Report of post doc project
|
|
|
- Horatio Clark
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Report of post doc project Researcher: Mohammad Hossein Mohammadi (SSTC fellowship) Supervisor: Professor Marnik Vanclooster Stay time: 21/July/2013 to 21/Nov/2013 Project title: AdvanCing the Hydrodynamic characterization of hillslopes (ACHILLES). 1-Introduction The important variability of intrinsic soil properties along a hillslope will subsequently be translated in a strong differentiation of soil hydrological and biogeochemical functioning. In terms of soil hydrological functioning, for instance, it is well known that the hillslope topography largely controls the soil moisture distribution and associated soil moisture fluxes. In addition, the systematic variation (organized patterns) of soil properties along the hillslope transect (or similarity between some characteristics) may allow predicting and modeling the soil functions with limited experimental data. The current project is embedded in an ARC project that aims to understand the controls of carbon dioxide fluxes in soils of a hillslope. (UCL-ARC: The hillslope as elementary unit for regional scale modeling of soil organic carbon emission ( )). The specific objective of the SSTC post-doc project is to understand the link between CO2 fluxes and hydraulic controls at the hillslope scale. The study is carried out in the Belgian loam belt along a cultivated hillslope of 150 meters length ( N, W) in the Marbaix experimental site in Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium. The experimental hillslope has been equipped for monitoring hydrological and carbon turnover fluxes with an unprecedented high spatial resolution within the framework of the SSTC projects HYDRASENS (HYDRASENS: Integrating radar remote sensing, hydrologic and hydraulic modelling for surface water management, SSTC, ) and the UCL- ARC project. In summary this post-doc project aims to reduce the uncertainty in modeling hydrodynamic processes and biogeochemical cycling at the hillslope scale, by reducing the uncertainty in the assessment of spatially distributed field of hydraulic properties (moisture retention and hydraulic conductivity) within the hillslope. 2- Research methodology 2-1 The experimental hillslope 2-1-1) Measurement stations. Detailed background data (soil map, geological map, land use and land use history map) are available for the site. In addition, 4 measurement stations were selected at different slope positions along the transect: the summit, the shoulder, the backslope and the footslope (fig 1). At each of the 4 stations, the following hydrogeophysical monitoring program is operational for the experimental hillslope from spring 2012 onwards: time lapse electrical resistivity measurements using a 164 surface electrode surface array; time lapse electrical resistivity measurements at 4 local stations using borehole and surface electrical resistivity measurements; and at 3 local stations, fully automated time lapse (hourly) TDR measurements using a 24 channel TDR device. In addition, at each of the 4 stations, soil surface CO 2 fluxes have been measured by means of a portable infra-red gas analyzer with an automated closed dynamic chamber (LI-8100A system, LI-COR, United-States), and also soil CO 2 concentrations have been measured by means of specific designed soil CO2probes.
2 2-1-2) Sampling locations. The sampling locations are shown in figure 1. At each of the 4 stations and also at the midway between two units, totally 9 positions were selected to take disturbed and undisturbed soil samples and to conduct soil physical experiments. Backslope 4 Measurement stations Shoulder Summit Footslope Toetslope 9 Sampling locations Fig. 1. Hillslope and schematic representation of the study site (profile view) and, 4 measurement stations and 9 soil sampling locations along the hillslope (plan view). Samples: 1- Small samples (5cm id * 5cm h): 3 small undisturbed soil samples were taken from each position and each pedogenic horizon. Total number is Large samples (4.5cm id * 100cm h). Undisturbed soil samples were taken along the transect. Total number is Disturbed samples: From each sampling position and pedogenic horizon, a ~2 Kg soil sample was taken. 2-2-Experiments In-situ experiments Gas conductivity experiment. A hand-made instrument was designed and constructed based on the "Marriot device" steady out flow. One-dimensional advective air flux in soils was measured for the top soil at each sampling position (with 5 replicates) according to the method of Iversen et al (2001). This experiment was repeated for different soil moisture contents (at least 5 moisture contents) to achieve the relationships between the soil moisture content and the gas conductivity. Double ring infiltration rate. Infiltration was measured using a double ring infiltrometer, with 32 cm inner diameter and 53 cm outer diameter rings (four replicates) installed in the each sampling position. Grass was carefully cut at the soil surface with shears in the inner and outer rings. A constant water head of approximately 2 cm was kept in both rings and amount of the water drop and the depth of added water were recorded.
3 Single ring infiltration rate. The infiltration rate was also measured in field with a single ring infiltrometer which is merely a thin ring that is pushed partly into the soil and then ponded with water (Reynolds et al 2002). For each sampling position, different size of rings (including; 5, 8.1, 11.2, 16.4, 32, 53 cm) were used to estimate the macroscopic length scale, saturated hydraulic conductivity and the eventual effect of preferential flow. Dye tracer experiments. At the end of in-situ experiments, a dye tracer experiment was conducted with 2 g/l Rhodamine B (CI 45170) and a soil vertical profile(width=1.2m) was diged up to depth of 150 cm for the each hillslope unit (five experiments). Image analysis was subsequently conducted on the vertical view for the each hillslope unit Laboratory experiments Soil moisture characteristic curve (SMC). The SMCs were obtained using a hanging water column ( kpa), pressure plate ( kpa), and pressure membrane apparatus ( kpa) (Dane and Hopmans, 2002). The soil bulk density and porosity were also measured during the measurement of the SMC. Soil particle size distribution (PSD). The PSD was determined using a hydrometer and the sieving method according to Gee and Or (2002).Totally 20 size fractions were measured. The pipette method was also used to determine the soil texture and to verify the hydrometer method. Aggregate size distributions.wet sieving was performed on soil aggregates smaller than 8 mm (Yoder 1936). An undisturbed sample was placed on the nest of sieves consisting of eight aperture sizes,8, 4.75, 2, 1, 0.5, 0.25, 0.15 and mm, and then gently submerged in the standard water. The samples were shaken for 10 min with a vertical stroke (~30 mm distance and speed of ~35 cycles min 1 ). Gas conductivity experiment. The field gas conductivity instrument was adopted to measure air flux in small soil samples (5cm id * 5cm h). This experiment was conducted for different soil moisture contents (at least 8 moisture contents) to achieve the relationships between the soil moisture content and the gas conductivity (Iversen et al., 2001). All laboratory experiments were conducted on the soil samples taken from each position and each pedogenic horizon with at least 3 replicates. Note that during the post-doc stay, the monitoring of hydraulic behavior was ensured by other members of the project team. This monitoring encompassed the measurement of soil moisture related attributes by means of TDR, GPR, and ERT probes. Soil thermal behavior was monitored through the use of CTN probes. Soil respiration was assessed by the infrared technique. 3-Results 3-1) Linking soil hydraulic characteristics to soil basic properties A priori-estimates of the hydraulic propertes of the macrostructural units of the hillslope can be obtained from pedo-transfer functions (PTFs) (e.g. Weynants et al., 2009; Mohammadi and Vanclooster, 2011). We studied the organized patterns of soil basic properties and eventual correlations with the soil carbon flux and hydraulic characteristics. We aim finding the control depth of infiltration processes and studying
4 the eventual relation with the pedogenics horizons along the transect. To this end, we first improved the theoretical concepts aiming to link basic physical attributes to hydraulic behavior of the soil. These improvement are currently in the process of publication (Meskini-Vishkaee et al,2014; Mohammadi et al., 2014). 3-2) Study the effect of the macropores and the sample size and scale on hydraulic properties and CO2 diffusion. Much progress has recently been made with the hydraulic characterization of the local flow properties using simple fast in-situ flow and tracer experiments (e.g. Lassabatère et al., 2006). The objective of this task is to carry out a set of fast in-situ flow and transport experiment and to use these in combination with existing conceptual models to assess flow parameters and associated uncertainty from insitu experiments, and their link with CO2 respiration. The experiments supporting this research task have been performed, but time is needed to improve the analysis and writing the research papers related to this topic. 4-Output (joint publications) During the first stay a conference paper was published, and two A1 research papers were submitted for publication (one has been accepted for publication, the other one is in review). Mohammadi, M.H., F. Wiaux, K. Van Oost, S. Lambot, M. Vanclooster, Linking the soil C0 2 emission to soil hydraulic properties at the hillslope scale. SOMpatic 2013 (Rauischholzhausen, Germany, du 20/11/2013 au 22/11/2013). In: Book of abstracts, Justus-Liebig Universität Giessen: Germany, F. Meskini-Vishkaee, M. H. Mohammadi and M. Vanclooster, A Scaling Approach, Predicting the Continuous Form of Soil Moisture Characteristics Curve, from Soil Particle Size Distribution and Bulk Density Data. Hydrology and Earth Sciences Systems. In review. Mohammadi, M.H., M. Khattar and M. Vanclooster, Combining a single hydraulic conductivity measurement data with soil particle size distribution data for estimating the full range partially saturated hydraulic conductivity curve. Soil Science Society of America Journal. In press. Two research papers are also in preparation as follows: 1- The effect of sample size and scale in prediction of soil hydraulic properties with using the BEST method. 2- The effect of the soil structure and macropores on CO2 emission at hilslope scale. 5) Perspectives for the second research stay 5-1) The quality and quantity of the organic carbon (OC) may affect the pore shape and size distribution (PSSD). Both the SMC and the air diffusivity are affected by PSSD.
