ORGANIC - BRUICE 8E CH CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III: REACTIONS AT THE ALPHA-CARBON
|
|
|
- Jordan French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 !!
2 CNCEPT: ALPHA CARBNS AND TAUTMERIZATIN We have discussed the high reactivity of the carbonyl carbon. However, carbonyls contain another highly reactive component. What is the acidity of the β-carbon? What is the acidity of the α-carbon? Which phenomenon is responsible for this difference? Tautomerization General Reaction: Acid-Catalyzed Mechanism: Base-Catalyzed Mechanism: Page 2
3 PRACTICE: Draw the enol tautomer for the following compound. Cyclopentanone Page 3
4 CNCEPT: ENLATES Upon deprotonation, the α-carbon forms a resonance-stabilized intermediate structure called an Both notations can be used to represent an enolate Note that the negative charge now rests on the This makes the α-carbon of the enolate a good General Reactions of Enolates: Page 4
5 CNCEPT: ELECTRPHILIC α-halgenatins Acid-Catalyzed α-halogenation: Always yields -halogenation PRACTICE: Provide the major product for the following reaction. Br 2 CH 3 H + Page 5
6 CNCEPT: ELECTRPHILIC α-halgenatins Base-Catalyzed α-halogenation: May yield -halogenation PRACTICE: Provide the major product for the following reaction. Br 2 excess NaH Page 6
7 CNCEPT: ELECTRPHILIC α-halgenatins The Haloform Reaction: Base-Catalyzed α-halogenation of The α-carbon is transformed into a good through successive halogenations. PRACTICE: Provide the major product for the following reaction. Br 2 excess NaH Page 7
8 CNCEPT: ELECTRPHILIC α-halgenatins The HVZ Reaction PRACTICE: Provide the major product after each step for the following reaction. Br 2, PBr 3 NH 3 H H 2 Page 8
9 CNCEPT: VERVIEW F α-carbn ALKYLATINS AND ACYLATINS Adding R groups to α-carbons of carbonyl compounds is synthetically important. There are main synthetic pathways that we use to accomplish this. Page 9
10 CNCEPT: ENLATE ALKYLATIN AND ACYLATIN We can expose enolates to alkyl halides to produce α-alkyations Using acid chlorides results in α-acylations. Directed Reactions: When we run α-alkyations with asymmetrical ketones, two enolates are possible. This leads to a mixture of products. We can use different bases to direct the direction of deprotonation The thermodynamic product is the product with the lowest overall energy The kinetic product is the product with the lowest activation energy Enolates of Esters: LDA can also be used in the alkylation of esters Use of alkoxide bases may yield transesterification (stay away!) Page 10
11 PRACTICE: The following molecule forms two products. Determine the products and determine if they follow thermodynamic control or kinetic control. 1) TBuK, TBuH 2) CH 3 Br 1) LiH 2) CH 3 Br Page 11
12 CNCEPT: ENAMINE ALKYLATIN AND ACYLATIN Carbonyls easily react with acid-catalyzed amine solvents to form imines and enamines. Secondary Amine Addition: Enamines Enamines have the ability to alkylate or acylate via the formation of an iminium salt EXAMPLE: Predict the products of the following reactions 1. Page 12
13 PRACTICE: Provide the major product after each step for the following reaction. H N Br H 3 + H + Acetone PRACTICE: Which of the following can NT be formed through the stork enamine reaction with 2-butanone? a) 3-pentanone b) 3-methyl-2-butanone c) 2-octanone d) 3-octanone Page 13
14 CNCEPT: TAUTMERS F DICARBNYL CMPUNDS Most carbonyl compounds favor the tautomer β-dicarbonyl compounds favor the tautomer due to and β-dicarbonyl compounds are exceptionally acidic due to the high stability of the conjugate base If the α-carbon exists as a chiral center, that carbon will ALWAYS BE EXAMPLE: Which of the following ketones is the most acidic? Page 14
15 CNCEPT: β-dicarbnyl ESTER SYNTHESIS PATHWAY β-dicarbonyl compounds are unusually acidic due to the incredible stability of the enolate. We can take advantage of this acidity to easily alkylate the central α-carbon through a predictable multi-step synthesis. β-dicarbonyl Ester Synthetic Pathway Page 15
16 CNCEPT: ACETACETIC ESTER SYNTHESIS GENERAL REACTINS EXAMPLE: Predict the products of the following multi-step reactions Page 16
17 PRACTICE: Provide the major product for the following reaction H 3 C CH 3 1. NaEt 2. PhCH 2 Br 3. H Δ PRACTICE: Beginning from ethyl acetoacetate, and using any other necessary reagents, show the necessary compounds needed to form the following compound. Page 17
18 CNCEPT: MALNIC ESTER SYNTHESIS GENERAL REACTINS EXAMPLE: Predict the products of the following multi-step reactions Page 18
19 PRACTICE: Provide the major product for the following reaction 1. 2 moles NaEt, EtH 2. BrCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 Br H 3 C CH 3 3. NaH, H 2, H LiAlH 4 PRACTICE: Provide the major product for the following reaction 1. NaEt, EtH 2. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 Br H 3 C CH 3 3. NaH, H 2, H Heat PRACTICE: Beginning from diethyl malonate, and using any other necessary reagents, show the necessary compounds needed to form the following compound. H Page 19
20 CNCEPT: CNDENSATIN REACTINS A condensation reaction spontaneously combines two or more molecules with the loss of a smaller molecule. Instead of just reacting with electophiles, enolates are able to react with themselves to self-condensate bviously, are required for this type of reaction to take place Example Reactions: Page 20
21 CNCEPT: ALDL CNDENSATIN Via enolates, ketones and aldehydes will react with to condensate into The final products are called aldols because they are part and part Mechanism: 1. Form the enolate 2. Nucleophilic attack the other carbonyl (which we will call the electrophile) 3. Protonate the tetrahedral intermediate: β-hydroxy carbonyls are to dehydrate than typical alcohols due to Many times, we will simply assume that the condensation product dehydrated on its own, without requiring an explanation. Page 21
22 PRACTICE: What product can be isolated from the following aldol condensation reaction? H Page 22
