The extreme flood event of Lago Maggiore in September 1993
|
|
|
- Tyrone Henderson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stucki, P., O. Martius, S. Brönnimann, and J. Franke (2013) The extreme flood event of Lago Maggiore in September In: Brönnimann, S. and O. Martius (Eds.) Weather extremes during the past 140 years. Geographica Bernensia G89, p , DOI: /GB2013.G The extreme flood event of Lago Maggiore in September 1993 Peter Stucki *, Olivia Martius, Stefan Brönnimann, and Jörg Franke Oeschger Centre for Climate Change Research and Institute of Geography, University of Bern, Switzerland Abstract In September 1993, the Valais and Ticino regions of Switzerland were affected by extreme flooding triggered by heavy precipitation. The meteorological situation leading to this event is studied in the Twentieth Century Reanalysis (20CR) data set. A strong cut-off low development is found to be the driving synoptic-scale atmospheric circulation pattern. The agreement with previous studies highlights the applicability of 20CR for extreme event analysis. 1. Introduction The central Alps show large heterogeneity with regard to precipitation due to shielding and slope effects. The southern slopes of the central Alps are particularly prone to episodes of heavy precipitation (Frei and Schaer, 1998). In synergy with hydro-meteorological preconditions such as saturated soils and snow melt, heavy precipitation episodes can lead to flood events (e.g., Stucki et al., 2012). In the Canton of Ticino, the largest flood events occur in the Ticino catchment (including the Lago Maggiore basin), which is characterized by very steep slopes, large elevation differences and by runoff of nearly 1500 mm/a (Spreafico and Weingartner, 2005). Since these floods can cause severe damage, it is relevant to understand the hydrological and atmospheric conditions prior to and during such events. Heavy precipitation events on the southern slope of the Alps are typically triggered by an upper-level trough that decays into a cut-off low (e.g., Massacand et al., 1998). The upper level trough ensures steady inflow of warm and moist air from the south. The warm air is typically accompanied by a very high snow line (3500 m a.s.l.; Grebner, 1993). * Corresponding author: Peter Stucki, University of Bern, Institute of Geography, Hallerstr. 12, CH-3012 Bern, Switzerland. peter.stucki@giub.unibe.ch
2 Figure 1. Photo of the Piazza Grande in Locarno on 3 October 1993 (Source: Repubblica e Cantone Ticino). In this paper, we study the flood event of September The event is known for the flooding and debris flows in Brig/Valais, but also for severe damage in the Lago Maggiore basin (Pfister, 1999). The lake level at Locarno rose 1.16 m per 24 h on 24 September and 2.8 m from 23 to 25 September, and it reached the third-highest water level since 1868 ( m a.s.l.) on 9 October Figure 1 shows the flooded Piazza Grande in the old town of Locarno on 3 October The flood event had been the costliest event in the area so far, with estimated losses of 650 Million Swiss Francs (Röthlisberger, 1994). The event is relatively well studied using traditional data sets (e.g., Grebner, 1993; Landeshydrologie und geologie, 1994; MeteoSwiss, 1995; Massacand et al., 1998; Buzzi and Foschini, 2000). It therefore serves as an interesting example to test the applicability of another, new data set, namely the Twentieth Century Reanalysis, version 2 (Compo et al., 2011), for the problem of studying heavy precipitation events. In the following, we present an analysis of the large-scale meteorological situation leading to the extreme flood events of September 1993 in the Valais and the Lago Maggiore basin. Section 2 describes data and methods used. In Section 3, we shortly describe the precipitation and the meteorological development during the extreme event of 22 to 25 September A discussion is given in Section 4. Conclusions are drawn in Section Data and Methods The analysis considers the Twentieth Century Reanalysis version 2 (20CR), which is a global three-dimensional atmospheric dataset that reaches back to 1871 (Compo et al., 2011). It is based on an assimilation of observed surface or sea-level pressure and on HadISST (Rayner et al., 2003) monthly sea surface temperature and sea ice distributions as boundary conditions for the Global Forecast System atmosphere/land model (NCEP/GFS) at a spatial resolution of 54
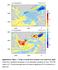
3 Figure 2. Map of the study area displaying the 20CR topography and land-sea mask. Dots indicate surface or sealevel pressure information assimilated into 20CR. Colours indicate the orography in 20CR and the land-sea mask as depicted in the Gaussian grid (192 x 94 cells). For orientation, the location of Milano is also indicated. T62. Assimilation is performed using an Ensemble Kalman filter, with 56 ensemble members. Here, we use the ensemble mean in the analysis and the figures. We focus on the 500 hpa geopotential height (GPH) and sea-level pressure (SLP) as an indicator of the general flow structure, 500 hpa vertical velocity (ω) as an indicator for lifting, equivalent potential temperature (θ e ) at 850 hpa to identify air mass boundaries as well as wind at 850 hpa and precipitable water to analyze the moisture flux. The 20CR data provide information only on the large-scale circulation. The resolution is 2 longitude x 2 latitude or approximately 200 x 200 km, and the orography of the Alps is smoothed substantially. Figure 2 shows the model orography, together with the surface and sea-level pressure data assimilated. As a consequence of the smooth orography, we do not expect very local extremes to be well depicted. Moreover, extremes are further expected to be smoothed because we analyze the mean of 56 realizations. As the data set does not resolve small-scale features in the precipitation field such as those caused by orographic effects, we supplement the data with daily amounts of precipitation from the MeteoSwiss station network. 3. Results Precipitation distribution After some days with little to no precipitation in the area, an episode of heavy precipitation on the south side of the Alps started on 22 September For instance, a precipitation rate of 127 mm within 24 hours was observed at the Airolo station at 1139 m a.s.l., located just south of the Alpine divide. The daily records in the area exceeded 100 mm on 25 September. 55
