The Jurassic Coast is an outdoor classroom for the study of geology, geomorphology, geography and biology.
|
|
|
- Scot Cross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
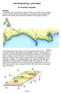
1 The Jurassic Coast is an outdoor classroom for the study of geology, geomorphology, geography and biology. The rocks at Kimmeridge Bay were once the floor of a fairly deep, subtropical sea rich in life. Within the bay, we find the type section for the Upper Jurassic Kimmeridge Clay Formation, which is the dominant source rock of the North Sea. It is also noteworthy that Kimmeridge is an international name; all around the world rocks of this age are known as Kimmeridgian. Blocks of stone from dolomite beds occur at intervals in the grey Kimmeridge Clay. They have formed during the generation of hydrocarbons in the organic-rich muds. A37 M5 A31 A30 Exeter Lyme Regis Dorchester Poole Bournemouth Sidmouth Exmouth Weymouth Lulworth Cove Durdle Door Kimmeridge Swanage 0 20 km Portland 58 GEO ExPro November 2006
2 The Jurassic Coast A few days of holiday can be well spent by walking leisurely through an almost complete Mesozoic succession along the south coast of England. Outcrops of colourful shales, sandstones and carbonates can be studied without the need for detailed prior knowledge. The rest of the family will also enjoy abundant fossils, beautiful beaches, lagoons and numerous bays, as well as small, picturesque towns next to the cliffs. Isle of Wight Portsmouth A27 Cartography: Masaoki Adachi Halfdan Carstens The Jurassic Coast, a narrow coastal strip of land lying between the top of the cliffs and the low water mark, was in 2001 awarded World Heritage Site status and became recognised as a place of outstanding universal value. The Jurassic Coast includes 155 km of unspoiled cliffs and beaches along the East Devon and Dorset coast. The main reason for its inscription as England s first natural World Heritage Site is the unique insight it gives to the Earth Sciences. Sedimentary rocks of Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous age record 185 million years of the Earth s history, and this rare geological display enables both the study of coastal geological processes that are changing the landscape, as well as the evolution of life through fossils that are easily found along almost the entire coast. Located on the south coast of Britain, the Jurassic Coast comprises a segment of undeveloped coast and countryside between East Devon in the west and Dorset in the east. More than 80% of this is cliffed coastline. This unique area has a combination of internationally renowned geological features considered by both palaeontologists and geomorphologists to be one of the most significant research sites for their respective fields of study.a World Heritage Site, it includes a nearcontinuous sequence of Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous rock exposures, representing almost the entire Mesozoic Era. The sequence of Jurassic strata exposed between Lyme Regis and Swanage is said to be among the best sections of marine Jurassic-age rocks to be found anywhere in the world. Impressive web-site Dr. Ian West has spent most of his life as a geologist amongst the coastal cliffs and has an intimate knowledge of the beaches, bays and lagoons of the Wessex Coast. After many years as a lecturer at Southampton University, he is now retired and working from home. The Dorset and East Devon World Heritage Coast provides classic and well-known exposures of the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous strata of southern England. It is important because they are varied, easily accessible, described in detail and in many cases, type sections or reference sections for understanding the Mesozoic geology of Europe, Ian explains. Because of rapid variation in rock type within a short distance, there is a wide variety of geomorphological features clearly visible. The coast is active and moving northwards rapidly as the English Channel continues its post-glacial expansion. The Jurassic Coast is not a static feature but is moving inland at a rate in places of a metre per annum. Remarkable geomorphological features such as Chesil Beach are the result of this, says Ian. Ian is now heavily involved in building and updating a web-site concerning the Jurassic Coast: ac.uk/~imw/. It is run in cooperation with the School of Ocean and Earth Science at the National Oceanographic Centre in Southampton and has an impressive content with both text and numerous photos. Nevertheless, he has some clear ambitions with respect to the web-site: My plan is to substantially expand this website over the coming years, he says. GEO ExPro November
3 Named by quarrymen As often as he can, he takes his car and drives down from Southampton to one of the many spectacular localities for another visit. With hammer and lens in hand, there are always new things to discover for the curious geologist. The large area of coastal cliffs provides a good opportunity to study the geological details which provide important information on the ancient environments. Because the cliffs of this classic area are within easy reach of London and Oxford, they have been studied in detail since In addition, geologists have given names and numbers to the strata of these cliffs. Names have also been applied to the strata by quarrymen in the past. Thus, individual beds of rocks have their own names: Glass Bottle, Cinder, Under Picking Cap, Skull Cap, Top Copper, Saurian Shales, Feather Bed, Spangle, Shrimp Bed, etc., etc. If you know a bed of rock by name you have a more personal interest in it and this increases one s enthusiasm to understand its history, Ian says. In addition to the Mesozoic strata, there are major features of geomorphological interest, including the famous Chesil Beach. The landslides involving the Lias in West Dorset and the Kimmeridge Clay in East Dorset are of great importance. The area is of special interest to petroleum geologists, partly because it lies close to the Wytch Farm Oil Field. It has the best Kimmeridge Clay exposures in the world and these include various bituminous shale source rocks and in particular, the Blackstone - the Kimmeridge oil shale. It has been worked since Iron Age times and was important to the Romans. The world famous section The Triassic rocks of East Devon are desert fluvial and sand dune sediments that were originally brown. They include the Sherwood Sandstone that constitutes the lower reservoir of the Wytch Farm oil field. The strata are red now because of water loss from ferric hydroxides during the heat of a long period of burial. The latitude was about 20 N and conditions were like those of the Sahara Desert. Gypsum and salt deposits are common. The halite is being used for gas storage on the Isle of Portland where these Triassic strata are deep underground, Ian explains. The Jurassic strata are from the shallow seas that flooded the rifted basins preceding the formation of the Atlantic Ocean. Dr. Ian West acquired an intimate knowledge of England s south coast by working the area throughout his entire career. He has made the geology of the Kimmeridge Bay and the Wessex Coast of southern