Name: Date: Period: Identifying & Analyzing Powders Lab [Adapted from
|
|
|
- Meghan Sharp
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Date: Period: Identifying & Analyzing Powders Lab [Adapted from ] In this lab, you will be observing physical and chemical properties of four different powders. Then you will use the physical and chemical properties that you observe to distinguish unknown mixtures of powders. Purpose To identify several household items by their physical and chemical properties To analyze mixtures of common household items of unknown composition To practice measuring matter and converting units To practice scientific writing Content Covered Describing and measuring matter Physical & chemical properties States of matter Introduction Part of the fun of chemistry is being able to identify different substances by tests. To identify substances, chemists use reagents which are known chemicals or mixtures of chemicals. When a reagent is added to a sample being tested, it may or it may not produce an observable change. Both the positive and the negative result will help identify the unknown sample being tested. In this simple system of common household chemicals, four powders and three liquid reagents are used: POWDERS: A: Baking Soda B: Corn Starch C: Alka Seltzer D: Table Salt LIQUID REAGENTS: I: White Vinegar II: Iodine Tincture III: Distilled Water A series of tests will be performed that will help you to find out how each of the powders behaves when the liquid reagent is added. When performing the tests, look for both POSITIVE RESULTS (chemical changes like color changes and the production of gas bubbles) as well as NEGATIVE RESULTS (no chemical change/no observable change) since both positive and negative results carry the same significance in chemical analysis. After you establish the tests that identify or indicate a difference between the four powders, you will analyze three samples of unknown composition: Two of your unknown samples will be mixtures of two powders (identified with a number between 10-99) One unknown sample will be a mixture of three powders (identified with a number between ). 1
2 Materials 2 grams of Baking soda 5 grams of Cornstarch 1 tablet of Alka-Seltzer 2 grams of Table Salt 4 ml of White Vinegar 4 ml of Tinctured Iodine 4 ml of Water 2 spot plates 3 pipets 3 test tubes labeled White Vinegar, Tinctured Iodine and Water 4 cups labeled Baking Soda, Cornstarch, Alkaseltzer, Table Salt 3 spoons 1 balance 3 unknown samples Procedure PART 1: IDENTIFICATION 1.) Write down 2 physical properties for each of the four powders and the three liquid reagents. Record the information in the data section. 2.) Weigh out 2 grams of table salt, 5 grams of cornstarch and 2 grams of baking soda. Record the actual weight of baking soda, cornstarch and table salt that you used and record the information in the data section. 3.) Break an Alkaseltzer tablet into two halves. Weigh the half of Alkaseltzer that you use in grams. Grind one half of the tablet into a powder. Use the bottom of your spoon to grind it up in a cup 4.) Place small amounts (use a spoon) of the four powers in each of the 12 depressions of your spot plate as show in the diagram below. 5.) Samples of white vinegar, iodine tincture and water have been placed for you into three clean test tubes. Make sure that the test tubes are labeled. Put a pipet into each of the test tubes. Throughout the experiment, make sure that the same pipet is always used for the same liquid reagent. 6.) To each of the 12 solid samples in the spot plate, add a few drops of the three liquid reagents according to the diagram below. 2
3 7.) Record your observations and briefly describe how you can identify each powder. PART 2: ANALYSIS 1.) Check out your three unknown mixtures and record their numbers below and in the table in #2. Unknown #1: (2 powders) Unknown #2: (2 powders) Unknown #3: (3 powders) 2.) Test the unknown sample with each of the three liquid reagents as you did in Part 1. Follow the diagram below when arranging the chemicals in your spot plate. White vinegar Unknown1 # Unknown2 # Unknown3 # empty Iodine tincture Unknown1 # Unknown2 # Unknown3 # empty Distilled water Unknown1 # Unknown2 # Unknown3 # empty 3.) State the composition of each mixture. 3
4 Data & Observations PART 1: IDENTIFICATION 1. ) Physical Properties Record at least 2 physical properties for each powder and for each liquid reagent. Powder/Reagent Physical Properties Baking Soda Cornstarch Alka-Seltzer Table Salt White Vinegar Tinctured Iodine Water 2.) Measurements Record the mass of the four powders that you used in this lab. Make sure you take significant figures into consideration. Powders Mass Baking Soda Cornstarch Alka-Seltzer Table Salt Here s the volume of the three liquid reagents that you used in this lab. Make sure you take significant figures into consideration. Reagents Volume White Vinegar Tinctured Iodine Water 4 ml 4 ml 4 ml 4
5 3.) Results Record what happened in each spot when you mixed the powders. Was there a chemical change? How do you know? Baking Soda Cornstarch Alka-Seltzer Table Salt White Vinegar Tinctured Iodine Water 4.) Conclusion Briefly describe how you can identify each powder using the results you got from this lab. Powder How can I identify this powder? Baking Soda Cornstarch Alka-Seltzer Table Salt 5
6 PART 2: ANALYSIS In this section, you will report the data you got when you tested the unknown samples. You will also analyze your results to figure out what powders are in each sample. 1.) Report your unknown numbers Two-power mixture #1 Two-powder mixture #2 Three-powder mixture 2.) Results Unknown #1 (2 powders) Unknown #2 (2 powders) Unknown #3 (3 powders) White Vinegar Tinctured Iodine Water 3.) Conclusion 1.) Write down what you think powders each unknown contains. Unknown #1 and #2 (with a 2-digit number) contains only 2 powders. Unknown #3 (with a 3-digit number) contains only 3 powders. a.) Unknown #1 : I think Unknown #1 contains and because. 6
7 b.) Unknown #2 : I think Unknown #1 contains and because. c.) Unknown #3 : I think Unknown #1 contains,, and because. 2.) What is matter and how do we know that the materials (the powders and the reagents) we used in this lab were matter? 3.) In this lab, we measured the mass of our powders in grams (g). Convert the mass of your baking soda sample to kilograms (kg). Show the math work you did for this conversion below. 4.) In this lab, we measured the volume of our liquids to be 4 milliliters (ml). Convert this measurement to liters (L). Show the math work you did for this conversions. 5.) In this lab, you recorded the mass each powder. In this table below, write each measurement in scientific notation also. Baking Soda Cornstarch Alka-Seltzer Table Salt Powders Recorded Mass Scientific Notation 7
8 6.) We saw all three states of matter in this lab. Name examples of where you saw solids, liquids and gases in this experiment. 7.) What are physical properties and how did we use them in this lab? Why are they useful in science and in describing matter? 8.) We saw chemical changes in this lab. What types of chemical changes did you see and when did you see these chemical changes happen? 9.) Explain in a paragraph how you figured out what unknown1, unknown 2 and unknown 3 were. 8
Name: Date: Period: Identifying & Analyzing Powders Lab [Adapted from
 Name: Date: Period: Identifying & Analyzing Powders Lab [Adapted from http://www.csun.edu/chemteach/activities/beginninganalysis.pdf ] In this lab, you will be observing physical and chemical properties
