Suppressing environmental noise in quantum computation through pulse control
|
|
|
- Marsha Dean
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ocober 999 Ž. Physics Leers A Suppressing environmenl noise in qunum compuion hrough pulse conrol Lu-Ming Dun ), Gung-Cn Guo Deprmen of Physics nd lborory of Qunum communicion, Qunum Compuion, UniÕersiy of Science, Technology of Chin, Hefei , PR Chin Received 9 July 999; cceped 22 Augus 999 Communiced by P.R. Hollnd Absrc A scheme bsed on pulse conrol is described for suppressing noise in qunum compuion wihou he cos of sringen qunum compuing resources. I is shown h environmen-induced noise nd decoherence, wheher in qunum memory or in ge operions, ll cn be much reduced by pplying suible sequence of bi-flipping nd phse-flipping pulses. q 999 Published by Elsevier Science B.V. All righs reserved. PACS: Hk; Dd; p Qunum compuion hs become very cive field ever since he discovery h qunum compuers cn be much more powerful hn heir clssicl counerprs w 3 x. Qunum compuers c s sophisiced qunum informion processors, in which clculions re mde by he conrolled ime evoluion of se of coupled wo-level qunum sysems Ž qubis.. Coherence in he evoluion is essenil for king dvnge of qunum prllelism. However, here is mjor obscle o he relizion of qunum compuion. Decoherence of he qubis cused by he inevible inercion wih noisy environmen will mke qunum informion oo frgile o be of ny prcicl use. Recenly, ineres in qunum compuion hs incresed drmiclly becuse of wo respecs of dvnces owrd overcoming he bove ) Corresponding uhor. E-mil: lmdun@vorex.uibk.c. E-mil: gcguo@usc.edu.cn difficuly. Firs, combinion of series of innovive discoveries, such s qunum error correcing codes w4,5 x, ful-olern error correcion echniques wx 6, nd concened coding wx 7, hs yielded he imporn hreshold resul w7,8 x, which promises h rbirrily ccure qunum compuion is possible provided h he error per operion is below hreshold vlue. Hence, noise below cerin level is no n obscle o relible qunum compuion. Second, gre progress hs been mde owrd buildw9 x. Some ing he necessry qunum hrdwres simple bu rel qunum compuions hve been demonsred in bulk spin resonnce qunum sysw2,3 x; nd rdicl scheme, using semicon- ems ducor physics o mnipule nucler spins, hs been recenly proposed, which indices promising roue o lrge-scle qunum compuion w4 x. Ful-olern qunum error correcion schemes re effecive only when he error re per operion is below hreshold vlue. Operions in qunum r99r$ - see fron mer q 999 Published by Elsevier Science B.V. All righs reserved. Ž. PII: S
2 40 ( ) L.-M. Dun, G.-C. GuorPhysics Leers A compuers include rnsmission or sorge of qunum ses nd qunum logic. For qunum logic, he y6 esimed hreshold error re is bou 0 w7,8 x. Wih he presen echnology, he rel noise seems necessrily beyond his hreshold, even for he mos promising qunum hrdwre wx 8. Therefore, i is essenilly imporn o furher suppress noise before king he procedure of ful-olern qunum error correcion. Here, we propose noise suppression scheme which operes by pplying sequence of bi-flipping nd phse-flipping pulses on he sysem, wih he pulse period less hn he noise correlion ime. I is shown h noise in he pulse-conrolled sysem cn be grely reduced. The scheme bsed on pulse conrol is relively esy o implemen in experimens. In fc, clever pulse mehods Ž clled refocusing echniques. hve been developed for yers in nucler mgneic resonnce specroscopy Ž NMR. o effecively remove mny kinds of inercions mong he spins h re considered unwned or unineresing w5 x. In rew6 x, Viol nd Lloyd used his echnique cen work o comb environmenl noise in compuer memory wih specific single-qubi dephsing model. Ler, he echnique ws immediely exended o more generl cses w7,8 x, nd generl heory for suppressing memory noise hs been developed in he group conex w9,20 x. In his pper, we consider he generl ype of environmenl noise, including clssicl or qunum dephsing nd dissipion s is specil cses. By pplying suible pulse sequences, i is found h he noise in he conrolled sysem is much reduced; nd furhermore, he scheme cn be redily exended o suppress noise in qunum ges Žreferring o wo-bi or muli-bi qunum ges, whose error res re much lrger hn h of single-qubi roions w9,4,2 x.. Suppose pg is he error re per operion, nd p0 is he ddiionl error re inroduced by ech pulse. Our resul shows h he error re per operion in he pulse-conrolled sysem pproximely reduces o p p r, g 0 dec c where dec nd c re respecively he decoherence ime nd he noise correlion ime. Since p is normlly very smll, he reducing fcor p r is 0 dec c less hn even h he noise correlion ime is considerbly smller hn he decoherence ime. Therefore, by his scheme i is possible for he reduced error re o in he hreshold vlue, sy, 0 0 y6. This is desirous resul for relible qunum compuion. The only requiremen in our scheme is h he pulses should be pplied frequenly so h he pulse period is less hn he noise correlion ime. The scheme coss no ddiionl qunum compuing resources. Firs we show how o use pulse conrol o comb decoherence of single qubi in qunum memory. The qubi is described by Puli s operor s. In he inercion picure, he mos generl form of he Hmilonin describing single-qubi decoherence due o environmenl noise cn be expressed s Žseing "s. Ž. Ž. Ž. HI s s G, sx, y, z where GŽ., generlly dependen of ime, re noise erms, which my be clssicl sochsic vribles or sochsic qunum operors, corresponding clssicl noise or qunum noise, respecively. For environmenl noise in qunum compuers, i is resonble o ssume h GŽ. Ž sx, y, z. sisfy he condiions ² G Ž. : s 0 nd ² : env G Ž. G Ž. sf Ž j., Ž 2. b env b where ² PPP : env denoes verge over he environ- men. In Eq. Ž. 2, ll fbž j. re correlion funcions nd jsžy. r c. The quniy c chrcerizes he order of mgniude of he noise correlion imes. Differen noise correlion erms my hve differen correlion imes. Bu we ssume h hey hve he sme order of mgniude, which is denoed by c. For simpliciy, in he following we direcly cll c he noise correlion ime. Suppose h he qubi is iniilly in pure se C Ž 0.:. Under he Hmilonin Ž., fer shor ime i evolves ino mixed se rž. fer king verge over he environmen. The difference beween he ses rž. nd C Ž 0. : snds for errors. The error re p cn be described by psyfž., where FŽ. is he inpu-oupu se fideliy, defined s FŽ. s² C Ž 0. rž. C Ž 0.:. From Eqs. Ž. nd Ž. 2, i is no difficul o obin n explici perurbive expression for he error re. Up o he second order of he Hmilonin, he resul is b 2 ps2 ² Ds Ds : shh fb d2d, Ž 3.,b ž 0 0 c
3 ( ) L.-M. Dun, G.-C. GuorPhysics Leers A where Ds s s y² s : s, nd ² PPP : s denoes v- erge over he sysem. Eq. Ž. 3 is derived wih pure inpu se. However, i remins rue when he qubi is iniilly in mixed se. In his cse, we define he error re by psyfež., where FeŽ. is he ennglemen fideliy w22 x, nurl exension of he inpu-oupu se fideliy o he mixed se circumsnce. Wih his definiion, he expression for he error re remins compleely sme s Eq. Ž. 3. Now we show how o use pulse conrol o reduce he error re in qunum memory. We pply sequence of bi-flipping nd phse-flipping pulses on he qubi, wih he pulse period D nd pulse widh w. I is required h w<d so h he environ- men-induced sysem evoluion during he shor ime w is negligible. A ime s0, no pulse is pplied, nd is operion is represened by he uni operor I. A ime s, we begin o pply in urn he bi-flipping nd he phse-flipping pulses. The pulse-induced operions re hus respecively I,s x,s z,s x,s z, PPP. Four pulse periods mke up conrol period. Le U 2 denoe 2 T½exp yih HIŽ. d 5, where T PPP 4 indices h ime-ordered produc is ken in he brcke. In he Ž nq. h conrol period Žform ime 4nD o ime 4Ž n q.., he effecive sysem evoluion under pulse conrol is represened by he following evoluion operor: z Ž 4nq4. D x Ž4 nq3.d nq Ž 4nq3. D Ž4 nq2.d U ss U s U =s z U Ž4 nq2. s x U Ž4 nq. ½ Ž Ž4 nq.d 4 nd syt exp yi H s H IŽ. s d Ž 4 nq4. z z 4 nq3. yi H s H IŽ. s d Ž 4 nq3. y y Ž 4 nq2. yi H s H IŽ. s d Ž 4 nq2. x x Ž 4 nq. Ž 4 nq. H D Ž. I 5 4n yi H d ½ syt exp yi H 4Ž nq. 4n 5 sx, y, z s G Ž. d. Ž 4. The effecive noise erms G Ž 4nD q. wih 0F- 4 in Eq. Ž. 4 re defined s follows: D ž 3 D j D D 4 js0 4 G Ž 4n q. s h G 4n qj q, Ž 5. where he 3=4 coefficien mrix y y hs wh jxs y y. Ž 6. y y Afer pulse conrol, he only difference in he sysem evoluion Ž. 4 is h he noise erms GŽ. re replced by he corresponding effecive noise erms G. Form Eqs. Ž. 2 nd Ž. Ž. 5, i is no difficul o ge he correlions of he