Lecture 3. Chlorophyta
|
|
|
- Shannon King
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 3 Chlorophyta Chlorophyta is a division of green algae contain chlorophylls a and b, and store food as starch in their plastids. There are many different species belonging to Chlorophyta; some are unicellular, some are multicelluar. The genome structures within Chlorophyta are all different. However, there are some common characteristics across species. Chlorophyta inhabit freshwater, marine and terrestrial habitats. Conditions for survival include light, carbon, essential nutrients, water quality, temperature and tidal exposure. Certain intertidal species such as the ulva, or sea lettuce, can tolerate a range of temperatures and survive drying at low tide. While most chlorophyta are aquatic, 1
2 1- General characteristics 1-Tend to grow well in summer, with ample light and nutrients and high temperature 2-Some filamentous forms may be inedible 3-Flagella may reduce tendency to sink 4-Many shapes and sizes but planktonic Chlorophyta tend to share a characteristic: rapid growth potential 2-Cell Structure and Metabolism Most Chlorophyta are unicelluar, but there are some multicelluar species. Some are free-living, some are colonial, others are coenocytic. Filamentous sporophytes have singluar lenticular nuclei, which are embedded in a thick cytoplasm. Chlorophyta usually have biflagellated gametes. Like other green plants, Chlorophyta contain chlorophylls a and b, although the major pigment is chlorophyll b. In addition, some tropical species are pigmented by siphonoxanthin and siphonein. They store starches made from photosynthesis in double-membrane bounded chloroplasts. Cell walls are made of cellulose. Parenchymatous Siphonocladous Figure 1: General Forms of Chlorophyta 2
3 Chlorophyta are photosynthetic organisms, obtaining starch from photosynthesis. They are autotrophic. Figure 2: General structure of Chlorophyta 3- Reproduction and Life cycle Chlorophyta reproduce both sexually and asexually, but usually sexually. Asexual reproduction can occurs by fission, fragmentation, or zoospores. Sexual reproduction can be isogamous, anisogamous, or oogamous. The species Ulva lobata experiences alternation of generations, alternating between haploid and diploid phases. In the haploid phase, gametes are formed; in the diploid phase, zoospores are formed. Not all species have this, however. For the species without alternation, meiosis occurs in the zygote. Chlorophyta can exist as single cells, multi-cellular filaments or colonies. As single cells, green algae may be motile or moving, or non- 3
4 motile. An example of this unicellular organism is the fast growing chlorella that live inside animals. Multi-cellular filaments can involve a life cycle that includes both sexual and asexual reproduction. The ulva, for example, goes through the process of alternation of generations or alternate forms of reproduction. Parents characteristics are recombined through the fusion of gametes, but reproduction also occurs through spores. Colonies may consist of loose aggregates of single cells or an arrangement of cells in a pattern. These cells lack specialized functions. Reproduction occurs more rapidly with nearby mating cells. An example of a colony is the volvox, which has strands of cytoplasm-bonding individual cells. Hundreds of thousands of bright green cells form a sphere-shaped colony that uses its flagella to spin in the water. Figure 3: General Life cycle of Chlorophyta 4
5 3-1 Oedogonium Life Cycle Asexual Reproduction Oedogonium is a form of filamentous green algae. It is capabable of reproducing asexually, which means that each oedogonium has both male and female reproductive organs. In asexual reproduction, the oedogonium fragments and produces zoospores. Zoospores are able to move spontaneously through the water. Once the zoospore is produced, it is released and is free to find a viable substrate. Once found, the zoospore's cells are able to divide and form a new filament of oedogonium. Sexual Reproduction: Zygote Production In addition to being able to reproduce asexually, the oedogonium is capable of reproducing sexually. In sexual reproduction, the filament portion of the oedogonium, called the antheridium, produces and releases sperm. The sperm sinks through the water until it meets with the filament portion of the oedogonium, called the oogonium, which contains a large egg. If the sperm successfully fertilizes the egg, a zygote is produced. Sexual Reproduction: Zoospores After the zygote is produced, it is released into the water and develops zoospores. The zoospores are similar to those created through asexual reproduction. Once the zoospores mature, the zygote splits open, releasing the zoospores. The zoospores then attach to the bottom of the sea and the cells in the zoospores divide to produce a new filament of oedogonium. 5
6 Figure 4: Life cycle of Oedogonium 4- Ecology Cholorophyta are adapted to shallow water, and live in both freshwater and marine habitats. 90% of Chlorophyta are freshwater species. Those that live in marine habitats largely inhabit tropical environments. There are a small number of terrestrial species; these largely dwell on rocks or trees. Some species form symbiotic relationships with fungi, producing lichens. There are a few instances in which Chlorophyta have formed symbiotic relationships with animals. The Chlorophyta species Caulerpa racemosa was introduced to the Mediterranean Sea in It was first observed in France in 1997, and has continued spreading. Many of the invaded locations are fishing areas. The Mediterranean Sea has many environmental factors that encourage the growth of Caulerpa racemosa, such as an ideal climate and substrata. The species Spirogyra insignis is known to adapt to harsh conditions through spontaneous mutation. Flores-Moya et. al. (2005) studied the adaptation of this species in sulpherous waters. At first, its growth and reproduction was inhibited. However, the culture survived due to the 6
