Uhlíkové nanostruktury-materiály ypro budoucnost?
|
|
|
- Julia Gardner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Uhlíkové nanostruktury-materiály ypro budoucnost? Martin Kalbáč IFW Dresden Ústav fyzikální chemie J. Heyrovského, Praha Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Cambridge,USA
2 Forms of carbon Nanotubes Fullerenes Diamond Graphite Graphene
3 Content: 1) Grafen 2) Fullereny 3) Nanotuby 4) Peapody 5) DWCNTs 6) Spektroelektrochemie
4
5 Graphite Forms of carbon
6 Graphene Forms of carbon
7 Graphene applications Ultrathin conductive films Graphene Used To Create World's Smallest ttransistor Liquid Crystal Device with electrodes made of graphene with different voltages applied. The overall width of the insert image is 30 microns. (Image: Mesoscopic Physics Group, University of Manchester) Dr Ponomarenko, who carried out this work, shows his research sample: graphene quantum dots on a chip.
8 Graphene applications Single molecule gas detection Ultracapacitors Spin transport Schematic of the resonator. The graphene is in contact with a gold electrode that can be used to electrostatically actuate the resonator. A red laser is used to detect the motion of the resonator by laser interferometry.
9 Forms of carbon Graphene 0.70 per μm per mm 2
10 Graphene Forms of carbon
11 Graphene Forms of carbon
12 Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) Cu or Ni Quartz substrate boat Quartz tube Electric furnace Ar H2/CH4 or Ar/H 2 Ethanol tank Hot bath
13 Chemical vapor deposition (CVD)
14 Transfer of graphene
15 Transfer of graphene
16 Chemical vapor deposition (CVD)
17 Expo '67 American Pavillion by R. Buckminster Fuller, on Ile Sainte-Hélène, Montreal
18 C 60 acc. to IUPAC: Hentriacontacyclo[ ,14.0 3,12.0 4,59.0 5,10.0 6,58.0 7,55.0 8,53.0 9, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ,46 ]hexaconta- 1,3,5(10),6,8,11,13(18),14,16,19,21,23,25,27,29(45), 11 13(18) (45) 30,32(44),33,35(43),36,38(54),39(51),40(48),41,46,49, 52,55,57, 59-triaconten Kroto, Allaf, Balm, Chem. Rev. 91, 1991, 1213
19 Fullerene gallery C 60 C 70 C 76 C 78 C 82 La@C 84 Sc 3 N@C 84 Endohedral Fullerene M@C 84
20 Carbon nanotubes
21 Rolling of SWCNT -zag zigarm-chair
22 Carbon nanotubes (CNT) SWCNT MWCNT DW CNT
23 SWCNT Bundles
24 SWCNT Bundles
25 Single wall carbon nanotubes (SWCNT) Size: Nanostructures with dimensions of ~1 nm diameter (~10 atoms around the cylinder) Physics: 1D density of electronic states. Single molecule Raman spectroscopy, luminescence, and transport properties. Electronic Properties: Can be either metallic or semiconducting depending on diameter and orientation of the hexagons Mechanical Properties: Very high strength. Good properties on both compression and extension.
26 Carbon nanotubes (CNT) mechanical properties Fiber material Specific E Strength Strain at break density (TPa) (GPa) (%) CNT HS Steel <10 CF-PAN Kevlar
27 Carbon nanotubes (CNT) mechanical properties
28 Single nanotube transistor Distinctive metallic and semiconducting transport properties IBM Ballistic transport Extremely high current carrying capacity
29 Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) Quartz boat Quartz tube Electric furnace Ar or Ar/H 2 Ethanol tank Hot bath
30 Quality vs. price
31 Commercial 90% carbon purity 500 $ /g Purity of carbon nanotubes
32 SWCNT from graphene A a 1 6 a 1 a 2 5a 2 C h B Chiral vector: C h = na 6a 1 + ma 5a 2 a 1, a 2. Unit vectors of 2D-hexagonal lattice (6,5)
33 SWCNT from graphene Armchair nt (n=m) metal Zig-zag nt (n-m) = 3i metal (n-m) 3i semicond. Chiral nt (n-m) =3i metal (n-m) 3i semicond.
34 Density of states (DOS) in SWCNT Van Hove singularities (5,5) Armchair tubes (5,5) 5) Zig-zag tubes (5,0) om/ev) (states/c-at DOS (10,10) (10,0) DOS (states/c-at tom/ev) (20,20) (20,0) Energy, ev Energy, ev
35 ΔE of singularities vs. diameter of SWCNT ( Kataura graph ) 2χ0 ac C ΔE = SWCNT d d nm (10,10) Ene ergy, ev Energy Sepa aration (ev) v 2 m c m 2 v s3 c 3 s v m1 c 1 m Energy, ev DOS v s2 c s 2 v s1 c s 1 (11,9) Nanotube diameter (nm) -1.0 (n, m) to (40,40) -1.5 DOS
36 Vis/NIR spectrum of SWCNT/ITO 0.5 hv Absorbance v s1 c s 1 v s2 c s 2 v m1 1 c m 0.1 SWCNT ITO Energy, ev
37 SWCNT Bundles
38 Sorting SWCNT
39 What is the Raman spectroscopy py about C. V. Raman
40 Resonance enhanced Raman spectroscopy Approximately 1 in 10 7 photons is inelastically scattered The signal is usally very weak 1) Use of lasers - intensive light 2) Resonance enhancement
41 Resonance enhanced Raman spectroscopy Virtual state E 1 V 0 Optical transition? E 0 V 1 E 0 V 0 Resonance enhanced spectra
42 Resonance Raman spectroscopy of SWCNT I = c ( E E iγ )( E + E E iγ ) L ii L ph ii 2 E L - laser photon energy E ii - optical transition energy E ph - phonon energy γ - damping constant Typical values for RBM E ph 0.02 ev γ 0.05 ev
43 Raman spectrum of SWCNT 1.83 ev 2.41 ev TG Raman int tensity, a. u. x 5 x 25 RBM D G Raman shift, cm Diameter = 234/ω RBM
44 Growth of CNT
45 Raman spectra of SWCNT, hv exc = 1.83 ev x 1.5 y, a.u. man intensity Bundle Ra Raman shift, cm
46 Creation of defects in SWCNT RF Ar plasma Individual SWCNT Mask Substrate
47 Defective SWCNT x 30 Raman inte ensity, a.u. x10 3 D mode Pristine part Defective part Raman shift, cm Diameter = 234/ω RBM
48 Formation of fullerene peapod (C C 60 (g) FULLERENE PEAPOD Nanotube, optimum 1.36 nm
49 Dy 3 N@C Dy 3 N@C Dysprosium (at approx. 154 ev) from EELS spectra J.Cech, M. Kalbáč, S.A. Curran, D. Zhang, U. Dettlaff-Weglikowska, L. Dunsch, S. Yang and S. Roth: Physica E: Low-dimensional Systems and Nanostructures, in press (2006) Distance (nm)
50 Raman spectra of Dy 3 N@C hv exc = 1.91 ev y, a. u. intensity Raman Dy 3 N@C SWCNT Dy 3 N@C 80 x Raman shift, cm
51 Double walled nanotubes RT C 800 o C 1200 o C DWCNT 1000 o C 1200 o C S. Bandow et al., Chem. Phys. Lett. 337 (2001) 48
52 Raman spectra of dry DWCNT, hv exc = 1.83 ev Raman intens sity, a. u. OUTER TUBES INNER TUBES Raman shift, cm
53 Double walled nanotubes from different peapod sources (The spectra are excited by 1.83 ev) C 60 -DWCNT C 70 -DWCNT C 78 -DWCNT Raman intensity, a. u. Raman intensity, a. u. Raman intensity, a. u Raman shift, cm Raman 300 shift, cm Raman shift, cm C 84 -DWCNT La@C 82 -DWCNT Dy 3 N@C 80 -DWCNT Raman in ntensity, a. u. Raman in ntensity, a. u. Raman in ntensity, a. u Raman shift, cm Raman shift, cm Raman shift, cm
54 In-situ spectroelectrochemistry The change of potential The change of electronic state The change of spectra Methods EPR UV-Vis-NIR Vis Raman FTIR Materials conducting polymers monomers, oligomers fullerenes CNT peapods
55 Cat2 An1 OCP Cat1 An2 In-situ electrochemical doping of SWCNT anodic/cathodic= extraction/insertion of e - Fermi level Fermi level Fermi level Fermi level Fermi level Fermi level Electrode
56 Vis-NIR spectra on ITO electrode of SWCNT (0.22 M LiClO 4 + acetonitrile) RE 0.50 Energy, ev CE WE hv bsorbance (A) DOS A 0.30 Energy, ev sample ITO Energy, ev E = 0.0V 0.2V 0.4V 0.6V 0.8V 1.0V 1.2V 1.4V 1.6V DOS
57 Raman spectra of SWCNT, hv exc = 2.54 ev (0.2 M LiClO 4 + acetonitrile) I = c ( E E iγ )( E + E E iγ ) L ii L ph ii V Spectroelectrochemical cell x40 RE (Ag/AgCl) Pyrex window N -outlet 2 N 2 -inlet CE (Pt) Electrolyte solution V an intens ity, a. u. Ram y, a. u. Raman intensity (vs. Fc/Fc + ) WE Raman shift, cm -1
58 Raman spectra of DWCNT, hv exc = 1.83 ev (0.2 M LiClO 4 + acetonitrile) 1.5 V 1.2 V 0.9 V Raman inten nsity, a. u. 0.6 V 0.3 V 0V -0.3 V -0.6 V -0.9 V -1.2 V -1.5 V Raman shift, cm M. Kalbáč, L. Kavan, M. Zukalová and L. Dunsch: Adv. Funct. Mater., 15, , (2005).
