Geography 128 Winter Quarter Lecture 4: A Transformational View of Cartography
|
|
|
- Raymond Johnson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Geography 128 Winter Quarter 2017 Lecture 4: A Transformational View of Cartography
2 Tobler, W. R. (1979). A Transformational View of Cartography. American Cartographer, vol. 6, no. 2, pp
3 A simplified view Map input Transformation Map output
4 Waldo Tobler s Classic Paper, 1979 the entire process of making, and using a map can be viewed as a sequence of transformations. Types of Cartographic Transformation Geometrical Transformations: to manipulate the locative aspects of the geographical data Map Projections Substantive Transformations: to modify the substantive geographical data Map Generalization Classification
5 Examples of a Cartographic Transformation Input data: World outline in Geographic Coordinates Software: Ingests data Establishes earth model (datum) Establishes transformation (Projection) Executes transformation Saves transformed data Displays transformed data
6 Cartographic Transformations The basis of Computer Cartography The core of Analytical Cartography Forms of Cartographic Transformation Geometry Attribute Symbolization Scale Data Structure and Data Model Map Type
7 Map Geometry Point, Line, Area, (Volume) and Text Properties, position, length, area, shape, content
8 Map Attributes
9 Symbolization
10 Map Scale
11 Data Structure and Model Raster, vector, object
12 Map Type
13 A simplified view Map input Transformation Inverse Transformation Map output
14 Invertibility whether or not a Cartographic Transformation can be undone or reversed to produce the initial starting conditions Clarke, 1995 Stable Transformation invertible controllable and therefore are effectively programmed and modeled, especially with respect to the error introduced Unstable Transformation NOT invertible the inverse transformation produces chaos
15 For example: Map generalization Detailed map to coarse: throw away points and detail Coarse map to detailed: not possible without new data
16 T1a: Earth to earth model
17 T1b: Ellipsoid to symbolized globe
18 T2: Globe to map projection A transformation of the spherical or ellipsoidal earth onto a flat map is called a map projection. The map projection can be onto a flat surface or a surface that can be made flat by cutting, such as a cylinder or a cone.
19 Our simplified view Map input Transformation Inverse Transformation Map output
20 For example Maps1: Mercator projection Map 2: Mollweide Could go directly from Mollweide to Mercator Better to go back to Geographic coordinates (inverse) then forward to Mercator Possible infinite set of pairwise map conversions!
21 Forward and Inverse Projection Techniques
22 Map Projection Transformations Map projections represent many different types of transformation Perfectly invertible (one-to-one) One-to-many Many-to-one Undefined (non-invertible) Imperfectly invertible, e.g. on ellipsoid and geoid, computational error, rounding etc. Some transformations use iterative methods i.e. algorithms, not formulas
23 Matrices: Review Has n rows Has m columns Has values Has a leading diagonal Identity matrix Matrix multiplication Matrix inversion (T -1 ) Powers, squares, etc
24 Maps as matrices
25 World Outline (or any set of points, lines or areas) Consists of many sets of coordinate pairs (x, y) Can be represented as a list or set X, where X is a 2 x n matrix of points Matrix multiplication: Possible when one dimension is equal in sequence E.g. 2 x 2 times a 2 x 10 The transformation can be represented also as a matrix multiplication, with transformation T Works across sequences of transformations
26 Generic map as a matrix [x 1, y 1, z 1 ] [x 2, y 2, z 2 ].. [xn, yn, zn] = X n nodes, n-1 segments
27 Sequences Data matrix X (n x 2) Transformation matrix T1 (2 x 2) Transformation matrix T2 ( 2 x 2) Multiply T1 by T2 gives a new 2 x 2 matrix that performs BOTH transformations! Can repeat as often as we want Examples: Scaling, rotations, changes of origin, projections, etc. Original matrix X, transformation T, result X
28 For example, in Inkscape
29 Rotate 60 deg CCW, then scale to 50%
30 Map Transformation Algebra Matrices have inverses, which reverse effect of multiplication to yield the identity matrix Error creeps in when inversion does not result in identity matrix
31 Equatorial Mercator Transformation
32 Planar Geometry vs. Spherical Geometry Rule of Sines Distance between points
33 Making projections Writing code modules Needs point data input Rasters create error, often autocorrelated Output must be stable Problems when crossing hemispheres Numerical handling Problem of repetition Store data in latitude and longitude, project on the fly? Tools for projections: Open source, code libraries, toolkits, web sites
34 Map projection software General Cartographic Transformation Package C-language (K&R style) version of GCTP PROJ.4 (Most popular) GEOTRANS (NGA) National Geodetic Survey (NOAA/NGS) GMT-3 The Generic Mapping Tools GeoConverter JMPL (Java Map Projections Library) PyProj (Python) GDAL Commercial GeoCart The Geographic Calculator
35 Some issues and research problems Display of pixel loss and replication in reprojecting raster data from the sinusoidal projection Denis White
36 Real Maps and Virtual Maps Joel Morrison (1974) called for an expanded definition of map in the computing era Harold Moellering (1977, 1980, and 1984) defined real and virtual maps Two crucial characteristics Whether a map is directly viewable as a cartographic image Whether it has a permanent tangible reality
37 Classes of Real & Virtual Maps Moellering, 1984, Real Maps, Virtual Maps and Interactive Cartography
38 Transformations between Real & Virtual Maps Moellering, 1984, Real Maps, Virtual Maps and Interactive Cartography Moellering, 2000, The Scope and Conceptual Content of Analytical Cartography
39 Summary Map input Transformation Times N Map output Plus E
Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections
 Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL. Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2
 Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2 What is GIS? A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing and
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2 What is GIS? A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing and
Map Projections. Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps
 Map Projections Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps Map projections Define the spatial relationship between locations on earth and their relative locations on a flat map Are mathematical expressions
Map Projections Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps Map projections Define the spatial relationship between locations on earth and their relative locations on a flat map Are mathematical expressions
Map Projections. What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL
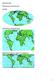 Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Lecture 4. Coordinate Systems & Projections
 Lecture 4 Coordinate Systems & Projections Outline Geodesy Geoids Ellipsoids Geographic Coordinate Systems Magnetic North vs. True North Datums Projections Applying Coordinate Systems and Projections Why
Lecture 4 Coordinate Systems & Projections Outline Geodesy Geoids Ellipsoids Geographic Coordinate Systems Magnetic North vs. True North Datums Projections Applying Coordinate Systems and Projections Why
Georeferencing. Place names Postal addresses Postal codes Coordinate systems (lat/long, UTM, etc.)
