Climate Variability Studies in the Ocean
|
|
|
- Aubrey Dennis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Climate Variability Studies in the Ocean Topic 1. Long-term variations of vertical profiles of nutrients in the western North Pacific Topic 2. Biogeochemical processes related to ocean carbon cycling: biogenic particle metal interaction.
2 Background Climate Changes and Oceans 1. Oceanic response to climate change 2. Effects to carbon cycling in the ocean 3. Ecological effects due to climate changes Why is the western North Pacific Ocean important ecologically and climatologically? Two major currents (Kuroshio and Oyashio) exist in the western North Pacific. Kuroshio: a western boundary current, warm and salty Oyashio: a subarctic current cold and less salty An important fishery exists in the western North Pacific. Fishing catches are affected by ecological variation due to climate change.
3 Increase of green-house gases in the atmosphere Climate change Oceanic change Change of nutrient supply Current systems into the euphotic layer Upwelling Eddy formation Feedback Feedback to atmosphere Change of primary Change of export fluxes Effect to carbon Production cycling Change of fish mass Change of fish catch
4 A typical example of Ecological regime shift Chavez et al., Science 299, 217 (2003)
5 Long-term variations of vertical profiles of nutrients in the western North Pacific K. Hirose Geochemical Research Laboratory, Meteorological Research Institute Objective Physical characteristics of the Kuroshio re-circulation and effect of distributions of nutrients Short history There were few studies on temporal variations of nutrients concentrations in seawater until Major research works were published in the last few years. analysis of variation of nutrient concentrations along isopicnal surface seasonal variation of nutrient concentrations in surface mixed layer
6 Do vertical profiles of nutrients in water columns vary temporally? Time-series observation Station HOT Subtropical Pacific Ocean BATS Atlantic Ocean JMA Observation line P9 along 137 E Start from 1970 winter and summer Our knowledge 1. Seasonal change 2. Inter-annual change 3. Decadal change
7 Trends in BATS time series data Trends in BATS time series data Interannual seasonal DIC + + Alkalinity - - δ 13 C + + pco NAO North Atlantic Oscillation Pressure difference between the Atlantic high and low (Azores) (Ireland) NAO + stronger pressure gradient Positive SST anomalies (subtropics) Negative SST anomalies (subpolar gyre) Detrend Internannual Correlation with NAO SST anomalies + + DIC + + δ 13 C + - pco Positive NAO deep convection Positive DIC anomaly Negative δ13c anomaly NCP increase DIC decrease Remove light carbon Gruber et al., Science, 298, 2374 (2002)
8 N/P ratios in nutrients The variation of N/P ratios of inorganic nutrients Example : ALOHA N/P ratios of inorganic nutrients in the western North Pacific Do N/P ratios vary spatially and temporally? What are factors controlling N/P ratios? How about relationships between N/P ratio in water column and Redfield ratio?
9
10
11
12
13 Oceanographic characteristics of the western North Pacific 1. Kuroshio current (a typical western boundary current) 2. Kuroshio recirculation area The western North Pacific subtropical mode water (NPSMW) The North Pacific Intermediate Water (NPIW) 3. The North Equatorial current Tropical Water (TW) 4. The Equatorial current system
14 Surface current system in the world ocean
15 Oceanographic observation JMA observation lines
16
17
18
19
20
21
22 Summary of Meso-scale eddies in the western North Pacific Ebuchi and Hanawa, (2001) Trajectory of mesoscale eddies in the Kuroshio recirculation region. J. Oceanogr., 57, Uehara et al., (2003) A role of eddies in formation and transport of North Pacific subtropical mode water. Geophy. Res. Lett., 30, Characteristics of meso-scale eddy Spatial scale 250 km Temporal scale 80 days Typical maximum surface velocity cm s-1 SSH anomaly 15 cm Advection velocity to southwest 7 cm s-1 Eddies with a strong nonlinear nature can trap a substantial amount of water parcels within them. (greater than 30-40% of volume)
23 Oceanic cycle of nutrients ( Comparison with inorganic carbon in the ocean) 1.Solubility pump (Air-Sea exchange) very small 2.Biological pump particle export DOC transport significant relatively small 3.Carbonate pump none 4.Other process N 2 fixation nitrification denitrification Residence time of phosphorus Very long y
24 Dose vertical profiles of nutrients vary? We examine the temporal variation of vertical profiles of nitrate and phosphate in 25 N 137. To use about 20 years dataset of nutrients observed by JMA. A result The temporal variation of nutrients systematically occurs at all of depth. Causes of variation 1. Chemical analysis offset --- no offset due to chemical analysis because of lack of surface nutrients in the subtropical North Pacific, slope --- inability to estimate the past data because of no standard materials 2. Natural variation Systematic variation of nutrient concentrations in deep waters Systematic variation of depths where the same nutrient concentrations occurred To separate these two variations Hirose s simple model
25 Concept of model Aeolian input NA(IN) NA(OUT) Advection ko N(inorg) N(org) ki N(part) Upwelling w F e Export flux Decomposition N(inorg) k rmremineralization
26 Movement of meso-scale eddies in the western North Pacific Cyclonic eddy Anticyclonic eddy Advection Horizontal scale: 250 km Vertical scale: 2 3 km Upwelling of deep waters due to global circulation
27 Scheme of model The differential equation governing the vertical distribution of nutrients Ni(z) in the steady state is expressed as follows: d/dz(wni(z)) - Si(z) = 0 (1) where z denotes depth and Si(z) is a biogeochemical term reflecting sources and sinks of nutrients. Si(z) is constructed from the consumption of the nutrients, Pi(z), and the regeneration of nutrients (or remineralization), Qi(z); Si(z) = Qi(z) - Pi(z). The upwelling velocity, w, is assumed to be constant. Hirose and Kamiya, J. Oceanogr., 59, 149 (2003)
28 Consumption scheme of nutrients We adopted a first-order kinetics for the consumption of nutrients to simplify the biological process. The differential consumption rate is given as Pi(z) = d/dz (kp(z)ni(z)). (2) The depth-dependent consumption rate of nutrients due to the biological process, kp(z), is represented as an exponential function of depth. kp(z) = ko/λp exp (-λp z) (3) where ko (unit: yr-1)and λp (unit: m-1) respectively stand for the consumption rate constant in the surface layer (100 m depth).
29 Export scheme of nutrients The regeneration of nutrients in the water column, from the biological decomposition of sinking particles, is related to the export flux of particulate matter, Fi(z). We assume that the change of the export flux at depth corresponds to the input of nutrients remineralized in the water column as a result of decomposition by bacterial activity. The differential regeneration of nutrients in the water column is given as follows: Qi(z) = d/dz Fi(z). (4) The particle export flux is represented as an exponential function of depth (Shaffer, 1989): Fi(z) = Fio exp( - λf z) (5) where Fio (unit: mol m-2yr-1) and λf (unit: m-1) denote the export flux of N and P in the surface and the particle flux decay constant, respectively.
