Evolu&on of Cellular Interac&on Networks. Pedro Beltrao Krogan and Lim UCSF
|
|
|
- Daisy Simmons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Evolu&on of Cellular Interac&on Networks Pedro Beltrao Krogan and Lim UCSF
2
3
4 Point muta&ons Recombina&on Duplica&ons
5 Mutants
6 Mutants
7 Point muta&ons Recombina&on Duplica&ons Changes in protein- protein, protein- DNA interac&ons, etc
8 Cellular interac&on networks
9 Output Point muta&ons Recombina&on Duplica&ons Input Phenotypic changes Changes in protein- protein, protein- DNA interac&ons, etc
10 Fitness differences Output Point muta&ons Recombina&on Duplica&ons Input Phenotypic changes Changes in protein- protein, protein- DNA interac&ons, etc
11 Muta&on/Change Model Consequence Codon change in open reading frames Gene&c code Amino acid changes Amino acid changes Sta&s&cal energy poten&als Impact on protein structure and/or interac&ons Changes in reac&on kine&cs or interac&ons Network model Output Input Network response
12 2 short stories
13 Details
14 Evolutionary dynamics of: 1 Protein phosphorylation 2 Drug-gene interactions
15 Evolu&onary dynamics of phosphoryla&on Mass- spec phosphoproteomics 3 yeast species Exponen&ally growing yeast cells Protein extrac&on Trypsin digest Phosphopep&de enrichment Mass- spectrometry S. cerevisiae C.albicans S.pombe Site iden&fica&on With UCSF Mass Spec facility Beltrao et al. PLoS Bio 2009
16 Phosphoryla&on is poorly conserved Phosphoryla&on sites from 3 yeast species shows they are poorly conserved
17 Phosphoryla&on of func&onal modules is well conserved Pathway or complex Average number of phosphosites per protein (normalized for proteome coverage)
18 How is phosphoryla&on translated to func&on? How many phosphoryla&on sites are func&onal? How much of this change is neutral?
19 Currently known phosphoryla&on sites Species Phospho Phospho proteins sites H.sapiens M.musculus R. norvegicus X.laevis C.elegans D.melanogaster S.pombe S.cerevisiae C.albicans A.thaliana O.sa=va > phosphorylation sites
20 Func&onal consequence of phosphoryla&on Globular regions Unstructured regions + Regula&ng interfaces Regula&ng domain ac&vity Phosphoryla&on switches ~20% ~80%
21 Phosphoryla&on of interfaces Control of protein- protein interac&ons by regula&ng interfaces Define models for protein- protein interac&on interfaces (ex. S. cerevisiae): 100 Xray structures of complexes (PDB) 1200 homology models of interac&ons (GWIDD database) 2700 docking solu&ons (Mosca et al PLoS Comp 2009) Map phosphosites to models of interfaces Evaluate conserva&on of phosphoryla&on (site and func&on)
22 Phosphoryla&on of interfaces RDI1 Phosphorylated in S. cerevisiae and C. albicans CDC42 Phosphorylated in H.sapiens Phosphorylated residues are 20 Amino- acids apart in sequence
23 Conserva&on of func&on vs conserva&on of psites Phosphosite Interfaces with psites (xray) In S. cerevisiae In S. cerevisiae Conserved in another species by aln (+/- 5 pos) Conserved in another species Frac9on conserved All In interface Frac9on conserved Interfaces with psites (docking) Interfaces with psites (compara9ve modeling) Posi9onal conserva9on under- predicts conserva9on of func9on
24 Regula&on of domain ac&vity 1. Pool all phosphosites and map them to representa&ve structures of domain families 2. Look for sequence / structural enrichment
25 Protein kinase domain phosphoryla&on propensity Ac9va9on loop (50% of psites) Regulatory hot- spot
26 HSP70 domain Phosphoryla&on propensity Substrate binding region Region 2 ATPase region Region 1 p-value < Region 2 Region 1
27 Regulatory hot- spots in S. cerevisiae Hsp70 SSA1 7 cytosolic Hsp70 (SSA1-4, SSB1-2 and SSZ1) Mutants generated for SSA1: Region 2 Region 1 mutant 1: SSA1 T492A mutant 2: SSA1 T492D mutant 7: SSA1 T492A, S495A mutant 8: SSA1 T492D, S495D mutant 9: SSA1 T492A, T499A mutant 10: SSA1 T492D, T499D mutant 15: SSA1 T492A, S495A, T499A mutant 16: SSA1 T492D, S495D, T499D mutant 19: SSA1 T495A mutant 20: SSA1 T495D mutant 23: SSA1 T36A mutant 24: SSA1 T36D mutant 25: SSA1 S38A mutant 26: SSA1 S38D mutant 27: SSA1 T36A S38A mutant 28: SSA1 T36D S38D Pep&de binding domain ATPase domain Collabora&on with: Veronique Albanese, Frydman Stanford
28 Complementa&on assay for the mutants Region 2 None of the SSA1 mutants complement the null
29 Preliminary func&onal assays Region 2 SSA1 T492A T492D Interaction of the mutants with cochaperone SSE1 Cell morphology
30 Post- transla&onal switches Different PTMs tend to co- occur in the same proteins More than 75% of ubi proteins are also phosphorylated Different PTMs cluster within proteins Phosphoacceptor phosphoryla&on increases near Ubi sites Phosphosites near other PTMs are more conserved 2X more than average? Ongoing: ~2000 Ubiquitylation sites for H.sapiens
31 Summary: evolu&on of protein phosphoryla&on Regula&on by protein phosphoryla&on diverges quickly Phosphosites with predicted func&on are more likely to be conserved Phosphosites at interfaces Phosphosites near other PTMs (phospho- switches) Regulatory hot- spots Some evidence for neutral varia&on Conserva&on of interface phosphoryla&on despite divergence of site Co- evolu&on of phospho- switches
32 Drug-gene interactions (Chemogenomics)
33 Drug- gene interac&ons in S. cerevisiae and S. pombe Kapitzky L, Beltrao P et al. MSB 2010
34 Drug- gene scores are reproducible 438 S. pombe KOs 727 S. cerevisiae KOs X 21 compounds 2 technical replicates 2 biological replicates
35 Drug- gene interac&ons are poorly conserved
36 Drug- gene vs. Drug- module interac&ons
37 Drug- gene vs. Drug- module interac&ons Gold-standard drug-gene and drug-complex (functional) interactions obtained from STITCH database for S. cerevisiae S. cerevisiae Drug-gene predictions S. cerevisiae Drug-complex predictions S. cerevisiae plus S. pombe S. pombe data S. cerevisiae data S.cerevisiae liquid+agar S. cerevisiae plus S. pombe S. pombe data S. cerevisiae data Area under the ROC curve 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9 0,5 0,6 0,7 0,8 0,9
