Treatment of Land-Use and Urbanization
|
|
|
- Jeremy Burke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Treatment of Land-Use and Urbanization LECTURE 9 Alexander Mahura Danish Meteorological Institute, DMI, Copenhagen, Denmark NetFAM Summer School on Integrated Modelling 7-12 July 2008, Zelenogorsk, Russia
2 Outline of the Lecture Land-cover and land-use: classification, datasets, etc.; Urban lands: some statistics; Urbanized areas: urban boundary layer, features, controls, characteristics, approaches for treatment, etc. Urbanization of Enviro-HIRLAM: modules, urban districts, anthropogenic heat flux, some results (on example of Copenhagen Metropolitan area, Denmark), applicability, etc.
3 LAND COVER and LAND USE
4 Land Cover and Land Use Land cover - defined as observed physical cover, as seen from the ground or through remote sensing, including natural or planted vegetation and human constructions (buildings, roads, etc.) which cover the earth's surface. Water, ice, bare rock or sand surfaces count as land cover. Land Use defined as a series of activities undertaken to produce one or more goods or services. A given land use may take place on one or several pieces of land, and several land uses may occur on the same piece of land.
5 Why There is a Need for Meteorological Modelling Simulate exchanges between surface and atmosphere (momentum, heat, water, chemical species, etc.); Take into account the climate variability from one region to another Separate the surface schemes from the atmospheric model - allows to use the same surface code for several atmospheric models (NWP models runs) - easy switch between surface schemes and options; All surface fields necessary to land surface schemes
6 CORINE: Coordination of Information on the Environment LCDB - based on interpretation of satellite images for 1989 and 1990, land cover types in 44 standard classes, GIS ARC/INFO format, at an original scale of 1:100,000 (consistent and comparable with similar land cover databases in other European countries. Update
7 CORINE : EU Countries Land cover map - CORINE dataset 250 m resolution, 44 classes
8 CORINE : Denmark : Classification Denmark: Land cover map - CORINE dataset (21 class, Sattler, 1999) Description of land-class Crops, Mixed Farming Irrigated Crops Bogs and Marshes Evergreen Needle-leaf Trees Deciduous Needle-leaf Tree Deciduous Broad-leaf Trees Evergreen Broad-leaf Trees Evergreen Shrubs Deciduous Shrubs Interrupted Forest Mixed Forest Tundra Short Grass Tall Grass Desert Semi-desert Ocean Inland Water Water and Land Mixtures Ice Caps and Glaciers Urban area
9 ECOCLIMAP, USGS, PELCOM, etc. Land cover map - ECOCLIMAP dataset 1 km resolution + Other datasets, USGS, PELCOM, etc.
10 URBAN LANDS
11 EU: Urban Land Development EU statistics from Drivers of urban land development (ha/year)
12 EU: Urban Land Uptake by Origin During from all areas converted to artificial land-use Origin of urban land uptake as percentage of total uptake
13 EU: Urban Land Uptake by Countries Urban land uptake by countries
14 EU: Urban Land Uptake by Metropolitan Areas Urban land uptake by megacities
15 URBANIZED AREAS
16 Urban Boundary Layer Urban Boundary Layer, UBL vs. rural homogeneous boundary layer is characterised by greatly enhanced mixing, resulting from both the large surface roughness and increased surface heating, and by horizontal inhomogeneity of meteorological fields due to variations in surface roughness and heating from rural, sub-urban, to central areas of cities.
17 Features for Urban Areas Local-scale inhomogeneties, sharp changes of roughness and heat fluxes; Wind velocity reduce effect due to buildings; Redistribution of eddies due to buildings, from large to small; Trapping of radiation in street canyons; Effect of urban soil structure, diffusivities heat and water vapour; Anthropogenic heat fluxes, urban heat island; Internal urban boundary layers, urban mixing height, Effects of pollutants (aerosols) on urban meteorology and climate; Urban effects on clouds, precipitation and thunderstorms.
18 Controls on Urban Climate Effects (including Urban Heat Island) Fixed City Location climate topography rural surrounds City Size fetch distance density of use Time day season Urban Climate City Metabolism energy/water use emissions Weather wind cloud stability City Form fabric structure cover (Oke et al., 1980) Modulators Controllable (policy, planning, design)
19 Surface Energy Balance, Characteristics of Urban Surfaces Q* = K -K + L -L = Q H + Q E + ΔQ S + Q [W/m 2 ] Q* - net all-wave radiation; K and K - incoming and outgoing reflected shortwave radiation; L and L - incoming and outgoing longwave radiation; Q H and Q E - turbulent sensible and latent heat fluxes, ΔQ S - storage heat flux, Q other sources/sinks. Altered albedo can be higher or lower, Higher heat capacity, Lower moisture flux to atmosphere, Larger roughness elements, Increased surface area, Source of anthropogenic heat and emissions, Impermeable to water, Decreased net longwave radiation loss.
20 Approaches for Treatment of Urban Boundary Layer Features Urban roughness effects (Bornstein, 1975, 2001; Hunt et al., 2003) Urban surface energy balance (Oke et al., 1999; Piringer et al., 2002) Town Energy Balance scheme (Masson, 2000) Urban surface exchange sub-layer model (Martilli et al., 2002) Soil model for sub-meso scales urban version (Dupont et al., 2006ab) Prognostic equations for UBL height (Zilitinkevich et al., 2002+; Gryning and Bartchvarova, 2002).