4 Figure 3. Precipitation and meteorological fields for 24 September, (a) Precipitation recorded at Swiss rain gauge stations (the inset shows the precipitation as a function of elevation) in mm/24 h. (b) GPH (black lines) in geopotential decametres and vertical motion (ω, in Pa/s, ascent in red, subsidence in steel blue shades) at 500 hpa. (c) SLP (lines, in hpa) and precipitation rate (shaded, in mm/h over 3 h around noon). (d) θ e at 850 hpa (blue, black and yellow lines mark 16, 24, and 32 C), wind (arrows), and precipitable water (mm, shades). (b) to (d) are from 20CR. Until 23 September, mainly the western Ticino was affected, and then the precipitation area expanded to the east and north across the Alpine divide. The situation on 24 September is depicted in Figure 3a. The heaviest precipitation occurred in the western Ticino/Domodossola area (145.8 mm at Cevio, 418 m a.s.l.). Precipitation amounts of more than 50 mm were observed from the Alpine divide (Uri, Valais) to Milano (Northern Italy) at all elevations. Compared to these local observations, the 20CR ensemble mean (Fig. 3b) shows relatively modest precipitation rates, and the main precipitation field is shifted to the western and especially the Maritime Alps on 24 September Meteorological situation By 22 September, a narrow upper-level trough had formed over Brittany upstream of a blocking ridge over southeastern Europe/Russia. The trough produced a meridionally elongated cut-off low, and a surface low developed over the Gulf of Lion, which moved slowly north-eastward over the next three days. The situation on 24 September is depicted in Figure 3. At 850 hpa, the low-level flow steered very moist and warm air from the south towards the Alps, as can be seen in the high values of 850 hpa θ e, wind, and precipitable water (Fig. 3c and d). 56
5 Strong uplift is indicated by negative values of ω at the 500 hpa level (Fig. 3b) on the eastern side of the cut-off low, i.e., at the southern slope of the Alps. Similar to precipitation, the area of strongest uplift is located over the Tyrrhenian Sea. 4. Discussion Our analysis shows that prior to the event, a mid-tropospheric trough formed of over Brittany and developed into an elongated cut-off low. The cut-off low triggered cyclogenesis over the Gulf of Lion. In fact, this process has been studied by various authors, who specifically addressed the role of the narrow, meridionally aligned trough in the upper troposphere (e.g. Massacand et al., 1998, 2001; Buzzi and Foschini, 2000; Hoinka et al., 2006). In this sense, the flood event of September 1993 is a typical example for the mechanisms responsible for heavy precipitation at the southern slope of the Alps (see also Stucki et al., 2012). The development of the trough and the cut-off low is relatively well depicted in the 20CR data. However, the mid-tropospheric lifting and the associated precipitation fields are shifted southward and the modelled precipitation rates are far below the observed extreme values. An almost-stationary, deep low over the Balearics/Ligurian Sea was the key element of low-level flow (Grebner, 1993). Mesoscale model simulations point to the central role of convection and illustrate the counterclockwise rotation of the frontal system, suggesting that the regional precipitation occurred in prefrontal circulation on 23 September and was associated with the cold front passage on 24 September (Buzzi and Foschini, 2000). In summary, the heavy precipitation on the south side of the Alps was likely due to a combination of synoptic and mesoscale forcings. Mid-tropospheric large-scale ascent supported deep convection over an area where abundant low-level moisture transport, convergence and orographic lift occurred. The importance of deep convection is indicated by the absence of an elevation gradient of precipitation (Fig. 3), i.e., heavy precipitation was observed at all elevations. 5. Conclusion The flood event of September 1993 in Ticino is studied using meteorological data from the Twentieth Century Reanalysis (20CR). The flood was triggered by heavy precipitation and led to one of the highest water levels of Lago Maggiore in the instrumental period. Our findings are in agreement with previous studies (Grebner, 1993; Röthlisberger, 1994; Massacand et al., 1998) in that the event was caused by continuous heavy precipitation induced by a quasi-stationary upper-level trough/cut-off system, warm and humid southerly inflow and high temperatures (with the snow line at 3000 m or even higher), and fast runoff formation on saturated soils. A narrow upper-level trough, from which a cut-off low developed, played an instrumental role in triggering the heavy precipitation event. Although just constrained by SLP, the Twentieth Century Reanalysis is able to reproduce the synoptic-scale atmospheric features which were essential for this anomalous precipitation event and flooding. However, the intensity of the precipitation event is underestimated in the ensemble mean and the regional-scale precipitation distribution is not well represented in 20CR. This is expected from the low spatial resolution of 2 longitude x 2 latitude and the resulting averaging over a large region and the coarsely resolved topography of the Alps. 57
6 Acknowledgements 20CR data were obtained courtesy of the NOAA/OAR/ESRL PSD, Boulder, Colorado, USA, from their Web site at Support for the Twentieth Century Reanalysis Project dataset is provided by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science Innovative and Novel Computational Impact on Theory and Experiment (DOE INCITE) program, and Office of Biological and Environmental Research (BER), and by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Climate Program Office. Precipitation data were provided by MeteoSwiss. The work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (NCCR Climate, Project PALVAREX III, project EVALUATE ) and the EU FP7 project ERA-CLIM. References Buzzi, A. and L. Foschini (2000) Mesoscale Meteorological Features Associated with Heavy Precipitation in the Southern Alpine Region. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys., 72, Compo, G. P., J. S. Whitaker, P. D. Sardeshmukh, N. Matsui, R. J. Allan, X. Yin, B. E. Gleason, R. S. Vose, G. Rutledge, P. Bessemoulin, S. Brönnimann, M. Brunet, R. I. Crouthamel, A. N. Grant, P. Y. Groisman, P. D. Jones, M. C. Kruk, A. C. Kruger, G. J. Marshall, M. Maugeri, H. Y. Mok, Ø. Nordli, T. F. Ross, R. M. Trigo, X. L. Wang, S. D. Woodruff, and S. J. Worley (2011) The Twentieth Century Reanalysis project. Q. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc., 137, Frei, C. and C. Schaer (1998) A precipitation climatology of the Alps from high-resolution rain-gauge observations. Int. J. Climatol., 18, Grebner, D. (1993) Meteorologische Analyse des Unwetters von Brig und Saas Almagell vom 24. September Geographisches Institut ETH Zürich. Hoinka, K. P., C. Schwierz, and O. Martius (2006) Synoptic-scale weather patterns during Alpine heavy rain events. Q. J. Roy. Meteorol. Soc. 132, Landeshydrologie und geologie (1994) Die Hochwasser 1993 im Wallis und im Tessin - Messdaten und ausgesuchte Auswertungen. Mitteilungen der Landeshydrologie und geologie Nr. 19. Massacand, A. C., H. Wernli, and H. C. Davies (1998) Heavy precipitation on the Alpine south side: An upperlevel precursor. Geophys. Res. Lett., 25, MeteoSwiss (1995) Le alluvione del 1993 sul versante sudalpino. Working reports of the SMI, No. 186, Pfister, C. (1999) Wetternachhersage: 500 Jahre Klimavariationen und Naturkatastrophen ( ). Verlag Paul Haupt, Bern. Rayner, N. A., D. E. Parker, E. B. Horton, C. K. Folland, L. V. Alexander, D. P. Rowell, E. C. Kent, and A. Kaplan (2003) Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J. Geophys. Res., 108, 4407, /2002JD Röthlisberger, G. (1994) Unwetterschäden in der Schweiz im Jahre wasser, energie, luft, 841/2. Spreafico, M., and R. Weingartner (2005): Hydrologie der Schweiz Ausgewählte Aspekte und Resultate. Berichte des BWG, Serie Wasser Nr. 7, Bern. Stucki, P., R. Rickli, S. Brönnimann, O. Martius, H. Wanner, D. Grebner, and J. Luterbacher (2012) Weather patterns and hydro-climatological precursors of extreme large-scale floods in Switzerland since Meteorol. Z., 21,
The link between atmospheric blockings and Central European flood events a case study
 Workshop on Atmospheric Blocking, 6-8 April 2016, Reading, UK The link between atmospheric blockings and Central European flood events a case study Sina Lenggenhager 1,2, Olivia Martius 1,2, Stefan Brönnimann
Workshop on Atmospheric Blocking, 6-8 April 2016, Reading, UK The link between atmospheric blockings and Central European flood events a case study Sina Lenggenhager 1,2, Olivia Martius 1,2, Stefan Brönnimann
The Great Appalachian Storm of 1950 in Reanalyses and Historical Weather Charts
 Burkart, K. and A.-M. Wyss (2017) The Great Appalachian Storm of 1950 in Reanalyses and Historical Weather Charts. In: Brönnimann, S. (Ed.) Historical Weather Extremes in Reanalyses. Geographica Bernensia
Burkart, K. and A.-M. Wyss (2017) The Great Appalachian Storm of 1950 in Reanalyses and Historical Weather Charts. In: Brönnimann, S. (Ed.) Historical Weather Extremes in Reanalyses. Geographica Bernensia
Coverage bias in the HadCRUT4 temperature series and its impact on recent temperature trends. UPDATE. 1 Temperature reconstruction by domain: version
 Coverage bias in the HadCRUT4 temperature series and its impact on recent temperature trends. UPDATE Temperature reconstruction by domain: version 2.0 temperature series Kevin Cowtan, Robert G. Way January
Coverage bias in the HadCRUT4 temperature series and its impact on recent temperature trends. UPDATE Temperature reconstruction by domain: version 2.0 temperature series Kevin Cowtan, Robert G. Way January
The 1872 Baltic Sea Storm Surge
 Feuchter, D., C. Jörg,, G. Rosenhagen, R. Auchmann, O. Martius, and S. Brönnimann (2013) The 1872 Baltic Sea storm surge. In: Brönnimann, S. and O. Martius (Eds.) Weather extremes during the past 140 years.
Feuchter, D., C. Jörg,, G. Rosenhagen, R. Auchmann, O. Martius, and S. Brönnimann (2013) The 1872 Baltic Sea storm surge. In: Brönnimann, S. and O. Martius (Eds.) Weather extremes during the past 140 years.
North Atlantic Amospheric Blocking and Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation in CESM1 Large Ensemble Simulations. Carlos Martinez
 North Atlantic Amospheric Blocking and Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation in CESM1 Large Ensemble Simulations ABSTRACT Carlos Martinez Academic Affiliation, Fall 2014: Junior, Texas A&M University SOARS
North Atlantic Amospheric Blocking and Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation in CESM1 Large Ensemble Simulations ABSTRACT Carlos Martinez Academic Affiliation, Fall 2014: Junior, Texas A&M University SOARS
L alluvione di Firenze del 1966 : an ensemble-based re-forecasting study
 from Newsletter Number 148 Summer 2016 METEOROLOGY L alluvione di Firenze del 1966 : an ensemble-based re-forecasting study Image from Mallivan/iStock/Thinkstock doi:10.21957/ nyvwteoz This article appeared
from Newsletter Number 148 Summer 2016 METEOROLOGY L alluvione di Firenze del 1966 : an ensemble-based re-forecasting study Image from Mallivan/iStock/Thinkstock doi:10.21957/ nyvwteoz This article appeared
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1840 RECENT MULTIDECADAL STRENGTHENING OF THE WALKER CIRCULATION ACROSS THE TROPICAL PACIFIC (1) Supplementary_Figures.pdf Adobe document 1.5MB SI Guide Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1840 RECENT MULTIDECADAL STRENGTHENING OF THE WALKER CIRCULATION ACROSS THE TROPICAL PACIFIC (1) Supplementary_Figures.pdf Adobe document 1.5MB SI Guide Supplementary
The Arctic Outbreak of 4-8 January 2014
 The Arctic Outbreak of 4-8 January 2014 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION An artic outbreak affected much of eastern North American to include the eastern
The Arctic Outbreak of 4-8 January 2014 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION An artic outbreak affected much of eastern North American to include the eastern
The 1956 Cold Wave in Western Europe
 Dizerens, C., S. Lenggenhager, M. Schwander, A. Buck, and S. Foffa (2017) The 1956 Cold Wave in Western Europe. In: Brönnimann, S. (Ed.) Historical Weather Extremes in Reanalyses. Geographica Bernensia
Dizerens, C., S. Lenggenhager, M. Schwander, A. Buck, and S. Foffa (2017) The 1956 Cold Wave in Western Europe. In: Brönnimann, S. (Ed.) Historical Weather Extremes in Reanalyses. Geographica Bernensia
J1.7 SOIL MOISTURE ATMOSPHERE INTERACTIONS DURING THE 2003 EUROPEAN SUMMER HEATWAVE
 J1.7 SOIL MOISTURE ATMOSPHERE INTERACTIONS DURING THE 2003 EUROPEAN SUMMER HEATWAVE E Fischer* (1), SI Seneviratne (1), D Lüthi (1), PL Vidale (2), and C Schär (1) 1 Institute for Atmospheric and Climate
J1.7 SOIL MOISTURE ATMOSPHERE INTERACTIONS DURING THE 2003 EUROPEAN SUMMER HEATWAVE E Fischer* (1), SI Seneviratne (1), D Lüthi (1), PL Vidale (2), and C Schär (1) 1 Institute for Atmospheric and Climate
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America
 Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific subtropical high
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L13701, doi:10.1029/2008gl034584, 2008 Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L13701, doi:10.1029/2008gl034584, 2008 Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific
Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L12704, doi:10.1029/2009gl038416, 2009 Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon A. S. Taschetto, 1
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L12704, doi:10.1029/2009gl038416, 2009 Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon A. S. Taschetto, 1
Weather Related Factors of the Adelaide floods ; 7 th to 8 th November 2005
