Zou Zou Kuzyk Assistant Professor Centre for Earth Observation Science (CEOS) & Geological Sciences, Clayton H. Riddell Faculty of Environment, Earth
|
|
|
- Ami Johns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Zou Zou Kuzyk Assistant Professor Centre for Earth Observation Science (CEOS) & Geological Sciences, Clayton H. Riddell Faculty of Environment, Earth and Resources University of Manitoba (with input from T. Papakyriakou, R. Wang, CEOS)
2 Motivation Continental shelf systems are very important in global C cycle Intermediary between terrestrial, atmospheric, oceanic C reservoirs Biologically and biogeochemically active and physically dynamic, so large transfers/fluxes Can be sink or source for atmospheric CO 2 Sensitive to climate changes Arctic margins generally sinks but rise in terrestrial C delivery, decrease in primary production, increase in oxidation, etc. may weaken CO 2 uptake potential
3 Motivation (continued) Hudson Bay System Large continental shelf area (~1.2 x 10 6 km 2 or 4.5% of total shelf area) Massive drainage basin with discharge representing ~23% of the Arctic Ocean s total riverine input Located at southern margin of the Arctic, where climate changes may be faster and more dramatic Indicator of future changes in Arctic Ocean shelves? Greater development in basin compared to more remote Arctic areas Offer insights into impact of local human activities?
4 Observations and measurements of C sources, stocks, sinks and fluxes Change in rates of processes, within atmosphere, watershed, oceanic systems Understanding of physical and biogeochemical processes influencing these fluxes (PP, respiration, sedimentation, coastal erosion, ocean circulation, sea ice formation) and model development Ability to extrapolate in time and space and predict shifts and net balance in C system
5 Terrestrial Organic Carbon Frozen soils in Arctic and sub-arctic regions hold ~50% of global terrestrial OC. Warming, increased river discharge, and other changes/activities in watersheds may mobilize more of this OC and transport it to the ocean. Terrestrial Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) ~18 rivers in HBS (HB, HS, FB) sampled to date - DOC concentrations varied um - Total riverine input of DOC estimated at ~ Tg C/yr (Mundy et al., 2010) =14%-22% of DOC input from rivers to Arctic Ocean (vs. receiving volume of HBS only ~1%) So DOC inputs from rivers to HB very significant! Mundy et al., 2010
6 Characterizing sources and composition of DOC (CDOM) Statistically significant differences in CDOM fluorescence and absorbance characteristics among various river/estuary systems (Granskog et al., 2007; Guéguen et al., 2011) Great Whale River Nelson/Hayes Rivers NE HB Rivers Marine sources of DOC and photobleaching (see also Granskog et al. 2009) Guéguen et al., 2011
7 Distribution, impact and fate of terrestrial DOC in Hudson Bay Distribution of river water River tracer experiment conducted using 3-D numerical model (left) and also conservative tracers (δ 18 O and S) were applied to differentiate RW vs SIM (right). - Most of the RW remains in coastal region in summer, with limited exchange into the interior of the Bay (at most 25% diverted into interior by winds). (St-Laurent et al., 2011) (Granskog et al., 2011)
8 Distribution, impact and fate of terrestrial DOC in Hudson Bay - CDOM distributed mostly along coast - influences light absorption and thus primary production, thermodynamics and stratification of the coastal waters Absorption coefficient at 355 nm (Granskog et al., 2007) - CDOM effects on light penetration through water column incorporated into 3D biophysical model (via RW tracer) (Sibert et al., 2011).
9 Distribution, impact and fate of terrestrial DOC in Hudson Bay - Quantification of fraction RW (vs SIM) allowed assessment of CDOM fate - CDOM almost conservative within estuaries but degraded >50% during regional mixing (as RW diminished to 5-10%, 1-3 month residence time) CDOM in southwest sector of the Bay Granskog et al., Photobleaching and/or micobial degradation represents important sink for DOC entering from rivers
10 CO 2 System Observations (raft-, boat- and ship-based) of river/marine dissolved gases and key variables have provided insight into local and regional air-sea CO 2 exchange budgets, metabolic function and CO 2 dynamics of rivers/estuaries. Strong relationships between pco 2 and RW distribution (as indicated by S and CDOM). Coastal waters are supersaturated in CO 2 with respect to atmosphere, while interior waters undersaturated. Estimated fluxes imply weaker net C sink in HBS compared to other Arctic shelf environments..but large seasonal and probably inter-annual variability - Ongoing work 2005 vs 2010 Relationship between pco 2 and SST Else et al., 2008a,b
11 Terrestrial POC Riverbank erosion often significant source of sediment and POC; supply enhanced by thermal degradation of permafrost, high river flows, ice jams, ice scouring, onshore winds, high tides, etc. Terrestrial POC generally efficiently buried in Arctic shelf sediments, representing important C sink. Sources and composition of river particulate, soils, and permafrost studied using OC/ N, δ 13 C, δ 15 N, lignin, Δ 14 C Kuzyk et al., 2008, 2009; Godin et al. in preparation
12 Terrestrial POC Terrestrial POC varies from river to river, reflecting differences in vegetation in watersheds. Currents redistribute POC throughout HB, preserving some regional differences (e.g., latitudinal trend). Modifications in POC composition imply some degradation (perhaps more than in other Arctic systems). Lignin compositional ratios Sediment core records show changes in POC over last ~100 yrs. NORTHWEST SOUTHWEST SOUTHEAST Kuzyk et al., 2008
13 Regional sediment core studies E.g., 8 sediment cores from small sedimentary basins at mouth of Great Whale River (Hulse et al., 2012). - Sediment accumulation rates calculated from 210 Pb and 137 Cs profiles suggest an offshore shift in the locus of fine sediment deposition in recent decades, which may be a sign of increased wave resuspension due to a more energetic environment (related to less sea-ice cover during fall?) - Periodic variation in sediment particle size over last ~100 yrs, which correlated across cores, imply variations in sediment discharge from river, changing sediment source, and/or winnowing (related to wave climate and/or sea-ice cover?) - Effects on POC still to come! Downcore grain diameter frequencies
14 Ongoing work with archived sediment boxcore and piston core samples, soil and permafrost samples Pollen (Heikkila et al., in prep.) Geochemical indicators of fire history and vegetation (Goni et al., in prep., Godin et al., in prep)
15 Marine POC Studies of biological processes - primary production, microbial recycling, particle export Geochemical studies effect of labile C metabolism on sediment geochemistry HB is fundamentally oligotrophic - 3-D biophysical coupled model (Sibert et al., 2011) - measures of primary productivity (Ferland et al., 2011) - measures of export fluxes (Lapoussière et al., 2009; Lalande & Fortier, 2011) - labile C flux to sediments inferred from sediment redox geochemistry (Kuzyk et al., 2011) Improved understanding of relationships with environmental conditions. Appreciation of inter-annual, regional and sub-regional variability. Coupled with short time-series, this means that temporal trends difficult to address.