5 However, PSSD variation due to OC will only be visible at the microscopic scale. Insights in the soil microstructure can improve the interpretation between soil gas diffusion in partially saturated soils. We will detect the PSSD data with using image analysis technique. This technique allows us to measure soil hydraulic properties at small scales. The OC can be measured at small scale, so it would be possible to investigate the eventual relationships between PSSD and OC along the soil horizons. Since we have prepared 28 large undisturbed soil sample, we analysis the OC micro-structure and variability and, we prepare thin section for eventual the X ray tomography or the micro morphology experiments (which is available) during the second stay. 5-2) Data fusion and hydrodynamic modeling. In this last workpackage, results from the previous experiments will be integrated to constrain the hydrodynamic inversion of the soil moisture maps for inferring the hydraulic parameters. The time lapse ERT and GPR- EMI data will be fused to obtain time lapse soil moisture fields of the hillslope using Bayesian approaches. These soil moisture time series will subsequently be inverted using an inverse hydrodynamic model (HYDRUS 2D) constrained by the a-priori estimates as assessed from PTFs and local scale fast in-situ flow experiments, using global parameter research strategies (e.g. Vrugt et al., 2008). References Iversen, B.V., Schjonning, P., Poulsen, T.G., and Moldrup, P.2001.In situ, on site and laboratory measurements of soil air permeability: Boundary conditions and measurement scale. Soil Sci. 166: Reynolds, W. D., Elrick, D. E., Youngs, E. G., Amoozegar, A., Booltink, H. W. G., and Bouma, J Saturated and field-saturated water flow parameters. In Dane, J. H. and Clake, G. C. (eds.) Methods of soil analysis. Part, 4. SSSA Book Series No. 5. SSSA, Madison. pp Dane, J. H. and Hopmans, J Water retention and storage. In Dane, J. H. and Clake, G. C. (eds.) Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 4. Physical Methods. SSSA Book Series No. 5. SSSA, Madison. pp Gee, G. W. and Or, D Particle-size analysis. In Dane, J. H. and Clake. G. C. (eds.) Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 4. Physical Methods. SSSA Book Series No. 5. SSSA, Madison. pp Yoder, R.E A direct method of aggregate analysis of soils and a study of the physical nature of erosion losses. J. Am.Soc. Agron. 28: Lassabatère, L., R. Angulo-Jaramillo, J. M. Soria Ugalde, R. Cuenca, I. Braud, and Haverkamp, R Beerkan stimation of soil transfer parameters through infiltration experiments BEST. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 70: Mohammadi, M. H., and Vanclooster, M Predicting the soil moisture characteristic curve from particle size distribution with a simple conceptual model. Vados. Zone J. 10:
6 Wiaux, F., J. T. Cornelis, K. Van Oost, and Vanclooster, M Space-time dynamics of soil respiration link to a C pool differentiation of the hillslope scale: an experimental study, paper presented at ENVITAM-GEPROC Ph D student day, Gembloux Agro- Biotec. Weynants, M., H. Vereecken, and Javaux, M Revisiting Vereecken pedotransfer functions: introducing a closed-form hydraulic model. Vados. Zone J. 8:
Site Characterization & Hydrogeophysics
 Site Characterization & Hydrogeophysics (Source: Matthew Becker, California State University) Site Characterization Definition: quantitative description of the hydraulic, geologic, and chemical properties
Site Characterization & Hydrogeophysics (Source: Matthew Becker, California State University) Site Characterization Definition: quantitative description of the hydraulic, geologic, and chemical properties
GLG 471; MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY INSTRUCTOR R.L. VAN DAM PROJECT: ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY
 GLG 471; MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY INSTRUCTOR R.L. VAN DAM PROJECT: ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY General information: This is a group (2-3 students) project requiring lab-, computer-, and fieldwork. Work will
GLG 471; MICHIGAN STATE UNIVERSITY INSTRUCTOR R.L. VAN DAM PROJECT: ELECTRICAL RESISTIVITY General information: This is a group (2-3 students) project requiring lab-, computer-, and fieldwork. Work will
11280 Electrical Resistivity Tomography Time-lapse Monitoring of Three-dimensional Synthetic Tracer Test Experiments
 11280 Electrical Resistivity Tomography Time-lapse Monitoring of Three-dimensional Synthetic Tracer Test Experiments M. Camporese (University of Padova), G. Cassiani* (University of Padova), R. Deiana
11280 Electrical Resistivity Tomography Time-lapse Monitoring of Three-dimensional Synthetic Tracer Test Experiments M. Camporese (University of Padova), G. Cassiani* (University of Padova), R. Deiana
2D Electrical Resistivity Tomography survey optimisation of solute transport in porous media
 ArcheoSciences Revue d'archéométrie 33 (suppl.) 2009 Mémoire du sol, espace des hommes 2D Electrical Resistivity Tomography survey optimisation of solute transport in porous media Gregory Lekmine, Marc
ArcheoSciences Revue d'archéométrie 33 (suppl.) 2009 Mémoire du sol, espace des hommes 2D Electrical Resistivity Tomography survey optimisation of solute transport in porous media Gregory Lekmine, Marc
Comparison of geophysical. techniques to determine depth to. bedrock in complex weathered. environments of the Mount Crawford. region, South Australia
 Comparison of geophysical techniques to determine depth to bedrock in complex weathered environments of the Mount Crawford region, South Australia Thesis submitted in accordance with the requirements of
Comparison of geophysical techniques to determine depth to bedrock in complex weathered environments of the Mount Crawford region, South Australia Thesis submitted in accordance with the requirements of
21 st century hydrological modelling for optimizing ancient water harvesting techniques
 21 st century hydrological modelling for optimizing ancient water harvesting techniques Wim Cornelis (1), Koen Verbist (1), Rob G.McLaren (2), Guido Soto (3), Donald Gabiels (1) (1) Ghent University, Dept.
21 st century hydrological modelling for optimizing ancient water harvesting techniques Wim Cornelis (1), Koen Verbist (1), Rob G.McLaren (2), Guido Soto (3), Donald Gabiels (1) (1) Ghent University, Dept.
