Seasonal associations between mid-tropospheric height patterns and precipitation in the western Great Basin, USA
|
|
|
- Cathleen Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Seasonal associations between mid-tropospheric height patterns and precipitation in the western Great Basin, USA By: Paul A. Knapp Knapp, P.A. (1994) Seasonal associations between mid-tropospheric pressure patterns and precipitation in the western Great Basin. Climate Research 4: Made available courtesy of Inter Research: ***Reprinted with permission. No further reproduction is authorized without written permission from Inter Research. This version of the document is not the version of record. Figures and/or pictures may be missing from this format of the document.*** Abstract: Associations between seasonal 700 mb height data and precipitation data in the western Great Basin, USA, are examined from 1947 through 1991 using bivariate regression. Results show that approximately one-third of precipitation variability in the study region is associated with changes in 700 mb heights during the autumn, winter, and spring months, but Little associated variance occurs during summer. When only wet seasons are examined (Z scores > 0.5), correlations increase substantially. However, dry season (Z scores <-0.5) data correlations had little interpretive value. Key Words: Great Basin 700 mb, Precipitation, Acid environments Article: Seasonal precipitation fluctuations in arid environments often are a topic of concern because precipitation variability influences stream runoff, agricultural productivity, and municipal planning. In the western Great Basin, USA, moderate deviations from 30 yr averages may cause severe flooding and dust storms, and they can adversely affect agriculture. Invariably, the consequences of either unusually wet or dry seasons heighten the discussion of what has caused the variability. One way to understand certain aspects of precipitation variability is to look at associations between 700 mb height data and precipitation. Studies have shown that 700 mb height data are best for predicting precipitation in mid-latitude locations (Houghton 1969, Cayan & Roads 1984, Klein & Bloom 1987, Leathers 1991). In general (summer excluded), 700 mb heights are correlated negatively with precipitation amounts, but this relationship is affected by the placement of ridges and troughs associated with meridional flow (Harman 1991). Areas under ridges are typically associated with dry conditions (e.g. Namias 1978), while areas affected by troughing may experience either wet or dry conditions depending on the exact placement of the trough axis (e.g. Yarnal & Leathers 1988). Variability in the latter case arises because the east side of the mean trough is a zone of frequent positive vorticity advection that favors precipitation, while the west side of the trough is a zone of frequent negative vorticity advection that suppresses precipitation events (Harman 1991). The objective of this paper is to examine seasonal associations between mid-tropospheric pressure heights and precipitation in the western Great Basin for a 45 yr period (1947 to 1991). Because interannual precipitation variability prevails within the study area, synoptic controls influencing wet and dry seasons are analyzed. Study area. The study sites lie within the western Great Basin, an area of approximately km2 comprising southeastern Oregon, extreme eastern California, northern and central Nevada, southern Idaho, and western Utah (Fig 1). The Great Basin is a high, mid-latitude desert interspersed with hundreds of north-south oriented fault-block mountains separated by broad, flat basins. Mean annual temperatures at the sites average approximately 9 C with both large annual and diurnal ranges. Annual precipitation averages 20 cm. Percentages of annual precipitation occurring during winter, spring, summer, and autumn are 31, 29, 17, and 23, respectively.
2 Data and methods. Precipitation data from December 1946 through November 1991 were used. The study group consisted of 9 stations, 7 from Nevada and 2 from Oregon (Fig. 1). All stations were between 1208 and 1712 m in elevation. The original potential data set contained all stations that fell within the western Great Basin all areas west of the 115 W boundary. This boundary delineation was made because the 115 meridian is the dividing line between frequent and infrequent summertime invasions of Gulf of Mexico air masses that are responsible for convective rain showers (Houghton 1969). The 9 stations were chosen because of their length of record (beginning no later than December 1946) and their completeness. The precipitation data were provided by the Western Regional Climate Center and were organized as monthly values by station. Standard seasonal definitions were used (i.e. winter = December, January, February) to calculate seasonal averages. Gridded seasonal 700 mb height data were provided by the Scripps Institution of Oceanography. Seasonal height data intersecting at 4 grid points, 40 N at 100, 110, 120, and 130 W, were used from 1947 through The grid points intersecting at 100, 110, and 130 W were not used in any direct association with data from the surface recordings, but rather were included to get a greater spatial perspective of temporal changes in the 700 mb height data. Seasons were the same as for the precipitation data. Data analyses (SAS 1985) involved bivariate regression of aggregate seasonal precipitation data with 700 mb height data using the height data as the independent variable. Mean seasonal precipitation values were standardized around a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1 to produce a set of Z scores. Three sets of regression analysis were run: first, all seasonal precipitation data were included; second, only seasonal precipitation values with Z score values of > 0.5 (indicating wet seasons) were analyzed; and finally, only seasonal precipitation values with Z scores <-0.5 (dry seasons) were used. Cook's D and studentized residual values were
3 used as diagnostic tools to check for possible statistical distortions (i.e. outliers and influential observations) associated with bivariate regression (SAS 1985, Clark & Hosking 1986). Results and discussion. Regression analyses used to predict seasonal precipitation as a function of 700 mb height were significant for all seasons (Table 1). For the complete record, the strongest associations occurred during autumn. Models for spring and winter provided less associated variance, and the weakest relationships were during the summer. When only wet seasons were included, the amount of associated variance increased during all seasons (Table 1), but the summer model was insignificant at the 0.05 level. Analyses of dry season data showed no significant r2 values and all values were below that for the complete record. Moisture for precipitation within the Great Basin comes from 2 regions: a flow from the Pacific Ocean providing moisture principally from October through April and an influx of warm, moist air streaming in from the Gulf of Mexico from mid to late summer Precipitation events are associated with 3 flows (Houghton 1969, Houghton et al. 1975). First, low pressure systems from the Pacific Ocean during winter produce the major precipitation events. These events are affected greatly by orographic features. The influence of this orographic lifting is most important in the western Great Basin where the Sierra Nevada creates a major rain shadow on its lee side. Second, cyclogenesis on the lee side of the Sierra Nevada mountains creates Great Basin lows and these lows cause precipitation from late fall through spring. Lee-side lows are most common in late spring. Third, during summer, a mid-continental high over the Mississippi Valley will often shift westward towards the Four Corners region (i.e. Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah). The anticyclonic flow around this high feeds moisture from the Gulf of Mexico providing sufficient conditions for convective showers; however, this summertime source is most important east of the 115 W meridian. Results of the regression analyses showed that wet winters were correlated better with 700 mb heights than either the complete record or dry (Z < 0.5) winters. Wet winters in the western Great Basin are caused most commonly by the presence of a well- developed low centered off the Pacific Coast. Concurrent midtropospheric flow is meridional, with southwesterly flow aloft bringing moisture inland. Upper-level lows off the Pacific Coast may remain anchored for several weeks, where a series of fronts triggered by traveling shortwaves can produce large precipitation totals (Houghton 1969). While the above conditions are most common, brief, wet conditions in the western Great Basin can occur during what is otherwise a winter characterized by high 700 mb heights. During February 1986, for example, almost all the annual average of precipitation fell during a 1 wk period. These rare events serve to complicate the association between lower 700 mb heights and increased precipitation. Dry winters can be associated with both high pressure (e.g. in 1977 when the second lowest amount of precipitation and the second highest 700 mb pressure occurred during the study period) and low pressure (e.g. in 1966 when the sixth driest winter and third lowest winter 700 nib heights occurred during the study period). In situations such as the latter, the position of the upper-level trough may be centered in the eastern Great Basin over Utah or even further east. As a result, air flow into the western Great Basin is northwesterly (with slight