38 Drug- gene interac&ons vs. Gene&c interac&ons S.pombe S.cerevisiae Gene&c int. Chemical gene&c int.
39 Summary: cross- species drug studies Drug- complex interac&ons more likely conserved than individual drug- gene interac&ons Combined cross- species improves predic&ons for drug mode- of- ac&on (MoA) Predicted MoA for 10 compounds (1 validated) Divergence of drug- gene interac&ons correlates with divergence of gene&c interac&ons What about drug combina&ons? (synergy)
40 Fitness differences Output Point muta&ons Recombina&on Duplica&ons Input Phenotypic changes Changes in protein- protein, protein- DNA interac&ons, etc
41 Supervisors: Nevan Krogan Wendell Lim Thank you! Collaborators: Fungal phosphoryla&on Jonathan Trinidad UCSF Alma Burlingame UCSF Ubiquityla&on Cell Signaling Judit Villen Uni. Wash Coprinus cinereus Jason Stajich UC Riverside Laura Kapitzky Krogan Lab Veronique Albanese Frydman lab Blog
Recombina*on and Linkage Disequilibrium (LD)
 Recombina*on and Linkage Disequilibrium (LD) A B a b r = recombina*on frac*on probability of an odd Number of crossovers occur Between our markers 0
Recombina*on and Linkage Disequilibrium (LD) A B a b r = recombina*on frac*on probability of an odd Number of crossovers occur Between our markers 0
Ch. 8 Metabolism and Energy BIOL 222
 Ch. 8 Metabolism and Energy BIOL 222 Metabolism Metabolism The totality of an organism s chemical reac:ons Sum of anabolism and catabolism emergent property of life that arises from interac:ons between
Ch. 8 Metabolism and Energy BIOL 222 Metabolism Metabolism The totality of an organism s chemical reac:ons Sum of anabolism and catabolism emergent property of life that arises from interac:ons between
Transcrip:on factor binding mo:fs
 Transcrip:on factor binding mo:fs BMMB- 597D Lecture 29 Shaun Mahony Transcrip.on factor binding sites Short: Typically between 6 20bp long Degenerate: TFs have favorite binding sequences but don t require
Transcrip:on factor binding mo:fs BMMB- 597D Lecture 29 Shaun Mahony Transcrip.on factor binding sites Short: Typically between 6 20bp long Degenerate: TFs have favorite binding sequences but don t require
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 8: Mechanisms of Cell Cycle Control and DNA Synthesis Gary Peter
 Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 8: Mechanisms of Cell Cycle Control and DNA Synthesis Gary Peter 9/10/2008 1 Learning Objectives Explain why a cell cycle was selected for during evolution
Plant Molecular and Cellular Biology Lecture 8: Mechanisms of Cell Cycle Control and DNA Synthesis Gary Peter 9/10/2008 1 Learning Objectives Explain why a cell cycle was selected for during evolution
Gene Regulatory Networks II Computa.onal Genomics Seyoung Kim
 Gene Regulatory Networks II 02-710 Computa.onal Genomics Seyoung Kim Goal: Discover Structure and Func;on of Complex systems in the Cell Identify the different regulators and their target genes that are
Gene Regulatory Networks II 02-710 Computa.onal Genomics Seyoung Kim Goal: Discover Structure and Func;on of Complex systems in the Cell Identify the different regulators and their target genes that are
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
BIOINF 4371 Drug Design 1 Oliver Kohlbacher & Jens Krüger
 BIOINF 4371 Drug Design 1 Oliver Kohlbacher & Jens Krüger Winter 2013/2014 11. Docking Part IV: Receptor Flexibility Overview Receptor flexibility Types of flexibility Implica5ons for docking Examples
BIOINF 4371 Drug Design 1 Oliver Kohlbacher & Jens Krüger Winter 2013/2014 11. Docking Part IV: Receptor Flexibility Overview Receptor flexibility Types of flexibility Implica5ons for docking Examples
Ch. 18 Regula'on of Gene Expression BIOL 222
 Ch. 18 Regula'on of Gene Expression BIOL 222 Overview: Conduc'ng the Gene'c Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In mul@cellular eukaryotes
Ch. 18 Regula'on of Gene Expression BIOL 222 Overview: Conduc'ng the Gene'c Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In mul@cellular eukaryotes
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
Principles of Gene Expression
 Principles of Gene Expression I. Introduc5on Genome : the en*re set of genes (transcrip*on units) of an organism Transcriptome : the en*re set of marns found in a cell at a given *me Proteome : the en*re
Principles of Gene Expression I. Introduc5on Genome : the en*re set of genes (transcrip*on units) of an organism Transcriptome : the en*re set of marns found in a cell at a given *me Proteome : the en*re
Introduction to Bioinformatics. Shifra Ben-Dor Irit Orr
 Introduction to Bioinformatics Shifra Ben-Dor Irit Orr Lecture Outline: Technical Course Items Introduction to Bioinformatics Introduction to Databases This week and next week What is bioinformatics? A
Introduction to Bioinformatics Shifra Ben-Dor Irit Orr Lecture Outline: Technical Course Items Introduction to Bioinformatics Introduction to Databases This week and next week What is bioinformatics? A
Computational methods for predicting protein-protein interactions
 Computational methods for predicting protein-protein interactions Tomi Peltola T-61.6070 Special course in bioinformatics I 3.4.2008 Outline Biological background Protein-protein interactions Computational
Computational methods for predicting protein-protein interactions Tomi Peltola T-61.6070 Special course in bioinformatics I 3.4.2008 Outline Biological background Protein-protein interactions Computational
From genes to func.on Gene regula.on and transcrip.on
 From genes to func.on Gene regula.on and transcrip.on Systems biology for system engineers Part 2 Sofia Pe(ersson Informa.on Coding Dept. of Electrical Engineering Linköping University The eukaryo.c cell
From genes to func.on Gene regula.on and transcrip.on Systems biology for system engineers Part 2 Sofia Pe(ersson Informa.on Coding Dept. of Electrical Engineering Linköping University The eukaryo.c cell
Yeast mrna cap- binding protein Cbc1/Sto1 is necessary for the rapid reprogramming of transla9on a:er hyperosmo9c shock (2012)
 Transla'on in Eucaryotes Yeast mrna cap- binding protein Cbc1/Sto1 is necessary for the rapid reprogramming of transla9on a:er hyperosmo9c shock (2012) Elena Garrea, Lorena Romero- Santacreua, Nikki De
Transla'on in Eucaryotes Yeast mrna cap- binding protein Cbc1/Sto1 is necessary for the rapid reprogramming of transla9on a:er hyperosmo9c shock (2012) Elena Garrea, Lorena Romero- Santacreua, Nikki De
Phylogene)cs. IMBB 2016 BecA- ILRI Hub, Nairobi May 9 20, Joyce Nzioki
 Phylogene)cs IMBB 2016 BecA- ILRI Hub, Nairobi May 9 20, 2016 Joyce Nzioki Phylogenetics The study of evolutionary relatedness of organisms. Derived from two Greek words:» Phle/Phylon: Tribe/Race» Genetikos:
Phylogene)cs IMBB 2016 BecA- ILRI Hub, Nairobi May 9 20, 2016 Joyce Nzioki Phylogenetics The study of evolutionary relatedness of organisms. Derived from two Greek words:» Phle/Phylon: Tribe/Race» Genetikos:
Biochemistry in Singulo:
 Biochemistry in Singulo: When Less Means More Carlos Bustamante University of California, Berkeley The Ensemble Approach The study of chemical transforma9ons has been dominated by the ensemble method:
Biochemistry in Singulo: When Less Means More Carlos Bustamante University of California, Berkeley The Ensemble Approach The study of chemical transforma9ons has been dominated by the ensemble method:
Lecture Notes for Fall Network Modeling. Ernest Fraenkel
 Lecture Notes for 20.320 Fall 2012 Network Modeling Ernest Fraenkel In this lecture we will explore ways in which network models can help us to understand better biological data. We will explore how networks
Lecture Notes for 20.320 Fall 2012 Network Modeling Ernest Fraenkel In this lecture we will explore ways in which network models can help us to understand better biological data. We will explore how networks
Proteomics. Yeast two hybrid. Proteomics - PAGE techniques. Data obtained. What is it?
