Numerical Taxonomy for Detecting the Azotobacterial Diversity
|
|
|
- Jasper Reynolds
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
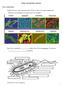
1 Numerical Taxonomy for Detecting the Azotobacterial Diversity Enny Zulaika 1 *, Maya Shovitri 2 and N.D. Kuswytasari 3 1,2,3. Department of Biology-Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, ITS-Surabaya *Corresponding author s. Tel: , enny@bio.its.ac.id Abstract Azotobacter was a non-symbiont of bacteria that were abundant in the land and it able to bind free nitrogen. The bacterial diversity required a holistic integration with a variety of methods, both at the level of the community, or functional structure of the bacteria. Each member of the bacterial population had varying responses to environmental factors and phenotypic variation in accordance with it genotype, so that required a grouping or classification to facilitate the study of bacterial diversity. Through a numerical taxonomy approach will hopefully reveal the diversity of Azotobacter and it similarity relations thus it enable bundling its potential in usage as bioremoval, or as eco-friendly biofertilizer for critical land. Azotobacter was isolated from soil of Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember (ITS) Eco Urban Farming, using selective media for Azotobacter. The Azotobacterial isolates were characterized by utilizing a numerical taxonomy method based on phenotypic characters, including morphological, biochemical and physiological characters. Based on the numerical taxonomy analysis the isolates separate into two different phenotypic groups at similarity level of 79-85%. Species members in one cluster included A5, A6, A7 that had a colony of white-beige and the other cluster with its members consist of A1a, A3 and A9 with their colonies of yellow-brown. Keyword: Azotobacter, diversity, numerical taxonomy, similarity Introduction Azotobacter was a non-symbiont genus of bacteria that were abundant in the land and it able to bind free nitrogen, some of its species were siderophore bacteria, phytohormones producer (Kizilkaya, 2009), and thus it potentially used as biofertilizer. Diversity of Azotobacter in it habitat affected by the physical and chemical properties of soil as well as interactions among microorganisms in the soil (Lenart, 2012). Some members of the Azotobacter was high salinity tolerant (Akhter et al., 2012) and resistant to mercury (Aleem et al., 2003), so it also potentially used as a mercury bioremediation on high salinity area. Mercury was one of heavy metals that were highly toxic and dangerous even in very low concentrations, may accumulate in the cells or tissues of organisms food chain (Oehmen et al., 2009). A minimum threshold of mercury in Indonesia based on the Government regulation of the Republic of Indonesia No. 82 in 2001 was mg/l. Bacteria were microorganisms that live in various habitats, either in normal or extreme environments. Inorganic mercury 5 µg/l shall be inhibited the growth of microorganisms, but naturally there were bacteria that able to live in these conditions, it was called Mercury Resistant Bacteria or MRB. MRB members were enzymatic mechanism that may turn toxic anorganic mercury (Hg 2+ ) into volatile mercury (Hg 0 ) so that mercury did not poison the cells (Brown et al., 2002). Characterization and identification of the bacteria was not as easy to identify specimens of plants or animals, therefore bacterial cell structure were microscopic, simple and difficult to distinguish just based on the visualization only. Study of bacterial diversity August 2014, Korea University, Seoul, Korea Page 1
2 required a holistic integration with a variety of methods, both at the level of the community, or functional structure of the bacteria itself (Schleifer, 2009). Each member of the bacterial population had varying responses to environmental factors and phenotypic variation in accordance with it genotype, so that required a grouping or classification to facilitate the study of bacterial diversity (Selvakumaran et al., 2008). Given the importance role of bacteria in nature for biogeochmical cycles within the ecosystem, it was necessary to understand the diversity of bacterial communities deeply and its role in habitats. Through a numerical taxonomy approach will hopefully reveal the diversity of Azotobacter and it similarity relations, thus it enable bundling its potential in usage as mercury bioremoval, bioremediation or as eco-friendly biofertilizer for critical land. Material and Methods Isolation of bacteria Using composite method, Azotobacter was isolated from soil of the Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember (ITS) Eco Urban Farming. Selective media (Himedia )- HgCl 2 0,1 mg/l used to grow its inoculum and incubated at room temperature for hours. The grown colony was a mercury resistant, isolate Azotobacter, a colony which had different colors and shapes then reisolated and replanted again. Identification, characterization, and generic assignment All the selected isolates characterized based on morphological, physiological and biochemistry reaction, then followed by generic assignment used profile matching to determine the key characters of the genus Azotobacter. Verification refers to the Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology (Holt et al., 1994). All methods of morphology, physiological characterization and biochemistry reaction above resulted from modification of several manuals laboratory (Harley & Prescott, 2002). Collection of data Data were obtained from morphological characterization of phenotypes, physiology and biochemistry reaction. Those data were include how colonies morphology on flat agar media (diameter, color, surface, shape, transparency, elevation, and the edges of the colony), colonies morphology on upright and oblique agar media (growth and a colony form), the cell morphology (shape, Gram staining characteristics, and the presence of cysta). It resisted to metals (Hg, Cd, Pb), antibiotics and NaCl osmotic pressure. Physiological reactions and biochemistry included oxygen demand (aerobic and anaerobic), carbohydrate metabolism (glucose, sucrose, maltose, galactose, fructose, manitol and sorbitol). The characters of the morphology, physiology and biochemistry reaction obtained from the characterization, then it converted with a positive value (+) or negative (-). Data tabulated into a matrix n x t, with n as the number of isolate Azotobacter and t as number of characters, then it inserted into Programmer's File Editor (PFE) August 2014, Korea University, Seoul, Korea Page 2
3 Settings and data processing Data in table n x t copied and inserted in the PFE as a program editor. Files edited in accordance the procedure of PFE, then it stored in a format.mvs that can be opened using MVSP (Multi Variate Statistical Package). Matrix n x t file that has been edited with PFE then processed with MVSP. So that it can be entered MVSP isolates coded. For Taxonomical Operational Unit (OTU), each isolate was codified with A, B, C and so on, as for the character code-named AA, AB, AC, and so on according to the number of characters used. Simple Matching Coeficient (S SM ) used to specify the similarity between isolates Azotobacter. Grouping was done using Unweighted algorithm Paired Group Method with Averages (UPGMA) arithmatic in form of a dendorgram (Sneath & Sokal, 1973). Result and Discussion Phenotypic characterization The results obtained by 79 isolates and only 6 isolates were resisted to HgCl 2 10 mg/l, which were A1a, A3, A5, A6, A7, A9, and those isolate then were characterized. All isolates had small colonies, only isolates A7 was punctiform and A1a isolates that had a large colony. Colonies were normally grouped into 4 colors, white or cream (A5, A6 and A7), brown (A1a), yellowish white (A9) and yellow (A3). They had circular form for colonies, except A9 and A1a with irregular shape (Figure 1.) A1a A3 A5 A6 A7 A9 Figure 1. The colony of Azotobacterial isolates The elevation varies between colonies drive from flat, convex into a pulvinate. They had colony margin such as entire, undulate, and erose. They also had all smooth colony texture, bright and opaque appearance (most were an opaque). Its growth of oblique and upright agar media were filiform and echinulate August 2014, Korea University, Seoul, Korea Page 3