21 URBANIZATION of Enviro-HIRLAM
22 Enviro-HIRLAM: Urbanization Modules anthropogenic heat flux and roughness (AHF+R) building effect parameterization (BEP) soil model for sub-meso scales urban version (SM2-U)
23 Enviro-HIRLAM : Urban : Land Surface Scheme, Tiles and Urban Areas, Modelling Domains, and Focus Land surface scheme: Interaction Soil-Biosphere-Atmosphere (ISBA) Tiles (low vegetation, forest, ice, snow, water, bare soil) + urban fraction High resolution domains: -U01/-I01 (horiz resol of 1.4 km) Climate Generation Files, + surface and meteorology related data Focus: Copenhagen metropolitan area (Island of Sjealland)
24 Urban Districts : Classification Residential (RD) City Center/High Buildings District (CC/HBD) GIS Industrial Commercial (ICD) Extraction of districts related characteristics (statistics): Morphology parameters (avg. height, volume, perimeter, compactness, space between buildings), Cover modes (surface density (SD) of buildings, of vegetation, hydrography, roads, N buildings), Aerodynamic parameters (roughness length, displacement height, frontal and lateral SD),
25 Anthropogenic Heat Flux in Urban Areas can be calculated based on assumption of dependency/ proportionality to other urban characteristics: 1. Population density maps with a high resolution in urban areas; 2. Satellite images of the night lightness over urban areas (but difficulties to use for industrial and developing countries, should be corrected); 3. Land-use classification as a percentage of urban classes (central part, urban, sub-urban, industrial, etc.); 4. Emission inventory for specific pollutants typical for urban areas (e.g., due to traffic emission, etc.); NASA, Monitoring or simulation of concentration fields for specific air pollutants typical for urban areas. Reference avg. value: up to 100 W/m 2
26 BEP : Building Effect Parameterization (Martilli et al., 2002) Drag Wake diffusion Radiation Momentum Turbulence Heat Roof Wall Street
27 MeteoModelling: BEP Module Difference between runs: 01 Aug 2004, 06 UTC (control vs. urbanized run) Difference field for wind at 10 m (control vs. urbanized run) Difference field for temperature at 2 m
28 MeteoModelling: BEP Module Urban station N-6180: Copenhagen area : Verification July 2004 August 2004 Diurnal variability for 00 UTC forecasts for the average wind velocity at 10 m for the urban station N 6180 in the Copenhagen metropolitan area as function of the forecast length based on the DMI HIRLAM I01+BEP /U0D/ and I01 CTRL /C0D/ model runs vs. observations
29 SM2-U : Soil Model for Sub-Meso scales Urbanized version : Thermal budget (Dupont et al., 2006ab) Net radiative flux = solar, atmospheric, and surface visible and IR radiations Sensible heat flux Latent heat flux Stored heat flux Anthropic heat flux T s roof T s veg T s bare Surface soil layer Return towards equilibrium T soil Ts 2 nd soil layer 3 rd soil layer art T s nat Surface soil layer T s wat Lake Sea
30 SM2-U : Soil Model for Sub-Meso scales Urbanized version : Water budget (Dupont et al., 2006ab) P Precipitations Evapotranspiration E bare E roof E art E nat E wat Buildings Run off Natural soil Drainage network Water drainage out of system Bare soil Superficial soil layer Drainage Artificial soil Infiltration 2 nd soil layer 3 rd soil layer Superficial soil layer Return towards equilibrium Lake Water Sea
31 Revised Land Use Classification : SM2-U Module BARE NAT VEGN VEGA ART BAT EAU Bare soil without vegetation Bare soil located between sparse vegetation elements Vegetation over bare soil Vegetation over paved surfaces Paved surfaces located between the sparse vegetation elements Building/roofs Water surfaces BAT type ART type VEGA type Dominated type
32 MeteoModelling: SM2-U Module Metropolitan area : Copenhagen : Surface temperature
33 MeteoModelling: SM2-U Module Metropolitan area : Copenhagen : Surface temperature : Urban districts CC/HBD ICD RD Non-urban City center / high buildings district Industrial commercial district Residential district Non-urban areas (no BAT type)
34 MeteoModelling: SM2-U Module Metropolitan area : Copenhagen : Storage and sensible heat fluxes : Types of surfaces BARE NAT VEGN VEGA ART BAT EAU Bare soil without vegetation Bare soil located between sparse vegetation elements Vegetation over bare soil Vegetation over paved surfaces Paved surfaces located between the sparse vegetation elements Building/roofs Water surfaces
35 Evaluation of Results : Items Specific dates/ short- and long-term periods selected, Diurnal cycle, Month-to-month variability, Difference between the control vs. urban runs, Meteorological variables of key importance, Urban districts of different nature: City Center, High Buildings District, Industrial Commercial District, Residential District, Types of surfaces (including urban variants), Focus: impact of urban areas on simulated meteorological fields
36 Urbanization: Applicability of Results Testing and verification of numerical weather prediction and climatological models performance over high resolution model domains, and especially, over the urbanized areas; Investigation of temporal and spatial variability of various meteorological and derived variables over urbanized areas; Improvements in land use classification and climate generation properties; Distinguishing and selection of types of urban districts and their properties; Urbanization of climate regional and global models.
37 Thanks DMI FM HIRLAM and Environmental Meteorology Groups, the ECN (France) and EPFL (Switzerland) research teams, FUMAPEX, COST Actions, MEGAPOLI, etc.
Strategy for Urbanization of Different Types of Models
 Chapter 3. Strategy for Urbanization of Different Types of Models 3.1 FUMAPEX Experience of Model Urbanisation Alexander Baklanov and FUMAPEX Team Danish Meteorological Institute, DMI, Copenhagen, Denmark
Chapter 3. Strategy for Urbanization of Different Types of Models 3.1 FUMAPEX Experience of Model Urbanisation Alexander Baklanov and FUMAPEX Team Danish Meteorological Institute, DMI, Copenhagen, Denmark
Environmental Fluid Dynamics
 Environmental Fluid Dynamics ME EN 7710 Spring 2015 Instructor: E.R. Pardyjak University of Utah Department of Mechanical Engineering Definitions Environmental Fluid Mechanics principles that govern transport,
Environmental Fluid Dynamics ME EN 7710 Spring 2015 Instructor: E.R. Pardyjak University of Utah Department of Mechanical Engineering Definitions Environmental Fluid Mechanics principles that govern transport,
Investigating the urban climate characteristics of two Hungarian cities with SURFEX/TEB land surface model
 Investigating the urban climate characteristics of two Hungarian cities with SURFEX/TEB land surface model Gabriella Zsebeházi Gabriella Zsebeházi and Gabriella Szépszó Hungarian Meteorological Service,
Investigating the urban climate characteristics of two Hungarian cities with SURFEX/TEB land surface model Gabriella Zsebeházi Gabriella Zsebeházi and Gabriella Szépszó Hungarian Meteorological Service,
WATER AND ENERGY BALANCE ESTIMATION IN PUERTO RICO USING SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING
 WATER AND ENERGY BALANCE ESTIMATION IN PUERTO RICO USING SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING Eric. W. Harmsen, Ariel Mercado Vargas, Pedro Tosado Cruz, Jonellys M Maldonado Morales and Angel O. Ortiz Lozada OCTAVA
WATER AND ENERGY BALANCE ESTIMATION IN PUERTO RICO USING SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING Eric. W. Harmsen, Ariel Mercado Vargas, Pedro Tosado Cruz, Jonellys M Maldonado Morales and Angel O. Ortiz Lozada OCTAVA
METR 130: Lecture 2 - Surface Energy Balance - Surface Moisture Balance. Spring Semester 2011 February 8, 10 & 14, 2011
 METR 130: Lecture 2 - Surface Energy Balance - Surface Moisture Balance Spring Semester 2011 February 8, 10 & 14, 2011 Reading Arya, Chapters 2 through 4 Surface Energy Fluxes (Ch2) Radiative Fluxes (Ch3)
METR 130: Lecture 2 - Surface Energy Balance - Surface Moisture Balance Spring Semester 2011 February 8, 10 & 14, 2011 Reading Arya, Chapters 2 through 4 Surface Energy Fluxes (Ch2) Radiative Fluxes (Ch3)
