A study of the large voids in the spatial distribution of galaxy clusters in the Northern Galactic Hemisphere
|
|
|
- Lester Robbins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS JUNE I 2, PAGE 323 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astrn. Astrphys. Suppl. Ser. 144, (2) A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters in the Nrthern Galactic Hemisphere K.Y. Stavrev Institute f Astrnmy, Bulgarian Academy f Sciences, 72 Tsarigradsk Shsse Blvd., BG-1784 Sfia, Bulgaria kstavrev@skyarchive.rg Received July 22, 1999; accepted March 23, 2 Abstract. We present a mapping f the large vids (D 5 h 1 Mpc) in the spatial distributin f clusters f galaxies in the Nrthern Galactic Hemisphere in a vlume defined by galactic latitude b +3 and redshift z.14. Rich clusters with spectrscpically measured r phtmetrically estimated redshifts are used as tracers f the large-scale structure f the Universe. An autmated vid-search and analysis prcedure which identifies a vid as a system f intersecting empty spheres is applied, allwing fr a descriptin f the vid dimensins, vlumes and shapes mre cmplete than in previus investigatins. A number f vid catalgues crrespnding t different tracer types, different surces f redshift data, and different versins f the search methd have been generated and analysed. Visualizatins f the 2-D and 3-D distributins f vids are presented. The estimated mean dimensins f the vids f R 1andR Abell/ACO clusters are D e = 15. ± 5.6 h 1 Mpc and D e = 87.2 ± 4.1 h 1 Mpc, respectively, where D e is the equivalent vid diameter. We have identified the pr clusters, grups, and galaxies ppulating the vids f rich clusters and cnstructed radial density prfiles f the vids, which shw the presence f a vid hierarchy. Key wrds: csmlgy: bservatins large-scale structure f Universe galaxies: clusters: general methds: data analysis 1. Intrductin The vids in the spatial distributin f galaxies and clusters f galaxies, discvered mre than tw decades ag (Tifft & Gregry 1976; Gregry & Thmpsn 1978; Jõeveer & Einast 1978; Kirshner et al. 1981; Bahcall & Sneira 1982a, 1982b), are a dminant feature f the largescale structure (LSS) f the Universe. The bservatinal Send ffprint requests t: K.Y.Stavrev studies f their prperties (gemetrical parameters, cntent, envirnment) are f great imprtance fr testing basic assumptins in the cntemprary theretical mdels and scenaris f the frmatin and evlutin f the LSS. One majr cmplicatin in vid studies arises frm the difficulty t btain spatial distributins f the tracers f the LSS with spectrscpically measured redshifts which are fairly cmplete in vlumes bth wide and deep. Frm this pint f view the use f rich clusters f galaxies as tracers allws t study the largest spatial vlumes. Wide-angle studies f the vids in the distributin f clusters f galaxies cntaining lists (catalgues) f the identified vids have been carried ut s far by Batuski & Burns (1985), Tully (1986), Stavrev (199a, 199b), and Einast et al. (1994). All f them are based n Abell/ACO clusters (Abell 1958; Abell et al. 1989) as tracers. Since then, new redshift data fr the clusters have been accumulated. An imprtant step in this directin is the MX Nrthern Abell Cluster Redshift Survey (Slinglend et al. 1998), nt nly because f the increased number f clusters with measured redshifts, but als because f the reliable determinatin f the cluster redshifts excluding t a great extent the fregrund/backgrund cntaminatin. The newly accumulated redshift data allws nw fr a mre cmplete and crrect mapping f the vids in the distributin f galaxy clusters. Recent bservatinal studies cnfirm a hierarchical structure f the vids, suggested frm theretical cnsideratins fr the vid evlutin by Dubinski et al. (1993), and van de Weygaert & van Kampen (1993). Accrding t Einast et al. (1994) the vids determined by rich clusters f galaxies are divided int smaller vids by filaments f very pr clusters and galaxies. Lindner et al. (1995, 1996) find a vid hierarchy in the Nrthern Lcal Supervid (Einast et al. 1983): vids defined by pr (Zwicky) clusters are divided int smaller vids by latetype galaxies. These vids cntain fainter galaxies which define still smaller vids. The presence f the vid hierarchy makes it reasnable t cmbine the bservatins f
