Synthetic possibilities Chem 315 Beauchamp 1
|
|
|
- Walter Clark
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Propose reasonable syntheses f the following target molecules (TM-#). You can use the given starting materials and any typical ganic reagents studied in our course ( even outside our course if you know them). eaction onditions (in our course) Alkane reagents h S/E reagents (react with methyl, primary, secondary, tertiary, allylic, benzylic X patterns via S/E S/E)) a a S S a LiAl a a K a a a hydroxide alkoxides carboxylates enolates hydrogen sulfur anion alkyl sulfur anion phthalimide anion azide Alkene reagents g(ac) ( S / ). g(ac) / ( S / ). g(ac) / ab ab ab. B / z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
2 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Alkyne reagents ( S / ) ( eq) ( eq.) g +. B-. a cat. / epoxide ( eq) ( eq.). a methyl primary X. a aldehyde ketone. a excess (zipper) wkup electrophile Alcohol reagents follow all reactions with a wkup step P S Ts-l, py.. Ts-l, py. a a. a Me o X r / pyridine P 9 0 Fischer 6 ester S. g(ac) r / ( S / ) Jones (- ) l alkene Ts- to ketone aldehyde Friedel-rafts ab eqs.of alkylation (- ) neutralize l Ts (- ) rearrangements possible Epoxides follow all reactions with a wkup step 6 7 Li 8 ( S / ) ( S / ) a/ a/ a a Li (Mg) aqueous acid acidic alcohol hydroxide alkoxide cyanide terminal acetylide enolate ganometallic S ab ab LiAl LiAl nucleophilic hydride nucleophilic deuteride nucleophilic hydride nucleophilic deuteride S Li dithiane anion Aldehyde reagents follow all reactions with a wkup step Li eqs S Li Ts (- ) Ts (- ) a a (Mg) Ph P make ketals make ketals slow addition of acid S Li Wittig reaction enolates & acetals & acetals make cyanohydrins terminal acetylides ganometallic dithiane anion makes alkenes aldol reactions 9 0 Li 6 r /. LA, -78 o Jones mpba p Zn / l a p X oxidize to oxidize to (- ) (- ) LA, -78 o carboxylic acids carboxylic acids make imines make enamines lemmenson reaction Wolff-Kishner rxn make enolates react enolates z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
3 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Ketone reagents follow all reactions with a wkup step Acid reagents Pb(Ac) /Li P (- ) Kochi reaction makes - Friedel-rafts acylation Acid chlide reagents Amides Anhydrides Amines z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
4 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp Ethers itriles Alpha-beta unsaturated carbonyl compounds,-dicarbonyl compounds Aromatic chemistry Template z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
5 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp epresentative X patterns from - 7: (), (), (), (), (8), 6 (7) and (9) examples, not counting stereoisomers such as enantiomers and diastereomers - in our course, many of these can be made from: a. free radical substitution, b. alcohols c. alkenes. You have to know the limitations (our rules) of S / E chemistry (strong vs weak), (me basic vs less basic), substitution patterns, substitution patterns, etc z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
6 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp 6 epresentative patterns from - 7: (), (), (), (), (8), 6 (7) and (9) examples, not counting stereoisomers such as enantiomers and diastereomers - many of these can be made from: a. X compounds, b. alkenes c. carbonyl compounds d. epoxides z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
7 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp 7 epresentative alkene patterns from - many of these can be made from: a. X compounds, b. c. Wittig reaction (= compounds) d. alkynes z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
8 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp 8 epresentative aldehyde and ketone patterns from - many of these can be made from a. alcohols, b. alkynes c. nitriles d. esters e. acid chlides f. carboxylic acids g. alkenes h. other reactions we don't know. The aldehydes can be made into caroboxylic acids, alcohols and alkenes, imines, enamines, enolates, enol ethers, acetals and me. Acids can be made into esters, acid chlides (many possibilities), alcohols, ketones and me. Ketones can be made into alcohols, alkenes, esters, enol ethers, enolates, enamines, imines and me z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
9 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp 9 z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc epresentative acid patterns from -manyofthesecanbemadefroma. o, b. alkenes ( )c
10 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp 0 z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc epresentative amide patterns ( o, o, o, = from - can be made from a. acid chlide +,ammonia a o o amine b. nitriles can make o amides 8 9 0
11 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
12 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp epresentative patterns ( = ) from - 7 skeletons: (), (), (), (), (8), 6 (7) and (9) examples, not counting stereoisomers such as enantiomers and diastereomers - many of these can be made from: a. X compounds and. phthalimidate b. a. a LiAl. wkup c. nitrile + LiAl wkup d. aldehydes ketones +, (-) a B. wkup itter rxn problem itter rxn f us problem f us itter rxn itter rxn 9 0 problem f us itter rxn itter rxn itter rxn problem f us itt er rxn problem f us itter rxn z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
13 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp The following are useful transfmations using the given alkane starting points. eagents are not given over the arrows, but possibilities are suggested below each list by number. h P S a. Tsl/py b. a S Li (Mg) a S.. a Li Mg Al LiAl metal a metal (aromatic chem) a a a a a a r /py r / X (P) (Jones) (S ). a X (S ) l Ts (- ) Fischer ester syn LiAl. ab P(Ph) r /. Li (Mg) p = (Jones) Wittig rxn (- ) imines a a l = unstable. a X (S ) only. LiAl Sl (but no good f acid). eqs. Li Assume all reactions finish with a wkup step. Assume all reactions finish with a wkup step. S Li (Mg) h. a (S ) (S ) a a S.. a Li Mg metal metal LiAl a a a a K Al (aromatic chem) Ts 6 P S a. Tsl/py b. a r /py (P). a r / X (Jones) X (=Me, o (= o, o X, S ) X, S ) a S / (E rxns) 6 Ts-l pyridine z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
