ROADMAP FOR REACTIONS Chapter 6
|
|
|
- Dominic Williams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 6 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: syn-addition Works well for methyl and 1 halo Stereochemistry: gives cis- as products Stereochemistry: gives trans- as products Reactivity of C H bonds follows 3 > 2 > 1 Works for methyl, 1, and 2 halo Works for 2 and 3 halo, may see rearrangements Works for all halo except methyl, although a bulky (non-nucleophilic) base must be used for 1 halo. Regiochemistry: follows Zaitzev s rules so the more substituted alkene predominates. Stereochemistry: requirement for the X and H to be eliminated with anti-periplanar geometry. PBr 3 and SX 2 works for methyl, 1, and 2 halo. HX can give rearrangements. For 1 For 2 Regiochemistry: the product with the more substituted alkene predominates Reactions that cleave carbon-carbon bonds are indicated by reagents that are circled. halohydrins 1) 3, 2) (CH 3 ) 2 S X 2 /H 2 (B) X 2 (B) 1) s 4 (D), 2) NaHS 3 diols 1) BH 3, 2) H 2 2, NaH (C, D) H 2 /Pd, Pt,or Ni (D) H 3 + /H 2 (A) 1) Hg(Ac) 2, H 2, 2) NaBH 4, (A) haloakanes
2 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapters 6 7 Chapter 6 Chapter 7 geminal tetrahalo Reactions that cleave carbon-carbon bonds are indicated by reagents that are circled. 2X 2 1) (sia)2 BH, 2) H 2 2, NaH (C) alkynes 1) BH 3, 2) H 2 2, NaH H 2 S 4, HgS 4 (A) CR (E) NaC H 2 /Pd, Pt, Ni Na /NH 3 (G) NaNH 2 /NH 3 H 2 /Lindlar Cat. (F) halohydrins 1) 3, 2) (CH 3 ) 2 S X 2 /H 2 (B) X 2 (B) 1) s 4 (D), 2) NaHS 3 diols 1) BH 3, 2) H 2 2, NaH (C, D) H 2 /Pd, Pt,or Ni (D) H 3 + /H 2 (A) 1) Hg(Ac) 2, H 2, 2) NaBH 4, (A) haloakanes
3 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapters Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 geminal tetrahalo Reactions that cleave carbon-carbon bonds are indicated by reagents that are circled. 2X 2 1) (sia)2 BH, 2) H 2 2, NaH (C) alkynes 1) BH 3, 2) H 2 2, NaH H 2 S 4, HgS 4 (A) RC CR (E) NaC H 2 /Pd, Pt, Ni Na /NH 3 (G) NaNH 2 /NH 3 H 2 /Lindlar Cat. (F) halohydrins 1) 3, 2) (CH 3 ) 2 S X 2 /H 2 (B) X 2 (B) 1) s 4 (D), 2) NaHS 3 diols 1) BH 3, 2) H 2 2, NaH (C, D) H 2 /Pd, Pt,or Ni (D) H 3 + /H 2 (A) 1) Hg(Ac) 2, H 2, 2) NaBH 4, (A) NBS () allylic halides X 2, hv or heat (H) HBr, peroxides (C) haloakanes (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: syn-addition Works well for methyl and 1 halo Stereochemistry: gives cis- as products Stereochemistry: gives trans- as products Reactivity of C H bonds follows 3 > 2 > 1 Works for methyl, 1, and 2 halo Works for 2 and 3 halo, may see rearrangements Works for all halo except methyl, although a bulky (non-nucleophilic) base must be used for 1 halo. Regiochemistry: follows Zaitzev s rules so the more substituted alkene predominates. Stereochemistry: requirement for the X and H to be eliminated with anti-periplanar geometry. PBr 3 and SX 2 works for methyl, 1, and 2 halo. HX can give rearrangements. For 1 For 2 Regiochemistry: the product with the more substituted alkene predominates
4 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapters geminal tetrahalo Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Reactions that cleave carbon-carbon bonds are indicated by reagents that are circled. 2X 2 1) (sia)2 BH, 2) H 2 2, NaH (C) alkynes 1) BH 3, 2) H 2 2, NaH H 2 S 4, HgS 4 (A) CLi (E) RC CR (E) NaC H 2 /Pd, Pt, Ni allylic halides NaCN (I) NaSH (I) Na /NH 3 (G) H 2 /Lindlar Cat. (F) NaSR (I) NaHR 2 (I) NaN 3 (I) NaNH 2 /NH 3 halohydrins 1) 3, 2) (CH 3 ) 2 S X 2 /H 2 (B) X 2 (B) 1) s 4 (D), 2) NaHS 3 diols 1) BH 3, 2) H 2 2, NaH (C, D) H 2 /Pd, Pt,or Ni (D) H 3 + /H 2 (A) 1) Hg(Ac) 2, H 2, 2) NaBH 4, (A) NBS () X 2, hv or heat (H) HBr, peroxides (C) NaR (K) NaR (E) ethers HR, acid (J) NaH (E) H 2, acid (J) haloakanes nitriles thiols thioethers amines alkyl azides
5 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapters geminal tetrahalo Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Chapter 10 Reactions that cleave carbon-carbon bonds are indicated by reagents that are circled. 2X 2 1) (sia)2 BH, 2) H 2 2, NaH (C) alkynes 1) BH 3, 2) H 2 2, NaH H 2 S 4, HgS 4 (A) CLi (E) RC CR (E) NaC H 2 /Pd, Pt, Ni Na /NH 3 (G) H 2 /Lindlar Cat. (F) allylic halides X 2, hv or heat (H) halohydrins H 2 /Pd, Pt,or Ni (D) NBS () X 2 /H 2 (B) HBr, peroxides (C) NaNH 2 /NH 3 X 2 (B) NaR (K) 1) 3, 2) (CH 3 ) 2 S 1) s 4 (D), 2) NaHS 3 diols 1) BH 3, 2) H 2 2, NaH (C, D) H 3 + /H 2 (A) 1) Hg(Ac) 2, H 2, 2) NaBH 4, (A) H 3 P 4 NaR (E) ethers HR, acid (J) NaH (E) HI 4 H 2, acid (J) H 2 Cr 4 (N) HX or PBr 3 or SCl 2 (L) H 2 Cr 4 PCC (M) haloakanes NaCN (I) NaSH (I) NaSR (I) NaHR 2 (I) NaN 3 (I) carboxylic acids nitriles thiols thioethers amines alkyl azides