4 subsidence) and provides little precipitation as fronts pass the Sierra Nevada crest. Higher associated variance also occurred during spring and autumn during wet (Z > 0.5) seasons than for either the complete record or dry seasons. The greater amount of associated variance during wetter years is likely the result of the same causes as for wet winters. In addition, Great Basin lows (i.e. upper- level, cut-off lows) form on the lee side of the Sierra Nevada. These closed lows, depending on their location, can produce upslope conditions (and great precipitation) and may persist for several days or longer (Houghton 1969), providing another cause of simultaneous low 700 mb height data and precipitation accumulation. Lower associated variance during dry spring and autumn seasons was caused by the same reasons as for winter, but with the additional confounding influences of the Great Basin lows. The most common position of the axis of these Great Basin lows is centered east of the recording stations (eastern Nevada and western Utah). Hence, as with the Pacific fronts, if the recording stations are slightly upstream of the low pressure core, the stations remain dry while simultaneously being located under lower 700 mb heights. Low r 2 values in the summer were not surprising. Summertime precipitation is a function of small-scale convectional uplift and is associated poorly with mid-tropospheric flow. Rainfall accumulations are spotty with this type of activity, so it is not unusual for one area to receive 0.5 cm or more precipitation from a storm while an area nearby remains dry. The likelihood of precipitation also increases in the Great Basin when high pressure and anticyclonic flow are centered slightly east of the Basin, and/or low pressure with accompanying cyclonic flow (often associated with tropical depressions) lie westward. Either individually or in concert, the result is an influx of moisture into the Basin that, when coupled with atmospheric instability, triggers showers, but is associated weakly with mid-tropospheric patterns. Conclusions. Results indicate that approximately one-third of the total precipitation variance can be explained by variations in the mid-tropospheric heights during autumn, winter, and spring, but substantially less during summer when looking at the complete record. These values are in rough agreement with previous, similar studies (e.g. Leathers 1991, Leathers et al. 1991). When wet seasons are examined, however, associated variance increases substantially, particularly during the winter and autumn seasons, and somewhat less during the spring. Conversely, examination of dry seasons indicates that associated variance is less in comparison to the complete record. These results suggest several key points. First, wet seasons are usually associated most strongly with upper-level lows centered offshore if circulation around the low causes a southwesterly (and moist) flow into the western Great Basin. Second, dry seasons may be caused either by the dominance of high pressure, if centered over the western Great Basin, or by the persistence of low pressure, if the axis of the upperlevel low is centered east of the recording stations. In conclusion, wet seasons are most often associated with 1 cause: lower 700 mb heights. Few wet years are characterized by a dominance of high pressure, hence the high degree of associated variance. Conversely, at least 2 causes for dry seasons exist: the dominance of either high or low 700 mb heights; therefore, bivariate regressions reveal little associated variance. LITERATURE CITED Cayan, D. R., Roads, J. 0. (1984). Local relationships between United States west coast precipitation and monthly mean circulation parameters. Mon. Weather Rev. 112: Clark, W. A. V., Hosking, P. L. (1986). Statistical methods for geographers. John Wiley and Sons, New York Harman, J. R. (1991). Synoptic climatology of the westerlies: processes and patterns. Association of American Geographers, Washington, DC Houghton, J. G. (1969). Characteristics of rainfall in the Great Basin. Desert Research Institute, Reno, NV Houghton, J. G., Sakamoto, C. M., Gifford, R. 0. (1975). Nevada's weather and climate. Nevada Bureau of Mines and Geology, Reno Klein, W. H., Bloom, H. J. (1987). Specification of monthly precipitation over the United States from the surrounding 700 mb height field. Mon. Weather Rev. 115: Leathers, D. J. (1991). Relationships between 700 mb circulation variations and Great Plains Climate. Great Plains Res. 1: Leathers, D. J., Yarnal, B., Palecki, M. A. (1991). The Pacific/ North American teleconnection pattern and
5 United States climate. Part I: Regional temperature and precipitation patterns. J. Clim. 4: Namias, J. (1978). Multiple causes of the North American abnormal winter Mon. Weather Rev. 106: SAS (1985). SAS user's guide: statistics, Version 5 edn. SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC Yarnal, B., Leathers, D. J. (1988). Relationships between interdecadal and interannual climatic variations and their effect on Pennsylvania climate. Ann. Ass. Am. Geogr. 78: Manuscript first received: June 3, 1993 Revised version accepted: February 28, 1994
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast February 2018 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast February 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College February 5, 2018 Summary: For the majority of the month of January the persistent ridge of high pressure
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast February 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College February 5, 2018 Summary: For the majority of the month of January the persistent ridge of high pressure
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter
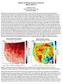 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter 2016-17 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University December 5, 2016 Well after an October that felt more like November, we just finished a November that
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter 2016-17 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University December 5, 2016 Well after an October that felt more like November, we just finished a November that
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2018 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College March 7, 2018 Summary: The ridge pattern that brought drier and warmer conditions from December through most
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College March 7, 2018 Summary: The ridge pattern that brought drier and warmer conditions from December through most
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast October 2017 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast October 2017 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College October 4, 2017 Summary: Typical variability in September temperatures with the onset of fall conditions evident
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast October 2017 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College October 4, 2017 Summary: Typical variability in September temperatures with the onset of fall conditions evident
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2017
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2017 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University August 4, 2017 July largely held true to forecast, although it ended with the start of one of the most extreme
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2017 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University August 4, 2017 July largely held true to forecast, although it ended with the start of one of the most extreme
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast December 2017 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast December 2017 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College December 5, 2017 Summary: November was relatively cool and wet from central California throughout most of
