodetic Activities in Latin America Prof. Luiz Paulo
UNIVERSIDADE DO ESTADO DO RIO DE JANEIRO CENTRO DE TECNOLOGIA E CIÊNCIAS FACULDADE DE ENGENHARIA DEPARTAMENTO DE ENGENHARIA CARTOGRÁFICA A Glimpse at Geodetic Activities in Latin America Prof. Luiz Paulo
Using Cascais GPS Permanent Station for geodynamic purposes.
 Using Cascais GPS Permanent Station for geodynamic purposes. Ribeiro, H. 1 e Pinto, J.T. 1 1 IPCC Instituto Português de Cartografia e Cadastro, Portugal SUMMARY Cascais GPS station, the first Portuguese
Using Cascais GPS Permanent Station for geodynamic purposes. Ribeiro, H. 1 e Pinto, J.T. 1 1 IPCC Instituto Português de Cartografia e Cadastro, Portugal SUMMARY Cascais GPS station, the first Portuguese
Assessment of the orbit-related sea level error budget for the TOPEX/Poseidon altimetry mission
 Assessment of the orbit-related sea level error budget for the TOPEX/Poseidon altimetry mission Sergei Rudenko (1,2), Saskia Esselborn (1), Tilo Schöne (1) (1) GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences,
Assessment of the orbit-related sea level error budget for the TOPEX/Poseidon altimetry mission Sergei Rudenko (1,2), Saskia Esselborn (1), Tilo Schöne (1) (1) GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences,
Deriving groundwater estimates in Australia from GRACE observations
 Deriving groundwater estimates in Australia from GRACE observations P. Tregoning 1 and S.C. McClusky 1 1 Research School of Earth Sciences, The Australian National University, Canberra, ACT, 0200, Australia,
Deriving groundwater estimates in Australia from GRACE observations P. Tregoning 1 and S.C. McClusky 1 1 Research School of Earth Sciences, The Australian National University, Canberra, ACT, 0200, Australia,
A Unique Reference Frame: Basis of the Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) for Geodynamics and Global Change
 SRTM (InSAR) A Unique Reference Frame: Basis of the Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) for Geodynamics and Global Change Hermann Drewes President IAG Commission 1 Reference Frames Deutsches Geodätisches
SRTM (InSAR) A Unique Reference Frame: Basis of the Global Geodetic Observing System (GGOS) for Geodynamics and Global Change Hermann Drewes President IAG Commission 1 Reference Frames Deutsches Geodätisches
Surface Mass Loads from GRACE, GPS, and Earth Rotation
 Surface Mass Loads from GRACE,, and Earth Rotation R. Gross *, G. Blewitt, H.-P. Plag, P. Clarke, D. Lavallée, T. van Dam *Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, USA Nevada
Surface Mass Loads from GRACE,, and Earth Rotation R. Gross *, G. Blewitt, H.-P. Plag, P. Clarke, D. Lavallée, T. van Dam *Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, USA Nevada
Call for space geodetic solutions corrected for non-tidal atmospheric loading (NT-ATML) at the observation level
 Call for space geodetic solutions corrected for non-tidal atmospheric loading (NT-ATML) at the observation level Xavier Collilieux, Tonie van Dam, Zuheir Altamimi Outline: Context Why correcting for non-tidal
Call for space geodetic solutions corrected for non-tidal atmospheric loading (NT-ATML) at the observation level Xavier Collilieux, Tonie van Dam, Zuheir Altamimi Outline: Context Why correcting for non-tidal
ITRF2014 Et la prise en compte des mouvements non linéaires
 ITRF2014 Et la prise en compte des mouvements non linéaires Zuheir Altamimi, Paul Rebischung, Laurent Métivier, Xavier Collilieux E-mail: zuheir.altamimi@ign.fr ITRF2014 Network Key Points Modelling of
ITRF2014 Et la prise en compte des mouvements non linéaires Zuheir Altamimi, Paul Rebischung, Laurent Métivier, Xavier Collilieux E-mail: zuheir.altamimi@ign.fr ITRF2014 Network Key Points Modelling of
A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin, F. Perosanz, F. Mercier and J. Marty. AVENUE project. June, 20
 Efficient QR Sequential Least Square algorithm for high frequency GNSS Precise Point Positioning A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin, F. Perosanz, F. Mercier and J. Marty AVENUE project June, 20 A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin,
Efficient QR Sequential Least Square algorithm for high frequency GNSS Precise Point Positioning A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin, F. Perosanz, F. Mercier and J. Marty AVENUE project June, 20 A. Barbu, J. Laurent-Varin,
GGOS Bureau for Standards and Conventions
 GGOS D. Angermann (1), T. Gruber (2), J. Bouman (1), M. Gerstl (1), R. Heinkelmann (1), U. Hugentobler (2), L. Sánchez (1), P. Steigenberger (2) (1) Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI), München
GGOS D. Angermann (1), T. Gruber (2), J. Bouman (1), M. Gerstl (1), R. Heinkelmann (1), U. Hugentobler (2), L. Sánchez (1), P. Steigenberger (2) (1) Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI), München
Deriving groundwater estimates in Australia from Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) observations
