EC Objective Paper I (Set - D)
|
|
|
- Robert Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 EC-Objective Paper-I ESE-5 EC Objective Paper I (Set - D). If a system produces frequencies in the output are not present in the input, then the system cannot be Minimum phase system (C) Stable and causal Linear shift invariant Stable and linear Since linearity and time-invariance (shift-invariance) doesn t effect the frequency of input to get the output the system can t be LTI.. In eddy current damping system, the disc employed should be of Conducting and magnetic material Conducting but non-magnetic material (C) Magnetic but non-conducting material Non-conducting and non-magnetic material 3. Which of the following can act as in inverse transducer? LVDT Strain (C) Piezo electric crystal Bimetal strip (C) 4. Which one of the following thermocouple pairs has maximum sensitivity around 73 K? Nichrome-constant Copper-Nickel (C) Platinum-constantan Nickel-constantan 5. Maximum power will be delivered from an ac source to a resistive load in a network when the magnitude of the source impedance is equal to Half the load resistance (C) The load resistance The equation of power for resistive load is P RL V S ZS RL R L So we can say power is maximum when Z S =, Double the load resistance Zero Note that maximum power transfer theorem is not applicable here as we are not calculating the value of R L (variable). We are going in reverse way. 6. The dc resistivity and permeability exhibited by a type superconductor are respectively: Zero and zero Zero and unity (C) Unity and zero Unity and Unity
3 xm r In super conductors r, xm (negative) super conductor has zero Resistivity. Directions: Each of the next Fourteen (4) items consists of two statements one labeled as the Statement (I) and the other as Statement (II). Examine these two statements carefully and select the answers to these items using the codes given below. Codes: Both Statement (I) and Statement (II) are individually true and Statement (II) is the correct explanation of Statement (I) Both Statement (I) and Statement (II) are individually true but Statement (II) is NOT the correct explanation of Statement (I) (C) Statement (I) is true but Statement (II) is false Statement (I) is false but Statement (II) is true 7. Statement (I): One of the mechanism by which a transistor s usefulness may be terminated, as the collector voltage is increased, is called punch through. Punch through results from the increased width of the collectorjunction transition region with increased collector-junction voltage. Punch through: When the base collector voltage reaches a certain (device specific) value, the base collector depletion region boundary meets the base emitter depletion region boundary. When in this state the transistor effectively has no base. The device thus loses all gain when in this state. 8. Statement (I): In ferroelectric materials, domains with permanent electric dipoles may be created that would align along external electric field. Ferroelectric materials undergo phase transformation of symmetric to asymmetric structure below a critical temperature. 9. Statement (I): Conduction takes place in an enhancement MOSFET only for gate voltages below the threshold level. V GS >V t conduction takes places V GS <V t no conduction take place in MOSFET In an enhancement MOSFET, a channel of semiconductor of the same type as the source and drain is induced in the substrate by a positive voltage applied to the gate.. Statement (I): MOSFET is a field effect transistor whose drain current is controlled by the voltage applied at the gate. MOSFET is an insulated gate FET
4 . Statement (I): All passive components can be fabricated in a single chip. As opposed to discrete circuits where all components are separately inserted and connected, in an integrated circuit, they are simultaneously created on a chip of semiconductor material during manufacturing.. Statement (I): The total energy of an energy signal falls between the limits and. The average power of an energy signal is zero. Energy signal is a signal with finite energy and zero average power. Thus statement (I) and (II). Both are correct but statement (II) is not giving explanation/reasoning to statement (I). 3. Statement (I): Sinusoidal signals are used as basic function in electrical systems. The response of a linear system to a sinusoidal input function remains sinusoidal. 4. Statement (I): Dirichlet s conditions restrict the periodic signal x(t), to be represented by Fourier series, to have only finite number of maximal and minima. x(t) should possess only a finite number of dis-continuities. Strong Dirichlet conditions states that the Fourier series exists if and only if the signal has a finite number of maxima and minima (or) finite number of discontinuities. 5. Statement (I): Ferrite cored coils are used in high frequency tuned circuits. Ferrite cored coils have high Q as compared to iron-cored coils. 6. Statement (I): A cylindrical conductor of radius R carries a current H.dl j.ds s L I H.r r R Ir H R H r statement (I) is correct I. The magnetic Field intensity within the conductor increases linearly with the radial distance r < R. The current enclosed increases as the square of the radial distance while the circumference increases linearly with the radial distance. Statement (II) is correct explanation to Statement (I).