6 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapters geminal tetrahalo Chapter 6 Chapter 7 Chapter 8 Chapter 9 Chapter 10 Chapter 11 Reactions that cleave carbon-carbon bonds are indicated by reagents that are circled. 2X 2 1) (sia)2 BH, 2) H 2 2, NaH (C) alkynes 1) BH 3, 2) H 2 2, NaH H 2 S 4, HgS 4 (A) CLi (E) RC CR (E) NaC H 2 /Pd, Pt, Ni Na /NH 3 (G) H 2 /Lindlar Cat. (F) allylic halides X 2, hv or heat (H) halohydrins H 2 /Pd, Pt,or Ni (D) NBS () X 2 /H 2 (B) HBr, peroxides (C) NaNH 2 /NH 3 X 2 (B) NaR (K) haloakanes 1) 3, 2) (CH 3 ) 2 S 1) s 4 (D), 2) NaHS 3 diols 1) Cl 2, H 2, 2) NaH, H 2 m-cbpa 1) BH 3, 2) H 2 2, NaH (C, D) H 3 + /H 2 (A) 1) Hg(Ac) 2, H 2, 2) NaBH 4, (A) RH/acid (J) HI H 3 P 4 ethers NaR (E) HR, acid (J) NaH (E) HI 4 H 2, acid (J) H 2 Cr 4 (N) HX or PBr 3 or SCl 2 (L) H 2 Cr 4 PCC (M) amino H 3 + /H 2 NH 3 epoxides 1) LiAlH 4 2) H 2 t-bume 3 SiCl/pyridine silyl ethers NaCN (I) NaSH (I) NaSR (I) NaHR 2 (I) NaN 3 (I) carboxylic acids nitriles thiols thioethers amines alkyl azides
7 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 15 reactions are indicated by reagents written with solid backgrounds geminal dihalo CHX 3 (CH 3 ) 3 CK CH 2 I 2 Zn (Cu) vinyl halides R 2 CuLi halo 1) Mg, 2), 3) H 3 + /H 2 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: syn-addition Works well for methyl and 1 halo Stereochemistry: gives cis- as products Stereochemistry: gives trans- as products Reactivity of C H bonds follows 3 > 2 > 1 Works for methyl, 1, and 2 halo Works for 2 and 3 halo, may see rearrangements Works for all halo except methyl, although a bulky (non-nucleophilic) base must be used for 1 halo. Regiochemistry: follows Zaitzev s rules so the more substituted alkene predominates. Stereochemistry: requirement for the X and H to be eliminated with anti-periplanar geometry. PBr 3 and SX 2 works for methyl, 1, and 2 halo. HX can give rearrangements. For 1 For 2 Regiochemistry: the product with the more substituted alkene predominates
8 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapters reactions are indicated by reagents written with solid backgrounds acetals, -unsaturated -halo -hydroxyalkynes cyanohydrins Chapter 15 Chapter 16 H 3 + /H 2 RH/H + hemiacetals 1) (Me) 2 P CH 2 C 2) Base RH/H + H 3 + /H 2 Et Br 2, acid 1) RC CNa 2) H 3 + /H 2 1) NaCN 2) H 2 Zn (Hg), HCl N 2 H 4, KH geminal dihalo CHX 3 (CH 3 ) 3 CK CH 2 I 2 Zn (Cu) Ph 3 P + CR 2 1) RMgX, 2) H 3 + 1) RLi, 2) H 3 + 1) NaBH 2, 2) H 3 + Pt, H 2 RNH 2 imines R 2 NH enamines amine, NaBH 3 CN vinyl halides R 2 CuLi amines halo 1) Mg, 2), 3) H 3 + /H 2
9 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapters acetals H 3 + /H 2 RH/H + hemiacetals 1), -unsaturated (Me) 2 P 2) Base RH/H + H 3 + /H 2 CH 2 C Et -halo -hydroxyalkynes cyanohydrins Br 2, acid 1) RC CNa 2) H 3 + /H 2 1) NaCN 2) H 2 Zn (Hg), HCl N 2 H 4, KH reactions are indicated by reagents written with solid backgrounds Chapter 15 Chapter 16 Chapter 17 geminal dihalo CHX 3 (CH 3 ) 3 CK CH 2 I 2 Zn (Cu) Ph 3 P + CR 2 1) RMgX, 2) H 3 + R 2 CuLi halo 1) Mg 2) C 2 3) H 3 + /H 2 1) Mg, 2), 3) H 3 + /H 2 1) LiAlH 4, 2) H 3 + /H 2 carboxylic acids CH 2 N 2 RH acid SCl 2 1) RLi, 2) H 3 + 1) NaBH 2, 2) H 3 + Pt, H 2 RNH 2 imines R 2 NH enamines amine, NaBH 3 CN vinyl halides amines acid chlorides
10 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapters acetals H 3 + /H 2 RH/H + hemiacetals 1), -unsaturated (Me) 2 P 2) Base RH/H + H 3 + /H 2 CH 2 C Et -halo -hydroxyalkynes cyanohydrins Br 2, acid 1) RC CNa 2) H 3 + /H 2 1) NaCN 2) H 2 Zn (Hg), HCl N 2 H 4, KH reactions are indicated by reagents written with solid backgrounds Chapter 15 Chapter 16 Chapter 17 Chapter 18 geminal dihalo CHX 3 (CH 3 ) 3 CK CH 2 I 2 Zn (Cu) Ph 3 P + CR 2 1) RMgX, 2) H 3 + 1) RLi, 2) H 3 + SCl 2 1) NaBH 2, 2) H 3 + Pt, H 2 1) DIBAL, 2) H 3 + RNH 2 halo 1) Mg 2) C 2 3) H 3 + /H 2 carboxylic acids R 2 CuLi 1) Mg, 2), 3) H 3 + /H 2 1) LiAlH 4, 2) H 3 + /H 2 H 2 acid or base CH 2 N 2 RH acid H 2 RH RH H 2 1) LiAlH 4, 2) H 3 + /H 2 NHR 2 imines R 2 NH enamines amine, NaBH 3 CN 1) R 2 CuLi, 2) H 2 vinyl halides 1) 2RMgX, 2) H 2 amines acid chlorides RC 2 H acid anhydrides NHR 2 amides 1) LiAlH 4, 2) H 3 + /H 2 NHR 2 H 2 acid or base H 2 acid or base nitriles 1) LiAlH 4, 2) H 3 + /H 2
