The Summer Flooding 2005 in Southern Bavaria A Climatological Review. J. Grieser, C. Beck, B. Rudolf
|
|
|
- Pauline Anthony
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
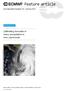
1 168 DWD Klimastatusbericht 2005 The Summer Flooding 2005 in Southern Bavaria A Climatological Review J. Grieser, C. Beck, B. Rudolf The Flood-Event During the second half of August 2005 severe floodings occurred in the northern central Alps. Following heavy precipitation on the 21 August major Swiss cities like Interlaken, Luzern and the capital Bern were flooded. On the following day a number of rivers in southern Bavaria including Lech, Iller, Isar, Inn and also Danube flooded vast areas. Amongst other cities Garmisch-Partenkirchen, Kempten and Regensburg were affected by major inundations. In some regions the river gauges even exceeded the level of the century flooding of The Synoptic Situation Although the floodings caused regionally disastrous effects the observed precipitation sums did not exceed former maxima of gauge observations at any station. Instead, the extraordinary flooding resulted from the particular interaction of several meteorological and hydrological processes. A detailed discussion can be found in Rudolf et al. (2006). Fig. 1 Infrared satellite image (METEOSAT 8) for 22 August 2005, 20:45 UTC resp. 22:45h Mean European Summer Time (MEST).
2 Klimastatusbericht 2005 DWD 169 Several days before the high precipitation amounts occurred a cut-off low was separated from the meandering flow over the south-western part of Europe. Crossing the northern part of the Mediterranean this low pressure system took up a considerable amount of humidity. On the 22nd, the South-western Bavarian region was located west of the cyclone under a dense and convective cloud band (see Fig. 1). The northern slope of the alps forced lifting of the air masses being advected with high velocity from the North, and led to a further amplification of condensation processes and locally extreme precipitation events. The emergence of the resulting floods was furthermore promoted through soil characteristics. Following a period of high precipitation during July and the beginning of August 2005 soils were already water saturated. Thus all the precipitated water was directly transferred into surface run-off. Forecast and Warning The weather development that led to the flooding was well observed and forecasted. The local model (LME) of the German Weather Service (DWD) predicted precipitation amounts close to the observed ones. As a consequence DWD informed the responsible agencies well in advance and gave the public warning of heavy precipitation. Fig. 2 (left panel) shows the precipitation forecast issued 22 August 2:00h Mean European Summer Time (MEST) for the 24h period starting 22 August 8:00h MEST. The right panel of Fig. 2 shows the interpolated observed precipitation from 1377 stations within the same period. The good agreement of both these maps obviously demonstrates that the daily precipitation total of this event was well forecasted. The regional Unwetterwarnzentrale (engl. storm warning centre) of DWD residing in Munich issued its first warning at 21 August 8:00h - well in advance of the event. Climatological Evaluation Fig. 3 shows the observed precipitation of 22 August for several stations within Bavaria and Austria. Only a small region of southern Bavaria faced extraordinary extreme precipitation. Most pronounced around Reutte and Oberstdorf with values above 100mm/day and an observed maximum precipitation of 189mm/day at Reutte/Tirol. However, precipitation rates of more than 100mm/day are not unusual within the Alps. Stations situated in the alpine foothills like Kempten (with 67.5mm/day) faced less extreme precipitation. Also at very high altitude stations like Zugspitze (2962m altitude) precipitation was less extreme (45.8mm/day). Fig. 2 Precipitation forecast issued 22 August, 2:00h for a 24-hours period starting 6 hours later (left panel) and observed precipitation interpolated from 1377 stations (right panel).
3 170 DWD Klimastatusbericht 2005 For some of the stations shown in Fig. 3 long time series of daily precipitation observations exist. Those time series allow estimating return periods. At the station Kempten observations since 1896 are available. From these nearly 40,000 observed daily precipitation sums 14 exceed the observation of 22 August This suggests a return period of less than 8 years. The precipitation amount at Mount Zugspitze usually is exceeded twice a year. However, at Garmisch, Oberstdorf and Oberstaufen the precipitation amount of 22 August 2005 was only exceeded once in their records consisting of more than 25,000 days each. At the station of Garmisch a considerably higher precipitation sum was observed during the precipitation event of 21 May 1999 which led to devastating floods. Assuming stationarity, i.e. the probability of an extreme precipitation event should not depend on time, we estimate a return period of the order of 100 years, given the observed records. Since the most extreme observed precipitation sums reflect small scale convective precipitation events, the estimated return period reflects the probability that the stations under consideration are affected by those events. However, if the meteorological situation had been only slightly different another but neighboured region would have been hit. Therefore, the probability that such an event occurs not exactly at the same location but shifted along the northern bounds of the Alps is higher. As a consequence the return period for such an event to occur somewhere in the alpine region is considerably below 100 years. Fig. 3 Observed precipitation in mm/day at 22 August 2005.
4 Klimastatusbericht 2005 DWD 171 Fig. 4 Time series (red) of highest daily precipitation sum per year (in mm/day) for the stations Oberstdorf, Garmisch und Kempten. Blue column is precipitation sum of 22 August Against the background of global climate change the question may be asked whether or not the probability for an extreme precipitation event like that under consideration has risen or fallen. In fact there is some conceptual framework arguing that heavy precipitation events should become more intensive in case of global climate change (Trenberth, 1999). In order to investigate whether or not the most extreme precipitation events lead to higher precipitation sums within the recent years Fig. 4 shows the records of the highest observed daily precipitation sum per year for the 3 stations Oberstdorf, Garmisch and Kempten. These time series do not reveal a systematic increase in the intensity of the highest daily precipitation sums per year. Finally we focus on the second point that was essential for generating the flood: the saturated soils. These resulted from fertile precipitation during the weeks before the extreme event. If monthly precipitation totals increase also soil saturation increases on average. This in turn promotes the vulnerability of river catchments to floods triggered by short-lived but extreme precipitation events.
5 172 DWD Klimastatusbericht 2005 Fig. 5 Time series of monthly mean August precipitation for the region 9-12 E and N (blue columns) and linear trend (red line). In order to investigate the regional trend in monthly August precipitation for the central northern alpine and pre-alpine region a 50-year gridded dataset with.5 spatial resolution of observed monthly precipitation sums created on the basis of homogeneity tested, long and nearly gap-free records is used (Beck et a., 2005). Spatially averaged August precipitation sums for the region bounded by 9-12 East and North are calculated and the respective time series since 1951 is shown in Fig. 5. A negative linear trend of about 7% over the period 1951 to 2000 becomes visible reducing average August precipitation from about 150mm at the beginning of this period to about 140mm at the end. However, given the high precipitation variability this negative trend is not significant on a 90% level of significance. Trömel and Schönwiese (2005) showed that temporal changes in precipitation variability exceed changes in precipitation averages which may suggest a decoupling of extreme and average precipitation. Grieser and Beck (2003) found significant increases in both, days with extreme precipitation and precipitation sums on days with extreme precipitation. However, they defined a day with extreme precipitation as a day having a return period of 100 days. Thus their statistics based on daily data for the period describe less extreme events. Moreover they found significant trends only in winter or for the shorter subperiod from 1961 to Summary and Conclusion The flood that occurred in the second half of August 2005 at the northern Alps resulted from extreme rainfall (with a return period of up to 100 years for a small region) on saturated soils. The extreme rainfall itself was caused by a rather rare meteorological situation implying the advection of warm and humid air masses from the Mediterranean that circled eastward around the Alps and cooled down on the northern side which led to condensation and continuous rainfall. Furthermore due to forced lifting at the northern slopes of the Alps precipitation locally reached outstanding intensities. The potential hydrometeorological effects resulting from this synoptic situation were early recognized by the German Meteorological Service (DWD) and respective warnings were issued well in advance of the event.