23 PRACTICE: Provide the mechanism for the following transformation. H H H Page 23
24 CNCEPT: DIRECTED CNDENSATINS When we run condensation reactions with asymmetrical ketones, two enolates may be possible. We can use different bases to direct the direction of deprotonation The thermodynamic enolate is the substituted one. Favored by bases. The kinetic enolate is the substituted one. Favored by bases. EXAMPLE: Predict the products of the following self-condensation. Page 24
25 CNCEPT: CRSSED ALDL When we run condensation reactions on two different ketones or aldehydes, mixed products are difficult to avoid. In general, condensation reactions with two different carbonyls work best when one carbonyl is nonenolizable. Nonenolizable Carbonyls: Page 25
26 PRACTICE: Give the structure of the aldehydes or ketones used to create the product prepared by a crossed aldol condensation reaction. PRACTICE: Give the structure of the aldehydes or ketones used to create the product prepared by a crossed aldol reaction. H PRACTICE: What product can be isolated from the following aldol condensation reaction? H H Page 26
27 CNCEPT: CLAISEN-SCHMIDT REACTIN When a crossed aldol contains an enolizable aldehyde and a ketone, one product does predominate. Aldehydes are more susceptible toward nucleophilic addition than ketones, favoring a single enolate. EXAMPLE: Predict the major product of the following condensation. Page 27
28 CNCEPT: CLAISEN CNDENSATIN Via enolates, esters will react with to condensate into Mechanism: 1. Form the enolate 2. Nucleophilic attack the other carbonyl (which we will call the electrophile) 3. Kick out the good leaving group: Example Application: Page 28
29 PRACTICE: Draw the structure of the Claisen condensation product for each of the following compounds. NaEt Et Et EtH PRACTICE: Draw the structure of the Claisen condensation product for each of the following compounds. NaMe MeH PRACTICE: Give the structure of the ester precursor for the following Claisen condensation product. Page 29
30 CNCEPT: INTRAMLECULAR CNDENSATIN Dicarbonyl compounds have the ability to self-condensate through cyclization if it will generate a or -membered ring. When a diketone or dialdehyde self-condensate, the resulting product is called a cyclic enone When a diester self-condensates, the resulting product is called a cyclic β-ketoester This is known as a Dieckmann Condensation Page 30
31 PRACTICE: Consider the following reaction. Provide a stepwise mechanism to explain the given transformation. Page 31
32 CNCEPT: CNJUGATE ADDITIN F ENNES nce an aldol condensation is completed, an electrophilic carbonyl still remains. Enones remain susceptible to nucleophilic attack, however they now have two electrophilic regions: Also known as 1,2 vs. 1,4 addition of enones, or nucleophilic addition vs. conjugate addition of carbonyls. Nucleophilic Addition vs. Conjugate Addition Page 32
33 CNCEPT: THE MICHAEL REACTIN The Michael Reaction is a 1,4-conjugate addition of an enone with an enolate. Basically Always forms 1,5-dicarbonyls Mechanism: Page 33
34 PRACTICE: Determine the product in the following conjugated addition reaction. PRACTICE: Determine the product in the following conjugated addition reaction. PRACTICE: Determine the product in the following conjugated addition reaction. Page 34
35 CNCEPT: RBINSN ANNULATIN 1,5-dicarbonyl compounds have the ability to undergo intramolecular self-condensation into 6-membered enones. When the 1,5-dicarbonyl is generated via Michael Reaction (enone + enolate), it is called a Robinson Annulation ` Basically EXAMPLE: Predict the major product of the following Robinson Annulation. Page 35
36 PRACTICE: Provide the product for the following Robinson Annulation Reaction. PRACTICE: How would you prepare the following compound using a Robinson annulation reaction between a di-ketone and an alpha, beta unsaturated ketone? PRACTICE: How would you prepare the following compound using a Robinson annulation reaction between a ketone and an alpha, beta unsaturated ketone? Page 36
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH CONDENSATION CHEMISTRY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: CNDENSATIN REACTINS A condensation reaction spontaneously combines two or more molecules with the loss of a smaller molecule. Instead of just reacting with electophiles, enolates
!! www.clutchprep.com CNCEPT: CNDENSATIN REACTINS A condensation reaction spontaneously combines two or more molecules with the loss of a smaller molecule. Instead of just reacting with electophiles, enolates
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III
 CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
CHAPTER 19: CARBONYL COMPOUNDS III A hydrogen bonded to a carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is sufficiently acidic to be removed by a strong base. The carbon adjacent to a carbonyl carbon is called
Enols and Enolates. A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl)
 Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
Enols and Enolates A type of reaction with carbonyl compounds is an α-substitution (an electrophile adds to the α carbon of a carbonyl) E+ E In the preceding chapters, we primarily studied nucleophiles
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon
 Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Chapter 19. Carbonyl Compounds III Reaction at the α-carbon There is a basic hydrogen (α hydrogen) on α carbon, which can be removed by a strong base. 19.1 The Acidity of α-hydrogens A hydrogen bonded
Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions. Alpha Substitution
 Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
 Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Lecture Notes Chem 51C S. King Chapter 24 Carbonyl Condensation Reactions I. Reaction of Enols & Enolates with ther Carbonyls Enols and enolates are electron rich nucleophiles that react with a number
Chapter 19. Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions. ß-dicarbonyl compounds. Why are ß-dicarbonyls useful?
 Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
CHEM Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25
 CHEM 2425. Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25 Student: 1. Which of the following statements about Aldol reactions with either aldehydes or ketones is true? Equilibrium favors the starting
CHEM 2425. Chapter 23. Carbonyl Condensation Reactions (quiz) W25 Student: 1. Which of the following statements about Aldol reactions with either aldehydes or ketones is true? Equilibrium favors the starting
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Aldehydes and Ketones : Aldol Reactions The Acidity of the a Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons a to carbonyls are unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by
Reactions at α-position
 Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
Reactions at α-position In preceding chapters on carbonyl chemistry, a common reaction mechanism observed was a nucleophile reacting at the electrophilic carbonyl carbon site NUC NUC Another reaction that
A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation:
 1 Chapter 22: Reactions of Enols and Enolates I. Alpha Substitution verview: A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation: Recall that the
1 Chapter 22: Reactions of Enols and Enolates I. Alpha Substitution verview: A. Review of Acidity and pk a Common way to examine acidity is to use the Bronsted-Lowry acid-base equation: Recall that the
CHAPTER 24 HW: CARBONYL CONDENSATIONS
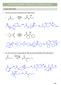 CAPTER 24 W: CARBNYL CNDENSATINS ALDL REACTIN 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism for each aldol reaction. Na 2 product Na Et prod. 2. Give the curved arrow mechanism for this aldol reaction (and dehydration
CAPTER 24 W: CARBNYL CNDENSATINS ALDL REACTIN 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism for each aldol reaction. Na 2 product Na Et prod. 2. Give the curved arrow mechanism for this aldol reaction (and dehydration
1/4/2011. Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds
 Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Chapter 19. Organic Chemistry. Carbonyl Compounds III. Reactions at the a-carbon. 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice
 Organic Chemistry 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 19 Carbonyl Compounds III Reactions at the a-carbon Disampaikan oleh: Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Irene Lee Case Western Reserve University Cleveland,
Organic Chemistry 4 th Edition Paula Yurkanis Bruice Chapter 19 Carbonyl Compounds III Reactions at the a-carbon Disampaikan oleh: Dr. Sri Handayani 2013 Irene Lee Case Western Reserve University Cleveland,
Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha ( ) Substitution
 Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha () Substitution The overall reaction replaces an H with an E + The acid-catalyzed reaction has an enol intermediate The base-catalyzed reaction has an enolate intermediate Keto-Enol
Ch 22 Carbonyl Alpha () Substitution The overall reaction replaces an H with an E + The acid-catalyzed reaction has an enol intermediate The base-catalyzed reaction has an enolate intermediate Keto-Enol
New bond. ph 4.0. Fischer esterification. New bond 2 O * New bond. New bond H 2N. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. O Cl.
 Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~ 20
 Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
Enolate Anions Chapter 17 Hydrogen on a carbons a to a carbonyl is unusually acidic The resulting anion is stabilized by resonance to the carbonyl Aldehydes and Ketones II Aldol Reactions pka of a-h ~
Organic Chemistry, Third Edition. Chapter 24 Carbonyl condensations
 rganic Chemistry, Third Edition Chapter 24 Carbonyl condensations 1 Review: enolates LDA, -78 C TF kinetic RX R = Me, 1 alkyl R Na TF, RT RX R = Me, 1 alkyl thermodynamic R enolates = nucleophiles React
rganic Chemistry, Third Edition Chapter 24 Carbonyl condensations 1 Review: enolates LDA, -78 C TF kinetic RX R = Me, 1 alkyl R Na TF, RT RX R = Me, 1 alkyl thermodynamic R enolates = nucleophiles React
Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds.
 1 Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds. 1. Enolates. a) Carbonyl compounds are acidic at the α C, can be deprotonated by bases to give enolates. i) Ketones and aldehydes have pk a = 18
1 Chapter 23. Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds. 1. Enolates. a) Carbonyl compounds are acidic at the α C, can be deprotonated by bases to give enolates. i) Ketones and aldehydes have pk a = 18
Michael and Aldol CH391 December 4, 2002
 Michael and Aldol H391 December 4, 2002 RH 2 H pk a = 16-20 + H RHH + Enolate anions... So.a basic solution contains comparable amounts of the aldehyde and its enolate. Which gives rise to..the Aldol ondensation
Michael and Aldol H391 December 4, 2002 RH 2 H pk a = 16-20 + H RHH + Enolate anions... So.a basic solution contains comparable amounts of the aldehyde and its enolate. Which gives rise to..the Aldol ondensation
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions and Condensation Reactions
 Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Chap 11. Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution eactions and Condensation eactions Four fundamental reactions of carbonyl compounds 1) Nucleophilic addition (aldehydes and ketones) ) Nucleophilic acyl substitution
ENOLATES IN ORGANIC SYNTHESIS
 ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS 1 ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS Recall Enolate alkylation, Aldol addition and condensation can provide access to a wide variety of multi-functional compounds, which can lend themselves
ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS 1 ENLATES IN RGANIC SYNTHESIS Recall Enolate alkylation, Aldol addition and condensation can provide access to a wide variety of multi-functional compounds, which can lend themselves
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and How Do They Work?