11 RADMAP FR REACTINS, aldehydes Chapter 19 reactions are indicated by reagents written with solid backgrounds Aldol Reaction NaR/HR -Hydroxy carbonyls R 3 H R 4 R 2 H 3 +, -Unsaturated carbonyls R 3 R 4 R 2 1) LDA 2) R-X 3) H 3 + /H 2 1) 2 -amine 2) R-X 3) H 3 + /H 2 Alkylated -carbons R 4 R 3 R 2 1) R 2 CuLi 2) H 3 + /H 2 -Alkylated carbonyls R 2 R 5 R 3 R 4 1) 2 -amine 2) acid chloride 3) H 3 + /H 2 -Dicarbonyls R 4 R 2 R 3 Michael Reaction various enolates or amines R 2 Nu R 3 R 4 Nu = enolate forming species or amines di malonic acetoacetic Claisen Condensation Dieckmann Condensation Malonic Ester Synthesis Acetoacetic Ester Sythesis 1) NaEt/HEt 2) H 3 + /H 2 1) NaEt/HEt 2) H 3 + /H 2 1) NaEt/HEt 2) R-X 3) NaH, H 2 4) H 3 + /H 2 5) 1) NaEt/HEt 2) R-X 3) NaH, H 2 4) H 3 + /H 2 5) -keto cyclic -keto alkylated carboxylic acids alylated methyl R 2 R 3 R 4 R 2 R 8 R 7 H H 3 C R 3 R 6 R 4 R 5 H R 2 H 3 C R 2
12 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 20 dienes alkene HX cyclohexenes allylic halides
13 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapters Chapter 20 Chapter 21 alkene cyclohexenes dienes HX allylic halides quinones H 2 Cr 4 phenols 1) NaH 2) C 2 3) H 3 + /H 2 carboxy phenols benzylic bromides NBS alkyl benzenes H 2 Cr 4 aryl carboxylic acids
14 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapters Chapter 20 Chapter 21 Chapter 22 alkene cyclohexenes dienes HX allylic halides quinones H 2 Cr 4 phenols 1) NaH 2) C 2 3) H 3 + /H 2 carboxy phenols benzylic bromides NBS alkyl benzenes H 2 Cr 4 aryl carboxylic acids H 3 P 4 3 -RH, H 3 P 4 RX, AlX 3 NaH, H 2 sulfobenzenes H 2 S 4, S 3 aryl rings acyl benzenes R(C)X, AlX 3 HN 3, H 2 S 4 nitrobenzenes 1) Fe, HCl 2) NaH H 2, Ni X 2, FeX 3 halobenzenes anilines NaNH 2, NH 3
15 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapters dienes alkene HX cyclohexenes allylic halides Chapter 20 Chapter 21 Chapter 22 Chapter 23 quinones H 2 Cr 4 phenols 1) NaH 2) C 2 3) H 3 + /H 2 carboxy phenols benzylic bromides NBS alkyl benzenes H 2 Cr 4 aryl carboxylic acids H 3 P 4 3 -RH, H 3 P 4 RX, AlX 3 NaH, H 2 sulfobenzenes H 2 S 4, S 3 X 2, FeX 3 halobenzenes aryl rings acyl benzenes R(C)X, AlX 3 HN 3, H 2 S 4 nitrobenzenes H 3 P 2 1) Fe, HCl 2) NaH H 2, Ni aryl nitriles H 2 KCN, CaCN aryl diazonium salts 1) HN 2, 2) HCl KI anilines aryl iodides NaNH 2, NH 3 amines epoxides 1) KN 3, 2) H 2, 3) LiAlH 4, 4) H 3 + /H 2 HBF 4 aryl fluorides amino HN 2 1) excess Mel 2) NaH, heat 1) H 2 2, 2) heat
New bond. ph 4.0. Fischer esterification. New bond 2 O * New bond. New bond H 2N. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. O Cl.
 Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
22.7 Reactions of Amines: A Review and a Preview
 22.7 Reactions of Amines: A Review and a Preview Preparation of Amines Two questions to answer: 1) How is the C N C N bond to be formed? 2) How do we obtain the correct oxidation state of nitrogen (and
22.7 Reactions of Amines: A Review and a Preview Preparation of Amines Two questions to answer: 1) How is the C N C N bond to be formed? 2) How do we obtain the correct oxidation state of nitrogen (and
Module9. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy - Chemical shift - Integration of signal area
 1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
20.5 Preparation of Amines
 RGANIC CHEMISTRY 20.5 Preparation of Amines RGANIC CHEMISTRY 20.5A Through Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Alkylation of Ammonia or Amines NaH NH 3 + R X RNH 3 X RNH2 R + R X R 2 X NaH R 2 NH R 2 NH
RGANIC CHEMISTRY 20.5 Preparation of Amines RGANIC CHEMISTRY 20.5A Through Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Alkylation of Ammonia or Amines NaH NH 3 + R X RNH 3 X RNH2 R + R X R 2 X NaH R 2 NH R 2 NH
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 15, 2010 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW
 REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
Chem 251 Fall Learning Objectives
 Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
Learning Objectives Chapter 8 (last semester) 1. Write an electron-pushing mechanism for an SN2 reaction between an alkyl halide and a nucleophile. 2. Describe the rate law and relative rate of reaction
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes. 2. Radical Substitution with Alkenes. 3. Electrophilic Addition
 1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis.
 Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK
 Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
A. B. C. D. 2. Which compound does not give a stable Grignard reagent when reacting with Mg metal?
 Practice Test, Chemistry 2220 Final Exam 1. Which structure has the MST signals for its proton NMR? 2. Which compound does not give a stable Grignard reagent when reacting with Mg metal? 3. Which of these
Practice Test, Chemistry 2220 Final Exam 1. Which structure has the MST signals for its proton NMR? 2. Which compound does not give a stable Grignard reagent when reacting with Mg metal? 3. Which of these
Appendix A. Common Abbreviations, Arrows, and Symbols. Abbreviations
 smi97462_apps.qxd 12/6/04 1:09 PM Page A-1 Appendix A ommon Abbreviations, Arrows, and Symbols Abbreviations Ac acetyl, 3 BBN 9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane BINAP 2,2'-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphthyl
smi97462_apps.qxd 12/6/04 1:09 PM Page A-1 Appendix A ommon Abbreviations, Arrows, and Symbols Abbreviations Ac acetyl, 3 BBN 9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane BINAP 2,2'-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphthyl
Score: Homework Problem Set 9 Iverson CH320N Due Monday, April 17. NAME (Print): Chemistry 320N Dr. Brent Iverson 9th Homework April 10, 2017
 omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0N Due Monday, April 7 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0N Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework April 0, 07 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes
omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0N Due Monday, April 7 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0N Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework April 0, 07 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes
Chapter 11 Reaction of Alcohols
 Chapter 11 eaction of Alcohols xidation of alcohols Alcohols are at the same oxidation level as alkenes Therefore alkenes can be converted to alcohols with acidic water PDC or PCC 2 C C 2 3 + X 3 C 3 C
Chapter 11 eaction of Alcohols xidation of alcohols Alcohols are at the same oxidation level as alkenes Therefore alkenes can be converted to alcohols with acidic water PDC or PCC 2 C C 2 3 + X 3 C 3 C
1. What is the major organic product obtained from the following sequence of reactions?
 CH320 N N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. Carefully record your answers on the Scantron
CH320 N N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. Carefully record your answers on the Scantron
Michael and Aldol CH391 December 4, 2002
 Michael and Aldol H391 December 4, 2002 RH 2 H pk a = 16-20 + H RHH + Enolate anions... So.a basic solution contains comparable amounts of the aldehyde and its enolate. Which gives rise to..the Aldol ondensation
Michael and Aldol H391 December 4, 2002 RH 2 H pk a = 16-20 + H RHH + Enolate anions... So.a basic solution contains comparable amounts of the aldehyde and its enolate. Which gives rise to..the Aldol ondensation
Tips for taking exams in 852
 Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Physical Properties. Alcohols can be: CH CH 2 OH CH 2 CH 3 C OH CH 3. Secondary alcohol. Primary alcohol. Tertiary alcohol
 Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Reducing Agents. Linda M. Sweeting 1998
 Reducing Agents Linda M. Sweeting 1998 Reduction is defined in chemistry as loss of oxygen, gain of hydrogen or gain of electrons; the gain of electrons enables you to calculate an oxidation state. Hydride
Reducing Agents Linda M. Sweeting 1998 Reduction is defined in chemistry as loss of oxygen, gain of hydrogen or gain of electrons; the gain of electrons enables you to calculate an oxidation state. Hydride
Double and Triple Bonds. The addition of an electrophile and a
 Chapter 11 Additions to Carbon-Carbon Double and Triple Bonds The addition of an electrophile and a nucleophile to a C-C C double or triple bonds 11.1 The General Mechanism Pi electrons of the double bond
Chapter 11 Additions to Carbon-Carbon Double and Triple Bonds The addition of an electrophile and a nucleophile to a C-C C double or triple bonds 11.1 The General Mechanism Pi electrons of the double bond
CHEM 234: Organic Chemistry II Reaction Sheets
 EM234:rganichemistry eactionsheets ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: Grignards and reducing agents u: u u u: u u = or = or l u u u ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: oxygen and nitrogen nucleophiles:
EM234:rganichemistry eactionsheets ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: Grignards and reducing agents u: u u u: u u = or = or l u u u ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: oxygen and nitrogen nucleophiles:
Chapter 9 Alkynes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 9 Alkynes Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1 Sources of Alkynes Acetylene Industrial preparation of acetylene is by dehydrogenation of
Chapter 9 Alkynes Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1 Sources of Alkynes Acetylene Industrial preparation of acetylene is by dehydrogenation of
Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions.
 ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds.
 1 Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds. 1. Enolates. a) Carbonyl compounds are acidic at the α C, can be deprotonated by bases to give enolates. i) Ketones and aldehydes have pk a = 18
1 Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds. 1. Enolates. a) Carbonyl compounds are acidic at the α C, can be deprotonated by bases to give enolates. i) Ketones and aldehydes have pk a = 18
Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions. Alpha Substitution
 Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Modern Organic Synthesis an Introduction
 Modern Organic Synthesis an Introduction G. S. Zweifel M. H. Nantz W.H. Freeman and Company Chapter 1 Synthetic Design 1 What is an ideal or viable synthesis, and how does one approach a synthetic project?
Modern Organic Synthesis an Introduction G. S. Zweifel M. H. Nantz W.H. Freeman and Company Chapter 1 Synthetic Design 1 What is an ideal or viable synthesis, and how does one approach a synthetic project?
Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides. Chapter Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry
 Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides Chapter 17-18 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry 1 Introduction Structure and Bonding Alcohols contain a hydroxy group (OH) bonded to an sp 3 hybridized carbon. 2
Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides Chapter 17-18 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry 1 Introduction Structure and Bonding Alcohols contain a hydroxy group (OH) bonded to an sp 3 hybridized carbon. 2
Exercise 15 - Preparation of a Key for Reaction-Map of Organic Chemistry (see Appendix C in student manual)
 125 Exercise 15 - Preparation of a Key for Reaction-Map of Organic Chemistry (see Appendix C in student manual) Abstract: The Reaction -Map of Organic Chemistry has been designed to give organic chemistry
125 Exercise 15 - Preparation of a Key for Reaction-Map of Organic Chemistry (see Appendix C in student manual) Abstract: The Reaction -Map of Organic Chemistry has been designed to give organic chemistry
ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
 ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS Alcohols contain an OH group connected to a a saturated C (sp3) They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to
ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS Alcohols contain an OH group connected to a a saturated C (sp3) They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to
Chapter 19. Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions. ß-dicarbonyl compounds. Why are ß-dicarbonyls useful?
 Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Dr. Sapna Gupta Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated.
Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Dr. Sapna Gupta Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated.
CHAPTER 12. Substituted Benzene
 CHAPTER 12 Substituted Benzene 12.1 Alkylbenzenes (Ar-R) Bezylic carbons: CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 CH(CH 3 ) 2 1 Reactions of Alkylbenzens 1. Free Radical Halogenation CH 2 CH 3 Br 2 hv Br CHCH 3 2 2- xidation R
CHAPTER 12 Substituted Benzene 12.1 Alkylbenzenes (Ar-R) Bezylic carbons: CH 3 CH 2 CH 3 CH(CH 3 ) 2 1 Reactions of Alkylbenzens 1. Free Radical Halogenation CH 2 CH 3 Br 2 hv Br CHCH 3 2 2- xidation R
Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman
 Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman Robert Robinson 1886-1975 Nobel Laureate 1947 April 17, 2018 tto Paul Hermann Diels 1876-1954 Nobel Laureates 1950 Kurt Alder 1902-1958 Exam III Tomorrow Wed April
Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman Robert Robinson 1886-1975 Nobel Laureate 1947 April 17, 2018 tto Paul Hermann Diels 1876-1954 Nobel Laureates 1950 Kurt Alder 1902-1958 Exam III Tomorrow Wed April
LECTURE #22 Thurs., Nov.15, 2007
 Provide a rxn sequence to make these as the major products Answers: 1. i Pr-Cl, AlCl 3 2. conc. fuming? H 2 S 4 3. Cl 2, FeCl 3 or AlCl 3 4. dilute H 2 S 4 note: normally aqueous workup after step 1, but
Provide a rxn sequence to make these as the major products Answers: 1. i Pr-Cl, AlCl 3 2. conc. fuming? H 2 S 4 3. Cl 2, FeCl 3 or AlCl 3 4. dilute H 2 S 4 note: normally aqueous workup after step 1, but
Organic Chemistry Lecture 2 - Hydrocarbons, Alcohols, Substitutions
 ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
ALKANES Water-insoluble, low density C-C single bonds Higher MW -> higher BP, higher MP Branching -> lower BP, higher MP Forms cycloalkanes which can have ring strain Cyclohexane: chair vs. boat configuration
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 18, 2013 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Your name: Final Exam December 18, 2013 ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3.
CEM 203 Your name: Final Exam December 18, 2013 ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3.
Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones
 Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes (RCHO), with the exception of formaldehyde (H 2 CO), are compounds with both an H and an organic group attached to a carbonyl. Ketones (R 2 CO) are compounds with
Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes (RCHO), with the exception of formaldehyde (H 2 CO), are compounds with both an H and an organic group attached to a carbonyl. Ketones (R 2 CO) are compounds with
Synthetic possibilities Chem 315 Beauchamp 1
 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Propose reasonable syntheses f the following target molecules (TM-#). You can use the given starting materials and any typical ganic reagents studied in our course
Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Propose reasonable syntheses f the following target molecules (TM-#). You can use the given starting materials and any typical ganic reagents studied in our course
ORGANIC - BRUICE 8E CH CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III: REACTIONS AT THE ALPHA-CARBON
 !! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: ALPHA CARBNS AND TAUTMERIZATIN We have discussed the high reactivity of the carbonyl carbon. However, carbonyls contain another highly reactive component. What is the acidity
!! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: ALPHA CARBNS AND TAUTMERIZATIN We have discussed the high reactivity of the carbonyl carbon. However, carbonyls contain another highly reactive component. What is the acidity
Suggested solutions for Chapter 28
 s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
Organic Chemistry Curriculum Content Outline
 Organic Chemistry 2014-15 Curriculum Content Outline CHEM 0203: Organic Structure and Reactivity 1. Structure & Bonding (Brief Review from General Chemistry) a. Ionic & Covalent Bonding b. Lewis Structures
Organic Chemistry 2014-15 Curriculum Content Outline CHEM 0203: Organic Structure and Reactivity 1. Structure & Bonding (Brief Review from General Chemistry) a. Ionic & Covalent Bonding b. Lewis Structures
The Claisen Condensation
 Lecture 22 The Claisen Condensation CH 3 CCH 2 CH 3 CH 2 CCH 2 CH 3 April 10, 2018 Hydrolysis of Amides Hydrolysis of amides is irreversible. In acid solution the amine product is protonated to give an
Lecture 22 The Claisen Condensation CH 3 CCH 2 CH 3 CH 2 CCH 2 CH 3 April 10, 2018 Hydrolysis of Amides Hydrolysis of amides is irreversible. In acid solution the amine product is protonated to give an
C h a p t e r T e n : Alkynes. Tazarotene, a synthetic acetylenic retinoid used to treat acne
 C h a p t e r T e n : Alkynes N S Tazarotene, a synthetic acetylenic retinoid used to treat acne CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter 10: Alkynes I. Structure and bonding A. sp-hybridization
C h a p t e r T e n : Alkynes N S Tazarotene, a synthetic acetylenic retinoid used to treat acne CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter 10: Alkynes I. Structure and bonding A. sp-hybridization
1. LiAlH4 :.. :.. 2. H3O +
 Ch 24 Amines Description of Amines - An amine is a compound with a nitrogen atom that has single bonds to carbon and hydrogen atoms. - An uncharged nitrogen atom normally has three bonds and a lone pair.