England, available to the whole world through his comprehensive website soton.ac.uk/~imw/. The area's important fossil sites and classic coastal geomorphologic features have contributed to the study of earth sciences for over 300 years. They originated in less arid conditions; the environment was warm Mediterranean and the palaeolatitude about 30 to 35 N. Most of the deposits are limestone and sandstones of very shallow seas and the dark shales of rather deeper water. The latter were at times poorly oxygenated and the Kimmeridge Blackstone and the Black Ven Marls are black because of some similarities to the modern Black Sea environment. In the organic-rich shales the skeletons of marine animals, such as ichthyosaurs and plesiosaurs, have been well-preserved. The Dorset coast, and in particular, Lyme Regis, has received its fame from the creatures of the black waters. The Cretaceous is very varied because of large fluctuations in sea level, connected with the opening of the Atlantic and large variations in the rate of sea-floor spreading. The lower part is the product of paralic lagoons and of rivers and shallow deltas. This was followed by a change to marine sediments, and in the warm greenhouse environment the iron-rich clay mineral glauconite was developed on a large scale. As sea level rose because of the high spreading rate, the land around was flooded and the supply of clastics was greatly reduced. Thus came the pure white chalk sea of planktonic algal debris, says Ian. 60 GEO ExPro November 2006
4 The coastal landscape results from the way the power of the sea has acted on rocks of different resistance. At Lulworth, only twenty or so kilometres from Bournemouth, limestone forms a massive barrier against the sea. A small stream has caused a horseshoe bay by allowing the sea to enter the valley and remove the softer clays lying behind the limestone barrier. The World Heritage Coast Scheme The value of the Dorset and East Devon World Heritage Coast is obvious. Says Ian: It is protecting from development or destruction some of the best, most important and classic coastal sections of Mesozoic strata in England. Many of these strata are richly fossiliferous and there is easy access in many places. Because the area has been studied for almost 200 years there are numerous publications on the strata and its fossils. The Dorset and East Devon World Heritage Coast was opened in 2001 by Prince Charles, and is now well known and well accepted. It is surprisingly narrow, in many places it is only a few metres wide, and it does not include the cliff top coastal footpath or any land at all at the top of the cliffs. It would have been even better if a reasonable amount of cliff top land could have been included. However, in many places this deficiency is made up for by the fact that the National Trust and Country Parks The Jurassic Coast is also renowned for the study of beach formation and evolution on a retreating coastline. Chesil Beach, famous for the volume, type and grading of pebbles, is one of the best-studied beaches in the world. It is an outstanding example of a barrier beach. The Isle of Portland is in the foreground. GEO ExPro November
5 The Jurassic Coast has a unique status in the history of geological science. Regarded for more than 200 years as among the best available research sites anywhere for geological inquiry, the output of research has fundamentally shaped the development of geological thinking. own parts of the cliff top. The councils enforce strict planning regulations. Thus most of it consists of good cliff exposures with relatively unspoilt cliff-top land above. A good, long-distance, coastal footpath is present above it, explains Ian. All in all, the Dorset and East Devon World Heritage Coast protects what is quite probably the world s most well-known coastal sections of Mesozoic strata. Most of it has changed little since the 1940 s and there has only been limited loss of sections near the main towns. However, if it had not been protected for the future, it could have become an ugly concrete and rock armoured coast, with expensive second homes littering the cliff top. It is now preserved for geology, research and education and as a general natural environment for the public. It is greatly valued and will continue as a national and international treasure, concludes Dr. Ian West, dedicated geologist and a frequent visitor to the sacred Jurassic Coast. For more information: The Jurassic Coast can boast a range of internationally important fossil localities that have produced well-preserved and diverse evidence of life throughout the Mesozoic. The nodding donkey on the cliff top has produced more than 3 million barrels of oil since 1959 (GEO ExPro no 5/6, 2005). The oil formed in rocks that were laid down on a stagnant sea floor in Early Jurassic times. In other places, oil seeps, where oil leaks to the surface from underground accumulations or mature source rocks, are evident. 62 GEO ExPro November 2006
Jurassic Coast Fieldtrip
 Field trip leaders: Members of the convener team Dates: Thursday 11 th and Friday 12 th April Jurassic Coast Fieldtrip Logistics: Note that the field trip will begin and end in Piccadilly, London (in front
Field trip leaders: Members of the convener team Dates: Thursday 11 th and Friday 12 th April Jurassic Coast Fieldtrip Logistics: Note that the field trip will begin and end in Piccadilly, London (in front
UK Field Training Courses
 UK Field Training Courses Bespoke courses for E&P companies For individual companies and/or partnerships Reservoir and exploration sedimentology oriented Integrated with company sedimentologist if desired
UK Field Training Courses Bespoke courses for E&P companies For individual companies and/or partnerships Reservoir and exploration sedimentology oriented Integrated with company sedimentologist if desired
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment
 Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Sediment and sedimentary rocks Sediment From sediments to sedimentary rocks (transportation, deposition, preservation and lithification) Types of sedimentary rocks (clastic, chemical and organic) Sedimentary
Hard Engineering: Lyme Regis
 Hard Engineering: Lyme Regis By The British Geographer Situation Lyme Regis, with a population of 4400 is located in the centre of the Heritage Jurassic Coast in Dorset, South England. It is exposed to
Hard Engineering: Lyme Regis By The British Geographer Situation Lyme Regis, with a population of 4400 is located in the centre of the Heritage Jurassic Coast in Dorset, South England. It is exposed to
Module 10: Resources and Virginia Geology Topic 4 Content: Virginia Geology Notes
 Virginia is composed of a very diverse landscape that extends from the beaches and barrier islands all of the way to the highly elevated Appalachian Plateau. Geologists have discovered ancient shallow
Virginia is composed of a very diverse landscape that extends from the beaches and barrier islands all of the way to the highly elevated Appalachian Plateau. Geologists have discovered ancient shallow
The Niagara Escarpment extends from western New York, through the GTA all the way up to Manitoulin Island and into Michigan and Wisconsin.