 Proteomics What is it? Reveal protein interactions Protein profiling in a sample Yeast two hybrid screening High throughput 2D PAGE Automatic analysis of 2D Page Yeast two hybrid Use two mating strains
Proteomics What is it? Reveal protein interactions Protein profiling in a sample Yeast two hybrid screening High throughput 2D PAGE Automatic analysis of 2D Page Yeast two hybrid Use two mating strains
comparative genomics of high throughput data between species and evolution of function
 Comparative Interactomics comparative genomics of high throughput data between species and evolution of function Function prediction, for what aspects of function from model organism to e.g. human is orthology
Comparative Interactomics comparative genomics of high throughput data between species and evolution of function Function prediction, for what aspects of function from model organism to e.g. human is orthology
Bioinformatics 2. Yeast two hybrid. Proteomics. Proteomics
 GENOME Bioinformatics 2 Proteomics protein-gene PROTEOME protein-protein METABOLISM Slide from http://www.nd.edu/~networks/ Citrate Cycle Bio-chemical reactions What is it? Proteomics Reveal protein Protein
GENOME Bioinformatics 2 Proteomics protein-gene PROTEOME protein-protein METABOLISM Slide from http://www.nd.edu/~networks/ Citrate Cycle Bio-chemical reactions What is it? Proteomics Reveal protein Protein
Whole-genome analysis of GCN4 binding in S.cerevisiae
 Whole-genome analysis of GCN4 binding in S.cerevisiae Lillian Dai Alex Mallet Gcn4/DNA diagram (CREB symmetric site and AP-1 asymmetric site: Song Tan, 1999) removed for copyright reasons. What is GCN4?
Whole-genome analysis of GCN4 binding in S.cerevisiae Lillian Dai Alex Mallet Gcn4/DNA diagram (CREB symmetric site and AP-1 asymmetric site: Song Tan, 1999) removed for copyright reasons. What is GCN4?
Genomics and bioinformatics summary. Finding genes -- computer searches
 Genomics and bioinformatics summary 1. Gene finding: computer searches, cdnas, ESTs, 2. Microarrays 3. Use BLAST to find homologous sequences 4. Multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) 5. Trees quantify sequence
Genomics and bioinformatics summary 1. Gene finding: computer searches, cdnas, ESTs, 2. Microarrays 3. Use BLAST to find homologous sequences 4. Multiple sequence alignments (MSAs) 5. Trees quantify sequence
CISC 636 Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (Fall 2016)
 CISC 636 Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (Fall 2016) Predicting Protein-Protein Interactions CISC636, F16, Lec22, Liao 1 Background Proteins do not function as isolated entities. Protein-Protein
CISC 636 Computational Biology & Bioinformatics (Fall 2016) Predicting Protein-Protein Interactions CISC636, F16, Lec22, Liao 1 Background Proteins do not function as isolated entities. Protein-Protein
Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division
 Chem*3560 Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division The eukaryotic cell cycle Actively growing mammalian cells divide roughly every 24 hours, and follow a precise sequence of events know as
Chem*3560 Lecture 10: Cyclins, cyclin kinases and cell division The eukaryotic cell cycle Actively growing mammalian cells divide roughly every 24 hours, and follow a precise sequence of events know as
Tracking Protein Allostery in Evolution
 Tracking Protein Allostery in Evolution Glycogen phosphorylase frees sugars to provide energy GP orthologs diverged 600,000,000 years can respond to transcription controls, metabolite concentrations and
Tracking Protein Allostery in Evolution Glycogen phosphorylase frees sugars to provide energy GP orthologs diverged 600,000,000 years can respond to transcription controls, metabolite concentrations and
CSCI1950 Z Computa3onal Methods for Biology Lecture 24. Ben Raphael April 29, hgp://cs.brown.edu/courses/csci1950 z/ Network Mo3fs
 CSCI1950 Z Computa3onal Methods for Biology Lecture 24 Ben Raphael April 29, 2009 hgp://cs.brown.edu/courses/csci1950 z/ Network Mo3fs Subnetworks with more occurrences than expected by chance. How to
CSCI1950 Z Computa3onal Methods for Biology Lecture 24 Ben Raphael April 29, 2009 hgp://cs.brown.edu/courses/csci1950 z/ Network Mo3fs Subnetworks with more occurrences than expected by chance. How to
Pathway Association Analysis Trey Ideker UCSD
 Pathway Association Analysis Trey Ideker UCSD A working network map of the cell Network evolutionary comparison / cross-species alignment to identify conserved modules The Working Map Network-based classification
Pathway Association Analysis Trey Ideker UCSD A working network map of the cell Network evolutionary comparison / cross-species alignment to identify conserved modules The Working Map Network-based classification
Mendelian Gene*cs & the Chromosome Theory of Inheritance
 Mendelian Gene*cs & the Chromosome Theory of Inheritance Mendel 1840s- 1860s Ignored Completely Darwin 1860 Theory incompa*ble with blending model of inheritance. Microscopy techniques constantly improving
Mendelian Gene*cs & the Chromosome Theory of Inheritance Mendel 1840s- 1860s Ignored Completely Darwin 1860 Theory incompa*ble with blending model of inheritance. Microscopy techniques constantly improving
6. Evolu)on, Co- evolu)on (and Ar)ficial Life) Part 1
 6. Evolu)on, Co- evolu)on (and Ar)ficial Life) Part 1 Modelling Social Interac)on in Informa)on Systems hep://davidhales.com/msiis David Hales, University of Szeged dave@davidhales.com 1 Summary How can
6. Evolu)on, Co- evolu)on (and Ar)ficial Life) Part 1 Modelling Social Interac)on in Informa)on Systems hep://davidhales.com/msiis David Hales, University of Szeged dave@davidhales.com 1 Summary How can
# shared OGs (spa, spb) Size of the smallest genome. dist (spa, spb) = 1. Neighbor joining. OG1 OG2 OG3 OG4 sp sp sp
 Bioinformatics and Evolutionary Genomics: Genome Evolution in terms of Gene Content 3/10/2014 1 Gene Content Evolution What about HGT / genome sizes? Genome trees based on gene content: shared genes Haemophilus
Bioinformatics and Evolutionary Genomics: Genome Evolution in terms of Gene Content 3/10/2014 1 Gene Content Evolution What about HGT / genome sizes? Genome trees based on gene content: shared genes Haemophilus