30 Basic equation of vertical profile of nutrients in the Kuroshio recirculation region Substituting eq. 2-5 in eq. 1, we obtain a following differential equation: d/dz(w(z)ni(z)) + d/dz (ko/λp exp (-λp z) Ni(z)) - d/dz (Fio exp( - λf z)) = 0. (6) This differential equation (eq. 6) can be solved under the conditions that concentrations of inorganic N and P in surface waters are negligible. Finally we have a simple equation as a result of integration: Ni(z) = A exp(λp -λf)z /{1 + B exp(λpz)} (7) where A and B are constant at each station; A = Fioλp/ko (unit: mol m-3) and B = w λp/ko (non-dimensional parameter). Equation 7 has been applied to fit the vertical distribution of inorganic N and P in the western North Pacific using adjustable parameters, A, B, λp and λf.
31
32 Relationship between adjustable parameters Information obtained from model fitting with the observed vertical profile. A, B, λp, λf (We used a constant λf value in all of the western North Pacific sites.) λf = 8x10-5 m -1 Fi,o/w = A/B Fi,o: export flux at 100 m depth w = Bλp -1 ko w: upwelling velocity (FN,o/FP.o)(ko,P/ko,N) = AN/AP (ko,p/ko,n) = BN/BP ko,p: consumption rate constant
33 Implication of parameters obtained by a simple model w/k w (k 1) upwelling velocity F/w :to be a linear relationship with maximum concentration of nutrients. To correspond to the variation of nutrient inventory kop/kon >1 : To preferentially consume phosphate. <1 : To preferentially consume nitrate.
34
35
36
37
38
39 Temporal variations of the vertical profiles of nutrients 25 N 137 E time-series data (winter, summer) started from 1970 by JMA. We used data from Temporal variations of the vertical profiles of nutrients reflect the values of upwelling velocity and F/w. The variation of upwelling velocity corresponds to passage of cyclonic and/or anticyclonic eddies.
40
41
42
43 2.Analysis of time-series data of nitrate and phosphate in 25 N 137 E The upwelling velocity varies according to path-through meso-scale eddies (cyclonic and anti-cyclonic). We observe a marked change of nutrient profiles in in the station of 25 N 137 E. There is no marked eddy during the period from 1992 to Nitrate was preferentially consumed by phytoplankton in the 1980s, whereas phosphate was consumed by phytoplankton in the 1990s The value of F/w corresponding to inventory for phosphate shows decadal variation.
44 3.Change spatial variation of nutrients in P3 to temporal variation A number of anticyclonic and cyclonic eddies are generated in the vicinity of the Kroshio Extension. Eddies move westward in the western North Pacific We assume a southwestward advection rate of 500 km y -1. Results Low phosphate in deep water around 1985 was observed by two independent observations (US and JMA). The N/P ratios in deep water around 1985 determined by JMA agreed with US observations. Phosphate and nitrate in deep waters may show decadal variation at an order of several percent.
45
46 Concluding remarks Nutrient concentrations in deep waters show decadal variations. The width of variation of phosphate concentrations in deep water is about 7%. The width of variation of nitrate concentrations in deep water is about 3.5 %. This variation is due to a natural variability in the western North Pacific. The variations of vertical profiles of nutrients are related to the formation and southwest motion of meso-scale eddies, which are produced in the Kuroshio extension region.
47 One possible ecological effect due to the climate change Cyclonic eddies steadily support a significant amount of biomass because nutrients continuously supply to the euphotic layer in eddies. Movement of eddies can transport a significant amount of biomass at the scale of basin. The variation of the formation of cyclonic eddies and their movement affects ecology of marine organisms. The climate change affects the formation of cyclonic eddies and their movement. The climate change affects marine ecosystems.
Upper Ocean Circulation
 Upper Ocean Circulation C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth 1 MAR555 Lecture 4: The Upper Oceanic Circulation The Oceanic Circulation
Upper Ocean Circulation C. Chen General Physical Oceanography MAR 555 School for Marine Sciences and Technology Umass-Dartmouth 1 MAR555 Lecture 4: The Upper Oceanic Circulation The Oceanic Circulation
Chemical Oceanography Spring 2000 Final Exam (Use the back of the pages if necessary)(more than one answer may be correct.)
 Ocean 421 Your Name Chemical Oceanography Spring 2000 Final Exam (Use the back of the pages if necessary)(more than one answer may be correct.) 1. Due to the water molecule's (H 2 O) great abundance in
Ocean 421 Your Name Chemical Oceanography Spring 2000 Final Exam (Use the back of the pages if necessary)(more than one answer may be correct.) 1. Due to the water molecule's (H 2 O) great abundance in
Lecture 1. Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature
 Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
Lecture 6 Lecture 1 Ocean circulation Forcing and large-scale features Amplitude of the seasonal cycle in temperature 1 Atmosphere and ocean heat transport Trenberth and Caron (2001) False-colour satellite
1 Carbon - Motivation
 1 Carbon - Motivation Figure 1: Atmospheric pco 2 over the past 400 thousand years as recorded in the ice core from Vostok, Antarctica (Petit et al., 1999). Figure 2: Air-sea flux of CO 2 (mol m 2 yr 1
1 Carbon - Motivation Figure 1: Atmospheric pco 2 over the past 400 thousand years as recorded in the ice core from Vostok, Antarctica (Petit et al., 1999). Figure 2: Air-sea flux of CO 2 (mol m 2 yr 1
TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS
 Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Notes of the tutorial lectures for the Natural Sciences part by Alice Grimm Fourth lecture TROPICAL-EXTRATROPICAL INTERACTIONS Anomalous tropical SST Anomalous convection Anomalous latent heat source Anomalous
Jeffrey Polovina 1, John Dunne 2, Phoebe Woodworth 1, and Evan Howell 1
 Projected expansion of the subtropical biome and contraction of the temperate and equatorial upwelling biomes in the North Pacific under global warming Jeffrey Polovina 1, John Dunne 2, Phoebe Woodworth
Projected expansion of the subtropical biome and contraction of the temperate and equatorial upwelling biomes in the North Pacific under global warming Jeffrey Polovina 1, John Dunne 2, Phoebe Woodworth
Catastrophic reduction of seaice in the Arctic Ocean - its impact on the marine ecosystems in the polar region-
 1/12 Catastrophic reduction of seaice in the Arctic Ocean - its impact on the marine ecosystems in the polar region- KAKENHI No.22221003 Naomi Harada (JAMSTEC) J. Onodera, E. Watanabe, K. Matsuno, K. Kimoto,
1/12 Catastrophic reduction of seaice in the Arctic Ocean - its impact on the marine ecosystems in the polar region- KAKENHI No.22221003 Naomi Harada (JAMSTEC) J. Onodera, E. Watanabe, K. Matsuno, K. Kimoto,
Ocean Mixing and Climate Change
 Ocean Mixing and Climate Change Factors inducing seawater mixing Different densities Wind stirring Internal waves breaking Tidal Bottom topography Biogenic Mixing (??) In general, any motion favoring turbulent
Ocean Mixing and Climate Change Factors inducing seawater mixing Different densities Wind stirring Internal waves breaking Tidal Bottom topography Biogenic Mixing (??) In general, any motion favoring turbulent
IPCC AR5 WG1 - Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Nandini Ramesh
 IPCC AR5 WG1 - Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis Nandini Ramesh Seminar in Atmospheric Science 21 st February, 2014 1. Introduc,on The ocean exchanges heat, freshwater, and C with the atmosphere.
