Termites: Here, There and Everywhere? Chris J. Peterson EARTH Vol. 55 (No. 1), p. 46
|
|
|
- Austen Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The American Geological Institute 4220 King Street, Alexandria, VA , U.S.A ; Fax: ; Termites: Here, There and Everywhere? Chris J. Peterson EARTH Vol. 55 (No. 1), p. 46 REPRODUCTION: More than one photocopy of an item from EARTH may be made provided that fees are paid directly to the Copyright Clearance Center, 222 Rosewood Dr., Danvers, MA 01923, USA. Phone: (978) Fax: (978) Any other form of reproduction requires special permission from and is subject to fees by EARTH. Information about obtaining reprints of this article or about obtaining permission to reproduce this article in whole or in part can be found by ing EARTH is published monthly for a base subscription rate of $34.50 a year (single copies $4.99) by the American Geological Institute American Geological Institute. Standard mail, nonprofit postage paid at Denver, Colo., and at other mailing offices. Claims for missing issues will be honored only up to six months. Issues undelivered through failure to notify EARTH of address change will not be replaced.
2 Above and below: Termites are not currently found across most of the northern part of the United States and Canada, which means forests like this one in Michigan s Upper Peninsula are choked with downed trees. Termites Here, There and Everywhere? Will climate change allow termite populations in North America to spread? Below: Termites, with the help of wood-decaying fungi, take care of any downed trees in short order in forests across the southern United States, such as in Mississippi. Chris J. Peterson As a child growing up in Iowa, every summer I looked forward to our family s annual trip to the woods in Michigan s Upper Peninsula. One of the highlights was going to camp, an old logging camp my grandfather purchased in the 1940s and maintained as a deer camp and weekend getaway. Off-road hiking in the Northwoods was slow. We had to maneuver our way around downed logs that sometimes piled two or three deep, and climb over a profusion of old stumps still charred from a massive fire that had burned through the area three or four decades before. Today, I live in Mississippi, where a trek through the woods is a different experience. If you re lucky enough to find a wooded area that isn t choked with yaupon, catbrier, holly and vines, you can walk freely, unencumbered by downed wood or stumps. In Mississippi, fallen logs decompose in a few years, and do not accumulate on the forest floor. A burned-out stump wouldn t last 30 or 40 months, let alone 30 or 40 years. Why the difference? Termites. Clockwise from bottom: Chris J. Peterson; B. J. Peterson, Kingsford, Mich.; B. J. Peterson, Kingsford, Mich.; istockphoto.com/jeridu 46 EARTH January
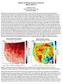
3 Termite Risk to Structures Map: Beth Dishong, Mississippi State University/U.S. Forest Service; background: Chris J. Peterson Relative risk of termite infestation in structures in the United States. In Canada, only southern British Columbia and southeastern Ontario experience risk of termite infestations. Termites are ubiquitous in Mississippi, where no wooden structure or dead log is immune to the insect s powerful jaws, but in Michigan s Upper Peninsula, termites are almost unheard of. My grandfather s camp is made entirely of wood and sits on a concrete slab with just a centimeter or two of clearance between the soil and the wood. The main part of the building is more than 70 years old and has never once had a termite. In fact, termites are so rare that preventative treatments for termites are not required in the Upper Peninsula. But someday my grandfather s camp may need some termite-proofing. With warmer conditions creeping northward as the climate changes, especially in the winter, termites will likely expand their territories to higher latitudes. And because those areas are not equipped to handle termites, this could cause untold billions of dollars in property damages, unless we prepare for the coming changes. Where are the termites now? In the United States, the most common and widespread termites, and therefore those that cause the most damage, are the subterranean termites, the family Rhinotermitidae and more specifically the genus Reticulitermes. Three species in this genus occur in the eastern United States, a fourth species occurs only on the West Coast, and a fifth species is primarily restricted to the Rocky Mountains. There are a couple of other species of termites in other genera that tend to be more localized and therefore cause localized destruction. The Formosan termite, which belongs to a different genus and originated in southern China, has garnered much attention because of the size of its colonies and the speed with which it can consume wood. But as of now, due mostly to quarantine efforts and the species temperature dependence, the Formosan termite is not widespread in North America and only causes damage in localized areas, most notably New Orleans, La. Generally speaking, termites in North America get more common the farther south you go. In EARTH January
4 Canada, termites are native only to British Columbia. Isolated infestations (now reportedly eradicated) have been found in southern Manitoba and Alberta, but are becoming more common in southern Ontario, especially in Toronto. Infestations outside of British Columbia, including those in Toronto, are likely due to accidental introduction through human activities. Taking all of these termites together and estimating the relative hazard of termites to structures, we find that currently the greatest risk of termite damage is still in the Southeast from North Carolina to central Texas and south to the Gulf Coast and Florida and in California. A lesser but still significant risk extends northward along both the East and West coasts, while the least risk is generally in the Great Plains although no part of North America is completely immune to a termite s appetite. Changes on the horizon Global climate change has implications for the abundance of termites in areas where they are not currently common. In 2007, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) released its predictions for worldwide climate change for the next 100 years, and reported that most of North America Predicted changes in the annual mean temperature, and during the winter and summer months over the Annual Winter Predicted changes in precipitation for the annual mean rainfall, and during the winter and summer Annual Winter Maps: From Christiansen et al., IPCC (2007); background: Chris J. Peterson 48 EARTH January
5 will become warmer and many parts will become wetter. The area of North America that is of immediate concern for termites from the Gulf of Mexico to the southern shores of Canada s Hudson Bay is predicted to see an increase in annual mean temperature of 3 degrees to more than 4 degrees Celsius over the next 100 years. Areas even farther north are expected to warm to an even greater degree and experience higher precipitation, especially in the East. But more than higher annual temperatures, it s the winter temperature increases that matter next 100 years in North America. Summer months over the next 100 years in North America. Summer the most. In the area of immediate concern, winter temperatures are predicted to increase by up to 7 degrees Celsius, and extreme cold events are expected to decrease in frequency. This portends problems. Most termites die off during the winter in areas where the ground freezes: Most species cannot survive sustained temperatures below 9 degrees Celsius, and even fewer can survive temperatures below 1 degree Celsius. Thus the increase in the winter temperature in the North will affect termite populations largely because as winter temperatures warm, termites may be better able to survive winters in more northern climates. Scientists don t know exactly how termites spend the winter in areas where the depth to which the soil freezes (the frost line) is significantly deep, but researchers assume that termites survive in soil below the frost line. Central heating might also help termites to survive, with the assumption being that heated basements keep soil above freezing throughout the year. This is consistent with observations by Timothy Myles, termite officer for the City of Guelph, Ontario, who notes that termites are found in residential areas and not in forests. It is also possible, and has been demonstrated in laboratory studies, that termites move downward in the soil in response to declining temperature the implication being that they do this to avoid freezing. A final possibility is that termites do not move in response to cold, and those above the frost line simply die, while those below the frost line survive to rebuild the colony the next year. If climate change causes progressively shallower frost lines in the winter, more termites should survive the winter, allowing populations to build and spread more easily. Meanwhile, higher summer temperatures in the North might allow any termite populations already present to increase in size. In southern states, a newly formed termite colony starts with two reproductive individuals and then builds for several years until it reaches a certain size. At that point, winged, or alate, termites capable of reproduction begin to appear. In the spring, thousands of these alates from many colonies take flight (sometimes called a swarm). Adults pair up and start new colonies, reinitiating the cycle. Termites in Toronto have produced alates, according to Myles, but they do not appear to fly to produce new colonies. This might be because the temperature remains too low for the necessary physical and behavioral changes to take place that allow the flights to happen. Any new colonies that do form are likely killed off by the winter freeze. But if temperatures in Toronto and across the North increase, all bets are off. EARTH January
