Homogeneous model: Horizontal pipe and horizontal well. Flow loops can't duplicate field conditions. Daniel D. Joseph. April 2001
|
|
|
- Morgan Gwendolyn O’Neal’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Homogeneous model of producton of heavy ol through horzontal ppelnes and wells based on the Naver-Stokes equatons n the ppelne or the well and Darcy's law n the reservor Homogeneous model: Danel D. Joseph Aprl 1 The gas and ol can be descrbed as a mture n whch the gas content s represented at every pont of the mture by a volume fracton φ of gas. I do not epect that the homogeneous model wll work well f slugs are the flow type and certanly t won't work f the gas s connected n streams as n stratfed or annular flow. The homogeneous model should work best n the case that all the gas (or most of t) s dspersed n small bubbles that move wth the ol, whch may be the case for foamy ols, heavy ol lke Zuata, Cerro Negro and other heavy ols n the Ornoco belt, Canada, Albana, etc. Emlo Guevara told me that n hs eperence wth multphase pumps t was always much easer to montor the flow of foamy ol because the gas was dspersed. I tred on my last vst n early March 1 to fnd out f the flow type was slugs or homogeneous n horzontal ppes and wells n reservors of heavy ol. No one that I asked seemed really to know the answer to ths mportant queston. Horzontal ppe and horzontal well. There s no flow through the wall of the ppe; all the ol s ntroduced at the entrance of the ppe. The well has lner wth many slots that allow the ol to enter the well by over n the reservor; probably ths can be modeled by the contnuty of velocty of the ol and gas normal to the lner wall. It s probable that the contnuty of velocty normal to the lner s modeled well by the contnuty of the normal component of velocty gven by Darcy's law n the reservor and Naver-Stokes n the ppe. Flow loops can't duplcate feld condtons In horzontal wells and ppe lve ol at saturaton s drven nto the ppe by a created by the drawdown at the pump. The gas evolves by outgassng of dssolved gas as the drops by gradents n the drecton of the pump. In flow loops the gas s ntroduced by pumpng n gas and ol and outgassng s not an mportant factor. Of course f a lot of dssolved gas s released by outgassng t mght collect nto slugs whch could be modeled n a flow loop.
2 Mathematcal model of homogeneous flow () Pressure P vs dspersed gas fracton φ (all of the gas s dspersed nto bobbles whch more or less move wth the flud). Aran Kamp and I derved the equaton of state (called a solublty sotherm) for dspersed as a functon of βφ P P (1) 1 φ P where β(t) depends on temperature and P s the saturaton or bubble pont. When P P there s no dspersed gas, φ. We computed β 3 for Cerro Negro and values dfferent but near 3.4 for Lloydmnster and Lndbergh heavy ol. Obvously the most severe outgassng occurs at the pump where P P ρ s the smallest. Usng (1) we may estmate φ 1 β 1 / P where P PT. If P 1 ps and P p 9 ps, the φ 1/3.6. If P 7 ps, P p 4 ps, then φ 1 /.6. These are the worst condtons; n the ppe or well φ s much smaller. It certanly appears that n many cases not very much gas wll come out ecept near the pump. Ths supports the dea that the homogeneous model mght hold mostly anywhere away from the pump. It wll be convenent to work wth the drop Then (1) 1 may be wrtten as π P - P. ρ βφ π 1 φ π P (1) () The vscosty (φ ) and densty ρ(φ) of the mture depend on φ. The vscosty s assumed n the separable form (φ) () f (φ) f (φ) () There are may emprcal formulas for f (φ ) but we really don't know the correct f (φ ) n the case of foamy ol. On the other hand, the mture densty can be consdered to be accurately descrbed by ρ (φ ) ρ (1-φ ) ρ g φ ρ (1-φ ) (3) Prnted 4/1/1 DDJ/1/homogeneous/model-NS-Darcy.doc
3 () The substantal dervatve n a flud and n a porous meda u φ Dt t n a pure flud (4) α q φ Dt t n a porous meda wth porosty α (5) (v) Darcy's Law q s the seepage velocty of the mture n the porous meda and t satsfes Darcy's law q π k( f φ) (6) where k s the permeablty (v) contnuty equaton Dρ( φ) d ρ α ρ (7) Dt dφ Dt Dt From Dρ ρ dv u Dt (8) we get Dt ( 1 φ ) dvu n the flud (9) Dt ( 1 φ ) dvq porous meda (1) The stress Ths doesn't est n the porous meda T ( u u ) 1 D[ u] (11) In the Naver-Stokes equaton we have a term correspondng to the vscosty part of the stress S( φ, u) dv ( D[ u] ) dv ( φ) D[ u] dv S( φ, u) T [ ( u u )] (1) Prnted 4/1/1 3 DDJ/1/homogeneous/model-NS-Darcy.doc
4 Naver-Stokes equaton for dspersed flow ρ u t (13) ( φ ) y y π S( φ, ) 1 u Horzontal well and ppelne: Boundary condtons H q - k π D R n a round hole P p s pump Naver-Stokes n the well or ppe P(H) s the bubble pont at a heght H L Fgure 1. H. We are gong to assume that there s one bubble pont P whch doesn t depend on (1.) Horzontal ppe. u at r R. The porous meda determnes the at the end of the ppe at L. P p s the lowest n the system. Flow s from reservor to ppe entrance; then from ppe entrance to pump. (.) Horzontal well. The normal component of velocty s contnuous across the lner from the porous meda nto the well The tangental component on the ppe lner vanshes (3.) Pressure at the nlet end L of a long ppe. k π u er q er at r R (14) r u e at r R (15) It can be shown that f the ppe s long the P L at L s very nearly the reservor P L P (16) Prnted 4/1/1 4 DDJ/1/homogeneous/model-NS-Darcy.doc
5 (4.) Reynolds number n a long ppe. Assume that the ol s homogeneous and n Poseulle flow n a long ppe. The mean velocty s gven by u R 8 L where s the vscosty The Reynolds number s P P p. Re 3 ur ρ R v 8 L Numercal estmate: P P L 5 ft / L 1 dynes/cm R 1n.5cm (.5) u (.5) Re 3 p 1 ps ρ cm 6 dynes/cm The Reynolds number s very small Re << 1 for heavy ol (5.) Concluson. The Reynolds number for heavy ol > 1 pose s very small. Neglect the nerta (left sde) n (13). Prnted 4/1/1 5 DDJ/1/homogeneous/model-NS-Darcy.doc
6 π P P π P -P < p βφ π 1 φ π P ( φ) p Pressure dfference prescrbed whch drves the flow Solublty sotherm Vscosty dfference The porous meda does not enter ths problem P p pump r u at r R u φ ( 1 φ) dvu t π Stokes flow Contnuty equaton. We can neglect / t. P reservor Fgure. Horzontal ppe (length L, Radus R r). The unknowns are φ and u; π may be elmnated. φ and u depend on or r. All the equatons n the horzontal ppe hold n the horzontal well. In addton, we need k q π Darcy law reservor equatons: α q φ (1 φ) dvq Contnuty equaton t P p pump r u e The equatons n the well are the same as n the ppe but the boundary condtons are dfferent. π k π u er q er at r R r P reservor Fgure 3. Horzontal well. The porous meda s very mportant. Flow s drven by the reservor reference π p toward the pump through the lner. The equatons n fgures and 3 should be made dmensonless n order to dentfy the controllng parameters. Qute frankly, I am not at all clear on how to do ths. It s easy to make the equatons dmensonless, but choces of scales must be made and I do not yet know the optmal choce. You could try your hand at gettng a good dmensonless formulaton. Prnted 4/1/1 6 DDJ/1/homogeneous/model-NS-Darcy.doc
Normally, in one phase reservoir simulation we would deal with one of the following fluid systems:
 TPG4160 Reservor Smulaton 2017 page 1 of 9 ONE-DIMENSIONAL, ONE-PHASE RESERVOIR SIMULATION Flud systems The term sngle phase apples to any system wth only one phase present n the reservor In some cases