4 According to Aquilanti et al. (2004), Azotobacter chroococcum colonies appear after 24 hours of incubation with the color white and wet colonies turned into dark brown after 3-5 days, Azotobacter paspali after 48 hours of incubation, colonies were yellow in center, Azotobacter agilis was yellowish white. The Azotobacter can be cysta forming that to protect the cell from a state of extreme environments, Azotobacter was an obligate anaerobic bacteria although it could grow under low O 2 conditions (Jímenez et al., 2011). All isolates were able to perform the metabolism of glucose, fructose, sucrose, maltose, galactose, manitol and sorbitol (Table 1.). The genus Azotobacter were able to ferment carbohydrates, types of carbohydrate which fermented depending on the species (Boone et al., 2005), Tabel 1. The Azotobacterial metobolism of carbohydrat Carbohydrate Isolates of Azotobacter A1a A3 A5 A6 A7 A9 Glucose Fructose Sucrose Maltose Galactose Manitol Sorbitol (+) positive test; (-) negative test All Azotobacter isolates resisted to HgCl 2, CdCl 2 dan PbCl 2 10 mg/l, moreover isolate A5, A6, and A7 resisted to HgCl 2 up to 20 mg/l. All isolates were also resistant to the antibiotic ampisilin, tetracycline, and chloramphenicol 30 µg either to NaCl salinity 5%. The mechanism of bacterial resistance to metal or heavy metals varies depending on the genera/species/strains of bacteria, the metal concentration and duration of contacts took place. The majority of bacterial resistant to heavy metals through active efflux transport mechanism or system involving the role of genes in the operon. Mercury involved mer-operon, on cadmium-involved cad-operon and at cuprum (copper) involves a cop-operon (Brown et al., 2002). The mechanisms of bacterial resistance toward heavy metal can be through bioadsorption by Exo Polysacharide (EPS) that located in the outer layer of the cell wall, had a covalent bond and formed a polysaccharide slime that easy off. Bioadsorption process with heavy metals by the EPS was a non-metabolic mechanism because of the ties between the organic acid residue ligand which has negatively charged with functional groups that has the positively charged metal (Aquilanti et al., 2004). All isolates of Azotobacter from soil in Eco Urban Farming had shown resistant to ampsilin, chloramphenicol and 30 µg tetracycline. All isolate Azotobacter were also tolerant to salinity (NaCl) 5%. On the research of Zulaika et al. (2012), Azotobacter S8 of the Kalimas Surabaya resistant to 10µg ampisilin, and 30µg chloramphenicol, tetracycline. And also tolerant of 10% NaCl August 2014, Korea University, Seoul, Korea Page 4
5 Numerical taxonomy The species concept used in this study was through the taxospesies approach. Based on numerical taxonomy analysis produced a dendogram that describes the similarity between Azotobacter isolates, dendogram clumped into two clusters were cluster A and B (Figure 2.). Cluster A Cluster B Figure 2. Dendogram which showed similarity phenotypic between isolates Azotobacter. The scale indicates the level of similaritas (S SM ). Numerical taxonomy used as a system of classification with a politetic phenentic character. Classification by numerical taxonomy of politetic phenentic was widely used and successfully explained isolates representing the diversity of natural habitats included soil, water and could decipher large and heterogeneous taxa (Priest & Austin, 1996). Based dendorgram on Figure 2., Azotobacter isolate form two clusters that included A cluster of isolates; A5, A6, A7 and cluster B isolates that encompassing A1a, A3, A9. Isolates members of A cluster and the cluster B had similarity > 70%, it was assumed that member within of A cluster of isolates be the same species, as well as the members of the cluster B (Table 2) Table 2. Index of Similarity Isolates Isolates A1a A3 A5 A6 A7 A9 A1a 1,000 A3 0,758 1,000 A5 0,613 0,694 1,000 A6 0,597 0,613 0,855 1,000 A7 0,677 0,661 0,839 0,887 1,000 A9 0,839 0,823 0,710 0,597 0,645 1,000 In accordance with the concept of taxospecies, which belongs to the strains of a species must have a similarity > 70% (Goodfellow & O Donnel, 1993). On cluster A had a similarity > 85% and cluster B > 79%. Members in A cluster had similarities in color August 2014, Korea University, Seoul, Korea Page 5
6 white-beige colony and that was capable to use sorbitol and galactose as carbon source and resistant to HgCl 2 for up to 20 mg/l. Members of cluster B had similarity in yellowbrown colour colonies and resistant to HgCl 2 only up to 10 mg/l. Between cluster A and B had similarity only 65%, according to the concept of taxsospecies, isolates in cluster A differed to isolates in cluster B Conclusion The genus of Azotobacter from ITS Eco Urban Farming were consist of isolates A1a, A3, A5, A6, A7 and A9 that resisted to HgCl 2 10 mg/l. Based on concept of taxospecies, the isolates had derived into two species clusters. Species members in A cluster included A5, A6, A7 that had a colony of white-beige and cluster B with its members consist of A1a, A3 and A9 with their colonies of yellow-brown. Acknowledgement We would like to thank to ITS for the financial support, with Contract Number: /IT2.7/PN.01.00/2014 We specially thanked to our students Kusnul Khotimah, Anjar Lulu Sakinah and Afina Dhuhaini who helped us conducting the experiments, they worked with their excellent scientific enthusiasm performing the laboratory works during the hard days. References Akhter, M.S., S.J. Hossain, S.A. Hossain, and R.K. Datta Isolation and characterization of salinity tolerant Azotobacter sp. Greener Journal of Biological Sciences. 2: Aleem, A., J. Isar, and A. Malik Impact of long-term application of industrial wastewater on the emergence of resistance traits in Azotobacter chrococcum isolated from rhizosperic soil. Bioresource Technology, 86: Aquilanti, L., F. Favili, and F. Clementi Comparison of different strategies for isolation and preliminary identification of Azotobacter from soil samples. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 36: Brown, N., Y. Shih, C. Leang, K. Glendinning, K., Hobman, J. and Wilson, J. (2002) Mercury Transport and Resistance.International Biometals Symposium, Biometals, Boone, R.D., R.W. Castenholz, D.J. Breener, N.R. Krieg, and J.T. Staley Bergey s Manual Systematic and Bacteriology 2 nd edition. USA: Springer. Goodfellow, M. and A. G. O Donnell, Handbook of New Bacterial Systematics. Academic Press, Inc. Harley, J.P. & Prescott, L.M Laboratory Exercises in Microbiology. 4 th Edition. The McGraw-Hill Companies: New York Holt, J.G., Krieg, N.R., Sneath, H.A., Staley, J.T. and Wiliam, S.T Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology 9 th Ed, William & Wilkins, Baltimor. Jiménez D.J., J.S. Montaña, and M.M. Martínez Characterization of Free Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria of the Genus Azotobacter in Organic Vegetable-grown Colombian Soils. Brazilian Journal of Microbiology, 42: August 2014, Korea University, Seoul, Korea Page 6