Ch 24 Amines Description of Amines - An amine is a compound with a nitrogen atom that has single bonds to carbon and hydrogen atoms. - An uncharged nitrogen atom normally has three bonds and a lone pair.
Enols and Enolates. A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl)
 Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
Chapter 7. Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis
 Chapter 7. Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis 1 Synthesis of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions 1. Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides. loss of requires CH 2 CH 2 Cl Zaitsev s Rule: CH 2 C 2. Dehydration of
Chapter 7. Alkenes: Reactions and Synthesis 1 Synthesis of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions 1. Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides. loss of requires CH 2 CH 2 Cl Zaitsev s Rule: CH 2 C 2. Dehydration of
Introduction & Definitions Catalytic Hydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of H- and H+ Oxidation of Alcohols Oxidation of
 CEM 241- UNIT 4 xidation/reduction Reactions Redox chemistry 1 utline Introduction & Definitions Catalytic ydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of - and + xidation of Alcohols
CEM 241- UNIT 4 xidation/reduction Reactions Redox chemistry 1 utline Introduction & Definitions Catalytic ydrogenations Dissolving Metal Reduction Reduction by Addition of - and + xidation of Alcohols
Allyl radicals are especially stable due to resonance ( and double bond switch places):
 Ch 10 Alkyl Halides Nomenclature Rules The parent is the longest alkyl chain or ring. The #1 C for a chain is at the end that is nearest to the first substituent. The #1 C for a ring possesses the first
Ch 10 Alkyl Halides Nomenclature Rules The parent is the longest alkyl chain or ring. The #1 C for a chain is at the end that is nearest to the first substituent. The #1 C for a ring possesses the first
2311A and B Practice Problems to help Prepare for Final from Previous Marder Exams.
 2311A and B Practice Problems to help Prepare for Final from Previous Marder Exams. Disclaimer.: Use only to help learn what you need to know and don t expect the final to be in the same form. 1 1. Short
2311A and B Practice Problems to help Prepare for Final from Previous Marder Exams. Disclaimer.: Use only to help learn what you need to know and don t expect the final to be in the same form. 1 1. Short
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis.
 Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation:
 1 Chapter 22: Reactions of Enols and Enolates I. Alpha Substitution verview: A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation: Recall that the
1 Chapter 22: Reactions of Enols and Enolates I. Alpha Substitution verview: A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation: Recall that the
Ch 17 Alcohols and Phenols
 Ch 17 Alcohols and Phenols Alcohols are compounds with a hydroxyl group (OH) attached to an sp 3 C. Phenols are compounds with a hydroxyl group (OH) attached to an aromatic sp 2 C. Classification of Alcohols
Ch 17 Alcohols and Phenols Alcohols are compounds with a hydroxyl group (OH) attached to an sp 3 C. Phenols are compounds with a hydroxyl group (OH) attached to an aromatic sp 2 C. Classification of Alcohols
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III
 CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
10. Organohalides. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 10. Organohalides Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain
10. Organohalides Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain
Name the following compounds (include stereochemistry, cis/trans, E/Z when appropriate). Cl E- 6 chloro, 5 ethyl, 4 methyl 3-octene
 Problem Set 6 Name the following compounds (include stereochemistry, cis/trans, E/Z when appropriate). E- 6 chlo, 5 ethyl, 4 methyl 3-octene 5 methyl, 3 vinyl cyclohexene 7Z- 7 bromo 4 ethyl, 6 methyl
Problem Set 6 Name the following compounds (include stereochemistry, cis/trans, E/Z when appropriate). E- 6 chlo, 5 ethyl, 4 methyl 3-octene 5 methyl, 3 vinyl cyclohexene 7Z- 7 bromo 4 ethyl, 6 methyl
Learning Guide for Chapter 12 - Alkenes (II)
 Learning Guide for Chapter 12 - Alkenes (II) I. Addition reactions of alkenes Introduction to addition reactions Catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes Hydroxylation of alkenes Epoxidation of alkenes Cyclopropanation
Learning Guide for Chapter 12 - Alkenes (II) I. Addition reactions of alkenes Introduction to addition reactions Catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes Hydroxylation of alkenes Epoxidation of alkenes Cyclopropanation
N_HW1 N_HW1. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this sequence?
 N_HW1 N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this
N_HW1 N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. 1. What is the purpose of the H 2 O in this
SYSTEMWIDE CHEM 2425 FINAL EXAM. Department Of Physical Sciences
 SYSTEMWIDE CHEM 2425 FINAL EXAM Department f Physical Sciences Morphine NAME: RGANIC CHEM 2425 FINAL EXAM DIRECTINS- A periodic table is attached at the end of this exam. Please answer all questions in
SYSTEMWIDE CHEM 2425 FINAL EXAM Department f Physical Sciences Morphine NAME: RGANIC CHEM 2425 FINAL EXAM DIRECTINS- A periodic table is attached at the end of this exam. Please answer all questions in
Ethers can be symmetrical or not:
 Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides 175 Physical Properties Ethers can be symmetrical or not: linear or cyclic. Ethers are inert and make excellent solvents for organic reactions. Epoxides are very
Chapter 14: Ethers, Epoxides, and Sulfides 175 Physical Properties Ethers can be symmetrical or not: linear or cyclic. Ethers are inert and make excellent solvents for organic reactions. Epoxides are very
Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols
 hapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols sp 3 alcohol phenol (aromatic alcohol) pka~ 16-18 pka~ 10 Alcohols contain an group connected to a saturated carbon (sp 3 ) Phenols contain an group connected to a carbon
hapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols sp 3 alcohol phenol (aromatic alcohol) pka~ 16-18 pka~ 10 Alcohols contain an group connected to a saturated carbon (sp 3 ) Phenols contain an group connected to a carbon
10. Alkyl Halides. What Is an Alkyl Halide. An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen
 10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
10. Alkyl Halides What Is an Alkyl Halide An organic compound containing at least one carbonhalogen bond (C-X) X (F, Cl, Br, I) replaces H Can contain many C-X bonds Properties and some uses Fire-resistant
Organic Chemistry. M. R. Naimi-Jamal. Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology
 Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 7-1. Alkyl Halides Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition What Is an Alkyl Halide? An
Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 7-1. Alkyl Halides Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition What Is an Alkyl Halide? An
CHEMISTRY MIDTERM # 2 November 02, The total number of points in this midterm is 100. The total exam time is 120 min (2 h). Good luck!
 CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 2 November 02, 2009 Name... The total number of points in this midterm is 100. The total exam time is 120 min (2 h). Good luck! 1. (8 pts) Mark as true (T) or false (F) the following
CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 2 November 02, 2009 Name... The total number of points in this midterm is 100. The total exam time is 120 min (2 h). Good luck! 1. (8 pts) Mark as true (T) or false (F) the following
HONORS ORGANIC CHEM. HAHS MRS. RICHARDS
 NRS RGANIC CEM. AS MRS. RICARDS RGANIC CEMISTRY: FINAL EXAM REVIEW List of Topics: While the exam will specifically focus on material from Quarter 2, an understanding of several important concepts from
NRS RGANIC CEM. AS MRS. RICARDS RGANIC CEMISTRY: FINAL EXAM REVIEW List of Topics: While the exam will specifically focus on material from Quarter 2, an understanding of several important concepts from
Lecture 23. Amines. Chemistry 328N. April 12, 2016
 Lecture 23 Amines April 12, 2016 Michael Reaction Michael reaction: conjugate addition of an enolate Arthur Michael anion to an, -unsaturated carbonyl compound!! Following are two examples in the first,
Lecture 23 Amines April 12, 2016 Michael Reaction Michael reaction: conjugate addition of an enolate Arthur Michael anion to an, -unsaturated carbonyl compound!! Following are two examples in the first,
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE MIDTERM EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 353 READ ALL THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY
 WEDNESDAY MARCH 9th, 2016 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE MIDTERM EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 353 Version 1 Time: 2 Hours READ ALL THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY PLEASE WRITE YOUR NAME, STUDENT I.D. NUMBER
WEDNESDAY MARCH 9th, 2016 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE MIDTERM EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 353 Version 1 Time: 2 Hours READ ALL THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY PLEASE WRITE YOUR NAME, STUDENT I.D. NUMBER
Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Why this Chapter? Much of organic chemistry involves the chemistry of carbonyl compounds Aldehydes/ketones are intermediates in synthesis of pharmaceutical
Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Why this Chapter? Much of organic chemistry involves the chemistry of carbonyl compounds Aldehydes/ketones are intermediates in synthesis of pharmaceutical
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 18, This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 18, 2013 Your name: This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3. / 30 4.
CEM 203 Final Exam December 18, 2013 Your name: This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3. / 30 4.
3) Oxidation of tertiary alcohol yields A) Aldehyde B) No reaction C) Ketone D) Carboxylic acid
 ALKYL HALIDES 18- The reaction of Propyl bromide with Na is A) Nucleophilic addition. B) Nucleophilic substitution. C) Electrophilic substitution. D) Electrophilic addition. 25) Which of the following
ALKYL HALIDES 18- The reaction of Propyl bromide with Na is A) Nucleophilic addition. B) Nucleophilic substitution. C) Electrophilic substitution. D) Electrophilic addition. 25) Which of the following
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and How Do They Work?
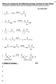 What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions and Condensation Reactions
 Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
ELECTROPHILIC ADDITIONS OF ALKENES AS THE COUNTERPART OF ELIMINATIONS
 ELECTRPHILIC ADDITINS F ALKENES AS THE CUNTERPART F ELIMINATINS INTRDUCTIN - Chapter 8 is mostly about alkene reactions. That is, how one can transform alkenes into other functional groups. Most of these
ELECTRPHILIC ADDITINS F ALKENES AS THE CUNTERPART F ELIMINATINS INTRDUCTIN - Chapter 8 is mostly about alkene reactions. That is, how one can transform alkenes into other functional groups. Most of these
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chem 315/316 Reactions. Bromo organic compounds C1 & C2 carbon skeletons C3 carbon skeletons C4 carbon skeletons. Alcohols. Chem 316 / Beauchamp 1
 hem 316 / Beauchamp 1 hem 315/316 eactions Name available sources of carbon 4 3 NaN methyl 3 2 ethyl 3 2 2 n-propyl 3 3 isopropyl 2 3 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 3 n-butyl sec butyl t-butyl phenyl available until topic
hem 316 / Beauchamp 1 hem 315/316 eactions Name available sources of carbon 4 3 NaN methyl 3 2 ethyl 3 2 2 n-propyl 3 3 isopropyl 2 3 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 3 n-butyl sec butyl t-butyl phenyl available until topic
1/4/2011. Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds
 Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
2.222 Practice Problems 2003
 2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
Advanced Organic Chemistry: Retrosynthesis
 123.312 Advanced rganic Chemistry: Retrosynthesis Tutorial Question 1. Propose a retrosynthetic analysis of the following two compounds. Your answer should include both the synthons, showing your thinking,
123.312 Advanced rganic Chemistry: Retrosynthesis Tutorial Question 1. Propose a retrosynthetic analysis of the following two compounds. Your answer should include both the synthons, showing your thinking,
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha ( ) Substitution
 Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha () Substitution The overall reaction replaces an H with an E + The acid-catalyzed reaction has an enol intermediate The base-catalyzed reaction has an enolate intermediate Keto-Enol
Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha () Substitution The overall reaction replaces an H with an E + The acid-catalyzed reaction has an enol intermediate The base-catalyzed reaction has an enolate intermediate Keto-Enol
Loudon Chapter 23 Review: Amines Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 4/22/2018
 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions that are specific to nitrogen. Amines can be subdivided based on how many
This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions that are specific to nitrogen. Amines can be subdivided based on how many
Mechanisms. . CCl2 F + Cl.
 Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Química Orgânica I. Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB QO I 2007/08 1
 Química rgânica I Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB Q I 2007/08 1 alcohols Adaptado de rganic Chemistry, 6th Edition; Wade rganic Chemistry, 6 th Edition; McMurry AFB Q I 2007/08 2 Typical
Química rgânica I Ciências Farmacêuticas Bioquímica Química AFB Q I 2007/08 1 alcohols Adaptado de rganic Chemistry, 6th Edition; Wade rganic Chemistry, 6 th Edition; McMurry AFB Q I 2007/08 2 Typical
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES.
 COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II
 KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
Cape Cod Community College
 Cape Cod Community College Departmental Syllabus Prepared by the Department of Natural Sciences & Applied Technology Date of Departmental Approval: February 3, 2014 Date Approved by Curriculum and Programs:
Cape Cod Community College Departmental Syllabus Prepared by the Department of Natural Sciences & Applied Technology Date of Departmental Approval: February 3, 2014 Date Approved by Curriculum and Programs:
Loudon Chapter 23 Review: Amines CHEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall Page 1
 Loudon Chapter 23 eview: Amines CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions
Loudon Chapter 23 eview: Amines CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions
Reactions at α-position
 Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Classification Tests
 3CLASFIC.DC 10/23/2008 Classification Tests 1. Classification Tests For Alcohols a) Sodium Metal: RH Na RNa H2(g) Positive Test: evolution of gas the rate is highly variable and depends upon the alcohol
3CLASFIC.DC 10/23/2008 Classification Tests 1. Classification Tests For Alcohols a) Sodium Metal: RH Na RNa H2(g) Positive Test: evolution of gas the rate is highly variable and depends upon the alcohol
Synthesis of Amines Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction II. Reductive Amination
 Synthesis of Amines I. Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction Amines can be alkylated in SN2 fashion by alkyl halides; primary halides are best for this purpose. This is not a practical reaction for formation
Synthesis of Amines I. Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction Amines can be alkylated in SN2 fashion by alkyl halides; primary halides are best for this purpose. This is not a practical reaction for formation
Organic Chemistry, 7 L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter , Prentice Hall
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although h benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although h benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic
Organic Chemistry I: Reactions and Overview
 Organic Chemistry I: Reactions and Overview Andrew Rosen Editor: Raghav Malik January 13, 2013 Contents I Library of Synthetic Reactions 3 II Organic Trends and Essentials 4 1 The Basics: Bonding and Molecular
Organic Chemistry I: Reactions and Overview Andrew Rosen Editor: Raghav Malik January 13, 2013 Contents I Library of Synthetic Reactions 3 II Organic Trends and Essentials 4 1 The Basics: Bonding and Molecular
Additions to the Carbonyl Groups
 Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups Nucleophilic substitution (S N 2andS N 1) reaction occurs at sp3 hybridized carbons with electronegative leaving groups Why? The carbon is electrophilic! Addition
Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups Nucleophilic substitution (S N 2andS N 1) reaction occurs at sp3 hybridized carbons with electronegative leaving groups Why? The carbon is electrophilic! Addition
Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Alcohols and Phenols Alcohols contain an OH group connected to a a saturated C (sp 3 ) They are important solvents and
Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Alcohols and Phenols Alcohols contain an OH group connected to a a saturated C (sp 3 ) They are important solvents and
Alkenes - Addition Reactions
 Alkenes - Addition Reactions Alkenes- reactions. Addition Ionic Free radical Reduction Oxidation Substitution Reactions, alkenes: 1. Addition of hydrogen (reduction). 2. Addition of halogens. 3. Addition
Alkenes - Addition Reactions Alkenes- reactions. Addition Ionic Free radical Reduction Oxidation Substitution Reactions, alkenes: 1. Addition of hydrogen (reduction). 2. Addition of halogens. 3. Addition
Keynotes in Organic Chemistry
 Keynotes in Organic Chemistry Second Edition ANDREW F. PARSONS Department of Chemistry, University of York, UK Wiley Contents Preface xi 1 Structure and bonding 1 1.1 Ionic versus covalent bonds 1 1.2
Keynotes in Organic Chemistry Second Edition ANDREW F. PARSONS Department of Chemistry, University of York, UK Wiley Contents Preface xi 1 Structure and bonding 1 1.1 Ionic versus covalent bonds 1 1.2
September [KV 804] Sub. Code: 3804
![September [KV 804] Sub. Code: 3804 September [KV 804] Sub. Code: 3804](/thumbs/89/97855699.jpg) September 2009 [KV 804] Sub. Code: 3804 (Regulations 2008-2009) (Candidates admitted from 2008-2009 onwards) Paper IV PHARMACEUTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Time : Three hours Maximum : 70 marks Answer All questions
September 2009 [KV 804] Sub. Code: 3804 (Regulations 2008-2009) (Candidates admitted from 2008-2009 onwards) Paper IV PHARMACEUTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Time : Three hours Maximum : 70 marks Answer All questions
C h a p t e r N i n e: Addition Reactions of Alkenes
 C h a p t e r N i n e: Addition Reactions of Alkenes. H C 2 H Biosynthesis of a prostaglandin from arachidonic acid: intermediate intramolecular radical addition CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts
C h a p t e r N i n e: Addition Reactions of Alkenes. H C 2 H Biosynthesis of a prostaglandin from arachidonic acid: intermediate intramolecular radical addition CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE MIDTERM EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 353 READ ALL THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY
 TUESDAY MARCH 3rd, 2015 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE MIDTERM EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 353 Version 1 Time: 2 Hours READ ALL THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY PLEASE WRITE YOUR NAME, STUDENT I.D. NUMBER
TUESDAY MARCH 3rd, 2015 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY FACULTY OF SCIENCE MIDTERM EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 353 Version 1 Time: 2 Hours READ ALL THE INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY PLEASE WRITE YOUR NAME, STUDENT I.D. NUMBER
