Coordinate Systems and Map James Frew ESM 263 Winter
|
|
|
- Sheryl Hamilton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Coordinate Systems and Map 1
2 Outline and longitude and coordinate systems Placenames Postal addresses and postal codes Linear referencing systems Cadasters georeferences 2
3 Georeferencing Linking to specific Unique = f (georeference) Shared means the same thing to everybody Persistent means the same thing tomorrow 3
4 Types of Georeferences Nominal Placenames Ordinal street addresses (in some of the world, anyway ) Interval or Cyclic linear or angular distance from fixed places e.g. from Equator or Greenwich Meridian 4
5 Geographic Coordinates Spherical coordinates Longitude defined by Center of mass Equator = f(rota@on) Zero meridian = f(poli@cs) Spherical Earth R km A km 2 5
6 Prime Meridian at Greenwich, UK Why the Greenwich meridian moved 6
7 Longitude Angle between planes of Zero meridian and axis 7
8 Requires model of Earth s shape Closer to an ellipsoid than a sphere an ellipse rotated about its minor axis N-S diameter ~ 1/300 less than E-W WGS 84 ellipsoid (current best model) Radius at Equator: km Flagening: 1/
9 and the Ellipsoid is angle between perpendicular to surface plane of the Equator Same pt, different ellipsoids: Same (almost) longitude Different 9
10 Why Different Ellipsoids? Before satellites: many Each country used local best fit ellipsoid US: North American Datum of 1927 (NAD 27) Clarke 1866 ellipsoid tangent to surface at Meades Ranch, KS US: North Amercian Datum of 1983 (NAD 83) GRS 1980 ellipsoid Earth-centered <=200 m offset from NAD 27 (in US) Aner satellites: WGS 84 Earth-centered ellipsoid <1 cm offset from NAD 83 (in US) 10
11 NAD27 NAD83 datum shin 11
12 Datum Connects Ellipsoid to Earth 12
13 What Happens When You Mix Datums USS LA MOURE COUNTY aground in Caleta Cifuncho Bay, Chile after navigating with GPS (WGS-84 datum) on a local chart on local datum. 13
14 Why project Earth s surface onto plane? See whole Earth surface at once GIS maps/displays scan, digi@ze print, plot Much easier to measure distance Represent Earth surface as a rectangular grid we ll talk more about this in the raster sec@on... 14
15 All distort the Earth in some way Which is most important? (Pick one) Shape? Use conformal same in all Area? Use equal area Distorts shapes to preserve area (No has both of these (And maybe add) Distance? Use equidistant Only from 1 or 2 points, or along 1 line. 15
16 Cylindrical Wrap a cylinder around the Earth 16
17 Cylindrical Example: Mercator 17
18 Conic Wrap a cone around the Earth Standard Parallel(s):where cone intersects Earth surface 18
19 Conic Example: Lambert Conformal Conic 19
20 The Unprojected (aka Plate Carrée) X = longitude, Y = la@tude Cylindrical projec@on Neither conformal nor equal area 20
21 Comparing U.S. Mercator Plate Carrée Lambert Conformal Conic 21
22 Comparing North America Albers Equal Area Lambert Conformal Conic 22
23 Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) standard Originally military System of 60 zones w/in zone <= 0.04% Transverse Cylindrical wrapped around Poles, not Equator 23
24 UTM Zones Zones are each six degrees of longitude, numbered from W to E 24
25 UTM Coordinates X: (meters east) Y: northing (meters north) X = 500 central meridian false eas@ng Y = Equator Eas@ngs and northings are both in meters allowing easy es@ma@on of distance on the projecaon UTM georeference zone number six-digit eas@ng seven-digit northing E.g., 14, E, N 25
26 UTM Zones: Each zone is a different projec@on Adjacent zones won t fit along border What about areas that span zones? Either: pick 1 zone accept >normal distor@ons in other zone Or: use other projec@on that spans area E.g. CA (zones 10 & 11) UTM zone 10½ Teale Albers (equal area conic) 26
27 State Plane Coordinates (SPC83) Defined in US by each state Many different Some states use zones 27
28 Which should I use? For data generally: equal-area so calcula@ons and comparisons make sense specifically: whatever your project/client already uses so you don t conver@ng stuff For maps generally: whatever s most familiar to the map s users specifically: conformal: if it s most important to recognize shapes equal-area: if it s most important to compare sizes (The smaller the area, the less important this dis@nc@on is.) 28
29 Placenames Earliest form of georeferencing & most commonly used in everyday Work at many different scales villages neighborhoods Evolve Peking Peip ing Beijing Taprobane Ceylon Sri Lanka Poland 29
30 Uniqueness: Which One? Domain-specific many instances of Springfield in the U.S. but only one per state Context-specific Paris, France vs Paris, Texas 30
31 Postal Address as Georeference Works iff mail (dwelling, office, ) is unique along: Street name is unique within: Local area (city, county, ) is unique within: Region (state, province, ) but not for... Rural areas e.g. Star Route 1 Box 198 changing to West 210th St. Natural features (lakes, mountains, rivers, ) Non-sequen@al street addresses e.g. Japan 31
32 Postcodes as Georeferences Defined in many countries US ZIP codes UK postcodes Hierarchically structured Leading characters large areas Trailing characters smaller areas vs. postal address? Ubiquitous Less precise 32
33 Linear Referencing on a network road, rail, river,... Expressed as name of link distance along link from fixed point e.g. intersec@on Used for Maintenance Public safety 33
34 Linear Referencing Problems Distance measurement inaccuracy e.g. car odometer Fixed points may be far apart Exacerbates measurement inaccuracy "street1 x street2" not always unique may intersect more than once 34
35 Cadasters Land ownership (property boundary) maps Parcel fabrics in ArcGIS US Public Land Survey System (PLSS) Georeferences local cadasters esp. in western US Natural resources Similar systems in other countries 35
36 Township and Range System (PLSS) land ownership in most of western US townships laid out in six mile squares on either side of accurately surveyed Principal Meridian. Square mile within township numbered as shown east of PM, reversed west the Principal Meridian. 36
37 Georeferences Transform coordinates to new ArcGIS projec,on and transforma,on tools Geocoding Convert street addresses to coordinates ArcGIS geocoding tools Google geocoding web service Gazegeer database of: place = (name, loca@on, type) U.S. Board on Geographic Names GeoNames 37
Georeferencing. Geography is the key to linking attributes. Georeferencing is the key to geography.