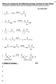 What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
What is in Common for the Following Reactions, and ow Do They Work? You should eventually be able to draw the mechanism for these (and other) reactions 13 Key Intermediate 1 Br-Br Na Br 2 C 3 -I Me NaMe
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Score: Homework Problem Set 9 Iverson CH320N Due Monday, April 17. NAME (Print): Chemistry 320N Dr. Brent Iverson 9th Homework April 10, 2017
 omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0N Due Monday, April 7 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0N Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework April 0, 07 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes
omework Problem Set 9 Iverson C0N Due Monday, April 7 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: Chemistry 0N Dr. ent Iverson 9th omework April 0, 07 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes
ζ ε δ γ β α α β γ δ ε ζ
 hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman
 Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman Robert Robinson 1886-1975 Nobel Laureate 1947 April 17, 2018 tto Paul Hermann Diels 1876-1954 Nobel Laureates 1950 Kurt Alder 1902-1958 Exam III Tomorrow Wed April
Lecture 24 Two Germans and an Englishman Robert Robinson 1886-1975 Nobel Laureate 1947 April 17, 2018 tto Paul Hermann Diels 1876-1954 Nobel Laureates 1950 Kurt Alder 1902-1958 Exam III Tomorrow Wed April
CHAPTER 23 HW: ENOLS + ENOLATES
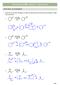 CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
CAPTER 23 W: ENLS + ENLATES KET-ENL TAUTMERSM 1. Draw the curved arrow mechanism to show the interconversion of the keto and enol form in either trace acid or base. trace - 2 trace 3 + 2 + E1 2 c. trace
Chapter 22 Enols and Enolates
 Chapter Enols and Enolates Acidity of the α hydrogen o The position next door to a carbonyl is called the α position o When an α proton is abstracted, the resulting carbanion is resonancestabilized. This
Chapter Enols and Enolates Acidity of the α hydrogen o The position next door to a carbonyl is called the α position o When an α proton is abstracted, the resulting carbanion is resonancestabilized. This
MCAT Organic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones
 MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
MCAT rganic Chemistry Problem Drill 10: Aldehydes and Ketones Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following is not a physical property of aldehydes and ketones? Question #01 (A) Hydrogen bonding
18: Reactions of Enolate Ions and Enols
 18: Reactions of Enolate Ions and Enols 18.1 Enolate Ions and Enols 18-3 Halogenation, Alkylation, and Condensation Reactions (18.1A) 18-3 Acidity of α-c-h's (18.1B) 18-4 Resonance Stabilization Enol Form
18: Reactions of Enolate Ions and Enols 18.1 Enolate Ions and Enols 18-3 Halogenation, Alkylation, and Condensation Reactions (18.1A) 18-3 Acidity of α-c-h's (18.1B) 18-4 Resonance Stabilization Enol Form
When we deprotonate we generate enolates or enols. Mechanism for deprotonation: Resonance form of the anion:
 Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
The problem is that your product still has a-protons, and can keep on forming enolates to get more methyl groups added:
 Lecture 13 Notes November 7, 2012 We are going to start with some examples of proline-catalyzed reactions. In each case, you can draw a mechanism that would involve proline as a chiral catalyst, and one
Lecture 13 Notes November 7, 2012 We are going to start with some examples of proline-catalyzed reactions. In each case, you can draw a mechanism that would involve proline as a chiral catalyst, and one
Lecture 23. Amines. Chemistry 328N. April 12, 2016
 Lecture 23 Amines April 12, 2016 Michael Reaction Michael reaction: conjugate addition of an enolate Arthur Michael anion to an, -unsaturated carbonyl compound!! Following are two examples in the first,
Lecture 23 Amines April 12, 2016 Michael Reaction Michael reaction: conjugate addition of an enolate Arthur Michael anion to an, -unsaturated carbonyl compound!! Following are two examples in the first,
Summary of π Bond Chemistry
 Chapter 10 Summary of π Bond Chemistry to π C=C 13.01 Chapter 11 at π C=C to π C=C Chapter 1 LG at π C=C Chapter 13 at α position C= activates position ow does C= activation α position? Via or. E base
Chapter 10 Summary of π Bond Chemistry to π C=C 13.01 Chapter 11 at π C=C to π C=C Chapter 1 LG at π C=C Chapter 13 at α position C= activates position ow does C= activation α position? Via or. E base
II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction
 P. Wipf - Chem 2320 1 3/20/2006 II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction Boger Notes: p. 147-206 (Chapter VIII) Carey/Sundberg: B p. 57-95 (Chapter B 2.1) Problem of the Day: Wang,
P. Wipf - Chem 2320 1 3/20/2006 II. Special Topics IIA. Enolate Chemistry & the Aldol Reaction Boger Notes: p. 147-206 (Chapter VIII) Carey/Sundberg: B p. 57-95 (Chapter B 2.1) Problem of the Day: Wang,
Lecture 23. The Aldol Condensation. an Aldol! April 12, 2018 O H O H - Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 23 The Aldol Condensation - b a an Aldol! April 12, 2018 Exam III - Wed April 18 WEL 2.122 7-9 PM Covers thru today omework ydrolysis Reactions Synthesis Get an A!!! Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA)
Lecture 23 The Aldol Condensation - b a an Aldol! April 12, 2018 Exam III - Wed April 18 WEL 2.122 7-9 PM Covers thru today omework ydrolysis Reactions Synthesis Get an A!!! Lithium diisopropylamide (LDA)
22.4 ALDOL ADDITION AND ALDOL CONDENSATION
 .4 ALDL ADDITIN AND ALDL CNDENATIN 06 H C $ C L C L CH ) H C H C $ CA CL CH ) H C not an important structure (.8) In addition, the carbocation is destabilized by its unfavorable electrostatic interaction
.4 ALDL ADDITIN AND ALDL CNDENATIN 06 H C $ C L C L CH ) H C H C $ CA CL CH ) H C not an important structure (.8) In addition, the carbocation is destabilized by its unfavorable electrostatic interaction
Conjugate Addition Reactions 2:02 PM
 1 Conjugate Addition vs Direct Addition What is Conjugate Addition? Conjugate addition refers to nucleophilic addition directed to the electrophilic carbon of the C=C (double bond) in a,bunsaturated systems.
1 Conjugate Addition vs Direct Addition What is Conjugate Addition? Conjugate addition refers to nucleophilic addition directed to the electrophilic carbon of the C=C (double bond) in a,bunsaturated systems.