7 growth of a resistant variant that formed before the culture was introduced to these sulfurous waters. This type of spontaneous mutation is what allows the species to survive. 5- Class Chlorophyceae This group contains the largest number of species of the division. They can have two or more flagella, near the apex of the cell. Mitosis in this class involves phycoplasts, microtubules that develop between and separate the daughter nuclei. This characteristic is not seen in any other organism, implying that no organisms have descended from this class. There are a variety of asexual and sexual reproductive techniques. Sexual reproduction is characterized by the formation of a zygospore (a dormant diploid zygote protected by a thick wall) that later undergoes meiosis. The class includes unicellular organisms such as those in the genus Chlamydomonas with their two apical flagella and nonmotile organisms such as Chlorella, which is being cultivated for use as a dietary supplement. Colonial genera of Chlorophyceae include Hydrodictyon (the "water net") and the so-called volvocine line of flagellated specimens that range from simple colonies of Gonium to the intricate spinning spheres of Volvox, which can consist of up to 60,000 cells and exhibit some cellular specialization. The most complex of the class are the filamentous members. 7
8 6- Class Ulvophyceae Ulvophyceae contains marine organisms that take a variety of shapes that may consist of a few cells, long filaments, thin sheets of cells, or coenocytic cells. Most approach being radially symmetrical. They have an alternation of generations and unlike in the other classes, meiosis occurs in the spores rather than the zygotes. When present, there can be two or more apical flagella. During mitosis, the nuclear envelope and the mitotic spindle persist, as they do in the Charophyceae. 7- Class Charophyceae Charophyceae are of great fossil age; the stoneworts date as far back as the late Silurian period. Cells of this class are asymetrical. Those that are motile have two flagella, at right angles near the apex of the cell. Sexual reproduction in this class, as in Chlorophyceae, is characterized by the formation of a zygospore and zygotic meiosis. Unlike in the other two common classes of green algae, but as with plants, the nuclear envelope disintegrates when mitosis begins. During cell division the mitotic spindle 8
9 is present; in some a phragmoplast similar to those seen in plants aids in the formation of a cell plate. Plants are thought to have evolved from early species of Charophyceae. The class includes Spirogyra, familiar filamentous algae that float on ponds and lakes in slimy masses. The desmids are single cells noted for their extraordinary symmetry and geometrical beauty. They are found only in fresh (usually still) water and often take an important place in the food chains of small nutrient-poor ponds and peat bogs. The stoneworts consist of a complex branched thallus with an erect stemlike structure and many whorls of short branches. 9
10 References Chapman VJ (1962) The algae. Macmillan and Co Ltd., New York, St Martin s Press London Chapman VJ, Chapman DJ (1981) The algae, 2nd edn. Macmillan Press Limited, London/ Basingstoke Chepurnov VA, Mann DG, Sabbe K, Vyverman W (2004) Experimental studies on sexual reproduction in diatoms. Int Rev Cytol 237: Cox EJ (2011) Morphology, cell wall, cytology, ultrastructure and morphogenetic studies. In: Seckbach J, Kociolek JP (eds) Cellular origin, life in extreme habitats and astrobiology volume 19: the diatom world, Springer Publishing House, London, pp Crawford SA, Higgins MJ, Mulvaney P, Wetherbee R (2001) Nanostructure of the diatom frustule as revealed by atomic force and scanning electron microscopy. J Phycol 37: Edlund MB, Stoermer EF (1997) Ecological, evolutionary, and systematic significance of diatom life histories. J Phycol 33: Eichler AW (1883) Syllabus der Vorlesungen über Phanerogamenkunde, Berlin: Borntraeger 3rd edn Engler A, Prantl K (1912) Die naturlichen Pflanzenfamilien, 23 vols. W. Engelmann, Leipzig Fritsch FE (1935) The structure and reproduction of algae, vol I. Cambridge University Press, London Geitler L (1927) Rhodospora sordida, nov. gen. et n. sp., eine neue Bangiacee des Süsswassers. sterreichische Botanisches Zeitschrift 76:
Biology. Slide 1of 39. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1of 39 2of 39 20-4 Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown and Green Algae Most of these algae are multicellular, like plants. Their reproductive cycles are
Biology 1of 39 2of 39 20-4 Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown and Green Algae Most of these algae are multicellular, like plants. Their reproductive cycles are
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta
 Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
Biology 11 Kingdom Plantae: Algae and Bryophyta Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 3 types of algae Why we believe land plants developed from algae Lifecycle of a bryophyte
Plantae. Rhodophyta Chlorophytes Charophytes Land Plants. II. Algal taxonomy. Division: Chlorophyta (green algae)
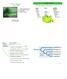 Division: Chlorophyta (green algae) I. General Characteristics II. Distinguishing Classes III. Morphology IV. Classes in Detail II. Algal taxonomy Hierarchical system of classification: Level: suffix:
Division: Chlorophyta (green algae) I. General Characteristics II. Distinguishing Classes III. Morphology IV. Classes in Detail II. Algal taxonomy Hierarchical system of classification: Level: suffix:
Have cell walls made of chitin (same material is found in the skeletons of arthropods)
 Fungi are multicellular eukaryotic heterotrophs that do not ingest their food but rather absorb it through their cell walls and cell membranes after breaking it down with powerful digestive enzymes. Fungi
Fungi are multicellular eukaryotic heterotrophs that do not ingest their food but rather absorb it through their cell walls and cell membranes after breaking it down with powerful digestive enzymes. Fungi
Kingdom Protista. The following organisms will be examined in the lab today: Volvox, Oedogonium, Spirogyra, Ulva
 Kingdom Protista I. Introduction The protists are a diverse group of organisms. In the past they have been classified as fungi, plants and animals. They can be green, autotrophs or nongreen heterotrophs.