2 324 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters different types f tracers f the LSS frm rich clusters f galaxies dwn t pr clusters, grups, and single galaxies. The usefulness f this apprach, hwever, is limited by the incmpleteness f the samples f pr clusters, grups and galaxies with measured redshifts in vlumes in which the rich clusters f galaxies frm cmplete samples. The chice f apprpriate numerical techniques fr vid search and analysis is an imprtant aspect f the vid studies. The methd f the largest empty sphere, nested in the vid, has been mst ften used in searches fr vids in the distributin f clusters. It has been first applied by Tully (1986), and later by Einast et al. (1989) and Stavrev (199a, 199b). Tifft & Gregry (1988) and Stavrev (1991) have prpsed an imprvement f this methd thrugh apprximatin f a vid by a system f intersecting spheres (spherids). Such an apprach allws fr a mre cmplete descriptin f the vid dimensins, vlumes and shapes. An applicatin f this versin f the methd is given in Stavrev (1998). Recently similar multisphere techniques were develped by El-Ad et al. (1996), as well as by Aiki & Mähönen (1998), and applied t the study f vids in the distributin f IRAS galaxies (El- Ad et al. 1997) and suthern sky galaxies (El-Ad & Piran 1997). The gals f this paper are (1) t map as cmpletely as pssible the large vids in the distributin f clusters f galaxies in the Nrthern Galactic Hemisphere ut t medium-large distances ( 4 h 1 Mpc) cmbining redshift data frm many surces, and using estimated redshifts, (2) t define vid parameters n the basis f a mre elabrate prcedure fr vid search and analysis, (3) t btain estimates f the mean characteristics f vids frm a statistical analysis f hmgeneus samples f vids, and (4) t identify the vid ppulatin and study its distributin in the light f the cncept f a vid hierarchy. T achieve these gals we have develped and applied an autmated system fr vid search and analysis. The bservatinal data used in this study are described in Sect. 2. The Autmated Vid Search and Analysis System is presented in Sect. 3, including the vid-search algrithm and the vid parameterizatin. Sme functins f the system are explained als in Sects. 5 and 6. Sectin 4 presents the generated vid catalgues, and Sect. 5 cntains the results frm their analysis, including an autmated cmparisn f the catalgues btained with different tracers, a cmparisn with vids knwn frm previus investigatins, and a statistical analysis. The vid ppulatin and vid shell are discussed in Sect. 6. Finally, Sect. 7 gives a summary f the results. 2. Cmpsitin f the bservatinal samples 2.1. Cmbining redshift data frm different surces The redshift data used in the present study which is limited t the Nrthern Galactic Hemisphere (NGH) have been cmpiled frm the fllwing surces: (1) A Cmpilatin f Clusters f Galaxies with Published Redshifts, versin 1996., by V.S. Lebedev and I.A. Lebedeva (a descriptin f an earlier versin is given in Lebedev & Lebedeva 1991), with redshifts fr 1 5 clusters and grups (with at least 2 member galaxies) in the NGH, 859 f which are Abell/ACO (A/ACO) clusters. (2) The NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database (NED), versin 1997 (see descriptin in Madre et al. 1992), with redshifts fr 968 clusters and 19 grups in the NGH, 759 f which are A/ACO clusters. (3) A Catalgue f Measured Redshifts f Abell Clusters f Galaxies, versin 1997 (Andernach & Tag 1998; Andernach 1997), with 944 A/ACO clusters in the NGH. (4) The MX Nrthern Abell Cluster Redshift Survey (Slinglend et al. 1998; Batuski et al. 1998), with redshifts fr 62 clusters and 81 galaxies in the NGH. (5) The Center fr Astrphysics (CfA) Redshift Catalgue (ZCAT), versin March 3, 1997 (see descriptin in Huchra et al. 1992), cntaining redshifts fr galaxies in the NGH. Fr cnvenience, we shall use the fllwing abbreviatins fr surces 1-5, respectively: LEB, NED, AND, MXS, CfA. As can be seen, we use fur cmpilatins, based n hundreds f riginal surces, and ne new redshift survey, nt yet included in any cmpilatin at the time f the present study. They reflect the status f the available redshift data fr the clusters, grups, and galaxies in the beginning f The numbers f the A/ACO clusters given abve include the supplementary suthern clusters (ACO S) as well. Let us nte that because f the limitatin t the NGH (galactic latitude b ) the great majrity (> 9%) f the cmpiled A/ACO clusters are nrthern Abell clusters (Abell 1958). Besides A/ACO clusters the cmpilatins LEB and NED cntain als Zwicky clusters (Zwicky et al. 1961), ther types f clusters like pr clusters (Mrgan et al. 1975; Albert et al. 1977), clusters frm the Shane-Wirtanen cunts (Shectman 1985), distant clusters (Gunn et al. 1986), clusters frm the Einstein Observatry Medium Sensitivity Survey (Giia et al. 199) and the ROSAT all-sky survey (Vges 1992). The grups f galaxies in LEB and NED are mainly nearby grups (Huchra & Geller 1982), cmpact grups (Hicksn 1982), grups in the tw CfA redshift surveys (Geller & Huchra 1983; Ramella et al. 1989), and grups in individual clusters and superclusters (e.g. Ciardull et al. 1983; Hpp & Materne 1985). N indicatin which bject is a grup is given in LEB. We have fund frm the riginal data surces referenced in LEB that the number f grups in this cmpilatin (in the NGH) is < 1.