6 Klimastatusbericht 2005 DWD 173 As the flooding arose from the combination of unfavourable hydrological preconditions (water saturated soils) on the one hand and a triggering meteorological event (extreme daily precipitation) on the other hand long-term variations of both factors were investigated in order to place this event in a broader context of global climate change. Given long records of station observations within the affected region neither a long term positive trend of monthly mean August precipitation (which can be used as an indicator for water saturation of soils) nor positive trends in the very extreme daily precipitation sums can be detected. Therefore, this individual event can not be regarded as a consequence of long-term global climate change. However, previous work suggests an increase in more moderate extreme precipitation (return times of 100 days) especially in recent years but mainly in the winter half-year. This may reflect a tendency of central european climate characteristics towards less continentality as assumed by Beck et al. (2006). Acknowledgements The authors wish to thank all the colleagues from German Met Service (DWD) who contributed information, data or even graphs to this study. References Beck, C., J. Grieser and B. Rudolf (2005): A New Monthly Precipitation Climatology for the Global Land Areas for the Period 1951 to DWD, Klimastatusbericht KSB 2004, ISBN , ISSN , Beck, C., J. Grieser, M. Kottek, F. Rubel and B. Rudolf (2006): Characterizing Global Climate Change by means of Köppen Climate Classification. DWD, Klimastatusbericht 2005, Deutscher Wetterdienst, ISBN Grieser, J. and C. Beck (2003): Extremniederschläge in Deutschland Zufall oder Zeichen?, Klimastatusbericht 2002, Deutscher Wetterdienst, ISBN , Rudolf, B., H. Frank, J. Grieser, G. Müller-Westermeier, J. Rapp, W. Trampf (2006): Das Hochwasser in Südbayern im August 2005: Niederschlagsvorhersage, Warnung und klimatologische Bewertung des DWD. Hochwasserschutz und Katastrophenmanagement, Ernst&Sohn, accepted. Trenberth, K. (1999): Conceptual framework for changes of extremes of the hydrological cycle with climate change. Climatic Change 42, Trömel, S., C.-D. Schönwiese: A generalized method of time series decomposition into significant components including probability assessments of extreme events and application to observational German precipitation data. Meteorol. Z. 14, (2005).
European Flooding, Summer 2013
 European Flooding, Summer 2013 Fredrik ikwetterhall Florian Pappenberger, Clement Albergel, Lorenzo Alfieri, Gianpaolo Balsamo, Konrad Bogner, Thomas Haiden, Tim Hewson, Linus Magnusson, Patricia de Rosnay,
European Flooding, Summer 2013 Fredrik ikwetterhall Florian Pappenberger, Clement Albergel, Lorenzo Alfieri, Gianpaolo Balsamo, Konrad Bogner, Thomas Haiden, Tim Hewson, Linus Magnusson, Patricia de Rosnay,
L alluvione di Firenze del 1966 : an ensemble-based re-forecasting study
 from Newsletter Number 148 Summer 2016 METEOROLOGY L alluvione di Firenze del 1966 : an ensemble-based re-forecasting study Image from Mallivan/iStock/Thinkstock doi:10.21957/ nyvwteoz This article appeared
from Newsletter Number 148 Summer 2016 METEOROLOGY L alluvione di Firenze del 1966 : an ensemble-based re-forecasting study Image from Mallivan/iStock/Thinkstock doi:10.21957/ nyvwteoz This article appeared
Meteorological similarities and differences of the great European floods
 Meteorological similarities and differences of the great European floods Nataša Strelec Mahović DHMZ Meteorological and Hydrological Service, Croatia Europe floods 1998-2008 Areas most frequently affected
Meteorological similarities and differences of the great European floods Nataša Strelec Mahović DHMZ Meteorological and Hydrological Service, Croatia Europe floods 1998-2008 Areas most frequently affected
Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007
 Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007 National Meteorological Administration Romania 1. Summary of major highlights The medium range forecast activity within the National Meteorological
Application and verification of the ECMWF products Report 2007 National Meteorological Administration Romania 1. Summary of major highlights The medium range forecast activity within the National Meteorological
The observed global warming of the lower atmosphere
 WATER AND CLIMATE CHANGE: CHANGES IN THE WATER CYCLE 3.1 3.1.6 Variability of European precipitation within industrial time CHRISTIAN-D. SCHÖNWIESE, SILKE TRÖMEL & REINHARD JANOSCHITZ SUMMARY: Precipitation
WATER AND CLIMATE CHANGE: CHANGES IN THE WATER CYCLE 3.1 3.1.6 Variability of European precipitation within industrial time CHRISTIAN-D. SCHÖNWIESE, SILKE TRÖMEL & REINHARD JANOSCHITZ SUMMARY: Precipitation
A New Monthly Precipitation Climatology for the Global Land Areas for the Period 1951 to Ch. Beck, J. Grieser and Bruno Rudolf
 Klimastatusbericht 2004 DWD 181 A New Monthly Precipitation Climatology for the Global Land Areas for the Period 1951 to 2000 Ch. Beck, J. Grieser and Bruno Rudolf 1 INTRODUCTION Globally gridded precipitation-data
Klimastatusbericht 2004 DWD 181 A New Monthly Precipitation Climatology for the Global Land Areas for the Period 1951 to 2000 Ch. Beck, J. Grieser and Bruno Rudolf 1 INTRODUCTION Globally gridded precipitation-data
DETECTION AND FORECASTING - THE CZECH EXPERIENCE
 1 STORM RAINFALL DETECTION AND FORECASTING - THE CZECH EXPERIENCE J. Danhelka * Czech Hydrometeorological Institute, Prague, Czech Republic Abstract Contribution presents the state of the art of operational
1 STORM RAINFALL DETECTION AND FORECASTING - THE CZECH EXPERIENCE J. Danhelka * Czech Hydrometeorological Institute, Prague, Czech Republic Abstract Contribution presents the state of the art of operational