59 THANK YOU!!! Financial support: GACR-DFG GA AV MSMT-USA Kontakt: 1) M. Kalbac, L. Kavan, L. Dunsch and M.S. Dresselhaus. Nanoletters, 8, (2008). 2) M. Kalbac, L. Kavan, M. Zukalová and L. Dunsch. Chemistry - A Eur. J., 14, (2008). 3) M. Kalbac, L. Kavan, L. Dunsch. J. Phys. Chem C. 112(43), (2008). 4) M. Kalbac, H. Farhat, L. Kavan, J. Kong, M.S. Dresselhaus. Nanoletters, 8 (10), (2008). 5) M. Kalbac, L. Kavan, L. Dunsch. J. Phys. Chem C. 113(4), (2009). 6) M. Kalbac, L. Kavan, H. Farhat, J. Kong, M.S. Dresselhaus. J. Phys. Chem C. 113(5), (2009). 7) M. Kalbac, L. Kavan, L. Dunsch: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131(12) , (2009). 8) M. Kalbac, H. Farhat, L. Kavan, J. Kong, K. Sasaki, R.Saito and M. S. Dresselhaus. ACS Nano, 3 (8), (2009). 9) M. Kalbac, A. A. Green, M. C. Hersam, and L. Kavan. ACS Nano, 4 (1), (2010). 10) M. Kalbac, V. Zólyomi, Á. Rusznyák, J. Koltai, J. Kürti and L. Kavan. J. Phys. Chem C. 114, (2010).
Determining Carbon Nanotube Properties from Raman. Scattering Measurements
 Determining Carbon Nanotube Properties from Raman Scattering Measurements Ying Geng 1, David Fang 2, and Lei Sun 3 1 2 3 The Institute of Optics, Electrical and Computer Engineering, Laboratory for Laser
Determining Carbon Nanotube Properties from Raman Scattering Measurements Ying Geng 1, David Fang 2, and Lei Sun 3 1 2 3 The Institute of Optics, Electrical and Computer Engineering, Laboratory for Laser
Control of Diameter Distribution of Single-walled Carbon Nanotubes Using the Zeolite-CCVD Method
 22 Special Issue Nano-structure Controls of Functional Powders Research Report Control of Diameter Distribution of Single-walled Carbon Nanotubes Using the Zeolite-CCVD Method Atsuto Okamoto, Hisanori
22 Special Issue Nano-structure Controls of Functional Powders Research Report Control of Diameter Distribution of Single-walled Carbon Nanotubes Using the Zeolite-CCVD Method Atsuto Okamoto, Hisanori
Metallic/semiconducting ratio of carbon nanotubes in a bundle prepared using CVD technique
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 2 journal of August 2006 physics pp. 395 400 Metallic/semiconducting ratio of carbon nanotubes in a bundle prepared using CVD technique KHURSHED AHMAD
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 67, No. 2 journal of August 2006 physics pp. 395 400 Metallic/semiconducting ratio of carbon nanotubes in a bundle prepared using CVD technique KHURSHED AHMAD
Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1
 Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1 ChiiDong Chen Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica chiidong@phys.sinica.edu.tw 02 27896766 Section 5.2.1 Nature of the Carbon Bond
Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1 ChiiDong Chen Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica chiidong@phys.sinica.edu.tw 02 27896766 Section 5.2.1 Nature of the Carbon Bond
Why are we so excited about carbon nanostructures? Mildred Dresselhaus Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA
 Why are we so excited about carbon nanostructures? Mildred Dresselhaus Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA Conference for Undergraduate Women in Physics at Yale January 18, 2009 Why are
Why are we so excited about carbon nanostructures? Mildred Dresselhaus Massachusetts Institute of Technology Cambridge, MA Conference for Undergraduate Women in Physics at Yale January 18, 2009 Why are
Tube tube interaction in double-wall carbon nanotubes
 phys. stat. sol. (b) 243, No. 13, 3268 3272 (2006) / DOI 10.1002/pssb.200669176 Tube tube interaction in double-wall carbon nanotubes R. Pfeiffer *, 1, F. Simon 1, 2, H. Kuzmany 1, V. N. Popov 3, V. Zólyomi
phys. stat. sol. (b) 243, No. 13, 3268 3272 (2006) / DOI 10.1002/pssb.200669176 Tube tube interaction in double-wall carbon nanotubes R. Pfeiffer *, 1, F. Simon 1, 2, H. Kuzmany 1, V. N. Popov 3, V. Zólyomi
Transport Properties of Novel Carbon Nanotubes and Nanopeapods
 Transport Properties of Novel Carbon Nanotubes and Nanopeapods Takashi Shimada, Yutaka Ohno, Toshiya Okazaki, Toshiki Sugai, Yousuke Nosho, Kazutomo Suenaga, Shigeru Kishimoto, Takashi Mizutani, and Hisanori
Transport Properties of Novel Carbon Nanotubes and Nanopeapods Takashi Shimada, Yutaka Ohno, Toshiya Okazaki, Toshiki Sugai, Yousuke Nosho, Kazutomo Suenaga, Shigeru Kishimoto, Takashi Mizutani, and Hisanori
Use of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for UV radiation detection
 Use of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for UV radiation detection Viviana Carillo 11th Topical Seminar on Innovative Particle and Radiation Detectors (IPRD08) 1-4 October 2008 Siena, Italy A new nanostructured
Use of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for UV radiation detection Viviana Carillo 11th Topical Seminar on Innovative Particle and Radiation Detectors (IPRD08) 1-4 October 2008 Siena, Italy A new nanostructured
Optical & Transport Properties of Carbon Nanotubes II
 Optical & Transport Properties of Carbon Nanotubes II Duncan J. Mowbray Nano-Bio Spectroscopy Group European Theoretical Spectroscopy Facility (ETSF) Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC) Universidad
Optical & Transport Properties of Carbon Nanotubes II Duncan J. Mowbray Nano-Bio Spectroscopy Group European Theoretical Spectroscopy Facility (ETSF) Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC) Universidad
Physics of Nanotubes, Graphite and Graphene Mildred Dresselhaus
 Quantum Transport and Dynamics in Nanostructures The 4 th Windsor Summer School on Condensed Matter Theory 6-18 August 2007, Great Park Windsor (UK) Physics of Nanotubes, Graphite and Graphene Mildred
Quantum Transport and Dynamics in Nanostructures The 4 th Windsor Summer School on Condensed Matter Theory 6-18 August 2007, Great Park Windsor (UK) Physics of Nanotubes, Graphite and Graphene Mildred
Interaction between Inner and Outer Tubes in DWCNTs
 Interaction between Inner and Outer Tubes in DWCNTs R. Pfeiffer, Ch. Kramberger, F. Simon, H. Kuzmany and V. N. Popov Institut für Materialphysik, Universität Wien, Vienna, Austria Faculty of Physics,
Interaction between Inner and Outer Tubes in DWCNTs R. Pfeiffer, Ch. Kramberger, F. Simon, H. Kuzmany and V. N. Popov Institut für Materialphysik, Universität Wien, Vienna, Austria Faculty of Physics,
Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1
 Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1 ChiiDong Chen Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica chiidong@phys.sinica.edu.tw 02 27896766 Carbon contains 6 electrons: (1s) 2,
Introduction to Nanotechnology Chapter 5 Carbon Nanostructures Lecture 1 ChiiDong Chen Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica chiidong@phys.sinica.edu.tw 02 27896766 Carbon contains 6 electrons: (1s) 2,
