PBBTC01 - CELL AND DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY UNIT I: CELLULAR ORGANIZATION
|
|
|
- Jeremy Bradford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PBBTC01 - CELL AND DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY UNIT I: CELLULAR ORGANIZATION PART-A 1. What is prokaryotic cell 2. Explain Eukaryotic cell 3. Major difference of prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells 4. Role of lipid bilayer 5. Explain cell wall 6. Role of Nucleus 7. What is nucleolus 8. Function of nucleolus 9. Major role of Golgi bodies in cell function 10. What is lsosomes 11. Importance of endoplasmic reticulum 12. What is peroxisomes 13. Define plasmid 14. Role of plasmid 15. Role of chloroplast 16. Importance of cytoskeleton 17. Major role in mitochondria 18. Define Powerhouse of the cells 19. Explain types of mitochondria 20. Explain the matrix in the mitochondria UNIT II: CELL CYCLE AND CELL SIGNALING 1. What is cell division 2. Explain different type of cell division 3. What is mitosis cell division 4. What is meiosis cell division 5. What is Interphase 6. What is Prophase 7. What is Metaphase 8. What is Anaphase 9. What is Telohase 10. What is cytokinesis 11. What are the different stages in mitosis cell division 12. What is gamete 13. What is oogenesis 14. What is speramatogenesis 15. What is G-Protein 16. What is cell surface receptor
2 17. Explain molecular chaperones 18. What is cell signaling 19. What is cellular communication 20. What is programmed death cells UNIT III: CELL SIGNALING, CELLULAR COMMUNICATION 1. Role of ligand in cell communication 2. What is receptor protein 3. What is Paracrine signaling 4. What is Autocrine signaling 5. What is Endocrine signaling 6. Explain synaptic signaling 7. What is Signal transduction 8. What is protein kinase 9. What is phosphatase 10. Types of receptor in cell signaling 11. What is Cell surface receptor 12. Explain enzymatic receptor 13. What is G protein coupled receptor 14. Role of steroid hormone cell signaling 15. What is Receptor tyrosine kinas 16. What is mitogen activated protein kinase 17. What is GPCRs 18. What is neurotransmission 19. What is quorum sensing? 20. Explain bacterial chemotaxis UNIT IV: BASIC CONCEPTS OF DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY 1. Explain Stem cell 2. Explain different types of stem cells 3. Explain Human development of stem cells 4. What s Sex chromosome 5. What is sex linkage 6. What is chromosome linkage 7. What is Gametogenesis 8. What is Oogenesis 9. What is Spermatogenesis 10. What is blastula 11. What is gastrula 12. What is Metamorphosis 13. What are the different stages of Embryonic development 14. What is organogenesis 15. What is cleavage 16. What is patterning 17. What is Differentiation in embryonic development 18. What is trimester 19. What is Morphogenesis 20. What is Organogenesis
3 UNIT V: ADVANCES IN DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY 1. What is Danio rerio 2. Major role of Danio rerio in Experimental research in developmental Biology 3. Physiological characterization of Danio rerio 4. What is postfertilization 5. What is Somitigenesis 6. What is geneknockting 7. What is nephronophthisis 8. Explain NPHP 9. Advantages of Experimental research in Danio rerio 10. Disadvantage of experimental research in Danio rerio 11. Write short notes on manipulation of Robust embryos 12. Uses of experiential research in developmental biology in drosophila 13. Disadvantage of experimental research in developmental biology in frogs 14. Role of animal ethical committee in experimental research in developmental biology 15. What is CPCSEA 16. Role of CPCSEA in experimental research in developmental biology 17. What is Xenopus Laevis 18. What is Blastula 19. What is Gastrula 20. What is Neurula **************
4 PART-B UNIT I: CELLULAR ORGANIZATION 1. Explain difference of prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells 2. Explain Structure and function of plasma membrane 3. Define structure and function of mitochondria 4. Write short on nucleolus 5. Explain the type of lysosome 6. Brief explain about nucleus 7. Give a details on the ultra structure of mitochondria 8. Cytoskeleton is the driving force behind function of cells substantiate the statement 9. Give a account on organismal theory 10. How DNA is packed so compactly inside a cells UNIT II: CELL CYCLE AND CELL SIGNALING 1. Explain different type of cell Surface receptor and cell signaling 2. Explain the extracellular matrix and the leucocytes migration 3. Describe the different stages in mitosis cell division 4. Describe the different stages of meiosis cell division 5. Write briefly about the protein synthesis 6. What are the molecular basic of mutation 7. Explain different stages of strategies of cell division 8. Give the significance of mitosis 9. Describe the brief cell ageing 10. Compare mitosis and meiosis cell division UNIT III: CELL SIGNALING, CELLULAR COMMUNICATION 1. Describe intracellular and extracellular communication 2. Define Cellular Hemolysis 3. Write general principle of cell communication 4. Define following a. Cell adhesion b. Extracellular matrix 5. Give a account on neurotransmission and its regulation 6. Describe the bacterial toxin with suitable example 7. Define Quorum sensing 8. Describe the cancer and cell cycle 9. Define Ongogenes and Oncovirus 10. What is apoptosis? Explain cancer therapy. UNIT IV: BASIC CONCEPTS OF DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY 1. Give a details account on Stem cell 2. Define following a. Potency b. Commitment 3. Explain chromosomal inheritance
5 4. Define chromosomal inheritance and extra-chromosomal inheritance 5. Explain Gametogenesis 6. Define fertilization in Animals? Different type of stages in Animals development during fertilization? 7. Write about different type stage of cell development during plant fertilization? 8. Brief Embryonic development 9. Define Metamorphosis and Regeneration 10. Define Morphogenesis and organogenesis in plants and animals UNIT V: ADVANCES IN DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY 1. Explain experimental system of animal model in pharmacological research 2. Write about role of animal model in during experimental research in developmental biology 3. Give a details account on Zebrafish in experimental system in developmental biology 4. Write about the different stages in experimental system in animals model 5. Define the experimental system of frog in developmental biology 6. Uses of Sea urchin in experimental systems in developmental biology 7. Discuss about a. Arabidopsis thaliana b. Dictyostelium discoideum 8. Give a details account on Programmed cell death? 9. Define a. Aging b. Senescence 10. Discuss about Drosophila melanogaster in experimental research in developmental biology ************