16 Preliminary OCterr and OCmar Budgets Marine OC (x 10 6 t yr -1 ) Relatively high burial of marine OM due to old OM, derived from resuspension? Terrestrial OC (x 10 6 t yr -1 ) Kuzyk et al., 2009 Partial degradation of terrestrial OM due to repeated cycles of deposition and resuspension?
17 Gaps & Priorities Limited observational record hinders assessment of C cycle, including development of budgets, and forecasts of sensitivity to environmental change (anthropogenic and natural) Propose strategic deployment of monitoring facilities/moorings Buoys suited for time-series observations of CO 2 and associated air-sea exchange parameters Improved temporal and spatial coverage
18 Gaps & Priorities δ 18 O data imply ~20% of RW exported into deep layer winter densification in polynyas (also supported by DOC data) Model results suggest spatial uncoupling PP/C deposition higher POC fluxes to seafloor on shallow W shelf of HB sediment records do not show particular accumulation points to resuspension and transport, perhaps with dense water? Propose sampling/moorings to examine dense water formation on W shelves and transports to interior Sibert et al., 2011
19 Gaps & Priorities Characterizing and tracing fate of C components from watersheds/rivers of origin, through estuaries and into HB marine system Apply fingerprinting tools in coordination with watershed researchers, collect observations to compare to model output Portion of RW from Nelson River (%) during 2005 field campaign (Wang et al., in prep.)
20 Conceptual model of C cycle, viewing HB as integrated system of land-atmosphere-ocean
21 Acknowledgements Contributors to Journal of Marine Systems, Special Issue on Hudson Bay ArcticNet and the MERICA-nord program
Carbon Exchanges between the Continental Margins and the Open Ocean
 Carbon Exchanges between the Continental Margins and the Open Ocean Outline: 1. Introduction to problem 2. Example of how circulation can export carbon to open ocean 3. Example of how particle transport
Carbon Exchanges between the Continental Margins and the Open Ocean Outline: 1. Introduction to problem 2. Example of how circulation can export carbon to open ocean 3. Example of how particle transport
Global Carbon Cycle - I
 Global Carbon Cycle - I Reservoirs and Fluxes OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 13 November 2012 Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 11 Outline 1. Overview of global C cycle 2. Global C reservoirs 3. The contemporary
Global Carbon Cycle - I Reservoirs and Fluxes OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems 13 November 2012 Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 11 Outline 1. Overview of global C cycle 2. Global C reservoirs 3. The contemporary
Global Carbon Cycle - I Systematics: Reservoirs and Fluxes
 OCN 401-10 Nov. 16, 2010 KCR Global Carbon Cycle - I Systematics: Reservoirs and Fluxes The Global carbon cycle Reservoirs: biomass on land in the oceans, atmosphere, soil and rocks, waters Processes:
OCN 401-10 Nov. 16, 2010 KCR Global Carbon Cycle - I Systematics: Reservoirs and Fluxes The Global carbon cycle Reservoirs: biomass on land in the oceans, atmosphere, soil and rocks, waters Processes:
Global Carbon Cycle - I
 Global Carbon Cycle - I OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 11 1. Overview of global C cycle 2. Global C reservoirs Outline 3. The contemporary global C cycle 4. Fluxes and residence
Global Carbon Cycle - I OCN 401 - Biogeochemical Systems Reading: Schlesinger, Chapter 11 1. Overview of global C cycle 2. Global C reservoirs Outline 3. The contemporary global C cycle 4. Fluxes and residence
The benthic processing of terrestrial organic matter on riverdominated margins
 The benthic processing of terrestrial organic matter on riverdominated margins Neal E. Blair Departments of Civil & Environmental Engineering and Earth & Planetary Sciences Northwestern University Elana
The benthic processing of terrestrial organic matter on riverdominated margins Neal E. Blair Departments of Civil & Environmental Engineering and Earth & Planetary Sciences Northwestern University Elana
New perspectives of climate change impacts on marine anthropogenic radioactivity in Arctic regions
 New perspectives of climate change impacts on marine anthropogenic radioactivity in Arctic regions M. Karcher 1,3, I. Harms 2, R. Gerdes 3, W.J.F. Standring 4, M. Dowdall 4, P. Strand 4 1 O.A.Sys Ocean
New perspectives of climate change impacts on marine anthropogenic radioactivity in Arctic regions M. Karcher 1,3, I. Harms 2, R. Gerdes 3, W.J.F. Standring 4, M. Dowdall 4, P. Strand 4 1 O.A.Sys Ocean
1. Introduction 2. Ocean circulation a) Temperature, salinity, density b) Thermohaline circulation c) Wind-driven surface currents d) Circulation and
 1. Introduction 2. Ocean circulation a) Temperature, salinity, density b) Thermohaline circulation c) Wind-driven surface currents d) Circulation and climate change e) Oceanic water residence times 3.
1. Introduction 2. Ocean circulation a) Temperature, salinity, density b) Thermohaline circulation c) Wind-driven surface currents d) Circulation and climate change e) Oceanic water residence times 3.