14 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp 6 7. LiAl. ab P(Ph) Wittig rxn mpba p = (- ) imines.. Li (Mg) 6 a a 7 z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
15 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp eaction Wksheet Possible Approaches. a + equivalents. a +. K + h available. a + equivalents. a +. K + h available a / Pd / quinoline (Lindlar's cat.) Pd / quinoline (Lindlar's cat.) Use any of these. Pd / 6 LiAl Use either of these. 6 S / S 7 Pd / / SS 7 Pd / a h 8 available 9. B / 9 r pyridine 9., -78 o S has to be made 0 + / (g + cat.) Either of these. 0 r / pyridine r / 0., -78 o S has to be made. B / a + + /. g(ac) / ab Any of these..lial ( ab ) Any of these.. a z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
16 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp 6. B / P. Ts-l, py. a Any of these. h 6. B / ( is prepared in 8) a 8,9,0,. B The other ethers / are prepared in a similar way using S and S reactions. f 8 f a f. B / 8 f. a. a r / 9,6,7,8,9,0 (similar). a. a (from ) a a a h available. a. a 6 is similar 6 6 is similar. B / available h.k + ( ) a mpba mpba mpba. /. / a a. / a z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
17 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp 7 0. a + / / 7 7. a 7. a 7 (from ) Ts. a 7 7 / / S 8 and S. a / / / / / / / / and SS a 8 S 0 and S a 9 + / / + / 8 / 9 / / 6 /. a 8. a /. a a 9 7 and 8 are similar with mpba. / a z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
18 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp 8. a 9. a 9 (from ) a 6. a 6. a 0 6. a 6. Li+ = (LA) Li+ = (LA) 9. Li+ = (LA). Li+ = (LA) Li+ = (LA) 70. Li+ = (LA). Li+ = (LA). Li+ = (LA) S (also S).LiAl 7.LiAl.LiAl 7 ( ab ) ( ab ) (also SS) ( ab ) 8 7.LiAl ( ab ) 9.LiAl 76 7 ( ab ) 77.LiAl ( ab ) 9 78.LiAl ( ab ) 0. Li+ = (LA) Li+ = (LA) 8. Li+ = (LA) 8., -78 o S., -78 o ab 8 8., -78 o / 8 z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
19 Synthetic possibilities hem Beauchamp 9. B / + / (g + cat.) r / pyridine r / r pyridine., -78 o S a + + /. B /. B / of P. Ts-l, py. a. a.lial. a. a. B /. B /. a (from ). a r / a h / + / / Ts. a. a 7., -78 o /., -78 o ab equivalents + / /.LiAl ( ab ) mpba. / a similar to 0. a 9 ( ab ). g(ac) / ab. Li+ = (LA) z:\files\classes\\ andouts\synthesis target molecules W 0doc
Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions.
 ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1 Available chemicals from the catalog (the starting sources of carbon compounds will continually decrease as we learn new reactions. ources of
Products from reactions of carbon nucleophiles and carbon electrophiles used in the 14 C Game and our course:
 synthesis strategies, hem / / Beauchamp roducts from reactions of carbon nucleophiles and carbon electrophiles used in the Game and our course: arbon electrophiles methyl primary organolithium reagents
synthesis strategies, hem / / Beauchamp roducts from reactions of carbon nucleophiles and carbon electrophiles used in the Game and our course: arbon electrophiles methyl primary organolithium reagents
S N 2 and E2 Mechanisms (strong base/nucleophile competition reacting at a carbon or reacting at a proton)
 Electrophile (Lewis Acid) = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor (can also be an acidic proton = onsted acid) ucleophile (Lewis Base) = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron pair
Electrophile (Lewis Acid) = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor (can also be an acidic proton = onsted acid) ucleophile (Lewis Base) = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron pair
Chem 315/316 Reactions. Bromo organic compounds C1 & C2 carbon skeletons C3 carbon skeletons C4 carbon skeletons. Alcohols. Chem 316 / Beauchamp 1
 hem 316 / Beauchamp 1 hem 315/316 eactions Name available sources of carbon 4 3 NaN methyl 3 2 ethyl 3 2 2 n-propyl 3 3 isopropyl 2 3 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 3 n-butyl sec butyl t-butyl phenyl available until topic
hem 316 / Beauchamp 1 hem 315/316 eactions Name available sources of carbon 4 3 NaN methyl 3 2 ethyl 3 2 2 n-propyl 3 3 isopropyl 2 3 2 3 3 2 2 3 3 3 n-butyl sec butyl t-butyl phenyl available until topic
Nucleophilic Substitution & Elimination Chemistry 1
 ucleophilic Substitution & Elimination hemistry 1 What kind of mechanisms are possible? What is the major mechanism occuring? Write in ALL mechanism details (lone pairs, formal charge, curved arrows, etc.).
ucleophilic Substitution & Elimination hemistry 1 What kind of mechanisms are possible? What is the major mechanism occuring? Write in ALL mechanism details (lone pairs, formal charge, curved arrows, etc.).
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 15, 2010 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
CEM 203 Final Exam December 15, 2010 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test contains 15 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 16 2. / 15 3. / 24
New bond. ph 4.0. Fischer esterification. New bond 2 O * New bond. New bond H 2N. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. New C-C bond. O Cl.
 Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Iverson C 0N KRE Table: For use in synthesis problems, count carbons in products and starting materials then identify location(s) of new s, especially C-C or C=C s. With that information, use the following
Suggested solutions for Chapter 28
 s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
s for Chapter 28 28 PBLEM 1 ow would you make these four compounds? Give your disconnections, explain why you chose them and then give reagents for the. 2 2 Me S Exercises in basic one- group C X disconnections.