Haiti and Dominican Republic Flash Flood Initial Planning Meeting
 Dr Rochelle Graham Climate Scientist Haiti and Dominican Republic Flash Flood Initial Planning Meeting September 7 th to 9 th, 2016 Hydrologic Research Center http://www.hrcwater.org Haiti and Dominican
Dr Rochelle Graham Climate Scientist Haiti and Dominican Republic Flash Flood Initial Planning Meeting September 7 th to 9 th, 2016 Hydrologic Research Center http://www.hrcwater.org Haiti and Dominican
Name SOLUTIONS T.A./Section Atmospheric Science 101 Homework #6 Due Thursday, May 30 th (in class)
 Name SOLUTIONS T.A./Section Atmospheric Science 101 Homework #6 Due Thursday, May 30 th (in class) 1. General Circulation Briefly describe where each of the following features is found in the earth s general
Name SOLUTIONS T.A./Section Atmospheric Science 101 Homework #6 Due Thursday, May 30 th (in class) 1. General Circulation Briefly describe where each of the following features is found in the earth s general
Bias correction of global daily rain gauge measurements
 Bias correction of global daily rain gauge measurements M. Ungersböck 1,F.Rubel 1,T.Fuchs 2,andB.Rudolf 2 1 Working Group Biometeorology, University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna 2 Global Precipitation
Bias correction of global daily rain gauge measurements M. Ungersböck 1,F.Rubel 1,T.Fuchs 2,andB.Rudolf 2 1 Working Group Biometeorology, University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna 2 Global Precipitation
AROME Nowcasting - tool based on a convective scale operational system
 AROME Nowcasting - tool based on a convective scale operational system RC - LACE stay report Supervisors (ZAMG): Yong Wang Florian Meier Christoph Wittmann Author: Mirela Pietrisi (NMA) 1. Introduction
AROME Nowcasting - tool based on a convective scale operational system RC - LACE stay report Supervisors (ZAMG): Yong Wang Florian Meier Christoph Wittmann Author: Mirela Pietrisi (NMA) 1. Introduction
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2015
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2015 Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera, I.P. 1. Summary of major highlights At Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera (IPMA) ECMWF products are
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2015 Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera, I.P. 1. Summary of major highlights At Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera (IPMA) ECMWF products are
A High Resolution Daily Gridded Rainfall Data Set ( ) for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies
 National Climate Centre Research Report No: 9/2008 A High Resolution Daily Gridded Rainfall Data Set (1971-2005) for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies M. Rajeevan and Jyoti Bhate National Climate Centre
National Climate Centre Research Report No: 9/2008 A High Resolution Daily Gridded Rainfall Data Set (1971-2005) for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies M. Rajeevan and Jyoti Bhate National Climate Centre
Nerushev A.F., Barkhatov A.E. Research and Production Association "Typhoon" 4 Pobedy Street, , Obninsk, Kaluga Region, Russia.
 DETERMINATION OF ATMOSPHERIC CHARACTERISTICS IN THE ZONE OF ACTION OF EXTRA-TROPICAL CYCLONE XYNTHIA (FEBRUARY 2010) INFERRED FROM SATELLITE MEASUREMENT DATA Nerushev A.F., Barkhatov A.E. Research and
DETERMINATION OF ATMOSPHERIC CHARACTERISTICS IN THE ZONE OF ACTION OF EXTRA-TROPICAL CYCLONE XYNTHIA (FEBRUARY 2010) INFERRED FROM SATELLITE MEASUREMENT DATA Nerushev A.F., Barkhatov A.E. Research and
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts
 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, 2018 ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts Each question is worth 4 points. Indicate your BEST CHOICE for each question on the Scantron
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, 2018 ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts Each question is worth 4 points. Indicate your BEST CHOICE for each question on the Scantron
Rainfall Analysis in Mumbai using Gumbel s Extreme Value Distribution Model
 Rainfall Analysis in Mumbai using Gumbel s Extreme Value Distribution Model S. Sangita Mishra 1, M. Solapure 2, R. Satpathy 3, K. Phadtare 4, S. Pawar 5 1 Assistant Professor, 2,3,4,5 Undergraduate students
Rainfall Analysis in Mumbai using Gumbel s Extreme Value Distribution Model S. Sangita Mishra 1, M. Solapure 2, R. Satpathy 3, K. Phadtare 4, S. Pawar 5 1 Assistant Professor, 2,3,4,5 Undergraduate students
Global Precipitation Analysis Products of the GPCC
 Global Precipitation Analysis Products of the GPCC Introduction U. Schneider, T. Fuchs, A. Meyer-Christoffer, B. Rudolf Global Precipitation Climatology Centre (GPCC) Deutscher Wetterdienst, Offenbach
Global Precipitation Analysis Products of the GPCC Introduction U. Schneider, T. Fuchs, A. Meyer-Christoffer, B. Rudolf Global Precipitation Climatology Centre (GPCC) Deutscher Wetterdienst, Offenbach
Assessment of ERA-20C reanalysis monthly precipitation totals on the basis of GPCC in-situ measurements
 Assessment of ERA-20C reanalysis monthly precipitation totals on the basis of GPCC in-situ measurements Elke Rustemeier, Markus Ziese, Andreas Becker, Anja Meyer-Christoffer, Udo Schneider, and Peter Finger
Assessment of ERA-20C reanalysis monthly precipitation totals on the basis of GPCC in-situ measurements Elke Rustemeier, Markus Ziese, Andreas Becker, Anja Meyer-Christoffer, Udo Schneider, and Peter Finger
What makes it difficult to predict extreme climate events in the long time scales?
