Generalization of a nonlinear friction relation for a dimer sliding on a periodic substrate
|
|
|
- Alban Jonah Henry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Eur. Phys. J. B 6, 59 6 (008 DOI: 0.0/epj/e THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL B Generlizion of nonliner fricion relion for dimer sliding on periodic susre M. Tiwri,,S.Gonçles, nd V.M. Kenkre Consorium of he Americs for Inerdisciplinry Science nd Deprmen of Physics nd Asronomy, Uniersiy of New Mexico, Aluquerque, New Mexico 873, USA Insiuo de Físic, Uniersidde Federl do Rio Grnde do Sul, Cix Posl 505, Poro Alegre RS, Brzil Receied 9 Ferury 008 / Receied in finl form 6 April 008 Pulished online My 008 c EDP Sciences, Socieà Ilin di Fisic, Springer-Verlg 008 Asrc. An omic cluser moing long solid surfce cn undergo dissipion of is rnslionl energy hrough direc mode, inoling he coupling of he cener-of-mss moion o herml exciions of he susre, nd n indirec mode, due o dmping of he inernl moion of he cluser, o which he cener-of-mss moion cn e coupled s resul of surfce poenil. Focusg only on he less well undersood indirec mode, on he sis of numericl soluions, we presen, deprures from recenly repored simple relionship eween he force nd elociy of nonliner fricion. A generlizion of he nlyic considerions h erlier led o h relionship is crried ou nd shown o explin he deprures sisfcorily. Our generlizion res for he sysem considered (dimer sliding oer periodic susre he complee dependence on seerl of he key prmeers, specificlly inernl dissipion, nurl frequency, susre corrugion, nd lengh rio. Furher predicions from our generlizions re found o gree wih new simulions. The sysem nlyzed is relen o nnosrucures moing oer crysl surfces. PACS. 8.0.Pq Fricion, luricion, nd wer d Triology nd mechnicl concs Inroducion The fricion experienced y oms, smll molecules nd dlyers moing on susres is n cie opic of curren reserch [ 7,6] ecuse of is relence o he fundmenl undersnding of riey of processes such s hose inoled in omic force microscopy [8,9]. Tking he nurl poin of iew h horough undersnding of he moion of idelized omic srucures oer idelized susres should precede he sudy of he moion of relisic omic eniies oer relisic surfces, seerl inesigors he explored he moion of dimers (wo-om sysems moing oer fixed surfce represened y usoidl [0 5] poenil. I is perhps surprig u rue h, in spie of he fc h numer of horough sudies of more relisic (e.g., exended sysems he lredy ppered in he lierure, inereg resuls coninue o e found in he simple dimer sysem. If dimer chrcerized y he mss m of ech om conneced y spring of spring consn m 0 is hrown wih n iniil cener of mss elociy 0 oer -dimensionl susre represened y usoidl poenil of mpliude u 0 nd welengh, one of hese recen numericl inesigions [0] showed h, if he only dmping in he sysem cs on he inernl coordine of he dimer, he cener of mss moion of he dimer is effecielydmpedinremrkle e-mil: mukesh@unm.edu fshion represened y nonliner fricion relion. Th relion ses h he effecie fricion force experienced y he dimer cener of mss moion is inersely proporionl o he cue of he cener of mss elociy. The purpose of he presen pper is o inesige he rnge of lidiy of h fricion relion. We crry ou numericl simulions h go eyond he limiing se of condiions explored in reference [0], show h cler deprures re oined in he ehior of he dimer including in he dependence of is sopping ime on rious sysem prmeers, nd proide sisfcory heoreicl explnion for our findings. The pper is se ou s follows. We firs inesige numericlly he deprures from he simple nonliner fricion relion of reference [0] wih chnge in sysem prmeers (Sec. nd hen gie simple explnion in erms of n exended nonliner fricion relion o suppor our numericl findings (Sec. 3. In Secion we mke predicions on he sis of our nlysis nd find h hey re erified y new numericl soluions. Concluding remrks re presened in Secion 5. Deprures from he / 3 fricion relion The equions of moion goerning he sysem under sudy, dimer moing on -dimensionl periodic
2 60 The Europen Physicl Journl B susre, re mẍ = k(x x + ( πu 0 mγ (ẋ ẋ mẍ = k(x x + ( πu 0 ( πx ( πx mγ (ẋ ẋ ( where x, re he coordines of he wo dimer pricles of equl mss m, oerdos denoe ime deriies, γ is he dmping coefficien nd k,,, u 0 re, respeciely, he spring consn, equilirium lengh of he dimer, welengh of he susre poenil nd hlf he mpliude of he poenil. Noe h he dmping of ech mss is proporionl no o is solue elociy u o he elociy relie o he oher mss. This mens h dmping cs only on he inernl coordine. Such siuion represens dissipion of energy hrough chnnels inernl o he moing srucure. We consider he sysem emperures low enough h rndom (Brownin moion erms need no e dded in equion (. This we do for simpliciy s in reference [0]. I hs een poined ou in rious ppers such s reference [] how he Brownin erms my e incorpored. The uhors of reference [0] he shown, hrough simulions nd nlyic indicions sring from equion (, h he dimer dynmics cn resul in he remrkly simple nonliner fricion relion: d d = γ ( u0 m ( π 3 ( Equion ( predics h he sopping ime (defined s heimewhichheelociyofhecenerofmssdrops o zero would e gien s: s = γ ( u 0 m ( (3 π This mens h he sopping ime for he cener of mss moion should ry inersely s he coefficien γ which conrols he dmping in he inernl coordine of he dimer. The firs of he deprures from he fricion relion gien y equion ( h we repor in he presen pper is he iolion of he monoonic γ-dependence of he sopping ime. We plo in Figure he riion, wih chnge in he dmping coefficien γ, of he sopping ime oined y soling numericlly equion (. The plo clerly shows h deprure. The soluion we oin (solid cure coincides wih he predicion of equions (, 3iniilly, showing decrese in sop wih increg γ. Howeer, furher increse in γ resuls in n increse in sop,in conrs o he predicions of equions (, 3. In exmining he dependence of sop on γ, wehefoundsriking liner relionship eween γ nd he relie difference eween sop nd he sopping ime s prediced y he / 3 relion se ou in reference [0]. We exhii his liner relionship in Figure. The second deprure from predicions of he relion in equions (, 3 h we found inoles he frequencydependence of he sopping ime. While equion ( is 0 sop γ presen work / 3 lw Fig.. Deprure from he fricion relion of reference [0]: comprison eween he non-monoonic sopping ime sop oined from numericl simulions (solid line wih he monoonic predicion (see Eq. (3 of he / 3 relion (dshed line of reference [0] for differen lues γ of dmping. Dmping is expressed in unis of (/ u 0/m nd sopping ime is in unis of m/u 0.Iniilelociy 0 is 5 u 0/m. Oher prmeers re / =0.5 ndk /u 0 =0.0. sop / s 0 0 numericl soluion liner fi γ Fig.. Liner relionship eween γ nd he relie difference eween he sopping ime nd he predicion of he fricion relion in reference [0]. The circles represens he numericl soluion while he solid line is n (excellen liner fi. Oher prmeers re s in Figure. independen of he nurl frequency 0 = k/m of he dimer, our numericl soluions show h sop does exhii dependence on 0, showing minimum nd increse on eiher side of he minimum. We disply his ehior in Figure 3, where we plo sop normlized o is limi 0 s 0 0. The mrked oscillory ehior o he lef of he minimum in Figure 3 is represenie of he resonnce s will e cler from Figure elow. The res of he jgged nure of he cure in Figure 3 hs no physicl significnce nd rises from numericl sources.