The Photophysics of Nano Carbons. Kavli Institute, UC Santa Barbara January 9, 2012 M. S. Dresselhaus, MIT
 The Photophysics of Nano Carbons Kavli Institute, UC Santa Barbara January 9, 2012 M. S. Dresselhaus, MIT The Electronic Structure of Graphene Near the K point E ( ) v F linear relation where and and 0
The Photophysics of Nano Carbons Kavli Institute, UC Santa Barbara January 9, 2012 M. S. Dresselhaus, MIT The Electronic Structure of Graphene Near the K point E ( ) v F linear relation where and and 0
Calculating Electronic Structure of Different Carbon Nanotubes and its Affect on Band Gap
 Calculating Electronic Structure of Different Carbon Nanotubes and its Affect on Band Gap 1 Rashid Nizam, 2 S. Mahdi A. Rizvi, 3 Ameer Azam 1 Centre of Excellence in Material Science, Applied Physics AMU,
Calculating Electronic Structure of Different Carbon Nanotubes and its Affect on Band Gap 1 Rashid Nizam, 2 S. Mahdi A. Rizvi, 3 Ameer Azam 1 Centre of Excellence in Material Science, Applied Physics AMU,
Raman study on single-walled carbon nanotubes with different laser excitation energies
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 30, No. 3, June 2007, pp. 295 299. Indian Academy of Sciences. Raman study on single-walled carbon nanotubes with different laser excitation energies S S ISLAM*, KHURSHED AHMAD
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 30, No. 3, June 2007, pp. 295 299. Indian Academy of Sciences. Raman study on single-walled carbon nanotubes with different laser excitation energies S S ISLAM*, KHURSHED AHMAD
2 Symmetry. 2.1 Structure of carbon nanotubes
 2 Symmetry Carbon nanotubes are hollow cylinders of graphite sheets. They can be viewed as single molecules, regarding their small size ( nm in diameter and µm length), or as quasi-one dimensional crystals
2 Symmetry Carbon nanotubes are hollow cylinders of graphite sheets. They can be viewed as single molecules, regarding their small size ( nm in diameter and µm length), or as quasi-one dimensional crystals
Carbon Nanomaterials
 Carbon Nanomaterials STM Image 7 nm AFM Image Fullerenes C 60 was established by mass spectrographic analysis by Kroto and Smalley in 1985 C 60 is called a buckminsterfullerene or buckyball due to resemblance
Carbon Nanomaterials STM Image 7 nm AFM Image Fullerenes C 60 was established by mass spectrographic analysis by Kroto and Smalley in 1985 C 60 is called a buckminsterfullerene or buckyball due to resemblance
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes
 Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes 1 atom thick films of graphite atomic chicken wire Novoselov et al - Science 306, 666 (004) 100μm Geim s group at Manchester Novoselov et al - Nature 438, 197 (005) Kim-Stormer
Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes 1 atom thick films of graphite atomic chicken wire Novoselov et al - Science 306, 666 (004) 100μm Geim s group at Manchester Novoselov et al - Nature 438, 197 (005) Kim-Stormer
CVD growth of Graphene. SPE ACCE presentation Carter Kittrell James M. Tour group September 9 to 11, 2014
 CVD growth of Graphene SPE ACCE presentation Carter Kittrell James M. Tour group September 9 to 11, 2014 Graphene zigzag armchair History 1500: Pencil-Is it made of lead? 1789: Graphite 1987: The first
CVD growth of Graphene SPE ACCE presentation Carter Kittrell James M. Tour group September 9 to 11, 2014 Graphene zigzag armchair History 1500: Pencil-Is it made of lead? 1789: Graphite 1987: The first
Wafer-scale fabrication of graphene
 Wafer-scale fabrication of graphene Sten Vollebregt, MSc Delft University of Technology, Delft Institute of Mircosystems and Nanotechnology Delft University of Technology Challenge the future Delft University
Wafer-scale fabrication of graphene Sten Vollebregt, MSc Delft University of Technology, Delft Institute of Mircosystems and Nanotechnology Delft University of Technology Challenge the future Delft University
Recap (so far) Low-Dimensional & Boundary Effects
 Recap (so far) Ohm s & Fourier s Laws Mobility & Thermal Conductivity Heat Capacity Wiedemann-Franz Relationship Size Effects and Breakdown of Classical Laws 1 Low-Dimensional & Boundary Effects Energy
Recap (so far) Ohm s & Fourier s Laws Mobility & Thermal Conductivity Heat Capacity Wiedemann-Franz Relationship Size Effects and Breakdown of Classical Laws 1 Low-Dimensional & Boundary Effects Energy
Carbon Nanomaterials: Nanotubes and Nanobuds and Graphene towards new products 2030
 Carbon Nanomaterials: Nanotubes and Nanobuds and Graphene towards new products 2030 Prof. Dr. Esko I. Kauppinen Helsinki University of Technology (TKK) Espoo, Finland Forecast Seminar February 13, 2009
Carbon Nanomaterials: Nanotubes and Nanobuds and Graphene towards new products 2030 Prof. Dr. Esko I. Kauppinen Helsinki University of Technology (TKK) Espoo, Finland Forecast Seminar February 13, 2009
Supplementary Figure S1. AFM images of GraNRs grown with standard growth process. Each of these pictures show GraNRs prepared independently,
 Supplementary Figure S1. AFM images of GraNRs grown with standard growth process. Each of these pictures show GraNRs prepared independently, suggesting that the results is reproducible. Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Figure S1. AFM images of GraNRs grown with standard growth process. Each of these pictures show GraNRs prepared independently, suggesting that the results is reproducible. Supplementary Figure
Manipulating and determining the electronic structure of carbon nanotubes
 Manipulating and determining the electronic structure of carbon nanotubes (06.12.2005 NTHU, Physics Department) Po-Wen Chiu Department of Electrical Engineering, Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan Max-Planck
Manipulating and determining the electronic structure of carbon nanotubes (06.12.2005 NTHU, Physics Department) Po-Wen Chiu Department of Electrical Engineering, Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan Max-Planck
status solidi Department of Biological Physics, Eötvös University, Pázmány Péter sétány 1/A, 1117 Budapest, Hungary 2
 physica pss www.pss-b.com status solidi basic solid state physics b Curvature effects in the D * band of small diameter carbon nanotubes J. Kürti,V. Zólyomi,,J. Koltai, F. Simon 3, 4,R. Pfeiffer 4, and
physica pss www.pss-b.com status solidi basic solid state physics b Curvature effects in the D * band of small diameter carbon nanotubes J. Kürti,V. Zólyomi,,J. Koltai, F. Simon 3, 4,R. Pfeiffer 4, and
Imaging Carbon materials with correlative Raman-SEM microscopy. Introduction. Raman, SEM and FIB within one chamber. Diamond.