Name: Date: Period: Identifying & Analyzing Powders Lab [Adapted from http://www.csun.edu/chemteach/activities/beginninganalysis.pdf ] In this lab, you will be observing physical and chemical properties
Exploring Acids & Bases
 Food Explorations Lab: Exploring Acids & Bases STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will use cabbage juice indicator to determine if two unknown samples are acids or
Food Explorations Lab: Exploring Acids & Bases STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will use cabbage juice indicator to determine if two unknown samples are acids or
Activity Sheet Chapter 6, Lesson 10 Carbon Dioxide Can Make a Solution Acidic
 Activity Sheet Chapter 6, Lesson 10 Carbon Dioxide Can Make a Solution Acidic Name Date DEMONSTRATION 1. Your teacher blew through a straw into a universal indicator solution until it changed color. Did
Activity Sheet Chapter 6, Lesson 10 Carbon Dioxide Can Make a Solution Acidic Name Date DEMONSTRATION 1. Your teacher blew through a straw into a universal indicator solution until it changed color. Did
Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes Lab
 Name: Date: Period: Group Members Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes Lab Station 1 Color Station Instruction: Describe the color of the following substances. Substance Color 1. Sulfur 2. Ammonium
Name: Date: Period: Group Members Physical and Chemical Properties and Changes Lab Station 1 Color Station Instruction: Describe the color of the following substances. Substance Color 1. Sulfur 2. Ammonium
CHEMICAL REACTION IN A BAGGY (MODIFIED FOR ADEED)
 CHEMICAL REACTION IN A BAGGY (MODIFIED FOR ADEED) Overview: Students investigate chemical reactions using given substances. Students identify chemical reactions in their daily lives. Objectives: The student
CHEMICAL REACTION IN A BAGGY (MODIFIED FOR ADEED) Overview: Students investigate chemical reactions using given substances. Students identify chemical reactions in their daily lives. Objectives: The student
Limiting Reactants Lab
 Name: Teacher s Name: Class: Block: Date: Partners: Limiting Reactants Lab Purpose: Through experimentation, determine the limiting reactant and the percent yield in a chemical reaction that generates
Name: Teacher s Name: Class: Block: Date: Partners: Limiting Reactants Lab Purpose: Through experimentation, determine the limiting reactant and the percent yield in a chemical reaction that generates
LEVEL ZERO VOICE CATALYST (10 minutes, individual work): 1. Counting atoms
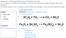 Assignment 4 Chemical Detectives at the Molecular Level LO: To explain the differences between chemical and physical changes through observable evidence. EQ: What evidence can be used to tell the difference
Assignment 4 Chemical Detectives at the Molecular Level LO: To explain the differences between chemical and physical changes through observable evidence. EQ: What evidence can be used to tell the difference
Name Period Date. Lab 1: Mass of Ice Materials: beaker, ice and balance.
 Name Period Date Testing the Law of Conservation of MASS! Introduction: Does mass change in a chemical or physical reaction? In this series of experiments you will find the answer to this question. Lab
Name Period Date Testing the Law of Conservation of MASS! Introduction: Does mass change in a chemical or physical reaction? In this series of experiments you will find the answer to this question. Lab
Physical and Chemical Changes Or How Do You Know When You ve Made Something New?
 Introduction Or How Do You Know When You ve Made Something New? Remember that all matter has characteristic physical and chemical properties. Matter can also undergo physical and chemical changes. How
Introduction Or How Do You Know When You ve Made Something New? Remember that all matter has characteristic physical and chemical properties. Matter can also undergo physical and chemical changes. How
Post-Show. Chemistry. Periodic Table of the Elements. After the Show. Traveling Science Shows
 Traveling Science Shows Post-Show Chemistry After the Show We recently presented a Chemistry show at your school, and thought you and your students might like to continue investigating this topic. The
Traveling Science Shows Post-Show Chemistry After the Show We recently presented a Chemistry show at your school, and thought you and your students might like to continue investigating this topic. The
T h e M yster y Pow der s L ab: Ph ysical an d Ch em ical Ch an ges
 T h e M yster y Pow der s L ab: Ph ysical an d Ch em ical Ch an ges Background Information: You have learned how to describe matter based on its physical and chemical properties. You have also learned
T h e M yster y Pow der s L ab: Ph ysical an d Ch em ical Ch an ges Background Information: You have learned how to describe matter based on its physical and chemical properties. You have also learned
Alka Seltzer Lab: Reaction rate - Factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions
 Alka Seltzer Lab: Reaction rate - Factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions Materials Lead Scribe Reporter/Questioner Clean-up WRITE ALL NOTES / DATA / OBSERVATIONS ON YOUR DATA SHEET The rate
Alka Seltzer Lab: Reaction rate - Factors that affect the rate of chemical reactions Materials Lead Scribe Reporter/Questioner Clean-up WRITE ALL NOTES / DATA / OBSERVATIONS ON YOUR DATA SHEET The rate
Matter: Chemical and Physical Changes
 PARAMUS ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PARAMUS, NEW JERSEY CURRICULUM OUTLINE DEPARTMENT: Science REVISION DATE: January, 2004 COURSE: Matter: Chemical and Physical Changes GRADE LEVEL: Grade 5 I. COURSE DESCRIPTION:
PARAMUS ELEMENTARY SCHOOL PARAMUS, NEW JERSEY CURRICULUM OUTLINE DEPARTMENT: Science REVISION DATE: January, 2004 COURSE: Matter: Chemical and Physical Changes GRADE LEVEL: Grade 5 I. COURSE DESCRIPTION:
5 th GRADE PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL TESTS
 5 th GRADE PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL TESTS Summary: Students investigate 5 unknown white powders. They gather clues by observing the physical and chemical changes of the powders. At the end of the activity,
5 th GRADE PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL TESTS Summary: Students investigate 5 unknown white powders. They gather clues by observing the physical and chemical changes of the powders. At the end of the activity,
Chapter 6, Lesson 10: Carbon Dioxide Can Make a Solution Acidic
 Chapter 6, Lesson 10: Carbon Dioxide Can Make a Solution Acidic Key Concepts Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) gas dissolved in water can cause water to become acidic. The acidity of water from dissolved CO 2 can
Chapter 6, Lesson 10: Carbon Dioxide Can Make a Solution Acidic Key Concepts Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) gas dissolved in water can cause water to become acidic. The acidity of water from dissolved CO 2 can
A physical property is any characteristic of a material that can be observed or measured without changing the composition of the substances in the
 Physical Properties A physical property is any characteristic of a material that can be observed or measured without changing the composition of the substances in the material. Examples of Physical Properties
Physical Properties A physical property is any characteristic of a material that can be observed or measured without changing the composition of the substances in the material. Examples of Physical Properties
Chapter 6, Lesson 9: Neutralizing Acids and Bases
 Chapter 6, Lesson 9: Neutralizing Acids and Bases Key Concepts ph is a measure of the concentration of H 3 O + ions in a solution. Adding an acid increases the concentration of H 3 O + ions in the solution.