 Georeferencing Geography is the key to linking attributes. Georeferencing is the key to geography. Why georeferencing? Many reasons for having georeferences Many different approaches to georeferencing
Georeferencing Geography is the key to linking attributes. Georeferencing is the key to geography. Why georeferencing? Many reasons for having georeferences Many different approaches to georeferencing
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts. -Coordinate Systems -Datum
 Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
Georeferencing, Map Projections, Cartographic Concepts -Map Projections -Coordinate Systems -Datum Map projection is "the process of systematically transforming positions on the Earth's spherical surface
Georeferencing. Place names Postal addresses Postal codes Coordinate systems (lat/long, UTM, etc.)
 Georeferencing Georeferencing Used to describe the act of assigning locations to data or information Certain requirements include that they are: unique, have shared meaning, and are persistent through
Georeferencing Georeferencing Used to describe the act of assigning locations to data or information Certain requirements include that they are: unique, have shared meaning, and are persistent through
SIG/GIS: Systèmes d Information Géographiques Geographical Information Systems. Principles
 SIG/GIS: Systèmes d Information Géographiques Geographical Information Systems Principles GEOREFERENCING Outlines 1- Representing Geography 2- The nature of Geographic Data 3- Geo-referencing 4-Uncertainty
SIG/GIS: Systèmes d Information Géographiques Geographical Information Systems Principles GEOREFERENCING Outlines 1- Representing Geography 2- The nature of Geographic Data 3- Geo-referencing 4-Uncertainty
REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING
 GIS in Ecology SPATIAL REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING : :1 Where on earth? Early mapmakers recognized the need for a system that could locate features on the earth's surface.
GIS in Ecology SPATIAL REFERENCING COORDINATE SYSTEMS MAP PROJECTIONS GEOREFERENCING : :1 Where on earth? Early mapmakers recognized the need for a system that could locate features on the earth's surface.
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL. Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2
 Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2 What is GIS? A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing and
Applied Cartography and Introduction to GIS GEOG 2017 EL Lecture-1 Chapters 1 and 2 What is GIS? A Geographic Information System (GIS) is a computer system for capturing, storing, querying, analyzing and
How does an ellipsoid differ from a sphere in approximating the shape and size of the Earth?
 Chapter 02 Test Bank Worksheet Questions 1. What is a map projection? Topic: Map Projection 2. How does an ellipsoid differ from a sphere in approximating the shape and size of the Earth? Topic: Ellipsoid
Chapter 02 Test Bank Worksheet Questions 1. What is a map projection? Topic: Map Projection 2. How does an ellipsoid differ from a sphere in approximating the shape and size of the Earth? Topic: Ellipsoid
Geographic coordinate systems
 1 Geographic coordinate systems In this chapter you ll learn about longitude and latitude. You ll also learn about the parts that comprise a geographic coordinate system including Spheres and spheroids
1 Geographic coordinate systems In this chapter you ll learn about longitude and latitude. You ll also learn about the parts that comprise a geographic coordinate system including Spheres and spheroids
The Elements of GIS. Organizing Data and Information. The GIS Database. MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION
 GIS s Roots in Cartography Getting Started With GIS Chapter 2 Dursun Z. Seker MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION Data (numbers and text) store as files refer to them collectively as a database gather inform.
GIS s Roots in Cartography Getting Started With GIS Chapter 2 Dursun Z. Seker MAP and ATRIBUTE INFORMATION Data (numbers and text) store as files refer to them collectively as a database gather inform.
Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems.
 Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems. A GIS without coordinates would simply be a database like Microsoft Excel
Welcome to Lesson 4. It is important for a GIS analyst to have a thorough understanding of map projections and coordinate systems. A GIS without coordinates would simply be a database like Microsoft Excel
ch02.pdf chap2.pdf chap02.pdf
 Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 8th Edition Karl Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/introduction-to-geographic-information-systems-8th-edition-karl-solutions-manu
Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 8th Edition Karl Solutions Manual Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/introduction-to-geographic-information-systems-8th-edition-karl-solutions-manu
Map projections. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens Coordinate systems Geographic coordinates f a: semi-major axis b: semi-minor axis Geographic latitude b Geodetic latitude a f: flattening = (a-b)/a Expresses as a fraction 1/f = about 300
Rüdiger Gens Coordinate systems Geographic coordinates f a: semi-major axis b: semi-minor axis Geographic latitude b Geodetic latitude a f: flattening = (a-b)/a Expresses as a fraction 1/f = about 300
Georeferencing. datum. projection. scale. The next few lectures will introduce you to these elements. on the Earth, you ll need to understand how
 Georeferencing GOAL: To assign a location to all the features represented in our geographic information data In order to do so, we need to make use of the following elements: ellipsoid/geoid To determine
Georeferencing GOAL: To assign a location to all the features represented in our geographic information data In order to do so, we need to make use of the following elements: ellipsoid/geoid To determine
Outline. Shape of the Earth. Geographic Coordinates (φ, λ, z) Ellipsoid or Spheroid Rotate an ellipse around an axis. Ellipse.
 Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Map Projections Outline Geodesy and map projections Prof. D. Nagesh Kumar Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Science Bangalore 560 012, India http://www.civil.iisc.ernet.in/~nagesh Shape
Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections
 Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
Organizing Data and Information Lesson 5: Map Scale and Projections Map Scales Projections Information can be organized as lists, numbers, tables, text, pictures, maps, or indexes. Clusters of information
GIST 3300 / Geographic Information Systems. Last Time. Today
 GIST 3300 / 5300 Last Time Ellipsoids and Datums Today Map Projections Map Projections Today we will build on the concepts of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Ellipsoids and Datums and add the concepts of
GIST 3300 / 5300 Last Time Ellipsoids and Datums Today Map Projections Map Projections Today we will build on the concepts of Geographic Coordinate Systems, Ellipsoids and Datums and add the concepts of
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems
 Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 9/7/2017 1 Why? Laying the Earth Flat Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveying instruments measure
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 9/7/2017 1 Why? Laying the Earth Flat Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveying instruments measure
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections
 NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections From http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ 1 Geographic coordinates Coordinates are expressed as Latitude and Longitude in Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources Lesson 4 Map Projections From http://www.or.blm.gov/gis/ 1 Geographic coordinates Coordinates are expressed as Latitude and Longitude in Degrees, Minutes, Seconds
Projections and Coordinate Systems
 Projections and Coordinate Systems Overview Projections Examples of different projections Coordinate systems Datums Projections Overview Projections and Coordinate Systems GIS must accurately represent
Projections and Coordinate Systems Overview Projections Examples of different projections Coordinate systems Datums Projections Overview Projections and Coordinate Systems GIS must accurately represent
Lecture 4. Coordinate Systems & Projections
 Lecture 4 Coordinate Systems & Projections Outline Geodesy Geoids Ellipsoids Geographic Coordinate Systems Magnetic North vs. True North Datums Projections Applying Coordinate Systems and Projections Why
Lecture 4 Coordinate Systems & Projections Outline Geodesy Geoids Ellipsoids Geographic Coordinate Systems Magnetic North vs. True North Datums Projections Applying Coordinate Systems and Projections Why
What is a Map Projection?
 What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
What is a Map Projection? It is how we represent a three dimensional Earth on a flat piece of paper However The process of transferring information from the Earth to a map causes every projection to distort
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012
 WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Datums Datums A reference surface of the Earth Used as the
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2012 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Datums Datums A reference surface of the Earth Used as the
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015
 WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
WHERE ARE YOU? Maps & Geospatial Concepts Fall 2015 Where are you? Relative location I m at school Absolute Location 45 26 18.07 122 43 50.78 Where is Boston? Introducing Geodesy, Ellipsoids & Geoids Geodesy
EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography
 EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 3 Geodesy Map Projections, Datums, and Coordinate Systems 1 Geodesy The science of measuring and representing the shape and size of the earth, and
EnvSci360 Computer and Analytical Cartography Lecture 3 Geodesy Map Projections, Datums, and Coordinate Systems 1 Geodesy The science of measuring and representing the shape and size of the earth, and
Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections
 Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections SHAPE OF THE EARTH Earth's Shape Geoid: shape of earth minus topographic features (irregular due to local variations in gravity) Ellipsoid: elongated
Intro to GIS Fall 2010 Georeferencing & Map Projections SHAPE OF THE EARTH Earth's Shape Geoid: shape of earth minus topographic features (irregular due to local variations in gravity) Ellipsoid: elongated
1. Geospatial technology rarely links geospatial data to nonspatial data. a. True *b. False
 Chapter 2 Where in the Geospatial World Are You? 1. Geospatial technology rarely links geospatial data to nonspatial data. 2. For geospatial technology to work, every location on Earth must be: a. inhabited
Chapter 2 Where in the Geospatial World Are You? 1. Geospatial technology rarely links geospatial data to nonspatial data. 2. For geospatial technology to work, every location on Earth must be: a. inhabited
Map Projections. Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps
 Map Projections Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps Map projections Define the spatial relationship between locations on earth and their relative locations on a flat map Are mathematical expressions
Map Projections Displaying the earth on 2 dimensional maps Map projections Define the spatial relationship between locations on earth and their relative locations on a flat map Are mathematical expressions
This week s topics. Week 6. FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications. Week 6
 FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 6 Week 6 Last week Chapter 8 Combining and splitting landscape features and merging GIS databases Chapter 11 Overlay processes Questions? Next week
FE 257. GIS and Forest Engineering Applications Week 6 Week 6 Last week Chapter 8 Combining and splitting landscape features and merging GIS databases Chapter 11 Overlay processes Questions? Next week
Modern Navigation. Thomas Herring
 12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Today s class Map Projections: Why projections are needed Types of map projections Classification by type of projection Classification by characteristics of projection
12.215 Modern Navigation Thomas Herring Today s class Map Projections: Why projections are needed Types of map projections Classification by type of projection Classification by characteristics of projection
Map projections. Rüdiger Gens
 Rüdiger Gens 2 Outline! Relevant terms! Why map projections?! Map projection categories " Projection surfaces " Features preserved from distortions! Map projection examples! Right choice Relevant terms!
Rüdiger Gens 2 Outline! Relevant terms! Why map projections?! Map projection categories " Projection surfaces " Features preserved from distortions! Map projection examples! Right choice Relevant terms!
Lab #3 Map Projections.