 WIRADA Science Symposium Proceedings, Melbourne, Australia, 1 5 August 2011 Deriving groundwater estimates in Australia from Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) observations Tregoning P 1 and
WIRADA Science Symposium Proceedings, Melbourne, Australia, 1 5 August 2011 Deriving groundwater estimates in Australia from Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) observations Tregoning P 1 and
COMBINATION OF SATELLITE PRECIPITATION ESTIMATES AND RAIN GAUGE FOR HIGH SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL RESOLUTIONS INTRODUCTION
 COMBINATION OF SATELLITE PRECIPITATION ESTIMATES AND RAIN GAUGE FOR HIGH SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL RESOLUTIONS Ferreira, Rute Costa¹ ; Herdies, D. L.¹; Vila, D.A.¹; Beneti, C.A. A.² ¹ Center for Weather Forecasts
COMBINATION OF SATELLITE PRECIPITATION ESTIMATES AND RAIN GAUGE FOR HIGH SPATIAL AND TEMPORAL RESOLUTIONS Ferreira, Rute Costa¹ ; Herdies, D. L.¹; Vila, D.A.¹; Beneti, C.A. A.² ¹ Center for Weather Forecasts
Warkworth geodetic station as a potential GGOS core site in New Zealand
 "Launching the Next-Generation IVS Network Session 2: Correlators, Stations and Operations Centers. 7th IVS General Meeting March 5, 2012 Madrid, Spain Warkworth geodetic station as a potential GGOS core
"Launching the Next-Generation IVS Network Session 2: Correlators, Stations and Operations Centers. 7th IVS General Meeting March 5, 2012 Madrid, Spain Warkworth geodetic station as a potential GGOS core
GRACE Gravity Model GGM02
 GRACE Gravity Model GGM02 The GGM02S gravity model was estimated with 363 days (spanning April 2002 through December 2003) of GRACE K-band range-rate, attitude, and accelerometer data. No Kaula constraint,
GRACE Gravity Model GGM02 The GGM02S gravity model was estimated with 363 days (spanning April 2002 through December 2003) of GRACE K-band range-rate, attitude, and accelerometer data. No Kaula constraint,
GNSS-specific local effects at the Geodetic Observatory Wettzell
 GNSS-specific local effects at the Geodetic Observatory Wettzell Peter Steigenberger, Urs Hugentobler, Ralf Schmid Technische Universität München (TUM) Uwe Hessels, Thomas Klügel Bundesamt für Kartographie
GNSS-specific local effects at the Geodetic Observatory Wettzell Peter Steigenberger, Urs Hugentobler, Ralf Schmid Technische Universität München (TUM) Uwe Hessels, Thomas Klügel Bundesamt für Kartographie
ESTIMATING THE RESIDUAL TROPOSPHERIC DELAY FOR AIRBORNE DIFFERENTIAL GPS POSITIONING (A SUMMARY)
 ESTIMATING THE RESIDUAL TROPOSPHERIC DELAY FOR AIRBORNE DIFFERENTIAL GPS POSITIONING (A SUMMARY) J. Paul Collins and Richard B. Langley Geodetic Research Laboratory Department of Geodesy and Geomatics
ESTIMATING THE RESIDUAL TROPOSPHERIC DELAY FOR AIRBORNE DIFFERENTIAL GPS POSITIONING (A SUMMARY) J. Paul Collins and Richard B. Langley Geodetic Research Laboratory Department of Geodesy and Geomatics
The BIFROST Project: 21 years of search for the true crustal deformation in Fennoscandia
 The BIFROST Project: 21 years of search for the true crustal deformation in Fennoscandia Martin Lidberg and Holger Steffen Lantmäteriet, Sweden Jan Johansson Chalmers University of Technology Halfdan Kierulf
The BIFROST Project: 21 years of search for the true crustal deformation in Fennoscandia Martin Lidberg and Holger Steffen Lantmäteriet, Sweden Jan Johansson Chalmers University of Technology Halfdan Kierulf
Summary of the 2012 Global Geophysical Fluid Center Workshop
 Summary of the 2012 Global Geophysical Fluid Center Workshop T. van Dam (Uni. Lux), J. Ray (NGS/NOAA), X. Collilieux (IGN) Introduction Review the history of the GGFC Discuss the 2012 Workshop Review recommendations
Summary of the 2012 Global Geophysical Fluid Center Workshop T. van Dam (Uni. Lux), J. Ray (NGS/NOAA), X. Collilieux (IGN) Introduction Review the history of the GGFC Discuss the 2012 Workshop Review recommendations
PRECISE ORBIT DETERMINATION OF GPS SATELLITES FOR REAL TIME APPLICATIONS
 J. Astron. Space Sci. 18(2), 129 136 (2001) GPS,,,, PRECISE ORBIT DETERMINATION OF GPS SATELLITES FOR REAL TIME APPLICATIONS Hyung-Chul Lim, Pil-Ho Park, Jong-Uk Park, Jung-Ho Cho, Yong-Won Ahn GPS Research
J. Astron. Space Sci. 18(2), 129 136 (2001) GPS,,,, PRECISE ORBIT DETERMINATION OF GPS SATELLITES FOR REAL TIME APPLICATIONS Hyung-Chul Lim, Pil-Ho Park, Jong-Uk Park, Jung-Ho Cho, Yong-Won Ahn GPS Research
IGS Reprocessing. and First Quality Assessment
 IGS Reprocessing Summary of Orbit/Clock Combination and First Quality Assessment Gerd Gendt, GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam Jake Griffiths, NOAA/National Geodetic Survey Thomas Nischan, GeoForschungsZentrum
IGS Reprocessing Summary of Orbit/Clock Combination and First Quality Assessment Gerd Gendt, GeoForschungsZentrum Potsdam Jake Griffiths, NOAA/National Geodetic Survey Thomas Nischan, GeoForschungsZentrum
Time Variable Gravity (TVG) in GRGS REPRO2 solution (GR2)