Chapter 6, Lesson 9: Neutralizing Acids and Bases Key Concepts ph is a measure of the concentration of H 3 O + ions in a solution. Adding an acid increases the concentration of H 3 O + ions in the solution.
Density. weight: a measure of the pull of gravity on an object
 Imagine that it is a very hot day. You decide to cool a glass of water by placing several ice cubes in the drink. What happens when you drop the ice into the water? Likely, when you place the first ice
Imagine that it is a very hot day. You decide to cool a glass of water by placing several ice cubes in the drink. What happens when you drop the ice into the water? Likely, when you place the first ice
Data Sheet for Task 1: Mixing It Up!
 Data Sheet for Task 1: Mixing It Up! 1. Mix 25 ml water and 1 ml of Mystery Material A in a small container. Then mix 25 ml water and 1 ml of Mystery Material B in another container. Put the lids on and
Data Sheet for Task 1: Mixing It Up! 1. Mix 25 ml water and 1 ml of Mystery Material A in a small container. Then mix 25 ml water and 1 ml of Mystery Material B in another container. Put the lids on and
Are Chemical Reactions Closed Systems?
 Measuring a Chemical Reaction 1. Place about 100 ml of vinegar in a large plastic cup. Carefully weigh the cup AND the vinegar all together, and write down the total mass. (Don t worry about subtracting
Measuring a Chemical Reaction 1. Place about 100 ml of vinegar in a large plastic cup. Carefully weigh the cup AND the vinegar all together, and write down the total mass. (Don t worry about subtracting
Name Period Date. Lab 9: Analysis of Commercial Bleach
 Name Period Date Lab 9: Analysis of Commercial Bleach Introduction Many common products are effective because they contain oxidizing agents. Some products, which contain oxidizing agents, are bleaches,
Name Period Date Lab 9: Analysis of Commercial Bleach Introduction Many common products are effective because they contain oxidizing agents. Some products, which contain oxidizing agents, are bleaches,
A simple equation of what happens when you add baking soda to vinegar:
 What s the Matter? Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. Mass is the stuff that matter is made of, or the amount of particles in a substance or object. Matter has physical and chemical properties
What s the Matter? Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. Mass is the stuff that matter is made of, or the amount of particles in a substance or object. Matter has physical and chemical properties
SNC2D CHEMISTRY 2/23/2013. CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Conservation of Mass (P ) Activity: Measuring Mass (Part 1) Activity: Measuring Mass (Part 1)
 SNC2D CHEMISTRY CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Conservation of Mass (P.176-177) Activity: Measuring Mass (Part 1) INSTRUCTIONS (CLOSED SYSTEM) A. Measure~ 30 ml of vinegar (acetic acid) into a small Erlenmeyer flask.
SNC2D CHEMISTRY CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Conservation of Mass (P.176-177) Activity: Measuring Mass (Part 1) INSTRUCTIONS (CLOSED SYSTEM) A. Measure~ 30 ml of vinegar (acetic acid) into a small Erlenmeyer flask.
MONDAY (12/12) TUESDAY (12/13) WEDNESDAY (12/14) THURSDAY (12/15) FRIDAY (12/16) Making Acid Rain (a lab) Quiz
 Homework Activities Name: Date: Period: This week, we will be using our knowledge of acids and bases and studying how acids, specifically acid rain, affect our lives and our environment. We will also end
Homework Activities Name: Date: Period: This week, we will be using our knowledge of acids and bases and studying how acids, specifically acid rain, affect our lives and our environment. We will also end
Directed Reading B. Section: What Is Matter? MATTER MATTER AND VOLUME. same time. the bottom of the curve at the surface of the water called. the.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: What Is Matter? MATTER (pp. 78 83) 1. What characteristic do a human, hot soup, the metal wires in a toaster, and the glowing gases in a neon sign have in common?
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading B Section: What Is Matter? MATTER (pp. 78 83) 1. What characteristic do a human, hot soup, the metal wires in a toaster, and the glowing gases in a neon sign have in common?
Chemical Change. Day 1: 70 minutes; Day 2: minutes
 Chemical Change Lesson Concept When one substance interacts with another substance, a chemical change may occur. There are five indicators that a chemical change has occurred: gas production (bubbles),
Chemical Change Lesson Concept When one substance interacts with another substance, a chemical change may occur. There are five indicators that a chemical change has occurred: gas production (bubbles),
Bio 105 Lab 3: Chemistry: ph and solutions
 1 Bio 105 Lab 3: Chemistry: ph and solutions Part 1. Acid and Base Chemistry A. Introduction BIO 105 Summer 2013 Name One of the most important concepts in biology is acid/base chemistry. We are familiar
1 Bio 105 Lab 3: Chemistry: ph and solutions Part 1. Acid and Base Chemistry A. Introduction BIO 105 Summer 2013 Name One of the most important concepts in biology is acid/base chemistry. We are familiar
CH 13 Solutions All Practice Problems
 CH 13 Solutions All Practice Problems CH 13 Solutions Practice #1 A chemical analysis shows that a sample contains 0.0044 grams of lead in 1.00 x 10 3 grams of water. Convert the measurement to parts per
CH 13 Solutions All Practice Problems CH 13 Solutions Practice #1 A chemical analysis shows that a sample contains 0.0044 grams of lead in 1.00 x 10 3 grams of water. Convert the measurement to parts per
How to Write a Lab Report
 How to Write a Lab Report Each section of your report should be clearly identified. Reports must be done on the computer. If you do not have access to a computer at home, you will have to use the computers
How to Write a Lab Report Each section of your report should be clearly identified. Reports must be done on the computer. If you do not have access to a computer at home, you will have to use the computers
Chemistry Foundations of Chemistry Test. This is due:
 Chemistry Foundations of Chemistry Test This is due: Directions: Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper (or on this paper if you have room), staple to this paper (if you used a separate
Chemistry Foundations of Chemistry Test This is due: Directions: Answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper (or on this paper if you have room), staple to this paper (if you used a separate
Goal: During this lab students will gain a quantitative understanding of limiting reagents.