CSCI1950 Z Computa3onal Methods for Biology* (*Working Title) Lecture 1. Ben Raphael January 21, Course Par3culars
 CSCI1950 Z Computa3onal Methods for Biology* (*Working Title) Lecture 1 Ben Raphael January 21, 2009 Course Par3culars Three major topics 1. Phylogeny: ~50% lectures 2. Func3onal Genomics: ~25% lectures
CSCI1950 Z Computa3onal Methods for Biology* (*Working Title) Lecture 1 Ben Raphael January 21, 2009 Course Par3culars Three major topics 1. Phylogeny: ~50% lectures 2. Func3onal Genomics: ~25% lectures
Written Exam 15 December Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no
 Technical University of Denmark Written Exam 15 December 2008 Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no. 27041 Aids allowed: Open book exam Provide your answers and calculations on separate
Technical University of Denmark Written Exam 15 December 2008 Course name: Introduction to Systems Biology Course no. 27041 Aids allowed: Open book exam Provide your answers and calculations on separate
Regulation of mycotoxin production and kinome analysis in Fusarium graminearum
 Regulation of mycotoxin production and kinome analysis in Fusarium graminearum Chenfang Wang Northwest Agricultural & Forestry University Regulation of mycotoxin production and kinome analysis in Fusarium
Regulation of mycotoxin production and kinome analysis in Fusarium graminearum Chenfang Wang Northwest Agricultural & Forestry University Regulation of mycotoxin production and kinome analysis in Fusarium
RNA-protein interac/ons and the structure of the gene/c code
 RNA-protein interac/ons and the structure of the gene/c code Bojan Zagrovic Department of Structural and Computa/onal Biology University of Vienna Evolu/on workshop, Salzburg, 07.07.2018 Physicochemical
RNA-protein interac/ons and the structure of the gene/c code Bojan Zagrovic Department of Structural and Computa/onal Biology University of Vienna Evolu/on workshop, Salzburg, 07.07.2018 Physicochemical
Tiffany Samaroo MB&B 452a December 8, Take Home Final. Topic 1
 Tiffany Samaroo MB&B 452a December 8, 2003 Take Home Final Topic 1 Prior to 1970, protein and DNA sequence alignment was limited to visual comparison. This was a very tedious process; even proteins with
Tiffany Samaroo MB&B 452a December 8, 2003 Take Home Final Topic 1 Prior to 1970, protein and DNA sequence alignment was limited to visual comparison. This was a very tedious process; even proteins with
Proteomics Systems Biology
 Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Proteomics Systems Biology IIT Bombay 2 1 DNA Genomics RNA Transcriptomics Global Cellular Protein Proteomics Global Cellular Metabolite Metabolomics Global Cellular
Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava IIT Bombay Proteomics Systems Biology IIT Bombay 2 1 DNA Genomics RNA Transcriptomics Global Cellular Protein Proteomics Global Cellular Metabolite Metabolomics Global Cellular
Tutorial 4 Substitution matrices and PSI-BLAST
 Tutorial 4 Substitution matrices and PSI-BLAST 1 Agenda Substitution Matrices PAM - Point Accepted Mutations BLOSUM - Blocks Substitution Matrix PSI-BLAST Cool story of the day: Why should we care about
Tutorial 4 Substitution matrices and PSI-BLAST 1 Agenda Substitution Matrices PAM - Point Accepted Mutations BLOSUM - Blocks Substitution Matrix PSI-BLAST Cool story of the day: Why should we care about
Lecture 4: Yeast as a model organism for functional and evolutionary genomics. Part II
 Lecture 4: Yeast as a model organism for functional and evolutionary genomics Part II A brief review What have we discussed: Yeast genome in a glance Gene expression can tell us about yeast functions Transcriptional
Lecture 4: Yeast as a model organism for functional and evolutionary genomics Part II A brief review What have we discussed: Yeast genome in a glance Gene expression can tell us about yeast functions Transcriptional
Introduction into Selected Reaction Monitoring (SRM) Christina Ludwig
 Introduction into Selected Reaction Monitoring (SRM) Christina Ludwig EuPA Bioinformatics course 28.11.2013 Overview A) What is selected reac/on monitoring, how does it work and why is it useful? B) How
Introduction into Selected Reaction Monitoring (SRM) Christina Ludwig EuPA Bioinformatics course 28.11.2013 Overview A) What is selected reac/on monitoring, how does it work and why is it useful? B) How
Biological Mass Spectrometry
 Biochemistry 412 Biological Mass Spectrometry February 13 th, 2007 Proteomics The study of the complete complement of proteins found in an organism Degrees of Freedom for Protein Variability Covalent Modifications
Biochemistry 412 Biological Mass Spectrometry February 13 th, 2007 Proteomics The study of the complete complement of proteins found in an organism Degrees of Freedom for Protein Variability Covalent Modifications
Exponen'al growth Limi'ng factors Environmental resistance Carrying capacity logis'c growth curve
 Exponen'al growth Popula)on increases by a fixed percent Fixed percent of a large number produces a large increase Graphed as a J- shaped curve Cannot be sustained indefinitely It occurs in nature With
Exponen'al growth Popula)on increases by a fixed percent Fixed percent of a large number produces a large increase Graphed as a J- shaped curve Cannot be sustained indefinitely It occurs in nature With
Prokaryo'c Operon Model Ac'vity
 Prokaryo'c Operon Model Ac'vity Differen'al Expression of Genes Prokaryotes and eukaryotes precisely regulate gene expression in response to environmental condi6ons In mul6cellular eukaryotes, gene expression
Prokaryo'c Operon Model Ac'vity Differen'al Expression of Genes Prokaryotes and eukaryotes precisely regulate gene expression in response to environmental condi6ons In mul6cellular eukaryotes, gene expression
Networks. Can (John) Bruce Keck Founda7on Biotechnology Lab Bioinforma7cs Resource
 Networks Can (John) Bruce Keck Founda7on Biotechnology Lab Bioinforma7cs Resource Networks in biology Protein-Protein Interaction Network of Yeast Transcriptional regulatory network of E.coli Experimental
Networks Can (John) Bruce Keck Founda7on Biotechnology Lab Bioinforma7cs Resource Networks in biology Protein-Protein Interaction Network of Yeast Transcriptional regulatory network of E.coli Experimental
Pedro Alexandrino Fernandes, Dep. Chemistry & Biochemistry, University of Porto, Portugal