3 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters 325 The preliminary examinatin f the spatial distributin f the different tracers frm data surces 1-5 shws that nly the A/ACO clusters can frm cmplete enugh samples in large vlumes suitable fr large vid studies. The cmpleteness limits fr all ther tracers (nn- A/ACO clusters, grups, galaxies) d nt g beynd z.3.4. Therefre, we use in this study fr vid identificatin nly distributins f A/ACO clusters. A limited applicatin f the ther tracers has been dne nly fr investigating the substructure f vids in the distributin f rich A/ACO clusters (Sect. 6). (Prcessing f samples cntaining galaxies, as well as grups and pr clusters, in smaller and nearer spatial vlumes in which the cmpleteness f these bjects is higher will be dne in a separate study.) The cmpilatins LEB, NED, and AND are maintained independently by their authrs. Furthermre, the cmpilatin versins we use refer t smewhat different times f last update. Therefre, they d nt verlap cmpletely and each ne f them cntains bjects which are nt present in the ther cmpilatins. It fllws that by merging them we can increase the ttal number f bjects with spectrscpically measured redshifts. We have first cmbined the data frm LEB, NED, and MXS. The data frm the new unpublished versin f AND, nly fr A/ACO clusters missing in the ther three surces, became available t us and was added later as a final enlargement f the data. After a preliminary check f the data in LEB and NED we have remved frm them several dzens f bjects which are predminantly subcmpnents f clusters with the same crdinates and redshift as the main cmpnent, r bjects which are errneusly included in the cmpilatins as spectrscpically bserved, while, in fact, their redshifts are phtmetric estimates (Andernach 1997). Befre cmbining the data, the redshifts, when helicentric (z h ), have been transfrmed t galactcentric (z g ) fllwing z g = z h + 3 sin l cs b, c where l and b are the galactic crdinates, and c is the speed f light. The distance r t the bjects has been derived frm the Hubble law assuming a Hubble cnstant H = 1 km s 1 Mpc 1. The Cartesian crdinates x, y, z f the bjects have been calculated frm their spherical crdinates r, l, b with the transfrmatin x = r cs l cs b, y = r sin l cs b, z = r sin b in a crdinate system centred in the Galaxy with axes x and y directed t l =, b = and l =9, b =,respectively, and axis z directed t the Nrth Galactic Ple (NGP). In rder t be able t cnstruct the 2-D distributin f bjects n the sky we have calculated als their z NED z LEB Fig. 1. Cmparisn f the redshifts f clusters and grups in the cmpilatin f Lebedev and Lebedeva (z LEB) with the redshifts in NED (z NED) fr galactic latitude b rectangular crdinates x L, y L in an azimuthal equal-area prjectin (Lambert prjectin) frm ( A =2sin 45 b ), 2 x L = A cs l, y L = A sin l, where b, fr a crdinate system centred n the NGP and axes x and y directed respectively t l =, b = and l = 27, b =. The cmbinatin f the data frm the different surces is cmplicated by the presence f discrepant redshifts fr a part f the bjects, as well as by the necessity t crss-identify crrectly (autmatically) the identical bjects whse designatins, crdinates, redshifts, etc. may nt exactly cincide in the different surces. The cmparisn f the LEB and NED cmpilatins gives 8 cinciding bjects whse redshifts are cmpared in Fig. 1 (fr z.4). As it is seen, mst f the clusters and grups are situated alng the line z LEB = z NED. Hwever, fr several dzens f bjects ( 1%) the differences z = z LEB z NED are significant. We have fund that in many cases the large z are an effect f the backgrund cntaminatin which splits clusters int tw r mre cmpnents at different distances alng the line-fsight. The MX Survey cntains the mst reliable data fr the cluster redshifts in cmparisn with the ther three surces f data. This is due t the large mean number N z = 9 f cluster members with measured redshifts per cluster, allwing fr the eliminatin f the backgrund cntaminatin. At the same time, nly less than half f the clusters in LEB, NED and AND have N z 3. We can use MXS as a cntrl sample t evaluate the quality f the redshift data in LEB and NED. The cmparisns LEB MXS and NED MXS fr 44 and 42 cmmn