The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes
 1of 18 The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes Vivek Arora Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis Meteorological Service of Canada Outline 2of 18
1of 18 The role of soil moisture in influencing climate and terrestrial ecosystem processes Vivek Arora Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis Meteorological Service of Canada Outline 2of 18
Land Surface Processes and Their Impact in Weather Forecasting
 Land Surface Processes and Their Impact in Weather Forecasting Andrea Hahmann NCAR/RAL with thanks to P. Dirmeyer (COLA) and R. Koster (NASA/GSFC) Forecasters Conference Summer 2005 Andrea Hahmann ATEC
Land Surface Processes and Their Impact in Weather Forecasting Andrea Hahmann NCAR/RAL with thanks to P. Dirmeyer (COLA) and R. Koster (NASA/GSFC) Forecasters Conference Summer 2005 Andrea Hahmann ATEC
A Subgrid Surface Scheme for the Analysis of the Urban Heat Island of Rome
 A Subgrid Surface Scheme for the Analysis of the Urban Heat Island of Rome Antonio Cantelli, Paolo Monti, Giovanni Leuzzi Dipartimento di Idraulica, Trasporti e Strade Summary Analysis of the atmospheric
A Subgrid Surface Scheme for the Analysis of the Urban Heat Island of Rome Antonio Cantelli, Paolo Monti, Giovanni Leuzzi Dipartimento di Idraulica, Trasporti e Strade Summary Analysis of the atmospheric
Climate Roles of Land Surface
 Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
Lecture 5: Land Surface and Cryosphere (Outline) Climate Roles Surface Energy Balance Surface Water Balance Sea Ice Land Ice (from Our Changing Planet) Surface Albedo Climate Roles of Land Surface greenhouse
SENSITIVITY OF THE SURFEX LAND SURFACE MODEL TO FORCING SETTINGS IN URBAN CLIMATE MODELLING
 SENSITIVITY OF THE SURFEX LAND SURFACE MODEL TO FORCING SETTINGS IN URBAN CLIMATE MODELLING Gabriella Zsebeházi PhD supervisor: Gabriella Szépszó Regional Climate Modelling Group, Hungarian Meteorological
SENSITIVITY OF THE SURFEX LAND SURFACE MODEL TO FORCING SETTINGS IN URBAN CLIMATE MODELLING Gabriella Zsebeházi PhD supervisor: Gabriella Szépszó Regional Climate Modelling Group, Hungarian Meteorological
Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI
 Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
Fundamentals of Climate Modelling Torben Königk Rossby Centre/ SMHI Outline Introduction Why do we need models? Basic processes Radiation Atmospheric/Oceanic circulation Model basics Resolution Parameterizations
MESOSCALE MODELLING OVER AREAS CONTAINING HEAT ISLANDS. Marke Hongisto Finnish Meteorological Institute, P.O.Box 503, Helsinki
 MESOSCALE MODELLING OVER AREAS CONTAINING HEAT ISLANDS Marke Hongisto Finnish Meteorological Institute, P.O.Box 503, 00101 Helsinki INTRODUCTION Urban heat islands have been suspected as being partially
MESOSCALE MODELLING OVER AREAS CONTAINING HEAT ISLANDS Marke Hongisto Finnish Meteorological Institute, P.O.Box 503, 00101 Helsinki INTRODUCTION Urban heat islands have been suspected as being partially
SENSITIVITY STUDY FOR SZEGED, HUNGARY USING THE SURFEX/TEB SCHEME COUPLED TO ALARO
 SENSITIVITY STUDY FOR SZEGED, HUNGARY USING THE SURFEX/TEB SCHEME COUPLED TO ALARO Report from the Flat-Rate Stay at the Royal Meteorological Institute, Brussels, Belgium 11.03.2015 01.04.2015 Gabriella
SENSITIVITY STUDY FOR SZEGED, HUNGARY USING THE SURFEX/TEB SCHEME COUPLED TO ALARO Report from the Flat-Rate Stay at the Royal Meteorological Institute, Brussels, Belgium 11.03.2015 01.04.2015 Gabriella
Quantifying the influence of wind advection on the urban heat island for an improvement of a climate change adaptation planning tool
 Quantifying the influence of wind advection on the urban heat island for an improvement of a climate change adaptation planning tool BEAR conference 15/12/2014 Bassett R., Cai X., Chapman L., Heaviside
Quantifying the influence of wind advection on the urban heat island for an improvement of a climate change adaptation planning tool BEAR conference 15/12/2014 Bassett R., Cai X., Chapman L., Heaviside
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
Towards improving the simulation of meteorological fields in urban areas through updated/advanced surface fluxes description
 Author(s) 2008. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Towards improving the simulation of meteorological fields in urban areas through updated/advanced
Author(s) 2008. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Towards improving the simulation of meteorological fields in urban areas through updated/advanced
Soil Moisture Prediction and Assimilation
 Soil Moisture Prediction and Assimilation Analysis and Prediction in Agricultural Landscapes Saskatoon, June 19-20, 2007 STEPHANE BELAIR Meteorological Research Division Prediction and Assimilation Atmospheric
Soil Moisture Prediction and Assimilation Analysis and Prediction in Agricultural Landscapes Saskatoon, June 19-20, 2007 STEPHANE BELAIR Meteorological Research Division Prediction and Assimilation Atmospheric
Case study of an urban heat island in London, UK: Comparison between observations and a high resolution numerical weather prediction model
 Case study of an urban heat island in London, UK: Comparison between observations and a high resolution numerical weather prediction model Siân Lane, Janet Barlow, Humphrey Lean With thanks to Christos
Case study of an urban heat island in London, UK: Comparison between observations and a high resolution numerical weather prediction model Siân Lane, Janet Barlow, Humphrey Lean With thanks to Christos
Lecture 10. Surface Energy Balance (Garratt )
 Lecture 10. Surface Energy Balance (Garratt 5.1-5.2) The balance of energy at the earth s surface is inextricably linked to the overlying atmospheric boundary layer. In this lecture, we consider the energy
Lecture 10. Surface Energy Balance (Garratt 5.1-5.2) The balance of energy at the earth s surface is inextricably linked to the overlying atmospheric boundary layer. In this lecture, we consider the energy
Urban micrometeorological flux observations and surface characterization State of art observational techniques and use of data in urban modeling"
 Urban micrometeorological flux observations and surface characterization State of art observational techniques and use of data in urban modeling" Sue Grimmond 1,2 1 Atmospheric Science Program, Geography,
Urban micrometeorological flux observations and surface characterization State of art observational techniques and use of data in urban modeling" Sue Grimmond 1,2 1 Atmospheric Science Program, Geography,
Danish Meteorological Institute Ministry of Transport and Energy
 Ministry of Transport and Energy DMI-HIRLAM Modelling with High Resolution Setup and Simulations for Areas of Denmark Alexander Mahura, Kai Sattler, Claus Petersen, Bjarne Amstrup, Alexander Baklanov Copenhagen
Ministry of Transport and Energy DMI-HIRLAM Modelling with High Resolution Setup and Simulations for Areas of Denmark Alexander Mahura, Kai Sattler, Claus Petersen, Bjarne Amstrup, Alexander Baklanov Copenhagen
CLIMATE CHANGE & CRITICAL RESOURCES. Iratxe González-Aparicio Tlfn:
 CLIMATE CHANGE & CRITICAL RESOURCES Iratxe González-Aparicio iratxe.gonzalez@tecnalia.com Tlfn: 0034 667 17 89 95 OUTLINE 1. Introduction. IPCC last releases 2. Regional Models and Data 3. Scenarios of
CLIMATE CHANGE & CRITICAL RESOURCES Iratxe González-Aparicio iratxe.gonzalez@tecnalia.com Tlfn: 0034 667 17 89 95 OUTLINE 1. Introduction. IPCC last releases 2. Regional Models and Data 3. Scenarios of
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales. John Houghton. C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth
 Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Climate Modeling Research & Applications in Wales John Houghton C 3 W conference, Aberystwyth 26 April 2011 Computer Modeling of the Atmosphere & Climate System has revolutionized Weather Forecasting and
Surface temperature what does this data tell us about micro-meteorological processes?