 LIMITING REAGENT LAB: THE REACTION BETWEEN VINEGAR AND BAKING SODA Goal: During this lab students will gain a quantitative understanding of limiting reagents. Safety: Safety goggles should be worn at all
LIMITING REAGENT LAB: THE REACTION BETWEEN VINEGAR AND BAKING SODA Goal: During this lab students will gain a quantitative understanding of limiting reagents. Safety: Safety goggles should be worn at all
Moles Lab Activity 1: PCU (Popcorn Counting Units)
 Moles Lab Activity 1: PCU (Popcorn Counting Units) Materials: A container of each of the following: Popcorn kernels Another type of beans A large unopened bag of popcorn Kernels Balance Safety goggles
Moles Lab Activity 1: PCU (Popcorn Counting Units) Materials: A container of each of the following: Popcorn kernels Another type of beans A large unopened bag of popcorn Kernels Balance Safety goggles
Jeopardy. Final Jeopardy. Other. Matter $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500
 Jeopardy Matter States of matter Physical changes and chemical changes Physical and chemical properties Other $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400
Jeopardy Matter States of matter Physical changes and chemical changes Physical and chemical properties Other $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400
Bellevue College CHEM& 121 Experiment: Stoichiometric Analysis of an Antacid 1
 Experiment: Stoichiometric Analysis of an Antacid 1 Introduction In this lab, you will use the concept of stoichiometry to solve two sequential problems. First, you will try to determine the products of
Experiment: Stoichiometric Analysis of an Antacid 1 Introduction In this lab, you will use the concept of stoichiometry to solve two sequential problems. First, you will try to determine the products of
FOSS Measuring Matter Module
 September, Teacher: test Concept IA: Matter exists in three states. Item: 4 Write a letter on the blank line next to each word on the left to math the properties UWT Erma, Penrod, Janet, Urmila, Magnus,
September, Teacher: test Concept IA: Matter exists in three states. Item: 4 Write a letter on the blank line next to each word on the left to math the properties UWT Erma, Penrod, Janet, Urmila, Magnus,
Energy Transformations Activities Students engage in different activities to observe energy changing form!
 Energy Transformations Activities Students engage in different activities to observe energy changing form! Name: Energy Labs and Activities Activity 1: Static Electricity Glue this side down Procedure:
Energy Transformations Activities Students engage in different activities to observe energy changing form! Name: Energy Labs and Activities Activity 1: Static Electricity Glue this side down Procedure:
Section 1: Four States of Matter (pages 60-67)
 Name: Sci Number: Period: Parent Signature: My little book of: Word: Pg found States of matter Solid Four States of Matter: Section 1 definitions: (pg60) My definition Chp 3 Draw/paste examples of all
Name: Sci Number: Period: Parent Signature: My little book of: Word: Pg found States of matter Solid Four States of Matter: Section 1 definitions: (pg60) My definition Chp 3 Draw/paste examples of all
PROPERTIES OF MATTER STATION 1. Where did the water droplets on the outside of this cup come from? What phase change is this?
 PROPERTIES OF MATTER STATION 1 Where did the water droplets on the outside of this cup come from? What phase change is this? PROPERTIES OF MATTER STATION 2 Make a copy of this graph on your paper. Label
PROPERTIES OF MATTER STATION 1 Where did the water droplets on the outside of this cup come from? What phase change is this? PROPERTIES OF MATTER STATION 2 Make a copy of this graph on your paper. Label
Creative Classroom Lessons
 Matter, Matter Everywhere! Solids, Liquids and Gases Unit Creative Classroom Lessons Contents: 1. Solids, Liquids and gases student folder cover 2. Introduction Activity: Mystery Box 3. Solids, Liquids
Matter, Matter Everywhere! Solids, Liquids and Gases Unit Creative Classroom Lessons Contents: 1. Solids, Liquids and gases student folder cover 2. Introduction Activity: Mystery Box 3. Solids, Liquids
MATTER. Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes that matter undergoes. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
 MATTER Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes that matter undergoes. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Properties of Matter Physical Properties Can be observed without changing
MATTER Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes that matter undergoes. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. Properties of Matter Physical Properties Can be observed without changing
Name: 1. Which of the following is probably true about 300 ml of sand and 300 ml of water?
 Name: Jaguar Review #2 Physical Sciences Benchmark A: Relate uses, properties and chemical processes to the behavior and/or arrangement of the small particles that compose matter. 1. Which of the following
Name: Jaguar Review #2 Physical Sciences Benchmark A: Relate uses, properties and chemical processes to the behavior and/or arrangement of the small particles that compose matter. 1. Which of the following
Materials: Micropipettes (2-20 µl range pipette, µl range, µl range), tips, test tubes with color dye, well plates
 Virtually every chemical reaction in a lab or manufacturing facility, as in cells, occurs in a watery environment or solution. A lab technician, therefore, must be able to quickly prepare any volume of
Virtually every chemical reaction in a lab or manufacturing facility, as in cells, occurs in a watery environment or solution. A lab technician, therefore, must be able to quickly prepare any volume of
ESSENTIAL EXPERIMENTS CHEMISTRY
 ESSENTIAL EXPERIMENTS for CHEMISTRY Morrison Scodellaro Sample Experiment Freezing Point Depression For additional information email: smg_order@smglabbooks.com Fax: 1-800-201-4587 Phone: 1-800-201-4587
ESSENTIAL EXPERIMENTS for CHEMISTRY Morrison Scodellaro Sample Experiment Freezing Point Depression For additional information email: smg_order@smglabbooks.com Fax: 1-800-201-4587 Phone: 1-800-201-4587
Chemistry and Measurement
 Chemistry and Measurement What Is Chemistry? Chemistry is the study of the composition, structure, and properties of matter and energy and changes that matter undergoes. Matter is anything that occupies
Chemistry and Measurement What Is Chemistry? Chemistry is the study of the composition, structure, and properties of matter and energy and changes that matter undergoes. Matter is anything that occupies
1 st Semester Exam Study Guide 1.) Which of the following is NOT a compound? Explain why. a. H2O b. O2
 1 st Semester Exam Study Guide 1.) Which of the following is NOT a compound? Explain why. a. H2O b. O2 2.) A chemist has discovered what she thinks is a new molecule. In order for it to be a molecule,
1 st Semester Exam Study Guide 1.) Which of the following is NOT a compound? Explain why. a. H2O b. O2 2.) A chemist has discovered what she thinks is a new molecule. In order for it to be a molecule,
Virtual Solution Lab::
 Name A Solution is a type of homogeneous mixture formed when one substance dissolves in another. The particles of the mixing substances are evenly spread throughout. The substance that is dissolved is
Name A Solution is a type of homogeneous mixture formed when one substance dissolves in another. The particles of the mixing substances are evenly spread throughout. The substance that is dissolved is
The Chemistry Summary Sheet Chemistry is the scientific study of matter.