effecive noise G Ž.. Then, subsiuing hese correlions ino Eq. Ž. 3, we obin he error re pc fer pulse conrol. The finl resul is ž c 2 pc D s, Ž 7. p where c is he noise correlion ime, nd is dimensionless ner-o- fcor Žis explici form cn be found in w7 x., which is unimporn o our resul nd will be omied in he following discussion. From Eq. Ž. 7, i follows h hrough pulse conrol he error re in qunum memory cn be reduced by fcor proporionl o he second order of he re of he pulse period o he noise correlion ime. In fc, by pplying more complice pulse sequences, he error re cn be furher reduced. For exmple, we my pply he pulse sequence I,s x,s z,s x, I,s x,s z, s x, I, PPP, wih he pulse period. In his sequence, conrol period consiss of eigh pulse periods. We cn similrly clcule he error re of he sysem conrolled by his pulse sequence. The resul is h he error re is reduced by fcor proporionl o Ž r. 4 D c. In generl, if we pply pulse sequence wih he conrol period consising of 2 nq pulse periods, he error re is ble o be reduced by fcor proporionl o Ž r. 2 n D c. In he bove, we considered decoherence of single qubi. Now, suppose h here re L qubis, described respecively by Puli s operors s. In l he inercion picure, he Hmilonin describing decoherence of L qubis cn be generlly expressed
4 42 ( ) L.-M. Dun, G.-C. GuorPhysics Leers A s Ž. Ž. Ž. HL s sl Gl, 8 l sx, y, z where he noise erms sisfy he condiions ² G Ž. : s0 nd l env y b b G Ž. G Ž. s f. Ž 9. ² : l l env ll ž c The bove descripion of mny qubi decoherence is quie generl. I includes independen decoherence nd cooperive decoherence s is specil cse w23 x. For reducing decoherence of his sysem, he conrol mehod is very simple. We need only pply he bove pulse sequence seprely on ech qubi. I is esy o know h he error re of he conrolled sysem will be reduced by fcor proporionl o Ž r. 2 n D c, where n depends on which pulse sequence is chosen. To mke ful-olern qunum compuion possible, noise in qunum ges should be suppressed s well s noise in qunum memory. The pulse conrol scheme cn be exended o include qunum ge operions. Any qunum ge cn be decomposed ino series of qunum conrolled-not Ž CNOT. ges ogeher wih some single-qubi row24 x. In relisic qunum compuer models ions w9,,4 x, he qunum CNOT ge is no described by single Hmilonin. I is composed of severl seps. The crucil seps re wo-qubi direc or indirec inercion processes, which re usully described by he following Heisenberg-like effecive Hmilonin w,4 x: H s g Ž. s Ps, Ž 0. g ll l l ll where g ll Ž., possibly dependen of ime, re coupling coefficiens. The Heisenberg-like inercion Ž 0., ogeher wih some single-qubi roions, suffice o consruc qunum CNOT. The ime required o perform he Heisenberg-like inercion is normlly much lrger hn he running ime of sinw,4 x. Hence, ny wo-bi or gle-qubi roions muli-bi qunum ge cn be decomposed ino series of slow Heisenberg-like inercions ogeher wih some fs single-qubi roions. The pulse conrol scheme is no used o reduce he error re of single-qubi roions. I is no prcicl o do so, since ech pulse Ž specil single-qubi operion. will inroduce n error re comprble wih h of single-qubi roions. However, he noise in he qunum ge minly comes from he slow Heisenberg-like inercion, nd we re mking progress if he environmenl noise in he Heisenberg-like inercion is suppressed by he scheme. This gol cn be esily ined. We need only synchronize he pulses cing on differen qubis, i.e., we pply he sme bi-flipping or phse-flipping pulses simulneously on ll of he qubis. The synchronized pulses induce eiher collecive bi flip mls l x or collecive phse flip mls l z, where ml denoes ensor produc. The Hmilonin Ž 0. remins unchnged under hese operions, i.e., Ž mls l x. HgŽ mls l x. sž mls l z. HgŽ mls l z. sh g. Ž. Hence, he Heisenberg-like inercion is no influenced by he pulses, wheres he environmenl noise in his process Ždescribed by he Hmilonin Ž 8.. is grely suppressed. There is remining quesion. Besides he Heisenberg-like inercions, ddiionl single-qubi roions re inroduced o perform qunum compuion. We need o show h hese roions cn be performed in wy h hey do no influence he noise-suppression pulse sequence. I is convenien o ke he pulse sequence I,s x,s z,s x,s z, PPP used in Eq. Ž. 4 s n exmple o illusre he generl resul. Firs, we should noe h he durion of single-qubi roions is comprble wih he pulse widh w nd hus much smller hn he pulse period. Hence, he roion is compleed in one of he pulse periods. To perform single-qubi roion R in he Ž nq. h conrol period Žsee Eq. Ž 4.., we my pply n ddiionl shor pulse R during he firs pule period, or pply shor pulse s x Rs x during he second pulse period, or pply s y Rs y Ž z s R s z. during he hird Ž fourh. pulse period. The effecive evoluion operor Ž. 4 in he Ž n q. h conrol period is hen replced by he following form: U ½ 4Ž nq. nq 4n 5 sx, y, z syt R exp yi H s G Ž. d. Ž 2.
5 ( ) L.-M. Dun, G.-C. GuorPhysics Leers A Obviously, single-qubi roion R is ined while he noise suppression is no influenced Žhe noise erms G re sill replced by he effecive. noise erms G. I is srighforwrd o exend his resul o include ny noise suppression pulse sequence. Hence, single-qubi roions cn be ined while suppressing noise in qunum memory nd he Heisenberg-like inercions by he pulse conrol mehod. This shows h our scheme is pplicble for reducing decoherence boh in qunum memory n in qunum compuion. We hve shown h by moduling he sysem hrough sequence of pulses much fser hn he decoherence process nd he Heisenberg-like inercions, bu sill much slower hn he single-qubi roions nd he free evoluion, he environmenl noise in qunum memory nd in qunum compuion cn be reduced while he oher dynmics remin unchnged. In he bove nlyses, we mke n idel ssumpion h he pulses inroduce no ddiionl noise. If he inccurcy of he pulse is considered, n ddiionl error re p0 will be inroduced by ech pulse Ž p0 is comprble wih he error re of single-qubi roions.. Now we esime in his circumsnce o wh moun he error re per qunum operion cn be reduced hrough pulse conrol Žhe qunum operion here refers o he sorge of qunum informion or he wo-bi or muli-bi qunum ges.. Le g nd pg denoe he running ime nd he environmen-induced error re of he operion, respecively, hen grd defines he num- ber of pulses pplied during he operion. Afer pulse conrol, he error re pproximely becomes ž 2 n D g p,p q p g g 0 c D g c p0g 2 nq GpgŽ 2nq., Ž 3 ž. 2np where he minimum is ined when ž 2 n p0gc 2 nq D s, 2np g which is he opiml vlue for he pulse period. The Ž. prmeer n in Eq. 3 depends on which pulse 2 n sequence is chosen. If 2 n is considerbly lrge, p rp, Ž p. rž p. g g 0 g g c. For environmen-induced error, p cn be pproximed by p, r w2 x g g g dec, where dec is he decoherence ime. Wih his pprox- imion, we hve p grp g,p0decr c. The error re is reduced by very smll fcor p0decr c. This suggess h he pulse conrol mehod is very effecive. Compred wih oher noise suppression schemes, he pulse conrol mehod hs severl remrkble feures. Firs, i coss no ddiionl qubis. This is n imporn feure since wih he presen echnology, qunum compuing resources re sill very sringen w0,,25 x. Only smll qunum sysems hve been demonsred experimenlly. For hese sysems, i is impossible o perform ful-olern qunum error correcion, bu he pulse conrol scheme works well. Second, in he pulse conrol scheme, no encoding, decoding, nd error correcion re required, nd no mesuremen is performed. Hence, in conrs o qunum error correcion, his scheme inroduces no slowdown of he compuion speed. Ls bu no he les, pulse conrol is relw9, x. The pulse conrol mehod, combined wih ful- ively mure echnology in experimens olern qunum error correcion, my ulimely mke relible qunum compuion possible. Acknowledgemens This projec ws suppored by he Nionl Nurl Science Foundion of Chin. References wx P.W. Shor, in Proc. of he 35h Annul Symposium on Foundions of Compuer Science ŽIEEE Press, Los Almios, CA, 994., pp wx 2 S. Lloyd, Science 273 Ž wx 3 L.K. Grover, Phys. Rev. Le. 79 Ž wx 4 P.W. Shor, Phys. Rev. A 52 Ž 995. R2493. wx 5 A.M. Sene, Phys. Rev. Le. 77 Ž wx 6 D.P. DiVincenzo, P.W. Shor, Phys. Rev. Le. 77 Ž wx 7 E. Knill, R. Lflmme, W.H. Zurek, Science 279 Ž wx 8 J. Preskill, Proc. R. Soc. London A 454 Ž wx 9 J.I. Circ, P. Zoller, Phys. Rev. Le. 74 Ž
