DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
|
|
|
- Geoffrey Mitchell Washington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS PAGE # An equaion conaining independen variable, dependen variable & differenial coeffeciens of dependen variables wr independen variable is called differenial equaion If all he differenial coeffeciens are presen wr one independen variable hen he differenial equaion is called ordinar differenial equ If he are presen wr more han one independen variables hen i is called parial differenial equ d d d d 3 ODE z 0 PDE 3 Differenial equaion represens a famil of curve which share some common characerisics d eg : 5 d = 5 + c famil of lines wih slope 5 eg : d 0 d k famil of hperbola wih cenre as (0, 0) & pair of asmpoes as = 4 The famil of curves obained afer inergraing he given differenial equ, free from differenial coeffeciens & conaining arbirar consans is called general soluion or soluion or inegral curves or primiive If all he arbirar consans presen in general sol are subsiued wih some specific values hen he obained equ is called paricular sol 5 Order & Degree : The order of highes order differenial coeffecien presen in he equaion is called order of differenial equaion eg : 3 8 d d 3 d 0 d order = 3 The eponen of highes order differenial coefficien presen in he equaion is called he degree of differenial equaion provided all he differenial coefficiens are presen in polnomial form Order of a differenial equ is alwas defined while degree need no o be defined eg : d d d d order 3 degree 7 eg: 5 d 5 d 4 e d / d 3 order 5 degree undefined eg: 3 e 4 d d 4 4 order 4 degree 3 7 "" eg: 4 ' sin 0 order 4 degree 3
2 PAGE # / 3 eg: 5 "" ' order - 4 degree (iv) 3 sin " n order degree FORMATION OF DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION : NOTE : (A) If he equaion of famil of curves is given hen (i) coun he no of independen arbirar consans sa n The no of independen arbirar consans will be he order of differenial equ o be formed eg : = = 3 sin k k 3 sin k order k eg : = k3 ke k4 k = ke k 4 order 3 eg3 : = A sin Bcos order eg4 : A sin c cos D order eg5 : sin cos k3 k4 sin k k (ii) Differeniae he given equaion n imes Eliminae hese n arbirar consans from hese n + equaions, one given and n obained (iii) The eliminan of above will be req differenial equ (B) If he equaions are given in erms of language hen form he corresponding mahemaical equaion & hence differenial equaion hus obained is Reqd DE Q Form he differenial equ for follow famil of curves (i) k e k ' k e e ' k e ' e " 0 = (ii) = k e k e ' k e k e " k e k e = (iii) k e k e ' k e k e = k e k e
3 PAGE # 3 (iv) = = 3 k 5 3k = 3 (v) ab e c = a ke ' ak e a c a e ' ak a a ae ' e " 0 = a = a (vi) Famil of circles cenred a origin k ' 0 (vii) Famil of circles having cenre a line = & radius = k 4 k ' 0 k ' 4 ' (viii) Famil of parabolas ais // o -ais & he vere a (4, 5) 5 a 4 5 ' a 5 5 ' ' (i) Circle ouching -ais a origin r r r 0 r 0
4 PAGE # 4 ' ' 0 ' () c c ' c ' c ' ' ' ' SOLUTION OF DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION : A soluion of a differenial equ will saisf i idenicall eg : Find which one of he follow/s is/are sol of differenial equ " 3 0 (i) = a sin bcos (ii) 3 asin b cos (iii) 3 a sin bcos (iv) 4sin 3 Sol Checking opion (ii) " a sin b cos " 3 as bc as bc Sol Checking opion (iv) " 4sin 4s 4s For a general curve (a) Tangen d Y X d (b) Normal Y X d d (c) Inerceps made b angen on boh he aes are A :, 0 ' & B : 0, ' 3 (a) RP = Lengh of angen Inerceped porion of angen b/w p & -ais (b) PS = Inerceped porion of normal b/w p & -ais Lengh of Normal (c) RQ = subangen = Projecion of lengh of angen on -ais (d) QS = Projecion of lengh of normal on -ais Subnormal Subnormal = QS = ang =
5 PAGE # 5 ' Lengh of normal = PS = subangen = ' Lengh of angen = ' 4 d = d d Lengh of curve = AB = B d A B = d d ' d A METHODS OF SOLVING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION : Variable separable : Take d on one side of equaion & d on oher side If all he erms conaining can be clubed wih d & he erms conaining can be clubed wih d hen i is variable separable form Separae he erms & hen inergrae (i) d sin cos 0 d sin d cos d cos sin c d cos an 3 0 d (ii) cos d 3co d sin 3n sin c (iii) sin 3 d d 0 sin 3 d d d d 0 sin 3 d sin3 d + = 0
6 PAGE # 6 3 sec d 3 3 an an + an c (iv) d d e 3 e sin d 3 e e e sin d 3 e d e sin d 3 e e cos c 3 (v) d d d n a b d e ab d a e e d b b a e d e d b a e e c b a (vi) Find c urve (which is no passing hrough origin) f or which lengh of normal a a poin is equal o radius vecor? Sol Lengh of normal = radius vecor ' ' = k (vii) Find curve for which segmen of angen conained b/w coordinae aes is biseced b he poin & he curve passes hrough (3, 4) A : ' A B p 0 ' '
7 PAGE # 7 d d n n c ( (3, 4) lies on he curve) = k = Q8 Find he curve pass ing hrough (, ) for which mid p of (lengh of ) angen is biseced a is p of wih -ais A P 0 0 ' d ' d n n c k (, ) k = 4 4 Q9 Find curve for which area bounded b curve, he coordinae aes & a variable ordinae is equal o he lengh of corresponding arc in s quad & given ha curve passes hrough (0, )? Ar OAPQ 0 PQ d = ' d 0 = f() f d 0 = ' ' ' = = d d n c
8 n PAGE # 8 e e e e e e & = (B) Reducial o Variable separable : d f a b c d le a + b + c = a + b = a bf a f d d d d sin 3 cos 3 4 d = + 3 = + 3 = d + 3(sin () + cos() + 4) = d d 3sin 3cos 4 d d 3 d d 4 d d 5 d an d
9 + = + = d PAGE # 9 + d d = + c = an 3 + = + = d d d d d = 4 + = ' d + d d d d 5 ' d an d
10 d = co PAGE # 0 c n sin 3 Variable separable using Trigonomeric subsiuion : (a) r sin & = r cos (b) r (c) an / (d) d d r dr (e) sec d d d r d d d T - : (a) r sec = r an (b) r (c) sin (d) d d r dr d d (e) cosd d d r secd d d d d = r dr r r sec d r dr r sec d n r r n sec an c d d d d 0 r cos r dr r sin r d 0 cos dr sind 0 dr an sec d 0
11 PAGE # r sec c 0 d d d d 3 4 d d d d 5 ' ' 3 r dr r d r r cos dr = sec r = an c d 4 r dr = r cosr d dr cos d r 5 c sin r ' ' r cos r sin' r r cos' r sin r + d d d r dr = d d d r d = r r dr r d d a b c d a b c ad bd cd ad bd cd bd cd ad cd ad bd 0 a b 0 If a d b d a d d
12 PAGE # eg: d d d 8d 9d 3d 4d 5d 8d 9d 3d 5d 4d d c eg : + 4 = eg3 : d 4 9 d 4 6 d 3 d 3 Inegrae erm b erm eg:4 : 3d 9 8 d 8 eg: 5: d 3 4 d 9 7 HOMOGENOUS DEs : The equaion of he form same degree d d P, Q, is called homogenous differenial equaion where P & Q are homogenous funcions of In his case RHS ca also be wrien as f [B cancelling n from numeraor & D r of RHS where n is he degree of P & Q] To solve pu / = = d d d f() = + d f() = d d f variable separable Q d 3 4 d 4 3 As i is homog diff equ using / =
13 PAGE # 3 d n d d 3 d d 4 sin d sin d 3 d d 5 d d d ln n c = / 3 d d d d 3 n = + c 4 d sin / d sin /
14 PAGE # 4 d sin sin n sin 5 d 3 d d = 3 n c 6 Find he curve for which subnormal is equals o summaion of coordinaes ' = d = 7 Find he curve for which raio of subnormal o he sum of coordinaes is equals o ha of ordinae & absicca? ' = 0 or = 8 If he area bounded b he curve b/w =, =, = 0 & he curve is = raio of cube of ordinae o absicca 3 d = 3 3 ' 3 3 ' 9 Find he curve for which angle formed b -ais a an p is wice he formed b polar radius of p of angenc wih -ais an = an '
15 PAGE # 5 ' / d 0 ' ' 0 = 4 4 = d / / e d e / d 0 / d e / d / e d e e d d 0 d d d Q3 d d REDUCIBLE TO HOMOGENOUS DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION :
16 PAGE # 6 T- d a b c d a b c = + h = + k d a b ah bk c d a b a h b k c If h & k are chosen such ha ah bk c 0 ah bk c 0 d a b d a b d a b a b E- d 5 d 3 4 = + h = + k d d 3 4 h + k 5 = 0 3h + 4k = 0 h =, k = d = 4 T-: If & is presen as f() & g() hen search f () wih d & g () wih d Q 3 d d = d d d d 4 5 8
17 PAGE # 7 3 d d c c d sec 3cos 4sin d cosec 4cos 5sin d d 0 d 4 e e e d 5 'sin cos sin cos d 3cos 4sin sin d 4cos 5sin d sin 3cos 4sin d cos 4cos 5sin = sin, = cos d 3 4 d = 3 c 3 d d 0 d d 0 d d 4 e d e d d e d e e e e e Now e & e d d Reducible separable mehod
18 5 'sin cos sin PAGE # 8 sin d sin cos sin d d d d = d d 7 d dy dx X Y X le X = X 7 Y = Y + 3 dx X = where Y = X Ulimael we will pu Y = Y + 3 & X = 7 LINEAR DE OF ST ORDER & FIRST DEGREE : General equaion : d p Q d Define inegraing facor IF = ep p d = e p d mulipl boh sides b IF p d e d p d e p Qe d d p d p d e Q e d p d pd p d e Q e d (i) NOTE : If an epression conains d d of ( Inegraing Facor) linearl added wih (where coefficiens could be funcions of ) hen i can be made perfec diff d d p Q is linear differenial equ where is dependen veriable and is independen variable d Q Q n n n d d d
19 PAGE # 9 d d d n Q3 Q4 d cos sin d Q5 d Q6 d 3 d Q7 d d 0 Q8 cos 3 Q9 d an d Q0 d Q d d 0 d / d 0 d Q sin cos sin d n d d IF = ep d = ep d = ep n = Using (i) = n d = n d = n c
20 PAGE # 0 IF = d ep n = ep nn = n From (i) n n d n n c d d 3 cos sin d d cos sin sin sin e sin e d 4 9 d n d d n d IF = = n d d an d e an an e an d 5 d d d IF = ep d ep n an c
21 PAGE # ep 6 IF = ep n d = ep = d d = d 7 d 3 d d d d IF = ep d d = an c = = an c d cos d 8 IF = ep d cos d sin c d d d 0 d 3 d 0 d 0 d 5 c d d
22 d d PAGE # IF = ep d e e e d d d co sin IF = ep co d ep nsin sin sin sin sin d DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION REDUCIBLE TO LINEAR DE : d f ' p f Q d f() = z (diff wr ) dz p z Q d Linear differenial equaion in z BERNOULI S EQUATION : d d n p Q d p Q n d n n z eg : ' ' / = d IF / d 3 '
23 PAGE # 3 3 ' n n 4 3 ' d 5 sin cos cos sin d 6 / ' e sin ' d d d d d IF = ep 4 = ep n 4 = / 4 / 4 / 4 d 3 d d n n / n d IF = / d 4 d d 3
24 d d PAGE # d 3 IF = ep 3d e 3 3 e 3 e d 5 d cos cos sin (cos ) d sin sin 6 d / e sin d / / e sin d = IF = ep d ep / / / e e e sin d e / e / cos c 7 Find he curve such ha he iniial ordinae of an angen is less han absicca of p of angenc b unis Y ' X Iniial ordinae = ' ' ', 0 pu = 0 8 Find he curve if he produc of iniial ordinae & absicca is consan? I O = ', 0 = ' c FORMING PERFECT DIFFERENTIALS : d d d
25 d d d PAGE # 5 d d 3 d d d d 4 5 d an d d Q Solve he followings : 3 d d d d = sec an d d sec an d d d d d sec an d sec an d = n sec an + n cos c 3 d d d d 3 cos d d 3 d d 4 d d 0 5 d d d 6 ' ' 7 d d sin cos d d sin d 0 cos cos
26 d d d d d / d PAGE # 6 = d d 3 cos d d cos d d sin c 4 d d d d 0 d d d 0 3 / c 3 5 d d d d d n c d d 6 d d d d d d d d
27 7 d d d 0 PAGE # 7 k 8 cos d d sin d sin d 0 an cos cos c d d d d 9 d d d d 3 / 3 / d d d an 0 c sin d 3 cos d 0 d 3 d cos d sin d 0 3 d d d cos 0 3 cos c d d d d d d d d d d ORTHOGONAL TRAJECTORY : (O T) : OT of a famil of curves is a famil of curves each member of which inersec wih each member of given famil a 90
28 PAGE # 8 To find equ of orhogonal rajecor s find differenial equ of given famil, hen replace d inegrae his DE o ge req OT Q Find orhogonal rajecor of follow : d d in his diff equ b d & hen (i) k ' 0 For OT = 0 ' ' 0 ' d d 0 d 0 = c (ii) r + = 0 For ORTHOGONAL TRAJECTORY 0 ' = 0 d d = 0 d d 0 n() n() = c n c = c ' (iii) / 3 / 3 / 3 a ' 0 / 3 / 3 For ORTHOGONAL TRAJECTORY 0 / 3 / 3 ' / 3 / 3 d d 0 '
29 4 / 3 4 / 3 k PAGE # 9 RATE CHANGE & FORMING CORRESPONDING DE : To analse he problem consider a ime inerval ie from o ( + ) In his ime inerval, a changing quani can be assumed as consan 3 Form DE for corresponding phsical phenomenon Inegrae he ob differenial equ The given informaion in he ques ma be used in limis of inegraion or for indefinie o evaluae arbirar consan Q Le a spherical ball losses is volume which is direcl proporional o is insananeous area Also a = 0, r = m & a = 3 monhs, r = m Find radius as funcion of ime? dv 4 r dv k 4 r d 4 r k 4 r dr 3r k 4r 3 dr k r = k + c = 0, r = c = = 3 r = 3k + = k = 3 r = 3 Q Le a cone is filled wih waer & waer evaporaes from i a he rae direcl proporional o suface area epossed o environmen proporionali consan being m/s Find he heigh of waer column as func of ime given a = 0, h = 00 m & he semiverical angle is 60 v r h han60 h 3 3 = h 3 dv r 6 h 3 d h 6h
30 dh 3h 6h PAGE # 30 dh h = + k h = 00 = 0 k = 00 h = + 00 Q3 Le a righ circular clinder of cross-secional area A is provided wih a circular opening a boom of area a, which is covered wih a diaphrogm z is opening a a consan rae & is compleel opened a he ime, = T The h of circular vessel is H & is comp filled column as a func of ime? (i) < T (ii) > T a a k a when = T k = a T a v a T reduced v ou Adh a v (v is he veloci of waer moving ou) Adh a gh dh a A gh T h A dh a g h T H 0 A h a h g H T 0 A a h H g T g a h H, < T 4TA > T A dh a gh Q4 Le a conainer conains v 0 L of fresh waer A ime = 0 a saled waer is run ino i a he rae v L/min, each lire of which conains a kg of sal A = 0 waer also sars flowing ou a he rae of v L/min hen find quani of sal presen in conainer as a funcion of ime, all he ime miure is kep uniform b sirring am = In ou
31 PAGE # 3 m av v = v0 v v v v v Volume of waer = 0 m dm av v v 0 v v dm v m av v v v ep 0 If = v v v v 0 v ep lnv v v v v = 0 = 0 v v v v v v v v v = m v v v 0 0 v vv av v v v v v v mv0 v v = av v v v 0 v vv v v v v v + c STQ: f () + p()f() Linear Diff Epression d Le for a given diff equaion f, d If g() is one of he soluion hen dg f, g d Q Le = f() be a soluion of differenial equ curve a a given poin? d 3 d T = + 4 = ( ) N 4 d 3 d 5 & i passes hrough (, 4) hen find equ of angen & normal o his
32 Q Le p() = 0 and d p d TPT p() > 0 p, PAGE # 3 dp p 0 d d p e 0 d f () > 0 f() ing hen if > f() > f() p() p() e p e e 0 p() > 0 Alernaive : d p e 0 d Inegraing boh sides wihin limis o p e p e 0 p() > 0 p e 0 Q3 Le f(,, c) = 0 be he inegral curves of he differenial equ d d g, k, where g & k are homogenous ep equ of same degree TPT angens drawn o all he inegral curves a heir p of inersecion wih a sraigh line passing hrough origin, will be parallel d d g, k, d d f d MT d, f m MT d d, f m Q4 Le wo curves are given = f() & = g() saisf he follow wo properies (i) angens drawn a he ps of equal absicca inersec on -ais (ii) normals drawn a he poin of equal absical inersec on -ais hen find he curves
33 df T Y f X d PAGE # 33 dg T Y g X d As boh passes hrough A f f ' g g' d N Y f X df d N Y g X dg As boh passes hrough B f f ' gg' (ii) f g c f g f g c (ii) f g f ' g' from (i) d f g f g d d f g d f g f g k (iv) from (iii) & (iv) k(f + g) = c f + g = c k f g = k c f = g = c k c k Q5 Le wo curves = f() & = g() are given where g() = f d & also angens drawn a ps wih equal absicca o boh curves inersec on -ais f ind he curves if f() passes hrough (0, ) & g() pas ses hrough 0, 4 As he inersec on -ais f g f ' g'
34 f ' g' f = kg() f g PAGE # 34 g() = f d g () = f() g () = kg() g' k g n g k c g() = f() = e kc kk e k k e k 0, 4 k = /4 (0, ) = k 4 k = 4 f() = 4 e g() = e 4 4 Q6 Le & are wo soluions of d p d = Q() & also z Q d TPT z = ae where a is arbirar consan d p d d p d z Q Q dz d z pz Q d d dz zq Q d dz Q z d dz Q d z Q nz d c z k e Q d