 Weather Related Factors of the Adelaide floods ; th to th November 2005 Extended Abstract Andrew Watson Regional Director Bureau of Meteorology, South Australian Region 1. Antecedent Weather 1.1 Rainfall
Weather Related Factors of the Adelaide floods ; th to th November 2005 Extended Abstract Andrew Watson Regional Director Bureau of Meteorology, South Australian Region 1. Antecedent Weather 1.1 Rainfall
COUPLING A DISTRIBUTED HYDROLOGICAL MODEL TO REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL OUTPUT: AN EVALUATION OF EXPERIMENTS FOR THE RHINE BASIN IN EUROPE
 P.1 COUPLING A DISTRIBUTED HYDROLOGICAL MODEL TO REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL OUTPUT: AN EVALUATION OF EXPERIMENTS FOR THE RHINE BASIN IN EUROPE Jan Kleinn*, Christoph Frei, Joachim Gurtz, Pier Luigi Vidale,
P.1 COUPLING A DISTRIBUTED HYDROLOGICAL MODEL TO REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL OUTPUT: AN EVALUATION OF EXPERIMENTS FOR THE RHINE BASIN IN EUROPE Jan Kleinn*, Christoph Frei, Joachim Gurtz, Pier Luigi Vidale,
Meteorological similarities and differences of the great European floods
 Meteorological similarities and differences of the great European floods Nataša Strelec Mahović DHMZ Meteorological and Hydrological Service, Croatia Europe floods 1998-2008 Areas most frequently affected
Meteorological similarities and differences of the great European floods Nataša Strelec Mahović DHMZ Meteorological and Hydrological Service, Croatia Europe floods 1998-2008 Areas most frequently affected
Synoptic Meteorology
 M.Sc. in Meteorology Synoptic Meteorology [MAPH P312] Prof Peter Lynch Second Semester, 2004 2005 Seminar Room Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Part 9 Extratropical Weather Systems These lectures
M.Sc. in Meteorology Synoptic Meteorology [MAPH P312] Prof Peter Lynch Second Semester, 2004 2005 Seminar Room Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. Part 9 Extratropical Weather Systems These lectures
Mid Atlantic Severe Event of 1 May 2017 Central Pennsylvania QLCS event By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803
 1. Overview Mid Atlantic Severe Event of 1 May 2017 Central Pennsylvania QLCS event By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803 A strong upper-level wave (Fig.1) moving into a
1. Overview Mid Atlantic Severe Event of 1 May 2017 Central Pennsylvania QLCS event By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service, State College, PA 16803 A strong upper-level wave (Fig.1) moving into a
Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical
 1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
1 2 3 Supplemental Information for Human influence on terrestrial precipitation trends revealed by dynamical adjustment 4 Ruixia Guo 1,2, Clara Deser 1,*, Laurent Terray 3 and Flavio Lehner 1 5 6 7 1 Climate
Climate Change and Runoff Statistics in the Rhine Basin: A Process Study with a Coupled Climate-Runoff Model
 IACETH Climate Change and Runoff Statistics in the Rhine Basin: A Process Study with a Coupled Climate-Runoff Model Jan KLEINN, Christoph Frei, Joachim Gurtz, Pier Luigi Vidale, and Christoph Schär Institute
IACETH Climate Change and Runoff Statistics in the Rhine Basin: A Process Study with a Coupled Climate-Runoff Model Jan KLEINN, Christoph Frei, Joachim Gurtz, Pier Luigi Vidale, and Christoph Schär Institute
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997)
 Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
Multiscale Analyses of Inland Tropical Cyclone Midlatitude Jet Interactions: Camille (1969) and Danny (1997) Matthew Potter, Lance Bosart, and Daniel Keyser Department of Atmospheric and Environmental
Reanalysis of the Hamburg Storm Surge of 1962
 Jochner, M., M. Schwander, and S. Brönnimann (2013) Reanalysis of the Hamburg Storm Surge of 1962. In: Brönnimann, S. and O. Martius (Eds.) Weather extremes during the past 140 years. Geographica Bernensia
Jochner, M., M. Schwander, and S. Brönnimann (2013) Reanalysis of the Hamburg Storm Surge of 1962. In: Brönnimann, S. and O. Martius (Eds.) Weather extremes during the past 140 years. Geographica Bernensia
A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS:
 2.6 A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS: 2000-2007 James V. Rudolph*, K. Friedrich, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Colorado at Boulder,
2.6 A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS: 2000-2007 James V. Rudolph*, K. Friedrich, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Colorado at Boulder,
A SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN ROMANIA DUE TO MEDITERRANEAN CYCLONIC ACTIVITY
 A SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN ROMANIA DUE TO MEDITERRANEAN CYCLONIC ACTIVITY Florinela Georgescu, Gabriela Bancila, Viorica Dima National Meteorological Administration, Bucharest, Romania Abstract Mediterranean
A SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN ROMANIA DUE TO MEDITERRANEAN CYCLONIC ACTIVITY Florinela Georgescu, Gabriela Bancila, Viorica Dima National Meteorological Administration, Bucharest, Romania Abstract Mediterranean
Numerical Simulation of a Severe Cold and Rainy Event over the East Mediterranean
 JKAU: Met., Env. & Arid Land Agric. Sci., Vol. 20, No. 2, pp: 95-109 (2009 A.D. / 1430 A.H.) Numerical Simulation of a Severe Cold and Rainy Event over the East Mediterranean Department of Meteorology,
JKAU: Met., Env. & Arid Land Agric. Sci., Vol. 20, No. 2, pp: 95-109 (2009 A.D. / 1430 A.H.) Numerical Simulation of a Severe Cold and Rainy Event over the East Mediterranean Department of Meteorology,
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events
 National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events Heavy rainfall of 23 November 2011 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College PA 16803 Abstract:. A fast moving mid-tropospheric
National Weather Service-Pennsylvania State University Weather Events Heavy rainfall of 23 November 2011 by Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College PA 16803 Abstract:. A fast moving mid-tropospheric
The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 1, 25 30 The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO HU Kai-Ming and HUANG Gang State Key
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 1, 25 30 The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO HU Kai-Ming and HUANG Gang State Key
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts. Lecture 12 AOS 101
 Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
Mid-Latitude Cyclones and Fronts Lecture 12 AOS 101 Homework 4 COLDEST TEMPS GEOSTROPHIC BALANCE Homework 4 FASTEST WINDS L Consider an air parcel rising through the atmosphere The parcel expands as it