5 I.H 7. Statement (I): Hall voltage is given by V H R H Where I is the current, H is t the magnetic field strength, t is the thickness of probe and R H is the Hall constant. (C) BI VH W R H BI So, VH R H. W W = t = width (or) thickness B H Hall effect does not sense the carrier concentration. Hall Effect measures density of the carries, and their sign (whether electron (or) holes) 8. Statement (I): For an energy meter, careful design and treatment of breaking magnet during its manufacture are essential in order to ensure consistency of break magnet during the use of meter. Steady rotational speed of energy meter disc is directly proportional to flux of the break magnet. 9. Statement (I): If the limiting errors of measurement of power consumed by and the current passing through a resistance are.5% and.% respectively, then the limiting error of resistance measurement will be.5%. Mathematically if f = xyz. Then f x yz xyz xy z It is given that the limiting error of power is Poweris.5%and Current is.% P R so the limiting error will be I.5. % 3.5%. Statement (I): Integrating DVM measures the true average value of the input voltage over a fixed measuring period. Since the display of measured signal is a decimal number, the errors due to parallax and observation error are eliminated.. Measurement of pressure can be done by using wire, foil or semiconductor type Strain Gauges. The disadvantage of the semiconductor type of strain gauge compared to other two is in terms of Gauge factor (C) Temperature sensitivity (C) Hysteresis characteristics Frequency response
6 . The Fourier series of a periodic function x T (t) with a period T is given by jko t Xske, where o T And the Fourier coefficient X s (K) is defined as, k jkot Xsk xtte dt T If xt t is real and odd, the Fourier coefficients X s (K) are Real and odd Complex (C) Real Imaginary T jkt xs k xt t e dt T T Consider Thus xs T T jkt jkt xtte dt xt te dt T k is imaginary. x t is odd, x t x t T T T T jkt jkt xsk e e xttdt T T j x k sin k t x t dt s T T 3. Consider a continuous time period signal x(t) with fundamental period T and Fourier series coefficient X[K]. What is the Fourier series coefficient of the signal y t x t t x t t?.cos Kt XK o T o o T sin Kt XK to to to to (C) e XK e X K e XK e XK y(t) = x(t-t ) + x(t+t ) x t FS x k By using time-shifting property of Fourier series, FS FS x t t x k e x t t x k e Fourierseriesof y t jkt jkt e e xk x k cosk t jkt jkt T x k cos kt o
7 4. Consider the following transfer functions:.. 3. j j j j The transfer functions which have a non linear phase are: and only and 3 only (C) and 3 only, and 3 5. A continuity equation is also called as the law of conservation of Mass Energy (C) Charge Power (C) Continuity equation is based upon the law of conservation at charge. 6. The basic structure of an avalanche photodiode is p i p n p i n (C) p p n i p n 7. Consider two infinite duration input sequences Convergence [ROC] of Z-transform of their superposition i.e. xn xn plane except possibly at Z = or Z? When their linear combination is of finite duration When they are left sided sequences (C) When they are right sided sequences When their linear combination is causal x n,x n. When will the Region of be entire Z For a finite duration sequence the ROC will be entire Z-plane except z = and/or Z. 8. If the lower limit of Region of Convergence (ROC) is greater than the upper limit of n ROC, the series XZ xnz (C) n Converges Zero (C) Does not converge None of the above z
8 If is lower limit and is upper limit of ROC then ROC is z. Accordingly, the signal corresponding to is Right-sided and the signal corresponding to is left sided. Since, it is given that, ROC does not converge. 9. For a random signal (continuous time) x(t) defined for t, its probability density function (pdf) at t = t o is such that It is non-negative and it s integral Need not be non-negative, but integral equals (C) It is non-negative, but integral is not None of the above 3. The response of a system to a complex input jt jt jt as yt t.e e. The system is definitely LTI (C) may be LTI x t e ;y t te e jt jt jt y(t) = tx(t) + x(-t) consider y(t) = y (t) + y (t) y (t) = t x(t) is linear but non-time invariant Similarly y (t) = x(-t) is also linear but non time-invariant Thus the system is non-lti. x t is definitely not-lti Information is insufficient e is specified 3. The rise time of the output response of a low pass filter circuit when a step input is applied will be Proportional to the band width (C) Half the value of band width t r.35 Bandwidth Inversely proportional to the band width of the band width 3. Consider an LTI system subjected to a wide sense stationary input xn white noise sequence. The cross correlation m is (C) x hm x hm x hm Where m m and xx x XY, which is a between input x(n) and output y(n) h. is impulse response x hm
9 33. For the active network shown in Figure, the value of V/I is R 4 I V R 6 I.4 (C) 3.6 (C) Since it is a dead network with dependent source to find V/I we have to connect an external source and measure it writing nodal equation at node A I V I A R 4 V 3.6 I V Ri 6 I 34. In a discrete-time Low pass Filter, the frequency response is A periodic A periodic with response restricted to, (C) Periodic with period Quasi periodic with response extending to infinity (C) c c 35. For the R-L circuit shown, the current i(t) for unit step input voltage will rise to.63 in s s (C).5s.5s Vi t i H t * I S SS S S
10 i t e u t t.63.5 e.6 e t t t e.6 No value of t will satisfy this equation 36. In the circuit the value of i x is i x V 3A ix A.6A (C).6A.4A Writing nodal equation A VA 3 i VA andix V i A Solving equation () and () i x =.4A and V A = 7.V x x 37. When the frequency of the applied voltage (sine wave) across an inductor is increased then the current will Decrease Increase (C) Remain same Be zero VL IL j L IL So when frequency increase current will decreases 38. A series resonant circuit is tuned to MHz and provides 3-dB bandwidth of khz. The quality factor Q of the circuit is 3 (C) (C)
11 IES PREVIOUS YEAR SOLVED QUESTION PAPERS ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - 5 Publisher : Faculty Notes Author : Panel of Experts Type the URL : Get this ebook
EC Objective Paper I (Set - D)
 EC-Objective Paper-I ESE-5 www.gateforum.com EC Objective Paper I (Set - D). If a system produces frequencies in the output are not present in the input, then the system cannot be Minimum phase system
EC-Objective Paper-I ESE-5 www.gateforum.com EC Objective Paper I (Set - D). If a system produces frequencies in the output are not present in the input, then the system cannot be Minimum phase system
ECE Branch GATE Paper The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2
 Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + = is (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 2. The Fourier series of a real periodic function has only P. Cosine terms if it is
GATE 2009 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2009 Electronics and Communication Engineering Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + y =e (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 is 2. The Fourier series of a
GATE 2009 Electronics and Communication Engineering Question 1 Question 20 carry one mark each. 1. The order of the differential equation + + y =e (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 is 2. The Fourier series of a
GATE EE Topic wise Questions SIGNALS & SYSTEMS
 www.gatehelp.com GATE EE Topic wise Questions YEAR 010 ONE MARK Question. 1 For the system /( s + 1), the approximate time taken for a step response to reach 98% of the final value is (A) 1 s (B) s (C)
www.gatehelp.com GATE EE Topic wise Questions YEAR 010 ONE MARK Question. 1 For the system /( s + 1), the approximate time taken for a step response to reach 98% of the final value is (A) 1 s (B) s (C)
EC- Objective Paper-I IES IES Paper-I
 EC- Objective Paper-I IES-03 www.gateforum.com IES-03- Paper-I. The resistances of two coils of a watt meter are 0.0Ω and 00 Ω respectively and both are non-inclusive. The current through a resistance
EC- Objective Paper-I IES-03 www.gateforum.com IES-03- Paper-I. The resistances of two coils of a watt meter are 0.0Ω and 00 Ω respectively and both are non-inclusive. The current through a resistance
Conventional Paper I (a) (i) What are ferroelectric materials? What advantages do they have over conventional dielectric materials?