 Time Variable Gravity (TVG) in GRGS REPRO2 solution (GR2) S. Loyer (1), J.-M. Lemoine (2) and F. Perosanz (2) (1) Collecte Localisation Satellites (CLS, Ramonville Saint-Agne, France) (2) Centre National
Time Variable Gravity (TVG) in GRGS REPRO2 solution (GR2) S. Loyer (1), J.-M. Lemoine (2) and F. Perosanz (2) (1) Collecte Localisation Satellites (CLS, Ramonville Saint-Agne, France) (2) Centre National
Strategy for the Realization of the International Height Reference System (IHRS)
 Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI-TUM) Technische Universität München Strategy for the Realization of the International Height Reference System (IHRS) Laura Sánchez 1, Johannes Ihde 2, Roland
Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut (DGFI-TUM) Technische Universität München Strategy for the Realization of the International Height Reference System (IHRS) Laura Sánchez 1, Johannes Ihde 2, Roland
Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate
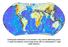 Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate interiors) Tectonic plates and their boundaries today -- continents
Earthquake distribution is not random: very narrow deforming zones (= plate boundaries) versus large areas with no earthquakes (= rigid plate interiors) Tectonic plates and their boundaries today -- continents
NATIONAL REPORT OF POLAND TO EUREF 2011
 NATIONAL REPORT OF POLAND TO EUREF 2011 Jan Krynski Institute of Geodesy and Cartography, Warsaw Jerzy B. Rogowski Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw Outline Main geodetic activities at the national
NATIONAL REPORT OF POLAND TO EUREF 2011 Jan Krynski Institute of Geodesy and Cartography, Warsaw Jerzy B. Rogowski Warsaw University of Technology, Warsaw Outline Main geodetic activities at the national
3.3 Analysis Coordinator
 1. Introduction 2. Analysis of ITRF2014 post-seismic parameterization In this report we outline the activities of the Analysis Coordinator during 2015. The main activities were analysis of the ITRF2014
1. Introduction 2. Analysis of ITRF2014 post-seismic parameterization In this report we outline the activities of the Analysis Coordinator during 2015. The main activities were analysis of the ITRF2014
Modeling and Observation of Loading Contribution to Time-Variable GPS Site Positions
 EGU2009-3768 Session G4 EGU General Assembly 2009 Vienna, Austria, 19 24 April 2009 Modeling and Observation of Loading Contribution to Time-Variable GPS Site Positions Are we able to Detect and Identify
EGU2009-3768 Session G4 EGU General Assembly 2009 Vienna, Austria, 19 24 April 2009 Modeling and Observation of Loading Contribution to Time-Variable GPS Site Positions Are we able to Detect and Identify
Vertical Reference Frame Pacific
 Vertical Reference Frame Pacific Andrick Lal SPC Geoscience Division GIS&RS User Conference 29 th November 2016 USP, Fiji. What does it mean? All buildings and features have a height. But what is it relative
Vertical Reference Frame Pacific Andrick Lal SPC Geoscience Division GIS&RS User Conference 29 th November 2016 USP, Fiji. What does it mean? All buildings and features have a height. But what is it relative
Analysis of the Accuracy of GMF, NMF, and VMF1 Mapping Functions with GPT 50 a Priori Zenith Constraint in Tropospheric Delay Modelling
 Analysis of the Accuracy of GMF, NMF, and VMF1 Mapping Functions with GPT 50 a Priori Zenith Constraint in Tropospheric Delay Modelling Brian Makabayi 1 Addisu Hunegnaw 2 1 Assistant Lecturer, Department
Analysis of the Accuracy of GMF, NMF, and VMF1 Mapping Functions with GPT 50 a Priori Zenith Constraint in Tropospheric Delay Modelling Brian Makabayi 1 Addisu Hunegnaw 2 1 Assistant Lecturer, Department
Evaluation of the impact of atmospheric pressure loading modeling on GNSS data analysis
 Evaluation of the impact of atmospheric pressure loading modeling on GNSS data analysis R. Dach a, J. Böhm b, S. Lutz a, and P. Steigenberger c a Astronomical Institute, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
Evaluation of the impact of atmospheric pressure loading modeling on GNSS data analysis R. Dach a, J. Böhm b, S. Lutz a, and P. Steigenberger c a Astronomical Institute, University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland
Modeling and Observation of Loading Contribution to Time-Variable GPS Site Positions
 EGU2009-3768 Session G4 EGU General Assembly 2009 Vienna, Austria, 19 24 April 2009 Modeling and Observation of Loading Contribution to Time-Variable GPS Site Positions Are we able to Detect and Identify
EGU2009-3768 Session G4 EGU General Assembly 2009 Vienna, Austria, 19 24 April 2009 Modeling and Observation of Loading Contribution to Time-Variable GPS Site Positions Are we able to Detect and Identify
PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF THE GNSS APPLICATION TO PRECIPITATION NOWCASTING Luiz Fernando Sapucci. Luiz Augusto Toledo Machado. Izabelly Carvalho.
 PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF THE GNSS APPLICATION TO PRECIPITATION NOWCASTING Luiz Fernando Sapucci. Luiz Augusto Toledo Machado. Izabelly Carvalho. Lucas Amarantes Avanço. Integrated water vapor from Global
PRELIMINARY STUDIES OF THE GNSS APPLICATION TO PRECIPITATION NOWCASTING Luiz Fernando Sapucci. Luiz Augusto Toledo Machado. Izabelly Carvalho. Lucas Amarantes Avanço. Integrated water vapor from Global
Shape of the Earth. Data Output by the Receiver
 It is quite common for confusion to arise about the process used during a hydrographic survey when GPS-derived water surface elevation is incorporated into the data as an RTK Tide correction. This article
It is quite common for confusion to arise about the process used during a hydrographic survey when GPS-derived water surface elevation is incorporated into the data as an RTK Tide correction. This article
Geodetic Observing Systems: tools in observing the Glacial Isostatic Adjustment. Markku Poutanen Finnish Geodetic Institute
 Geodetic Observing Systems: tools in observing the Glacial Isostatic Adjustment Markku Poutanen Finnish Geodetic Institute Glacial Isostatic Adjustment Land uplift is just one consequence of the physical
Geodetic Observing Systems: tools in observing the Glacial Isostatic Adjustment Markku Poutanen Finnish Geodetic Institute Glacial Isostatic Adjustment Land uplift is just one consequence of the physical
The Role of CORS GNSS Data for Climate Monitoring: Case Study using NIGNET Network BY
 The Role of CORS GNSS Data for Climate Monitoring: Case Study using NIGNET Network BY Abayomi AYOOLA, Adeyemi ADEBOMEHIN, Kufre Eko (Nigeria) and SÁ ANDRÉ (Portugal). Introduction The 2012 rainy season
The Role of CORS GNSS Data for Climate Monitoring: Case Study using NIGNET Network BY Abayomi AYOOLA, Adeyemi ADEBOMEHIN, Kufre Eko (Nigeria) and SÁ ANDRÉ (Portugal). Introduction The 2012 rainy season
GEOID UNDULATIONS OF SUDAN USING ORTHOMETRIC HEIGHTS COMPARED WITH THE EGM96 ANG EGM2008
 GEOID UNDULATIONS OF SUDAN USING ORTHOMETRIC HEIGHTS COMPARED Dr. Abdelrahim Elgizouli Mohamed Ahmed* WITH THE EGM96 ANG EGM2008 Abstract: Positioning by satellite system determine the normal height above
GEOID UNDULATIONS OF SUDAN USING ORTHOMETRIC HEIGHTS COMPARED Dr. Abdelrahim Elgizouli Mohamed Ahmed* WITH THE EGM96 ANG EGM2008 Abstract: Positioning by satellite system determine the normal height above
Frequent epoch reference frames instead of instant station positions and constant velocities
 Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut Technische Universität München (DGFI-TUM) Frequent epoch reference frames instead of instant station positions and constant velocities Hermann Drewes Deutsches
Deutsches Geodätisches Forschungsinstitut Technische Universität München (DGFI-TUM) Frequent epoch reference frames instead of instant station positions and constant velocities Hermann Drewes Deutsches
Modernization of National Geodetic Datum in China *
 UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.102/IP.16 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Nineteenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 29 October 1 November 2012 Item 6(b) of the provisional
UNITED NATIONS E/CONF.102/IP.16 ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL COUNCIL Nineteenth United Nations Regional Cartographic Conference for Asia and the Pacific Bangkok, 29 October 1 November 2012 Item 6(b) of the provisional
Co-location of VLBI with other techniques in space: a simulation study
 Co-location of VLBI with other techniques in space: a simulation study B. Männel, M. Rothacher ETH Zürich, Geodesy and Geodynamics Lab 7 th IGS General Meeting, Madrid 212 1 Reference frame and local ties
Co-location of VLBI with other techniques in space: a simulation study B. Männel, M. Rothacher ETH Zürich, Geodesy and Geodynamics Lab 7 th IGS General Meeting, Madrid 212 1 Reference frame and local ties
The role of CORS GNSS data for climate monitoring: case study using NIGNET network
 The role of CORS GNSS data for climate monitoring: case study using NIGNET network Adeyemi ADEBOMEHIN, A. AYOOLA, Kufrey EKO, Nigeria and André SÁ, Portugal Key words: GNSS, CORS, Climate, Water Vapor
The role of CORS GNSS data for climate monitoring: case study using NIGNET network Adeyemi ADEBOMEHIN, A. AYOOLA, Kufrey EKO, Nigeria and André SÁ, Portugal Key words: GNSS, CORS, Climate, Water Vapor
Introduction to geodetic VLBI
 Introduction to geodetic VLBI David Mayer Andreas Hellerschmied Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
Introduction to geodetic VLBI David Mayer Andreas Hellerschmied Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
Consideration of a Global Vertical Reference System (GVRS) in the IERS Conventions
 Consideration of a Global Vertical Reference System (GVRS) in the IERS Conventions Johannes Ihde Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy (BKG) Chair of IAG ICP1.2 (2003-2007) Vertical Reference Frames
