The Pituitary Gland. Pituitary Gland
|
|
|
- Wesley Holt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Pituitary Gland Pituitary Gland
2 The Hypophysis (Pituitary gland) Is the master gland, produces several hormones which influence the activity of other endocrine glands. Suspended from hypothalamus by means of a short stalk. Tissue derived from two different sources. Adenohypophysis from oral ectoderm, Neurohypophysis arises as a ventral evagination from the floor of diencephalon (forebrain). Oral component originates as an out pocketing of ectoderm, known as Rathke's pouch, which grows cranially from the primitive mouth (stomodeum) of embryo. Next slide
3 The Pituitary Gland
4 Pituitary Gland Anterior wall of Rathke's pouch becomes greatly thickened, so that the lumen of pouch is reduced to a narrow fissure. Ant. lobe is divided by residual lumen of Rathke's pouch into two unequal parts: Pars distalis and Pars intermedia Thicker pars distalis lies anterior to the fissure. An extension of the pars distalis, called pars tuberalis, surrounds the infundibulum. Posterior to the fissure lies pars intermedia. which forms a thin cellular partition between the pars distalis and Neurohypophysis.
5
6
7
8 PITUITARY GLAND Anterior lobe (Adenohypophysis) comprises pars distalis, pars tuberalis & pars Intermedia. Posterior lobe (Neurohypophysis) includes pars nervosa, Infundibular stem and Median eminence.
9 Neurohypophysis comprises three parts: 1.Pars nervosa 2. Infundibular stem 3. Median eminence (of the hypothalamus). Pars nervosa lies immediately posterior to pars intermedia, continuous above with infundibular stem and median eminence, which together constitute the infundibulum. Hypophyseal stalk comprises infundibulum and pars tuberalis. PITUITARY GLAND
10 THE ADENOHYPOPHYSIS Adenohypophysis comprises Pars distalis, Pars intermedia and Pars tuberalis. Pars distalis constitutes about 75 % of hypophysis, surrounded by a dense fibrous capsule. Parenchyma of pars distalis consists of cords and clusters of cells, supported by a scanty stroma composed of fibroblasts and reticular fibers. Between cellular masses are present sinusoidal capillaries.
11
12
13 THE ADENOHYPOPHYSIS Depending on their affinity for ordinary stains, cells of pars distalis are classified into two main types: (1) Chromophobes, and (2) Chromophils. 1) Chromophobes, have little or no affinity for stains (chroma = color, phobein = to be afraid of), about 50% of the cells in pars distalis.
14 THE ADENOHYPOPHYSIS Under L.M, Chromophobes are rounded or polygonal cells, boundaries of which are not clearly distinguishable. Cytoplasm does not exhibit any secretory granules. Formerly it was believed that the chromophobes represent undifferentiated or reserve cells which give rise to chromophils: But now it has been established that chromophobes are actually degranulated chromophils, i.e., they represent those cells which have secreted their cytoplasmic granules into the blood.
15 THE ADENOHYPOPHYSIS 2) Chromophils, 50% of the pars distalis cells, rounded or polygonal in shape, but they have distinct boundaries. Chroma = color, philein = to love Chromophils exhibit affinity for stains, due to presence of cytoplasmic granules which are either acidophilic or basophilic. Chromophils are divided into two types: Basophils and Acidophils, which are more abundant, constituting about 70% of the total chromophils.
16
17 THE ADENOHYPOPHYSIS ACIDOPHILS, are larger than chromophobes, but smaller than basophils. Cytoplasm has small secretory granules which stain with acid dyes like eosin, acid fuchsin, orange G and azocarmine. On the basis of staining reaction of the cytoplasmic granules, acidophils are subclassified into two varieties: (i) alpha acidophils (ii) epsilon acidophils
18
19 THE ADENOHYPOPHYSIS i) Alpha Acidophils. are commoner of the 'two varieties. Their cytoplasmic granules stain well with orange G; hence these cells are also known as orangeophils. E-M. secretory granules 300 to 400 nm in diameter. Secrete growth hormone (somatotropin) hence known as somatotropes.
20 THE ADENOHYPOPHYSIS ii) Epsilon Acidophils. Cytoplasmic granules of these cells stain intensely with azocarmine; hence, these cells are also called carminophils. EM. cytoplasmic granules are larger (average diameter 600 nm) than those of alpha acidophils. Epsilon acidophils secrete prolactin (lactogenic hormone) and are also known as mammotropes or lactotropes. Their size and number increase during pregnancy and lactation.
21 The Adenohypophysis BASOPHILS are larger in size than acidophils Cytoplasmic granules are smaller and fewer than those of acidophils. Cytoplasmic granules of a basophil do not stain well with hematoxylin but stain intensely with methylene blue. Strongly positive reaction when stained by PAS technique. Secretory granules are stained by aldehyde fuchsin, and are classified. into three subtypes: (i) beta basophils, (ii) delta basophils, and (iii) corticotropes.
22
23 i) Beta basophils relatively large cells which stain intensely with aldehyde fuchsin. E-M. secretory granules 100 to 150 nm in diameter. Beta basophils secrete TSH and are also known as Thyrotropes. The Adenohypophysis ii) Delta Basophils. do not stain with aldehyde fuchsin. secrete gonadotropic hormones and, hence, are also termed Gonadotropes.
24 The Adenohypophysis Gonadotropes are distinguished into two varieties First variety, secretory granules, 100 nm in diameter. secrete follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). Second variety, granules, about 150 nm in diameter which are concentrated to one side of the cell. secrete luteinizing hormone (LH) which in the male is also known as interstitial cell stimulating hormone (ICSH).