 Conventional Paper I-03.(a) (i) What are ferroelectric materials? What advantages do they have over conventional dielectric materials? (ii) Give one example each of a dielectric and a ferroelectric material
Conventional Paper I-03.(a) (i) What are ferroelectric materials? What advantages do they have over conventional dielectric materials? (ii) Give one example each of a dielectric and a ferroelectric material
Basic Electronics. Introductory Lecture Course for. Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011
 Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory drake@anl.gov
Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory drake@anl.gov
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 GATE 5 SET- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - EC Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. The bilateral Laplace transform of a function is if a t b f() t = otherwise (A) a b s (B) s e ( a b) s (C) e as
GATE 5 SET- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING - EC Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. The bilateral Laplace transform of a function is if a t b f() t = otherwise (A) a b s (B) s e ( a b) s (C) e as
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Consider a system of linear equations: x y 3z =, x 3y 4z =, and x 4y 6 z = k. The value of k for which the system has infinitely many solutions is. Q. A function 3 = is
Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q. Consider a system of linear equations: x y 3z =, x 3y 4z =, and x 4y 6 z = k. The value of k for which the system has infinitely many solutions is. Q. A function 3 = is
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1
 Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
Electronics and Communication Exercise 1 1. For matrices of same dimension M, N and scalar c, which one of these properties DOES NOT ALWAYS hold? (A) (M T ) T = M (C) (M + N) T = M T + N T (B) (cm)+ =
4. Given a range of frequencies, which of the following systems is best for transmission line load matching?
 IES-00- Paper-I. Consider the following statements: For a rectangular waveguide with dimensions a b where b is the narrow dimension, small value of b. Gives a larger separation between cutoff frequencies
IES-00- Paper-I. Consider the following statements: For a rectangular waveguide with dimensions a b where b is the narrow dimension, small value of b. Gives a larger separation between cutoff frequencies
Conventional Paper I-2010
 Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
Conventional Paper I-010 1. (a) Sketch the covalent bonding of Si atoms in a intrinsic Si crystal Illustrate with sketches the formation of bonding in presence of donor and acceptor atoms. Sketch the energy
II/IV B.Tech (Regular/Supplementary) DEGREE EXAMINATION. Answer ONE question from each unit.
 14ECEI302/EC 212 1. Answer all questions (1X12=12 Marks) a What are the applications of linked list? b Compare singly linked list and doubly linked list. c Define ADT. d What are the basic operations of
14ECEI302/EC 212 1. Answer all questions (1X12=12 Marks) a What are the applications of linked list? b Compare singly linked list and doubly linked list. c Define ADT. d What are the basic operations of
EE 3324 Electromagnetics Laboratory
 EE 3324 Electromagnetics Laboratory Experiment #3 Inductors and Inductance 1. Objective The objective of Experiment #3 is to investigate the concepts of inductors and inductance. Several inductor geometries
EE 3324 Electromagnetics Laboratory Experiment #3 Inductors and Inductance 1. Objective The objective of Experiment #3 is to investigate the concepts of inductors and inductance. Several inductor geometries
ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
 Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
Chapter 31: ELECTROMAGNETIC OSCILLATIONS AND ALTERNATING CURRENT 1 A charged capacitor and an inductor are connected in series At time t = 0 the current is zero, but the capacitor is charged If T is the
SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING. Paper -1. Please read the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper -1 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks ; 300 Instructions
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(02)-I ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Paper -1 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks ; 300 Instructions
a. Type 0 system. b. Type I system. c. Type 2 system. d. Type 3 system.
 1-The steady-state error of a feedback control system with an acceleration input becomes finite in a a. Type 0 system. b. Type I system. c. Type 2 system. d. Type 3 system. 2-A good control system has
1-The steady-state error of a feedback control system with an acceleration input becomes finite in a a. Type 0 system. b. Type I system. c. Type 2 system. d. Type 3 system. 2-A good control system has
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE
 Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Review of Basic Electrical and Magnetic Circuit Concepts EE 442-642 Sinusoidal Linear Circuits: Instantaneous voltage, current and power, rms values Average (real) power, reactive power, apparent power,
Force and Displacement Measurement
 Force and Displacement Measurement Prof. R.G. Longoria Updated Fall 20 Simple ways to measure a force http://scienceblogs.com/dotphysics/200/02/diy_force_probe.php Example: Key Force/Deflection measure
Force and Displacement Measurement Prof. R.G. Longoria Updated Fall 20 Simple ways to measure a force http://scienceblogs.com/dotphysics/200/02/diy_force_probe.php Example: Key Force/Deflection measure
2. The following diagram illustrates that voltage represents what physical dimension?
 BioE 1310 - Exam 1 2/20/2018 Answer Sheet - Correct answer is A for all questions 1. A particular voltage divider with 10 V across it consists of two resistors in series. One resistor is 7 KΩ and the other
BioE 1310 - Exam 1 2/20/2018 Answer Sheet - Correct answer is A for all questions 1. A particular voltage divider with 10 V across it consists of two resistors in series. One resistor is 7 KΩ and the other
SOME USEFUL NETWORK THEOREMS
 APPENDIX D SOME USEFUL NETWORK THEOREMS Introduction In this appendix we review three network theorems that are useful in simplifying the analysis of electronic circuits: Thévenin s theorem Norton s theorem
APPENDIX D SOME USEFUL NETWORK THEOREMS Introduction In this appendix we review three network theorems that are useful in simplifying the analysis of electronic circuits: Thévenin s theorem Norton s theorem
6.003 Homework #10 Solutions
 6.3 Homework # Solutions Problems. DT Fourier Series Determine the Fourier Series coefficients for each of the following DT signals, which are periodic in N = 8. x [n] / n x [n] n x 3 [n] n x 4 [n] / n
6.3 Homework # Solutions Problems. DT Fourier Series Determine the Fourier Series coefficients for each of the following DT signals, which are periodic in N = 8. x [n] / n x [n] n x 3 [n] n x 4 [n] / n
Module 4. Related web links and videos. 1. FT and ZT
 Module 4 Laplace transforms, ROC, rational systems, Z transform, properties of LT and ZT, rational functions, system properties from ROC, inverse transforms Related web links and videos Sl no Web link
Module 4 Laplace transforms, ROC, rational systems, Z transform, properties of LT and ZT, rational functions, system properties from ROC, inverse transforms Related web links and videos Sl no Web link
The initial magnetization curve shows the magnetic flux density that would result when an increasing magnetic field is applied to an initially
 MAGNETIC CIRCUITS The study of magnetic circuits is important in the study of energy systems since the operation of key components such as transformers and rotating machines (DC machines, induction machines,
MAGNETIC CIRCUITS The study of magnetic circuits is important in the study of energy systems since the operation of key components such as transformers and rotating machines (DC machines, induction machines,
Objective Paper-I-2013
 EE-Objective Paper-I IES-03 www.gateforum.com Objective Paper-I-03 Directions: Each of the next Ten (0) items consists of two statements, one labeled as the Statement (I) and the other as Statement (II).