3 M. Tiwri e l.: Generlizion of nonliner fricion relion... 6 sop / presen work / 3 lw Fig. 3. Deprure from he fricion relion of reference [0]s seen in he dependence of he sopping ime on he dimer nurl frequency 0. Shown is he sopping ime (normlized o is lue 0 for 0 0, see ex from our numericl soluions (solid line nd from he predicion of equions (, 3 (dshed line, i.e., of he erlier nlysis reference [0]. Frequency is expressed in unis of (/ u 0/m nd γ (m/u 0=.Oher prmeers re s in Figures,. 3 Anlyic sudies from n exended ersion of he fricion relion In order o undersnd he source of he deprures from he / 3 relion repored in Secion, weexminehe equions of moion ( y following he procedure se ou in reference [0]. By defining scled nd rnsled coordine ξ, hrough ξ = (x x, ( we oin he equion of moion gien in reference [0], d ξ d + γ dξ d + 0 ξ = πu { 0 π } m ( + ξ cos(ζ, (5 where ζ, he scled cener of mss coordine oeys d ζ d = [ (π (u0 ζ = π(x + x, (6 m ] { π } cos ( + ξ (ζ (7 I ws rgued in reference [0] h, lhough equion (7 predics n inoled dependence of ζ on ξ nd, herefore, eenully on, he simple liner pproximion ζ( where = π(/ is he so clled wshord frequency, ( eing he elociy of he cener of mss, leds, for smll ξ (ξ, o d ξ d + γ dξ d + 0ξ = πu ( 0 π m cos ( (8 Wih equion (8 s he sring poin, pproximing he ssumed wekly -dependen o e consn, one cn sole for he inernl coordine ξ( = πu ( 0 π m ( 0 + γ cos( δ (9 where δ is he phse ngle gien y n(δ =γ /(0. The uhors of reference [0] deried he nonliner fricion lw y ug power lnce condiion. To e le o ddress he deprures repored y us in Figures 3 oe, we inroduce n imporn modificion in h rgumen. Insed of neglecing 0 nd γ erms in d d = γ ( u0 m ( π [ ( 0 π ] ( + γ π, (0 we elec o use equion (0 s our generlized fricion relion. Clerly, under he pproximion h he wshord frequency is much lrger hn oh he nurl frequency 0 nd dmping γ, one ges he / 3 relion of reference [0]. Insed of simplifying equion (0 for 0 /π nd γ/π, wesole equion (0 excly: [{ ( } = 0 + η 0 { ( } 0 ( ( γ π ( ( ] 0 ln ( π0 0 where, η = γ ( u0 m ( π. The definiion of he frequency =π 0 /, whichisheiniil lue of,nd corresponds o he iniil cener of mss elociy of he dimer, llows us o rewrie our soluion ( s [ ( ] ( [ ( ] = 0 + γ 0 0 s ( 0 ( ln 0 ( where s = 0 η.equion( is one of he principl nlyic resuls of he presen pper. 3. Anlysis of he γ dependence of he sopping ime for smll inernl frequency ( 0 The ide of puing = 0 in equion(, nd clculing he corresponding sopping ime sop, nurlly suggess iself. Howeer, i is no lid in generl: he exisence of he logrihmic erm ensures h he elociy hs longime il which mens h he sopping ime is, sricly, lwys infinie. On he oher hnd, he simulions do show sopping ime wihin which he dimer flls ino one of he susre wells, nd hen rles ck nd forh. A good esime of sop cn e oined from equion ( for lues of 0 / sufficienly smll h he logrihmic
4 6 The Europen Physicl Journl B erm cn e negleced. Then, if he inernl irion frequency is smll enough ( 0, u if specificlly we llow he dmping γ o e unresriced, we oin s = [ ( 0 ] + γ [ ( ] ( c = numericl nlyicl fi Puing =0inequion(3, we ge he sopping ime ( γ ] sop = s [+ ( sop c = /5 Equion (, noher of he new resuls of he presen nlysis, displys he sopping ime sop s he produc of wo fcors. The firs fcor is he sopping ime s = 0 η gien y he / 3 relion of reference [0]. The second fcor is he correcion proided y our presen nlysis: +(γ/. If dmping is reliely smll, which ws he cse reed erlier, (γ/ my e negleced nd here is negligile correcion. If, howeer, dmping is susnil, sop s gien y equion (cnincrese wih γ. Indeed, ( ledso sop s = γ. (5 Our nlyic resul (5 proides he highly ccure fi o he simulions displyed in Figure. 3. Anlysis of he 0 dependence of he sopping ime for smll dmping (γ If, inequion(, we mke he pproximion h he dmping in inernl coordine is smll (γ, u llow he frequency 0 o e unresriced, we oin s = [ ( ] 0 ( 0 ( [ 0 ( ln 0 ( ] 0 (6 Unlike in equion ( we cnno oin sop in his cse y puing =0inequion(6, ecuse, s explined oe, he sopping ime is lwys infinie. To ge n esime of sop from (6, we pu / 0 equl o sufficienly smll non-zero lue c nd sole (6 numericlly. We cll he sopping ime hus oined sop rher hn sop (ecuse c 0, lhough smll nd disply is dependence on he oscillor frequency in Figure. Thelue of c we he ken is oined y equing he cener of mss kineic energy o he susre poenil energy. The significn feure in he oe cse is he deelopmen of long ils of ( h rise from he logrihmic erm in he righ hnd side of (6. In he low-elociy limi ( 0 /π he denominor of he righ hnd side of equion (0 ecomes independen of nd we recoer he liner fricion relion. d d = γ ( u0 m s ( π, ( Fig.. Dependence of he ppren sopping ime sop on he oscillor frequency 0 showing close greemen eween he numericl (solid line nd nlyic expression gien y equion (6 (dshed line s explined, for differen lues of he nurl frequency of he oscillor. The rio c (see ex is ken o e /5. Frequency is expressed in unis of (u0/m/ nd γ (m/u 0 =. Oher prmeers re he sme s in Figure. Inse shows he comprison for smller lue of c = 0.0 which shows poor greemen of simulion nd heory. where, s = 0 π is he sliding elociy corresponding o he nurl frequency of he oscillor. By fixing / 0 = c nd puing d/d 0 = 0 in our nlyic equion (6, we cn oin resonle lue of 0 which he minimum of sop occurs in Figure : [(c /lnc] /. This mnner of geing sopping ime would e compleely useless if he resuls we oin were srongly dependen on he chosen lue of c. Wehecrriedou numerous clculions for differen c s nd found h for c 0. we ge fine greemen eween simulion nd nlyic predicion. For smller lues, we sill find quliie greemen (e.g. in he exisence nd pproxime locion of he minimum which ecomes worse s c is mde smller (see inse of Fig.. The oscillions seen o he lef of he minimum occur when he driing frequency is close o resonnce. This is oiously no presen in our simple nlyic resuls. The resonnce is eween he nurl frequency of he dimer 0 nd he wshord frequency =π/ (see Eq. (9. Comprison of he predicions of he generlized fricion relion wih simulions Gien he sisfcory greemen of he nlyic expression, equion (, for he sopping ime deried here, we presen Figures 5, 6, where we compre he cener of mss elociy ccording o our nlyic expression ( wih numericl simulions. In Figure 5 we he kep he dmping coefficien γ unchnged nd he ried he nurl frequency of he dimer o produce cures,, c from our nlyic predicion for hree differen lues of 0 s
5 M. Tiwri e l.: Generlizion of nonliner fricion relion c,, c 3 c 0 c Fig. 5. Comprison eween our presen nlyic predicion from he generlized fricion relion (dshed lines nd numericl simulions (solid lines wih oscillions for he cener of mss elociy (. Iniil elociy 0 is 5 u 0/m. Oherprmeers re / =0.5 ndγ m/u 0 =. The differen lues of frequency 0 re 3.6, 0 nd. expressed in unis of (u0/m/. They correspond o he spring consn k eing in he rio :0:0 respeciely. The lines, nd c re he predicions of he / 3 fricion relion of reference [0] nd coincide wih one noher ecuse of he lck of ppernce of he nurl frequency in h relion. Velociy is expressed in unis of u 0/m nd ime is in unis of m/u 0.Inseshows he resonnce srucure h is isile in he min figure round = 0. shown. Our prediced cures si righ ono he simulion resuls unil he ler rek ino oscillions which our nlyic predicions cnno descrie. Clerly, our presen nlysis does considerly eer is--is he simulions hn he / 3 relion which, eing insensiie o 0, produces he gle cure denoed,,c in Figure 5. The oher feure our presen simulions show is he resonnce phenomenon when he wshord frequency equls he nurl frequency. I is responsile for he srucure seen in Figure 5 round = 0 (mgnified in he inse nd is he sme s he one h produces he srucure o he lef of he minimum in Figure. In Figure 6 we he lef 0 consn nd ried he dmping. Once gin our nlyic predicions, cures,, c (for γ = 5, 50, 00 respeciely in unis (u 0 /m/ do ery well wih respec o he simulions. No only do hey si on op of he simulion cures (excep for he oscillions while cures,,c oined from he / 3 relion do no, u hey lso exhii non-monoonic ehior s γ is ried: cure is o he lef of u cure c is o he righ of. By conrs, cures,,c exhii monoonic endency in h hey moe lefwrd in he - -c progression. 