Kingdom Protista I. Introduction The protists are a diverse group of organisms. In the past they have been classified as fungi, plants and animals. They can be green, autotrophs or nongreen heterotrophs.
Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants. Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR
 Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR In single cell organisms (protists) all life functions are performed by specialized organelles within one cell (a.k.a.
Chapter 9. Fungi and Aquatic Plants Introduction: The Big Step: DIVISION OF LABOUR In single cell organisms (protists) all life functions are performed by specialized organelles within one cell (a.k.a.
Major groups of algae
 Algae general features. All are protists They require moist environments because they lack a cuticle They lack vascular tissues Algae are photosynthetic and reproduce both sexually and asexually Major
Algae general features. All are protists They require moist environments because they lack a cuticle They lack vascular tissues Algae are photosynthetic and reproduce both sexually and asexually Major
Protist Classification the Saga Continues
 Protist Classification the Saga Continues Learning Objectives Explain what a protist is. Describe how protists are related to other eukaryotes. What Are Protists? Photosynthetic Motile Unicellular Multicellular
Protist Classification the Saga Continues Learning Objectives Explain what a protist is. Describe how protists are related to other eukaryotes. What Are Protists? Photosynthetic Motile Unicellular Multicellular
ALGAE (L. Seaweed) HABITAT:
 ALGAE (L. Seaweed) SALIENT FEATURES: 1. Algae are autotrophic organisms and they have chlorophyll. 2. They are O2 producing photosynthetic organisms. 3. In algae the plant body shows no differentiation
ALGAE (L. Seaweed) SALIENT FEATURES: 1. Algae are autotrophic organisms and they have chlorophyll. 2. They are O2 producing photosynthetic organisms. 3. In algae the plant body shows no differentiation
Division: Chlorophyta! The mean Greens!
 8/12/14 Division: Chlorophyta The mean Greens I. Taxonomy II. Unifying Characteristics III. Distinguishing Classes IV. Classes in Detail Easiest division of Chlorophyta from other algae: - usually bright
8/12/14 Division: Chlorophyta The mean Greens I. Taxonomy II. Unifying Characteristics III. Distinguishing Classes IV. Classes in Detail Easiest division of Chlorophyta from other algae: - usually bright
Biology 11. Day 4 Classification of Algae
 Biology 11 Day 4 Classification of Algae Learning Objectives: Become familiar with biological nomenclature Distinguish between Rhodophyta, Phaeophyta, and Chlorophyta Identify features of each body type
Biology 11 Day 4 Classification of Algae Learning Objectives: Become familiar with biological nomenclature Distinguish between Rhodophyta, Phaeophyta, and Chlorophyta Identify features of each body type
Chlamydomonas. Organelle?
 Chlamydomonas Organelle? Structure? Organelle? Unicellular thalli typically spherical to subspherical. Eyespot prominent in many species, at cell anterior embedded in chloroplast. Nucleus single and typically
Chlamydomonas Organelle? Structure? Organelle? Unicellular thalli typically spherical to subspherical. Eyespot prominent in many species, at cell anterior embedded in chloroplast. Nucleus single and typically
Biology. Slide 1of 34. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists 2of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists Similarities and differences between funguslike protists and fungi Like fungi, g, funguslike protists are heterotrophs that absorb
Biology 1of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists 2of 34 20 5 Funguslike Protists Similarities and differences between funguslike protists and fungi Like fungi, g, funguslike protists are heterotrophs that absorb
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome
 Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
What Are the Protists?