EE-Objective Paper-I IES-03 www.gateforum.com Objective Paper-I-03 Directions: Each of the next Ten (0) items consists of two statements, one labeled as the Statement (I) and the other as Statement (II).
Exercise The determinant of matrix A is 5 and the determinant of matrix B is 40. The determinant of matrix AB is.
 Exercise 1. The determinant of matrix A is 5 and the determinant of matrix B is 40. The determinant of matrix AB is.. Let X be a random variable which is uniformly chosen from the set of positive odd numbers
Exercise 1. The determinant of matrix A is 5 and the determinant of matrix B is 40. The determinant of matrix AB is.. Let X be a random variable which is uniformly chosen from the set of positive odd numbers
Conventional Paper-I-2011 PART-A
 Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Conventional Paper-I-0 PART-A.a Give five properties of static magnetic field intensity. What are the different methods by which it can be calculated? Write a Maxwell s equation relating this in integral
Objective of Lecture Discuss resistivity and the three categories of materials Chapter 2.1 Show the mathematical relationships between charge,
 Objective of Lecture Discuss resistivity and the three categories of materials Chapter 2.1 Show the mathematical relationships between charge, current, voltage, and energy. Chapter 2.2-2.4 Define resistance
Objective of Lecture Discuss resistivity and the three categories of materials Chapter 2.1 Show the mathematical relationships between charge, current, voltage, and energy. Chapter 2.2-2.4 Define resistance
ME 515 Mechatronics. Overview of Computer based Control System
 ME 515 Mechatronics Introduction to Sensors I Asanga Ratnaweera Department of Faculty of Engineering University of Peradeniya Tel: 081239 (3627) Email: asangar@pdn.ac.lk Overview of Computer based Control
ME 515 Mechatronics Introduction to Sensors I Asanga Ratnaweera Department of Faculty of Engineering University of Peradeniya Tel: 081239 (3627) Email: asangar@pdn.ac.lk Overview of Computer based Control
Homework Assignment 08
 Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
Homework Assignment 08 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. Give one phrase/sentence that describes the primary advantage of an active load. Answer: Large effective resistance
ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation MEP382: Design of Applied Measurement Systems Lecture #2: Transduction Mechanisms
 ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation MEP382: Design of Applied Measurement Systems Lecture #2: Transduction Mechanisms Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. April 28 th 2014 Slides are borrowed from Dr. Moahmed Elshiekh
ECE421: Electronics for Instrumentation MEP382: Design of Applied Measurement Systems Lecture #2: Transduction Mechanisms Mostafa Soliman, Ph.D. April 28 th 2014 Slides are borrowed from Dr. Moahmed Elshiekh
MAGNETIC PROBLEMS. (d) Sketch B as a function of d clearly showing the value for maximum value of B.
 PHYS2012/2912 MAGNETC PROBLEMS M014 You can investigate the behaviour of a toroidal (dough nut shape) electromagnet by changing the core material (magnetic susceptibility m ) and the length d of the air
PHYS2012/2912 MAGNETC PROBLEMS M014 You can investigate the behaviour of a toroidal (dough nut shape) electromagnet by changing the core material (magnetic susceptibility m ) and the length d of the air
Conventional Paper-I Part A. 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy
 EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
EE-Conventional Paper-I IES-01 www.gateforum.com Conventional Paper-I-01 Part A 1. (a) Define intrinsic wave impedance for a medium and derive the equation for intrinsic vy impedance for a lossy dielectric
PAPER I I.E.S. (OBJ) of 16
 csir.hrdg/ I.E.S. (OBJ) - 2004 1 of 16 ELECTRONICS & TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING 1. Which on of the following statements is A right circularly polarized wave is incident from air onto a polysterene (
csir.hrdg/ I.E.S. (OBJ) - 2004 1 of 16 ELECTRONICS & TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING 1. Which on of the following statements is A right circularly polarized wave is incident from air onto a polysterene (
Electronic Circuits 1. Transistor Devices. Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations. Prof. C.K. Tse: Transistor devices
 Electronic Circuits 1 Transistor Devices Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations 1 What is a transistor? Three-terminal device whose voltage-current relationship is controlled by a third voltage
Electronic Circuits 1 Transistor Devices Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations 1 What is a transistor? Three-terminal device whose voltage-current relationship is controlled by a third voltage
An Introduction to Electrical Machines. P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy
 An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
An Introduction to Electrical Machines P. Di Barba, University of Pavia, Italy Academic year 0-0 Contents Transformer. An overview of the device. Principle of operation of a single-phase transformer 3.
6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 10 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Exam No. 2 Thursday, November 5, 2009 7:30 to
Page 1 of 10 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits Exam No. 2 Thursday, November 5, 2009 7:30 to
Electrical Circuit & Network
 Electrical Circuit & Network January 1 2017 Website: www.electricaledu.com Electrical Engg.(MCQ) Question and Answer for the students of SSC(JE), PSC(JE), BSNL(JE), WBSEDCL, WBSETCL, WBPDCL, CPWD and State
Electrical Circuit & Network January 1 2017 Website: www.electricaledu.com Electrical Engg.(MCQ) Question and Answer for the students of SSC(JE), PSC(JE), BSNL(JE), WBSEDCL, WBSETCL, WBPDCL, CPWD and State
ONE MARK QUESTIONS. 1. The condition on R, L and C such that the step response y(t) in the figure has no oscillations, is
 ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ONE MARK QUESTIONS. The condition on R, L and C such that the step response y(t) in the figure has no oscillations, is (a.) R L C (b.) R L C (c.) R L C (d.) R LC
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ONE MARK QUESTIONS. The condition on R, L and C such that the step response y(t) in the figure has no oscillations, is (a.) R L C (b.) R L C (c.) R L C (d.) R LC
Section 8: Magnetic Components
 Section 8: Magnetic omponents Inductors and transformers used in power electronic converters operate at quite high frequency. The operating frequency is in khz to MHz. Magnetic transformer steel which
Section 8: Magnetic omponents Inductors and transformers used in power electronic converters operate at quite high frequency. The operating frequency is in khz to MHz. Magnetic transformer steel which
3. Frequency-Domain Analysis of Continuous- Time Signals and Systems
 3. Frequency-Domain Analysis of Continuous- ime Signals and Systems 3.. Definition of Continuous-ime Fourier Series (3.3-3.4) 3.2. Properties of Continuous-ime Fourier Series (3.5) 3.3. Definition of Continuous-ime
3. Frequency-Domain Analysis of Continuous- ime Signals and Systems 3.. Definition of Continuous-ime Fourier Series (3.3-3.4) 3.2. Properties of Continuous-ime Fourier Series (3.5) 3.3. Definition of Continuous-ime
EC-Objective-Paper-I (Set-D)
 EC-Objective-Paper-I (Set-D). Consider an LTI system representing a passive electrical network. If the input is a sinusoidal signal, then the steady-state output of the network is (A) Sinusoidal with the
EC-Objective-Paper-I (Set-D). Consider an LTI system representing a passive electrical network. If the input is a sinusoidal signal, then the steady-state output of the network is (A) Sinusoidal with the