Consideration of a Global Vertical Reference System (GVRS) in the IERS Conventions Johannes Ihde Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy (BKG) Chair of IAG ICP1.2 (2003-2007) Vertical Reference Frames
Towards an improved ILRS TRF contribution
 Towards an improved ILRS TRF contribution Erricos C. Pavlis ILRS Analysis Coordinator JCET/ & NASA Goddard IERS Workshop on Conventions 2007 20-21 Sept. 2007, Sèvres, France Overview The ILRS Network Geometry
Towards an improved ILRS TRF contribution Erricos C. Pavlis ILRS Analysis Coordinator JCET/ & NASA Goddard IERS Workshop on Conventions 2007 20-21 Sept. 2007, Sèvres, France Overview The ILRS Network Geometry
State-of-the-art physical models for calculating atmospheric pressure loading effects
 State-of-the-art physical models for calculating atmospheric pressure loading effects Dudy D. Wijaya, Böhm J., Schindelegger M., Karbon M., Schuh H. Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics, TU Vienna Geodätische
State-of-the-art physical models for calculating atmospheric pressure loading effects Dudy D. Wijaya, Böhm J., Schindelegger M., Karbon M., Schuh H. Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics, TU Vienna Geodätische
Report for 15th PCGIAP Meeting at 18th UNRCC-AP Working Group 1 Regional Geodesy
 Report for 15th PCGIAP Meeting at 18th UNRCC-AP Working Group 1 Regional Geodesy Chairman Shigeru Matsuzaka, Japan - shigeru@gsi.go.jp Vice Chairman Prof. Pengfei Cheng, China - chengpf@casm.ac.cn John
Report for 15th PCGIAP Meeting at 18th UNRCC-AP Working Group 1 Regional Geodesy Chairman Shigeru Matsuzaka, Japan - shigeru@gsi.go.jp Vice Chairman Prof. Pengfei Cheng, China - chengpf@casm.ac.cn John
Improving the long-term stability of the GDR orbit solutions
 Improving the long-term stability of the GDR orbit solutions L. Cerri 1, A. Couhert 1, S. Houry 1, F. Mercier 1 (1) CNES Toulouse OSTST Meeting 19-21 Oct. 2011 POD Splinter Session Status of the POD standards
Improving the long-term stability of the GDR orbit solutions L. Cerri 1, A. Couhert 1, S. Houry 1, F. Mercier 1 (1) CNES Toulouse OSTST Meeting 19-21 Oct. 2011 POD Splinter Session Status of the POD standards
GPS time series and sea level
 GPS time series and sea level M. Poutanen 1, H. Koivula 1, M. Tervo 1,2, K. Kahma 3, M. Ollikainen 1, H. Virtanen 1 1 Finnish Geodetic Institute, 2 University of Helsinki, 3 Finnish Institute of Marine
GPS time series and sea level M. Poutanen 1, H. Koivula 1, M. Tervo 1,2, K. Kahma 3, M. Ollikainen 1, H. Virtanen 1 1 Finnish Geodetic Institute, 2 University of Helsinki, 3 Finnish Institute of Marine
Comparison of Terrestrial and Martian TEC at Dawn and Dusk during Solstices
 Comparison of Terrestrial and Martian TEC at Dawn and Dusk during Solstices Angeline G. Burrell 1 Beatriz Sanchez-Cano 2, Mark Lester 2, Russell Stoneback 1, Olivier Witasse 3, Marco Cartacci 4 1 Center
Comparison of Terrestrial and Martian TEC at Dawn and Dusk during Solstices Angeline G. Burrell 1 Beatriz Sanchez-Cano 2, Mark Lester 2, Russell Stoneback 1, Olivier Witasse 3, Marco Cartacci 4 1 Center
UNB Neutral Atmosphere Models: Development and Performance
 UNB Neutral Atmosphere Models: Development and Performance Rodrigo Leandro, Marcelo Santos, and Richard B. Langley Geodetic Research Laboratory, Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering University
UNB Neutral Atmosphere Models: Development and Performance Rodrigo Leandro, Marcelo Santos, and Richard B. Langley Geodetic Research Laboratory, Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering University
IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST. (a) (b) (c)
 9B.3 IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST Tetsuya Iwabuchi *, J. J. Braun, and T. Van Hove UCAR, Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
9B.3 IMPACT OF GROUND-BASED GPS PRECIPITABLE WATER VAPOR AND COSMIC GPS REFRACTIVITY PROFILE ON HURRICANE DEAN FORECAST Tetsuya Iwabuchi *, J. J. Braun, and T. Van Hove UCAR, Boulder, Colorado 1. INTRODUCTION
Basins-Level Heavy Rainfall and Flood Analyses
 Basins-Level Heavy Rainfall and Flood Analyses Peng Gao, Greg Carbone, and Junyu Lu Department of Geography, University of South Carolina (gaop@mailbox.sc.edu, carbone@mailbox.sc.edu, jlu@email.sc.edu)
Basins-Level Heavy Rainfall and Flood Analyses Peng Gao, Greg Carbone, and Junyu Lu Department of Geography, University of South Carolina (gaop@mailbox.sc.edu, carbone@mailbox.sc.edu, jlu@email.sc.edu)
Status. EUREF TWG Meeting November 8 9, 2004, Praha
 ECGN was initiated by IAG Sub-Commission for Europe EUREF (SC1.3a) and IAG Sub-Commission for Europe of the International Gravity and Geoid Commission (IGGC) with relationship to Joint Research Centre
ECGN was initiated by IAG Sub-Commission for Europe EUREF (SC1.3a) and IAG Sub-Commission for Europe of the International Gravity and Geoid Commission (IGGC) with relationship to Joint Research Centre
From Global to National Geodetic Reference Frames: how are they connected and why are they needed?