24. WHAT CAUSED THE RECORD-BREAKING HEAT ACROSS AUSTRALIA IN OCTOBER 2015?
 24. WHAT CAUSED THE RECORD-BREAKING HEAT ACROSS AUSTRALIA IN OCTOBER 2015? Pandora Hope, Guomin Wang, Eun-Pa Lim, Harry H. Hendon, and Julie M. Arblaster Using a seasonal forecasting framework for attribution,
24. WHAT CAUSED THE RECORD-BREAKING HEAT ACROSS AUSTRALIA IN OCTOBER 2015? Pandora Hope, Guomin Wang, Eun-Pa Lim, Harry H. Hendon, and Julie M. Arblaster Using a seasonal forecasting framework for attribution,
Figure ES1 demonstrates that along the sledging
 UPPLEMENT AN EXCEPTIONAL SUMMER DURING THE SOUTH POLE RACE OF 1911/12 Ryan L. Fogt, Megan E. Jones, Susan Solomon, Julie M. Jones, and Chad A. Goergens This document is a supplement to An Exceptional Summer
UPPLEMENT AN EXCEPTIONAL SUMMER DURING THE SOUTH POLE RACE OF 1911/12 Ryan L. Fogt, Megan E. Jones, Susan Solomon, Julie M. Jones, and Chad A. Goergens This document is a supplement to An Exceptional Summer
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
Name: 1) As the difference between the dewpoint temperature and the air temperature decreases, the probability of precipitation increases remains the same decreases 2) Which statement best explains why
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
ANALYZING EL NIÑO- SOUTHERN OSCILLATION SENSITIVITY IN A LARGE ENSEMBLE OF OCEAN REANALYSES. A Thesis KELLEY BRADLEY
 ANALYZING EL NIÑO- SOUTHERN OSCILLATION SENSITIVITY IN A LARGE ENSEMBLE OF OCEAN REANALYSES A Thesis by KELLEY BRADLEY Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University
ANALYZING EL NIÑO- SOUTHERN OSCILLATION SENSITIVITY IN A LARGE ENSEMBLE OF OCEAN REANALYSES A Thesis by KELLEY BRADLEY Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University
Name of research institute or organization: Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss
 Name of research institute or organization: Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Title of project: The weather in 2016 Report by: Stephan Bader, Climate Division MeteoSwiss English
Name of research institute or organization: Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Title of project: The weather in 2016 Report by: Stephan Bader, Climate Division MeteoSwiss English
Arctic Winds in the Twentieth Century Reanalysis
 Brönnimann, S., M. Wegmann, R. Wartenburger, and A. Stickler (2013) Arctic Winds in the Twentieth Century Reanalysis. In: Brönnimann, S. and O. Martius (Eds.) Weather extremes during the past 140 years.
Brönnimann, S., M. Wegmann, R. Wartenburger, and A. Stickler (2013) Arctic Winds in the Twentieth Century Reanalysis. In: Brönnimann, S. and O. Martius (Eds.) Weather extremes during the past 140 years.
ICRC-CORDEX Sessions A: Benefits of Downscaling Session A1: Added value of downscaling Stockholm, Sweden, 18 May 2016
 ICRC-CORDEX Sessions A: Benefits of Downscaling Session A1: Added value of downscaling Stockholm, Sweden, 18 May 2016 Challenges in the quest for added value of climate dynamical downscaling: Evidence
ICRC-CORDEX Sessions A: Benefits of Downscaling Session A1: Added value of downscaling Stockholm, Sweden, 18 May 2016 Challenges in the quest for added value of climate dynamical downscaling: Evidence
P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002
 P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002 Ari-Juhani Punkka* and Jenni Teittinen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland 1. INTRODUCTION On 5 July 2002 a fast propagating
P4.9 THE SEVERE THUNDERSTORM OUTBREAK IN FINLAND ON 5 JULY 2002 Ari-Juhani Punkka* and Jenni Teittinen Finnish Meteorological Institute, Helsinki, Finland 1. INTRODUCTION On 5 July 2002 a fast propagating
4/29/2011. Mid-latitude cyclones form along a
 Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
Seasonal associations between mid-tropospheric height patterns and precipitation in the western Great Basin, USA
 Seasonal associations between mid-tropospheric height patterns and precipitation in the western Great Basin, USA By: Paul A. Knapp Knapp, P.A. (1994) Seasonal associations between mid-tropospheric pressure
Seasonal associations between mid-tropospheric height patterns and precipitation in the western Great Basin, USA By: Paul A. Knapp Knapp, P.A. (1994) Seasonal associations between mid-tropospheric pressure
FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic areas for Risk mitigation in the Alpine space
 Natural Risk Management in a changing climate: Experiences in Adaptation Strategies from some European Projekts Milano - December 14 th, 2011 FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic
Natural Risk Management in a changing climate: Experiences in Adaptation Strategies from some European Projekts Milano - December 14 th, 2011 FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic
Stormiest winter on record for Ireland and UK
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Stormiest winter on record for Ireland and UK This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation:
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Stormiest winter on record for Ireland and UK This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation:
Romanian Contribution in Quantitative Precipitation Forecasts Project
 3 Working Group on Physical Aspects 29 Romanian Contribution in Quantitative Precipitation Forecasts Project Rodica Dumitrache, Victor Pescaru, Liliana Velea, Cosmin Barbu National Meteorological Administration,
3 Working Group on Physical Aspects 29 Romanian Contribution in Quantitative Precipitation Forecasts Project Rodica Dumitrache, Victor Pescaru, Liliana Velea, Cosmin Barbu National Meteorological Administration,
Diabatic processes and the structure of the warm conveyor belt
 2 nd European Windstorm Workshop Leeds, 3-4 September 2012 Diabatic processes and the structure of the warm conveyor belt Oscar Martínez-Alvarado J. Chagnon, S. Gray, R. Plant, J. Methven Department of
2 nd European Windstorm Workshop Leeds, 3-4 September 2012 Diabatic processes and the structure of the warm conveyor belt Oscar Martínez-Alvarado J. Chagnon, S. Gray, R. Plant, J. Methven Department of
The Summer Flooding 2005 in Southern Bavaria A Climatological Review. J. Grieser, C. Beck, B. Rudolf
 168 DWD Klimastatusbericht 2005 The Summer Flooding 2005 in Southern Bavaria A Climatological Review J. Grieser, C. Beck, B. Rudolf The Flood-Event During the second half of August 2005 severe floodings
168 DWD Klimastatusbericht 2005 The Summer Flooding 2005 in Southern Bavaria A Climatological Review J. Grieser, C. Beck, B. Rudolf The Flood-Event During the second half of August 2005 severe floodings
A Cyclogenesis south of the Alps. Manfred Kurz Neustadt/Weinstraße
 A Cyclogenesis south of the Alps Manfred Kurz Neustadt/Weinstraße A cyclogenesis south of the Alps Surface maps 06-11-99, 00 UTC The occluded frontal system of a quasi-stationary low above the North Sea
A Cyclogenesis south of the Alps Manfred Kurz Neustadt/Weinstraße A cyclogenesis south of the Alps Surface maps 06-11-99, 00 UTC The occluded frontal system of a quasi-stationary low above the North Sea
Forecasting summer convective activity over the Po Valley: insights from MAP D-PHASE
 Forecasting summer convective activity over the Po Valley: insights from MAP D-PHASE S. Davolio, O. Drofa and P. Malguzzi ISAC - CNR, Bologna, Italy Introduction The Po Valley is an area prone to convective
Forecasting summer convective activity over the Po Valley: insights from MAP D-PHASE S. Davolio, O. Drofa and P. Malguzzi ISAC - CNR, Bologna, Italy Introduction The Po Valley is an area prone to convective
Winter Storm of 15 December 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 Winter Storm of 15 December 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A complex winter storm brought snow, sleet, and freezing rain to central Pennsylvania.