6 PART-C UNIT I: CELLULAR ORGANIZATION 1. Give a details account on prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells with suitable diagram? 2. Brief Structure and function of plasma membrane? Different type of lysosome 3. Give a details account on structure and function of mitochondria 4. Brief explain on nucleolus? Structure and function of nucleus. 5. Explain the type of lysosome? Define power hours of the cells. 6. Brief explain about nucleus? Function of nucleus. 7. Give details on the ultra structure of mitochondria? Write about the organisms theory. 8. Write about Cytoskeleton is the driving force behind function of cells substantiate the statement 9. How DNA is packed so compactly inside a cells 10. Explain structure and function of Chloroplast? Define cytoskeleton. UNIT II: CELL CYCLE AND CELL SIGNALING 1. Brief different type of cell Surface receptor and cell signaling 2. Give a details account on extracellular matrix and the leucocytes migration 3. Write about the different stages in mitosis cell division with suitable diagram? 4. Write about the different stages of meiosis cell division with suitable diagram? 5. Give a details account on protein synthesis in cells 6. Brief the molecular basic of mutation 7. Write about the different stages of strategies of cell division 8. Write about the significance of mitosis 9. Give a details account on cell ageing 10. Write about Compare mitosis and meiosis cell division with suitable diagram UNIT III: CELL SIGNALING, CELLULAR COMMUNICATION 1. Write about the intracellular and extracellular communication 2. Define Cellular Hemolysis? Explain Cell adhesion 3. Write about the general principle of cell communication? Define the extracellular matrix? 4. Give a detail account on neurotransmission and its regulation with suitable example 5. Describe the bacterial toxin with suitable example? Write about the Quorum sensing 6. Describe the cancer and cell cycle? Brief Metastasis? 7. Define Ongogenes and Oncovirus 8. What is apoptosis? Explain cancer therapy. 9. Define interaction of cancer cells with normal cells? 10. Write about the types of cancer therapy-types and approaches. UNIT IV: BASIC CONCEPTS OF DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY 1. Give a details account on Stem cell research in developmental biology 2. Write about the Potency? Define Commitment? 3. Brief chromosomal inheritance with suitable diagram? 4. Write about the chromosomal inheritance and extra-chromosomal inheritance 5. Write about the Gametogenesis with suitable diagram?
7 6. Write about the fertilization in Animals? Different type of stages in Animals development during fertilization? 7. Write about different type stage of cell development during plant fertilization? 8. Brief Embryonic development? 9. Give a detail account on Metamorphosis and Regeneration 10. Write about the Morphogenesis and organogenesis in plants and animals UNIT V: ADVANCES IN DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY 1. Write about the experimental system of animal model in pharmacological research? 2. Write about role of animal model in during experimental research in developmental biology? 3. Give a details account on Zebra fish in experimental system in developmental biology 4. Write about the different stages in experimental system in animals model 5. Define the experimental system of frog in developmental biology 6. Discuss about the Uses of Sea urchin in experimental systems in developmental biology 7. Write about the different developmental stages in Arabidopsis thaliana in experimental research? Write about the experimental research on developmental biology on Dictyostelium discoideum? 8. Give a details account on Programmed cell death? 9. Write about the Aging? Discuss about the Senescence? 10. Write about the Drosophila melanogaster in experimental research in developmental biology **********
Unit 5: Cell Division and Development Guided Reading Questions (45 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Unit 5: Cell Division and Development Guided
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Unit 5: Cell Division and Development Guided
Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle
 Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis
 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis Omnis cellula e cellula Cell Div. In Eukaryotic cells Chromosome structure Biparental inheritance and diploidy Mitosis: Karyokinesis and cytokinesis 5 stages: PPMAT Regulating
Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis Omnis cellula e cellula Cell Div. In Eukaryotic cells Chromosome structure Biparental inheritance and diploidy Mitosis: Karyokinesis and cytokinesis 5 stages: PPMAT Regulating
Science 9 Unit 2 pack: Reproduction
 Science 9 Unit 2 pack: Reproduction Name Ch 4: The Nucleus Ch 5: Mitosis Ch 6: Meiosis Students will develop an understanding of the processes of cell division as they pertain to reproduction. 0 Section
Science 9 Unit 2 pack: Reproduction Name Ch 4: The Nucleus Ch 5: Mitosis Ch 6: Meiosis Students will develop an understanding of the processes of cell division as they pertain to reproduction. 0 Section
Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018
 Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Class: Date: Honors Biology-CW/HW Cell Biology 2018 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Hooke s discovery of cells was made observing a. living
Honors Biology Midterm Exam Study Guide--January 2019
 Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
Objective Response Reflection 3 = I totally know this! :) 2 = I remember this somewhat 1 = I don't remember this at all Explain the difference between independent and dependent variables. Explain what
NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions
 NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions Directions: Using your notes and book as a guide, complete the following questions to review everything we have learned about cells, their parts, and any functions
NAME: PERIOD: The Cell and Its Functions Directions: Using your notes and book as a guide, complete the following questions to review everything we have learned about cells, their parts, and any functions
Biology: Life on Earth
 Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 11 The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Cellular Reproduction Intracellular activity between one cell division to the next is the cell
Biology: Life on Earth Eighth Edition Lecture for Chapter 11 The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Cellular Reproduction Intracellular activity between one cell division to the next is the cell
Reading Assignments. A. Systems of Cell Division. Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Death Read Chapter 19 Cell Division Read Chapter 20 pages 659-672 672 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections)
Station What are the statements to the cell theory? 2. What are the two categories of cells?