5 Concluding remrks The simple sysem of dimer sliding on periodic susre offers eg ground for heoreicl pproches Fig. 6. Comprison eween our presen nlyic predicion from he generlized fricion relion (dshed lines nd numericl simulions (solid lines wih oscillions for he cener of mss elociy ( s.ime. Iniilelociy 0 is 5 u 0/m. Oher prmeers re / =0.5 ndk /u 0 =0.0. The differen lues of dmping γ expressed in unis of (u 0/m/ re 5, 50 nd 00. The doed lines, nd c show he predicions of he / 3 fricion relion. Velociy is expressed in unis of u 0/m nd ime is in unis of m/u 0. imed undersnding he nure of omic fricion on meril susres. In exmining recenly repored nonliner fricion relion [0], we he found, i, our simulions, deprures from he predicion of h relion. The deprures re inereg, re displyed in Figures 3, nd cn e explined heoreiclly, s we he shown. Predicions mde on he sis of our nlysis re orne ou excellenly y simulions s shown in Figures 5, 6. Our new nlyic resuls re equion ( for he sopping ime of he dimer when hrown oer he susre wih n iniil elociy, is pproxime forms equions (3, 6, nd deried expressions such s equions (, 5. All hese resuls sem from he generlizion, equion (, of he fricion relion of reference [0]. Much of he ehior seen in he eoluion of he cener of mss elociy cn e undersood physiclly from he concep of resonnce. The ell shpe of he resonnce gien y equion (0 is conrolled y dmping nd he nurl frequency of he dimer. Mximum energy is los in he irionl moion nd close o resonnce. A smll lues of dmping he mximum lue of he ell shpe is lrge u he widh is nrrow so he inernl mode does no lose much energy nd hence he sopping ime is lrge. Increg he lue of dmping rings down he resonnce pek u he sme ime increses he widh of he ell shpe. Thus he dimer loses more energy s i spends more ime in he resonnce region. Lrge lues of dmping desroys he widh of he resonnce cure nd gin he inernl mode is no le o lose much energy; hence he increse in sopping ime. The nurl frequency deermines he posiion of he pek. Iniilly, he driing frequency is fr wy from resonnce nd no much
6 6 The Europen Physicl Journl B energy is eing rnsferred o he inernl coordine. As he cener of mss elociy drops down o close o resonnce, he rnsfer of energy reches locl mximum. Howeer, ecuse he dmping is no lrge he energy cnno e dissiped wy immediely nd hence is rnsferred ck ino rnslionl moion. This ck nd forh rnsfer of energy eween rnslionl nd irionl moion leds o srong periodic oscillions elociies close o resonnce. The nonliner fricion relion gien y equion (0 is no le o cpure hese oscillions. The coupling dries he dimer ou of resonnce window o where he driing frequency ecomes much smller hn he resonn frequency nd hence he elociy decys exponenilly wih ime (see Eq. (7 nd he oscillions ecome periodic. This srong oscillory ehior cn e wshed ou y increg he dmping of he sysem due o resons lredy menioned efore. Increse in he lue of nurl frequency shifs he resonnce pek o lrger lues nd hus he dimer goes ino resonnce region lrger driing frequencies. Our im in he presen pper hs een o ddress some feures of omisic fricion. Excep for he simplificion h he model is confined o gle spil dimension, i hs he necessry ingrediens o represen rel dimer or molecule in conrolled microscopic sliding experimen (e.g. [] low emperures, o he exen h exernl dmping my e considered negligile. Dissipion of rnslionl energy of n ojec long surfce cn occur in wo wys, direcly nd indirecly. Indeed, here hs een n ongoing dee in he lierure ou he relie impornce of he source of sliding fricion: wheher i is elecronic or phononic. As explined in deil in he conclusion secion of recen pper y some of he presen uhors [] i migh mke sense o idenify ckground liner fricion wih elecronic, nd resonnce fricion wih phononic, sources. For sufficienly lrge corrugions of he susre, he ler (he only chnnel considered in he presen pper cn domine in principle. Neerheless if he modulion rio / is smll, he chnnel we he considered cn e unimporn y comprison, nd dlyer elociies relie o he susre migh need o e s high s m/s for he resonnce fricion o e pprecile. Experimens repored so fr do no inole such high elociies. Our sudy hs no ddressed ps oserions u rges relizle fuure scenrios. We hope h in he ligh of he cler nlysis presened in his pper nd elsewhere [0], he focus on he resonnce fricion chnnel used oe will e of help in fuure oserions where h chnnel my no e oerlooked. I is plesure o hnk Birk Reichench for numerous discussions. This work ws suppored in pr y he NSF under grn INT References. M. Urkh, J. Klfer, D. Gourdon, J. Isrelchili, Nure (London 30, 55 (00. B.N.J. Persson, Phys. Re. B 8, 80 ( J. Krim, Surf. Sci 500, 7 (00. J.B. Sokoloff, Phys. Re. B, 760 ( A.S. Kole, A.I. Lndu, Low Temp. Phys. 8, 3 (00 6. O.M. Brun, R. Ferrndo, D.E. Tommei, Phys. Re. E 68, 050 ( L. Consoli, H.J.F. Knops, A. Fsolino, Phys. Re. Le. 85, 30 ( C.M. Me, G.M. McClellnd, R. Erlndsson, S. Ching, Phys. Re. Le. 59, 9 ( E. Gnecco, R. Bennewiz, T. Gylog, E. Meyer, J. Phys.: Condens. Mer 3, R69 (00 0. S. Gonçles, V.M. Kenkre, A.R. Bishop, Phys. Re. B 70, 955 (00. S. Gonçles, C. Fusco, A.R. Bishop, V.M. Kenkre, Phys. Re. B 7, 958 (005. C. Fusco, A. Fsolino, T. Jnssen, Eur. Phys J. B 3, 95 ( C. Fusco, A. Fsolino, Thin Solid Films 8, 3 (003. A.H. Romero, A.M. Lcs, J.M. Sncho, Phys. Re. E 69, 0505 (00 5. O.M. Brun, Phys. Re. E 63, 00 (00 6. S.Yu. Krylo, K.B. Jinesh, H. Vlk, M. Dienwieel, J.W.M. Frenken, Phys. Re. E 7, 0650(R (005
A Kalman filtering simulation
 A Klmn filering simulion The performnce of Klmn filering hs been esed on he bsis of wo differen dynmicl models, ssuming eiher moion wih consn elociy or wih consn ccelerion. The former is epeced o beer
A Klmn filering simulion The performnce of Klmn filering hs been esed on he bsis of wo differen dynmicl models, ssuming eiher moion wih consn elociy or wih consn ccelerion. The former is epeced o beer
0 for t < 0 1 for t > 0
 8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
1. Consider a PSA initially at rest in the beginning of the left-hand end of a long ISS corridor. Assume xo = 0 on the left end of the ISS corridor.
 In Eercise 1, use sndrd recngulr Cresin coordine sysem. Le ime be represened long he horizonl is. Assume ll ccelerions nd decelerions re consn. 1. Consider PSA iniilly res in he beginning of he lef-hnd
In Eercise 1, use sndrd recngulr Cresin coordine sysem. Le ime be represened long he horizonl is. Assume ll ccelerions nd decelerions re consn. 1. Consider PSA iniilly res in he beginning of he lef-hnd
Motion. Part 2: Constant Acceleration. Acceleration. October Lab Physics. Ms. Levine 1. Acceleration. Acceleration. Units for Acceleration.
 Moion Accelerion Pr : Consn Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion is he re of chnge of velociy. = v - vo = Δv Δ ccelerion = = v - vo chnge of velociy elpsed ime Accelerion is vecor, lhough in one-dimensionl
Moion Accelerion Pr : Consn Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion is he re of chnge of velociy. = v - vo = Δv Δ ccelerion = = v - vo chnge of velociy elpsed ime Accelerion is vecor, lhough in one-dimensionl
Contraction Mapping Principle Approach to Differential Equations
 epl Journl of Science echnology 0 (009) 49-53 Conrcion pping Principle pproch o Differenil Equions Bishnu P. Dhungn Deprmen of hemics, hendr Rn Cmpus ribhuvn Universiy, Khmu epl bsrc Using n eension of
epl Journl of Science echnology 0 (009) 49-53 Conrcion pping Principle pproch o Differenil Equions Bishnu P. Dhungn Deprmen of hemics, hendr Rn Cmpus ribhuvn Universiy, Khmu epl bsrc Using n eension of
ENGR 1990 Engineering Mathematics The Integral of a Function as a Function
 ENGR 1990 Engineering Mhemics The Inegrl of Funcion s Funcion Previously, we lerned how o esime he inegrl of funcion f( ) over some inervl y dding he res of finie se of rpezoids h represen he re under
ENGR 1990 Engineering Mhemics The Inegrl of Funcion s Funcion Previously, we lerned how o esime he inegrl of funcion f( ) over some inervl y dding he res of finie se of rpezoids h represen he re under
e t dt e t dt = lim e t dt T (1 e T ) = 1
 Improper Inegrls There re wo ypes of improper inegrls - hose wih infinie limis of inegrion, nd hose wih inegrnds h pproch some poin wihin he limis of inegrion. Firs we will consider inegrls wih infinie
Improper Inegrls There re wo ypes of improper inegrls - hose wih infinie limis of inegrion, nd hose wih inegrnds h pproch some poin wihin he limis of inegrion. Firs we will consider inegrls wih infinie
1.0 Electrical Systems
 . Elecricl Sysems The ypes of dynmicl sysems we will e sudying cn e modeled in erms of lgeric equions, differenil equions, or inegrl equions. We will egin y looking fmilir mhemicl models of idel resisors,
. Elecricl Sysems The ypes of dynmicl sysems we will e sudying cn e modeled in erms of lgeric equions, differenil equions, or inegrl equions. We will egin y looking fmilir mhemicl models of idel resisors,
HW #1 Solutions. Lewis Structures: Using the above rules, determine the molecular structure for Cl2CO. Hint: C is at the center.