Arctic-Coastal Land Ocean Interactions
 Arctic- Project PIs: Maria Tzortziou (CCNY / CUNY) Antonio Mannino (NASA/GSFC) Joseph Salisbury (Univ. of NH) Peter Hernes (UC Davis) Carlos Del Castillo (NASA/GSFC) Marjorie Friedrichs (VIMS) Patricia
Arctic- Project PIs: Maria Tzortziou (CCNY / CUNY) Antonio Mannino (NASA/GSFC) Joseph Salisbury (Univ. of NH) Peter Hernes (UC Davis) Carlos Del Castillo (NASA/GSFC) Marjorie Friedrichs (VIMS) Patricia
OCB Summer Workshop WHOI, July 16-19,
 Transformation and fluxes of carbon in a changing Arctic Ocean and it s impact on ocean acidification, the Atlantic view Leif G. Anderson Department t of Chemistry and Molecular l Biology University of
Transformation and fluxes of carbon in a changing Arctic Ocean and it s impact on ocean acidification, the Atlantic view Leif G. Anderson Department t of Chemistry and Molecular l Biology University of
Global phosphorus cycle
 Global phosphorus cycle OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 11 April 2013 2013 Arisa Okazaki and Kathleen Ruttenberg Outline 1. Introduction on global phosphorus (P) cycle 2. Terrestrial environment 3. Atmospheric
Global phosphorus cycle OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 11 April 2013 2013 Arisa Okazaki and Kathleen Ruttenberg Outline 1. Introduction on global phosphorus (P) cycle 2. Terrestrial environment 3. Atmospheric
XI. the natural carbon cycle. with materials from J. Kasting (Penn State)
 XI. the natural carbon cycle with materials from J. Kasting (Penn State) outline properties of carbon the terrestrial biological cycle of carbon the ocean cycle of carbon carbon in the rock cycle overview
XI. the natural carbon cycle with materials from J. Kasting (Penn State) outline properties of carbon the terrestrial biological cycle of carbon the ocean cycle of carbon carbon in the rock cycle overview
Carbon Dioxide, Alkalinity and ph
 Carbon Dioxide, Alkalinity and ph OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 15 March 2018 Reading: Libes, Chapter 15, pp. 383 389 (Remainder of chapter will be used with the classes Global Carbon Dioxide and Biogenic
Carbon Dioxide, Alkalinity and ph OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 15 March 2018 Reading: Libes, Chapter 15, pp. 383 389 (Remainder of chapter will be used with the classes Global Carbon Dioxide and Biogenic
SCOPE 35 Scales and Global Change (1988)
 1. Types and origins of marine sediments 2. Distribution of sediments: controls and patterns 3. Sedimentary diagenesis: (a) Sedimentary and organic matter burial (b) Aerobic and anaerobic decomposition
1. Types and origins of marine sediments 2. Distribution of sediments: controls and patterns 3. Sedimentary diagenesis: (a) Sedimentary and organic matter burial (b) Aerobic and anaerobic decomposition
Atmospheric Evolution: Earth s s Oxidation
 Earth s s Atmosphere Thematic Questions about the Atmosphere Observations of the Modern Atmosphere What is its structure and composition? What controls atmospheric dynamics? Information from the Rock Record
Earth s s Atmosphere Thematic Questions about the Atmosphere Observations of the Modern Atmosphere What is its structure and composition? What controls atmospheric dynamics? Information from the Rock Record
Part 2. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling. Lecture Outline. 1. Net Primary Production (NPP) a) Global Patterns b) Fate of NPP
 OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.25.16) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 2. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling Lecture Outline 1. Net Primary Production (NPP) a) Global Patterns b) Fate of NPP 2. Sediment
OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.25.16) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 2. Oceanic Carbon and Nutrient Cycling Lecture Outline 1. Net Primary Production (NPP) a) Global Patterns b) Fate of NPP 2. Sediment
Terrestrial Plants 900 GT C Terrestrial Primary Production 75 GT C/yr. River flux 0.5 GT C/yr. Carbonates 60,000,000 GT C
 Most of the organic carbon on earth is stored in long term deposits (shales, coals, sedimentary rocks) that represent a leak from the contemporary C cycle Terrestrial Plants 900 GT C Terrestrial Primary
Most of the organic carbon on earth is stored in long term deposits (shales, coals, sedimentary rocks) that represent a leak from the contemporary C cycle Terrestrial Plants 900 GT C Terrestrial Primary
International Arctic Research Center
 International Arctic Research Center IARC Project Reducing Uncertainty in Arctic Climate Change Prediction Distinguishing Natural and Anthropogenic Changes Testing Carbon Cycle Hydrologic Cycle Integration
International Arctic Research Center IARC Project Reducing Uncertainty in Arctic Climate Change Prediction Distinguishing Natural and Anthropogenic Changes Testing Carbon Cycle Hydrologic Cycle Integration
Where is all the water?
 Where is all the water? The distribution of water at the Earth's surface % of total Oceans 97.25 Ice caps and glaciers 2.05 Groundwater 0.68 Lakes 0.01 Soils 0.005 Atmosphere (as vapour) 0.001 Rivers 0.0001
Where is all the water? The distribution of water at the Earth's surface % of total Oceans 97.25 Ice caps and glaciers 2.05 Groundwater 0.68 Lakes 0.01 Soils 0.005 Atmosphere (as vapour) 0.001 Rivers 0.0001
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 10, Day 1
 Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 10, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Beaches are created by the actions of waves, tides,
Earth Science Lesson Plan Quarter 2, Week 10, Day 1 Outcomes for Today Standard Focus: PREPARE 1. Background knowledge necessary for today s reading. Beaches are created by the actions of waves, tides,
Earth s Heat Budget. What causes the seasons? Seasons
 Earth s Heat Budget Solar energy and the global heat budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation A. Rotation of the Earth B. Distance from the Sun C. Variations of Earth s orbit
Earth s Heat Budget Solar energy and the global heat budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation A. Rotation of the Earth B. Distance from the Sun C. Variations of Earth s orbit
Time-series observations in the Northern Indian Ocean V.V.S.S. Sarma National Institute of Oceanography Visakhapatnam, India
 The Second GEOSS Asia-Pacific Symposium, Tokyo, 14-16 th April 28 Time-series observations in the Northern Indian Ocean V.V.S.S. Sarma National Institute of Oceanography Visakhapatnam, India Seasonal variations
The Second GEOSS Asia-Pacific Symposium, Tokyo, 14-16 th April 28 Time-series observations in the Northern Indian Ocean V.V.S.S. Sarma National Institute of Oceanography Visakhapatnam, India Seasonal variations
Research Programme Polar, Marine and Coastal Systems. Current and future Arctic research priorities of Germany Nicole Biebow, AWI
 Research Programme Polar, Marine and Coastal Systems Current and future Arctic research priorities of Germany Nicole Biebow, AWI Arctic Science and Technology (S&T) Collaboration and Engagement Workshop,
Research Programme Polar, Marine and Coastal Systems Current and future Arctic research priorities of Germany Nicole Biebow, AWI Arctic Science and Technology (S&T) Collaboration and Engagement Workshop,
IPCC AR5 WG1 - Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Nandini Ramesh
 IPCC AR5 WG1 - Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis Nandini Ramesh Seminar in Atmospheric Science 21 st February, 2014 1. Introduc,on The ocean exchanges heat, freshwater, and C with the atmosphere.
IPCC AR5 WG1 - Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis Nandini Ramesh Seminar in Atmospheric Science 21 st February, 2014 1. Introduc,on The ocean exchanges heat, freshwater, and C with the atmosphere.
Lake Levels and Climate Change in Maine and Eastern North America during the last 12,000 years
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities December, 2000 Lake Levels and Climate Change in Maine and Eastern North America during the last 12,000 years Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture,
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities December, 2000 Lake Levels and Climate Change in Maine and Eastern North America during the last 12,000 years Text by Robert A. Johnston, Department of Agriculture,
Summary. The Ice Ages and Global Climate
 The Ice Ages and Global Climate Summary Earth s climate system involves the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. Changes affecting it operate on time scales ranging from decades to millions
The Ice Ages and Global Climate Summary Earth s climate system involves the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. Changes affecting it operate on time scales ranging from decades to millions
Oil. Oil. Early common mistakes in the oil business.