 Imaging Carbon materials with correlative Raman-SEM microscopy Application Example Carbon materials are widely used in many industries for their exceptional properties. Electric conductance, light weight,
Imaging Carbon materials with correlative Raman-SEM microscopy Application Example Carbon materials are widely used in many industries for their exceptional properties. Electric conductance, light weight,
Energy Storage. Light-emitting. Nano-Carbons. H 2 Energy. CNT synthesis. Graphene synthesis Top-down. Solar H 2 generation
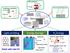 Nano-Carbon battery Graphene synthesis Top-down CNT synthesis CVD reactor hydrocarbon gas Catalyst CNTs Chemical Modification COO O NO 2 COO COO COO Bottom-up O O NO NO 2 2 COO COO Nano-Carbons 20 nm Light-emitting
Nano-Carbon battery Graphene synthesis Top-down CNT synthesis CVD reactor hydrocarbon gas Catalyst CNTs Chemical Modification COO O NO 2 COO COO COO Bottom-up O O NO NO 2 2 COO COO Nano-Carbons 20 nm Light-emitting
What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them?
 Growth and Properties of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them? - Interconnects of the future? - our vision Where do we stand - our
Growth and Properties of Multiwalled Carbon Nanotubes What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them? - Interconnects of the future? - our vision Where do we stand - our
METAL/CARBON-NANOTUBE INTERFACE EFFECT ON ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT
 METAL/CARBON-NANOTUBE INTERFACE EFFECT ON ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT S. Krompiewski Institute of Molecular Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, M. Smoluchowskiego 17, 60-179 Poznań, Poland OUTLINE 1. Introductory
METAL/CARBON-NANOTUBE INTERFACE EFFECT ON ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT S. Krompiewski Institute of Molecular Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, M. Smoluchowskiego 17, 60-179 Poznań, Poland OUTLINE 1. Introductory
Carbon Nanotubes in Interconnect Applications
 Carbon Nanotubes in Interconnect Applications Page 1 What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them? - Interconnects of the future? Comparison of electrical properties
Carbon Nanotubes in Interconnect Applications Page 1 What are Carbon Nanotubes? What are they good for? Why are we interested in them? - Interconnects of the future? Comparison of electrical properties
status solidi The effects of inhomogeneous isotope distribution on the vibrational properties of isotope enriched double walled carbon nanotubes
 physica pss www.pss-b.com status solidi basic solid state physics b The effects of inhomogeneous isotope distribution on the vibrational properties of isotope enriched double walled carbon nanotubes V.
physica pss www.pss-b.com status solidi basic solid state physics b The effects of inhomogeneous isotope distribution on the vibrational properties of isotope enriched double walled carbon nanotubes V.
Transparent Electrode Applications
 Transparent Electrode Applications LCD Solar Cells Touch Screen Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) Zinc Oxide (ZnO) - High conductivity - High transparency - Resistant to environmental effects - Rare material (Indium)
Transparent Electrode Applications LCD Solar Cells Touch Screen Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) Zinc Oxide (ZnO) - High conductivity - High transparency - Resistant to environmental effects - Rare material (Indium)
Rahul Sen 1, Hiromichi Kataura 2, Yohsuke Ohtsuka 1, Toshinobu Ishigaki 1, Shinzo Suzuki 1 and Yohji Achiba 1 ABSTRACT
 EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE GRADIENT NEAR THE TARGET AND GAS FLOW RATE ON THE DIAMETER DISTRIBUTION OF SINGLE-WALLED CARBON NANOTUBES GROWN BY THE LASER ABLATION TECHNIQUE Rahul Sen 1, Hiromichi Kataura 2, Yohsuke
EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE GRADIENT NEAR THE TARGET AND GAS FLOW RATE ON THE DIAMETER DISTRIBUTION OF SINGLE-WALLED CARBON NANOTUBES GROWN BY THE LASER ABLATION TECHNIQUE Rahul Sen 1, Hiromichi Kataura 2, Yohsuke
Understanding Irreducible and Reducible Oxides as Catalysts for Carbon Nanotubes and Graphene Formation
 Wright State University CORE Scholar Special Session 5: Carbon and Oxide Based Nanostructured Materials (2011) Special Session 5 6-2011 Understanding Irreducible and Reducible Oxides as Catalysts for Carbon
Wright State University CORE Scholar Special Session 5: Carbon and Oxide Based Nanostructured Materials (2011) Special Session 5 6-2011 Understanding Irreducible and Reducible Oxides as Catalysts for Carbon
FMM, 15 th Feb Simon Zihlmann
 FMM, 15 th Feb. 2013 Simon Zihlmann Outline Motivation Basics about graphene lattice and edges Introduction to Raman spectroscopy Scattering at the edge Polarization dependence Thermal rearrangement of
FMM, 15 th Feb. 2013 Simon Zihlmann Outline Motivation Basics about graphene lattice and edges Introduction to Raman spectroscopy Scattering at the edge Polarization dependence Thermal rearrangement of
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2017. Supporting Information for Adv. Energy Mater., DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201701456 Selective Etching of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon by Steam
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2017. Supporting Information for Adv. Energy Mater., DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201701456 Selective Etching of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon by Steam
Quantized Electrical Conductance of Carbon nanotubes(cnts)
 Quantized Electrical Conductance of Carbon nanotubes(cnts) By Boxiao Chen PH 464: Applied Optics Instructor: Andres L arosa Abstract One of the main factors that impacts the efficiency of solar cells is
Quantized Electrical Conductance of Carbon nanotubes(cnts) By Boxiao Chen PH 464: Applied Optics Instructor: Andres L arosa Abstract One of the main factors that impacts the efficiency of solar cells is
Carbon Nanotubes. Andrea Goldoni. Elettra- Sincrotrone Trieste S.C.p.A., s.s. 14 Km 163,5 in Area Science Park, Trieste, Italy
 Carbon Nanotubes Andrea Goldoni Elettra- Sincrotrone Trieste S.C.p.A., s.s. 14 Km 163,5 in Area Science Park, 34012 Trieste, Italy Up to 1985 the only two allotropic form of carbon were known: graphite
Carbon Nanotubes Andrea Goldoni Elettra- Sincrotrone Trieste S.C.p.A., s.s. 14 Km 163,5 in Area Science Park, 34012 Trieste, Italy Up to 1985 the only two allotropic form of carbon were known: graphite
Optical Science of Nano-graphene (graphene oxide and graphene quantum dot) Introduction of optical properties of nano-carbon materials
 Optical Science of Nano-graphene (graphene oxide and graphene quantum dot) J Kazunari Matsuda Institute of Advanced Energy, Kyoto University Introduction of optical properties of nano-carbon materials
Optical Science of Nano-graphene (graphene oxide and graphene quantum dot) J Kazunari Matsuda Institute of Advanced Energy, Kyoto University Introduction of optical properties of nano-carbon materials
Fig. 1: Raman spectra of graphite and graphene. N indicates the number of layers of graphene. Ref. [1]
![Fig. 1: Raman spectra of graphite and graphene. N indicates the number of layers of graphene. Ref. [1] Fig. 1: Raman spectra of graphite and graphene. N indicates the number of layers of graphene. Ref. [1]](/thumbs/90/102653942.jpg) Vibrational Properties of Graphene and Nanotubes: The Radial Breathing and High Energy Modes Presented for the Selected Topics Seminar by Pierce Munnelly 09/06/11 Supervised by Sebastian Heeg Abstract
Vibrational Properties of Graphene and Nanotubes: The Radial Breathing and High Energy Modes Presented for the Selected Topics Seminar by Pierce Munnelly 09/06/11 Supervised by Sebastian Heeg Abstract
chiral m = n Armchair m = 0 or n = 0 Zigzag m n Chiral Three major categories of nanotube structures can be identified based on the values of m and n
 zigzag armchair Three major categories of nanotube structures can be identified based on the values of m and n m = n Armchair m = 0 or n = 0 Zigzag m n Chiral Nature 391, 59, (1998) chiral J. Tersoff,
zigzag armchair Three major categories of nanotube structures can be identified based on the values of m and n m = n Armchair m = 0 or n = 0 Zigzag m n Chiral Nature 391, 59, (1998) chiral J. Tersoff,
Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)
 Carbon Nanotubes (s) Seminar: Quantendynamik in mesoskopischen Systemen Florian Figge Fakultät für Physik Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg July 7th, 2010 F. Figge (University of Freiburg) Carbon Nanotubes