6 The development rate of insects is dependent on temperature. For certain developmental and behavioral changes to take place (such as the foundation of new colonies), the high temperatures must be sustained. The required temperature and time are genetic, and vary with species and the particular change being considered. Currently, it seems that the Toronto summer does not stay warm enough for long enough for dispersal flights to occur and thus for termites to spread farther into the region. But with warmer winters, termite colonies could survive; with a warmer spring, developmental changes might start occurring earlier in the year. And a warmer summer might accelerate these changes, allowing termite colonies to initiate flights. Precipitation changes will also have an effect. Termites, being soft-bodied, are prone to water loss and death by desiccation in soils with less than about 8 to 10 percent moisture by weight. So regions such as the Southwest, east Texas and parts of Louisiana, which are predicted to experience less rainfall and higher temperatures over the next 100 years, may see a decline in termite populations. However, although populations of less heat-tolerant and more moisture-dependent species might suffer due to hotter and drier conditions, other species that are better adapted to higher heat and lower humidity might become more common in those areas, exchanging one headache for another. Increase in summer rainfall in the North, meanwhile, coupled with the warmer temperatures, should favor termite growth in areas where moisture is presently limiting their growth. As conditions in these areas approach those seen to the south, any termite populations already present might expand. Although there is evidence that termite populations can be suppressed by inundation in wet years, this effect is likely only seen locally in poorly drained soils. Termites can survive almost indefinitely in saturated soil, provided that there is no standing water to flood their tunnels. How bad will it get? Climate change has already affected the lives of North American insects. The first greenness in the North American spring has come 10 to 14 days earlier since 1981, according to the IPCC. The average first spring flight of 23 species of butterflies in California occurs earlier now than it did in And the skipper butterfly has expanded its northernmost range on the West Coast by more than 300 kilometers over the past 30 years into areas that were previously too cold to support a full life cycle. If these examples are any indication of the response by termites to changes in Left: istockphoto.com/michael Pettigrew; background: Chris J. Peterson 50 EARTH January
7 Houses in the northern United States and most of Canada don t need termite protection today, but that may change as the climate warms. Top: istockphoto.com/dan Barnes; background: Chris J. Peterson climate, then we should expect them to develop more quickly and to expand northward too. At what rate? We don t yet know. However, because termites, barring human activities, move slowly on their own, it may take longer to notice the effects than it does for butterflies. Furthermore, there aren t formal abundance surveys for termites, so we don t have a good sense yet of what termite populations might be doing. The areas most vulnerable to expanded termite populations will be New England, the upper Midwest and southern Canada. How quickly and how drastically temperatures and precipitation change across northern regions will determine how quickly termite populations move. It is likely that changes in termite populations will keep pace with gradual warming. How much termite damage will increase in these areas will thus depend on the degree to which the climate changes, but also the degree to which termite-preventative measures are taken. In terms of termite preventative measures, the North is again most likely to see the biggest changes. The Southeast should not see many effects because most of their structures have already been treated or are otherwise constructed to minimize termite infestation. Few (if any) preventative measures have been taken farther north. In upper New England, the upper Midwest and into Canada and Alaska, where few to no structures are treated, damage will become more severe and widespread. These regions will incur costs for repairs and treatment. In addition, legislators and building code boards in these areas will have to decide which, if any, preventative measures to incorporate. Preventative treatments usually consist of soil-applied termiticides, termiticidal baits, treated wood or physical barriers, but the allowed treatments vary from state to state. Only a handful of states Alabama, Arizona, Florida, Hawaii and North Carolina require termite preventative treatments in their EARTH January
8 Above: States where termite inspections (and treatment if termites are found) are required to secure a loan from the Federal Housing Administration. Left: Termiticide treatments, although costly and disruptive to property, are usually necessary in areas where termites are known to damage structures. building codes at the state level. Other states are discussing the issue but have not yet adopted any formal measures. Many, if not most, states allow county or municipal governments to incorporate these requirements into their building codes if they so choose. At least some communities in most states have done so, and in some southern states, all counties have. Although states might not require termite preventative measures, many mortgage-lending institutions do. The U.S. Federal Housing Authority (FHA), part of the Department of Housing and Urban Development, has established that termite inspections or preventative treatments are required to secure a loan in all or parts of 40 states. Private mortgage Bottom and background: Chris J. Peterson; map: prepared by Michael Carr, U.S. Forest Service, Forest Inventory and Analysis, Knoxville, Tenn. 52 EARTH January
9 w Bottom left: istockphoto.com/jeridu; bottom right: B.J. Peterson, Kingsford, Mich.; top right: istockphoto.com/don Wilkie lending institutions might follow different guidelines, but they probably do not differ significantly from FHA s. In the future, if termite populations do spread, more states, counties and local governments will need to adopt these termite regulations and policies. Furthermore, short of requiring retroactive treatment of all existing structures, those structures that were built before the new policies were in place will remain vulnerable to attack. Unfortunately, we cannot accurately project how much potential termite damage may cost as a result of climate change. We do not precisely know the effect of temperature and rainfall on termite population growth, and we know even less about how termite population affects the amount of damage to a structure. We can only say in a general sense that termite populations will likely increase everywhere, with the possible exception of the Southwest and eastern Texas, and structures with no treatment or a failed treatment will be more likely to be damaged by termites. And though termites in northern areas have so far been easily eradicated once they are found, once warming temperatures allow them to become more established, infestations will become much more difficult to eliminate, and control strategies will have to switch to management instead of eradication. Does this mean those of you in the Northwoods should immediately pick up the phone and schedule a termite treatment? Not just yet. The climate changes predicted by the IPCC are 100-year projections and termite populations move slowly. So if you do not have termites in your area now, you probably have at least a few years until you ll start seeing them. But when you do start to see them pop up, schedule a formal termite inspection of your property and discuss which, if any, treatment options are available that meet your needs. Peterson is a research entomologist with the U.S. Forest Service, Insects, Diseases and Invasive Plants Unit in Starkville, Miss. cjpeterson@fs.fed.us. EARTH January