Modeling soil hydrologic processes at hillslope or catchment scales requires
 Soil Pysics Note Analysis of te Role of Tortuosity and Infiltration Constants in te Beerkan Metod Paolo Nasta* Dep. of Land, Air and Water Resources Univ. of California Davis, CA 95618 Laurent Lassabatere
Soil Pysics Note Analysis of te Role of Tortuosity and Infiltration Constants in te Beerkan Metod Paolo Nasta* Dep. of Land, Air and Water Resources Univ. of California Davis, CA 95618 Laurent Lassabatere
Oak Ridge IFRC. Quantification of Plume-Scale Flow Architecture and Recharge Processes
 Oak Ridge IFRC Quantification of Plume-Scale Flow Architecture and Recharge Processes S. Hubbard *1, G.S. Baker *2, D. Watson *3, D. Gaines *3, J. Chen *1, M. Kowalsky *1, E. Gasperikova *1, B. Spalding
Oak Ridge IFRC Quantification of Plume-Scale Flow Architecture and Recharge Processes S. Hubbard *1, G.S. Baker *2, D. Watson *3, D. Gaines *3, J. Chen *1, M. Kowalsky *1, E. Gasperikova *1, B. Spalding
On the hydraulic properties of coarse-textured sediments at intermediate water contents
 WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 39, NO. 9, 1233, doi:10.1029/2003wr002387, 2003 On the hydraulic properties of coarse-textured sediments at intermediate water contents Raziuddin Khaleel Fluor Federal Services,
WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 39, NO. 9, 1233, doi:10.1029/2003wr002387, 2003 On the hydraulic properties of coarse-textured sediments at intermediate water contents Raziuddin Khaleel Fluor Federal Services,
SUMMER SCHOOL on PESTICIDE AND ENVIRONMENT Ancona, Italy, September Transport processes determining pesticide behaviour in soil. M.
 SUMMER SCHOOL on PESTICIDE AND ENVIRONMENT Ancona, Italy, September 2003 Transport processes determining pesticide behaviour in soil M. Vanclooster Department of environmental sciences and land use planning
SUMMER SCHOOL on PESTICIDE AND ENVIRONMENT Ancona, Italy, September 2003 Transport processes determining pesticide behaviour in soil M. Vanclooster Department of environmental sciences and land use planning
SASKATCHEWAN STRATIGRAPHY GLACIAL EXAMPLE BOULDERS IN GLACIAL DEPOSITS
 SASKATCHEWAN STRATIGRAPHY GLACIAL EXAMPLE BOULDERS IN GLACIAL DEPOSITS 51 SASKATCHEWAN STRATIGRAPHY GLACIAL SURFICIAL STRATIFIED DEPOSITS 52 SASKATCHEWAN STRATIGRAPHY GLACIAL EXAMPLE OF SEDIMENT DEPOSITION
SASKATCHEWAN STRATIGRAPHY GLACIAL EXAMPLE BOULDERS IN GLACIAL DEPOSITS 51 SASKATCHEWAN STRATIGRAPHY GLACIAL SURFICIAL STRATIFIED DEPOSITS 52 SASKATCHEWAN STRATIGRAPHY GLACIAL EXAMPLE OF SEDIMENT DEPOSITION
Imaging Critical Zone Processes
 Imaging Critical Zone Processes Kamini Singha Hydrologic Science and Engineering Colorado School of Mines With contributions from: Xavier Comas, Jorden Hayes, and Andy Parsekian Key critical zone processes
Imaging Critical Zone Processes Kamini Singha Hydrologic Science and Engineering Colorado School of Mines With contributions from: Xavier Comas, Jorden Hayes, and Andy Parsekian Key critical zone processes
C18 Hydrogeophysical Monitoring of Landslide Processes Using Automated Time-Lapse Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ALERT)
 C18 Hydrogeophysical Monitoring of Landslide Processes Using Automated Time-Lapse Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ALERT) J.E. Chambers* (British Geological Survey), P.I. Meldrum (British Geological
C18 Hydrogeophysical Monitoring of Landslide Processes Using Automated Time-Lapse Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ALERT) J.E. Chambers* (British Geological Survey), P.I. Meldrum (British Geological
Each basin is surrounded & defined by a drainage divide (high point from which water flows away) Channel initiation
 DRAINAGE BASINS A drainage basin or watershed is defined from a downstream point, working upstream, to include all of the hillslope & channel areas which drain to that point Each basin is surrounded &
DRAINAGE BASINS A drainage basin or watershed is defined from a downstream point, working upstream, to include all of the hillslope & channel areas which drain to that point Each basin is surrounded &
Liquefaction Resistance and Internal Erosion Potential of Non-Plastic Silty Sand
 Liquefaction Resistance and Internal Erosion Potential of Non-Plastic Silty Sand Jing-Wen CHEN 1, Wei F. LEE 2, Chun-Chi CHEN 3 1 Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, National Chen-Kung University
Liquefaction Resistance and Internal Erosion Potential of Non-Plastic Silty Sand Jing-Wen CHEN 1, Wei F. LEE 2, Chun-Chi CHEN 3 1 Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, National Chen-Kung University
PHYSICO-MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF ROCKS LECTURE 2. Contents
 PHYSICO-MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF ROCKS LECTURE 2 Contents 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Rock coring and logging 2.3 Physico-mechanical properties 2.3.1 Physical Properties 2.3.1.1 Density, unit weight and specific
PHYSICO-MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF ROCKS LECTURE 2 Contents 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Rock coring and logging 2.3 Physico-mechanical properties 2.3.1 Physical Properties 2.3.1.1 Density, unit weight and specific
ψ ae is equal to the height of the capillary rise in the soil. Ranges from about 10mm for gravel to 1.5m for silt to several meters for clay.
 Contents 1 Infiltration 1 1a Hydrologic soil horizons...................... 1 1b Infiltration Process......................... 2 1c Measurement............................ 2 1d Richard s Equation.........................
Contents 1 Infiltration 1 1a Hydrologic soil horizons...................... 1 1b Infiltration Process......................... 2 1c Measurement............................ 2 1d Richard s Equation.........................
On the influence of coarse fragments on soil water retention
 WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 45, W07408, doi:10.1029/2008wr007402, 2009 On the influence of coarse fragments on soil water retention J. M. Baetens, 1 K. Verbist, 1,2 W. M. Cornelis, 1 D. Gabriels, 1
WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 45, W07408, doi:10.1029/2008wr007402, 2009 On the influence of coarse fragments on soil water retention J. M. Baetens, 1 K. Verbist, 1,2 W. M. Cornelis, 1 D. Gabriels, 1
In situ estimation of soil hydraulic functions using a multistep soil-water extraction technique
 WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 34, NO. 5, PAGES 1035 1050, MAY 1998 In situ estimation of soil hydraulic functions using a multistep soil-water extraction technique M. Inoue Arid Land Research Center,
WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH, VOL. 34, NO. 5, PAGES 1035 1050, MAY 1998 In situ estimation of soil hydraulic functions using a multistep soil-water extraction technique M. Inoue Arid Land Research Center,
Infiltration Characteristics of Granitic Residual Soil of Various Weathering Grades
 American Journal of Environmental Sciences (): 64-68, 25 ISSN 553-345X Science Publications, 25 Infiltration Characteristics of Granitic Residual Soil of Various Weathering Grades Faisal Hj. Ali, 2 Bujang
American Journal of Environmental Sciences (): 64-68, 25 ISSN 553-345X Science Publications, 25 Infiltration Characteristics of Granitic Residual Soil of Various Weathering Grades Faisal Hj. Ali, 2 Bujang
Custom Soil Resource Report Soil Map
 77 35' 22'' W Custom Soil Resource Report Soil Map 77 35' 0'' W 282170 282220 282270 282320 282370 282420 282470 282520 282570 282620 40 59' 2'' N 40 58' 52'' N 4539900 4539950 4540000 4540050 4540100
77 35' 22'' W Custom Soil Resource Report Soil Map 77 35' 0'' W 282170 282220 282270 282320 282370 282420 282470 282520 282570 282620 40 59' 2'' N 40 58' 52'' N 4539900 4539950 4540000 4540050 4540100
Workshop Opening Presentation of the DYNAS Project
 Workshop Opening Presentation of the DYNAS Project Alexandre Ern, Eric Gaume, Cyril Kao, Jérôme Jaffré CERMICS École Nationale des Ponts et Chausées Marne-la-Vallée, France DYNAS Workshop 06-08/12/04 p.1
Workshop Opening Presentation of the DYNAS Project Alexandre Ern, Eric Gaume, Cyril Kao, Jérôme Jaffré CERMICS École Nationale des Ponts et Chausées Marne-la-Vallée, France DYNAS Workshop 06-08/12/04 p.1
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10)
 Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
Surface Processes Focus on Mass Wasting (Chapter 10) 1. What is the distinction between weathering, mass wasting, and erosion? 2. What is the controlling force in mass wasting? What force provides resistance?