Module No and Title. PAPER No: 5 ; TITLE : Organic Chemistry-II MODULE No: 25 ; TITLE: S E 1 reactions
 Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 5; Organic Chemistry-II 25; S E 1 reactions CHE_P5_M25 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. S E 1 reactions 3.1
Subject Chemistry Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 5; Organic Chemistry-II 25; S E 1 reactions CHE_P5_M25 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. S E 1 reactions 3.1
20.10 Conjugate Additions
 894 APTER 20 ELATE AD THER CARB UCLEPHILES 2010 Conjugate Additions The conjugate addition of nucleophiles to,-unsaturated carbonyl compounds at the -position was described in Section 1810 Enolate and
894 APTER 20 ELATE AD THER CARB UCLEPHILES 2010 Conjugate Additions The conjugate addition of nucleophiles to,-unsaturated carbonyl compounds at the -position was described in Section 1810 Enolate and
2.222 Practice Problems 2003
 2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
2.222 Practice Problems 2003 Set #1 1. Provide the missing starting compound(s), reagent/solvent, or product to correctly complete each of the following. Most people in the class have not done this type
Practice Synthetic Problems: CHEM 235 Page 2
 Practice Synthetic Problems: CM 235 Page 2 Syntheses based on diethyl malonate, ethyl acetoacetate, etc. Using diethyl malonate and any other necessary organic reagents, show a synthesis of: a) 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine
Practice Synthetic Problems: CM 235 Page 2 Syntheses based on diethyl malonate, ethyl acetoacetate, etc. Using diethyl malonate and any other necessary organic reagents, show a synthesis of: a) 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine
Important Concepts. Problems. Chapter Problems. Cuprate additions followed by enolate alkylations. 15. Michael Addition (Section 18-11)
 Problems hapter 18 861 uprate additions followed by enolate alkylations P 1. R 2uLi, TF 2. RX A A R R N 15. Michael Addition (Section 18-11) D P D R P R A RR 16. Robinson Annulation (Section 18-11) Important
Problems hapter 18 861 uprate additions followed by enolate alkylations P 1. R 2uLi, TF 2. RX A A R R N 15. Michael Addition (Section 18-11) D P D R P R A RR 16. Robinson Annulation (Section 18-11) Important
MITOCW watch?v=gboyppj9ok4
 MITOCW watch?v=gboyppj9ok4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=gboyppj9ok4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high quality educational resources for free. To
Chem 263 Nov 19, Cl 2
 Chem 263 Nov 19, 2013 eactions of Enolates: X X alogenation X C 2 Alkylation C Aldol eaction X C Acylation Example: halogenation LDA 2 Chloroacetone is used in tear gas. chloroacetone In this reaction,
Chem 263 Nov 19, 2013 eactions of Enolates: X X alogenation X C 2 Alkylation C Aldol eaction X C Acylation Example: halogenation LDA 2 Chloroacetone is used in tear gas. chloroacetone In this reaction,
Name. Department of Chemistry SUNY/Oneonta. Chem Organic Chemistry II Examination #3 - March 31, 2003
 INSTRUTINS Name Department of hemistry SUNY/neonta hem 322 - rganic hemistry II Examination #3 - March 31, 2003 This examination has two parts. Part I is in multiple choice format and the answers should
INSTRUTINS Name Department of hemistry SUNY/neonta hem 322 - rganic hemistry II Examination #3 - March 31, 2003 This examination has two parts. Part I is in multiple choice format and the answers should
Suggested solutions for Chapter 28
 s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
Chem 263 Nov 14, e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents)
 hem 263 ov 14, 2013 More examples: e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents) Br 2 hv Br a 2 r 4 S 2 or swern oxidation Mg Li 0 0 MgBr Li e.g. : Fill the reagents (any reagents
hem 263 ov 14, 2013 More examples: e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents) Br 2 hv Br a 2 r 4 S 2 or swern oxidation Mg Li 0 0 MgBr Li e.g. : Fill the reagents (any reagents
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis.
 Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
Chem 22 Final Exam Practice
 Chem 22 Final Exam Practice Questions taken from regular tests given during the previous semesters. Only one answer is correct unless the question says otherwise. The questions are somewhat scrambled with
Chem 22 Final Exam Practice Questions taken from regular tests given during the previous semesters. Only one answer is correct unless the question says otherwise. The questions are somewhat scrambled with
20.3 Alkylation of Enolate Anions
 864 APTER 20 ELATE AD TER ARB ULEPILES which precipitates as a yellow solid, provides a positive test for the presence of a methyl ketone The reaction can also be used in synthesis to convert a methyl
864 APTER 20 ELATE AD TER ARB ULEPILES which precipitates as a yellow solid, provides a positive test for the presence of a methyl ketone The reaction can also be used in synthesis to convert a methyl
Another Equilibrium: Reaction At The α-position
 Another Equilibrium: Reaction At The α-position D 3 + D 3 C CD 3 2 C 2 the keto form the enol form chanism: + C 2 C 2 C 2 D D 2 D 2 repeat 5 times D 3 C CD 3 alogenation At The α-position Br 2, 2 C 2 Br
Another Equilibrium: Reaction At The α-position D 3 + D 3 C CD 3 2 C 2 the keto form the enol form chanism: + C 2 C 2 C 2 D D 2 D 2 repeat 5 times D 3 C CD 3 alogenation At The α-position Br 2, 2 C 2 Br
The problem is that your product still has a-protons, and can keep on forming enolates to get more methyl groups added:
 Lecture 14 ovember 3, 2011 OK I want to continue briefly with the topic of proline catalysis that we discussed last time. In particular, the idea of using secondary amines to catalyze carbonyl chemistry
Lecture 14 ovember 3, 2011 OK I want to continue briefly with the topic of proline catalysis that we discussed last time. In particular, the idea of using secondary amines to catalyze carbonyl chemistry
Chapter 21 Ester Enolates
 hapter 21 Ester Enolates Introduction R R' H H The preparation and reactions of β-dicarbonyl compounds, especially β-keto esters, is the main focus of this chapter. A proton on the carbon flanked by the
hapter 21 Ester Enolates Introduction R R' H H The preparation and reactions of β-dicarbonyl compounds, especially β-keto esters, is the main focus of this chapter. A proton on the carbon flanked by the
CHEM 234: Organic Chemistry II Reaction Sheets
 EM234:rganichemistry eactionsheets ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: Grignards and reducing agents u: u u u: u u = or = or l u u u ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: oxygen and nitrogen nucleophiles:
EM234:rganichemistry eactionsheets ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: Grignards and reducing agents u: u u u: u u = or = or l u u u ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: oxygen and nitrogen nucleophiles:
1. What is the major organic product obtained from the following sequence of reactions?
 CH320 N N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. Carefully record your answers on the Scantron
CH320 N N_HW1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. Carefully record your answers on the Scantron
State University of New York at Stony Brook Department of Chemistry. CHE 322, Organic Chemistry II Exam II March 17, 2004 Form 1
 State University of New York at Stony Brook Department of Chemistry CHE 22, rganic Chemistry II Exam II March 17, 2004 Form 1 Please answer all questions specifically, concisely, and readably in the spaces
State University of New York at Stony Brook Department of Chemistry CHE 22, rganic Chemistry II Exam II March 17, 2004 Form 1 Please answer all questions specifically, concisely, and readably in the spaces
The Claisen Condensation
 Lecture 22 The Claisen Condensation CH 3 CCH 2 CH 3 CH 2 CCH 2 CH 3 April 10, 2018 Hydrolysis of Amides Hydrolysis of amides is irreversible. In acid solution the amine product is protonated to give an
Lecture 22 The Claisen Condensation CH 3 CCH 2 CH 3 CH 2 CCH 2 CH 3 April 10, 2018 Hydrolysis of Amides Hydrolysis of amides is irreversible. In acid solution the amine product is protonated to give an
Tautomerism and Keto Enol Equilibrium
 Tautomerism and Keto Enol Equilibrium Enols & enolates are important nucleophiles in organic & biochemistry. Keto-Enol Equilibrium: Tautomerisation can be catalyzed by either acids or bases. Relative stability
Tautomerism and Keto Enol Equilibrium Enols & enolates are important nucleophiles in organic & biochemistry. Keto-Enol Equilibrium: Tautomerisation can be catalyzed by either acids or bases. Relative stability
2 - ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND DERIVATIVES
 2 - ALDEYDES, KETNES AND DEIVATIVES Carbonyl chemistry is one of the most important areas of organic chemistry. You have been introduced to the chemistry of carboxylic acids in CEM*2700, and in this course
2 - ALDEYDES, KETNES AND DEIVATIVES Carbonyl chemistry is one of the most important areas of organic chemistry. You have been introduced to the chemistry of carboxylic acids in CEM*2700, and in this course
Nucleophilic Addition Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
 Lecture 5: bjectives: Nucleophilic Addition eactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: draw the mechanism of a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction with
Lecture 5: bjectives: Nucleophilic Addition eactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: draw the mechanism of a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction with
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis.
 Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
You must have your answers written in PERMANENT ink if you want a regrade!!!! This means no test written in pencil or ERASABLE INK will be regraded.
 NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: hemistry 320N Dr. Brent Iverson 3rd Midterm April 20, 2017 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes Please Note: This test may be a bit long, but
NAME (Print): SIGNATURE: hemistry 320N Dr. Brent Iverson 3rd Midterm April 20, 2017 Please print the first three letters of your last name in the three boxes Please Note: This test may be a bit long, but
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES.
 COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
COURSE OBJECTIVES / OUTCOMES / COMPETENCIES. By the end of the course, students should be able to do the following: See Test1-4 Objectives/Competencies as listed in the syllabus and on the main course
Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Relative Reactivity of carbonyls: Hydration of Ketones and Aldehydes
 Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Weak nucleophiles, such as water, alcohols, and amines, require acid or base catalysis to undergo addition to carbonyl compounds Relative Reactivity
Reversible Additions to carbonyls: Weak Nucleophiles Weak nucleophiles, such as water, alcohols, and amines, require acid or base catalysis to undergo addition to carbonyl compounds Relative Reactivity
Background Information
 ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
ackground nformation ntroduction to Condensation eactions Condensation reactions occur between the α-carbon of one carbonyl-containing functional group and the carbonyl carbon of a second carbonyl-containing
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Answers to HT2, Chemistry A
 Answers to T2, hemistry 302-302A - 2004 1. There are many ways to do these problems - here is just one. For all three parts we can use diphenyl ketone (benzophenone) so let s make that first: 1. 2 Eq.
Answers to T2, hemistry 302-302A - 2004 1. There are many ways to do these problems - here is just one. For all three parts we can use diphenyl ketone (benzophenone) so let s make that first: 1. 2 Eq.