25 The Adenohypophysis iii) Corticotropes. do not stain with aldehyde fuchsin. E-M. secretory granules, about 200 nm in diameter, well-developed Golgi apparatus. Nucleus occupies an eccentric position in the cell. Corticotropes constitute the most numerous variety of basophils, secrete Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) which is also called corticotropin.
26 The Adenohypophysis PARS INTERMEDIA In humans, pars intermedia is rudimentary, composed mainly of cords of basophilic, polygonal cells. Some follicles are also seen which are lined by cuboidal cells and contain colloid material. In some lower animals, pars intermedia is well developed. In humans the amount of melanin pigment in the skin is believed, to be controlled by ACTH and function of pars intermedia is not well understood.
27
28 The Adenohypophysis PARS TUBERALIS Pars tuberalis surrounds infundibular stem in the form of a collar. Composed of groups or cords of faintly basophilic cuboidal cells associated with blood vessels of the hypophyseal portal system. Function of the pars tuberalis is unknown.
29 The Neurohypophysis Neurohypophysis consists of unmyelinated nerve fibers (axons), b.vs and neuroglialike cells called Pituicytes. Axons, about 100,000 in number, originate mainly from neurons located in the supraoptic & paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus.
30 The Neurohypophysis These axons converge at the median eminence to form a bundle of nerve fibers called Hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract. This tract passes through the infundibular stem to pars nervosa, where the axons terminate in dilated nerve endings close to a rich plexus of fenesterated capillaries. Dilated axonal terminations contain neurosecretory granules having a diameter of nm.
31 The Neurohypophysis Neurosecretory material from neurons moves into pars nervosa Is stored at the dilated axonal terminations and released into circulation as needed. Two hormones are stored and released from Neurohypophysis: (I) Oxytocin, and (2) Vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone (ADH). Hormone communication
32 The Neurohypophysis H&E, neurohypophysis is rather undistinguishable, because the individual axons and nerve terminations can not be identified. Large accumulations of the neurosecretory material are seen as basophilic masses called Herring bodies. Most easily seen in substance of neurohypophysis, are round pale staining nuclei of the pituicytes and numerous capillaries.
33
34
35
36
37
38 The Neurohypophysis Pituicyte has a small cell body with a number of cytoplasmic processes. These processes often end in close relation to blood vessels. In routine preparations, cytoplasm processes can not be seen. Pituicytes are considered to be a special type of neuroglial cells.
39 Pituicytes & Herring bodies
40 Pituicytes & Herring bodies
41 BLOOD SUPPLY Hypophyseal arteries arise from internal carotid arteries and circle of Willis. These arteries divide into superior and inferior sets of branches. Superior hypophyseal arteries pass to the region of median eminence and give rise to capillaries. Capillaries reunite to form veins which run downwards around the hypophyseal stalk to reach pars distalis Here these veins open into the sinusoidal capillaries of anterior lobe. The Hypophysis
42 The Hypophysis This connection between capillaries of median eminence and sinusoidal capillaries of anterior lobe constitutes the hypothalamohypophyseal portal system. Through this pathway hormone-releasing (or releaseinhibiting) factors from hypothalamus pass to pars distalis. Inferior hypophyseal arteries pass directly to posterior lobe of pituitary gland to supply it. Veins from the anterior and posterior lobes of the hypophysis drain into the cavernous sinus.
43 Pituitary gland
The Development of the Human Fetal Adenohypophysis '
 The Development of the Human Fetal Adenohypophysis ' JAMES L. CONKLIN Department of Anatomy, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan ABSTRACT Understanding the development of the human adenohypophysis
The Development of the Human Fetal Adenohypophysis ' JAMES L. CONKLIN Department of Anatomy, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan ABSTRACT Understanding the development of the human adenohypophysis
BASOPHILS OF PARS DISTALIS ADENOHYPOPHYSIS IN MADRAS RED SHEEP (Ovis aries) HISTOLOGY WITH REFERENCE TO VARIOUS AGE GROUPS
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 1, 2017, 866 871 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) BASOPHILS OF PARS DISTALIS ADENOHYPOPHYSIS IN MADRAS RED SHEEP (Ovis aries) HISTOLOGY
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 1, 2017, 866 871 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) BASOPHILS OF PARS DISTALIS ADENOHYPOPHYSIS IN MADRAS RED SHEEP (Ovis aries) HISTOLOGY
A Histochemical Study of Mucoid Cells in the Pars Distalis of the Human Hypophysis '
 A Histochemical Study of Mucoid Cells in the Pars Distalis of the Human Hypophysis ' JAMES L. CONKLIN Department of Anatomy, The Univefsity of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan ABSTRACT Sections of the human
A Histochemical Study of Mucoid Cells in the Pars Distalis of the Human Hypophysis ' JAMES L. CONKLIN Department of Anatomy, The Univefsity of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan ABSTRACT Sections of the human
Neurosecretion Protein hormones make on RER. Sequestered in granuels Released by exocytosis
 Comparative Physiology Withers CH 11 Endocrinology Communication Pathways Among Cells endocrine: fluid-born transport of chemical mediators (ex., insulin in regulation of glucose metabolism) paracrine:
Comparative Physiology Withers CH 11 Endocrinology Communication Pathways Among Cells endocrine: fluid-born transport of chemical mediators (ex., insulin in regulation of glucose metabolism) paracrine:
Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue.
 Plant Tissues Class- IX Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. PLANT TISSUES ANIMAL TISSUES 1. Most of the plant tissues are Most of the tissues
Plant Tissues Class- IX Tissues: - A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. PLANT TISSUES ANIMAL TISSUES 1. Most of the plant tissues are Most of the tissues
A Note on the Morphology of the Hypophysis in the Gymnophione Schistomepum thomense
 Okajimas Fol. anat. Op., 46: 307-319, 1970 A Note on the Morphology of the Hypophysis in the Gymnophione Schistomepum thomense By Hartwig Kuhlenbeck (Laboratory of Morphologic Brain Research, Prof. Dr.