7 Kizilkaya, R Nitrogen fixation capacity of Azotobacter spp. strains isolated from soils in different ecosystems and relationship between them and the microbiological properties of soils. Journal Environmental Biology, 30: Lenart, A Occurance, characteristics, and genetic diversity of Azotobacter chroccocum in various soils of Shotern Poland. Poland Journal Environmental Study, 21: Oehmen, A., J. Fradinho, S.Serra, G. Carvalho, J.L. Capelo, S. Velizarov, and J.G. Crespo The effect of carbon source on the biological reduction of ionic mercury. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165: Priest, F., and Austin, B Modern Bacterial Taxonomy Second Edition. London: Chapman and Hall. Schleifer, K.H Classification of bacteria and archaea: Past, present and future. Systematic and Applied Microbiology, 32: Selvakumaran, S., Kapley, A., Kalia, V.C. & Purohit, H.J Phenotypic and phylogenic groups to evaluate the diversity of Citrobacter isolates from activated biomass of effluent treatment plants. Bioresource Technology, 99: Sneath, P. H. A Thirty years of numerical taxonomy. Systematic Biology, 44 (3): Zulaika, E., L. Sembiring, and A. Soegianto Characterization and Identification Of Mercury-resistant Bacteria From Kalimas River Surabaya-Indonesia by Numerical Phenetic Taxonomy. Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research, 7: August 2014, Korea University, Seoul, Korea Page 7
KILGORE COLLEGE BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT Biology 2421 Syllabus
 COURSE: BIOL 2421 (4-3-4) TITLE: CATALOG DESCRIPTION: Microbiology and Pathology A study of the morphology, physiology, genetics, taxonomy and control of microorganisms. This course includes a study of
COURSE: BIOL 2421 (4-3-4) TITLE: CATALOG DESCRIPTION: Microbiology and Pathology A study of the morphology, physiology, genetics, taxonomy and control of microorganisms. This course includes a study of
Intro to Prokaryotes Lecture 1 Spring 2014
 Intro to Prokaryotes Lecture 1 Spring 2014 Meet the Prokaryotes 1 Meet the Prokaryotes 2 Meet the Prokaryotes 3 Why study prokaryotes? Deep Time 4 Fig. 25.7 Fossilized stromatolite (above) and living stromatolite
Intro to Prokaryotes Lecture 1 Spring 2014 Meet the Prokaryotes 1 Meet the Prokaryotes 2 Meet the Prokaryotes 3 Why study prokaryotes? Deep Time 4 Fig. 25.7 Fossilized stromatolite (above) and living stromatolite
SYLLABUS. Meeting Basic of competence Topic Strategy Reference
 SYLLABUS Faculty : Mathematics and science Study Program : Biology education Lecture/Code : Microbiology/BIO 236 Credits : 2 unit of semester credit Semester : 5 Prerequisites lecture : Biochemistry, Cell
SYLLABUS Faculty : Mathematics and science Study Program : Biology education Lecture/Code : Microbiology/BIO 236 Credits : 2 unit of semester credit Semester : 5 Prerequisites lecture : Biochemistry, Cell
Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity
 19 Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Taxonomy Introduction to Microbial Taxonomy
19 Microbial Taxonomy and the Evolution of Diversity Copyright McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Taxonomy Introduction to Microbial Taxonomy
Taxonomy. Content. How to determine & classify a species. Phylogeny and evolution
 Taxonomy Content Why Taxonomy? How to determine & classify a species Domains versus Kingdoms Phylogeny and evolution Why Taxonomy? Classification Arrangement in groups or taxa (taxon = group) Nomenclature
Taxonomy Content Why Taxonomy? How to determine & classify a species Domains versus Kingdoms Phylogeny and evolution Why Taxonomy? Classification Arrangement in groups or taxa (taxon = group) Nomenclature
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology
 Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology Ex. 13-1: INVESTIGATING CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA Lab Study A: Colony Morphology Table 13.1 Characteristics of Bacterial Colonies Name of Bacteria
Worksheet for Morgan/Carter Laboratory #13 Bacteriology Ex. 13-1: INVESTIGATING CHARACTERISTICS OF BACTERIA Lab Study A: Colony Morphology Table 13.1 Characteristics of Bacterial Colonies Name of Bacteria
THE IDENTIFICATION OF TWO UNKNOWN BACTERIA AFUA WILLIAMS BIO 3302 TEST TUBE 3 PROF. N. HAQUE 5/14/18
 THE IDENTIFICATION OF TWO UNKNOWN BACTERIA AFUA WILLIAMS BIO 3302 TEST TUBE 3 PROF. N. HAQUE Introduction: The identification of bacteria is important in order for us to differentiate one microorganism
THE IDENTIFICATION OF TWO UNKNOWN BACTERIA AFUA WILLIAMS BIO 3302 TEST TUBE 3 PROF. N. HAQUE Introduction: The identification of bacteria is important in order for us to differentiate one microorganism
The Prokaryotic World
 The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
The Prokaryotic World A. An overview of prokaryotic life There is no doubt that prokaryotes are everywhere. By everywhere, I mean living in every geographic region, in extremes of environmental conditions,
Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words)
 Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Biology II BACTERIA Vocabulary- Bacteria (34 words) 1. Prokaryote 21. phototroph 2. Peptidoglycan 22. chemotroph 3. Methanogen 23. obligate anaerobe 4. Halophile 24. facultative anaerobe 5. Thermoacidophile
Introduction to Microbiology. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 Introduction to Microbiology CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Microbiology Micro- means very small (that needs a microscope to see). Microbiology is the study of very small living organisms.
Introduction to Microbiology CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani Microbiology Micro- means very small (that needs a microscope to see). Microbiology is the study of very small living organisms.
P-solubilizing Microorganisms from The Poteran Island, Madura
 P-solubilizing Microorganisms from The Poteran Island, Madura M.Shovitri 1*, N.D. Kuswytasari and E. Zulaika 2 1 Department of Biology, InstitutTeknologiSepuluhNopember, Surabaya, Indonesia 2 Department
P-solubilizing Microorganisms from The Poteran Island, Madura M.Shovitri 1*, N.D. Kuswytasari and E. Zulaika 2 1 Department of Biology, InstitutTeknologiSepuluhNopember, Surabaya, Indonesia 2 Department
Chapter 19. Microbial Taxonomy
 Chapter 19 Microbial Taxonomy 12-17-2008 Taxonomy science of biological classification consists of three separate but interrelated parts classification arrangement of organisms into groups (taxa; s.,taxon)
Chapter 19 Microbial Taxonomy 12-17-2008 Taxonomy science of biological classification consists of three separate but interrelated parts classification arrangement of organisms into groups (taxa; s.,taxon)
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA 10/15/2012
 BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
BACTERIA AND ARCHAEA Chapter 27 KEY CONCEPTS: Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Rapid reproduction, mutation, and genetic recombination promote genetic diversity in
Azospirillum brasilense Triticum sativum
 Triticum sativum Flint Ca - Bentonite clay CFU Ca - Bentonite N 210 Azospirillum C17 N Montmorillonite 8 NFB 214 sand Silt Clay 215 Chloraminet NFB 7) Biochemical Flint Clay Azospirillum brasilens M.P.N.
Triticum sativum Flint Ca - Bentonite clay CFU Ca - Bentonite N 210 Azospirillum C17 N Montmorillonite 8 NFB 214 sand Silt Clay 215 Chloraminet NFB 7) Biochemical Flint Clay Azospirillum brasilens M.P.N.