 Lab #3 Map Projections http://visual.merriam-webster.com/images/earth/geography/cartography/map-projections.jpg Map Projections Projection: a systematic arrangement of parallels and meridians on a plane
Lab #3 Map Projections http://visual.merriam-webster.com/images/earth/geography/cartography/map-projections.jpg Map Projections Projection: a systematic arrangement of parallels and meridians on a plane
Shape e o f f the e Earth
 1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
1 Coordinate Systems & Projections Coordinate Systems Two map layers are not going to register spatially unless they are based on the same coordinate system. 2 Contents Shape of the earth Datum Projections
Introduction to Geographic Information Science. Updates/News. Last Lecture. Geography 4103 / Map Projections and Coordinate Systems
 Geography 4103 / 5103 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Map Projections and Coordinate Systems Updates/News Thursday s lecture Reading discussion 1 find the readings online open questions,
Geography 4103 / 5103 Introduction to Geographic Information Science Map Projections and Coordinate Systems Updates/News Thursday s lecture Reading discussion 1 find the readings online open questions,
Coordinate Systems. Location on earth is defined by coordinates
 Coordinate Systems We think of the earth as a sphere It is actually a spheroid (ellipsoid), slightly larger in radius at the equator than at the poles Shape of the Earth Location on earth is defined by
Coordinate Systems We think of the earth as a sphere It is actually a spheroid (ellipsoid), slightly larger in radius at the equator than at the poles Shape of the Earth Location on earth is defined by
Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP)
 Workshop on : Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP) 14-15 April 2016 Venue: Tehran, Iran GIS definitions GIS: A simplified view of the real
Workshop on : Dr. ABOLGHASEM AKBARI Faculty of Civil Engineering & Earth Resources, University Malaysia Pahang (UMP) 14-15 April 2016 Venue: Tehran, Iran GIS definitions GIS: A simplified view of the real
Mapping coordinate systems
 Mapping coordinate systems 1. The Earth's Graticule Latitude and Longitude The graticule is the imaginary grid of lines running east-west (lines of latitude = parallels) and north-south lines of longitude
Mapping coordinate systems 1. The Earth's Graticule Latitude and Longitude The graticule is the imaginary grid of lines running east-west (lines of latitude = parallels) and north-south lines of longitude
Lecture 2. Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems. Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University
 Lecture 2 Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Map Projections Map projections are mathematical formulas
Lecture 2 Map Projections and GIS Coordinate Systems Tomislav Sapic GIS Technologist Faculty of Natural Resources Management Lakehead University Map Projections Map projections are mathematical formulas
Projections & GIS Data Collection: An Overview
 Projections & GIS Data Collection: An Overview Projections Primary data capture Secondary data capture Data transfer Capturing attribute data Managing a data capture project Geodesy Basics for Geospatial
Projections & GIS Data Collection: An Overview Projections Primary data capture Secondary data capture Data transfer Capturing attribute data Managing a data capture project Geodesy Basics for Geospatial
Understanding Projections for GIS
 Presented by John Schaeffer Juniper GIS Services, Inc. This PowerPoint is available at JuniperGIS.com Presentation Objectives To understand basic concepts on projections and coordinate systems for the
Presented by John Schaeffer Juniper GIS Services, Inc. This PowerPoint is available at JuniperGIS.com Presentation Objectives To understand basic concepts on projections and coordinate systems for the
2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS
 2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS What are geographic information systems and what are they used for? ArcGIS: ArcMap, ArcCatalog and ArcToolbox Vector data vs. raster data vs. attribute tables Polygons, polylines,
2. GETTING STARTED WITH GIS What are geographic information systems and what are they used for? ArcGIS: ArcMap, ArcCatalog and ArcToolbox Vector data vs. raster data vs. attribute tables Polygons, polylines,
Plane coordinates ~~~~~~~~~~
 Coordinate Systems & Map Projections Geographic coordinates A Basic Introduction to Coordinate Systems & Map Projections Latitude & longitude Angles Parallels & meridians Lines Plane coordinates ~~~~~~~~~~
Coordinate Systems & Map Projections Geographic coordinates A Basic Introduction to Coordinate Systems & Map Projections Latitude & longitude Angles Parallels & meridians Lines Plane coordinates ~~~~~~~~~~
MAR-E1004 Basics of GIS: Georeferencing Jaakko Madetoja Slides adopted from Paula Ahonen-Rainio
 MAR-E1004 Basics of GIS: Georeferencing Jaakko Madetoja Slides adopted from Paula Ahonen-Rainio Learning goals In this session you will learn To describe the basics of different types of referencing systems
MAR-E1004 Basics of GIS: Georeferencing Jaakko Madetoja Slides adopted from Paula Ahonen-Rainio Learning goals In this session you will learn To describe the basics of different types of referencing systems
Georeferencing. Where on earth are we? Critical for importing and combining layers for mapping
 Georeferencing Where on earth are we? Critical for importing and combining layers for mapping 1. The Geoid Earth is not a perfect sphere, it is ellipsoidal.. earth is the 'Geoid'. The difference between
Georeferencing Where on earth are we? Critical for importing and combining layers for mapping 1. The Geoid Earth is not a perfect sphere, it is ellipsoidal.. earth is the 'Geoid'. The difference between
12/26/2012. Geographic Information Systems * * * * GIS (... yrezaei
 ( - Geographic Information Systems ( ( 1 2 3 Information System Data base DB IS IS DB (Knowledge ( ( (System (Information System - (Georefrence Analysis Data + Knowledge ======== Information 4 5 ( < 10%
( - Geographic Information Systems ( ( 1 2 3 Information System Data base DB IS IS DB (Knowledge ( ( (System (Information System - (Georefrence Analysis Data + Knowledge ======== Information 4 5 ( < 10%
Map Projections. What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL
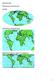 Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
Map Projections What does the world look like? AITOFF AZIMUTHAL EQUIDISTANT BEHRMANN EQUAL AREA CYLINDRICAL 1 CYLINDRICAL EQUAL AREA BONNE CRASTER PARABOLIC 2 ECKERT I ECKERT III ECKERT V There are many
The Nature of Spatial Data. Keith C. Clarke Geography UCSB
 The Nature of Spatial Data Keith C. Clarke Geography UCSB Geographic primitives G = g (x, y, z, s, A, t) [x, y, z] = f(λ, φ, d) Geography also highly dependent upon model First, the datum (d) Models of
The Nature of Spatial Data Keith C. Clarke Geography UCSB Geographic primitives G = g (x, y, z, s, A, t) [x, y, z] = f(λ, φ, d) Geography also highly dependent upon model First, the datum (d) Models of
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I. Lecture 15
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 15 Lecture Plan Midterm Multiple choice part graded (+ solutions) Jump to Ch. 11 for one lecture Coordinate systems Projections, datums, spheroids Unprojected
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 15 Lecture Plan Midterm Multiple choice part graded (+ solutions) Jump to Ch. 11 for one lecture Coordinate systems Projections, datums, spheroids Unprojected
Fri. Jan. 26, Demonstration of QGIS with GPS tracks. Types of data, simple vector (shapefile) formats
 Fri. Jan. 26, 2018 Demonstration of QGIS with GPS tracks Types of data, simple vector (shapefile) formats Map projections, Coordinate Reference Systems Demonstration of QGIS with geologic map 1 Raster
Fri. Jan. 26, 2018 Demonstration of QGIS with GPS tracks Types of data, simple vector (shapefile) formats Map projections, Coordinate Reference Systems Demonstration of QGIS with geologic map 1 Raster
Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections.
 Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections. 1 It is extremely important that you gain an understanding of coordinate systems and map projections. GIS works with spatial data, and,
Importance of Understanding Coordinate Systems and Map Projections. 1 It is extremely important that you gain an understanding of coordinate systems and map projections. GIS works with spatial data, and,
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 1/25/2018
 Map Projections & Coordinate Sstems Laing the Earth Flat How? Projections transformation of curved earth to a flat map; sstematic rendering of the lat. & lon. graticule to rectangular coordinate sstem.
Map Projections & Coordinate Sstems Laing the Earth Flat How? Projections transformation of curved earth to a flat map; sstematic rendering of the lat. & lon. graticule to rectangular coordinate sstem.
Working with georeferenced data. What is georeferencing? Coordinate Systems. Geographic and Projected Coordinate System
 GIS501 Fundamentals of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) Coordinate Systems Working with georeferenced data What is georeferencing? Geographically referenced data which is, in some way, referenced
GIS501 Fundamentals of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) Coordinate Systems Working with georeferenced data What is georeferencing? Geographically referenced data which is, in some way, referenced
Map Projections 2/4/2013. Map Projections. Rhumb Line (Loxodrome) Great Circle. The GLOBE. Line of constant bearing (e.g., 292.
 The GLOBE ADVANTAGES Directions True Distances True Shapes True Area True DISADVANTAGES Very small scale with little detail. Costly to reproduce and update. Difficult to carry around. Bulky to store. FACTS
The GLOBE ADVANTAGES Directions True Distances True Shapes True Area True DISADVANTAGES Very small scale with little detail. Costly to reproduce and update. Difficult to carry around. Bulky to store. FACTS
ArcGIS for Applied Economists Session 2
 ArcGIS for Applied Economists Session 2 Mark Westcott LMU Munich June 15, 2015 1 / 31 Topics for this session: Geographic Coordinate Systems Projections Projected Coordinate Systems Geocoding 2 / 31 Some
ArcGIS for Applied Economists Session 2 Mark Westcott LMU Munich June 15, 2015 1 / 31 Topics for this session: Geographic Coordinate Systems Projections Projected Coordinate Systems Geocoding 2 / 31 Some
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 9/10/2013. Why? M. Helper GEO327G/386G, UT Austin 2. M. Helper GEO327G/386G, UT Austin 4
 Map Projections & Coordinates Laing the earth flat Wh? Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveing instruments measure in meters or feet,
Map Projections & Coordinates Laing the earth flat Wh? Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveing instruments measure in meters or feet,
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 PROJECTS Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WEEK THREE Lecture 5 PROJECT DATA/IDEAS, PROJECTIONS (Cont.) & LAB REVIEW Joe Wheaton GUEST LECTURE HOUSEKEEPING: LAB 01 GRADES This
PROJECTS Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WEEK THREE Lecture 5 PROJECT DATA/IDEAS, PROJECTIONS (Cont.) & LAB REVIEW Joe Wheaton GUEST LECTURE HOUSEKEEPING: LAB 01 GRADES This
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth. 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth. 3.1 Objectives
 Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Chapter 3 Models of the Earth 3.1 Finding Locations on the Earth 3.1 Objectives Explain latitude and longitude. How can latitude and longitude be used to find locations on Earth? How can a magnetic compass
Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910
 Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910 Where are you? 31UFT8361 174,7 441,2 51 58' NB 5 40' OL 2/60 Who are they? 3/60 Do geo data describe Earth s phenomena perfectly? Georeference systems ellipsoid
Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910 Where are you? 31UFT8361 174,7 441,2 51 58' NB 5 40' OL 2/60 Who are they? 3/60 Do geo data describe Earth s phenomena perfectly? Georeference systems ellipsoid
Chapter 3 Geographic Location Systems
 Chapter 3 Geographic Location Systems In this chapter you will learn about: Latitude and longitude Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) U.S. Public Land Survey Other geographic location systems Geographic
Chapter 3 Geographic Location Systems In this chapter you will learn about: Latitude and longitude Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) U.S. Public Land Survey Other geographic location systems Geographic
Control Surveys and Coordinate Systems
 Control Surveys and Coordinate Systems The Earth is Round Basic Shape of the Earth: Oblate Spheroid of Revolution The length of the equatorial axis is approximately 27 miles greater than the polar axis.
Control Surveys and Coordinate Systems The Earth is Round Basic Shape of the Earth: Oblate Spheroid of Revolution The length of the equatorial axis is approximately 27 miles greater than the polar axis.
Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections
 Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections Coordinate systems and map projections if we want to integrate geographic data from many different sources, we need to use a consistent
Referencing map features: Coordinate systems and map projections Coordinate systems and map projections if we want to integrate geographic data from many different sources, we need to use a consistent
Spatial locations. Spatial locations. Spatial locations. Spatial locations
 Where am I? sounds simple, but definitely not huge amount of picky detail Cartographers make a career from the details focus on the minimum you need to know c Philip M. Dixon (Iowa State Univ.) Spatial
Where am I? sounds simple, but definitely not huge amount of picky detail Cartographers make a career from the details focus on the minimum you need to know c Philip M. Dixon (Iowa State Univ.) Spatial
Boolean Operators and Topological OVERLAY FUNCTIONS IN GIS
 Boolean Operators and Topological OVERLAY FUNCTIONS IN GIS Query asking a question of the attribute data Standard Query Language (SQL) is used to query the data There are 4 basic statements used to get
Boolean Operators and Topological OVERLAY FUNCTIONS IN GIS Query asking a question of the attribute data Standard Query Language (SQL) is used to query the data There are 4 basic statements used to get
What is a map? A simple representation of the real world Two types of maps
 Mapping with GIS What is a map? A simple representation of the real world Two types of maps Reference maps showing reference features such as roads, locations, political boundaries, cities etc. Thematic
Mapping with GIS What is a map? A simple representation of the real world Two types of maps Reference maps showing reference features such as roads, locations, political boundaries, cities etc. Thematic
Map Projections & Coordinate Systems 9/7/2017
 Map Projections & Coordinate Sstems Laing the Earth Flat Wh? Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveing instruments measure in meters or
Map Projections & Coordinate Sstems Laing the Earth Flat Wh? Need convenient means of measuring and comparing distances, directions, areas, shapes. Traditional surveing instruments measure in meters or
Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910
 Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910 Where are you? 31UFT8361 174,7 441,2 51 58' NB 5 40' OL 2/60 Who are they? 3/60 Do geo data describe Earth s phenomena perfectly? Georeference systems ellipsoid
Geo Referencing & Map projections CGI-GIRS 0910 Where are you? 31UFT8361 174,7 441,2 51 58' NB 5 40' OL 2/60 Who are they? 3/60 Do geo data describe Earth s phenomena perfectly? Georeference systems ellipsoid
Lecture 10-14: Map Projections and Coordinate System
 URP 1281 Surveying and Cartography Lecture 10-14: Map Projections and Coordinate System December 27, 2015 Course Teacher: Md. Esraz-Ul-Zannat Assistant Professor Department of Urban and Regional Planning
URP 1281 Surveying and Cartography Lecture 10-14: Map Projections and Coordinate System December 27, 2015 Course Teacher: Md. Esraz-Ul-Zannat Assistant Professor Department of Urban and Regional Planning
GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATE SYSTEMS
 GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATE SYSTEMS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 What is Georeferencing? Used to establish a location on the Earth s surface 1 st order polynomial transformation Georeferencing toolbar What
GEOGRAPHIC COORDINATE SYSTEMS Introduction to GIS Winter 2015 What is Georeferencing? Used to establish a location on the Earth s surface 1 st order polynomial transformation Georeferencing toolbar What
Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006
 I. Introduction and References Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006 The world is, approximately, a sphere. Maps are flat. Making maps requires some method of putting
I. Introduction and References Projections Part I - Categories and Properties James R. Clynch February 2006 The world is, approximately, a sphere. Maps are flat. Making maps requires some method of putting
The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet. Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about!
 Georeferencing I GEOG 300, Lecture 4 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet Quiz Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about! 5:30 7:30 PM, Wednesday September
Georeferencing I GEOG 300, Lecture 4 Dr. Anthony Jjumba 1 The Wildlife Society Meet and Greet Quiz Come learn about what the UNBC Student Chapter of TWS is all about! 5:30 7:30 PM, Wednesday September
Spatial Reference Systems. Introduction
 Spatial Reference Systems Wolfgang Kainz Professor of Cartography and Geoinformation Department of Geography and Regional Research University of Vienna wolfgang.kainz@univie.ac.at Introduction Historic
Spatial Reference Systems Wolfgang Kainz Professor of Cartography and Geoinformation Department of Geography and Regional Research University of Vienna wolfgang.kainz@univie.ac.at Introduction Historic
Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook Chang 2006 and the practical manual)
 Introduction Geo-information Science (GRS-10306) Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook 2006 and the practical manual) Introduction Chapter 1 Geographic information system (GIS) Geographically
Introduction Geo-information Science (GRS-10306) Overview key concepts and terms (based on the textbook 2006 and the practical manual) Introduction Chapter 1 Geographic information system (GIS) Geographically
Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E. Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections
 Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections What is Geodesy? The science of geodesy determines: Earth s shape and Interrelation of different points on earth s surface The
Introduction to Cartography GEOG 2016 E Lecture-2 Geodesy and Projections What is Geodesy? The science of geodesy determines: Earth s shape and Interrelation of different points on earth s surface The
Geographers Perspectives on the World
 What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
What is Geography? Geography is not just about city and country names Geography is not just about population and growth Geography is not just about rivers and mountains Geography is a broad field that
How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity
 Map projections How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity http://www.mapovasbirka.cz/english/index_eng.html The world could be mapped like
Map projections How can we project a 3D globe onto a 2D display? - Ellipsoids and Datums deal with earth non-sphericity http://www.mapovasbirka.cz/english/index_eng.html The world could be mapped like
2. Which geometric model has been used at some time to describe the earth? a. Sphere b. Oblate ellipsoid c. Flat disk. d. Geoid e.