 Oil www.priweb.org/ed/pgws/history/pennsylvania/pennsylvania.html Early common mistakes in the oil business Oil www.priweb.org/ed/pgws/history/pennsylvania/pennsylvania.html 1 Climate More recent common
Oil www.priweb.org/ed/pgws/history/pennsylvania/pennsylvania.html Early common mistakes in the oil business Oil www.priweb.org/ed/pgws/history/pennsylvania/pennsylvania.html 1 Climate More recent common
1. Oceans. Example 2. oxygen.
 1. Oceans a) Basic facts: There are five oceans on earth, making up about 72% of the planet s surface and holding 97% of the hydrosphere. Oceans supply the planet with most of its oxygen, play a vital
1. Oceans a) Basic facts: There are five oceans on earth, making up about 72% of the planet s surface and holding 97% of the hydrosphere. Oceans supply the planet with most of its oxygen, play a vital
Geol 117 Lecture 18 Beaches & Coastlines. I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition:
 I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
I. Types of Coastlines A. Definition: 1. Shore = narrow zone where ocean meets land (e.g. beach) 2. Coast is a broad area where both ocean and land processes act a. Includes onshore marshes, dunes, sea
Today s Lecture: Land, biosphere, cryosphere (All that stuff we don t have equations for... )
 Today s Lecture: Land, biosphere, cryosphere (All that stuff we don t have equations for... ) 4 Land, biosphere, cryosphere 1. Introduction 2. Atmosphere 3. Ocean 4. Land, biosphere, cryosphere 4.1 Land
Today s Lecture: Land, biosphere, cryosphere (All that stuff we don t have equations for... ) 4 Land, biosphere, cryosphere 1. Introduction 2. Atmosphere 3. Ocean 4. Land, biosphere, cryosphere 4.1 Land
Productivity in a Changing Southern Ocean. Kevin R. Arrigo Stanford University
 Productivity in a Changing Southern Ocean Kevin R. Arrigo Stanford University 1 Productivity in a Changing Southern Ocean A Paleo-perspective Satellite view of the Southern Ocean Role of ice and iron Controls
Productivity in a Changing Southern Ocean Kevin R. Arrigo Stanford University 1 Productivity in a Changing Southern Ocean A Paleo-perspective Satellite view of the Southern Ocean Role of ice and iron Controls
The Exploration of the Coastal Zone in the Arctic seas: Siberian Shelf Studies
 The Exploration of the Coastal Zone in the Arctic seas: Siberian Shelf Studies V.I. Sergienko, FEBRAS NEESPI Summit Helsinki, Finland May 3-4, 2007 SCIENTIFIC MOTIVATION 1. Artic Ocean is small (~4% from
The Exploration of the Coastal Zone in the Arctic seas: Siberian Shelf Studies V.I. Sergienko, FEBRAS NEESPI Summit Helsinki, Finland May 3-4, 2007 SCIENTIFIC MOTIVATION 1. Artic Ocean is small (~4% from
The Biogeochemical Carbon Cycle: CO 2,the greenhouse effect, & climate feedbacks. Assigned Reading: Kump et al. (1999) The Earth System, Chap. 7.
 The Biogeochemical Carbon Cycle: CO 2,the greenhouse effect, & climate feedbacks Assigned Reading: Kump et al. (1999) The Earth System, Chap. 7. Overhead Transparencies Faint Faint Young Sun Paradox Young
The Biogeochemical Carbon Cycle: CO 2,the greenhouse effect, & climate feedbacks Assigned Reading: Kump et al. (1999) The Earth System, Chap. 7. Overhead Transparencies Faint Faint Young Sun Paradox Young
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 )
 3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Basic information on CO 2 with regard to environmental issues Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is a significant greenhouse gas that has strong absorption bands in the infrared region and
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Basic information on CO 2 with regard to environmental issues Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is a significant greenhouse gas that has strong absorption bands in the infrared region and
Marine Science and Oceanography
 Marine Science and Oceanography Marine geology- study of the ocean floor Physical oceanography- study of waves, currents, and tides Marine biology study of nature and distribution of marine organisms Chemical
Marine Science and Oceanography Marine geology- study of the ocean floor Physical oceanography- study of waves, currents, and tides Marine biology study of nature and distribution of marine organisms Chemical
GEOCHEMICAL TRACERS OF ARCTIC OCEAN CIRCULATION
 GEOCHEMICAL TRACERS OF ARCTIC OCEAN CIRCULATION Earth Sciences Division Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Fresh Water Cycle Maintains Stratification of Upper Arctic Ocean Stably stratified surface
GEOCHEMICAL TRACERS OF ARCTIC OCEAN CIRCULATION Earth Sciences Division Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Fresh Water Cycle Maintains Stratification of Upper Arctic Ocean Stably stratified surface
Natural U-Th series radio-nuclides reveal important estuarine biogeochemical processes in the Delaware and Chesapeake Bays, USA
 Presentation to the 10th IEBC Meeting Xiamen, CHINA, 21 May 2008 Natural U-Th series radio-nuclides reveal important estuarine biogeochemical processes in the Delaware and Chesapeake Bays, USA Thomas M.
Presentation to the 10th IEBC Meeting Xiamen, CHINA, 21 May 2008 Natural U-Th series radio-nuclides reveal important estuarine biogeochemical processes in the Delaware and Chesapeake Bays, USA Thomas M.
Characterizing the Physical Oceanography of Coastal Waters Off Rhode Island
 Characterizing the Physical Oceanography of Coastal Waters Off Rhode Island Dan Codiga and Dave Ullman Graduate School of Oceanography University of Rhode Island RI OSAMP Stakeholder Meeting January 5,
Characterizing the Physical Oceanography of Coastal Waters Off Rhode Island Dan Codiga and Dave Ullman Graduate School of Oceanography University of Rhode Island RI OSAMP Stakeholder Meeting January 5,
/ Past and Present Climate
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.842 / 12.301 Past and Present Climate Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. The Faint Young
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.842 / 12.301 Past and Present Climate Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. The Faint Young
6. What has been the most effective erosive agent in the climate system? a. Water b. Ice c. Wind
 Multiple Choice. 1. Heinrich Events a. Show increased abundance of warm-water species of planktic foraminifera b. Show greater intensity since the last deglaciation c. Show increased accumulation of ice-rafted
Multiple Choice. 1. Heinrich Events a. Show increased abundance of warm-water species of planktic foraminifera b. Show greater intensity since the last deglaciation c. Show increased accumulation of ice-rafted
OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography
 OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography Reading: Libes, Chapters 22 & 23 (much detail on subject) Note: You can skim the details on compound classes (22.4) Operational definitions! 1 POM 2 Organic compounds display
OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography Reading: Libes, Chapters 22 & 23 (much detail on subject) Note: You can skim the details on compound classes (22.4) Operational definitions! 1 POM 2 Organic compounds display
Coastal Antarctic polynyas: A coupled process requiring high model resolution in the ocean and atmosphere
 Coastal Antarctic polynyas: A coupled process requiring high model resolution in the ocean and atmosphere Mike Dinniman and John Klinck Center for Coastal Physical Oceanography Old Dominion University
Coastal Antarctic polynyas: A coupled process requiring high model resolution in the ocean and atmosphere Mike Dinniman and John Klinck Center for Coastal Physical Oceanography Old Dominion University
Terrestrial Organic Carbon inputs to the Oceans - II. Carbon isotopic compositions of leaf wax biomarkers
 Terrestrial Organic Carbon inputs to the Oceans - II Some additional light reading: Guo et al., 2004. Characterization of Siberian Arctic coastal sediments: Implications for terrestrial organic carbon
Terrestrial Organic Carbon inputs to the Oceans - II Some additional light reading: Guo et al., 2004. Characterization of Siberian Arctic coastal sediments: Implications for terrestrial organic carbon
Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent
 Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent 1979-2012 Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent 1979-2012 Notes: The month of September has the minimum sea ice cover each year. Passive microwave instruments on
Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent 1979-2012 Annual September Arctic Sea ice extent 1979-2012 Notes: The month of September has the minimum sea ice cover each year. Passive microwave instruments on
Figure 65: Reservoir in a steady state condition where the input flux is equal to the output flux and the reservoir size remains constant.