 Pedro Alexandrino Fernandes, Dep. Chemistry & Biochemistry, University of Porto, Portugal pedro.fernandes@fc.up.pt 1. Introduc3on Intermolecular Associa3ons 1. Introduc3on What type of forces govern these
Pedro Alexandrino Fernandes, Dep. Chemistry & Biochemistry, University of Porto, Portugal pedro.fernandes@fc.up.pt 1. Introduc3on Intermolecular Associa3ons 1. Introduc3on What type of forces govern these
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Biology I
 EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Biology I Course Design 2013-2014 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 181 (SUN# BIO 1181) Title General Biology I Credits 4 Developed by David J. Henson
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE General Biology I Course Design 2013-2014 Course Information Division Science Course Number BIO 181 (SUN# BIO 1181) Title General Biology I Credits 4 Developed by David J. Henson
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.22 EVOLUTIONARY GENETICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF EVOLUTION Evolution is a process through which variation in individuals makes it more likely for them to survive and reproduce There are principles to the theory
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF EVOLUTION Evolution is a process through which variation in individuals makes it more likely for them to survive and reproduce There are principles to the theory
Organismal & Evolutionary Biology in Ocean Acidification Research. Ron Burton Scripps Institution of Oceanography
 Organismal & Evolutionary Biology in Ocean Acidification Research Ron Burton Scripps Institution of Oceanography Marine calcifiers exhibit mixed responses to CO 2 -induced ocean acidification Justin B.
Organismal & Evolutionary Biology in Ocean Acidification Research Ron Burton Scripps Institution of Oceanography Marine calcifiers exhibit mixed responses to CO 2 -induced ocean acidification Justin B.
Proteomics and Mass Spectrometry
 Molecular Cell Biology Lecture. Oct. 16, 2014 Proteomics and Mass Spectrometry Ron Bose, MD PhD Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology Programs Washington University School of Medicine Introduction Definition
Molecular Cell Biology Lecture. Oct. 16, 2014 Proteomics and Mass Spectrometry Ron Bose, MD PhD Biochemistry and Molecular Cell Biology Programs Washington University School of Medicine Introduction Definition
Chemical Reac+ons and Enzymes. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview. 2.4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Lesson Overview Chemical Reac+ons and Enzymes Lesson Overview 2.4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes THINK ABOUT IT Living things are made up of chemical compounds, but chemistry isn t just what life is made
Lesson Overview Chemical Reac+ons and Enzymes Lesson Overview 2.4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes THINK ABOUT IT Living things are made up of chemical compounds, but chemistry isn t just what life is made
Purging of inbreeding load in par;ally selfing popula;ons
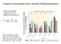 Purging of inbreeding load in par;ally selfing popula;ons Given an inbreeding coefficient of f, the equilibrium frequency is q e µ ( h(1 f ) + f )s Data from various Schiedea species with different extent
Purging of inbreeding load in par;ally selfing popula;ons Given an inbreeding coefficient of f, the equilibrium frequency is q e µ ( h(1 f ) + f )s Data from various Schiedea species with different extent
Basics on bioinforma-cs Lecture 7. Nunzio D Agostino
 Basics on bioinforma-cs Lecture 7 Nunzio D Agostino nunzio.dagostino@entecra.it; nunzio.dagostino@gmail.com Multiple alignments One sequence plays coy a pair of homologous sequence whisper many aligned
Basics on bioinforma-cs Lecture 7 Nunzio D Agostino nunzio.dagostino@entecra.it; nunzio.dagostino@gmail.com Multiple alignments One sequence plays coy a pair of homologous sequence whisper many aligned
PTM Bioinformatics Yu Xue
 PTM Bioinformatics Yu Xue Huazhong University of Science and Technology Wuhan, China Huazhong University of Science and Technology http://www.uniprot.org/docs/ptmlist Post-translational modification POST:
PTM Bioinformatics Yu Xue Huazhong University of Science and Technology Wuhan, China Huazhong University of Science and Technology http://www.uniprot.org/docs/ptmlist Post-translational modification POST:
BMB 170 Lecture 13 Nucleic Acids, Nov 7th
 BMB 170 Lecture 13 Nucleic Acids, Nov 7th Chloroplast Ribosome h"p://www.bangroup.ethz.ch/research/nomenclature-of-ribosomal-proteins.html Ban N, Beckmann R, Cate JH, Dinman JD, Dragon F, Ellis SR, Lafontaine
BMB 170 Lecture 13 Nucleic Acids, Nov 7th Chloroplast Ribosome h"p://www.bangroup.ethz.ch/research/nomenclature-of-ribosomal-proteins.html Ban N, Beckmann R, Cate JH, Dinman JD, Dragon F, Ellis SR, Lafontaine
Orthology Part I concepts and implications Toni Gabaldón Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), Barcelona
 Orthology Part I concepts and implications Toni Gabaldón Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), Barcelona Toni Gabaldón Contact: tgabaldon@crg.es Group website: http://gabaldonlab.crg.es Science blog: http://treevolution.blogspot.com
Orthology Part I concepts and implications Toni Gabaldón Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG), Barcelona Toni Gabaldón Contact: tgabaldon@crg.es Group website: http://gabaldonlab.crg.es Science blog: http://treevolution.blogspot.com
CSE182-L8. Mass Spectrometry
 CSE182-L8 Mass Spectrometry Project Notes Implement a few tools for proteomics C1:11/2/04 Answer MS questions to get started, select project partner, select a project. C2:11/15/04 (All but web-team) Plan
CSE182-L8 Mass Spectrometry Project Notes Implement a few tools for proteomics C1:11/2/04 Answer MS questions to get started, select project partner, select a project. C2:11/15/04 (All but web-team) Plan
Three different fusions led to three basic ideas: 1) If one fuses a cell in mitosis with a cell in any other stage of the cell cycle, the chromosomes
 Section Notes The cell division cycle presents an interesting system to study because growth and division must be carefully coordinated. For many cells it is important that it reaches the correct size