 The Chemistry Summary Sheet Chemistry is the scientific study of matter. ATOMIC STRUCTURE: -an atom is composed of three fundamental particles: proton, electron, neutron. -atom size mostly consists of
The Chemistry Summary Sheet Chemistry is the scientific study of matter. ATOMIC STRUCTURE: -an atom is composed of three fundamental particles: proton, electron, neutron. -atom size mostly consists of
Conservation of Mass in Chemical Reactions Lab. Experiment Question: What happens to the total mass of substances when a chemical reaction occurs?
 Conservation of Mass in Chemical Reactions Lab Name: 5 th Grade PSI Science Score: / 5 Experiment Question: What happens to the total mass of substances when a chemical reaction occurs? Hypothesis Starters:
Conservation of Mass in Chemical Reactions Lab Name: 5 th Grade PSI Science Score: / 5 Experiment Question: What happens to the total mass of substances when a chemical reaction occurs? Hypothesis Starters:
White Before Your Eyes
 Name Class Date You have learned how to describe matter based on its physical and chemical properties. You have also learned some signs that can help you determine whether a change in matter is a physical
Name Class Date You have learned how to describe matter based on its physical and chemical properties. You have also learned some signs that can help you determine whether a change in matter is a physical
I. INTRODUCTION AND LABORATORY SAFETY
 EXPERIMENT 1 Chemistry 100 Measurement Techniques and Safety Purpose: To Learn the basic techniques of laboratory measurement of mass, temperature, volume and length and the concepts of safety I. INTRODUCTION
EXPERIMENT 1 Chemistry 100 Measurement Techniques and Safety Purpose: To Learn the basic techniques of laboratory measurement of mass, temperature, volume and length and the concepts of safety I. INTRODUCTION
1. Write date, topic and purpose in notebook. 2. Answer in your notebook: What are two signs that a chemical reaction is happening?
 Warm Up (5 min) Date: Monday, 1/4/16 Topic: Alka Seltzer Lab Purpose: To assess the Law of Conservation of Mass by designing an experiment to determine mass before and after a chemical reaction. 1. Write
Warm Up (5 min) Date: Monday, 1/4/16 Topic: Alka Seltzer Lab Purpose: To assess the Law of Conservation of Mass by designing an experiment to determine mass before and after a chemical reaction. 1. Write
Bubbles and Colors and Smells Oh My! A lesson about physical and chemical changes By Glenda Kitts, Arlene Cuellar, and Maritza Aquino
 Glenda Kitts, Arlene Cuellar, Maritza Aquino Last Updated on 9/17/2017 Bubbles and Colors and Smells Oh My! A lesson about physical and chemical changes By Glenda Kitts, Arlene Cuellar, and Maritza Aquino
Glenda Kitts, Arlene Cuellar, Maritza Aquino Last Updated on 9/17/2017 Bubbles and Colors and Smells Oh My! A lesson about physical and chemical changes By Glenda Kitts, Arlene Cuellar, and Maritza Aquino
Chapter 6, Lesson 1: What is a Chemical Reaction?
 Chapter 6, Lesson 1: What is a Chemical Reaction? Key Concepts: A physical change, such as a state change or dissolving, does not create a new substance, but a chemical change does. In a chemical reaction,
Chapter 6, Lesson 1: What is a Chemical Reaction? Key Concepts: A physical change, such as a state change or dissolving, does not create a new substance, but a chemical change does. In a chemical reaction,
Chemistry Unit Test 1 Review
 Chemistry Unit Test 1 Review Name: S8P1a. Students will distinguish between atoms and molecules. 1. Which of the following particles combine to form molecules? a. Atoms b. Protons c. Electrons d. Compounds
Chemistry Unit Test 1 Review Name: S8P1a. Students will distinguish between atoms and molecules. 1. Which of the following particles combine to form molecules? a. Atoms b. Protons c. Electrons d. Compounds
Lab Activity 3: Gravimetric Stoichiometry 2
 Chemistry 2202 Gravimetric Stoichiometry Lab 2 1 Lab Activity 3: Gravimetric Stoichiometry 2 Introduction: Stoichiometry involves making predictions about how much of one substance should react or be produced
Chemistry 2202 Gravimetric Stoichiometry Lab 2 1 Lab Activity 3: Gravimetric Stoichiometry 2 Introduction: Stoichiometry involves making predictions about how much of one substance should react or be produced
Use quantitative and qualitative analyses to identify the powder in Mr. Orlow s car.
 Case File 7 Drug Tests: Identifying an unknown chemical Use quantitative and qualitative analyses to identify the powder in Mr. Orlow s car. Police Report Patrol officers pulled over Mr. Yuri Orlow for
Case File 7 Drug Tests: Identifying an unknown chemical Use quantitative and qualitative analyses to identify the powder in Mr. Orlow s car. Police Report Patrol officers pulled over Mr. Yuri Orlow for
Individual Benchmark Specifications for Grade 5
 Individual Benchmark Specifications for This section of the FCAT Science Test Item and Performance Task Specifications describes how the benchmarks are assessed on the FCAT. The benchmarks are defined
Individual Benchmark Specifications for This section of the FCAT Science Test Item and Performance Task Specifications describes how the benchmarks are assessed on the FCAT. The benchmarks are defined
1 gram = kg = 1.0 x 10 3 kg. 1 milligram (1 mg) = 1.0 x 10 3 g. 1 microgram (1µg) = 1.0 x 10 6 g
 1.1 Chemistry & Measurements Scientists throughout the world use the International System of Units, abbreviated SI, for their measurements. There are seven base units in the SI system. Measurements can
1.1 Chemistry & Measurements Scientists throughout the world use the International System of Units, abbreviated SI, for their measurements. There are seven base units in the SI system. Measurements can
SYLLABUS INDEX CARD NAME MAJOR (IF YOU DON T HAVE ONE INTEREST) WHAT DO YOU WANT TO BE WHEN YOU GROW UP?