 Protists 1 What Are the Protists? 2 Protists are all the eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals. Protists are a paraphyletic group. Protists exhibit wide variation in morphology, size, and nutritional
Protists 1 What Are the Protists? 2 Protists are all the eukaryotes that are not fungi, plants, or animals. Protists are a paraphyletic group. Protists exhibit wide variation in morphology, size, and nutritional
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual S Section 1: S Gamete: Haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote. S Zygote: The cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual S Section 1: S Gamete: Haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote. S Zygote: The cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11. Reproduction Section 1
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11 Reproduction Section 1 Reproduction Key Idea: An individual formed by asexual reproduction is genetically identical to its parent. Asexual Reproduction In asexual
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11 Reproduction Section 1 Reproduction Key Idea: An individual formed by asexual reproduction is genetically identical to its parent. Asexual Reproduction In asexual
SG 9.2 notes Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants
 Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
Ideas about targets and terms: 9.2 In the past, all living things were classified in either the kingdom of animals or plants Euglena are singled celled organisms in pond water They are green, so contain,
GREEN ALGAE DIVISION CHLOROPHYTA
 GREEN ALGAE DIVISION CHLOROPHYTA Introduction Of the approximately 16,000 species of green algae, 90% are restricted to the freshwater environment: damp soil, rivers, lakes, ponds, puddles, tree bark,
GREEN ALGAE DIVISION CHLOROPHYTA Introduction Of the approximately 16,000 species of green algae, 90% are restricted to the freshwater environment: damp soil, rivers, lakes, ponds, puddles, tree bark,
A. Difference between bacteria (Monera) and other algae (Eukaryotes). -normal stuff: circular v. linear DNA; organelles or not; nucleus or not.
 Cyanophyta (Cyanobacteria; blue-green algae). A. Difference between bacteria (Monera) and other algae (Eukaryotes). -normal stuff: circular v. linear DNA; organelles or not; nucleus or not. B. Differences
Cyanophyta (Cyanobacteria; blue-green algae). A. Difference between bacteria (Monera) and other algae (Eukaryotes). -normal stuff: circular v. linear DNA; organelles or not; nucleus or not. B. Differences
Chapter 13- Reproduction, Meiosis, and Life Cycles. Many plants and other organisms depend on sexual reproduction.
 Chapter 13- Reproduction, Meiosis, and Life Cycles Many plants and other organisms depend on sexual reproduction. Flowers are the sexual reproductive organ systems of angiosperms. Sexual reproduction gametes
Chapter 13- Reproduction, Meiosis, and Life Cycles Many plants and other organisms depend on sexual reproduction. Flowers are the sexual reproductive organ systems of angiosperms. Sexual reproduction gametes
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014
 Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Meet the algae 1 Protist Phylogeny Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular From phytoplankton to kelp forests
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Meet the algae 1 Protist Phylogeny Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular From phytoplankton to kelp forests
Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring Protist Phylogeny. Meet the algae. Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis. Endosymbiosis. Secondary Endosymbiosis
 Meet the algae Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Protist Phylogeny 1 Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis 2 Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular
Meet the algae Protists: Algae Lecture 5 Spring 2014 Protist Phylogeny 1 Primary & Secondary Endosymbiosis 2 Algae - Not monophyletic What unites them as a group? Range from unicellular to multicellular
Aquatic Ancestors of Land Plants
 Aquatic Ancestors of Land Plants Distinguishing Characteristics: Photosynthetic Live in aqueous environments (ie. In or near water) Lack internal tubes to move water and materials from one part of the
Aquatic Ancestors of Land Plants Distinguishing Characteristics: Photosynthetic Live in aqueous environments (ie. In or near water) Lack internal tubes to move water and materials from one part of the
Cells. Unit Review: Cells MEIOSIS. TECHBOOK UNIT 0 Views. Essential Questions and Answers for Review Sheet. What is meiosis?