6 44 ( ) L.-M. Dun, G.-C. GuorPhysics Leers A w0x C. Monroe e l., ibid 75 Ž wx N.A. Gershenfeld, I.L. Chung, Science 275 Ž w2x I.L. Chung, Nure 393 Ž w3x D.G. Cory e l., LANL e-prin qun-phr w4x B.E. Kne, Nure 393 Ž ; D.P. DiVincenzo, ibid 393 Ž w5x C.P. Slicher, Principles of Mgneic Resonnce, 3rd. ed. Springer-Verlg, New York, 990. w6x L. Viol, S. Lloyd, Phys. Rev. A 58 Ž w7x L.M. Dun, G.C. Guo, LANL e-prin qun-phr w8x D. Vili, P. Tombesi, Phys. Rev. A 59 Ž w9x L. Viol, E. Knill, S. Lloyd, Phys. Rev. Le. 82 Ž w20x P. Znrdi, Phys. Le. A 258 Ž w2x D.P. DiVincenzo, Science 270 Ž w22x B. Schumcher, Phys. Rev. A 54 Ž w23x L.M. Dun, G.C. Guo Phys. Rev. A 56 Ž ; Phys. Rev. Le. 79 Ž w24x S. Lloyd, ibid 75 Ž w25x W.S. Wrren, N.A. Gershenfeld, I.L. Chung, Science 277 Ž
Contraction Mapping Principle Approach to Differential Equations
 epl Journl of Science echnology 0 (009) 49-53 Conrcion pping Principle pproch o Differenil Equions Bishnu P. Dhungn Deprmen of hemics, hendr Rn Cmpus ribhuvn Universiy, Khmu epl bsrc Using n eension of
epl Journl of Science echnology 0 (009) 49-53 Conrcion pping Principle pproch o Differenil Equions Bishnu P. Dhungn Deprmen of hemics, hendr Rn Cmpus ribhuvn Universiy, Khmu epl bsrc Using n eension of
4.8 Improper Integrals
 4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
4.8 Improper Inegrls Well you ve mde i hrough ll he inegrion echniques. Congrs! Unforunely for us, we sill need o cover one more inegrl. They re clled Improper Inegrls. A his poin, we ve only del wih inegrls
e t dt e t dt = lim e t dt T (1 e T ) = 1
 Improper Inegrls There re wo ypes of improper inegrls - hose wih infinie limis of inegrion, nd hose wih inegrnds h pproch some poin wihin he limis of inegrion. Firs we will consider inegrls wih infinie
Improper Inegrls There re wo ypes of improper inegrls - hose wih infinie limis of inegrion, nd hose wih inegrnds h pproch some poin wihin he limis of inegrion. Firs we will consider inegrls wih infinie
September 20 Homework Solutions
 College of Engineering nd Compuer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Mechnicl Engineering A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll 7 Number 66 Insrucor: Lrry Creo Sepember Homework Soluions Find he specrum
College of Engineering nd Compuer Science Mechnicl Engineering Deprmen Mechnicl Engineering A Seminr in Engineering Anlysis Fll 7 Number 66 Insrucor: Lrry Creo Sepember Homework Soluions Find he specrum
22.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Systems Prof. Freidberg Lecture 9: The High Beta Tokamak
 .65, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 9: The High e Tokmk Summry of he Properies of n Ohmic Tokmk. Advnges:. good euilibrium (smll shif) b. good sbiliy ( ) c. good confinemen ( τ nr )
.65, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 9: The High e Tokmk Summry of he Properies of n Ohmic Tokmk. Advnges:. good euilibrium (smll shif) b. good sbiliy ( ) c. good confinemen ( τ nr )
Motion. Part 2: Constant Acceleration. Acceleration. October Lab Physics. Ms. Levine 1. Acceleration. Acceleration. Units for Acceleration.
 Moion Accelerion Pr : Consn Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion is he re of chnge of velociy. = v - vo = Δv Δ ccelerion = = v - vo chnge of velociy elpsed ime Accelerion is vecor, lhough in one-dimensionl
Moion Accelerion Pr : Consn Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion Accelerion is he re of chnge of velociy. = v - vo = Δv Δ ccelerion = = v - vo chnge of velociy elpsed ime Accelerion is vecor, lhough in one-dimensionl
0 for t < 0 1 for t > 0
 8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
8.0 Sep nd del funcions Auhor: Jeremy Orloff The uni Sep Funcion We define he uni sep funcion by u() = 0 for < 0 for > 0 I is clled he uni sep funcion becuse i kes uni sep = 0. I is someimes clled he Heviside
The solution is often represented as a vector: 2xI + 4X2 + 2X3 + 4X4 + 2X5 = 4 2xI + 4X2 + 3X3 + 3X4 + 3X5 = 4. 3xI + 6X2 + 6X3 + 3X4 + 6X5 = 6.
 [~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
[~ o o :- o o ill] i 1. Mrices, Vecors, nd Guss-Jordn Eliminion 1 x y = = - z= The soluion is ofen represened s vecor: n his exmple, he process of eliminion works very smoohly. We cn elimine ll enries
A Kalman filtering simulation
 A Klmn filering simulion The performnce of Klmn filering hs been esed on he bsis of wo differen dynmicl models, ssuming eiher moion wih consn elociy or wih consn ccelerion. The former is epeced o beer
A Klmn filering simulion The performnce of Klmn filering hs been esed on he bsis of wo differen dynmicl models, ssuming eiher moion wih consn elociy or wih consn ccelerion. The former is epeced o beer
S Radio transmission and network access Exercise 1-2
 S-7.330 Rdio rnsmission nd nework ccess Exercise 1 - P1 In four-symbol digil sysem wih eqully probble symbols he pulses in he figure re used in rnsmission over AWGN-chnnel. s () s () s () s () 1 3 4 )
S-7.330 Rdio rnsmission nd nework ccess Exercise 1 - P1 In four-symbol digil sysem wih eqully probble symbols he pulses in he figure re used in rnsmission over AWGN-chnnel. s () s () s () s () 1 3 4 )
Minimum Squared Error
 Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i = i for ll smples
Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i = i for ll smples
Minimum Squared Error
 Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > 0 for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i i for ll smples
Minimum Squred Error LDF: Minimum Squred-Error Procedures Ide: conver o esier nd eer undersood prolem Percepron y i > 0 for ll smples y i solve sysem of liner inequliies MSE procedure y i i for ll smples
f t f a f x dx By Lin McMullin f x dx= f b f a. 2
 Accumulion: Thoughs On () By Lin McMullin f f f d = + The gols of he AP* Clculus progrm include he semen, Sudens should undersnd he definie inegrl s he ne ccumulion of chnge. 1 The Topicl Ouline includes
Accumulion: Thoughs On () By Lin McMullin f f f d = + The gols of he AP* Clculus progrm include he semen, Sudens should undersnd he definie inegrl s he ne ccumulion of chnge. 1 The Topicl Ouline includes
Convergence of Singular Integral Operators in Weighted Lebesgue Spaces
 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS Vol. 10, No. 2, 2017, 335-347 ISSN 1307-5543 www.ejpm.com Published by New York Business Globl Convergence of Singulr Inegrl Operors in Weighed Lebesgue
EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED MATHEMATICS Vol. 10, No. 2, 2017, 335-347 ISSN 1307-5543 www.ejpm.com Published by New York Business Globl Convergence of Singulr Inegrl Operors in Weighed Lebesgue
ENGR 1990 Engineering Mathematics The Integral of a Function as a Function
 ENGR 1990 Engineering Mhemics The Inegrl of Funcion s Funcion Previously, we lerned how o esime he inegrl of funcion f( ) over some inervl y dding he res of finie se of rpezoids h represen he re under
ENGR 1990 Engineering Mhemics The Inegrl of Funcion s Funcion Previously, we lerned how o esime he inegrl of funcion f( ) over some inervl y dding he res of finie se of rpezoids h represen he re under
1 jordan.mcd Eigenvalue-eigenvector approach to solving first order ODEs. -- Jordan normal (canonical) form. Instructor: Nam Sun Wang
 jordnmcd Eigenvlue-eigenvecor pproch o solving firs order ODEs -- ordn norml (cnonicl) form Insrucor: Nm Sun Wng Consider he following se of coupled firs order ODEs d d x x 5 x x d d x d d x x x 5 x x
jordnmcd Eigenvlue-eigenvecor pproch o solving firs order ODEs -- ordn norml (cnonicl) form Insrucor: Nm Sun Wng Consider he following se of coupled firs order ODEs d d x x 5 x x d d x d d x x x 5 x x
REAL ANALYSIS I HOMEWORK 3. Chapter 1
 REAL ANALYSIS I HOMEWORK 3 CİHAN BAHRAN The quesions re from Sein nd Shkrchi s e. Chper 1 18. Prove he following sserion: Every mesurble funcion is he limi.e. of sequence of coninuous funcions. We firs
REAL ANALYSIS I HOMEWORK 3 CİHAN BAHRAN The quesions re from Sein nd Shkrchi s e. Chper 1 18. Prove he following sserion: Every mesurble funcion is he limi.e. of sequence of coninuous funcions. We firs
3. Renewal Limit Theorems
 Virul Lborories > 14. Renewl Processes > 1 2 3 3. Renewl Limi Theorems In he inroducion o renewl processes, we noed h he rrivl ime process nd he couning process re inverses, in sens The rrivl ime process
Virul Lborories > 14. Renewl Processes > 1 2 3 3. Renewl Limi Theorems In he inroducion o renewl processes, we noed h he rrivl ime process nd he couning process re inverses, in sens The rrivl ime process
An integral having either an infinite limit of integration or an unbounded integrand is called improper. Here are two examples.