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast December 2017 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College December 5, 2017 Summary: November was relatively cool and wet from central California throughout most of
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast November 2017 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast November 2017 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College November 7, 2017 Summary: October was relatively cool and wet north, while warm and very dry south. Dry conditions
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast November 2017 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College November 7, 2017 Summary: October was relatively cool and wet north, while warm and very dry south. Dry conditions
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2018 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College January 5, 2018 Summary: A persistent ridge of high pressure over the west in December produced strong inversions
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College January 5, 2018 Summary: A persistent ridge of high pressure over the west in December produced strong inversions
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts
 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, 2018 ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts Each question is worth 4 points. Indicate your BEST CHOICE for each question on the Scantron
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES Name SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, 2018 ERTH 360 Test #2 200 pts Each question is worth 4 points. Indicate your BEST CHOICE for each question on the Scantron
Variability Across Space
 Variability and Vulnerability of Western US Snowpack Potential impacts of Climactic Change Mark Losleben, Kurt Chowanski Mountain Research Station, University of Colorado Introduction The Western United
Variability and Vulnerability of Western US Snowpack Potential impacts of Climactic Change Mark Losleben, Kurt Chowanski Mountain Research Station, University of Colorado Introduction The Western United
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast April 2018 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast April 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College April 4, 2018 Summary: A near Miracle March played out bringing cooler and wetter conditions to the majority
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast April 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College April 4, 2018 Summary: A near Miracle March played out bringing cooler and wetter conditions to the majority
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2019 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2019 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College March 2, 2019 Summary: Dramatic flip from a mild winter to a top five coldest February on record in many locations
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast March 2019 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College March 2, 2019 Summary: Dramatic flip from a mild winter to a top five coldest February on record in many locations
California 120 Day Precipitation Outlook Issued Tom Dunklee Global Climate Center
 California 120 Day Precipitation Outlook Issued 11-01-2008 Tom Dunklee Global Climate Center This is my second updated outlook for precipitation patterns and amounts for the next 4 s of the current rainy
California 120 Day Precipitation Outlook Issued 11-01-2008 Tom Dunklee Global Climate Center This is my second updated outlook for precipitation patterns and amounts for the next 4 s of the current rainy
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Fall/Winter 2016
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Fall/Winter 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University November 5, 2016 After a year where we were seemingly off by a month in terms of temperatures (March
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Fall/Winter 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University November 5, 2016 After a year where we were seemingly off by a month in terms of temperatures (March
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2019 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2019 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College January 4, 2019 Summary: December was mild and dry over much of the west, while the east was much warmer than
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast January 2019 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College January 4, 2019 Summary: December was mild and dry over much of the west, while the east was much warmer than
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10
 Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America
 Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Impacts of the April 2013 Mean trough over central North America By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA Abstract: The mean 500 hpa flow over North America featured a trough over
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast August 2018 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast August 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College August 5, 2018 Summary: July 2018 will likely go down as one of the top five warmest July s on record for many
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast August 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College August 5, 2018 Summary: July 2018 will likely go down as one of the top five warmest July s on record for many
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter 2016-17 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University February 7, 2017 What a difference from last year at this time. Temperatures in January and February
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Winter 2016-17 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University February 7, 2017 What a difference from last year at this time. Temperatures in January and February
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast October 2018 Report
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast October 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College October 4, 2018 Summary: Much of Washington, Oregon, coastal California and the Bay Area and delta region
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast October 2018 Report Gregory V. Jones Linfield College October 4, 2018 Summary: Much of Washington, Oregon, coastal California and the Bay Area and delta region
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer into Harvest 2016
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer into Harvest 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University September 3, 2016 With school and football season starting a hint of fall is right on time
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer into Harvest 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University September 3, 2016 With school and football season starting a hint of fall is right on time
Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains
 Abstract: Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A deep 500 hpa cutoff developed in the southern Plains on 3 May 2013. It produced a
Abstract: Early May Cut-off low and Mid-Atlantic rains By Richard H. Grumm National Weather Service State College, PA A deep 500 hpa cutoff developed in the southern Plains on 3 May 2013. It produced a
Satellites, Weather and Climate Module??: Polar Vortex
 Satellites, Weather and Climate Module??: Polar Vortex SWAC Jan 2014 AKA Circumpolar Vortex Science or Hype? Will there be one this year? Today s objectives Pre and Post exams What is the Polar Vortex
Satellites, Weather and Climate Module??: Polar Vortex SWAC Jan 2014 AKA Circumpolar Vortex Science or Hype? Will there be one this year? Today s objectives Pre and Post exams What is the Polar Vortex
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2016
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University June 6, 2016 May 2016 continued the warm trend for portions of the west, while providing some relief for
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University June 6, 2016 May 2016 continued the warm trend for portions of the west, while providing some relief for
MET Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16)
 MET 4300 Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16) Learning Objectives Provide an overview of the importance and impacts of mountain snowstorms in the western US Describe how topography influence precipitation
MET 4300 Lecture 20 Mountain Snowstorms (CH16) Learning Objectives Provide an overview of the importance and impacts of mountain snowstorms in the western US Describe how topography influence precipitation
The following information is provided for your use in describing climate and water supply conditions in the West as of April 1, 2003.