Section Notes The cell division cycle presents an interesting system to study because growth and division must be carefully coordinated. For many cells it is important that it reaches the correct size
Proteomics. 2 nd semester, Department of Biotechnology and Bioinformatics Laboratory of Nano-Biotechnology and Artificial Bioengineering
 Proteomics 2 nd semester, 2013 1 Text book Principles of Proteomics by R. M. Twyman, BIOS Scientific Publications Other Reference books 1) Proteomics by C. David O Connor and B. David Hames, Scion Publishing
Proteomics 2 nd semester, 2013 1 Text book Principles of Proteomics by R. M. Twyman, BIOS Scientific Publications Other Reference books 1) Proteomics by C. David O Connor and B. David Hames, Scion Publishing
The Signal Hypothesis and the Targe3ng of Nascent Polypep3des to the Secretory Pathway. Tuesday 8/31/2017 Mike Mueckler
 The Signal Hypothesis and the Targe3ng of Nascent Polypep3des to the Secretory Pathway Tuesday 8/31/2017 Mike Mueckler mmueckler@wustl.edu Figure 6-63 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008)
The Signal Hypothesis and the Targe3ng of Nascent Polypep3des to the Secretory Pathway Tuesday 8/31/2017 Mike Mueckler mmueckler@wustl.edu Figure 6-63 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008)
Map of AP-Aligned Bio-Rad Kits with Learning Objectives
 Map of AP-Aligned Bio-Rad Kits with Learning Objectives Cover more than one AP Biology Big Idea with these AP-aligned Bio-Rad kits. Big Idea 1 Big Idea 2 Big Idea 3 Big Idea 4 ThINQ! pglo Transformation
Map of AP-Aligned Bio-Rad Kits with Learning Objectives Cover more than one AP Biology Big Idea with these AP-aligned Bio-Rad kits. Big Idea 1 Big Idea 2 Big Idea 3 Big Idea 4 ThINQ! pglo Transformation
Functional Characterization of Molecular Interaction Networks
 Functional Characterization of Molecular Interaction Networks Mehmet Koyutürk Case Western Reserve University Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Computer Science Colloquium Texas Tech
Functional Characterization of Molecular Interaction Networks Mehmet Koyutürk Case Western Reserve University Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science Computer Science Colloquium Texas Tech
Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg Lapets ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies 2004, 2:
 1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
1 3/1/2005 A Quantitative Cell-Based High-Content Screening Assay for the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Specific Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Richik N. Ghosh, Linnette Grove, and Oleg
Proteomics. Areas of Interest
 Introduction to BioMEMS & Medical Microdevices Proteomics and Protein Microarrays Companion lecture to the textbook: Fundamentals of BioMEMS and Medical Microdevices, by Prof., http://saliterman.umn.edu/
Introduction to BioMEMS & Medical Microdevices Proteomics and Protein Microarrays Companion lecture to the textbook: Fundamentals of BioMEMS and Medical Microdevices, by Prof., http://saliterman.umn.edu/
Functional Characterization and Topological Modularity of Molecular Interaction Networks
 Functional Characterization and Topological Modularity of Molecular Interaction Networks Jayesh Pandey 1 Mehmet Koyutürk 2 Ananth Grama 1 1 Department of Computer Science Purdue University 2 Department
Functional Characterization and Topological Modularity of Molecular Interaction Networks Jayesh Pandey 1 Mehmet Koyutürk 2 Ananth Grama 1 1 Department of Computer Science Purdue University 2 Department
Cryodetectors in Life Science Mass Spectrometry. Damian Twerenbold
 Cryodetectors in Life Science Mass Spectrometry Damian Twerenbold Institut de Physique de l'université Neuchâtel, Paul Scherrer Institut,Villigen GenSpec SA, Boudry Switzerland LTD-10, Genova, 2003 Université
Cryodetectors in Life Science Mass Spectrometry Damian Twerenbold Institut de Physique de l'université Neuchâtel, Paul Scherrer Institut,Villigen GenSpec SA, Boudry Switzerland LTD-10, Genova, 2003 Université
Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Generating function, alignment and assembly
 Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Generating function, alignment and assembly With slides from Sangtae Kim and from Jones & Pevzner 2004 Determining reliability of identifications Can we use Target/Decoy to estimate
Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Generating function, alignment and assembly With slides from Sangtae Kim and from Jones & Pevzner 2004 Determining reliability of identifications Can we use Target/Decoy to estimate
networks in molecular biology Wolfgang Huber
 networks in molecular biology Wolfgang Huber networks in molecular biology Regulatory networks: components = gene products interactions = regulation of transcription, translation, phosphorylation... Metabolic
networks in molecular biology Wolfgang Huber networks in molecular biology Regulatory networks: components = gene products interactions = regulation of transcription, translation, phosphorylation... Metabolic
V19 Metabolic Networks - Overview
 V19 Metabolic Networks - Overview There exist different levels of computational methods for describing metabolic networks: - stoichiometry/kinetics of classical biochemical pathways (glycolysis, TCA cycle,...
V19 Metabolic Networks - Overview There exist different levels of computational methods for describing metabolic networks: - stoichiometry/kinetics of classical biochemical pathways (glycolysis, TCA cycle,...
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Evolu&on Cont d. h:p:// content/uploads/2009/09/evolu&on.jpg. 7 th Grade Biology Mr. Joanides
 Evolu&on Cont d h:p://www.buildamovement.com/blog/wp- content/uploads/2009/09/evolu&on.jpg 7 th Grade Biology Mr. Joanides The Fossil Record Fossil Preserved remains or markings lem by organisms that live
Evolu&on Cont d h:p://www.buildamovement.com/blog/wp- content/uploads/2009/09/evolu&on.jpg 7 th Grade Biology Mr. Joanides The Fossil Record Fossil Preserved remains or markings lem by organisms that live
(Lys), resulting in translation of a polypeptide without the Lys amino acid. resulting in translation of a polypeptide without the Lys amino acid.