SRM UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING. Subject code: EN0701- Environmental Microbiology. Topic / Content Book Learning outcomes
 SRM UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING Subject code: EN0701- Environmental Microbiology Semester: I Course: M. Tech Envn. Eng. LESSON PLAN Year: 2011 Lecture in hours Topic / Content Book Learning
SRM UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING Subject code: EN0701- Environmental Microbiology Semester: I Course: M. Tech Envn. Eng. LESSON PLAN Year: 2011 Lecture in hours Topic / Content Book Learning
Classifying Prokaryotes: Eubacteria Plasma Membrane. Ribosomes. Plasmid (DNA) Capsule. Cytoplasm. Outer Membrane DNA. Flagellum.
 Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
Bacteria The yellow band surrounding this hot spring is sulfur, a waste product of extremophilic prokaryotes, probably of the Domain Archaea, Kingdom Archaebacteria. Bacteria are prokaryotic cells (no
9/8/2017. Bacteria and Archaea. Three domain system: The present tree of life. Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success
 5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
5 m 2 m 9/8/2017 Three domain system: The present tree of life Bacteria and Archaea Chapter 27 Structural and functional adaptations contribute to prokaryotic success Unicellular Small Variety of shapes
(DMB 01) M.Sc. (Previous) DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER First Year. Microbiology. Paper I INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS
 wk 7 (DMB 01) Paper I INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS PART A (5 8 = 40 marks) 1. Explain the growth of microbiology in the twentieth century. 2. Describe the structure of eukaryotic cell with a neat-labeled
wk 7 (DMB 01) Paper I INTRODUCTION TO MICROORGANISMS PART A (5 8 = 40 marks) 1. Explain the growth of microbiology in the twentieth century. 2. Describe the structure of eukaryotic cell with a neat-labeled
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC
 BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
BIOLOGY STANDARDS BASED RUBRIC STUDENTS WILL UNDERSTAND THAT THE FUNDAMENTAL PROCESSES OF ALL LIVING THINGS DEPEND ON A VARIETY OF SPECIALIZED CELL STRUCTURES AND CHEMICAL PROCESSES. First Semester Benchmarks:
CHAPTER 2 LIFE'S CHEMICAL BASIS MULTIPLE CHOICE. ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate OBJ: Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge. Mercury Rising
 TEST BANK FOR BIOLOGY THE UNITY AND DIVERSITY OF LIFE 13TH EDITION BY CECEI STARR Link download full:https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-for-biology-the-unity-and-div ersity-of-life-13th-edition-by-cecei-starr
TEST BANK FOR BIOLOGY THE UNITY AND DIVERSITY OF LIFE 13TH EDITION BY CECEI STARR Link download full:https://digitalcontentmarket.org/download/test-bank-for-biology-the-unity-and-div ersity-of-life-13th-edition-by-cecei-starr
GUJARAT UNIVERSITY Syllabus for First Year Microbiology Semester I and II Effective from June 2017
 GUJARAT UNIVERSITY Syllabus for First Year Microbiology Semester I and II Effective from June 2017 1. A student offering Microbiology programme will be offered two theory papers of core course MI 101 and
GUJARAT UNIVERSITY Syllabus for First Year Microbiology Semester I and II Effective from June 2017 1. A student offering Microbiology programme will be offered two theory papers of core course MI 101 and
Chapter 4.0 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification
 Chapter 4.0 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification 8/20/2017 MDufilho 1 Classification and Identification of Microorganisms Taxonomy consists of classification, nomenclature, and identification Organize
Chapter 4.0 Microscopy, Staining, and Classification 8/20/2017 MDufilho 1 Classification and Identification of Microorganisms Taxonomy consists of classification, nomenclature, and identification Organize
Ledyard Public Schools Science Curriculum. Biology. Level-2. Instructional Council Approval June 1, 2005
 Ledyard Public Schools Science Curriculum Biology Level-2 1422 Instructional Council Approval June 1, 2005 Suggested Time: Approximately 9 weeks Essential Question Cells & Cell Processes 1. What compounds
Ledyard Public Schools Science Curriculum Biology Level-2 1422 Instructional Council Approval June 1, 2005 Suggested Time: Approximately 9 weeks Essential Question Cells & Cell Processes 1. What compounds
Microbiology / Active Lecture Questions Chapter 10 Classification of Microorganisms 1 Chapter 10 Classification of Microorganisms
 1 2 Bergey s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology differs from Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former a. groups bacteria into species. b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic
1 2 Bergey s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology differs from Bergey s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology in that the former a. groups bacteria into species. b. groups bacteria according to phylogenetic
Microbiology Helmut Pospiech
 Microbiology http://researchmagazine.uga.edu/summer2002/bacteria.htm 05.04.2018 Helmut Pospiech The Species Concept in Microbiology No universally accepted concept of species for prokaryotes Current definition
Microbiology http://researchmagazine.uga.edu/summer2002/bacteria.htm 05.04.2018 Helmut Pospiech The Species Concept in Microbiology No universally accepted concept of species for prokaryotes Current definition
Interactions Between Microorganisms and Higher Plants from Competition to Symbiosis p. 184
 Introduction What Are Soils? p. 3 Introduction p. 3 Soil Genesis p. 4 Rock Weathering or Decay p. 4 Importance of Soil Texture p. 5 Input of Organic Matter into Soils and Aggregation p. 7 Migration Processes
Introduction What Are Soils? p. 3 Introduction p. 3 Soil Genesis p. 4 Rock Weathering or Decay p. 4 Importance of Soil Texture p. 5 Input of Organic Matter into Soils and Aggregation p. 7 Migration Processes
Unit # - Title Intro to Biology Unit 1 - Scientific Method Unit 2 - Chemistry
 Intro to Biology Unit 1 - Scientific Method Unit 2 - Chemistry What is Biology? What is Science? What tools, skills, knowledge, and dispositions are needed to conduct scientific inquiry? How do the rules
Intro to Biology Unit 1 - Scientific Method Unit 2 - Chemistry What is Biology? What is Science? What tools, skills, knowledge, and dispositions are needed to conduct scientific inquiry? How do the rules
BACTERIAL TOLERANCE TO HEAVY METALS UNDER THE INFLUENCE OF ph, TEMPERATURE AND SALINITY
 BACTERIAL TOLERANCE TO HEAVY METALS UNDER THE INFLUENCE OF ph, TEMPERATURE AND SALINITY 1 J. JOONU, 2 KAVITHA.P, 3 SUGANYA.T 1, 2, 3 Department of Zoology, Bishop Heber College, Trichy 17, Tamilnadu. India
BACTERIAL TOLERANCE TO HEAVY METALS UNDER THE INFLUENCE OF ph, TEMPERATURE AND SALINITY 1 J. JOONU, 2 KAVITHA.P, 3 SUGANYA.T 1, 2, 3 Department of Zoology, Bishop Heber College, Trichy 17, Tamilnadu. India
P e a r s o n : M a t t e r a n d t h e E n v i r o n m e n t
 Quizlet P e a r s o n : M a t t e r a n d t h e E n v i r o n m e n t Study online at quizlet. com/_atb84 a t o m carbonhydrates compound element hydrocarbon lipids macromolecules m a t t e r molecule
Quizlet P e a r s o n : M a t t e r a n d t h e E n v i r o n m e n t Study online at quizlet. com/_atb84 a t o m carbonhydrates compound element hydrocarbon lipids macromolecules m a t t e r molecule
Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea
 Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Section 5.1 Kingdom Bacteria Kingdom Archaea p. 132-139 Kingdom Bacteria General Characteristics: Cell Type: all are prokaryotic. Body Form: most are unicellular, some are colonial. Three main shapes are:
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES
 Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
Chapter 21 PROKARYOTES AND VIRUSES Bozeman Video classification of life http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tyl_8gv 7RiE Impacts, Issues: West Nile Virus Takes Off Alexander the Great, 336 B.C., conquered a
Basic Chemistry. Chapter 2 BIOL1000 Dr. Mohamad H. Termos
 Basic Chemistry Chapter 2 BIOL1000 Dr. Mohamad H. Termos Chapter 2 Objectives Following this chapter, you should be able to describe: - Atoms, molecules, and ions - Composition and properties - Types of
Basic Chemistry Chapter 2 BIOL1000 Dr. Mohamad H. Termos Chapter 2 Objectives Following this chapter, you should be able to describe: - Atoms, molecules, and ions - Composition and properties - Types of
Day 2 - Viewing a prepared slide of mixed bacteria on high power.