TPG4160 Reservor Smulaton 2017 page 1 of 9 ONE-DIMENSIONAL, ONE-PHASE RESERVOIR SIMULATION Flud systems The term sngle phase apples to any system wth only one phase present n the reservor In some cases
STUDY ON TWO PHASE FLOW IN MICRO CHANNEL BASED ON EXPERI- MENTS AND NUMERICAL EXAMINATIONS
 Blucher Mechancal Engneerng Proceedngs May 0, vol., num. www.proceedngs.blucher.com.br/evento/0wccm STUDY ON TWO PHASE FLOW IN MICRO CHANNEL BASED ON EXPERI- MENTS AND NUMERICAL EXAMINATIONS Takahko Kurahash,
Blucher Mechancal Engneerng Proceedngs May 0, vol., num. www.proceedngs.blucher.com.br/evento/0wccm STUDY ON TWO PHASE FLOW IN MICRO CHANNEL BASED ON EXPERI- MENTS AND NUMERICAL EXAMINATIONS Takahko Kurahash,
Lecture 12: Discrete Laplacian
 Lecture 12: Dscrete Laplacan Scrbe: Tanye Lu Our goal s to come up wth a dscrete verson of Laplacan operator for trangulated surfaces, so that we can use t n practce to solve related problems We are mostly
Lecture 12: Dscrete Laplacan Scrbe: Tanye Lu Our goal s to come up wth a dscrete verson of Laplacan operator for trangulated surfaces, so that we can use t n practce to solve related problems We are mostly
Publication 2006/01. Transport Equations in Incompressible. Lars Davidson
 Publcaton 2006/01 Transport Equatons n Incompressble URANS and LES Lars Davdson Dvson of Flud Dynamcs Department of Appled Mechancs Chalmers Unversty of Technology Göteborg, Sweden, May 2006 Transport
Publcaton 2006/01 Transport Equatons n Incompressble URANS and LES Lars Davdson Dvson of Flud Dynamcs Department of Appled Mechancs Chalmers Unversty of Technology Göteborg, Sweden, May 2006 Transport
The Second Anti-Mathima on Game Theory
 The Second Ant-Mathma on Game Theory Ath. Kehagas December 1 2006 1 Introducton In ths note we wll examne the noton of game equlbrum for three types of games 1. 2-player 2-acton zero-sum games 2. 2-player
The Second Ant-Mathma on Game Theory Ath. Kehagas December 1 2006 1 Introducton In ths note we wll examne the noton of game equlbrum for three types of games 1. 2-player 2-acton zero-sum games 2. 2-player
Turbulent Flow. Turbulent Flow
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xoll2kedog&feature=related http://br.youtube.com/watch?v=7kkftgx2any http://br.youtube.com/watch?v=vqhxihpvcvu 1. Caothc fluctuatons wth a wde range of frequences and
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xoll2kedog&feature=related http://br.youtube.com/watch?v=7kkftgx2any http://br.youtube.com/watch?v=vqhxihpvcvu 1. Caothc fluctuatons wth a wde range of frequences and
Module 1 : The equation of continuity. Lecture 1: Equation of Continuity
 1 Module 1 : The equaton of contnuty Lecture 1: Equaton of Contnuty 2 Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer: Modules 1. THE EQUATION OF CONTINUITY : Lectures 1-6 () () () (v) (v) Overall Mass Balance Momentum
1 Module 1 : The equaton of contnuty Lecture 1: Equaton of Contnuty 2 Advanced Heat and Mass Transfer: Modules 1. THE EQUATION OF CONTINUITY : Lectures 1-6 () () () (v) (v) Overall Mass Balance Momentum
Math1110 (Spring 2009) Prelim 3 - Solutions
 Math 1110 (Sprng 2009) Solutons to Prelm 3 (04/21/2009) 1 Queston 1. (16 ponts) Short answer. Math1110 (Sprng 2009) Prelm 3 - Solutons x a 1 (a) (4 ponts) Please evaluate lm, where a and b are postve numbers.
Math 1110 (Sprng 2009) Solutons to Prelm 3 (04/21/2009) 1 Queston 1. (16 ponts) Short answer. Math1110 (Sprng 2009) Prelm 3 - Solutons x a 1 (a) (4 ponts) Please evaluate lm, where a and b are postve numbers.
2 Finite difference basics
 Numersche Methoden 1, WS 11/12 B.J.P. Kaus 2 Fnte dfference bascs Consder the one- The bascs of the fnte dfference method are best understood wth an example. dmensonal transent heat conducton equaton T
Numersche Methoden 1, WS 11/12 B.J.P. Kaus 2 Fnte dfference bascs Consder the one- The bascs of the fnte dfference method are best understood wth an example. dmensonal transent heat conducton equaton T
Computational Study of Transition of Oil-water Flow Morphology due to Sudden Contraction in Microfluidic Channel
 Computatonal Study of Transton of Ol-water Flow Morphology due to Sudden Contracton n Mcrofludc Channel J. Chaudhur 1, S. Tmung 1, T. K. Mandal 1,2, and D. Bandyopadhyay *1,2 1 Department of Chemcal Engneerng,
Computatonal Study of Transton of Ol-water Flow Morphology due to Sudden Contracton n Mcrofludc Channel J. Chaudhur 1, S. Tmung 1, T. K. Mandal 1,2, and D. Bandyopadhyay *1,2 1 Department of Chemcal Engneerng,
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION
 NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 Introducton Dfferentaton s a method to compute the rate at whch a dependent output y changes wth respect to the change n the ndependent nput x. Ths rate of change s called the
NUMERICAL DIFFERENTIATION 1 Introducton Dfferentaton s a method to compute the rate at whch a dependent output y changes wth respect to the change n the ndependent nput x. Ths rate of change s called the
NUMERICAL MODEL FOR NON-DARCY FLOW THROUGH COARSE POROUS MEDIA USING THE MOVING PARTICLE SIMULATION METHOD
 THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 2018, Vol. 22, No. 5, pp. 1955-1962 1955 NUMERICAL MODEL FOR NON-DARCY FLOW THROUGH COARSE POROUS MEDIA USING THE MOVING PARTICLE SIMULATION METHOD Introducton by Tomok IZUMI a* and
THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 2018, Vol. 22, No. 5, pp. 1955-1962 1955 NUMERICAL MODEL FOR NON-DARCY FLOW THROUGH COARSE POROUS MEDIA USING THE MOVING PARTICLE SIMULATION METHOD Introducton by Tomok IZUMI a* and
MATH 5630: Discrete Time-Space Model Hung Phan, UMass Lowell March 1, 2018
 MATH 5630: Dscrete Tme-Space Model Hung Phan, UMass Lowell March, 08 Newton s Law of Coolng Consder the coolng of a well strred coffee so that the temperature does not depend on space Newton s law of collng
MATH 5630: Dscrete Tme-Space Model Hung Phan, UMass Lowell March, 08 Newton s Law of Coolng Consder the coolng of a well strred coffee so that the temperature does not depend on space Newton s law of collng
PERMEABILITY-POROSITY RELATIONSHIP ASSESSMENT BY 2-D NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS
 ISTP-16, 005, PRAGUE 16 TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA PERMEABILITY-POROSITY RELATIONSHIP ASSESSMENT BY -D NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS J. Pnela*, S. Kruz*, A. F. Mguel* +, A. H. Res*, M. Aydn**
ISTP-16, 005, PRAGUE 16 TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA PERMEABILITY-POROSITY RELATIONSHIP ASSESSMENT BY -D NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS J. Pnela*, S. Kruz*, A. F. Mguel* +, A. H. Res*, M. Aydn**
PES 1120 Spring 2014, Spendier Lecture 6/Page 1
 PES 110 Sprng 014, Spender Lecture 6/Page 1 Lecture today: Chapter 1) Electrc feld due to charge dstrbutons -> charged rod -> charged rng We ntroduced the electrc feld, E. I defned t as an nvsble aura
PES 110 Sprng 014, Spender Lecture 6/Page 1 Lecture today: Chapter 1) Electrc feld due to charge dstrbutons -> charged rod -> charged rng We ntroduced the electrc feld, E. I defned t as an nvsble aura
ACTM State Calculus Competition Saturday April 30, 2011