IPCC AR5 WG1 - Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis Nandini Ramesh Seminar in Atmospheric Science 21 st February, 2014 1. Introduc,on The ocean exchanges heat, freshwater, and C with the atmosphere.
Typical Arctic profiles. How to form halocline water? 2012 Changing Arctic Ocean 506E/497E - Lecture 7 - Woodgate
 Schematic Surface and Atlantic Circulation Typical Arctic profiles MIXED LAYER Usually thin (no wind stirring) PACIFIC WATER High nutrients Shallow (
Schematic Surface and Atlantic Circulation Typical Arctic profiles MIXED LAYER Usually thin (no wind stirring) PACIFIC WATER High nutrients Shallow (
Project Retrograde imagine Earth rotated in the opposite direction
 Project Retrograde imagine Earth rotated in the opposite direction The rotation of Earth shapes our climate system in various ways: It controls the major wind directions, lets the weather systems swirl,
Project Retrograde imagine Earth rotated in the opposite direction The rotation of Earth shapes our climate system in various ways: It controls the major wind directions, lets the weather systems swirl,
Thermohaline and wind-driven circulation
 Thermohaline and wind-driven circulation Annalisa Bracco Georgia Institute of Technology School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences NCAR ASP Colloquium: Carbon climate connections in the Earth System Tracer
Thermohaline and wind-driven circulation Annalisa Bracco Georgia Institute of Technology School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences NCAR ASP Colloquium: Carbon climate connections in the Earth System Tracer
Time-series observations in the Northern Indian Ocean V.V.S.S. Sarma National Institute of Oceanography Visakhapatnam, India
 The Second GEOSS Asia-Pacific Symposium, Tokyo, 14-16 th April 28 Time-series observations in the Northern Indian Ocean V.V.S.S. Sarma National Institute of Oceanography Visakhapatnam, India Seasonal variations
The Second GEOSS Asia-Pacific Symposium, Tokyo, 14-16 th April 28 Time-series observations in the Northern Indian Ocean V.V.S.S. Sarma National Institute of Oceanography Visakhapatnam, India Seasonal variations
Phytoplankton. The Biological Pump. Nutrient Cycling and the Marine Biological Pump. Phytoplankton and Zooplankton. CSU ATS Sco9 Denning 1
 Nutrient Cycling and the Marine Biological Pump Readings: SelecGons from Williams & Follows (2011) Sabine et al (2004): Ocean Sink for Anthropogenic CO 2 Phytoplankton Diameter: < 1 mm to over 100 mm ConcentraGon:
Nutrient Cycling and the Marine Biological Pump Readings: SelecGons from Williams & Follows (2011) Sabine et al (2004): Ocean Sink for Anthropogenic CO 2 Phytoplankton Diameter: < 1 mm to over 100 mm ConcentraGon:
Dynamics of particulate organic carbon flux in a global ocean model
 Biogeosciences, 11, 1177 1198, 2014 doi:10.5194/bg-11-1177-2014 Authors 2014. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Biogeosciences Open Access Dynamics of particulate organic carbon flux in a global ocean model
Biogeosciences, 11, 1177 1198, 2014 doi:10.5194/bg-11-1177-2014 Authors 2014. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Biogeosciences Open Access Dynamics of particulate organic carbon flux in a global ocean model
The Planetary Circulation System
 12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
12 The Planetary Circulation System Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe and account for the global patterns of pressure, wind patterns and ocean currents
Strengthening seasonal marine CO 2 variations due to increasing atmospheric CO 2 - Supplementary material
 Strengthening seasonal marine CO 2 variations due to increasing atmospheric CO 2 - Supplementary material Peter Landschützer 1, Nicolas Gruber 2, Dorothee C. E. Bakker 3, Irene Stemmler 1, Katharina D.
Strengthening seasonal marine CO 2 variations due to increasing atmospheric CO 2 - Supplementary material Peter Landschützer 1, Nicolas Gruber 2, Dorothee C. E. Bakker 3, Irene Stemmler 1, Katharina D.
OCN/ATM/ESS 587. Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics.
 OCN/ATM/ESS 587 Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics. Equation of state for seawater General T/S properties of the upper ocean Heat balance of the upper ocean Upper ocean circulation Deep circulation
OCN/ATM/ESS 587 Ocean circulation, dynamics and thermodynamics. Equation of state for seawater General T/S properties of the upper ocean Heat balance of the upper ocean Upper ocean circulation Deep circulation
Decadal variability in the Kuroshio and Oyashio Extension frontal regions in an eddy-resolving OGCM
 Decadal variability in the Kuroshio and Oyashio Extension frontal regions in an eddy-resolving OGCM Masami Nonaka 1, Hisashi Nakamura 1,2, Youichi Tanimoto 1,3, Takashi Kagimoto 1, and Hideharu Sasaki
Decadal variability in the Kuroshio and Oyashio Extension frontal regions in an eddy-resolving OGCM Masami Nonaka 1, Hisashi Nakamura 1,2, Youichi Tanimoto 1,3, Takashi Kagimoto 1, and Hideharu Sasaki
Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models
 WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models Jerry Tjiputra 1, K. Lindsay 2, J. Orr 3, J. Segschneider 4, I. Totterdell 5, and C. Heinze 1 1 Bjerknes Centre for Climate
WWW.BJERKNES.UIB.NO Ocean carbon cycle feedbacks in the tropics from CMIP5 models Jerry Tjiputra 1, K. Lindsay 2, J. Orr 3, J. Segschneider 4, I. Totterdell 5, and C. Heinze 1 1 Bjerknes Centre for Climate
The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact
 1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
1 The North Atlantic Oscillation: Climatic Significance and Environmental Impact James W. Hurrell National Center for Atmospheric Research Climate and Global Dynamics Division, Climate Analysis Section
Winds and Global Circulation
 Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
Winds and Global Circulation Atmospheric Pressure Winds Global Wind and Pressure Patterns Oceans and Ocean Currents El Nino How is Energy Transported to its escape zones? Both atmospheric and ocean transport
The biological importance of the major ocean currents
 The biological importance of the major ocean currents Squid and the western boundary currents Illex illecebrosus, the short-finned squid Squid use the Gulf Stream to facilitate their migration. The center
The biological importance of the major ocean currents Squid and the western boundary currents Illex illecebrosus, the short-finned squid Squid use the Gulf Stream to facilitate their migration. The center
Mechanisms of air-sea CO 2 flux variability in the equatorial Pacific and the North Atlantic
 GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 18,, doi:10.1029/2003gb002179, 2004 Mechanisms of air-sea CO 2 flux variability in the equatorial Pacific and the North Atlantic Galen A. McKinley, 1,2 Michael J. Follows,
GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 18,, doi:10.1029/2003gb002179, 2004 Mechanisms of air-sea CO 2 flux variability in the equatorial Pacific and the North Atlantic Galen A. McKinley, 1,2 Michael J. Follows,
Climate/Ocean dynamics
 Interannual variations of the East-Kamchatka and East-Sakhalin Currents volume transports and their impact on the temperature and chemical parameters in the Okhotsk Sea Andrey G. Andreev V.I. Il ichev
Interannual variations of the East-Kamchatka and East-Sakhalin Currents volume transports and their impact on the temperature and chemical parameters in the Okhotsk Sea Andrey G. Andreev V.I. Il ichev
Hiromichi Igarashi 1,2, Y. Ishikawa 1, T. Wakamatsu 1, Y. Tanaka 1, M. Kamachi 1,3, N. Usui 3, M. Sakai 4, S. Saitoh 2 and Y.