Okajimas Fol. anat. Op., 46: 307-319, 1970 A Note on the Morphology of the Hypophysis in the Gymnophione Schistomepum thomense By Hartwig Kuhlenbeck (Laboratory of Morphologic Brain Research, Prof. Dr.
QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY"
 QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY" 1. The structure of the Plasmolemma. 2. Characteristic of receptive and transport functions of the plasmolemma. 3. The structure of intercellular contacts: Simple contact,
QUESTIONS TO MODULE "CYTOLOGY" 1. The structure of the Plasmolemma. 2. Characteristic of receptive and transport functions of the plasmolemma. 3. The structure of intercellular contacts: Simple contact,
C. L. FOSTER. (From the Dept. of Biology & Histology, Middlesex Hospital Medical School, London, W.i) With one Text-figure and one Plate INTRODUCTION
 Some Observations upon the Golgi Elements of the Anterior Pituitary Cells of Normal and Stilboestrol-treated Male Rats, using the Sudan Black Technique BY C. L. FOSTER (From the Dept. of Biology & Histology,
Some Observations upon the Golgi Elements of the Anterior Pituitary Cells of Normal and Stilboestrol-treated Male Rats, using the Sudan Black Technique BY C. L. FOSTER (From the Dept. of Biology & Histology,
Organization of Vertebrate Body. Organization of Vertebrate Body
 The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES
 NAME: DATE: PARTNER: CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES For ease of study, multicellular animals are often examined at various levels of structural organization. Starting from the most
NAME: DATE: PARTNER: CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES For ease of study, multicellular animals are often examined at various levels of structural organization. Starting from the most
7. CONTROL AND COORDINATION
 7. CONTROL AND COORDINATION Multicellular animals, except sponges, have specialized cells called neurons, for responding to stimuli. A neuron or nerve cell is the structural and functional unit of the
7. CONTROL AND COORDINATION Multicellular animals, except sponges, have specialized cells called neurons, for responding to stimuli. A neuron or nerve cell is the structural and functional unit of the
Unicellular vs. Multicellular Organisms Worksheet
 Name Date Unicellular vs. Multicellular Organisms Worksheet Instructions for VIVED Science 1. Open the Plant Cell Structures and Animal (Human) Cell Structures sessions and follow the instructions. 2.
Name Date Unicellular vs. Multicellular Organisms Worksheet Instructions for VIVED Science 1. Open the Plant Cell Structures and Animal (Human) Cell Structures sessions and follow the instructions. 2.
Chapter 6: Tissues. KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept]
![Chapter 6: Tissues. KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] Chapter 6: Tissues. KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept]](/thumbs/78/78538656.jpg) Chapter 6: Tissues KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] CONCEPTS RATING Meristems in plants ** Permanent tissues in plants **** Animal tissues ***** 1. Tissue is a group of cells
Chapter 6: Tissues KEY CONCEPTS : [ *rating as per the significance of concept] CONCEPTS RATING Meristems in plants ** Permanent tissues in plants **** Animal tissues ***** 1. Tissue is a group of cells
Cellular events in adenohypophysis of Trichogaster trichopterus (Pallas) during final oocyte maturation
 Indian J. Fish., 52(1) : 1-13, Jan.-Mar., 2005 1 Cellular events in adenohypophysis of Trichogaster trichopterus (Pallas) during final oocyte maturation K. JACKSON, M. ABRAHAM* AND G. DEGANI ** School
Indian J. Fish., 52(1) : 1-13, Jan.-Mar., 2005 1 Cellular events in adenohypophysis of Trichogaster trichopterus (Pallas) during final oocyte maturation K. JACKSON, M. ABRAHAM* AND G. DEGANI ** School
Developmental Zoology. Ectodermal derivatives (ZOO ) Developmental Stages. Developmental Stages
 Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
Seasonal Histology and Histochemistry of the Adenohypophysis of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)
 Seasonal Histology and Histochemistry of the Adenohypophysis of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) El-Sakhawy, M.A; El-Shammaa, M.A; Abd Rabou, M.I; El- Saba, A.A and Hussein, S.H Department of Cytology
Seasonal Histology and Histochemistry of the Adenohypophysis of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) El-Sakhawy, M.A; El-Shammaa, M.A; Abd Rabou, M.I; El- Saba, A.A and Hussein, S.H Department of Cytology
Head and Face Development
 Head and Face Development Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical Sciences,
Head and Face Development Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical Sciences,
Prelab Exercise 1. Cell structure
 Prelab Exercise 1 CELLS, EPITHELIA, GLANDS AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Prelab guide: this will function as a review of material that will be important to your performance of the lab. The first lab will examine
Prelab Exercise 1 CELLS, EPITHELIA, GLANDS AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Prelab guide: this will function as a review of material that will be important to your performance of the lab. The first lab will examine
Neuroectodermal origin of avian hypothalamo-hypophyseal complex: the role of the ventral neural ridge
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 34, 2,pp. 311-325, 1975 1>\\ Printed in Great Britain Neuroectodermal origin of avian hypothalamo-hypophyseal complex: the role of the ventral neural ridge By T. TAKOR TAKOR
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 34, 2,pp. 311-325, 1975 1>\\ Printed in Great Britain Neuroectodermal origin of avian hypothalamo-hypophyseal complex: the role of the ventral neural ridge By T. TAKOR TAKOR
The pituitary adrenocorticotropes originate from neural ridge tissue in Xenopus laevis
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. 95, 1-14 (1986) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1986 1 The pituitary adrenocorticotropes originate from neural ridge tissue in Xenopus laevis GERALD W.