1 P a g e.
 1. Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to complete the following sentence. Communication and interpersonal skills are important in their own ways. each B. both C. all either.
1. Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to complete the following sentence. Communication and interpersonal skills are important in their own ways. each B. both C. all either.
GATE 2017 ECE Session 3 Answer Key
 1. Three pair cubical dice are thrown simultaneously. What is the probability that all three dice have same number is... Ans. ( 1 36 ). The one of the eigen value is real, rest are imaginary the real value
1. Three pair cubical dice are thrown simultaneously. What is the probability that all three dice have same number is... Ans. ( 1 36 ). The one of the eigen value is real, rest are imaginary the real value
(A) (B) (D) (C) 1.5. Amplitude (volts) 1.5. Amplitude (volts) Time (seconds) Time (seconds)
 Reminder: Lab #1 : Limitations of A/D conversion Lab #2 : Thermocouple, static and dynamic calibration Lab #3 : Conversion of work into heat Lab #4 : Pressure transducer, static and dynamic calibration
Reminder: Lab #1 : Limitations of A/D conversion Lab #2 : Thermocouple, static and dynamic calibration Lab #3 : Conversion of work into heat Lab #4 : Pressure transducer, static and dynamic calibration
Biasing the CE Amplifier
 Biasing the CE Amplifier Graphical approach: plot I C as a function of the DC base-emitter voltage (note: normally plot vs. base current, so we must return to Ebers-Moll): I C I S e V BE V th I S e V th
Biasing the CE Amplifier Graphical approach: plot I C as a function of the DC base-emitter voltage (note: normally plot vs. base current, so we must return to Ebers-Moll): I C I S e V BE V th I S e V th
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 1. "Electrical Eng Science"
 ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 1 COURSE NAME: "Electrical Eng Science" CODE: GROUP: "[ADET 2]" DATE: December 2010 TIME: DURATION: 9:00 am "Two hours" INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This
ASSOCIATE DEGREE IN ENGINEERING RESIT EXAMINATIONS SEMESTER 1 COURSE NAME: "Electrical Eng Science" CODE: GROUP: "[ADET 2]" DATE: December 2010 TIME: DURATION: 9:00 am "Two hours" INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers. Final Examination.
 Name: Number: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Examination December 17, 2001 Closed Book and Notes 1. Be sure to fill in your
Name: Number: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Examination December 17, 2001 Closed Book and Notes 1. Be sure to fill in your
Digital Electronics Part II - Circuits
 Digital Electronics Part - Circuits Dr.. J. Wassell Gates from Transistors ntroduction Logic circuits are non-linear, consequently we will introduce a graphical technique for analysing such circuits The
Digital Electronics Part - Circuits Dr.. J. Wassell Gates from Transistors ntroduction Logic circuits are non-linear, consequently we will introduce a graphical technique for analysing such circuits The
MOS Transistor Theory
 MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
MOS Transistor Theory So far, we have viewed a MOS transistor as an ideal switch (digital operation) Reality: less than ideal EE 261 Krish Chakrabarty 1 Introduction So far, we have treated transistors
QUESTION BANK SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS (4 th SEM ECE)
 QUESTION BANK SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS (4 th SEM ECE) 1. For the signal shown in Fig. 1, find x(2t + 3). i. Fig. 1 2. What is the classification of the systems? 3. What are the Dirichlet s conditions of Fourier
QUESTION BANK SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS (4 th SEM ECE) 1. For the signal shown in Fig. 1, find x(2t + 3). i. Fig. 1 2. What is the classification of the systems? 3. What are the Dirichlet s conditions of Fourier
Physics 142 AC Circuits Page 1. AC Circuits. I ve had a perfectly lovely evening but this wasn t it. Groucho Marx
 Physics 142 A ircuits Page 1 A ircuits I ve had a perfectly lovely evening but this wasn t it. Groucho Marx Alternating current: generators and values It is relatively easy to devise a source (a generator
Physics 142 A ircuits Page 1 A ircuits I ve had a perfectly lovely evening but this wasn t it. Groucho Marx Alternating current: generators and values It is relatively easy to devise a source (a generator
Operation and Modeling of. The MOS Transistor. Second Edition. Yannis Tsividis Columbia University. New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS
 Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
Operation and Modeling of The MOS Transistor Second Edition Yannis Tsividis Columbia University New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS Chapter 1 l.l 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Chapter 2 2.1 2.2
Chapter 31 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current LC Oscillations, Qualitatively
 Chapter 3 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current LC Oscillations, Qualitatively In the LC circuit the charge, current, and potential difference vary sinusoidally (with period T and angular
Chapter 3 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Alternating Current LC Oscillations, Qualitatively In the LC circuit the charge, current, and potential difference vary sinusoidally (with period T and angular
AC Circuits. The Capacitor
 The Capacitor Two conductors in close proximity (and electrically isolated from one another) form a capacitor. An electric field is produced by charge differences between the conductors. The capacitance
The Capacitor Two conductors in close proximity (and electrically isolated from one another) form a capacitor. An electric field is produced by charge differences between the conductors. The capacitance
MARKING SCHEME SET 55/1/G Q. No. Expected Answer / Value Points Marks Total Marks
 MARKING SCHEME SET 55//G Q. No. Expected Answer / Value Points Marks Total Marks Set,Q Set2,Q5 Set,Q2 Set,Q2 Set2,Q4 Set,Q5 Set,Q Set2,Q2 Set,Q4 Set,Q4 Set2,Q Set,Q Set,Q5 Set2,Q Set,Q Set,Q6 Set2,Q7 Set,Q0
MARKING SCHEME SET 55//G Q. No. Expected Answer / Value Points Marks Total Marks Set,Q Set2,Q5 Set,Q2 Set,Q2 Set2,Q4 Set,Q5 Set,Q Set2,Q2 Set,Q4 Set,Q4 Set2,Q Set,Q Set,Q5 Set2,Q Set,Q Set,Q6 Set2,Q7 Set,Q0
Electrical Eng. fundamental Lecture 1
 Electrical Eng. fundamental Lecture 1 Contact details: h-elhelw@staffs.ac.uk Introduction Electrical systems pervade our lives; they are found in home, school, workplaces, factories,
Electrical Eng. fundamental Lecture 1 Contact details: h-elhelw@staffs.ac.uk Introduction Electrical systems pervade our lives; they are found in home, school, workplaces, factories,
Electric Currents & Resistance
 Electric Currents & Resistance Electric Battery A battery produces electricity by transforming chemical energy into electrical energy. The simplest battery contains two plates or rods made of dissimilar
Electric Currents & Resistance Electric Battery A battery produces electricity by transforming chemical energy into electrical energy. The simplest battery contains two plates or rods made of dissimilar
ONE MARK QUESTIONS. 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a tree of this graph?
 ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ONE MARK QUESTIONS 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a tree of this graph? (a.) (b.) (c.) (d.). The equivalent
ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING ONE MARK QUESTIONS 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a tree of this graph? (a.) (b.) (c.) (d.). The equivalent
Chapter 14: Inductor design
 Chapter 14 Inductor Design 14.1 Filter inductor design constraints 14.2 A step-by-step design procedure 14.3 Multiple-winding magnetics design using the K g method 14.4 Examples 14.5 Summary of key points
Chapter 14 Inductor Design 14.1 Filter inductor design constraints 14.2 A step-by-step design procedure 14.3 Multiple-winding magnetics design using the K g method 14.4 Examples 14.5 Summary of key points
11. AC Circuit Power Analysis
 . AC Circuit Power Analysis Often an integral part of circuit analysis is the determination of either power delivered or power absorbed (or both). In this chapter First, we begin by considering instantaneous
. AC Circuit Power Analysis Often an integral part of circuit analysis is the determination of either power delivered or power absorbed (or both). In this chapter First, we begin by considering instantaneous
Fourier Series Representation of
 Fourier Series Representation of Periodic Signals Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University it Email: ruiwang@tongji.edu.cn Outline The response of LIT system
Fourier Series Representation of Periodic Signals Rui Wang, Assistant professor Dept. of Information and Communication Tongji University it Email: ruiwang@tongji.edu.cn Outline The response of LIT system
Transistor Noise Lecture 10 High Speed Devices
 Transistor Noise 1 Transistor Noise A very brief introduction to circuit and transistor noise. I an not an expert regarding noise Maas: Noise in Linear and Nonlinear Circuits Lee: The Design of CMOS RFIC
Transistor Noise 1 Transistor Noise A very brief introduction to circuit and transistor noise. I an not an expert regarding noise Maas: Noise in Linear and Nonlinear Circuits Lee: The Design of CMOS RFIC
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering
 GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
GATE 2010 Electrical Engineering Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each 1. The value of the quantity P, where P = xe dx, is equal to (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) e (D) 1/e 2. Divergence of the three-dimensional radial vector
INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester. Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE
 INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE Detailed Contents Objectives Sensors and transducer Classification of transducers Temperature transducers Resistance
INSTRUMENTATION ECE Fourth Semester Presented By:- Sumit Grover Lect., Deptt. of ECE Detailed Contents Objectives Sensors and transducer Classification of transducers Temperature transducers Resistance
Basic Electronics. Introductory Lecture Course for. Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011
 Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 2
Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 2
3.2 Complex Sinusoids and Frequency Response of LTI Systems
 3. Introduction. A signal can be represented as a weighted superposition of complex sinusoids. x(t) or x[n]. LTI system: LTI System Output = A weighted superposition of the system response to each complex
3. Introduction. A signal can be represented as a weighted superposition of complex sinusoids. x(t) or x[n]. LTI system: LTI System Output = A weighted superposition of the system response to each complex
Electronic Circuits Summary
 Electronic Circuits Summary Andreas Biri, D-ITET 6.06.4 Constants (@300K) ε 0 = 8.854 0 F m m 0 = 9. 0 3 kg k =.38 0 3 J K = 8.67 0 5 ev/k kt q = 0.059 V, q kt = 38.6, kt = 5.9 mev V Small Signal Equivalent
Electronic Circuits Summary Andreas Biri, D-ITET 6.06.4 Constants (@300K) ε 0 = 8.854 0 F m m 0 = 9. 0 3 kg k =.38 0 3 J K = 8.67 0 5 ev/k kt q = 0.059 V, q kt = 38.6, kt = 5.9 mev V Small Signal Equivalent
MCT151: Introduction to Mechatronics Lecture 10: Sensors & Transduction Mechanisms
 Faculty of Engineering MCT151: Introduction to Mechatronics Lecture 10: Sensors & Transduction Mechanisms Slides are borrowed from Dr. Mohamed Elshiekh lectures Types of sensors Sensors are considered
Faculty of Engineering MCT151: Introduction to Mechatronics Lecture 10: Sensors & Transduction Mechanisms Slides are borrowed from Dr. Mohamed Elshiekh lectures Types of sensors Sensors are considered
Module 4 : Laplace and Z Transform Problem Set 4
 Module 4 : Laplace and Z Transform Problem Set 4 Problem 1 The input x(t) and output y(t) of a causal LTI system are related to the block diagram representation shown in the figure. (a) Determine a differential
Module 4 : Laplace and Z Transform Problem Set 4 Problem 1 The input x(t) and output y(t) of a causal LTI system are related to the block diagram representation shown in the figure. (a) Determine a differential
Module I Module I: traditional test instrumentation and acquisition systems. Prof. Ramat, Stefano
 Preparatory Course (task NA 3.6) Basics of experimental testing and theoretical background Module I Module I: traditional test instrumentation and acquisition systems Prof. Ramat, Stefano Transducers A
Preparatory Course (task NA 3.6) Basics of experimental testing and theoretical background Module I Module I: traditional test instrumentation and acquisition systems Prof. Ramat, Stefano Transducers A
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors
 ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
ECE 546 Lecture 10 MOS Transistors Spring 2018 Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical & Computer Engineering University of Illinois jesa@illinois.edu NMOS Transistor NMOS Transistor N-Channel MOSFET Built on p-type
Transformer Fundamentals
 Transformer Fundamentals 1 Introduction The physical basis of the transformer is mutual induction between two circuits linked by a common magnetic field. Transformer is required to pass electrical energy
Transformer Fundamentals 1 Introduction The physical basis of the transformer is mutual induction between two circuits linked by a common magnetic field. Transformer is required to pass electrical energy