 ACTM State Calculus Competton Saturday Aprl 30, 2011 ACTM State Calculus Competton Sprng 2011 Page 1 Instructons: For questons 1 through 25, mark the best answer choce on the answer sheet provde Afterward
ACTM State Calculus Competton Saturday Aprl 30, 2011 ACTM State Calculus Competton Sprng 2011 Page 1 Instructons: For questons 1 through 25, mark the best answer choce on the answer sheet provde Afterward
Supplementary Notes for Chapter 9 Mixture Thermodynamics
 Supplementary Notes for Chapter 9 Mxture Thermodynamcs Key ponts Nne major topcs of Chapter 9 are revewed below: 1. Notaton and operatonal equatons for mxtures 2. PVTN EOSs for mxtures 3. General effects
Supplementary Notes for Chapter 9 Mxture Thermodynamcs Key ponts Nne major topcs of Chapter 9 are revewed below: 1. Notaton and operatonal equatons for mxtures 2. PVTN EOSs for mxtures 3. General effects
Some modelling aspects for the Matlab implementation of MMA
 Some modellng aspects for the Matlab mplementaton of MMA Krster Svanberg krlle@math.kth.se Optmzaton and Systems Theory Department of Mathematcs KTH, SE 10044 Stockholm September 2004 1. Consdered optmzaton
Some modellng aspects for the Matlab mplementaton of MMA Krster Svanberg krlle@math.kth.se Optmzaton and Systems Theory Department of Mathematcs KTH, SE 10044 Stockholm September 2004 1. Consdered optmzaton
SOLUTION - Examination paper for TPG4160 Reservoir Simulation
 Department of Petroleum Engneerng and Appled Geophyscs SOLUTION - Examnaton paper for TPG4160 Reservor Smulaton Academc contact durng examnaton: Jon Kleppe Phone: 91897300/73594925 Examnaton date: May
Department of Petroleum Engneerng and Appled Geophyscs SOLUTION - Examnaton paper for TPG4160 Reservor Smulaton Academc contact durng examnaton: Jon Kleppe Phone: 91897300/73594925 Examnaton date: May
in a horizontal wellbore in a heavy oil reservoir
 498 n a horzontal wellbore n a heavy ol reservor L Mngzhong, Wang Ypng and Wang Weyang Abstract: A novel model for dynamc temperature dstrbuton n heavy ol reservors s derved from and axal dfference equatons
498 n a horzontal wellbore n a heavy ol reservor L Mngzhong, Wang Ypng and Wang Weyang Abstract: A novel model for dynamc temperature dstrbuton n heavy ol reservors s derved from and axal dfference equatons
Linear Approximation with Regularization and Moving Least Squares
 Lnear Approxmaton wth Regularzaton and Movng Least Squares Igor Grešovn May 007 Revson 4.6 (Revson : March 004). 5 4 3 0.5 3 3.5 4 Contents: Lnear Fttng...4. Weghted Least Squares n Functon Approxmaton...
Lnear Approxmaton wth Regularzaton and Movng Least Squares Igor Grešovn May 007 Revson 4.6 (Revson : March 004). 5 4 3 0.5 3 3.5 4 Contents: Lnear Fttng...4. Weghted Least Squares n Functon Approxmaton...
Lattice Boltzmann Method and its Application to Flow Analysis in Porous Media
 Specal Issue Multscale Smulatons for Materals 7 Research Report Lattce Boltzmann Method and ts Applcaton to Flow Analyss n Porous Meda Hdemtsu Hayash Abstract Under the exstence of an external force, a
Specal Issue Multscale Smulatons for Materals 7 Research Report Lattce Boltzmann Method and ts Applcaton to Flow Analyss n Porous Meda Hdemtsu Hayash Abstract Under the exstence of an external force, a
Open Systems: Chemical Potential and Partial Molar Quantities Chemical Potential
 Open Systems: Chemcal Potental and Partal Molar Quanttes Chemcal Potental For closed systems, we have derved the followng relatonshps: du = TdS pdv dh = TdS + Vdp da = SdT pdv dg = VdP SdT For open systems,
Open Systems: Chemcal Potental and Partal Molar Quanttes Chemcal Potental For closed systems, we have derved the followng relatonshps: du = TdS pdv dh = TdS + Vdp da = SdT pdv dg = VdP SdT For open systems,
Numerical Heat and Mass Transfer
 Master degree n Mechancal Engneerng Numercal Heat and Mass Transfer 06-Fnte-Dfference Method (One-dmensonal, steady state heat conducton) Fausto Arpno f.arpno@uncas.t Introducton Why we use models and
Master degree n Mechancal Engneerng Numercal Heat and Mass Transfer 06-Fnte-Dfference Method (One-dmensonal, steady state heat conducton) Fausto Arpno f.arpno@uncas.t Introducton Why we use models and
PHYS 705: Classical Mechanics. Calculus of Variations II
 1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Calculus of Varatons II 2 Calculus of Varatons: Generalzaton (no constrant yet) Suppose now that F depends on several dependent varables : We need to fnd such that has a statonary
1 PHYS 705: Classcal Mechancs Calculus of Varatons II 2 Calculus of Varatons: Generalzaton (no constrant yet) Suppose now that F depends on several dependent varables : We need to fnd such that has a statonary
Optimal Control of Temperature in Fluid Flow
 Kawahara Lab. 5 March. 27 Optmal Control of Temperature n Flud Flow Dasuke YAMAZAKI Department of Cvl Engneerng, Chuo Unversty Kasuga -3-27, Bunkyou-ku, Tokyo 2-855, Japan E-mal : d33422@educ.kc.chuo-u.ac.jp
Kawahara Lab. 5 March. 27 Optmal Control of Temperature n Flud Flow Dasuke YAMAZAKI Department of Cvl Engneerng, Chuo Unversty Kasuga -3-27, Bunkyou-ku, Tokyo 2-855, Japan E-mal : d33422@educ.kc.chuo-u.ac.jp
Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics
 Introducton to Computatonal Flud Dynamcs M. Zanub 1, T. Mahalakshm 2 1 (PG MATHS), Department of Mathematcs, St. Josephs College of Arts and Scence for Women-Hosur, Peryar Unversty 2 Assstance professor,
Introducton to Computatonal Flud Dynamcs M. Zanub 1, T. Mahalakshm 2 1 (PG MATHS), Department of Mathematcs, St. Josephs College of Arts and Scence for Women-Hosur, Peryar Unversty 2 Assstance professor,
DUE: WEDS FEB 21ST 2018
 HOMEWORK # 1: FINITE DIFFERENCES IN ONE DIMENSION DUE: WEDS FEB 21ST 2018 1. Theory Beam bendng s a classcal engneerng analyss. The tradtonal soluton technque makes smplfyng assumptons such as a constant
HOMEWORK # 1: FINITE DIFFERENCES IN ONE DIMENSION DUE: WEDS FEB 21ST 2018 1. Theory Beam bendng s a classcal engneerng analyss. The tradtonal soluton technque makes smplfyng assumptons such as a constant
Week3, Chapter 4. Position and Displacement. Motion in Two Dimensions. Instantaneous Velocity. Average Velocity
 Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Week3, Chapter 4 Moton n Two Dmensons Lecture Quz A partcle confned to moton along the x axs moves wth constant acceleraton from x =.0 m to x = 8.0 m durng a 1-s tme nterval. The velocty of the partcle
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. D Alembert s Principle and The Lagrangian-1
 P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
P. Guterrez Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs D Alembert s Prncple and The Lagrangan 1 Introducton The prncple of vrtual work provdes a method of solvng problems of statc equlbrum wthout havng to consder the
Chapter 12. Ordinary Differential Equation Boundary Value (BV) Problems
 Chapter. Ordnar Dfferental Equaton Boundar Value (BV) Problems In ths chapter we wll learn how to solve ODE boundar value problem. BV ODE s usuall gven wth x beng the ndependent space varable. p( x) q(
Chapter. Ordnar Dfferental Equaton Boundar Value (BV) Problems In ths chapter we wll learn how to solve ODE boundar value problem. BV ODE s usuall gven wth x beng the ndependent space varable. p( x) q(
Limited Dependent Variables
 Lmted Dependent Varables. What f the left-hand sde varable s not a contnuous thng spread from mnus nfnty to plus nfnty? That s, gven a model = f (, β, ε, where a. s bounded below at zero, such as wages