 PICES2015,Qingdao Oct.20,2015 Relationships between ocean conditions and interannual variability of habitat suitability index (HSI) distribution for neon flying squid in central North Pacific examined
PICES2015,Qingdao Oct.20,2015 Relationships between ocean conditions and interannual variability of habitat suitability index (HSI) distribution for neon flying squid in central North Pacific examined
Estimates of Rates of Biological Productivity at BATS: Is there convergence?
 Estimates of Rates of Biological Productivity at BATS: Is there convergence? Rachel H. R. Stanley Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Outline 1) Introduction to Bermuda Atlantic Time-series Site (BATS)
Estimates of Rates of Biological Productivity at BATS: Is there convergence? Rachel H. R. Stanley Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Outline 1) Introduction to Bermuda Atlantic Time-series Site (BATS)
Global-scale variations of the ratios of carbon to phosphorus in exported marine organic matter
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2303 Global-scale variations of the ratios of carbon to phosphorus in exported marine organic matter Yi-Cheng Teng 1, Francois W. Primeau 1, J. Keith Moore 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO2303 Global-scale variations of the ratios of carbon to phosphorus in exported marine organic matter Yi-Cheng Teng 1, Francois W. Primeau 1, J. Keith Moore 1,
Ocean Circulation. In partnership with Dr. Zafer Top
 Ocean Circulation In partnership with Dr. Zafer Top Samantha Hampton Honors Science December 15, 2014 Ocean Circulation is the large scale movement of waters in the ocean basins. Dr. Zafer Top studies
Ocean Circulation In partnership with Dr. Zafer Top Samantha Hampton Honors Science December 15, 2014 Ocean Circulation is the large scale movement of waters in the ocean basins. Dr. Zafer Top studies
Cycling and transport of nutrients and carbon
 Chapter 11 Cycling and transport of nutrients and carbon Phytoplankton require sunlight and nutrients to grow in the surface ocean. Sustaining phytoplankton growth is difficult in the open ocean because
Chapter 11 Cycling and transport of nutrients and carbon Phytoplankton require sunlight and nutrients to grow in the surface ocean. Sustaining phytoplankton growth is difficult in the open ocean because
Eddy and Chlorophyll-a Structure in the Kuroshio Extension Detected from Altimeter and SeaWiFS
 14th Symposium on Integrated Observing and Assimilation Systems for the Atmosphere, Oceans, and Land Surface (IOAS-AOLS), AMS Atlanta, January 17-21, 21 Eddy and Chlorophyll-a Structure in the Kuroshio
14th Symposium on Integrated Observing and Assimilation Systems for the Atmosphere, Oceans, and Land Surface (IOAS-AOLS), AMS Atlanta, January 17-21, 21 Eddy and Chlorophyll-a Structure in the Kuroshio
The role of sub-antarctic mode water in global biological production. Jorge Sarmiento
 The role of sub-antarctic mode water in global biological production Jorge Sarmiento Original motivation Sediment traps suggest that ~one-third of the particulate organic matter flux at 200 m continues
The role of sub-antarctic mode water in global biological production Jorge Sarmiento Original motivation Sediment traps suggest that ~one-third of the particulate organic matter flux at 200 m continues
Modeled biogeochemical responses to mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2010jc006800, 2011 Modeled biogeochemical responses to mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea Peng Xiu 1 and Fei Chai 1 Received 11 November 2010;
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2010jc006800, 2011 Modeled biogeochemical responses to mesoscale eddies in the South China Sea Peng Xiu 1 and Fei Chai 1 Received 11 November 2010;
Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS Apr 2006
 Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp. 957-960 (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS 513 12 Apr 2006 Questions 1. What is the proposed mechanism by which a uniform
Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp. 957-960 (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS 513 12 Apr 2006 Questions 1. What is the proposed mechanism by which a uniform
Impact of atmospheric CO 2 doubling on the North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06602, doi:10.1029/2008gl037075, 2009 Impact of atmospheric CO 2 doubling on the North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water Hyun-Chul Lee 1,2 Received 19 December 2008;
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06602, doi:10.1029/2008gl037075, 2009 Impact of atmospheric CO 2 doubling on the North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water Hyun-Chul Lee 1,2 Received 19 December 2008;
Ocean Dynamics. The Great Wave off Kanagawa Hokusai
 Ocean Dynamics The Great Wave off Kanagawa Hokusai LO: integrate relevant oceanographic processes with factors influencing survival and growth of fish larvae Physics Determining Ocean Dynamics 1. Conservation
Ocean Dynamics The Great Wave off Kanagawa Hokusai LO: integrate relevant oceanographic processes with factors influencing survival and growth of fish larvae Physics Determining Ocean Dynamics 1. Conservation
Upper ocean control on the solubility pump of CO 2
 Journal of Marine Research, 61, 465 489, 2003 Upper ocean control on the solubility pump of CO 2 by Takamitsu Ito 1 and Michael J. Follows 1 ABSTRACT We develop and test a theory for the relationship of
Journal of Marine Research, 61, 465 489, 2003 Upper ocean control on the solubility pump of CO 2 by Takamitsu Ito 1 and Michael J. Follows 1 ABSTRACT We develop and test a theory for the relationship of
Cold air outbreak over the Kuroshio Extension Region
 Cold air outbreak over the Kuroshio Extension Region Jensen, T. G. 1, T. Campbell 1, T. A. Smith 1, R. J. Small 2 and R. Allard 1 1 Naval Research Laboratory, 2 Jacobs Engineering NRL, Code 7320, Stennis
Cold air outbreak over the Kuroshio Extension Region Jensen, T. G. 1, T. Campbell 1, T. A. Smith 1, R. J. Small 2 and R. Allard 1 1 Naval Research Laboratory, 2 Jacobs Engineering NRL, Code 7320, Stennis
1: JAMSTEC; 2: Tohoku University; 3: MWJ *Deceased. POC Paper Session PICES-2014 October 16-26, 2014, Yeosu, Republic of Korea
 Western North Pacific Integrated Physical- Biogeochemical Ocean Observation Experiment: Summary of the Intensive Observation around the Biogeochemical Mooring S1 (S1-INBOX) Toshio Suga 1,2, Ryuichiro Inoue