 HW # Soluions Cron Mss Prolem: ssuming n erge surfce pressure of m, n erge ropospheric emperure of 55 K, n glol CO mixing rio of 385 ppm, wh is he curren mospheric Cron reseroir (in unis of g m -? Compre
HW # Soluions Cron Mss Prolem: ssuming n erge surfce pressure of m, n erge ropospheric emperure of 55 K, n glol CO mixing rio of 385 ppm, wh is he curren mospheric Cron reseroir (in unis of g m -? Compre
MTH 146 Class 11 Notes
 8.- Are of Surfce of Revoluion MTH 6 Clss Noes Suppose we wish o revolve curve C round n is nd find he surfce re of he resuling solid. Suppose f( ) is nonnegive funcion wih coninuous firs derivive on he
8.- Are of Surfce of Revoluion MTH 6 Clss Noes Suppose we wish o revolve curve C round n is nd find he surfce re of he resuling solid. Suppose f( ) is nonnegive funcion wih coninuous firs derivive on he
22.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Systems Prof. Freidberg Lecture 9: The High Beta Tokamak
 .65, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 9: The High e Tokmk Summry of he Properies of n Ohmic Tokmk. Advnges:. good euilibrium (smll shif) b. good sbiliy ( ) c. good confinemen ( τ nr )
.65, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 9: The High e Tokmk Summry of he Properies of n Ohmic Tokmk. Advnges:. good euilibrium (smll shif) b. good sbiliy ( ) c. good confinemen ( τ nr )
Average & instantaneous velocity and acceleration Motion with constant acceleration
 Physics 7: Lecure Reminders Discussion nd Lb secions sr meeing ne week Fill ou Pink dd/drop form if you need o swich o differen secion h is FULL. Do i TODAY. Homework Ch. : 5, 7,, 3,, nd 6 Ch.: 6,, 3 Submission
Physics 7: Lecure Reminders Discussion nd Lb secions sr meeing ne week Fill ou Pink dd/drop form if you need o swich o differen secion h is FULL. Do i TODAY. Homework Ch. : 5, 7,, 3,, nd 6 Ch.: 6,, 3 Submission
PHYSICS 1210 Exam 1 University of Wyoming 14 February points
 PHYSICS 1210 Em 1 Uniersiy of Wyoming 14 Februry 2013 150 poins This es is open-noe nd closed-book. Clculors re permied bu compuers re no. No collborion, consulion, or communicion wih oher people (oher
PHYSICS 1210 Em 1 Uniersiy of Wyoming 14 Februry 2013 150 poins This es is open-noe nd closed-book. Clculors re permied bu compuers re no. No collborion, consulion, or communicion wih oher people (oher
An object moving with speed v around a point at distance r, has an angular velocity. m/s m
 Roion The mosphere roes wih he erh n moions wihin he mosphere clerly follow cure phs (cyclones, nicyclones, hurricnes, ornoes ec.) We nee o epress roion quniiely. For soli objec or ny mss h oes no isor
Roion The mosphere roes wih he erh n moions wihin he mosphere clerly follow cure phs (cyclones, nicyclones, hurricnes, ornoes ec.) We nee o epress roion quniiely. For soli objec or ny mss h oes no isor
3. Renewal Limit Theorems
 Virul Lborories > 14. Renewl Processes > 1 2 3 3. Renewl Limi Theorems In he inroducion o renewl processes, we noed h he rrivl ime process nd he couning process re inverses, in sens The rrivl ime process
Virul Lborories > 14. Renewl Processes > 1 2 3 3. Renewl Limi Theorems In he inroducion o renewl processes, we noed h he rrivl ime process nd he couning process re inverses, in sens The rrivl ime process
Minimum Squared Error
 Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > 0 for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i i for ll smples
Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > 0 for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i i for ll smples
Introduction to LoggerPro
 Inroducion o LoggerPro Sr/Sop collecion Define zero Se d collecion prmeers Auoscle D Browser Open file Sensor seup window To sr d collecion, click he green Collec buon on he ool br. There is dely of second
Inroducion o LoggerPro Sr/Sop collecion Define zero Se d collecion prmeers Auoscle D Browser Open file Sensor seup window To sr d collecion, click he green Collec buon on he ool br. There is dely of second
A 1.3 m 2.5 m 2.8 m. x = m m = 8400 m. y = 4900 m 3200 m = 1700 m
 PHYS : Soluions o Chper 3 Home Work. SSM REASONING The displcemen is ecor drwn from he iniil posiion o he finl posiion. The mgniude of he displcemen is he shores disnce beween he posiions. Noe h i is onl
PHYS : Soluions o Chper 3 Home Work. SSM REASONING The displcemen is ecor drwn from he iniil posiion o he finl posiion. The mgniude of he displcemen is he shores disnce beween he posiions. Noe h i is onl
(b) 10 yr. (b) 13 m. 1.6 m s, m s m s (c) 13.1 s. 32. (a) 20.0 s (b) No, the minimum distance to stop = 1.00 km. 1.
 Answers o Een Numbered Problems Chper. () 7 m s, 6 m s (b) 8 5 yr 4.. m ih 6. () 5. m s (b).5 m s (c).5 m s (d) 3.33 m s (e) 8. ().3 min (b) 64 mi..3 h. ().3 s (b) 3 m 4..8 mi wes of he flgpole 6. (b)
Answers o Een Numbered Problems Chper. () 7 m s, 6 m s (b) 8 5 yr 4.. m ih 6. () 5. m s (b).5 m s (c).5 m s (d) 3.33 m s (e) 8. ().3 min (b) 64 mi..3 h. ().3 s (b) 3 m 4..8 mi wes of he flgpole 6. (b)
September 20 Homework Solutions
 College of Engineering nd Compuer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Mechnicl Engineering A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll 7 Number 66 Insrucor: Lrry Creo Sepember Homework Soluions Find he specrum
College of Engineering nd Compuer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Mechnicl Engineering A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll 7 Number 66 Insrucor: Lrry Creo Sepember Homework Soluions Find he specrum
Minimum Squared Error
 Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i = i for ll smples
Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i = i for ll smples
A new model for limit order book dynamics
 Anewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics JeffreyR.Russell UniversiyofChicgo,GrdueSchoolofBusiness TejinKim UniversiyofChicgo,DeprmenofSisics Absrc:Thispperproposesnewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics.Thelimiorderbookconsiss
Anewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics JeffreyR.Russell UniversiyofChicgo,GrdueSchoolofBusiness TejinKim UniversiyofChicgo,DeprmenofSisics Absrc:Thispperproposesnewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics.Thelimiorderbookconsiss
2D Motion WS. A horizontally launched projectile s initial vertical velocity is zero. Solve the following problems with this information.
 Nme D Moion WS The equions of moion h rele o projeciles were discussed in he Projecile Moion Anlsis Acii. ou found h projecile moes wih consn eloci in he horizonl direcion nd consn ccelerion in he ericl
Nme D Moion WS The equions of moion h rele o projeciles were discussed in he Projecile Moion Anlsis Acii. ou found h projecile moes wih consn eloci in he horizonl direcion nd consn ccelerion in he ericl
3 Motion with constant acceleration: Linear and projectile motion
 3 Moion wih consn ccelerion: Liner nd projecile moion cons, In he precedin Lecure we he considered moion wih consn ccelerion lon he is: Noe h,, cn be posiie nd neie h leds o rie of behiors. Clerl similr
3 Moion wih consn ccelerion: Liner nd projecile moion cons, In he precedin Lecure we he considered moion wih consn ccelerion lon he is: Noe h,, cn be posiie nd neie h leds o rie of behiors. Clerl similr
Motion in a Straight Line
 Moion in Srigh Line. Preei reched he mero sion nd found h he esclor ws no working. She wlked up he sionry esclor in ime. On oher dys, if she remins sionry on he moing esclor, hen he esclor kes her up in
Moion in Srigh Line. Preei reched he mero sion nd found h he esclor ws no working. She wlked up he sionry esclor in ime. On oher dys, if she remins sionry on he moing esclor, hen he esclor kes her up in
RESPONSE UNDER A GENERAL PERIODIC FORCE. When the external force F(t) is periodic with periodτ = 2π
 RESPONSE UNDER A GENERAL PERIODIC FORCE When he exernl force F() is periodic wih periodτ / ω,i cn be expnded in Fourier series F( ) o α ω α b ω () where τ F( ) ω d, τ,,,... () nd b τ F( ) ω d, τ,,... (3)
RESPONSE UNDER A GENERAL PERIODIC FORCE When he exernl force F() is periodic wih periodτ / ω,i cn be expnded in Fourier series F( ) o α ω α b ω () where τ F( ) ω d, τ,,,... () nd b τ F( ) ω d, τ,,... (3)
Solutions to Problems from Chapter 2
 Soluions o Problems rom Chper Problem. The signls u() :5sgn(), u () :5sgn(), nd u h () :5sgn() re ploed respecively in Figures.,b,c. Noe h u h () :5sgn() :5; 8 including, bu u () :5sgn() is undeined..5
Soluions o Problems rom Chper Problem. The signls u() :5sgn(), u () :5sgn(), nd u h () :5sgn() re ploed respecively in Figures.,b,c. Noe h u h () :5sgn() :5; 8 including, bu u () :5sgn() is undeined..5
Chapter 2. Motion along a straight line. 9/9/2015 Physics 218
 Chper Moion long srigh line 9/9/05 Physics 8 Gols for Chper How o describe srigh line moion in erms of displcemen nd erge elociy. The mening of insnneous elociy nd speed. Aerge elociy/insnneous elociy
Chper Moion long srigh line 9/9/05 Physics 8 Gols for Chper How o describe srigh line moion in erms of displcemen nd erge elociy. The mening of insnneous elociy nd speed. Aerge elociy/insnneous elociy