4 326 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters bjects, respectively, shw large redshift discrepancies fr abut 1% f the cmpared clusters in bth cases. We cnclude that (1) the cmpilatins LEB and NED cntain similar amunts f large redshift errrs, and (2) such errrs strngly affect nly a cmparatively small part f the clusters. Therefre, we accept that bth cmpilatins are equally suitable fr studies f the large ( 5 h 1 Mpc) vids in the spatial distributin f clusters f galaxies. The cmbinatin f the data frm LEB, NED, and MXS has been dne by assigning different pririties t them. If an bject is present in mre than ne surce it btains the redshift frm that surce with the higher pririty. We give the highest pririty t MXS, and lwer, but equal pririties t LEB and NED. Because f this equality we merge the data int tw parallel cmpilatins: in the first ne the bjects which are bth in LEB and NED have the redshifts frm LEB (cmpilatin CL), and in the secnd ne the redshifts frm NED (cmpilatin CN). After adding the data frm AND, the tw versins f the final cmpilatin cntain bjects each, 1 14 f which are A/ACO clusters ( 45% f all A/ACO clusters in the NGH). The different data surces cntribute t cmpilatins CL and CN as fllws: MXS 62 A/ACO clusters bth in CL and CN, LEB bjects (812 A/ACO clusters) in CL and 679 (15) in CN, NED 267 (37) in CL and 1 24 (699) in CN, AND 13 A/ACO clusters bth in CL and CN. The cmbinatin f several surces has led t a 25% increase in cmparisn with the largest cmpilatin LEB (1 5 clusters and grups). Fr the A/ACO clusters alne, the increase is abut 1% cmpared t AND (944 clusters). Cnsequently, ur cmpilatins ffer the pssibility f a mre cmplete mapping f the large vids in the spatial distributin f cncentratins f galaxies in the NGH. Besides the tw cmpilatins CL and CN we have cmpsed als a cmpilatin f galaxies, hereafter referred t as CG, by merging the data frm CfA (ZCAT) and MXS. CG cntains galaxies with b.itisusedin Sect. 6 t examine hw galaxies ppulate the vids in the cluster distributin. In rder t define a vlume suitable fr vid investigatins we have first studied the variatins f the surface and spatial number densities with decreasing galactic latitude and with increasing redshift, respectively, fr the A/ACO clusters frm the cmpilatins CL and CN. The surface number density as a functin f galactic latitude fr 5 bins in b is shwn in Fig. 2 fr samples frm CL separately fr all A/ACO clusters (richness class R, including the ACO S clusters) and fr the R 1 clusters. It is well seen that the effect f galactic bscuratin is nt strng dwn t b =+4. The spatial number density as a functin f redshift (Fig. 3) is cmputed fr cncentric shells f thickness z =.1. Only bjects with b +3 have been cnsidered in rder t reduce the effect f galactic bscuratin. Figure 3a shws the variatin f the number density with NUMBER DENSITY [1-2 deg -2 ] A/ACO clusters R>1 R> GALACTIC LATITUDE Fig. 2. Surface number density as a functin f galactic latitude fr A/ACO clusters f richness classes R 1andR z fr the R 1andR A/ACO clusters frm CL. As can be seen, the spatial density f the R 1 clusters remains cmparatively high up t z.9. In this range the average density is in gd agreement with the estimate by Bahcall & Cen (1993) n =61 6 h 3 Mpc 3 fr the mean spatial density f the R 1 A/ACO clusters. In the redshift range.9.14 the density f the R 1 clusters with measured redshifts drps by mre than 5%, remaining, hwever, cmparatively cnstant in this range. Fr z>.14 the density is belw 25% f the mean estimate f Bahcall & Cen. Figure 3a shws that the spatial distributin f the R A/ACO clusters is affected by the bservatinal selectin even in the redshift range z <.9. This is expected since the R = clusters represent an incmplete class f bjects in Abell s catalgue. While the density f the R clusters fr z =.4.9 agrees well with the estimate by Bahcall & Cen (1993) n = h 3 Mpc 3 fr this class f bjects, in the nearest vlume fr z<.4 the density agrees better with the mre recent estimate n =261 6 h 3 Mpc 3 f Einast et al. (1997). Fr z >.9 the