 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 Geography 12 Sample Mid-Term Examination Before you
01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 Geography 12 Sample Mid-Term Examination Before you
Notes on Projections Part II - Common Projections James R. Clynch February 2006
 Notes on Projections Part II - Common Projections James R. Clynch February 2006 I. Common Projections There are several areas where maps are commonly used and a few projections dominate these fields. An
Notes on Projections Part II - Common Projections James R. Clynch February 2006 I. Common Projections There are several areas where maps are commonly used and a few projections dominate these fields. An
Introduction to GIS. Phil Guertin School of Natural Resources and the Environment GeoSpatial Technologies
 Introduction to GIS Phil Guertin School of Natural Resources and the Environment dguertin@cals.arizona.edu Mapping GeoSpatial Technologies Traditional Survey Global Positioning Systems (GPS) Remote Sensing
Introduction to GIS Phil Guertin School of Natural Resources and the Environment dguertin@cals.arizona.edu Mapping GeoSpatial Technologies Traditional Survey Global Positioning Systems (GPS) Remote Sensing
A PRIMER ON COORDINATE SYSTEMS Commonly Used in Michigan
 A PRIMER ON COORDINATE SYSTEMS Commonly Used in Michigan David P. Lusch, Ph.D., GISP Department of Geography Remote Sensing & GIS Research and Outreach Services Group Michigan State University September,
A PRIMER ON COORDINATE SYSTEMS Commonly Used in Michigan David P. Lusch, Ph.D., GISP Department of Geography Remote Sensing & GIS Research and Outreach Services Group Michigan State University September,
P R O J E C T I O N S. Map Projections. Introduction to. Map Projections. with. TNTmips. TNTedit TNTview. page 1
 P R O J E C T I O N S Introduction to Map Projections Map Projections with TNTmips page 1 TNTedit TNTview Before Getting Started Positions in a georeferenced spatial object must refer to a particular coordinate
P R O J E C T I O N S Introduction to Map Projections Map Projections with TNTmips page 1 TNTedit TNTview Before Getting Started Positions in a georeferenced spatial object must refer to a particular coordinate
Lecture Plan. GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I. Why use Projections? Lecture 15 - chapter 11. Different types of Projections
 GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 15 - chapter 11 Lecture Plan Ch. 11, one lecture Coordinate systems Projection, Datums, Dpheroid Unprojected (geographic) coord. syst., UTM On the fly projection
GEOL 452/552 - GIS for Geoscientists I Lecture 15 - chapter 11 Lecture Plan Ch. 11, one lecture Coordinate systems Projection, Datums, Dpheroid Unprojected (geographic) coord. syst., UTM On the fly projection
GIS in Water Resources Fall 2018 Homework #1
 GIS in Water Resources Fall 2018 Homework #1 Goal The goal of this homework is to reinforce the lecture material on Geodesy, Map Projections and Coordinate Systems by having you identify attributes and
GIS in Water Resources Fall 2018 Homework #1 Goal The goal of this homework is to reinforce the lecture material on Geodesy, Map Projections and Coordinate Systems by having you identify attributes and
Wed. Apr. 25, 2018 GIS DEMO. Reading: Ch Comparing Image Types (Death Valley) Treat as review of techniques already studied
 Wed. Apr. 25, 2018 GIS DEMO Reading: Ch. 14 -- Comparing Image Types (Death Valley) Treat as review of techniques already studied 1 GIS: Geographic Information Systems Way to organize data obtained by
Wed. Apr. 25, 2018 GIS DEMO Reading: Ch. 14 -- Comparing Image Types (Death Valley) Treat as review of techniques already studied 1 GIS: Geographic Information Systems Way to organize data obtained by
When the Earth Was Flat. Measurements were made using a plumb bob, a spirit level, and a stick. Also, the Stars.
 ABSTRACT Defining the shape of the Earth geoid. Mathematical models spheroid or ellipsoid Mathematical projection of geodetic systems GIS/GPS technology The need for a unified projection systems World
ABSTRACT Defining the shape of the Earth geoid. Mathematical models spheroid or ellipsoid Mathematical projection of geodetic systems GIS/GPS technology The need for a unified projection systems World
Chapter 02 Maps. Multiple Choice Questions
 Chapter 02 Maps Multiple Choice Questions 1. Every projection has some degree of distortion because A. a curved surface cannot be represented on a flat surface without distortion. B. parallels and meridians
Chapter 02 Maps Multiple Choice Questions 1. Every projection has some degree of distortion because A. a curved surface cannot be represented on a flat surface without distortion. B. parallels and meridians
Introduction to Geography
 Introduction to Geography ropic of Cancer 3½ N Arctic Circle 90 N Prime Meridian 0 Arctic Ocean Mississippi R. Appalachian Mts. Europe Rocky Mountains N. America Atlantic Gulf of Ocean Mexico Caribbean
Introduction to Geography ropic of Cancer 3½ N Arctic Circle 90 N Prime Meridian 0 Arctic Ocean Mississippi R. Appalachian Mts. Europe Rocky Mountains N. America Atlantic Gulf of Ocean Mexico Caribbean
GIS in Water Resources Midterm Exam Fall 2008 There are 4 questions on this exam. Please do all 4.
 Page 1 of 8 Name: GIS in Water Resources Midterm Exam Fall 2008 There are 4 questions on this exam. Please do all 4. 1. Basic Concepts [20 points] Find the letter with the best answer for each term: 1.
Page 1 of 8 Name: GIS in Water Resources Midterm Exam Fall 2008 There are 4 questions on this exam. Please do all 4. 1. Basic Concepts [20 points] Find the letter with the best answer for each term: 1.