Winter Storm of 15 December 2005 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION A complex winter storm brought snow, sleet, and freezing rain to central Pennsylvania.
27. NATURAL VARIABILITY NOT CLIMATE CHANGE DROVE THE RECORD WET WINTER IN SOUTHEAST AUSTRALIA
 27. NATURAL VARIABILITY NOT CLIMATE CHANGE DROVE THE RECORD WET WINTER IN SOUTHEAST AUSTRALIA Andrew D. King Warmth in the east Indian Ocean increased the likelihood of the record wet July September in
27. NATURAL VARIABILITY NOT CLIMATE CHANGE DROVE THE RECORD WET WINTER IN SOUTHEAST AUSTRALIA Andrew D. King Warmth in the east Indian Ocean increased the likelihood of the record wet July September in
MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology. Lecture 8: September 16, AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2)
 MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology Lecture 8: September 16, 2010 AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2) Identifying a cold front on a surface weather map: 1. Surface front is located at the leading edge
MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology Lecture 8: September 16, 2010 AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2) Identifying a cold front on a surface weather map: 1. Surface front is located at the leading edge
and 24 mm, hPa lapse rates between 3 and 4 K km 1, lifted index values
 3.2 Composite analysis 3.2.1 Pure gradient composites The composite initial NE report in the pure gradient northwest composite (N = 32) occurs where the mean sea level pressure (MSLP) gradient is strongest
3.2 Composite analysis 3.2.1 Pure gradient composites The composite initial NE report in the pure gradient northwest composite (N = 32) occurs where the mean sea level pressure (MSLP) gradient is strongest
Introduction of products for Climate System Monitoring
 Introduction of products for Climate System Monitoring 1 Typical flow of making one month forecast Textbook P.66 Observed data Atmospheric and Oceanic conditions Analysis Numerical model Ensemble forecast
Introduction of products for Climate System Monitoring 1 Typical flow of making one month forecast Textbook P.66 Observed data Atmospheric and Oceanic conditions Analysis Numerical model Ensemble forecast
Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty
 Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty David R. Easterling National Climatic Data Center Asheville, North Carolina Overview Some examples of observed climate
Observed Climate Variability and Change: Evidence and Issues Related to Uncertainty David R. Easterling National Climatic Data Center Asheville, North Carolina Overview Some examples of observed climate
Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate
 Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate Will Perrie, Lanli Guo, Zhenxia Long, Bash Toulany Fisheries and Oceans Canada, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Dartmouth, NS Abstract
Impacts of Climate Change on Autumn North Atlantic Wave Climate Will Perrie, Lanli Guo, Zhenxia Long, Bash Toulany Fisheries and Oceans Canada, Bedford Institute of Oceanography, Dartmouth, NS Abstract
Supplemental Material for Evolution of the Atlantic Multidecadal. Variability in a model with an improved North Atlantic Current
 1 Supplemental Material for Evolution of the Atlantic Multidecadal 2 Variability in a model with an improved North Atlantic Current 3 Annika Drews 4 GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, Kiel,
1 Supplemental Material for Evolution of the Atlantic Multidecadal 2 Variability in a model with an improved North Atlantic Current 3 Annika Drews 4 GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, Kiel,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
Figure S1. Summary of the climatic responses to the Gulf Stream. On the offshore flank of the SST front (black dashed curve) of the Gulf Stream (green long arrow), surface wind convergence associated with
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Guðrún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts issued at IMO are mainly
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Guðrún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts issued at IMO are mainly
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns
 Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 4: Weather forecasters use advanced technologies Ch. 3 Weather Fronts and Storms Objective(s) 7.E.1.3
Ch. 3: Weather Patterns Sect. 1: Air Mass & Fronts Sect. 2: Storms Sect. 3: Predicting the Weather Sect. 4: Weather forecasters use advanced technologies Ch. 3 Weather Fronts and Storms Objective(s) 7.E.1.3
Blocking precursors to stratospheric sudden warming events
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L14806, doi:10.1029/2009gl038776, 2009 Blocking precursors to stratospheric sudden warming events O. Martius, 1 L. M. Polvani, 2 and H. C. Davies 1 Received 27 April
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L14806, doi:10.1029/2009gl038776, 2009 Blocking precursors to stratospheric sudden warming events O. Martius, 1 L. M. Polvani, 2 and H. C. Davies 1 Received 27 April
High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl044119, 2010 High initial time sensitivity of medium range forecasting observed for a stratospheric sudden warming Yuhji Kuroda 1 Received 27 May
TROPICAL-LIKE CYCLONES IN THE MEDITERRANEAN: IMPACTS AND COMPOSITE DAILY MEANS AND ANOMALIES OF SYNOPTIC CONDITIONS
 Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 TROPICAL-LIKE CYCLONES IN THE MEDITERRANEAN: IMPACTS AND COMPOSITE DAILY MEANS
Proceedings of the 14 th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology Rhodes, Greece, 3-5 September 2015 TROPICAL-LIKE CYCLONES IN THE MEDITERRANEAN: IMPACTS AND COMPOSITE DAILY MEANS
WWOSC 2014, MONTREAL
 WWOSC 2014, MONTREAL Forecast Errors of Rossby Waveguides Evi Giannakaki, Olivia Martius University of Bern, Switzerland Rossby waves (PV perspective) 07/10/2011_06 PV @ 325K PVU 2 Rossby waves (PV perspective)
WWOSC 2014, MONTREAL Forecast Errors of Rossby Waveguides Evi Giannakaki, Olivia Martius University of Bern, Switzerland Rossby waves (PV perspective) 07/10/2011_06 PV @ 325K PVU 2 Rossby waves (PV perspective)
Atmospheric patterns for heavy rain events in the Balearic Islands
 Adv. Geosci., 12, 27 32, 2007 Author(s) 2007. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Advances in Geosciences Atmospheric patterns for heavy rain events in the Balearic Islands A. Lana,
Adv. Geosci., 12, 27 32, 2007 Author(s) 2007. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Advances in Geosciences Atmospheric patterns for heavy rain events in the Balearic Islands A. Lana,
Heavy rains and precipitable water anomalies August 2010 By Richard H. Grumm And Jason Krekeler National Weather Service State College, PA 16803
 Heavy rains and precipitable water anomalies 17-19 August 2010 By Richard H. Grumm And Jason Krekeler National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION Heavy rain fell over the Gulf States,
Heavy rains and precipitable water anomalies 17-19 August 2010 By Richard H. Grumm And Jason Krekeler National Weather Service State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION Heavy rain fell over the Gulf States,
ATMOSPHERIC PATTERNS FOR HEAVY PRECIPITATION IN BULGARIA