 Improper Inegrls To his poin we hve only considered inegrls f(x) wih he is of inegrion nd b finie nd he inegrnd f(x) bounded (nd in fc coninuous excep possibly for finiely mny jump disconinuiies) An inegrl
Improper Inegrls To his poin we hve only considered inegrls f(x) wih he is of inegrion nd b finie nd he inegrnd f(x) bounded (nd in fc coninuous excep possibly for finiely mny jump disconinuiies) An inegrl
GENERALIZATION OF SOME INEQUALITIES VIA RIEMANN-LIOUVILLE FRACTIONAL CALCULUS
 - TAMKANG JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 5, Number, 7-5, June doi:5556/jkjm555 Avilble online hp://journlsmhkueduw/ - - - GENERALIZATION OF SOME INEQUALITIES VIA RIEMANN-LIOUVILLE FRACTIONAL CALCULUS MARCELA
- TAMKANG JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Volume 5, Number, 7-5, June doi:5556/jkjm555 Avilble online hp://journlsmhkueduw/ - - - GENERALIZATION OF SOME INEQUALITIES VIA RIEMANN-LIOUVILLE FRACTIONAL CALCULUS MARCELA
1.0 Electrical Systems
 . Elecricl Sysems The ypes of dynmicl sysems we will e sudying cn e modeled in erms of lgeric equions, differenil equions, or inegrl equions. We will egin y looking fmilir mhemicl models of idel resisors,
. Elecricl Sysems The ypes of dynmicl sysems we will e sudying cn e modeled in erms of lgeric equions, differenil equions, or inegrl equions. We will egin y looking fmilir mhemicl models of idel resisors,
Probability, Estimators, and Stationarity
 Chper Probbiliy, Esimors, nd Sionriy Consider signl genered by dynmicl process, R, R. Considering s funcion of ime, we re opering in he ime domin. A fundmenl wy o chrcerize he dynmics using he ime domin
Chper Probbiliy, Esimors, nd Sionriy Consider signl genered by dynmicl process, R, R. Considering s funcion of ime, we re opering in he ime domin. A fundmenl wy o chrcerize he dynmics using he ime domin
Systems Variables and Structural Controllability: An Inverted Pendulum Case
 Reserch Journl of Applied Sciences, Engineering nd echnology 6(: 46-4, 3 ISSN: 4-7459; e-issn: 4-7467 Mxwell Scienific Orgniion, 3 Submied: Jnury 5, 3 Acceped: Mrch 7, 3 Published: November, 3 Sysems Vribles
Reserch Journl of Applied Sciences, Engineering nd echnology 6(: 46-4, 3 ISSN: 4-7459; e-issn: 4-7467 Mxwell Scienific Orgniion, 3 Submied: Jnury 5, 3 Acceped: Mrch 7, 3 Published: November, 3 Sysems Vribles
NMR Spectroscopy: Principles and Applications. Nagarajan Murali Advanced Tools Lecture 4
 NMR Specroscop: Principles nd Applicions Ngrjn Murli Advnced Tools Lecure 4 Advnced Tools Qunum Approch We know now h NMR is rnch of Specroscop nd he MNR specrum is n oucome of nucler spin inercion wih
NMR Specroscop: Principles nd Applicions Ngrjn Murli Advnced Tools Lecure 4 Advnced Tools Qunum Approch We know now h NMR is rnch of Specroscop nd he MNR specrum is n oucome of nucler spin inercion wih
MATH 124 AND 125 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 2008)
 MATH 14 AND 15 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 8) The following quesions cn be used s review for Mh 14/ 15 These quesions re no cul smples of quesions h will pper on he finl em, bu hey will provide
MATH 14 AND 15 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PACKET (Revised spring 8) The following quesions cn be used s review for Mh 14/ 15 These quesions re no cul smples of quesions h will pper on he finl em, bu hey will provide
Physics 2A HW #3 Solutions
 Chper 3 Focus on Conceps: 3, 4, 6, 9 Problems: 9, 9, 3, 41, 66, 7, 75, 77 Phsics A HW #3 Soluions Focus On Conceps 3-3 (c) The ccelerion due o grvi is he sme for boh blls, despie he fc h he hve differen
Chper 3 Focus on Conceps: 3, 4, 6, 9 Problems: 9, 9, 3, 41, 66, 7, 75, 77 Phsics A HW #3 Soluions Focus On Conceps 3-3 (c) The ccelerion due o grvi is he sme for boh blls, despie he fc h he hve differen
Magnetostatics Bar Magnet. Magnetostatics Oersted s Experiment
 Mgneosics Br Mgne As fr bck s 4500 yers go, he Chinese discovered h cerin ypes of iron ore could rc ech oher nd cerin mels. Iron filings "mp" of br mgne s field Crefully suspended slivers of his mel were
Mgneosics Br Mgne As fr bck s 4500 yers go, he Chinese discovered h cerin ypes of iron ore could rc ech oher nd cerin mels. Iron filings "mp" of br mgne s field Crefully suspended slivers of his mel were
INTEGRALS. Exercise 1. Let f : [a, b] R be bounded, and let P and Q be partitions of [a, b]. Prove that if P Q then U(P ) U(Q) and L(P ) L(Q).
![INTEGRALS. Exercise 1. Let f : [a, b] R be bounded, and let P and Q be partitions of [a, b]. Prove that if P Q then U(P ) U(Q) and L(P ) L(Q). INTEGRALS. Exercise 1. Let f : [a, b] R be bounded, and let P and Q be partitions of [a, b]. Prove that if P Q then U(P ) U(Q) and L(P ) L(Q).](/thumbs/78/77677920.jpg) INTEGRALS JOHN QUIGG Eercise. Le f : [, b] R be bounded, nd le P nd Q be priions of [, b]. Prove h if P Q hen U(P ) U(Q) nd L(P ) L(Q). Soluion: Le P = {,..., n }. Since Q is obined from P by dding finiely
INTEGRALS JOHN QUIGG Eercise. Le f : [, b] R be bounded, nd le P nd Q be priions of [, b]. Prove h if P Q hen U(P ) U(Q) nd L(P ) L(Q). Soluion: Le P = {,..., n }. Since Q is obined from P by dding finiely
Chapter Direct Method of Interpolation
 Chper 5. Direc Mehod of Inerpolion Afer reding his chper, you should be ble o:. pply he direc mehod of inerpolion,. sole problems using he direc mehod of inerpolion, nd. use he direc mehod inerpolns o
Chper 5. Direc Mehod of Inerpolion Afer reding his chper, you should be ble o:. pply he direc mehod of inerpolion,. sole problems using he direc mehod of inerpolion, nd. use he direc mehod inerpolns o
Tax Audit and Vertical Externalities
 T Audi nd Vericl Eernliies Hidey Ko Misuyoshi Yngihr Ngoy Keizi Universiy Ngoy Universiy 1. Inroducion The vericl fiscl eernliies rise when he differen levels of governmens, such s he federl nd se governmens,
T Audi nd Vericl Eernliies Hidey Ko Misuyoshi Yngihr Ngoy Keizi Universiy Ngoy Universiy 1. Inroducion The vericl fiscl eernliies rise when he differen levels of governmens, such s he federl nd se governmens,
A Time Truncated Improved Group Sampling Plans for Rayleigh and Log - Logistic Distributions
 ISSNOnline : 39-8753 ISSN Prin : 347-67 An ISO 397: 7 Cerified Orgnizion Vol. 5, Issue 5, My 6 A Time Trunced Improved Group Smpling Plns for Ryleigh nd og - ogisic Disribuions P.Kvipriy, A.R. Sudmni Rmswmy
ISSNOnline : 39-8753 ISSN Prin : 347-67 An ISO 397: 7 Cerified Orgnizion Vol. 5, Issue 5, My 6 A Time Trunced Improved Group Smpling Plns for Ryleigh nd og - ogisic Disribuions P.Kvipriy, A.R. Sudmni Rmswmy
A LIMIT-POINT CRITERION FOR A SECOND-ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR IAN KNOWLES
 A LIMIT-POINT CRITERION FOR A SECOND-ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR j IAN KNOWLES 1. Inroducion Consider he forml differenil operor T defined by el, (1) where he funcion q{) is rel-vlued nd loclly
A LIMIT-POINT CRITERION FOR A SECOND-ORDER LINEAR DIFFERENTIAL OPERATOR j IAN KNOWLES 1. Inroducion Consider he forml differenil operor T defined by el, (1) where he funcion q{) is rel-vlued nd loclly
Average & instantaneous velocity and acceleration Motion with constant acceleration
 Physics 7: Lecure Reminders Discussion nd Lb secions sr meeing ne week Fill ou Pink dd/drop form if you need o swich o differen secion h is FULL. Do i TODAY. Homework Ch. : 5, 7,, 3,, nd 6 Ch.: 6,, 3 Submission
Physics 7: Lecure Reminders Discussion nd Lb secions sr meeing ne week Fill ou Pink dd/drop form if you need o swich o differen secion h is FULL. Do i TODAY. Homework Ch. : 5, 7,, 3,, nd 6 Ch.: 6,, 3 Submission
EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE BOUNDARY-VALUE PROBLEM
 Elecronic Journl of Differenil Equions, Vol. 208 (208), No. 50, pp. 6. ISSN: 072-669. URL: hp://ejde.mh.xse.edu or hp://ejde.mh.un.edu EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE
Elecronic Journl of Differenil Equions, Vol. 208 (208), No. 50, pp. 6. ISSN: 072-669. URL: hp://ejde.mh.xse.edu or hp://ejde.mh.un.edu EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS OF SOLUTIONS FOR A SECOND-ORDER ITERATIVE
PHYSICS 1210 Exam 1 University of Wyoming 14 February points
 PHYSICS 1210 Em 1 Uniersiy of Wyoming 14 Februry 2013 150 poins This es is open-noe nd closed-book. Clculors re permied bu compuers re no. No collborion, consulion, or communicion wih oher people (oher
PHYSICS 1210 Em 1 Uniersiy of Wyoming 14 Februry 2013 150 poins This es is open-noe nd closed-book. Clculors re permied bu compuers re no. No collborion, consulion, or communicion wih oher people (oher
Neural assembly binding in linguistic representation
 Neurl ssembly binding in linguisic represenion Frnk vn der Velde & Mrc de Kmps Cogniive Psychology Uni, Universiy of Leiden, Wssenrseweg 52, 2333 AK Leiden, The Neherlnds, vdvelde@fsw.leidenuniv.nl Absrc.