 Georeferencing Georeferencing Used to describe the act of assigning locations to data or information Certain requirements include that they are: unique, have shared meaning, and are persistent through
Georeferencing Georeferencing Used to describe the act of assigning locations to data or information Certain requirements include that they are: unique, have shared meaning, and are persistent through
Map projections. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens Coordinate systems Geographic coordinates f a: semi-major axis b: semi-minor axis Geographic latitude b Geodetic latitude a f: flattening = (a-b)/a Expresses as a fraction 1/f = about 300
Rüdiger Gens Coordinate systems Geographic coordinates f a: semi-major axis b: semi-minor axis Geographic latitude b Geodetic latitude a f: flattening = (a-b)/a Expresses as a fraction 1/f = about 300
GIST 3300 / Geographic Information Systems. Last Time. Today
 GIST 3300 / 5300 Last Time Ellipsoids and Datums Today Map Projections Map Projections Today we will build on the concepts of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Ellipsoids and Datums and add the concepts of
GIST 3300 / 5300 Last Time Ellipsoids and Datums Today Map Projections Map Projections Today we will build on the concepts of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Ellipsoids and Datums and add the concepts of
Recall: The scale transformation
 Recall: The scale transformation Geography 12: Maps and Spatial Reasoning Lecture 3: Map Projection Basics Professor Keith Clarke 1:400M The real world A representation of the world A cartographic problem
Recall: The scale transformation Geography 12: Maps and Spatial Reasoning Lecture 3: Map Projection Basics Professor Keith Clarke 1:400M The real world A representation of the world A cartographic problem
Outline. Shape of the Earth. Geographic Coordinates (φ, λ, z) Ellipsoid or Spheroid Rotate an ellipse around an axis. Ellipse.
 Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Lecture 2. A Review: Geographic Information Systems & ArcGIS Basics
 Lecture 2 A Review: Geographic Information Systems & ArcGIS Basics GIS Overview Types of Maps Symbolization & Classification Map Elements GIS Data Models Coordinate Systems and Projections Scale Geodatabases
Lecture 2 A Review: Geographic Information Systems & ArcGIS Basics GIS Overview Types of Maps Symbolization & Classification Map Elements GIS Data Models Coordinate Systems and Projections Scale Geodatabases
Georeferencing. datum. projection. scale. The next few lectures will introduce you to these elements. on the Earth, you ll need to understand how
 Georeferencing GOAL: To assign a location to all the features represented in our geographic information data In order to do so, we need to make use of the following elements: ellipsoid/geoid To determine
Georeferencing GOAL: To assign a location to all the features represented in our geographic information data In order to do so, we need to make use of the following elements: ellipsoid/geoid To determine
The Elements of GIS. Organizing Data and Information. The GIS Database. MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION
 GIS s Roots in Cartography Getting Started With GIS Chapter 2 Dursun Z. Seker MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION Data (numbers and text) store as files refer to them collectively as a database gather inform.
GIS s Roots in Cartography Getting Started With GIS Chapter 2 Dursun Z. Seker MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION Data (numbers and text) store as files refer to them collectively as a database gather inform.
ch02.pdf chap2.pdf chap02.pdf
 Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 8th Edition Karl Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/introduction-to-geographic-information-systems-8th-edition-karl-solutions-manu
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 8th Edition Karl Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/introduction-to-geographic-information-systems-8th-edition-karl-solutions-manu
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I. Lecture 15
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 15 Lecture Plan Midterm Multiple choice part graded (+ solutions) Jump to Ch. 11 for one lecture Coordinate systems Projections, datums, spheroids Unprojected
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 15 Lecture Plan Midterm Multiple choice part graded (+ solutions) Jump to Ch. 11 for one lecture Coordinate systems Projections, datums, spheroids Unprojected
Fri. Jan. 26, Demonstration of QGIS with GPS tracks. Types of data, simple vector (shapefile) formats
 Fri. Jan. 26, 2018 Demonstration of QGIS with GPS tracks Types of data, simple vector (shapefile) formats Map projections, Coordinate Reference Systems Demonstration of QGIS with geologic map 1 Raster
Fri. Jan. 26, 2018 Demonstration of QGIS with GPS tracks Types of data, simple vector (shapefile) formats Map projections, Coordinate Reference Systems Demonstration of QGIS with geologic map 1 Raster
Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E. Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections
 Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections What is Geodesy? The science of geodesy determines: Earth s shape and Interrelation of different points on earth s surface The
Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections What is Geodesy? The science of geodesy determines: Earth s shape and Interrelation of different points on earth s surface The
EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography
 EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 3 Geodesy Map Projections, Datums, and Coordinate Systems 1 Geodesy The science of measuring and representing the shape and size of the earth, and
EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 3 Geodesy Map Projections, Datums, and Coordinate Systems 1 Geodesy The science of measuring and representing the shape and size of the earth, and
Dirty REMOTE SENSING : Lecture 8 A mapping interlude..