relative decrease f the density is strnger than fr the R 1 clusters. We cnclude frm the examinatin f Figs. 2 and 3a that (1) bth the R 1andR A/ACO clusters shw a weak effect f the galactic bscuratin fr b +4, and (2) the sample f R 1 A/ACO clusters seems t be cmplete up t z.9 while the sample f R clusters is incmplete even in this clser range Clusters with estimated redshifts One pssibility t cmpensate fr the grwing incmpleteness with distance f the clusters is the usage f estimated distances t the clusters with unmeasured redshifts. A disadvantage f this apprach are the large errrs (2 3%) f the estimated redshifts (Peacck & West 1992). The unfavurable effect frm the large errrs may be reduced by keeping small the fractin f clusters with estimated
5 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters 327 NUMBER DENSITY [1-6 h 3 Mpc -3 ] a A/ACO clusters, b> REDSHIFT R>1 R> NUMBER DENSITY [1-6 h 3 Mpc -3 ] b A/ACO clusters, R>1, b> REDSHIFT measured z measured r estimated z Fig. 3. Spatial number density as a functin f redshift fr: a) A/ACO clusters f richness classes R 1andR, b) R 1 A/ACO clusters with measured redshifts, cmpared with that fr the R 1 A/ACO clusters with measured r estimated redshifts redshifts when cmbining them with clusters with measured redshifts. T estimate the distances t the A/ACO clusters we use the calibratin equatin (Kalinkv et al. 1985) lg z = m 1, ±829 ±5 btained fr a sample f 529 Abell clusters with measured redshifts, where m 1 is the magnitude f the 1th brightest cluster member frm Abell (1958). We have applied this calibratin fr A/ACO clusters in the NGH (b ) fr which n measured redshifts are available. The clusters with phtmetrically estimated redshifts have been mixed with the clusters with measured redshifts frm cmpilatins CL and CN. It is seen frm Fig. 3b, where the spatial number density f the R 1 A/ACO clusters with measured r estimated redshifts is cmpared with that f the same type f clusters with measured redshifts (frm CL), that after the additin f the clusters with estimated z a deep minimum in the number density distributin is frmed at z =.1.11, fllwed by a strng enhancement fr z = The latter feature is prbably due t systematic effects in Abell s catalgue (Abell 1958). A similar density enhancement in the distance range 3 45 h 1 Mpc has been fund by Scaramella et al. (1991) fr a sample f Abell clusters, abut 45% f which had estimated redshifts, and has been explained as an effect f a systematic verestimate f m 1 fr the distant clusters in Abell s catalgue. Hwever, in spite f the large errrs f the estimated distances, the reality f the maximum in this range cannt be definitely ruled ut. It is interesting that the density enhancement in the range cincides well with the third f the peaks in the number f galaxies twards the NGP discvered in the ne-dimensinal deep survey f Bradhurst et al. (199). If the density distributin is cut at z =.14 the crrespnding selectin functin fr the R 1 A/ACO clusters with measured r estimated redshifts becmes flat at adensitylevelf61 6 h 3 Mpc 3, in gd agreement Table 1. Cluster samples fr b +2 and z.16 with the Bahcall & Cen estimate. Therefre, we cnclude that this redshift limit is apprpriate fr the samples cntaining clusters with measured r estimated redshifts. Let us nte that if the deep minimum at z =.1.11 in Fig. 3b is real then the sample f R 1 A/ACO clusters with measured redshifts may be cmplete t z.12, i.e. nearly 1 h 1 Mpc mre than the adpted cmpleteness limit z = The cluster samples Taking int accunt the analysis f the cmpleteness f the cmpilatins CL and CN, we define a vlume V 2 in the NGH with b +3 and z.14 in which the R 1 A/ACO clusters with measured r estimated redshifts frm a cmplete sample and delimit in it a subvlume V 1 with b +4 and z.9 in which the sample f R 1 A/ACO clusters with measured redshifts is cmplete. T reduce the bundary effects we intrduce additinally an enlargement f vlume V 2dwntb =+2 and up t z =.16. While the vid search is limited t vlume V 2 (i.e. vid centres must lie in V 2), the bjects utside f vlume V 2 are used nly t cnstrain the vids which intersect the vlume bundaries.