 Cells TECHBOOK UNIT 0 Views Unit Review: Cells MEIOSIS Essential Questions and Answers for Review Sheet What is meiosis? Answer: Meiosis is the process by which specialized cells called gametes form in
Cells TECHBOOK UNIT 0 Views Unit Review: Cells MEIOSIS Essential Questions and Answers for Review Sheet What is meiosis? Answer: Meiosis is the process by which specialized cells called gametes form in
Biology. Slide 1 of 34. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 34 2 of 34 What are the similarities and differences between funguslike protists and fungi? 3 of 34 Funguslike protists are heterotrophs that absorb nutrients from dead or decaying organic
Biology 1 of 34 2 of 34 What are the similarities and differences between funguslike protists and fungi? 3 of 34 Funguslike protists are heterotrophs that absorb nutrients from dead or decaying organic
Lecture-1- Introduction to Algae
 Lecture-1- Introduction to 1-General Characteristics 1-Size Criterion: picoplankton ( 20 mm) 2- Most reproduce asexually 3- Both heterotrophic and autotrophic
Lecture-1- Introduction to 1-General Characteristics 1-Size Criterion: picoplankton ( 20 mm) 2- Most reproduce asexually 3- Both heterotrophic and autotrophic
MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU
 MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes such as animals, plants and fungi The number of sets of chromosomes
MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes such as animals, plants and fungi The number of sets of chromosomes
Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants
 Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants Land plants descended from a green algae ancestor Some key characteristics of land plants are shared with green algae, like Multicellular, eukaryotic,
Domain Eukarya: Kingdom Plantae non-vascular plants Land plants descended from a green algae ancestor Some key characteristics of land plants are shared with green algae, like Multicellular, eukaryotic,
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.29 - PROTISTS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Eukrayotic cells are large, have a nucleus, contain membrane-bound organelles, and use a cytoskeleton The nucleus is the synapomorphy that unifies eukaryotes Endosymbiotic theory
!! www.clutchprep.com Eukrayotic cells are large, have a nucleus, contain membrane-bound organelles, and use a cytoskeleton The nucleus is the synapomorphy that unifies eukaryotes Endosymbiotic theory
Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land
 Chapter 29, 30. Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land 1 The first plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the seas 1st photosynthetic
Chapter 29, 30. Diversity of Plants How Plants Colonized the Land 1 The first plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the seas 1st photosynthetic
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
Kingdom Protista. The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists
 Kingdom Protista The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists DOMAIN EUKARYA PROTISTS KINGDOM PROTISTA Any eukaryote that is not classified as a fungus, plant, or
Kingdom Protista The world of Protists: Animal-like Protists Plant-like Protists Fungus-like Protists DOMAIN EUKARYA PROTISTS KINGDOM PROTISTA Any eukaryote that is not classified as a fungus, plant, or
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity
 http://animal.discovery.com/tvshows/monsters-insideme/videos/the-brain-eatingamoeba.htm The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Introduction to the protists Kingdom Protista split into as many as 20 kingdoms
http://animal.discovery.com/tvshows/monsters-insideme/videos/the-brain-eatingamoeba.htm The Origins of Eukaryotic Diversity Introduction to the protists Kingdom Protista split into as many as 20 kingdoms
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28
 Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Major Events in the History of Earth
 Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
Major Events in the History of Earth Cenozoic Humans Land plants Animals Origin of solar system and Earth Multicellular eukaryotes 1 Proterozoic eon 2 Archaean eon 3 4 Single-celled eukaryotes Atmospheric
1. If a eukaryotic cell has a single set of chromosomes, it is called A. haploid B. diploid C. polypoid
 Reproduction 1. If a eukaryotic cell has a single set of chromosomes, it is called A. haploid B. diploid C. polypoid 2. Which of the following cell functions are maintained by cell division? A. growth,
Reproduction 1. If a eukaryotic cell has a single set of chromosomes, it is called A. haploid B. diploid C. polypoid 2. Which of the following cell functions are maintained by cell division? A. growth,
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Planktonic Chlorophytes I. Chlorophyceae
 Planktonic Chlorophytes Chlorophyta are commonly known as green algae. This is the most diverse group of algae, with over 10,000 species. The majority of organisms in this group are unicelluar, but there
Planktonic Chlorophytes Chlorophyta are commonly known as green algae. This is the most diverse group of algae, with over 10,000 species. The majority of organisms in this group are unicelluar, but there
Chlorophyta. I. Diversity of Form Among the Chlorophyta--A First Gauntlet!
 ` Chlorophyta Name I. Diversity of Form Among the Chlorophyta--A First Gauntlet! Work as part of the class team to set up all prepared slides and wet-mount(s) at ten microscopes. When all are ready, the
` Chlorophyta Name I. Diversity of Form Among the Chlorophyta--A First Gauntlet! Work as part of the class team to set up all prepared slides and wet-mount(s) at ten microscopes. When all are ready, the
Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s
 Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s somatic cells: all the cells in the body except for specialized sex cells each somatic cell has a specific # of chromosomes - ( humans have 46, 23
Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s somatic cells: all the cells in the body except for specialized sex cells each somatic cell has a specific # of chromosomes - ( humans have 46, 23
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation
 Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms Are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview: Hereditary Similarity and Variation Living organisms Are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell
Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Eukaryotic microorganisms Fungi Algae Water
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 12 Characterizing and Classifying Eukaryotes Eukaryotic microorganisms Fungi Algae Water
Cellular Division. copyright cmassengale
 Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis. Genetics Terminology: Homologous chromosomes
 For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis Genetics Terminology: Autosomes Somatic cell Gamete Karyotype Homologous chromosomes Meiosis Sex chromosomes Diploid Haploid Zygote Synapsis
For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis Genetics Terminology: Autosomes Somatic cell Gamete Karyotype Homologous chromosomes Meiosis Sex chromosomes Diploid Haploid Zygote Synapsis
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
Frequently asked questions (FAQs).