with Termidor. Rest Assured termiticide/insecticide
 with Termidor. Rest Assured termiticide/insecticide America s #1 Termite Defense. n Works without question n Represents the latest technology available n Formulated with your family and the environment
with Termidor. Rest Assured termiticide/insecticide America s #1 Termite Defense. n Works without question n Represents the latest technology available n Formulated with your family and the environment
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 18, 2017 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP,
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 18, 2017 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sroot@weatherbank.com MARCH 2017 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average contiguous
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 18, 2017 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sroot@weatherbank.com MARCH 2017 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average contiguous
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: NOVEMBER 16, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: NOVEMBER 16, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales sroot@weatherbank.com OCTOBER 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: NOVEMBER 16, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales sroot@weatherbank.com OCTOBER 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 25, 2016 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 25, 2016 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales sroot@weatherbank.com MARCH 2016 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The March
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: APRIL 25, 2016 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales sroot@weatherbank.com MARCH 2016 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The March
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast November 2017 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast November 2017 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College November 7, 2017 Summary: October was relatively cool and wet north, while warm and very dry south. Dry conditions
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast November 2017 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College November 7, 2017 Summary: October was relatively cool and wet north, while warm and very dry south. Dry conditions
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter 2016-17 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University February 7, 2017 What a difference from last year at this time. Temperatures in January and February
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter 2016-17 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University February 7, 2017 What a difference from last year at this time. Temperatures in January and February
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: SEPTEMBER 19, 2016 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP,
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: SEPTEMBER 19, 2016 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sroot@weatherbank.com SEPTEMBER 2016 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The contiguous
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: SEPTEMBER 19, 2016 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sroot@weatherbank.com SEPTEMBER 2016 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The contiguous
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast August 2018 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast August 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College August 5, 2018 Summary: July 2018 will likely go down as one of the top five warmest July s on record for many
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast August 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College August 5, 2018 Summary: July 2018 will likely go down as one of the top five warmest July s on record for many
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast October 2017 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast October 2017 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College October 4, 2017 Summary: Typical variability in September temperatures with the onset of fall conditions evident
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast October 2017 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College October 4, 2017 Summary: Typical variability in September temperatures with the onset of fall conditions evident
National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook
 National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook National Interagency Fire Center Predictive Services Issued: April 1, 2008 Next Issue: May 1, 2008 Wildland Fire Outlook April 2008 through July 2008
National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook National Interagency Fire Center Predictive Services Issued: April 1, 2008 Next Issue: May 1, 2008 Wildland Fire Outlook April 2008 through July 2008
National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook
 National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook National Interagency Fire Center Predictive Services Issued: September, 2007 Wildland Fire Outlook September through December 2007 Significant fire
National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook National Interagency Fire Center Predictive Services Issued: September, 2007 Wildland Fire Outlook September through December 2007 Significant fire
Guided Reading Activity
 Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 Physical Features Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? A Vast Land Directions: Read the lesson and use your text to decide whether each
Guided Reading Activity Lesson 1 Physical Features Essential Question: How does geography influence the way people live? A Vast Land Directions: Read the lesson and use your text to decide whether each
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2018 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College January 5, 2018 Summary: A persistent ridge of high pressure over the west in December produced strong inversions
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College January 5, 2018 Summary: A persistent ridge of high pressure over the west in December produced strong inversions
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast December 2017 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast December 2017 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College December 5, 2017 Summary: November was relatively cool and wet from central California throughout most of
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast December 2017 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College December 5, 2017 Summary: November was relatively cool and wet from central California throughout most of
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2019 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2019 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College January 4, 2019 Summary: December was mild and dry over much of the west, while the east was much warmer than
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2019 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College January 4, 2019 Summary: December was mild and dry over much of the west, while the east was much warmer than
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2018 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College March 7, 2018 Summary: The ridge pattern that brought drier and warmer conditions from December through most
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College March 7, 2018 Summary: The ridge pattern that brought drier and warmer conditions from December through most
Protect your most valuable assets
 Protect your most valuable assets Premise eliminates termites right around your home Termites are a very serious pest in Australia, causing damage that costs hundreds of millions of dollars to repair each
Protect your most valuable assets Premise eliminates termites right around your home Termites are a very serious pest in Australia, causing damage that costs hundreds of millions of dollars to repair each
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2017