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. 95, 1-14 (1986) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1986 1 The pituitary adrenocorticotropes originate from neural ridge tissue in Xenopus laevis GERALD W.
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
Is there a ventral neural ridge in chick embryos? Implications for the origin of adenohypophyseal and other APUD cells
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 57, pp. 71-78, 1980 7 \ Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited 1980 Is there a ventral neural ridge in chick embryos? Implications for the origin of adenohypophyseal
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 57, pp. 71-78, 1980 7 \ Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited 1980 Is there a ventral neural ridge in chick embryos? Implications for the origin of adenohypophyseal
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes
 Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
Year 7 - Cells Summary Notes Life Processes All living things do all seven of the life processes. Things that are not living may do some but do not do all seven of the life processes. These are: Movement
Introduction to Cellular Communication *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m53235 1 Introduction to Cellular Communication * Steven Telleen This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 Why Cells Communicate
OpenStax-CNX module: m53235 1 Introduction to Cellular Communication * Steven Telleen This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 1 Why Cells Communicate
Science Honors: Human Anatomy and Physiology Unit 3: The Endocrine System
 Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge The endocrine system maintains homeostasis by releasing chemicals called hormones, and it controls prolonged or continuous processes such
Essential Understandings Essential Questions Essential Knowledge The endocrine system maintains homeostasis by releasing chemicals called hormones, and it controls prolonged or continuous processes such
Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology
 Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The study of the human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye is. a. anatomy c. biology b. physiology d. pathology Anatomy is the
Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The study of the human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye is. a. anatomy c. biology b. physiology d. pathology Anatomy is the
HSC HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Midterm Exam October 17, 2001 Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology and Department of Physiology Time: 50 minutes 1.
 HSC 208.6 - HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Midterm Exam October 17, 2001 Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology and Department of Physiology Time: 50 minutes 1. An organ: A. is the smallest independent unit of life
HSC 208.6 - HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS Midterm Exam October 17, 2001 Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology and Department of Physiology Time: 50 minutes 1. An organ: A. is the smallest independent unit of life
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE. Cells, Tissues, and Membranes
 NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
NATIONAL REVIEW COURSE Cells, Tissues, and Membranes I. Cell Types A. Prokaryote bacteria cells; a cell that does not have a nucleus in which to store its genetic material. B. Eukaryote plant or animal
Plant Tissues. Parenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma
 BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, NOIDA CLASS-IX BIOLOGY TOPIC- TISSUES BY: UMESH VERMA Defination- A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. Also this group od
BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, NOIDA CLASS-IX BIOLOGY TOPIC- TISSUES BY: UMESH VERMA Defination- A group of cells similar in structure and performing a particular function forms a tissue. Also this group od
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill
 Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Sioux Falls School District Anatomy and Physiology Holes Anatomy and Physiology Authors: Shier, Butler, and Lewis Glencoe/ McGraw hill Semester 1 Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
Introduction Chpt 1. Study Slides
 Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
II. SIMPLE TISSUES Bot 404--Fall A. Introduction to Tissues (DIAGRAM allow a full page)
 II. SIMPLE TISSUES Bot 404--Fall 2004 A. Introduction to Tissues (DIAGRAM allow a full page) B. Definitions Adaxial = facing the axil; upper surface of leaf Abaxial = facing away from the axil; lower surface
II. SIMPLE TISSUES Bot 404--Fall 2004 A. Introduction to Tissues (DIAGRAM allow a full page) B. Definitions Adaxial = facing the axil; upper surface of leaf Abaxial = facing away from the axil; lower surface
Developmental Biology
 Developmental Biology 352 (2011) 215 227 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Birthdating studies reshape models for pituitary
Developmental Biology 352 (2011) 215 227 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Birthdating studies reshape models for pituitary
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY)
 PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
PREFACE O-LEVEL TOPICAL SCIENCE (BIOLOGY) provides a thorough revision for students taking the GCE O-Level Science (Biology) Examination. Past examination questions have been carefully classified into
2. Examine the external anatomy of the squid and identify the following structures: tentacles, arms, fins, siphon, mantle, eyes and collar.
 Cephalopod Anatomy As their name implies, members of the class Cephalopoda have modified head-foot which bears an array of prehensile tentacles and arms at the cranial end of the body. The visceral mass
Cephalopod Anatomy As their name implies, members of the class Cephalopoda have modified head-foot which bears an array of prehensile tentacles and arms at the cranial end of the body. The visceral mass
Nerve cells have many branches that help them send signals throughout the body.