Name: Per: L o s A l t o s H i g h S c h o o l. Physics Unit 1 Workbook. 1D Kinematics. Mr. Randall Room 705
 Nme: Per: L o s A l o s H i g h S c h o o l Physics Uni 1 Workbook 1D Kinemics Mr. Rndll Room 705 Adm.Rndll@ml.ne www.laphysics.com Uni 1 - Objecies Te: Physics 6 h Ediion Cunel & Johnson The objecies
Nme: Per: L o s A l o s H i g h S c h o o l Physics Uni 1 Workbook 1D Kinemics Mr. Rndll Room 705 Adm.Rndll@ml.ne www.laphysics.com Uni 1 - Objecies Te: Physics 6 h Ediion Cunel & Johnson The objecies
Phys 221 Fall Chapter 2. Motion in One Dimension. 2014, 2005 A. Dzyubenko Brooks/Cole
 Phys 221 Fall 2014 Chaper 2 Moion in One Dimension 2014, 2005 A. Dzyubenko 2004 Brooks/Cole 1 Kinemaics Kinemaics, a par of classical mechanics: Describes moion in erms of space and ime Ignores he agen
Phys 221 Fall 2014 Chaper 2 Moion in One Dimension 2014, 2005 A. Dzyubenko 2004 Brooks/Cole 1 Kinemaics Kinemaics, a par of classical mechanics: Describes moion in erms of space and ime Ignores he agen
4.8 Improper Integrals
 4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
Chapter Direct Method of Interpolation
 Chper 5. Direc Mehod of Inerpolion Afer reding his chper, you should be ble o:. pply he direc mehod of inerpolion,. sole problems using he direc mehod of inerpolion, nd. use he direc mehod inerpolns o
Chper 5. Direc Mehod of Inerpolion Afer reding his chper, you should be ble o:. pply he direc mehod of inerpolion,. sole problems using he direc mehod of inerpolion, nd. use he direc mehod inerpolns o
5.1-The Initial-Value Problems For Ordinary Differential Equations
 5.-The Iniil-Vlue Problems For Ordinry Differenil Equions Consider solving iniil-vlue problems for ordinry differenil equions: (*) y f, y, b, y. If we know he generl soluion y of he ordinry differenil
5.-The Iniil-Vlue Problems For Ordinry Differenil Equions Consider solving iniil-vlue problems for ordinry differenil equions: (*) y f, y, b, y. If we know he generl soluion y of he ordinry differenil
P441 Analytical Mechanics - I. Coupled Oscillators. c Alex R. Dzierba
 Lecure 3 Mondy - Deceber 5, 005 Wrien or ls upded: Deceber 3, 005 P44 Anlyicl Mechnics - I oupled Oscillors c Alex R. Dzierb oupled oscillors - rix echnique In Figure we show n exple of wo coupled oscillors,
Lecure 3 Mondy - Deceber 5, 005 Wrien or ls upded: Deceber 3, 005 P44 Anlyicl Mechnics - I oupled Oscillors c Alex R. Dzierb oupled oscillors - rix echnique In Figure we show n exple of wo coupled oscillors,
f t f a f x dx By Lin McMullin f x dx= f b f a. 2
 Accumulion: Thoughs On () By Lin McMullin f f f d = + The gols of he AP* Clculus progrm include he semen, Sudens should undersnd he definie inegrl s he ne ccumulion of chnge. 1 The Topicl Ouline includes
Accumulion: Thoughs On () By Lin McMullin f f f d = + The gols of he AP* Clculus progrm include he semen, Sudens should undersnd he definie inegrl s he ne ccumulion of chnge. 1 The Topicl Ouline includes
Phys 110. Answers to even numbered problems on Midterm Map
 Phys Answers o een numbered problems on Miderm Mp. REASONING The word per indices rio, so.35 mm per dy mens.35 mm/d, which is o be epressed s re in f/cenury. These unis differ from he gien unis in boh
Phys Answers o een numbered problems on Miderm Mp. REASONING The word per indices rio, so.35 mm per dy mens.35 mm/d, which is o be epressed s re in f/cenury. These unis differ from he gien unis in boh
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( y )
 8. Lengh of Plne Curve The mos fmous heorem in ll of mhemics is he Pyhgoren Theorem. I s formulion s he disnce formul is used o find he lenghs of line segmens in he coordine plne. In his secion you ll
8. Lengh of Plne Curve The mos fmous heorem in ll of mhemics is he Pyhgoren Theorem. I s formulion s he disnce formul is used o find he lenghs of line segmens in he coordine plne. In his secion you ll
Probability, Estimators, and Stationarity
 Chper Probbiliy, Esimors, nd Sionriy Consider signl genered by dynmicl process, R, R. Considering s funcion of ime, we re opering in he ime domin. A fundmenl wy o chrcerize he dynmics using he ime domin
Chper Probbiliy, Esimors, nd Sionriy Consider signl genered by dynmicl process, R, R. Considering s funcion of ime, we re opering in he ime domin. A fundmenl wy o chrcerize he dynmics using he ime domin
FM Applications of Integration 1.Centroid of Area
 FM Applicions of Inegrion.Cenroid of Are The cenroid of ody is is geomeric cenre. For n ojec mde of uniform meril, he cenroid coincides wih he poin which he ody cn e suppored in perfecly lnced se ie, is
FM Applicions of Inegrion.Cenroid of Are The cenroid of ody is is geomeric cenre. For n ojec mde of uniform meril, he cenroid coincides wih he poin which he ody cn e suppored in perfecly lnced se ie, is
Collision Detection and Bouncing
 Collision Deecion nd Bouncing Collisions re Hndled in Two Prs. Deecing he collision Mike Biley mj@cs.oregonse.edu. Hndling he physics of he collision collision-ouncing.ppx If You re Lucky, You Cn Deec
Collision Deecion nd Bouncing Collisions re Hndled in Two Prs. Deecing he collision Mike Biley mj@cs.oregonse.edu. Hndling he physics of he collision collision-ouncing.ppx If You re Lucky, You Cn Deec
The solution is often represented as a vector: 2xI + 4X2 + 2X3 + 4X4 + 2X5 = 4 2xI + 4X2 + 3X3 + 3X4 + 3X5 = 4. 3xI + 6X2 + 6X3 + 3X4 + 6X5 = 6.
 [~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
[~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
Observability of flow dependent structure functions and their use in data assimilation
 Oserviliy of flow dependen srucure funcions nd heir use in d ssimilion Pierre Guhier nd Crisin Lupu Collorion wih Séphne Lroche, Mrk Buehner nd Ahmed Mhidji (Env. Cnd) 3rd meeing of he HORPEX DAOS-WG Monrél
Oserviliy of flow dependen srucure funcions nd heir use in d ssimilion Pierre Guhier nd Crisin Lupu Collorion wih Séphne Lroche, Mrk Buehner nd Ahmed Mhidji (Env. Cnd) 3rd meeing of he HORPEX DAOS-WG Monrél
M r. d 2. R t a M. Structural Mechanics Section. Exam CT5141 Theory of Elasticity Friday 31 October 2003, 9:00 12:00 hours. Problem 1 (3 points)
 Delf Universiy of Technology Fculy of Civil Engineering nd Geosciences Srucurl echnics Secion Wrie your nme nd sudy numer he op righ-hnd of your work. Exm CT5 Theory of Elsiciy Fridy Ocoer 00, 9:00 :00
Delf Universiy of Technology Fculy of Civil Engineering nd Geosciences Srucurl echnics Secion Wrie your nme nd sudy numer he op righ-hnd of your work. Exm CT5 Theory of Elsiciy Fridy Ocoer 00, 9:00 :00
Soliton Scattering on the External Potential in Weakly Nonlocal Nonlinear Media
 Mlysin Journl of Mhemicl Sciences 1(S) Februry: 219 226 (216) Specil Issue: The 3 rd Inernionl Conference on Mhemicl Applicions in Engineering 214 (ICMAE 14) MALAYSIAN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES
Mlysin Journl of Mhemicl Sciences 1(S) Februry: 219 226 (216) Specil Issue: The 3 rd Inernionl Conference on Mhemicl Applicions in Engineering 214 (ICMAE 14) MALAYSIAN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICAL SCIENCES
An integral having either an infinite limit of integration or an unbounded integrand is called improper. Here are two examples.
 Improper Inegrls To his poin we hve only considered inegrls f(x) wih he is of inegrion nd b finie nd he inegrnd f(x) bounded (nd in fc coninuous excep possibly for finiely mny jump disconinuiies) An inegrl
Improper Inegrls To his poin we hve only considered inegrls f(x) wih he is of inegrion nd b finie nd he inegrnd f(x) bounded (nd in fc coninuous excep possibly for finiely mny jump disconinuiies) An inegrl
22.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Systems Prof. Freidberg Lecture 10: The High Beta Tokamak Con d and the High Flux Conserving Tokamak.
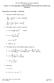 .615, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 1: The High Be Tokmk Con d nd he High Flux Conserving Tokmk Proeries of he High Tokmk 1. Evlue he MHD sfey fcor: ψ B * ( ) 1 3 ρ 1+ ν ρ ρ cosθ *
.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 1: The High Be Tokmk Con d nd he High Flux Conserving Tokmk Proeries of he High Tokmk 1. Evlue he MHD sfey fcor: ψ B * ( ) 1 3 ρ 1+ ν ρ ρ cosθ *
EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEM
 Elecronic Journl of Differenil Equions, Vol. 208 (208), No. 50, pp. 6. ISSN: 072-669. URL: hp://ejde.mh.xse.edu or hp://ejde.mh.un.edu EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE
Elecronic Journl of Differenil Equions, Vol. 208 (208), No. 50, pp. 6. ISSN: 072-669. URL: hp://ejde.mh.xse.edu or hp://ejde.mh.un.edu EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE
NEWTON S SECOND LAW OF MOTION
 Course and Secion Dae Names NEWTON S SECOND LAW OF MOTION The acceleraion of an objec is defined as he rae of change of elociy. If he elociy changes by an amoun in a ime, hen he aerage acceleraion during
Course and Secion Dae Names NEWTON S SECOND LAW OF MOTION The acceleraion of an objec is defined as he rae of change of elociy. If he elociy changes by an amoun in a ime, hen he aerage acceleraion during
Version 001 test-1 swinney (57010) 1. is constant at m/s.