 Surface temperature what does this data tell us about micro-meteorological processes? Prof. Dr. Eberhard Parlow Meteorology, Climatology and Remote Sensing (MCR Lab) Department of Environmental Sciences
Surface temperature what does this data tell us about micro-meteorological processes? Prof. Dr. Eberhard Parlow Meteorology, Climatology and Remote Sensing (MCR Lab) Department of Environmental Sciences
Mesoscale meteorological models. Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen
 Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
Mesoscale meteorological models Claire L. Vincent, Caroline Draxl and Joakim R. Nielsen Outline Mesoscale and synoptic scale meteorology Meteorological models Dynamics Parametrizations and interactions
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
Surface issues for High Resolution NWP
 Surface issues for High Resolution NWP François Bouyssel - Jean-François Mahfouf with many contributors High Resolution NWP Workshop, 17-20 May 2010, Brac, Croatia Outline Introduction (specificities of
Surface issues for High Resolution NWP François Bouyssel - Jean-François Mahfouf with many contributors High Resolution NWP Workshop, 17-20 May 2010, Brac, Croatia Outline Introduction (specificities of
ATMOS 5140 Lecture 1 Chapter 1
 ATMOS 5140 Lecture 1 Chapter 1 Atmospheric Radiation Relevance for Weather and Climate Solar Radiation Thermal Infrared Radiation Global Heat Engine Components of the Earth s Energy Budget Relevance for
ATMOS 5140 Lecture 1 Chapter 1 Atmospheric Radiation Relevance for Weather and Climate Solar Radiation Thermal Infrared Radiation Global Heat Engine Components of the Earth s Energy Budget Relevance for
Atmospheric Processes
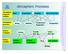 Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Atmospheric Processes Atmospheric prognostic variables Wind Temperature Humidity Cloud Water/Ice Atmospheric processes Mixing Radiation Condensation/ Evaporation Precipitation Surface exchanges Friction
Seasonal Variations of the Urban Heat Island Effect:
 Seasonal Variations of the Urban Heat Island Effect: Examining the Differences in Temperature Between the City of Philadelphia and its Outlying Suburbs By: Frank Vecchio 1 P a g e We re calling for a high
Seasonal Variations of the Urban Heat Island Effect: Examining the Differences in Temperature Between the City of Philadelphia and its Outlying Suburbs By: Frank Vecchio 1 P a g e We re calling for a high
The inputs and outputs of energy within the earth-atmosphere system that determines the net energy available for surface processes is the Energy
 Energy Balance The inputs and outputs of energy within the earth-atmosphere system that determines the net energy available for surface processes is the Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic
Energy Balance The inputs and outputs of energy within the earth-atmosphere system that determines the net energy available for surface processes is the Energy Balance Electromagnetic Radiation Electromagnetic
What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology.
 What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology. Climatology is the study of Earth s climate and the factors that affect past, present, and future climatic
What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology. Climatology is the study of Earth s climate and the factors that affect past, present, and future climatic
dt urb (z)/dt = M(z) (T rur (z) T urb (z)) / x (1)
 5.5 SENSITIVITY TESTING OF AN URBAN SURFACE SCHEME COUPLED TO A 1-D BOUNDARY LAYER MODEL E. Scott Krayenhoff * and James A. Voogt University of Western Ontario, London ON Canada 1. INTRODUCTION Many applications
5.5 SENSITIVITY TESTING OF AN URBAN SURFACE SCHEME COUPLED TO A 1-D BOUNDARY LAYER MODEL E. Scott Krayenhoff * and James A. Voogt University of Western Ontario, London ON Canada 1. INTRODUCTION Many applications
The Atmosphere. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems. Topic 3: Global Cycles and Physical Systems
 The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
The Atmosphere 1 How big is the atmosphere? Why is it cold in Geneva? Why do mountaineers need oxygen on Everest? 2 A relatively thin layer of gas over the Earths surface Earth s radius ~ 6400km Atmospheric
Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks. Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC
 Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC Outline Three Snow Lectures: 1. Why you should care about snow: Snow and the cryosphere Classes of
Terrestrial Snow Cover: Properties, Trends, and Feedbacks Chris Derksen Climate Research Division, ECCC Outline Three Snow Lectures: 1. Why you should care about snow: Snow and the cryosphere Classes of
Lecture 3. Background materials. Planetary radiative equilibrium TOA outgoing radiation = TOA incoming radiation Figure 3.1
 Lecture 3. Changes in planetary albedo. Is there a clear signal caused by aerosols and clouds? Outline: 1. Background materials. 2. Papers for class discussion: Palle et al., Changes in Earth s reflectance
Lecture 3. Changes in planetary albedo. Is there a clear signal caused by aerosols and clouds? Outline: 1. Background materials. 2. Papers for class discussion: Palle et al., Changes in Earth s reflectance
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Model physical parameterizations: The study uses the single-layer urban canopy model (SLUCM: Kusaka et al. 2001; Kusaka and Kimura 2004; Liu et al. 2006; Chen and Dudhia 2001; Chen
Supplementary Material Model physical parameterizations: The study uses the single-layer urban canopy model (SLUCM: Kusaka et al. 2001; Kusaka and Kimura 2004; Liu et al. 2006; Chen and Dudhia 2001; Chen
Remote Sensing Applications for Land/Atmosphere: Earth Radiation Balance
 Remote Sensing Applications for Land/Atmosphere: Earth Radiation Balance - Introduction - Deriving surface energy balance fluxes from net radiation measurements - Estimation of surface net radiation from
Remote Sensing Applications for Land/Atmosphere: Earth Radiation Balance - Introduction - Deriving surface energy balance fluxes from net radiation measurements - Estimation of surface net radiation from
Glaciology HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION
 HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION A Heat Budget 1 Black body radiation Definition. A perfect black body is defined as a body that absorbs all radiation that falls on it. The intensity of radiation emitted by a
HEAT BUDGET AND RADIATION A Heat Budget 1 Black body radiation Definition. A perfect black body is defined as a body that absorbs all radiation that falls on it. The intensity of radiation emitted by a
Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting
 Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting www.cawcr.gov.au Imtiaz Dharssi and Peter Steinle February 2011 SMOS/SMAP workshop, Monash University Summary In preparation of the
Assimilation of satellite derived soil moisture for weather forecasting www.cawcr.gov.au Imtiaz Dharssi and Peter Steinle February 2011 SMOS/SMAP workshop, Monash University Summary In preparation of the
GEOG415 Mid-term Exam 110 minute February 27, 2003
 GEOG415 Mid-term Exam 110 minute February 27, 2003 1 Name: ID: 1. The graph shows the relationship between air temperature and saturation vapor pressure. (a) Estimate the relative humidity of an air parcel
GEOG415 Mid-term Exam 110 minute February 27, 2003 1 Name: ID: 1. The graph shows the relationship between air temperature and saturation vapor pressure. (a) Estimate the relative humidity of an air parcel
1. GLACIER METEOROLOGY - ENERGY BALANCE
 Summer School in Glaciology McCarthy, Alaska, 5-15 June 2018 Regine Hock Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, Fairbanks 1. GLACIER METEOROLOGY - ENERGY BALANCE Ice and snow melt at 0 C, but this
Summer School in Glaciology McCarthy, Alaska, 5-15 June 2018 Regine Hock Geophysical Institute, University of Alaska, Fairbanks 1. GLACIER METEOROLOGY - ENERGY BALANCE Ice and snow melt at 0 C, but this
Creating Meteorology for CMAQ
 Creating Meteorology for CMAQ Tanya L. Otte* Atmospheric Sciences Modeling Division NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Research Triangle Park, NC * On assignment to the National Exposure Research Laboratory,
Creating Meteorology for CMAQ Tanya L. Otte* Atmospheric Sciences Modeling Division NOAA Air Resources Laboratory Research Triangle Park, NC * On assignment to the National Exposure Research Laboratory,