35 PAGE # 35 Q d z = k e
Check in: 1 If m = 2(x + 1) and n = find y when. b y = 2m n 2
 7 Parameric equaions This chaer will show ou how o skech curves using heir arameric equaions conver arameric equaions o Caresian equaions find oins of inersecion of curves and lines using arameric equaions
7 Parameric equaions This chaer will show ou how o skech curves using heir arameric equaions conver arameric equaions o Caresian equaions find oins of inersecion of curves and lines using arameric equaions
15. Vector Valued Functions
 1. Vecor Valued Funcions Up o his poin, we have presened vecors wih consan componens, for example, 1, and,,4. However, we can allow he componens of a vecor o be funcions of a common variable. For example,
1. Vecor Valued Funcions Up o his poin, we have presened vecors wih consan componens, for example, 1, and,,4. However, we can allow he componens of a vecor o be funcions of a common variable. For example,
Challenge Problems. DIS 203 and 210. March 6, (e 2) k. k(k + 2). k=1. f(x) = k(k + 2) = 1 x k
 Challenge Problems DIS 03 and 0 March 6, 05 Choose one of he following problems, and work on i in your group. Your goal is o convince me ha your answer is correc. Even if your answer isn compleely correc,
Challenge Problems DIS 03 and 0 March 6, 05 Choose one of he following problems, and work on i in your group. Your goal is o convince me ha your answer is correc. Even if your answer isn compleely correc,
MA 214 Calculus IV (Spring 2016) Section 2. Homework Assignment 1 Solutions
 MA 14 Calculus IV (Spring 016) Secion Homework Assignmen 1 Soluions 1 Boyce and DiPrima, p 40, Problem 10 (c) Soluion: In sandard form he given firs-order linear ODE is: An inegraing facor is given by
MA 14 Calculus IV (Spring 016) Secion Homework Assignmen 1 Soluions 1 Boyce and DiPrima, p 40, Problem 10 (c) Soluion: In sandard form he given firs-order linear ODE is: An inegraing facor is given by
1 1 + x 2 dx. tan 1 (2) = ] ] x 3. Solution: Recall that the given integral is improper because. x 3. 1 x 3. dx = lim dx.
![1 1 + x 2 dx. tan 1 (2) = ] ] x 3. Solution: Recall that the given integral is improper because. x 3. 1 x 3. dx = lim dx. 1 1 + x 2 dx. tan 1 (2) = ] ] x 3. Solution: Recall that the given integral is improper because. x 3. 1 x 3. dx = lim dx.](/thumbs/71/65799522.jpg) . Use Simpson s rule wih n 4 o esimae an () +. Soluion: Since we are using 4 seps, 4 Thus we have [ ( ) f() + 4f + f() + 4f 3 [ + 4 4 6 5 + + 4 4 3 + ] 5 [ + 6 6 5 + + 6 3 + ]. 5. Our funcion is f() +.
. Use Simpson s rule wih n 4 o esimae an () +. Soluion: Since we are using 4 seps, 4 Thus we have [ ( ) f() + 4f + f() + 4f 3 [ + 4 4 6 5 + + 4 4 3 + ] 5 [ + 6 6 5 + + 6 3 + ]. 5. Our funcion is f() +.
KEY. Math 334 Midterm I Fall 2008 sections 001 and 003 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 1 KEY Mah 4 Miderm I Fall 8 secions 1 and Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his eam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on our own paper, preferabl engineering
1 KEY Mah 4 Miderm I Fall 8 secions 1 and Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his eam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on our own paper, preferabl engineering
MA Study Guide #1
 MA 66 Su Guide #1 (1) Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Firs Order Linear Equaion (FOL): + p() = g() Soluion : = 1 µ() [ ] µ()g() + C, where µ() = e p() II. Separable Equaion (SEP): dx = h(x) g()
MA 66 Su Guide #1 (1) Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Firs Order Linear Equaion (FOL): + p() = g() Soluion : = 1 µ() [ ] µ()g() + C, where µ() = e p() II. Separable Equaion (SEP): dx = h(x) g()
Math 2214 Solution Test 1A Spring 2016
 Mah 14 Soluion Tes 1A Spring 016 sec Problem 1: Wha is he larges -inerval for which ( 4) = has a guaraneed + unique soluion for iniial value (-1) = 3 according o he Exisence Uniqueness Theorem? Soluion
Mah 14 Soluion Tes 1A Spring 016 sec Problem 1: Wha is he larges -inerval for which ( 4) = has a guaraneed + unique soluion for iniial value (-1) = 3 according o he Exisence Uniqueness Theorem? Soluion
ME 391 Mechanical Engineering Analysis
 Fall 04 ME 39 Mechanical Engineering Analsis Eam # Soluions Direcions: Open noes (including course web posings). No books, compuers, or phones. An calculaor is fair game. Problem Deermine he posiion of
Fall 04 ME 39 Mechanical Engineering Analsis Eam # Soluions Direcions: Open noes (including course web posings). No books, compuers, or phones. An calculaor is fair game. Problem Deermine he posiion of
Solutions to Assignment 1
 MA 2326 Differenial Equaions Insrucor: Peronela Radu Friday, February 8, 203 Soluions o Assignmen. Find he general soluions of he following ODEs: (a) 2 x = an x Soluion: I is a separable equaion as we
MA 2326 Differenial Equaions Insrucor: Peronela Radu Friday, February 8, 203 Soluions o Assignmen. Find he general soluions of he following ODEs: (a) 2 x = an x Soluion: I is a separable equaion as we
3, so θ = arccos
 Mahemaics 210 Professor Alan H Sein Monday, Ocober 1, 2007 SOLUTIONS This problem se is worh 50 poins 1 Find he angle beween he vecors (2, 7, 3) and (5, 2, 4) Soluion: Le θ be he angle (2, 7, 3) (5, 2,
Mahemaics 210 Professor Alan H Sein Monday, Ocober 1, 2007 SOLUTIONS This problem se is worh 50 poins 1 Find he angle beween he vecors (2, 7, 3) and (5, 2, 4) Soluion: Le θ be he angle (2, 7, 3) (5, 2,
MATH 31B: MIDTERM 2 REVIEW. x 2 e x2 2x dx = 1. ue u du 2. x 2 e x2 e x2] + C 2. dx = x ln(x) 2 2. ln x dx = x ln x x + C. 2, or dx = 2u du.
![MATH 31B: MIDTERM 2 REVIEW. x 2 e x2 2x dx = 1. ue u du 2. x 2 e x2 e x2] + C 2. dx = x ln(x) 2 2. ln x dx = x ln x x + C. 2, or dx = 2u du. MATH 31B: MIDTERM 2 REVIEW. x 2 e x2 2x dx = 1. ue u du 2. x 2 e x2 e x2] + C 2. dx = x ln(x) 2 2. ln x dx = x ln x x + C. 2, or dx = 2u du.](/thumbs/86/93221008.jpg) MATH 3B: MIDTERM REVIEW JOE HUGHES. Inegraion by Pars. Evaluae 3 e. Soluion: Firs make he subsiuion u =. Then =, hence 3 e = e = ue u Now inegrae by pars o ge ue u = ue u e u + C and subsiue he definiion
MATH 3B: MIDTERM REVIEW JOE HUGHES. Inegraion by Pars. Evaluae 3 e. Soluion: Firs make he subsiuion u =. Then =, hence 3 e = e = ue u Now inegrae by pars o ge ue u = ue u e u + C and subsiue he definiion
1 st order ODE Initial Condition
 Mah-33 Chapers 1-1 s Order ODE Sepember 1, 17 1 1 s order ODE Iniial Condiion f, sandard form LINEAR NON-LINEAR,, p g differenial form M x dx N x d differenial form is equivalen o a pair of differenial
Mah-33 Chapers 1-1 s Order ODE Sepember 1, 17 1 1 s order ODE Iniial Condiion f, sandard form LINEAR NON-LINEAR,, p g differenial form M x dx N x d differenial form is equivalen o a pair of differenial
Math 333 Problem Set #2 Solution 14 February 2003
 Mah 333 Problem Se #2 Soluion 14 February 2003 A1. Solve he iniial value problem dy dx = x2 + e 3x ; 2y 4 y(0) = 1. Soluion: This is separable; we wrie 2y 4 dy = x 2 + e x dx and inegrae o ge The iniial
Mah 333 Problem Se #2 Soluion 14 February 2003 A1. Solve he iniial value problem dy dx = x2 + e 3x ; 2y 4 y(0) = 1. Soluion: This is separable; we wrie 2y 4 dy = x 2 + e x dx and inegrae o ge The iniial
Math 2214 Solution Test 1B Fall 2017
 Mah 14 Soluion Tes 1B Fall 017 Problem 1: A ank has a capaci for 500 gallons and conains 0 gallons of waer wih lbs of sal iniiall. A soluion conaining of 8 lbsgal of sal is pumped ino he ank a 10 galsmin.