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2017 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University August 4, 2017 July largely held true to forecast, although it ended with the start of one of the most extreme
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2017 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University August 4, 2017 July largely held true to forecast, although it ended with the start of one of the most extreme
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast February 2018 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast February 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College February 5, 2018 Summary: For the majority of the month of January the persistent ridge of high pressure
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast February 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College February 5, 2018 Summary: For the majority of the month of January the persistent ridge of high pressure
L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment
 Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
SEPTEMBER 2013 REVIEW
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: October 21, 2013 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com SEPTEMBER 2013 REVIEW Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average temperature
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: October 21, 2013 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com SEPTEMBER 2013 REVIEW Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average temperature
remain on the trees all year long) Example: Beaverlodge, Alberta, Canada
 Coniferous Forest Temperature: -40 C to 20 C, average summer temperature is 10 C Precipitation: 300 to 900 millimeters of rain per year Vegetation: Coniferous-evergreen trees (trees that produce cones
Coniferous Forest Temperature: -40 C to 20 C, average summer temperature is 10 C Precipitation: 300 to 900 millimeters of rain per year Vegetation: Coniferous-evergreen trees (trees that produce cones
Ocean s Influence on Weather and Climate
 Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
Earth is often called the Blue Planet because so much of its surface (about 71%) is covered by water. Of all the water on Earth, about 96.5%, is held in the world s oceans. As you can imagine, these oceans
but 2012 was dry Most farmers pulled in a crop
 After a winter that wasn t, conditions late in the year pointed to a return to normal snow and cold conditions Most farmers pulled in a crop but 2012 was dry b y M i k e Wr o b l e w s k i, w e a t h e
After a winter that wasn t, conditions late in the year pointed to a return to normal snow and cold conditions Most farmers pulled in a crop but 2012 was dry b y M i k e Wr o b l e w s k i, w e a t h e
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: SEPTEMBER 19, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: SEPTEMBER 19, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales sroot@weatherbank.com AUGUST 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: SEPTEMBER 19, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales sroot@weatherbank.com AUGUST 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The
discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms and bodies of
 Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter 2016-17 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University December 5, 2016 Well after an October that felt more like November, we just finished a November that
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter 2016-17 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University December 5, 2016 Well after an October that felt more like November, we just finished a November that
CLIMATE READY BOSTON. Climate Projections Consensus ADAPTED FROM THE BOSTON RESEARCH ADVISORY GROUP REPORT MAY 2016
 CLIMATE READY BOSTON Sasaki Steering Committee Meeting, March 28 nd, 2016 Climate Projections Consensus ADAPTED FROM THE BOSTON RESEARCH ADVISORY GROUP REPORT MAY 2016 WHAT S IN STORE FOR BOSTON S CLIMATE?
CLIMATE READY BOSTON Sasaki Steering Committee Meeting, March 28 nd, 2016 Climate Projections Consensus ADAPTED FROM THE BOSTON RESEARCH ADVISORY GROUP REPORT MAY 2016 WHAT S IN STORE FOR BOSTON S CLIMATE?
Climate. Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) January Temperature. July Temperature. Average Precipitation (Last 30 Years)
 Climate Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) Average Annual High Temp. (F)70, (C)21 Average Annual Low Temp. (F)43, (C)6 January Temperature Average January High Temp. (F)48, (C)9 Average January Low Temp.
Climate Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) Average Annual High Temp. (F)70, (C)21 Average Annual Low Temp. (F)43, (C)6 January Temperature Average January High Temp. (F)48, (C)9 Average January Low Temp.
THE CANADIAN CENTRE FOR CLIMATE MODELLING AND ANALYSIS
 THE CANADIAN CENTRE FOR CLIMATE MODELLING AND ANALYSIS As Canada s climate changes, and weather patterns shift, Canadian climate models provide guidance in an uncertain future. CANADA S CLIMATE IS CHANGING
THE CANADIAN CENTRE FOR CLIMATE MODELLING AND ANALYSIS As Canada s climate changes, and weather patterns shift, Canadian climate models provide guidance in an uncertain future. CANADA S CLIMATE IS CHANGING
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2016
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University June 6, 2016 May 2016 continued the warm trend for portions of the west, while providing some relief for
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University June 6, 2016 May 2016 continued the warm trend for portions of the west, while providing some relief for
Pacific Decadal Oscillation ( PDO ):
 Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2015-2016. El Nino / La Nina: When looking
Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2015-2016. El Nino / La Nina: When looking
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer into Harvest 2016
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer into Harvest 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University September 3, 2016 With school and football season starting a hint of fall is right on time
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer into Harvest 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University September 3, 2016 With school and football season starting a hint of fall is right on time
A heat source is any device or natural body that supplies heat.
 Heat Source and Heat Sinks Heat Source: A heat source is any device or natural body that supplies heat. Examples of a heat source: The sun, gas stove, fire, volcano, hot spring, radiator, electric heater,
Heat Source and Heat Sinks Heat Source: A heat source is any device or natural body that supplies heat. Examples of a heat source: The sun, gas stove, fire, volcano, hot spring, radiator, electric heater,
Climate change in the U.S. Northeast
 Climate change in the U.S. Northeast By U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, adapted by Newsela staff on 04.10.17 Word Count 1,109 Killington Ski Resort is located in Vermont. As temperatures increase
Climate change in the U.S. Northeast By U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, adapted by Newsela staff on 04.10.17 Word Count 1,109 Killington Ski Resort is located in Vermont. As temperatures increase
What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
 IPCC WG1 FAQ What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change The IPCC is a scientific intergovernmental body set up by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and by the United Nations
IPCC WG1 FAQ What is the IPCC? Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change The IPCC is a scientific intergovernmental body set up by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and by the United Nations
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: July 18, 2014 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: July 18, 2014 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com JUNE 2014 REVIEW Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average temperature for
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: July 18, 2014 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com JUNE 2014 REVIEW Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average temperature for
Erik Kabela and Greg Carbone, Department of Geography, University of South Carolina
 Downscaling climate change information for water resources Erik Kabela and Greg Carbone, Department of Geography, University of South Carolina As decision makers evaluate future water resources, they often
Downscaling climate change information for water resources Erik Kabela and Greg Carbone, Department of Geography, University of South Carolina As decision makers evaluate future water resources, they often
EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles.
 EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles. Places & Terms for Discussion Appalachian Mountains Great Plains Canadian Shield
EQ: Discuss main geographic landforms of the U.S. & Canada and examine varied landforms in relation to their lifestyles. Places & Terms for Discussion Appalachian Mountains Great Plains Canadian Shield
UNITED STATES AND SOUTH AMERICA WEATHER ROUNDUP Sunday, December 17, 2017
 T-storm Weather Summary Extreme heat was followed by heavy rain in some key areas of Argentina yesterday. T-storms affect much of the driest Argentina, southern Brazil, and Paraguay through 7 to 10 days,
T-storm Weather Summary Extreme heat was followed by heavy rain in some key areas of Argentina yesterday. T-storms affect much of the driest Argentina, southern Brazil, and Paraguay through 7 to 10 days,
Current Climate Trends and Implications
 Current Climate Trends and Implications Dr. Mark Seeley Professor emeritus Department of Soil, Water, and Climate University of Minnesota St Paul, MN 55108 Crop Insurance Conference September 12, 2018
Current Climate Trends and Implications Dr. Mark Seeley Professor emeritus Department of Soil, Water, and Climate University of Minnesota St Paul, MN 55108 Crop Insurance Conference September 12, 2018
2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW
 2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW 1 INTRODUCTION Recently, three of the major centres for global climate monitoring determined with high confidence that 2015 was the warmest year on record, globally.
2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW 1 INTRODUCTION Recently, three of the major centres for global climate monitoring determined with high confidence that 2015 was the warmest year on record, globally.
Crop / Weather Update
 Crop / Weather Update This is our last for the 2018 planting, growing and harvesting seasons. USDA will publish their Crop Progress Report again in April 2019, and we will continue our coverage sometime
Crop / Weather Update This is our last for the 2018 planting, growing and harvesting seasons. USDA will publish their Crop Progress Report again in April 2019, and we will continue our coverage sometime
Unit 1 Test - Version A
 Unit 1 Test - Version A 1. Approximately, how many degrees of longitude equal one time zone change? a. 5 b. 10 c. 15 d. 20 e. 25 2. The city of Lewisville has a population of 1,000 people living in 100
Unit 1 Test - Version A 1. Approximately, how many degrees of longitude equal one time zone change? a. 5 b. 10 c. 15 d. 20 e. 25 2. The city of Lewisville has a population of 1,000 people living in 100
Climate Change & Extreme Weather: Perception vs Reality
 Climate Change & Extreme Weather: Perception vs Reality Madhav Khandekar Expert Reviewer IPCC 2007 Climate Change Are Extreme Weather (EW) events on the rise? A short answer: NO! A long answer: NO! NO!
Climate Change & Extreme Weather: Perception vs Reality Madhav Khandekar Expert Reviewer IPCC 2007 Climate Change Are Extreme Weather (EW) events on the rise? A short answer: NO! A long answer: NO! NO!
Historical and Projected National and Regional Climate Trends
 Climate Change Trends for Planning at Sand Creek Massacre National Historic Site Prepared by Nicholas Fisichelli, NPS Climate Change Response Program April 18, 2013 Climate change and National Parks Climate
Climate Change Trends for Planning at Sand Creek Massacre National Historic Site Prepared by Nicholas Fisichelli, NPS Climate Change Response Program April 18, 2013 Climate change and National Parks Climate
Drought Impacts in the Southern Great Plains. Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK
 Drought Impacts in the Southern Great Plains Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK Causes of Drought: Large-Scale, Stationary High Pressure Air rotates clockwise around high pressure steers storms
Drought Impacts in the Southern Great Plains Mark Shafer University of Oklahoma Norman, OK Causes of Drought: Large-Scale, Stationary High Pressure Air rotates clockwise around high pressure steers storms
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast October 2018 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast October 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College October 4, 2018 Summary: Much of Washington, Oregon, coastal California and the Bay Area and delta region
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast October 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College October 4, 2018 Summary: Much of Washington, Oregon, coastal California and the Bay Area and delta region
COMMUNITY EMERGENCY RESPONSE TEAM FLOODS INTRODUCTION
 INTRODUCTION Floods are one of the most common hazards in the United States. A flood occurs any time a body of water rises to cover what is usually dry land. Flood effects can be local, impacting a neighborhood
INTRODUCTION Floods are one of the most common hazards in the United States. A flood occurs any time a body of water rises to cover what is usually dry land. Flood effects can be local, impacting a neighborhood
2011 Year in Review TORNADOES
 2011 Year in Review The year 2011 had weather events that will be remembered for a long time. Two significant tornado outbreaks in April, widespread damage and power outages from Hurricane Irene in August
2011 Year in Review The year 2011 had weather events that will be remembered for a long time. Two significant tornado outbreaks in April, widespread damage and power outages from Hurricane Irene in August
Figure 1. Carbon dioxide time series in the North Pacific Ocean (
 Evidence #1: Since 1950, Earth s atmosphere and oceans have changed. The amount of carbon released to the atmosphere has risen. Dissolved carbon in the ocean has also risen. More carbon has increased ocean
Evidence #1: Since 1950, Earth s atmosphere and oceans have changed. The amount of carbon released to the atmosphere has risen. Dissolved carbon in the ocean has also risen. More carbon has increased ocean
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 3 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 3 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
4 Changes in Climate. TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why is more land exposed during glacial periods than at other times?