Lmted Dependent Varables. What f the left-hand sde varable s not a contnuous thng spread from mnus nfnty to plus nfnty? That s, gven a model = f (, β, ε, where a. s bounded below at zero, such as wages
MMA and GCMMA two methods for nonlinear optimization
 MMA and GCMMA two methods for nonlnear optmzaton Krster Svanberg Optmzaton and Systems Theory, KTH, Stockholm, Sweden. krlle@math.kth.se Ths note descrbes the algorthms used n the author s 2007 mplementatons
MMA and GCMMA two methods for nonlnear optmzaton Krster Svanberg Optmzaton and Systems Theory, KTH, Stockholm, Sweden. krlle@math.kth.se Ths note descrbes the algorthms used n the author s 2007 mplementatons
Buckingham s pi-theorem
 TMA495 Mathematcal modellng 2004 Buckngham s p-theorem Harald Hanche-Olsen hanche@math.ntnu.no Theory Ths note s about physcal quanttes R,...,R n. We lke to measure them n a consstent system of unts, such
TMA495 Mathematcal modellng 2004 Buckngham s p-theorem Harald Hanche-Olsen hanche@math.ntnu.no Theory Ths note s about physcal quanttes R,...,R n. We lke to measure them n a consstent system of unts, such
The Tangential Force Distribution on Inner Cylinder of Power Law Fluid Flowing in Eccentric Annuli with the Inner Cylinder Reciprocating Axially
 Open Journal of Flud Dynamcs, 2015, 5, 183-187 Publshed Onlne June 2015 n ScRes. http://www.scrp.org/journal/ojfd http://dx.do.org/10.4236/ojfd.2015.52020 The Tangental Force Dstrbuton on Inner Cylnder
Open Journal of Flud Dynamcs, 2015, 5, 183-187 Publshed Onlne June 2015 n ScRes. http://www.scrp.org/journal/ojfd http://dx.do.org/10.4236/ojfd.2015.52020 The Tangental Force Dstrbuton on Inner Cylnder
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Solutions to Example Problems on Heat Transfer
 Prncples of Food and Boprocess Engneerng (FS 31) Solutons to Example Problems on Heat Transfer 1. We start wth Fourer s law of heat conducton: Q = k A ( T/ x) Rearrangng, we get: Q/A = k ( T/ x) Here,
Prncples of Food and Boprocess Engneerng (FS 31) Solutons to Example Problems on Heat Transfer 1. We start wth Fourer s law of heat conducton: Q = k A ( T/ x) Rearrangng, we get: Q/A = k ( T/ x) Here,
Implicit Integration Henyey Method
 Implct Integraton Henyey Method In realstc stellar evoluton codes nstead of a drect ntegraton usng for example the Runge-Kutta method one employs an teratve mplct technque. Ths s because the structure
Implct Integraton Henyey Method In realstc stellar evoluton codes nstead of a drect ntegraton usng for example the Runge-Kutta method one employs an teratve mplct technque. Ths s because the structure
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM
 ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
ELASTIC WAVE PROPAGATION IN A CONTINUOUS MEDIUM An elastc wave s a deformaton of the body that travels throughout the body n all drectons. We can examne the deformaton over a perod of tme by fxng our look
Module 3: Element Properties Lecture 1: Natural Coordinates
 Module 3: Element Propertes Lecture : Natural Coordnates Natural coordnate system s bascally a local coordnate system whch allows the specfcaton of a pont wthn the element by a set of dmensonless numbers
Module 3: Element Propertes Lecture : Natural Coordnates Natural coordnate system s bascally a local coordnate system whch allows the specfcaton of a pont wthn the element by a set of dmensonless numbers
(Online First)A Lattice Boltzmann Scheme for Diffusion Equation in Spherical Coordinate
 Internatonal Journal of Mathematcs and Systems Scence (018) Volume 1 do:10.494/jmss.v1.815 (Onlne Frst)A Lattce Boltzmann Scheme for Dffuson Equaton n Sphercal Coordnate Debabrata Datta 1 *, T K Pal 1
Internatonal Journal of Mathematcs and Systems Scence (018) Volume 1 do:10.494/jmss.v1.815 (Onlne Frst)A Lattce Boltzmann Scheme for Dffuson Equaton n Sphercal Coordnate Debabrata Datta 1 *, T K Pal 1
TURBULENT FLOW A BEGINNER S APPROACH. Tony Saad March
 TURBULENT FLOW A BEGINNER S APPROACH Tony Saad March 2004 http://tsaad.uts.edu - tsaad@uts.edu CONTENTS Introducton Random processes The energy cascade mechansm The Kolmogorov hypotheses The closure problem
TURBULENT FLOW A BEGINNER S APPROACH Tony Saad March 2004 http://tsaad.uts.edu - tsaad@uts.edu CONTENTS Introducton Random processes The energy cascade mechansm The Kolmogorov hypotheses The closure problem
Flow Induced Vibration
 Flow Induced Vbraton Project Progress Report Date: 16 th November, 2005 Submtted by Subhrajt Bhattacharya Roll no.: 02ME101 Done under the gudance of Prof. Anrvan Dasgupta Department of Mechancal Engneerng,
Flow Induced Vbraton Project Progress Report Date: 16 th November, 2005 Submtted by Subhrajt Bhattacharya Roll no.: 02ME101 Done under the gudance of Prof. Anrvan Dasgupta Department of Mechancal Engneerng,
MEASUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTIA
 1. measurement MESUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTI The am of ths measurement s to determne the moment of nerta of the rotor of an electrc motor. 1. General relatons Rotatng moton and moment of nerta Let us
1. measurement MESUREMENT OF MOMENT OF INERTI The am of ths measurement s to determne the moment of nerta of the rotor of an electrc motor. 1. General relatons Rotatng moton and moment of nerta Let us
Bindel, Spring 2014 Applications of Parallel Computers (CS 5220)
 Bndel, Sprng 2014 Applcatons of Parallel Computers (CS 5220) 1 Dervng SPH The Naver-Stokes equatons wth gravty are ρa = p + µ 2 v + ρg. The acceleraton s the materal dervatve of velocty, and we usually
Bndel, Sprng 2014 Applcatons of Parallel Computers (CS 5220) 1 Dervng SPH The Naver-Stokes equatons wth gravty are ρa = p + µ 2 v + ρg. The acceleraton s the materal dervatve of velocty, and we usually
2.29 Numerical Fluid Mechanics Fall 2011 Lecture 6
 REVIEW of Lecture 5 2.29 Numercal Flud Mechancs Fall 2011 Lecture 6 Contnuum Hypothess and conservaton laws Macroscopc Propertes Materal covered n class: Dfferental forms of conservaton laws Materal Dervatve
REVIEW of Lecture 5 2.29 Numercal Flud Mechancs Fall 2011 Lecture 6 Contnuum Hypothess and conservaton laws Macroscopc Propertes Materal covered n class: Dfferental forms of conservaton laws Materal Dervatve
Lecture 5.8 Flux Vector Splitting
 Lecture 5.8 Flux Vector Splttng 1 Flux Vector Splttng The vector E n (5.7.) can be rewrtten as E = AU (5.8.1) (wth A as gven n (5.7.4) or (5.7.6) ) whenever, the equaton of state s of the separable form
Lecture 5.8 Flux Vector Splttng 1 Flux Vector Splttng The vector E n (5.7.) can be rewrtten as E = AU (5.8.1) (wth A as gven n (5.7.4) or (5.7.6) ) whenever, the equaton of state s of the separable form
1.72, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #3: Hydraulic Head and Fluid Potential. p o. p o + p
 1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #3: Hydraulc Head and Flud Potental What makes water flow? Consder ressure Water Level o A Water Level C o o + B Pressure at A atmosherc (
1.7, Groundwater Hydrology Prof. Charles Harvey Lecture Packet #3: Hydraulc Head and Flud Potental What makes water flow? Consder ressure Water Level o A Water Level C o o + B Pressure at A atmosherc (
For all questions, answer choice E) NOTA" means none of the above answers is correct.