Carbon Nanotubes (s) Seminar: Quantendynamik in mesoskopischen Systemen Florian Figge Fakultät für Physik Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg July 7th, 2010 F. Figge (University of Freiburg) Carbon Nanotubes
Raman Imaging and Electronic Properties of Graphene
 Raman Imaging and Electronic Properties of Graphene F. Molitor, D. Graf, C. Stampfer, T. Ihn, and K. Ensslin Laboratory for Solid State Physics, ETH Zurich, 8093 Zurich, Switzerland ensslin@phys.ethz.ch
Raman Imaging and Electronic Properties of Graphene F. Molitor, D. Graf, C. Stampfer, T. Ihn, and K. Ensslin Laboratory for Solid State Physics, ETH Zurich, 8093 Zurich, Switzerland ensslin@phys.ethz.ch
Graphene. Tianyu Ye November 30th, 2011
 Graphene Tianyu Ye November 30th, 2011 Outline What is graphene? How to make graphene? (Exfoliation, Epitaxial, CVD) Is it graphene? (Identification methods) Transport properties; Other properties; Applications;
Graphene Tianyu Ye November 30th, 2011 Outline What is graphene? How to make graphene? (Exfoliation, Epitaxial, CVD) Is it graphene? (Identification methods) Transport properties; Other properties; Applications;
Conference Return Seminar- NANO2014,Moscow State University,Moscow,Russia Date: th July 2014
 Conference Return Seminar- NANO2014,Moscow State University,Moscow,Russia Date:13-1818 th July 2014 An electrochemical method for the synthesis of single and few layers graphene sheets for high temperature
Conference Return Seminar- NANO2014,Moscow State University,Moscow,Russia Date:13-1818 th July 2014 An electrochemical method for the synthesis of single and few layers graphene sheets for high temperature
Supplementary Information
 Emiss. Inten. (arb. unit) Emiss. Inten. (arb. unit) Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures S-S a b..5. c.2 d.2 (6,5) (7,5) (6,5).8 (7,6).8.6.4.2 (9,) (8,4) (9,4) (8,6) (,2).6.4.2 (7,5) (7,6)(8,4)
Emiss. Inten. (arb. unit) Emiss. Inten. (arb. unit) Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures S-S a b..5. c.2 d.2 (6,5) (7,5) (6,5).8 (7,6).8.6.4.2 (9,) (8,4) (9,4) (8,6) (,2).6.4.2 (7,5) (7,6)(8,4)
Carbon Nanotube: The Inside Story
 Krasnoyarsk: 24 th August, 2009 Carbon Nanotube: The Inside Story Review written for Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Yoshinori ANDO Dean of Faculty of Science and Technology, Meijo University
Krasnoyarsk: 24 th August, 2009 Carbon Nanotube: The Inside Story Review written for Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Yoshinori ANDO Dean of Faculty of Science and Technology, Meijo University
Carbon nanotubes and Graphene
 16 October, 2008 Solid State Physics Seminar Main points 1 History and discovery of Graphene and Carbon nanotubes 2 Tight-binding approximation Dynamics of electrons near the Dirac-points 3 Properties
16 October, 2008 Solid State Physics Seminar Main points 1 History and discovery of Graphene and Carbon nanotubes 2 Tight-binding approximation Dynamics of electrons near the Dirac-points 3 Properties
Thermal Transport in Graphene and other Two-Dimensional Systems. Li Shi. Department of Mechanical Engineering & Texas Materials Institute
 Thermal Transport in Graphene and other Two-Dimensional Systems Li Shi Department of Mechanical Engineering & Texas Materials Institute Outline Thermal Transport Theories and Simulations of Graphene Raman
Thermal Transport in Graphene and other Two-Dimensional Systems Li Shi Department of Mechanical Engineering & Texas Materials Institute Outline Thermal Transport Theories and Simulations of Graphene Raman
PH575 Spring Lecture #28 Nanoscience: the case study of graphene and carbon nanotubes.
 PH575 Spring 2014 Lecture #28 Nanoscience: the case study of graphene and carbon nanotubes. Nanoscience scale 1-100 nm "Artificial atoms" Small size => discrete states Large surface to volume ratio Bottom-up
PH575 Spring 2014 Lecture #28 Nanoscience: the case study of graphene and carbon nanotubes. Nanoscience scale 1-100 nm "Artificial atoms" Small size => discrete states Large surface to volume ratio Bottom-up
Resonance Raman scattering from phonon overtones in double-wall carbon nanotubes
 Resonance Raman scattering from phonon overtones in double-wall carbon nanotubes R. Pfeiffer, 1 H. Kuzmany, 1 F. Simon, 1 S. N. Bokova, 2 and E. Obraztsova 2 1 Universität Wien, Institut für Materialphysik,
Resonance Raman scattering from phonon overtones in double-wall carbon nanotubes R. Pfeiffer, 1 H. Kuzmany, 1 F. Simon, 1 S. N. Bokova, 2 and E. Obraztsova 2 1 Universität Wien, Institut für Materialphysik,
Carbon Nanotubes for Interconnect Applications Franz Kreupl, Andrew P. Graham, Maik Liebau, Georg S. Duesberg, Robert Seidel, Eugen Unger
 Carbon Nanotubes for Interconnect Applications Franz Kreupl, Andrew P. Graham, Maik Liebau, Georg S. Duesberg, Robert Seidel, Eugen Unger Infineon Technologies Corporate Research Munich, Germany Outline
Carbon Nanotubes for Interconnect Applications Franz Kreupl, Andrew P. Graham, Maik Liebau, Georg S. Duesberg, Robert Seidel, Eugen Unger Infineon Technologies Corporate Research Munich, Germany Outline
Multicolor Graphene Nanoribbon/Semiconductor Nanowire. Heterojunction Light-Emitting Diodes
 Multicolor Graphene Nanoribbon/Semiconductor Nanowire Heterojunction Light-Emitting Diodes Yu Ye, a Lin Gan, b Lun Dai, *a Hu Meng, a Feng Wei, a Yu Dai, a Zujin Shi, b Bin Yu, a Xuefeng Guo, b and Guogang
Multicolor Graphene Nanoribbon/Semiconductor Nanowire Heterojunction Light-Emitting Diodes Yu Ye, a Lin Gan, b Lun Dai, *a Hu Meng, a Feng Wei, a Yu Dai, a Zujin Shi, b Bin Yu, a Xuefeng Guo, b and Guogang
Isotope Engineering in Nanotube Research
 Isotope Engineering in Nanotube Research Ferenc Simon Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Institute of Physics and Condensed Matter Research Group of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences H-1521,
Isotope Engineering in Nanotube Research Ferenc Simon Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Institute of Physics and Condensed Matter Research Group of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences H-1521,
VIBRATION CHARACTERISTICS OF EMBEDDED DOUBLE WALLED CARBON NANOTUBES SUBJECTED TO AN AXIAL PRESSURE
 18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS VIBRATION CHARACTERISTICS OF EMBEDDED DOUBLE WALLED CARBON NANOTUBES SUBJECTED TO AN AXIAL PRESSURE X. W. Lei 1, T. Natsuki 2, J. X. Shi 1, Q. Q. Ni
18 TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS VIBRATION CHARACTERISTICS OF EMBEDDED DOUBLE WALLED CARBON NANOTUBES SUBJECTED TO AN AXIAL PRESSURE X. W. Lei 1, T. Natsuki 2, J. X. Shi 1, Q. Q. Ni
Random Telegraph Signal in Carbon Nanotube Device
 Random Telegraph Signal in Carbon Nanotube Device Tsz Wah Chan Feb 28, 2008 1 Introduction 1. Structure of Single-walled Carbon Nanotube (SWCNT) 2. Electronic properties of SWCNT 3. Sample preparation:
Random Telegraph Signal in Carbon Nanotube Device Tsz Wah Chan Feb 28, 2008 1 Introduction 1. Structure of Single-walled Carbon Nanotube (SWCNT) 2. Electronic properties of SWCNT 3. Sample preparation:
Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics
 Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics 09 02 200802 2008 ME class Outline driving force for the carbon nanomaterial electronic properties of fullerene exploration of electronic carbon nanotube gold rush of
Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics 09 02 200802 2008 ME class Outline driving force for the carbon nanomaterial electronic properties of fullerene exploration of electronic carbon nanotube gold rush of
Metallic: 2n 1. +n 2. =3q Armchair structure always metallic = 2
 Properties of CNT d = 2.46 n 2 2 1 + n1n2 + n2 2π Metallic: 2n 1 +n 2 =3q Armchair structure always metallic a) Graphite Valence(π) and Conduction(π*) states touch at six points(fermi points) Carbon Nanotube:
Properties of CNT d = 2.46 n 2 2 1 + n1n2 + n2 2π Metallic: 2n 1 +n 2 =3q Armchair structure always metallic a) Graphite Valence(π) and Conduction(π*) states touch at six points(fermi points) Carbon Nanotube:
In today s lecture, we will cover:
 In today s lecture, we will cover: Metal and Metal oxide Nanoparticles Semiconductor Nanocrystals Carbon Nanotubes 1 Week 2: Nanoparticles Goals for this section Develop an understanding of the physical
In today s lecture, we will cover: Metal and Metal oxide Nanoparticles Semiconductor Nanocrystals Carbon Nanotubes 1 Week 2: Nanoparticles Goals for this section Develop an understanding of the physical
Lectures Graphene and
 Lectures 15-16 Graphene and carbon nanotubes Graphene is atomically thin crystal of carbon which is stronger than steel but flexible, is transparent for light, and conducts electricity (gapless semiconductor).