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of atoms or cells. You might even say you are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of atoms or cells. You might even say you are made of organs, like skin and a heart. These answers are all correct. Each focuses on a different
Assignment 7 Due February 26
 Assignment 7 Due February 26 Cells of Multicellular organisms 1. File upload (3 points) View this electron micrograph of spinach leaf cells. The central cell has a thin cell wall; it is difficult to distinguish
Assignment 7 Due February 26 Cells of Multicellular organisms 1. File upload (3 points) View this electron micrograph of spinach leaf cells. The central cell has a thin cell wall; it is difficult to distinguish
Lack of the ventral anterior homeodomain transcription factor VAX1 leads to induction of a second pituitary
 Page nos Page total Colour pages: Facing pages: Issue Ms order Access Development the most First recent posted version epress online at on online http://dev.biologists.org/lookup/doi/10.1242/dev.056465
Page nos Page total Colour pages: Facing pages: Issue Ms order Access Development the most First recent posted version epress online at on online http://dev.biologists.org/lookup/doi/10.1242/dev.056465
Class IX Chapter 6 Tissues Science
 Question 1: What is a tissue? Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and are organised together to perform a specific task. Question 2: What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular
Question 1: What is a tissue? Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and are organised together to perform a specific task. Question 2: What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular
SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS
 SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Course Number: BIOL 132 Department: Biological Sciences Course Title: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Semester: Spring Year: 1997 Objectives/ 1. Recognize
SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Course Number: BIOL 132 Department: Biological Sciences Course Title: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Semester: Spring Year: 1997 Objectives/ 1. Recognize
Cells - Chapter 3. Transport into and out of cells. The Cell Theory. Hooke (1665) Leeuwenhoek ( ) Simple Cells Cell Tutorial
 Cells - Chapter 3 Cells Alive Intro Video Transport into and out of cells Organization/Review Simple Cells Cell Tutorial http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/framz.asp?objid=ap11604 Cell Death http://www.whfreeman.com/kuby/content/anm/kb04an01.htm
Cells - Chapter 3 Cells Alive Intro Video Transport into and out of cells Organization/Review Simple Cells Cell Tutorial http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/framz.asp?objid=ap11604 Cell Death http://www.whfreeman.com/kuby/content/anm/kb04an01.htm
WNT Signaling Affects Gene Expression in the Ventral Diencephalon and Pituitary Gland Growth
 DEVELOPMENTAL DYNAMICS 237:1006 1020, 2008 RESEARCH ARTICLE WNT Signaling Affects Gene Expression in the Ventral Diencephalon and Pituitary Gland Growth Mary Anne Potok, 1 Kelly B. Cha, 1 Andrea Hunt,
DEVELOPMENTAL DYNAMICS 237:1006 1020, 2008 RESEARCH ARTICLE WNT Signaling Affects Gene Expression in the Ventral Diencephalon and Pituitary Gland Growth Mary Anne Potok, 1 Kelly B. Cha, 1 Andrea Hunt,
and its origins G. E. Schneider 2009 Part 1: Introduction MIT 9.14 Class 1 Brain talk, and
 A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins G. E. Schneider 2009 Part 1: Introduction MIT 9.14 Class 1 Brain talk, and the ancient activities of brain cells 1. Introduction a) b) The plan for
A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins G. E. Schneider 2009 Part 1: Introduction MIT 9.14 Class 1 Brain talk, and the ancient activities of brain cells 1. Introduction a) b) The plan for
Inhibition of Sox2-dependent activation of Shh in the ventral diencephalon by Tbx3 is required for formation of the neurohypophysis
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 2299 Development 140, 2299-2309 (2013) doi:10.1242/dev.094524 2013. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Inhibition of Sox2-dependent activation of Shh in the ventral diencephalon
RESEARCH ARTICLE 2299 Development 140, 2299-2309 (2013) doi:10.1242/dev.094524 2013. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Inhibition of Sox2-dependent activation of Shh in the ventral diencephalon
BIOLOGY 5090/21. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 Theory May/June 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 Theory May/June 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and
Intercellular Communication. Department of Physiology School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara
 Intercellular Communication Department of Physiology School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara Intercellular Communication and Signal Transduction The ability of cells to communicate with each other
Intercellular Communication Department of Physiology School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara Intercellular Communication and Signal Transduction The ability of cells to communicate with each other
TU/Zoology/Pre-Ph.D. Course Work Syllabus/2010
 Pre- Ph.D. Course of Zoology Department will consist of four papers and each paper will be of 100 marks of which 20 marks will be of internal assessment. The outline of the course structure will be as
Pre- Ph.D. Course of Zoology Department will consist of four papers and each paper will be of 100 marks of which 20 marks will be of internal assessment. The outline of the course structure will be as
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 211 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. 4 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Deborah Allen. Revised date: July, 2014
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 211 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Deborah Allen Revised date: July, 2014 Linda Abernathy, Division Chair for Math, Science, and Business Shirley
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 211 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Deborah Allen Revised date: July, 2014 Linda Abernathy, Division Chair for Math, Science, and Business Shirley
VOCABULARY. Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System
 CELLS VOCABULARY Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System THE IMPORTANCE OF CELLS Cells are the smallest unit of life in all living things They are organized structures
CELLS VOCABULARY Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System THE IMPORTANCE OF CELLS Cells are the smallest unit of life in all living things They are organized structures
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which body fluid compartment contains high levels of K +, large anions, and proteins?
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which body fluid compartment contains high levels of K +, large anions, and proteins?
Announcements: Test4: Wednesday on: week4 material CH5 CH6 & NIA CAPE Evaluations please do them for me!! ask questions...discuss listen learn.
 Announcements: Test4: Wednesday on: week4 material CH5 CH6 & NIA CAPE Evaluations please do them for me!! ask questions...discuss listen learn. The Chemical Senses: Olfaction Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department
Announcements: Test4: Wednesday on: week4 material CH5 CH6 & NIA CAPE Evaluations please do them for me!! ask questions...discuss listen learn. The Chemical Senses: Olfaction Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department
PERIODIC-ACID-SCHIFF METHOD FOR THE DIFFERENTIATION OF BASOPHILS IN THE
 J. clin. Path. (1960), 13, 256. THE BUFFERED PERFORMIC-ACID-ALCIAN-BLUE- PERIODIC-ACID-SCHIFF METHOD FOR THE DIFFERENTIATION OF BASOPHILS IN THE HUMAN AND RAT PITUITARY BY From the Bernhard Baron Institute
J. clin. Path. (1960), 13, 256. THE BUFFERED PERFORMIC-ACID-ALCIAN-BLUE- PERIODIC-ACID-SCHIFF METHOD FOR THE DIFFERENTIATION OF BASOPHILS IN THE HUMAN AND RAT PITUITARY BY From the Bernhard Baron Institute
(Q.) Mention the layer outside the plasma membrane of a plant cell. (1 Mark) (Ans) Cell wall is the layer outside the plasma membrane of a plant cell.