 Dirty REMOTE SENSING : Lecture 8 A mapping interlude.. Stuart Green Teagasc Spatial Analysis Group Stuart.green@teagasc.ie Web for the Week: http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/gps.htm http://www.cstars.ucdavis.edu/classes/ers186-w03/lecture17/lecture17.ppt
Dirty REMOTE SENSING : Lecture 8 A mapping interlude.. Stuart Green Teagasc Spatial Analysis Group Stuart.green@teagasc.ie Web for the Week: http://electronics.howstuffworks.com/gps.htm http://www.cstars.ucdavis.edu/classes/ers186-w03/lecture17/lecture17.ppt
The Nature of Spatial Data. Keith C. Clarke Geography UCSB
 The Nature of Spatial Data Keith C. Clarke Geography UCSB Geographic primitives G = g (x, y, z, s, A, t) [x, y, z] = f(λ, φ, d) Geography also highly dependent upon model First, the datum (d) Models of
The Nature of Spatial Data Keith C. Clarke Geography UCSB Geographic primitives G = g (x, y, z, s, A, t) [x, y, z] = f(λ, φ, d) Geography also highly dependent upon model First, the datum (d) Models of
Modern Navigation. Thomas Herring
 12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Today s class Map Projections: Why projections are needed Types of map projections Classification by type of projection Classification by characteristics of projection
12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Today s class Map Projections: Why projections are needed Types of map projections Classification by type of projection Classification by characteristics of projection
Projections and Coordinate Systems
 Projections and Coordinate Systems Overview Projections Examples of different projections Coordinate systems Datums Projections Overview Projections and Coordinate Systems GIS must accurately represent
Projections and Coordinate Systems Overview Projections Examples of different projections Coordinate systems Datums Projections Overview Projections and Coordinate Systems GIS must accurately represent
Lab #3 Map Projections.
 Lab #3 Map Projections http://visual.merriam-webster.com/images/earth/geography/cartography/map-projections.jpg Map Projections Projection: a systematic arrangement of parallels and meridians on a plane
Lab #3 Map Projections http://visual.merriam-webster.com/images/earth/geography/cartography/map-projections.jpg Map Projections Projection: a systematic arrangement of parallels and meridians on a plane
Analytical and Computer Cartography Lecture 3: Review: Coordinate Systems
 Analytical and Computer Cartography Lecture 3: Review: Coordinate Systems Geographic Coordinates NAD83 NAD27 remained in use until the earthcentered international GRS80 was complete (Geodetic Reference
Analytical and Computer Cartography Lecture 3: Review: Coordinate Systems Geographic Coordinates NAD83 NAD27 remained in use until the earthcentered international GRS80 was complete (Geodetic Reference
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections
 NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections From http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ 1 Geographic coordinates Coordinates are expressed as Latitude and Longitude in Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections From http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ 1 Geographic coordinates Coordinates are expressed as Latitude and Longitude in Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS
 2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS What are geographic information systems and what are they used for? ArcGIS: ArcMap, ArcCatalog and ArcToolbox Vector data vs. raster data vs. attribute tables Polygons, polylines,
2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS What are geographic information systems and what are they used for? ArcGIS: ArcMap, ArcCatalog and ArcToolbox Vector data vs. raster data vs. attribute tables Polygons, polylines,
Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP)
 Workshop on : Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP) 14-15 April 2016 Venue: Tehran, Iran GIS definitions GIS: A simplified view of the real
Workshop on : Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP) 14-15 April 2016 Venue: Tehran, Iran GIS definitions GIS: A simplified view of the real
Geographers Perspectives on the World
 What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012
 WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Datums Datums A reference surface of the Earth Used as the
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Datums Datums A reference surface of the Earth Used as the
The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet. Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about!
 Georeferencing I GEOG 300, Lecture 4 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet Quiz Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about! 5:30 7:30 PM, Wednesday September
Georeferencing I GEOG 300, Lecture 4 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet Quiz Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about! 5:30 7:30 PM, Wednesday September
How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity
 Map projections How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity http://www.mapovasbirka.cz/english/index_eng.html The world could be mapped like
Map projections How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity http://www.mapovasbirka.cz/english/index_eng.html The world could be mapped like
Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems.
 Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems. A GIS without coordinates would simply be a database like Microsoft Excel
Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems. A GIS without coordinates would simply be a database like Microsoft Excel
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015
 WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
Version 1.1 GIS Syllabus
 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CERTIFICATION Version 1.1 GIS Syllabus Endorsed 1 Version 1 January 2007 GIS Certification Programme 1. Target The GIS certification is aimed at: Those who wish to demonstrate
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS CERTIFICATION Version 1.1 GIS Syllabus Endorsed 1 Version 1 January 2007 GIS Certification Programme 1. Target The GIS certification is aimed at: Those who wish to demonstrate
This week s topics. Week 6. FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications. Week 6
 FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 6 Week 6 Last week Chapter 8 Combining and splitting landscape features and merging GIS databases Chapter 11 Overlay processes Questions? Next week
FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 6 Week 6 Last week Chapter 8 Combining and splitting landscape features and merging GIS databases Chapter 11 Overlay processes Questions? Next week
YYT-C3002 Application Programming in Engineering GIS I. Anas Altartouri Otaniemi
 YYT-C3002 Application Programming in Engineering GIS I Otaniemi Overview: GIS lectures & exercise We will deal with GIS application development in two lectures. Because of the versatility of GIS data models
YYT-C3002 Application Programming in Engineering GIS I Otaniemi Overview: GIS lectures & exercise We will deal with GIS application development in two lectures. Because of the versatility of GIS data models
EUROPEAN COMPUTER DRIVING LICENCE. GIS Cartography. Syllabus
 EUROPEAN COMPUTER DRIVING LICENCE GIS Cartography Syllabus Purpose This document details the syllabus for ECDL GIS Module 1 Cartography. The syllabus describes, through learning outcomes, the knowledge
EUROPEAN COMPUTER DRIVING LICENCE GIS Cartography Syllabus Purpose This document details the syllabus for ECDL GIS Module 1 Cartography. The syllabus describes, through learning outcomes, the knowledge
MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts.
 MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts. Types of Maps General Purpose Topographic Thematic/Choropleth Dot Graduated Circle Isometric/Isolines Isopleth Mental Maps Scale Small-scale
MAP PROJECTIONS but before let s review some basic concepts. Types of Maps General Purpose Topographic Thematic/Choropleth Dot Graduated Circle Isometric/Isolines Isopleth Mental Maps Scale Small-scale
Karsten Vennemann, Seattle. QGIS Workshop CUGOS Spring Fling 2015
 Karsten Vennemann, Seattle 2015 a very capable and flexible Desktop GIS QGIS QGIS Karsten Workshop Vennemann, Seattle slide 2 of 13 QGIS - Desktop GIS originally a GIS viewing environment QGIS for the
Karsten Vennemann, Seattle 2015 a very capable and flexible Desktop GIS QGIS QGIS Karsten Workshop Vennemann, Seattle slide 2 of 13 QGIS - Desktop GIS originally a GIS viewing environment QGIS for the
DATA 301 Introduction to Data Analytics Geographic Information Systems
 DATA 301 Introduction to Data Analytics Geographic Information Systems Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca DATA 301: Data Analytics (2) Why learn Geographic
DATA 301 Introduction to Data Analytics Geographic Information Systems Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca DATA 301: Data Analytics (2) Why learn Geographic
Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections
 Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections Coordinate systems and map projections if we want to integrate geographic data from many different sources, we need to use a consistent
Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections Coordinate systems and map projections if we want to integrate geographic data from many different sources, we need to use a consistent
Where on Earth are We? Projections and Coordinate Reference Systems
 Where on Earth are We? Projections and Coordinate Reference Systems Nick Eubank February 11, 2018 If I told you that there was a treasure chest buried at the coordinates p2, 5q, your first response might
Where on Earth are We? Projections and Coordinate Reference Systems Nick Eubank February 11, 2018 If I told you that there was a treasure chest buried at the coordinates p2, 5q, your first response might
Lecture 2. Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 Lecture 2 Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Map Projections Map projections are mathematical formulas
Lecture 2 Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Map Projections Map projections are mathematical formulas
Illustrator: Vector base Each line/point store some sort of information Mapping Representation of the world
 Illustrator: Vector base Each line/point store some sort of information Mapping Representation of the world Photoshop Raster base Images can be overlaid Pixel vector data model: [data models] A representation
Illustrator: Vector base Each line/point store some sort of information Mapping Representation of the world Photoshop Raster base Images can be overlaid Pixel vector data model: [data models] A representation
Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook Chang 2006 and the practical manual)
 Introduction Geo-information Science (GRS-10306) Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook 2006 and the practical manual) Introduction Chapter 1 Geographic information system (GIS) Geographically
Introduction Geo-information Science (GRS-10306) Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook 2006 and the practical manual) Introduction Chapter 1 Geographic information system (GIS) Geographically
Introduction to GIS - 2
 Introduction to GIS - 2 Outline Using GIS Representation of spatial objects in GIS Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh
Introduction to GIS - 2 Outline Using GIS Representation of spatial objects in GIS Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh
Shape e o f f the e Earth
 1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
Introduction to Geographic Information Science. Updates/News. Last Lecture. Geography 4103 / Map Projections and Coordinate Systems
 Geography 4103 / 5103 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Map Projections and Coordinate Systems Updates/News Thursday s lecture Reading discussion 1 find the readings online open questions,
Geography 4103 / 5103 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Map Projections and Coordinate Systems Updates/News Thursday s lecture Reading discussion 1 find the readings online open questions,
What you learned. Lecture 27: Class Summary. Maps and geodesy. How you learned it
 What you learned Geography 12: Maps and Spatial Reasoning Lecture 27: Class Summary Professor Keith Clarke Map geometry, construction and content Practical map use, reading and navigation Map representation
What you learned Geography 12: Maps and Spatial Reasoning Lecture 27: Class Summary Professor Keith Clarke Map geometry, construction and content Practical map use, reading and navigation Map representation
Representation of Geographic Data
 GIS 5210 Week 2 The Nature of Spatial Variation Three principles of the nature of spatial variation: proximity effects are key to understanding spatial variation issues of geographic scale and level of
GIS 5210 Week 2 The Nature of Spatial Variation Three principles of the nature of spatial variation: proximity effects are key to understanding spatial variation issues of geographic scale and level of
12/26/2012. Geographic Information Systems * * * * GIS (... yrezaei
 ( - Geographic Information Systems ( ( 1 2 3 Information System Data base DB IS IS DB (Knowledge ( ( (System (Information System - (Georefrence Analysis Data + Knowledge ======== Information 4 5 ( < 10%
( - Geographic Information Systems ( ( 1 2 3 Information System Data base DB IS IS DB (Knowledge ( ( (System (Information System - (Georefrence Analysis Data + Knowledge ======== Information 4 5 ( < 10%
THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION
 UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
UNIT 7 THE EARTH AND ITS REPRESENTATION TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 THE EARTH AND THE SOLAR SYSTEM... 2 2 THE EARTH S MOVEMENTS... 2 2.1 Rotation.... 2 2.2 The revolution of the Earth: seasons of the year....