FLOOD1 report: Appendix 3
 FLOOD1 report: Appendix 3 Summary of Laboratory Testing Programme Part of the investigation into the behaviour of groundwater in the unsaturated zone of the Chalk required testing samples to determine
FLOOD1 report: Appendix 3 Summary of Laboratory Testing Programme Part of the investigation into the behaviour of groundwater in the unsaturated zone of the Chalk required testing samples to determine
EXAMPLE PROBLEMS. 1. Example 1 - Column Infiltration
 EXAMPLE PROBLEMS The module UNSATCHEM is developed from the variably saturated solute transport model HYDRUS-1D [Šimůnek et al., 1997], and thus the water flow and solute transport parts of the model have
EXAMPLE PROBLEMS The module UNSATCHEM is developed from the variably saturated solute transport model HYDRUS-1D [Šimůnek et al., 1997], and thus the water flow and solute transport parts of the model have
Experimental study of the hydromechanical coupling in argillaceous rocks: the example of Boom clay
 Experimental study of the hydromechanical coupling in argillaceous rocks: the example of Boom clay Financial support of the EU: SELFRAC scientific project DIGA network Cécile Coll (GeomaC, Liège) Jacques
Experimental study of the hydromechanical coupling in argillaceous rocks: the example of Boom clay Financial support of the EU: SELFRAC scientific project DIGA network Cécile Coll (GeomaC, Liège) Jacques
Boreholes. Implementation. Boring. Boreholes may be excavated by one of these methods: 1. Auger Boring 2. Wash Boring 3.
 Implementation Boreholes 1. Auger Boring 2. Wash Boring 3. Rotary Drilling Boring Boreholes may be excavated by one of these methods: 4. Percussion Drilling The right choice of method depends on: Ground
Implementation Boreholes 1. Auger Boring 2. Wash Boring 3. Rotary Drilling Boring Boreholes may be excavated by one of these methods: 4. Percussion Drilling The right choice of method depends on: Ground
Electrical Resistivity of Compacted Kaolin and its Relation with Suction
 Electrical Resistivity of Compacted Kaolin and its Relation with Suction Dias, Ana Sofia ana.sofia.dias@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Summary The electrical characteristics of compacted kaolin were studied and related
Electrical Resistivity of Compacted Kaolin and its Relation with Suction Dias, Ana Sofia ana.sofia.dias@tecnico.ulisboa.pt Summary The electrical characteristics of compacted kaolin were studied and related
Landscapes & Hydric Soils Bruce Vasilas University of Delaware
 Landscapes & Hydric Soils Bruce Vasilas University of Delaware Hydric soils are defined as soils that formed under conditions of saturation, flooding, or ponding long enough during the growing season to
Landscapes & Hydric Soils Bruce Vasilas University of Delaware Hydric soils are defined as soils that formed under conditions of saturation, flooding, or ponding long enough during the growing season to
HYDROPEDOLOGY AND WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT: CASE STUDY OF AL-KHOUD RECHARGE DAM- OMAN
 HYDROPEDOLOGY AND WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT: CASE STUDY OF AL-KHOUD RECHARGE DAM- OMAN Dr. Ali Al-Maktoumi Sultan Qaboos University, Oman Gulf Water Conference 11 th 20-22 October 2014 Co-authors: Al-Saqri,
HYDROPEDOLOGY AND WATER RESOURCES MANAGEMENT: CASE STUDY OF AL-KHOUD RECHARGE DAM- OMAN Dr. Ali Al-Maktoumi Sultan Qaboos University, Oman Gulf Water Conference 11 th 20-22 October 2014 Co-authors: Al-Saqri,
NHBRA SOIL LABORATORY SECTION INTERIM REVISED TEST RATES FOR THE MATERIALS LABORATORY
 NHBRA SOIL LABORATORY SECTION INTERIM REVISED TEST RATES FOR THE MATERIALS LABORATORY DATE OF REVISION: ) 10th October 2010 S/N TEST DESCRIPTION UNIT RATE REMARKS 1 Sieve Analysis (wet and dry methods
NHBRA SOIL LABORATORY SECTION INTERIM REVISED TEST RATES FOR THE MATERIALS LABORATORY DATE OF REVISION: ) 10th October 2010 S/N TEST DESCRIPTION UNIT RATE REMARKS 1 Sieve Analysis (wet and dry methods
Procedure for Determining Near-Surface Pollution Sensitivity
 Procedure for Determining Near-Surface Pollution Sensitivity Minnesota Department of Natural Resources Division of Ecological and Water Resources County Geologic Atlas Program March 2014 Version 2.1 I.
Procedure for Determining Near-Surface Pollution Sensitivity Minnesota Department of Natural Resources Division of Ecological and Water Resources County Geologic Atlas Program March 2014 Version 2.1 I.
Schedule of Accreditation issued by United Kingdom Accreditation Service 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK
 2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK Parkside Lane Dewsbury Road Leeds LS11 5SX Contact: Mr K Walker Tel: +44 (0)113 385 9157 Fax: +44 (0)113 276 0472 E-Mail: Kevin.Walker@soil-engineering.co.uk
2 Pine Trees, Chertsey Lane, Staines-upon-Thames, TW18 3HR, UK Parkside Lane Dewsbury Road Leeds LS11 5SX Contact: Mr K Walker Tel: +44 (0)113 385 9157 Fax: +44 (0)113 276 0472 E-Mail: Kevin.Walker@soil-engineering.co.uk
2nd International Conference Mechanics of Unsaturated Soils 7 th 9 th March 2007
 2nd International Conference Determination of the Soil Water Retention Curve and the Unsaturated Hydraulic Conductivity from the Particle Size Distribution Alexander Scheuermann & Andreas Bieberstein Motivation
2nd International Conference Determination of the Soil Water Retention Curve and the Unsaturated Hydraulic Conductivity from the Particle Size Distribution Alexander Scheuermann & Andreas Bieberstein Motivation
Joint inversion of geophysical and hydrological data for improved subsurface characterization
 Joint inversion of geophysical and hydrological data for improved subsurface characterization Michael B. Kowalsky, Jinsong Chen and Susan S. Hubbard, Lawrence Berkeley National Lab., Berkeley, California,
Joint inversion of geophysical and hydrological data for improved subsurface characterization Michael B. Kowalsky, Jinsong Chen and Susan S. Hubbard, Lawrence Berkeley National Lab., Berkeley, California,
1. Water in Soils: Infiltration and Redistribution
 Contents 1 Water in Soils: Infiltration and Redistribution 1 1a Material Properties of Soil..................... 2 1b Soil Water Flow........................... 4 i Incorporating K - θ and ψ - θ Relations
Contents 1 Water in Soils: Infiltration and Redistribution 1 1a Material Properties of Soil..................... 2 1b Soil Water Flow........................... 4 i Incorporating K - θ and ψ - θ Relations
Instructional Objectives
 GE 6477 DISCONTINUOUS ROCK 8. Fracture Detection Dr. Norbert H. Maerz Missouri University of Science and Technology (573) 341-6714 norbert@mst.edu Instructional Objectives 1. List the advantages and disadvantages
GE 6477 DISCONTINUOUS ROCK 8. Fracture Detection Dr. Norbert H. Maerz Missouri University of Science and Technology (573) 341-6714 norbert@mst.edu Instructional Objectives 1. List the advantages and disadvantages
CHAPTER 2. SOIL-WATER POTENTIAL: CONCEPTS AND MEASUREMENT
 SSC107 Fall 2000 Chapter 2, Page - 1 - CHAPTER 2. SOIL-WATER POTENTIAL: CONCEPTS AND MEASUREMENT Contents: Transport mechanisms Water properties Definition of soil-water potential Measurement of soil-water
SSC107 Fall 2000 Chapter 2, Page - 1 - CHAPTER 2. SOIL-WATER POTENTIAL: CONCEPTS AND MEASUREMENT Contents: Transport mechanisms Water properties Definition of soil-water potential Measurement of soil-water
Prediction of Soil Properties Using Fuzzy Membership