6 328 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters 9 9 A/ACO clusters R>1 Sample AR/L n=415 A/ACO clusters,r>1 measured r estimated z Sample ARE/L n=813 l= 18 l= 18 a b= b b= A/ACO clusters R> Sample A/L n=79 A/ACO clusters,r> measured r estimated z Sample AE/L n=1455 l= 18 l= 18 c b= d b= Fig. 4. Surface distributins in galactic crdinates fr samples f A/ACO clusters with b +2 and z.16 (see Table 1) in Lambert equal-area prjectin centred n the NGP: a) R 1 clusters with measured redshifts, b) R 1 clusters with measured r estimated redshifts, c and d) same as a and b) but fr the R clusters The samples used in the present study t search fr vids are frmed by extracting frm the cmpilatins CL and CN all A/ACO clusters with b +2 and z.16 separately fr (1) the R 1 clusters, and (2) all (R ) A/ACO clusters, and fr each f these tw tracer types separately fr the clusters (1) with measured redshifts, and (2) with measured r estimated redshifts. Thus, a ttal f 8 samples are cmpsed. Table 1 cntains the adpted sample designatins and the number f bjects in each sample. Letter L r N in the sample designatin means extractin frm CL r CN, respectively, and E means that the sample cntains clusters with estimated redshifts. Fr z.14 the fractin f clusters with estimated redshifts is abut 1/3 f the ttal number (33% fr the R 1 clusters and 36% fr the R clusters). Hwever, fr z>.12 the number f clusters with estimated redshifts is already larger than that f the measured clusters (see Fig. 3b). There are almst n clusters with nly estimated redshifts in the clseby subvlume V 1. Figures 4a d and 5a d shw 2-D and 3-D visualizatins, respectively, f the samples frm Table 1 (nly the samples extracted frm CL are shwn). The 2-D distributins are Lambert equal-area prjectins, centred n the NGP, while the 3-D visualizatins are perspective graphs. The 2-D distributins (Fig. 4) shw that the NGH is cvered satisfactrily by the bservatins with the exceptin f the sparsely ppulated regin at lw galactic latitudes arund l = affected strngly by the galactic bscuratin (Abell 1958; Bahcall & Sneira 1982b). The inclusin f clusters with estimated redshifts (Figs. 5b and d) increases the cmpleteness but sme stratificatin in
7 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters z (h -1 Mpc) z (h -1 Mpc) -4 x (h -1 Mpc) 4-4 A/ACO clusters, R>1, Sample AR/L (n=415) y (h -1 Mpc) 4 a -4 x (h -1 Mpc) 4-4 y (h -1 Mpc) A/ACO clusters, R>1, measured r estimated z, Sample ARE/L (n=813) 4 b z (h -1 Mpc) z (h -1 Mpc) -4 A/ACO clusters, R>, Sample A/L (n=79) x (h -1 Mpc) 4-4 y (h -1 Mpc) 4 c -4 x (h -1 Mpc) 4-4 y (h -1 Mpc) A/ACO clusters, R>, measured r estimated z, Sample AE/L (n=1455) 4 d Fig. 5. Spatial distributins fr samples f A/ACO clusters with b +2 and z.16 (see Table 1) shwn as perspective graphs with the crdinate system centred n the Galaxy, axes x and y directed twards l =, b =,andl =9, b =, respectively, axis z directed twards the NGP, and lcatin f the view pint at b +18, l 32 : a) R 1 clusters with measured redshifts, b) R 1 clusters with measured r estimated redshifts, c and d) same as a and b) but fr the R clusters the spatial distributin appears at larger distances, mst prbably due t the systematic verestimate f m 1 in Abell s catalgue. 