What is Geodesy? Types of Geodesy terrestrial or classical geodesy space geodesy theoretical geodesy
 What is Geodesy? Geodesy is the study of: The size, shape and motion of the earth The measurement of the position and motion of points on the earth's surface, and The study of the earth's gravity field
What is Geodesy? Geodesy is the study of: The size, shape and motion of the earth The measurement of the position and motion of points on the earth's surface, and The study of the earth's gravity field
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS
 Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WEEK TWO Lecture PROJECTIONS Joe Wheaton Some of slides in this lecture adapted from content in Paul Bolstad s Fundamentals of GIS HOUSEKEEPING
Watershed Sciences 4930 & 6920 GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION SYSTEMS WEEK TWO Lecture PROJECTIONS Joe Wheaton Some of slides in this lecture adapted from content in Paul Bolstad s Fundamentals of GIS HOUSEKEEPING
HP-35s Calculator Program Lambert 1
 Convert Latitude and Longitude to Lambert Conformal Conic Projection Co-ordinates (SPCS) Programmer: Dr. Bill Hazelton Date: July, 2010. Version: 1.2 Line Instruction Display User Instructions N001 LBL
Convert Latitude and Longitude to Lambert Conformal Conic Projection Co-ordinates (SPCS) Programmer: Dr. Bill Hazelton Date: July, 2010. Version: 1.2 Line Instruction Display User Instructions N001 LBL
Illustrator: Vector base Each line/point store some sort of information Mapping Representation of the world
 Illustrator: Vector base Each line/point store some sort of information Mapping Representation of the world Photoshop Raster base Images can be overlaid Pixel vector data model: [data models] A representation
Illustrator: Vector base Each line/point store some sort of information Mapping Representation of the world Photoshop Raster base Images can be overlaid Pixel vector data model: [data models] A representation
1/28/16. EGM101 Skills Toolbox. Oblate spheroid. The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections. Geoid
 EGM101 Skills Toolbox Oblate spheroid The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections The geoid is the shape that the surface of the oceans would take under the influence of Earth's gravitation
EGM101 Skills Toolbox Oblate spheroid The shape of the earth Co-ordinate systems Map projections The geoid is the shape that the surface of the oceans would take under the influence of Earth's gravitation
Lab#3: GIS Projections and Coordinate Systems. Start Arcmap and create a data frame for each of the above coordinate systems.
 NRM338 Fall 2017 Lab#3 Page#1 of 18 In this lab, you will Lab#3: GIS Projections and Coordinate Systems 1) Define the geographic coordinate system of two GIS themes. 2) Determine the geographic coordinates
NRM338 Fall 2017 Lab#3 Page#1 of 18 In this lab, you will Lab#3: GIS Projections and Coordinate Systems 1) Define the geographic coordinate system of two GIS themes. 2) Determine the geographic coordinates
Navigation. Longitude and Latitude Foundations of Navigation. MTPs:
 Navigation 3.01 Foundations of Navigation References: FTGU pages 177-178, 184-190 Transport Canada Study and Reference Guide Glider Pilot Canada Flight Training Manual Pilot Navigation http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/transverse_mercator_projection#spherical_transverse_mercator
Navigation 3.01 Foundations of Navigation References: FTGU pages 177-178, 184-190 Transport Canada Study and Reference Guide Glider Pilot Canada Flight Training Manual Pilot Navigation http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/transverse_mercator_projection#spherical_transverse_mercator
Lecture 9: Reference Maps & Aerial Photography
 Lecture 9: Reference Maps & Aerial Photography I. Overview of Reference and Topographic Maps There are two basic types of maps? Reference Maps - General purpose maps & Thematic Maps - maps made for a specific
Lecture 9: Reference Maps & Aerial Photography I. Overview of Reference and Topographic Maps There are two basic types of maps? Reference Maps - General purpose maps & Thematic Maps - maps made for a specific
GIS in Water Resources. Fall Homework #1
 GIS in Water Resources Fall 2015 Homework #1 Goal The goal of this homework is to reinforce the lecture material on Geodesy, Map Projections and Coordinate Systems by having you identify attributes and
GIS in Water Resources Fall 2015 Homework #1 Goal The goal of this homework is to reinforce the lecture material on Geodesy, Map Projections and Coordinate Systems by having you identify attributes and
Coordinate Systems and Datum Transformation in ArcGIS. Brittney White and Melita Kennedy
 Coordinate Systems and Datum Transformation in ArcGIS Brittney White and Melita Kennedy Where is my data? Problem Horizontal Vertical Projections Transformations Horizontal coordinate systems Geographic
Coordinate Systems and Datum Transformation in ArcGIS Brittney White and Melita Kennedy Where is my data? Problem Horizontal Vertical Projections Transformations Horizontal coordinate systems Geographic
GCSAR Navigation -- Maps
 GCSAR Navigation -- Maps From the GCSAR Certification Standards Identify and explain all the border information on a topographic map. Identify and explain the following aspects of maps: index and intermediate
GCSAR Navigation -- Maps From the GCSAR Certification Standards Identify and explain all the border information on a topographic map. Identify and explain the following aspects of maps: index and intermediate
Mapping Earth. How are Earth s surface features measured and modeled?
 Name Mapping Earth How are Earth s surface features measured and modeled? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about maps Record your thoughts in the first column Pair
Name Mapping Earth How are Earth s surface features measured and modeled? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about maps Record your thoughts in the first column Pair
Military Map Reading 201
 Military Map Reading 201 This information paper is designed to resolve the confusion between the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) and the Military Grid Reference System (MGRS) coordinates. The two systems
Military Map Reading 201 This information paper is designed to resolve the confusion between the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) and the Military Grid Reference System (MGRS) coordinates. The two systems
4 Survey Datums. 4.1 Horizontal Datum Policy SURVEY DATUMS SEPTEMBER 2006
 4 Survey Datums Today s multi-organizational Project Development efforts require the use of common, accurate horizontal and vertical survey datums and consistent, precise control-survey procedures to ensure
4 Survey Datums Today s multi-organizational Project Development efforts require the use of common, accurate horizontal and vertical survey datums and consistent, precise control-survey procedures to ensure