 Station 1 1. What are the statements to the cell theory? 2. What are the two categories of cells? Station 2 3. List the main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 4. What are the similarities
Station 1 1. What are the statements to the cell theory? 2. What are the two categories of cells? Station 2 3. List the main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes? 4. What are the similarities
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES
 CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
The facts about cells
 The facts about cells By Regina Bailey, ThoughtCo.com on 10.18.17 Word Count 867 Level MAX An illustration of cells. Photo from Pixabay. Cells are the fundamental units of life. Whether they be unicellular
The facts about cells By Regina Bailey, ThoughtCo.com on 10.18.17 Word Count 867 Level MAX An illustration of cells. Photo from Pixabay. Cells are the fundamental units of life. Whether they be unicellular
Mitosis & Meiosis. PPT Questions. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete copy of the original cell s DNA?
 1. From where do new cells arise? Mitosis & Meiosis PPT Questions 2. Why does the body constantly make new cells? 3. Is cell division the same in all cells? Explain. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete
1. From where do new cells arise? Mitosis & Meiosis PPT Questions 2. Why does the body constantly make new cells? 3. Is cell division the same in all cells? Explain. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete
Introduction to Cells
 Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology
 2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from p. 93-121, mostly skimming Concept 6.1 on microscopy. Figure 6.8 on pp. 100-101 is really helpful in showing
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from p. 93-121, mostly skimming Concept 6.1 on microscopy. Figure 6.8 on pp. 100-101 is really helpful in showing
Chapter 2: Chromosomes and cellular reproduction
 Chapter 2: Chromosomes and cellular reproduction I. Contrast between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. See Figure 2.1 Nucleus absent Small diameter 1 to 10 µm Genome usually 1 circular molecule Small genome;
Chapter 2: Chromosomes and cellular reproduction I. Contrast between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. See Figure 2.1 Nucleus absent Small diameter 1 to 10 µm Genome usually 1 circular molecule Small genome;
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division. Chapter 2 Human Heredity by Michael Cummings 2006 Brooks/Cole-Thomson Learning
 Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division Cells The basic functional units of all living things Human cells vary widely but all have similar basic structure Cells vary widely in morphology Neuron Hair cell http://umech.mit.edu/hearing/intro/big/hccomp.000.gif
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division Cells The basic functional units of all living things Human cells vary widely but all have similar basic structure Cells vary widely in morphology Neuron Hair cell http://umech.mit.edu/hearing/intro/big/hccomp.000.gif
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division
 Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in: A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in: A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
Life of the Cell. Learning Objectives
 Life of the Cell Society on a micro-scale 1 Learning Objectives 1. What are the characteristics that distinguish prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Which type of cell is believed to be older (more primitive)?
Life of the Cell Society on a micro-scale 1 Learning Objectives 1. What are the characteristics that distinguish prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Which type of cell is believed to be older (more primitive)?
CELL REPRODUCTION VOCABULARY- CHAPTER 8 (33 words)
 CELL REPRODUCTION- CHAPTER 8 CELL REPRODUCTION VOCABULARY- CHAPTER 8 (33 words) 1. Chromosome 2. histone 3. chromatid 4. Centromere 5. chromatin 6. autosome 7. Sex chromosome 8. homologous chromosome 9.
CELL REPRODUCTION- CHAPTER 8 CELL REPRODUCTION VOCABULARY- CHAPTER 8 (33 words) 1. Chromosome 2. histone 3. chromatid 4. Centromere 5. chromatin 6. autosome 7. Sex chromosome 8. homologous chromosome 9.
Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle
 Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Example 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Concept 12.1
Name Period Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle Overview: 1. What are the three key roles of cell division? State each role, and give an example. Key Role Example 2. What is meant by the cell cycle? Concept 12.1
Know how to read a balance, graduated cylinder, ruler. Know the SI unit of each measurement.
 Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2012-2013 Due the day of your final for a maximum of 5 extra credit points. You will be able to use this review on your exam for 15 minutes! Safety and Lab Measurement:
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2012-2013 Due the day of your final for a maximum of 5 extra credit points. You will be able to use this review on your exam for 15 minutes! Safety and Lab Measurement:
Introduction to Cells
 Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Life Science Introduction to Cells All life forms on our planet are made up of cells. In ALL organisms, cells have the same basic structure. The scientist Robert Hooke was the first to see cells under
Introduction to Botany
 Introduction to Botany Alexey Shipunov Minot State University Lecture 13 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany Lecture 13 1 / 27 Outline 1 Questions and answers Quiz 2 Plant cell Cell boundaries Protein
Introduction to Botany Alexey Shipunov Minot State University Lecture 13 Shipunov (MSU) Introduction to Botany Lecture 13 1 / 27 Outline 1 Questions and answers Quiz 2 Plant cell Cell boundaries Protein
Chapter 4. Table of Contents. Section 1 The History of Cell Biology. Section 2 Introduction to Cells. Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features
 Cell Structure and Function Table of Contents Section 1 The History of Cell Biology Section 2 Introduction to Cells Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features Section 4 Unique Features of Plant Cells Section
Cell Structure and Function Table of Contents Section 1 The History of Cell Biology Section 2 Introduction to Cells Section 3 Cell Organelles and Features Section 4 Unique Features of Plant Cells Section
REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL DIVISION UNIT. A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned:
 Period Date REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL DIVISION UNIT A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes No internal membranes vs. membrane-bound organelles
Period Date REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL DIVISION UNIT A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes No internal membranes vs. membrane-bound organelles
Anaphase. Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell
 Anaphase Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell Antony Van Leevwenhoek 1643- Dutch microscope maker and merchant, observed and described
Anaphase Third phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. Animal Cell Antony Van Leevwenhoek 1643- Dutch microscope maker and merchant, observed and described
Chapter 7.2. Cell Structure
 Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Chapter 7.2 Cell Structure Daily Objectives Describe the structure and function of the cell nucleus. Describe the function and structure of membrane bound organelles found within the cell. Describe the
Microorganisms Answer Key
 Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Microorganisms Answer Key 1. What is NOT a part of the water cycle? a. condensation b. evaporation c. transpiration d. bacteria 2. Unicellular prokaryotes that may be spherical, rod or spiral shaped. a.
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1
 Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Cell Growth and Reproduction Module B, Anchor 1 Key Concepts: - The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, a larger cell is less efficient in moving nutrients
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell The cell is the basic unit of life Although cells differ substantially from one another, they all share certain characteristics that reflect a common ancestry and remind us
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell The cell is the basic unit of life Although cells differ substantially from one another, they all share certain characteristics that reflect a common ancestry and remind us
CHAPTER 12 - THE CELL CYCLE (pgs )
 CHAPTER 12 - THE CELL CYCLE (pgs. 228-245) CHAPTER SEVEN TARGETS I. Describe the importance of mitosis in single-celled and multi-cellular organisms. II. Explain the organization of DNA molecules and their
CHAPTER 12 - THE CELL CYCLE (pgs. 228-245) CHAPTER SEVEN TARGETS I. Describe the importance of mitosis in single-celled and multi-cellular organisms. II. Explain the organization of DNA molecules and their
Biology. Chapter 10 Cell Reproduction. I. Chromosomes
 Biology Chapter 10 Cell Reproduction I. Chromosomes Long thin molecules that store genetic information. A. Chromosome Structure 1. Rod shaped structure composed of DNA and protein. 2. DNA is wrapped around
Biology Chapter 10 Cell Reproduction I. Chromosomes Long thin molecules that store genetic information. A. Chromosome Structure 1. Rod shaped structure composed of DNA and protein. 2. DNA is wrapped around
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Normal diploid somatic (body) cells of the mosquito Culex pipiens contain six chromosomes.
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Normal diploid somatic (body) cells of the mosquito Culex pipiens contain six chromosomes.