 Natural Resources Conservation Service National Water and Climate Center 101 SW Main Street, Suite 1600 Portland, OR 97204-3224 Date: April 8, 2003 Subject: April 1, 2003 Western Snowpack Conditions and
Natural Resources Conservation Service National Water and Climate Center 101 SW Main Street, Suite 1600 Portland, OR 97204-3224 Date: April 8, 2003 Subject: April 1, 2003 Western Snowpack Conditions and
National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook
 National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook National Interagency Fire Center Predictive Services Issued: September, 2007 Wildland Fire Outlook September through December 2007 Significant fire
National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook National Interagency Fire Center Predictive Services Issued: September, 2007 Wildland Fire Outlook September through December 2007 Significant fire
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
Climate. Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) January Temperature. July Temperature. Average Precipitation (Last 30 Years)
 Climate Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) Average Annual High Temp. (F)70, (C)21 Average Annual Low Temp. (F)43, (C)6 January Temperature Average January High Temp. (F)48, (C)9 Average January Low Temp.
Climate Annual Temperature (Last 30 Years) Average Annual High Temp. (F)70, (C)21 Average Annual Low Temp. (F)43, (C)6 January Temperature Average January High Temp. (F)48, (C)9 Average January Low Temp.
Flood Risk Assessment
 Flood Risk Assessment February 14, 2008 Larry Schick Army Corps of Engineers Seattle District Meteorologist General Assessment As promised, La Nina caused an active winter with above to much above normal
Flood Risk Assessment February 14, 2008 Larry Schick Army Corps of Engineers Seattle District Meteorologist General Assessment As promised, La Nina caused an active winter with above to much above normal
MAURITIUS METEOROLOGICAL SERVICES
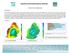 MAURITIUS METEOROLOGICAL SERVICES CLIMATE NOVEMBER 2018 Introduction Climatologically speaking, November is a relatively dry month for Mauritius with a long term monthly mean rainfall of 78 mm. However,
MAURITIUS METEOROLOGICAL SERVICES CLIMATE NOVEMBER 2018 Introduction Climatologically speaking, November is a relatively dry month for Mauritius with a long term monthly mean rainfall of 78 mm. However,
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2016
 Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University August 5, 2016 The month of July saw the continued flip, flop of the western US temperatures. It was warm
Weather and Climate Summary and Forecast Summer 2016 Gregory V. Jones Southern Oregon University August 5, 2016 The month of July saw the continued flip, flop of the western US temperatures. It was warm
March 1, 2003 Western Snowpack Conditions and Water Supply Forecasts
 Natural Resources Conservation Service National Water and Climate Center 101 SW Main Street, Suite 1600 Portland, OR 97204-3224 Date: March 17, 2003 Subject: March 1, 2003 Western Snowpack Conditions and
Natural Resources Conservation Service National Water and Climate Center 101 SW Main Street, Suite 1600 Portland, OR 97204-3224 Date: March 17, 2003 Subject: March 1, 2003 Western Snowpack Conditions and
Long-Term Trend of Summer Rainfall at Selected Stations in the Republic of Korea
 Long-Term Trend of Summer Rainfall at Selected Stations in the Republic of Korea Il-Kon Kim Professor, Department of Region Information Rafique Ahmed Professor, Geography and Earth Science Silla University
Long-Term Trend of Summer Rainfall at Selected Stations in the Republic of Korea Il-Kon Kim Professor, Department of Region Information Rafique Ahmed Professor, Geography and Earth Science Silla University
Keys to Climate Climate Classification Low Latitude Climates Midlatitude Climates High Latitude Climates Highland Climates Our Changing Climate
 Climate Global Climates Keys to Climate Climate Classification Low Latitude Climates Midlatitude Climates High Latitude Climates Highland Climates Our Changing Climate Keys to Climate Climate the average
Climate Global Climates Keys to Climate Climate Classification Low Latitude Climates Midlatitude Climates High Latitude Climates Highland Climates Our Changing Climate Keys to Climate Climate the average
4/29/2011. Mid-latitude cyclones form along a
 Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
Chapter 10: Cyclones: East of the Rocky Mountain Extratropical Cyclones Environment prior to the development of the Cyclone Initial Development of the Extratropical Cyclone Early Weather Along the Fronts
ATSC 2000 Final Fall 2005
 ATSC 2000 Final Fall 2005 true/false /25 multiple choice /25 short answer /23 essay /10 total /83 or % True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. (25 questions 1% each) 1.
ATSC 2000 Final Fall 2005 true/false /25 multiple choice /25 short answer /23 essay /10 total /83 or % True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. (25 questions 1% each) 1.
CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Viewed from above in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds about a subtropical high blow a. clockwise and inward. b. counterclockwise.
CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Viewed from above in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds about a subtropical high blow a. clockwise and inward. b. counterclockwise.
PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Event Response
 PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2014 - RMS Event Response 2014 SEASON OUTLOOK The 2013 North Atlantic hurricane season saw the fewest hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin
PRMS WHITE PAPER 2014 NORTH ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2014 - RMS Event Response 2014 SEASON OUTLOOK The 2013 North Atlantic hurricane season saw the fewest hurricanes in the Atlantic Basin
National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook
 National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook National Interagency Fire Center Predictive Services Issued: April 1, 2008 Next Issue: May 1, 2008 Wildland Fire Outlook April 2008 through July 2008
National Wildland Significant Fire Potential Outlook National Interagency Fire Center Predictive Services Issued: April 1, 2008 Next Issue: May 1, 2008 Wildland Fire Outlook April 2008 through July 2008
CHAPTER IV THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN OCEANOGRAPHY AND METEOROLOGY
 CHAPTER IV THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN OCEANOGRAPHY AND METEOROLOGY THE relationship between oceanography and meteorology is of an order different from that between it and geology or biology, because meteorologic
CHAPTER IV THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN OCEANOGRAPHY AND METEOROLOGY THE relationship between oceanography and meteorology is of an order different from that between it and geology or biology, because meteorologic
P2.4 THE IMPACT OF TROPICAL CYCLONE REMNANTS ON THE RAINFALL OF THE NORTH AMERICAN SOUTHWEST REGION
 P2.4 THE IMPACT OF TROPICAL CYCLONE REMNANTS ON THE RAINFALL OF THE NORTH AMERICAN SOUTHWEST REGION by Elizabeth A. Ritchie 1 and David Szenasi University of New Mexico 1. INTRODUCTION New Mexico has a
P2.4 THE IMPACT OF TROPICAL CYCLONE REMNANTS ON THE RAINFALL OF THE NORTH AMERICAN SOUTHWEST REGION by Elizabeth A. Ritchie 1 and David Szenasi University of New Mexico 1. INTRODUCTION New Mexico has a
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: February 15, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: February 15, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com JANUARY 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review During January, the average
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: February 15, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com JANUARY 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review During January, the average
Diagnosing the Climatology and Interannual Variability of North American Summer Climate with the Regional Atmospheric Modeling System (RAMS)
 Diagnosing the Climatology and Interannual Variability of North American Summer Climate with the Regional Atmospheric Modeling System (RAMS) Christopher L. Castro and Roger A. Pielke, Sr. Department of
Diagnosing the Climatology and Interannual Variability of North American Summer Climate with the Regional Atmospheric Modeling System (RAMS) Christopher L. Castro and Roger A. Pielke, Sr. Department of
Lecture #14 March 29, 2010, Monday. Air Masses & Fronts
 Lecture #14 March 29, 2010, Monday Air Masses & Fronts General definitions air masses source regions fronts Air masses formation types Fronts formation types Air Masses General Definitions a large body
Lecture #14 March 29, 2010, Monday Air Masses & Fronts General definitions air masses source regions fronts Air masses formation types Fronts formation types Air Masses General Definitions a large body
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Cat Response
 2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF OKLAHOMA'S PRECIPITATION REGIME FOR TWO EXTENDED TIME PERIODS BY USE OF EIGENVECTORS
 85 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF OKLAHOMA'S PRECIPITATION REGIME FOR TWO EXTENDED TIME PERIODS BY USE OF EIGENVECTORS Elias Johnson Department of Geography, Southwest Missouri State University, Springfield, MO
85 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF OKLAHOMA'S PRECIPITATION REGIME FOR TWO EXTENDED TIME PERIODS BY USE OF EIGENVECTORS Elias Johnson Department of Geography, Southwest Missouri State University, Springfield, MO
L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment
 Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
Name L.O Students will learn about factors that influences the environment Date 1. At the present time, glaciers occur mostly in areas of A) high latitude or high altitude B) low latitude or low altitude
3) What is the difference between latitude and longitude and what is their affect on local and world weather and climate?
 www.discoveryeducation.com 1) Describe the difference between climate and weather citing an example of each. Describe how water (ocean, lake, river) has a local effect on weather and climate and provide
www.discoveryeducation.com 1) Describe the difference between climate and weather citing an example of each. Describe how water (ocean, lake, river) has a local effect on weather and climate and provide
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: NOVEMBER 16, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: NOVEMBER 16, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales sroot@weatherbank.com OCTOBER 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: NOVEMBER 16, 2015 Steven A. Root, CCM, Chief Analytics Officer, Sr. VP, sales sroot@weatherbank.com OCTOBER 2015 Climate Highlights The Month in Review The
Fig Major air masses of the world
 Fig. 9.3 Major air masses of the world CLASSIFICATION FOUR BASIC CATEGORIES OF AIR MASSES: POLAR - P ARCTIC - A TROPICAL - T EQUATORIAL - E TWO DESIGNATIONS OF SURFACE IN SOURCE REGION MARITIME - m. CONTINENTAL
Fig. 9.3 Major air masses of the world CLASSIFICATION FOUR BASIC CATEGORIES OF AIR MASSES: POLAR - P ARCTIC - A TROPICAL - T EQUATORIAL - E TWO DESIGNATIONS OF SURFACE IN SOURCE REGION MARITIME - m. CONTINENTAL
Type of storm viewed by Spotter A Ordinary, multi-cell thunderstorm. Type of storm viewed by Spotter B Supecell thunderstorm
 ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
ANSWER KEY Part I: Locating Geographical Features 1. The National Weather Service s Storm Prediction Center (www.spc.noaa.gov) has issued a tornado watch on a warm spring day. The watch covers a large
Global Wind Patterns
 Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
Name: Earth Science: Date: Period: Global Wind Patterns 1. Which factor causes global wind patterns? a. changes in the distance between Earth and the Moon b. unequal heating of Earth s surface by the Sun
Mozambique. General Climate. UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles. C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1
 UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Mozambique C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2.Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
UNDP Climate Change Country Profiles Mozambique C. McSweeney 1, M. New 1,2 and G. Lizcano 1 1. School of Geography and Environment, University of Oxford. 2.Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk
2011 National Seasonal Assessment Workshop for the Eastern, Southern, & Southwest Geographic Areas
 2011 National Seasonal Assessment Workshop for the Eastern, Southern, & Southwest Geographic Areas On January 11-13, 2011, wildland fire, weather, and climate met virtually for the ninth annual National
2011 National Seasonal Assessment Workshop for the Eastern, Southern, & Southwest Geographic Areas On January 11-13, 2011, wildland fire, weather, and climate met virtually for the ninth annual National
True or false: The atmosphere is always in hydrostatic balance. A. True B. False
 Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
Clicker Questions and Clicker Quizzes Clicker Questions Chapter 7 Of the four forces that affect the motion of air in our atmosphere, which is to thank for opposing the vertical pressure gradient force