 Purpose Bacteria Lab To compare the quantity and the different types of bacteria from four different locations within the school. To identify 3 different bacterial colonies on a prepared slide. Materials
Purpose Bacteria Lab To compare the quantity and the different types of bacteria from four different locations within the school. To identify 3 different bacterial colonies on a prepared slide. Materials
BIO 181 GENERAL BIOLOGY I (MAJORS) with Lab (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) Course Package
 GENERAL BIOLOGY I (MAJORS) with Lab (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) Course Package COURSE INFORMATION Is this a new course or a proposed modification to an existing course? Please check the appropriate box.
GENERAL BIOLOGY I (MAJORS) with Lab (Title change ONLY Oct. 2013) Course Package COURSE INFORMATION Is this a new course or a proposed modification to an existing course? Please check the appropriate box.
Lidia Sas Paszt The Rhizosphere Laboratory, Research Institute of Horticulture, Skierniewice, Poland,
 Lidia Sas Paszt lidia.sas@inhort.pl The Rhizosphere Laboratory, Research Institute of Horticulture, Skierniewice, Poland, www.inhort.pl - Research on the role of roots & rhizosphere in growth & yelding
Lidia Sas Paszt lidia.sas@inhort.pl The Rhizosphere Laboratory, Research Institute of Horticulture, Skierniewice, Poland, www.inhort.pl - Research on the role of roots & rhizosphere in growth & yelding
Prokaryotes. Chapter 27. PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition. Lectures by Chris Romero. Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 27 Prokaryotes PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: They re (Almost) Everywhere! Most prokaryotes are microscopic But
Chapter 27 Prokaryotes PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero Overview: They re (Almost) Everywhere! Most prokaryotes are microscopic But
Biology Curriculum Pacing Guide MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Biology Curriculum Pacing Guide 1 st 9 Weeks SOL Objectives Vocabulary 7 Days 14 Days BIO.1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific reasoning, logic,
MONTGOMERY COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS Biology Curriculum Pacing Guide 1 st 9 Weeks SOL Objectives Vocabulary 7 Days 14 Days BIO.1 The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific reasoning, logic,
Big Idea 1: Does the process of evolution drive the diversity and unit of life?
 AP Biology Syllabus 2016-2017 Course Overview: AP Biology is equivalent to an introductory college level biology program in order to develop student led inquiry into science. The class is designed to go
AP Biology Syllabus 2016-2017 Course Overview: AP Biology is equivalent to an introductory college level biology program in order to develop student led inquiry into science. The class is designed to go
ADVANCED PLACEMENT BIOLOGY
 ADVANCED PLACEMENT BIOLOGY Description Advanced Placement Biology is designed to be the equivalent of a two-semester college introductory course for Biology majors. The course meets seven periods per week
ADVANCED PLACEMENT BIOLOGY Description Advanced Placement Biology is designed to be the equivalent of a two-semester college introductory course for Biology majors. The course meets seven periods per week
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1)
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) 1) Which of the following statements about the atom A) It has 12 neutrons in its nucleus. B) It
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) 1) Which of the following statements about the atom A) It has 12 neutrons in its nucleus. B) It
13. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Name 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and
Environmental Science and Technology
 Environmental Science and Technology Are You Ready for the June Exam? THE MATERIAL WORLD Properties of solutions: Concentration I can determine the concentration of an aqueous solution (g/l, percentage,
Environmental Science and Technology Are You Ready for the June Exam? THE MATERIAL WORLD Properties of solutions: Concentration I can determine the concentration of an aqueous solution (g/l, percentage,
belonging to the Genus Pantoea
 Emerging diseases of maize and onion caused by bacteria belonging to the Genus Pantoea by Teresa Goszczynska Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree Philosophiae Doctoriae in
Emerging diseases of maize and onion caused by bacteria belonging to the Genus Pantoea by Teresa Goszczynska Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree Philosophiae Doctoriae in
TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY
 Washington Educator Skills Tests Endorsements (WEST E) TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY BIOLOGY Copyright 2014 by the Washington Professional Educator Standards Board 1 Washington Educator Skills
Washington Educator Skills Tests Endorsements (WEST E) TEST SUMMARY AND FRAMEWORK TEST SUMMARY BIOLOGY Copyright 2014 by the Washington Professional Educator Standards Board 1 Washington Educator Skills
Behavioral Science, Math, Science, and Physical Education Fall COURSE OUTLINE Critical Concepts in Biology
 Butler County Community College Susan Forrest/ William Langley Behavioral Science, Math, Science, and Physical Education Fall 2003 COURSE OUTLINE Critical Concepts in Biology Course Description: BI 106.
Butler County Community College Susan Forrest/ William Langley Behavioral Science, Math, Science, and Physical Education Fall 2003 COURSE OUTLINE Critical Concepts in Biology Course Description: BI 106.
CELL AND MICROBIOLOGY Nadia Iskandarani
 7Course Title: Head of Department: Teacher(s) + e-mail: Cycle/Division: Biology IA: CELL AND MICROBIOLOGY Nadia Iskandarani Ms.Ibtessam: ibtissam.h@greenwood.sch.ae High School Grade Level: Grade 10 Credit
7Course Title: Head of Department: Teacher(s) + e-mail: Cycle/Division: Biology IA: CELL AND MICROBIOLOGY Nadia Iskandarani Ms.Ibtessam: ibtissam.h@greenwood.sch.ae High School Grade Level: Grade 10 Credit
Ch 10. Classification of Microorganisms
 Ch 10 Classification of Microorganisms Student Learning Outcomes Define taxonomy, taxon, and phylogeny. List the characteristics of the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya domains. Differentiate among eukaryotic,
Ch 10 Classification of Microorganisms Student Learning Outcomes Define taxonomy, taxon, and phylogeny. List the characteristics of the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya domains. Differentiate among eukaryotic,
If you are looking for the book by R. C. W. Berkeley The Aerobic Endospore-Forming Bacteria: Classification and Identification (Special publications
 The Aerobic Endospore-Forming Bacteria: Classification And Identification (Special Publications Of The Society For General Microbiology) By R. C. W. Berkeley READ ONLINE If you are looking for the book
The Aerobic Endospore-Forming Bacteria: Classification And Identification (Special Publications Of The Society For General Microbiology) By R. C. W. Berkeley READ ONLINE If you are looking for the book
Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes
 The Microbial World Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Mircrobes of the Ocean Primary Producers Are the organisms that produce bio-mass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). -Photosynthetic autotrophs Phytoplankton
The Microbial World Prokaryotes Vs. Eukaryotes Mircrobes of the Ocean Primary Producers Are the organisms that produce bio-mass from inorganic compounds (autotrophs). -Photosynthetic autotrophs Phytoplankton
Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz The Chemical Basis for Life - (BIO.A ) Water Properties, (BIO.A ) Carbon, (BIO.A.2.2.
 Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz The Chemical Basis for Life - (BIO.A.2.1.1 ) Water Properties, (BIO.A.2.2.1 ) Carbon, (BIO.A.2.2.2 ) Macromolecules Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared George 1) The first
Biology Keystone (PA Core) Quiz The Chemical Basis for Life - (BIO.A.2.1.1 ) Water Properties, (BIO.A.2.2.1 ) Carbon, (BIO.A.2.2.2 ) Macromolecules Student Name: Teacher Name: Jared George 1) The first
Cell Respiration Star 2
 Cell Respiration Star 2 Name: Date: 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the provided information and on your knowledge of biology. small green plant was placed in a flask as shown below.
Cell Respiration Star 2 Name: Date: 1. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the provided information and on your knowledge of biology. small green plant was placed in a flask as shown below.
What do plants compete for? What do animals compete for? What is a gamete and what do they carry? What is a gene?
 How are these animals adapted to their surroundings: - a) Polar bear b) Camel c) Cactus What do plants compete for? What do animals compete for? What is a gamete and what do they carry? What is a gene?
How are these animals adapted to their surroundings: - a) Polar bear b) Camel c) Cactus What do plants compete for? What do animals compete for? What is a gamete and what do they carry? What is a gene?
Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table:
 Practical Microbiology 30/11/2018 University of Sulaimani college of Pharmacy Year2 Lab. 5: Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table: Major Bacterial
Practical Microbiology 30/11/2018 University of Sulaimani college of Pharmacy Year2 Lab. 5: Overview of the major bacterial pathogens The major bacterial pathogens are presented in this table: Major Bacterial
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Chapter 2
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 2 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CHAPTER 2 CHEMICAL BASIS OF
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 2 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. CHAPTER 2 CHEMICAL BASIS OF
ISSN: IJBPAS, December, 2014, 3(12):
 : 2753-2762 ISSN: 2277 4998 MICROBIAL DIVERSITY OF FOREST ECOSYSTEM OF ACHANAKMAR TIGER RESERVE IN CHHATTISGARH STATE OF INDIA BARIK K*, SAO S AND PARIHAR DK 2 Department of Microbiology, Dr. C.V. Raman
: 2753-2762 ISSN: 2277 4998 MICROBIAL DIVERSITY OF FOREST ECOSYSTEM OF ACHANAKMAR TIGER RESERVE IN CHHATTISGARH STATE OF INDIA BARIK K*, SAO S AND PARIHAR DK 2 Department of Microbiology, Dr. C.V. Raman
Abiotic Stress in Crop Plants
 1 Abiotic Stress in Crop Plants Mirza Hasanuzzaman, PhD Professor Department of Agronomy Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University E-mail: mhzsauag@yahoo.com Stress Stress is usually defined as an external
1 Abiotic Stress in Crop Plants Mirza Hasanuzzaman, PhD Professor Department of Agronomy Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University E-mail: mhzsauag@yahoo.com Stress Stress is usually defined as an external
Chapter 1. Basics of Microbiology
 Chapter 1 Basics of Microbiology Objectives How microorganisms are classified (taxonomy) What they look like (morphology) The major divisions among microorganisms based upon their function in the environment
Chapter 1 Basics of Microbiology Objectives How microorganisms are classified (taxonomy) What they look like (morphology) The major divisions among microorganisms based upon their function in the environment
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 ch 2 chemical basis of life Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Fill in the blank or provide a short answer: 1) When a change in matter
ch 2 chemical basis of life Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Fill in the blank or provide a short answer: 1) When a change in matter
C. Schedule Description: An introduction to biological principles, emphasizing molecular and cellular bases for the functions of the human body.
 I. CATALOG DESCRIPTION: A. Division: Science Department: Biology Course ID: BIOL 102 Course Title: Human Biology Units: 4 Lecture: 3 hours Laboratory: 3 hours Prerequisite: None B. Course Description:
I. CATALOG DESCRIPTION: A. Division: Science Department: Biology Course ID: BIOL 102 Course Title: Human Biology Units: 4 Lecture: 3 hours Laboratory: 3 hours Prerequisite: None B. Course Description:
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math
 Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/37 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours 1/37 *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not
Connecticut State Department of Education Science - Core Curriculum Standards High School Grades 9-12
 Connecticut State Department of Education Science - Core Curriculum Standards High School Grades 9-12 Essential Questions Scientific Inquiry, Literacy and Numeracy How is scientific knowledge created and
Connecticut State Department of Education Science - Core Curriculum Standards High School Grades 9-12 Essential Questions Scientific Inquiry, Literacy and Numeracy How is scientific knowledge created and
Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages )
 Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages 471 477) How do the two groups of prokaryotes differ? What factors are used to identify prokaryotes? What is the importance of bacteria? 13.
Chapter 19 Bacteria and Viruses Section 19 1 Bacteria (pages 471 477) How do the two groups of prokaryotes differ? What factors are used to identify prokaryotes? What is the importance of bacteria? 13.
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)
 PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
Notes - Microbiology Monera
 Notes - Microbiology Monera Part 1 Classification - Kingdom moneran is more commonly known as bacteria. This is the largest kingdom with inhabitants covering almost every square metre of the planet! -
Notes - Microbiology Monera Part 1 Classification - Kingdom moneran is more commonly known as bacteria. This is the largest kingdom with inhabitants covering almost every square metre of the planet! -
Chemical Basis of Life
 Chemical Basis of Life Jan 30 11:42 AM In order to understand digestion and nutrition, we need some basic biochemistry Chemistry studies the composition of matter and its changes as well as the change
Chemical Basis of Life Jan 30 11:42 AM In order to understand digestion and nutrition, we need some basic biochemistry Chemistry studies the composition of matter and its changes as well as the change
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Sediment Microbiology. Guangyi Wang POST 103B
 OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Sediment Microbiology Guangyi Wang POST 103B guangyi@hawaii.edu Three Domains of Life 1) Unrooted phylogenetic tree constructed based on small-subunit rrna genes; 2) Members
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Sediment Microbiology Guangyi Wang POST 103B guangyi@hawaii.edu Three Domains of Life 1) Unrooted phylogenetic tree constructed based on small-subunit rrna genes; 2) Members
Announcements KEY CONCEPTS
 What do these things have in common? Announcements Lab this week: bring textbook and photo atlas. Relevant reading BEFORE lab: Ch. 30 http://i.cnn.net/cnn/specials/2001/trade.center/images/anthrax.jpg
What do these things have in common? Announcements Lab this week: bring textbook and photo atlas. Relevant reading BEFORE lab: Ch. 30 http://i.cnn.net/cnn/specials/2001/trade.center/images/anthrax.jpg
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition. Chapter 2
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier w Butler w Lewis Chapter 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier w Butler w Lewis Chapter 2 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
2. Draw two water molecules. Using a dotted line, show a hydrogen bond that could form between them.
 Biology Final Review Packet Directions: Answer the questions below. You may use any notes, worksheets, or your textbook to find the answers. The questions are divided up based on the different units we
Biology Final Review Packet Directions: Answer the questions below. You may use any notes, worksheets, or your textbook to find the answers. The questions are divided up based on the different units we
CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
 CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and mitigate potential
Common Effects of Abiotic Stress Factors on Plants
 Common Effects of Abiotic Stress Factors on Plants Plants are living organisms which lack ability of locomotion. Animals can move easily from one location to other. Immovable property of plants makes it
Common Effects of Abiotic Stress Factors on Plants Plants are living organisms which lack ability of locomotion. Animals can move easily from one location to other. Immovable property of plants makes it
In vitro the effect of intestinal normal flora on some pathogenic bacteria.