 From Global to National Geodetic Reference Frames: how are they connected and why are they needed? Zuheir ALTAMIMI Institut National de l Information Géographique et Forestière, France Vice-President,
From Global to National Geodetic Reference Frames: how are they connected and why are they needed? Zuheir ALTAMIMI Institut National de l Information Géographique et Forestière, France Vice-President,
Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 91 (2012), REALIZATION OF ETRF2000 AS A NEW TERRESTRIAL REFERENCE FRAME IN REPUBLIC OF SERBIA
 Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 91 (2012), 199-206 Contributed paper REALIZATION OF ETRF2000 AS A NEW TERRESTRIAL REFERENCE FRAME IN REPUBLIC OF SERBIA D. BLAGOJEVIĆ and V. VASILIĆ Faculty of Civil Engineering,
Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 91 (2012), 199-206 Contributed paper REALIZATION OF ETRF2000 AS A NEW TERRESTRIAL REFERENCE FRAME IN REPUBLIC OF SERBIA D. BLAGOJEVIĆ and V. VASILIĆ Faculty of Civil Engineering,
Height systems. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens 2 Outline! Why bother about height systems?! Relevant terms! Coordinate systems! Reference surfaces! Geopotential number! Why bother about height systems?! give a meaning to a value defined
Rüdiger Gens 2 Outline! Why bother about height systems?! Relevant terms! Coordinate systems! Reference surfaces! Geopotential number! Why bother about height systems?! give a meaning to a value defined
GOCE based Gravity Field Models Signal and Error Assessment
 GOCE based Gravity Field Models Signal and Error Assessment Th. Gruber, M. Willberg Institute of Astronomical & Physical Geodesy (IAPG) Technical University Munich GOCE Reprocessing Status Expected Results
GOCE based Gravity Field Models Signal and Error Assessment Th. Gruber, M. Willberg Institute of Astronomical & Physical Geodesy (IAPG) Technical University Munich GOCE Reprocessing Status Expected Results
Towards a Rigorous Combination of Space Geodetic Techniques
 Towards a Rigorous Combination of Space Geodetic Techniques Markus Rothacher Forschungseinrichtung Satellitengeodäsie, TU Munich, Germany Abstract: The with all its different components and products, ranging
Towards a Rigorous Combination of Space Geodetic Techniques Markus Rothacher Forschungseinrichtung Satellitengeodäsie, TU Munich, Germany Abstract: The with all its different components and products, ranging
SLR and the Gravity Field
 SLR and the Gravity Field Daniela Thaller With contributions by: Krzysztof Sośnica (University of Wroclaw, Poland) Mathis Bloßfeld (DGFI-TUM, Germany) Gravity Field Determination Dedicated gravity field
SLR and the Gravity Field Daniela Thaller With contributions by: Krzysztof Sośnica (University of Wroclaw, Poland) Mathis Bloßfeld (DGFI-TUM, Germany) Gravity Field Determination Dedicated gravity field
Workshop on Numerical Weather Models for Space Geodesy Positioning
 Workshop on Numerical Weather Models for Space Geodesy Positioning Marcelo C. Santos University of New Brunswick, Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, Fredericton, NB Room C25 (ADI Room), Head
Workshop on Numerical Weather Models for Space Geodesy Positioning Marcelo C. Santos University of New Brunswick, Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, Fredericton, NB Room C25 (ADI Room), Head
Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry
 Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry Johannes Böhm Harald Schuh and Johannes Böhm, Very Long Baseline Interferometry for Geodesy and Astrometry, in Guochang Xu (editor): Sciences
Initial Results of Altimetry Assimilation in POP2 Ocean Model
 Initial Results of Altimetry Assimilation in POP2 Ocean Model Svetlana Karol and Alicia R. Karspeck With thanks to the DART Group, CESM Software Development Group, Climate Modeling Development Group POP-DART
Initial Results of Altimetry Assimilation in POP2 Ocean Model Svetlana Karol and Alicia R. Karspeck With thanks to the DART Group, CESM Software Development Group, Climate Modeling Development Group POP-DART
Sebastian Strasser, Torsten Mayer-Gürr
 Sebastian Strasser, Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, Graz University of Technology WG Theoretical Geodesy and Satellite Geodesy Geodetic Week 2015, Stuttgart, Germany Sebastian Strasser 16.09.2015
Sebastian Strasser, Torsten Mayer-Gürr Institute of Geodesy, Graz University of Technology WG Theoretical Geodesy and Satellite Geodesy Geodetic Week 2015, Stuttgart, Germany Sebastian Strasser 16.09.2015
The GOCE Geoid in Support to Sea Level Analysis
 The GOCE Geoid in Support to Sea Level Analysis The geoid is a very useful quantity for oceanographers Thomas Gruber Astronomical & Physical Geodesy (IAPG) Technische Universität München 1. Characteristics
The GOCE Geoid in Support to Sea Level Analysis The geoid is a very useful quantity for oceanographers Thomas Gruber Astronomical & Physical Geodesy (IAPG) Technische Universität München 1. Characteristics
New developments in using solar cells as remote sensors to gauge climate change
 New developments in using solar cells as remote sensors to gauge climate change Nelson Veissid ABSTRACT Earth s albedo is the fraction between the radiation reflected outside and the incident solar radiation,
New developments in using solar cells as remote sensors to gauge climate change Nelson Veissid ABSTRACT Earth s albedo is the fraction between the radiation reflected outside and the incident solar radiation,
Determination of Current Velocity Field (Rate) of North Anatolian Fault in Izmit-Sapanca Segment