Western North Pacific Integrated Physical- Biogeochemical Ocean Observation Experiment: Summary of the Intensive Observation around the Biogeochemical Mooring S1 (S1-INBOX) Toshio Suga 1,2, Ryuichiro Inoue
E-FLUX: An Investigation of Eddy Dynamics in the Lee of Hawaii. OCN 621: Biological Oceanography Bob Bidigare
 E-FLUX: An Investigation of Eddy Dynamics in the Lee of Hawaii OCN 621: Biological Oceanography Bob Bidigare 17 February 2006 Isolated Vortices Isolated vortices (IVs) are formed via numerous processes
E-FLUX: An Investigation of Eddy Dynamics in the Lee of Hawaii OCN 621: Biological Oceanography Bob Bidigare 17 February 2006 Isolated Vortices Isolated vortices (IVs) are formed via numerous processes
CGSN Overview. GSN Sites CSN Sites Shore Facilities
 GSN Sites CSN Sites Shore Facilities CGSN Overview Coastal Pioneer Array Endurance Array Global Irminger Sea Southern Ocean Station Papa Fixed assets Surface mooring Subsurface mooring Mobile assets Ocean
GSN Sites CSN Sites Shore Facilities CGSN Overview Coastal Pioneer Array Endurance Array Global Irminger Sea Southern Ocean Station Papa Fixed assets Surface mooring Subsurface mooring Mobile assets Ocean
ROLES OF THE OCEAN MESOSCALE IN THE LATERAL SUPPLY OF MASS, HEAT, CARBON AND NUTRIENTS TO THE NORTHERN HEMISPHERE SUBTROPICAL GYRE
 ROLES OF THE OCEAN MESOSCALE IN THE LATERAL SUPPLY OF MASS, HEAT, CARBON AND NUTRIENTS TO THE NORTHERN HEMISPHERE SUBTROPICAL GYRE AYAKO YAMAMOTO 1*, JAIME B. PALTER 1,2, CAROLINA O. DUFOUR 1,3, STEPHEN
ROLES OF THE OCEAN MESOSCALE IN THE LATERAL SUPPLY OF MASS, HEAT, CARBON AND NUTRIENTS TO THE NORTHERN HEMISPHERE SUBTROPICAL GYRE AYAKO YAMAMOTO 1*, JAIME B. PALTER 1,2, CAROLINA O. DUFOUR 1,3, STEPHEN
Eddy-resolving Simulation of the World Ocean Circulation by using MOM3-based OGCM Code (OFES) Optimized for the Earth Simulator
 Chapter 1 Atmospheric and Oceanic Simulation Eddy-resolving Simulation of the World Ocean Circulation by using MOM3-based OGCM Code (OFES) Optimized for the Earth Simulator Group Representative Hideharu
Chapter 1 Atmospheric and Oceanic Simulation Eddy-resolving Simulation of the World Ocean Circulation by using MOM3-based OGCM Code (OFES) Optimized for the Earth Simulator Group Representative Hideharu
How to form halocline water?
 How to form halocline water? Atlantic water - cannot form Halocline water simply by mixing (Aagaard, 1981) Surface Water Adapted from Steele and Boyd, 1998 ADVECTIVE HC Temp Fresh Salty Aagaard et al,
How to form halocline water? Atlantic water - cannot form Halocline water simply by mixing (Aagaard, 1981) Surface Water Adapted from Steele and Boyd, 1998 ADVECTIVE HC Temp Fresh Salty Aagaard et al,
Using preformed nitrate to infer decadal changes in DOM remineralization in the subtropical North Pacific
 GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 19,, doi:10.1029/2004gb002285, 2005 Using preformed nitrate to infer decadal changes in DOM remineralization in the subtropical North Pacific Jeffrey Abell Department
GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 19,, doi:10.1029/2004gb002285, 2005 Using preformed nitrate to infer decadal changes in DOM remineralization in the subtropical North Pacific Jeffrey Abell Department
Almost of Earth is covered by water. On a map, the continents appear as huge islands surrounded by a vast global ocean.
 Earth s Oceans & Ocean Floor Date: Feelin Blue What are Earth s five main oceans? Almost of Earth is covered by water. On a map, the continents appear as huge islands surrounded by a vast global ocean.
Earth s Oceans & Ocean Floor Date: Feelin Blue What are Earth s five main oceans? Almost of Earth is covered by water. On a map, the continents appear as huge islands surrounded by a vast global ocean.
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
Interannual variability of Black Sea's hydrodynamics and connection to atmospheric patterns
 P. Alechinsky,The Black Sea, 1990 Interannual variability of Black Sea's hydrodynamics and connection to atmospheric patterns Capet Arthur, Barth Alexander, Beckers Jean-Marie, Grégoire Marilaure Context
P. Alechinsky,The Black Sea, 1990 Interannual variability of Black Sea's hydrodynamics and connection to atmospheric patterns Capet Arthur, Barth Alexander, Beckers Jean-Marie, Grégoire Marilaure Context
Weather & Ocean Currents
 Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
Weather & Ocean Currents Earth is heated unevenly Causes: Earth is round Earth is tilted on an axis Earth s orbit is eliptical Effects: Convection = vertical circular currents caused by temperature differences
A role of eddies in formation and transport of North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water
 1 A role of eddies in formation and transport of North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water Hiroki Uehara 1, Toshio Suga 1,2, Kimio Hanawa 1 and Nobuyuki Shikama 2 1 Department of Geophysics, Graduate School
1 A role of eddies in formation and transport of North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water Hiroki Uehara 1, Toshio Suga 1,2, Kimio Hanawa 1 and Nobuyuki Shikama 2 1 Department of Geophysics, Graduate School
OCB Summer Workshop WHOI, July 16-19,
 Transformation and fluxes of carbon in a changing Arctic Ocean and it s impact on ocean acidification, the Atlantic view Leif G. Anderson Department t of Chemistry and Molecular l Biology University of
Transformation and fluxes of carbon in a changing Arctic Ocean and it s impact on ocean acidification, the Atlantic view Leif G. Anderson Department t of Chemistry and Molecular l Biology University of
THE OCEAN CARBON CYCLE
 THE OCEAN CARBON CYCLE 21st February 2018 1 Box-model of the global ocean phosphorus, alkalinity, carbon 2 Pre-industrial model 3 Evolution during the industrial period 4 13 C isotopic evolution BOX-MODEL
THE OCEAN CARBON CYCLE 21st February 2018 1 Box-model of the global ocean phosphorus, alkalinity, carbon 2 Pre-industrial model 3 Evolution during the industrial period 4 13 C isotopic evolution BOX-MODEL
1. Introduction 2. Ocean circulation a) Temperature, salinity, density b) Thermohaline circulation c) Wind-driven surface currents d) Circulation and
 1. Introduction 2. Ocean circulation a) Temperature, salinity, density b) Thermohaline circulation c) Wind-driven surface currents d) Circulation and climate change e) Oceanic water residence times 3.
1. Introduction 2. Ocean circulation a) Temperature, salinity, density b) Thermohaline circulation c) Wind-driven surface currents d) Circulation and climate change e) Oceanic water residence times 3.