 In vitro the effect of intestinal normal flora on some pathogenic bacteria. Abstract: Dr.abbass shaker Ali adel Leena abd Al-Redha The effect of two types of intestinal bacterial normal floral ( and klebsiella)
In vitro the effect of intestinal normal flora on some pathogenic bacteria. Abstract: Dr.abbass shaker Ali adel Leena abd Al-Redha The effect of two types of intestinal bacterial normal floral ( and klebsiella)
Range of Competencies
 BIOLOGY Content Domain Range of Competencies l. Nature of Science 0001 0003 20% ll. Biochemistry and Cell Biology 0004 0005 13% lll. Genetics and Evolution 0006 0009 27% lv. Biological Unity and Diversity
BIOLOGY Content Domain Range of Competencies l. Nature of Science 0001 0003 20% ll. Biochemistry and Cell Biology 0004 0005 13% lll. Genetics and Evolution 0006 0009 27% lv. Biological Unity and Diversity
Biology 160 Cell Lab. Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm. Student Learning Outcomes:
 Biology 160 Cell Lab Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm Student Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of today s lab you will be able to do the following: Properly use a compound light microscope Discuss the
Biology 160 Cell Lab Name Lab Section: 1:00pm 3:00 pm Student Learning Outcomes: Upon completion of today s lab you will be able to do the following: Properly use a compound light microscope Discuss the
Monday EOC Notecard Review
 Monday EOC Notecard Review #117 AEROBIC process which requires oxygen to occur (i.e. cellular respiration). #118 HETEROTROPH an organism which needs to consume their food to survive. Create an antonym,
Monday EOC Notecard Review #117 AEROBIC process which requires oxygen to occur (i.e. cellular respiration). #118 HETEROTROPH an organism which needs to consume their food to survive. Create an antonym,
Biology. Lessons: 15% Quizzes: 25% Projects: 30% Tests: 30% Assignment Weighting per Unit Without Projects. Lessons: 21% Quizzes: 36% Tests: 43%
 Biology This course consists of 12 units, which provide an overview of the basic concepts and natural laws of Biology. Unit 1 deals with the organization of living organisms. Unit 2 addresses the chemistry
Biology This course consists of 12 units, which provide an overview of the basic concepts and natural laws of Biology. Unit 1 deals with the organization of living organisms. Unit 2 addresses the chemistry
Microbiology: An Introduction, 12e (Tortora) Chapter 2 Chemical Principles. 2.1 Multiple Choice Questions
 Microbiology An Introduction 12th Edition Tortora TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/microbiology-an-introduction-12thedition-tortora-test-bank/ Microbiology An Introduction
Microbiology An Introduction 12th Edition Tortora TEST BANK Full download at: https://testbankreal.com/download/microbiology-an-introduction-12thedition-tortora-test-bank/ Microbiology An Introduction
FINAL VERSION_ Secondary Preservice Teacher Standards -- Life Science AFK12SE/NGSS Strand Disciplinary Core Idea
 Secondary Preservice Teacher Standards -- Life Science AFK12SE/NGSS Strand Disciplinary Core Idea LS1: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes LS1.A: Structure and Function How do the structures
Secondary Preservice Teacher Standards -- Life Science AFK12SE/NGSS Strand Disciplinary Core Idea LS1: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes LS1.A: Structure and Function How do the structures
Prereq: Concurrent 3 CH
 0201107 0201101 General Biology (1) General Biology (1) is an introductory course which covers the basics of cell biology in a traditional order, from the structure and function of molecules to the structure
0201107 0201101 General Biology (1) General Biology (1) is an introductory course which covers the basics of cell biology in a traditional order, from the structure and function of molecules to the structure
Biosorption of aqueous chromium VI by living mycelium of phanerochaete chrysosporium
 Biosorption of aqueous chromium VI by living mycelium of phanerochaete chrysosporium Nikazar, M.*, Davarpanah, L., Vahabzadeh, F. * Professor of Department of Chemical Engineering, Amirkabir University
Biosorption of aqueous chromium VI by living mycelium of phanerochaete chrysosporium Nikazar, M.*, Davarpanah, L., Vahabzadeh, F. * Professor of Department of Chemical Engineering, Amirkabir University
Stockton Unified School District Instructional Guide for BIOLOGY NGSS Pilot for both 4X4 and Traditional. 1st Quarter
 1st Quarter Unit NGSS Standards Required Labs Supporting Text Content Academic Suggested Labs and Activities Biochemistry HS-LS-1-6 Ch. 1 & 2 molecules elements amino acids Carbon-based Carbon Hydrogen
1st Quarter Unit NGSS Standards Required Labs Supporting Text Content Academic Suggested Labs and Activities Biochemistry HS-LS-1-6 Ch. 1 & 2 molecules elements amino acids Carbon-based Carbon Hydrogen
PLANT BIOLOGY (PBIO) Plant Biology (PBIO) 1
 Plant Biology (PBIO) 1 PLANT BIOLOGY (PBIO) PBIO 1052 How Plants Shaped Our World (LN) Description: This course is an eclectic dive into the world of plants and their influence on human society. Students
Plant Biology (PBIO) 1 PLANT BIOLOGY (PBIO) PBIO 1052 How Plants Shaped Our World (LN) Description: This course is an eclectic dive into the world of plants and their influence on human society. Students
Peddie Summer Day School
 Peddie Summer Day School Course Syllabus: BIOLOGY Teacher: Mr. Jeff Tuliszewski Text: Biology by Miller and Levine, Prentice Hall, 2010 edition ISBN 9780133669510 Guided Reading Workbook for Biology ISBN
Peddie Summer Day School Course Syllabus: BIOLOGY Teacher: Mr. Jeff Tuliszewski Text: Biology by Miller and Levine, Prentice Hall, 2010 edition ISBN 9780133669510 Guided Reading Workbook for Biology ISBN
Enumeration and Identification of Microorganisms in Plantation White Sugar from Factories in Thailand
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 321-327 (2008) Enumeration and Identification of Microorganisms in Plantation White Sugar from Factories in Thailand Sirivatana Chittrepol 1, Malai Boonyaratanakornkit 2 *
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 42 : 321-327 (2008) Enumeration and Identification of Microorganisms in Plantation White Sugar from Factories in Thailand Sirivatana Chittrepol 1, Malai Boonyaratanakornkit 2 *
Bacterial Morphology and Structure م.م رنا مشعل
 Bacterial Morphology and Structure م.م رنا مشعل SIZE OF BACTERIA Unit for measurement : Micron or micrometer, μm: 1μm=10-3 mm Size: Varies with kinds of bacteria, and also related to their age and external
Bacterial Morphology and Structure م.م رنا مشعل SIZE OF BACTERIA Unit for measurement : Micron or micrometer, μm: 1μm=10-3 mm Size: Varies with kinds of bacteria, and also related to their age and external
Microbial Diversity and Assessment (II) Spring, 2007 Guangyi Wang, Ph.D. POST103B
 Microbial Diversity and Assessment (II) Spring, 007 Guangyi Wang, Ph.D. POST03B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/marinefungi/ocn403webpage.htm General introduction and overview Taxonomy [Greek