Lectures 15-16 Graphene and carbon nanotubes Graphene is atomically thin crystal of carbon which is stronger than steel but flexible, is transparent for light, and conducts electricity (gapless semiconductor).
Lithium-ion Batteries Based on Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotubes and Ionic Liquid
 Electronic Supplementary Information Lithium-ion Batteries Based on Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotubes and Ionic Liquid Electrolytes Wen Lu, * Adam Goering, Liangti Qu, and Liming Dai * 1. Synthesis of
Electronic Supplementary Information Lithium-ion Batteries Based on Vertically-Aligned Carbon Nanotubes and Ionic Liquid Electrolytes Wen Lu, * Adam Goering, Liangti Qu, and Liming Dai * 1. Synthesis of
Manifestation of Structure of Electron Bands in Double-Resonant Raman Spectra of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
 Stubrov et al. Nanoscale Research Letters (2016) 11:2 DOI 10.1186/s11671-015-1213-8 NANO EXPRESS Manifestation of Structure of Electron Bands in Double-Resonant Raman Spectra of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
Stubrov et al. Nanoscale Research Letters (2016) 11:2 DOI 10.1186/s11671-015-1213-8 NANO EXPRESS Manifestation of Structure of Electron Bands in Double-Resonant Raman Spectra of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
on Self-Assembly of Fullerene Molecules
 Effect of Surface Preparation of Copper on Self-Assembly of Fullerene Molecules Dongni Ma, Selene Sandoval, Krishna Muralidharan, Srini Raghavan University of Arizona Department of Materials Science and
Effect of Surface Preparation of Copper on Self-Assembly of Fullerene Molecules Dongni Ma, Selene Sandoval, Krishna Muralidharan, Srini Raghavan University of Arizona Department of Materials Science and
CHAPTER 3. OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES
 42 CHAPTER 3 OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In recent years, considerable interest has been shown on semiconducting nanostructures owing to their enhanced optical and electrical
42 CHAPTER 3 OPTICAL STUDIES ON SnS NANOPARTICLES 3.1 INTRODUCTION In recent years, considerable interest has been shown on semiconducting nanostructures owing to their enhanced optical and electrical
Carbon nanomaterials. Gavin Lawes Wayne State University.
 Carbon nanomaterials Gavin Lawes Wayne State University glawes@wayne.edu Outline 1. Carbon structures 2. Carbon nanostructures 3. Potential applications for Carbon nanostructures Periodic table from bpc.edu
Carbon nanomaterials Gavin Lawes Wayne State University glawes@wayne.edu Outline 1. Carbon structures 2. Carbon nanostructures 3. Potential applications for Carbon nanostructures Periodic table from bpc.edu
NiCl2 Solution concentration. Etching Duration. Aspect ratio. Experiment Atmosphere Temperature. Length(µm) Width (nm) Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa
 Experiment Atmosphere Temperature #1 # 2 # 3 # 4 # 5 # 6 # 7 # 8 # 9 # 10 Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1,
Experiment Atmosphere Temperature #1 # 2 # 3 # 4 # 5 # 6 # 7 # 8 # 9 # 10 Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1, 150Pa Ar:H2=9:1,
Session V: Graphene. Matteo Bruna CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ENGINEERING
 Session V: Graphene Matteo Bruna Graphene: Material in the Flatland Graphite Graphene Properties: Thinnest imaginable material Good(and tunable) electrical conductor Strongest ever measured Stiffest known
Session V: Graphene Matteo Bruna Graphene: Material in the Flatland Graphite Graphene Properties: Thinnest imaginable material Good(and tunable) electrical conductor Strongest ever measured Stiffest known
The Young s Modulus of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
 The Young s Modulus of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Douglas Vodnik Faculty Advisor: Dr. Kevin Crosby Department of Physics, Carthage College, Kenosha, WI Abstract A new numerical method for calculating
The Young s Modulus of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Douglas Vodnik Faculty Advisor: Dr. Kevin Crosby Department of Physics, Carthage College, Kenosha, WI Abstract A new numerical method for calculating
Clar Sextet Theory for low-dimensional carbon nanostructures: an efficient approach based on chemical criteria
 Clar Sextet Theory for low-dimensional carbon nanostructures: an efficient approach based on chemical criteria Matteo Baldoni Fachbereich Chemie, Technische Universität Dresden, Germany Department of Chemistry
Clar Sextet Theory for low-dimensional carbon nanostructures: an efficient approach based on chemical criteria Matteo Baldoni Fachbereich Chemie, Technische Universität Dresden, Germany Department of Chemistry
G raphene, which is a gapless material, has gathered much attention due to its prospective fascinating
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: ELECTRONIC PROPERTIES AND DEVICES MECHANICAL AND STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES AND DEVICES SURFACES, INTERFACES AND THIN FILMS SYNTHESIS OF GRAPHENE Mass-related inversion symmetry breaking
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: ELECTRONIC PROPERTIES AND DEVICES MECHANICAL AND STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES AND DEVICES SURFACES, INTERFACES AND THIN FILMS SYNTHESIS OF GRAPHENE Mass-related inversion symmetry breaking
GRAPHENE the first 2D crystal lattice
 GRAPHENE the first 2D crystal lattice dimensionality of carbon diamond, graphite GRAPHENE realized in 2004 (Novoselov, Science 306, 2004) carbon nanotubes fullerenes, buckyballs what s so special about
GRAPHENE the first 2D crystal lattice dimensionality of carbon diamond, graphite GRAPHENE realized in 2004 (Novoselov, Science 306, 2004) carbon nanotubes fullerenes, buckyballs what s so special about
Supporting Information Available:
 Supporting Information Available: Photoresponsive and Gas Sensing Field-Effect Transistors based on Multilayer WS 2 Nanoflakes Nengjie Huo 1, Shengxue Yang 1, Zhongming Wei 2, Shu-Shen Li 1, Jian-Bai Xia
Supporting Information Available: Photoresponsive and Gas Sensing Field-Effect Transistors based on Multilayer WS 2 Nanoflakes Nengjie Huo 1, Shengxue Yang 1, Zhongming Wei 2, Shu-Shen Li 1, Jian-Bai Xia
Raman study of pressure screening effects in double-wall carbon nanotubes
 Raman study of pressure screening effects in double-wall carbon nanotubes J. Arvanitidis a,b, D. Christofilos a, K. Papagelis c, K. S. Andrikopoulos a, G. A. Kourouklis a, S. Ves b,*, T. Takenobu d,e,
Raman study of pressure screening effects in double-wall carbon nanotubes J. Arvanitidis a,b, D. Christofilos a, K. Papagelis c, K. S. Andrikopoulos a, G. A. Kourouklis a, S. Ves b,*, T. Takenobu d,e,
Controlling Graphene Ultrafast Hot Carrier Response from Metal-like. to Semiconductor-like by Electrostatic Gating
 Controlling Graphene Ultrafast Hot Carrier Response from Metal-like to Semiconductor-like by Electrostatic Gating S.-F. Shi, 1,2* T.-T. Tang, 1 B. Zeng, 1 L. Ju, 1 Q. Zhou, 1 A. Zettl, 1,2,3 F. Wang 1,2,3
Controlling Graphene Ultrafast Hot Carrier Response from Metal-like to Semiconductor-like by Electrostatic Gating S.-F. Shi, 1,2* T.-T. Tang, 1 B. Zeng, 1 L. Ju, 1 Q. Zhou, 1 A. Zettl, 1,2,3 F. Wang 1,2,3
2011 GCEP Report. Project title: Self-sorting of Carbon Nanotubes for High Performance Large Area Transparent Electrodes for Solar Cells
 2011 GCEP Report Project title: Self-sorting of Carbon Nanotubes for High Performance Large Area Transparent Electrodes for Solar Cells Investigators Zhenan Bao, Associate Professor, Chemical Engineering