Mah 14 Soluion Tes 1B Fall 017 Problem 1: A ank has a capaci for 500 gallons and conains 0 gallons of waer wih lbs of sal iniiall. A soluion conaining of 8 lbsgal of sal is pumped ino he ank a 10 galsmin.
PROBLEMS FOR MATH 162 If a problem is starred, all subproblems are due. If only subproblems are starred, only those are due. SLOPES OF TANGENT LINES
 PROBLEMS FOR MATH 6 If a problem is sarred, all subproblems are due. If onl subproblems are sarred, onl hose are due. 00. Shor answer quesions. SLOPES OF TANGENT LINES (a) A ball is hrown ino he air. Is
PROBLEMS FOR MATH 6 If a problem is sarred, all subproblems are due. If onl subproblems are sarred, onl hose are due. 00. Shor answer quesions. SLOPES OF TANGENT LINES (a) A ball is hrown ino he air. Is
( ) 2. Review Exercise 2. cos θ 2 3 = = 2 tan. cos. 2 x = = x a. Since π π, = 2. sin = = 2+ = = cotx. 2 sin θ 2+
 Review Eercise sin 5 cos sin an cos 5 5 an 5 9 co 0 a sinθ 6 + 4 6 + sin θ 4 6+ + 6 + 4 cos θ sin θ + 4 4 sin θ + an θ cos θ ( ) + + + + Since π π, < θ < anθ should be negaive. anθ ( + ) Pearson Educaion
Review Eercise sin 5 cos sin an cos 5 5 an 5 9 co 0 a sinθ 6 + 4 6 + sin θ 4 6+ + 6 + 4 cos θ sin θ + 4 4 sin θ + an θ cos θ ( ) + + + + Since π π, < θ < anθ should be negaive. anθ ( + ) Pearson Educaion
Chapter 2. First Order Scalar Equations
 Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
AP Calculus BC Chapter 10 Part 1 AP Exam Problems
 AP Calculus BC Chaper Par AP Eam Problems All problems are NO CALCULATOR unless oherwise indicaed Parameric Curves and Derivaives In he y plane, he graph of he parameric equaions = 5 + and y= for, is a
AP Calculus BC Chaper Par AP Eam Problems All problems are NO CALCULATOR unless oherwise indicaed Parameric Curves and Derivaives In he y plane, he graph of he parameric equaions = 5 + and y= for, is a
!!"#"$%&#'()!"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./0)1-*23)
 "#"$%&#'()"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./)1-*) #$%&'()*+,&',-.%,/)*+,-&1*#$)()5*6$+$%*,7&*-'-&1*(,-&*6&,7.$%$+*&%'(*8$&',-,%'-&1*(,-&*6&,79*(&,%: ;..,*&1$&$.$%&'()*1$$.,'&',-9*(&,%)?%*,('&5
"#"$%&#'()"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./)1-*) #$%&'()*+,&',-.%,/)*+,-&1*#$)()5*6$+$%*,7&*-'-&1*(,-&*6&,7.$%$+*&%'(*8$&',-,%'-&1*(,-&*6&,79*(&,%: ;..,*&1$&$.$%&'()*1$$.,'&',-9*(&,%)?%*,('&5
Math 334 Test 1 KEY Spring 2010 Section: 001. Instructor: Scott Glasgow Dates: May 10 and 11.
 1 Mah 334 Tes 1 KEY Spring 21 Secion: 1 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Daes: Ma 1 and 11. Do NOT wrie on his problem saemen bookle, excep for our indicaion of following he honor code jus below. No credi will be
1 Mah 334 Tes 1 KEY Spring 21 Secion: 1 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Daes: Ma 1 and 11. Do NOT wrie on his problem saemen bookle, excep for our indicaion of following he honor code jus below. No credi will be
ln 2 1 ln y x c y C x
 Lecure 14 Appendi B: Some sample problems from Boas Here are some soluions o he sample problems assigned for Chaper 8 8: 6 Soluion: We wan o find he soluion o he following firs order equaion using separaion
Lecure 14 Appendi B: Some sample problems from Boas Here are some soluions o he sample problems assigned for Chaper 8 8: 6 Soluion: We wan o find he soluion o he following firs order equaion using separaion
u(x) = e x 2 y + 2 ) Integrate and solve for x (1 + x)y + y = cos x Answer: Divide both sides by 1 + x and solve for y. y = x y + cos x
 . 1 Mah 211 Homework #3 February 2, 2001 2.4.3. y + (2/x)y = (cos x)/x 2 Answer: Compare y + (2/x) y = (cos x)/x 2 wih y = a(x)x + f(x)and noe ha a(x) = 2/x. Consequenly, an inegraing facor is found wih
. 1 Mah 211 Homework #3 February 2, 2001 2.4.3. y + (2/x)y = (cos x)/x 2 Answer: Compare y + (2/x) y = (cos x)/x 2 wih y = a(x)x + f(x)and noe ha a(x) = 2/x. Consequenly, an inegraing facor is found wih
23.2. Representing Periodic Functions by Fourier Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Answers to 1 Homework
 Answers o Homework. x + and y x 5 y To eliminae he parameer, solve for x. Subsiue ino y s equaion o ge y x.. x and y, x y x To eliminae he parameer, solve for. Subsiue ino y s equaion o ge x y, x. (Noe:
Answers o Homework. x + and y x 5 y To eliminae he parameer, solve for x. Subsiue ino y s equaion o ge y x.. x and y, x y x To eliminae he parameer, solve for. Subsiue ino y s equaion o ge x y, x. (Noe:
Elementary Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems
 Elemenar Differenial Equaions and Boundar Value Problems Boce. & DiPrima 9 h Ediion Chaper 1: Inroducion 1006003 คณ ตศาสตร ว ศวกรรม 3 สาขาว ชาว ศวกรรมคอมพ วเตอร ป การศ กษา 1/2555 ผศ.ดร.อร ญญา ผศ.ดร.สมศ
Elemenar Differenial Equaions and Boundar Value Problems Boce. & DiPrima 9 h Ediion Chaper 1: Inroducion 1006003 คณ ตศาสตร ว ศวกรรม 3 สาขาว ชาว ศวกรรมคอมพ วเตอร ป การศ กษา 1/2555 ผศ.ดร.อร ญญา ผศ.ดร.สมศ
Chapters 6 & 7: Trigonometric Functions of Angles and Real Numbers. Divide both Sides by 180
 Algebra Chapers & : Trigonomeric Funcions of Angles and Real Numbers Chapers & : Trigonomeric Funcions of Angles and Real Numbers - Angle Measures Radians: - a uni (rad o measure he size of an angle. rad
Algebra Chapers & : Trigonomeric Funcions of Angles and Real Numbers Chapers & : Trigonomeric Funcions of Angles and Real Numbers - Angle Measures Radians: - a uni (rad o measure he size of an angle. rad
( ) = 0.43 kj = 430 J. Solutions 9 1. Solutions to Miscellaneous Exercise 9 1. Let W = work done then 0.
 Soluions 9 Soluions o Miscellaneous Exercise 9. Le W work done hen.9 W PdV Using Simpson's rule (9.) we have. W { 96 + [ 58 + 6 + 77 + 5 ] + [ + 99 + 6 ]+ }. kj. Using Simpson's rule (9.) again: W.5.6
Soluions 9 Soluions o Miscellaneous Exercise 9. Le W work done hen.9 W PdV Using Simpson's rule (9.) we have. W { 96 + [ 58 + 6 + 77 + 5 ] + [ + 99 + 6 ]+ }. kj. Using Simpson's rule (9.) again: W.5.6
Math 2142 Exam 1 Review Problems. x 2 + f (0) 3! for the 3rd Taylor polynomial at x = 0. To calculate the various quantities:
 Mah 4 Eam Review Problems Problem. Calculae he 3rd Taylor polynomial for arcsin a =. Soluion. Le f() = arcsin. For his problem, we use he formula f() + f () + f ()! + f () 3! for he 3rd Taylor polynomial
Mah 4 Eam Review Problems Problem. Calculae he 3rd Taylor polynomial for arcsin a =. Soluion. Le f() = arcsin. For his problem, we use he formula f() + f () + f ()! + f () 3! for he 3rd Taylor polynomial
MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS 4758
 OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS Advanced Subsidiary General Cerificae of Educaion Advanced General Cerificae of Educaion MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS 4758 Differenial Equaions Thursday 5 JUNE 006 Afernoon
OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS Advanced Subsidiary General Cerificae of Educaion Advanced General Cerificae of Educaion MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS 4758 Differenial Equaions Thursday 5 JUNE 006 Afernoon
ENGI 9420 Engineering Analysis Assignment 2 Solutions
 ENGI 940 Engineering Analysis Assignmen Soluions 0 Fall [Second order ODEs, Laplace ransforms; Secions.0-.09]. Use Laplace ransforms o solve he iniial value problem [0] dy y, y( 0) 4 d + [This was Quesion
ENGI 940 Engineering Analysis Assignmen Soluions 0 Fall [Second order ODEs, Laplace ransforms; Secions.0-.09]. Use Laplace ransforms o solve he iniial value problem [0] dy y, y( 0) 4 d + [This was Quesion
ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS PAPER 1
 000-CE A MATH PAPER HONG KONG EXAMINATIONS AUTHORITY HONG KONG CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION EXAMINATION 000 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS PAPER 8.0 am 0.0 am ( hours This paper mus be answered in English. Answer
000-CE A MATH PAPER HONG KONG EXAMINATIONS AUTHORITY HONG KONG CERTIFICATE OF EDUCATION EXAMINATION 000 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICS PAPER 8.0 am 0.0 am ( hours This paper mus be answered in English. Answer
Problem Set 7-7. dv V ln V = kt + C. 20. Assume that df/dt still equals = F RF. df dr = =
 20. Assume ha df/d sill equals = F + 0.02RF. df dr df/ d F+ 0. 02RF = = 2 dr/ d R 0. 04RF 0. 01R 10 df 11. 2 R= 70 and F = 1 = = 0. 362K dr 31 21. 0 F (70, 30) (70, 1) R 100 Noe ha he slope a (70, 1) is
20. Assume ha df/d sill equals = F + 0.02RF. df dr df/ d F+ 0. 02RF = = 2 dr/ d R 0. 04RF 0. 01R 10 df 11. 2 R= 70 and F = 1 = = 0. 362K dr 31 21. 0 F (70, 30) (70, 1) R 100 Noe ha he slope a (70, 1) is
APPM 2360 Homework Solutions, Due June 10
 2.2.2: Find general soluions for he equaion APPM 2360 Homework Soluions, Due June 10 Soluion: Finding he inegraing facor, dy + 2y = 3e µ) = e 2) = e 2 Muliplying he differenial equaion by he inegraing
2.2.2: Find general soluions for he equaion APPM 2360 Homework Soluions, Due June 10 Soluion: Finding he inegraing facor, dy + 2y = 3e µ) = e 2) = e 2 Muliplying he differenial equaion by he inegraing
MA 366 Review - Test # 1
 MA 366 Review - Tes # 1 Fall 5 () Resuls from Calculus: differeniaion formulas, implici differeniaion, Chain Rule; inegraion formulas, inegraion b pars, parial fracions, oher inegraion echniques. (1) Order
MA 366 Review - Tes # 1 Fall 5 () Resuls from Calculus: differeniaion formulas, implici differeniaion, Chain Rule; inegraion formulas, inegraion b pars, parial fracions, oher inegraion echniques. (1) Order
Differential Equations
 Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
10.1 EXERCISES. y 2 t 2. y 1 t y t 3. y e
 66 CHAPTER PARAMETRIC EQUATINS AND PLAR CRDINATES SLUTIN We use a graphing device o produce he graphs for he cases a,,.5,.,,.5,, and shown in Figure 7. Noice ha all of hese curves (ecep he case a ) have
66 CHAPTER PARAMETRIC EQUATINS AND PLAR CRDINATES SLUTIN We use a graphing device o produce he graphs for he cases a,,.5,.,,.5,, and shown in Figure 7. Noice ha all of hese curves (ecep he case a ) have
4.6 One Dimensional Kinematics and Integration
 4.6 One Dimensional Kinemaics and Inegraion When he acceleraion a( of an objec is a non-consan funcion of ime, we would like o deermine he ime dependence of he posiion funcion x( and he x -componen of
4.6 One Dimensional Kinemaics and Inegraion When he acceleraion a( of an objec is a non-consan funcion of ime, we would like o deermine he ime dependence of he posiion funcion x( and he x -componen of
Mathematics Paper- II
 R Prerna Tower, Road No -, Conracors Area, Bisupur, Jamsedpur - 8, Tel - (65789, www.prernaclasses.com Maemaics Paper- II Jee Advance PART III - MATHEMATICS SECTION - : (One or more opions correc Type
R Prerna Tower, Road No -, Conracors Area, Bisupur, Jamsedpur - 8, Tel - (65789, www.prernaclasses.com Maemaics Paper- II Jee Advance PART III - MATHEMATICS SECTION - : (One or more opions correc Type
Math Final Exam Solutions
 Mah 246 - Final Exam Soluions Friday, July h, 204 () Find explici soluions and give he inerval of definiion o he following iniial value problems (a) ( + 2 )y + 2y = e, y(0) = 0 Soluion: In normal form,
Mah 246 - Final Exam Soluions Friday, July h, 204 () Find explici soluions and give he inerval of definiion o he following iniial value problems (a) ( + 2 )y + 2y = e, y(0) = 0 Soluion: In normal form,
Math 10B: Mock Mid II. April 13, 2016
 Name: Soluions Mah 10B: Mock Mid II April 13, 016 1. ( poins) Sae, wih jusificaion, wheher he following saemens are rue or false. (a) If a 3 3 marix A saisfies A 3 A = 0, hen i canno be inverible. True.
Name: Soluions Mah 10B: Mock Mid II April 13, 016 1. ( poins) Sae, wih jusificaion, wheher he following saemens are rue or false. (a) If a 3 3 marix A saisfies A 3 A = 0, hen i canno be inverible. True.
dy dx = xey (a) y(0) = 2 (b) y(1) = 2.5 SOLUTION: See next page
 Assignmen 1 MATH 2270 SOLUTION Please wrie ou complee soluions for each of he following 6 problems (one more will sill be added). You may, of course, consul wih your classmaes, he exbook or oher resources,
Assignmen 1 MATH 2270 SOLUTION Please wrie ou complee soluions for each of he following 6 problems (one more will sill be added). You may, of course, consul wih your classmaes, he exbook or oher resources,
Topics covered in tutorial 01: 1. Review of definite integrals 2. Physical Application 3. Area between curves. 1. Review of definite integrals
 MATH4 Calculus II (8 Spring) MATH 4 Tuorial Noes Tuorial Noes (Phyllis LIANG) IA: Phyllis LIANG Email: masliang@us.hk Homepage: hps://masliang.people.us.hk Office: Room 3 (Lif/Lif 3) Phone number: 3587453
MATH4 Calculus II (8 Spring) MATH 4 Tuorial Noes Tuorial Noes (Phyllis LIANG) IA: Phyllis LIANG Email: masliang@us.hk Homepage: hps://masliang.people.us.hk Office: Room 3 (Lif/Lif 3) Phone number: 3587453
Additional Exercises for Chapter What is the slope-intercept form of the equation of the line given by 3x + 5y + 2 = 0?
 ddiional Eercises for Caper 5 bou Lines, Slopes, and Tangen Lines 39. Find an equaion for e line roug e wo poins (, 7) and (5, ). 4. Wa is e slope-inercep form of e equaion of e line given by 3 + 5y +
ddiional Eercises for Caper 5 bou Lines, Slopes, and Tangen Lines 39. Find an equaion for e line roug e wo poins (, 7) and (5, ). 4. Wa is e slope-inercep form of e equaion of e line given by 3 + 5y +
23.5. Half-Range Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Half-Range Series 2.5 Inroducion In his Secion we address he following problem: Can we find a Fourier series expansion of a funcion defined over a finie inerval? Of course we recognise ha such a funcion
Half-Range Series 2.5 Inroducion In his Secion we address he following problem: Can we find a Fourier series expansion of a funcion defined over a finie inerval? Of course we recognise ha such a funcion
8. Basic RL and RC Circuits
 8. Basic L and C Circuis This chaper deals wih he soluions of he responses of L and C circuis The analysis of C and L circuis leads o a linear differenial equaion This chaper covers he following opics
8. Basic L and C Circuis This chaper deals wih he soluions of he responses of L and C circuis The analysis of C and L circuis leads o a linear differenial equaion This chaper covers he following opics
UCLA: Math 3B Problem set 3 (solutions) Fall, 2018
 UCLA: Mah 3B Problem se 3 (soluions) Fall, 28 This problem se concenraes on pracice wih aniderivaives. You will ge los of pracice finding simple aniderivaives as well as finding aniderivaives graphically
UCLA: Mah 3B Problem se 3 (soluions) Fall, 28 This problem se concenraes on pracice wih aniderivaives. You will ge los of pracice finding simple aniderivaives as well as finding aniderivaives graphically
Exam 1 Solutions. 1 Question 1. February 10, Part (A) 1.2 Part (B) To find equilibrium solutions, set P (t) = C = dp
 Exam Soluions Februar 0, 05 Quesion. Par (A) To find equilibrium soluions, se P () = C = = 0. This implies: = P ( P ) P = P P P = P P = P ( + P ) = 0 The equilibrium soluion are hus P () = 0 and P () =..
Exam Soluions Februar 0, 05 Quesion. Par (A) To find equilibrium soluions, se P () = C = = 0. This implies: = P ( P ) P = P P P = P P = P ( + P ) = 0 The equilibrium soluion are hus P () = 0 and P () =..
LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION
 CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
System of Linear Differential Equations
 Sysem of Linear Differenial Equaions In "Ordinary Differenial Equaions" we've learned how o solve a differenial equaion for a variable, such as: y'k5$e K2$x =0 solve DE yx = K 5 2 ek2 x C_C1 2$y''C7$y
Sysem of Linear Differenial Equaions In "Ordinary Differenial Equaions" we've learned how o solve a differenial equaion for a variable, such as: y'k5$e K2$x =0 solve DE yx = K 5 2 ek2 x C_C1 2$y''C7$y
Math 116 Second Midterm March 21, 2016
 Mah 6 Second Miderm March, 06 UMID: EXAM SOLUTIONS Iniials: Insrucor: Secion:. Do no open his exam unil you are old o do so.. Do no wrie your name anywhere on his exam. 3. This exam has pages including
Mah 6 Second Miderm March, 06 UMID: EXAM SOLUTIONS Iniials: Insrucor: Secion:. Do no open his exam unil you are old o do so.. Do no wrie your name anywhere on his exam. 3. This exam has pages including
Lecture 13 RC/RL Circuits, Time Dependent Op Amp Circuits
 Lecure 13 RC/RL Circuis, Time Dependen Op Amp Circuis RL Circuis The seps involved in solving simple circuis conaining dc sources, resisances, and one energy-sorage elemen (inducance or capaciance) are:
Lecure 13 RC/RL Circuis, Time Dependen Op Amp Circuis RL Circuis The seps involved in solving simple circuis conaining dc sources, resisances, and one energy-sorage elemen (inducance or capaciance) are:
ACCUMULATION. Section 7.5 Calculus AP/Dual, Revised /26/2018 7:27 PM 7.5A: Accumulation 1
 ACCUMULATION Secion 7.5 Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 2019 vie.dang@humbleisd.ne 12/26/2018 7:27 PM 7.5A: Accumulaion 1 APPLICATION PROBLEMS A. Undersand he quesion. I is ofen no necessary o as much compuaion
ACCUMULATION Secion 7.5 Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 2019 vie.dang@humbleisd.ne 12/26/2018 7:27 PM 7.5A: Accumulaion 1 APPLICATION PROBLEMS A. Undersand he quesion. I is ofen no necessary o as much compuaion
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Kinematics. Position. Lectures 3 and 4 Motion in One Dimension. A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan
 Ground Rules PC11 Fundamenals of Physics I Lecures 3 and 4 Moion in One Dimension A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan 1 Swich off your handphone and pager Swich off your lapop compuer and keep i No alking while lecure
Ground Rules PC11 Fundamenals of Physics I Lecures 3 and 4 Moion in One Dimension A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan 1 Swich off your handphone and pager Swich off your lapop compuer and keep i No alking while lecure
Some Basic Information about M-S-D Systems
 Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Review - Quiz # 1. 1 g(y) dy = f(x) dx. y x. = u, so that y = xu and dy. dx (Sometimes you may want to use the substitution x y
 Review - Quiz # 1 (1) Solving Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Separable Equaions (SE). d = f() g() Mehod of Soluion : 1 g() d = f() (The soluions ma be given implicil b he above formula. Remember,
Review - Quiz # 1 (1) Solving Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Separable Equaions (SE). d = f() g() Mehod of Soluion : 1 g() d = f() (The soluions ma be given implicil b he above formula. Remember,
Class Notes 1: Introduction. MAE 82 Engineering Mathematics
 Class Noes 1: Inroducion MAE 82 Engineering Mahemaics CHANGE Rae of Change Basic Mahemaical Models Man of he principles or laws underling he behavior of he naural world are saemens or relaions involving
Class Noes 1: Inroducion MAE 82 Engineering Mahemaics CHANGE Rae of Change Basic Mahemaical Models Man of he principles or laws underling he behavior of he naural world are saemens or relaions involving
Complete solutions to Exercise 14(b) 1. Very similar to EXAMPLE 4. We have same characteristic equation:
 Soluions 4(b) Complee soluions o Exercise 4(b). Very similar o EXAMPE 4. We have same characerisic equaion: 5 i Ae = + Be By using he given iniial condiions we obain he simulaneous equaions A+ B= 0 5A
Soluions 4(b) Complee soluions o Exercise 4(b). Very similar o EXAMPE 4. We have same characerisic equaion: 5 i Ae = + Be By using he given iniial condiions we obain he simulaneous equaions A+ B= 0 5A
Section 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equations; Method of Undetermined Coefficients
 Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Chaper 5 Eponenial and Logarihmic Funcions Chaper 5 Prerequisie Skills Chaper 5 Prerequisie Skills Quesion 1 Page 50 a) b) c) Answers may vary. For eample: The equaion of he inverse is y = log since log
Chaper 5 Eponenial and Logarihmic Funcions Chaper 5 Prerequisie Skills Chaper 5 Prerequisie Skills Quesion 1 Page 50 a) b) c) Answers may vary. For eample: The equaion of he inverse is y = log since log
Second Order Linear Differential Equations
 Second Order Linear Differenial Equaions Second order linear equaions wih consan coefficiens; Fundamenal soluions; Wronskian; Exisence and Uniqueness of soluions; he characerisic equaion; soluions of homogeneous
Second Order Linear Differenial Equaions Second order linear equaions wih consan coefficiens; Fundamenal soluions; Wronskian; Exisence and Uniqueness of soluions; he characerisic equaion; soluions of homogeneous
Kinematics Vocabulary. Kinematics and One Dimensional Motion. Position. Coordinate System in One Dimension. Kinema means movement 8.