 7. The carbon cycle 7.1. Box model of the carbon cycle Without the greenhouse effect, our planet would experience a permanent ice age and life as we know it would not be possible. The main contributors
7. The carbon cycle 7.1. Box model of the carbon cycle Without the greenhouse effect, our planet would experience a permanent ice age and life as we know it would not be possible. The main contributors
Chapter 3 Sedimentation of clay minerals
 Chapter 3 Sedimentation of clay minerals 3.1 Clay sedimentation on land 3.2 From land to sea 3.3 Clay sedimentation in the sea 1 3.1 Clay sedimentation on land Deserts Glaciers Rivers Lacustrine 2 University
Chapter 3 Sedimentation of clay minerals 3.1 Clay sedimentation on land 3.2 From land to sea 3.3 Clay sedimentation in the sea 1 3.1 Clay sedimentation on land Deserts Glaciers Rivers Lacustrine 2 University
Problem Set #4 ANSWER KEY Fall 2009 Due: 9:30, Monday, Nov 30
 OCN 520 Problem Set #4 ANSWER KEY Fall 2009 Due: 9:30, Monday, Nov 30 1. Two-Box Ocean Model The B Flux Using a 2 box model like the one you have worked on in problem set #4 (question 1) assume the following
OCN 520 Problem Set #4 ANSWER KEY Fall 2009 Due: 9:30, Monday, Nov 30 1. Two-Box Ocean Model The B Flux Using a 2 box model like the one you have worked on in problem set #4 (question 1) assume the following
Sediment Transport and Strata Formation in the Adriatic Sea
 Sediment Transport and Strata Formation in the Adriatic Sea Wayne R. Geyer James D. Irish Peter A. Traykovski Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543 Tel. (508) 289-2868, Fax: (508) 457-2194,
Sediment Transport and Strata Formation in the Adriatic Sea Wayne R. Geyer James D. Irish Peter A. Traykovski Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543 Tel. (508) 289-2868, Fax: (508) 457-2194,
Regional Ocean Climate Model Projections for the British Columbia Continental Shelf
 Regional Ocean Climate Model Projections for the British Columbia Continental Shelf Mike Foreman, Wendy Callendar, John Morrison, Diane Masson, Isaac Fine Institute of Ocean Sciences Fisheries and Oceans
Regional Ocean Climate Model Projections for the British Columbia Continental Shelf Mike Foreman, Wendy Callendar, John Morrison, Diane Masson, Isaac Fine Institute of Ocean Sciences Fisheries and Oceans
Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures
 Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Name: Lab 7: Sedimentary Structures Sedimentary rocks account for a negligibly small fraction of Earth s mass, yet they are commonly encountered because the processes that form them are ubiquitous in the
Seasonal Changes in the Mekong River Delta's Distributary Channels and Nearshore Sedimentary Environments
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Seasonal Changes in the Mekong River Delta's Distributary Channels and Nearshore Sedimentary Environments Paul Liu & David
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Seasonal Changes in the Mekong River Delta's Distributary Channels and Nearshore Sedimentary Environments Paul Liu & David
Carbon and Nutrient Cycles on Continental Shelves - Current Advances and Thoughts for Future Research
 Carbon and Nutrient Cycles on Continental Shelves - Current Advances and Thoughts for Future Research 1. Brief summary of N-based productivity measures. 2. Thoughts for future studies of the ocean margin
Carbon and Nutrient Cycles on Continental Shelves - Current Advances and Thoughts for Future Research 1. Brief summary of N-based productivity measures. 2. Thoughts for future studies of the ocean margin
Long-term Change of Ocean Productivity: A case study in the Bay of Bengal
 Long-term Change of Ocean Productivity: A case study in the Bay of Bengal The 3 rd Asian /12 th Korean-Japan Workshop on Ocean Color Dr.Md.Latifur Rahman Sarker, UTM, Malaysia & RU, Bangladesh & Noor Saadah
Long-term Change of Ocean Productivity: A case study in the Bay of Bengal The 3 rd Asian /12 th Korean-Japan Workshop on Ocean Color Dr.Md.Latifur Rahman Sarker, UTM, Malaysia & RU, Bangladesh & Noor Saadah
Earth s Heat Budget. What causes the seasons? Seasons
 Earth s Heat Budget Solar energy and the global heat budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation A. Rotation of the Earth B. Distance from the Sun C. Variations of Earth s orbit
Earth s Heat Budget Solar energy and the global heat budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation A. Rotation of the Earth B. Distance from the Sun C. Variations of Earth s orbit
Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface
 Oceanography Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface An ocean must be large and have features which set it apart from other oceans (currents, water
Oceanography Oceanography is the scientific study of oceans Oceans make up over 70% of the Earth s surface An ocean must be large and have features which set it apart from other oceans (currents, water
NOAA/OAR Observing Systems
 NOAA/OAR Observing Systems Dr. Christopher L. Sabine Director NOAA s Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory Workshop on Hydroclimate Monitoring Systems and Measurement Needs June, 2014 Global Ocean Observing
NOAA/OAR Observing Systems Dr. Christopher L. Sabine Director NOAA s Pacific Marine Environmental Laboratory Workshop on Hydroclimate Monitoring Systems and Measurement Needs June, 2014 Global Ocean Observing
Sediment and Sedimentary rock
 Sediment and Sedimentary rock Sediment: An accumulation of loose mineral grains, such as boulders, pebbles, sand, silt or mud, which are not cemented together. Mechanical and chemical weathering produces
Sediment and Sedimentary rock Sediment: An accumulation of loose mineral grains, such as boulders, pebbles, sand, silt or mud, which are not cemented together. Mechanical and chemical weathering produces
THE BC SHELF ROMS MODEL
 THE BC SHELF ROMS MODEL Diane Masson & Isaac Fine, Institute of Ocean Sciences The Canadian west coast perspective (filling the gap ) AVISO, Eddy Kinetic Energy (cm 2 s -2 ) In this talk Model set-up and
THE BC SHELF ROMS MODEL Diane Masson & Isaac Fine, Institute of Ocean Sciences The Canadian west coast perspective (filling the gap ) AVISO, Eddy Kinetic Energy (cm 2 s -2 ) In this talk Model set-up and
Coastal Oceanography. Coastal Oceanography. Coastal Waters
 Coastal Oceanography Coastal Oceanography 95% of ocean life is in coastal waters (320 km from shore) Estuaries and wetlands are among most productive ecosystems on Earth Major shipping routes, oil and
Coastal Oceanography Coastal Oceanography 95% of ocean life is in coastal waters (320 km from shore) Estuaries and wetlands are among most productive ecosystems on Earth Major shipping routes, oil and
EARTH SURFACE PROCESSES AND SEDIMENTATION!