 Frequently asked questions (FAQs). Q.1. What is The term algae (singular: alga), has been derived from a Latin word algere, meaning seaweeds. Algae include a diverse group of mostly autotrophic, eukaryotic
Frequently asked questions (FAQs). Q.1. What is The term algae (singular: alga), has been derived from a Latin word algere, meaning seaweeds. Algae include a diverse group of mostly autotrophic, eukaryotic
Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Algae Eukaryotic Algae
 Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Algae Eukaryotic Algae I. General Characteristics II. Reproduction and Life History Patterns III. Photosynthetic Pigments IV. Chloroplast types V. Major Polysaccharide Reserves
Characteristics Of Eukaryotic Algae Eukaryotic Algae I. General Characteristics II. Reproduction and Life History Patterns III. Photosynthetic Pigments IV. Chloroplast types V. Major Polysaccharide Reserves
2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
 Human Heredity Chapter 2 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis 2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
Human Heredity Chapter 2 Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis 2:1 Chromosomes DNA Genes Chromatin Chromosomes CHROMATIN: nuclear material in non-dividing cell, composed of DNA/protein in thin uncoiled strands
THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS. Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent.
 THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent. Sexual Reproduction: The fusion of two separate parent cells that produce offspring with
THE CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction: Production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent. Sexual Reproduction: The fusion of two separate parent cells that produce offspring with
Topic 10: Cyanobacteria & Algae
 BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Spring 2009 Topic 10: Cyanobacteria & Algae A. Introduction Plants are not the only organisms that are photosynthetic. In fact, photosynthetic lineages have popped up here and
BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Spring 2009 Topic 10: Cyanobacteria & Algae A. Introduction Plants are not the only organisms that are photosynthetic. In fact, photosynthetic lineages have popped up here and
The Cellular Basis of Inheritance
 CHAPTER 9 The Cellular Basis of Inheritance Summary of Key Concepts Concept 9.1 All cells come from cells. (pp. 180 181) Cell reproduction is an important process. Three functions of cell reproduction
CHAPTER 9 The Cellular Basis of Inheritance Summary of Key Concepts Concept 9.1 All cells come from cells. (pp. 180 181) Cell reproduction is an important process. Three functions of cell reproduction
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Introduction Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles 2004-05 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. -Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely
Introduction Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles 2004-05 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. -Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely
The Producers: The Plant Kingdom An Introduction to Plants and the Mosses
 The Producers: The Plant Kingdom An Introduction to Plants and the Mosses Mosses Phylum Bryophyta - ~12,000 species Liverworts - Phylum Hepaticophyta - ~8,500 species Hornworts - Phylum Anthocerophyta
The Producers: The Plant Kingdom An Introduction to Plants and the Mosses Mosses Phylum Bryophyta - ~12,000 species Liverworts - Phylum Hepaticophyta - ~8,500 species Hornworts - Phylum Anthocerophyta
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Single parent produces offspring All offspring are genetically identical to one another and to parent Produces identical somatic (body) cells Sexual
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Single parent produces offspring All offspring are genetically identical to one another and to parent Produces identical somatic (body) cells Sexual
Chapter 20 Protists Section Review 20-1
 Chapter 20 Protists Section Review 20-1 1. What are protists? 2. Why is it easier to define protists by what they are not, rather than by what they are? Completion On the lines provided, complete the following
Chapter 20 Protists Section Review 20-1 1. What are protists? 2. Why is it easier to define protists by what they are not, rather than by what they are? Completion On the lines provided, complete the following
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Name Hour. Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages )
 Name Hour Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages 506-509) Introduction (Page 506) 1. Plantlike protists are commonly called 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Algae include
Name Hour Section 20-3 Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae (pages 506-509) Introduction (Page 506) 1. Plantlike protists are commonly called 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Algae include
Importance of Protists
 Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
Protists Protists The kingdom Protista is a very diverse kingdom. Eukaryotes that are not classified as fungi, plants, or animals are classified as protists. However, even though they are officially in
3/22/2011. Review. Review. Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell
 Review Review Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell Meiosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with one-half
Review Review Mitosis: division of cells that results in two identical daughter cells with same genetic information as the first cell Meiosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with one-half
Kingdom Protista. Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 EXIT 2/16/2005
 Kingdom Protista Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 Kingdom Protista General Characteristics Animal-Like Protists Plant-Like Protists Fungus-Like Protists General Characteristics Protozoa - Greek name
Kingdom Protista Mr. Krause Edina Public Schools ISD273 Kingdom Protista General Characteristics Animal-Like Protists Plant-Like Protists Fungus-Like Protists General Characteristics Protozoa - Greek name
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis
 Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Outline Overview Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Outline Overview Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less