 is southern Ontario s most prominent topographic feature, extending more than 500 kilometres from western New York, through Niagara Falls and the western part of the Greater Toronto Area (GTA), and north
is southern Ontario s most prominent topographic feature, extending more than 500 kilometres from western New York, through Niagara Falls and the western part of the Greater Toronto Area (GTA), and north
Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018
 Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018 Quiz 2 scheduled for Friday Feb 23 (Interlude B, Chapters 6,7) Questions? Chapter 6 Pages of the Past: Sedimentary Rocks Key Points for today Be
Lecture Outline Wednesday - Friday February 14-16, 2018 Quiz 2 scheduled for Friday Feb 23 (Interlude B, Chapters 6,7) Questions? Chapter 6 Pages of the Past: Sedimentary Rocks Key Points for today Be
Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures
 Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Depositional Environments. Depositional Environments
 Depositional Environments Geographic area in which sediment is deposited Characterized by a combination of geological process & environmental conditions Depositional Environments Geological processes:
Depositional Environments Geographic area in which sediment is deposited Characterized by a combination of geological process & environmental conditions Depositional Environments Geological processes:
Fossil Clues Teacher s Notes
 Fossils are the remains of living things which have been changed into rock. The father of modern geology, James Hutton, said that we can interpret the nature of creatures from the past and the environment
Fossils are the remains of living things which have been changed into rock. The father of modern geology, James Hutton, said that we can interpret the nature of creatures from the past and the environment
Paleo Lab #4 - Sedimentary Environments
 Paleo Lab #4 - Sedimentary Environments page - 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF SEDIMENT Grain size and grain shape: The sizes and shapes of sedimentary particles (grains) are modified considerably during their transportation
Paleo Lab #4 - Sedimentary Environments page - 1. CHARACTERISTICS OF SEDIMENT Grain size and grain shape: The sizes and shapes of sedimentary particles (grains) are modified considerably during their transportation
Sedimentary Rocks, our most Valuable Rocks. Or, what you will probably find when you are outdoors exploring.
 Sedimentary Rocks, our most Valuable Rocks Or, what you will probably find when you are outdoors exploring. Sedimentary rocks give us evidence to earth s earlier history. We look at processes happening
Sedimentary Rocks, our most Valuable Rocks Or, what you will probably find when you are outdoors exploring. Sedimentary rocks give us evidence to earth s earlier history. We look at processes happening
Sedimentary Rocks. Weathering. Mechanical & Chemical Weathering. Sediments. Lithification. Deposition. Transport. Erosion.
 Lithification Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Deposition Transport Erosion Weathering Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Mechanical Weathering
Lithification Sedimentary Rocks Sediments Deposition Transport Erosion Weathering Weathering The sediments that make up sedimentary rocks are produced by: Mechanical & Chemical Weathering Mechanical Weathering
Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks
 Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks Introduction! Drilling into the bottom of the North Sea, we encounter: " Soft mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: " Similar materials
Chapter 6 Pages of Earth s Past: Sedimentary Rocks Introduction! Drilling into the bottom of the North Sea, we encounter: " Soft mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: " Similar materials
Sediment and Sedimentary rock
 Sediment and Sedimentary rock Sediment: An accumulation of loose mineral grains, such as boulders, pebbles, sand, silt or mud, which are not cemented together. Mechanical and chemical weathering produces
Sediment and Sedimentary rock Sediment: An accumulation of loose mineral grains, such as boulders, pebbles, sand, silt or mud, which are not cemented together. Mechanical and chemical weathering produces
Depositional Environment
 Depositional Environment Sedimentary depositional environment describes the combination of physical, chemical and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment. Types
Depositional Environment Sedimentary depositional environment describes the combination of physical, chemical and biological processes associated with the deposition of a particular type of sediment. Types
Lyme Regis. Environmental Improvements Phase 2. Securing the future of Lyme Regis
 Lyme Regis Environmental Improvements Phase 2 Securing the future of Lyme Regis Wave attack on Marine Parade The spectacular scenery around Lyme Regis is a result of erosion by the sea and landsliding
Lyme Regis Environmental Improvements Phase 2 Securing the future of Lyme Regis Wave attack on Marine Parade The spectacular scenery around Lyme Regis is a result of erosion by the sea and landsliding
Cretaceous, Dakota Formation, Terra Cotta Member South Side of I-70, Salina County, Kansas
 Cretaceous, Dakota Formation, Terra Cotta Member South Side of I-70, Salina County, Kansas Written By: Steven D.J. Baumann G-102010-1A Outcrop looking southeast Photo taken by: Steven Baumann on 10-20-2010
Cretaceous, Dakota Formation, Terra Cotta Member South Side of I-70, Salina County, Kansas Written By: Steven D.J. Baumann G-102010-1A Outcrop looking southeast Photo taken by: Steven Baumann on 10-20-2010
MUHAMMAD S TAMANNAI, DOUGLAS WINSTONE, IAN DEIGHTON & PETER CONN, TGS Nopec Geological Products and Services, London, United Kingdom
 Geological and Geophysical Evaluation of Offshore Morondava Frontier Basin based on Satellite Gravity, Well and regional 2D Seismic Data Interpretation MUHAMMAD S TAMANNAI, DOUGLAS WINSTONE, IAN DEIGHTON
Geological and Geophysical Evaluation of Offshore Morondava Frontier Basin based on Satellite Gravity, Well and regional 2D Seismic Data Interpretation MUHAMMAD S TAMANNAI, DOUGLAS WINSTONE, IAN DEIGHTON
EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks
 Name: EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 5 Introduction In this lab we will classify sedimentary rocks and investigate the relationship between environmental conditions and
Name: EPS 50 Lab 4: Sedimentary Rocks Grotzinger and Jordan, Chapter 5 Introduction In this lab we will classify sedimentary rocks and investigate the relationship between environmental conditions and
UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS
 UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS WHAT ARE SEDIMENTS Sediments are loose Earth materials (unconsolidated materials) such as sand which are transported by the action of water, wind, glacial ice and gravity. These
UNIT 4 SEDIMENTARY ROCKS WHAT ARE SEDIMENTS Sediments are loose Earth materials (unconsolidated materials) such as sand which are transported by the action of water, wind, glacial ice and gravity. These
Sedimentary rocks. Mechanical Weathering. Weathering. Chemical weathering. Rates of weathering. Fossil Fuel Resources. Two kinds of weathering
 Sedimentary rocks Fossil Fuel Resources Exam next Tuesday February 14 Bring Scantron and Review Questions About 75% of all rock outcrops on the continents Important to reconstruct much of Earth's history
Sedimentary rocks Fossil Fuel Resources Exam next Tuesday February 14 Bring Scantron and Review Questions About 75% of all rock outcrops on the continents Important to reconstruct much of Earth's history
Mammoth Cave National Park, Kentucky
 Mammoth Cave National Park, Kentucky Objectives of Today s Lecture Refresher on Sedimentary Depositional Systems and Rock Classifications Transgressive and Regressive Marine Environments Carbonate Depositional
Mammoth Cave National Park, Kentucky Objectives of Today s Lecture Refresher on Sedimentary Depositional Systems and Rock Classifications Transgressive and Regressive Marine Environments Carbonate Depositional
NC Earth Science Essential Standards
 NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
NC Earth Science Essential Standards EEn. 2.1 Explain how processes and forces affect the Lithosphere. EEn. 2.1.1 Explain how the rock cycle, plate tectonics, volcanoes, and earthquakes impact the Lithosphere.