 Sed and Strat EARTH SURFACE PROCESSES AND SEDIMENTATION! 2/27 Lecture 7- Exposure: Weathering and the Sediment Factory 3/04 Lecture 8 - Rivers and Landscapes 3/06 Lecture 9 - Waves (not Tides) 3/11 Lecture
Sed and Strat EARTH SURFACE PROCESSES AND SEDIMENTATION! 2/27 Lecture 7- Exposure: Weathering and the Sediment Factory 3/04 Lecture 8 - Rivers and Landscapes 3/06 Lecture 9 - Waves (not Tides) 3/11 Lecture
The performance expectation above was developed using the following elements from the NRC document A Framework for K-12 Science Education:
 MS-ESS2-1 Earth's Systems Students who demonstrate understanding can: MS-ESS2-1. Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth's materials and the flow of energy that drives this process. [Clarification
MS-ESS2-1 Earth's Systems Students who demonstrate understanding can: MS-ESS2-1. Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth's materials and the flow of energy that drives this process. [Clarification
Early diagenesis in marine sediments
 Early diagenesis in marine sediments Why study this part of the ocean? Particle flux to the sea floor ocean surface sediments early diagenesis layer Biogeochemical reactions Why study this part of the
Early diagenesis in marine sediments Why study this part of the ocean? Particle flux to the sea floor ocean surface sediments early diagenesis layer Biogeochemical reactions Why study this part of the
The Rare Earth Elements (REEs) from lanthanum to lutetium are members of Group IlIA in the periodic table and all have very similar chemical and
 The Rare Earth Elements (REEs) from lanthanum to lutetium are members of Group IlIA in the periodic table and all have very similar chemical and physical properties. REEs along with certain other trace
The Rare Earth Elements (REEs) from lanthanum to lutetium are members of Group IlIA in the periodic table and all have very similar chemical and physical properties. REEs along with certain other trace
Earth s Heat Budget. What causes the seasons?
 Earth s Heat Budget Solar Energy and the global Heat Budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation Should we talk about this? What causes the seasons? Before you answer, think. What
Earth s Heat Budget Solar Energy and the global Heat Budget Transfer of heat drives weather and climate Ocean circulation Should we talk about this? What causes the seasons? Before you answer, think. What
Terrestrial Climate Change Variables
 Terrestrial Climate Change Variables Content Terrestrial Climate Change Variables Surface Air Temperature Land Surface Temperature Sea Level Ice Level Aerosol Particles (acid rain) Terrestrial Climate
Terrestrial Climate Change Variables Content Terrestrial Climate Change Variables Surface Air Temperature Land Surface Temperature Sea Level Ice Level Aerosol Particles (acid rain) Terrestrial Climate
Variations in chemical and phase speciation of phosphorus during estuarine mixing in the Bay of Saint Louis. Laodong Guo and Peng Lin
 Variations in chemical and phase speciation of phosphorus during estuarine mixing in the Bay of Saint Louis Laodong Guo and Peng Lin Department of Marine Science University of Southern Mississippi Acknowledgements
Variations in chemical and phase speciation of phosphorus during estuarine mixing in the Bay of Saint Louis Laodong Guo and Peng Lin Department of Marine Science University of Southern Mississippi Acknowledgements
Section 4 Professor Donald McFarlane
 Carbon cycle Present in atmosphere in low concentrations Autotrophs incorporate it into organic matter via photosynthesis Section 4 Professor Donald McFarlane Lecture 23 and Climate Carbon Cycle Respiration
Carbon cycle Present in atmosphere in low concentrations Autotrophs incorporate it into organic matter via photosynthesis Section 4 Professor Donald McFarlane Lecture 23 and Climate Carbon Cycle Respiration
ATOC OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow
![ATOC OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow ATOC OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow](/thumbs/95/126309683.jpg) ATOC 1060-002 OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow cover, permafrost, river and lake ice, ; [3]Glaciers and
ATOC 1060-002 OUR CHANGING ENVIRONMENT Class 19 (Chp 6) Objectives of Today s Class: The Cryosphere [1] Components, time scales; [2] Seasonal snow cover, permafrost, river and lake ice, ; [3]Glaciers and
Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2
 Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2 Create a mind map with the driving question, Why are Oceans Important? Remember: Why are oceans so important? Why are oceans so important? Primary water source
Unit 1: Water Systems on Earth Chapter 2 Create a mind map with the driving question, Why are Oceans Important? Remember: Why are oceans so important? Why are oceans so important? Primary water source
What makes the Arctic hot?