Statistical Forecast of the 2001 Western Wildfire Season Using Principal Components Regression. Experimental Long-Lead Forecast Bulletin
 Statistical Forecast of the 2001 Western Wildfire Season Using Principal Components Regression contributed by Anthony L. Westerling 1, Daniel R. Cayan 1,2, Alexander Gershunov 1, Michael D. Dettinger 2
Statistical Forecast of the 2001 Western Wildfire Season Using Principal Components Regression contributed by Anthony L. Westerling 1, Daniel R. Cayan 1,2, Alexander Gershunov 1, Michael D. Dettinger 2
but 2012 was dry Most farmers pulled in a crop
 After a winter that wasn t, conditions late in the year pointed to a return to normal snow and cold conditions Most farmers pulled in a crop but 2012 was dry b y M i k e Wr o b l e w s k i, w e a t h e
After a winter that wasn t, conditions late in the year pointed to a return to normal snow and cold conditions Most farmers pulled in a crop but 2012 was dry b y M i k e Wr o b l e w s k i, w e a t h e
8.1 Attachment 1: Ambient Weather Conditions at Jervoise Bay, Cockburn Sound
 8.1 Attachment 1: Ambient Weather Conditions at Jervoise Bay, Cockburn Sound Cockburn Sound is 20km south of the Perth-Fremantle area and has two features that are unique along Perth s metropolitan coast
8.1 Attachment 1: Ambient Weather Conditions at Jervoise Bay, Cockburn Sound Cockburn Sound is 20km south of the Perth-Fremantle area and has two features that are unique along Perth s metropolitan coast
Middle-Latitude Cyclone
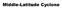 Middle-Latitude Cyclone What is a mid-latitude cyclone? - The mid-latitude cyclone is a synoptic scale low pressure system that has cyclonic (counter-clockwise in northern hemisphere) flow that is found
Middle-Latitude Cyclone What is a mid-latitude cyclone? - The mid-latitude cyclone is a synoptic scale low pressure system that has cyclonic (counter-clockwise in northern hemisphere) flow that is found
United States Streamflow Probabilities based on Forecasted La Niña, Winter-Spring 2000
 United States Streamflow Probabilities based on Forecasted La Niña, Winter-Spring 2000 contributed by Michael D. Dettinger 1, Daniel R. Cayan 1, and Kelly T. Redmond 2 1 U.S. Geological Survey, Scripps
United States Streamflow Probabilities based on Forecasted La Niña, Winter-Spring 2000 contributed by Michael D. Dettinger 1, Daniel R. Cayan 1, and Kelly T. Redmond 2 1 U.S. Geological Survey, Scripps
LAB J - WORLD CLIMATE ZONES
 Introduction LAB J - WORLD CLIMATE ZONES The objective of this lab is to familiarize the student with the various climates around the world and the climate controls that influence these climates. Students
Introduction LAB J - WORLD CLIMATE ZONES The objective of this lab is to familiarize the student with the various climates around the world and the climate controls that influence these climates. Students
Summer 2018 Southern Company Temperature/Precipitation Forecast
 Scott A. Yuknis High impact weather forecasts, climate assessment and prediction. 14 Boatwright s Loop Plymouth, MA 02360 Phone/Fax 508.927.4610 Cell: 508.813.3499 ClimateImpact@comcast.net Climate Impact
Scott A. Yuknis High impact weather forecasts, climate assessment and prediction. 14 Boatwright s Loop Plymouth, MA 02360 Phone/Fax 508.927.4610 Cell: 508.813.3499 ClimateImpact@comcast.net Climate Impact
Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak
 Chapter 14: Cold Waves Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak 1 Cold Wave A cold wave is an influx of unusually cold air into middle or lower latitudes. Cold waves affect much larger areas than
Chapter 14: Cold Waves Formation of Cold Airmasses Cold Air Outbreak 1 Cold Wave A cold wave is an influx of unusually cold air into middle or lower latitudes. Cold waves affect much larger areas than
Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997
 Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997 Tim Hollfelder May 10 th, 2006 Abstract Synoptic scale forcings were very weak for these thunderstorms on August 7-8, 1997 over the
Investigation of the Arizona Severe Weather Event of August 8 th, 1997 Tim Hollfelder May 10 th, 2006 Abstract Synoptic scale forcings were very weak for these thunderstorms on August 7-8, 1997 over the
The Pennsylvania Observer
 The Pennsylvania Observer October 1, 2015 September 2015 - Pennsylvania Weather Recap By: Quinn Lease The month of September will be remembered for its above normal temperatures and dry conditions that
The Pennsylvania Observer October 1, 2015 September 2015 - Pennsylvania Weather Recap By: Quinn Lease The month of September will be remembered for its above normal temperatures and dry conditions that
Forecasting Challenges
 Forecasting Challenges 2017-18 Alex Tardy- NWS San Diego Alexander.Tardy@noaa.gov CW3E meetings April 2018 Atmospheric Rivers Climate Forecast System by NOAA 100-h fuel moisture all-time low for South
Forecasting Challenges 2017-18 Alex Tardy- NWS San Diego Alexander.Tardy@noaa.gov CW3E meetings April 2018 Atmospheric Rivers Climate Forecast System by NOAA 100-h fuel moisture all-time low for South
Role of Multiple-Level Tropospheric Circulations in Forcing ENSO Winter Precipitation Anomalies
 3102 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW Role of Multiple-Level Tropospheric Circulations in Forcing ENSO Winter Precipitation Anomalies SHAWN R. SMITH, PHAEDRA M. GREEN,* ALAN P. LEONARDI, AND JAMES J. O BRIEN Center
3102 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW Role of Multiple-Level Tropospheric Circulations in Forcing ENSO Winter Precipitation Anomalies SHAWN R. SMITH, PHAEDRA M. GREEN,* ALAN P. LEONARDI, AND JAMES J. O BRIEN Center
MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology. Lecture 8: September 16, AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2)
 MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology Lecture 8: September 16, 2010 AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2) Identifying a cold front on a surface weather map: 1. Surface front is located at the leading edge
MET 3502 Synoptic Meteorology Lecture 8: September 16, 2010 AIRMASSES, FRONTS and FRONTAL ANALYSIS (2) Identifying a cold front on a surface weather map: 1. Surface front is located at the leading edge
ONE-YEAR EXPERIMENT IN NUMERICAL PREDICTION OF MONTHLY MEAN TEMPERATURE IN THE ATMOSPHERE-OCEAN-CONTINENT SYSTEM
 71 4 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW Vol. 96, No. 10 ONE-YEAR EXPERIMENT IN NUMERICAL PREDICTION OF MONTHLY MEAN TEMPERATURE IN THE ATMOSPHERE-OCEAN-CONTINENT SYSTEM JULIAN ADEM and WARREN J. JACOB Extended Forecast
71 4 MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW Vol. 96, No. 10 ONE-YEAR EXPERIMENT IN NUMERICAL PREDICTION OF MONTHLY MEAN TEMPERATURE IN THE ATMOSPHERE-OCEAN-CONTINENT SYSTEM JULIAN ADEM and WARREN J. JACOB Extended Forecast
Arizona Climate Summary February 2012
 Arizona Climate Summary February 2012 Summary of conditions for January 2012 January 2012 Temperature and Precipitation Summary January 1 st 20 th : The New Year has started on a very dry note. The La
Arizona Climate Summary February 2012 Summary of conditions for January 2012 January 2012 Temperature and Precipitation Summary January 1 st 20 th : The New Year has started on a very dry note. The La
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain
 ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain References: Forecaster s Guide to Tropical Meteorology (updated), Ramage Tropical Climatology, McGregor and Nieuwolt Climate and Weather
ESCI 344 Tropical Meteorology Lesson 7 Temperature, Clouds, and Rain References: Forecaster s Guide to Tropical Meteorology (updated), Ramage Tropical Climatology, McGregor and Nieuwolt Climate and Weather
2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW
 2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW 1 INTRODUCTION Recently, three of the major centres for global climate monitoring determined with high confidence that 2015 was the warmest year on record, globally.