 Romanian Journal of Meteorology vol. 10 nr.1-2010 ATMOSPHERIC PATTERNS FOR HEAVY PRECIPITATION IN BULGARIA I. TSONEVSKY 1, J. CAMPINS 2, A. GENOVÉS 2, A. JANSÁ 2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and
Romanian Journal of Meteorology vol. 10 nr.1-2010 ATMOSPHERIC PATTERNS FOR HEAVY PRECIPITATION IN BULGARIA I. TSONEVSKY 1, J. CAMPINS 2, A. GENOVÉS 2, A. JANSÁ 2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and
Shawn M. Milrad Atmospheric Science Program Department of Geography University of Kansas Lawrence, Kansas
 Shawn M. Milrad Atmospheric Science Program Department of Geography University of Kansas Lawrence, Kansas Eyad H. Atallah and John R. Gyakum Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences McGill University
Shawn M. Milrad Atmospheric Science Program Department of Geography University of Kansas Lawrence, Kansas Eyad H. Atallah and John R. Gyakum Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences McGill University
General Circulation. Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
 General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1
 APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1 1 By David B. Fissel, Mar Martínez de Saavedra Álvarez, and Randy C. Kerr, ASL Environmental Sciences Inc. (Feb. 2012) West Greenland Seismic
APPENDIX B PHYSICAL BASELINE STUDY: NORTHEAST BAFFIN BAY 1 1 By David B. Fissel, Mar Martínez de Saavedra Álvarez, and Randy C. Kerr, ASL Environmental Sciences Inc. (Feb. 2012) West Greenland Seismic
Hydrologic Research Laboratory Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of California, Davis
 Physically-Based Estimation of Maximum Precipitation: Preliminary Results on Application to American River Basin for the December,1996-January,1997 Flood Event Hydrologic Research Laboratory Department
Physically-Based Estimation of Maximum Precipitation: Preliminary Results on Application to American River Basin for the December,1996-January,1997 Flood Event Hydrologic Research Laboratory Department
August 2005 intense rainfall event in Switzerland: Not necessarily an analog for strong convective events in a greenhouse climate
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L05701, doi:10.1029/2005gl025573, 2006 August 2005 intense rainfall event in Switzerland: Not necessarily an analog for strong convective events in a greenhouse climate
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L05701, doi:10.1029/2005gl025573, 2006 August 2005 intense rainfall event in Switzerland: Not necessarily an analog for strong convective events in a greenhouse climate
Mid-West Heavy rains 18 April 2013
 Abstract: Mid-West Heavy rains 18 April 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA The relatively wet conditions during the first 16 days of April 2013 set the
Abstract: Mid-West Heavy rains 18 April 2013 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA The relatively wet conditions during the first 16 days of April 2013 set the
Daily, Monthly and Yearly Norm Temperature ( ): TnormD8110, TnormM8110 and TnormY8110
 Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Documentation of MeteoSwiss Grid-Data Products Daily, Monthly and Yearly Norm Temperature (1981-2010): TnormD8110,
Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Documentation of MeteoSwiss Grid-Data Products Daily, Monthly and Yearly Norm Temperature (1981-2010): TnormD8110,
The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 6, 371 375 The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height HUANG Yan-Yan and
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2015, VOL. 8, NO. 6, 371 375 The Interdecadal Variation of the Western Pacific Subtropical High as Measured by 500 hpa Eddy Geopotential Height HUANG Yan-Yan and
Minor Winter Flooding Event in northwestern Pennsylvania January 2017
 1. Overview Minor Winter Flooding Event in northwestern Pennsylvania 12-13 January 2017 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A combination of snow melt, frozen ground, and areas
1. Overview Minor Winter Flooding Event in northwestern Pennsylvania 12-13 January 2017 By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A combination of snow melt, frozen ground, and areas
No pause in the increase of hot temperature extremes
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2145 No pause in the increase of hot temperature extremes Sonia I. Seneviratne 1, Markus G. Donat 2,3, Brigitte Mueller 4,1, and Lisa V. Alexander 2,3 1 Institute
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2145 No pause in the increase of hot temperature extremes Sonia I. Seneviratne 1, Markus G. Donat 2,3, Brigitte Mueller 4,1, and Lisa V. Alexander 2,3 1 Institute
Introduction of climate monitoring and analysis products for one-month forecast
 Introduction of climate monitoring and analysis products for one-month forecast TCC Training Seminar on One-month Forecast on 13 November 2018 10:30 11:00 1 Typical flow of making one-month forecast Observed
Introduction of climate monitoring and analysis products for one-month forecast TCC Training Seminar on One-month Forecast on 13 November 2018 10:30 11:00 1 Typical flow of making one-month forecast Observed
Global Atmospheric Circulation
 Global Atmospheric Circulation Polar Climatology & Climate Variability Lecture 11 Nov. 22, 2010 Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation The Polar Vortex
Global Atmospheric Circulation Polar Climatology & Climate Variability Lecture 11 Nov. 22, 2010 Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation Global Atmospheric Circulation The Polar Vortex
A Synoptic Climatology of Heavy Precipitation Events in California
 A Synoptic Climatology of Heavy Precipitation Events in California Alan Haynes Hydrometeorological Analysis and Support (HAS) Forecaster National Weather Service California-Nevada River Forecast Center
A Synoptic Climatology of Heavy Precipitation Events in California Alan Haynes Hydrometeorological Analysis and Support (HAS) Forecaster National Weather Service California-Nevada River Forecast Center
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011 National Meteorological Administration 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts are primarily based on the results of ECMWF and
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011 National Meteorological Administration 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts are primarily based on the results of ECMWF and
Maximum and minimum temperature trends for the globe: An update through 2004
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L23822, doi:10.1029/2005gl024379, 2005 Maximum and minimum temperature trends for the globe: An update through 2004 Russell S. Vose, David R. Easterling, and Byron
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L23822, doi:10.1029/2005gl024379, 2005 Maximum and minimum temperature trends for the globe: An update through 2004 Russell S. Vose, David R. Easterling, and Byron
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox
 Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
p = ρrt p = ρr d = T( q v ) dp dz = ρg
 Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
MET Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16)