 Name Class CHAPTER 3 Date Climate 4 Changes in Climate SECTION National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: ES 1k, 2a
Name Class CHAPTER 3 Date Climate 4 Changes in Climate SECTION National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: ES 1k, 2a
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2019 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2019 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College March 2, 2019 Summary: Dramatic flip from a mild winter to a top five coldest February on record in many locations
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2019 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College March 2, 2019 Summary: Dramatic flip from a mild winter to a top five coldest February on record in many locations
KCC White Paper: The 100 Year Hurricane. Could it happen this year? Are insurers prepared? KAREN CLARK & COMPANY. June 2014
 KAREN CLARK & COMPANY KCC White Paper: The 100 Year Hurricane Could it happen this year? Are insurers prepared? June 2014 Copyright 2014 Karen Clark & Company The 100 Year Hurricane Page 1 2 COPLEY PLACE
KAREN CLARK & COMPANY KCC White Paper: The 100 Year Hurricane Could it happen this year? Are insurers prepared? June 2014 Copyright 2014 Karen Clark & Company The 100 Year Hurricane Page 1 2 COPLEY PLACE
Unit 2. United States Physical Geography
 Unit 2 United States Physical Geography Physical Geography U.S. extends from the Atlantic to Pacific U.S. is the 3rd largest country U.S. has fertile soils, vast forests, and variety of minerals All major
Unit 2 United States Physical Geography Physical Geography U.S. extends from the Atlantic to Pacific U.S. is the 3rd largest country U.S. has fertile soils, vast forests, and variety of minerals All major
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast April 2018 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast April 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College April 4, 2018 Summary: A near Miracle March played out bringing cooler and wetter conditions to the majority
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast April 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College April 4, 2018 Summary: A near Miracle March played out bringing cooler and wetter conditions to the majority
Severe Weather: Tornadoes and Hurricanes
 Severe Weather: Tornadoes and Hurricanes Tornadoes Grab Toto!! TORNADOES Are a low pressure storm that usually forms over land in an average year, 800 tornadoes are reported in the U.S. a tornado is defined
Severe Weather: Tornadoes and Hurricanes Tornadoes Grab Toto!! TORNADOES Are a low pressure storm that usually forms over land in an average year, 800 tornadoes are reported in the U.S. a tornado is defined
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: May 15, 2014 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: May 15, 2014 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com APRIL 2014 REVIEW Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average temperature for
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: May 15, 2014 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com APRIL 2014 REVIEW Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average temperature for
Unit 2 Text Worksheet # 2
 Unit 2 Text Worksheet # 2 Read Pages 74-77 1. Using fig. 5.1 on page 75 identify: Climatic Region the most widespread climatic region in the low latitudes two climatic subregions with dry conditions for
Unit 2 Text Worksheet # 2 Read Pages 74-77 1. Using fig. 5.1 on page 75 identify: Climatic Region the most widespread climatic region in the low latitudes two climatic subregions with dry conditions for
3) What is the difference between latitude and longitude and what is their affect on local and world weather and climate?
 www.discoveryeducation.com 1) Describe the difference between climate and weather citing an example of each. Describe how water (ocean, lake, river) has a local effect on weather and climate and provide
www.discoveryeducation.com 1) Describe the difference between climate and weather citing an example of each. Describe how water (ocean, lake, river) has a local effect on weather and climate and provide
GLOBAL CLIMATES FOCUS
 which you will learn more about in Chapter 6. Refer to the climate map and chart on pages 28-29 as you read the rest of this chapter. FOCUS GLOBAL CLIMATES What are the major influences on climate? Where
which you will learn more about in Chapter 6. Refer to the climate map and chart on pages 28-29 as you read the rest of this chapter. FOCUS GLOBAL CLIMATES What are the major influences on climate? Where
2011 National Seasonal Assessment Workshop for the Eastern, Southern, & Southwest Geographic Areas
 2011 National Seasonal Assessment Workshop for the Eastern, Southern, & Southwest Geographic Areas On January 11-13, 2011, wildland fire, weather, and climate met virtually for the ninth annual National
2011 National Seasonal Assessment Workshop for the Eastern, Southern, & Southwest Geographic Areas On January 11-13, 2011, wildland fire, weather, and climate met virtually for the ninth annual National
Detecting Climate Change through Means and Extremes
 Detecting Climate Change through Means and Extremes New Mexico Supercomputing Challenge Final Report April 6, 2016 Team 55 Los Alamos Middle School Team Member: Lillian Petersen Teacher: Adam Drew Mentor:
Detecting Climate Change through Means and Extremes New Mexico Supercomputing Challenge Final Report April 6, 2016 Team 55 Los Alamos Middle School Team Member: Lillian Petersen Teacher: Adam Drew Mentor:
CHAPTER 1. Geo Challenges 1A to 1D. & World Map Activity
 CHAPTER 1 Geo Challenges 1A to 1D & World Map Activity SELECT YOUR CHALLENGE World Map Activity Challenge 1A Challenge 1B Challenge 1C Challenge 1D Challenge 1A WS PG. 2 STEP #1 Label the largest continent
CHAPTER 1 Geo Challenges 1A to 1D & World Map Activity SELECT YOUR CHALLENGE World Map Activity Challenge 1A Challenge 1B Challenge 1C Challenge 1D Challenge 1A WS PG. 2 STEP #1 Label the largest continent
JEFF JOHNSON S Winter Weather Outlook
 JEFF JOHNSON S 2017-2018 Winter Weather Outlook TABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT THE AUTHOR Components of the seasonal outlook... 2 ENSO state/ocean temperatures... 3 Sub-seasonal outlooks... 4 Forecast models...
JEFF JOHNSON S 2017-2018 Winter Weather Outlook TABLE OF CONTENTS ABOUT THE AUTHOR Components of the seasonal outlook... 2 ENSO state/ocean temperatures... 3 Sub-seasonal outlooks... 4 Forecast models...