 0 MA Natonal Conventon For all questons, answer choce " means none of the above answers s correct.. In calculus, one learns of functon representatons that are nfnte seres called power 3 4 5 seres. For
0 MA Natonal Conventon For all questons, answer choce " means none of the above answers s correct.. In calculus, one learns of functon representatons that are nfnte seres called power 3 4 5 seres. For
= z 20 z n. (k 20) + 4 z k = 4
 Problem Set #7 solutons 7.2.. (a Fnd the coeffcent of z k n (z + z 5 + z 6 + z 7 + 5, k 20. We use the known seres expanson ( n+l ( z l l z n below: (z + z 5 + z 6 + z 7 + 5 (z 5 ( + z + z 2 + z + 5 5
Problem Set #7 solutons 7.2.. (a Fnd the coeffcent of z k n (z + z 5 + z 6 + z 7 + 5, k 20. We use the known seres expanson ( n+l ( z l l z n below: (z + z 5 + z 6 + z 7 + 5 (z 5 ( + z + z 2 + z + 5 5
Physics 5153 Classical Mechanics. Principle of Virtual Work-1
 P. Guterrez 1 Introducton Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs Prncple of Vrtual Work The frst varatonal prncple we encounter n mechancs s the prncple of vrtual work. It establshes the equlbrum condton of a mechancal
P. Guterrez 1 Introducton Physcs 5153 Classcal Mechancs Prncple of Vrtual Work The frst varatonal prncple we encounter n mechancs s the prncple of vrtual work. It establshes the equlbrum condton of a mechancal
Nice plotting of proteins II
 Nce plottng of protens II Fnal remark regardng effcency: It s possble to wrte the Newton representaton n a way that can be computed effcently, usng smlar bracketng that we made for the frst representaton
Nce plottng of protens II Fnal remark regardng effcency: It s possble to wrte the Newton representaton n a way that can be computed effcently, usng smlar bracketng that we made for the frst representaton
Chapter 3. r r. Position, Velocity, and Acceleration Revisited
 Chapter 3 Poston, Velocty, and Acceleraton Revsted The poston vector of a partcle s a vector drawn from the orgn to the locaton of the partcle. In two dmensons: r = x ˆ+ yj ˆ (1) The dsplacement vector
Chapter 3 Poston, Velocty, and Acceleraton Revsted The poston vector of a partcle s a vector drawn from the orgn to the locaton of the partcle. In two dmensons: r = x ˆ+ yj ˆ (1) The dsplacement vector
Physics 106a, Caltech 11 October, Lecture 4: Constraints, Virtual Work, etc. Constraints
 Physcs 106a, Caltech 11 October, 2018 Lecture 4: Constrants, Vrtual Work, etc. Many, f not all, dynamcal problems we want to solve are constraned: not all of the possble 3 coordnates for M partcles (or
Physcs 106a, Caltech 11 October, 2018 Lecture 4: Constrants, Vrtual Work, etc. Many, f not all, dynamcal problems we want to solve are constraned: not all of the possble 3 coordnates for M partcles (or
Lectures - Week 4 Matrix norms, Conditioning, Vector Spaces, Linear Independence, Spanning sets and Basis, Null space and Range of a Matrix
 Lectures - Week 4 Matrx norms, Condtonng, Vector Spaces, Lnear Independence, Spannng sets and Bass, Null space and Range of a Matrx Matrx Norms Now we turn to assocatng a number to each matrx. We could
Lectures - Week 4 Matrx norms, Condtonng, Vector Spaces, Lnear Independence, Spannng sets and Bass, Null space and Range of a Matrx Matrx Norms Now we turn to assocatng a number to each matrx. We could
Electrostatic Potential from Transmembrane Currents
 Electrostatc Potental from Transmembrane Currents Let s assume that the current densty j(r, t) s ohmc;.e., lnearly proportonal to the electrc feld E(r, t): j = σ c (r)e (1) wth conductvty σ c = σ c (r).
Electrostatc Potental from Transmembrane Currents Let s assume that the current densty j(r, t) s ohmc;.e., lnearly proportonal to the electrc feld E(r, t): j = σ c (r)e (1) wth conductvty σ c = σ c (r).