1. Weather and climate.
 Lecture 31. Introduction to climate and climate change. Part 1. Objectives: 1. Weather and climate. 2. Earth s radiation budget. 3. Clouds and radiation field. Readings: Turco: p. 320-349; Brimblecombe:
Lecture 31. Introduction to climate and climate change. Part 1. Objectives: 1. Weather and climate. 2. Earth s radiation budget. 3. Clouds and radiation field. Readings: Turco: p. 320-349; Brimblecombe:
Estimation of Wavelet Based Spatially Enhanced Evapotranspiration Using Energy Balance Approach
 Estimation of Wavelet Based Spatially Enhanced Evapotranspiration Using Energy Balance Approach Dr.Gowri 1 Dr.Thirumalaivasan 2 1 Associate Professor, Jerusalem College of Engineering, Department of Civil
Estimation of Wavelet Based Spatially Enhanced Evapotranspiration Using Energy Balance Approach Dr.Gowri 1 Dr.Thirumalaivasan 2 1 Associate Professor, Jerusalem College of Engineering, Department of Civil
How Researchers Measure Urban Heat Islands. James Voogt Department of Geography, University of Western Ontario London ON Canada
 How Researchers Measure Urban Heat Islands James Voogt Department of Geography, University of Western Ontario London ON Canada Outline What is the urban heat island? What types of urban heat islands exist?
How Researchers Measure Urban Heat Islands James Voogt Department of Geography, University of Western Ontario London ON Canada Outline What is the urban heat island? What types of urban heat islands exist?
May 3, :41 AOGS - AS 9in x 6in b951-v16-ch13 LAND SURFACE ENERGY BUDGET OVER THE TIBETAN PLATEAU BASED ON SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING DATA
 Advances in Geosciences Vol. 16: Atmospheric Science (2008) Eds. Jai Ho Oh et al. c World Scientific Publishing Company LAND SURFACE ENERGY BUDGET OVER THE TIBETAN PLATEAU BASED ON SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING
Advances in Geosciences Vol. 16: Atmospheric Science (2008) Eds. Jai Ho Oh et al. c World Scientific Publishing Company LAND SURFACE ENERGY BUDGET OVER THE TIBETAN PLATEAU BASED ON SATELLITE REMOTE SENSING
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer. The Surface Energy Balance (9.2)
 The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) Atm S 547 Lecture 4,
The Atmospheric Boundary Layer Turbulence (9.1) The Surface Energy Balance (9.2) Vertical Structure (9.3) Evolution (9.4) Special Effects (9.5) The Boundary Layer in Context (9.6) Atm S 547 Lecture 4,
Light Up Your World Adapted from Reflecting on Reflectivity,
 Climate Change I m Supposed To Know What That Is? Light Up Your World Adapted from Reflecting on Reflectivity, http://www.climatechangenorth.ca Overview: Students often confuse global warming and the depletion
Climate Change I m Supposed To Know What That Is? Light Up Your World Adapted from Reflecting on Reflectivity, http://www.climatechangenorth.ca Overview: Students often confuse global warming and the depletion
2. EVOLUTION OF URBAN CLIMATE OF PARIS AND ITS AREA WITH REGARD TO CLIMATE CHANGE
 EPICEA PROJECT [2008-2010] MULTIDISCIPLINARY STUDY OF THE IMPACTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON THE SCALE OF PARIS J. Desplat*, J-L. Salagnac***, R. Kounkou*, A. Lemonsu**, M.Colombert***, M. Lauffenburger***,
EPICEA PROJECT [2008-2010] MULTIDISCIPLINARY STUDY OF THE IMPACTS OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON THE SCALE OF PARIS J. Desplat*, J-L. Salagnac***, R. Kounkou*, A. Lemonsu**, M.Colombert***, M. Lauffenburger***,
Soil Water Atmosphere Plant (SWAP) Model: I. INTRODUCTION AND THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
 Soil Water Atmosphere Plant (SWAP) Model: I. INTRODUCTION AND THEORETICAL BACKGROUND Reinder A.Feddes Jos van Dam Joop Kroes Angel Utset, Main processes Rain fall / irrigation Transpiration Soil evaporation
Soil Water Atmosphere Plant (SWAP) Model: I. INTRODUCTION AND THEORETICAL BACKGROUND Reinder A.Feddes Jos van Dam Joop Kroes Angel Utset, Main processes Rain fall / irrigation Transpiration Soil evaporation
M.Sc. in Meteorology. Physical Meteorology Prof Peter Lynch. Mathematical Computation Laboratory Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield.