Bowen s Chemical Stability Series
 Lab 5 - Identification of Sedimentary Rocks Page - Introduction Sedimentary rocks are the second great rock group. Although they make up only a small percentage of the rocks in the earth s crust (~5%)
Lab 5 - Identification of Sedimentary Rocks Page - Introduction Sedimentary rocks are the second great rock group. Although they make up only a small percentage of the rocks in the earth s crust (~5%)
The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks
 The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are composed of: Fragments of other rocks Chemical precipitates Organic matter or biochemically produced materials The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary
The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are composed of: Fragments of other rocks Chemical precipitates Organic matter or biochemically produced materials The Nature of Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary
Igneous Rocks. Sedimentary Rocks
 Earth Sciences 083F Plate Tectonics Exercises Plate tectonics is a model for the dynamic behaviour of Earth s lithosphere. Outlining stable areas of lithosphere are narrow zones (plate boundaries) in which
Earth Sciences 083F Plate Tectonics Exercises Plate tectonics is a model for the dynamic behaviour of Earth s lithosphere. Outlining stable areas of lithosphere are narrow zones (plate boundaries) in which
EROSION, DEPOSITION AND SEDIMENTARY ROCKS. Reading: Earth Science Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5: pages Chapter 3: pages 52-54, 61-69
 EROSION, DEPOSITION AND SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Reading: Earth Science Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5: pages 124-133 Chapter 3: pages 52-54, 61-69 Base Level Resistant bed Resistant bed creates a local base level
EROSION, DEPOSITION AND SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Reading: Earth Science Tarbuck and Lutgens Chapter 5: pages 124-133 Chapter 3: pages 52-54, 61-69 Base Level Resistant bed Resistant bed creates a local base level
The Mesozoic. Wednesday, November 30, 11
 The Mesozoic Periods of the Mesozoic Triassic- First period of the Mesozoic era Jurassic Cretaceous- Last period of the Mesozoic era Breakup of Pangaea Stage one (Triassic) Rifting and volcanism, normal
The Mesozoic Periods of the Mesozoic Triassic- First period of the Mesozoic era Jurassic Cretaceous- Last period of the Mesozoic era Breakup of Pangaea Stage one (Triassic) Rifting and volcanism, normal
Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6
 Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6 I. What is a sedimentary rock? A. Sedimentary rock 1) Rock made of detrital sediments (such as sand) or inorganic/organic chemical precipitates (such as calcite) 2) Detrital
Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 6 I. What is a sedimentary rock? A. Sedimentary rock 1) Rock made of detrital sediments (such as sand) or inorganic/organic chemical precipitates (such as calcite) 2) Detrital
MOR SEAWAY TEACHERS. A CHANGING LANDSCAPE Activity Overview BIG IDEA
 MOR SEAWAY 03 Activity Overview BIG IDEA The Earth and its landscapes change over time. Scientists use the fossil record to understand the Earth s environments and climates millions of years ago. OBJECTIVE
MOR SEAWAY 03 Activity Overview BIG IDEA The Earth and its landscapes change over time. Scientists use the fossil record to understand the Earth s environments and climates millions of years ago. OBJECTIVE
Earth Science 11: Earth Materials, Sedimentary Rocks
 Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials, Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 1, pages 56 to 66 2.4: Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary Rock Formation All sedimentary rocks form through compaction and cementation
Name: Date: Earth Science 11: Earth Materials, Sedimentary Rocks Chapter 1, pages 56 to 66 2.4: Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary Rock Formation All sedimentary rocks form through compaction and cementation
Black Point & Bihler Point
 Black Point & Bihler Point Conglomerate Photo: looking north toward end of Black Point (south of post 1) All of the rocks in this photo are conglomerate. Both Black Point and Bihler Point are formed from
Black Point & Bihler Point Conglomerate Photo: looking north toward end of Black Point (south of post 1) All of the rocks in this photo are conglomerate. Both Black Point and Bihler Point are formed from
Ecoregions Glossary. 7.8B: Changes To Texas Land Earth and Space
 Ecoregions Glossary Ecoregions The term ecoregions was developed by combining the terms ecology and region. Ecology is the study of the interrelationship of organisms and their environments. The term,
Ecoregions Glossary Ecoregions The term ecoregions was developed by combining the terms ecology and region. Ecology is the study of the interrelationship of organisms and their environments. The term,
Name: Period: Date: ID: A. Circle the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question and write the letter on the blank.
 Name: Period: _ Date: _ ID: A Unit 7 Practice Circle the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question and write the letter on the blank. 1. What term describes the movement of rock
Name: Period: _ Date: _ ID: A Unit 7 Practice Circle the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question and write the letter on the blank. 1. What term describes the movement of rock
Coso Red Hill and Coso Playa field trip, Prof. Alessandro Grippo, Ph.D.
 HISTORICAL GEOLOGY fall 2016 Professor: Dr. Alessandro Grippo, Ph.D. FIELD TRIP REPORT: Friday, October 21, 2016: Coso Red Hill & Playa, Coso Junction CA YOUR NAME part 1: COSO RED HILL (you can sample
HISTORICAL GEOLOGY fall 2016 Professor: Dr. Alessandro Grippo, Ph.D. FIELD TRIP REPORT: Friday, October 21, 2016: Coso Red Hill & Playa, Coso Junction CA YOUR NAME part 1: COSO RED HILL (you can sample
Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators
 Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators Table of Contents Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Correlation Chart... 7 Benchmarks Chapter 1 The Practice of Science...................... 11
Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators Table of Contents Next Generation Sunshine State Standards Correlation Chart... 7 Benchmarks Chapter 1 The Practice of Science...................... 11
Rocks and Landscapes of Ogden Clough, Halifax. A group on a guided walk, looking at rock features in Ogden Kirk Quarries.