 Science Class 8 (CBSE) Page: 1 Mention the layer outside the plasma membrane of a plant cell. Cell wall is the layer outside the plasma membrane of a plant cell. Name the outermost layer of an animal cell.
Science Class 8 (CBSE) Page: 1 Mention the layer outside the plasma membrane of a plant cell. Cell wall is the layer outside the plasma membrane of a plant cell. Name the outermost layer of an animal cell.
The Continuity between the Cavities of the Premandibular Somites and of Rathke's Pocket in Torpedo By SIR GAVIN DE BEER, F.R.S.
 279 The Continuity between the Cavities of the Premandibular Somites and of Rathke's Pocket in Torpedo By SIR GAVIN DE BEER, F.R.S. (Correspondant de Vlnstitut de France; Director of the British Museum
279 The Continuity between the Cavities of the Premandibular Somites and of Rathke's Pocket in Torpedo By SIR GAVIN DE BEER, F.R.S. (Correspondant de Vlnstitut de France; Director of the British Museum
Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards. Anatomical terms. Homeostatic mechanisms. Characteristics of Life. Requirements for life
 Honors Anatomy & Physiology 2012 Michael Harshaw, Melissa Castone Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards Month Introduction September- 1.5 weeks How do Anatomy and Physiology relate to
Honors Anatomy & Physiology 2012 Michael Harshaw, Melissa Castone Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards Month Introduction September- 1.5 weeks How do Anatomy and Physiology relate to
Physiology. Organization of the Body. Assumptions in Physiology. Chapter 1. Physiology is the study of how living organisms function
 Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis Chapter 1 Physiology Physiology is the study of how living organisms function On the street explanations are in terms of meeting a bodily need Physiologic explanations
Introduction to Physiology and Homeostasis Chapter 1 Physiology Physiology is the study of how living organisms function On the street explanations are in terms of meeting a bodily need Physiologic explanations
Ion Channels and Signaling in the Pituitary Gland
 Ion Channels and Signaling in the Pituitary Gland Stanko S. Stojilkovic, Joël Tabak and Richard Bertram Endocr. Rev. 2010 31:845-915 originally published online Jul 21, 2010;, doi: 10.1210/er.2010-0005
Ion Channels and Signaling in the Pituitary Gland Stanko S. Stojilkovic, Joël Tabak and Richard Bertram Endocr. Rev. 2010 31:845-915 originally published online Jul 21, 2010;, doi: 10.1210/er.2010-0005
Lab Exercise 4: Primary Growth and Tissues in Stems
 Lab Exercise 4: Primary Growth and Tissues in Stems Tissues of the plant body can be classified in a variety of ways: functionally (based on the tissue function, e.g. vascular tissue ), morphologically
Lab Exercise 4: Primary Growth and Tissues in Stems Tissues of the plant body can be classified in a variety of ways: functionally (based on the tissue function, e.g. vascular tissue ), morphologically
D.C.H.S BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT
 D.C.H.S BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT NAT 5 Homework Booklet Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms 1 HOMEWORK 1- Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. (a) Multicellular organisms are composed of different types of cells which are
D.C.H.S BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT NAT 5 Homework Booklet Unit 2 Multicellular Organisms 1 HOMEWORK 1- Cells, Tissues and Organs 1. (a) Multicellular organisms are composed of different types of cells which are
active transport active transport support
 1 Which row matches the cell membrane and cell wall of a palisade cell to their functions? cell membrane active transport active transport support support cell wall active transport support active transport
1 Which row matches the cell membrane and cell wall of a palisade cell to their functions? cell membrane active transport active transport support support cell wall active transport support active transport
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms. Gene Families
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Gene Families In metazoans,
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 19: Eukaryotic genes & Multicellular Organisms http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Gene Families In metazoans,
Slide 1 / Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system.
 Slide 1 / 64 1 Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system. Slide 2 / 64 2 List the four major groups of tissues in animals. Slide 3 /
Slide 1 / 64 1 Arrange the following in order from least complex to most complex: organ, tissue, cell, organism, organ system. Slide 2 / 64 2 List the four major groups of tissues in animals. Slide 3 /
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125
 Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2010-2011 catalog ANAT 125 Human Anatomy 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record ANAT 125 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2010-2011 catalog ANAT 125 Human Anatomy 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory completion
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Chapter 3. Cells and Tissues. Slides Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L.
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Slides 3.1 3.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Slides 3.1 3.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical
Organelles & Cells Student Edition. A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole
 Name: Date: 1. Which structure is outside the nucleus of a cell and contains DNA? A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole 2. A potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure
Name: Date: 1. Which structure is outside the nucleus of a cell and contains DNA? A. chromosome B. gene C. mitochondrion D. vacuole 2. A potato core was placed in a beaker of water as shown in the figure
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology - II Week 1; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Review of Early Development of Humans.
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology - II Week 1; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Review of Early Development of Humans Special Senses Review: Historical and Developmental Perspectives Ontogeny
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology - II Week 1; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Review of Early Development of Humans Special Senses Review: Historical and Developmental Perspectives Ontogeny
Signaling mechanisms in pituitary morphogenesis and cell fate determination Jeremy S Dasen* and Michael G Rosenfeld
 669 Signaling mechanisms in pituitary morphogenesis and cell fate determination Jeremy S Dasen* and Michael G Rosenfeld The development of the pituitary gland has provided an instructive model system for
669 Signaling mechanisms in pituitary morphogenesis and cell fate determination Jeremy S Dasen* and Michael G Rosenfeld The development of the pituitary gland has provided an instructive model system for
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION. Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos
 Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
Introduction. The study of animal form and function is integrated by the common set of problems that all animals must solve.