 Version 001 es-1 swinne (57010) 1 This prin-ou should hve 20 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions m coninue on he nex column or pge find ll choices before nswering. CubeUniVec1x76 001 10.0 poins Acubeis1.4fee
Version 001 es-1 swinne (57010) 1 This prin-ou should hve 20 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions m coninue on he nex column or pge find ll choices before nswering. CubeUniVec1x76 001 10.0 poins Acubeis1.4fee
Properties of Logarithms. Solving Exponential and Logarithmic Equations. Properties of Logarithms. Properties of Logarithms. ( x)
 Properies of Logrihms Solving Eponenil nd Logrihmic Equions Properies of Logrihms Produc Rule ( ) log mn = log m + log n ( ) log = log + log Properies of Logrihms Quoien Rule log m = logm logn n log7 =
Properies of Logrihms Solving Eponenil nd Logrihmic Equions Properies of Logrihms Produc Rule ( ) log mn = log m + log n ( ) log = log + log Properies of Logrihms Quoien Rule log m = logm logn n log7 =
Lecture 3: 1-D Kinematics. This Week s Announcements: Class Webpage: visit regularly
 Lecure 3: 1-D Kinemics This Week s Announcemens: Clss Webpge: hp://kesrel.nm.edu/~dmeier/phys121/phys121.hml isi regulrly Our TA is Lorrine Bowmn Week 2 Reding: Chper 2 - Gincoli Week 2 Assignmens: Due:
Lecure 3: 1-D Kinemics This Week s Announcemens: Clss Webpge: hp://kesrel.nm.edu/~dmeier/phys121/phys121.hml isi regulrly Our TA is Lorrine Bowmn Week 2 Reding: Chper 2 - Gincoli Week 2 Assignmens: Due:
Physics Worksheet Lesson 4: Linear Motion Section: Name:
 Physics Workshee Lesson 4: Liner Moion Secion: Nme: 1. Relie Moion:. All moion is. b. is n rbirry coorine sysem wih reference o which he posiion or moion of somehing is escribe or physicl lws re formule.
Physics Workshee Lesson 4: Liner Moion Secion: Nme: 1. Relie Moion:. All moion is. b. is n rbirry coorine sysem wih reference o which he posiion or moion of somehing is escribe or physicl lws re formule.
Chapter 2: Evaluative Feedback
 Chper 2: Evluive Feedbck Evluing cions vs. insrucing by giving correc cions Pure evluive feedbck depends olly on he cion ken. Pure insrucive feedbck depends no ll on he cion ken. Supervised lerning is
Chper 2: Evluive Feedbck Evluing cions vs. insrucing by giving correc cions Pure evluive feedbck depends olly on he cion ken. Pure insrucive feedbck depends no ll on he cion ken. Supervised lerning is
Physic 231 Lecture 4. Mi it ftd l t. Main points of today s lecture: Example: addition of velocities Trajectories of objects in 2 = =
 Mi i fd l Phsic 3 Lecure 4 Min poins of od s lecure: Emple: ddiion of elociies Trjecories of objecs in dimensions: dimensions: g 9.8m/s downwrds ( ) g o g g Emple: A foobll pler runs he pern gien in he
Mi i fd l Phsic 3 Lecure 4 Min poins of od s lecure: Emple: ddiion of elociies Trjecories of objecs in dimensions: dimensions: g 9.8m/s downwrds ( ) g o g g Emple: A foobll pler runs he pern gien in he
Magnetostatics Bar Magnet. Magnetostatics Oersted s Experiment
 Mgneosics Br Mgne As fr bck s 4500 yers go, he Chinese discovered h cerin ypes of iron ore could rc ech oher nd cerin mels. Iron filings "mp" of br mgne s field Crefully suspended slivers of his mel were
Mgneosics Br Mgne As fr bck s 4500 yers go, he Chinese discovered h cerin ypes of iron ore could rc ech oher nd cerin mels. Iron filings "mp" of br mgne s field Crefully suspended slivers of his mel were
6. Gas dynamics. Ideal gases Speed of infinitesimal disturbances in still gas
 6. Gs dynmics Dr. Gergely Krisóf De. of Fluid echnics, BE Februry, 009. Seed of infiniesiml disurbnces in sill gs dv d, dv d, Coninuiy: ( dv)( ) dv omenum r r heorem: ( ( dv) ) d 3443 4 q m dv d dv llievi
6. Gs dynmics Dr. Gergely Krisóf De. of Fluid echnics, BE Februry, 009. Seed of infiniesiml disurbnces in sill gs dv d, dv d, Coninuiy: ( dv)( ) dv omenum r r heorem: ( ( dv) ) d 3443 4 q m dv d dv llievi
MATH 124 AND 125 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 2008)
 MATH 14 AND 15 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 8) The following quesions cn be used s review for Mh 14/ 15 These quesions re no cul smples of quesions h will pper on he finl em, bu hey will provide
MATH 14 AND 15 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 8) The following quesions cn be used s review for Mh 14/ 15 These quesions re no cul smples of quesions h will pper on he finl em, bu hey will provide
The order of reaction is defined as the number of atoms or molecules whose concentration change during the chemical reaction.
 www.hechemisryguru.com Re Lw Expression Order of Recion The order of recion is defined s he number of oms or molecules whose concenrion chnge during he chemicl recion. Or The ol number of molecules or
www.hechemisryguru.com Re Lw Expression Order of Recion The order of recion is defined s he number of oms or molecules whose concenrion chnge during he chemicl recion. Or The ol number of molecules or
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Some basic notation and terminology. Deterministic Finite Automata. COMP218: Decision, Computation and Language Note 1
 COMP28: Decision, Compuion nd Lnguge Noe These noes re inended minly s supplemen o he lecures nd exooks; hey will e useful for reminders ou noion nd erminology. Some sic noion nd erminology An lphe is
COMP28: Decision, Compuion nd Lnguge Noe These noes re inended minly s supplemen o he lecures nd exooks; hey will e useful for reminders ou noion nd erminology. Some sic noion nd erminology An lphe is
Physics 2A HW #3 Solutions
 Chper 3 Focus on Conceps: 3, 4, 6, 9 Problems: 9, 9, 3, 41, 66, 7, 75, 77 Phsics A HW #3 Soluions Focus On Conceps 3-3 (c) The ccelerion due o grvi is he sme for boh blls, despie he fc h he hve differen
Chper 3 Focus on Conceps: 3, 4, 6, 9 Problems: 9, 9, 3, 41, 66, 7, 75, 77 Phsics A HW #3 Soluions Focus On Conceps 3-3 (c) The ccelerion due o grvi is he sme for boh blls, despie he fc h he hve differen
Solutions for Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations By Tan-Cot Method
 IOSR Journl of Mhemics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578. Volume 5, Issue 3 (Jn. - Feb. 13), PP 6-11 Soluions for Nonliner Pril Differenil Equions By Tn-Co Mehod Mhmood Jwd Abdul Rsool Abu Al-Sheer Al -Rfidin Universiy
IOSR Journl of Mhemics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578. Volume 5, Issue 3 (Jn. - Feb. 13), PP 6-11 Soluions for Nonliner Pril Differenil Equions By Tn-Co Mehod Mhmood Jwd Abdul Rsool Abu Al-Sheer Al -Rfidin Universiy
Some Basic Information about M-S-D Systems
 Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Brock University Physics 1P21/1P91 Fall 2013 Dr. D Agostino. Solutions for Tutorial 3: Chapter 2, Motion in One Dimension
 Brock Uniersiy Physics 1P21/1P91 Fall 2013 Dr. D Agosino Soluions for Tuorial 3: Chaper 2, Moion in One Dimension The goals of his uorial are: undersand posiion-ime graphs, elociy-ime graphs, and heir
Brock Uniersiy Physics 1P21/1P91 Fall 2013 Dr. D Agosino Soluions for Tuorial 3: Chaper 2, Moion in One Dimension The goals of his uorial are: undersand posiion-ime graphs, elociy-ime graphs, and heir
Thermal neutron self-shielding factor in foils: a universal curve
 Proceedings of he Inernionl Conference on Reserch Recor Uilizion, Sfey, Decommissioning, Fuel nd Wse Mngemen (Snigo, Chile, -4 Nov.3) Pper IAEA-CN-/, IAEA Proceedings Series, Vienn, 5 Therml neuron self-shielding
Proceedings of he Inernionl Conference on Reserch Recor Uilizion, Sfey, Decommissioning, Fuel nd Wse Mngemen (Snigo, Chile, -4 Nov.3) Pper IAEA-CN-/, IAEA Proceedings Series, Vienn, 5 Therml neuron self-shielding
3D Transformations. Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 1/26/07 1
 D Trnsformions Compuer Grphics COMP 770 (6) Spring 007 Insrucor: Brndon Lloyd /6/07 Geomery Geomeric eniies, such s poins in spce, exis wihou numers. Coordines re nming scheme. The sme poin cn e descried
D Trnsformions Compuer Grphics COMP 770 (6) Spring 007 Insrucor: Brndon Lloyd /6/07 Geomery Geomeric eniies, such s poins in spce, exis wihou numers. Coordines re nming scheme. The sme poin cn e descried
Honours Introductory Maths Course 2011 Integration, Differential and Difference Equations
 Honours Inroducory Mhs Course 0 Inegrion, Differenil nd Difference Equions Reding: Ching Chper 4 Noe: These noes do no fully cover he meril in Ching, u re men o supplemen your reding in Ching. Thus fr
Honours Inroducory Mhs Course 0 Inegrion, Differenil nd Difference Equions Reding: Ching Chper 4 Noe: These noes do no fully cover he meril in Ching, u re men o supplemen your reding in Ching. Thus fr
Calculation method of flux measurements by static chambers
 lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers P.S. Kroon Presened he NiroEurope Workshop, 15h - 17h December 28, openhgen, Denmrk EN-L--9-11 December 28 lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers
lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers P.S. Kroon Presened he NiroEurope Workshop, 15h - 17h December 28, openhgen, Denmrk EN-L--9-11 December 28 lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers
1. Introduction. 1 b b
 Journl of Mhemicl Inequliies Volume, Number 3 (007), 45 436 SOME IMPROVEMENTS OF GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITY N. ELEZOVIĆ, LJ. MARANGUNIĆ AND J. PEČARIĆ (communiced b A. Čižmešij) Absrc. In his pper some inequliies
Journl of Mhemicl Inequliies Volume, Number 3 (007), 45 436 SOME IMPROVEMENTS OF GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITY N. ELEZOVIĆ, LJ. MARANGUNIĆ AND J. PEČARIĆ (communiced b A. Čižmešij) Absrc. In his pper some inequliies
Chapter 10. Simple Harmonic Motion and Elasticity. Goals for Chapter 10
 Chper 0 Siple Hronic Moion nd Elsiciy Gols or Chper 0 o ollow periodic oion o sudy o siple hronic oion. o sole equions o siple hronic oion. o use he pendulu s prooypicl syse undergoing siple hronic oion.