The Weather Wire. Contents: Summer 2018 Outlook. Summer 2018 Outlook Drought Monitor May Summary/Statistics June Preview Rainfall Totals
 The Weather Wire June 2018 Volume 25 Number 6 Contents: Summer 2018 Outlook Drought Monitor May Summary/Statistics June Preview Rainfall Totals Summer 2018 Outlook June 1 st marked the first day of meteorological
The Weather Wire June 2018 Volume 25 Number 6 Contents: Summer 2018 Outlook Drought Monitor May Summary/Statistics June Preview Rainfall Totals Summer 2018 Outlook June 1 st marked the first day of meteorological
NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information State Summaries 149-FL. Observed and Projected Temperature Change
 19-FL FLORIDA Key Messages Under a higher emissions pathway, historically unprecedented warming is projected by the end of the 1st century. Rising temperatures will likely increase the intensity of naturally-occurring
19-FL FLORIDA Key Messages Under a higher emissions pathway, historically unprecedented warming is projected by the end of the 1st century. Rising temperatures will likely increase the intensity of naturally-occurring
Winter. Here s what a weak La Nina usually brings to the nation with tempseraures:
 2017-2018 Winter Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2017-2018. El Nino /
2017-2018 Winter Time again for my annual Winter Weather Outlook. Here's just a small part of the items I considered this year and how I think they will play out with our winter of 2017-2018. El Nino /
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America
 Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2016
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University August 5, 2016 The month of July saw the continued flip, flop of the western US temperatures. It was warm
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University August 5, 2016 The month of July saw the continued flip, flop of the western US temperatures. It was warm
MIDDAY WEATHER SUMMARY
 MIDDAY WEATHER SUMMARY Weather Headlines TS Cindy will move inland tonight or early tomorrow morning near the Texas/Louisiana border. The latest GFS model run is cooler late in the 6-10 and early in the
MIDDAY WEATHER SUMMARY Weather Headlines TS Cindy will move inland tonight or early tomorrow morning near the Texas/Louisiana border. The latest GFS model run is cooler late in the 6-10 and early in the
TERMITES. Pillar To Post Continuing Education Program
 TERMITES Pillar To Post Continuing Education Program Table of Contents Chapter 1: Overview and Objectives Chapter 2: Introduction to Termites Chapter 3: Termite Damage Chapter 4: Getting Rid of Termites
TERMITES Pillar To Post Continuing Education Program Table of Contents Chapter 1: Overview and Objectives Chapter 2: Introduction to Termites Chapter 3: Termite Damage Chapter 4: Getting Rid of Termites
Cookie Settings Accept Cookies
 1 of 10 10/7/2018, 3:07 PM The U.S. East Coast is sinking, worsening floods from sea level rise 2 of 10 10/7/2018, 3:07 PM sea level rise, which has been occurring faster in the western Atlantic Ocean
1 of 10 10/7/2018, 3:07 PM The U.S. East Coast is sinking, worsening floods from sea level rise 2 of 10 10/7/2018, 3:07 PM sea level rise, which has been occurring faster in the western Atlantic Ocean
Tropical Moist Rainforest
 Tropical or Lowlatitude Climates: Controlled by equatorial tropical air masses Tropical Moist Rainforest Rainfall is heavy in all months - more than 250 cm. (100 in.). Common temperatures of 27 C (80 F)
Tropical or Lowlatitude Climates: Controlled by equatorial tropical air masses Tropical Moist Rainforest Rainfall is heavy in all months - more than 250 cm. (100 in.). Common temperatures of 27 C (80 F)
 Contributors: Arlene Fiore 1, Lee Murray 1, Luke Valin 1, Olivia Clifton 1, Jean Guo 1 Author: Melissa Seto 1 Analysis of Wisconsin 2007 High-Ozone event Section 1A: Can satellite NO 2 columns inform us
Contributors: Arlene Fiore 1, Lee Murray 1, Luke Valin 1, Olivia Clifton 1, Jean Guo 1 Author: Melissa Seto 1 Analysis of Wisconsin 2007 High-Ozone event Section 1A: Can satellite NO 2 columns inform us
Markville. CGC 1DL/PL Geography. Geography of Canada. Natural Environment Unit Test
 Markville CGC 1DL/PL Geography Geography of Canada Natural Environment Unit Test Name: Thinking /10 Knowledge /10 Application /10 Communication /10 Part A: Blanks (1 mark each) Thinking Choose the correct
Markville CGC 1DL/PL Geography Geography of Canada Natural Environment Unit Test Name: Thinking /10 Knowledge /10 Application /10 Communication /10 Part A: Blanks (1 mark each) Thinking Choose the correct
WeatherManager Weekly
 Issue 222 March 26, 2015 Welcome to this week s WeatherManager, your weekly journal for ideas and developments in the weather risk market, brought to you by eweatherrisk. Articles talk about the expanding
Issue 222 March 26, 2015 Welcome to this week s WeatherManager, your weekly journal for ideas and developments in the weather risk market, brought to you by eweatherrisk. Articles talk about the expanding
Weather Report 04 April 2018
 Weather Report 04 April 2018 South Africa - Weather Alternating periods of rain and sunshine will evolve across South Africa during the coming week. Moisture totals through next Tuesday morning will range
Weather Report 04 April 2018 South Africa - Weather Alternating periods of rain and sunshine will evolve across South Africa during the coming week. Moisture totals through next Tuesday morning will range
HURRICANES AND TORNADOES
 HURRICANES AND TORNADOES The most severe weather systems are hurricanes and tornadoes. They occur in extremely low pressure systems, or cyclones, when the air spirals rapidly into the center of a low.
HURRICANES AND TORNADOES The most severe weather systems are hurricanes and tornadoes. They occur in extremely low pressure systems, or cyclones, when the air spirals rapidly into the center of a low.
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: February 15, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: February 15, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com JANUARY 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review During January, the average
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: February 15, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com JANUARY 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review During January, the average
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale
 The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale is a one to five categorization based on the hurricane's intensity at the indicated time. The scale provides examples of
The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale The Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale is a one to five categorization based on the hurricane's intensity at the indicated time. The scale provides examples of
Crop / Weather Update
 Crop / Weather Update Corn Crop Condition Percent of Acreage Rated Good or Excellent 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 45 The U.S. corn crop was rated 69% good-to-excellent on September 23, up 1% from week-ago,
Crop / Weather Update Corn Crop Condition Percent of Acreage Rated Good or Excellent 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 45 The U.S. corn crop was rated 69% good-to-excellent on September 23, up 1% from week-ago,
Climates of NYS. Definitions. Climate Regions of NYS. Storm Tracks. Climate Controls 10/13/2011. Characteristics of NYS s Climates
 Definitions Climates of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande 2011 Weather and Climate Weather the state of the atmosphere at one point in time. The elements of weather are temperature, air pressure, wind and moisture.
Definitions Climates of NYS Prof. Anthony Grande 2011 Weather and Climate Weather the state of the atmosphere at one point in time. The elements of weather are temperature, air pressure, wind and moisture.