2011 GCEP Report Project title: Self-sorting of Carbon Nanotubes for High Performance Large Area Transparent Electrodes for Solar Cells Investigators Zhenan Bao, Associate Professor, Chemical Engineering
TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE
 International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, Nos. 12 & 13 (2009) 2641 2646 World Scientific Publishing Company TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE TARIQ M. G. MOHIUDDIN, A. A. ZHUKOV, D. C. ELIAS,
International Journal of Modern Physics B Vol. 23, Nos. 12 & 13 (2009) 2641 2646 World Scientific Publishing Company TRANSVERSE SPIN TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE TARIQ M. G. MOHIUDDIN, A. A. ZHUKOV, D. C. ELIAS,
The World of Carbon Nanotubes
 The World of Carbon Nanotubes Carbon Nanotubes Presentation by Jan Felix Eschermann at JASS05 from March 31st to April 9th, 2005 1 Outline Introduction Physical Properties Manufacturing Techniques Applications
The World of Carbon Nanotubes Carbon Nanotubes Presentation by Jan Felix Eschermann at JASS05 from March 31st to April 9th, 2005 1 Outline Introduction Physical Properties Manufacturing Techniques Applications
Supplementary Figure 1 XPS, Raman and TGA characterizations on GO and freeze-dried HGF and GF. (a) XPS survey spectra and (b) C1s spectra.
 Supplementary Figure 1 XPS, Raman and TGA characterizations on GO and freeze-dried HGF and GF. (a) XPS survey spectra and (b) C1s spectra. (c) Raman spectra. (d) TGA curves. All results confirm efficient
Supplementary Figure 1 XPS, Raman and TGA characterizations on GO and freeze-dried HGF and GF. (a) XPS survey spectra and (b) C1s spectra. (c) Raman spectra. (d) TGA curves. All results confirm efficient
From Graphene to Nanotubes
 From Graphene to Nanotubes Zone Folding and Quantum Confinement at the Example of the Electronic Band Structure Christian Krumnow christian.krumnow@fu-berlin.de Freie Universität Berlin June 6, Zone folding
From Graphene to Nanotubes Zone Folding and Quantum Confinement at the Example of the Electronic Band Structure Christian Krumnow christian.krumnow@fu-berlin.de Freie Universität Berlin June 6, Zone folding
Processing and Properties of Highly Enriched Double-Walled. Carbon Nanotubes: Supplementary Information
 Processing and Properties of Highly Enriched Double-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Supplementary Information Alexander A. Green and Mark C. Hersam* Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Department
Processing and Properties of Highly Enriched Double-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Supplementary Information Alexander A. Green and Mark C. Hersam* Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Department
Saturable absorbers incorporating carbon nanotubes directly synthesized onto substrates/fibers and their application to mode-locked fiber lasers
 Saturable absorbers incorporating carbon nanotubes directly synthesized onto substrates/fibers and their application to mode-locked fiber lasers S. Yamashita (1), S. Maruyama (2), Y. Murakami (2), Y. Inoue
Saturable absorbers incorporating carbon nanotubes directly synthesized onto substrates/fibers and their application to mode-locked fiber lasers S. Yamashita (1), S. Maruyama (2), Y. Murakami (2), Y. Inoue
SYNTHESIS OF CARBON NANOTUBES BY CATALYTIC CVD USING Fe-Mo/MgO AND Fe- Mo/Al 2 O 3 CATALYSTS. Abstract. Introduction. Experimental
 SYNTHESIS OF CARBON NANOTUBES BY CATALYTIC CVD USING Fe-Mo/MgO AND Fe- Mo/Al 2 O 3 CATALYSTS Shinn-Shyong Tzeng, Ting-Bin Liang, Sheng-Chuan Wang, Ting-Yu Wu and Yu-Hun Lin Department of Materials Engineering,
SYNTHESIS OF CARBON NANOTUBES BY CATALYTIC CVD USING Fe-Mo/MgO AND Fe- Mo/Al 2 O 3 CATALYSTS Shinn-Shyong Tzeng, Ting-Bin Liang, Sheng-Chuan Wang, Ting-Yu Wu and Yu-Hun Lin Department of Materials Engineering,
Arc-synthesis of Single-walled Carbon Nanotubes in Nitrogen Atmosphere
 Fullerenes, Nanotubes and Carbon Nanostructures, 16: 330 334, 2008 Copyright # Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN 1536-383X print/1536-4046 online DOI: 10.1080/15363830802219849 Arc-synthesis of Single-walled
Fullerenes, Nanotubes and Carbon Nanostructures, 16: 330 334, 2008 Copyright # Taylor & Francis Group, LLC ISSN 1536-383X print/1536-4046 online DOI: 10.1080/15363830802219849 Arc-synthesis of Single-walled
Chirality and energy dependence of first and second order resonance Raman intensity
 NT06: 7 th International Conference on the Science and Application of Nanotubes, June 18-23, 2006 Nagano, JAPAN Chirality and energy dependence of first and second order resonance Raman intensity R. Saito
NT06: 7 th International Conference on the Science and Application of Nanotubes, June 18-23, 2006 Nagano, JAPAN Chirality and energy dependence of first and second order resonance Raman intensity R. Saito
In Situ Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction Studies of Single-walled Carbon Nanotubes for Electric Double-layer Capacitors
 J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 9 (2015) 509-513 doi: 10.17265/1934-7375/2015.08.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING In Situ Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction Studies of Single-walled Carbon Nanotubes for Electric Double-layer Capacitors
J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 9 (2015) 509-513 doi: 10.17265/1934-7375/2015.08.005 D DAVID PUBLISHING In Situ Synchrotron X-ray Diffraction Studies of Single-walled Carbon Nanotubes for Electric Double-layer Capacitors
Yan Li *, Supporting Information
 Decoration of Gold Nanoparticles on Surface-Grown Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Detection of Every Nanotube by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Haibin Chu,, Jinyong Wang, Lei Ding, Dongning Yuan,
Decoration of Gold Nanoparticles on Surface-Grown Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Detection of Every Nanotube by Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Haibin Chu,, Jinyong Wang, Lei Ding, Dongning Yuan,
Self-Charged Graphene Battery Harvests Electricity. from Thermal Energy of the Environment
 Self-Charged Graphene Battery Harvests Electricity from Thermal Energy of the Environment Zihan Xu 1 *, Guoan Tai 1,3, Yungang Zhou 2, Fei Gao 2, Kim Hung Wong 1 1 Department of Applied Physics and Materials
Self-Charged Graphene Battery Harvests Electricity from Thermal Energy of the Environment Zihan Xu 1 *, Guoan Tai 1,3, Yungang Zhou 2, Fei Gao 2, Kim Hung Wong 1 1 Department of Applied Physics and Materials
Physics of Nanotubes, Graphite and Graphene Mildred Dresselhaus
 Quantum Transport and Dynamics in Nanostructures The 4 th Windsor Summer School on Condensed Matter Theory 6-18 August 2007, Great Park Windsor (UK) Physics of Nanotubes, Graphite and Graphene Mildred
Quantum Transport and Dynamics in Nanostructures The 4 th Windsor Summer School on Condensed Matter Theory 6-18 August 2007, Great Park Windsor (UK) Physics of Nanotubes, Graphite and Graphene Mildred
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Phonon populations and electrical power dissipation in carbon nanotube transistors Supplemental Information Mathias Steiner 1, Marcus Freitag 1, Vasili Perebeinos 1, James C.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Phonon populations and electrical power dissipation in carbon nanotube transistors Supplemental Information Mathias Steiner 1, Marcus Freitag 1, Vasili Perebeinos 1, James C.