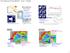 1/3 total USA UN Environ Prog What makes the Arctic hot? Local communities subsistence Arctic Shipping Routes? Decreasing Ice cover Sept 2007 -ice extent (Pink=1979-2000 mean min) Source: NSIDC Oil/Gas
1/3 total USA UN Environ Prog What makes the Arctic hot? Local communities subsistence Arctic Shipping Routes? Decreasing Ice cover Sept 2007 -ice extent (Pink=1979-2000 mean min) Source: NSIDC Oil/Gas
Impact of changing Siberian land-shelf-basin on the Arctic Ocean biogeochemical dynamics
 Impact of changing Siberian land-shelf-basin on the Arctic Ocean biogeochemical dynamics PI: Shigeto Nishino (JAMSTEC) Co-PI: Igor Semiletov (IARC/UAF) Other Investigators: Natalia Shakhova (IARC/UAF),
Impact of changing Siberian land-shelf-basin on the Arctic Ocean biogeochemical dynamics PI: Shigeto Nishino (JAMSTEC) Co-PI: Igor Semiletov (IARC/UAF) Other Investigators: Natalia Shakhova (IARC/UAF),
The Field Research Facility, Duck, NC Warming Ocean Observations and Forecast of Effects
 The Field Research Facility, Duck, NC Warming Ocean Observations and Forecast of Effects A potential consequence of a warming ocean is more frequent and more intense wind events (Hurricanes & Typhoons)
The Field Research Facility, Duck, NC Warming Ocean Observations and Forecast of Effects A potential consequence of a warming ocean is more frequent and more intense wind events (Hurricanes & Typhoons)
Carbon pathways in the South Atlantic
 Carbon pathways in the South Atlantic Olga T. Sato, Ph.D. Paulo Polito, Ph.D. olga.sato@usp.br - polito@usp.br Oceanographic Institute University of São Paulo Olga Sato and Paulo Polito (IOUSP) Carbon
Carbon pathways in the South Atlantic Olga T. Sato, Ph.D. Paulo Polito, Ph.D. olga.sato@usp.br - polito@usp.br Oceanographic Institute University of São Paulo Olga Sato and Paulo Polito (IOUSP) Carbon
GEOL/ENVS 3520 Spring 2009 Hour Exam #2
 GEOL/ENVS 3520 Spring 2009 Hour Exam #2 Enter your name, the date, your ID number, and a made-up 4-digit code (for later recall and identification of your test results) on the separate test sheet. Carefully
GEOL/ENVS 3520 Spring 2009 Hour Exam #2 Enter your name, the date, your ID number, and a made-up 4-digit code (for later recall and identification of your test results) on the separate test sheet. Carefully
Hydrosphere The hydrosphere includes all water on Earth.
 Hydrosphere The hydrosphere includes all water on Earth. The abundance of water on Earth is a unique feature that clearly distinguishes our "Blue Planet" from others in the solar system. Not a drop of
Hydrosphere The hydrosphere includes all water on Earth. The abundance of water on Earth is a unique feature that clearly distinguishes our "Blue Planet" from others in the solar system. Not a drop of
All objects emit radiation. Radiation Energy that travels in the form of waves Waves release energy when absorbed by an object. Earth s energy budget
 Radiation Energy that travels in the form of waves Waves release energy when absorbed by an object Example: Sunlight warms your face without necessarily heating the air Shorter waves carry more energy
Radiation Energy that travels in the form of waves Waves release energy when absorbed by an object Example: Sunlight warms your face without necessarily heating the air Shorter waves carry more energy
Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models
 WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models Jerry Tjiputra 1, K. Lindsay 2, J. Orr 3, J. Segschneider 4, I. Totterdell 5, and C. Heinze 1 1 Bjerknes Centre for Climate
WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models Jerry Tjiputra 1, K. Lindsay 2, J. Orr 3, J. Segschneider 4, I. Totterdell 5, and C. Heinze 1 1 Bjerknes Centre for Climate
Supplemental Slides. Shore: Junction of Land & Water. Junction of Land & Water. Sea Level Variations. Shore vs. Coast. Sea Level Variations
 Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water. Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents
 Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Shore: Junction of Land & Water Supplemental Slides Sediments come off land Most get dumped at the beach Sediment interacts with ocean waves and currents Junction of Land & Water Features: Breaking waves,
Part 1. Ocean Composition & Circulation
 OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.19.17) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 1. Ocean Composition & Circulation 1. Introduction Lecture Outline 2. Ocean Circulation a) Global Patterns in T, S, ρ b) Thermohaline
OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.19.17) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 1. Ocean Composition & Circulation 1. Introduction Lecture Outline 2. Ocean Circulation a) Global Patterns in T, S, ρ b) Thermohaline
Semi-enclosed seas. Estuaries are only a particular type of semi-enclosed seas which are influenced by tides and rivers
 Semi-enclosed seas Estuaries are only a particular type of semi-enclosed seas which are influenced by tides and rivers Other semi-enclosed seas vary from each other, mostly by topography: Separated from
Semi-enclosed seas Estuaries are only a particular type of semi-enclosed seas which are influenced by tides and rivers Other semi-enclosed seas vary from each other, mostly by topography: Separated from
Chemical Oceanography Spring 2000 Final Exam (Use the back of the pages if necessary)(more than one answer may be correct.)
 Ocean 421 Your Name Chemical Oceanography Spring 2000 Final Exam (Use the back of the pages if necessary)(more than one answer may be correct.) 1. Due to the water molecule's (H 2 O) great abundance in
Ocean 421 Your Name Chemical Oceanography Spring 2000 Final Exam (Use the back of the pages if necessary)(more than one answer may be correct.) 1. Due to the water molecule's (H 2 O) great abundance in
Ice Sheets and Sea Level -- Concerns at the Coast (Teachers Guide)
 Ice Sheets and Sea Level -- Concerns at the Coast (Teachers Guide) Roughly 153 million Americans (~53% of the US population) live in coastal counties. World wide some 3 billion people live within 200 km
Ice Sheets and Sea Level -- Concerns at the Coast (Teachers Guide) Roughly 153 million Americans (~53% of the US population) live in coastal counties. World wide some 3 billion people live within 200 km
1 IntroductIon to the cryosphere
 1 IntroductIon to the cryosphere in this place, nostalgia roams, patient as slow hands on skin, transparent as melt-water. nights are light and long. Shadows settle on the shoulders of air. time steps
1 IntroductIon to the cryosphere in this place, nostalgia roams, patient as slow hands on skin, transparent as melt-water. nights are light and long. Shadows settle on the shoulders of air. time steps
Contents. Preface. IC. Introductory Chapter. 1. The Ocean in the Earth System. Ocean Studies and Pedagogy Acknowledgments
 Contents Preface Ocean Studies and Pedagogy Acknowledgments IC. Introductory Chapter IC.1 Why the Ocean is Important to Us? IC.1.1 Biological Resources IC.1.1.1 Fisheries IC.1.1.2 Other Biological Resources
Contents Preface Ocean Studies and Pedagogy Acknowledgments IC. Introductory Chapter IC.1 Why the Ocean is Important to Us? IC.1.1 Biological Resources IC.1.1.1 Fisheries IC.1.1.2 Other Biological Resources
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES
 BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES BASICS Biogeochemical Cycle: The complete path a chemical takes through the four major components, or reservoirs, of Earth s system (atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere)
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES BASICS Biogeochemical Cycle: The complete path a chemical takes through the four major components, or reservoirs, of Earth s system (atmosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere)
Oceanography Curriculum Mapping and Pacing Guide
 Oceanography Curriculum Mapping and Pacing Guide 203-4 Grade/Course Oceanography (information for this map/pacing guide copied and adapted from Ocean Literacy: Essential Principles and Fundamental Concepts);
Oceanography Curriculum Mapping and Pacing Guide 203-4 Grade/Course Oceanography (information for this map/pacing guide copied and adapted from Ocean Literacy: Essential Principles and Fundamental Concepts);
Modeling the Formation and Offshore Transport of Dense Water from High-Latitude Coastal Polynyas
 Modeling the Formation and Offshore Transport of Dense Water from High-Latitude Coastal Polynyas David C. Chapman Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543 phone: (508) 289-2792 fax: (508)
Modeling the Formation and Offshore Transport of Dense Water from High-Latitude Coastal Polynyas David C. Chapman Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Woods Hole, MA 02543 phone: (508) 289-2792 fax: (508)
Potential Impact of climate change and variability on the Intra-Americas Sea (IAS)
 Potential Impact of climate change and variability on the Intra-Americas Sea (IAS) Sang-Ki Lee 1, Yanyun Liu 1 and Barbara Muhling 2 1 CIMAS-University of Miami and AOML-NOAA 2 Princeton University and
Potential Impact of climate change and variability on the Intra-Americas Sea (IAS) Sang-Ki Lee 1, Yanyun Liu 1 and Barbara Muhling 2 1 CIMAS-University of Miami and AOML-NOAA 2 Princeton University and
Lecture 6 - Determinants of Seawater Composition. Sets up electric dipole because O is more electronegative A o. Figure 3.