 Rocks and Landscapes of Ogden Clough, Halifax A group on a guided walk, looking at rock features in Ogden Kirk Quarries. Rocks and Landscapes of Ogden Clough, Halifax 2 Ogden Clough Local Geological Site
Rocks and Landscapes of Ogden Clough, Halifax A group on a guided walk, looking at rock features in Ogden Kirk Quarries. Rocks and Landscapes of Ogden Clough, Halifax 2 Ogden Clough Local Geological Site
General Geology Lab #4: Sedimentary Rocks and Environments
 Name General Geology Lab #4: Sedimentary Rocks and Environments Please identify the following group of sedimentary rocks. Please determine whether they clastic, biogenic or chemical. Also, answer the sample
Name General Geology Lab #4: Sedimentary Rocks and Environments Please identify the following group of sedimentary rocks. Please determine whether they clastic, biogenic or chemical. Also, answer the sample
Objectives: Define Relative Age, Absolute Age
 S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks
 Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 2) Science 330 Summer 2005 What is a sedimentary rock? Products of mechanical and chemical weathering Account for about 5 percent of Earth
Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks (Shaping Earth s Surface, Part 2) Science 330 Summer 2005 What is a sedimentary rock? Products of mechanical and chemical weathering Account for about 5 percent of Earth
GLG Chapter 7 Sedimentary Environments & Rocks
 GLG 101 - Chapter 7 Sedimentary Environments & Rocks Name Note, Oct 11: I ll be writing this study sheet over the next few days. Each day I will add questions until the entire chapter is done, hopefully
GLG 101 - Chapter 7 Sedimentary Environments & Rocks Name Note, Oct 11: I ll be writing this study sheet over the next few days. Each day I will add questions until the entire chapter is done, hopefully
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Geology Laboratory GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Sedimentary & Metamorphic Rocks
 GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Sedimentary & Metamorphic Rocks Name I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give
GEOL.3250 Geology for Engineers Sedimentary & Metamorphic Rocks Name I. Introduction The bulk of the earth's crust is composed of relatively few minerals. These can be mixed together, however, to give
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5 Sedimentation Rocks Formed by Surface Processes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Mineralogy of sandstones Key Figure 5.12
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5 Sedimentation Rocks Formed by Surface Processes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Mineralogy of sandstones Key Figure 5.12
Weathering and Erosion
 Have you ever looked at the land around you and wondered how it was shaped? The geologic features that help define the world are still being shaped by the natural processes of weathering, erosion, and
Have you ever looked at the land around you and wondered how it was shaped? The geologic features that help define the world are still being shaped by the natural processes of weathering, erosion, and
Sedimentary Environments Chapter 8
 Sedimentary Environments Chapter 8 Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. What is a sedimentary rock? Sedimentary rocks are products of
Sedimentary Environments Chapter 8 Does not contain complete lecture notes. To be used to help organize lecture notes and home/test studies. What is a sedimentary rock? Sedimentary rocks are products of
Geology and Natural Resources
 Geology and Natural Resources Brought to you by: Western Michigan University Department of Geosciences and The Michigan Geological Repository for Research and Education s K-12 Outreach Program Core Kids
Geology and Natural Resources Brought to you by: Western Michigan University Department of Geosciences and The Michigan Geological Repository for Research and Education s K-12 Outreach Program Core Kids
The boundary between two formations (or any distinct layers) is called a contact. Sedimentary rocks cover 75% of continents.
 Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks form at the Earth s surface through interactions of the hydrologic system and the crust. Fortunately, many of these processes are in operation today, and geologists
Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks form at the Earth s surface through interactions of the hydrologic system and the crust. Fortunately, many of these processes are in operation today, and geologists
Section 7. Reading the Geologic History of Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Outline 16: The Mesozoic World: Formation of Oil Deposits (with a side trip to the Devonian Marcellus Shale)
 Outline 16: The Mesozoic World: Formation of Oil Deposits (with a side trip to the Devonian Marcellus Shale) The first commercial oil well was drilled by Colonel Edwin Drake in Titusville, Pennsylvania,
Outline 16: The Mesozoic World: Formation of Oil Deposits (with a side trip to the Devonian Marcellus Shale) The first commercial oil well was drilled by Colonel Edwin Drake in Titusville, Pennsylvania,
Quiz 12 Bonus 2 (9:30-9:35 AM)
 Quiz 12 Bonus 2 (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lectures 32 and 33: Mesozoic Sedimentation Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time Mesozoic Tectonics A) The Triassic
Quiz 12 Bonus 2 (9:30-9:35 AM) UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 112: Earth History Lectures 32 and 33: Mesozoic Sedimentation Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time Mesozoic Tectonics A) The Triassic
Hiking the Bold Coast, Cutler, Maine
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2010 Hiking the Bold Coast, Cutler, Maine 44 o 39 36.34 N, 67 o 12 46.99 W Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2010 Hiking the Bold Coast, Cutler, Maine 44 o 39 36.34 N, 67 o 12 46.99 W Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map
Higher National Unit specification. General information for centres. Geology and Geomorphology. Unit title: Unit code: F3SL 34
 Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Geology and Geomorphology Unit code: F3SL 34 Unit purpose: This Unit provides an introduction to geology and geomorphology.
Higher National Unit specification General information for centres Unit title: Geology and Geomorphology Unit code: F3SL 34 Unit purpose: This Unit provides an introduction to geology and geomorphology.