 Introduction The study of animal form and function is integrated by the common set of problems that all animals must solve. These include how to extract oxygen from the environment, how to nourish themselves,
Introduction The study of animal form and function is integrated by the common set of problems that all animals must solve. These include how to extract oxygen from the environment, how to nourish themselves,
JEFFERSON COLLEGE VERTEBRATE ANATOMY
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
ORGANISATION IN THE LIVING THINGS
 2 ORGANISATION IN THE LIVING THINGS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. A group of similar cells which perform a particular function is called (a) organism (b) tissue (c) organelle
2 ORGANISATION IN THE LIVING THINGS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. A group of similar cells which perform a particular function is called (a) organism (b) tissue (c) organelle
WHAT UNIVERSITY GENERAL EDUCATION OUTCOMES GUIDE STUDENT LEARNING IN COURSES THAT CARRY NATURAL SCIENCES CREDIT?
 Ralph Henry Contact: ralph.henry@uark.edu, 479-283-0154 A plan to assess student learning in a University General Education Core Curriculum course: BIOL2213/BIOL2211L Human Physiology/Human Physiology
Ralph Henry Contact: ralph.henry@uark.edu, 479-283-0154 A plan to assess student learning in a University General Education Core Curriculum course: BIOL2213/BIOL2211L Human Physiology/Human Physiology
Form and Function. Physical Laws and Form. Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function. AP Biology Fig Figs & 40.
 Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function AP Biology 2013 1 Form and Function Comparative studies show that form and function are closely related Natural selection can fit the form (anatomy)
Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function AP Biology 2013 1 Form and Function Comparative studies show that form and function are closely related Natural selection can fit the form (anatomy)
UNIT 6 - STRUCTURES OF FLOWERING PLANTS & THEIR FUNCTIONS
 6.1 Plant Tissues A tissue is a group of cells with common function, structures or both. In plants we can find 2 types of tissues: Meristem Permanent tissues Meristem is found in regions with continuous
6.1 Plant Tissues A tissue is a group of cells with common function, structures or both. In plants we can find 2 types of tissues: Meristem Permanent tissues Meristem is found in regions with continuous
Chapter 9. Benefits of Being Large. Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity. Hierarchical Organization of Animal Complexity. Fig. 9.
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity Zoologists recognize
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity Zoologists recognize
Cell Organelles. 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism Cells tissues organ organ system organism
 Cell Organelles What are some of the differences you see between these two cells? A. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism
Cell Organelles What are some of the differences you see between these two cells? A. Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of organization in an organism
Plants. Tissues, Organs, and Systems
 Plants Tissues, Organs, and Systems Meristematic cells Specialized cells that are responsible for producing specialized cells, they produce three types of tissue in the body of a plant. Meristematic Cells
Plants Tissues, Organs, and Systems Meristematic cells Specialized cells that are responsible for producing specialized cells, they produce three types of tissue in the body of a plant. Meristematic Cells
2 nd Term - Helping Questions for Final Exam of Bio 110
 2 nd Term - Helping Questions for Final Exam of Bio 110 1) requires a continuous supply of O 2 and the disposal of CO 2. A) Transpiration B) Cellular respiration C) Tissue respiration D) Photosynthesis
2 nd Term - Helping Questions for Final Exam of Bio 110 1) requires a continuous supply of O 2 and the disposal of CO 2. A) Transpiration B) Cellular respiration C) Tissue respiration D) Photosynthesis
Cell Theory and Structure. Discoveries What are Cells? Cell Theory Cell Structures Organelles
 Cell Theory and Structure Discoveries What are Cells? Cell Theory Cell Structures Organelles Discoveries In 1665 Robert Hooke observed a thin slice of cork from an oak tree What he saw reminded him of
Cell Theory and Structure Discoveries What are Cells? Cell Theory Cell Structures Organelles Discoveries In 1665 Robert Hooke observed a thin slice of cork from an oak tree What he saw reminded him of
Cells to systems. 1) Chemical Level All matter is a combination of atoms: - Oxygen - Carbon - Nitrogen - Hydrogen Make up 96% of total body chemistry
 Cells to systems Organisation of the Human body: 1. Chemical level 2. Cellular level 3. Tissue level 4. Organ level 5. Body system level 6. Organism level 1) Chemical Level All matter is a combination
Cells to systems Organisation of the Human body: 1. Chemical level 2. Cellular level 3. Tissue level 4. Organ level 5. Body system level 6. Organism level 1) Chemical Level All matter is a combination
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Muscle Cells skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle
 Muscle Cells Muscle tissue, one of the four major tissue types, plays the vital role of providing movement and heat generation to the organs of the body. Within muscle tissue are three distinct groups
Muscle Cells Muscle tissue, one of the four major tissue types, plays the vital role of providing movement and heat generation to the organs of the body. Within muscle tissue are three distinct groups
PRELIMINARY REPORT ON THE EFFECT OF PITUITARY AUTOTRANSPLANTATION ON THE PARS INTERMEDIA OF THE SEAW ATER GOBY, G1LLICHTHYS MIRABILIS1
 Bol. Zool. e Biol. Mar., N.S., n. 30, pp. 69-79, São Paulo, 1973 PRELIMINARY REPORT ON THE EFFECT OF PITUITARY AUTOTRANSPLANTATION ON THE PARS INTERMEDIA OF THE SEAW ATER GOBY, G1LLICHTHYS MIRABILIS1 RICHARD
Bol. Zool. e Biol. Mar., N.S., n. 30, pp. 69-79, São Paulo, 1973 PRELIMINARY REPORT ON THE EFFECT OF PITUITARY AUTOTRANSPLANTATION ON THE PARS INTERMEDIA OF THE SEAW ATER GOBY, G1LLICHTHYS MIRABILIS1 RICHARD
The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY
 The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY The topography of organs and organ systems 1. The organs are: a. clusters of identical tissues; b. different tissue groups; c. morphological units that fulfill the function
The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY The topography of organs and organ systems 1. The organs are: a. clusters of identical tissues; b. different tissue groups; c. morphological units that fulfill the function
Non Permanent Tissues - Meristematic Tissue
 PLANT TISSUES Non Permanent Tissues - Meristematic Tissue Undifferentiated plant cells that are continually dividing by mitosis Large thin walled cells No vacuole Dense cytoplasm Large nucleus Found at
PLANT TISSUES Non Permanent Tissues - Meristematic Tissue Undifferentiated plant cells that are continually dividing by mitosis Large thin walled cells No vacuole Dense cytoplasm Large nucleus Found at
2.5 : Cells are grouped into tissue
 2.5 : Cells are grouped into tissue 1 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Structures & functions: Cell membrane and organelles Animal Cells are grouped into tissue Plant Cell
2.5 : Cells are grouped into tissue 1 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Structures & functions: Cell membrane and organelles Animal Cells are grouped into tissue Plant Cell
Human Physiology Part - 02
 Episode No 32 Telecast: 16/04/2017 Faculty: prof. M J H Shafi Human Physiology Part - 02 01. Read the statements A and B Pick the correct option. Statement A: All kinds of movements seen in humans are
Episode No 32 Telecast: 16/04/2017 Faculty: prof. M J H Shafi Human Physiology Part - 02 01. Read the statements A and B Pick the correct option. Statement A: All kinds of movements seen in humans are
human cell Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function.