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division
 Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in. A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in. A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
SOALAN ULANGKAJI BAB 5 BIOLOGI TINGKATAN 4
 SOALAN ULANGKAJI BAB 5 BIOLOGI TINGKATAN 4 SECTION A: OBJECTIVES QUESTIONS. Diagram shows the phases in a cell cycle. Diagram 3 Diagram What is V? A Mitosis B Cytokinesis C Stage S D Stage G What is the
SOALAN ULANGKAJI BAB 5 BIOLOGI TINGKATAN 4 SECTION A: OBJECTIVES QUESTIONS. Diagram shows the phases in a cell cycle. Diagram 3 Diagram What is V? A Mitosis B Cytokinesis C Stage S D Stage G What is the
Chapter 9 Active Reading Guide The Cell Cycle
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 9 Active Reading Guide The Cell Cycle 1. Give an example of the three key roles of cell division. Key Role Reproduction Example Growth and Development Tissue Renewal
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 9 Active Reading Guide The Cell Cycle 1. Give an example of the three key roles of cell division. Key Role Reproduction Example Growth and Development Tissue Renewal
Biology 1 Semester Review
 Chapter 1 What is Science? 1 1 What Is Science? Key Concept The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural world, and to use those explanations
Chapter 1 What is Science? 1 1 What Is Science? Key Concept The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural world, and to use those explanations
CAPE Biology Unit 1 Scheme of Work
 CAPE Biology Unit 1 Scheme of Work 2011-2012 Term 1 DATE SYLLABUS OBJECTIVES TEXT PAGES ASSIGNMENTS COMMENTS Orientation Introduction to CAPE Biology syllabus content and structure of the exam Week 05-09
CAPE Biology Unit 1 Scheme of Work 2011-2012 Term 1 DATE SYLLABUS OBJECTIVES TEXT PAGES ASSIGNMENTS COMMENTS Orientation Introduction to CAPE Biology syllabus content and structure of the exam Week 05-09
Anaphase, Telophase. Animal cells divide their cytoplasm by forming? Cleavage furrow. Bacteria, Paramecium, Amoeba, etc. reproduce by...
 The 4 phases of mitosis Animal cells divide their cytoplasm by forming? Bacteria, Paramecium, Amoeba, etc. reproduce by... Cell which after division is identical to the original is called a Prophase, Metaphase,
The 4 phases of mitosis Animal cells divide their cytoplasm by forming? Bacteria, Paramecium, Amoeba, etc. reproduce by... Cell which after division is identical to the original is called a Prophase, Metaphase,
Biology. 7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure 10/29/2013. Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Biology Biology 1of 49 2of 49 Eukaryotic Cell Structures Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists
Biology Biology 1of 49 2of 49 Eukaryotic Cell Structures Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists
Cell Organelles. Wednesday, October 22, 14
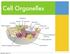 Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Cell Organelles Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells have a cell membrane It is the layer that surrounds the cell and controls what goes in and out Bacteria (Prokaryotic Cell) Cell/Plasma Membrane ALL cells
Compare and contrast the cellular structures and degrees of complexity of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms.
 Subject Area - 3: Science and Technology and Engineering Education Standard Area - 3.1: Biological Sciences Organizing Category - 3.1.A: Organisms and Cells Course - 3.1.B.A: BIOLOGY Standard - 3.1.B.A1:
Subject Area - 3: Science and Technology and Engineering Education Standard Area - 3.1: Biological Sciences Organizing Category - 3.1.A: Organisms and Cells Course - 3.1.B.A: BIOLOGY Standard - 3.1.B.A1:
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis
 Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Biology Unit 6 Chromosomes and Mitosis 6:1 Chromosomes DNA GENES CHROMATIN/CHROMOSOMES CHROMOSOMES/CHROMATIN are made of units called GENES. GENES are made of a compound called deoxyribonucleic acid or
Topic 2: Cells (12 hours)
 Topic : Cells ( hours). Cell theory hours.. Outline the cell theory. Include the following. Living organisms are composed of cells. Cells are the smallest unit of life. Cells come from pre-existing cells...
Topic : Cells ( hours). Cell theory hours.. Outline the cell theory. Include the following. Living organisms are composed of cells. Cells are the smallest unit of life. Cells come from pre-existing cells...
Investigation 7 Part 1: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS
 Investigation 7 Part 1: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS How do eukaryotic cells divide to produce genetically identical cells? BACKGROUND One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate
Investigation 7 Part 1: CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS How do eukaryotic cells divide to produce genetically identical cells? BACKGROUND One of the characteristics of living things is the ability to replicate
Signal Transduction. Dr. Chaidir, Apt
 Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Signal Transduction Dr. Chaidir, Apt Background Complex unicellular organisms existed on Earth for approximately 2.5 billion years before the first multicellular organisms appeared.this long period for
Biology Semester Review
 Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Biology Semester Review 1 1 What is Science? One goal of science is to provide natural explanations for events in the natural world. Science also aims to use those explanations
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Biology Semester Review 1 1 What is Science? One goal of science is to provide natural explanations for events in the natural world. Science also aims to use those explanations
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division. Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms
 Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
5.1. Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. G 1. Cell Growth and Division CHAPTER 5 THE CELL CYCLE KEY CONCEPT
 SECTION 5.1 THE CELL CYCLE Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. VOCABULARY cell cycle mitosis cytokinesis The cell cycle has four main stages.
SECTION 5.1 THE CELL CYCLE Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. VOCABULARY cell cycle mitosis cytokinesis The cell cycle has four main stages.
Biology 1 Notebook. Review Answers Pages 17 -?
 Biology 1 Notebook Review Answers Pages 17 -? The History of Cell Studies 1. Robert Hook (1665) used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. The little boxes he observed reminded him of the small
Biology 1 Notebook Review Answers Pages 17 -? The History of Cell Studies 1. Robert Hook (1665) used a microscope to examine a thin slice of cork. The little boxes he observed reminded him of the small
The Cell Cycle. The Cell Cycle
 The Cell Cycle Cells divide by Mitosis or Meiosis. Mitosis allows the organism to replace cells that have died or aren't working, and is how living things grow. It makes an exact copy of the parent cell.