Carbon pathways in the South Atlantic
 Carbon pathways in the South Atlantic Olga T. Sato, Ph.D. Paulo Polito, Ph.D. olga.sato@usp.br - polito@usp.br Oceanographic Institute University of São Paulo Olga Sato and Paulo Polito (IOUSP) Carbon
Carbon pathways in the South Atlantic Olga T. Sato, Ph.D. Paulo Polito, Ph.D. olga.sato@usp.br - polito@usp.br Oceanographic Institute University of São Paulo Olga Sato and Paulo Polito (IOUSP) Carbon
Carbon Dioxide, Alkalinity and ph
 Carbon Dioxide, Alkalinity and ph OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 15 March 2018 Reading: Libes, Chapter 15, pp. 383 389 (Remainder of chapter will be used with the classes Global Carbon Dioxide and Biogenic
Carbon Dioxide, Alkalinity and ph OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography 15 March 2018 Reading: Libes, Chapter 15, pp. 383 389 (Remainder of chapter will be used with the classes Global Carbon Dioxide and Biogenic
Size matters: another reason why the Atlantic is saltier than the Pacific C.S. Jones and Paola Cessi
 Size matters: another reason why the Atlantic is saltier than the Pacific C.S. Jones and Paola Cessi Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego Proposed reasons for Atlantic
Size matters: another reason why the Atlantic is saltier than the Pacific C.S. Jones and Paola Cessi Scripps Institution of Oceanography University of California, San Diego Proposed reasons for Atlantic
CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation Pearson Education, Inc.
 CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Types of Ocean Currents Surface currents Deep currents 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Measuring Surface Currents Direct methods Floating device tracked
CHAPTER 7 Ocean Circulation 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Types of Ocean Currents Surface currents Deep currents 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Measuring Surface Currents Direct methods Floating device tracked
CO2 in atmosphere is influenced by pco2 of surface water (partial pressure of water is the CO2 (gas) that would be in equilibrium with water).
 EART 254, Lecture on April 6 & 11, 2011 Introduction (skipped most of this) Will look at C and N (maybe) cycles with respect to how they influence CO2 levels in the atmosphere. Ocean chemistry controls
EART 254, Lecture on April 6 & 11, 2011 Introduction (skipped most of this) Will look at C and N (maybe) cycles with respect to how they influence CO2 levels in the atmosphere. Ocean chemistry controls
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10
 Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Wind: Global Systems Chapter 10 General Circulation of the Atmosphere General circulation of the atmosphere describes average wind patterns and is useful for understanding climate Over the earth, incoming
Water mass formation, subduction, and the oceanic heat budget
 Chapter 5 Water mass formation, subduction, and the oceanic heat budget In the first four chapters we developed the concept of Ekman pumping, Rossby wave propagation, and the Sverdrup circulation as the
Chapter 5 Water mass formation, subduction, and the oceanic heat budget In the first four chapters we developed the concept of Ekman pumping, Rossby wave propagation, and the Sverdrup circulation as the
Phytoplankton. Zooplankton. Nutrients
 Phytoplankton Zooplankton Nutrients Patterns of Productivity There is a large Spring Bloom in the North Atlantic (temperate latitudes remember the Gulf Stream!) What is a bloom? Analogy to terrestrial
Phytoplankton Zooplankton Nutrients Patterns of Productivity There is a large Spring Bloom in the North Atlantic (temperate latitudes remember the Gulf Stream!) What is a bloom? Analogy to terrestrial
FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA
 FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA AKIO KITOH, MASAHIRO HOSAKA, YUKIMASA ADACHI, KENJI KAMIGUCHI Meteorological Research Institute Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0052, Japan It is anticipated
FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA AKIO KITOH, MASAHIRO HOSAKA, YUKIMASA ADACHI, KENJI KAMIGUCHI Meteorological Research Institute Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0052, Japan It is anticipated
Nutrient streams and their induction into the mixed layer
 GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 20,, doi:10.1029/2005gb002586, 2006 Nutrient streams and their induction into the mixed layer Richard G. Williams, 1 Vassil Roussenov, 1 and Michael J. Follows 2 Received
GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 20,, doi:10.1029/2005gb002586, 2006 Nutrient streams and their induction into the mixed layer Richard G. Williams, 1 Vassil Roussenov, 1 and Michael J. Follows 2 Received
CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Viewed from above in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds about a subtropical high blow a. clockwise and inward. b. counterclockwise.
CHAPTER 9 ATMOSPHERE S PLANETARY CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Viewed from above in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds about a subtropical high blow a. clockwise and inward. b. counterclockwise.
Oceanography of the tropical Pacific Ocean Part 2 Historical changes and future projections
 Oceanography of the tropical Pacific Ocean Part 2 Historical changes and future projections A. Ganachaud 1, A. Sen Gupta 2, J. Brown 3, L. Muir 3, with contributions from J. Orr, S. Wijffels, K. Ridgway,
Oceanography of the tropical Pacific Ocean Part 2 Historical changes and future projections A. Ganachaud 1, A. Sen Gupta 2, J. Brown 3, L. Muir 3, with contributions from J. Orr, S. Wijffels, K. Ridgway,
Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research. Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes
 Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes Acknowledgments Anders Levermann Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact
Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes Acknowledgments Anders Levermann Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact
A modeling study of the North Pacific shallow overturning circulation. Takao Kawasaki, H. Hasumi, 2 M. Kurogi
 PICES 2011 Annual Meeting, Khabarovsk, Russia A modeling study of the North Pacific shallow overturning circulation 1 Takao Kawasaki, H. Hasumi, 2 M. Kurogi 1 Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute, University
PICES 2011 Annual Meeting, Khabarovsk, Russia A modeling study of the North Pacific shallow overturning circulation 1 Takao Kawasaki, H. Hasumi, 2 M. Kurogi 1 Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute, University
Anthropogenic CO 2 accumulation rates in the North Atlantic Ocean from changes in the 13 C/ 12 C of dissolved inorganic carbon
 Click Here for Full Article GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 21,, doi:10.1029/2006gb002761, 2007 Anthropogenic CO 2 accumulation rates in the North Atlantic Ocean from changes in the 13 C/ 12 C of dissolved
Click Here for Full Article GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 21,, doi:10.1029/2006gb002761, 2007 Anthropogenic CO 2 accumulation rates in the North Atlantic Ocean from changes in the 13 C/ 12 C of dissolved
Possible mechanism of bi-decadal North Pacific ocean/climate variability in relation to 18.6-year nodal tidal cycle
 Possible mechanism of bi-decadal North Pacific ocean/climate variability in relation to 18.6-year nodal tidal cycle Ichiro Yasuda and Satoshi Osafune (Ocean Research Institute, Univ. Tokyo) Hiroaki Tatebe
Possible mechanism of bi-decadal North Pacific ocean/climate variability in relation to 18.6-year nodal tidal cycle Ichiro Yasuda and Satoshi Osafune (Ocean Research Institute, Univ. Tokyo) Hiroaki Tatebe
SIO 210 Final Exam December 10, :30 2:30 NTV 330 No books, no notes. Calculators can be used.