 M.Sc. in Meteorology Physical Meteorology Prof Peter Lynch Mathematical Computation Laboratory Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Climate Change???????????????? Tourists run through a swarm of pink
M.Sc. in Meteorology Physical Meteorology Prof Peter Lynch Mathematical Computation Laboratory Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Climate Change???????????????? Tourists run through a swarm of pink
A R C T E X Results of the Arctic Turbulence Experiments Long-term Monitoring of Heat Fluxes at a high Arctic Permafrost Site in Svalbard
 A R C T E X Results of the Arctic Turbulence Experiments www.arctex.uni-bayreuth.de Long-term Monitoring of Heat Fluxes at a high Arctic Permafrost Site in Svalbard 1 A R C T E X Results of the Arctic
A R C T E X Results of the Arctic Turbulence Experiments www.arctex.uni-bayreuth.de Long-term Monitoring of Heat Fluxes at a high Arctic Permafrost Site in Svalbard 1 A R C T E X Results of the Arctic
Evaluation of a New Land Surface Model for JMA-GSM
 Evaluation of a New Land Surface Model for JMA-GSM using CEOP EOP-3 reference site dataset Masayuki Hirai Takuya Sakashita Takayuki Matsumura (Numerical Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological Agency)
Evaluation of a New Land Surface Model for JMA-GSM using CEOP EOP-3 reference site dataset Masayuki Hirai Takuya Sakashita Takayuki Matsumura (Numerical Prediction Division, Japan Meteorological Agency)
Lecture 3A: Interception
 3-1 GEOG415 Lecture 3A: Interception What is interception? Canopy interception (C) Litter interception (L) Interception ( I = C + L ) Precipitation (P) Throughfall (T) Stemflow (S) Net precipitation (R)
3-1 GEOG415 Lecture 3A: Interception What is interception? Canopy interception (C) Litter interception (L) Interception ( I = C + L ) Precipitation (P) Throughfall (T) Stemflow (S) Net precipitation (R)
Sun and Earth s Climate
 Kevin E Trenberth Sun and Earth s Climate BAMS cover March 2009 NCAR Here comes the sun So where does all that solar radiation go? If the sun keeps shining why don t we continue to get warmer? Aaagh! But
Kevin E Trenberth Sun and Earth s Climate BAMS cover March 2009 NCAR Here comes the sun So where does all that solar radiation go? If the sun keeps shining why don t we continue to get warmer? Aaagh! But
Observation: predictable patterns of ecosystem distribution across Earth. Observation: predictable patterns of ecosystem distribution across Earth 1.
 Climate Chap. 2 Introduction I. Forces that drive climate and their global patterns A. Solar Input Earth s energy budget B. Seasonal cycles C. Atmospheric circulation D. Oceanic circulation E. Landform
Climate Chap. 2 Introduction I. Forces that drive climate and their global patterns A. Solar Input Earth s energy budget B. Seasonal cycles C. Atmospheric circulation D. Oceanic circulation E. Landform
Lecture notes: Interception and evapotranspiration
 Lecture notes: Interception and evapotranspiration I. Vegetation canopy interception (I c ): Portion of incident precipitation (P) physically intercepted, stored and ultimately evaporated from vegetation
Lecture notes: Interception and evapotranspiration I. Vegetation canopy interception (I c ): Portion of incident precipitation (P) physically intercepted, stored and ultimately evaporated from vegetation
METRIC tm. Mapping Evapotranspiration at high Resolution with Internalized Calibration. Shifa Dinesh
 METRIC tm Mapping Evapotranspiration at high Resolution with Internalized Calibration Shifa Dinesh Outline Introduction Background of METRIC tm Surface Energy Balance Image Processing Estimation of Energy
METRIC tm Mapping Evapotranspiration at high Resolution with Internalized Calibration Shifa Dinesh Outline Introduction Background of METRIC tm Surface Energy Balance Image Processing Estimation of Energy
DO WE NEED URBAN PARAMETERIZATION IN HIGH RESOLUTION SIMULATIONS?
 Charles University Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Dept. of Atmospheric Physics V Holešovičkách 2, Prague Czech Republic DO WE NEED URBAN PARAMETERIZATION IN HIGH RESOLUTION SIMULATIONS? Tomáš Halenka,
Charles University Faculty of Mathematics and Physics Dept. of Atmospheric Physics V Holešovičkách 2, Prague Czech Republic DO WE NEED URBAN PARAMETERIZATION IN HIGH RESOLUTION SIMULATIONS? Tomáš Halenka,
Evapotranspiration monitoring with Meteosat Second Generation satellites: method, products and utility in drought detection.
 Evapotranspiration monitoring with Meteosat Second Generation satellites: method, products and utility in drought detection. Nicolas Ghilain Royal Meteorological Institute Belgium EUMeTrain Event week
Evapotranspiration monitoring with Meteosat Second Generation satellites: method, products and utility in drought detection. Nicolas Ghilain Royal Meteorological Institute Belgium EUMeTrain Event week
Atmospheric Composition and Structure
 Atmospheric Composition and Structure Weather and Climate What is weather? The state of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. Defined by: Humidity, temperature, wind speed, clouds, precipitation,
Atmospheric Composition and Structure Weather and Climate What is weather? The state of the atmosphere at a specific time and place. Defined by: Humidity, temperature, wind speed, clouds, precipitation,
Weather and Wind Modeling in Egypt Meso-scale Meteorological (Weather Forecast) Modeling
 Weather and Wind Modeling in Egypt Meso-scale Meteorological (Weather Forecast) Modeling Presented By; Atef O. Sherif Aerospace Department Faculty of Engineering Cairo University Collaborators Hamada Sultan
Weather and Wind Modeling in Egypt Meso-scale Meteorological (Weather Forecast) Modeling Presented By; Atef O. Sherif Aerospace Department Faculty of Engineering Cairo University Collaborators Hamada Sultan
1. Current atmospheric DA systems 2. Coupling surface/atmospheric DA 3. Trends & ideas
 1 Current issues in atmospheric data assimilation and its relationship with surfaces François Bouttier GAME/CNRM Météo-France 2nd workshop on remote sensing and modeling of surface properties, Toulouse,
1 Current issues in atmospheric data assimilation and its relationship with surfaces François Bouttier GAME/CNRM Météo-France 2nd workshop on remote sensing and modeling of surface properties, Toulouse,
An Introduction to Climate Modeling
 An Introduction to Climate Modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline What is Climate & why do we care Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
An Introduction to Climate Modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline What is Climate & why do we care Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
P1.34 MULTISEASONALVALIDATION OF GOES-BASED INSOLATION ESTIMATES. Jason A. Otkin*, Martha C. Anderson*, and John R. Mecikalski #
 P1.34 MULTISEASONALVALIDATION OF GOES-BASED INSOLATION ESTIMATES Jason A. Otkin*, Martha C. Anderson*, and John R. Mecikalski # *Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies, University of
P1.34 MULTISEASONALVALIDATION OF GOES-BASED INSOLATION ESTIMATES Jason A. Otkin*, Martha C. Anderson*, and John R. Mecikalski # *Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies, University of
THE OFFLINE VERSION OF SURFEX COUPLED TO THE
 SURFEX@RMI THE OFFLINE VERSION OF SURFEX COUPLED TO THE OPERATIONAL ALADIN FORECAST OVER BELGIUM: A TOOL TO IMPROVE WINTER SCREEN TEMPERATURE Royal Meteorological Institute, Brussels, Belgium Corresponding