COURSE UNIT DESCRIPTION. Dept. Organic Chemistry, Vilnius University. Type of the course unit
 Course unit title Organic Chemistry II Lecturer(s) Rimantas Vaitkus COURSE UNIT DESCRIPTION Department Dept. Organic Chemistry, Vilnius University Cycle First Type of the course unit Mode of delivery Period
Course unit title Organic Chemistry II Lecturer(s) Rimantas Vaitkus COURSE UNIT DESCRIPTION Department Dept. Organic Chemistry, Vilnius University Cycle First Type of the course unit Mode of delivery Period
ROADMAP FOR REACTIONS Chapter 6
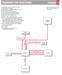 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 6 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition
RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 6 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition
O O O CH 2 O 7. 2 = C=O hydration H B. 6 = reverse aldol H O. 9b = acetal formation add alcohol (step 2)
 1 equences For Practice 1. 1 2 3 7 2 6 5 4 8 9 Possible Key 3 = AD + oxidation 1 2 3 4 5 3 2 1 AD + 7 1 = AD + oxidation 7 = aldol AD 2 = = hydration 2 6 6 = aldol AD + AD 5 5 = β-keto decarboxylation
1 equences For Practice 1. 1 2 3 7 2 6 5 4 8 9 Possible Key 3 = AD + oxidation 1 2 3 4 5 3 2 1 AD + 7 1 = AD + oxidation 7 = aldol AD 2 = = hydration 2 6 6 = aldol AD + AD 5 5 = β-keto decarboxylation
Organic Chemistry CHM 224
 rganic Chemistry CM 224 Final Exam Review Questions This is a compilation example final exam questions. Provide IUPAC names for each of the structures below. 2 ! Propose a structure for the compound that
rganic Chemistry CM 224 Final Exam Review Questions This is a compilation example final exam questions. Provide IUPAC names for each of the structures below. 2 ! Propose a structure for the compound that
The Final Learning Experience
 Chemistry 212 and 300 rganic Chemistry II Winter Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #5 Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions, Sugars & Nucleic Acids The Final Learning Experience Friday, May 5,
Chemistry 212 and 300 rganic Chemistry II Winter Semester 2000 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #5 Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions, Sugars & Nucleic Acids The Final Learning Experience Friday, May 5,
Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones
 Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes (RCHO), with the exception of formaldehyde (H 2 CO), are compounds with both an H and an organic group attached to a carbonyl. Ketones (R 2 CO) are compounds with
Ch 19 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes (RCHO), with the exception of formaldehyde (H 2 CO), are compounds with both an H and an organic group attached to a carbonyl. Ketones (R 2 CO) are compounds with
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
NH 2 O O O O OCH (6 pts) Provide an acceptable name for each of the following compounds: NH 2 COOH HOOC COOH. piperidine
 CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 4 April 1, 2003 Statistics: Average: 87 pts (72%); ighest: 116 pts (97%); Lowest: 49 pts (41%) umber of students performing at or above average: 13 (62%) 1. (9 pts) Mark as true
CEMISTRY 314-01 MIDTERM # 4 April 1, 2003 Statistics: Average: 87 pts (72%); ighest: 116 pts (97%); Lowest: 49 pts (41%) umber of students performing at or above average: 13 (62%) 1. (9 pts) Mark as true
Exam 1 (Monday, July 6, 2015)
 Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections:
 Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections: 9.14-9.19 Aldehydes and ketones are found in many fragrant odors of many fruits, fine perfumes, hormones etc. some examples are listed below. Aldehydes
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections: 9.14-9.19 Aldehydes and ketones are found in many fragrant odors of many fruits, fine perfumes, hormones etc. some examples are listed below. Aldehydes
Carbonyl Condensation Reactions
 24 arbonyl ondensation eactions 24.1 The aldol reaction 24.2 rossed aldol reactions 24.3 Directed aldol reactions 24.4 Intramolecular aldol reactions 24.5 The laisen reaction 24.6 The crossed laisen and
24 arbonyl ondensation eactions 24.1 The aldol reaction 24.2 rossed aldol reactions 24.3 Directed aldol reactions 24.4 Intramolecular aldol reactions 24.5 The laisen reaction 24.6 The crossed laisen and
Chapter 22 The Chemistry of Enolate Ions, Enols, and
 Organic Chemistry, 5th ed. Marc Loudon Chapter 22 The Chemistry of Enolate Ions, Enols, and α,β Unsaturated Carbonyl Compounds Eric J. Kantorowski California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo,
Organic Chemistry, 5th ed. Marc Loudon Chapter 22 The Chemistry of Enolate Ions, Enols, and α,β Unsaturated Carbonyl Compounds Eric J. Kantorowski California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo,
Amines Reading Study Problems Key Concepts and Skills Lecture Topics: Amines: structure and nomenclature
 Amines Reading: Wade chapter 19, sections 19-1-19-19 Study Problems: 19-37, 19-39, 19-40, 19-41, 19-44, 19-46, 19-47, 19-48, 19-51, 19-54 Key Concepts and Skills: Explain how the basicity of amines varies
Amines Reading: Wade chapter 19, sections 19-1-19-19 Study Problems: 19-37, 19-39, 19-40, 19-41, 19-44, 19-46, 19-47, 19-48, 19-51, 19-54 Key Concepts and Skills: Explain how the basicity of amines varies
Keynotes in Organic Chemistry
 Keynotes in Organic Chemistry Second Edition ANDREW F. PARSONS Department of Chemistry, University of York, UK Wiley Contents Preface xi 1 Structure and bonding 1 1.1 Ionic versus covalent bonds 1 1.2
Keynotes in Organic Chemistry Second Edition ANDREW F. PARSONS Department of Chemistry, University of York, UK Wiley Contents Preface xi 1 Structure and bonding 1 1.1 Ionic versus covalent bonds 1 1.2
Suggested solutions for Chapter 30
 s for Chapter 30 30 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this synthesis of a tricyclic aromatic heterocycle. 2 Cl base A simple exercise in the synthesis of a pyridine fused to a pyrrole (or an indole with
s for Chapter 30 30 PRBLEM 1 uggest a mechanism for this synthesis of a tricyclic aromatic heterocycle. 2 Cl base A simple exercise in the synthesis of a pyridine fused to a pyrrole (or an indole with
CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018
 CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018 HW 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. (5 pts each) 1. Which
CH 320/328 N Summer II 2018 HW 1 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. There is only one correct response for each question. (5 pts each) 1. Which
Modern Organic Synthesis an Introduction
 Modern Organic Synthesis an Introduction G. S. Zweifel M. H. Nantz W.H. Freeman and Company Chapter 1 Synthetic Design 1 What is an ideal or viable synthesis, and how does one approach a synthetic project?