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [Chapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ' ketone aldehyde f both aldehydes and ketones, the parent chain is the longest
Electrophile = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor = Lewis acid, (often an acidic proton)
 314 Arrow Pushing practice/eauchamp 1 Electrophile = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor = Lewis acid, (often an acidic proton) ucleophile = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron
314 Arrow Pushing practice/eauchamp 1 Electrophile = electron loving = any general electron pair acceptor = Lewis acid, (often an acidic proton) ucleophile = nucleus/positive loving = any general electron
Chapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones
 hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [hapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ketone ' aldehyde 2. eview of the Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones Br Br f
hapter 20: Aldehydes and Ketones [hapter 20 Sections: 20.1-20.7, 20.9-10.10, 20.13] 1. Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones ketone ' aldehyde 2. eview of the Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones Br Br f
Appendix A. Common Abbreviations, Arrows, and Symbols. Abbreviations
 smi97462_apps.qxd 12/6/04 1:09 PM Page A-1 Appendix A ommon Abbreviations, Arrows, and Symbols Abbreviations Ac acetyl, 3 BBN 9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane BINAP 2,2'-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphthyl
smi97462_apps.qxd 12/6/04 1:09 PM Page A-1 Appendix A ommon Abbreviations, Arrows, and Symbols Abbreviations Ac acetyl, 3 BBN 9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane BINAP 2,2'-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphthyl
These same reaction schemes are available without the mechanistic details, so you can practice filling in those details.
 314/315 reactions and mechanisms through topic 11 and some of topic 12 1 These same reaction schemes are available without the mechanistic details, so you can practice filling in those details. Problems
314/315 reactions and mechanisms through topic 11 and some of topic 12 1 These same reaction schemes are available without the mechanistic details, so you can practice filling in those details. Problems
CHEM 203. Midterm Exam 1 October 31, 2008 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Midterm Exam 1 ctober 31, 2008 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This exam contains 8 pages Time: 1h 30 min 1. / 15 2. / 16 3. /
CEM 203 Midterm Exam 1 ctober 31, 2008 Your name: ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This exam contains 8 pages Time: 1h 30 min 1. / 15 2. / 16 3. /
Nomenclature Question
 Topic 13: i-licker Slides Beauchamp 1 omenclature Question 2 2 a. 1,2-diamino-5,11-dioxo-6-isopropoxy-7-hydroxy-9-cyanoundec-3E-en-1-one b. 3-cyano-5-hydroxy-6-isopropoxy-7,11-dioxo-10,11-diaminoundec-8E-enal
Topic 13: i-licker Slides Beauchamp 1 omenclature Question 2 2 a. 1,2-diamino-5,11-dioxo-6-isopropoxy-7-hydroxy-9-cyanoundec-3E-en-1-one b. 3-cyano-5-hydroxy-6-isopropoxy-7,11-dioxo-10,11-diaminoundec-8E-enal
CHEM 234: Organic Chemistry II Reaction Sheets
 EM234:rganichemistry eactionsheets ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: Grignards and reducing agents u: u u u: u u = or = or l u u u ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: oxygen and nitrogen nucleophiles:
EM234:rganichemistry eactionsheets ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: Grignards and reducing agents u: u u u: u u = or = or l u u u ucleophilic addition at carbonyl groups: oxygen and nitrogen nucleophiles:
Chapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones
 hapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones arbonyl Groups polarized (1) Aldehydes and Ketones ' aldehydes ketones : and : are poor leaving groups (2) arboxylic Acid Derivatives l ' ' 2 carboxylic acid substituent
hapter 17 Aldehydes and Ketones arbonyl Groups polarized (1) Aldehydes and Ketones ' aldehydes ketones : and : are poor leaving groups (2) arboxylic Acid Derivatives l ' ' 2 carboxylic acid substituent
Lecture Notes Chemistry Mukund P. Sibi Lecture 36 Synthesis of Amines
 Lecture otes hemistry 42-2008 Mukund P. Sibi Synthesis of Amines Amines can be prepared from a variety of starting materials. All of these methods involve functional group transformations. The main methods
Lecture otes hemistry 42-2008 Mukund P. Sibi Synthesis of Amines Amines can be prepared from a variety of starting materials. All of these methods involve functional group transformations. The main methods
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones
 Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Lecture 3: Aldehydes and ketones I want to start by talking about the mechanism of hydroboration/ oxidation, which is a way to get alcohols from alkenes. This gives the anti-markovnikov product, primarily
Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. Recognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 12: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. Recognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chem 342 Organic Chemistry II Final Exam 13 May 2009
 hem 342 rganic hemistry II Final Exam 13 May 2009 KEY Please read through each question carefully and answer in the spaces provided. A good strategy is to go through the test and answer all the questions
hem 342 rganic hemistry II Final Exam 13 May 2009 KEY Please read through each question carefully and answer in the spaces provided. A good strategy is to go through the test and answer all the questions
Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
 Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Why this Chapter? Much of organic chemistry involves the chemistry of carbonyl compounds Aldehydes/ketones are intermediates in synthesis of pharmaceutical
Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions Why this Chapter? Much of organic chemistry involves the chemistry of carbonyl compounds Aldehydes/ketones are intermediates in synthesis of pharmaceutical
Chem 316/422 Beauchamp 1 Match the step number in the synthesis with the letter of the reagents listed just below.