Microbial Diversity and Assessment (II) Spring, 007 Guangyi Wang, Ph.D. POST03B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/marinefungi/ocn403webpage.htm General introduction and overview Taxonomy [Greek
Missouri Educator Gateway Assessments
 Missouri Educator Gateway Assessments June 2014 Content Domain Range of Competencies Approximate Percentage of Test Score I. Science and Engineering Practices 0001 0003 21% II. Biochemistry and Cell Biology
Missouri Educator Gateway Assessments June 2014 Content Domain Range of Competencies Approximate Percentage of Test Score I. Science and Engineering Practices 0001 0003 21% II. Biochemistry and Cell Biology
Scientific names allow scientists to talk about particular species without confusion
 Unit 9 Test Review KEY a. Explain the history, purpose, and methods of taxonomy What is taxonomy? the science of naming and classifying organisms Who came up with it? Linnaeus Why do we use taxonomy? Scientific
Unit 9 Test Review KEY a. Explain the history, purpose, and methods of taxonomy What is taxonomy? the science of naming and classifying organisms Who came up with it? Linnaeus Why do we use taxonomy? Scientific
Marine Resources Development Foundation/MarineLab Grades: 9, 10, 11, 12 States: AP Biology Course Description Subjects: Science
 Marine Resources Development Foundation/MarineLab Grades: 9, 10, 11, 12 States: AP Biology Course Description Subjects: Science Highlighted components are included in Tallahassee Museum s 2016 program
Marine Resources Development Foundation/MarineLab Grades: 9, 10, 11, 12 States: AP Biology Course Description Subjects: Science Highlighted components are included in Tallahassee Museum s 2016 program
ASSIGNMENT-1. M.Sc. ( Previous ) DEGREE EXAMINATION, MAY 2018 First Year MICROBIOLOGY Introduction Microorganisms
 ASSIGNMENT-1 Introduction Microorganisms (DMB 01) Q1) Germ theory of diseases. Q2) Leeuwenhoek. Q3) Mycoplasmas. Q4) Rhizobium. Q5) T4 Q6) Viroids. Q7) Protozoa classification. ASSIGNMENT-2 Introduction
ASSIGNMENT-1 Introduction Microorganisms (DMB 01) Q1) Germ theory of diseases. Q2) Leeuwenhoek. Q3) Mycoplasmas. Q4) Rhizobium. Q5) T4 Q6) Viroids. Q7) Protozoa classification. ASSIGNMENT-2 Introduction
Fungal Identification Practical Manual Microbiology READ ONLINE
 Fungal Identification Practical Manual Microbiology READ ONLINE If you are searched for the book Fungal identification practical manual microbiology in pdf form, then you have come on to correct site.
Fungal Identification Practical Manual Microbiology READ ONLINE If you are searched for the book Fungal identification practical manual microbiology in pdf form, then you have come on to correct site.
Text of objective. Investigate and describe the structure and functions of cells including: Cell organelles
 This document is designed to help North Carolina educators teach the s (Standard Course of Study). NCDPI staff are continually updating and improving these tools to better serve teachers. Biology 2009-to-2004
This document is designed to help North Carolina educators teach the s (Standard Course of Study). NCDPI staff are continually updating and improving these tools to better serve teachers. Biology 2009-to-2004
DNA fingerprinting of Bacillus cereus from diverse sources by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis
 Advances in Bioscience and Biotechnology, 2010, 1, 136-144 doi:10.4236/abb.2010.12019 Published Online June 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/abb/) DNA fingerprinting of Bacillus cereus from diverse sources
Advances in Bioscience and Biotechnology, 2010, 1, 136-144 doi:10.4236/abb.2010.12019 Published Online June 2010 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/abb/) DNA fingerprinting of Bacillus cereus from diverse sources
Branches of Science. How many branches of science do you know Copyright 2010 Ryan P. Murphy
 Branches of Science How many branches of science do you know. - - - - - - - - Types of scientists Biology The study of life. Geology The study of Earth. Chemistry The study of Matter. Physics The study
Branches of Science How many branches of science do you know. - - - - - - - - Types of scientists Biology The study of life. Geology The study of Earth. Chemistry The study of Matter. Physics The study
BUNGOMA JOINT INTER-SCHOOLS EVALUTION TEST (JISET) Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education 2012
 NAME:. INDEX...... SCHOOL:.. SIGNATURE DATE. 231/1 BIOLOGY PAPER 1 (Theory) JULY/AUGUST 2012 TIME: 2HOURS BUNGOMA JOINT INTER-SCHOOLS EVALUTION TEST (JISET) Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education 2012
NAME:. INDEX...... SCHOOL:.. SIGNATURE DATE. 231/1 BIOLOGY PAPER 1 (Theory) JULY/AUGUST 2012 TIME: 2HOURS BUNGOMA JOINT INTER-SCHOOLS EVALUTION TEST (JISET) Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education 2012
Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1
 Name I. Multiple Choice (1 point each) Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1 B 1. Which is possessed by eukaryotes but not by prokaryotes? A. Cell wall B. Distinct nucleus
Name I. Multiple Choice (1 point each) Introduction to Microbiology BIOL 220 Summer Session I, 1996 Exam # 1 B 1. Which is possessed by eukaryotes but not by prokaryotes? A. Cell wall B. Distinct nucleus
Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani
 Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Why Study Microbes? Microbiology is the branch of biological sciences concerned with the study of the microbes. 1. Microbes and Man in Sickness and Health
Introductory Microbiology Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Why Study Microbes? Microbiology is the branch of biological sciences concerned with the study of the microbes. 1. Microbes and Man in Sickness and Health
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & Eubacteria)
 Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Kingdom Monera(Archaebacteria & All bacteria are prokaryotes Characteristics: 1. No nucleus Eubacteria) 2. No membrane bound organelles 3. Smaller & less ribosomes 4. Most are smaller than eukaryotes 5.
Evolution in Action: The Power of Mutation in E. coli
 Evolution in Action: The Power of Mutation in E. coli by Merle K. Heidemann, College of Natural Science, Emeritus Peter J. T. White, Lyman Briggs College James J. Smith, Lyman Briggs College Michigan State
Evolution in Action: The Power of Mutation in E. coli by Merle K. Heidemann, College of Natural Science, Emeritus Peter J. T. White, Lyman Briggs College James J. Smith, Lyman Briggs College Michigan State
Microbial Taxonomy. Classification of living organisms into groups. A group or level of classification
 Lec 2 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Purpose Microbial Taxonomy Classification Systems provide an easy way grouping of diverse and huge numbers of microbes To provide an overview of how physicians think
Lec 2 Oral Microbiology Dr. Chatin Purpose Microbial Taxonomy Classification Systems provide an easy way grouping of diverse and huge numbers of microbes To provide an overview of how physicians think