SURFEX@RMI THE OFFLINE VERSION OF SURFEX COUPLED TO THE OPERATIONAL ALADIN FORECAST OVER BELGIUM: A TOOL TO IMPROVE WINTER SCREEN TEMPERATURE Royal Meteorological Institute, Brussels, Belgium Corresponding
Atmospheric Sciences 321. Science of Climate. Lecture 14: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4
 Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 14: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Today, HW#5 is posted Quiz Today on Chapter 3, too. Mid Term
Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 14: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Today, HW#5 is posted Quiz Today on Chapter 3, too. Mid Term
Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra
 Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra emanuel.dutra@ecmwf.int Slide 1 Parameterizations training course 2015, Land-surface: Snow ECMWF Outline Snow in the climate system, an overview: Observations; Modeling;
Land Surface: Snow Emanuel Dutra emanuel.dutra@ecmwf.int Slide 1 Parameterizations training course 2015, Land-surface: Snow ECMWF Outline Snow in the climate system, an overview: Observations; Modeling;
Global Climate Change
 Global Climate Change Definition of Climate According to Webster dictionary Climate: the average condition of the weather at a place over a period of years exhibited by temperature, wind velocity, and
Global Climate Change Definition of Climate According to Webster dictionary Climate: the average condition of the weather at a place over a period of years exhibited by temperature, wind velocity, and
Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Class Web Site: Lecture 27 Dec
 Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Climate Natural Variations Feedback Mechanisms Lecture 27 Dec 4 2018 1 Climate
Weather Forecasts and Climate AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Climate Natural Variations Feedback Mechanisms Lecture 27 Dec 4 2018 1 Climate
J17.3 Impact Assessment on Local Meteorology due to the Land Use Changes During Urban Development in Seoul
 J17.3 Impact Assessment on Local Meteorology due to the Land Use Changes During Urban Development in Seoul Hae-Jung Koo *, Kyu Rang Kim, Young-Jean Choi, Tae Heon Kwon, Yeon-Hee Kim, and Chee-Young Choi
J17.3 Impact Assessment on Local Meteorology due to the Land Use Changes During Urban Development in Seoul Hae-Jung Koo *, Kyu Rang Kim, Young-Jean Choi, Tae Heon Kwon, Yeon-Hee Kim, and Chee-Young Choi
Inclusion of a Drag Approach in the Town Energy Balance (TEB) Scheme: Offline 1D Evaluation in a Street Canyon
 OCTOBER 2008 H A M D I A N D M A S S O N 2627 Inclusion of a Drag Approach in the Town Energy Balance (TEB) Scheme: Offline 1D Evaluation in a Street Canyon R. HAMDI Royal Meteorological Institute, Brussels,
OCTOBER 2008 H A M D I A N D M A S S O N 2627 Inclusion of a Drag Approach in the Town Energy Balance (TEB) Scheme: Offline 1D Evaluation in a Street Canyon R. HAMDI Royal Meteorological Institute, Brussels,
Atmospheric Sciences 321. Science of Climate. Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4
 Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Wednesday Quiz #2 Wednesday Mid Term is Wednesday May 6 Practice
Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 13: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Wednesday Quiz #2 Wednesday Mid Term is Wednesday May 6 Practice
Applications of GIS and Remote Sensing for Analysis of Urban Heat Island
 Chuanxin Zhu Professor Peter V. August Professor Yeqiao Wang NRS 509 December 15, 2016 Applications of GIS and Remote Sensing for Analysis of Urban Heat Island Since the last century, the global mean surface
Chuanxin Zhu Professor Peter V. August Professor Yeqiao Wang NRS 509 December 15, 2016 Applications of GIS and Remote Sensing for Analysis of Urban Heat Island Since the last century, the global mean surface
Local Meteorology. Changes In Geometry
 Energy Balance Climate Local Meteorology Surface Mass And Energy Exchange Net Mass Balance Dynamic Response Effect on Landscape Changes In Geometry Water Flow Climate Local Meteorology Surface Mass And
Energy Balance Climate Local Meteorology Surface Mass And Energy Exchange Net Mass Balance Dynamic Response Effect on Landscape Changes In Geometry Water Flow Climate Local Meteorology Surface Mass And
ATM S 111, Global Warming Climate Models
 ATM S 111, Global Warming Climate Models Jennifer Fletcher Day 27: July 29, 2010 Using Climate Models to Build Understanding Often climate models are thought of as forecast tools (what s the climate going
ATM S 111, Global Warming Climate Models Jennifer Fletcher Day 27: July 29, 2010 Using Climate Models to Build Understanding Often climate models are thought of as forecast tools (what s the climate going
F. Chen 1, H. Kusaka 2, M. Tewari 1, J.-W. Bao 3, and H. Hirakuchi
 9.11 UTILIZIN THE COUPLED WF/LSM/UBAN MODELIN SYSTEM WITH DETAILED UBAN CLASSIFICATION TO SIMULATE THE UBAN HEAT ISLAND PHENOMENA OVE THE EATE HOUSTON AEA F. Chen 1 H. Kusaka 2 M. Tewari 1 J.-W. Bao 3
9.11 UTILIZIN THE COUPLED WF/LSM/UBAN MODELIN SYSTEM WITH DETAILED UBAN CLASSIFICATION TO SIMULATE THE UBAN HEAT ISLAND PHENOMENA OVE THE EATE HOUSTON AEA F. Chen 1 H. Kusaka 2 M. Tewari 1 J.-W. Bao 3
Features of Global Warming Review. GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 23 Ahrens: Chapter 16
 Features of Global Warming Review GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 23 Ahrens: Chapter 16 The Greenhouse Effect 255 K 288 K Ahrens, Fig. 2.12 What can change the global energy balance? Incoming energy Solar strength
Features of Global Warming Review GEOG/ENST 2331 Lecture 23 Ahrens: Chapter 16 The Greenhouse Effect 255 K 288 K Ahrens, Fig. 2.12 What can change the global energy balance? Incoming energy Solar strength
Lecture 3a: Surface Energy Balance
 Lecture 3a: Surface Energy Balance Instructor: Prof. Johnny Luo http://www.sci.ccny.cuny.edu/~luo Total: 50 pts Absorption of IR radiation O 3 band ~ 9.6 µm Vibration-rotation interaction of CO 2 ~
Lecture 3a: Surface Energy Balance Instructor: Prof. Johnny Luo http://www.sci.ccny.cuny.edu/~luo Total: 50 pts Absorption of IR radiation O 3 band ~ 9.6 µm Vibration-rotation interaction of CO 2 ~
NCEP non-hydrostatic regional model and surface scheme LAPS: A dynamical scaling tool for use in agricultural models
 NCEP non-hydrostatic regional model and surface scheme LAPS: A dynamical scaling tool for use in agricultural models D.T. Mihailović and B. Lalić Faculty of Agriculture, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad,
NCEP non-hydrostatic regional model and surface scheme LAPS: A dynamical scaling tool for use in agricultural models D.T. Mihailović and B. Lalić Faculty of Agriculture, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad,
The Challenge of. Guy Brasseur
 The Challenge of Monitoring and Predicting Chemical Weather Guy Brasseur Introduction: What is Chemical Weather? What is Chemical Weather? Local, regional, and global distributions of important trace gases
The Challenge of Monitoring and Predicting Chemical Weather Guy Brasseur Introduction: What is Chemical Weather? What is Chemical Weather? Local, regional, and global distributions of important trace gases
Flux Tower Data Quality Analysis in the North American Monsoon Region
 Flux Tower Data Quality Analysis in the North American Monsoon Region 1. Motivation The area of focus in this study is mainly Arizona, due to data richness and availability. Monsoon rains in Arizona usually