2015: A YEAR IN REVIEW F.S. ANSLOW 1 INTRODUCTION Recently, three of the major centres for global climate monitoring determined with high confidence that 2015 was the warmest year on record, globally.
Grade 9 Geography Chapter 11 - Climate Connections
 Grade 9 Geography Chapter 11 - Climate Connections 1. Define: Weather. 2. In what way has weather affected your activities in the last two weeks? 3. Define: Climate. 4. Canada s climate is a function of
Grade 9 Geography Chapter 11 - Climate Connections 1. Define: Weather. 2. In what way has weather affected your activities in the last two weeks? 3. Define: Climate. 4. Canada s climate is a function of
Transient and Eddy. Transient/Eddy Flux. Flux Components. Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance. Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean
 Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Lecture 3: Weather/Disturbance Transients and Eddies Climate Roles Mid-Latitude Cyclones Tropical Hurricanes Mid-Ocean Eddies Transient and Eddy Transient: deviations from time mean Time Mean Eddy: deviations
Presentation Overview. Southwestern Climate: Past, present and future. Global Energy Balance. What is climate?
 Southwestern Climate: Past, present and future Mike Crimmins Climate Science Extension Specialist Dept. of Soil, Water, & Env. Science & Arizona Cooperative Extension The University of Arizona Presentation
Southwestern Climate: Past, present and future Mike Crimmins Climate Science Extension Specialist Dept. of Soil, Water, & Env. Science & Arizona Cooperative Extension The University of Arizona Presentation
Name SOLUTIONS T.A./Section Atmospheric Science 101 Homework #6 Due Thursday, May 30 th (in class)
 Name SOLUTIONS T.A./Section Atmospheric Science 101 Homework #6 Due Thursday, May 30 th (in class) 1. General Circulation Briefly describe where each of the following features is found in the earth s general
Name SOLUTIONS T.A./Section Atmospheric Science 101 Homework #6 Due Thursday, May 30 th (in class) 1. General Circulation Briefly describe where each of the following features is found in the earth s general
Climate Outlook through 2100 South Florida Ecological Services Office Vero Beach, FL September 9, 2014
 Climate Outlook through 2100 South Florida Ecological Services Office Vero Beach, FL September 9, 2014 Short Term Drought Map: Short-term (
Climate Outlook through 2100 South Florida Ecological Services Office Vero Beach, FL September 9, 2014 Short Term Drought Map: Short-term (
INVISIBLE WATER COSTS
 Every Drop Every Counts... Drop Counts... INVISIBLE WATER COSTS Corn - 108.1 gallons per pound How much water it takes to produce... Apple - 18.5 gallons to grow Beef - 1,581 gallons per pound Oats - 122.7
Every Drop Every Counts... Drop Counts... INVISIBLE WATER COSTS Corn - 108.1 gallons per pound How much water it takes to produce... Apple - 18.5 gallons to grow Beef - 1,581 gallons per pound Oats - 122.7
A Synoptic Climatology of Heavy Precipitation Events in California
 A Synoptic Climatology of Heavy Precipitation Events in California Alan Haynes Hydrometeorological Analysis and Support (HAS) Forecaster National Weather Service California-Nevada River Forecast Center
A Synoptic Climatology of Heavy Precipitation Events in California Alan Haynes Hydrometeorological Analysis and Support (HAS) Forecaster National Weather Service California-Nevada River Forecast Center
Weather Outlook: 2015 Growing Season
 Weather Outlook: 2015 Growing Season Leon F. Osborne Chester Fritz Distinguished Professor Regional Weather Information Center University of North Dakota Grand Forks, North Dakota Why Should We Be Concerned?
Weather Outlook: 2015 Growing Season Leon F. Osborne Chester Fritz Distinguished Professor Regional Weather Information Center University of North Dakota Grand Forks, North Dakota Why Should We Be Concerned?
3. HYDROMETEROLOGY. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Hydro-meteorological Aspect. 3.3 Rain Gauge Stations
 3. HYDROMETEROLOGY 3.1 Introduction Hydrometeorology is a branch of meteorology and hydrology that studies the transfer of water and energy between the land surface and the lower atmosphere. Detailed hydrological
3. HYDROMETEROLOGY 3.1 Introduction Hydrometeorology is a branch of meteorology and hydrology that studies the transfer of water and energy between the land surface and the lower atmosphere. Detailed hydrological
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
Weather and Climate Risks and Effects on Agriculture
 Weather and Climate Risks and Effects on Agriculture Dr. Eric Snodgrass Official Journal of the Fluid Fertilizer Foundation Vol. 26, No. 2, Issue #100 DOWNLOAD Summary: So, what do we need to watch for?
Weather and Climate Risks and Effects on Agriculture Dr. Eric Snodgrass Official Journal of the Fluid Fertilizer Foundation Vol. 26, No. 2, Issue #100 DOWNLOAD Summary: So, what do we need to watch for?