 WELCOME CHEMISTRY 131: PRINCIPLES OF CHEMISTRY Mrs. DeVos September 19, 2011 SYLLABUS INDEX CARD NAME MAJOR (IF YOU DON T HAVE ONE INTEREST) WHAT DO YOU WANT TO BE WHEN YOU GROW UP? WHY ARE YOU TAKING
WELCOME CHEMISTRY 131: PRINCIPLES OF CHEMISTRY Mrs. DeVos September 19, 2011 SYLLABUS INDEX CARD NAME MAJOR (IF YOU DON T HAVE ONE INTEREST) WHAT DO YOU WANT TO BE WHEN YOU GROW UP? WHY ARE YOU TAKING
Stoichiometry: Baking Soda and Vinegar Reactions Teacher Version
 Stoichiometry: Baking Soda and Vinegar Reactions Teacher Version In this lab, students will examine the chemical reaction between baking soda and vinegar, and mix different amounts of these household chemicals
Stoichiometry: Baking Soda and Vinegar Reactions Teacher Version In this lab, students will examine the chemical reaction between baking soda and vinegar, and mix different amounts of these household chemicals
Forensics with TI-Nspire Technology
 Forensics with TI-Nspire Technology 2013 Texas Instruments Incorporated 1 education.ti.com About the Lesson This lab uses the identification of an unknown drug to demonstrate the differences between chemical
Forensics with TI-Nspire Technology 2013 Texas Instruments Incorporated 1 education.ti.com About the Lesson This lab uses the identification of an unknown drug to demonstrate the differences between chemical
Lab 9: Over-the-Counter Drugs
 Lab 9: Over-the-Counter Drugs Report: You work in a clinical lab for a hospital. A doctor has sent down an unknown sample for you to identify. A small child got into his parent s drug cabinet and swallowed
Lab 9: Over-the-Counter Drugs Report: You work in a clinical lab for a hospital. A doctor has sent down an unknown sample for you to identify. A small child got into his parent s drug cabinet and swallowed
Physical Changes vs Chemical Changes Lab
 Physical Changes vs Chemical Changes Lab What was done? What can you observe? Is it a physical or chemical change and why? What else have you learned during the demonstration? #1) Crumpling Paper Notice
Physical Changes vs Chemical Changes Lab What was done? What can you observe? Is it a physical or chemical change and why? What else have you learned during the demonstration? #1) Crumpling Paper Notice
MiSP CHEMICAL REACTIONS, L3 Teacher Guide. Introduction
 MiSP CHEMICAL REACTIONS, L3 Teacher Guide Introduction This weeklong unit should be included with other chemistry content teaching and learning. It is designed to follow Intermediate Level Science Core
MiSP CHEMICAL REACTIONS, L3 Teacher Guide Introduction This weeklong unit should be included with other chemistry content teaching and learning. It is designed to follow Intermediate Level Science Core
Lesson 2. Color change
 Lesson 2 Color change T E A C H E R G U I D E Lesson summary Students meet marine chemist Sera Tuikabe, who is studying ocean acidification in the water surrounding the Republic of the Fiji Islands. Students
Lesson 2 Color change T E A C H E R G U I D E Lesson summary Students meet marine chemist Sera Tuikabe, who is studying ocean acidification in the water surrounding the Republic of the Fiji Islands. Students
Name Partner Lab Section M Tu W Th F Chemistry 130 Experiment 6: Titration and Analysis
 Name Partner Lab Section M Tu W Th F Chemistry 130 Experiment 6: Titration and Analysis Introduction A neutralization reaction is one in which an acid (proton donor) and a base (proton acceptor) react
Name Partner Lab Section M Tu W Th F Chemistry 130 Experiment 6: Titration and Analysis Introduction A neutralization reaction is one in which an acid (proton donor) and a base (proton acceptor) react
How Do I Make New Stuff From Old Stuff?
 How Do I Make New Stuff From Old Stuff? 7 th Grade Chemistry Unit Materials Jay Bingaman & Karen Ostrowski www.south7thscience.com Twitter: @South7thScience YouTube.com: South7thScience How Will I Be Graded?
How Do I Make New Stuff From Old Stuff? 7 th Grade Chemistry Unit Materials Jay Bingaman & Karen Ostrowski www.south7thscience.com Twitter: @South7thScience YouTube.com: South7thScience How Will I Be Graded?
Liquid X Lab. Station 1 The Penny Lab Water is cohesive, adhesive, and has surface tension. Does Liquid X have the same properties?
 Names Block Date Liquid X Lab Station 1 The Penny Lab Water is cohesive, adhesive, and has surface tension. Does Liquid X have the same properties? 1. Use a pipette to carefully place drops of each liquid
Names Block Date Liquid X Lab Station 1 The Penny Lab Water is cohesive, adhesive, and has surface tension. Does Liquid X have the same properties? 1. Use a pipette to carefully place drops of each liquid
Milwaukie HS Chemistry Linman. Period Date / /
 Milwaukie HS Chemistry Linman A701 Name Solutions Classify the following mixtures as homogeneous or heterogeneous: A: Freshly squeezed orange juice B: Tap water C: Human Blood D: Sand 1. Does a solution
Milwaukie HS Chemistry Linman A701 Name Solutions Classify the following mixtures as homogeneous or heterogeneous: A: Freshly squeezed orange juice B: Tap water C: Human Blood D: Sand 1. Does a solution
Acids and Bases. G.10 Science Chemistry Shaftesbury High School
 G.10 Science Chemistry Acids and Bases 2240 Grant Avenue Winnipeg, Manitoba R3P 0P7 Phone: 204-888-5898 Fax: 204-896-5492 http://www.pembinatrails.ca/shaftesbury/ G.10 Science Acids and Bases What is
G.10 Science Chemistry Acids and Bases 2240 Grant Avenue Winnipeg, Manitoba R3P 0P7 Phone: 204-888-5898 Fax: 204-896-5492 http://www.pembinatrails.ca/shaftesbury/ G.10 Science Acids and Bases What is
Observations. Direct Observations Those observations we make ourselves
 Observations Direct Observations Those observations we make ourselves Indirect Observations Those observations that we figure out from direct observations Observing Milk Consumption The cafeteria is considering
Observations Direct Observations Those observations we make ourselves Indirect Observations Those observations that we figure out from direct observations Observing Milk Consumption The cafeteria is considering
Identification of an Unknown Compound through Mass Correlations
 EXPERIMENT Identification of an Unknown Compound through Mass Correlations PURPOSE To carry out a series of decomposition reactions for five different unknown, and use stoichiometry in order to identify
EXPERIMENT Identification of an Unknown Compound through Mass Correlations PURPOSE To carry out a series of decomposition reactions for five different unknown, and use stoichiometry in order to identify
PROPERTIES OF MATTER Review Stations
 PROPERTIES OF MATTER Review Stations PROPERTIES OF MATTER STATION 1 Where did the water droplets on the outside of this cup come from? Answer: The droplets came from the air surrounding the cup. What phase
PROPERTIES OF MATTER Review Stations PROPERTIES OF MATTER STATION 1 Where did the water droplets on the outside of this cup come from? Answer: The droplets came from the air surrounding the cup. What phase
Chapter 6, Lesson 7: Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions
 Chapter 6, Lesson 7: Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions Key Concepts If two substances react and the temperature of the mixture decreases, the reaction is endothermic. If two substances react and the
Chapter 6, Lesson 7: Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions Key Concepts If two substances react and the temperature of the mixture decreases, the reaction is endothermic. If two substances react and the
What are the three different types of elements and what are their properties?