Asymptotics of the Solution of a Boundary Value. Problem for One-Characteristic Differential. Equation Degenerating into a Parabolic Equation
 Nonl. Analyss and Dfferental Equatons, ol., 4, no., 5 - HIKARI Ltd, www.m-har.com http://dx.do.org/.988/nade.4.456 Asymptotcs of the Soluton of a Boundary alue Problem for One-Characterstc Dfferental Equaton
Nonl. Analyss and Dfferental Equatons, ol., 4, no., 5 - HIKARI Ltd, www.m-har.com http://dx.do.org/.988/nade.4.456 Asymptotcs of the Soluton of a Boundary alue Problem for One-Characterstc Dfferental Equaton
THE CHINESE REMAINDER THEOREM. We should thank the Chinese for their wonderful remainder theorem. Glenn Stevens
 THE CHINESE REMAINDER THEOREM KEITH CONRAD We should thank the Chnese for ther wonderful remander theorem. Glenn Stevens 1. Introducton The Chnese remander theorem says we can unquely solve any par of
THE CHINESE REMAINDER THEOREM KEITH CONRAD We should thank the Chnese for ther wonderful remander theorem. Glenn Stevens 1. Introducton The Chnese remander theorem says we can unquely solve any par of
Solution Thermodynamics
 Soluton hermodynamcs usng Wagner Notaton by Stanley. Howard Department of aterals and etallurgcal Engneerng South Dakota School of nes and echnology Rapd Cty, SD 57701 January 7, 001 Soluton hermodynamcs
Soluton hermodynamcs usng Wagner Notaton by Stanley. Howard Department of aterals and etallurgcal Engneerng South Dakota School of nes and echnology Rapd Cty, SD 57701 January 7, 001 Soluton hermodynamcs
Answers Problem Set 2 Chem 314A Williamsen Spring 2000
 Answers Problem Set Chem 314A Wllamsen Sprng 000 1) Gve me the followng crtcal values from the statstcal tables. a) z-statstc,-sded test, 99.7% confdence lmt ±3 b) t-statstc (Case I), 1-sded test, 95%
Answers Problem Set Chem 314A Wllamsen Sprng 000 1) Gve me the followng crtcal values from the statstcal tables. a) z-statstc,-sded test, 99.7% confdence lmt ±3 b) t-statstc (Case I), 1-sded test, 95%
Homogenization of reaction-diffusion processes in a two-component porous medium with a non-linear flux-condition on the interface
 Homogenzaton of reacton-dffuson processes n a two-component porous medum wth a non-lnear flux-condton on the nterface Internatonal Conference on Numercal and Mathematcal Modelng of Flow and Transport n
Homogenzaton of reacton-dffuson processes n a two-component porous medum wth a non-lnear flux-condton on the nterface Internatonal Conference on Numercal and Mathematcal Modelng of Flow and Transport n
More metrics on cartesian products
 More metrcs on cartesan products If (X, d ) are metrc spaces for 1 n, then n Secton II4 of the lecture notes we defned three metrcs on X whose underlyng topologes are the product topology The purpose of
More metrcs on cartesan products If (X, d ) are metrc spaces for 1 n, then n Secton II4 of the lecture notes we defned three metrcs on X whose underlyng topologes are the product topology The purpose of
Measurement Uncertainties Reference
 Measurement Uncertantes Reference Introducton We all ntutvely now that no epermental measurement can be perfect. It s possble to mae ths dea quanttatve. It can be stated ths way: the result of an ndvdual
Measurement Uncertantes Reference Introducton We all ntutvely now that no epermental measurement can be perfect. It s possble to mae ths dea quanttatve. It can be stated ths way: the result of an ndvdual
Solutions for Euler and Navier-Stokes Equations in Powers of Time
 Solutons for Euler and Naver-Stokes Equatons n Powers of Tme Valdr Montero dos Santos Godo valdr.msgodo@gmal.com Abstract We present a soluton for the Euler and Naver-Stokes equatons for ncompressble case
Solutons for Euler and Naver-Stokes Equatons n Powers of Tme Valdr Montero dos Santos Godo valdr.msgodo@gmal.com Abstract We present a soluton for the Euler and Naver-Stokes equatons for ncompressble case
Finite-Volume Groundwater Modeling With Non-Orthogonal Grids, Using A Coordinate Transformation Method
 Fnte-Volume Groundwater Modelng Wth Non-Orthogonal Grds, Usng A Coordnate Transformaton Method W. Rühaak 1, V. Rath 2, A. Wolf, C. Clauser 2 1 Lebnz Insttute for Appled Geoscences, w.ruehaak@gga-hannover.de,
Fnte-Volume Groundwater Modelng Wth Non-Orthogonal Grds, Usng A Coordnate Transformaton Method W. Rühaak 1, V. Rath 2, A. Wolf, C. Clauser 2 1 Lebnz Insttute for Appled Geoscences, w.ruehaak@gga-hannover.de,
Homework Assignment 3 Due in class, Thursday October 15
 Homework Assgnment 3 Due n class, Thursday October 15 SDS 383C Statstcal Modelng I 1 Rdge regresson and Lasso 1. Get the Prostrate cancer data from http://statweb.stanford.edu/~tbs/elemstatlearn/ datasets/prostate.data.
Homework Assgnment 3 Due n class, Thursday October 15 SDS 383C Statstcal Modelng I 1 Rdge regresson and Lasso 1. Get the Prostrate cancer data from http://statweb.stanford.edu/~tbs/elemstatlearn/ datasets/prostate.data.
Perfect Fluid Cosmological Model in the Frame Work Lyra s Manifold
 Prespacetme Journal December 06 Volume 7 Issue 6 pp. 095-099 Pund, A. M. & Avachar, G.., Perfect Flud Cosmologcal Model n the Frame Work Lyra s Manfold Perfect Flud Cosmologcal Model n the Frame Work Lyra
Prespacetme Journal December 06 Volume 7 Issue 6 pp. 095-099 Pund, A. M. & Avachar, G.., Perfect Flud Cosmologcal Model n the Frame Work Lyra s Manfold Perfect Flud Cosmologcal Model n the Frame Work Lyra
Electrical double layer: revisit based on boundary conditions
 Electrcal double layer: revst based on boundary condtons Jong U. Km Department of Electrcal and Computer Engneerng, Texas A&M Unversty College Staton, TX 77843-318, USA Abstract The electrcal double layer
Electrcal double layer: revst based on boundary condtons Jong U. Km Department of Electrcal and Computer Engneerng, Texas A&M Unversty College Staton, TX 77843-318, USA Abstract The electrcal double layer
CFD simulation with multiphase flows in porous media and open mineral storage pile
 Computatonal Methods n Multphase Flow V 421 CFD smulaton wth multphase flows n porous meda and open mneral storage ple S. Torno, J. Toraño, I. Dego, M. Menéndez, M. Gent & J. Velasco School of Mnes, Unversty
Computatonal Methods n Multphase Flow V 421 CFD smulaton wth multphase flows n porous meda and open mneral storage ple S. Torno, J. Toraño, I. Dego, M. Menéndez, M. Gent & J. Velasco School of Mnes, Unversty
Lecture Notes on Linear Regression
 Lecture Notes on Lnear Regresson Feng L fl@sdueducn Shandong Unversty, Chna Lnear Regresson Problem In regresson problem, we am at predct a contnuous target value gven an nput feature vector We assume
Lecture Notes on Lnear Regresson Feng L fl@sdueducn Shandong Unversty, Chna Lnear Regresson Problem In regresson problem, we am at predct a contnuous target value gven an nput feature vector We assume
CSci 6974 and ECSE 6966 Math. Tech. for Vision, Graphics and Robotics Lecture 21, April 17, 2006 Estimating A Plane Homography
 CSc 6974 and ECSE 6966 Math. Tech. for Vson, Graphcs and Robotcs Lecture 21, Aprl 17, 2006 Estmatng A Plane Homography Overvew We contnue wth a dscusson of the major ssues, usng estmaton of plane projectve
CSc 6974 and ECSE 6966 Math. Tech. for Vson, Graphcs and Robotcs Lecture 21, Aprl 17, 2006 Estmatng A Plane Homography Overvew We contnue wth a dscusson of the major ssues, usng estmaton of plane projectve
Introduction to Vapor/Liquid Equilibrium, part 2. Raoult s Law:
 CE304, Sprng 2004 Lecture 4 Introducton to Vapor/Lqud Equlbrum, part 2 Raoult s Law: The smplest model that allows us do VLE calculatons s obtaned when we assume that the vapor phase s an deal gas, and
CE304, Sprng 2004 Lecture 4 Introducton to Vapor/Lqud Equlbrum, part 2 Raoult s Law: The smplest model that allows us do VLE calculatons s obtaned when we assume that the vapor phase s an deal gas, and
Mass Transfer Processes
 Mass Transfer Processes S. Majd Hassanzadeh Department of Earth Scences Faculty of Geoscences Utrecht Unversty Outlne: 1. Measures of Concentraton 2. Volatlzaton and Dssoluton 3. Adsorpton Processes 4.
Mass Transfer Processes S. Majd Hassanzadeh Department of Earth Scences Faculty of Geoscences Utrecht Unversty Outlne: 1. Measures of Concentraton 2. Volatlzaton and Dssoluton 3. Adsorpton Processes 4.