 Determination of Current Velocity Field (Rate) of North Anatolian Fault in Izmit-Sapanca Segment Cetin MEKIK, Bulent TURGUT, Haluk OZENER, Turkish Republic INTRODUCTION Turkey is geologically the part
Determination of Current Velocity Field (Rate) of North Anatolian Fault in Izmit-Sapanca Segment Cetin MEKIK, Bulent TURGUT, Haluk OZENER, Turkish Republic INTRODUCTION Turkey is geologically the part
Geophysical Correction Application in Level 2 CryoSat Data Products
 ESRIN-EOP-GQ / IDEAS IDEAS-VEG-IPF-MEM-1288 Version 2.0 29 July 2014 Geophysical Correction Application in Level 2 CryoSat Data Products TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 Purpose and Scope... 3
ESRIN-EOP-GQ / IDEAS IDEAS-VEG-IPF-MEM-1288 Version 2.0 29 July 2014 Geophysical Correction Application in Level 2 CryoSat Data Products TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 Purpose and Scope... 3
Understanding the hydrology of the large wetlands of the Bolivian Amazon using remote sensing and hydrological modeling
 Understanding the hydrology of the large wetlands of the Bolivian Amazon using remote sensing and hydrological modeling Preliminary results 6 th SO HYBAM Scientific Meeting Cusco, Octubre 2015 Alex Ovando
Understanding the hydrology of the large wetlands of the Bolivian Amazon using remote sensing and hydrological modeling Preliminary results 6 th SO HYBAM Scientific Meeting Cusco, Octubre 2015 Alex Ovando
Past, present and possible updates to the IERS Conventions. J. Ray, NGS G. Petit, BIPM
 Past, present and possible updates to the IERS Conventions J. Ray, NGS G. Petit, BIPM IERS Conventions update: electronic access http://tai.bipm.org/iers/convupdt/listupdt.html Introduction Add a set of
Past, present and possible updates to the IERS Conventions J. Ray, NGS G. Petit, BIPM IERS Conventions update: electronic access http://tai.bipm.org/iers/convupdt/listupdt.html Introduction Add a set of
Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia
 Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Meiry Sakamoto Uiversidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil Colombia Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Convective System (CS)
Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Meiry Sakamoto Uiversidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil Colombia Life Cycle of Convective Systems over Western Colombia Convective System (CS)
GNSS METEOROLOGY AND WATER VAPOUR ESTIMATION IN TURKEY
 GNSS METEOROLOGY AND WATER VAPOUR ESTIMATION IN TURKEY DR. CETIN MEKIK ASSOC. PROF., THE DEPT. OF GEOMATICS ENGINEERING BULENT ECEVIT UNIVERSITY, ZONGULDAK/TURKEY GNSS4SWEC MC&WG Meeting, Varna, Bulgaria,
GNSS METEOROLOGY AND WATER VAPOUR ESTIMATION IN TURKEY DR. CETIN MEKIK ASSOC. PROF., THE DEPT. OF GEOMATICS ENGINEERING BULENT ECEVIT UNIVERSITY, ZONGULDAK/TURKEY GNSS4SWEC MC&WG Meeting, Varna, Bulgaria,
The progress of the geoid in south America under GRACE and EGM08 models
 University of São Paulo The progress of the geoid in south America under GRACE and EGM08 models Polytechnic School Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics D. Blitzkow (E-mail: dblitzko@usp.br)
University of São Paulo The progress of the geoid in south America under GRACE and EGM08 models Polytechnic School Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics D. Blitzkow (E-mail: dblitzko@usp.br)
Modern Navigation. Thomas Herring
 12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Today s Class Latitude and Longitude Simple spherical definitions Geodetic definition: For an ellipsoid Astronomical definition: Based on direction of gravity Relationships
12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Today s Class Latitude and Longitude Simple spherical definitions Geodetic definition: For an ellipsoid Astronomical definition: Based on direction of gravity Relationships
PGM2016: A new geoid model for the. Philippines
 PGM2016: A new geoid model for the Philippines United Nations/Nepal Workshop on the Applications of Global Navigation Satellite Systems Kathmandu, Nepal December 12-16, 2016 Ronaldo Gatchalian, Chief Geodesy
PGM2016: A new geoid model for the Philippines United Nations/Nepal Workshop on the Applications of Global Navigation Satellite Systems Kathmandu, Nepal December 12-16, 2016 Ronaldo Gatchalian, Chief Geodesy
The International Terrestrial Reference System and ETRS89: Part I : General concepts
 The International Terrestrial Reference System and ETRS89: Part I : General concepts Zuheir ALTAMIMI Laboratoire de Recherche en Géodésie Institut national de l information géographique et forestière (IGN),
The International Terrestrial Reference System and ETRS89: Part I : General concepts Zuheir ALTAMIMI Laboratoire de Recherche en Géodésie Institut national de l information géographique et forestière (IGN),
2 nd Tidal and Water Level Working Group Meeting
 2 nd Tidal and Water Level Working Group Meeting Norwegian Hydrographic Service, Stavanger, Norway 27 29 April 2010 Vertical Offshore Reference Framework (VORF) Chris Jones United Kingdom Hydrographic
2 nd Tidal and Water Level Working Group Meeting Norwegian Hydrographic Service, Stavanger, Norway 27 29 April 2010 Vertical Offshore Reference Framework (VORF) Chris Jones United Kingdom Hydrographic
Contributions of Geodesy to Oceanography
 Contributions of Geodesy to Oceanography B. Tapley and J. Ries Center for Space Research, The University of Texas at Austin Dynamic Planet 2005 Cairns, Australia August 22-26, 2005 August 22-26, 2005 Dynam