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 101 Lab Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
ESC102. Sedimentary Rocks. Our keys to the past. Monday, February 11, 13
 ESC102 Sedimentary Rocks Our keys to the past Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are rocks that form through the accumulation of sediment and the process of lithification. Lithification occurs after deposition
ESC102 Sedimentary Rocks Our keys to the past Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary rocks are rocks that form through the accumulation of sediment and the process of lithification. Lithification occurs after deposition
Glacial Deposition and Groundwater in Dutchess County
 Glacial Deposition and Groundwater in Dutchess County Name: Period: Thousands of years ago an enormous ice sheet blanketed the Hudson Valley in what was called the Wisconsinan Glaciation. The ice reshaped
Glacial Deposition and Groundwater in Dutchess County Name: Period: Thousands of years ago an enormous ice sheet blanketed the Hudson Valley in what was called the Wisconsinan Glaciation. The ice reshaped
Tuesday 6 June 2017 Afternoon
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA Tuesday 6 June 2017 Afternoon A2 GCE GEOLOGY F794/01 Environmental Geology *6783378785* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
Oxford Cambridge and RSA Tuesday 6 June 2017 Afternoon A2 GCE GEOLOGY F794/01 Environmental Geology *6783378785* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
What are the different ways rocks can be weathered?
 Romano - 223 What are the different ways rocks can be weathered? Weathering - the breakdown of rocks and minerals at the Earth s surface 1. 2. PHYSICAL WEATHERING Rock is broken into smaller pieces with
Romano - 223 What are the different ways rocks can be weathered? Weathering - the breakdown of rocks and minerals at the Earth s surface 1. 2. PHYSICAL WEATHERING Rock is broken into smaller pieces with
Chapter 7 Case study. Sand dune coastal environment: Studland Bay
 Sand dune coastal environment: Studland Bay Sand dunes are common features of low-lying stretches of coastline in the UK and elsewhere in the world. They form in places where there is a plentiful supply
Sand dune coastal environment: Studland Bay Sand dunes are common features of low-lying stretches of coastline in the UK and elsewhere in the world. They form in places where there is a plentiful supply
What is a sedimentary rock?
 Sedimentary Rocks What is a sedimentary rock? Sedimentary rocks are products of mechanical and chemical weathering They account for only 5% of the top 10 miles of the outer crust, yet most of the earth
Sedimentary Rocks What is a sedimentary rock? Sedimentary rocks are products of mechanical and chemical weathering They account for only 5% of the top 10 miles of the outer crust, yet most of the earth
The Geology of Two Lights State Park. Cape Elizabeth, Maine
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2002 Cape Elizabeth, Maine 43 33 33.48 N, 70 12 13.32 W Text by Henry N. Berry IV and Robert G. Marvinney, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities June, 2002 Cape Elizabeth, Maine 43 33 33.48 N, 70 12 13.32 W Text by Henry N. Berry IV and Robert G. Marvinney, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1
13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p )
 13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p. 194-208) Sediment Deposition Weathering results in rock being broken down into smaller fragments, called regolith. This regolith is then broken down to form soil. The regolith
13. Sedimentary Rocks I (p. 194-208) Sediment Deposition Weathering results in rock being broken down into smaller fragments, called regolith. This regolith is then broken down to form soil. The regolith
WJEC Eduqas GCSE (9-1) GEOGRAPHY B
 WJEC Eduqas GCSE (9-1) GEOGRAPHY B Additional sample questions for Theme 2 Candidate name.. Question Mark (a) (i) /2 (a) (ii) /4 (a) (iii) /4 (a) (iv) /3 (b) (i) /4 (b) (ii) /6 (c) (i) /2 (c) (ii) /1 (c)
WJEC Eduqas GCSE (9-1) GEOGRAPHY B Additional sample questions for Theme 2 Candidate name.. Question Mark (a) (i) /2 (a) (ii) /4 (a) (iii) /4 (a) (iv) /3 (b) (i) /4 (b) (ii) /6 (c) (i) /2 (c) (ii) /1 (c)
Sediment. Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface
 Sediment Some basic terminology Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface Erosion: removal of weathered rock and minerals from one place to
Sediment Some basic terminology Weathering: mechanical and chemical decomposition and disintegration of rock and minerals at the surface Erosion: removal of weathered rock and minerals from one place to
Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks
 Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Rocks formed from material derived from preexisting rocks by surfacial processes followed by diagenesis There are two main classes of sedimentary rocks Clastic
Module 9 Sedimentary Rocks SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Rocks formed from material derived from preexisting rocks by surfacial processes followed by diagenesis There are two main classes of sedimentary rocks Clastic
The Geology of Sebago Lake State Park
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
Erosion and Deposition along Rivers and Seashores - Part 1: Modeling in the Classroom
 Erosion and Deposition along Rivers and Seashores - Part 1: Modeling in the Classroom Lesson Focus: Erosion and Deposition Learning Objectives: Students will learn to recognize landforms found on Earth.
Erosion and Deposition along Rivers and Seashores - Part 1: Modeling in the Classroom Lesson Focus: Erosion and Deposition Learning Objectives: Students will learn to recognize landforms found on Earth.
Sand. Sand is any eroded material (igneous, metamorphic or sedimentary) that has a grain size from 1/16 th to 2 millimeters in size.