Simulation of Heat Transfer during Artificial Ground Freezing Combined with Groundwater Flow
 Smulaton of Heat Transfer durng Artfcal Ground Freezng Combned th Groundater Flo Ru Hu *1, Quan Lu 1 1 School of Earth Scence and Engneerng, Hoha Unversty, Nanjng, Chna *Correspondng author: No.8 Fochengx
Smulaton of Heat Transfer durng Artfcal Ground Freezng Combned th Groundater Flo Ru Hu *1, Quan Lu 1 1 School of Earth Scence and Engneerng, Hoha Unversty, Nanjng, Chna *Correspondng author: No.8 Fochengx
How Differential Equations Arise. Newton s Second Law of Motion
 page 1 CHAPTER 1 Frst-Order Dfferental Equatons Among all of the mathematcal dscplnes the theory of dfferental equatons s the most mportant. It furnshes the explanaton of all those elementary manfestatons
page 1 CHAPTER 1 Frst-Order Dfferental Equatons Among all of the mathematcal dscplnes the theory of dfferental equatons s the most mportant. It furnshes the explanaton of all those elementary manfestatons
Section 8.1 Exercises
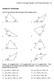 Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Secton 8.1 Non-rght Trangles: Law of Snes and Cosnes 519 Secton 8.1 Exercses Solve for the unknown sdes and angles of the trangles shown. 10 70 50 1.. 18 40 110 45 5 6 3. 10 4. 75 15 5 6 90 70 65 5. 6.
Statistical analysis using matlab. HY 439 Presented by: George Fortetsanakis
 Statstcal analyss usng matlab HY 439 Presented by: George Fortetsanaks Roadmap Probablty dstrbutons Statstcal estmaton Fttng data to probablty dstrbutons Contnuous dstrbutons Contnuous random varable X
Statstcal analyss usng matlab HY 439 Presented by: George Fortetsanaks Roadmap Probablty dstrbutons Statstcal estmaton Fttng data to probablty dstrbutons Contnuous dstrbutons Contnuous random varable X
ENGN 40 Dynamics and Vibrations Homework # 7 Due: Friday, April 15
 NGN 40 ynamcs and Vbratons Homework # 7 ue: Frday, Aprl 15 1. Consder a concal hostng drum used n the mnng ndustry to host a mass up/down. A cable of dameter d has the mass connected at one end and s wound/unwound
NGN 40 ynamcs and Vbratons Homework # 7 ue: Frday, Aprl 15 1. Consder a concal hostng drum used n the mnng ndustry to host a mass up/down. A cable of dameter d has the mass connected at one end and s wound/unwound
A new Approach for Solving Linear Ordinary Differential Equations
 , ISSN 974-57X (Onlne), ISSN 974-5718 (Prnt), Vol. ; Issue No. 1; Year 14, Copyrght 13-14 by CESER PUBLICATIONS A new Approach for Solvng Lnear Ordnary Dfferental Equatons Fawz Abdelwahd Department of
, ISSN 974-57X (Onlne), ISSN 974-5718 (Prnt), Vol. ; Issue No. 1; Year 14, Copyrght 13-14 by CESER PUBLICATIONS A new Approach for Solvng Lnear Ordnary Dfferental Equatons Fawz Abdelwahd Department of
n α j x j = 0 j=1 has a nontrivial solution. Here A is the n k matrix whose jth column is the vector for all t j=0
 MODULE 2 Topcs: Lnear ndependence, bass and dmenson We have seen that f n a set of vectors one vector s a lnear combnaton of the remanng vectors n the set then the span of the set s unchanged f that vector
MODULE 2 Topcs: Lnear ndependence, bass and dmenson We have seen that f n a set of vectors one vector s a lnear combnaton of the remanng vectors n the set then the span of the set s unchanged f that vector
STAT 511 FINAL EXAM NAME Spring 2001
 STAT 5 FINAL EXAM NAME Sprng Instructons: Ths s a closed book exam. No notes or books are allowed. ou may use a calculator but you are not allowed to store notes or formulas n the calculator. Please wrte
STAT 5 FINAL EXAM NAME Sprng Instructons: Ths s a closed book exam. No notes or books are allowed. ou may use a calculator but you are not allowed to store notes or formulas n the calculator. Please wrte
Ph.D. Qualifying Examination in Kinetics and Reactor Design
 Knetcs and Reactor Desgn Ph.D.Qualfyng Examnaton January 2006 Instructons Ph.D. Qualfyng Examnaton n Knetcs and Reactor Desgn January 2006 Unversty of Texas at Austn Department of Chemcal Engneerng 1.
Knetcs and Reactor Desgn Ph.D.Qualfyng Examnaton January 2006 Instructons Ph.D. Qualfyng Examnaton n Knetcs and Reactor Desgn January 2006 Unversty of Texas at Austn Department of Chemcal Engneerng 1.
Polynomial Regression Models
 LINEAR REGRESSION ANALYSIS MODULE XII Lecture - 6 Polynomal Regresson Models Dr. Shalabh Department of Mathematcs and Statstcs Indan Insttute of Technology Kanpur Test of sgnfcance To test the sgnfcance
LINEAR REGRESSION ANALYSIS MODULE XII Lecture - 6 Polynomal Regresson Models Dr. Shalabh Department of Mathematcs and Statstcs Indan Insttute of Technology Kanpur Test of sgnfcance To test the sgnfcance
(b) i(t) for t 0. (c) υ 1 (t) and υ 2 (t) for t 0. Solution: υ 2 (0 ) = I 0 R 1 = = 10 V. υ 1 (0 ) = 0. (Given).