Magnetic Force on a Moving Charge
 Magnetic Force on a Moving Charge Electric charges moving in a magnetic field experience a force due to the magnetic field. Given a charge Q moving with velocity u in a magnetic flux density B, the vector
Magnetic Force on a Moving Charge Electric charges moving in a magnetic field experience a force due to the magnetic field. Given a charge Q moving with velocity u in a magnetic flux density B, the vector
I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE
 I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE Most frequent measurement and control Direct contact: thermometer, Indirect contact: pyrometer (detect generated heat or sensing optical properties) 1. Definition of temperature
I. MEASUREMENT OF TEMPERATURE Most frequent measurement and control Direct contact: thermometer, Indirect contact: pyrometer (detect generated heat or sensing optical properties) 1. Definition of temperature
Electric Circuits I. Inductors. Dr. Firas Obeidat
 Electric Circuits I Inductors Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Inductors An inductor is a passive element designed to store energy in its magnetic field. They are used in power supplies, transformers, radios, TVs,
Electric Circuits I Inductors Dr. Firas Obeidat 1 Inductors An inductor is a passive element designed to store energy in its magnetic field. They are used in power supplies, transformers, radios, TVs,
Grades will be determined by the correctness of your answers (explanations are not required).
 6.00 (Fall 2011) Final Examination December 19, 2011 Name: Kerberos Username: Please circle your section number: Section Time 2 11 am 1 pm 4 2 pm Grades will be determined by the correctness of your answers
6.00 (Fall 2011) Final Examination December 19, 2011 Name: Kerberos Username: Please circle your section number: Section Time 2 11 am 1 pm 4 2 pm Grades will be determined by the correctness of your answers
Exercise: 4. 1 converges. 1. The series. (D) e. (A) 2 ln 2 (C) 2 (B) 2. equal to. 4. If. a and b equation. d x 2. (D) ae 2t. (A) ae t.
 Exercise: 4 1. The series n 1 = 0 n! converges to (A) ln (B) (C) (D) e. The magnitude of the gradient for the function f(x, y, z) = x =3y +z 3 at the point (1, 1, 1) is. 3. Let X be a zero mean unit variance
Exercise: 4 1. The series n 1 = 0 n! converges to (A) ln (B) (C) (D) e. The magnitude of the gradient for the function f(x, y, z) = x =3y +z 3 at the point (1, 1, 1) is. 3. Let X be a zero mean unit variance
3 The non-linear elements
 3.1 Introduction The inductor and the capacitor are the two important passive circuit elements which have the ability to store and deliver finite amount of energy [49]. In an inductor, the energy is stored
3.1 Introduction The inductor and the capacitor are the two important passive circuit elements which have the ability to store and deliver finite amount of energy [49]. In an inductor, the energy is stored
e453.eps 1 Change (or the absolute value) in the measured physical variable 2 Change in the sensor property is translated into low-power-level
 3 Basic Phenomenon in Effect in Sensor Operation Sensors Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of
3 Basic Phenomenon in Effect in Sensor Operation Sensors Prof. Dr. M. Zahurul Haq zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd http://teacher.buet.ac.bd/zahurul/ Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of
Alternating Current Circuits
 Alternating Current Circuits AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source. The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal and varies with time according
Alternating Current Circuits AC Circuit An AC circuit consists of a combination of circuit elements and an AC generator or source. The output of an AC generator is sinusoidal and varies with time according
CBSE_2014_SET_3 Physics
 CBSE_2014_SET_3 Physics 1. A conducting loop is held below a current carrying wire PQ as shown. Predict the direction of the induced current in the loop when the current in the wire is constantly increasing.
CBSE_2014_SET_3 Physics 1. A conducting loop is held below a current carrying wire PQ as shown. Predict the direction of the induced current in the loop when the current in the wire is constantly increasing.
5. ELECTRIC CURRENTS
 5. ELECTRIC CURRENTS TOPIC OUTLINE Section Recommended Time Giancoli Section 5.1 Potential Difference, Current, Resistance 5.2 Electric Circuits 3h 19.1, 19.2 6.2 Electric Field and Force 6.3 Magnetic
5. ELECTRIC CURRENTS TOPIC OUTLINE Section Recommended Time Giancoli Section 5.1 Potential Difference, Current, Resistance 5.2 Electric Circuits 3h 19.1, 19.2 6.2 Electric Field and Force 6.3 Magnetic
EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, pm, Room TBA
 EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, 2006 6-7 pm, Room TBA First retrieve your EE2110 final and other course papers and notes! The test will be closed book
EE 3120 Electric Energy Systems Study Guide for Prerequisite Test Wednesday, Jan 18, 2006 6-7 pm, Room TBA First retrieve your EE2110 final and other course papers and notes! The test will be closed book
1.1 An excitation is applied to a system at t = T and its response is zero for < t < T. Such a system is (a) non-causal system.
 . An excitation is applied to a system at t = T and its response is zero for < t < T. Such a system is (a) non-causal system x(t) (b) stable system (c) causal system (d) unstable system t=t t. In a series
. An excitation is applied to a system at t = T and its response is zero for < t < T. Such a system is (a) non-causal system x(t) (b) stable system (c) causal system (d) unstable system t=t t. In a series
2 π Hz. 2π and 1 π Hz
 GATE/EC-009 EC : ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Page GATE EC 009 Q. - Q.0 carry one mark each. MCQ. SOL. MCQ. The order of the differential equation 3 dy dy 4 y e dt dt t + c m + is (A) (B)
GATE/EC-009 EC : ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Page GATE EC 009 Q. - Q.0 carry one mark each. MCQ. SOL. MCQ. The order of the differential equation 3 dy dy 4 y e dt dt t + c m + is (A) (B)
Transducer. A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity. Transducer. (Input) Sensor.