 Sedimentology 001 What is sedimentology? Sedimentology...encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand [1], mud (silt) [2] andclay [3] and understanding the processes that deposit them.[4] It
Sedimentology 001 What is sedimentology? Sedimentology...encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand [1], mud (silt) [2] andclay [3] and understanding the processes that deposit them.[4] It
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, and Landscape Development
 Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, and Landscape Development I. Weathering - the breakdown of rocks into smaller particles, also called sediments, by natural processes. Weathering is further divided into
Weathering, Erosion, Deposition, and Landscape Development I. Weathering - the breakdown of rocks into smaller particles, also called sediments, by natural processes. Weathering is further divided into
Sedimentary Rocks. Origin, Properties and Identification. Physical Geology GEOL 100. Ray Rector - Instructor
 Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Sedimentary Rocks Origin, Properties and Identification Physical Geology GEOL 100 Ray Rector - Instructor Sedimentary Rock Origin and Identification Lab Pre-Lab Internet Link Resources 1) http://www.rockhounds.com/rockshop/rockkey/index.html
Concretions are accumulation of one or more minerals within the body of a sedimentary rock, or within
 Tibooburra concretions Page 1 Concretions are accumulation of one or more minerals within the body of a sedimentary rock, or within cracks and cavities in a rock. They form when minerals such as quartz,
Tibooburra concretions Page 1 Concretions are accumulation of one or more minerals within the body of a sedimentary rock, or within cracks and cavities in a rock. They form when minerals such as quartz,
To get you thinking Explain how these different layers of rock formed? Why are these layers different colors? Sedimentary Rocks
 To get you thinking Explain how these different layers of rock formed? Why are these layers different colors? Sedimentary Rocks Bryce Canyon, Utah Badlands, South Dakota Weathering Whenever rock is exposed
To get you thinking Explain how these different layers of rock formed? Why are these layers different colors? Sedimentary Rocks Bryce Canyon, Utah Badlands, South Dakota Weathering Whenever rock is exposed
Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
 Sedimentary Rocks & Surface Processes Quest Name: Earth Science 2013 Block: Date: Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
Sedimentary Rocks & Surface Processes Quest Name: Earth Science 2013 Block: Date: Section I: Multiple Choice Select the best answer to each question. Mark your final answer on the answer sheet. (1 pt each)
Pine Hill Serpentinized Peridotite,
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities November, 2016 Pine Hill Serpentinized Peridotite, Little Deer Isle, Maine 44 o 17 6.0 N, 68 o 42 7.2 W Text and photos by Robert G. Marvinney, Department of Agriculture,
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities November, 2016 Pine Hill Serpentinized Peridotite, Little Deer Isle, Maine 44 o 17 6.0 N, 68 o 42 7.2 W Text and photos by Robert G. Marvinney, Department of Agriculture,
The Welsh Borderland. Geologically recent surface deposits. The Welsh Borderland
 The Welsh Borderland This account provides a broad perspective of the geology of the Welsh Borderland region which comprises the southeast of Powys, southern Shropshire, northern Gwent, the western half
The Welsh Borderland This account provides a broad perspective of the geology of the Welsh Borderland region which comprises the southeast of Powys, southern Shropshire, northern Gwent, the western half
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition
 Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 5: SEDIMENTATION: Rocks Formed by Surface Processes Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright
Understanding Earth Fifth Edition Grotzinger Jordan Press Siever Chapter 5: SEDIMENTATION: Rocks Formed by Surface Processes Lecturer: H Mohammadzadeh Assistant professors, Department of Geology, FUM Copyright
The Geology of the Marginal Way, Ogunquit, Maine
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities February, 2002 The Geology of the Marginal Way, Ogunquit, Maine 43 14 23.88 N, 70 35 18.36 W Text by Arthur M. Hussey II, Bowdoin College and Robert G. Marvinney,, Department
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities February, 2002 The Geology of the Marginal Way, Ogunquit, Maine 43 14 23.88 N, 70 35 18.36 W Text by Arthur M. Hussey II, Bowdoin College and Robert G. Marvinney,, Department
1. Canadian Energy Use
 1 Unit 3 Energy 2 1. Canadian Energy Use Why are Canadians the sixth highest energy users in the world? Our major industries are energy intensive, overall industry consumes 31% of all energy in Canada.
1 Unit 3 Energy 2 1. Canadian Energy Use Why are Canadians the sixth highest energy users in the world? Our major industries are energy intensive, overall industry consumes 31% of all energy in Canada.
Unit 5 Possible Test Questions Mesozoic and Cenozoic Eras HISTORICAL GEOLOGY
 Revised 8/16 Unit 5 Possible Test Questions Mesozoic and Cenozoic Eras HISTORICAL GEOLOGY Mesozoic Era Eons, Eras and Periods 1. List the Mesozoic periods in order (oldest to youngest). End of the Paleozoic
Revised 8/16 Unit 5 Possible Test Questions Mesozoic and Cenozoic Eras HISTORICAL GEOLOGY Mesozoic Era Eons, Eras and Periods 1. List the Mesozoic periods in order (oldest to youngest). End of the Paleozoic
STUDENT SOIL PRESENTATIONS
 STUDENT SOIL PRESENTATIONS Soil Order (and informal name) Student Name(s) Alfisol = deciduous forest soil Andisol = formed on volcanic ash Aridisol = desert soil Entisol = alluvium soil Gelisol = tundra
STUDENT SOIL PRESENTATIONS Soil Order (and informal name) Student Name(s) Alfisol = deciduous forest soil Andisol = formed on volcanic ash Aridisol = desert soil Entisol = alluvium soil Gelisol = tundra
Oil & Gas. From exploration to distribution. Week 1 V05 Origin of hydrocarbon resources part 1. Jean-Pierre Deflandre
 Oil & Gas From exploration to distribution Week 1 V05 Origin of hydrocarbon resources part 1 Jean-Pierre Deflandre W1V5 Origin of hydrocarbon resources1 p. 1 Introduction to hydrocarbon resources You will
Oil & Gas From exploration to distribution Week 1 V05 Origin of hydrocarbon resources part 1 Jean-Pierre Deflandre W1V5 Origin of hydrocarbon resources1 p. 1 Introduction to hydrocarbon resources You will
Geology 109L Lab 3: Modern Sedimentary Environments --Field Trip to Bodega Bay--
 Geology 109L Lab 3: Modern Sedimentary Environments --Field Trip to Bodega Bay-- Goal: The purpose of this lab is to recognize characteristics of modern sedimentary environments, which will aid you in
Geology 109L Lab 3: Modern Sedimentary Environments --Field Trip to Bodega Bay-- Goal: The purpose of this lab is to recognize characteristics of modern sedimentary environments, which will aid you in
GEOL Lab #11 Information (Guidelines for Student Soil Presentations on April 8)
 GEOL 333 - Lab #11 Information (Guidelines for Student Soil Presentations on April 8) Assignment During Lab on April 8, you will give an oral presentation about one of the 12 soil orders (categories).
GEOL 333 - Lab #11 Information (Guidelines for Student Soil Presentations on April 8) Assignment During Lab on April 8, you will give an oral presentation about one of the 12 soil orders (categories).