Chapter Introduction. Earth. Change. Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Climates of Earth Chapter Wrap-Up Climate Cycles Recent Climate Change What is climate and how does it impact life on Earth? What do you think? Before you
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3 Climates of Earth Chapter Wrap-Up Climate Cycles Recent Climate Change What is climate and how does it impact life on Earth? What do you think? Before you
Keys to Climate Climate Classification Low Latitude Climates Midlatitude Climates High Latitude Climates Highland Climates Our Changing Climate
 Climate Global Climates Keys to Climate Climate Classification Low Latitude Climates Midlatitude Climates High Latitude Climates Highland Climates Our Changing Climate Keys to Climate Climate the average
Climate Global Climates Keys to Climate Climate Classification Low Latitude Climates Midlatitude Climates High Latitude Climates Highland Climates Our Changing Climate Keys to Climate Climate the average
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
WeatherManager Weekly
 Issue 288 July 14, 2016 WeatherManager Weekly Industries We Serve Agriculture Energy/Utilities Construction Transportation Retail Our Weather Protection Products Standard Temperature Products Lowest Daily
Issue 288 July 14, 2016 WeatherManager Weekly Industries We Serve Agriculture Energy/Utilities Construction Transportation Retail Our Weather Protection Products Standard Temperature Products Lowest Daily
WeatherManager Weekly
 Issue 242 August 13, 2015 Welcome to this week s WeatherManager, your weekly journal for ideas and developments in the weather risk market, brought to you by eweatherrisk. The articles talk about the volatile
Issue 242 August 13, 2015 Welcome to this week s WeatherManager, your weekly journal for ideas and developments in the weather risk market, brought to you by eweatherrisk. The articles talk about the volatile
UNITED STATES AND SOUTH AMERICA OUTLOOK (FULL REPORT) Thursday, December 28, 2017
 T-storm Weather Summary Despite scattered t-storms Sat.-Sun. in central and northern areas in Argentina, more will likely be needed especially in sunflower areas of the southwest. Some t-storms likely
T-storm Weather Summary Despite scattered t-storms Sat.-Sun. in central and northern areas in Argentina, more will likely be needed especially in sunflower areas of the southwest. Some t-storms likely
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
Colorado CoCoRaHS. Colorado CoCoRaHS. Because Every Drop Counts! October 2014 Volume 2, Issue 10
 U.S. PRECIPITATION (% OF AVERAGE) LOOKING BACK AT SEPTEMBER 2014 September was dry for much of the nation with a few exceptions; one of those being the central Rockies. In Colorado, it was wetter-than-average
U.S. PRECIPITATION (% OF AVERAGE) LOOKING BACK AT SEPTEMBER 2014 September was dry for much of the nation with a few exceptions; one of those being the central Rockies. In Colorado, it was wetter-than-average
Module 3, Investigation 1: Briefing 2 The ENSO game: Predicting and managing for El Niño and La Niña
 Part 5. The ENSO game How can prediction help avoid ENSO s tragic human consequences? Scientists from around the world are involved in forecasting, with computer models and sophisticated measurements,
Part 5. The ENSO game How can prediction help avoid ENSO s tragic human consequences? Scientists from around the world are involved in forecasting, with computer models and sophisticated measurements,
An assessment of the risk of aerial transport of rust pathogens to the Western Hemisphere and within North America
 An assessment of the risk of aerial transport of rust pathogens to the Western Hemisphere and within North America Scott A. Isard Departments of Plant Pathology and Meteorology Pennsylvania State University
An assessment of the risk of aerial transport of rust pathogens to the Western Hemisphere and within North America Scott A. Isard Departments of Plant Pathology and Meteorology Pennsylvania State University
The following information is provided for your use in describing climate and water supply conditions in the West as of April 1, 2003.
 Natural Resources Conservation Service National Water and Climate Center 101 SW Main Street, Suite 1600 Portland, OR 97204-3224 Date: April 8, 2003 Subject: April 1, 2003 Western Snowpack Conditions and
Natural Resources Conservation Service National Water and Climate Center 101 SW Main Street, Suite 1600 Portland, OR 97204-3224 Date: April 8, 2003 Subject: April 1, 2003 Western Snowpack Conditions and
Weekly Weather. Europe. February Flash. This Week: Warm East and Cold West; Heavy Rain and Snow in Some Areas
 Weekly Weather February 12 25 Flash US This Week: Warm East and Cold West; Heavy Rain and Snow in Some Areas A Look Ahead: Temperatures Run ; Severe Rain in the West Europe This Week: Cold Air Retreats
Weekly Weather February 12 25 Flash US This Week: Warm East and Cold West; Heavy Rain and Snow in Some Areas A Look Ahead: Temperatures Run ; Severe Rain in the West Europe This Week: Cold Air Retreats
Meteorology. Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer
 Chapter 3 Worksheet 1 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, the daily
Chapter 3 Worksheet 1 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) If the maximum temperature for a particular day is 26 C and the minimum temperature is 14 C, the daily
Projected Changes in Climate for Alberta and Forest Tree Improvement Program Regions
 Projected Changes in Climate for Alberta and Forest Tree Improvement Program Regions Laura K. Gray and Andreas Hamann Department of Renewable Resources University of Alberta, Edmonton June 2015 Tree Species
Projected Changes in Climate for Alberta and Forest Tree Improvement Program Regions Laura K. Gray and Andreas Hamann Department of Renewable Resources University of Alberta, Edmonton June 2015 Tree Species
CropCast Daily Agro-Highlights Don Keeney Friday, April 22, 2016
 VHI Image Date: Apr 14, 2016 USA Wheat Corn Soybeans Vegetative Health Index Map and Crop Condition Tendency EUROPE Wheat Rapeseed FSU Wheat CHINA Wheat Rapeseed ARGENTINA Corn Soybeans BRAZIL Corn Soybeans
VHI Image Date: Apr 14, 2016 USA Wheat Corn Soybeans Vegetative Health Index Map and Crop Condition Tendency EUROPE Wheat Rapeseed FSU Wheat CHINA Wheat Rapeseed ARGENTINA Corn Soybeans BRAZIL Corn Soybeans
Global Climate Change and the Implications for Oklahoma. Gary McManus Associate State Climatologist Oklahoma Climatological Survey
 Global Climate Change and the Implications for Oklahoma Gary McManus Associate State Climatologist Oklahoma Climatological Survey OCS LEGISLATIVE MANDATES Conduct and report on studies of climate and weather
Global Climate Change and the Implications for Oklahoma Gary McManus Associate State Climatologist Oklahoma Climatological Survey OCS LEGISLATIVE MANDATES Conduct and report on studies of climate and weather