 Name: Partners name(s): Stamp: Laboratory 5: Types of Matter and its changes Compounds, mixtures, elements, chemical /physical properties Classify several different compounds, elements and mixtures by
Name: Partners name(s): Stamp: Laboratory 5: Types of Matter and its changes Compounds, mixtures, elements, chemical /physical properties Classify several different compounds, elements and mixtures by
States of Matter Part 1: Lab Stations A. Initial Observations
 States of Matter POGIL Activity Name Date Block Part 1: Lab Stations A. Initial Observations At your station you will find some solid aluminum, liquid water, and gaseous air. Observe these three objects
States of Matter POGIL Activity Name Date Block Part 1: Lab Stations A. Initial Observations At your station you will find some solid aluminum, liquid water, and gaseous air. Observe these three objects
3. Kira makes 93 greeting cards for a craft fair. She sells the cards in packs of 5. How many full packs of greeting cards does Kira make?
 Chapter 4 Test 1. 2. 3. Kira makes 93 greeting cards for a craft fair. She sells the cards in packs of 5. How many full packs of greeting cards does Kira make? packs Work Space: 5. A kennel is moving 160
Chapter 4 Test 1. 2. 3. Kira makes 93 greeting cards for a craft fair. She sells the cards in packs of 5. How many full packs of greeting cards does Kira make? packs Work Space: 5. A kennel is moving 160
1. What is the difference between a qualitative and quantitative observation? Give at least one example of each.
 1 st 9wks Exam Review Name Per. Chemistry 1H Scientific Skills Unit - Lab Safety & Equipment: KEY EQUIPMENT TO KNOW: +beaker +Erlenmeyer flask +beaker tongs +balance +graduated cylinder +test tube +test
1 st 9wks Exam Review Name Per. Chemistry 1H Scientific Skills Unit - Lab Safety & Equipment: KEY EQUIPMENT TO KNOW: +beaker +Erlenmeyer flask +beaker tongs +balance +graduated cylinder +test tube +test
The number of stars in a galaxy is an example of an estimate that should be expressed in scientific notation.
 3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements A measurement is a quantity that has both a number and a unit. Using and Expressing Measurements In scientific notation, a given number is written as the product of
3.1 Using and Expressing Measurements A measurement is a quantity that has both a number and a unit. Using and Expressing Measurements In scientific notation, a given number is written as the product of
Safety: Safety goggles should be worn at all times. Students should hold the balloons on the test tubes tightly while the reaction takes place.
 LIMITING REAGENT LAB: THE REACTION BETWEEN VINEGAR AND BAKING SODA Goal: During this lab students will gain a quantitative understanding of limiting reagents. Safety: Safety goggles should be worn at all
LIMITING REAGENT LAB: THE REACTION BETWEEN VINEGAR AND BAKING SODA Goal: During this lab students will gain a quantitative understanding of limiting reagents. Safety: Safety goggles should be worn at all
OBJECTIVES: By the end of class, students will be able to
 7 th Grade Science Unit: Matter and Periodic Table Lesson: Matter 11 Law of Conservation of Mass Review Name: Date: Monday, December 12, 2016 Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of class, students will be
7 th Grade Science Unit: Matter and Periodic Table Lesson: Matter 11 Law of Conservation of Mass Review Name: Date: Monday, December 12, 2016 Homeroom: OBJECTIVES: By the end of class, students will be
Chemistry Unit Test 2 Review 8HPS
 Chemistry Unit Test 2 Review 8HPS 2015-2016 Name: S8P1a. Students will distinguish between atoms and molecules. 1. Molecules are a combination of a. Mixtures b. Neutrons c. Atoms d. Compounds 2. The picture
Chemistry Unit Test 2 Review 8HPS 2015-2016 Name: S8P1a. Students will distinguish between atoms and molecules. 1. Molecules are a combination of a. Mixtures b. Neutrons c. Atoms d. Compounds 2. The picture
What Do You Think? Investigate GOALS
 Activity 3 Atoms and Their Masses GOALS In this activity you will: Explore the idea of atoms by trying to isolate a single atom. Measure how many times greater the mass of a copper atom is than a magnesium
Activity 3 Atoms and Their Masses GOALS In this activity you will: Explore the idea of atoms by trying to isolate a single atom. Measure how many times greater the mass of a copper atom is than a magnesium
ANSWER KEY. Introduction to Matter
 Chapter Project Worksheet 1 1. The object to be massed is placed on one side of the balance. Objects with known masses are placed on the other side of the arm until the balance arm is level. 2. Sample
Chapter Project Worksheet 1 1. The object to be massed is placed on one side of the balance. Objects with known masses are placed on the other side of the arm until the balance arm is level. 2. Sample
2002 D Required 2001 D Required
 2002 D Required A student is asked to determine the molar enthalpy of neutralization, H neut, for the reaction represented above. The student combines equal volumes of 1.0 M HCl and 1.0 M NaOH in an open
2002 D Required A student is asked to determine the molar enthalpy of neutralization, H neut, for the reaction represented above. The student combines equal volumes of 1.0 M HCl and 1.0 M NaOH in an open
Pre-lab vocabulary (must be complete before lab begins) Name: Date: 1. acid- 2. base- 3. ph. 4. neutral- 5. neutralize- 6. electrolytes- 7.
 Name: Date: Gen Bio 1 Lab #2: Acids & Bases Pre-lab reading assignment Pages 51-53 in Campbell 10 th edition. Watch the following for more information TED talk on acids & bases: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dupxdd87ohc
Name: Date: Gen Bio 1 Lab #2: Acids & Bases Pre-lab reading assignment Pages 51-53 in Campbell 10 th edition. Watch the following for more information TED talk on acids & bases: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dupxdd87ohc
Non-Newtonian Fluids How slow can you go?