 What makes it difficult to predict extreme climate events in the long time scales? Monirul Mirza Department of Physical and Environmental Sciences University of Toronto at Scarborough Email: monirul.mirza@utoronto.ca
What makes it difficult to predict extreme climate events in the long time scales? Monirul Mirza Department of Physical and Environmental Sciences University of Toronto at Scarborough Email: monirul.mirza@utoronto.ca
Climate Classification Chapter 7
 Climate Classification Chapter 7 Climate Systems Earth is extremely diverse No two places exactly the same Similarities between places allow grouping into regions Climates influence ecosystems Why do we
Climate Classification Chapter 7 Climate Systems Earth is extremely diverse No two places exactly the same Similarities between places allow grouping into regions Climates influence ecosystems Why do we
Climate and tourism potential in Freiburg
 291 Climate and tourism potential in Freiburg Christina Endler, Andreas Matzatrakis Meteorological Institute, Albert-Ludwigs-University of Freiburg, Germany Abstract In our study, the modelled data, based
291 Climate and tourism potential in Freiburg Christina Endler, Andreas Matzatrakis Meteorological Institute, Albert-Ludwigs-University of Freiburg, Germany Abstract In our study, the modelled data, based
Description of the case study
 Description of the case study During the night and early morning of the 14 th of July 011 the significant cloud layer expanding in the West of the country and slowly moving East produced precipitation
Description of the case study During the night and early morning of the 14 th of July 011 the significant cloud layer expanding in the West of the country and slowly moving East produced precipitation
Winter and summer weather studies using high resolution radar data
 Winter and summer weather studies using high resolution radar data Tim Böhme 1 1 Deutscher Wetterdienst, Frankfurter Str. 135, 63067 Offenbach am Main, Germany (Dated: 29 August 2014) Tim Böhme 1. Introduction
Winter and summer weather studies using high resolution radar data Tim Böhme 1 1 Deutscher Wetterdienst, Frankfurter Str. 135, 63067 Offenbach am Main, Germany (Dated: 29 August 2014) Tim Böhme 1. Introduction
INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS, NW GREECE), ON PRECIPITATION, DURING THE WARM PERIOD OF THE YEAR
 Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference of Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS,
Proceedings of the 13 th International Conference of Environmental Science and Technology Athens, Greece, 5-7 September 2013 INVESTIGATION FOR A POSSIBLE INFLUENCE OF IOANNINA AND METSOVO LAKES (EPIRUS,
Rainfall analysis for Indian monsoon region using the merged rain gauge observations and satellite estimates: Evaluation of monsoon rainfall features
 Rainfall analysis for Indian monsoon region using the merged rain gauge observations and satellite estimates: Evaluation of monsoon rainfall features SKRoyBhowmikand Ananda K Das India Meteorological Department,
Rainfall analysis for Indian monsoon region using the merged rain gauge observations and satellite estimates: Evaluation of monsoon rainfall features SKRoyBhowmikand Ananda K Das India Meteorological Department,
Atmospheric patterns for heavy rain events in the Balearic Islands
 Adv. Geosci., 12, 27 32, 2007 Author(s) 2007. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Advances in Geosciences Atmospheric patterns for heavy rain events in the Balearic Islands A. Lana,
Adv. Geosci., 12, 27 32, 2007 Author(s) 2007. This work is licensed under a Creative Commons License. Advances in Geosciences Atmospheric patterns for heavy rain events in the Balearic Islands A. Lana,
Torrential events on the Spanish Mediterranean coast (Valencian Region). Spatial precipitation patterns and their relation to synoptic circulation
 Torrential events on the Spanish Mediterranean coast (Valencian Region). Spatial precipitation patterns and their relation to synoptic circulation M. ESTRELA, D. PEÑARROCHA, F. PASTOR & M. MILLAN Fundación
Torrential events on the Spanish Mediterranean coast (Valencian Region). Spatial precipitation patterns and their relation to synoptic circulation M. ESTRELA, D. PEÑARROCHA, F. PASTOR & M. MILLAN Fundación
Use of climate reanalysis for EEA climate change assessment. Blaz Kurnik. European Environment Agency (EEA)
 Use of climate reanalysis for EEA climate change assessment Blaz Kurnik European Environment Agency (EEA) 2016: EEA content priorities Circular economy Climate and Energy Sustainable Development Goals
Use of climate reanalysis for EEA climate change assessment Blaz Kurnik European Environment Agency (EEA) 2016: EEA content priorities Circular economy Climate and Energy Sustainable Development Goals
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Weather Patterns and Severe Weather Foundations, 6e - Chapter 14 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Air masses Characteristics Large body
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Weather Patterns and Severe Weather Foundations, 6e - Chapter 14 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Air masses Characteristics Large body
MSG FOR NOWCASTING - EXPERIENCES OVER SOUTHERN AFRICA
 MSG FOR NOWCASTING - EXPERIENCES OVER SOUTHERN AFRICA Estelle de Coning and Marianne König South African Weather Service, Private Bag X097, Pretoria 0001, South Africa EUMETSAT, Am Kavalleriesand 31, D-64295
MSG FOR NOWCASTING - EXPERIENCES OVER SOUTHERN AFRICA Estelle de Coning and Marianne König South African Weather Service, Private Bag X097, Pretoria 0001, South Africa EUMETSAT, Am Kavalleriesand 31, D-64295
QualiMET 2.0. The new Quality Control System of Deutscher Wetterdienst
 QualiMET 2.0 The new Quality Control System of Deutscher Wetterdienst Reinhard Spengler Deutscher Wetterdienst Department Observing Networks and Data Quality Assurance of Meteorological Data Michendorfer
QualiMET 2.0 The new Quality Control System of Deutscher Wetterdienst Reinhard Spengler Deutscher Wetterdienst Department Observing Networks and Data Quality Assurance of Meteorological Data Michendorfer
Figure 1: Tephigram for radiosonde launched from Bath at 1100 UTC on 15 June 2005 (IOP 1). The CAPE and CIN are shaded dark and light gray,
 Figure 1: Tephigram for radiosonde launched from Bath at 1100 UTC on 1 June 200 (IOP 1). The CAPE and CIN are shaded dark and light gray, respectively; the thin solid line partially bounding these areas
Figure 1: Tephigram for radiosonde launched from Bath at 1100 UTC on 1 June 200 (IOP 1). The CAPE and CIN are shaded dark and light gray, respectively; the thin solid line partially bounding these areas
Measures Also Significant Factors of Flood Disaster Reduction
 Non-Structual Measures Also Significant Factors of Flood Disaster Reduction Babiaková Gabriela, Leškov ková Danica Slovak Hydrometeorological Institute, Bratislava Hydrological Forecasts and Warning Department
Non-Structual Measures Also Significant Factors of Flood Disaster Reduction Babiaková Gabriela, Leškov ková Danica Slovak Hydrometeorological Institute, Bratislava Hydrological Forecasts and Warning Department
Climate Change and Runoff Statistics in the Rhine Basin: A Process Study with a Coupled Climate-Runoff Model
 IACETH Climate Change and Runoff Statistics in the Rhine Basin: A Process Study with a Coupled Climate-Runoff Model Jan KLEINN, Christoph Frei, Joachim Gurtz, Pier Luigi Vidale, and Christoph Schär Institute
IACETH Climate Change and Runoff Statistics in the Rhine Basin: A Process Study with a Coupled Climate-Runoff Model Jan KLEINN, Christoph Frei, Joachim Gurtz, Pier Luigi Vidale, and Christoph Schär Institute
Precipitation processes in the Middle East
 Precipitation processes in the Middle East J. Evans a, R. Smith a and R.Oglesby b a Dept. Geology & Geophysics, Yale University, Connecticut, USA. b Global Hydrology and Climate Center, NASA, Alabama,
Precipitation processes in the Middle East J. Evans a, R. Smith a and R.Oglesby b a Dept. Geology & Geophysics, Yale University, Connecticut, USA. b Global Hydrology and Climate Center, NASA, Alabama,
Characterizing Global Climate Change by means of Köppen Climate Classification. C. Beck, J. Grieser, M. Kottek, F. Rubel, B.