 1. A change that makes a polypeptide defective has been discovered in its amino acid sequence. The normal and defective amino acid sequences are shown below. Researchers are attempting to reproduce the
1. A change that makes a polypeptide defective has been discovered in its amino acid sequence. The normal and defective amino acid sequences are shown below. Researchers are attempting to reproduce the
V14 extreme pathways
 V14 extreme pathways A torch is directed at an open door and shines into a dark room... What area is lighted? Instead of marking all lighted points individually, it would be sufficient to characterize
V14 extreme pathways A torch is directed at an open door and shines into a dark room... What area is lighted? Instead of marking all lighted points individually, it would be sufficient to characterize
Drug targets, Protein Structures and Crystallography
 Drug targets, Protein Structures and Crystallography NS5B viral RNA polymerase (RNA dep) Hepa88s C drug Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) FDA 2013 Epclusa - combina8on with Velpatasvir approved in in 2016) Prodrug
Drug targets, Protein Structures and Crystallography NS5B viral RNA polymerase (RNA dep) Hepa88s C drug Sofosbuvir (Sovaldi) FDA 2013 Epclusa - combina8on with Velpatasvir approved in in 2016) Prodrug
Structure to Function. Molecular Bioinformatics, X3, 2006
 Structure to Function Molecular Bioinformatics, X3, 2006 Structural GeNOMICS Structural Genomics project aims at determination of 3D structures of all proteins: - organize known proteins into families
Structure to Function Molecular Bioinformatics, X3, 2006 Structural GeNOMICS Structural Genomics project aims at determination of 3D structures of all proteins: - organize known proteins into families
Gene Regula*on, ChIP- X and DNA Mo*fs. Statistics in Genomics Hongkai Ji
 Gene Regula*on, ChIP- X and DNA Mo*fs Statistics in Genomics Hongkai Ji (hji@jhsph.edu) Genetic information is stored in DNA TCAGTTGGAGCTGCTCCCCCACGGCCTCTCCTCACATTCCACGTCCTGTAGCTCTATGACCTCCACCTTTGAGTCCCTCCTC
Gene Regula*on, ChIP- X and DNA Mo*fs Statistics in Genomics Hongkai Ji (hji@jhsph.edu) Genetic information is stored in DNA TCAGTTGGAGCTGCTCCCCCACGGCCTCTCCTCACATTCCACGTCCTGTAGCTCTATGACCTCCACCTTTGAGTCCCTCCTC
Molecular Dynamics. Molecules in motion
 Molecular Dynamics Molecules in motion 1 Molecules in mo1on Molecules are not sta1c, but move all the 1me Source: h9p://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/kine1c_theory 2 Gasses, liquids and solids Gasses, liquids
Molecular Dynamics Molecules in motion 1 Molecules in mo1on Molecules are not sta1c, but move all the 1me Source: h9p://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/kine1c_theory 2 Gasses, liquids and solids Gasses, liquids
Lecture 1: CS 425 Introduc3on. Spring 2017 January 17, 2017
 Lecture 1: CS 425 Introduc3on Spring 2017 January 17, 2017 In this lecture Logis3cs of the course Introduc3on to basic biology which will con3nue in the following lecture Logis3cs of the Course Logis3cs
Lecture 1: CS 425 Introduc3on Spring 2017 January 17, 2017 In this lecture Logis3cs of the course Introduc3on to basic biology which will con3nue in the following lecture Logis3cs of the Course Logis3cs
Genome-wide multilevel spatial interactome model of rice
 Sino-German Workshop on Multiscale Spatial Computational Systems Biology, Beijing, Oct 8-12, 2015 Genome-wide multilevel spatial interactome model of rice Ming CHEN ( 陈铭 ) mchen@zju.edu.cn College of Life
Sino-German Workshop on Multiscale Spatial Computational Systems Biology, Beijing, Oct 8-12, 2015 Genome-wide multilevel spatial interactome model of rice Ming CHEN ( 陈铭 ) mchen@zju.edu.cn College of Life
Sec$on 9. Evolu$onary Rela$onships
 Sec$on 9 Evolu$onary Rela$onships Sec$on 9 Learning Goals Explain why the ribosomal 16S gene is a good marker for molecular phylogene$c comparisons. Be able to interpret a phylogene$c tree. Explain the
Sec$on 9 Evolu$onary Rela$onships Sec$on 9 Learning Goals Explain why the ribosomal 16S gene is a good marker for molecular phylogene$c comparisons. Be able to interpret a phylogene$c tree. Explain the
MS Based Proteomics: Recent Case Studies Using Advanced Instrumentation
 MS Based Proteomics: Recent Case Studies Using Advanced Instrumentation Chris Adams, PH.D. Stanford University Mass Spectrometry http://mass-spec.stanford.edu/ For personal use only. Please do not reuse
MS Based Proteomics: Recent Case Studies Using Advanced Instrumentation Chris Adams, PH.D. Stanford University Mass Spectrometry http://mass-spec.stanford.edu/ For personal use only. Please do not reuse
Comparative Network Analysis
 Comparative Network Analysis BMI/CS 776 www.biostat.wisc.edu/bmi776/ Spring 2016 Anthony Gitter gitter@biostat.wisc.edu These slides, excluding third-party material, are licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0 by
Comparative Network Analysis BMI/CS 776 www.biostat.wisc.edu/bmi776/ Spring 2016 Anthony Gitter gitter@biostat.wisc.edu These slides, excluding third-party material, are licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0 by
Activation of a receptor. Assembly of the complex
 Activation of a receptor ligand inactive, monomeric active, dimeric When activated by growth factor binding, the growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates the neighboring receptor. Assembly
Activation of a receptor ligand inactive, monomeric active, dimeric When activated by growth factor binding, the growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase phosphorylates the neighboring receptor. Assembly
Chemical Labeling Strategy for Generation of Internal Standards for Targeted Quantitative Proteomics
 Chemical Labeling Strategy for Generation of Internal Standards for Targeted Quantitative Proteomics mtraq Reagents Triplex Christie Hunter, Brian Williamson, Marjorie Minkoff AB SCIEX, USA The utility
Chemical Labeling Strategy for Generation of Internal Standards for Targeted Quantitative Proteomics mtraq Reagents Triplex Christie Hunter, Brian Williamson, Marjorie Minkoff AB SCIEX, USA The utility
Name Period The Control of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes Notes
 Bacterial DNA contains genes that encode for many different proteins (enzymes) so that many processes have the ability to occur -not all processes are carried out at any one time -what allows expression
Bacterial DNA contains genes that encode for many different proteins (enzymes) so that many processes have the ability to occur -not all processes are carried out at any one time -what allows expression
Identification of TARP Phosphorylation Sites and Their Significance in the Brain
 Identification of TARP Phosphorylation Sites and Their Significance in the Brain Susumu Tomita @ SHM BE17 Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology NIDA Neuroproteomics Center, December 13, 2008
Identification of TARP Phosphorylation Sites and Their Significance in the Brain Susumu Tomita @ SHM BE17 Department of Cellular and Molecular Physiology NIDA Neuroproteomics Center, December 13, 2008
UNIT 6 PART 3 *REGULATION USING OPERONS* Hillis Textbook, CH 11
 UNIT 6 PART 3 *REGULATION USING OPERONS* Hillis Textbook, CH 11 REVIEW: Signals that Start and Stop Transcription and Translation BUT, HOW DO CELLS CONTROL WHICH GENES ARE EXPRESSED AND WHEN? First of