Chper 0 Siple Hronic Moion nd Elsiciy Gols or Chper 0 o ollow periodic oion o sudy o siple hronic oion. o sole equions o siple hronic oion. o use he pendulu s prooypicl syse undergoing siple hronic oion.
Convergence of Singular Integral Operators in Weighted Lebesgue Spaces
 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS Vol. 10, No. 2, 2017, 335-347 ISSN 1307-5543 www.ejpm.com Published by New York Business Globl Convergence of Singulr Inegrl Operors in Weighed Lebesgue
EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS Vol. 10, No. 2, 2017, 335-347 ISSN 1307-5543 www.ejpm.com Published by New York Business Globl Convergence of Singulr Inegrl Operors in Weighed Lebesgue
A LIMIT-POINT CRITERION FOR A SECOND-ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR IAN KNOWLES
 A LIMIT-POINT CRITERION FOR A SECOND-ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR j IAN KNOWLES 1. Inroducion Consider he forml differenil operor T defined by el, (1) where he funcion q{) is rel-vlued nd loclly
A LIMIT-POINT CRITERION FOR A SECOND-ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR j IAN KNOWLES 1. Inroducion Consider he forml differenil operor T defined by el, (1) where he funcion q{) is rel-vlued nd loclly
Road noise sensitivity analysis with respect to suspension geometry
 Rod noise sensiiviy nlysis wih respec o suspension geomery Fumihiko KOSAKA 1 ; Hiroki MIZUNO ; Tsuyoshi INOUE 3 ; Kenro TAKAGI 4 1, MITSUBISHI MOTORS ORPORATION, Jpn 3, 4 Ngoy Universiy, Jpn ABSTRAT In
Rod noise sensiiviy nlysis wih respec o suspension geomery Fumihiko KOSAKA 1 ; Hiroki MIZUNO ; Tsuyoshi INOUE 3 ; Kenro TAKAGI 4 1, MITSUBISHI MOTORS ORPORATION, Jpn 3, 4 Ngoy Universiy, Jpn ABSTRAT In
Hermite-Hadamard-Fejér type inequalities for convex functions via fractional integrals
 Sud. Univ. Beş-Bolyi Mh. 6(5, No. 3, 355 366 Hermie-Hdmrd-Fejér ype inequliies for convex funcions vi frcionl inegrls İmd İşcn Asrc. In his pper, firsly we hve eslished Hermie Hdmrd-Fejér inequliy for
Sud. Univ. Beş-Bolyi Mh. 6(5, No. 3, 355 366 Hermie-Hdmrd-Fejér ype inequliies for convex funcions vi frcionl inegrls İmd İşcn Asrc. In his pper, firsly we hve eslished Hermie Hdmrd-Fejér inequliy for
Physics 101 Lecture 4 Motion in 2D and 3D
 Phsics 11 Lecure 4 Moion in D nd 3D Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Phsics Deprmen www.ogun.com Vecor nd is componens The componens re he legs of he righ ringle whose hpoenuse is A A A A A n ( θ ) A Acos( θ) A A A nd
Phsics 11 Lecure 4 Moion in D nd 3D Dr. Ali ÖVGÜN EMU Phsics Deprmen www.ogun.com Vecor nd is componens The componens re he legs of he righ ringle whose hpoenuse is A A A A A n ( θ ) A Acos( θ) A A A nd
Chapter 2. First Order Scalar Equations
 Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
ECE Microwave Engineering
 EE 537-635 Microwve Engineering Adped from noes y Prof. Jeffery T. Willims Fll 8 Prof. Dvid R. Jcson Dep. of EE Noes Wveguiding Srucures Pr 7: Trnsverse Equivlen Newor (N) Wveguide Trnsmission Line Model
EE 537-635 Microwve Engineering Adped from noes y Prof. Jeffery T. Willims Fll 8 Prof. Dvid R. Jcson Dep. of EE Noes Wveguiding Srucures Pr 7: Trnsverse Equivlen Newor (N) Wveguide Trnsmission Line Model
Procedia Computer Science
 Procedi Compuer Science 00 (0) 000 000 Procedi Compuer Science www.elsevier.com/loce/procedi The Third Informion Sysems Inernionl Conference The Exisence of Polynomil Soluion of he Nonliner Dynmicl Sysems
Procedi Compuer Science 00 (0) 000 000 Procedi Compuer Science www.elsevier.com/loce/procedi The Third Informion Sysems Inernionl Conference The Exisence of Polynomil Soluion of he Nonliner Dynmicl Sysems
Neural assembly binding in linguistic representation
 Neurl ssembly binding in linguisic represenion Frnk vn der Velde & Mrc de Kmps Cogniive Psychology Uni, Universiy of Leiden, Wssenrseweg 52, 2333 AK Leiden, The Neherlnds, vdvelde@fsw.leidenuniv.nl Absrc.
Neurl ssembly binding in linguisic represenion Frnk vn der Velde & Mrc de Kmps Cogniive Psychology Uni, Universiy of Leiden, Wssenrseweg 52, 2333 AK Leiden, The Neherlnds, vdvelde@fsw.leidenuniv.nl Absrc.
T-Match: Matching Techniques For Driving Yagi-Uda Antennas: T-Match. 2a s. Z in. (Sections 9.5 & 9.7 of Balanis)
 3/0/018 _mch.doc Pge 1 of 6 T-Mch: Mching Techniques For Driving Ygi-Ud Anenns: T-Mch (Secions 9.5 & 9.7 of Blnis) l s l / l / in The T-Mch is shun-mching echnique h cn be used o feed he driven elemen
3/0/018 _mch.doc Pge 1 of 6 T-Mch: Mching Techniques For Driving Ygi-Ud Anenns: T-Mch (Secions 9.5 & 9.7 of Blnis) l s l / l / in The T-Mch is shun-mching echnique h cn be used o feed he driven elemen
Module 3: The Damped Oscillator-II Lecture 3: The Damped Oscillator-II
 Module 3: The Damped Oscillaor-II Lecure 3: The Damped Oscillaor-II 3. Over-damped Oscillaions. This refers o he siuaion where β > ω (3.) The wo roos are and α = β + α 2 = β β 2 ω 2 = (3.2) β 2 ω 2 = 2
Module 3: The Damped Oscillaor-II Lecure 3: The Damped Oscillaor-II 3. Over-damped Oscillaions. This refers o he siuaion where β > ω (3.) The wo roos are and α = β + α 2 = β β 2 ω 2 = (3.2) β 2 ω 2 = 2
S Radio transmission and network access Exercise 1-2
 S-7.330 Rdio rnsmission nd nework ccess Exercise 1 - P1 In four-symbol digil sysem wih eqully probble symbols he pulses in he figure re used in rnsmission over AWGN-chnnel. s () s () s () s () 1 3 4 )
S-7.330 Rdio rnsmission nd nework ccess Exercise 1 - P1 In four-symbol digil sysem wih eqully probble symbols he pulses in he figure re used in rnsmission over AWGN-chnnel. s () s () s () s () 1 3 4 )
Lecture 2-1 Kinematics in One Dimension Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Everything in the world is moving. Nothing stays still.
 Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Hamilton-Jacobi irrotational hydrodynamics for binary neutron star inspiral
 Hmilon-Jcoi irroionl hydrodynmics for inry neuron sr inspirl Chrlmpos Mrkkis Mhemicl Sciences, Universiy of Souhmpon work in progress in collorion wih: John Friedmn, Msru Shi, Nils Andersson, Nicls Moldenhuer,
Hmilon-Jcoi irroionl hydrodynmics for inry neuron sr inspirl Chrlmpos Mrkkis Mhemicl Sciences, Universiy of Souhmpon work in progress in collorion wih: John Friedmn, Msru Shi, Nils Andersson, Nicls Moldenhuer,
Physics for Scientists and Engineers I
 Physics for Scieniss nd Engineers I PHY 48, Secion 4 Dr. Beriz Roldán Cueny Uniersiy of Cenrl Florid, Physics Deprmen, Orlndo, FL Chper - Inroducion I. Generl II. Inernionl Sysem of Unis III. Conersion
Physics for Scieniss nd Engineers I PHY 48, Secion 4 Dr. Beriz Roldán Cueny Uniersiy of Cenrl Florid, Physics Deprmen, Orlndo, FL Chper - Inroducion I. Generl II. Inernionl Sysem of Unis III. Conersion
Inventory Management Models with Variable Holding Cost and Salvage value
 OSR Journl of Business nd Mngemen OSR-JBM e-ssn: -X p-ssn: 9-. Volume ssue Jul. - Aug. PP - www.iosrjournls.org nvenory Mngemen Models wi Vrile Holding os nd Slvge vlue R.Mon R.Venkeswrlu Memics Dep ollege
OSR Journl of Business nd Mngemen OSR-JBM e-ssn: -X p-ssn: 9-. Volume ssue Jul. - Aug. PP - www.iosrjournls.org nvenory Mngemen Models wi Vrile Holding os nd Slvge vlue R.Mon R.Venkeswrlu Memics Dep ollege
RC, RL and RLC circuits
 Name Dae Time o Complee h m Parner Course/ Secion / Grade RC, RL and RLC circuis Inroducion In his experimen we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors.
Name Dae Time o Complee h m Parner Course/ Secion / Grade RC, RL and RLC circuis Inroducion In his experimen we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors.
Chapter 12: Velocity, acceleration, and forces
 To Feel a Force Chaper Spring, Chaper : A. Saes of moion For moion on or near he surface of he earh, i is naural o measure moion wih respec o objecs fixed o he earh. The 4 hr. roaion of he earh has a measurable
To Feel a Force Chaper Spring, Chaper : A. Saes of moion For moion on or near he surface of he earh, i is naural o measure moion wih respec o objecs fixed o he earh. The 4 hr. roaion of he earh has a measurable
1 jordan.mcd Eigenvalue-eigenvector approach to solving first order ODEs. -- Jordan normal (canonical) form. Instructor: Nam Sun Wang
 jordnmcd Eigenvlue-eigenvecor pproch o solving firs order ODEs -- ordn norml (cnonicl) form Insrucor: Nm Sun Wng Consider he following se of coupled firs order ODEs d d x x 5 x x d d x d d x x x 5 x x
jordnmcd Eigenvlue-eigenvecor pproch o solving firs order ODEs -- ordn norml (cnonicl) form Insrucor: Nm Sun Wng Consider he following se of coupled firs order ODEs d d x x 5 x x d d x d d x x x 5 x x
CHAPTER 11 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES
 CHAPTER PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES. PARAMETRIZATIONS OF PLANE CURVES., 9, _ _ Ê.,, Ê or, Ÿ. 5, 7, _ _.,, Ÿ Ÿ Ê Ê 5 Ê ( 5) Ê ˆ Ê 6 Ê ( 5) 7 Ê Ê, Ÿ Ÿ $ 5. cos, sin, Ÿ Ÿ 6. cos ( ), sin (
CHAPTER PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES. PARAMETRIZATIONS OF PLANE CURVES., 9, _ _ Ê.,, Ê or, Ÿ. 5, 7, _ _.,, Ÿ Ÿ Ê Ê 5 Ê ( 5) Ê ˆ Ê 6 Ê ( 5) 7 Ê Ê, Ÿ Ÿ $ 5. cos, sin, Ÿ Ÿ 6. cos ( ), sin (
Temperature Rise of the Earth
 Avilble online www.sciencedirec.com ScienceDirec Procedi - Socil nd Behviorl Scien ce s 88 ( 2013 ) 220 224 Socil nd Behviorl Sciences Symposium, 4 h Inernionl Science, Socil Science, Engineering nd Energy
Avilble online www.sciencedirec.com ScienceDirec Procedi - Socil nd Behviorl Scien ce s 88 ( 2013 ) 220 224 Socil nd Behviorl Sciences Symposium, 4 h Inernionl Science, Socil Science, Engineering nd Energy
What distance must an airliner travel down a runway before reaching
 2 LEARNING GALS By sudying his chper, you will lern: How o describe srigh-line moion in erms of erge elociy, insnneous elociy, erge ccelerion, nd insnneous ccelerion. How o inerpre grphs of posiion ersus
2 LEARNING GALS By sudying his chper, you will lern: How o describe srigh-line moion in erms of erge elociy, insnneous elociy, erge ccelerion, nd insnneous ccelerion. How o inerpre grphs of posiion ersus
Physics 100: Lecture 1
 Physics : Lecure Agen for Toy Aice Scope of his course Mesuremen n Unis Funmenl unis Sysems of unis Conering beween sysems of unis Dimensionl Anlysis -D Kinemics (reiew) Aerge & insnneous elociy n ccelerion
Physics : Lecure Agen for Toy Aice Scope of his course Mesuremen n Unis Funmenl unis Sysems of unis Conering beween sysems of unis Dimensionl Anlysis -D Kinemics (reiew) Aerge & insnneous elociy n ccelerion
Effects of Vehicle Heat on Road Surface Temperature of Dry Condition
 Effecs of Vehicle He on Rod Surfce Temperure of Dry Condiion A. Fujimoo 1, H. Wnbe 1 nd T. Fukuhr 1 1 The Uniersiy of Fukui 3-9-1 Bunkyo Fukui-ciy 910-8507, Jpn. Emil: fujimo@nc.nc-d.fukui-u.c.jp ABSTRACT
Effecs of Vehicle He on Rod Surfce Temperure of Dry Condiion A. Fujimoo 1, H. Wnbe 1 nd T. Fukuhr 1 1 The Uniersiy of Fukui 3-9-1 Bunkyo Fukui-ciy 910-8507, Jpn. Emil: fujimo@nc.nc-d.fukui-u.c.jp ABSTRACT
LAB # 2 - Equilibrium (static)
 AB # - Equilibrium (saic) Inroducion Isaac Newon's conribuion o physics was o recognize ha despie he seeming compleiy of he Unierse, he moion of is pars is guided by surprisingly simple aws. Newon's inspiraion
AB # - Equilibrium (saic) Inroducion Isaac Newon's conribuion o physics was o recognize ha despie he seeming compleiy of he Unierse, he moion of is pars is guided by surprisingly simple aws. Newon's inspiraion
ECE Microwave Engineering. Fall Prof. David R. Jackson Dept. of ECE. Notes 10. Waveguides Part 7: Transverse Equivalent Network (TEN)
 EE 537-635 Microwve Engineering Fll 7 Prof. Dvid R. Jcson Dep. of EE Noes Wveguides Pr 7: Trnsverse Equivlen Newor (N) Wveguide Trnsmission Line Model Our gol is o come up wih rnsmission line model for
EE 537-635 Microwve Engineering Fll 7 Prof. Dvid R. Jcson Dep. of EE Noes Wveguides Pr 7: Trnsverse Equivlen Newor (N) Wveguide Trnsmission Line Model Our gol is o come up wih rnsmission line model for
graph of unit step function t
 .5 Piecewie coninuou forcing funcion...e.g. urning he forcing on nd off. The following Lplce rnform meril i ueful in yem where we urn forcing funcion on nd off, nd when we hve righ hnd ide "forcing funcion"
.5 Piecewie coninuou forcing funcion...e.g. urning he forcing on nd off. The following Lplce rnform meril i ueful in yem where we urn forcing funcion on nd off, nd when we hve righ hnd ide "forcing funcion"
Tax Audit and Vertical Externalities
 T Audi nd Vericl Eernliies Hidey Ko Misuyoshi Yngihr Ngoy Keizi Universiy Ngoy Universiy 1. Inroducion The vericl fiscl eernliies rise when he differen levels of governmens, such s he federl nd se governmens,
T Audi nd Vericl Eernliies Hidey Ko Misuyoshi Yngihr Ngoy Keizi Universiy Ngoy Universiy 1. Inroducion The vericl fiscl eernliies rise when he differen levels of governmens, such s he federl nd se governmens,
A Time Truncated Improved Group Sampling Plans for Rayleigh and Log - Logistic Distributions
 ISSNOnline : 39-8753 ISSN Prin : 347-67 An ISO 397: 7 Cerified Orgnizion Vol. 5, Issue 5, My 6 A Time Trunced Improved Group Smpling Plns for Ryleigh nd og - ogisic Disribuions P.Kvipriy, A.R. Sudmni Rmswmy
ISSNOnline : 39-8753 ISSN Prin : 347-67 An ISO 397: 7 Cerified Orgnizion Vol. 5, Issue 5, My 6 A Time Trunced Improved Group Smpling Plns for Ryleigh nd og - ogisic Disribuions P.Kvipriy, A.R. Sudmni Rmswmy
ON NEW INEQUALITIES OF SIMPSON S TYPE FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVES ABSOLUTE VALUES ARE CONVEX.
 ON NEW INEQUALITIES OF SIMPSON S TYPE FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVES ABSOLUTE VALUES ARE CONVEX. MEHMET ZEKI SARIKAYA?, ERHAN. SET, AND M. EMIN OZDEMIR Asrc. In his noe, we oin new some ineuliies
ON NEW INEQUALITIES OF SIMPSON S TYPE FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVES ABSOLUTE VALUES ARE CONVEX. MEHMET ZEKI SARIKAYA?, ERHAN. SET, AND M. EMIN OZDEMIR Asrc. In his noe, we oin new some ineuliies