 hem 316/422 Beauchamp 1 Match the step number in the synthesis with the letter of the reagents listed just below. TP l Et step 8 4 5 eagents used in synthesis A B D E F a DMF (solvent) 1. (i-pr) 2 Li (LDA)/TF
hem 316/422 Beauchamp 1 Match the step number in the synthesis with the letter of the reagents listed just below. TP l Et step 8 4 5 eagents used in synthesis A B D E F a DMF (solvent) 1. (i-pr) 2 Li (LDA)/TF
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY. Fifth Edition. Stanley H. Pine
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Fifth Edition Stanley H. Pine Professor of Chemistry California State University, Los Angeles McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Fifth Edition Stanley H. Pine Professor of Chemistry California State University, Los Angeles McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London
Chapter 17: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 17: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 17: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chem 263 March 7, 2006
 Chem 263 March 7, 2006 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group, in which the carbon atom is doubly bonded to an oxygen atom. The carbonyl group is highly polarized, with a
Chem 263 March 7, 2006 Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group, in which the carbon atom is doubly bonded to an oxygen atom. The carbonyl group is highly polarized, with a
Four new mechanisms to learn: S N 2 vs E2 and S N 1 vs E1
 cleophilic ubstitution & Elimination hemistry 1 Four new mechanisms to learn: vs E2 and 1 vs E1 = substitution = a leaving group () is lost from a carbon atom () and replaced by nucleophile (:) = nucleophilic
cleophilic ubstitution & Elimination hemistry 1 Four new mechanisms to learn: vs E2 and 1 vs E1 = substitution = a leaving group () is lost from a carbon atom () and replaced by nucleophile (:) = nucleophilic
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
2Dstructuredrawing Chem314 Beauchamp
 2Dstructuredrawing hem314 Beauchamp 3 2 3 3 2 2 3 2 2 3 2 2 (neutral) (cation) (anion) (free radical) use zig-zag drawing for sp 3 chains 1 o carbocation 1 o carbanion 1 o free radical 3 3 3 3 3 3 (cation)
2Dstructuredrawing hem314 Beauchamp 3 2 3 3 2 2 3 2 2 3 2 2 (neutral) (cation) (anion) (free radical) use zig-zag drawing for sp 3 chains 1 o carbocation 1 o carbanion 1 o free radical 3 3 3 3 3 3 (cation)
Nucleophilic Substitution & Elimination Chemistry Beauchamp 1
 ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination hemistry Beauchamp 1 Problem 1 - ow can you tell whether the 2 reaction occurs with front side attack, backside attack or front and backside attack? Use the two molecules
ucleophilic ubstitution & Elimination hemistry Beauchamp 1 Problem 1 - ow can you tell whether the 2 reaction occurs with front side attack, backside attack or front and backside attack? Use the two molecules
Synthesis of Nitriles a. dehydration of 1 amides using POCl 3 : b. SN2 reaction of cyanide ion on halides:
 I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
I. Nitriles Nitriles consist of the CN functional group, and are linear with sp hybridization on C and N. Nitriles are non-basic at nitrogen, since the lone pair exists in an sp orbital (50% s character
Chem 263 Nov 14, e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents)
 hem 263 ov 14, 2013 More examples: e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents) Br 2 hv Br a 2 r 4 S 2 or swern oxidation Mg Li 0 0 MgBr Li e.g. : Fill the reagents (any reagents
hem 263 ov 14, 2013 More examples: e.g.: Fill the reagents to finish the reactions (only inorganic reagents) Br 2 hv Br a 2 r 4 S 2 or swern oxidation Mg Li 0 0 MgBr Li e.g. : Fill the reagents (any reagents
CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK
 Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Lecture Topics: CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Module7: Hydrogenation of Alkenes Hydrogenation - syn and anti- addition - hydrogenation of alkynes - synthesis of cis-alkenes -synthesis of trans-alkenes Text sections:
Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Dr. Sapna Gupta Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated.
Aldehydes and Ketones Reactions Dr. Sapna Gupta Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones Nucleophilic Addition A strong nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming an alkoxide ion that is then protonated.
CH 3 CHCH 3 CH 3 CHCH 3 Isopropyl cation. Oxomium ion intermediate. intermediate (an electrophile)
 Understanding (as opposed to memorizing) mechanisms is critical to mastering organic chemistry. Although the mechanisms you encounter throughout the course may seem entirely different, they are actually
Understanding (as opposed to memorizing) mechanisms is critical to mastering organic chemistry. Although the mechanisms you encounter throughout the course may seem entirely different, they are actually
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
ucleophilic Acyl Substitution hapter 20 arboxylic Acid Derivatives ucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y (1) need to have Y as a u Y u u + Y (2) could not happen with aldehydes or ketones as : and : are poor
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II
 KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
Organic Chemistry Curriculum Content Outline
 Organic Chemistry 2014-15 Curriculum Content Outline CHEM 0203: Organic Structure and Reactivity 1. Structure & Bonding (Brief Review from General Chemistry) a. Ionic & Covalent Bonding b. Lewis Structures
Organic Chemistry 2014-15 Curriculum Content Outline CHEM 0203: Organic Structure and Reactivity 1. Structure & Bonding (Brief Review from General Chemistry) a. Ionic & Covalent Bonding b. Lewis Structures
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Loudon Chapter 19 Review: Aldehydes and Ketones CHEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall Page 1
 Loudon Chapter 19 eview: Aldehydes and Ketones CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 Beginning with this chapter, we re looking at a very important functional group: the carbonyl. We ve seen
Loudon Chapter 19 eview: Aldehydes and Ketones CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 Beginning with this chapter, we re looking at a very important functional group: the carbonyl. We ve seen
acetaldehyde (ethanal)
 hem 263 Nov 2, 2010 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alkenes zonolysis 1. 3 2. Zn acetone 1. 3 2. Zn acetone acetaldehyde (ethanal) Mechanism: 3 3 3 + - oncerted reaction 3 3 3 + ozonide (explosive)
hem 263 Nov 2, 2010 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alkenes zonolysis 1. 3 2. Zn acetone 1. 3 2. Zn acetone acetaldehyde (ethanal) Mechanism: 3 3 3 + - oncerted reaction 3 3 3 + ozonide (explosive)
Alpha Substitution and Condensations of Enols and Enolate Ions. Alpha Substitution
 Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Alpha Substitution and ondensations of Enols and Enolate Ions hap 23 W: 27, 28, 30, 31, 37, 39, 42-44, 47, 51, 54-56 Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,
Additions to the Carbonyl Groups
 Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups Nucleophilic substitution (S N 2andS N 1) reaction occurs at sp3 hybridized carbons with electronegative leaving groups Why? The carbon is electrophilic! Addition
Chapter 18 Additions to the Carbonyl Groups Nucleophilic substitution (S N 2andS N 1) reaction occurs at sp3 hybridized carbons with electronegative leaving groups Why? The carbon is electrophilic! Addition
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Aldehydes are named by replacing the -e of the corresponding parent alkane with -al
When we deprotonate we generate enolates or enols. Mechanism for deprotonation: Resonance form of the anion:
 Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Lecture 5 Carbonyl Chemistry III September 26, 2013 Ketone substrates form tertiary alcohol products, and aldehyde substrates form secondary alcohol products. The second step (treatment with aqueous acid)
Mechanism Summary for A-level AQA Chemistry
 Mechanism Summary for Alevel AQA hemistry Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with omine Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with sulphuric acid 3 S 2 3 3 S 2 S 2 Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with hydrogen
Mechanism Summary for Alevel AQA hemistry Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with omine Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with sulphuric acid 3 S 2 3 3 S 2 S 2 Electrophilic Addition of Alkenes with hydrogen
Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II
 Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
Chapter 18: Carbonyl Compounds II Learning bjectives: 1. ecognize and assign names to aldehydes and ketones. 2. Write the mechanism for nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic addition-elimination reactions
ORGANIC - CLUTCH CH ALDEHYDES AND KETONES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALDEHYDE NOMENCLATURE Replace the suffix of the alkane -e with the suffix On the parent chain, the carbonyl is always terminal, and receive a location As substituents, they
Carbon-heteroatom single bonds basic C N C X. X= F, Cl, Br, I Alkyl Halide C O. epoxide Chapter 14 H. alcohols acidic H C S C. thiols.
 hapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols 13.1 Structure and Properties of Alcohols Alkanes arbon - arbon Multiple Bonds arbon-heteroatom single bonds basic Alkenes X X= F, l,, I Alkyl alide amines hapter 23 nitro
hapter 13: Alcohols and Phenols 13.1 Structure and Properties of Alcohols Alkanes arbon - arbon Multiple Bonds arbon-heteroatom single bonds basic Alkenes X X= F, l,, I Alkyl alide amines hapter 23 nitro
Exam 1 (Monday, July 6, 2015)
 Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Chem 231 Summer 2015 Assigned Homework Problems Last updated: Friday, July 24, 2015 Problems Assigned from Essential Organic Chemistry, 2 nd Edition, Paula Yurkanis Bruice, Prentice Hall, New York, NY,
Module9. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy - Chemical shift - Integration of signal area
 1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
1 CHEMISTRY 263 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: Module7. Hydrogenation of Alkenes The Function of the Catalyst - Syn and anti- addition Hydrogenation of Alkynes - Syn- addition of hydrogen: Synthesis of cis-alkenes
Chapter 19. Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions. ß-dicarbonyl compounds. Why are ß-dicarbonyls useful?
 Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Chapter 19 Synthesis and Reactions of b-dicarbonyl Compounds: More Chemistry of Enolate Anions ß-dicarbonyl compounds Two carbonyl groups separated by a carbon Three common types ß-diketone ß-ketoester
Chapter 22: Amines. Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH 3. Nitrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic
 hapter 22: Amines. rganic derivatives of ammonia, 3. itrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic 22.1: Amines omenclature. (please read) sp 3 Amines are classified
hapter 22: Amines. rganic derivatives of ammonia, 3. itrogen atom have a lone pair of electrons, making the amine both basic and nucleophilic 22.1: Amines omenclature. (please read) sp 3 Amines are classified
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections:
 Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections: 9.14-9.19 Aldehydes and ketones are found in many fragrant odors of many fruits, fine perfumes, hormones etc. some examples are listed below. Aldehydes
Chapter 9 Aldehydes and Ketones Excluded Sections: 9.14-9.19 Aldehydes and ketones are found in many fragrant odors of many fruits, fine perfumes, hormones etc. some examples are listed below. Aldehydes
Tips for taking exams in 852
 Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Comprehensive Tactical Methods in rganic Synthesis W. D. Wulff 1) Know the relative reactivity of carbonyl compounds Tips for taking exams in 852 Cl > > ' > > ' N2 eg: 'Mg Et ' 1equiv. 1equiv. ' ' Et 50%
Loudon Chapter 23 Review: Amines CHEM 3331, Jacquie Richardson, Fall Page 1
 Loudon Chapter 23 eview: Amines CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions
Loudon Chapter 23 eview: Amines CEM 3331, Jacquie ichardson, Fall 2010 - Page 1 This chapter is about the chemistry of nitrogen. We ve seen it before in several places, but now we can look at several reactions
1/4/2011. Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds
 Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Chapter 18 Aldehydes and Ketones Reaction at the -carbon of carbonyl compounds The Acidity of the Hydrogens of Carbonyl Compounds: Enolate Anions Hydrogens on carbons to carbonyls are unusually acidic
Physical Properties. Alcohols can be: CH CH 2 OH CH 2 CH 3 C OH CH 3. Secondary alcohol. Primary alcohol. Tertiary alcohol
 Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Chapter 10: Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols 100 Physical Properties Alcohols can be: CH 3 CH 3 CH CH 2 OH * Primary alcohol CH 3 OH CH * CH 2 CH 3 Secondary alcohol CH 3 CH 3 * C OH CH 3 Tertiary alcohol
Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy
 By Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College of Science, King Saud University http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/melnewehy Aldehydes and Ketones 1 Structure of Aldehydes and Ketones - Aldehydes and ketones
By Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College of Science, King Saud University http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/melnewehy Aldehydes and Ketones 1 Structure of Aldehydes and Ketones - Aldehydes and ketones
18.8 Oxidation. Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium
 18.8 Oxidation Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium Test for detecting aldehydes Tollens reagent to prevent precipitation of the insoluble silver oxide, a complexing agent is added: ammonia
18.8 Oxidation Oxidation by silver ion requires an alkaline medium Test for detecting aldehydes Tollens reagent to prevent precipitation of the insoluble silver oxide, a complexing agent is added: ammonia
Chapter 11 Reaction of Alcohols
 Chapter 11 eaction of Alcohols xidation of alcohols Alcohols are at the same oxidation level as alkenes Therefore alkenes can be converted to alcohols with acidic water PDC or PCC 2 C C 2 3 + X 3 C 3 C
Chapter 11 eaction of Alcohols xidation of alcohols Alcohols are at the same oxidation level as alkenes Therefore alkenes can be converted to alcohols with acidic water PDC or PCC 2 C C 2 3 + X 3 C 3 C
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis.
 Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
Objective 14. Develop synthesis strategies for organic synthesis. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features and reactive sites (alpha C, beta C, LG, etc.) ID Nu - and E + use curved arrows to show
Detailed Course Content
 Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Chapter 16. Aldehydes and Ketones I. Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl Group. Physical Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones. Synthesis of Aldehydes
 Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Aldehydes replace the -e of the parent alkane with -al The functional group needs no number Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl
Nomenclature of Aldehydes and Ketones Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones I. Aldehydes replace the -e of the parent alkane with -al The functional group needs no number Nucleophilic Addition to the Carbonyl
CH 19: Aldehydes and Ketones
 rganic hemistry otes by Jim Maxka 19: Aldehydes and Ketones Topics aming, structure, and properties Formation of = eactions with weak nucleophiles: and Derivatives: imines and enamines. eactions with strong
rganic hemistry otes by Jim Maxka 19: Aldehydes and Ketones Topics aming, structure, and properties Formation of = eactions with weak nucleophiles: and Derivatives: imines and enamines. eactions with strong
Synthesis of Amines Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction II. Reductive Amination
 Synthesis of Amines I. Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction Amines can be alkylated in SN2 fashion by alkyl halides; primary halides are best for this purpose. This is not a practical reaction for formation
Synthesis of Amines I. Amine Alkylation by SN2 reaction Amines can be alkylated in SN2 fashion by alkyl halides; primary halides are best for this purpose. This is not a practical reaction for formation
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes. 2. Radical Substitution with Alkenes. 3. Electrophilic Addition
 1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
1. Radical Substitution on Alkanes Only Cl and Br are useful at the laboratory level. Alkane reactivity: tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl Numbers below products give their relative yield. Relative
Aldehydes and Ketones
 Aldehydes and Ketones Preparation of Aldehydes xidation of Primary Alcohols --- 2 P 1o alcohol ydroboration of a Terminal Alkyne, followed by Tautomerization --- 1. B 3, TF 2. 2 2, K 2 terminal alkyne
Aldehydes and Ketones Preparation of Aldehydes xidation of Primary Alcohols --- 2 P 1o alcohol ydroboration of a Terminal Alkyne, followed by Tautomerization --- 1. B 3, TF 2. 2 2, K 2 terminal alkyne
Learning Guide for Chapter 15 - Alcohols (II)
 Learning Guide for Chapter 15 - Alcohols (II) I. Introduction to alcohol reactivity II. Reactions of alcohols with acids III. Reactions of alcohols with electrophiles alogenated phosphorus and sulfur compounds
Learning Guide for Chapter 15 - Alcohols (II) I. Introduction to alcohol reactivity II. Reactions of alcohols with acids III. Reactions of alcohols with electrophiles alogenated phosphorus and sulfur compounds
Chem 263 Nov 7, elimination reaction. There are many reagents that can be used for this reaction. Only three are given in this course:
 hem 263 Nov 7, 2013 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alcohols xidation of Alcohols [] must have at least 1 E elimination reaction [] = oxidation; removal of electrons [] = reduction; addition
hem 263 Nov 7, 2013 Preparation of Ketones and Aldehydes from Alcohols xidation of Alcohols [] must have at least 1 E elimination reaction [] = oxidation; removal of electrons [] = reduction; addition
When H and OH add to the alkyne, an enol is formed, which rearranges to form a carbonyl (C=O) group:
 Next Up: Addition of, : The next two reactions are the Markovnikov and non-markovnikov additions of and to an alkyne But you will not see alcohols form in this reaction! When and add to the alkyne, an
Next Up: Addition of, : The next two reactions are the Markovnikov and non-markovnikov additions of and to an alkyne But you will not see alcohols form in this reaction! When and add to the alkyne, an
ζ ε δ γ β α α β γ δ ε ζ
 hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
hem 263 Nov 17, 2016 eactions at the α-arbon The alpha carbon is the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. Beta is the next one, followed by gamma, delta, epsilon, and so on. 2 ε 2 δ 2 γ 2 2 β α The
Hyperlearning MCAT Instructor Qualifying Exam Organic Chemistry
 Hyperlearning MCAT Instructor Qualifying Exam Organic Chemistry 30 Questions (5 pages); Time limit = 45 minutes Use of books or notes is not permitted. 1. When analyzed with a polarimeter, which of the
Hyperlearning MCAT Instructor Qualifying Exam Organic Chemistry 30 Questions (5 pages); Time limit = 45 minutes Use of books or notes is not permitted. 1. When analyzed with a polarimeter, which of the
O C. Aldehyde: O C H 3 CH 2 C H propanal propionaldehyde. O C H 3 CH 2 C CH 2 CH 3 3-pentanone diethylketone
 Aldehydes and Ketones Both contain the functional group Aldehyde: R Ketone R R' Aldehydes omenclature. IUPA: drop the 'e' from the name of the alkane and add 'al'. There are also common names which are
Aldehydes and Ketones Both contain the functional group Aldehyde: R Ketone R R' Aldehydes omenclature. IUPA: drop the 'e' from the name of the alkane and add 'al'. There are also common names which are
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006
 Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
Chem 263 Notes March 2, 2006 Average for the midterm is 102.5 / 150 (approx. 68%). Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones There are several methods to prepare aldehydes and ketones. We will only deal with
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 18, 2013 ANSWERS. This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Your name: Final Exam December 18, 2013 ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3.