 Prediction of Soil Properties Using Fuzzy Membership Zhu, A.X. 1,2 ; Moore, A. 3 ; Burt, J. E. 2 1 State Key Lab of Resources and Environmental Information System, Institute of Geographical Sciences and
Prediction of Soil Properties Using Fuzzy Membership Zhu, A.X. 1,2 ; Moore, A. 3 ; Burt, J. E. 2 1 State Key Lab of Resources and Environmental Information System, Institute of Geographical Sciences and
Measuring soil respiration in the field different chamber designs
 Measuring soil respiration in the field different chamber designs Introduction Earliest studies on soil respiration were conducted by incubating soil cores in laboratory (Lundegårdh 1922). Later a need
Measuring soil respiration in the field different chamber designs Introduction Earliest studies on soil respiration were conducted by incubating soil cores in laboratory (Lundegårdh 1922). Later a need
A COMPARISON BETWEEN IN SITU AND LABORATORY MEASUREMENTS OF PORE WATER PRESSURE GENERATION
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 1220 A COMPARISON BETWEEN IN SITU AND LABORATORY MEASUREMENTS OF PORE WATER PRESSURE GENERATION Kenan
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 1220 A COMPARISON BETWEEN IN SITU AND LABORATORY MEASUREMENTS OF PORE WATER PRESSURE GENERATION Kenan
Geo-imaging: An Introduction to Engineering Geophysics
 Geo-imaging: An Introduction to Engineering Geophysics Chih-Ping Lin Distinguished Professor, Department of Civil Engineering & Natural Hazard Mitigation Research Center National Chiao Tung University,
Geo-imaging: An Introduction to Engineering Geophysics Chih-Ping Lin Distinguished Professor, Department of Civil Engineering & Natural Hazard Mitigation Research Center National Chiao Tung University,
Tournemire Underground Laboratory: Geophysical Monitoring of Claystone Desaturation in a Ventilated Borehole.
 Tournemire Underground Laboratory: Geophysical Monitoring of Claystone Desaturation in a Ventilated Borehole. U.Zimmer, A. Genty, T. Rothfuchs, B. Bonin, J. Cabrera 1 Introduction With this paper, we will
Tournemire Underground Laboratory: Geophysical Monitoring of Claystone Desaturation in a Ventilated Borehole. U.Zimmer, A. Genty, T. Rothfuchs, B. Bonin, J. Cabrera 1 Introduction With this paper, we will
2017 NACTA Contest FAQs for 2-Year and 4-Year Universities
 2017 NACTA Contest FAQs for 2-Year and 4-Year Universities 1. Have you determined how many practice days there will be? a. We plan on having 10 practice sites. They will be open on Tuesday, Wednesday,
2017 NACTA Contest FAQs for 2-Year and 4-Year Universities 1. Have you determined how many practice days there will be? a. We plan on having 10 practice sites. They will be open on Tuesday, Wednesday,
Breakout Session III Evolving landscapes and global environmental change
 Breakout Session III Evolving landscapes and global environmental change 1. Hydrology and critical zone imaging 2. Glaciology: Instrumenting glaciers and ice sheets 3. Polar networks and glacial isostatic
Breakout Session III Evolving landscapes and global environmental change 1. Hydrology and critical zone imaging 2. Glaciology: Instrumenting glaciers and ice sheets 3. Polar networks and glacial isostatic
6.6 Solute Transport During Variably Saturated Flow Inverse Methods
 6.6 Solute Transport During Variably Saturated Flow Inverse Methods JIÌÍ ŠIMæNEK AND MARTINUS TH. VAN GENUCHTEN, USDA-ARS, George E. Brown, Jr. Salinity Laboratory, Riverside, California DIEDERIK JACQUES,
6.6 Solute Transport During Variably Saturated Flow Inverse Methods JIÌÍ ŠIMæNEK AND MARTINUS TH. VAN GENUCHTEN, USDA-ARS, George E. Brown, Jr. Salinity Laboratory, Riverside, California DIEDERIK JACQUES,
FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING GEOLOGY
 FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Prof. Dr. HUSSEIN HAMEED KARIM Building and Construction Engineering Department 2012 Preface The impulse to write this book stemmed from a course of geology given by
FUNDAMENTALS OF ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Prof. Dr. HUSSEIN HAMEED KARIM Building and Construction Engineering Department 2012 Preface The impulse to write this book stemmed from a course of geology given by
Towards modelling global soil erosion and its importance for the terrestrial carbon cycle
 Towards modelling global soil erosion and its importance for the terrestrial carbon cycle Tom Vanwalleghem 1 and Jed Kaplan 2 1 - Group for Rural Hydrology and Hydraulics, Department of Agronomy, University
Towards modelling global soil erosion and its importance for the terrestrial carbon cycle Tom Vanwalleghem 1 and Jed Kaplan 2 1 - Group for Rural Hydrology and Hydraulics, Department of Agronomy, University
2. RESPONSIBILITIES AND QUALIFICATIONS
 Questa Rock Pile Stability Study 65v1 Page 1 Standard Operating Procedure No. 65 Density by the sand-cone method used for volumetric moisture content REVISION LOG Revision Number Description Date 65.0
Questa Rock Pile Stability Study 65v1 Page 1 Standard Operating Procedure No. 65 Density by the sand-cone method used for volumetric moisture content REVISION LOG Revision Number Description Date 65.0
Measuring Ammonia in Water and Wastewater using the Thermo Scientific Orion Dual Star ph/ise Meter
 Measuring Ammonia in Water and Wastewater using the Thermo Scientific Orion Dual Star ph/ise Meter Water and Lab Products, Thermo Fisher Scientific Technical Note 505 Key Words Thermo Scientific Orion
Measuring Ammonia in Water and Wastewater using the Thermo Scientific Orion Dual Star ph/ise Meter Water and Lab Products, Thermo Fisher Scientific Technical Note 505 Key Words Thermo Scientific Orion
Development of multi-functional measurement devices for vadose zone characterization
 Development of multi-functional measurement devices for vadose zone characterization Jan Hopmans University of California, Davis, CA, USA Yasushi Mori Shimane University, Japan Annette Pia Mortensen Geological
Development of multi-functional measurement devices for vadose zone characterization Jan Hopmans University of California, Davis, CA, USA Yasushi Mori Shimane University, Japan Annette Pia Mortensen Geological
The impact of vegetation on the characteristics of the flow in an inclined open channel using the piv method
 Water Resources and Ocean Science 2012;1(1):1-6 Published online December 30, 2012 (http:// www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/wors) doi:.11648/j.wors.201201.11 The impact of vegetation on the characteristics
Water Resources and Ocean Science 2012;1(1):1-6 Published online December 30, 2012 (http:// www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/wors) doi:.11648/j.wors.201201.11 The impact of vegetation on the characteristics
Forest Hydrology: Lect. 9. Contents. Runoff, soil water and infiltration
 Forest Hydrology: Lect. 9 Contents Runoff, soil water and infiltration Learning objectives:. - Hillslope runoff generation processes; - Dynamics of runoff generation processes; - Hortonian and Dunnian
Forest Hydrology: Lect. 9 Contents Runoff, soil water and infiltration Learning objectives:. - Hillslope runoff generation processes; - Dynamics of runoff generation processes; - Hortonian and Dunnian
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Statement of the Problem Engineering properties of geomaterials are very important for civil engineers because almost everything we build - tunnels, bridges, dams and others
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Statement of the Problem Engineering properties of geomaterials are very important for civil engineers because almost everything we build - tunnels, bridges, dams and others
EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC METHODS FOR EARTHWORK ASSESSMENT
 Vol. 11, Issue 1/, 38-44 DOI:./cee--000 EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC METHODS FOR EARTHWORK ASSESSMENT Jozef VLČEK 1,*, Dominika ĎUREKOVÁ 2, Katarína ZGÚTOVÁ 2 1 Department of Geotechnics, Faculty of Civil Engineering,
Vol. 11, Issue 1/, 38-44 DOI:./cee--000 EVALUATION OF DYNAMIC METHODS FOR EARTHWORK ASSESSMENT Jozef VLČEK 1,*, Dominika ĎUREKOVÁ 2, Katarína ZGÚTOVÁ 2 1 Department of Geotechnics, Faculty of Civil Engineering,
1 EX/P4-8. Hydrogen Concentration of Co-deposited Carbon Films Produced in the Vicinity of Local Island Divertor in Large Helical Device
 1 EX/P4-8 Hydrogen Concentration of Co-deposited Carbon Films Produced in the Vicinity of Local Island Divertor in Large Helical Device T. Hino 1,2), T. Hirata 1), N. Ashikawa 2), S. Masuzaki 2), Y. Yamauchi
1 EX/P4-8 Hydrogen Concentration of Co-deposited Carbon Films Produced in the Vicinity of Local Island Divertor in Large Helical Device T. Hino 1,2), T. Hirata 1), N. Ashikawa 2), S. Masuzaki 2), Y. Yamauchi
1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND MODELS
 1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND ODELS 1.1 INTRODUCTION This Volume III in the series of textbooks is focused on applications of environmental isotopes in surface water hydrology. The term environmental means that
1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND ODELS 1.1 INTRODUCTION This Volume III in the series of textbooks is focused on applications of environmental isotopes in surface water hydrology. The term environmental means that
Kristine E. Baker. Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the. Masters of Science in Hydrology
 INVESTIGATION OF DIRECT AND INDIRECT HYDRAULIC PROPERTY LABORATORY CHARACTERIZATION METHODS FOR HETEROGENEOUS ALLUVIAL DEPOSITS: APPLICATION TO THE SANDIA-TECH VADOSE ZONE INFILTRATION TEST SITE by Kristine
INVESTIGATION OF DIRECT AND INDIRECT HYDRAULIC PROPERTY LABORATORY CHARACTERIZATION METHODS FOR HETEROGENEOUS ALLUVIAL DEPOSITS: APPLICATION TO THE SANDIA-TECH VADOSE ZONE INFILTRATION TEST SITE by Kristine
Agry 465 Exam October 18, 2006 (100 points) (9 pages)
 Agry 465 Exam October 18, 2006 (100 points) (9 pages) Name (4) 1. In each of the following pairs of soils, indicate which one would have the greatest volumetric heat capacity, and which would have the
Agry 465 Exam October 18, 2006 (100 points) (9 pages) Name (4) 1. In each of the following pairs of soils, indicate which one would have the greatest volumetric heat capacity, and which would have the
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING University of Engineering & Technology, Lahore. Fluid Mechanics Lab
 DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING University of Engineering & Technology, Lahore Fluid Mechanics Lab Introduction Fluid Mechanics laboratory provides a hands on environment that is crucial for developing
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING University of Engineering & Technology, Lahore Fluid Mechanics Lab Introduction Fluid Mechanics laboratory provides a hands on environment that is crucial for developing
Advanced Hydrology Prof. Dr. Ashu Jain Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Lecture 6
 Advanced Hydrology Prof. Dr. Ashu Jain Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 6 Good morning and welcome to the next lecture of this video course on Advanced Hydrology.
Advanced Hydrology Prof. Dr. Ashu Jain Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 6 Good morning and welcome to the next lecture of this video course on Advanced Hydrology.
Modeling effect of initial soil moisture on sorptivity and infiltration
 Modeling effect of initial soil moisture on sorptivity and infiltration Stewart, R. D., D. E. Rupp, M. R. Abou Najm, and J. S. Selker (213), Modeling effect of initial soil moisture on sorptivity and infiltration,
Modeling effect of initial soil moisture on sorptivity and infiltration Stewart, R. D., D. E. Rupp, M. R. Abou Najm, and J. S. Selker (213), Modeling effect of initial soil moisture on sorptivity and infiltration,
KINEROS2/AGWA. Fig. 1. Schematic view (Woolhiser et al., 1990).
 KINEROS2/AGWA Introduction Kineros2 (KINematic runoff and EROSion) (K2) model was originated at the USDA-ARS in late 1960s and released until 1990 (Smith et al., 1995; Woolhiser et al., 1990). The spatial
KINEROS2/AGWA Introduction Kineros2 (KINematic runoff and EROSion) (K2) model was originated at the USDA-ARS in late 1960s and released until 1990 (Smith et al., 1995; Woolhiser et al., 1990). The spatial
10. FIELD APPLICATION: 1D SOIL MOISTURE PROFILE ESTIMATION
 Chapter 1 Field Application: 1D Soil Moisture Profile Estimation Page 1-1 CHAPTER TEN 1. FIELD APPLICATION: 1D SOIL MOISTURE PROFILE ESTIMATION The computationally efficient soil moisture model ABDOMEN,
Chapter 1 Field Application: 1D Soil Moisture Profile Estimation Page 1-1 CHAPTER TEN 1. FIELD APPLICATION: 1D SOIL MOISTURE PROFILE ESTIMATION The computationally efficient soil moisture model ABDOMEN,
HYDRAULIC MODELING OF SOIL ERORION
 18-21 August 28, Daejeon, Korea HYDRAULIC MODELING OF SOIL ERORION Liu Qing-quan Institute of Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 18, China. Email: qqliu@imech.ac.cn ABSTRACT: The prediction
18-21 August 28, Daejeon, Korea HYDRAULIC MODELING OF SOIL ERORION Liu Qing-quan Institute of Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 18, China. Email: qqliu@imech.ac.cn ABSTRACT: The prediction
APPENDIX F CORRELATION EQUATIONS. F 1 In-Situ Tests
 APPENDIX F 1 APPENDIX F CORRELATION EQUATIONS F 1 In-Situ Tests 1. SPT (1) Sand (Hatanaka and Uchida, 1996), = effective vertical stress = effective friction angle = atmosphere pressure (Shmertmann, 1975)
APPENDIX F 1 APPENDIX F CORRELATION EQUATIONS F 1 In-Situ Tests 1. SPT (1) Sand (Hatanaka and Uchida, 1996), = effective vertical stress = effective friction angle = atmosphere pressure (Shmertmann, 1975)
GEOL151 Fall 2016: Lab for Week #4 Gooseneck Bend Slump
 GEOL151 Fall 2016: Lab for Week #4 Gooseneck Bend Slump Overview This week, we will investigate a recent example of dynamic hillslope processes: a slump (Figs. 1 and 2) that has caused damage to a road
GEOL151 Fall 2016: Lab for Week #4 Gooseneck Bend Slump Overview This week, we will investigate a recent example of dynamic hillslope processes: a slump (Figs. 1 and 2) that has caused damage to a road
Principles of soil water and heat transfer in JULES
 Principles of soil water and heat transfer in JULES Anne Verhoef 1, Pier Luigi Vidale 2, Raquel Garcia- Gonzalez 1,2, and Marie-Estelle Demory 2 1. Soil Research Centre, Reading (UK); 2. NCAS-Climate,
Principles of soil water and heat transfer in JULES Anne Verhoef 1, Pier Luigi Vidale 2, Raquel Garcia- Gonzalez 1,2, and Marie-Estelle Demory 2 1. Soil Research Centre, Reading (UK); 2. NCAS-Climate,
Estimating soil specific surface area using the summation of the number of spherical particles and geometric mean particle-size diameter
 African Journal of Agricultural Research Vol. 6(7), pp. 1758-1762, 4 April, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajar DOI: 10.5897/AJAR11.199 ISSN 1991-637X 2011 Academic Journals Full
African Journal of Agricultural Research Vol. 6(7), pp. 1758-1762, 4 April, 2011 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ajar DOI: 10.5897/AJAR11.199 ISSN 1991-637X 2011 Academic Journals Full