 12.742 - Marine Chemistry Fall 2004 Lecture 6 - Determinants of Seawater Composition Prof. Scott Doney What is seawater? Water Dissolved inorganic salts (major ions) Trace species, organics, colloids,
12.742 - Marine Chemistry Fall 2004 Lecture 6 - Determinants of Seawater Composition Prof. Scott Doney What is seawater? Water Dissolved inorganic salts (major ions) Trace species, organics, colloids,
Components of the Climate System. Lecture 2: Earth s Climate System. Pop Quiz. Sub-components Global cycles What comes in What goes out
 Lecture 2: Earth s Climate System Components of the Climate System terrestrial radiation Atmosphere Ocean solar radiation Land Energy, Water, and Biogeochemistry Cycles Sub-components Global cycles What
Lecture 2: Earth s Climate System Components of the Climate System terrestrial radiation Atmosphere Ocean solar radiation Land Energy, Water, and Biogeochemistry Cycles Sub-components Global cycles What
Earth-Space Science 6 12
 Earth-Space Science 6 12 Section 08 1 Knowledge of the nature of science 1. Identify the components of scientific inquiry. 2. Identify the consistent patterns that govern the occurrence of most natural
Earth-Space Science 6 12 Section 08 1 Knowledge of the nature of science 1. Identify the components of scientific inquiry. 2. Identify the consistent patterns that govern the occurrence of most natural
Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle
 Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle Source: Sulfate aerosols are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception
Implications of Sulfate Aerosols on Clouds, Precipitation and Hydrological Cycle Source: Sulfate aerosols are produced by chemical reactions in the atmosphere from gaseous precursors (with the exception
Biogeochemical changes over long time scales
 Biogeochemical changes over long time scales Eric Galbraith McGill University, Montreal, Canada Overview What is a long time? Long timescale observations from marine sediments Very quick look at biogeochemical
Biogeochemical changes over long time scales Eric Galbraith McGill University, Montreal, Canada Overview What is a long time? Long timescale observations from marine sediments Very quick look at biogeochemical
CLIMATE CHANGE AND REGIONAL HYDROLOGY ACROSS THE NORTHEAST US: Evidence of Changes, Model Projections, and Remote Sensing Approaches
 CLIMATE CHANGE AND REGIONAL HYDROLOGY ACROSS THE NORTHEAST US: Evidence of Changes, Model Projections, and Remote Sensing Approaches Michael A. Rawlins Dept of Geosciences University of Massachusetts OUTLINE
CLIMATE CHANGE AND REGIONAL HYDROLOGY ACROSS THE NORTHEAST US: Evidence of Changes, Model Projections, and Remote Sensing Approaches Michael A. Rawlins Dept of Geosciences University of Massachusetts OUTLINE
SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2. Implications for Coastal Engineering
 SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2 Implications for Coastal Engineering Objectives of the lecture: Part 2 Show examples of coastal engineering Discuss the practical difficulties of ocean engineering
SHORELINE AND BEACH PROCESSES: PART 2 Implications for Coastal Engineering Objectives of the lecture: Part 2 Show examples of coastal engineering Discuss the practical difficulties of ocean engineering
1 Earth s Oceans. TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify What are the five main oceans?
 CHAPTER 13 1 Earth s Oceans SECTION Exploring the Oceans BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What affects the salinity of ocean water? What affects
CHAPTER 13 1 Earth s Oceans SECTION Exploring the Oceans BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What affects the salinity of ocean water? What affects
APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1
 APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1 1 By David B. Fissel, Mar Martínez de Saavedra Álvarez, and Randy C. Kerr, ASL Environmental Sciences Inc. (Feb. 2012) West Greenland Seismic
APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1 1 By David B. Fissel, Mar Martínez de Saavedra Álvarez, and Randy C. Kerr, ASL Environmental Sciences Inc. (Feb. 2012) West Greenland Seismic
Lecture 2: Earth s Climate System
 Lecture 2: Earth s Climate System terrestrial radiation solar radiation Atmosphere Ocean Solid Earth Land Energy, Water, and Biogeochemistry Cycles Sub-components Global cycles What comes in What goes
Lecture 2: Earth s Climate System terrestrial radiation solar radiation Atmosphere Ocean Solid Earth Land Energy, Water, and Biogeochemistry Cycles Sub-components Global cycles What comes in What goes
Almost of Earth is covered by water. On a map, the continents appear as huge islands surrounded by a vast global ocean.
 Earth s Oceans & Ocean Floor Date: Feelin Blue What are Earth s five main oceans? Almost of Earth is covered by water. On a map, the continents appear as huge islands surrounded by a vast global ocean.
Earth s Oceans & Ocean Floor Date: Feelin Blue What are Earth s five main oceans? Almost of Earth is covered by water. On a map, the continents appear as huge islands surrounded by a vast global ocean.
The Marine Nitrogen Cycle Experiments
 Current Science Editorial Board Meet: 30 th Nov 2015 The Marine Nitrogen Cycle Experiments R. Ramesh Physical Research Laboratory Ahmedabad Solubility, Biological Pumps & New production Redfield Ratio
Current Science Editorial Board Meet: 30 th Nov 2015 The Marine Nitrogen Cycle Experiments R. Ramesh Physical Research Laboratory Ahmedabad Solubility, Biological Pumps & New production Redfield Ratio