The Cell Cycle Cells divide by Mitosis or Meiosis. Mitosis allows the organism to replace cells that have died or aren't working, and is how living things grow. It makes an exact copy of the parent cell.
Cellular Division. copyright cmassengale
 Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Cellular Division 1 Cell Division All cells are derived from pre- existing cells New cells are produced for growth and to replace damaged or old cells Differs in prokaryotes (bacteria) and eukaryotes (protists,
Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab
 Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab Station 1: Microscopes allow scientists to study cells. Microscopes: How do light microscopes differ from electron microscopes? (How does each work? How much can each
Introduction to Cells- Stations Lab Station 1: Microscopes allow scientists to study cells. Microscopes: How do light microscopes differ from electron microscopes? (How does each work? How much can each
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Read Chapter 19 pages 651-663 663 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections these are in Chapter
Lecture Series 5 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Reading Assignments Read Chapter 18 Cell Cycle & Cell Division Read Chapter 19 pages 651-663 663 only (Benefits of Sex & Meiosis sections these are in Chapter
Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle. 2. What is the meaning of genome? Compare your genome to that of a prokaryotic cell.
 Name: AP Bio Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle 12.1 Cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells 1. What is meant by the cell cycle? 2. What is the meaning of genome? Compare your genome to that
Name: AP Bio Chapter 12: The Cell Cycle 12.1 Cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells 1. What is meant by the cell cycle? 2. What is the meaning of genome? Compare your genome to that
Cellular Growth & Reproduction. Biology 1B Ms. Morris
 Cellular Growth & Reproduction Biology 1B Ms. Morris Friday, February 7, 2014 Warm Up: Look around at the other people in the classroom. What types of variation (differences) do you see? What similarities
Cellular Growth & Reproduction Biology 1B Ms. Morris Friday, February 7, 2014 Warm Up: Look around at the other people in the classroom. What types of variation (differences) do you see? What similarities
Biology Midterm Review
 Biology Midterm Review Unit 1 Keystone Objectives: A.1.1, A.1.2, B.4.1.1 1.1 Biology explores life from the global to the microscopic level. Put the levels of organization in order, starting with subatomic
Biology Midterm Review Unit 1 Keystone Objectives: A.1.1, A.1.2, B.4.1.1 1.1 Biology explores life from the global to the microscopic level. Put the levels of organization in order, starting with subatomic
Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 3: Cell Structures and Functions
 Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 3: Cell Structures and Functions Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: Overview of Cell Structures and Functions Vocabulary
Wake Acceleration Academy - Biology Note Guide Unit 3: Cell Structures and Functions Extra Resources Website: http://waa-science.weebly.com Module 1: Overview of Cell Structures and Functions Vocabulary
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division
 Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. 1. DNA/information overload As a cell increases in size,
Mitosis and Meiosis Cell growth and division The larger the cell, the more trouble the cell has moving nutrients and waste across the cell membrane. 1. DNA/information overload As a cell increases in size,
AS Biology Summer Work 2015
 AS Biology Summer Work 2015 You will be following the OCR Biology A course and in preparation for this you are required to do the following for September 2015: Activity to complete Date done Purchased
AS Biology Summer Work 2015 You will be following the OCR Biology A course and in preparation for this you are required to do the following for September 2015: Activity to complete Date done Purchased
Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW
 Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW 2013-2014 CP Biology Student Name: School/Teacher: Date: SPS CP Biology Midterm Review, January 2014 Page 1 Dear Biology Student,
Stamford Public Schools Science Department District Midterm Examination REVIEW 2013-2014 CP Biology Student Name: School/Teacher: Date: SPS CP Biology Midterm Review, January 2014 Page 1 Dear Biology Student,
WarmUp 1. C. a phosphate group is removed
 WarmUp 1 1. Energy is released from ATP when C. a phosphate group is removed 2. During normal mitotic cell division, a parent cell with four chromosomes will produce two daughter cells, each containing-
WarmUp 1 1. Energy is released from ATP when C. a phosphate group is removed 2. During normal mitotic cell division, a parent cell with four chromosomes will produce two daughter cells, each containing-
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014
 Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014 Biomolecules and Enzymes (Chapter 2) 8 questions Macromolecules, Biomolecules, Organic Compunds Elements *From the Periodic Table of Elements Subunits Monomers,
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014 Biomolecules and Enzymes (Chapter 2) 8 questions Macromolecules, Biomolecules, Organic Compunds Elements *From the Periodic Table of Elements Subunits Monomers,
Answer Key. Cell Growth and Division
 Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE Cell Cycle: (1) Gap1 (G 1): cells grow, carry out normal functions, and copy their organelles. (2) Synthesis (S): cells replicate DNA. (3)
Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE Cell Cycle: (1) Gap1 (G 1): cells grow, carry out normal functions, and copy their organelles. (2) Synthesis (S): cells replicate DNA. (3)
Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines
 Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines Lecture 01: Introduction Course content Developmental Biology Obsolete hypotheses Current theory Lecture 02: Gametogenesis Spermatozoa Spermatozoon function Spermatozoon
Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines Lecture 01: Introduction Course content Developmental Biology Obsolete hypotheses Current theory Lecture 02: Gametogenesis Spermatozoa Spermatozoon function Spermatozoon
Midterm Review Guide. Unit 1 : Biochemistry: 1. Give the ph values for an acid and a base. 2. What do buffers do? 3. Define monomer and polymer.