 SIO 210 Final Exam December 10, 2003 11:30 2:30 NTV 330 No books, no notes. Calculators can be used. There are three sections to the exam: multiple choice, short answer, and long problems. Points are given
SIO 210 Final Exam December 10, 2003 11:30 2:30 NTV 330 No books, no notes. Calculators can be used. There are three sections to the exam: multiple choice, short answer, and long problems. Points are given
Physical-biological interactions in North Pacific oxygen variability
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jc003179, 2006 Physical-biological interactions in North Pacific oxygen variability Curtis Deutsch, 1 Steven Emerson,
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 111,, doi:10.1029/2005jc003179, 2006 Physical-biological interactions in North Pacific oxygen variability Curtis Deutsch, 1 Steven Emerson,
Chemical Oceanography 14 March 2012 Points are in parentheses (show all your work) Final Exam
 Ocean 400 Name: Chemical Oceanography 14 March 2012 Winter 2012 Points are in parentheses (show all your work) (give as much detail as you can) (use back if necessary) Final Exam 1. Sarmiento and Gruber
Ocean 400 Name: Chemical Oceanography 14 March 2012 Winter 2012 Points are in parentheses (show all your work) (give as much detail as you can) (use back if necessary) Final Exam 1. Sarmiento and Gruber
A Synthesis of Results from the Norwegian ESSAS (N-ESSAS) Project
 A Synthesis of Results from the Norwegian ESSAS (N-ESSAS) Project Ken Drinkwater Institute of Marine Research Bergen, Norway ken.drinkwater@imr.no ESSAS has several formally recognized national research
A Synthesis of Results from the Norwegian ESSAS (N-ESSAS) Project Ken Drinkwater Institute of Marine Research Bergen, Norway ken.drinkwater@imr.no ESSAS has several formally recognized national research
Basic Ocean Current Systems. Basic Ocean Structures. The State of Oceans. Lecture 6: The Ocean General Circulation and Climate. Temperature.
 Lecture 6: The Ocean General Circulation and Climate Basic Ocean Current Systems Upper Ocean surface circulation Basic Structures Mixed Layer Wind-Driven Circulation Theories Thermohaline Circulation Ocean
Lecture 6: The Ocean General Circulation and Climate Basic Ocean Current Systems Upper Ocean surface circulation Basic Structures Mixed Layer Wind-Driven Circulation Theories Thermohaline Circulation Ocean
Interdecadal variability of the thermocline along the west coast of South America
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L20307, doi:10.1029/2004gl020998, 2004 Interdecadal variability of the thermocline along the west coast of South America Oscar Pizarro Departamento de Física de la
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L20307, doi:10.1029/2004gl020998, 2004 Interdecadal variability of the thermocline along the west coast of South America Oscar Pizarro Departamento de Física de la
Long-Term Variability of North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water in Response to Spin-Up of the Subtropical Gyre
 Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 59, pp. 279 to 290, 2003 Long-Term Variability of North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water in Response to Spin-Up of the Subtropical Gyre TAMAKI YASUDA* and YOSHITERU KITAMURA
Journal of Oceanography, Vol. 59, pp. 279 to 290, 2003 Long-Term Variability of North Pacific Subtropical Mode Water in Response to Spin-Up of the Subtropical Gyre TAMAKI YASUDA* and YOSHITERU KITAMURA
Dynamics and Kinematics
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics () Syllabus Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3,
Hydrography and biological resources in the western Bering Sea. Gennady V. Khen, Eugeny O. Basyuk. Pacific Research Fisheries Centre (TINRO-Centre)
 Hydrography and biological resources in the western Bering Sea Gennady V. Khen, Eugeny O. Basyuk Pacific Research Fisheries Centre (TINRO-Centre) Bering Sea: deep-sea basin, shelf, and US-Russia convention
Hydrography and biological resources in the western Bering Sea Gennady V. Khen, Eugeny O. Basyuk Pacific Research Fisheries Centre (TINRO-Centre) Bering Sea: deep-sea basin, shelf, and US-Russia convention
Annual net community production and the biological carbon flux in the ocean
 GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 28, 1 12, doi:10.1002/2013gb004680, 2014 Annual net community production and the biological carbon flux in the ocean Steven Emerson 1 Received 28 June 2013; revised 6
GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES, VOL. 28, 1 12, doi:10.1002/2013gb004680, 2014 Annual net community production and the biological carbon flux in the ocean Steven Emerson 1 Received 28 June 2013; revised 6
Nutrients; Aerobic Carbon Production and Consumption
 Nutrients; Aerobic Carbon Production and Consumption OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography Reading: Libes, Chapters 8 and 9 Formation and respiration of organic matter DINutrients POM Primary Producers Autotrophs
Nutrients; Aerobic Carbon Production and Consumption OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography Reading: Libes, Chapters 8 and 9 Formation and respiration of organic matter DINutrients POM Primary Producers Autotrophs
8 Mechanisms for tropical rainfall responses to equatorial
 8 Mechanisms for tropical rainfall responses to equatorial heating More reading: 1. Hamouda, M. and Kucharski, F. (2019) Ekman pumping Mechanism driving Precipitation anomalies in Response to Equatorial
8 Mechanisms for tropical rainfall responses to equatorial heating More reading: 1. Hamouda, M. and Kucharski, F. (2019) Ekman pumping Mechanism driving Precipitation anomalies in Response to Equatorial
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228)
 Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Geophysics Fluid Dynamics (ESS228) Course Time Lectures: Tu, Th 09:30-10:50 Discussion: 3315 Croul Hall Text Book J. R. Holton, "An introduction to Dynamic Meteorology", Academic Press (Ch. 1, 2, 3, 4,
Arne Biastoch Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel. Modelling the Agulhas Current and its Coupling with the Atlantic Circulation
 Arne Biastoch Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel Modelling the Agulhas Current and its Coupling with the Atlantic Circulation The Agulhas System as a Key Region of the Global Oceanic Circulation
Arne Biastoch Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel Modelling the Agulhas Current and its Coupling with the Atlantic Circulation The Agulhas System as a Key Region of the Global Oceanic Circulation
The Agulhas Current system: its dynamics and climatic importance
 The Agulhas Current system: its dynamics and climatic importance BJØRN BACKEBERG 1 NANSEN-TUTU CENTRE FOR MARINE ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH 2 DEPTARTMENT OF OCEANOGRAPHY, UNIVERSITY OF CAPE TOWN Nansen Centers
The Agulhas Current system: its dynamics and climatic importance BJØRN BACKEBERG 1 NANSEN-TUTU CENTRE FOR MARINE ENVIRONMENTAL RESEARCH 2 DEPTARTMENT OF OCEANOGRAPHY, UNIVERSITY OF CAPE TOWN Nansen Centers
Where is all the water?