Contributions of Geodesy to Oceanography B. Tapley and J. Ries Center for Space Research, The University of Texas at Austin Dynamic Planet 2005 Cairns, Australia August 22-26, 2005 August 22-26, 2005 Dynam
THE OPEN UNIVERSITY OF SRI LANKA
 THE OPEN UNIVERSITY OF SRI LANKA Extended Abstracts Open University Research Sessions (OURS 2017) 16 th & 17 th November, 2017 The Open University of Sri Lanka - 2017 All rights reserved. No part of this
THE OPEN UNIVERSITY OF SRI LANKA Extended Abstracts Open University Research Sessions (OURS 2017) 16 th & 17 th November, 2017 The Open University of Sri Lanka - 2017 All rights reserved. No part of this
Evaluation of height network in Latvia
 Evaluation of height network in Latvia Kaminskis J. (,), Balodis J. (), Janpaule I. (,), Normand M. (,), Rubans A. (), Silabriedis G. (,), Zvirgzds J. (,) AFFILIATION: () Riga Technical University; ()
Evaluation of height network in Latvia Kaminskis J. (,), Balodis J. (), Janpaule I. (,), Normand M. (,), Rubans A. (), Silabriedis G. (,), Zvirgzds J. (,) AFFILIATION: () Riga Technical University; ()
GRACE Measurement of Total Water Storage Variations Over Texas
 GRACE Measurement of Total Water Storage Variations Over Texas Byron Tapley, Srinivas Bettadpur Himanshu Save, Tatyana Pekker University of Texas Center for Space Research First Texas Water Forum - Drought
GRACE Measurement of Total Water Storage Variations Over Texas Byron Tapley, Srinivas Bettadpur Himanshu Save, Tatyana Pekker University of Texas Center for Space Research First Texas Water Forum - Drought
Using non-tidal atmospheric loading model in space geodetic data processing: Preliminary results of the IERS analysis campaign
 Using non-tidal atmospheric loading model in space geodetic data processing: Preliminary results of the IERS analysis campaign Xavier Collilieux (1), Zuheir Altamimi (1), Laurent Métivier (1), Tonie van
Using non-tidal atmospheric loading model in space geodetic data processing: Preliminary results of the IERS analysis campaign Xavier Collilieux (1), Zuheir Altamimi (1), Laurent Métivier (1), Tonie van
Assimilation of satellite altimetry referenced to the new GRACE geoid estimate
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L06601, doi:10.1029/2004gl021329, 2005 Assimilation of satellite altimetry referenced to the new GRACE geoid estimate F. Birol, 1 J. M. Brankart, 1 J. M. Lemoine,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L06601, doi:10.1029/2004gl021329, 2005 Assimilation of satellite altimetry referenced to the new GRACE geoid estimate F. Birol, 1 J. M. Brankart, 1 J. M. Lemoine,
We have processed RO data for climate research and for validation of weather data since 1995 as illustrated in Figure 1.
 Real-time Analysis of COSMIC Data Christian Rocken, Doug Hunt, Bill Schreiner University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) COSMIC Project Office Boulder, CO Abstract UCAR has analyzed GPS radio
Real-time Analysis of COSMIC Data Christian Rocken, Doug Hunt, Bill Schreiner University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) COSMIC Project Office Boulder, CO Abstract UCAR has analyzed GPS radio
Geog Lecture 29 Mapping and GIS Continued
 Geog 1000 - Lecture 29 Mapping and GIS Continued http://scholar.ulethbridge.ca/chasmer/classes/ Today s Lecture (Pgs 13-25, 28-29) 1. Hand back Assignment 3 2. Review of Dr. Peddle s lecture last week
Geog 1000 - Lecture 29 Mapping and GIS Continued http://scholar.ulethbridge.ca/chasmer/classes/ Today s Lecture (Pgs 13-25, 28-29) 1. Hand back Assignment 3 2. Review of Dr. Peddle s lecture last week
Application of Satellite Data for Flood Forecasting and Early Warning in the Mekong River Basin in South-east Asia
 MEKONG RIVER COMMISSION Vientiane, Lao PDR Application of Satellite Data for Flood Forecasting and Early Warning in the Mekong River Basin in South-east Asia 4 th World Water Forum March 2006 Mexico City,
MEKONG RIVER COMMISSION Vientiane, Lao PDR Application of Satellite Data for Flood Forecasting and Early Warning in the Mekong River Basin in South-east Asia 4 th World Water Forum March 2006 Mexico City,
Use of ground-based GNSS measurements in data assimilation. Reima Eresmaa Finnish Meteorological Institute
 Use of ground-based GNSS measurements in data assimilation Reima Eresmaa Finnish Meteorological Institute 16 June 2006 Outline 1) Introduction GNSS * positioning Tropospheric delay 2) GNSS as a meteorological
Use of ground-based GNSS measurements in data assimilation Reima Eresmaa Finnish Meteorological Institute 16 June 2006 Outline 1) Introduction GNSS * positioning Tropospheric delay 2) GNSS as a meteorological
How significant is the dynamic component of the North American vertical datum?
 CGU Annual Scientific Meeting -8 June 212, Banff, Canada How significant is the dynamic component of the North American vertical datum? E. Rangelova, M.G. Sideris (University of Calgary) W. van der Wal
CGU Annual Scientific Meeting -8 June 212, Banff, Canada How significant is the dynamic component of the North American vertical datum? E. Rangelova, M.G. Sideris (University of Calgary) W. van der Wal
GG S. Internal Vision of GGOS. Markus Rothacher. GFZ Potsdam
 Internal Vision of GGOS Markus Rothacher GFZ Potsdam GGOS Retreat DGFI in Munich February 15-16, 2006 Contents Motivation Four Levels of Products of the IAG Services: First Level: Raw Data Collection Second
Internal Vision of GGOS Markus Rothacher GFZ Potsdam GGOS Retreat DGFI in Munich February 15-16, 2006 Contents Motivation Four Levels of Products of the IAG Services: First Level: Raw Data Collection Second