CEM 203 Your name: Final Exam December 18, 2013 ANSWERS This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3.
Keynotes in Organic Chemistry
 Keynotes in Organic Chemistry Second Edition ANDREW F. PARSONS Department of Chemistry, University of York, UK Wiley Contents Preface xi 1 Structure and bonding 1 1.1 Ionic versus covalent bonds 1 1.2
Keynotes in Organic Chemistry Second Edition ANDREW F. PARSONS Department of Chemistry, University of York, UK Wiley Contents Preface xi 1 Structure and bonding 1 1.1 Ionic versus covalent bonds 1 1.2
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Why this Chapter? Carboxylic acids present in many industrial processes and most biological processes They are the starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Why this Chapter? Carboxylic acids present in many industrial processes and most biological processes They are the starting materials from which other acyl derivatives are
I. Write Structures for the compounds named below: (12 points) H 2 N NH 2. Acetone Hydrazine Cyclohexane carbaldehyde H 3 C
 I. Write Structures for the compounds named below: (12 points) 3 2 N N 2 Acetone ydrazine yclohexane carbaldehyde N P( 6 5 ) 3 3 An ethyl ylide of Any imine 3-xo-6-phenylhexanal triphenylphosphine II.
I. Write Structures for the compounds named below: (12 points) 3 2 N N 2 Acetone ydrazine yclohexane carbaldehyde N P( 6 5 ) 3 3 An ethyl ylide of Any imine 3-xo-6-phenylhexanal triphenylphosphine II.
CHEM 203. Final Exam December 18, This a closed-notes, closed-book exam. You may use your set of molecular models
 CEM 203 Final Exam December 18, 2013 Your name: This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3. / 30 4.
CEM 203 Final Exam December 18, 2013 Your name: This a closed-notes, closed-book exam You may use your set of molecular models This test consists of 10 pages Time: 2h 30 min 1. / 20 2. / 20 3. / 30 4.
Alcohol Synthesis. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Alcohol Synthesis Dr. Sapna Gupta Synthesis of Alcohols Alcohols can be synthesized from several functional groups. Nucleophilic substitution of O - on alkyl halide ydration of alkenes water in acid solution
Alcohol Synthesis Dr. Sapna Gupta Synthesis of Alcohols Alcohols can be synthesized from several functional groups. Nucleophilic substitution of O - on alkyl halide ydration of alkenes water in acid solution
TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See
 Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
 Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
 Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Nomenclature: In carboxylic acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters and amides, the parent is the carboxylic acid. In each case be sure
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Nomenclature: In carboxylic acid chlorides, anhydrides, esters and amides, the parent is the carboxylic acid. In each case be sure
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
 Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic
ROADMAP FOR REACTIONS Chapter 6
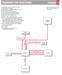 RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 6 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition
RADMAP FR REACTINS Chapter 6 (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) (F) (G) (H) (I) (J) (K) (L) (M) (N) () Regiochemistry: Markovnikov addition to a bond Stereochemistry: anti-addition Regiochemistry: non-markovnikov addition
Carbonyl Chemistry IV + C O C. Lecture 10. Chemistry /30/02
 arbonyl hemistry IV Ō - + Lecture 10 Addition of Nitrogen Nucleophiles Primary Amines RN 2 Imines Secondary Amines R 2 N Enamines ydrazine derivatives RNN 2 ydrazones ydroxyl Amine N 2 ximes Imine Formation
arbonyl hemistry IV Ō - + Lecture 10 Addition of Nitrogen Nucleophiles Primary Amines RN 2 Imines Secondary Amines R 2 N Enamines ydrazine derivatives RNN 2 ydrazones ydroxyl Amine N 2 ximes Imine Formation
b.p.=100 C b.p.=65 C b.p.=-25 C µ=1.69 D µ=2.0 D µ=1.3 D
 Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Alcohols I eading: Wade chapter 10, sections 10-1- 10-12 Study Problems: 10-35, 10-37, 10-38, 10-39, 10-40, 10-42, 10-43 Key Concepts and Skills: Show how to convert alkenes, alkyl halides, and and carbonyl
Cape Cod Community College
 Cape Cod Community College Departmental Syllabus Prepared by the Department of Natural Sciences & Applied Technology Date of Departmental Approval: February 3, 2014 Date Approved by Curriculum and Programs:
Cape Cod Community College Departmental Syllabus Prepared by the Department of Natural Sciences & Applied Technology Date of Departmental Approval: February 3, 2014 Date Approved by Curriculum and Programs:
Chapter 9 Alkynes. Introduction
 hapter 9 Alkynes Introduction Alkynes contain a triple bond. General formula is n 2n-2. Two elements of unsaturation for each triple bond. MST reactions are like alkenes: addition and oxidation. Some reactions
hapter 9 Alkynes Introduction Alkynes contain a triple bond. General formula is n 2n-2. Two elements of unsaturation for each triple bond. MST reactions are like alkenes: addition and oxidation. Some reactions
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 6 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Oxidation States Easy for inorganic salts: CrO 4 2- reduced to Cr 2 O 3. KMnO 4 reduced to MnO 2. Oxidation: Gain of O,
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 6 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Oxidation States Easy for inorganic salts: CrO 4 2- reduced to Cr 2 O 3. KMnO 4 reduced to MnO 2. Oxidation: Gain of O,
(Neither an oxidation or reduction: Addition or loss of H +, H 2 O, HX).
 eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
eactions of Alcohols Alcohols are versatile organic compounds since they undergo a wide variety of transformations the majority of which are either oxidation or reduction type reactions. xidation is a
Chem 345 Reaction List: Chem 343 Reactions: Page 1 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes).
 Chem 345 eaction List: Chem 343 eactions: Page 1 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). uc - optically active LG 2 optically active uc Alpha carbon (carbon attached to
Chem 345 eaction List: Chem 343 eactions: Page 1 (You do not need to know the mechanism for the reactions in the boxes). uc - optically active LG 2 optically active uc Alpha carbon (carbon attached to
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids
 1 Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids I. Introduction: Carboxylic acid structure: Classification of carboxylic acids: A carboxylic acid donates protons by the heterocyclic cleavage of the O-H bond, generating
1 Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids I. Introduction: Carboxylic acid structure: Classification of carboxylic acids: A carboxylic acid donates protons by the heterocyclic cleavage of the O-H bond, generating
Chapter 18: Ketones and Aldehydes. I. Introduction
 1 Chapter 18: Ketones and Aldehydes I. Introduction We have already encountered numerous examples of this functional group (ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, etc). The three-dimensional
1 Chapter 18: Ketones and Aldehydes I. Introduction We have already encountered numerous examples of this functional group (ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, etc). The three-dimensional
Chemistry 335 Supplemental Slides: Interlude 1. Reduction: addition of hydrogen to the substrate. Oxidation: addition of oxygen to the substrate
 Interlude 1: Oxidations, Reductions & Other Functional Group Interconversions (FGI) 1. Definition of Oxidation and Reduction For practical purposes in organic chemistry, oxidation and reduction are defined
Interlude 1: Oxidations, Reductions & Other Functional Group Interconversions (FGI) 1. Definition of Oxidation and Reduction For practical purposes in organic chemistry, oxidation and reduction are defined
O O O CH 2 O 7. 2 = C=O hydration H B. 6 = reverse aldol H O. 9b = acetal formation add alcohol (step 2)
 1 equences For Practice 1. 1 2 3 7 2 6 5 4 8 9 Possible Key 3 = AD + oxidation 1 2 3 4 5 3 2 1 AD + 7 1 = AD + oxidation 7 = aldol AD 2 = = hydration 2 6 6 = aldol AD + AD 5 5 = β-keto decarboxylation
1 equences For Practice 1. 1 2 3 7 2 6 5 4 8 9 Possible Key 3 = AD + oxidation 1 2 3 4 5 3 2 1 AD + 7 1 = AD + oxidation 7 = aldol AD 2 = = hydration 2 6 6 = aldol AD + AD 5 5 = β-keto decarboxylation
Ketones and Aldehydes Reading Study Problems Key Concepts and Skills Lecture Topics: Structure of Ketones and Aldehydes Structure:
 Ketones and Aldehydes Reading: Wade chapter 18, sections 18-1- 18-21 Study Problems: 18-43, 18-44,18-50, 18-51, 18-52, 18-59, 18-60, 18-62, 18-64, 18-72. Key Concepts and Skills: Interpret the IR, NMR,
Ketones and Aldehydes Reading: Wade chapter 18, sections 18-1- 18-21 Study Problems: 18-43, 18-44,18-50, 18-51, 18-52, 18-59, 18-60, 18-62, 18-64, 18-72. Key Concepts and Skills: Interpret the IR, NMR,
Reducing Agents. Linda M. Sweeting 1998
 Reducing Agents Linda M. Sweeting 1998 Reduction is defined in chemistry as loss of oxygen, gain of hydrogen or gain of electrons; the gain of electrons enables you to calculate an oxidation state. Hydride
Reducing Agents Linda M. Sweeting 1998 Reduction is defined in chemistry as loss of oxygen, gain of hydrogen or gain of electrons; the gain of electrons enables you to calculate an oxidation state. Hydride
Practice Synthetic Problems: CHEM 235 Page 2
 Practice Synthetic Problems: CM 235 Page 2 Syntheses based on diethyl malonate, ethyl acetoacetate, etc. Using diethyl malonate and any other necessary organic reagents, show a synthesis of: a) 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine
Practice Synthetic Problems: CM 235 Page 2 Syntheses based on diethyl malonate, ethyl acetoacetate, etc. Using diethyl malonate and any other necessary organic reagents, show a synthesis of: a) 2,2-dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine