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts. -Coordinate Systems -Datum
 Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING
 GIS in Ecology SPATIAL REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING : :1 Where on earth? Early mapmakers recognized the need for a system that could locate features on the earth's surface.
GIS in Ecology SPATIAL REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING : :1 Where on earth? Early mapmakers recognized the need for a system that could locate features on the earth's surface.
1/28/16. EGM101 Skills Toolbox. Oblate spheroid. The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections. Geoid
 EGM101 Skills Toolbox Oblate spheroid The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections The geoid is the shape that the surface of the oceans would take under the influence of Earth's gravitation
EGM101 Skills Toolbox Oblate spheroid The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections The geoid is the shape that the surface of the oceans would take under the influence of Earth's gravitation
Coordinate systems, measured surveys for BIM, total station for BIM, as-built surveys, setting-out
 Coordinate systems, measured surveys for BIM, total station for BIM, as-built surveys, setting-out What is a BIM What does a BIM do Why use a BIM BIM Software BIM and the Surveyor How do they relate to
Coordinate systems, measured surveys for BIM, total station for BIM, as-built surveys, setting-out What is a BIM What does a BIM do Why use a BIM BIM Software BIM and the Surveyor How do they relate to
Mapping Census Data in ArcView 3.x
 Mapping Census Data in ArcView 3.x Nancy Lemay University of Ottawa Barbara Znamirowski Trent University Workshop Outline Defining certain concepts and terms: Map scale, coordinate systems, datum and projections.
Mapping Census Data in ArcView 3.x Nancy Lemay University of Ottawa Barbara Znamirowski Trent University Workshop Outline Defining certain concepts and terms: Map scale, coordinate systems, datum and projections.
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth. 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth. 3.1 Objectives
 Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
1. Geospatial technology rarely links geospatial data to nonspatial data. a. True *b. False
 Chapter 2 Where in the Geospatial World Are You? 1. Geospatial technology rarely links geospatial data to nonspatial data. 2. For geospatial technology to work, every location on Earth must be: a. inhabited
Chapter 2 Where in the Geospatial World Are You? 1. Geospatial technology rarely links geospatial data to nonspatial data. 2. For geospatial technology to work, every location on Earth must be: a. inhabited
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS (GIS)
 AN INTRODUCTION TO GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS (GIS) Joana Magos Brehm 1, Ali Shehadeh 2 1 Botanical Garden, National Museum of Natural History, University of Lisbon (Portugal) 2 Genetic Resources Unit,
AN INTRODUCTION TO GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS (GIS) Joana Magos Brehm 1, Ali Shehadeh 2 1 Botanical Garden, National Museum of Natural History, University of Lisbon (Portugal) 2 Genetic Resources Unit,
Map Projections (Part 1)
 1 Earth is a round, maps are not. Four projection families. Equivalent (Equal Area) projections Preserves relative areas Commonly used for thematic maps Ex: Albers Conformal projections Preserve angles,
1 Earth is a round, maps are not. Four projection families. Equivalent (Equal Area) projections Preserves relative areas Commonly used for thematic maps Ex: Albers Conformal projections Preserve angles,
Hydrology and Floodplain Analysis, Chapter 10
 Hydrology and Floodplain Analysis, Chapter 10 Hydrology and Floodplain Analysis, Chapter 10.1 Introduction to GIS GIS Geographical Information System Spatial Data Data linked with geographical location
Hydrology and Floodplain Analysis, Chapter 10 Hydrology and Floodplain Analysis, Chapter 10.1 Introduction to GIS GIS Geographical Information System Spatial Data Data linked with geographical location
Scott A. True Project Scientist Geodesy & Geophysics Division Basic and Applied Research Office InnoVision Directorate
 EGM96 Variable Resolution Geoid Implementation Error in GEOTRANS 2.3 Scott A. True Project Scientist Geodesy & Geophysics Division Basic and Applied Research Office InnoVision Directorate Introduction
EGM96 Variable Resolution Geoid Implementation Error in GEOTRANS 2.3 Scott A. True Project Scientist Geodesy & Geophysics Division Basic and Applied Research Office InnoVision Directorate Introduction
Coordinate Systems. Location on earth is defined by coordinates
 Coordinate Systems We think of the earth as a sphere It is actually a spheroid (ellipsoid), slightly larger in radius at the equator than at the poles Shape of the Earth Location on earth is defined by
Coordinate Systems We think of the earth as a sphere It is actually a spheroid (ellipsoid), slightly larger in radius at the equator than at the poles Shape of the Earth Location on earth is defined by
Understanding Projections for GIS
 Presented by John Schaeffer Juniper GIS Services, Inc. This PowerPoint is available at JuniperGIS.com Presentation Objectives To understand basic concepts on projections and coordinate systems for the
Presented by John Schaeffer Juniper GIS Services, Inc. This PowerPoint is available at JuniperGIS.com Presentation Objectives To understand basic concepts on projections and coordinate systems for the
Spatial Data, 16 th Century Dutchmen, GPS and GIS. Martin Charlton, National Centre for Geocomputation National University of Ireland Maynooth
 Spatial Data, 16 th Century Dutchmen, GPS and GIS Martin Charlton, National Centre for Geocomputation National University of Ireland Maynooth Maps as truth Maps are cultural artifacts, comparable in history
Spatial Data, 16 th Century Dutchmen, GPS and GIS Martin Charlton, National Centre for Geocomputation National University of Ireland Maynooth Maps as truth Maps are cultural artifacts, comparable in history
Intro to GIS In Review
 Intro to GIS In Review GIS Analysis Winter 2016 GIS A quarter in review Geographic data types Acquiring GIS data Projections / Coordinate systems Working with attribute tables Data classification Map design
Intro to GIS In Review GIS Analysis Winter 2016 GIS A quarter in review Geographic data types Acquiring GIS data Projections / Coordinate systems Working with attribute tables Data classification Map design
Wed. Apr. 25, 2018 GIS DEMO. Reading: Ch Comparing Image Types (Death Valley) Treat as review of techniques already studied
 Wed. Apr. 25, 2018 GIS DEMO Reading: Ch. 14 -- Comparing Image Types (Death Valley) Treat as review of techniques already studied 1 GIS: Geographic Information Systems Way to organize data obtained by
Wed. Apr. 25, 2018 GIS DEMO Reading: Ch. 14 -- Comparing Image Types (Death Valley) Treat as review of techniques already studied 1 GIS: Geographic Information Systems Way to organize data obtained by
Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University
 Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University TTU Graduate Certificate Geographic Information Science and Technology (GIST) 3 Core Courses and
Spatial Analysis and Modeling (GIST 4302/5302) Guofeng Cao Department of Geosciences Texas Tech University TTU Graduate Certificate Geographic Information Science and Technology (GIST) 3 Core Courses and
Susan Cutter et al. Aug, 2002, The Professional Geographer, 54(3): David Tenenbaum GEOG 070 UNC-CH Spring 2005
 What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
Georeferencing. Geography is the key to linking attributes. Georeferencing is the key to geography.
 Georeferencing Geography is the key to linking attributes. Georeferencing is the key to geography. Why georeferencing? Many reasons for having georeferences Many different approaches to georeferencing
Georeferencing Geography is the key to linking attributes. Georeferencing is the key to geography. Why georeferencing? Many reasons for having georeferences Many different approaches to georeferencing
What is a Map Projection?
 What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910
 Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910 Where are you? 31UFT8361 174,7 441,2 51 58' NB 5 40' OL 2/60 Who are they? 3/60 Do geo data describe Earth s phenomena perfectly? Georeference systems ellipsoid
Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910 Where are you? 31UFT8361 174,7 441,2 51 58' NB 5 40' OL 2/60 Who are they? 3/60 Do geo data describe Earth s phenomena perfectly? Georeference systems ellipsoid
The Sinusoidal Projection: A New Importance in Relation to Global Image Data*
 The Sinusoidal Projection: A New Importance in Relation to Global Image Data* Jeong Chang Seong Northern Michigan University Karen A. Mulcahy East Carolina University E. Lynn Usery University of Georgia
The Sinusoidal Projection: A New Importance in Relation to Global Image Data* Jeong Chang Seong Northern Michigan University Karen A. Mulcahy East Carolina University E. Lynn Usery University of Georgia
Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910
 Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910 Where are you? 31UFT8361 174,7 441,2 51 58' NB 5 40' OL 2/60 Who are they? 3/60 Do geo data describe Earth s phenomena perfectly? Georeference systems ellipsoid
Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910 Where are you? 31UFT8361 174,7 441,2 51 58' NB 5 40' OL 2/60 Who are they? 3/60 Do geo data describe Earth s phenomena perfectly? Georeference systems ellipsoid
Map Projections. Chapter 4 MAP PROJECTION
 Map Projections Chapter 4 Map Projections What is map projection? Why are map projections drawn? What are the different types of projections? Which projection is most suitably used for which area? In this
Map Projections Chapter 4 Map Projections What is map projection? Why are map projections drawn? What are the different types of projections? Which projection is most suitably used for which area? In this
Keith C. Clarke Department of Geologyand Geography Hunter College-CUNY 695 Park Avenue New York, NY 10021,USA
 DISTORTION ON THE INTERRUPTED MODIFIED COLLIGNON PROJECTION Keith C. Clarke Department of Geologyand Geography Hunter College-CUNY 695 Park Avenue New York, NY 10021,USA and Karen A. Mulcahy Earth and
DISTORTION ON THE INTERRUPTED MODIFIED COLLIGNON PROJECTION Keith C. Clarke Department of Geologyand Geography Hunter College-CUNY 695 Park Avenue New York, NY 10021,USA and Karen A. Mulcahy Earth and
Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections.
 Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections. 1 It is extremely important that you gain an understanding of coordinate systems and map projections. GIS works with spatial data, and,
Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections. 1 It is extremely important that you gain an understanding of coordinate systems and map projections. GIS works with spatial data, and,
Chapter 1 Learning Guide Thinking Geographically
 Chapter 1 Learning Guide Thinking Geographically Key Issue 1 How Do Geographers Address Where Things Are? Pgs. 2 13 1. Define map: 2. Define cartography: Maps 3. Give an example of early mapmaking and
Chapter 1 Learning Guide Thinking Geographically Key Issue 1 How Do Geographers Address Where Things Are? Pgs. 2 13 1. Define map: 2. Define cartography: Maps 3. Give an example of early mapmaking and
Lab 1: Importing Data, Rectification, Datums, Projections, and Output (Mapping)
 Lab 1: Importing Data, Rectification, Datums, Projections, and Output (Mapping) Topics covered in this lab: i. Importing spatial data to TAS ii. Rectification iii. Conversion from latitude/longitude to
Lab 1: Importing Data, Rectification, Datums, Projections, and Output (Mapping) Topics covered in this lab: i. Importing spatial data to TAS ii. Rectification iii. Conversion from latitude/longitude to
First Exam: New Date. 6 Geographers Tools Maps and their Parts 9/14/2017 MAP MAKING MAP MAKING MAP PROJECTIONS MAP PROJECTIONS
 6 Geographers Tools Maps and their Parts Prof. nthony Grande Hunter ollege Geography Lecture design, content and presentation FG 0917. Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright.
6 Geographers Tools Maps and their Parts Prof. nthony Grande Hunter ollege Geography Lecture design, content and presentation FG 0917. Individual images and illustrations may be subject to prior copyright.
2. Which geometric model has been used at some time to describe the earth? a. Sphere b. Oblate ellipsoid c. Flat disk. d. Geoid e.
 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 Geography 12 Sample Mid-Term Examination Before you
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 Geography 12 Sample Mid-Term Examination Before you
Big Data and Geospatial with HPCC Systems
 Big Data and Geospatial with HPCC Systems Powered by LexisNexis Risk Solutions Ignacio Calvo Greg McRandal 10/05/2016 Concepts in Geospatial How to use them with HPCC Use cases @HPCCSystems Definition
Big Data and Geospatial with HPCC Systems Powered by LexisNexis Risk Solutions Ignacio Calvo Greg McRandal 10/05/2016 Concepts in Geospatial How to use them with HPCC Use cases @HPCCSystems Definition
Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections
 Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections SHAPE OF THE EARTH Earth's Shape Geoid: shape of earth minus topographic features (irregular due to local variations in gravity) Ellipsoid: elongated
Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections SHAPE OF THE EARTH Earth's Shape Geoid: shape of earth minus topographic features (irregular due to local variations in gravity) Ellipsoid: elongated
1. Define map: 2. Name and define the five concepts that guide geographers a) 3. Define cartography: MAPS 4. A map serves two purposes a)
 1. Define map: 2. Name and define the five concepts that guide geographers c) d) e) 3. Define cartography: MAPS 4. A map serves two purposes 5. Give two examples of early mapmaking and its (unusual?) materials
1. Define map: 2. Name and define the five concepts that guide geographers c) d) e) 3. Define cartography: MAPS 4. A map serves two purposes 5. Give two examples of early mapmaking and its (unusual?) materials
P R O J E C T I O N S. Map Projections. Introduction to. Map Projections. with. TNTmips. TNTedit TNTview. page 1
 P R O J E C T I O N S Introduction to Map Projections Map Projections with TNTmips page 1 TNTedit TNTview Before Getting Started Positions in a georeferenced spatial object must refer to a particular coordinate
P R O J E C T I O N S Introduction to Map Projections Map Projections with TNTmips page 1 TNTedit TNTview Before Getting Started Positions in a georeferenced spatial object must refer to a particular coordinate
Geographic coordinate systems
 1 Geographic coordinate systems In this chapter you ll learn about longitude and latitude. You ll also learn about the parts that comprise a geographic coordinate system including Spheres and spheroids
1 Geographic coordinate systems In this chapter you ll learn about longitude and latitude. You ll also learn about the parts that comprise a geographic coordinate system including Spheres and spheroids
Chapter 1: The World of Geography
 Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
Chapter 1: The World of Geography Chapter 1: What is Geography? *It is the study of our earth; our home. OR *Anything that can be mapped! *Geography mixes up the physical and human aspects of our world
Projection and Reprojection
 Using Quantum GIS Tutorial ID: IGET_GIS_002 This tutorial has been developed by BVIEER as part of the IGET web portal intended to provide easy access to geospatial education. This tutorial is released
Using Quantum GIS Tutorial ID: IGET_GIS_002 This tutorial has been developed by BVIEER as part of the IGET web portal intended to provide easy access to geospatial education. This tutorial is released
Lab 1: Importing Data, Rectification, Datums, Projections, and Coordinate Systems
 Lab 1: Importing Data, Rectification, Datums, Projections, and Coordinate Systems Topics covered in this lab: i. Importing spatial data to TAS ii. Rectification iii. Conversion from latitude/longitude
Lab 1: Importing Data, Rectification, Datums, Projections, and Coordinate Systems Topics covered in this lab: i. Importing spatial data to TAS ii. Rectification iii. Conversion from latitude/longitude
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2018 Lecture Notes Note Introduction to Linear Algebra the EECS Way
 EECS 16A Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 018 Lecture Notes Note 1 1.1 Introduction to Linear Algebra the EECS Way In this note, we will teach the basics of linear algebra and relate
EECS 16A Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 018 Lecture Notes Note 1 1.1 Introduction to Linear Algebra the EECS Way In this note, we will teach the basics of linear algebra and relate
Military Map Reading 201
 Military Map Reading 201 This information paper is designed to resolve the confusion between the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) and the Military Grid Reference System (MGRS) coordinates. The two systems
Military Map Reading 201 This information paper is designed to resolve the confusion between the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) and the Military Grid Reference System (MGRS) coordinates. The two systems
I. Numerical Computing
 I. Numerical Computing A. Lectures 1-3: Foundations of Numerical Computing Lecture 1 Intro to numerical computing Understand difference and pros/cons of analytical versus numerical solutions Lecture 2
I. Numerical Computing A. Lectures 1-3: Foundations of Numerical Computing Lecture 1 Intro to numerical computing Understand difference and pros/cons of analytical versus numerical solutions Lecture 2
Geog Lecture 29 Mapping and GIS Continued
 Geog 1000 - Lecture 29 Mapping and GIS Continued http://scholar.ulethbridge.ca/chasmer/classes/ Today s Lecture (Pgs 13-25, 28-29) 1. Hand back Assignment 3 2. Review of Dr. Peddle s lecture last week
Geog 1000 - Lecture 29 Mapping and GIS Continued http://scholar.ulethbridge.ca/chasmer/classes/ Today s Lecture (Pgs 13-25, 28-29) 1. Hand back Assignment 3 2. Review of Dr. Peddle s lecture last week
Map Projections 2/4/2013. Map Projections. Rhumb Line (Loxodrome) Great Circle. The GLOBE. Line of constant bearing (e.g., 292.
 The GLOBE ADVANTAGES Directions True Distances True Shapes True Area True DISADVANTAGES Very small scale with little detail. Costly to reproduce and update. Difficult to carry around. Bulky to store. FACTS
The GLOBE ADVANTAGES Directions True Distances True Shapes True Area True DISADVANTAGES Very small scale with little detail. Costly to reproduce and update. Difficult to carry around. Bulky to store. FACTS
GPS Remote Sensing. GIS Photogrammetry. GEODESY Equipment (total station) CARTOGRAPHY Survey Software. Map Projection Coordinate Systems
 GPS Remote Sensing GIS Photogrammetry GEODESY Equipment (total station) CARTOGRAPHY Survey Software Map Projection Coordinate Systems 1 Coordinate Systems, Datum and Map Projection Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq
GPS Remote Sensing GIS Photogrammetry GEODESY Equipment (total station) CARTOGRAPHY Survey Software Map Projection Coordinate Systems 1 Coordinate Systems, Datum and Map Projection Dr. Maher A. El-Hallaq
6. Provide an example of developments in geography for each of the following:
 Thinking Geographically: Key Issue 1 How Do Geographers Describe Where Things Are? Rubenstein, p. 5-13 1. Define map: 2. Define cartography: MAPS 3. Give two examples of developments in early mapmaking.
Thinking Geographically: Key Issue 1 How Do Geographers Describe Where Things Are? Rubenstein, p. 5-13 1. Define map: 2. Define cartography: MAPS 3. Give two examples of developments in early mapmaking.
INTRODUCTION TO GIS. Dr. Ori Gudes
 INTRODUCTION TO GIS Dr. Ori Gudes Outline of the Presentation What is GIS? What s the rational for using GIS, and how GIS can be used to solve problems? Explore a GIS map and get information about map
INTRODUCTION TO GIS Dr. Ori Gudes Outline of the Presentation What is GIS? What s the rational for using GIS, and how GIS can be used to solve problems? Explore a GIS map and get information about map
CHAPTER EXIT CHAPTER. Models of Earth. 3.1 Modeling the Planet. 3.2 Mapmaking and Technology. 3.3 Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE
 EXIT CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet.2 Mapmaking and Technology. Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet A flat of Earth is a convenient tool, but it can distort the shape, distance,
EXIT CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet.2 Mapmaking and Technology. Topographic Maps CHAPTER OUTLINE CHAPTER.1 Modeling the Planet A flat of Earth is a convenient tool, but it can distort the shape, distance,
AP Human Geography Chapter 1: Thinking Geographically Key Issue 1: How do Geographers describe where things are?
 AP Human Geography Chapter 1: Thinking Geographically Key Issue 1: How do Geographers describe where things are? Studying Human Geography Physical Geography Physical geography deals with Earth s natural
AP Human Geography Chapter 1: Thinking Geographically Key Issue 1: How do Geographers describe where things are? Studying Human Geography Physical Geography Physical geography deals with Earth s natural