Neurl ssembly binding in linguisic represenion Frnk vn der Velde & Mrc de Kmps Cogniive Psychology Uni, Universiy of Leiden, Wssenrseweg 52, 2333 AK Leiden, The Neherlnds, vdvelde@fsw.leidenuniv.nl Absrc.
A new model for limit order book dynamics
 Anewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics JeffreyR.Russell UniversiyofChicgo,GrdueSchoolofBusiness TejinKim UniversiyofChicgo,DeprmenofSisics Absrc:Thispperproposesnewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics.Thelimiorderbookconsiss
Anewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics JeffreyR.Russell UniversiyofChicgo,GrdueSchoolofBusiness TejinKim UniversiyofChicgo,DeprmenofSisics Absrc:Thispperproposesnewmodelforlimiorderbookdynmics.Thelimiorderbookconsiss
A Simple Method to Solve Quartic Equations. Key words: Polynomials, Quartics, Equations of the Fourth Degree INTRODUCTION
 Ausrlin Journl of Bsic nd Applied Sciences, 6(6): -6, 0 ISSN 99-878 A Simple Mehod o Solve Quric Equions Amir Fhi, Poo Mobdersn, Rhim Fhi Deprmen of Elecricl Engineering, Urmi brnch, Islmic Ad Universi,
Ausrlin Journl of Bsic nd Applied Sciences, 6(6): -6, 0 ISSN 99-878 A Simple Mehod o Solve Quric Equions Amir Fhi, Poo Mobdersn, Rhim Fhi Deprmen of Elecricl Engineering, Urmi brnch, Islmic Ad Universi,
Linear Response Theory: The connection between QFT and experiments
 Phys540.nb 39 3 Linear Response Theory: The connecion beween QFT and experimens 3.1. Basic conceps and ideas Q: How do we measure he conduciviy of a meal? A: we firs inroduce a weak elecric field E, and
Phys540.nb 39 3 Linear Response Theory: The connecion beween QFT and experimens 3.1. Basic conceps and ideas Q: How do we measure he conduciviy of a meal? A: we firs inroduce a weak elecric field E, and
Chapter 2. First Order Scalar Equations
 Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Mathematics 805 Final Examination Answers
 . 5 poins Se he Weiersrss M-es. Mhemics 85 Finl Eminion Answers Answer: Suppose h A R, nd f n : A R. Suppose furher h f n M n for ll A, nd h Mn converges. Then f n converges uniformly on A.. 5 poins Se
. 5 poins Se he Weiersrss M-es. Mhemics 85 Finl Eminion Answers Answer: Suppose h A R, nd f n : A R. Suppose furher h f n M n for ll A, nd h Mn converges. Then f n converges uniformly on A.. 5 poins Se
Version 001 test-1 swinney (57010) 1. is constant at m/s.
 Version 001 es-1 swinne (57010) 1 This prin-ou should hve 20 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions m coninue on he nex column or pge find ll choices before nswering. CubeUniVec1x76 001 10.0 poins Acubeis1.4fee
Version 001 es-1 swinne (57010) 1 This prin-ou should hve 20 quesions. Muliple-choice quesions m coninue on he nex column or pge find ll choices before nswering. CubeUniVec1x76 001 10.0 poins Acubeis1.4fee
Solutions to Problems from Chapter 2
 Soluions o Problems rom Chper Problem. The signls u() :5sgn(), u () :5sgn(), nd u h () :5sgn() re ploed respecively in Figures.,b,c. Noe h u h () :5sgn() :5; 8 including, bu u () :5sgn() is undeined..5
Soluions o Problems rom Chper Problem. The signls u() :5sgn(), u () :5sgn(), nd u h () :5sgn() re ploed respecively in Figures.,b,c. Noe h u h () :5sgn() :5; 8 including, bu u () :5sgn() is undeined..5
d 1 = c 1 b 2 - b 1 c 2 d 2 = c 1 b 3 - b 1 c 3
 and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
ON NEW INEQUALITIES OF SIMPSON S TYPE FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVES ABSOLUTE VALUES ARE CONVEX
 Journl of Applied Mhemics, Sisics nd Informics JAMSI), 9 ), No. ON NEW INEQUALITIES OF SIMPSON S TYPE FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVES ABSOLUTE VALUES ARE CONVEX MEHMET ZEKI SARIKAYA, ERHAN. SET
Journl of Applied Mhemics, Sisics nd Informics JAMSI), 9 ), No. ON NEW INEQUALITIES OF SIMPSON S TYPE FOR FUNCTIONS WHOSE SECOND DERIVATIVES ABSOLUTE VALUES ARE CONVEX MEHMET ZEKI SARIKAYA, ERHAN. SET
(b) 10 yr. (b) 13 m. 1.6 m s, m s m s (c) 13.1 s. 32. (a) 20.0 s (b) No, the minimum distance to stop = 1.00 km. 1.
 Answers o Een Numbered Problems Chper. () 7 m s, 6 m s (b) 8 5 yr 4.. m ih 6. () 5. m s (b).5 m s (c).5 m s (d) 3.33 m s (e) 8. ().3 min (b) 64 mi..3 h. ().3 s (b) 3 m 4..8 mi wes of he flgpole 6. (b)
Answers o Een Numbered Problems Chper. () 7 m s, 6 m s (b) 8 5 yr 4.. m ih 6. () 5. m s (b).5 m s (c).5 m s (d) 3.33 m s (e) 8. ().3 min (b) 64 mi..3 h. ().3 s (b) 3 m 4..8 mi wes of he flgpole 6. (b)
A 1.3 m 2.5 m 2.8 m. x = m m = 8400 m. y = 4900 m 3200 m = 1700 m
 PHYS : Soluions o Chper 3 Home Work. SSM REASONING The displcemen is ecor drwn from he iniil posiion o he finl posiion. The mgniude of he displcemen is he shores disnce beween he posiions. Noe h i is onl
PHYS : Soluions o Chper 3 Home Work. SSM REASONING The displcemen is ecor drwn from he iniil posiion o he finl posiion. The mgniude of he displcemen is he shores disnce beween he posiions. Noe h i is onl
LAPLACE TRANSFORMS. 1. Basic transforms
 LAPLACE TRANSFORMS. Bic rnform In hi coure, Lplce Trnform will be inroduced nd heir properie exmined; ble of common rnform will be buil up; nd rnform will be ued o olve ome dierenil equion by rnforming
LAPLACE TRANSFORMS. Bic rnform In hi coure, Lplce Trnform will be inroduced nd heir properie exmined; ble of common rnform will be buil up; nd rnform will be ued o olve ome dierenil equion by rnforming
Chapter 2: Evaluative Feedback
 Chper 2: Evluive Feedbck Evluing cions vs. insrucing by giving correc cions Pure evluive feedbck depends olly on he cion ken. Pure insrucive feedbck depends no ll on he cion ken. Supervised lerning is
Chper 2: Evluive Feedbck Evluing cions vs. insrucing by giving correc cions Pure evluive feedbck depends olly on he cion ken. Pure insrucive feedbck depends no ll on he cion ken. Supervised lerning is
10. State Space Methods
 . Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
. Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
5.1-The Initial-Value Problems For Ordinary Differential Equations
 5.-The Iniil-Vlue Problems For Ordinry Differenil Equions Consider solving iniil-vlue problems for ordinry differenil equions: (*) y f, y, b, y. If we know he generl soluion y of he ordinry differenil
5.-The Iniil-Vlue Problems For Ordinry Differenil Equions Consider solving iniil-vlue problems for ordinry differenil equions: (*) y f, y, b, y. If we know he generl soluion y of he ordinry differenil
Solutions for Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations By Tan-Cot Method
 IOSR Journl of Mhemics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578. Volume 5, Issue 3 (Jn. - Feb. 13), PP 6-11 Soluions for Nonliner Pril Differenil Equions By Tn-Co Mehod Mhmood Jwd Abdul Rsool Abu Al-Sheer Al -Rfidin Universiy
IOSR Journl of Mhemics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578. Volume 5, Issue 3 (Jn. - Feb. 13), PP 6-11 Soluions for Nonliner Pril Differenil Equions By Tn-Co Mehod Mhmood Jwd Abdul Rsool Abu Al-Sheer Al -Rfidin Universiy
Think of the Relationship Between Time and Space Again
 Repor nd Opinion, 1(3),009 hp://wwwsciencepubne sciencepub@gmilcom Think of he Relionship Beween Time nd Spce Agin Yng F-cheng Compny of Ruid Cenre in Xinjing 15 Hongxing Sree, Klmyi, Xingjing 834000,
Repor nd Opinion, 1(3),009 hp://wwwsciencepubne sciencepub@gmilcom Think of he Relionship Beween Time nd Spce Agin Yng F-cheng Compny of Ruid Cenre in Xinjing 15 Hongxing Sree, Klmyi, Xingjing 834000,
Nonlinear System Modelling: How to Estimate the. Highest Significant Order
 IEEE Insrumenion nd Mesuremen Technology Conference nchorge,, US, - My Nonliner Sysem Modelling: ow o Esime he ighes Significn Order Neophyos Chirs, Ceri Evns nd Dvid Rees, Michel Solomou School of Elecronics,
IEEE Insrumenion nd Mesuremen Technology Conference nchorge,, US, - My Nonliner Sysem Modelling: ow o Esime he ighes Significn Order Neophyos Chirs, Ceri Evns nd Dvid Rees, Michel Solomou School of Elecronics,
Lecture 2-1 Kinematics in One Dimension Displacement, Velocity and Acceleration Everything in the world is moving. Nothing stays still.
 Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
Lecure - Kinemaics in One Dimension Displacemen, Velociy and Acceleraion Everyhing in he world is moving. Nohing says sill. Moion occurs a all scales of he universe, saring from he moion of elecrons in
3D Transformations. Computer Graphics COMP 770 (236) Spring Instructor: Brandon Lloyd 1/26/07 1
 D Trnsformions Compuer Grphics COMP 770 (6) Spring 007 Insrucor: Brndon Lloyd /6/07 Geomery Geomeric eniies, such s poins in spce, exis wihou numers. Coordines re nming scheme. The sme poin cn e descried
D Trnsformions Compuer Grphics COMP 770 (6) Spring 007 Insrucor: Brndon Lloyd /6/07 Geomery Geomeric eniies, such s poins in spce, exis wihou numers. Coordines re nming scheme. The sme poin cn e descried
Phys 110. Answers to even numbered problems on Midterm Map
 Phys Answers o een numbered problems on Miderm Mp. REASONING The word per indices rio, so.35 mm per dy mens.35 mm/d, which is o be epressed s re in f/cenury. These unis differ from he gien unis in boh
Phys Answers o een numbered problems on Miderm Mp. REASONING The word per indices rio, so.35 mm per dy mens.35 mm/d, which is o be epressed s re in f/cenury. These unis differ from he gien unis in boh
T-Match: Matching Techniques For Driving Yagi-Uda Antennas: T-Match. 2a s. Z in. (Sections 9.5 & 9.7 of Balanis)
 3/0/018 _mch.doc Pge 1 of 6 T-Mch: Mching Techniques For Driving Ygi-Ud Anenns: T-Mch (Secions 9.5 & 9.7 of Blnis) l s l / l / in The T-Mch is shun-mching echnique h cn be used o feed he driven elemen
3/0/018 _mch.doc Pge 1 of 6 T-Mch: Mching Techniques For Driving Ygi-Ud Anenns: T-Mch (Secions 9.5 & 9.7 of Blnis) l s l / l / in The T-Mch is shun-mching echnique h cn be used o feed he driven elemen
SOLUTIONS TO ECE 3084
 SOLUTIONS TO ECE 384 PROBLEM 2.. For each sysem below, specify wheher or no i is: (i) memoryless; (ii) causal; (iii) inverible; (iv) linear; (v) ime invarian; Explain your reasoning. If he propery is no
SOLUTIONS TO ECE 384 PROBLEM 2.. For each sysem below, specify wheher or no i is: (i) memoryless; (ii) causal; (iii) inverible; (iv) linear; (v) ime invarian; Explain your reasoning. If he propery is no
Development of a New Scheme for the Solution of Initial Value Problems in Ordinary Differential Equations
 IOS Journl o Memics IOSJM ISSN: 78-78 Volume Issue July-Aug PP -9 www.iosrjournls.org Developmen o New Sceme or e Soluion o Iniil Vlue Problems in Ordinry Dierenil Equions Ogunrinde. B. dugb S. E. Deprmen
IOS Journl o Memics IOSJM ISSN: 78-78 Volume Issue July-Aug PP -9 www.iosrjournls.org Developmen o New Sceme or e Soluion o Iniil Vlue Problems in Ordinry Dierenil Equions Ogunrinde. B. dugb S. E. Deprmen
MTH 146 Class 11 Notes
 8.- Are of Surfce of Revoluion MTH 6 Clss Noes Suppose we wish o revolve curve C round n is nd find he surfce re of he resuling solid. Suppose f( ) is nonnegive funcion wih coninuous firs derivive on he
8.- Are of Surfce of Revoluion MTH 6 Clss Noes Suppose we wish o revolve curve C round n is nd find he surfce re of he resuling solid. Suppose f( ) is nonnegive funcion wih coninuous firs derivive on he
Temperature Rise of the Earth
 Avilble online www.sciencedirec.com ScienceDirec Procedi - Socil nd Behviorl Scien ce s 88 ( 2013 ) 220 224 Socil nd Behviorl Sciences Symposium, 4 h Inernionl Science, Socil Science, Engineering nd Energy
Avilble online www.sciencedirec.com ScienceDirec Procedi - Socil nd Behviorl Scien ce s 88 ( 2013 ) 220 224 Socil nd Behviorl Sciences Symposium, 4 h Inernionl Science, Socil Science, Engineering nd Energy
Bipartite Matching. Matching. Bipartite Matching. Maxflow Formulation
 Mching Inpu: undireced grph G = (V, E). Biprie Mching Inpu: undireced, biprie grph G = (, E).. Mching Ern Myr, Hrld äcke Biprie Mching Inpu: undireced, biprie grph G = (, E). Mflow Formulion Inpu: undireced,
Mching Inpu: undireced grph G = (V, E). Biprie Mching Inpu: undireced, biprie grph G = (, E).. Mching Ern Myr, Hrld äcke Biprie Mching Inpu: undireced, biprie grph G = (, E). Mflow Formulion Inpu: undireced,
Estimating the population parameter, r, q and K based on surplus production model. Wang, Chien-Hsiung
 SCTB15 Working Pper ALB 7 Esiming he populion prmeer, r, q nd K bsed on surplus producion model Wng, Chien-Hsiung Biologicl nd Fishery Division Insiue of Ocenogrphy Nionl Tiwn Universiy Tipei, Tiwn Tile:
SCTB15 Working Pper ALB 7 Esiming he populion prmeer, r, q nd K bsed on surplus producion model Wng, Chien-Hsiung Biologicl nd Fishery Division Insiue of Ocenogrphy Nionl Tiwn Universiy Tipei, Tiwn Tile:
Properties of Logarithms. Solving Exponential and Logarithmic Equations. Properties of Logarithms. Properties of Logarithms. ( x)
 Properies of Logrihms Solving Eponenil nd Logrihmic Equions Properies of Logrihms Produc Rule ( ) log mn = log m + log n ( ) log = log + log Properies of Logrihms Quoien Rule log m = logm logn n log7 =
Properies of Logrihms Solving Eponenil nd Logrihmic Equions Properies of Logrihms Produc Rule ( ) log mn = log m + log n ( ) log = log + log Properies of Logrihms Quoien Rule log m = logm logn n log7 =
Green s Functions and Comparison Theorems for Differential Equations on Measure Chains
 Green s Funcions nd Comprison Theorems for Differenil Equions on Mesure Chins Lynn Erbe nd Alln Peerson Deprmen of Mhemics nd Sisics, Universiy of Nebrsk-Lincoln Lincoln,NE 68588-0323 lerbe@@mh.unl.edu
Green s Funcions nd Comprison Theorems for Differenil Equions on Mesure Chins Lynn Erbe nd Alln Peerson Deprmen of Mhemics nd Sisics, Universiy of Nebrsk-Lincoln Lincoln,NE 68588-0323 lerbe@@mh.unl.edu
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Thermal neutron self-shielding factor in foils: a universal curve
 Proceedings of he Inernionl Conference on Reserch Recor Uilizion, Sfey, Decommissioning, Fuel nd Wse Mngemen (Snigo, Chile, -4 Nov.3) Pper IAEA-CN-/, IAEA Proceedings Series, Vienn, 5 Therml neuron self-shielding
Proceedings of he Inernionl Conference on Reserch Recor Uilizion, Sfey, Decommissioning, Fuel nd Wse Mngemen (Snigo, Chile, -4 Nov.3) Pper IAEA-CN-/, IAEA Proceedings Series, Vienn, 5 Therml neuron self-shielding
Online Appendix to Solution Methods for Models with Rare Disasters
 Online Appendix o Soluion Mehods for Models wih Rare Disasers Jesús Fernández-Villaverde and Oren Levinal In his Online Appendix, we presen he Euler condiions of he model, we develop he pricing Calvo block,
Online Appendix o Soluion Mehods for Models wih Rare Disasers Jesús Fernández-Villaverde and Oren Levinal In his Online Appendix, we presen he Euler condiions of he model, we develop he pricing Calvo block,
22.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Systems Prof. Freidberg Lecture 10: The High Beta Tokamak Con d and the High Flux Conserving Tokamak.