 Kinemaics Vocabulary Kinemaics and One Dimensional Moion 8.1 WD1 Kinema means movemen Mahemaical descripion of moion Posiion Time Inerval Displacemen Velociy; absolue value: speed Acceleraion Averages
Kinemaics Vocabulary Kinemaics and One Dimensional Moion 8.1 WD1 Kinema means movemen Mahemaical descripion of moion Posiion Time Inerval Displacemen Velociy; absolue value: speed Acceleraion Averages
Solutionbank Edexcel AS and A Level Modular Mathematics
 Page of 4 Soluionbank Edexcel AS and A Level Modular Mahemaics Exercise A, Quesion Quesion: Skech he graphs of (a) y = e x + (b) y = 4e x (c) y = e x 3 (d) y = 4 e x (e) y = 6 + 0e x (f) y = 00e x + 0
Page of 4 Soluionbank Edexcel AS and A Level Modular Mahemaics Exercise A, Quesion Quesion: Skech he graphs of (a) y = e x + (b) y = 4e x (c) y = e x 3 (d) y = 4 e x (e) y = 6 + 0e x (f) y = 00e x + 0
CHAPTER 6: FIRST-ORDER CIRCUITS
 EEE5: CI CUI T THEOY CHAPTE 6: FIST-ODE CICUITS 6. Inroducion This chaper considers L and C circuis. Applying he Kirshoff s law o C and L circuis produces differenial equaions. The differenial equaions
EEE5: CI CUI T THEOY CHAPTE 6: FIST-ODE CICUITS 6. Inroducion This chaper considers L and C circuis. Applying he Kirshoff s law o C and L circuis produces differenial equaions. The differenial equaions
AP CALCULUS AB 2003 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Quesion A blood vessel is 6 millimeers (mm) long Disance wih circular cross secions of varying diameer. x (mm) 6 8 4 6 Diameer The able above gives he measuremens of he B(x)
SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Quesion A blood vessel is 6 millimeers (mm) long Disance wih circular cross secions of varying diameer. x (mm) 6 8 4 6 Diameer The able above gives he measuremens of he B(x)
3 at MAC 1140 TEST 3 NOTES. 5.1 and 5.2. Exponential Functions. Form I: P is the y-intercept. (0, P) When a > 1: a = growth factor = 1 + growth rate
 1 5.1 and 5. Eponenial Funcions Form I: Y Pa, a 1, a > 0 P is he y-inercep. (0, P) When a > 1: a = growh facor = 1 + growh rae The equaion can be wrien as The larger a is, he seeper he graph is. Y P( 1
1 5.1 and 5. Eponenial Funcions Form I: Y Pa, a 1, a > 0 P is he y-inercep. (0, P) When a > 1: a = growh facor = 1 + growh rae The equaion can be wrien as The larger a is, he seeper he graph is. Y P( 1
y = (y 1)*(y 3) t
 MATH 66 SPR REVIEW DEFINITION OF SOLUTION A funcion = () is a soluion of he differenial equaion d=d = f(; ) on he inerval ff < < fi if (d=d)() =f(; ()) for each so ha ff
MATH 66 SPR REVIEW DEFINITION OF SOLUTION A funcion = () is a soluion of he differenial equaion d=d = f(; ) on he inerval ff < < fi if (d=d)() =f(; ()) for each so ha ff
Math 115 Final Exam December 14, 2017
 On my honor, as a suden, I have neiher given nor received unauhorized aid on his academic work. Your Iniials Only: Iniials: Do no wrie in his area Mah 5 Final Exam December, 07 Your U-M ID # (no uniqname):
On my honor, as a suden, I have neiher given nor received unauhorized aid on his academic work. Your Iniials Only: Iniials: Do no wrie in his area Mah 5 Final Exam December, 07 Your U-M ID # (no uniqname):
INDEX. Transient analysis 1 Initial Conditions 1
 INDEX Secion Page Transien analysis 1 Iniial Condiions 1 Please inform me of your opinion of he relaive emphasis of he review maerial by simply making commens on his page and sending i o me a: Frank Mera
INDEX Secion Page Transien analysis 1 Iniial Condiions 1 Please inform me of your opinion of he relaive emphasis of he review maerial by simply making commens on his page and sending i o me a: Frank Mera
Parametrics and Vectors (BC Only)
 Paramerics and Vecors (BC Only) The following relaionships should be learned and memorized. The paricle s posiion vecor is r() x(), y(). The velociy vecor is v(),. The speed is he magniude of he velociy
Paramerics and Vecors (BC Only) The following relaionships should be learned and memorized. The paricle s posiion vecor is r() x(), y(). The velociy vecor is v(),. The speed is he magniude of he velociy
WEEK-3 Recitation PHYS 131. of the projectile s velocity remains constant throughout the motion, since the acceleration a x
 WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
PMT. Version 1.0: abc. General Certificate of Education. Mathematics MPC4 Pure Core 4. Mark Scheme examination - January series
 Version.: 8 abc General Cerificae of Educaion Mahemaics 66 MPC Pure Core Mark Scheme 8 eaminaion - January series Mark schemes are prepared by he Principal Eaminer and considered, ogeher wih he relevan
Version.: 8 abc General Cerificae of Educaion Mahemaics 66 MPC Pure Core Mark Scheme 8 eaminaion - January series Mark schemes are prepared by he Principal Eaminer and considered, ogeher wih he relevan
Second Order Linear Differential Equations
 Second Order Linear Differenial Equaions Second order linear equaions wih consan coefficiens; Fundamenal soluions; Wronskian; Exisence and Uniqueness of soluions; he characerisic equaion; soluions of homogeneous
Second Order Linear Differenial Equaions Second order linear equaions wih consan coefficiens; Fundamenal soluions; Wronskian; Exisence and Uniqueness of soluions; he characerisic equaion; soluions of homogeneous
Solutions from Chapter 9.1 and 9.2
 Soluions from Chaper 9 and 92 Secion 9 Problem # This basically boils down o an exercise in he chain rule from calculus We are looking for soluions of he form: u( x) = f( k x c) where k x R 3 and k is
Soluions from Chaper 9 and 92 Secion 9 Problem # This basically boils down o an exercise in he chain rule from calculus We are looking for soluions of he form: u( x) = f( k x c) where k x R 3 and k is
10. State Space Methods
 . Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
. Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Additional materials (enclosed):
 ADVANCED GCE 78/0 MATHEMATICS (MEI) Differenial Equaions THURSDAY JANUARY 008 Morning Time: hour 30 minues Addiional maerials (enclosed): None Addiional maerials (required): Answer Bookle (8 pages) Graph
ADVANCED GCE 78/0 MATHEMATICS (MEI) Differenial Equaions THURSDAY JANUARY 008 Morning Time: hour 30 minues Addiional maerials (enclosed): None Addiional maerials (required): Answer Bookle (8 pages) Graph
Motion along a Straight Line
 chaper 2 Moion along a Sraigh Line verage speed and average velociy (Secion 2.2) 1. Velociy versus speed Cone in he ebook: fer Eample 2. Insananeous velociy and insananeous acceleraion (Secions 2.3, 2.4)
chaper 2 Moion along a Sraigh Line verage speed and average velociy (Secion 2.2) 1. Velociy versus speed Cone in he ebook: fer Eample 2. Insananeous velociy and insananeous acceleraion (Secions 2.3, 2.4)
AP Calculus BC - Parametric equations and vectors Chapter 9- AP Exam Problems solutions
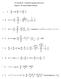 AP Calculus BC - Parameric equaions and vecors Chaper 9- AP Exam Problems soluions. A 5 and 5. B A, 4 + 8. C A, 4 + 4 8 ; he poin a is (,). y + ( x ) x + 4 4. e + e D A, slope.5 6 e e e 5. A d hus d d
AP Calculus BC - Parameric equaions and vecors Chaper 9- AP Exam Problems soluions. A 5 and 5. B A, 4 + 8. C A, 4 + 4 8 ; he poin a is (,). y + ( x ) x + 4 4. e + e D A, slope.5 6 e e e 5. A d hus d d
AP CALCULUS BC 2016 SCORING GUIDELINES
 6 SCORING GUIDELINES Quesion A ime, he posiion of a paricle moving in he xy-plane is given by he parameric funcions ( x ( ), y ( )), where = + sin ( ). The graph of y, consising of hree line segmens, is
6 SCORING GUIDELINES Quesion A ime, he posiion of a paricle moving in he xy-plane is given by he parameric funcions ( x ( ), y ( )), where = + sin ( ). The graph of y, consising of hree line segmens, is
Chapter 7: Solving Trig Equations
 Haberman MTH Secion I: The Trigonomeric Funcions Chaper 7: Solving Trig Equaions Le s sar by solving a couple of equaions ha involve he sine funcion EXAMPLE a: Solve he equaion sin( ) The inverse funcions
Haberman MTH Secion I: The Trigonomeric Funcions Chaper 7: Solving Trig Equaions Le s sar by solving a couple of equaions ha involve he sine funcion EXAMPLE a: Solve he equaion sin( ) The inverse funcions
2610 MEI Differential Equations January 2005 Mark Scheme
 60 MEI Differenial Equaions January 00 Mark Scheme (i) I ep( ) = M = e A d ( ) e y e e y + = M muliply d ( e y) = e F follow heir inegraing facor e y = e M inegrae = + A e A ( e A ) y = e + F divide by
60 MEI Differenial Equaions January 00 Mark Scheme (i) I ep( ) = M = e A d ( ) e y e e y + = M muliply d ( e y) = e F follow heir inegraing facor e y = e M inegrae = + A e A ( e A ) y = e + F divide by
1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION
 1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION 1.1 Kinemaics Equaions s = u + 1 a and s = v 1 a s = 1 (u + v) v = u + as 1. Displacemen-Time Graph Gradien = speed 1.3 Velociy-Time Graph Gradien = acceleraion Area under
1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION 1.1 Kinemaics Equaions s = u + 1 a and s = v 1 a s = 1 (u + v) v = u + as 1. Displacemen-Time Graph Gradien = speed 1.3 Velociy-Time Graph Gradien = acceleraion Area under
dt = C exp (3 ln t 4 ). t 4 W = C exp ( ln(4 t) 3) = C(4 t) 3.
 Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
Week 1 Lecture 2 Problems 2, 5. What if something oscillates with no obvious spring? What is ω? (problem set problem)
 Week 1 Lecure Problems, 5 Wha if somehing oscillaes wih no obvious spring? Wha is ω? (problem se problem) Sar wih Try and ge o SHM form E. Full beer can in lake, oscillaing F = m & = ge rearrange: F =
Week 1 Lecure Problems, 5 Wha if somehing oscillaes wih no obvious spring? Wha is ω? (problem se problem) Sar wih Try and ge o SHM form E. Full beer can in lake, oscillaing F = m & = ge rearrange: F =
Math 1b. Calculus, Series, and Differential Equations. Final Exam Solutions
 Mah b. Calculus, Series, and Differenial Equaions. Final Exam Soluions Spring 6. (9 poins) Evaluae he following inegrals. 5x + 7 (a) (x + )(x + ) dx. (b) (c) x arcan x dx x(ln x) dx Soluion. (a) Using
Mah b. Calculus, Series, and Differenial Equaions. Final Exam Soluions Spring 6. (9 poins) Evaluae he following inegrals. 5x + 7 (a) (x + )(x + ) dx. (b) (c) x arcan x dx x(ln x) dx Soluion. (a) Using
AQA Maths M2. Topic Questions from Papers. Differential Equations. Answers
 AQA Mahs M Topic Quesions from Papers Differenial Equaions Answers PhysicsAndMahsTuor.com Q Soluion Marks Toal Commens M 600 0 = A Applying Newonís second law wih 0 and. Correc equaion = 0 dm Separaing
AQA Mahs M Topic Quesions from Papers Differenial Equaions Answers PhysicsAndMahsTuor.com Q Soluion Marks Toal Commens M 600 0 = A Applying Newonís second law wih 0 and. Correc equaion = 0 dm Separaing
6.2 Transforms of Derivatives and Integrals.
 SEC. 6.2 Transforms of Derivaives and Inegrals. ODEs 2 3 33 39 23. Change of scale. If l( f ()) F(s) and c is any 33 45 APPLICATION OF s-shifting posiive consan, show ha l( f (c)) F(s>c)>c (Hin: In Probs.
SEC. 6.2 Transforms of Derivaives and Inegrals. ODEs 2 3 33 39 23. Change of scale. If l( f ()) F(s) and c is any 33 45 APPLICATION OF s-shifting posiive consan, show ha l( f (c)) F(s>c)>c (Hin: In Probs.
The equation to any straight line can be expressed in the form:
 Sring Graphs Par 1 Answers 1 TI-Nspire Invesigaion Suden min Aims Deermine a series of equaions of sraigh lines o form a paern similar o ha formed by he cables on he Jerusalem Chords Bridge. Deermine he
Sring Graphs Par 1 Answers 1 TI-Nspire Invesigaion Suden min Aims Deermine a series of equaions of sraigh lines o form a paern similar o ha formed by he cables on he Jerusalem Chords Bridge. Deermine he
2.1: What is physics? Ch02: Motion along a straight line. 2.2: Motion. 2.3: Position, Displacement, Distance
 Ch: Moion along a sraigh line Moion Posiion and Displacemen Average Velociy and Average Speed Insananeous Velociy and Speed Acceleraion Consan Acceleraion: A Special Case Anoher Look a Consan Acceleraion
Ch: Moion along a sraigh line Moion Posiion and Displacemen Average Velociy and Average Speed Insananeous Velociy and Speed Acceleraion Consan Acceleraion: A Special Case Anoher Look a Consan Acceleraion
Ch.1. Group Work Units. Continuum Mechanics Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPC
 Ch.. Group Work Unis Coninuum Mechanics Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPC Uni 2 Jusify wheher he following saemens are rue or false: a) Two sreamlines, corresponding o a same insan of ime, can never inersec
Ch.. Group Work Unis Coninuum Mechanics Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPC Uni 2 Jusify wheher he following saemens are rue or false: a) Two sreamlines, corresponding o a same insan of ime, can never inersec
Chapter 5 Kinematics
 Chaper 5 Kinemaics In he firs place, wha do we mean b ime and space? I urns ou ha hese deep philosophical quesions have o be analzed ver carefull in phsics, and his is no eas o do. The heor of relaivi
Chaper 5 Kinemaics In he firs place, wha do we mean b ime and space? I urns ou ha hese deep philosophical quesions have o be analzed ver carefull in phsics, and his is no eas o do. The heor of relaivi
THE SINE INTEGRAL. x dt t
 THE SINE INTEGRAL As one learns in elemenary calculus, he limi of sin(/ as vanishes is uniy. Furhermore he funcion is even and has an infinie number of zeros locaed a ±n for n1,,3 Is plo looks like his-
THE SINE INTEGRAL As one learns in elemenary calculus, he limi of sin(/ as vanishes is uniy. Furhermore he funcion is even and has an infinie number of zeros locaed a ±n for n1,,3 Is plo looks like his-
- If one knows that a magnetic field has a symmetry, one may calculate the magnitude of B by use of Ampere s law: The integral of scalar product
 11.1 APPCATON OF AMPEE S AW N SYMMETC MAGNETC FEDS - f one knows ha a magneic field has a symmery, one may calculae he magniude of by use of Ampere s law: The inegral of scalar produc Closed _ pah * d
11.1 APPCATON OF AMPEE S AW N SYMMETC MAGNETC FEDS - f one knows ha a magneic field has a symmery, one may calculae he magniude of by use of Ampere s law: The inegral of scalar produc Closed _ pah * d
MA6151 MATHEMATICS I PART B UNIVERSITY QUESTIONS. (iv) ( i = 1, 2, 3,., n) are the non zero eigen values of A, then prove that (1) k i.
 UNIT MATRICES METHOD EIGEN VALUES AND EIGEN VECTORS Find he Eigen values and he Eigenvecors of he following marices (i) ** 3 6 3 (ii) 6 (iii) 3 (iv) 0 3 Prove ha he Eigen values of a real smmeric mari
UNIT MATRICES METHOD EIGEN VALUES AND EIGEN VECTORS Find he Eigen values and he Eigenvecors of he following marices (i) ** 3 6 3 (ii) 6 (iii) 3 (iv) 0 3 Prove ha he Eigen values of a real smmeric mari
CH.7. PLANE LINEAR ELASTICITY. Continuum Mechanics Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPC
 CH.7. PLANE LINEAR ELASTICITY Coninuum Mechanics Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPC Overview Plane Linear Elasici Theor Plane Sress Simplifing Hpohesis Srain Field Consiuive Equaion Displacemen Field The Linear
CH.7. PLANE LINEAR ELASTICITY Coninuum Mechanics Course (MMC) - ETSECCPB - UPC Overview Plane Linear Elasici Theor Plane Sress Simplifing Hpohesis Srain Field Consiuive Equaion Displacemen Field The Linear
Math 116 Practice for Exam 2
 Mah 6 Pracice for Exam Generaed Ocober 3, 7 Name: SOLUTIONS Insrucor: Secion Number:. This exam has 5 quesions. Noe ha he problems are no of equal difficuly, so you may wan o skip over and reurn o a problem
Mah 6 Pracice for Exam Generaed Ocober 3, 7 Name: SOLUTIONS Insrucor: Secion Number:. This exam has 5 quesions. Noe ha he problems are no of equal difficuly, so you may wan o skip over and reurn o a problem
6. 6 v ; degree = 7; leading coefficient = 6; 7. The expression has 3 terms; t p no; subtracting x from 3x ( 3x x 2x)
 70. a =, r = 0%, = 0. 7. a = 000, r = 0.%, = 00 7. a =, r = 00%, = 7. ( ) = 0,000 0., where = ears 7. ( ) = + 0.0, where = weeks 7 ( ) =,000,000 0., where = das 7 = 77. = 9 7 = 7 geomeric 0. geomeric arihmeic,
70. a =, r = 0%, = 0. 7. a = 000, r = 0.%, = 00 7. a =, r = 00%, = 7. ( ) = 0,000 0., where = ears 7. ( ) = + 0.0, where = weeks 7 ( ) =,000,000 0., where = das 7 = 77. = 9 7 = 7 geomeric 0. geomeric arihmeic,
1.6. Slopes of Tangents and Instantaneous Rate of Change
 1.6 Slopes of Tangens and Insananeous Rae of Change When you hi or kick a ball, he heigh, h, in meres, of he ball can be modelled by he equaion h() 4.9 2 v c. In his equaion, is he ime, in seconds; c represens
1.6 Slopes of Tangens and Insananeous Rae of Change When you hi or kick a ball, he heigh, h, in meres, of he ball can be modelled by he equaion h() 4.9 2 v c. In his equaion, is he ime, in seconds; c represens
1998 Calculus AB Scoring Guidelines
 AB{ / BC{ 1999. The rae a which waer ows ou of a pipe, in gallons per hour, is given by a diereniable funcion R of ime. The able above shows he rae as measured every hours for a {hour period. (a) Use a
AB{ / BC{ 1999. The rae a which waer ows ou of a pipe, in gallons per hour, is given by a diereniable funcion R of ime. The able above shows he rae as measured every hours for a {hour period. (a) Use a