UNIT 6 PART 3 *REGULATION USING OPERONS* Hillis Textbook, CH 11 REVIEW: Signals that Start and Stop Transcription and Translation BUT, HOW DO CELLS CONTROL WHICH GENES ARE EXPRESSED AND WHEN? First of
Bioinformatics. Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics
 Bioinformatics Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 3 Bioinformatics - play with sequences & structures Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 4 ORGANIZATION OF LIFE ROLE OF BIOINFORMATICS
Bioinformatics Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 3 Bioinformatics - play with sequences & structures Dept. of Computational Biology & Bioinformatics 4 ORGANIZATION OF LIFE ROLE OF BIOINFORMATICS
Systems biology and biological networks
 Systems Biology Workshop Systems biology and biological networks Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Networks in electronics Radio kindly provided by Lazebnik, Cancer Cell, 2002 Systems Biology Workshop,
Systems Biology Workshop Systems biology and biological networks Center for Biological Sequence Analysis Networks in electronics Radio kindly provided by Lazebnik, Cancer Cell, 2002 Systems Biology Workshop,
Supplementary online material
 Supplementary online material A probabilistic functional network of yeast genes Insuk Lee, Shailesh V. Date, Alex T. Adai & Edward M. Marcotte DATA SETS Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome This study is based
Supplementary online material A probabilistic functional network of yeast genes Insuk Lee, Shailesh V. Date, Alex T. Adai & Edward M. Marcotte DATA SETS Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome This study is based
32 Gene regulation, continued Lecture Outline 11/21/05
 32 Gene regulation, continued Lecture Outline 11/21/05 Review the operon concept Repressible operons (e.g. trp) Inducible operons (e.g. lac) Positive regulation of lac () Practice applying the operon concept
32 Gene regulation, continued Lecture Outline 11/21/05 Review the operon concept Repressible operons (e.g. trp) Inducible operons (e.g. lac) Positive regulation of lac () Practice applying the operon concept
Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm
 Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm Urmila Kulkarni-Kale Bioinformatics Centre University of Pune, Pune 411 007. urmila@bioinfo.ernet.in Genome sequence: Fact file 1995: The first
Comparative genomics: Overview & Tools + MUMmer algorithm Urmila Kulkarni-Kale Bioinformatics Centre University of Pune, Pune 411 007. urmila@bioinfo.ernet.in Genome sequence: Fact file 1995: The first
What modern day animals could have evolved from the above extinct animals?
 1 2 3 Wooly Mammoth Saber tooth tiger Mesonychid What modern day animals could have evolved from the above extinct animals? 1 1. Fossil Records 2. Homologous Structures 3. Vestigial Structures 4. DNA Evidence
1 2 3 Wooly Mammoth Saber tooth tiger Mesonychid What modern day animals could have evolved from the above extinct animals? 1 1. Fossil Records 2. Homologous Structures 3. Vestigial Structures 4. DNA Evidence
Protein structure prediction. CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 10 and 12, 2017 Ron Dror
 Protein structure prediction CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 10 and 12, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Outline Why predict protein structure? Can we use (pure) physics-based methods? Knowledge-based methods Two major
Protein structure prediction CS/CME/BioE/Biophys/BMI 279 Oct. 10 and 12, 2017 Ron Dror 1 Outline Why predict protein structure? Can we use (pure) physics-based methods? Knowledge-based methods Two major
Name: TF: Section Time: LS1a ICE 5. Practice ICE Version B
 Name: TF: Section Time: LS1a ICE 5 Practice ICE Version B 1. (8 points) In addition to ion channels, certain small molecules can modulate membrane potential. a. (4 points) DNP ( 2,4-dinitrophenol ), as
Name: TF: Section Time: LS1a ICE 5 Practice ICE Version B 1. (8 points) In addition to ion channels, certain small molecules can modulate membrane potential. a. (4 points) DNP ( 2,4-dinitrophenol ), as
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit, and respond to information essential to life processes.
 Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit, and respond to information essential to life processes. Enduring understanding 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. Essential
Big Idea 3: Living systems store, retrieve, transmit, and respond to information essential to life processes. Enduring understanding 3.A: Heritable information provides for continuity of life. Essential
Sta$s$cal Physics, Inference and Applica$ons to Biology
 Sta$s$cal Physics, Inference and Applica$ons to Biology Physics Department, Ecole Normale Superieure, Paris, France. Simona Cocco Office:GH301 mail:cocco@lps.ens.fr Deriving Protein Structure and Func$on
Sta$s$cal Physics, Inference and Applica$ons to Biology Physics Department, Ecole Normale Superieure, Paris, France. Simona Cocco Office:GH301 mail:cocco@lps.ens.fr Deriving Protein Structure and Func$on
The geneticist s questions
 The geneticist s questions a) What is consequence of reduced gene function? 1) gene knockout (deletion, RNAi) b) What is the consequence of increased gene function? 2) gene overexpression c) What does
The geneticist s questions a) What is consequence of reduced gene function? 1) gene knockout (deletion, RNAi) b) What is the consequence of increased gene function? 2) gene overexpression c) What does
Copyright Mark Brandt, Ph.D A third method, cryogenic electron microscopy has seen increasing use over the past few years.
 Structure Determination and Sequence Analysis The vast majority of the experimentally determined three-dimensional protein structures have been solved by one of two methods: X-ray diffraction and Nuclear
Structure Determination and Sequence Analysis The vast majority of the experimentally determined three-dimensional protein structures have been solved by one of two methods: X-ray diffraction and Nuclear
Optimality, Robustness, and Noise in Metabolic Network Control
 Optimality, Robustness, and Noise in Metabolic Network Control Muxing Chen Gal Chechik Daphne Koller Department of Computer Science Stanford University May 18, 2007 Abstract The existence of noise, or
Optimality, Robustness, and Noise in Metabolic Network Control Muxing Chen Gal Chechik Daphne Koller Department of Computer Science Stanford University May 18, 2007 Abstract The existence of noise, or
Meiosis. Varia%on - The art of crossing over
 Meiosis Varia%on - The art of crossing over Vocabulary You Need to Know! Chroma%d Chroma%n Sister Chroma%ds Chromosomes Homologous Chromosomes Tetrad Centromere Daughter Cell Parent Cell Haploid Diploid
Meiosis Varia%on - The art of crossing over Vocabulary You Need to Know! Chroma%d Chroma%n Sister Chroma%ds Chromosomes Homologous Chromosomes Tetrad Centromere Daughter Cell Parent Cell Haploid Diploid
!"#$%&!"&'(&%")(*(+& '4567,846/-&*,/69450.:&*,.;42/9450&<ᶫ.=097,.4.& #259,40& &95&523/0,--,.
 1 2 Contact Information Dr. Sonish Azam Office: SP 375.23 Tel: 514-848-2424 ex 3488 Email: sonish.azam@concordia.ca (Please mention BIOL 266 in subject) Office hours: after the class or by appointment
1 2 Contact Information Dr. Sonish Azam Office: SP 375.23 Tel: 514-848-2424 ex 3488 Email: sonish.azam@concordia.ca (Please mention BIOL 266 in subject) Office hours: after the class or by appointment