Flux Tower Data Quality Analysis in the North American Monsoon Region 1. Motivation The area of focus in this study is mainly Arizona, due to data richness and availability. Monsoon rains in Arizona usually
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate
 Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
Energy Systems, Structures and Processes Essential Standard: Analyze patterns of global climate change over time Learning Objective: Differentiate between weather and climate Global Climate Focus Question
ATMOSPHERIC ENERGY and GLOBAL TEMPERATURES. Physical Geography (Geog. 300) Prof. Hugh Howard American River College
 ATMOSPHERIC ENERGY and GLOBAL TEMPERATURES Physical Geography (Geog. 300) Prof. Hugh Howard American River College RADIATION FROM the SUN SOLAR RADIATION Primarily shortwave (UV-SIR) Insolation Incoming
ATMOSPHERIC ENERGY and GLOBAL TEMPERATURES Physical Geography (Geog. 300) Prof. Hugh Howard American River College RADIATION FROM the SUN SOLAR RADIATION Primarily shortwave (UV-SIR) Insolation Incoming
ATMET Technical Note. Modifications for the Transition From LEAF-2 to LEAF-3
 ATMET Technical Note Number 1 Modifications for the Transition From LEAF-2 to LEAF-3 Prepared by: ATMET, LLC PO Box 19195 Boulder, Colorado 80308-2195 Robert L. Walko Craig J. Tremback October 2005 Table
ATMET Technical Note Number 1 Modifications for the Transition From LEAF-2 to LEAF-3 Prepared by: ATMET, LLC PO Box 19195 Boulder, Colorado 80308-2195 Robert L. Walko Craig J. Tremback October 2005 Table
Application and impacts of the GlobeLand30 land cover dataset on the Beijing Climate Center Climate Model
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Application and impacts of the GlobeLand30 land cover dataset on the Beijing Climate Center Climate Model To cite this article:
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Application and impacts of the GlobeLand30 land cover dataset on the Beijing Climate Center Climate Model To cite this article:
Evaluation of land surface temperature (LST) patterns in the urban agglomeration of Krakow using different satellite data and GIS
 Evaluation of land surface temperature (LST) patterns in the urban agglomeration of Krakow using different satellite data and GIS Jakub P. Walawender 1,2 1 Satellite Remote Sensing Centre, Institute of
Evaluation of land surface temperature (LST) patterns in the urban agglomeration of Krakow using different satellite data and GIS Jakub P. Walawender 1,2 1 Satellite Remote Sensing Centre, Institute of
The Effects of Improved Land Use on the Meteorological Modeling in Klang Valley Region Malaysia
 EnvironmentAsia The international journal published by the Thai Society of Higher Education Institutes on Environment Available online at www.tshe.org/ea EnvironmentAsia 3(special issue) (2010) 117-123
EnvironmentAsia The international journal published by the Thai Society of Higher Education Institutes on Environment Available online at www.tshe.org/ea EnvironmentAsia 3(special issue) (2010) 117-123
A PHYSICALLY-BASED SCHEME FOR THE URBAN ENERGY BUDGET IN ATMOSPHERIC MODELS
 A PHYSICALLY-BASED SCHEME FOR THE URBAN ENERGY BUDGET IN ATMOSPHERIC MODELS VALÉRY MASSON Centre National de Recherches Météorologiques, Toulouse, France (Received in final form 29 September 1999) Abstract.
A PHYSICALLY-BASED SCHEME FOR THE URBAN ENERGY BUDGET IN ATMOSPHERIC MODELS VALÉRY MASSON Centre National de Recherches Météorologiques, Toulouse, France (Received in final form 29 September 1999) Abstract.
Physical Aspects of Surface Energy Balance and Earth Observation Systems in Agricultural Practice
 Physical Aspects of Surface Energy Balance and Earth Observation Systems in Agricultural Practice Henk de Bruin During the visit to Pachacamac we contemplate about the 4 elements, fire, air, water and
Physical Aspects of Surface Energy Balance and Earth Observation Systems in Agricultural Practice Henk de Bruin During the visit to Pachacamac we contemplate about the 4 elements, fire, air, water and
Remote sensing derived evapotranspiration: comparisons to observations and models and results over the full MSG disk and selected basins
 4 th LSA-SAF WORKSHOP Toulouse,France, 15 th to 17 th November 2010 Remote sensing derived evapotranspiration: comparisons to observations and models and results over the full MSG disk and selected basins
4 th LSA-SAF WORKSHOP Toulouse,France, 15 th to 17 th November 2010 Remote sensing derived evapotranspiration: comparisons to observations and models and results over the full MSG disk and selected basins
Tropical Climates Zone
 Tropical Climates Zone RAIN FOREST CENTRAL AFRICA, SOUTH AMERICA (AMAZON), CENTRAL AMERICA, S.E. ASIA HUMID/WARM ANNUAL RAINFALL 200 CM TYPE #1: TROPICAL DESERT N. AFRICA (SAHARA) & S.W. ASIA < 25 CM
Tropical Climates Zone RAIN FOREST CENTRAL AFRICA, SOUTH AMERICA (AMAZON), CENTRAL AMERICA, S.E. ASIA HUMID/WARM ANNUAL RAINFALL 200 CM TYPE #1: TROPICAL DESERT N. AFRICA (SAHARA) & S.W. ASIA < 25 CM
The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget
 The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth MAR 555 Lecture 2: The Oceanic Heat Budget Q
The Ocean-Atmosphere System II: Oceanic Heat Budget C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth MAR 555 Lecture 2: The Oceanic Heat Budget Q
Global Water Cycle. Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere. Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40.
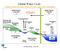 Global Water Cycle Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere Water Vapour over Land 3 Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40 Water Vapour over Sea 10 Glaciers and Snow 24,064 Permafrost
Global Water Cycle Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere Water Vapour over Land 3 Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40 Water Vapour over Sea 10 Glaciers and Snow 24,064 Permafrost
First steps toward a comparison of modelled thermal comfort during a heatwave in Melbourne, Australia
 First steps toward a comparison of modelled thermal comfort during a heatwave in Melbourne, Australia Stephanie Jacobs PhD supervisors: Ailie Gallant and Nigel Tapper Outline of talk Motivation for research
First steps toward a comparison of modelled thermal comfort during a heatwave in Melbourne, Australia Stephanie Jacobs PhD supervisors: Ailie Gallant and Nigel Tapper Outline of talk Motivation for research
Some remarks on climate modeling
 Some remarks on climate modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Selected overheads by Doug Nychka Outline Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
Some remarks on climate modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Selected overheads by Doug Nychka Outline Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models
 An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline Frame broader scientific problem Hierarchy
An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline Frame broader scientific problem Hierarchy
Areas of the World with high Insolation
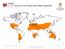 Areas of the World with high Insolation 22 /43 Africa Annual Average Global Horizontal Solar Radiation Map 19 Jul 2006 A map depicting model estimates of monthly average daily total radiation using inputs
Areas of the World with high Insolation 22 /43 Africa Annual Average Global Horizontal Solar Radiation Map 19 Jul 2006 A map depicting model estimates of monthly average daily total radiation using inputs