 MET 4300 Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16) Learning Objectives Provide an overview of the importance and impacts of mountain snowstorms in the western US Describe how topography influence precipitation
MET 4300 Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16) Learning Objectives Provide an overview of the importance and impacts of mountain snowstorms in the western US Describe how topography influence precipitation
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2010
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2010 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Guðrún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts issued at IMO are mainly
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2010 Icelandic Meteorological Office (www.vedur.is) Guðrún Nína Petersen 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts issued at IMO are mainly
Heavy Rainfall and Flooding of 23 July 2009 By Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803
 Heavy Rainfall and Flooding of 23 July 2009 By Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION Heavy rains fall over Pennsylvania and eastern New
Heavy Rainfall and Flooding of 23 July 2009 By Richard H. Grumm And Ron Holmes National Weather Service Office State College, PA 16803 1. INTRODUCTION Heavy rains fall over Pennsylvania and eastern New
INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS
 INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS C.G. Georgiev1 and P. Santurette2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Tsarigradsko chaussee 66, 1784 Sofia, Bulgaria 2 Météo-France, 42,
INTERPRETATION GUIDE TO MSG WATER VAPOUR CHANNELS C.G. Georgiev1 and P. Santurette2 1 National Institute of Meteorology and Hydrology, Tsarigradsko chaussee 66, 1784 Sofia, Bulgaria 2 Météo-France, 42,
Nonlinear atmospheric response to Arctic sea-ice loss under different sea ice scenarios
 Nonlinear atmospheric response to Arctic sea-ice loss under different sea ice scenarios Hans Chen, Fuqing Zhang and Richard Alley Advanced Data Assimilation and Predictability Techniques The Pennsylvania
Nonlinear atmospheric response to Arctic sea-ice loss under different sea ice scenarios Hans Chen, Fuqing Zhang and Richard Alley Advanced Data Assimilation and Predictability Techniques The Pennsylvania
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Summary of November Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge
 Summary of November 12-13 2010 Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge Event Overview The first significant snowfall of the 2010-2011 season affected portions of the plains and upper Mississippi
Summary of November 12-13 2010 Central U.S. Winter Storm By Christopher Hedge Event Overview The first significant snowfall of the 2010-2011 season affected portions of the plains and upper Mississippi
Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation
 Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation Renhe Zhang 1,2 Ruonan Zhang 2 Zhiyan Zuo 2 1 Institute of Atmospheric Sciences, Fudan University 2 Chinese Academy of Meteorological
Impact of Eurasian spring snow decrement on East Asian summer precipitation Renhe Zhang 1,2 Ruonan Zhang 2 Zhiyan Zuo 2 1 Institute of Atmospheric Sciences, Fudan University 2 Chinese Academy of Meteorological
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather
 Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream
 Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
Air Masses, Fronts, Storm Systems, and the Jet Stream Air Masses When a large bubble of air remains over a specific area of Earth long enough to take on the temperature and humidity characteristics of
Fronts in November 1998 Storm
 Fronts in November 1998 Storm Much of the significant weather observed in association with extratropical storms tends to be concentrated within narrow bands called frontal zones. Fronts in November 1998
Fronts in November 1998 Storm Much of the significant weather observed in association with extratropical storms tends to be concentrated within narrow bands called frontal zones. Fronts in November 1998
Diabatic processes and the structure of extratropical cyclones
 Geophysical and Nonlinear Fluid Dynamics Seminar AOPP, Oxford, 23 October 2012 Diabatic processes and the structure of extratropical cyclones Oscar Martínez-Alvarado R. Plant, J. Chagnon, S. Gray, J. Methven
Geophysical and Nonlinear Fluid Dynamics Seminar AOPP, Oxford, 23 October 2012 Diabatic processes and the structure of extratropical cyclones Oscar Martínez-Alvarado R. Plant, J. Chagnon, S. Gray, J. Methven
Cyclogenesis in the Western Mediterranean causing Heavy-Rain Events (NEPTUN)
 Cyclogenesis in the Western Mediterranean causing Heavy-Rain Events (NEPTUN) A Proposal for a coordinated mission of the HALO research aircraft in the field Transport processes and atmospheric dynamics
Cyclogenesis in the Western Mediterranean causing Heavy-Rain Events (NEPTUN) A Proposal for a coordinated mission of the HALO research aircraft in the field Transport processes and atmospheric dynamics
Precipitation in climate modeling for the Mediterranean region
 Precipitation in climate modeling for the Mediterranean region Simon Krichak Dept. of Geophysics Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, Tel Aviv University, Israel Concepts for Convective Parameterizations
Precipitation in climate modeling for the Mediterranean region Simon Krichak Dept. of Geophysics Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, Tel Aviv University, Israel Concepts for Convective Parameterizations
Orography and Monsoons: winter snow-storms over the Himalayas
 Orography and Monsoons: winter snow-storms over the Himalayas Massimo Bollasina1 and Laura Bertolani2 1Experimental 2Epson Climate Prediction Center, CA Meteo Center - Milan CEOP/IGWCO Joint Meeting, Tokyo,
Orography and Monsoons: winter snow-storms over the Himalayas Massimo Bollasina1 and Laura Bertolani2 1Experimental 2Epson Climate Prediction Center, CA Meteo Center - Milan CEOP/IGWCO Joint Meeting, Tokyo,
Eastern United States Wild Weather April 2014-Draft
 1. Overview Eastern United States Wild Weather 27-30 April 2014-Draft Significant quantitative precipitation bust By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA and Joel Maruschak Over
1. Overview Eastern United States Wild Weather 27-30 April 2014-Draft Significant quantitative precipitation bust By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA and Joel Maruschak Over
Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017
 Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A strong shortwave produced a stripe of precipitation
Northeastern United States Snowstorm of 9 February 2017 By Richard H. Grumm and Charles Ross National Weather Service State College, PA 1. Overview A strong shortwave produced a stripe of precipitation
East-west SST contrast over the tropical oceans and the post El Niño western North Pacific summer monsoon
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L15706, doi:10.1029/2005gl023010, 2005 East-west SST contrast over the tropical oceans and the post El Niño western North Pacific summer monsoon Toru Terao Faculty
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L15706, doi:10.1029/2005gl023010, 2005 East-west SST contrast over the tropical oceans and the post El Niño western North Pacific summer monsoon Toru Terao Faculty
