Math 2214 Solution Test 1B Fall 2017
|
|
|
- Noreen Rosaline Flowers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mah 14 Soluion Tes 1B Fall 017 Problem 1: A ank has a capaci for 500 gallons and conains 0 gallons of waer wih lbs of sal iniiall. A soluion conaining of 8 lbsgal of sal is pumped ino he ank a 10 galsmin. A well sirred mixure flows ou of he ank a he same rae. a) Se up he differenial equaion ha models his siuaion and hen find he soluion ha gives he amoun of sal in he ank a an ime using he inegraing facor. b) Find and explain he limiing value of our soluion. c) Suppose he rae a which he soluion flows ou changes o 8 galsmin. Deermine how long i will ake o fill he ank. Soluion: (18)ps The DE model for amoun of sal a an ime is (0) = lbs of sal 80 wih iniial value The inegraing facor u() = e 80e e d 80e d so e 400e C 400 Ce where C =-398 when (0) = and he soluion is e e 1d e o give us ) ( ) b Limi Limi e lbs of sal of he long erm period. c) The volumn will now be V = 0 + se 500 = 0 + o ge ha = 100 min or 1hr and 40 min. so i will ake one hours and 40 min o fill he ank.
2 Problem : Consider he iniial value problem an( ), (0) 3 ( 1) Find he larges open recangular region on which he soluion for his iniial value problem is guaraneed and is unique. Soluion: (14ps) Since his is a non-linear DE we will consider i o be muli-variable equaion f(,) = an( ) Therefore f (, ), for (0) = 3 ( 1) f an( ) and he parial derivaive is ( 1) Noice ha for boh he funcion and he parial derivaive wih he iniial value (0) = -3, he region mus be and 0 Problem 3: Given he differenial equaion p g ( ) ( ) wih he paricular soluion 5 e, find p() and g(). Show all work and explain reasoning. Soluion: (1ps) Consider he given soluion and work backward in he process o solve a 1 s order linear DE o find he original DE for his soluion. e e e e e e 10e 0e e Now noice ha p() = 10 and g() = 0 for he DE +P() = g()
3 Problem 4: Given he following direcion field, find he possible auonomous differenial equaion associaed wih i and clearl jusif our answer b indicaing exacl wh or wh no each DE is valid or no valid. 1) ( 3)( 1) ) ( 3)( 1) 3) ( 3)( 1) Soluion: (14ps) Since his is an auonomous DE, all isoclines are horizonal. We are ineresed in he equilibrium soluions which are he isoclines wih zero slopes a ever poin. The equilibrium soluions in he Direcion field occur a = -1 and a = -3. When we invesigae he DE in 1) we see ha when = 0 he equilibrium soluions occur a = -1 and = 3. Therefore his is no he correc DE for his direcion field. When we invesigae he DE in ) we see ha he equilibrium are correc when = 0. Bu on furher invesigaion we noice he isocline a = 0 will be = (0 + 3)(0 +1) > 0 bu = 0 clearl has negaive slopes and does no fi his DE. When we invesigae he DE in 3) we see ha he equilibrium are correc when = 0. And on furher invesigaion we noice he isocline a = 0 will be = (-0-3)(0 +1) < 0. B esing a few oher isoclines such as = o ge = (--3)(+1) = - 15 < 0, he direcion field seems o be a correc fi. So 3) is he correc answer.
4 Problem 5: A bod of weigh 18 lbs falls downward wih no iniial veloci. The resisance consan due o air is given o be k = 8. a) Se up iniial value differenial equaion ha models his scenario bu do no solve. b) Is veloci posiive or negaive in he scenario? Wh? c) Is resisance posiive or negaive in he scenario? Wh? d) Suppose ha air resisance is now given o be R = S0 where S is speed. Express R in erms of veloci. Soluion: (15ps) Using he equaion mv mg kv, we have he following; Since weigh is given o be 18 lbs and we know ha mg = weigh, we have ha m(3) = 18 and mass m = 4. So 4v 18 8 v wih iniial value v(0) = 0 To pu in he proper form for a 1 s order linear DE, we have 4v 8v 18 b) Veloci of a dropped falling objec is consider negaive. c) The resisance force is consider o be opposie in sign o he veloci and is herefore posiive. d)-the resisance in he above formula is defined o be R = kv bu is now express as R = S0 where S is speed and R = v 0 where v is negaive so R = -v0
5 Problem 6: Suppose a viral disease is spreading hrough a large populaion a a rae of change modeled b he differenial equaion k where he iniial number of people infeced was equal o 100. In a week a oal of 500 people were infeced. Use he mehod separaion of variables o solve for he number people infeced a an ime. Soluion: (15ps) Given k, wih iniial value = 0, = 100 and = 1 (in weeks), = 500 we have ha 1 d kd 1 1 k C, and C = for = 0 and = and k = 4500 for = 1, = 500 So k C (4 500) ( 1100) 500 people a ime. Problem 7: Given he iniial value problem 0, (), 1) Use Euler s Mehod o esimae (4) wih sep value h = 1. ) Do ou hink his esimae would be close? Explain wh or wh no. Soluion: (1ps) I) Since () = - we have he slope a he poin (, -) will be = -3 and he equaion of he angen line is = We will now evaluae he nex poin = 3 o ge ha (3) = -5. II) Our new poin is now ( 3, -5) wih new slope = 8-5. The equaion of he angen line will be = (-85) + -(15). Now evaluae he nex poin, = 4, o ge ha (4) = -335.
6
Math 2214 Solution Test 1A Spring 2016
 Mah 14 Soluion Tes 1A Spring 016 sec Problem 1: Wha is he larges -inerval for which ( 4) = has a guaraneed + unique soluion for iniial value (-1) = 3 according o he Exisence Uniqueness Theorem? Soluion
Mah 14 Soluion Tes 1A Spring 016 sec Problem 1: Wha is he larges -inerval for which ( 4) = has a guaraneed + unique soluion for iniial value (-1) = 3 according o he Exisence Uniqueness Theorem? Soluion
Math 2214 Solution Test 1 B Spring 2016
 Mah 14 Soluion Te 1 B Spring 016 Problem 1: Ue eparaion of ariable o ole he Iniial alue DE Soluion (14p) e =, (0) = 0 d = e e d e d = o = ln e d uing u-du b leing u = e 1 e = + where C = for he iniial
Mah 14 Soluion Te 1 B Spring 016 Problem 1: Ue eparaion of ariable o ole he Iniial alue DE Soluion (14p) e =, (0) = 0 d = e e d e d = o = ln e d uing u-du b leing u = e 1 e = + where C = for he iniial
MA Study Guide #1
 MA 66 Su Guide #1 (1) Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Firs Order Linear Equaion (FOL): + p() = g() Soluion : = 1 µ() [ ] µ()g() + C, where µ() = e p() II. Separable Equaion (SEP): dx = h(x) g()
MA 66 Su Guide #1 (1) Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Firs Order Linear Equaion (FOL): + p() = g() Soluion : = 1 µ() [ ] µ()g() + C, where µ() = e p() II. Separable Equaion (SEP): dx = h(x) g()
Exam 1 Solutions. 1 Question 1. February 10, Part (A) 1.2 Part (B) To find equilibrium solutions, set P (t) = C = dp
 Exam Soluions Februar 0, 05 Quesion. Par (A) To find equilibrium soluions, se P () = C = = 0. This implies: = P ( P ) P = P P P = P P = P ( + P ) = 0 The equilibrium soluion are hus P () = 0 and P () =..
Exam Soluions Februar 0, 05 Quesion. Par (A) To find equilibrium soluions, se P () = C = = 0. This implies: = P ( P ) P = P P P = P P = P ( + P ) = 0 The equilibrium soluion are hus P () = 0 and P () =..
Math 333 Problem Set #2 Solution 14 February 2003
 Mah 333 Problem Se #2 Soluion 14 February 2003 A1. Solve he iniial value problem dy dx = x2 + e 3x ; 2y 4 y(0) = 1. Soluion: This is separable; we wrie 2y 4 dy = x 2 + e x dx and inegrae o ge The iniial
Mah 333 Problem Se #2 Soluion 14 February 2003 A1. Solve he iniial value problem dy dx = x2 + e 3x ; 2y 4 y(0) = 1. Soluion: This is separable; we wrie 2y 4 dy = x 2 + e x dx and inegrae o ge The iniial
Math 1b. Calculus, Series, and Differential Equations. Final Exam Solutions
 Mah b. Calculus, Series, and Differenial Equaions. Final Exam Soluions Spring 6. (9 poins) Evaluae he following inegrals. 5x + 7 (a) (x + )(x + ) dx. (b) (c) x arcan x dx x(ln x) dx Soluion. (a) Using
Mah b. Calculus, Series, and Differenial Equaions. Final Exam Soluions Spring 6. (9 poins) Evaluae he following inegrals. 5x + 7 (a) (x + )(x + ) dx. (b) (c) x arcan x dx x(ln x) dx Soluion. (a) Using
1 1 + x 2 dx. tan 1 (2) = ] ] x 3. Solution: Recall that the given integral is improper because. x 3. 1 x 3. dx = lim dx.
![1 1 + x 2 dx. tan 1 (2) = ] ] x 3. Solution: Recall that the given integral is improper because. x 3. 1 x 3. dx = lim dx. 1 1 + x 2 dx. tan 1 (2) = ] ] x 3. Solution: Recall that the given integral is improper because. x 3. 1 x 3. dx = lim dx.](/thumbs/71/65799522.jpg) . Use Simpson s rule wih n 4 o esimae an () +. Soluion: Since we are using 4 seps, 4 Thus we have [ ( ) f() + 4f + f() + 4f 3 [ + 4 4 6 5 + + 4 4 3 + ] 5 [ + 6 6 5 + + 6 3 + ]. 5. Our funcion is f() +.
. Use Simpson s rule wih n 4 o esimae an () +. Soluion: Since we are using 4 seps, 4 Thus we have [ ( ) f() + 4f + f() + 4f 3 [ + 4 4 6 5 + + 4 4 3 + ] 5 [ + 6 6 5 + + 6 3 + ]. 5. Our funcion is f() +.
u(x) = e x 2 y + 2 ) Integrate and solve for x (1 + x)y + y = cos x Answer: Divide both sides by 1 + x and solve for y. y = x y + cos x
 . 1 Mah 211 Homework #3 February 2, 2001 2.4.3. y + (2/x)y = (cos x)/x 2 Answer: Compare y + (2/x) y = (cos x)/x 2 wih y = a(x)x + f(x)and noe ha a(x) = 2/x. Consequenly, an inegraing facor is found wih
. 1 Mah 211 Homework #3 February 2, 2001 2.4.3. y + (2/x)y = (cos x)/x 2 Answer: Compare y + (2/x) y = (cos x)/x 2 wih y = a(x)x + f(x)and noe ha a(x) = 2/x. Consequenly, an inegraing facor is found wih
Math Final Exam Solutions
 Mah 246 - Final Exam Soluions Friday, July h, 204 () Find explici soluions and give he inerval of definiion o he following iniial value problems (a) ( + 2 )y + 2y = e, y(0) = 0 Soluion: In normal form,
Mah 246 - Final Exam Soluions Friday, July h, 204 () Find explici soluions and give he inerval of definiion o he following iniial value problems (a) ( + 2 )y + 2y = e, y(0) = 0 Soluion: In normal form,
EXERCISES FOR SECTION 1.5
 1.5 Exisence and Uniqueness of Soluions 43 20. 1 v c 21. 1 v c 1 2 4 6 8 10 1 2 2 4 6 8 10 Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler s mehod wih = 0.1. Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler
1.5 Exisence and Uniqueness of Soluions 43 20. 1 v c 21. 1 v c 1 2 4 6 8 10 1 2 2 4 6 8 10 Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler s mehod wih = 0.1. Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler
1 st order ODE Initial Condition
 Mah-33 Chapers 1-1 s Order ODE Sepember 1, 17 1 1 s order ODE Iniial Condiion f, sandard form LINEAR NON-LINEAR,, p g differenial form M x dx N x d differenial form is equivalen o a pair of differenial
Mah-33 Chapers 1-1 s Order ODE Sepember 1, 17 1 1 s order ODE Iniial Condiion f, sandard form LINEAR NON-LINEAR,, p g differenial form M x dx N x d differenial form is equivalen o a pair of differenial
Math 334 Test 1 KEY Spring 2010 Section: 001. Instructor: Scott Glasgow Dates: May 10 and 11.
 1 Mah 334 Tes 1 KEY Spring 21 Secion: 1 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Daes: Ma 1 and 11. Do NOT wrie on his problem saemen bookle, excep for our indicaion of following he honor code jus below. No credi will be
1 Mah 334 Tes 1 KEY Spring 21 Secion: 1 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Daes: Ma 1 and 11. Do NOT wrie on his problem saemen bookle, excep for our indicaion of following he honor code jus below. No credi will be
dy dx = xey (a) y(0) = 2 (b) y(1) = 2.5 SOLUTION: See next page
 Assignmen 1 MATH 2270 SOLUTION Please wrie ou complee soluions for each of he following 6 problems (one more will sill be added). You may, of course, consul wih your classmaes, he exbook or oher resources,
Assignmen 1 MATH 2270 SOLUTION Please wrie ou complee soluions for each of he following 6 problems (one more will sill be added). You may, of course, consul wih your classmaes, he exbook or oher resources,
Solutions to Assignment 1
 MA 2326 Differenial Equaions Insrucor: Peronela Radu Friday, February 8, 203 Soluions o Assignmen. Find he general soluions of he following ODEs: (a) 2 x = an x Soluion: I is a separable equaion as we
MA 2326 Differenial Equaions Insrucor: Peronela Radu Friday, February 8, 203 Soluions o Assignmen. Find he general soluions of he following ODEs: (a) 2 x = an x Soluion: I is a separable equaion as we
MA 366 Review - Test # 1
 MA 366 Review - Tes # 1 Fall 5 () Resuls from Calculus: differeniaion formulas, implici differeniaion, Chain Rule; inegraion formulas, inegraion b pars, parial fracions, oher inegraion echniques. (1) Order
MA 366 Review - Tes # 1 Fall 5 () Resuls from Calculus: differeniaion formulas, implici differeniaion, Chain Rule; inegraion formulas, inegraion b pars, parial fracions, oher inegraion echniques. (1) Order
3.6 Derivatives as Rates of Change
 3.6 Derivaives as Raes of Change Problem 1 John is walking along a sraigh pah. His posiion a he ime >0 is given by s = f(). He sars a =0from his house (f(0) = 0) and he graph of f is given below. (a) Describe
3.6 Derivaives as Raes of Change Problem 1 John is walking along a sraigh pah. His posiion a he ime >0 is given by s = f(). He sars a =0from his house (f(0) = 0) and he graph of f is given below. (a) Describe
Math 2142 Exam 1 Review Problems. x 2 + f (0) 3! for the 3rd Taylor polynomial at x = 0. To calculate the various quantities:
 Mah 4 Eam Review Problems Problem. Calculae he 3rd Taylor polynomial for arcsin a =. Soluion. Le f() = arcsin. For his problem, we use he formula f() + f () + f ()! + f () 3! for he 3rd Taylor polynomial
Mah 4 Eam Review Problems Problem. Calculae he 3rd Taylor polynomial for arcsin a =. Soluion. Le f() = arcsin. For his problem, we use he formula f() + f () + f ()! + f () 3! for he 3rd Taylor polynomial
ln 2 1 ln y x c y C x
 Lecure 14 Appendi B: Some sample problems from Boas Here are some soluions o he sample problems assigned for Chaper 8 8: 6 Soluion: We wan o find he soluion o he following firs order equaion using separaion
Lecure 14 Appendi B: Some sample problems from Boas Here are some soluions o he sample problems assigned for Chaper 8 8: 6 Soluion: We wan o find he soluion o he following firs order equaion using separaion
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
APPM 2360 Homework Solutions, Due June 10
 2.2.2: Find general soluions for he equaion APPM 2360 Homework Soluions, Due June 10 Soluion: Finding he inegraing facor, dy + 2y = 3e µ) = e 2) = e 2 Muliplying he differenial equaion by he inegraing
2.2.2: Find general soluions for he equaion APPM 2360 Homework Soluions, Due June 10 Soluion: Finding he inegraing facor, dy + 2y = 3e µ) = e 2) = e 2 Muliplying he differenial equaion by he inegraing
Physics 180A Fall 2008 Test points. Provide the best answer to the following questions and problems. Watch your sig figs.
 Physics 180A Fall 2008 Tes 1-120 poins Name Provide he bes answer o he following quesions and problems. Wach your sig figs. 1) The number of meaningful digis in a number is called he number of. When numbers
Physics 180A Fall 2008 Tes 1-120 poins Name Provide he bes answer o he following quesions and problems. Wach your sig figs. 1) The number of meaningful digis in a number is called he number of. When numbers
ME 391 Mechanical Engineering Analysis
 Fall 04 ME 39 Mechanical Engineering Analsis Eam # Soluions Direcions: Open noes (including course web posings). No books, compuers, or phones. An calculaor is fair game. Problem Deermine he posiion of
Fall 04 ME 39 Mechanical Engineering Analsis Eam # Soluions Direcions: Open noes (including course web posings). No books, compuers, or phones. An calculaor is fair game. Problem Deermine he posiion of
WEEK-3 Recitation PHYS 131. of the projectile s velocity remains constant throughout the motion, since the acceleration a x
 WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
Math 2214 Sol Test 2B Spring 2015
 Mah 14 Sol Tes B Sring 015 roblem 1: An objec weighing ounds sreches a verical sring 8 fee beond i naural lengh before coming o res a equilibrium The objec is ushed u 6 fee from i s equilibrium osiion
Mah 14 Sol Tes B Sring 015 roblem 1: An objec weighing ounds sreches a verical sring 8 fee beond i naural lengh before coming o res a equilibrium The objec is ushed u 6 fee from i s equilibrium osiion
Note: For all questions, answer (E) NOTA means none of the above answers is correct.
 Thea Logarihms & Eponens 0 ΜΑΘ Naional Convenion Noe: For all quesions, answer means none of he above answers is correc.. The elemen C 4 has a half life of 70 ears. There is grams of C 4 in a paricular
Thea Logarihms & Eponens 0 ΜΑΘ Naional Convenion Noe: For all quesions, answer means none of he above answers is correc.. The elemen C 4 has a half life of 70 ears. There is grams of C 4 in a paricular
Some Basic Information about M-S-D Systems
 Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
ACCUMULATION. Section 7.5 Calculus AP/Dual, Revised /26/2018 7:27 PM 7.5A: Accumulation 1
 ACCUMULATION Secion 7.5 Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 2019 vie.dang@humbleisd.ne 12/26/2018 7:27 PM 7.5A: Accumulaion 1 APPLICATION PROBLEMS A. Undersand he quesion. I is ofen no necessary o as much compuaion
ACCUMULATION Secion 7.5 Calculus AP/Dual, Revised 2019 vie.dang@humbleisd.ne 12/26/2018 7:27 PM 7.5A: Accumulaion 1 APPLICATION PROBLEMS A. Undersand he quesion. I is ofen no necessary o as much compuaion
dt = C exp (3 ln t 4 ). t 4 W = C exp ( ln(4 t) 3) = C(4 t) 3.
 Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
Chapter 15: Phenomena. Chapter 15 Chemical Kinetics. Reaction Rates. Reaction Rates R P. Reaction Rates. Rate Laws
 Chaper 5: Phenomena Phenomena: The reacion (aq) + B(aq) C(aq) was sudied a wo differen emperaures (98 K and 35 K). For each emperaure he reacion was sared by puing differen concenraions of he 3 species
Chaper 5: Phenomena Phenomena: The reacion (aq) + B(aq) C(aq) was sudied a wo differen emperaures (98 K and 35 K). For each emperaure he reacion was sared by puing differen concenraions of he 3 species
Challenge Problems. DIS 203 and 210. March 6, (e 2) k. k(k + 2). k=1. f(x) = k(k + 2) = 1 x k
 Challenge Problems DIS 03 and 0 March 6, 05 Choose one of he following problems, and work on i in your group. Your goal is o convince me ha your answer is correc. Even if your answer isn compleely correc,
Challenge Problems DIS 03 and 0 March 6, 05 Choose one of he following problems, and work on i in your group. Your goal is o convince me ha your answer is correc. Even if your answer isn compleely correc,
MA 214 Calculus IV (Spring 2016) Section 2. Homework Assignment 1 Solutions
 MA 14 Calculus IV (Spring 016) Secion Homework Assignmen 1 Soluions 1 Boyce and DiPrima, p 40, Problem 10 (c) Soluion: In sandard form he given firs-order linear ODE is: An inegraing facor is given by
MA 14 Calculus IV (Spring 016) Secion Homework Assignmen 1 Soluions 1 Boyce and DiPrima, p 40, Problem 10 (c) Soluion: In sandard form he given firs-order linear ODE is: An inegraing facor is given by
!!"#"$%&#'()!"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./0)1-*23)
 "#"$%&#'()"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./)1-*) #$%&'()*+,&',-.%,/)*+,-&1*#$)()5*6$+$%*,7&*-'-&1*(,-&*6&,7.$%$+*&%'(*8$&',-,%'-&1*(,-&*6&,79*(&,%: ;..,*&1$&$.$%&'()*1$$.,'&',-9*(&,%)?%*,('&5
"#"$%&#'()"#&'(*%)+,&',-)./)1-*) #$%&'()*+,&',-.%,/)*+,-&1*#$)()5*6$+$%*,7&*-'-&1*(,-&*6&,7.$%$+*&%'(*8$&',-,%'-&1*(,-&*6&,79*(&,%: ;..,*&1$&$.$%&'()*1$$.,'&',-9*(&,%)?%*,('&5
KEY. Math 334 Midterm I Fall 2008 sections 001 and 003 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 1 KEY Mah 4 Miderm I Fall 8 secions 1 and Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his eam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on our own paper, preferabl engineering
1 KEY Mah 4 Miderm I Fall 8 secions 1 and Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his eam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on our own paper, preferabl engineering
5.1 - Logarithms and Their Properties
 Chaper 5 Logarihmic Funcions 5.1 - Logarihms and Their Properies Suppose ha a populaion grows according o he formula P 10, where P is he colony size a ime, in hours. When will he populaion be 2500? We
Chaper 5 Logarihmic Funcions 5.1 - Logarihms and Their Properies Suppose ha a populaion grows according o he formula P 10, where P is he colony size a ime, in hours. When will he populaion be 2500? We
Solutions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Math 246, Spring 2011, Professor David Levermore
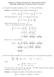 Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
y = (y 1)*(y 3) t
 MATH 66 SPR REVIEW DEFINITION OF SOLUTION A funcion = () is a soluion of he differenial equaion d=d = f(; ) on he inerval ff < < fi if (d=d)() =f(; ()) for each so ha ff
MATH 66 SPR REVIEW DEFINITION OF SOLUTION A funcion = () is a soluion of he differenial equaion d=d = f(; ) on he inerval ff < < fi if (d=d)() =f(; ()) for each so ha ff
Elementary Differential Equations and Boundary Value Problems
 Elemenar Differenial Equaions and Boundar Value Problems Boce. & DiPrima 9 h Ediion Chaper 1: Inroducion 1006003 คณ ตศาสตร ว ศวกรรม 3 สาขาว ชาว ศวกรรมคอมพ วเตอร ป การศ กษา 1/2555 ผศ.ดร.อร ญญา ผศ.ดร.สมศ
Elemenar Differenial Equaions and Boundar Value Problems Boce. & DiPrima 9 h Ediion Chaper 1: Inroducion 1006003 คณ ตศาสตร ว ศวกรรม 3 สาขาว ชาว ศวกรรมคอมพ วเตอร ป การศ กษา 1/2555 ผศ.ดร.อร ญญา ผศ.ดร.สมศ
Math Wednesday March 3, , 4.3: First order systems of Differential Equations Why you should expect existence and uniqueness for the IVP
 Mah 2280 Wednesda March 3, 200 4., 4.3: Firs order ssems of Differenial Equaions Wh ou should epec eisence and uniqueness for he IVP Eample: Consider he iniial value problem relaed o page 4 of his eserda
Mah 2280 Wednesda March 3, 200 4., 4.3: Firs order ssems of Differenial Equaions Wh ou should epec eisence and uniqueness for he IVP Eample: Consider he iniial value problem relaed o page 4 of his eserda
Module 2 F c i k c s la l w a s o s f dif di fusi s o i n
 Module Fick s laws of diffusion Fick s laws of diffusion and hin film soluion Adolf Fick (1855) proposed: d J α d d d J (mole/m s) flu (m /s) diffusion coefficien and (mole/m 3 ) concenraion of ions, aoms
Module Fick s laws of diffusion Fick s laws of diffusion and hin film soluion Adolf Fick (1855) proposed: d J α d d d J (mole/m s) flu (m /s) diffusion coefficien and (mole/m 3 ) concenraion of ions, aoms
Differential Equations
 Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
1.6. Slopes of Tangents and Instantaneous Rate of Change
 1.6 Slopes of Tangens and Insananeous Rae of Change When you hi or kick a ball, he heigh, h, in meres, of he ball can be modelled by he equaion h() 4.9 2 v c. In his equaion, is he ime, in seconds; c represens
1.6 Slopes of Tangens and Insananeous Rae of Change When you hi or kick a ball, he heigh, h, in meres, of he ball can be modelled by he equaion h() 4.9 2 v c. In his equaion, is he ime, in seconds; c represens
Comparison between the Discrete and Continuous Time Models
 Comparison beween e Discree and Coninuous Time Models D. Sulsky June 21, 2012 1 Discree o Coninuous Recall e discree ime model Î = AIS Ŝ = S Î. Tese equaions ell us ow e populaion canges from one day o
Comparison beween e Discree and Coninuous Time Models D. Sulsky June 21, 2012 1 Discree o Coninuous Recall e discree ime model Î = AIS Ŝ = S Î. Tese equaions ell us ow e populaion canges from one day o
ln y t 2 t c where c is an arbitrary real constant
 SOLUTION TO THE PROBLEM.A y y subjec o condiion y 0 8 We recognize is as a linear firs order differenial equaion wi consan coefficiens. Firs we sall find e general soluion, and en we sall find one a saisfies
SOLUTION TO THE PROBLEM.A y y subjec o condiion y 0 8 We recognize is as a linear firs order differenial equaion wi consan coefficiens. Firs we sall find e general soluion, and en we sall find one a saisfies
Displacement ( x) x x x
 Kinemaics Kinemaics is he branch of mechanics ha describes he moion of objecs wihou necessarily discussing wha causes he moion. 1-Dimensional Kinemaics (or 1- Dimensional moion) refers o moion in a sraigh
Kinemaics Kinemaics is he branch of mechanics ha describes he moion of objecs wihou necessarily discussing wha causes he moion. 1-Dimensional Kinemaics (or 1- Dimensional moion) refers o moion in a sraigh
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Kinematics. Position. Lectures 3 and 4 Motion in One Dimension. A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan
 Ground Rules PC11 Fundamenals of Physics I Lecures 3 and 4 Moion in One Dimension A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan 1 Swich off your handphone and pager Swich off your lapop compuer and keep i No alking while lecure
Ground Rules PC11 Fundamenals of Physics I Lecures 3 and 4 Moion in One Dimension A/Prof Tay Seng Chuan 1 Swich off your handphone and pager Swich off your lapop compuer and keep i No alking while lecure
IB Physics Kinematics Worksheet
 IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
IB Physics Kinemaics Workshee Wrie full soluions and noes for muliple choice answers. Do no use a calculaor for muliple choice answers. 1. Which of he following is a correc definiion of average acceleraion?
AP Calculus BC Chapter 10 Part 1 AP Exam Problems
 AP Calculus BC Chaper Par AP Eam Problems All problems are NO CALCULATOR unless oherwise indicaed Parameric Curves and Derivaives In he y plane, he graph of he parameric equaions = 5 + and y= for, is a
AP Calculus BC Chaper Par AP Eam Problems All problems are NO CALCULATOR unless oherwise indicaed Parameric Curves and Derivaives In he y plane, he graph of he parameric equaions = 5 + and y= for, is a
( ) a system of differential equations with continuous parametrization ( T = R + These look like, respectively:
 XIII. DIFFERENCE AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Ofen funcions, or a sysem of funcion, are paramerized in erms of some variable, usually denoed as and inerpreed as ime. The variable is wrien as a funcion of
XIII. DIFFERENCE AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Ofen funcions, or a sysem of funcion, are paramerized in erms of some variable, usually denoed as and inerpreed as ime. The variable is wrien as a funcion of
Basic Circuit Elements Professor J R Lucas November 2001
 Basic Circui Elemens - J ucas An elecrical circui is an inerconnecion of circui elemens. These circui elemens can be caegorised ino wo ypes, namely acive and passive elemens. Some Definiions/explanaions
Basic Circui Elemens - J ucas An elecrical circui is an inerconnecion of circui elemens. These circui elemens can be caegorised ino wo ypes, namely acive and passive elemens. Some Definiions/explanaions
Phys1112: DC and RC circuits
 Name: Group Members: Dae: TA s Name: Phys1112: DC and RC circuis Objecives: 1. To undersand curren and volage characerisics of a DC RC discharging circui. 2. To undersand he effec of he RC ime consan.
Name: Group Members: Dae: TA s Name: Phys1112: DC and RC circuis Objecives: 1. To undersand curren and volage characerisics of a DC RC discharging circui. 2. To undersand he effec of he RC ime consan.
MEI Mechanics 1 General motion. Section 1: Using calculus
 Soluions o Exercise MEI Mechanics General moion Secion : Using calculus. s 4 v a 6 4 4 When =, v 4 a 6 4 6. (i) When = 0, s = -, so he iniial displacemen = - m. s v 4 When = 0, v = so he iniial velociy
Soluions o Exercise MEI Mechanics General moion Secion : Using calculus. s 4 v a 6 4 4 When =, v 4 a 6 4 6. (i) When = 0, s = -, so he iniial displacemen = - m. s v 4 When = 0, v = so he iniial velociy
8. Basic RL and RC Circuits
 8. Basic L and C Circuis This chaper deals wih he soluions of he responses of L and C circuis The analysis of C and L circuis leads o a linear differenial equaion This chaper covers he following opics
8. Basic L and C Circuis This chaper deals wih he soluions of he responses of L and C circuis The analysis of C and L circuis leads o a linear differenial equaion This chaper covers he following opics
1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION
 1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION 1.1 Kinemaics Equaions s = u + 1 a and s = v 1 a s = 1 (u + v) v = u + as 1. Displacemen-Time Graph Gradien = speed 1.3 Velociy-Time Graph Gradien = acceleraion Area under
1. VELOCITY AND ACCELERATION 1.1 Kinemaics Equaions s = u + 1 a and s = v 1 a s = 1 (u + v) v = u + as 1. Displacemen-Time Graph Gradien = speed 1.3 Velociy-Time Graph Gradien = acceleraion Area under
PROBLEMS FOR MATH 162 If a problem is starred, all subproblems are due. If only subproblems are starred, only those are due. SLOPES OF TANGENT LINES
 PROBLEMS FOR MATH 6 If a problem is sarred, all subproblems are due. If onl subproblems are sarred, onl hose are due. 00. Shor answer quesions. SLOPES OF TANGENT LINES (a) A ball is hrown ino he air. Is
PROBLEMS FOR MATH 6 If a problem is sarred, all subproblems are due. If onl subproblems are sarred, onl hose are due. 00. Shor answer quesions. SLOPES OF TANGENT LINES (a) A ball is hrown ino he air. Is
Math 10B: Mock Mid II. April 13, 2016
 Name: Soluions Mah 10B: Mock Mid II April 13, 016 1. ( poins) Sae, wih jusificaion, wheher he following saemens are rue or false. (a) If a 3 3 marix A saisfies A 3 A = 0, hen i canno be inverible. True.
Name: Soluions Mah 10B: Mock Mid II April 13, 016 1. ( poins) Sae, wih jusificaion, wheher he following saemens are rue or false. (a) If a 3 3 marix A saisfies A 3 A = 0, hen i canno be inverible. True.
Math Week 14 April 16-20: sections first order systems of linear differential equations; 7.4 mass-spring systems.
 Mah 2250-004 Week 4 April 6-20 secions 7.-7.3 firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions; 7.4 mass-spring sysems. Mon Apr 6 7.-7.2 Sysems of differenial equaions (7.), and he vecor Calculus we need
Mah 2250-004 Week 4 April 6-20 secions 7.-7.3 firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions; 7.4 mass-spring sysems. Mon Apr 6 7.-7.2 Sysems of differenial equaions (7.), and he vecor Calculus we need
= ( ) ) or a system of differential equations with continuous parametrization (T = R
 XIII. DIFFERENCE AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Ofen funcions, or a sysem of funcion, are paramerized in erms of some variable, usually denoed as and inerpreed as ime. The variable is wrien as a funcion of
XIII. DIFFERENCE AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Ofen funcions, or a sysem of funcion, are paramerized in erms of some variable, usually denoed as and inerpreed as ime. The variable is wrien as a funcion of
AP CALCULUS AB/CALCULUS BC 2016 SCORING GUIDELINES. Question 1. 1 : estimate = = 120 liters/hr
 AP CALCULUS AB/CALCULUS BC 16 SCORING GUIDELINES Quesion 1 (hours) R ( ) (liers / hour) 1 3 6 8 134 119 95 74 7 Waer is pumped ino a ank a a rae modeled by W( ) = e liers per hour for 8, where is measured
AP CALCULUS AB/CALCULUS BC 16 SCORING GUIDELINES Quesion 1 (hours) R ( ) (liers / hour) 1 3 6 8 134 119 95 74 7 Waer is pumped ino a ank a a rae modeled by W( ) = e liers per hour for 8, where is measured
Math 115 Final Exam December 14, 2017
 On my honor, as a suden, I have neiher given nor received unauhorized aid on his academic work. Your Iniials Only: Iniials: Do no wrie in his area Mah 5 Final Exam December, 07 Your U-M ID # (no uniqname):
On my honor, as a suden, I have neiher given nor received unauhorized aid on his academic work. Your Iniials Only: Iniials: Do no wrie in his area Mah 5 Final Exam December, 07 Your U-M ID # (no uniqname):
d = ½(v o + v f) t distance = ½ (initial velocity + final velocity) time
 BULLSEYE Lab Name: ANSWER KEY Dae: Pre-AP Physics Lab Projecile Moion Weigh = 1 DIRECTIONS: Follow he insrucions below, build he ramp, ake your measuremens, and use your measuremens o make he calculaions
BULLSEYE Lab Name: ANSWER KEY Dae: Pre-AP Physics Lab Projecile Moion Weigh = 1 DIRECTIONS: Follow he insrucions below, build he ramp, ake your measuremens, and use your measuremens o make he calculaions
The fundamental mass balance equation is ( 1 ) where: I = inputs P = production O = outputs L = losses A = accumulation
 Hea (iffusion) Equaion erivaion of iffusion Equaion The fundamenal mass balance equaion is I P O L A ( 1 ) where: I inpus P producion O oupus L losses A accumulaion Assume ha no chemical is produced or
Hea (iffusion) Equaion erivaion of iffusion Equaion The fundamenal mass balance equaion is I P O L A ( 1 ) where: I inpus P producion O oupus L losses A accumulaion Assume ha no chemical is produced or
and v y . The changes occur, respectively, because of the acceleration components a x and a y
 Week 3 Reciaion: Chaper3 : Problems: 1, 16, 9, 37, 41, 71. 1. A spacecraf is raveling wih a veloci of v0 = 5480 m/s along he + direcion. Two engines are urned on for a ime of 84 s. One engine gives he
Week 3 Reciaion: Chaper3 : Problems: 1, 16, 9, 37, 41, 71. 1. A spacecraf is raveling wih a veloci of v0 = 5480 m/s along he + direcion. Two engines are urned on for a ime of 84 s. One engine gives he
Direct Current Circuits. February 19, 2014 Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2, Chapter 26 1
 Direc Curren Circuis February 19, 2014 Physics for Scieniss & Engineers 2, Chaper 26 1 Ammeers and Volmeers! A device used o measure curren is called an ammeer! A device used o measure poenial difference
Direc Curren Circuis February 19, 2014 Physics for Scieniss & Engineers 2, Chaper 26 1 Ammeers and Volmeers! A device used o measure curren is called an ammeer! A device used o measure poenial difference
Review - Quiz # 1. 1 g(y) dy = f(x) dx. y x. = u, so that y = xu and dy. dx (Sometimes you may want to use the substitution x y
 Review - Quiz # 1 (1) Solving Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Separable Equaions (SE). d = f() g() Mehod of Soluion : 1 g() d = f() (The soluions ma be given implicil b he above formula. Remember,
Review - Quiz # 1 (1) Solving Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Separable Equaions (SE). d = f() g() Mehod of Soluion : 1 g() d = f() (The soluions ma be given implicil b he above formula. Remember,
MATH 31B: MIDTERM 2 REVIEW. x 2 e x2 2x dx = 1. ue u du 2. x 2 e x2 e x2] + C 2. dx = x ln(x) 2 2. ln x dx = x ln x x + C. 2, or dx = 2u du.
![MATH 31B: MIDTERM 2 REVIEW. x 2 e x2 2x dx = 1. ue u du 2. x 2 e x2 e x2] + C 2. dx = x ln(x) 2 2. ln x dx = x ln x x + C. 2, or dx = 2u du. MATH 31B: MIDTERM 2 REVIEW. x 2 e x2 2x dx = 1. ue u du 2. x 2 e x2 e x2] + C 2. dx = x ln(x) 2 2. ln x dx = x ln x x + C. 2, or dx = 2u du.](/thumbs/86/93221008.jpg) MATH 3B: MIDTERM REVIEW JOE HUGHES. Inegraion by Pars. Evaluae 3 e. Soluion: Firs make he subsiuion u =. Then =, hence 3 e = e = ue u Now inegrae by pars o ge ue u = ue u e u + C and subsiue he definiion
MATH 3B: MIDTERM REVIEW JOE HUGHES. Inegraion by Pars. Evaluae 3 e. Soluion: Firs make he subsiuion u =. Then =, hence 3 e = e = ue u Now inegrae by pars o ge ue u = ue u e u + C and subsiue he definiion
3 at MAC 1140 TEST 3 NOTES. 5.1 and 5.2. Exponential Functions. Form I: P is the y-intercept. (0, P) When a > 1: a = growth factor = 1 + growth rate
 1 5.1 and 5. Eponenial Funcions Form I: Y Pa, a 1, a > 0 P is he y-inercep. (0, P) When a > 1: a = growh facor = 1 + growh rae The equaion can be wrien as The larger a is, he seeper he graph is. Y P( 1
1 5.1 and 5. Eponenial Funcions Form I: Y Pa, a 1, a > 0 P is he y-inercep. (0, P) When a > 1: a = growh facor = 1 + growh rae The equaion can be wrien as The larger a is, he seeper he graph is. Y P( 1
System of Linear Differential Equations
 Sysem of Linear Differenial Equaions In "Ordinary Differenial Equaions" we've learned how o solve a differenial equaion for a variable, such as: y'k5$e K2$x =0 solve DE yx = K 5 2 ek2 x C_C1 2$y''C7$y
Sysem of Linear Differenial Equaions In "Ordinary Differenial Equaions" we've learned how o solve a differenial equaion for a variable, such as: y'k5$e K2$x =0 solve DE yx = K 5 2 ek2 x C_C1 2$y''C7$y
UCLA: Math 3B Problem set 3 (solutions) Fall, 2018
 UCLA: Mah 3B Problem se 3 (soluions) Fall, 28 This problem se concenraes on pracice wih aniderivaives. You will ge los of pracice finding simple aniderivaives as well as finding aniderivaives graphically
UCLA: Mah 3B Problem se 3 (soluions) Fall, 28 This problem se concenraes on pracice wih aniderivaives. You will ge los of pracice finding simple aniderivaives as well as finding aniderivaives graphically
23.5. Half-Range Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Half-Range Series 2.5 Inroducion In his Secion we address he following problem: Can we find a Fourier series expansion of a funcion defined over a finie inerval? Of course we recognise ha such a funcion
Half-Range Series 2.5 Inroducion In his Secion we address he following problem: Can we find a Fourier series expansion of a funcion defined over a finie inerval? Of course we recognise ha such a funcion
Solutionbank Edexcel AS and A Level Modular Mathematics
 Page of 4 Soluionbank Edexcel AS and A Level Modular Mahemaics Exercise A, Quesion Quesion: Skech he graphs of (a) y = e x + (b) y = 4e x (c) y = e x 3 (d) y = 4 e x (e) y = 6 + 0e x (f) y = 00e x + 0
Page of 4 Soluionbank Edexcel AS and A Level Modular Mahemaics Exercise A, Quesion Quesion: Skech he graphs of (a) y = e x + (b) y = 4e x (c) y = e x 3 (d) y = 4 e x (e) y = 6 + 0e x (f) y = 00e x + 0
3.1.3 INTRODUCTION TO DYNAMIC OPTIMIZATION: DISCRETE TIME PROBLEMS. A. The Hamiltonian and First-Order Conditions in a Finite Time Horizon
 3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
Announcements: Warm-up Exercise:
 Fri Apr 13 7.1 Sysems of differenial equaions - o model muli-componen sysems via comparmenal analysis hp//en.wikipedia.org/wiki/muli-comparmen_model Announcemens Warm-up Exercise Here's a relaively simple
Fri Apr 13 7.1 Sysems of differenial equaions - o model muli-componen sysems via comparmenal analysis hp//en.wikipedia.org/wiki/muli-comparmen_model Announcemens Warm-up Exercise Here's a relaively simple
PHYSICS 220 Lecture 02 Motion, Forces, and Newton s Laws Textbook Sections
 PHYSICS 220 Lecure 02 Moion, Forces, and Newon s Laws Texbook Secions 2.2-2.4 Lecure 2 Purdue Universiy, Physics 220 1 Overview Las Lecure Unis Scienific Noaion Significan Figures Moion Displacemen: Δx
PHYSICS 220 Lecure 02 Moion, Forces, and Newon s Laws Texbook Secions 2.2-2.4 Lecure 2 Purdue Universiy, Physics 220 1 Overview Las Lecure Unis Scienific Noaion Significan Figures Moion Displacemen: Δx
MOMENTUM CONSERVATION LAW
 1 AAST/AEDT AP PHYSICS B: Impulse and Momenum Le us run an experimen: The ball is moving wih a velociy of V o and a force of F is applied on i for he ime inerval of. As he resul he ball s velociy changes
1 AAST/AEDT AP PHYSICS B: Impulse and Momenum Le us run an experimen: The ball is moving wih a velociy of V o and a force of F is applied on i for he ime inerval of. As he resul he ball s velociy changes
Practicing Problem Solving and Graphing
 Pracicing Problem Solving and Graphing Tes 1: Jan 30, 7pm, Ming Hsieh G20 The Bes Ways To Pracice for Tes Bes If need more, ry suggesed problems from each new opic: Suden Response Examples A pas opic ha
Pracicing Problem Solving and Graphing Tes 1: Jan 30, 7pm, Ming Hsieh G20 The Bes Ways To Pracice for Tes Bes If need more, ry suggesed problems from each new opic: Suden Response Examples A pas opic ha
EEEB113 CIRCUIT ANALYSIS I
 9/14/29 1 EEEB113 CICUIT ANALYSIS I Chaper 7 Firs-Order Circuis Maerials from Fundamenals of Elecric Circuis 4e, Alexander Sadiku, McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 2 Firs-Order Circuis -Chaper 7 7.2 The Source-Free
9/14/29 1 EEEB113 CICUIT ANALYSIS I Chaper 7 Firs-Order Circuis Maerials from Fundamenals of Elecric Circuis 4e, Alexander Sadiku, McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 2 Firs-Order Circuis -Chaper 7 7.2 The Source-Free
Problem Set 7-7. dv V ln V = kt + C. 20. Assume that df/dt still equals = F RF. df dr = =
 20. Assume ha df/d sill equals = F + 0.02RF. df dr df/ d F+ 0. 02RF = = 2 dr/ d R 0. 04RF 0. 01R 10 df 11. 2 R= 70 and F = 1 = = 0. 362K dr 31 21. 0 F (70, 30) (70, 1) R 100 Noe ha he slope a (70, 1) is
20. Assume ha df/d sill equals = F + 0.02RF. df dr df/ d F+ 0. 02RF = = 2 dr/ d R 0. 04RF 0. 01R 10 df 11. 2 R= 70 and F = 1 = = 0. 362K dr 31 21. 0 F (70, 30) (70, 1) R 100 Noe ha he slope a (70, 1) is
Suggested Practice Problems (set #2) for the Physics Placement Test
 Deparmen of Physics College of Ars and Sciences American Universiy of Sharjah (AUS) Fall 014 Suggesed Pracice Problems (se #) for he Physics Placemen Tes This documen conains 5 suggesed problems ha are
Deparmen of Physics College of Ars and Sciences American Universiy of Sharjah (AUS) Fall 014 Suggesed Pracice Problems (se #) for he Physics Placemen Tes This documen conains 5 suggesed problems ha are
Biol. 356 Lab 8. Mortality, Recruitment, and Migration Rates
 Biol. 356 Lab 8. Moraliy, Recruimen, and Migraion Raes (modified from Cox, 00, General Ecology Lab Manual, McGraw Hill) Las week we esimaed populaion size hrough several mehods. One assumpion of all hese
Biol. 356 Lab 8. Moraliy, Recruimen, and Migraion Raes (modified from Cox, 00, General Ecology Lab Manual, McGraw Hill) Las week we esimaed populaion size hrough several mehods. One assumpion of all hese
Predator - Prey Model Trajectories and the nonlinear conservation law
 Predaor - Prey Model Trajecories and he nonlinear conservaion law James K. Peerson Deparmen of Biological Sciences and Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Clemson Universiy Ocober 28, 213 Ouline Drawing Trajecories
Predaor - Prey Model Trajecories and he nonlinear conservaion law James K. Peerson Deparmen of Biological Sciences and Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Clemson Universiy Ocober 28, 213 Ouline Drawing Trajecories
Reading from Young & Freedman: For this topic, read sections 25.4 & 25.5, the introduction to chapter 26 and sections 26.1 to 26.2 & 26.4.
 PHY1 Elecriciy Topic 7 (Lecures 1 & 11) Elecric Circuis n his opic, we will cover: 1) Elecromoive Force (EMF) ) Series and parallel resisor combinaions 3) Kirchhoff s rules for circuis 4) Time dependence
PHY1 Elecriciy Topic 7 (Lecures 1 & 11) Elecric Circuis n his opic, we will cover: 1) Elecromoive Force (EMF) ) Series and parallel resisor combinaions 3) Kirchhoff s rules for circuis 4) Time dependence
Giambattista, Ch 3 Problems: 9, 15, 21, 27, 35, 37, 42, 43, 47, 55, 63, 76
 Giambaisa, Ch 3 Problems: 9, 15, 21, 27, 35, 37, 42, 43, 47, 55, 63, 76 9. Sraeg Le be direced along he +x-axis and le be 60.0 CCW from Find he magniude of 6.0 B 60.0 4.0 A x 15. (a) Sraeg Since he angle
Giambaisa, Ch 3 Problems: 9, 15, 21, 27, 35, 37, 42, 43, 47, 55, 63, 76 9. Sraeg Le be direced along he +x-axis and le be 60.0 CCW from Find he magniude of 6.0 B 60.0 4.0 A x 15. (a) Sraeg Since he angle
Section 3.8, Mechanical and Electrical Vibrations
 Secion 3.8, Mechanical and Elecrical Vibraions Mechanical Unis in he U.S. Cusomary and Meric Sysems Disance Mass Time Force g (Earh) Uni U.S. Cusomary MKS Sysem CGS Sysem fee f slugs seconds sec pounds
Secion 3.8, Mechanical and Elecrical Vibraions Mechanical Unis in he U.S. Cusomary and Meric Sysems Disance Mass Time Force g (Earh) Uni U.S. Cusomary MKS Sysem CGS Sysem fee f slugs seconds sec pounds
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions
 Chaper 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS PREVIEW Two-dimensional moion includes objecs which are moing in wo direcions a he same ime, such as a projecile, which has boh horizonal and erical moion. These wo
Chaper 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS PREVIEW Two-dimensional moion includes objecs which are moing in wo direcions a he same ime, such as a projecile, which has boh horizonal and erical moion. These wo
t + t sin t t cos t sin t. t cos t sin t dt t 2 = exp 2 log t log(t cos t sin t) = Multiplying by this factor and then integrating, we conclude that
 ODEs, Homework #4 Soluions. Check ha y ( = is a soluion of he second-order ODE ( cos sin y + y sin y sin = 0 and hen use his fac o find all soluions of he ODE. When y =, we have y = and also y = 0, so
ODEs, Homework #4 Soluions. Check ha y ( = is a soluion of he second-order ODE ( cos sin y + y sin y sin = 0 and hen use his fac o find all soluions of he ODE. When y =, we have y = and also y = 0, so
University Physics with Modern Physics 14th Edition Young TEST BANK
 Universi Phsics wih Modern Phsics 14h Ediion Young SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formaing errors) a: hps://esbankreal.com/download/universi-phsics-modern-phsics- 14h-ediion-oung-soluions-manual-/
Universi Phsics wih Modern Phsics 14h Ediion Young SOLUTIONS MANUAL Full clear download (no formaing errors) a: hps://esbankreal.com/download/universi-phsics-modern-phsics- 14h-ediion-oung-soluions-manual-/
AP CALCULUS AB 2003 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Quesion A blood vessel is 6 millimeers (mm) long Disance wih circular cross secions of varying diameer. x (mm) 6 8 4 6 Diameer The able above gives he measuremens of he B(x)
SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Quesion A blood vessel is 6 millimeers (mm) long Disance wih circular cross secions of varying diameer. x (mm) 6 8 4 6 Diameer The able above gives he measuremens of he B(x)
Math 116 Second Midterm March 21, 2016
 Mah 6 Second Miderm March, 06 UMID: EXAM SOLUTIONS Iniials: Insrucor: Secion:. Do no open his exam unil you are old o do so.. Do no wrie your name anywhere on his exam. 3. This exam has pages including
Mah 6 Second Miderm March, 06 UMID: EXAM SOLUTIONS Iniials: Insrucor: Secion:. Do no open his exam unil you are old o do so.. Do no wrie your name anywhere on his exam. 3. This exam has pages including
AP CALCULUS AB 2003 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 SCING GUIDELINES (Form B) Quesion 4 A paricle moves along he x-axis wih velociy a ime given by v( ) = 1 + e1. (a) Find he acceleraion of he paricle a ime =. (b) Is he speed of he paricle increasing a ime
SCING GUIDELINES (Form B) Quesion 4 A paricle moves along he x-axis wih velociy a ime given by v( ) = 1 + e1. (a) Find he acceleraion of he paricle a ime =. (b) Is he speed of he paricle increasing a ime
Chapter 7 Response of First-order RL and RC Circuits
 Chaper 7 Response of Firs-order RL and RC Circuis 7.- The Naural Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.3 The Sep Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.4 A General Soluion for Sep and Naural Responses 7.5 Sequenial
Chaper 7 Response of Firs-order RL and RC Circuis 7.- The Naural Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.3 The Sep Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.4 A General Soluion for Sep and Naural Responses 7.5 Sequenial
Theory of! Partial Differential Equations!
 hp://www.nd.edu/~gryggva/cfd-course/! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 011! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
hp://www.nd.edu/~gryggva/cfd-course/! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 011! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
Section 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equations; Method of Undetermined Coefficients
 Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION
 CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
(1) (2) Differentiation of (1) and then substitution of (3) leads to. Therefore, we will simply consider the second-order linear system given by (4)
 Phase Plane Analysis of Linear Sysems Adaped from Applied Nonlinear Conrol by Sloine and Li The general form of a linear second-order sysem is a c b d From and b bc d a Differeniaion of and hen subsiuion
Phase Plane Analysis of Linear Sysems Adaped from Applied Nonlinear Conrol by Sloine and Li The general form of a linear second-order sysem is a c b d From and b bc d a Differeniaion of and hen subsiuion
AP Chemistry--Chapter 12: Chemical Kinetics
 AP Chemisry--Chaper 12: Chemical Kineics I. Reacion Raes A. The area of chemisry ha deals wih reacion raes, or how fas a reacion occurs, is called chemical kineics. B. The rae of reacion depends on he
AP Chemisry--Chaper 12: Chemical Kineics I. Reacion Raes A. The area of chemisry ha deals wih reacion raes, or how fas a reacion occurs, is called chemical kineics. B. The rae of reacion depends on he
23.2. Representing Periodic Functions by Fourier Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Simulation-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010
 Simulaion-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010 Week Descripion Reading Maerial 2 Compuer Simulaion of Dynamic Models Finie Difference, coninuous saes, discree ime Simple Mehods Euler Trapezoid
Simulaion-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010 Week Descripion Reading Maerial 2 Compuer Simulaion of Dynamic Models Finie Difference, coninuous saes, discree ime Simple Mehods Euler Trapezoid
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS PAGE # An equaion conaining independen variable, dependen variable & differenial coeffeciens of dependen variables wr independen variable is called differenial equaion If all he
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS PAGE # An equaion conaining independen variable, dependen variable & differenial coeffeciens of dependen variables wr independen variable is called differenial equaion If all he