Chapter outline. Reference 12/13/2016
 Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
Chapter 2. observation CC EST 5103 Climate Change Science Rezaul Karim Environmental Science & Technology Jessore University of science & Technology Chapter outline Temperature in the instrumental record
The Climate of Oregon Climate Zone 4 Northern Cascades
 /05 E55 Unbound issue No. 9/ is Does not circulate Special Report 916 May 1993 The Climate of Oregon Climate Zone 4 Property of OREGON STATE UNIVERSITY Library Serials Corvallis, OR 97331-4503 Agricultural
/05 E55 Unbound issue No. 9/ is Does not circulate Special Report 916 May 1993 The Climate of Oregon Climate Zone 4 Property of OREGON STATE UNIVERSITY Library Serials Corvallis, OR 97331-4503 Agricultural
Analysis of meteorological measurements made over three rainy seasons in Sinazongwe District, Zambia.
 Analysis of meteorological measurements made over three rainy seasons in Sinazongwe District, Zambia. 1 Hiromitsu Kanno, 2 Hiroyuki Shimono, 3 Takeshi Sakurai, and 4 Taro Yamauchi 1 National Agricultural
Analysis of meteorological measurements made over three rainy seasons in Sinazongwe District, Zambia. 1 Hiromitsu Kanno, 2 Hiroyuki Shimono, 3 Takeshi Sakurai, and 4 Taro Yamauchi 1 National Agricultural
Science Olympiad Meteorology Quiz #2 Page 1 of 8
 1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
1) The prevailing general direction of the jet stream is from west to east in the northern hemisphere: 2) Advection is the vertical movement of an air mass from one location to another: 3) Thunderstorms
ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING. GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13
 ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13 Agenda for February 3 Assignment 3: Due on Friday Lecture Outline Numerical modelling Long-range forecasts Oscillations
ATMOSPHERIC MODELLING GEOG/ENST 3331 Lecture 9 Ahrens: Chapter 13; A&B: Chapters 12 and 13 Agenda for February 3 Assignment 3: Due on Friday Lecture Outline Numerical modelling Long-range forecasts Oscillations
Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses
 Lab 9 Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses This lab will introduce students to the patterns of surface winds around the center of a midlatitude cyclone of low pressure. The types of weather associated with
Lab 9 Mid-latitude Cyclones & Air Masses This lab will introduce students to the patterns of surface winds around the center of a midlatitude cyclone of low pressure. The types of weather associated with
Air Masses of North America cp and ca air masses Air mass characterized by very cold and dry conditions
 Chapter 8: Air Masses, Fronts, and Middle-Latitude Cyclones Air masses Fronts Middle-latitude cyclones Air Masses Air mass an extremely large body of air whose properties of temperature and humidity are
Chapter 8: Air Masses, Fronts, and Middle-Latitude Cyclones Air masses Fronts Middle-latitude cyclones Air Masses Air mass an extremely large body of air whose properties of temperature and humidity are
TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS
 Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
General Circulation. Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory
 General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
General Circulation Nili Harnik DEES, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory nili@ldeo.columbia.edu Latitudinal Radiation Imbalance The annual mean, averaged around latitude circles, of the balance between the
MAURITIUS METEOROLOGICAL SERVICES
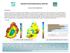 MAURITIUS METEOROLOGICAL SERVICES CLIMATE SEPTEMBER 2018 Introduction Synoptic weather pattern over the region portrayed September as a transition month. The month started with wintry characteristics.
MAURITIUS METEOROLOGICAL SERVICES CLIMATE SEPTEMBER 2018 Introduction Synoptic weather pattern over the region portrayed September as a transition month. The month started with wintry characteristics.
National Situation Report As of 5:00 a.m. EDT Tuesday, April 4, 2017
 Overview National Situation Report As of 5:00 a.m. EDT Tuesday, April 4, 2017 Table Of Contents Current Operations Monitoring Recovery National Response Coordination Center: Not Activated National Watch
Overview National Situation Report As of 5:00 a.m. EDT Tuesday, April 4, 2017 Table Of Contents Current Operations Monitoring Recovery National Response Coordination Center: Not Activated National Watch
Why There Is Weather?
 Lecture 6: Weather, Music Of Our Sphere Weather and Climate WEATHER The daily fluctuations in atmospheric conditions. The atmosphere on its own can produce weather. (From Understanding Weather & Climate)
Lecture 6: Weather, Music Of Our Sphere Weather and Climate WEATHER The daily fluctuations in atmospheric conditions. The atmosphere on its own can produce weather. (From Understanding Weather & Climate)
What is the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO)?
 What is the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO)? Planetary scale, 30 90 day oscillation in zonal wind, precipitation, surface pressure, humidity, etc., that propagates slowly eastward Wavelength = 12,000 20,000
What is the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO)? Planetary scale, 30 90 day oscillation in zonal wind, precipitation, surface pressure, humidity, etc., that propagates slowly eastward Wavelength = 12,000 20,000
PERSISTENT PLANETARY SCALE CIRCULATION PATTERNS AND THEIR RELATIONSHIP WITH COLD AIR OUTBREAK ACTIVITY OVER THE EASTERN UNITED STATES.
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 18: 1209 1221 (1998) PERSISTENT PLANETARY SCALE CIRCULATION PATTERNS AND THEIR RELATIONSHIP WITH COLD AIR OUTBREAK ACTIVITY OVER THE EASTERN UNITED
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CLIMATOLOGY Int. J. Climatol. 18: 1209 1221 (1998) PERSISTENT PLANETARY SCALE CIRCULATION PATTERNS AND THEIR RELATIONSHIP WITH COLD AIR OUTBREAK ACTIVITY OVER THE EASTERN UNITED
ERTH 360 Test #2 Key Fall pts
 DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, 2016 ERTH 360 Test #2 Key Fall 2016 200 pts Each question is worth 4 points. Indicate your BEST CHOICE for each question on
DEPARTMENT OF EARTH & CLIMATE SCIENCES SAN FRANCISCO STATE UNIVERSITY Nov 29, 2016 ERTH 360 Test #2 Key Fall 2016 200 pts Each question is worth 4 points. Indicate your BEST CHOICE for each question on
SEPTEMBER 2013 REVIEW
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: October 21, 2013 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com SEPTEMBER 2013 REVIEW Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average temperature
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: October 21, 2013 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com SEPTEMBER 2013 REVIEW Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average temperature