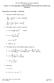 .615, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 1: The High Be Tokmk Con d nd he High Flux Conserving Tokmk Proeries of he High Tokmk 1. Evlue he MHD sfey fcor: ψ B * ( ) 1 3 ρ 1+ ν ρ ρ cosθ *
.615, MHD Theory of Fusion Sysems Prof. Freidberg Lecure 1: The High Be Tokmk Con d nd he High Flux Conserving Tokmk Proeries of he High Tokmk 1. Evlue he MHD sfey fcor: ψ B * ( ) 1 3 ρ 1+ ν ρ ρ cosθ *
For the reaction, R P, the is given by,
 Dr JADU SAMUEL CHEMICAL KINETICS Inroducion Chemicl ineics is brnch of physicl chemisry, which dels wih he sudy of he re of chemicl recions nd he vrious fcors ffecing i Such sudies lso enble us o elucide
Dr JADU SAMUEL CHEMICAL KINETICS Inroducion Chemicl ineics is brnch of physicl chemisry, which dels wih he sudy of he re of chemicl recions nd he vrious fcors ffecing i Such sudies lso enble us o elucide
Some basic notation and terminology. Deterministic Finite Automata. COMP218: Decision, Computation and Language Note 1
 COMP28: Decision, Compuion nd Lnguge Noe These noes re inended minly s supplemen o he lecures nd exooks; hey will e useful for reminders ou noion nd erminology. Some sic noion nd erminology An lphe is
COMP28: Decision, Compuion nd Lnguge Noe These noes re inended minly s supplemen o he lecures nd exooks; hey will e useful for reminders ou noion nd erminology. Some sic noion nd erminology An lphe is
Bias in Conditional and Unconditional Fixed Effects Logit Estimation: a Correction * Tom Coupé
 Bias in Condiional and Uncondiional Fixed Effecs Logi Esimaion: a Correcion * Tom Coupé Economics Educaion and Research Consorium, Naional Universiy of Kyiv Mohyla Academy Address: Vul Voloska 10, 04070
Bias in Condiional and Uncondiional Fixed Effecs Logi Esimaion: a Correcion * Tom Coupé Economics Educaion and Research Consorium, Naional Universiy of Kyiv Mohyla Academy Address: Vul Voloska 10, 04070
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( y )
 8. Lengh of Plne Curve The mos fmous heorem in ll of mhemics is he Pyhgoren Theorem. I s formulion s he disnce formul is used o find he lenghs of line segmens in he coordine plne. In his secion you ll
8. Lengh of Plne Curve The mos fmous heorem in ll of mhemics is he Pyhgoren Theorem. I s formulion s he disnce formul is used o find he lenghs of line segmens in he coordine plne. In his secion you ll
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2019 Lecture Notes Note 17
 EES 16A Designing Informaion Devices and Sysems I Spring 019 Lecure Noes Noe 17 17.1 apaciive ouchscreen In he las noe, we saw ha a capacior consiss of wo pieces on conducive maerial separaed by a nonconducive
EES 16A Designing Informaion Devices and Sysems I Spring 019 Lecure Noes Noe 17 17.1 apaciive ouchscreen In he las noe, we saw ha a capacior consiss of wo pieces on conducive maerial separaed by a nonconducive
STATE-SPACE MODELLING. A mass balance across the tank gives:
 B. Lennox and N.F. Thornhill, 9, Sae Space Modelling, IChemE Process Managemen and Conrol Subjec Group Newsleer STE-SPACE MODELLING Inroducion: Over he pas decade or so here has been an ever increasing
B. Lennox and N.F. Thornhill, 9, Sae Space Modelling, IChemE Process Managemen and Conrol Subjec Group Newsleer STE-SPACE MODELLING Inroducion: Over he pas decade or so here has been an ever increasing
Math 334 Fall 2011 Homework 11 Solutions
 Dec. 2, 2 Mah 334 Fall 2 Homework Soluions Basic Problem. Transform he following iniial value problem ino an iniial value problem for a sysem: u + p()u + q() u g(), u() u, u () v. () Soluion. Le v u. Then
Dec. 2, 2 Mah 334 Fall 2 Homework Soluions Basic Problem. Transform he following iniial value problem ino an iniial value problem for a sysem: u + p()u + q() u g(), u() u, u () v. () Soluion. Le v u. Then
..,..,.,
 57.95. «..» 7, 9,,. 3 DOI:.459/mmph7..,..,., E-mil: yshr_ze@mil.ru -,,. -, -.. -. - - ( ). -., -. ( - ). - - -., - -., - -, -., -. -., - - -, -., -. : ; ; - ;., -,., - -, []., -, [].,, - [3, 4]. -. 3 (
57.95. «..» 7, 9,,. 3 DOI:.459/mmph7..,..,., E-mil: yshr_ze@mil.ru -,,. -, -.. -. - - ( ). -., -. ( - ). - - -., - -., - -, -., -. -., - - -, -., -. : ; ; - ;., -,., - -, []., -, [].,, - [3, 4]. -. 3 (
Reinforcement Learning. Markov Decision Processes
 einforcemen Lerning Mrkov Decision rocesses Mnfred Huber 2014 1 equenil Decision Mking N-rmed bi problems re no good wy o model sequenil decision problem Only dels wih sic decision sequences Could be miiged
einforcemen Lerning Mrkov Decision rocesses Mnfred Huber 2014 1 equenil Decision Mking N-rmed bi problems re no good wy o model sequenil decision problem Only dels wih sic decision sequences Could be miiged
LAPLACE TRANSFORM OVERCOMING PRINCIPLE DRAWBACKS IN APPLICATION OF THE VARIATIONAL ITERATION METHOD TO FRACTIONAL HEAT EQUATIONS
 Wu, G.-.: Lplce Trnsform Overcoming Principle Drwbcks in Applicion... THERMAL SIENE: Yer 22, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 257-26 257 Open forum LAPLAE TRANSFORM OVEROMING PRINIPLE DRAWBAKS IN APPLIATION OF THE VARIATIONAL
Wu, G.-.: Lplce Trnsform Overcoming Principle Drwbcks in Applicion... THERMAL SIENE: Yer 22, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 257-26 257 Open forum LAPLAE TRANSFORM OVEROMING PRINIPLE DRAWBAKS IN APPLIATION OF THE VARIATIONAL
The order of reaction is defined as the number of atoms or molecules whose concentration change during the chemical reaction.
 www.hechemisryguru.com Re Lw Expression Order of Recion The order of recion is defined s he number of oms or molecules whose concenrion chnge during he chemicl recion. Or The ol number of molecules or
www.hechemisryguru.com Re Lw Expression Order of Recion The order of recion is defined s he number of oms or molecules whose concenrion chnge during he chemicl recion. Or The ol number of molecules or
1. Introduction. 1 b b
 Journl of Mhemicl Inequliies Volume, Number 3 (007), 45 436 SOME IMPROVEMENTS OF GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITY N. ELEZOVIĆ, LJ. MARANGUNIĆ AND J. PEČARIĆ (communiced b A. Čižmešij) Absrc. In his pper some inequliies
Journl of Mhemicl Inequliies Volume, Number 3 (007), 45 436 SOME IMPROVEMENTS OF GRÜSS TYPE INEQUALITY N. ELEZOVIĆ, LJ. MARANGUNIĆ AND J. PEČARIĆ (communiced b A. Čižmešij) Absrc. In his pper some inequliies
2D Motion WS. A horizontally launched projectile s initial vertical velocity is zero. Solve the following problems with this information.
 Nme D Moion WS The equions of moion h rele o projeciles were discussed in he Projecile Moion Anlsis Acii. ou found h projecile moes wih consn eloci in he horizonl direcion nd consn ccelerion in he ericl
Nme D Moion WS The equions of moion h rele o projeciles were discussed in he Projecile Moion Anlsis Acii. ou found h projecile moes wih consn eloci in he horizonl direcion nd consn ccelerion in he ericl
Inventory Analysis and Management. Multi-Period Stochastic Models: Optimality of (s, S) Policy for K-Convex Objective Functions
 Muli-Period Sochasic Models: Opimali of (s, S) Polic for -Convex Objecive Funcions Consider a seing similar o he N-sage newsvendor problem excep ha now here is a fixed re-ordering cos (> 0) for each (re-)order.
Muli-Period Sochasic Models: Opimali of (s, S) Polic for -Convex Objecive Funcions Consider a seing similar o he N-sage newsvendor problem excep ha now here is a fixed re-ordering cos (> 0) for each (re-)order.