Modern Organic Synthesis an Introduction G. S. Zweifel M. H. Nantz W.H. Freeman and Company Chapter 1 Synthetic Design 1 What is an ideal or viable synthesis, and how does one approach a synthetic project?
CHEM 330. Topics Discussed on Oct 5. Irreversible nature of the reaction of carbonyl enolates with the electrophiles discussed on Oct 2
 CEM 330 Topics Discussed on ct 5 Irreversible nature of the reaction of carbonyl enolates with the electrophiles discussed on ct 2 Kinetic control in an irreversible reaction: the product that is obtained
CEM 330 Topics Discussed on ct 5 Irreversible nature of the reaction of carbonyl enolates with the electrophiles discussed on ct 2 Kinetic control in an irreversible reaction: the product that is obtained
B X A X. In this case the star denotes a chiral center.
 Lecture 13 Chirality III October 29, 2013 We can also access chiral molecules through the use of something called chiral auxiliaries, which basically is a chiral attachment that you add to your molecule
Lecture 13 Chirality III October 29, 2013 We can also access chiral molecules through the use of something called chiral auxiliaries, which basically is a chiral attachment that you add to your molecule
Answers to Hour Examination #3, Chemistry 302X, 2006
 Answers to our Examination #, Chemistry 02X, 2006 1. (a). That SN2 shown just can t happen with the required inversion. The back of that methyl group is not reachable by the putative nucleophile, the pi
Answers to our Examination #, Chemistry 02X, 2006 1. (a). That SN2 shown just can t happen with the required inversion. The back of that methyl group is not reachable by the putative nucleophile, the pi
Carbonyl Chemistry IV: Enolate Alkylations and Aldols. Aldol Madness O O O N M + substrate. aldehyde. (Z)-enolate H
 Carbonyl Chemistry IV: nolate Alkylations and Aldols Paul Bracher Chem 30 Section 9 Section Agenda 1) o office hours Thursday 2) The Great Joe Young is covering section next onday 3) andout: Carbonyl Chemistry
Carbonyl Chemistry IV: nolate Alkylations and Aldols Paul Bracher Chem 30 Section 9 Section Agenda 1) o office hours Thursday 2) The Great Joe Young is covering section next onday 3) andout: Carbonyl Chemistry
CuI CuI eage lic R tal ome rgan gbr ommon
 Common rganometallic eagents Li Et 2 Li Mg Et 2 Li alkyllithium rignard Mg Mg Li Zn TF ZnCl 2 TF dialkylzinc Zn 2 2 Zn Li CuI TF ganocuprate CuI 2 2 CuI common electrophile pairings ' Cl ' '' ' ' ' ' '
Common rganometallic eagents Li Et 2 Li Mg Et 2 Li alkyllithium rignard Mg Mg Li Zn TF ZnCl 2 TF dialkylzinc Zn 2 2 Zn Li CuI TF ganocuprate CuI 2 2 CuI common electrophile pairings ' Cl ' '' ' ' ' ' '
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key
 CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
CHM 292 Final Exam Answer Key 1. Predict the product(s) of the following reactions (5 points each; 35 points total). May 7, 2013 Acid catalyzed elimination to form the most highly substituted alkene possible
Aldehydes and Ketones
 9 Aldehydes and Ketones hapter Summary The carbonyl group, =, is present in both aldehydes (=) and ketones ( 2 =). The IUPA ending for naming aldehydes is -al, and numbering begins with the carbonyl carbon.
9 Aldehydes and Ketones hapter Summary The carbonyl group, =, is present in both aldehydes (=) and ketones ( 2 =). The IUPA ending for naming aldehydes is -al, and numbering begins with the carbonyl carbon.
Carbonyl Compounds. Introduction
 Carbonyl Compounds Introduction 1 Introduction Two broad classes of compounds contain the carbonyl group: [1] Compounds that have only carbon and hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbonyl [2] Compounds that
Carbonyl Compounds Introduction 1 Introduction Two broad classes of compounds contain the carbonyl group: [1] Compounds that have only carbon and hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbonyl [2] Compounds that
How to make pyridines: the Hantzsch pyridine synthesis
 ow to make pyridines: the antzsch pyridine synthesis 1191 Zinc in acetic acid (Chapter 24) reduces the oxime to the amine and we can start the synthesis by doing the conjugate addition and then reducing
ow to make pyridines: the antzsch pyridine synthesis 1191 Zinc in acetic acid (Chapter 24) reduces the oxime to the amine and we can start the synthesis by doing the conjugate addition and then reducing
Synthesis of Nitriles a. dehydration of 1 amides using POCl 3 : b. SN2 reaction of cyanide ion on halides:
 I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides
 Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides Alcohols Structure and Bonding Enols and Phenols Compounds having a hydroxy group on a sp 2 hybridized carbon enols and phenols undergo different reactions than alcohols. Chapter
Alcohols, Ethers, & Epoxides Alcohols Structure and Bonding Enols and Phenols Compounds having a hydroxy group on a sp 2 hybridized carbon enols and phenols undergo different reactions than alcohols. Chapter
Luckily this intermediate has three saturated carbons between the carbonyls, which again points to a Michael reaction:
 Retrosynthesis Practice Problems Answer Key October 1, 2013 1. Draw a retrosynthesis for how to make the compound shown below from starting materials with eight or fewer carbon atoms. The first step is
Retrosynthesis Practice Problems Answer Key October 1, 2013 1. Draw a retrosynthesis for how to make the compound shown below from starting materials with eight or fewer carbon atoms. The first step is