 Klimastatusbericht 2005 DWD 139 Characterizing Global Climate Change by means of Köppen Climate Classification C. Beck, J. Grieser, M. Kottek, F. Rubel, B. Rudolf INTRODUCTION Global climate classifications
Klimastatusbericht 2005 DWD 139 Characterizing Global Climate Change by means of Köppen Climate Classification C. Beck, J. Grieser, M. Kottek, F. Rubel, B. Rudolf INTRODUCTION Global climate classifications
Romanian Contribution in Quantitative Precipitation Forecasts Project
 3 Working Group on Physical Aspects 29 Romanian Contribution in Quantitative Precipitation Forecasts Project Rodica Dumitrache, Victor Pescaru, Liliana Velea, Cosmin Barbu National Meteorological Administration,
3 Working Group on Physical Aspects 29 Romanian Contribution in Quantitative Precipitation Forecasts Project Rodica Dumitrache, Victor Pescaru, Liliana Velea, Cosmin Barbu National Meteorological Administration,
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016 RHMS of Serbia 1 Summary of major highlights ECMWF forecast products became the backbone in operational work during last several years. Starting from
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2016 RHMS of Serbia 1 Summary of major highlights ECMWF forecast products became the backbone in operational work during last several years. Starting from
Chapter outline. Reference 12/13/2016
 Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
25.1 Air Masses. Section 25.1 Objectives
 Section 25.1 Objectives Explain how an air mass forms. List the four main types of air masses. Describe how air masses affect the weather of North America. Air Masses 25.1 Air Masses Differences in air
Section 25.1 Objectives Explain how an air mass forms. List the four main types of air masses. Describe how air masses affect the weather of North America. Air Masses 25.1 Air Masses Differences in air
Heavier summer downpours with climate change revealed by weather forecast resolution model
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2258 Heavier summer downpours with climate change revealed by weather forecast resolution model Number of files = 1 File #1 filename: kendon14supp.pdf File
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2258 Heavier summer downpours with climate change revealed by weather forecast resolution model Number of files = 1 File #1 filename: kendon14supp.pdf File
Calibrating forecasts of heavy precipitation in river catchments
 from Newsletter Number 152 Summer 217 METEOROLOGY Calibrating forecasts of heavy precipitation in river catchments Hurricane Patricia off the coast of Mexico on 23 October 215 ( 215 EUMETSAT) doi:1.21957/cf1598
from Newsletter Number 152 Summer 217 METEOROLOGY Calibrating forecasts of heavy precipitation in river catchments Hurricane Patricia off the coast of Mexico on 23 October 215 ( 215 EUMETSAT) doi:1.21957/cf1598
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox
 Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
Charles A. Doswell III, Harold E. Brooks, and Robert A. Maddox Flash floods account for the greatest number of fatalities among convective storm-related events but it still remains difficult to forecast
The Australian Operational Daily Rain Gauge Analysis
 The Australian Operational Daily Rain Gauge Analysis Beth Ebert and Gary Weymouth Bureau of Meteorology Research Centre, Melbourne, Australia e.ebert@bom.gov.au Daily rainfall data and analysis procedure
The Australian Operational Daily Rain Gauge Analysis Beth Ebert and Gary Weymouth Bureau of Meteorology Research Centre, Melbourne, Australia e.ebert@bom.gov.au Daily rainfall data and analysis procedure
C o p e r n i c u s E m e r g e n c y M a n a g e m e n t S e r v i c e f o r e c a s t i n g f l o o d s
 C o p e r n i c u s E m e r g e n c y M a n a g e m e n t S e r v i c e f o r e c a s t i n g f l o o d s Copernicus & Copernicus Services Copernicus EU Copernicus EU Copernicus EU www.copernicus.eu W
C o p e r n i c u s E m e r g e n c y M a n a g e m e n t S e r v i c e f o r e c a s t i n g f l o o d s Copernicus & Copernicus Services Copernicus EU Copernicus EU Copernicus EU www.copernicus.eu W
The Contribution Of Fine Scale Atmospheric Numerical Models In Improving The Quality Of Hydraulic Modelling Outputs
 City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works International Conference on Hydroinformatics 8-1-2014 The Contribution Of Fine Scale Atmospheric Numerical Models In Improving The Quality Of Hydraulic
City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works International Conference on Hydroinformatics 8-1-2014 The Contribution Of Fine Scale Atmospheric Numerical Models In Improving The Quality Of Hydraulic
Observed rainfall trends and precipitation uncertainty in the vicinity of the Mediterranean, Middle East and North Africa
 SCIENTIFIC WORKSHOP 16-17 ΜΑΥ 2018 Nicosia, Cyprus Observed rainfall trends and precipitation uncertainty in the vicinity of the Mediterranean, Middle East and North Africa George Zittis, Associate Research
SCIENTIFIC WORKSHOP 16-17 ΜΑΥ 2018 Nicosia, Cyprus Observed rainfall trends and precipitation uncertainty in the vicinity of the Mediterranean, Middle East and North Africa George Zittis, Associate Research
Evaluating extreme flood characteristics of small mountainous basins of the Black Sea coastal area, Northern Caucasus
 Proc. IAHS, 7, 161 165, 215 proc-iahs.net/7/161/215/ doi:1.5194/piahs-7-161-215 Author(s) 215. CC Attribution. License. Evaluating extreme flood characteristics of small mountainous basins of the Black
Proc. IAHS, 7, 161 165, 215 proc-iahs.net/7/161/215/ doi:1.5194/piahs-7-161-215 Author(s) 215. CC Attribution. License. Evaluating extreme flood characteristics of small mountainous basins of the Black
A SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN ROMANIA DUE TO MEDITERRANEAN CYCLONIC ACTIVITY
 A SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN ROMANIA DUE TO MEDITERRANEAN CYCLONIC ACTIVITY Florinela Georgescu, Gabriela Bancila, Viorica Dima National Meteorological Administration, Bucharest, Romania Abstract Mediterranean
A SEVERE WEATHER EVENT IN ROMANIA DUE TO MEDITERRANEAN CYCLONIC ACTIVITY Florinela Georgescu, Gabriela Bancila, Viorica Dima National Meteorological Administration, Bucharest, Romania Abstract Mediterranean
COUPLING A DISTRIBUTED HYDROLOGICAL MODEL TO REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL OUTPUT: AN EVALUATION OF EXPERIMENTS FOR THE RHINE BASIN IN EUROPE
 P.1 COUPLING A DISTRIBUTED HYDROLOGICAL MODEL TO REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL OUTPUT: AN EVALUATION OF EXPERIMENTS FOR THE RHINE BASIN IN EUROPE Jan Kleinn*, Christoph Frei, Joachim Gurtz, Pier Luigi Vidale,
P.1 COUPLING A DISTRIBUTED HYDROLOGICAL MODEL TO REGIONAL CLIMATE MODEL OUTPUT: AN EVALUATION OF EXPERIMENTS FOR THE RHINE BASIN IN EUROPE Jan Kleinn*, Christoph Frei, Joachim Gurtz, Pier Luigi Vidale,
RR#5 - Free Response
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the data table below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. The table shows the area, in million square kilometers, of the Arctic Ocean covered by ice from
Base your answers to questions 1 through 3 on the data table below and on your knowledge of Earth Science. The table shows the area, in million square kilometers, of the Arctic Ocean covered by ice from
CLIMATE. UNIT TWO March 2019
 CLIMATE UNIT TWO March 2019 OUTCOME 9.2.1Demonstrate an understanding of the basic features of Canada s landscape and climate. identify and locate major climatic regions of Canada explain the characteristics
CLIMATE UNIT TWO March 2019 OUTCOME 9.2.1Demonstrate an understanding of the basic features of Canada s landscape and climate. identify and locate major climatic regions of Canada explain the characteristics
Regional Climate Centre Network (RCC) in RA VI as a GFCS contribution
 Regional Climate Centre Network (RCC) in RA VI as a GFCS contribution Stefan Rösner and Peter Bissolli Deutscher Wetterdienst (German Meteorological Service) Dep. Climate Monitoring, Offenbach, Germany
Regional Climate Centre Network (RCC) in RA VI as a GFCS contribution Stefan Rösner and Peter Bissolli Deutscher Wetterdienst (German Meteorological Service) Dep. Climate Monitoring, Offenbach, Germany
Severe weather. Some case studies for medium-range forecasting. T. La Rocca, Department of Synoptic Meteorology, Italian Met. Service, Rome.