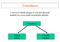 Transducer A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity Transducer (Input) Sensor (Output) Actuator Sensor A device which senses and detects the physical
Transducer A device to which change or converts physical quantity in a more easily measurable quantity Transducer (Input) Sensor (Output) Actuator Sensor A device which senses and detects the physical
Slide 1. Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic Fields Strain Pressure Displacement and Rotation Acceleration Electronic Sensors
 Slide 1 Electronic Sensors Electronic sensors can be designed to detect a variety of quantitative aspects of a given physical system. Such quantities include: Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic
Slide 1 Electronic Sensors Electronic sensors can be designed to detect a variety of quantitative aspects of a given physical system. Such quantities include: Temperatures Light (Optoelectronics) Magnetic
Most matter is electrically neutral; its atoms and molecules have the same number of electrons as protons.
 Magnetism Electricity Magnetism Magnetic fields are produced by the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin. -> permanent magnets Magnetic
Magnetism Electricity Magnetism Magnetic fields are produced by the intrinsic magnetic moments of elementary particles associated with a fundamental quantum property, their spin. -> permanent magnets Magnetic
Chapter 1 The Electric Force
 Chapter 1 The Electric Force 1. Properties of the Electric Charges 1- There are two kinds of the electric charges in the nature, which are positive and negative charges. - The charges of opposite sign
Chapter 1 The Electric Force 1. Properties of the Electric Charges 1- There are two kinds of the electric charges in the nature, which are positive and negative charges. - The charges of opposite sign
Lecture 24. April 5 th, Magnetic Circuits & Inductance
 Lecture 24 April 5 th, 2005 Magnetic Circuits & Inductance Reading: Boylestad s Circuit Analysis, 3 rd Canadian Edition Chapter 11.1-11.5, Pages 331-338 Chapter 12.1-12.4, Pages 341-349 Chapter 12.7-12.9,
Lecture 24 April 5 th, 2005 Magnetic Circuits & Inductance Reading: Boylestad s Circuit Analysis, 3 rd Canadian Edition Chapter 11.1-11.5, Pages 331-338 Chapter 12.1-12.4, Pages 341-349 Chapter 12.7-12.9,
Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs
 EECS 142 Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California,
EECS 142 Lecture 23: Negative Resistance Osc, Differential Osc, and VCOs Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California,
NEPTUNE -code: KAUVG11ONC Prerequisites:... Knowledge description:
 Subject name: Electrical Machines Credits: 9 Requirement : Course director: Dr. Vajda István Position: Assessment and verification procedures: NEPTUNE -code: KAUVG11ONC Prerequisites:... Number of hours:
Subject name: Electrical Machines Credits: 9 Requirement : Course director: Dr. Vajda István Position: Assessment and verification procedures: NEPTUNE -code: KAUVG11ONC Prerequisites:... Number of hours:
SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS
 Electrical Measurements International Program Department of Electrical Engineering UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA ANDRITTO ABDUL GHAFFAR ANDHIKA ADIEL INSANI Lecturer : Ir. Chairul Hudaya, ST, M.Eng., Ph.D., IPM
Electrical Measurements International Program Department of Electrical Engineering UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA ANDRITTO ABDUL GHAFFAR ANDHIKA ADIEL INSANI Lecturer : Ir. Chairul Hudaya, ST, M.Eng., Ph.D., IPM
3. (a) Figure 3(a) shows a Bridge T network used in control systems. The element values are clearly marked in the figure.
 I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
I.E.S.-(Conv.) 1987 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING PAPER - I PART A 1. (a) Define precisely unit step and unit impulse functions. Sketch the following function from t = 0 to t = 10 units, indicating all salient
CBSE Physics Set I Outer Delhi Board 2012
 Q28. a) In Young s double slit experiment, derive the condition for (I) constructive interference and (II) destructive interference at a point on the screen. b) A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths,
Q28. a) In Young s double slit experiment, derive the condition for (I) constructive interference and (II) destructive interference at a point on the screen. b) A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths,
ECE137B Final Exam. There are 5 problems on this exam and you have 3 hours There are pages 1-19 in the exam: please make sure all are there.
 ECE37B Final Exam There are 5 problems on this exam and you have 3 hours There are pages -9 in the exam: please make sure all are there. Do not open this exam until told to do so Show all work: Credit
ECE37B Final Exam There are 5 problems on this exam and you have 3 hours There are pages -9 in the exam: please make sure all are there. Do not open this exam until told to do so Show all work: Credit
Chip Inductors. LCCM Series Chip Common Mode Filter FEATURES CONSTRUCTION
 FEATURES Small wire wound chip inductor with ferrite core and 2 common mode lines. Highly effective in noise suppression High common-mode impedance at noise band an low differential mode impedance at signal
FEATURES Small wire wound chip inductor with ferrite core and 2 common mode lines. Highly effective in noise suppression High common-mode impedance at noise band an low differential mode impedance at signal
To find the step response of an RC circuit
 To find the step response of an RC circuit v( t) v( ) [ v( t) v( )] e tt The time constant = RC The final capacitor voltage v() The initial capacitor voltage v(t ) To find the step response of an RL circuit
To find the step response of an RC circuit v( t) v( ) [ v( t) v( )] e tt The time constant = RC The final capacitor voltage v() The initial capacitor voltage v(t ) To find the step response of an RL circuit
Sol: Semiconductor diode.
 48 49 1. What is the resistance value of a resistor of colour code Brown, Black, Red and silver? Sol: Brown-1, Black-0, Red-2, Silver- 10%. Resistance, R = 10 X 10-2 ±10Ω. 2. Mention a non-ohmic device.
48 49 1. What is the resistance value of a resistor of colour code Brown, Black, Red and silver? Sol: Brown-1, Black-0, Red-2, Silver- 10%. Resistance, R = 10 X 10-2 ±10Ω. 2. Mention a non-ohmic device.