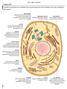 human cell CELL AND TISSUES Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function. Golgi apparatus Organelle composed of a series
human cell CELL AND TISSUES Smallest living structure and constituent unit of human beings; the sizes and shapes of cells vary according to their function. Golgi apparatus Organelle composed of a series
KRSN BIO 2030 Anatomy and Physiology - 8 credit hours KRSN BIO 2031 Anatomy and Physiology KRSN BIO 2032 Anatomy and Physiology Lab
 KRSN BIO 2030 Anatomy and Physiology - 8 credit hours KRSN BIO 2031 Anatomy and Physiology KRSN BIO 2032 Anatomy and Physiology Lab For institutional specific information, visit the University & College
KRSN BIO 2030 Anatomy and Physiology - 8 credit hours KRSN BIO 2031 Anatomy and Physiology KRSN BIO 2032 Anatomy and Physiology Lab For institutional specific information, visit the University & College
Endocrine Physiology. Introduction to Endocrine Principles
 Endocrine Physiology Introduction to Endocrine Principles There are TWO major groups of hormones Peptide and protein hormones Amine hormones Peptide and protein hormones act through cell membrane receptors
Endocrine Physiology Introduction to Endocrine Principles There are TWO major groups of hormones Peptide and protein hormones Amine hormones Peptide and protein hormones act through cell membrane receptors
Direct and indirect roles of Fgf3 and Fgf10 in innervation and vascularisation of the vertebrate hypothalamic neurohypophysis
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 1111 Development 140, 1111-1122 (2013) doi:10.1242/dev.080226 2013. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Direct and indirect roles of Fgf3 and Fgf10 in innervation and vascularisation
RESEARCH ARTICLE 1111 Development 140, 1111-1122 (2013) doi:10.1242/dev.080226 2013. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Direct and indirect roles of Fgf3 and Fgf10 in innervation and vascularisation
Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis. Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis
 Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis 1 Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis 2 Biological Explanations Proximate Proximate causation: an explanation of an animal's behavior based on
Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis 1 Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis 2 Biological Explanations Proximate Proximate causation: an explanation of an animal's behavior based on
Sample paper 6. Question: 1. Which of the following pairing is incorrect?
 Sample paper 6 Question: 1 Which of the following pairing is incorrect? A. Mesosomes : infolding of bacterial cell wall B. Ribosomes : sites of protein synthesis C. Flagella : locomotory organ of bacteria
Sample paper 6 Question: 1 Which of the following pairing is incorrect? A. Mesosomes : infolding of bacterial cell wall B. Ribosomes : sites of protein synthesis C. Flagella : locomotory organ of bacteria
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record AP 150
 Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record AP 150 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2012-2013 catalog AP 150 Integrative Anatomy and Physiology 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory
Modesto Junior College Course Outline of Record AP 150 I. OVERVIEW The following information will appear in the 2012-2013 catalog AP 150 Integrative Anatomy and Physiology 5 Units Prerequisite: Satisfactory
Introduction to the Human Body. Cells. Body Functions. Tissues. Organs. Systems. Body Functions & Life Process
 complex functions for the body. Ten major systems compose the human body: Introduction to the Human Body Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic
complex functions for the body. Ten major systems compose the human body: Introduction to the Human Body Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic
Architectural Pattern of an animal. Chapter 9
 Architectural Pattern of an animal Chapter 9 What is an animal? Levels of organization and organismal complexity 5 major levels of complexity Unicellular Metazoan? Tissue Organ Organ systems Levels of
Architectural Pattern of an animal Chapter 9 What is an animal? Levels of organization and organismal complexity 5 major levels of complexity Unicellular Metazoan? Tissue Organ Organ systems Levels of
Plant Anatomy AP Biology
 Plant Anatomy 2006-2007 Basic plant anatomy 1 root root tip root hairs Roots 1 Roots anchor plant in soil, absorb minerals & water, & store food fibrous roots (1) mat of thin roots that spread out monocots
Plant Anatomy 2006-2007 Basic plant anatomy 1 root root tip root hairs Roots 1 Roots anchor plant in soil, absorb minerals & water, & store food fibrous roots (1) mat of thin roots that spread out monocots