 Severe weather. Some case studies for medium-range forecasting T. La Rocca, Department of Synoptic Meteorology, Italian Met. Service, Rome. The Met Alert Messages by the Watch Office of the Public Safety
Severe weather. Some case studies for medium-range forecasting T. La Rocca, Department of Synoptic Meteorology, Italian Met. Service, Rome. The Met Alert Messages by the Watch Office of the Public Safety
ALARO experience in Romania
 ALARO experience in Romania S. Briceag, M. Pietrisi, S. Tascu, A. Craciun, R. Iordache National Meteorological Administration, Romania Operational model setup ALARO cy36t1: 1 January 2014 31 March 2016
ALARO experience in Romania S. Briceag, M. Pietrisi, S. Tascu, A. Craciun, R. Iordache National Meteorological Administration, Romania Operational model setup ALARO cy36t1: 1 January 2014 31 March 2016
Verification of the Seasonal Forecast for the 2005/06 Winter
 Verification of the Seasonal Forecast for the 2005/06 Winter Shingo Yamada Tokyo Climate Center Japan Meteorological Agency 2006/11/02 7 th Joint Meeting on EAWM Contents 1. Verification of the Seasonal
Verification of the Seasonal Forecast for the 2005/06 Winter Shingo Yamada Tokyo Climate Center Japan Meteorological Agency 2006/11/02 7 th Joint Meeting on EAWM Contents 1. Verification of the Seasonal
Name of research institute or organization: Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss
 Name of research institute or organization: Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Title of project: The weather in 2016 Report by: Stephan Bader, Climate Division MeteoSwiss English
Name of research institute or organization: Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology MeteoSwiss Title of project: The weather in 2016 Report by: Stephan Bader, Climate Division MeteoSwiss English
Covered Area Rainfall Event (18-20 October 2017) Excess Rainfall
 Covered Area Rainfall Event (18-20 October 2017) Excess Rainfall Event Briefing Trinidad 29 October 2017 Registered Office: CCRIF SPC c/o Sagicor Insurance Managers Ltd., 198 North Church Street 2nd Floor
Covered Area Rainfall Event (18-20 October 2017) Excess Rainfall Event Briefing Trinidad 29 October 2017 Registered Office: CCRIF SPC c/o Sagicor Insurance Managers Ltd., 198 North Church Street 2nd Floor
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather
 Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Science 1206 Chapter 1 - Inquiring about Weather 1.1 - The Atmosphere: Energy Transfer and Properties (pp. 10-25) Weather and the Atmosphere weather the physical conditions of the atmosphere at a specific
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011 National Meteorological Administration 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts are primarily based on the results of ECMWF and
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2011 National Meteorological Administration 1. Summary of major highlights Medium range weather forecasts are primarily based on the results of ECMWF and
Meteorology. Chapter 15 Worksheet 1
 Chapter 15 Worksheet 1 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) The Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle are examples of locations determined by: a) measuring systems.
Chapter 15 Worksheet 1 Meteorology Name: Circle the letter that corresponds to the correct answer 1) The Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle are examples of locations determined by: a) measuring systems.
Visualising and communicating probabilistic flow forecasts in The Netherlands
 Visualising and communicating probabilistic flow forecasts in The Netherlands Eric Sprokkereef Centre for Water Management Division Crisis Management & Information Supply 2-2-2009 Content The basins Forecasting
Visualising and communicating probabilistic flow forecasts in The Netherlands Eric Sprokkereef Centre for Water Management Division Crisis Management & Information Supply 2-2-2009 Content The basins Forecasting
August 2005 intense rainfall event in Switzerland: Not necessarily an analog for strong convective events in a greenhouse climate
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L05701, doi:10.1029/2005gl025573, 2006 August 2005 intense rainfall event in Switzerland: Not necessarily an analog for strong convective events in a greenhouse climate
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L05701, doi:10.1029/2005gl025573, 2006 August 2005 intense rainfall event in Switzerland: Not necessarily an analog for strong convective events in a greenhouse climate
Global Challenges - Partnering with Service Providers. World Meteorological Organization. J. Lengoasa WMO Deputy Secretary-General
 WMO World Meteorological Organization Working together in weather, climate and water Global Challenges - Partnering with Service Providers J. Lengoasa WMO Deputy Secretary-General jlengoasa@wmo.int http://www.wmo.int/pages/gfcs/gfcs_en.html
WMO World Meteorological Organization Working together in weather, climate and water Global Challenges - Partnering with Service Providers J. Lengoasa WMO Deputy Secretary-General jlengoasa@wmo.int http://www.wmo.int/pages/gfcs/gfcs_en.html
A Synoptic Climatology of Heavy Precipitation Events in California
 A Synoptic Climatology of Heavy Precipitation Events in California Alan Haynes Hydrometeorological Analysis and Support (HAS) Forecaster National Weather Service California-Nevada River Forecast Center
A Synoptic Climatology of Heavy Precipitation Events in California Alan Haynes Hydrometeorological Analysis and Support (HAS) Forecaster National Weather Service California-Nevada River Forecast Center
Our climate system is based on the location of hot and cold air mass regions and the atmospheric circulation created by trade winds and westerlies.
 CLIMATE REGIONS Have you ever wondered why one area of the world is a desert, another a grassland, and another a rainforest? Or have you wondered why are there different types of forests and deserts with
CLIMATE REGIONS Have you ever wondered why one area of the world is a desert, another a grassland, and another a rainforest? Or have you wondered why are there different types of forests and deserts with
III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms
 III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxwbr60tflg&feature=relmfu A. Thunderstorms form from rising moist air Electrical charges build up near the tops
III. Section 3.3 Vertical air motion can cause severe storms http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nxwbr60tflg&feature=relmfu A. Thunderstorms form from rising moist air Electrical charges build up near the tops
A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS:
 2.6 A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS: 2000-2007 James V. Rudolph*, K. Friedrich, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Colorado at Boulder,
2.6 A RADAR-BASED CLIMATOLOGY OF HIGH PRECIPITATION EVENTS IN THE EUROPEAN ALPS: 2000-2007 James V. Rudolph*, K. Friedrich, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, University of Colorado at Boulder,
Judit Kerényi. OMSZ - Hungarian Meteorological Service, Budapest, Hungary. H-1525 Budapest, P.O.Box 38, Hungary.