 Midterm Review Guide Name: Unit 1 : Biochemistry: 1. Give the ph values for an acid and a base. 2. What do buffers do? 3. Define monomer and polymer. 4. Fill in the Organic Compounds chart : Elements Monomer
Midterm Review Guide Name: Unit 1 : Biochemistry: 1. Give the ph values for an acid and a base. 2. What do buffers do? 3. Define monomer and polymer. 4. Fill in the Organic Compounds chart : Elements Monomer
Biology 2018 Final Review. Miller and Levine
 Biology 2018 Final Review Miller and Levine bones blood cells elements All living things are made up of. cells If a cell of an organism contains a nucleus, the organism is a(n). eukaryote prokaryote plant
Biology 2018 Final Review Miller and Levine bones blood cells elements All living things are made up of. cells If a cell of an organism contains a nucleus, the organism is a(n). eukaryote prokaryote plant
Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) Biomolecules & Enzymes
 Unit Biomolecules & Enzymes Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) on Exam 8 questions 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
Unit Biomolecules & Enzymes Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) on Exam 8 questions 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Explain
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Name them. 2. Explain
Highland Park Science Curriculum
 08/08/20115:20 PM 1 Biology I Semester I Unit IV Highland Park Science Curriculum Components Biology I Biology I Pre AP Extensions Biology I Pre AP TAG Extensions Unit Overview Cells and Cellular Mechanisms
08/08/20115:20 PM 1 Biology I Semester I Unit IV Highland Park Science Curriculum Components Biology I Biology I Pre AP Extensions Biology I Pre AP TAG Extensions Unit Overview Cells and Cellular Mechanisms
To help you complete this review activity and to help you study for your test, you should read SC State Standards B
 Name: Test Date: PAGE: Biology I: Unit 3 Cell Structure Review for Unit Test Directions: You should use this as a guide to help you study for your test. You should also read through your notes, worksheets,
Name: Test Date: PAGE: Biology I: Unit 3 Cell Structure Review for Unit Test Directions: You should use this as a guide to help you study for your test. You should also read through your notes, worksheets,
Biology Mid-Term Study Guide
 Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
Name: Date: Chapter 1: The Science of Biology 1. List the 8 characteristics of all living things: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 2. What is biology? 3. What is homeostasis? 4. Define sexual and asexual reproduction.
Meiosis produces haploid gametes.
 Section 1: produces haploid gametes. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of
Section 1: produces haploid gametes. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of
Build a STRUCTURAL concept map of has part starting with cell cycle and using all of the following: Metaphase Prophase Interphase Cell division phase
 Build a STRUCTURAL concept map of has part starting with cell cycle and using all of the following: Metaphase Prophase Interphase Cell division phase Telophase S phase G1 phase G2 phase Anaphase Cytokinesis
Build a STRUCTURAL concept map of has part starting with cell cycle and using all of the following: Metaphase Prophase Interphase Cell division phase Telophase S phase G1 phase G2 phase Anaphase Cytokinesis
Cells. Structural and functional units of living organisms
 Cells Structural and functional units of living organisms Eukaryotic ( true nucleus ) vs. Prokaryotic ( before nucleus ) cells Proks Eukaryotic ( true nucleus ) vs. Prokaryotic ( before nucleus ) cells
Cells Structural and functional units of living organisms Eukaryotic ( true nucleus ) vs. Prokaryotic ( before nucleus ) cells Proks Eukaryotic ( true nucleus ) vs. Prokaryotic ( before nucleus ) cells
Chapter 4: Cells: The Working Units of Life
 Name Period Chapter 4: Cells: The Working Units of Life 1. What are the three critical components of the cell theory? 2. What are the two important conceptual implications of the cell theory? 3. Which
Name Period Chapter 4: Cells: The Working Units of Life 1. What are the three critical components of the cell theory? 2. What are the two important conceptual implications of the cell theory? 3. Which
Cell Biology Review. The key components of cells that concern us are as follows: 1. Nucleus
 Cell Biology Review Development involves the collective behavior and activities of cells, working together in a coordinated manner to construct an organism. As such, the regulation of development is intimately
Cell Biology Review Development involves the collective behavior and activities of cells, working together in a coordinated manner to construct an organism. As such, the regulation of development is intimately
02/02/ Living things are organized. Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures. Learning Outcome B1
 Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
2. Draw two water molecules. Using a dotted line, show a hydrogen bond that could form between them.
 Biology Final Review Packet Directions: Answer the questions below. You may use any notes, worksheets, or your textbook to find the answers. The questions are divided up based on the different units we
Biology Final Review Packet Directions: Answer the questions below. You may use any notes, worksheets, or your textbook to find the answers. The questions are divided up based on the different units we
Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES.
 Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
Name: Period: Date: Biology Mid-Year Review Packet This packet will be collected on the day of the exam for 2 HOMEWORK GRADES. Topics: Observations & Inferences Making A Hypothesis Characteristics of Life
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS
 LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial cells have a single circular chromosome,
LAB 8 EUKARYOTIC CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS Name: Date: INTRODUCTION BINARY FISSION: Prokaryotic cells (bacteria) reproduce asexually by binary fission. Bacterial cells have a single circular chromosome,
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Cell Growth and Division. SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE 1. a; d; b; c 2. gaps 3. c and d 4. c 5. b and d 6.
 Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE 1. a; d; b; c 2. gaps 3. c and d 4. c 5. b and d 6. G 1 7. G 0 8. c 9. faster; too large 10. volume 11. a and b 12. repeating pattern or repetition
Cell Growth and Division Answer Key SECTION 1. THE CELL CYCLE 1. a; d; b; c 2. gaps 3. c and d 4. c 5. b and d 6. G 1 7. G 0 8. c 9. faster; too large 10. volume 11. a and b 12. repeating pattern or repetition
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions.
 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle Why must cells divide? Growth and Repair -
5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle Why must cells divide? Growth and Repair -
Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The receptors for a group of signaling molecules known as growth factors are
Study Guide 11 & 12 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The receptors for a group of signaling molecules known as growth factors are
Objective: The Cell. The Cell Theory. Question of the day: The Plasma Membrane 11/2/09. The Generalized Cell: Parts and Organelles:
 Objective: The Cell Basic Unit of Life The student will become familiar with the structure and function of the basic cell :) The student will know the differences between and animal cell and a plant cell
Objective: The Cell Basic Unit of Life The student will become familiar with the structure and function of the basic cell :) The student will know the differences between and animal cell and a plant cell
ACCELERATE ITS BIOCHEMICAL PROCESSES WHICH WERE SLOWED DOWN BY MITOSIS. THE LENGTH OF THE G1 PHASE CREATES THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FAST DIVIDING
 CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
CHAPTER 1: OVERVIEW OF THE CELL CYCLE THE THREE STAGES OF INTERPHASE: INTERPHASE BEFORE A CELL CAN ENTER CELL DIVISION, IT NEEDS TO PREPARE ITSELF BY REPLICATING ITS GENETIC INFORMATION AND ALL OF THE
Now starts the fun stuff Cell structure and function
 Now starts the fun stuff Cell structure and function Cell Theory The three statements of the cell theory are: All organisms are composed of one or more cells and the processes of life occur in these cells.
Now starts the fun stuff Cell structure and function Cell Theory The three statements of the cell theory are: All organisms are composed of one or more cells and the processes of life occur in these cells.
CELL : THE UNIT OF LIFE
 38 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 8 CELL : THE UNIT OF LIFE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A common characteristic feature of plant sieve tube cells and most of mammalian erythrocytes is a. Absence of
38 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 8 CELL : THE UNIT OF LIFE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A common characteristic feature of plant sieve tube cells and most of mammalian erythrocytes is a. Absence of
Unit 3: Cells. Objective: To be able to compare and contrast the differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells.
 Unit 3: Cells Objective: To be able to compare and contrast the differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. The Cell Theory All living things are composed of cells (unicellular or multicellular).
Unit 3: Cells Objective: To be able to compare and contrast the differences between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells. The Cell Theory All living things are composed of cells (unicellular or multicellular).
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction
 Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Human Development: Mitosis and Meiosis Division of the Cell Before a cell grows too large, it divides into two new daughter cells in a process called cell division.
Cell Growth, Division, and Reproduction Human Development: Mitosis and Meiosis Division of the Cell Before a cell grows too large, it divides into two new daughter cells in a process called cell division.
Cell Structure Vocab. Plasma membrane. Vacuole. Cell wall. Nuclear envelope. Chloroplast. Nucleus. Cytoskeleton. Nucleolus. Cytoplasm.
 The Cell Cell Structure Vocab Plasma membrane Nuclear envelope Nucleus Nucleolus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Lysosome Vacuole Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Centriole
The Cell Cell Structure Vocab Plasma membrane Nuclear envelope Nucleus Nucleolus Cytoplasm Mitochondria Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Lysosome Vacuole Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Centriole
The diagram below represents levels of organization within a cell of a multicellular organism.
 STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
STATION 1 1. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have the capacity to a. assemble into multicellular organisms b. establish symbiotic relationships with other organisms c. obtain energy from the
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis
 Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
Roles of Cell Division. Reproduction - Like begets like, more or less. Examples of Cell Numbers. Outline Cell Reproduction
 Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis 4. Sexual Life
Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis 4. Sexual Life
Eukaryotic Cell Structure. 7.2 Biology Mr. Hines
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure 7.2 Biology Mr. Hines Comparing the cell to a factory In order for a cell to maintain its internal environment (homeostasis), many things must go on. This is similar to a factory.
Eukaryotic Cell Structure 7.2 Biology Mr. Hines Comparing the cell to a factory In order for a cell to maintain its internal environment (homeostasis), many things must go on. This is similar to a factory.
Typical Life Cycle of Algae and Fungi. 5 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Module 3B Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this module, we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells called meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell
Module 3B Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles In this module, we will examine a second type of cell division used by eukaryotic cells called meiosis. In addition, we will see how the 2 types of eukaryotic cell
Biology. Mrs. Michaelsen. Types of cells. Cells & Cell Organelles. Cell size comparison. The Cell. Doing Life s Work. Hooke first viewed cork 1600 s
 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell most