LAB - Rock Classification
 NAME: LAB - Rock Classification Date: Introduction: A rock is any naturally occurring aggregate of minerals, mineral-like solids, glass, or organic particles. The properties that can be observed in a rock
NAME: LAB - Rock Classification Date: Introduction: A rock is any naturally occurring aggregate of minerals, mineral-like solids, glass, or organic particles. The properties that can be observed in a rock
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands
 Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 12 19 February 2004 A B C D F 97 94 92 91 88 87 86 85 85 84 82 77 73 73 mean 66 64 60 69 60 57 51 29 Exam Scores Mean = 71 Median = 82/77 Any Questions? Sedimentary
Geology of the Hawaiian Islands Class 12 19 February 2004 A B C D F 97 94 92 91 88 87 86 85 85 84 82 77 73 73 mean 66 64 60 69 60 57 51 29 Exam Scores Mean = 71 Median = 82/77 Any Questions? Sedimentary
COASTLINES MARINE EROSION PROCESSES. Read the course booklet.
 MARINE EROSION Read the course booklet. PROCESSES. You will need to know and be able to explain the four methods of coastal erosion and two of weathering The next few slides illustrate these processes.
MARINE EROSION Read the course booklet. PROCESSES. You will need to know and be able to explain the four methods of coastal erosion and two of weathering The next few slides illustrate these processes.
NAME: GEL 109 Final Winter 2010
 GEL 109 Final Winter 2010 1. The following stratigraphic sections represents a single event followed by the slow accumulation of background sedimentation of shale. Describe the flows that produced the
GEL 109 Final Winter 2010 1. The following stratigraphic sections represents a single event followed by the slow accumulation of background sedimentation of shale. Describe the flows that produced the
Dalhousie University- Petroleum Geoscience Field Methods- Trinidad Summary Report
 Dalhousie University- Petroleum Geoscience Field Methods- Trinidad Summary Report Submitted to: Offshore Energy Research Association of Nova Scotia (OERA) To fulfill requirements of the Undergraduate Student
Dalhousie University- Petroleum Geoscience Field Methods- Trinidad Summary Report Submitted to: Offshore Energy Research Association of Nova Scotia (OERA) To fulfill requirements of the Undergraduate Student
Chapter 5 Sedimentary Environments
 Chapter 3 Notes 1 Chapter 5 Sedimentary Environments A. The Tectonic Setting 1.Factors that determine the kind of sedimentary rock that will be formed in a particular area: a. the climate under which processes
Chapter 3 Notes 1 Chapter 5 Sedimentary Environments A. The Tectonic Setting 1.Factors that determine the kind of sedimentary rock that will be formed in a particular area: a. the climate under which processes
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy. Thanks to Rob Viens for slides
 Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
Sedimentology & Stratigraphy Thanks to Rob Viens for slides Sedimentology The study of the processes that erode, transport and deposit sediments Sedimentary Petrology The study of the characteristics and
Chapter 7: Sediment and Sedimentary Rocks
 Chapter 7: Sediment and Sedimentary Rocks Chapter Outline 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Sediment Sources, Transport, and Deposition 7.3 How Does Sediment Become Sedimentary Rock? 7.4 Types of Sedimentary Rocks
Chapter 7: Sediment and Sedimentary Rocks Chapter Outline 7.1 Introduction 7.2 Sediment Sources, Transport, and Deposition 7.3 How Does Sediment Become Sedimentary Rock? 7.4 Types of Sedimentary Rocks
Weathering, Erosion and Deposition
 Weathering, Erosion and Deposition Shaping the Earth s Surface Weathering the process of breaking down rocks into smaller fragments Erosion the transport of rock fragments from one location to another
Weathering, Erosion and Deposition Shaping the Earth s Surface Weathering the process of breaking down rocks into smaller fragments Erosion the transport of rock fragments from one location to another
GY 112L Earth History
 GY 112L Earth History Lab 2 Vertical Successions and Sequences of Events GY 112L Instructors: Douglas Haywick, James Connors, Mary Anne Connors Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama
GY 112L Earth History Lab 2 Vertical Successions and Sequences of Events GY 112L Instructors: Douglas Haywick, James Connors, Mary Anne Connors Department of Earth Sciences, University of South Alabama
Massive cross-bedded sandstone strata in Mt Zion USA (courtesy of Lawrie Davidson)
 Sedimentary rocks are formed from clasts (broken pieces) of earlier rock and organic material. They are the product of weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction and cementation. 1. Sedimentary strata
Sedimentary rocks are formed from clasts (broken pieces) of earlier rock and organic material. They are the product of weathering, erosion, deposition, compaction and cementation. 1. Sedimentary strata
PLATE TECTONICS THEORY
 PLATE TECTONICS THEORY Continental drift Sea floor spreading CONTINENTAL DRIFT CONTINENTAL DRIFT 1. The fitness of continents and Continental Reconstruction Earth ~200 million years ago 1.1 Geometrical
PLATE TECTONICS THEORY Continental drift Sea floor spreading CONTINENTAL DRIFT CONTINENTAL DRIFT 1. The fitness of continents and Continental Reconstruction Earth ~200 million years ago 1.1 Geometrical
Geology 229 Engineering Geology. Lecture 6. Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5)
 Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 6 Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5) Outline of this Lecture 1. Rock types and rock cycle 2. Geological and engineering
Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 6 Basic Rock Classification and Engineering Considerations (West, Chs. 2, 3, 4, 5) Outline of this Lecture 1. Rock types and rock cycle 2. Geological and engineering
DOMINANT SEDIMENTS TYPE IN ROCK Loose fragments of rocks or minerals broken off of bedrock Mineral crystals that precipitate directly out of water
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 7. SEDIMENTARY PROCESSES, ROCKS, AND ENVIRONMENTS Instructions: Refer to Laboratory 6 in your Lab Book on pages 153-186 to answer the questions in this work sheet.
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 7. SEDIMENTARY PROCESSES, ROCKS, AND ENVIRONMENTS Instructions: Refer to Laboratory 6 in your Lab Book on pages 153-186 to answer the questions in this work sheet.
Shallow marine facies. Outline 13: The Paleozoic World. Shallow marine and terrestrial facies
 Outline 13: The Paleozoic World Shallow marine and terrestrial facies Shallow marine facies Sea level was much higher than today during much of the Paleozoic. Shallow epicontinental seas flooded continental
Outline 13: The Paleozoic World Shallow marine and terrestrial facies Shallow marine facies Sea level was much higher than today during much of the Paleozoic. Shallow epicontinental seas flooded continental