 Non-Newtonian Fluids How slow can you go? Background Have you heard of Sir Isaac Newton? Newton (1643-1727) is a famous scientist and mathematician who discovered gravity! In addition, he created the three
Non-Newtonian Fluids How slow can you go? Background Have you heard of Sir Isaac Newton? Newton (1643-1727) is a famous scientist and mathematician who discovered gravity! In addition, he created the three
11. Introduction to Acids, Bases, ph, and Buffers
 11. Introduction to Acids, Bases, ph, and Buffers What you will accomplish in this experiment You ll use an acid-base indicating paper to: Determine the acidity or basicity of some common household substances
11. Introduction to Acids, Bases, ph, and Buffers What you will accomplish in this experiment You ll use an acid-base indicating paper to: Determine the acidity or basicity of some common household substances
Physical and Chemical Properties of Matter Lab
 Physical and Chemical Properties of Matter Lab Purpose To introduce the student to physical and chemical properties of matter and their use for the identification and separation of compounds. Each student
Physical and Chemical Properties of Matter Lab Purpose To introduce the student to physical and chemical properties of matter and their use for the identification and separation of compounds. Each student
LESSON 1. Chemical Reactions. Fireflies, also called lightning bugs, are small insects that generate their own light using chemical reactions.
 LESSON 1 Chemical Reactions Fireflies, also called lightning bugs, are small insects that generate their own light using chemical reactions. By the end of this lesson... you will be able to explain ways
LESSON 1 Chemical Reactions Fireflies, also called lightning bugs, are small insects that generate their own light using chemical reactions. By the end of this lesson... you will be able to explain ways
Acids and Bases. How does ph affect biological solutions? Introduction. Prelab Preparation Review Section 2.3 on acids and bases in your textbook.
 Acids and Bases How does ph affect biological solutions? Learning Objectives To relate the ph scale to how acidic or basic a solution is. To explain how a buffer affects the ph of a solution. Process Objectives
Acids and Bases How does ph affect biological solutions? Learning Objectives To relate the ph scale to how acidic or basic a solution is. To explain how a buffer affects the ph of a solution. Process Objectives
KEY. Chemistry Baseline Cornerstone Assessment: Part A. Experimental Design. Directions: Read the paragraph below and then respond to the questions.
 Chemistry Baseline Cornerstone Assessment: Part A. Experimental Design Directions: Read the paragraph below and then respond to the questions. Hydrogen peroxide is a liquid that breaks down and releases
Chemistry Baseline Cornerstone Assessment: Part A. Experimental Design Directions: Read the paragraph below and then respond to the questions. Hydrogen peroxide is a liquid that breaks down and releases
2/22/2019 NEW UNIT! Chemical Interactions. Atomic Basics #19
 NEW UNIT! Chemical Interactions Atomic Basics #19 1 Vocabulary: Matter: Anything that has mass and takes up space. Atom: the smallest particle of matter. Element: A pure substance made up of only one type
NEW UNIT! Chemical Interactions Atomic Basics #19 1 Vocabulary: Matter: Anything that has mass and takes up space. Atom: the smallest particle of matter. Element: A pure substance made up of only one type
Name: Period: Date: UNIT 1: Introduction to Matter Lesson 8: Baby, you look good
 Name: Period: Date: UNIT 1: Introduction to Matter Lesson 8: Baby, you look good Do Now: By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How do we describe and identify matter? Draw a particle diagram
Name: Period: Date: UNIT 1: Introduction to Matter Lesson 8: Baby, you look good Do Now: By the end of today, you will have an answer to: How do we describe and identify matter? Draw a particle diagram
Maintaining Mass Created By: Allyn Short
 Maintaining Mass Created By: Allyn Short Focus on Inquiry The student will demonstrate that mass is conserved when substances undergo chemical and/or physical changes through experimentation and evaluation
Maintaining Mass Created By: Allyn Short Focus on Inquiry The student will demonstrate that mass is conserved when substances undergo chemical and/or physical changes through experimentation and evaluation
Activity Sheet Chapter 3, Lesson 3 Density of water
 Activity Sheet Chapter 3, Lesson 3 Density of water Name Date DEMONSTRATION 1. One of your classmates lifted different amounts of water. The largest amount of water also had the most mass. You know how
Activity Sheet Chapter 3, Lesson 3 Density of water Name Date DEMONSTRATION 1. One of your classmates lifted different amounts of water. The largest amount of water also had the most mass. You know how
Drinking water is allowed to contain up to 1.3 parts per million of copper (by mass) and be considered safe. What does parts per million (ppm) mean?
 E One in a Million Drinking water is allowed to contain up to 1. parts per million of copper (by mass) and be considered safe. What does parts per million (ppm) mean? Living things and the environment
E One in a Million Drinking water is allowed to contain up to 1. parts per million of copper (by mass) and be considered safe. What does parts per million (ppm) mean? Living things and the environment
Today is: Friday, October 21st
 Today is: Friday, October 21st 10/21/2016 #followyourdreamsfriday 1. What are some of your biggest goals in life? 2. Which of the following is an example of a chemical change? Why? Justify your answer.
Today is: Friday, October 21st 10/21/2016 #followyourdreamsfriday 1. What are some of your biggest goals in life? 2. Which of the following is an example of a chemical change? Why? Justify your answer.
INTRODUCTION. Seltzer relieves upset stomach, provides pain relief, breaks fevers, and reduces inflammation.
 Effervescence Laboratory Experiment Developed by: Alex Jannini, David Krause, Heather Malino and Kevin Sweeney, Rowan University, Department of Chemical Engineering Edited by: C. Stewart Slater and Mariano
Effervescence Laboratory Experiment Developed by: Alex Jannini, David Krause, Heather Malino and Kevin Sweeney, Rowan University, Department of Chemical Engineering Edited by: C. Stewart Slater and Mariano
Test #1. Materials: jar measuring cup water unflavored gelatin (in packets)
 Test #1 Materials: jar measuring cup water unflavored gelatin (in packets) Methods: 1. Add ~ one-half cup of (warm or room-temperature) water to a jar. 2. Stir in one packet of unflavored gelatin. 3. Allow
Test #1 Materials: jar measuring cup water unflavored gelatin (in packets) Methods: 1. Add ~ one-half cup of (warm or room-temperature) water to a jar. 2. Stir in one packet of unflavored gelatin. 3. Allow