New Inequalities in Fractional Integrals
 ISSN 1749-3889 (prin), 1749-3897 (online) Inernionl Journl of Nonliner Science Vol.9(21) No.4,pp.493-497 New Inequliies in Frcionl Inegrls Zoubir Dhmni Zoubir DAHMANI Lborory of Pure nd Applied Mhemics,
ISSN 1749-3889 (prin), 1749-3897 (online) Inernionl Journl of Nonliner Science Vol.9(21) No.4,pp.493-497 New Inequliies in Frcionl Inegrls Zoubir Dhmni Zoubir DAHMANI Lborory of Pure nd Applied Mhemics,
M r. d 2. R t a M. Structural Mechanics Section. Exam CT5141 Theory of Elasticity Friday 31 October 2003, 9:00 12:00 hours. Problem 1 (3 points)
 Delf Universiy of Technology Fculy of Civil Engineering nd Geosciences Srucurl echnics Secion Wrie your nme nd sudy numer he op righ-hnd of your work. Exm CT5 Theory of Elsiciy Fridy Ocoer 00, 9:00 :00
Delf Universiy of Technology Fculy of Civil Engineering nd Geosciences Srucurl echnics Secion Wrie your nme nd sudy numer he op righ-hnd of your work. Exm CT5 Theory of Elsiciy Fridy Ocoer 00, 9:00 :00
More Digital Logic. t p output. Low-to-high and high-to-low transitions could have different t p. V in (t)
 EECS 4 Spring 23 Lecure 2 EECS 4 Spring 23 Lecure 2 More igial Logic Gae delay and signal propagaion Clocked circui elemens (flip-flop) Wriing a word o memory Simplifying digial circuis: Karnaugh maps
EECS 4 Spring 23 Lecure 2 EECS 4 Spring 23 Lecure 2 More igial Logic Gae delay and signal propagaion Clocked circui elemens (flip-flop) Wriing a word o memory Simplifying digial circuis: Karnaugh maps
Procedia Computer Science
 Procedi Compuer Science 00 (0) 000 000 Procedi Compuer Science www.elsevier.com/loce/procedi The Third Informion Sysems Inernionl Conference The Exisence of Polynomil Soluion of he Nonliner Dynmicl Sysems
Procedi Compuer Science 00 (0) 000 000 Procedi Compuer Science www.elsevier.com/loce/procedi The Third Informion Sysems Inernionl Conference The Exisence of Polynomil Soluion of he Nonliner Dynmicl Sysems
An introduction to the theory of SDDP algorithm
 An inroducion o he heory of SDDP algorihm V. Leclère (ENPC) Augus 1, 2014 V. Leclère Inroducion o SDDP Augus 1, 2014 1 / 21 Inroducion Large scale sochasic problem are hard o solve. Two ways of aacking
An inroducion o he heory of SDDP algorihm V. Leclère (ENPC) Augus 1, 2014 V. Leclère Inroducion o SDDP Augus 1, 2014 1 / 21 Inroducion Large scale sochasic problem are hard o solve. Two ways of aacking
HUI-HSIUNG KUO, ANUWAT SAE-TANG, AND BENEDYKT SZOZDA
 Communicions on Sochsic Anlysis Vol 6, No 4 2012 603-614 Serils Publicions wwwserilspublicionscom THE ITÔ FORMULA FOR A NEW STOCHASTIC INTEGRAL HUI-HSIUNG KUO, ANUWAT SAE-TANG, AND BENEDYKT SZOZDA Absrc
Communicions on Sochsic Anlysis Vol 6, No 4 2012 603-614 Serils Publicions wwwserilspublicionscom THE ITÔ FORMULA FOR A NEW STOCHASTIC INTEGRAL HUI-HSIUNG KUO, ANUWAT SAE-TANG, AND BENEDYKT SZOZDA Absrc
Section 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equations; Method of Undetermined Coefficients
 Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
1. Find a basis for the row space of each of the following matrices. Your basis should consist of rows of the original matrix.
 Mh 7 Exm - Prcice Prolem Solions. Find sis for he row spce of ech of he following mrices. Yor sis shold consis of rows of he originl mrix. 4 () 7 7 8 () Since we wn sis for he row spce consising of rows
Mh 7 Exm - Prcice Prolem Solions. Find sis for he row spce of ech of he following mrices. Yor sis shold consis of rows of he originl mrix. 4 () 7 7 8 () Since we wn sis for he row spce consising of rows
How to Prove the Riemann Hypothesis Author: Fayez Fok Al Adeh.
 How o Prove he Riemnn Hohesis Auhor: Fez Fok Al Adeh. Presiden of he Srin Cosmologicl Socie P.O.Bo,387,Dmscus,Sri Tels:963--77679,735 Emil:hf@scs-ne.org Commens: 3 ges Subj-Clss: Funcionl nlsis, comle
How o Prove he Riemnn Hohesis Auhor: Fez Fok Al Adeh. Presiden of he Srin Cosmologicl Socie P.O.Bo,387,Dmscus,Sri Tels:963--77679,735 Emil:hf@scs-ne.org Commens: 3 ges Subj-Clss: Funcionl nlsis, comle
Orientation. Connections between network coding and stochastic network theory. Outline. Bruce Hajek. Multicast with lost packets
 Connecions beween nework coding and sochasic nework heory Bruce Hajek Orienaion On Thursday, Ralf Koeer discussed nework coding: coding wihin he nework Absrac: Randomly generaed coded informaion blocks
Connecions beween nework coding and sochasic nework heory Bruce Hajek Orienaion On Thursday, Ralf Koeer discussed nework coding: coding wihin he nework Absrac: Randomly generaed coded informaion blocks
Physical Limitations of Logic Gates Week 10a
 Physical Limiaions of Logic Gaes Week 10a In a compuer we ll have circuis of logic gaes o perform specific funcions Compuer Daapah: Boolean algebraic funcions using binary variables Symbolic represenaion
Physical Limiaions of Logic Gaes Week 10a In a compuer we ll have circuis of logic gaes o perform specific funcions Compuer Daapah: Boolean algebraic funcions using binary variables Symbolic represenaion
Hermite-Hadamard-Fejér type inequalities for convex functions via fractional integrals
 Sud. Univ. Beş-Bolyi Mh. 6(5, No. 3, 355 366 Hermie-Hdmrd-Fejér ype inequliies for convex funcions vi frcionl inegrls İmd İşcn Asrc. In his pper, firsly we hve eslished Hermie Hdmrd-Fejér inequliy for
Sud. Univ. Beş-Bolyi Mh. 6(5, No. 3, 355 366 Hermie-Hdmrd-Fejér ype inequliies for convex funcions vi frcionl inegrls İmd İşcn Asrc. In his pper, firsly we hve eslished Hermie Hdmrd-Fejér inequliy for
A new model for solving fuzzy linear fractional programming problem with ranking function
 J. ppl. Res. Ind. Eng. Vol. 4 No. 07 89 96 Journl of pplied Reserch on Indusril Engineering www.journl-prie.com new model for solving fuzzy liner frcionl progrmming prolem wih rning funcion Spn Kumr Ds
J. ppl. Res. Ind. Eng. Vol. 4 No. 07 89 96 Journl of pplied Reserch on Indusril Engineering www.journl-prie.com new model for solving fuzzy liner frcionl progrmming prolem wih rning funcion Spn Kumr Ds
FURTHER GENERALIZATIONS. QI Feng. The value of the integral of f(x) over [a; b] can be estimated in a variety ofways. b a. 2(M m)
![FURTHER GENERALIZATIONS. QI Feng. The value of the integral of f(x) over [a; b] can be estimated in a variety ofways. b a. 2(M m) FURTHER GENERALIZATIONS. QI Feng. The value of the integral of f(x) over [a; b] can be estimated in a variety ofways. b a. 2(M m)](/thumbs/75/72845579.jpg) Univ. Beogrd. Pul. Elekroehn. Fk. Ser. M. 8 (997), 79{83 FUTHE GENEALIZATIONS OF INEQUALITIES FO AN INTEGAL QI Feng Using he Tylor's formul we prove wo inegrl inequliies, h generlize K. S. K. Iyengr's
Univ. Beogrd. Pul. Elekroehn. Fk. Ser. M. 8 (997), 79{83 FUTHE GENEALIZATIONS OF INEQUALITIES FO AN INTEGAL QI Feng Using he Tylor's formul we prove wo inegrl inequliies, h generlize K. S. K. Iyengr's
1. Consider a PSA initially at rest in the beginning of the left-hand end of a long ISS corridor. Assume xo = 0 on the left end of the ISS corridor.
 In Eercise 1, use sndrd recngulr Cresin coordine sysem. Le ime be represened long he horizonl is. Assume ll ccelerions nd decelerions re consn. 1. Consider PSA iniilly res in he beginning of he lef-hnd
In Eercise 1, use sndrd recngulr Cresin coordine sysem. Le ime be represened long he horizonl is. Assume ll ccelerions nd decelerions re consn. 1. Consider PSA iniilly res in he beginning of he lef-hnd
Calculation method of flux measurements by static chambers
 lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers P.S. Kroon Presened he NiroEurope Workshop, 15h - 17h December 28, openhgen, Denmrk EN-L--9-11 December 28 lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers
lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers P.S. Kroon Presened he NiroEurope Workshop, 15h - 17h December 28, openhgen, Denmrk EN-L--9-11 December 28 lculion mehod of flux mesuremens by sic chmbers