 Problem 5.37 Pror to t =, capactor C 1 n the crcut of Fg. P5.37 was uncharged. For I = 5 ma, R 1 = 2 kω, = 5 kω, C 1 = 3 µf, and C 2 = 6 µf, determne: (a) The equvalent crcut nvolvng the capactors for
Problem 5.37 Pror to t =, capactor C 1 n the crcut of Fg. P5.37 was uncharged. For I = 5 ma, R 1 = 2 kω, = 5 kω, C 1 = 3 µf, and C 2 = 6 µf, determne: (a) The equvalent crcut nvolvng the capactors for
Transfer Functions. Convenient representation of a linear, dynamic model. A transfer function (TF) relates one input and one output: ( ) system
 Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Transfer Functons Convenent representaton of a lnear, dynamc model. A transfer functon (TF) relates one nput and one output: x t X s y t system Y s The followng termnology s used: x y nput output forcng
Week 9 Chapter 10 Section 1-5
 Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
Week 9 Chapter 10 Secton 1-5 Rotaton Rgd Object A rgd object s one that s nondeformable The relatve locatons of all partcles makng up the object reman constant All real objects are deformable to some extent,
10.34 Numerical Methods Applied to Chemical Engineering Fall Homework #3: Systems of Nonlinear Equations and Optimization
 10.34 Numercal Methods Appled to Chemcal Engneerng Fall 2015 Homework #3: Systems of Nonlnear Equatons and Optmzaton Problem 1 (30 ponts). A (homogeneous) azeotrope s a composton of a multcomponent mxture
10.34 Numercal Methods Appled to Chemcal Engneerng Fall 2015 Homework #3: Systems of Nonlnear Equatons and Optmzaton Problem 1 (30 ponts). A (homogeneous) azeotrope s a composton of a multcomponent mxture
Application of the Adjoint Method for Vehicle Aerodynamic Optimization. Dr. Thomas Blacha, Audi AG
 Applcaton of the Adjont Method for Vehcle Aerodynamc Optmzaton Dr. Thomas Blacha, Aud AG GoFun, Braunschweg 22.3.2017 2 AUDI AG, Dr. Thomas Blacha, Applcaton of the Adjont Method for Vehcle Aerodynamc
Applcaton of the Adjont Method for Vehcle Aerodynamc Optmzaton Dr. Thomas Blacha, Aud AG GoFun, Braunschweg 22.3.2017 2 AUDI AG, Dr. Thomas Blacha, Applcaton of the Adjont Method for Vehcle Aerodynamc
Formal solvers of the RT equation
 Formal solvers of the RT equaton Formal RT solvers Runge- Kutta (reference solver) Pskunov N.: 979, Master Thess Long characterstcs (Feautrer scheme) Cannon C.J.: 970, ApJ 6, 55 Short characterstcs (Hermtan
Formal solvers of the RT equaton Formal RT solvers Runge- Kutta (reference solver) Pskunov N.: 979, Master Thess Long characterstcs (Feautrer scheme) Cannon C.J.: 970, ApJ 6, 55 Short characterstcs (Hermtan
The Feynman path integral
 The Feynman path ntegral Aprl 3, 205 Hesenberg and Schrödnger pctures The Schrödnger wave functon places the tme dependence of a physcal system n the state, ψ, t, where the state s a vector n Hlbert space
The Feynman path ntegral Aprl 3, 205 Hesenberg and Schrödnger pctures The Schrödnger wave functon places the tme dependence of a physcal system n the state, ψ, t, where the state s a vector n Hlbert space
CIS526: Machine Learning Lecture 3 (Sept 16, 2003) Linear Regression. Preparation help: Xiaoying Huang. x 1 θ 1 output... θ M x M
 CIS56: achne Learnng Lecture 3 (Sept 6, 003) Preparaton help: Xaoyng Huang Lnear Regresson Lnear regresson can be represented by a functonal form: f(; θ) = θ 0 0 +θ + + θ = θ = 0 ote: 0 s a dummy attrbute
CIS56: achne Learnng Lecture 3 (Sept 6, 003) Preparaton help: Xaoyng Huang Lnear Regresson Lnear regresson can be represented by a functonal form: f(; θ) = θ 0 0 +θ + + θ = θ = 0 ote: 0 s a dummy attrbute
ANSWERS. Problem 1. and the moment generating function (mgf) by. defined for any real t. Use this to show that E( U) var( U)
 Econ 413 Exam 13 H ANSWERS Settet er nndelt 9 deloppgaver, A,B,C, som alle anbefales å telle lkt for å gøre det ltt lettere å stå. Svar er gtt . Unfortunately, there s a prntng error n the hnt of
Econ 413 Exam 13 H ANSWERS Settet er nndelt 9 deloppgaver, A,B,C, som alle anbefales å telle lkt for å gøre det ltt lettere å stå. Svar er gtt . Unfortunately, there s a prntng error n the hnt of
x yi In chapter 14, we want to perform inference (i.e. calculate confidence intervals and perform tests of significance) in this setting.
 The Practce of Statstcs, nd ed. Chapter 14 Inference for Regresson Introducton In chapter 3 we used a least-squares regresson lne (LSRL) to represent a lnear relatonshp etween two quanttatve explanator
The Practce of Statstcs, nd ed. Chapter 14 Inference for Regresson Introducton In chapter 3 we used a least-squares regresson lne (LSRL) to represent a lnear relatonshp etween two quanttatve explanator
χ x B E (c) Figure 2.1.1: (a) a material particle in a body, (b) a place in space, (c) a configuration of the body
 Secton.. Moton.. The Materal Body and Moton hyscal materals n the real world are modeled usng an abstract mathematcal entty called a body. Ths body conssts of an nfnte number of materal partcles. Shown
Secton.. Moton.. The Materal Body and Moton hyscal materals n the real world are modeled usng an abstract mathematcal entty called a body. Ths body conssts of an nfnte number of materal partcles. Shown
coordinates. Then, the position vectors are described by
 Revewng, what we have dscussed so far: Generalzed coordnates Any number of varables (say, n) suffcent to specfy the confguraton of the system at each nstant to tme (need not be the mnmum number). In general,
Revewng, what we have dscussed so far: Generalzed coordnates Any number of varables (say, n) suffcent to specfy the confguraton of the system at each nstant to tme (need not be the mnmum number). In general,
In this section is given an overview of the common elasticity models.
 Secton 4.1 4.1 Elastc Solds In ths secton s gven an overvew of the common elastcty models. 4.1.1 The Lnear Elastc Sold The classcal Lnear Elastc model, or Hooean model, has the followng lnear relatonshp
Secton 4.1 4.1 Elastc Solds In ths secton s gven an overvew of the common elastcty models. 4.1.1 The Lnear Elastc Sold The classcal Lnear Elastc model, or Hooean model, has the followng lnear relatonshp
Line Drawing and Clipping Week 1, Lecture 2
 CS 43 Computer Graphcs I Lne Drawng and Clppng Week, Lecture 2 Davd Breen, Wllam Regl and Maxm Peysakhov Geometrc and Intellgent Computng Laboratory Department of Computer Scence Drexel Unversty http://gcl.mcs.drexel.edu
CS 43 Computer Graphcs I Lne Drawng and Clppng Week, Lecture 2 Davd Breen, Wllam Regl and Maxm Peysakhov Geometrc and Intellgent Computng Laboratory Department of Computer Scence Drexel Unversty http://gcl.mcs.drexel.edu
FORCED CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER FROM A RECTANGULAR CYLINDER: EFFECT OF ASPECT RATIO
 ISTP-,, PRAGUE TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA FORCED CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER FROM A RECTANGULAR CYLINDER: EFFECT OF ASPECT RATIO Mohammad Rahnama*, Seyed-Mad Hasheman*, Mousa Farhad**
ISTP-,, PRAGUE TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA FORCED CONVECTION HEAT TRANSFER FROM A RECTANGULAR CYLINDER: EFFECT OF ASPECT RATIO Mohammad Rahnama*, Seyed-Mad Hasheman*, Mousa Farhad**
SMOOTHED PARTICLE HYDRODYNAMICS METHOD FOR TWO-DIMENSIONAL STEFAN PROBLEM
 The 5th Internatonal Symposum on Computatonal Scences (ISCS) 28 May 2012, Yogyakarta, Indonesa SMOOTHED PARTICLE HYDRODYNAMICS METHOD FOR TWO-DIMENSIONAL STEFAN PROBLEM Dede Tarwd 1,2 1 Graduate School
The 5th Internatonal Symposum on Computatonal Scences (ISCS) 28 May 2012, Yogyakarta, Indonesa SMOOTHED PARTICLE HYDRODYNAMICS METHOD FOR TWO-DIMENSIONAL STEFAN PROBLEM Dede Tarwd 1,2 1 Graduate School
Summary with Examples for Root finding Methods -Bisection -Newton Raphson -Secant
 Summary wth Eamples or Root ndng Methods -Bsecton -Newton Raphson -Secant Nonlnear Equaton Solvers Bracketng Graphcal Open Methods Bsecton False Poston (Regula-Fals) Newton Raphson Secant All Iteratve
Summary wth Eamples or Root ndng Methods -Bsecton -Newton Raphson -Secant Nonlnear Equaton Solvers Bracketng Graphcal Open Methods Bsecton False Poston (Regula-Fals) Newton Raphson Secant All Iteratve
Energy configuration optimization of submerged propeller in oxidation ditch based on CFD
 IOP Conference Seres: Earth and Envronmental Scence Energy confguraton optmzaton of submerged propeller n oxdaton dtch based on CFD To cte ths artcle: S Y Wu et al 01 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Envron. Sc.
IOP Conference Seres: Earth and Envronmental Scence Energy confguraton optmzaton of submerged propeller n oxdaton dtch based on CFD To cte ths artcle: S Y Wu et al 01 IOP Conf. Ser.: Earth Envron. Sc.