19.1 Diversity of Protists. KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms.
 19.1 Diversity of Protists KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. 19.1 Diversity of Protists Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. Protists are eukaryotes
19.1 Diversity of Protists KEY CONCEPT Kingdom Protista is the most diverse of all the kingdoms. 19.1 Diversity of Protists Protists can be animal-like, plantlike, or funguslike. Protists are eukaryotes
Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists
 Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists This organism consists of a single cell with several flagella. Is it a prokaryote, such as a bacterium? Actually, it s larger than a prokaryotic cell, and it also has
Unit 14.1: Introduction to Protists This organism consists of a single cell with several flagella. Is it a prokaryote, such as a bacterium? Actually, it s larger than a prokaryotic cell, and it also has
Kingdom: Plantae. Domain Archaea. Domain Eukarya. Domain Bacteria. Common ancestor
 Kingdom: Plantae Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor The First Plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the
Kingdom: Plantae Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor The First Plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll
 Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
2. The development of revolutionized the of life.
 Science 10 Unit 7 Worksheet Chapter 15, Part 1. 1. Briefly describe the three main parts of cell theory: 2. The development of revolutionized the of life. 3. Individual cells need to take in to build and
Science 10 Unit 7 Worksheet Chapter 15, Part 1. 1. Briefly describe the three main parts of cell theory: 2. The development of revolutionized the of life. 3. Individual cells need to take in to build and
CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND. Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution
 CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution 1. Evolutionary adaptations to terrestrial living characterize the four main groups of land plants
CHAPTER 29 PLANT DIVERSITY I: HOW PLANTS COLONIZED LAND Section A: An Overview of Land Plant Evolution 1. Evolutionary adaptations to terrestrial living characterize the four main groups of land plants
Kingdom Fungi. 1. Student will be able to describe the characteristic features in the kingdom Fungi.
 Kingdom Fungi Molds, Sac Fungi, Mushrooms, and Lichens Essential Question(s): What makes fungi have their own kingdom? Objectives: 1. Student will be able to describe the characteristic features in the
Kingdom Fungi Molds, Sac Fungi, Mushrooms, and Lichens Essential Question(s): What makes fungi have their own kingdom? Objectives: 1. Student will be able to describe the characteristic features in the
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Variations on a Theme Living
13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Variations on a Theme Living
Groups of Fungi. Section 2
 Groups of Fungi Section 2 Chytrid Fungi Key Idea: The chytrids are a group of aquatic fungi that provide clues about the evolution of fungi. Chytrid Fungi Chytrids were once classified with protists because
Groups of Fungi Section 2 Chytrid Fungi Key Idea: The chytrids are a group of aquatic fungi that provide clues about the evolution of fungi. Chytrid Fungi Chytrids were once classified with protists because
MGC New Life Christian Academy
 A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
more than 380,000 species, of which more than two-thirds
 The plant world contains more than 380,000 species, of which more than two-thirds are green plants. From the most complex flowering plants to single-cell sea algae, plants present a surprising diversity
The plant world contains more than 380,000 species, of which more than two-thirds are green plants. From the most complex flowering plants to single-cell sea algae, plants present a surprising diversity
10.2 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
 10.2 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis There are thousands of different species of organisms. Each species produces more of its own. A species of bacteria splits to make two identical bacteria. A eucalyptus
10.2 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis There are thousands of different species of organisms. Each species produces more of its own. A species of bacteria splits to make two identical bacteria. A eucalyptus
Reading Assignments. A. Systems of Cell Division. Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Mitosis and Meiosis. 2. The distribution of chromosomes in one type of cell division is shown in the diagram below.
 Name: Date: 1. Jack bought a small turtle. Three months later, the turtle had grown to twice its original size. Which of the following statements best describes why Jack s turtle got bigger? A. Parts of
Name: Date: 1. Jack bought a small turtle. Three months later, the turtle had grown to twice its original size. Which of the following statements best describes why Jack s turtle got bigger? A. Parts of
CHAPTERS 16 & 17: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 2012 PROKARYOTES PROKARYOTES. Fig Lived alone on Earth for over 1 billion years
 CHAPTERS 6 & 7: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 0 PROKARYOTES Lived alone on Earth for over billion years Most numerous and widespread organisms (total biomass of prokaryotes is ten times
CHAPTERS 6 & 7: PROKARYOTES, FUNGI, AND PLANTS Honors Biology 0 PROKARYOTES Lived alone on Earth for over billion years Most numerous and widespread organisms (total biomass of prokaryotes is ten times
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division. Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms
 Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Topic 20. Protista II: The Stramenopiles
 Topic 20. Protista II: The Stramenopiles The Stramenopiles (heterokonts) are a phylogenetic group within the kingdom, Protista. These organisms were derived from an ancestor with two dissimilar flagella,
Topic 20. Protista II: The Stramenopiles The Stramenopiles (heterokonts) are a phylogenetic group within the kingdom, Protista. These organisms were derived from an ancestor with two dissimilar flagella,
11-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
ALGAE. Biol 165: Diversity of Life :24 PM
 Biol 165: Diversity of Life 2013-04-21 9:24 PM ALGAE Introduction Eukaryotic Algae are members of the Kingdom Protoctista Cyanobacteria is a Prokaryotic bacterial Algae, and part of the Domain Bacteria,
Biol 165: Diversity of Life 2013-04-21 9:24 PM ALGAE Introduction Eukaryotic Algae are members of the Kingdom Protoctista Cyanobacteria is a Prokaryotic bacterial Algae, and part of the Domain Bacteria,
Protists & Fungi. Words to Know: Chapters 19 & 20. Label the paramecium diagram above. (pg. 548)
 Words to Know: Protozoan Chapters 19 & 20 Protists & Fungi Microsporidium Contractile vacuole Pseudopod Bioluminescent Colony Plasmodium Chitin Hypha Septum Spore Sporangium Rhizoid Lichen Mycorrhiza Label
Words to Know: Protozoan Chapters 19 & 20 Protists & Fungi Microsporidium Contractile vacuole Pseudopod Bioluminescent Colony Plasmodium Chitin Hypha Septum Spore Sporangium Rhizoid Lichen Mycorrhiza Label
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.9 MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MITOSIS Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces daughter cells Interphase is the initial stage of the cell cycle, and is the period between divisions - G1, which
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MITOSIS Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces daughter cells Interphase is the initial stage of the cell cycle, and is the period between divisions - G1, which
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction
 Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction NC Essential Standard: 1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 5: Cellular Reproduction NC Essential Standard: 1.2.2 Analyze how cells grow and reproduce in terms of interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis
Why do cells divide? Why do cells divide? What would happen if they didn t?
 1 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 2 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Why do cells divide? 3 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Why do cells divide? What would happen if they didn t? Organisms would only ever exist as single
1 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 2 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Why do cells divide? 3 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Why do cells divide? What would happen if they didn t? Organisms would only ever exist as single
Polyphyletic group: multiple genealogies Prokaryotic algae (cyanobacteria) and Eukaryotic algae (protistans; not true plants) Autotrophy Body form:
 Algae Seaweeds Polyphyletic group: multiple genealogies Prokaryotic algae (cyanobacteria) and Eukaryotic algae (protistans; not true plants) Autotrophy Body form: unicellular, filamentous, and multicellular
Algae Seaweeds Polyphyletic group: multiple genealogies Prokaryotic algae (cyanobacteria) and Eukaryotic algae (protistans; not true plants) Autotrophy Body form: unicellular, filamentous, and multicellular
Intitial Question: How can the mathematically impossible become the biologically possiblenamely,
 Intitial Question: How can the mathematically impossible become the biologically possiblenamely, a cell with 46 chromosomes splits to form tow cells each with 46 chromosomes/ This means 46 divided by 2
Intitial Question: How can the mathematically impossible become the biologically possiblenamely, a cell with 46 chromosomes splits to form tow cells each with 46 chromosomes/ This means 46 divided by 2
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 10 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 10 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
True or false? Comprehension Section The nucleolus directs and controls all of the cell s activities.
 Use with textbook pages 131 132. True or false? Comprehension Section 4.1 Read the statements given below. If the statement is true, write T on the line in front of the statement. If it is false, write
Use with textbook pages 131 132. True or false? Comprehension Section 4.1 Read the statements given below. If the statement is true, write T on the line in front of the statement. If it is false, write
SCIENCE M E I O S I S
 SCIENCE 9 6. 1 - M E I O S I S OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the process of meiosis Compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis Explain why meiosis is needed MEIOSIS
SCIENCE 9 6. 1 - M E I O S I S OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the process of meiosis Compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis Explain why meiosis is needed MEIOSIS
BIOLOGY. Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Variations on a Theme Living
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Variations on a Theme Living
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction. What is Cellular Reproduction?
 Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of Each Daughter Cell: 1) Necessary genomic
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of Each Daughter Cell: 1) Necessary genomic
Sexual Reproduction. The two parent cells needed for sexual reproduction are called gametes. They are formed during a process known as meiosis.
 Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
Chapter 8 Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida
 Chapter 8 The Continuity of Life: How Cells Reproduce Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 8.1 Why Do Cells Divide? Cells reproduce by cell division.
Chapter 8 The Continuity of Life: How Cells Reproduce Lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 8.1 Why Do Cells Divide? Cells reproduce by cell division.
Meiosis. Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
 Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis and Life Cycles - 1
 Meiosis and Life Cycles - 1 We have just finished looking at the process of mitosis, a process that produces cells genetically identical to the original cell. Mitosis ensures that each cell of an organism
Meiosis and Life Cycles - 1 We have just finished looking at the process of mitosis, a process that produces cells genetically identical to the original cell. Mitosis ensures that each cell of an organism