 SATELLITE-DERIVED PRECIPITATION ESTIMATIONS DEVELOPED BY THE HYDROLOGY SAF PROJECT CASE STUDIES FOR THE INVESTIGATION OF THEIR ACCURACY AND FEATURES IN HUNGARY Judit Kerényi OMSZ - Hungarian Meteorological
SATELLITE-DERIVED PRECIPITATION ESTIMATIONS DEVELOPED BY THE HYDROLOGY SAF PROJECT CASE STUDIES FOR THE INVESTIGATION OF THEIR ACCURACY AND FEATURES IN HUNGARY Judit Kerényi OMSZ - Hungarian Meteorological
Severe storms over the Mediterranean Sea: A satellite and model analysis
 National Research Council of Italy Severe storms over the Mediterranean Sea: A satellite and model analysis V. Levizzani, S. Laviola, A. Malvaldi, M. M. Miglietta, and E. Cattani 6 th International Precipitation
National Research Council of Italy Severe storms over the Mediterranean Sea: A satellite and model analysis V. Levizzani, S. Laviola, A. Malvaldi, M. M. Miglietta, and E. Cattani 6 th International Precipitation
Climate Change or Climate Variability?
 Climate Change or Climate Variability? Key Concepts: Greenhouse Gas Climate Climate change Climate variability Climate zones Precipitation Temperature Water cycle Weather WHAT YOU WILL LEARN 1. You will
Climate Change or Climate Variability? Key Concepts: Greenhouse Gas Climate Climate change Climate variability Climate zones Precipitation Temperature Water cycle Weather WHAT YOU WILL LEARN 1. You will
DOWNLOAD PDF SCENERY OF SWITZERLAND, AND THE CAUSES TO WHICH IT IS DUE.
 Chapter 1 : The Scenery of Switzerland (Sir John Lubbock - ) (ID) ebay The scenery of Switzerland and the causes to which it is due / Related Titles Series: Collection of British authors ; vol. These diseases
Chapter 1 : The Scenery of Switzerland (Sir John Lubbock - ) (ID) ebay The scenery of Switzerland and the causes to which it is due / Related Titles Series: Collection of British authors ; vol. These diseases
The Ihtiman Flood Event in Bulgaria, Ilian Gospodinov
 The Ihtiman Flood Event in Bulgaria, 04-07.08.2005 Ilian Gospodinov Introduction The Ihtiman flood event in Bulgaria in the beginning of August 2005 provoked an outrage of polemics concerning the weather
The Ihtiman Flood Event in Bulgaria, 04-07.08.2005 Ilian Gospodinov Introduction The Ihtiman flood event in Bulgaria in the beginning of August 2005 provoked an outrage of polemics concerning the weather
The Global Scope of Climate. The Global Scope of Climate. Keys to Climate. Chapter 8
 The Global Scope of Climate Chapter 8 The Global Scope of Climate In its most general sense, climate is the average weather of a region, but except where conditions change very little during the course
The Global Scope of Climate Chapter 8 The Global Scope of Climate In its most general sense, climate is the average weather of a region, but except where conditions change very little during the course
Severe Freezing Rain in Slovenia
 Severe Freezing Rain in Slovenia Janez Markosek, Environmental Agency, Slovenia Introduction At the end of January and at the beginning of February 2014, severe and long-lasting freezing rain affected
Severe Freezing Rain in Slovenia Janez Markosek, Environmental Agency, Slovenia Introduction At the end of January and at the beginning of February 2014, severe and long-lasting freezing rain affected
Climate change and natural disasters, Athens, Greece October 31, 2018
 Flood early warning systems: operational approaches and challenges Climate change and natural disasters, Athens, Greece October 31, 2018 Athens, October 31, 2018 Marco Borga University of Padova, Italy
Flood early warning systems: operational approaches and challenges Climate change and natural disasters, Athens, Greece October 31, 2018 Athens, October 31, 2018 Marco Borga University of Padova, Italy
The Model SNOW 4. A Tool to Operationally Estimate Precipitation Supply
 The Model SNOW 4 A Tool to Operationally Estimate Precipitation Supply Uwe BöhmB hm,, Thomas Reich, Gerold Schneider Deutscher Wetterdienst, Dep. Hydrometeorology, Germany Conceptual Design of SNOW 4 Conceptual
The Model SNOW 4 A Tool to Operationally Estimate Precipitation Supply Uwe BöhmB hm,, Thomas Reich, Gerold Schneider Deutscher Wetterdienst, Dep. Hydrometeorology, Germany Conceptual Design of SNOW 4 Conceptual
Diabatic processes and the structure of the warm conveyor belt
 2 nd European Windstorm Workshop Leeds, 3-4 September 2012 Diabatic processes and the structure of the warm conveyor belt Oscar Martínez-Alvarado J. Chagnon, S. Gray, R. Plant, J. Methven Department of
2 nd European Windstorm Workshop Leeds, 3-4 September 2012 Diabatic processes and the structure of the warm conveyor belt Oscar Martínez-Alvarado J. Chagnon, S. Gray, R. Plant, J. Methven Department of
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION There is now unequivocal evidence from direct observations of a warming of the climate system (IPCC, 2007). Despite remaining uncertainties, it is now clear that the upward trend
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION There is now unequivocal evidence from direct observations of a warming of the climate system (IPCC, 2007). Despite remaining uncertainties, it is now clear that the upward trend
Development and applications of regional reanalyses for Europe and Germany based on DWD s NWP models: Status and outlook
 Development and applications of regional reanalyses for Europe and Germany based on DWD s NWP models: Status and outlook Frank Kaspar 1, Michael Borsche 1, Natacha Fery 1, Andrea K. Kaiser-Weiss 1, Jan
Development and applications of regional reanalyses for Europe and Germany based on DWD s NWP models: Status and outlook Frank Kaspar 1, Michael Borsche 1, Natacha Fery 1, Andrea K. Kaiser-Weiss 1, Jan
Lecture 5: Precipitation
 Lecture 5: Precipitation Key Questions 1. What physical concepts control the formation of precipitation (air pressure, expanding gases and cooling, and vapor pressure)? 2. What are some air mass lifting
Lecture 5: Precipitation Key Questions 1. What physical concepts control the formation of precipitation (air pressure, expanding gases and cooling, and vapor pressure)? 2. What are some air mass lifting
1 What Is Climate? TAKE A LOOK 2. Explain Why do areas near the equator tend to have high temperatures?
 CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
CHAPTER 17 1 What Is Climate? SECTION Climate BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is climate? What factors affect climate? How do climates differ
2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW
 2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW 1 INTRODUCTION Recently, three of the major centres for global climate monitoring determined with high confidence that 2015 was the warmest year on record, globally.