 Where is all the water? The distribution of water at the Earth's surface % of total Oceans 97.25 Ice caps and glaciers 2.05 Groundwater 0.68 Lakes 0.01 Soils 0.005 Atmosphere (as vapour) 0.001 Rivers 0.0001
Where is all the water? The distribution of water at the Earth's surface % of total Oceans 97.25 Ice caps and glaciers 2.05 Groundwater 0.68 Lakes 0.01 Soils 0.005 Atmosphere (as vapour) 0.001 Rivers 0.0001
Surface Circulation. Key Ideas
 Surface Circulation The westerlies and the trade winds are two of the winds that drive the ocean s surface currents. 1 Key Ideas Ocean water circulates in currents. Surface currents are caused mainly by
Surface Circulation The westerlies and the trade winds are two of the winds that drive the ocean s surface currents. 1 Key Ideas Ocean water circulates in currents. Surface currents are caused mainly by
EI Nino Induced Ocean Eddies in the Gulf of Alaska
 EI Nino Induced Ocean Eddies in the Gulf of Alaska Arne Melsom, Harley E. Hurlburt, E. Joseph Metzger, Steven D. Meyers and James J. O'Brien Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies The Florida
EI Nino Induced Ocean Eddies in the Gulf of Alaska Arne Melsom, Harley E. Hurlburt, E. Joseph Metzger, Steven D. Meyers and James J. O'Brien Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies The Florida
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
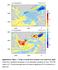 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Nutrients; Aerobic Carbon Production and Consumption
 Nutrients; Aerobic Carbon Production and Consumption OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography Reading: Libes, Chapters 8 and 9 Formation and respiration of organic matter DINutrients POM Primary Producers Autotrophs
Nutrients; Aerobic Carbon Production and Consumption OCN 623 Chemical Oceanography Reading: Libes, Chapters 8 and 9 Formation and respiration of organic matter DINutrients POM Primary Producers Autotrophs
Part 1. Ocean Composition & Circulation
 OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.19.17) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 1. Ocean Composition & Circulation 1. Introduction Lecture Outline 2. Ocean Circulation a) Global Patterns in T, S, ρ b) Thermohaline
OCN 401 Biogeochemical Systems (10.19.17) (Schlesinger: Chapter 9) Part 1. Ocean Composition & Circulation 1. Introduction Lecture Outline 2. Ocean Circulation a) Global Patterns in T, S, ρ b) Thermohaline
Seasonal and Intra-Seasonal Variability of Chlorophyll-a in the North Pacific: Model and Satellite data
 Journal of the Earth Simulator, Volume 8, November 7, 3 11 Seasonal and Intra-Seasonal Variability of Chlorophyll-a in the North Pacific: Model and Satellite data Yoshikazu Sasai 1 *, Kosei Sasaoka 1,
Journal of the Earth Simulator, Volume 8, November 7, 3 11 Seasonal and Intra-Seasonal Variability of Chlorophyll-a in the North Pacific: Model and Satellite data Yoshikazu Sasai 1 *, Kosei Sasaoka 1,
Ocean cycles and climate ENSO, PDO, AMO, AO
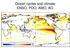 Ocean cycles and climate ENSO, PDO, AMO, AO 3 2.5 2 enso-index 1.5 1 0.5 0-0.5-1 enso 3.4 -index - 1996 to 1999-1.5 1996 1997 1998 1999 Bob Tisdale Bob Tisdale Bob Tisdale ENSO mechanisms animation http://esminfo.prenhall.com/science/geoanimations/animations/26_ninonina.html
Ocean cycles and climate ENSO, PDO, AMO, AO 3 2.5 2 enso-index 1.5 1 0.5 0-0.5-1 enso 3.4 -index - 1996 to 1999-1.5 1996 1997 1998 1999 Bob Tisdale Bob Tisdale Bob Tisdale ENSO mechanisms animation http://esminfo.prenhall.com/science/geoanimations/animations/26_ninonina.html
Tracer transport and meridional overturn in the equatorial ocean
 OFES workshops, February 2006 Tracer transport and meridional overturn in the equatorial ocean Akio Ishida with Yoshikazu Sasai, Yasuhiro Yamanaka, Hideharu Sasaki, and the OFES members Chlorofluorocarbon
OFES workshops, February 2006 Tracer transport and meridional overturn in the equatorial ocean Akio Ishida with Yoshikazu Sasai, Yasuhiro Yamanaka, Hideharu Sasaki, and the OFES members Chlorofluorocarbon
INSIGHTS INTO PARTICLE FORMATION AND REMINERALIZATION USING THE SHORT-LIVED RADIONUCLIDE, THORUIM-234 LA Woods Hole, MA 02543
 1 1 2 3 4 INSIGHTS INTO PARTICLE FORMATION AND REMINERALIZATION USING THE SHORT-LIVED RADIONUCLIDE, THORUIM-234 Kanchan Maiti 1,2, Claudia R. Benitez-Nelson 3 and Ken O. Buesseler 2 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 Department
1 1 2 3 4 INSIGHTS INTO PARTICLE FORMATION AND REMINERALIZATION USING THE SHORT-LIVED RADIONUCLIDE, THORUIM-234 Kanchan Maiti 1,2, Claudia R. Benitez-Nelson 3 and Ken O. Buesseler 2 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 Department
JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN
 JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN Soon-Il An 1, Fei-Fei Jin 1, Jong-Seong Kug 2, In-Sik Kang 2 1 School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology, University
JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN Soon-Il An 1, Fei-Fei Jin 1, Jong-Seong Kug 2, In-Sik Kang 2 1 School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology, University
Environmental changes
 Environmental changes What are the fishery, environmental, and trophic effects in historical data? Can we use short-term predictions from multiple regression models? Two kind of predictions: What happens
Environmental changes What are the fishery, environmental, and trophic effects in historical data? Can we use short-term predictions from multiple regression models? Two kind of predictions: What happens
The seasonal and interannual variability of circulation in the eastern and western Okhotsk Sea and its impact on plankton biomass
 The seasonal and interannual variability of circulation in the eastern and western Okhotsk Sea and its impact on plankton biomass Andrey G. Andreev, Sergey V. Prants, Maxim V. Budyansky and Michael Yu.
The seasonal and interannual variability of circulation in the eastern and western Okhotsk Sea and its impact on plankton biomass Andrey G. Andreev, Sergey V. Prants, Maxim V. Budyansky and Michael Yu.
U.S. CLIVAR VPM7 Guayaquil March 2004
 U.S. CLIVAR VPM7 Guayaquil 22-24 March 2004 CLIVAR Climate Variability and Predictability What causes the variability of the earth's climate on time scales from seasons to centuries and can we predict
U.S. CLIVAR VPM7 Guayaquil 22-24 March 2004 CLIVAR Climate Variability and Predictability What causes the variability of the earth's climate on time scales from seasons to centuries and can we predict
- vertical and horizontal segregation Univ. Washington - case studies (Fe and N) (10/29/01)
 Chapter 10: Biolimiting Elements James W. Murray - vertical and horizontal segregation Univ. Washington - case studies (Fe and N) (10/29/01) By definition, biolimiting elements are those: necessary to
Chapter 10: Biolimiting Elements James W. Murray - vertical and horizontal segregation Univ. Washington - case studies (Fe and N) (10/29/01) By definition, biolimiting elements are those: necessary to
XI. the natural carbon cycle. with materials from J. Kasting (Penn State)
 XI. the natural carbon cycle with materials from J. Kasting (Penn State) outline properties of carbon the terrestrial biological cycle of carbon the ocean cycle of carbon carbon in the rock cycle overview
XI. the natural carbon cycle with materials from J. Kasting (Penn State) outline properties of carbon the terrestrial biological cycle of carbon the ocean cycle of carbon carbon in the rock cycle overview