Experimental program in the URL
 Experimental program in the URL Jacques Delay Deputy Scientific Director July 21-24 th 2009 AGENCE NATIONALE POUR LA GESTION DES DÉCHETS RADIOACTIFS URL First construction step (2000 2006) Experimental
Experimental program in the URL Jacques Delay Deputy Scientific Director July 21-24 th 2009 AGENCE NATIONALE POUR LA GESTION DES DÉCHETS RADIOACTIFS URL First construction step (2000 2006) Experimental
Measurement, Monitoring & Verification. Dr. Lee H. Spangler, Director Zero Emission Research and Technology Center
 Measurement, Monitoring & Verification Dr. Lee H. Spangler, Director Zero Emission Research and Technology Center The Need for MMV Demonstration / Research Stage Health, Safety and Environmental concerns
Measurement, Monitoring & Verification Dr. Lee H. Spangler, Director Zero Emission Research and Technology Center The Need for MMV Demonstration / Research Stage Health, Safety and Environmental concerns
dynamics of f luids in porous media
 dynamics of f luids in porous media Jacob Bear Department of Civil Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York Contents Preface xvii CHAPTER 1 Introduction
dynamics of f luids in porous media Jacob Bear Department of Civil Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa DOVER PUBLICATIONS, INC. New York Contents Preface xvii CHAPTER 1 Introduction
Quantifying shallow subsurface flow and salt transport in the Canadian Prairies
 Quantifying shallow subsurface flow and salt transport in the Canadian Prairies Andrew Ireson GIWS, University of Saskatchewan www.usask.ca/water Uri Nachshon Garth van der Kamp GIWS, University of Saskatchewan
Quantifying shallow subsurface flow and salt transport in the Canadian Prairies Andrew Ireson GIWS, University of Saskatchewan www.usask.ca/water Uri Nachshon Garth van der Kamp GIWS, University of Saskatchewan
Patterns in Geophysical Data and Models
 Patterns in Geophysical Data and Models Jens Tronicke Angewandte Geophysik Institut für Geowissenschaften Universität Potsdam jens@geo.uni-potsdam.de Near-surface geophysics Using geophysical tools to
Patterns in Geophysical Data and Models Jens Tronicke Angewandte Geophysik Institut für Geowissenschaften Universität Potsdam jens@geo.uni-potsdam.de Near-surface geophysics Using geophysical tools to
Frost Determination by Electrical Resistance
 Frost Determination by Electrical Resistance ELMER F. ROWLAND, Engineering Aide, LEWIS H. STOLZY, Soil Conservationist, and GEORGE A. CRABB, Jr., Hydraulic Engineer Division of Soils Research, U. S. Department
Frost Determination by Electrical Resistance ELMER F. ROWLAND, Engineering Aide, LEWIS H. STOLZY, Soil Conservationist, and GEORGE A. CRABB, Jr., Hydraulic Engineer Division of Soils Research, U. S. Department
Geotechnical / Geophysical Investigation
 FEATURES TerraDol provides innovative geotechnical and geophysical exploration for civil construction projects including highway, railroad, subway, tunnel, bridge, port, and underground storage projects.
FEATURES TerraDol provides innovative geotechnical and geophysical exploration for civil construction projects including highway, railroad, subway, tunnel, bridge, port, and underground storage projects.
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1)
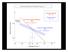 Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
The Afar Rift Consortium
 The Afar Rift Consortium University of Bristol University of Oxford University of Cambridge British Geological Survey University of Rochester University of Auckland, NZ Opportunistic programme following
The Afar Rift Consortium University of Bristol University of Oxford University of Cambridge British Geological Survey University of Rochester University of Auckland, NZ Opportunistic programme following
Remote Sensing and GIS Applications for Hilly Watersheds SUBASHISA DUTTA DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING IIT GUWAHATI
 Remote Sensing and GIS Applications for Hilly Watersheds SUBASHISA DUTTA DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING IIT GUWAHATI Deciding Alternative Land Use Options in a Watershed Using GIS Source: Anita Prakash
Remote Sensing and GIS Applications for Hilly Watersheds SUBASHISA DUTTA DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING IIT GUWAHATI Deciding Alternative Land Use Options in a Watershed Using GIS Source: Anita Prakash
Directorate E: Sectoral and regional statistics Unit E-4: Regional statistics and geographical information LUCAS 2018.
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate E: Sectoral and regional statistics Unit E-4: Regional statistics and geographical information Doc. WG/LCU 52 LUCAS 2018 Eurostat Unit E4 Working Group for Land
EUROPEAN COMMISSION EUROSTAT Directorate E: Sectoral and regional statistics Unit E-4: Regional statistics and geographical information Doc. WG/LCU 52 LUCAS 2018 Eurostat Unit E4 Working Group for Land
The Influence of Antecedent Soil Moisture Conditions on Inter-rill Soil Erosion
 The Influence of Antecedent Soil Moisture Conditions on Inter-rill Soil Erosion Ilja van Meerveld Ilja.van.meerveld@vu.nl Acknowledgements p Andrew Barry p Graham Sanders p Jean-Yves Parlange p Seifeddine
The Influence of Antecedent Soil Moisture Conditions on Inter-rill Soil Erosion Ilja van Meerveld Ilja.van.meerveld@vu.nl Acknowledgements p Andrew Barry p Graham Sanders p Jean-Yves Parlange p Seifeddine
Hydrological process simulation in the earth dam and dike by the Program PCSiWaPro
 Fakultät Umweltwissenschaften, Fachrichtung Hydrowissenschaften. Hydrological process simulation in the earth dam and dike by the Program PCSiWaPro Jinxing Guo, Peter-Wolfgang Graeber Table of contents
Fakultät Umweltwissenschaften, Fachrichtung Hydrowissenschaften. Hydrological process simulation in the earth dam and dike by the Program PCSiWaPro Jinxing Guo, Peter-Wolfgang Graeber Table of contents
Hydrological geophysical relationships
 International PhD Course in HYDROGEOPHYSICS Hydrological geophysical relationships Andrew Binley Lancaster University Overview In the course we will concentrate on electrical, electromagnetic and radar
International PhD Course in HYDROGEOPHYSICS Hydrological geophysical relationships Andrew Binley Lancaster University Overview In the course we will concentrate on electrical, electromagnetic and radar
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Flood and Flood Hazards Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG, Legon College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Flood and Flood Hazards Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG, Legon College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
Supporting Information. Methane bubble growth and migration in aquatic sediments observed by X-ray µct
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supporting Information Methane bubble growth and migration in aquatic sediments observed by X-ray µct Liu Liu, 1,* Tim De Kock, 2 Jeremy Wilkinson, 1 Veerle Cnudde, 2 Shangbin Xiao,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supporting Information Methane bubble growth and migration in aquatic sediments observed by X-ray µct Liu Liu, 1,* Tim De Kock, 2 Jeremy Wilkinson, 1 Veerle Cnudde, 2 Shangbin Xiao,
Groundwater Resource Evaluation in Support of Dewatering a South Carolina Limestone Quarry