Acoustic metamaterials in nanoscale
 Acoustic metamaterials in nanoscale Dr. Ari Salmi www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 12.2.2014 1 Revisit to resonances Matemaattis-luonnontieteellinen tiedekunta / Henkilön nimi / Esityksen nimi www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto
Acoustic metamaterials in nanoscale Dr. Ari Salmi www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto 12.2.2014 1 Revisit to resonances Matemaattis-luonnontieteellinen tiedekunta / Henkilön nimi / Esityksen nimi www.helsinki.fi/yliopisto
Effect of dimensionality in polymeric fullerenes and single-wall nanotubes
 Physica B 244 (1998) 186 191 Effect of dimensionality in polymeric fullerenes and single-wall nanotubes H. Kuzmany*, B. Burger, M. Fally, A.G. Rinzler, R.E. Smalley Institut fu( r Materialphysik, Universita(
Physica B 244 (1998) 186 191 Effect of dimensionality in polymeric fullerenes and single-wall nanotubes H. Kuzmany*, B. Burger, M. Fally, A.G. Rinzler, R.E. Smalley Institut fu( r Materialphysik, Universita(
vapour deposition. Raman peaks of the monolayer sample grown by chemical vapour
 Supplementary Figure 1 Raman spectrum of monolayer MoS 2 grown by chemical vapour deposition. Raman peaks of the monolayer sample grown by chemical vapour deposition (S-CVD) are peak which is at 385 cm
Supplementary Figure 1 Raman spectrum of monolayer MoS 2 grown by chemical vapour deposition. Raman peaks of the monolayer sample grown by chemical vapour deposition (S-CVD) are peak which is at 385 cm
Supplementary Figure S1. AFM image and height profile of GO. (a) AFM image
 Supplementary Figure S1. AFM image and height profile of GO. (a) AFM image and (b) height profile of GO obtained by spin-coating on silicon wafer, showing a typical thickness of ~1 nm. 1 Supplementary
Supplementary Figure S1. AFM image and height profile of GO. (a) AFM image and (b) height profile of GO obtained by spin-coating on silicon wafer, showing a typical thickness of ~1 nm. 1 Supplementary
High-Performance Flexible Asymmetric Supercapacitors Based on 3D. Electrodes
 Supporting Information for: High-Performance Flexible Asymmetric Supercapacitors Based on 3D Porous Graphene/MnO 2 Nanorod and Graphene/Ag Hybrid Thin-Film Electrodes Yuanlong Shao, a Hongzhi Wang,* a
Supporting Information for: High-Performance Flexible Asymmetric Supercapacitors Based on 3D Porous Graphene/MnO 2 Nanorod and Graphene/Ag Hybrid Thin-Film Electrodes Yuanlong Shao, a Hongzhi Wang,* a
Nanostrukturphysik Übung 2 (Class 3&4)
 Nanostrukturphysik Übung 2 (Class 3&4) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu 2017.05.03 Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de (3748), yang.xu@tuilmenau.de (4902)
Nanostrukturphysik Übung 2 (Class 3&4) Prof. Yong Lei & Dr. Yang Xu 2017.05.03 Fachgebiet 3D-Nanostrukturierung, Institut für Physik Contact: yong.lei@tu-ilmenau.de (3748), yang.xu@tuilmenau.de (4902)
The calculation of energy gaps in small single-walled carbon nanotubes within a symmetry-adapted tight-binding model
 The calculation of energy gaps in small single-walled carbon nanotubes within a symmetry-adapted tight-binding model Yang Jie( ) a), Dong Quan-Li( ) a), Jiang Zhao-Tan( ) b), and Zhang Jie( ) a) a) Beijing
The calculation of energy gaps in small single-walled carbon nanotubes within a symmetry-adapted tight-binding model Yang Jie( ) a), Dong Quan-Li( ) a), Jiang Zhao-Tan( ) b), and Zhang Jie( ) a) a) Beijing
status solidi Raman spectroscopy of ( n, m )-identified individual single-walled carbon nanotubes
 physica pss status solidi basic solid state physics b Raman spectroscopy of ( n, m )-identified individual single-walled carbon nanotubes T. Michel 1, M. Paillet 1, J. C. Meyer 2, V. N. Popov 3, L. Henrard
physica pss status solidi basic solid state physics b Raman spectroscopy of ( n, m )-identified individual single-walled carbon nanotubes T. Michel 1, M. Paillet 1, J. C. Meyer 2, V. N. Popov 3, L. Henrard
Selective Manipulation of Molecules by Electrostatic Force and Detection of Single Molecules in Aqueous Solution
 Supporting Information Selective Manipulation of Molecules by Electrostatic Force and Detection of Single Molecules in Aqueous Solution Zhongbo Yan, Ming Xia, Pei Zhang, and Ya-Hong Xie* Department of
Supporting Information Selective Manipulation of Molecules by Electrostatic Force and Detection of Single Molecules in Aqueous Solution Zhongbo Yan, Ming Xia, Pei Zhang, and Ya-Hong Xie* Department of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Flexible, high-performance carbon nanotube integrated circuits Dong-ming Sun, Marina Y. Timmermans, Ying Tian, Albert G. Nasibulin, Esko I. Kauppinen, Shigeru Kishimoto, Takashi
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Flexible, high-performance carbon nanotube integrated circuits Dong-ming Sun, Marina Y. Timmermans, Ying Tian, Albert G. Nasibulin, Esko I. Kauppinen, Shigeru Kishimoto, Takashi
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Chemical and Bandgap Engineering in Monolayer Hexagonal Boron Nitride Kun Ba 1,, Wei Jiang 1,,Jingxin Cheng 2, Jingxian Bao 1, Ningning Xuan 1,Yangye Sun 1, Bing Liu 1, Aozhen
Supplementary Information Chemical and Bandgap Engineering in Monolayer Hexagonal Boron Nitride Kun Ba 1,, Wei Jiang 1,,Jingxin Cheng 2, Jingxian Bao 1, Ningning Xuan 1,Yangye Sun 1, Bing Liu 1, Aozhen