2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW 1 INTRODUCTION Recently, three of the major centres for global climate monitoring determined with high confidence that 2015 was the warmest year on record, globally.
Unseasonable weather conditions in Japan in August 2014
 Unseasonable weather conditions in Japan in August 2014 Summary of analysis by the TCC Advisory Panel on Extreme Climatic Events In an extraordinary session held at the Japan Meteorological Agency on 3
Unseasonable weather conditions in Japan in August 2014 Summary of analysis by the TCC Advisory Panel on Extreme Climatic Events In an extraordinary session held at the Japan Meteorological Agency on 3
MODELING PRECIPITATION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN IN ICELAND
 MODELING PRECIPITATION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN IN ICELAND Philippe Crochet 1, Tómas Jóhannesson 1, Oddur Sigurðsson 2, Helgi Björnsson 3 and Finnur Pálsson 3 1 Icelandic Meteorological Office, Bústadavegur
MODELING PRECIPITATION OVER COMPLEX TERRAIN IN ICELAND Philippe Crochet 1, Tómas Jóhannesson 1, Oddur Sigurðsson 2, Helgi Björnsson 3 and Finnur Pálsson 3 1 Icelandic Meteorological Office, Bústadavegur
Mesoscale and High Impact Weather in the South American Monsoon Leila M. V. Carvalho 1 and Maria A. F. Silva Dias 2 1
 Mesoscale and High Impact Weather in the South American Monsoon Leila M. V. Carvalho 1 and Maria A. F. Silva Dias 2 1 University of California, Santa Barbara 2 University of Sao Paulo, Brazil Objectives
Mesoscale and High Impact Weather in the South American Monsoon Leila M. V. Carvalho 1 and Maria A. F. Silva Dias 2 1 University of California, Santa Barbara 2 University of Sao Paulo, Brazil Objectives
p = ρrt p = ρr d = T( q v ) dp dz = ρg
 Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Dust Storm: An Extreme Climate Event in China
 Dust Storm: An Extreme Climate Event in China ZHENG Guoguang China Meteorological Administration Beijing, China, 100081 zgg@cma.gov.cn CONTENTS 1. Climatology of dust storms in China 2. Long-term variation
Dust Storm: An Extreme Climate Event in China ZHENG Guoguang China Meteorological Administration Beijing, China, 100081 zgg@cma.gov.cn CONTENTS 1. Climatology of dust storms in China 2. Long-term variation
Mediterranean Climates (Csa, Csb)
 Climatic Zones & Types Part II I've lived in good climate, and it bores the hell out of me. I like weather rather than climate. 1 John Steinbeck Mediterranean Climates (Csa, Csb) Main locations Western
Climatic Zones & Types Part II I've lived in good climate, and it bores the hell out of me. I like weather rather than climate. 1 John Steinbeck Mediterranean Climates (Csa, Csb) Main locations Western
1990 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Impacts Assessment
 1990 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Impacts Assessment Although the variability of weather and associated shifts in the frequency and magnitude of climate events were not available from the
1990 Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Impacts Assessment Although the variability of weather and associated shifts in the frequency and magnitude of climate events were not available from the
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2012
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2012 Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera, I.P. (IPMA) 1. Summary of major highlights ECMWF products are used as the main source of data for operational
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2012 Instituto Português do Mar e da Atmosfera, I.P. (IPMA) 1. Summary of major highlights ECMWF products are used as the main source of data for operational
Climate of Columbus. Aaron Wilson. Byrd Polar & Climate Research Center State Climate Office of Ohio.
 Climate of Columbus Aaron Wilson Byrd Polar & Climate Research Center http://bpcrc.osu.edu/greenteam Overview Historical Climatology Climate Change & Impacts Projected Changes Summary 2 Historical Climatology
Climate of Columbus Aaron Wilson Byrd Polar & Climate Research Center http://bpcrc.osu.edu/greenteam Overview Historical Climatology Climate Change & Impacts Projected Changes Summary 2 Historical Climatology
SPECIAL PROJECT FINAL REPORT
 SPECIAL PROJECT FINAL REPORT All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Project Title: The role of soil moisture and surface- and subsurface water flows on predictability of convection
SPECIAL PROJECT FINAL REPORT All the following mandatory information needs to be provided. Project Title: The role of soil moisture and surface- and subsurface water flows on predictability of convection
FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic areas for Risk mitigation in the Alpine space
 Natural Risk Management in a changing climate: Experiences in Adaptation Strategies from some European Projekts Milano - December 14 th, 2011 FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic
Natural Risk Management in a changing climate: Experiences in Adaptation Strategies from some European Projekts Milano - December 14 th, 2011 FLORA: FLood estimation and forecast in complex Orographic
What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology.
 What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology. Climatology is the study of Earth s climate and the factors that affect past, present, and future climatic
What is Climate? Understanding and predicting climatic changes are the basic goals of climatology. Climatology is the study of Earth s climate and the factors that affect past, present, and future climatic
Extremes Events in Climate Change Projections Jana Sillmann
 Extremes Events in Climate Change Projections Jana Sillmann Max Planck Institute for Meteorology International Max Planck Research School on Earth System Modeling Temperature distribution IPCC (2001) Outline
Extremes Events in Climate Change Projections Jana Sillmann Max Planck Institute for Meteorology International Max Planck Research School on Earth System Modeling Temperature distribution IPCC (2001) Outline
USE OF SATELLITE INFORMATION IN THE HUNGARIAN NOWCASTING SYSTEM
 USE OF SATELLITE INFORMATION IN THE HUNGARIAN NOWCASTING SYSTEM Mária Putsay, Zsófia Kocsis and Ildikó Szenyán Hungarian Meteorological Service, Kitaibel Pál u. 1, H-1024, Budapest, Hungary Abstract The
USE OF SATELLITE INFORMATION IN THE HUNGARIAN NOWCASTING SYSTEM Mária Putsay, Zsófia Kocsis and Ildikó Szenyán Hungarian Meteorological Service, Kitaibel Pál u. 1, H-1024, Budapest, Hungary Abstract The
Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses
 Lab 9 Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses This lab will introduce students to the patterns of surface winds around the center of a midlatitude cyclone of low pressure. The types of weather associated with
Lab 9 Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses This lab will introduce students to the patterns of surface winds around the center of a midlatitude cyclone of low pressure. The types of weather associated with
Water Balance in the Murray-Darling Basin and the recent drought as modelled with WRF
 18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 2009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 Water Balance in the Murray-Darling Basin and the recent drought as modelled with WRF Evans, J.P. Climate
18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 2009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 Water Balance in the Murray-Darling Basin and the recent drought as modelled with WRF Evans, J.P. Climate
Module 11: Meteorology Topic 5 Content: Weather Maps Notes
 Introduction A variety of weather maps are produced by the National Weather Service and National Oceanographic Atmospheric Administration. These maps are used to help meteorologists accurately predict
Introduction A variety of weather maps are produced by the National Weather Service and National Oceanographic Atmospheric Administration. These maps are used to help meteorologists accurately predict