 Groundwater Resource Evaluation in Support of Dewatering a South Carolina Limestone Quarry Daniel T. Brantley 1, John M. Shafer 2, and Michael G. Waddell 3 AUTHORS: 1 Research Associate, Earth Sciences
Groundwater Resource Evaluation in Support of Dewatering a South Carolina Limestone Quarry Daniel T. Brantley 1, John M. Shafer 2, and Michael G. Waddell 3 AUTHORS: 1 Research Associate, Earth Sciences
CONCEPTS Conservational Channel Evolution and Pollutant Transport System
 CONCEPTS Conservational Channel Evolution and Pollutant Transport System Eddy J. Langendoen Watershed Physical Processes Research Unit National Sedimentation Laboratory USDA Agricultural Research Service
CONCEPTS Conservational Channel Evolution and Pollutant Transport System Eddy J. Langendoen Watershed Physical Processes Research Unit National Sedimentation Laboratory USDA Agricultural Research Service
Permafrost monitoring at Mölltaler Glacier and Magnetköpfl
 Permafrost monitoring at Mölltaler Glacier and Magnetköpfl DAVID OTTOWITZ 1, BIRGIT JOCHUM 1, ROBERT SUPPER 1, ALEXANDER RÖMER 1, STEFAN PFEILER 1 and MARKUS KEUSCHNIG 2, 3 1 Department of Geophysics,
Permafrost monitoring at Mölltaler Glacier and Magnetköpfl DAVID OTTOWITZ 1, BIRGIT JOCHUM 1, ROBERT SUPPER 1, ALEXANDER RÖMER 1, STEFAN PFEILER 1 and MARKUS KEUSCHNIG 2, 3 1 Department of Geophysics,
Cyclic Triaxial Behavior of an Unsaturated Silty Soil Subjected to Suction Changes
 6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 215 Christchurch, New Zealand Cyclic Triaxial Behavior of an Unsaturated Silty Soil Subjected to Suction Changes T. Nishimura
6 th International Conference on Earthquake Geotechnical Engineering 1-4 November 215 Christchurch, New Zealand Cyclic Triaxial Behavior of an Unsaturated Silty Soil Subjected to Suction Changes T. Nishimura
Monitoring and Characterization of the Meadowview Lane Landslide: Boyd County, KY
 Monitoring and Characterization of the Meadowview Lane Landslide: Boyd County, KY Matt Crawford Appalachian Coalition for Geologic Hazards in Transportation 13 th Annual Technical Forum Harrisonburg, VA
Monitoring and Characterization of the Meadowview Lane Landslide: Boyd County, KY Matt Crawford Appalachian Coalition for Geologic Hazards in Transportation 13 th Annual Technical Forum Harrisonburg, VA
Application of Multivariate Geostatistics in Delineating Management Zones within a gravelly vineyard using geo-electrical electrical sensors
 Application of Multivariate Geostatistics in Delineating Management Zones within a gravelly vineyard using geo-electrical electrical sensors Francesco Morari, DAAPV, Università di Padova Annamaria Castrignanò,
Application of Multivariate Geostatistics in Delineating Management Zones within a gravelly vineyard using geo-electrical electrical sensors Francesco Morari, DAAPV, Università di Padova Annamaria Castrignanò,
Triaxial Shear Test. o The most reliable method now available for determination of shear strength parameters.
 TOPICS Introduction Components of Shear Strength of Soils Normal and Shear Stresses on a Plane Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criterion Laboratory Shear Strength Testing Direct Shear Test Triaxial Compression Test
TOPICS Introduction Components of Shear Strength of Soils Normal and Shear Stresses on a Plane Mohr-Coulomb Failure Criterion Laboratory Shear Strength Testing Direct Shear Test Triaxial Compression Test
Drainage Basin Geomorphology. Nick Odoni s Slope Profile Model
 Drainage Basin Geomorphology Nick Odoni s Slope Profile Model Odoni s Slope Profile Model This model is based on solving the mass balance (sediment budget) equation for a hillslope profile This is achieved
Drainage Basin Geomorphology Nick Odoni s Slope Profile Model Odoni s Slope Profile Model This model is based on solving the mass balance (sediment budget) equation for a hillslope profile This is achieved
DOWN-HOLE SEISMIC SURVEY AND VERTICAL ELECTRIC SOUNDINGS RABASKA PROJECT, LÉVIS, QUÉBEC. Presented to :
 DOWN-HOLE SEISMIC SURVEY AND VERTICAL ELECTRIC SOUNDINGS RABASKA PROJECT, LÉVIS, QUÉBEC Presented to : TERRATECH 455, René-Lévesque Blvd. West Montreal, Québec HZ 1Z3 Presented by : GEOPHYSICS GPR INTERNATIONAL
DOWN-HOLE SEISMIC SURVEY AND VERTICAL ELECTRIC SOUNDINGS RABASKA PROJECT, LÉVIS, QUÉBEC Presented to : TERRATECH 455, René-Lévesque Blvd. West Montreal, Québec HZ 1Z3 Presented by : GEOPHYSICS GPR INTERNATIONAL
Nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in restored riverine floodplains in intensively managed watersheds
 Nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in restored riverine floodplains in intensively managed watersheds Sara McMillan 1, Alex Johnson 1, Celena Alford 1, Greg Noe 2, Venkatesh Merwade 1, Sayan Dey, 1 Siddharth
Nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in restored riverine floodplains in intensively managed watersheds Sara McMillan 1, Alex Johnson 1, Celena Alford 1, Greg Noe 2, Venkatesh Merwade 1, Sayan Dey, 1 Siddharth
A Short Course in Contaminated Fractured Rock Hydrogeology and Geophysics
 A Short Course in Contaminated Fractured Rock Hydrogeology and Geophysics An Eight Hour Geophysics Course Offered Through the Environmental Professionals' Organization of Connecticut Date: Nov 19, Nov
A Short Course in Contaminated Fractured Rock Hydrogeology and Geophysics An Eight Hour Geophysics Course Offered Through the Environmental Professionals' Organization of Connecticut Date: Nov 19, Nov
Geophysics for Environmental and Geotechnical Applications
 Geophysics for Environmental and Geotechnical Applications Dr. Katherine Grote University of Wisconsin Eau Claire Why Use Geophysics? Improve the quality of site characterization (higher resolution and
Geophysics for Environmental and Geotechnical Applications Dr. Katherine Grote University of Wisconsin Eau Claire Why Use Geophysics? Improve the quality of site characterization (higher resolution and
Spatial Survey of Surface Soil Moisture in a Sub-alpine Watershed Colloquium Presentation, University of Denver, Department of Geography
 Thank you all for coming today. I will be talking about my thesis work concerning the spatial distribution of soil moisture in an alpine catchment. But first we need some background in soil moisture. Why
Thank you all for coming today. I will be talking about my thesis work concerning the spatial distribution of soil moisture in an alpine catchment. But first we need some background in soil moisture. Why
Calculation types: drained, undrained and fully coupled material behavior. Dr Francesca Ceccato
 Calculation types: drained, undrained and fully coupled material behavior Dr Francesca Ceccato Summary Introduction Applications: Piezocone penetration (CPTU) Submerged slope Conclusions Introduction Porous
Calculation types: drained, undrained and fully coupled material behavior Dr Francesca Ceccato Summary Introduction Applications: Piezocone penetration (CPTU) Submerged slope Conclusions Introduction Porous
Grimsel In-situ Stimulation and Circulation experiment: First results SCCER Annual meeting , Birmensdorf, Switzerland
 Grimsel In-situ Stimulation and Circulation experiment: First results SCCER Annual meeting 14 15.09.2017, Birmensdorf, Switzerland J. Doetsch, F. Amann, V. Gischig, M. Jalali, H. Krietsch, B. Valley, C.
Grimsel In-situ Stimulation and Circulation experiment: First results SCCER Annual meeting 14 15.09.2017, Birmensdorf, Switzerland J. Doetsch, F. Amann, V. Gischig, M. Jalali, H. Krietsch, B. Valley, C.