3. Autmated vid search and analysis In rder t facilitate the quantitative studies f vids we have develped an Autmated Vid Search and Analysis System (AVSAS). Applicatins f earlier versins f this system are given in Stavrev (199a, 199b, 199c, 1991, 1998). AVSAS is a prgramme package f abut 5 mdules executing the fllwing functins: (1) preliminary data analysis hmgenizatin, cmparisn and cmbinatin f data frm different surces; (2) lcal analysis f galaxy and cluster samples cnstructin and visualizatin f the nearest-neighbur distance field, search fr and parameterizatin f vids (generatin f vid catalgues), visualizatin f the 2-D and 3-D distributins f vids, cmparisn f vid catalgues, identificatin f the vid ppulatin and the shell ppulatin, cnstructin f vid prfiles; (3) statistical analysis statistical cmparisn f bserved samples with randm samples, statistical analysis f vid catalgues The vid-search algrithm The vid-search algrithm in AVSAS is based n a definitin f the vids as space regins cmpletely devid f a certain type f bjects (clusters, grups, galaxies). T cnstruct the search algrithm we intrduce the cncept f a distance field (Stavrev 199a). Such an apprach has been applied als by Frisch et al. (1995), Lindner et al. (1995), and recently by Aiki & Mähönen (1998). Let S be a sample f n bjects A i, i = 1,..., n, with Cartesian crdinates x i, y i, z i in a 3-D crdinate system as described in Sect We cnstruct in the spatial vlume V S f sample S a cubic grid G, riented alng the axes x, y, z, with grid cnstant k [h 1 Mpc] and grid ndes g j with crdinates x j, y j, z j,wherej = 1,..., m. Fr each nde the distance t its nearest neighburing bject is cmputed frm d j =min{[(x i x j ) 2 +(y i y j ) 2 +(z i z j ) 2 ] 1/2 }, i where i = 1,..., n. The set f distances d j in the ndes g j frms a 3-D discrete scalar field d (x, y, z), which we shall call nearest-neighbur distance field, rd-field fr brevity. The lcal maxima f the d-field indicate regins devid f bjects, while the lcal minima indicate regins ppulated by bjects. Thus, the task f identificatin f vids is
8 33 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters reduced t the task f determinatin f the lcal maxima f a 3-D field. The lcal maxima (LM) f the d-field crrespnd in real space t the centres f the largest empty spheres embedded in the vids. A better apprximatin f a vid (its psitin, dimensin, shape) can be achieved by a system f crssing (verlapping) empty spheres, i.e. by a grup f grid ndes defining a lcal enhancement f the d-field (Stavrev 1991; see als Stavrev 199c). Similar methds fr vid search have been develped by El-Ad et al. (1996) and Aiki & Mähönen (1998).The apprximatin f a vid by mre than ne sphere is shwn schematically in Fig. 6. T determine the LM we intrduce first a threshld value d min crrespnding t the radius f the smallest vids which are t be identified, i.e. the search fr the LM is restricted ver the pints f the d-field with d d min. The neighburhd f a pint f the d-field with value d i in which a LM is searched is a sphere with radius r i just equal t d i. This means that the search prcedure uses a variable neighburhd which depends n the lcal prperties f the distributin f bjects: the neighburhd is larger in the mre sparsely ppulated regins and smaller in the denser regins. This feature f the prcedure makes it suitable fr prcessing spatial distributins f incmplete samples f bjects when the number density varies strngly depending n the distance r the galactic latitude. AVSAS ffers tw different methds fr determining the LM: (1) by direct cmparisn f the d-field values in the neighburhd f the d-field pints, and (2) by a criterin νσ fr the standard deviatin f the d-field values in the neighburhd f the d-field pints. Let di d min be the value f the d-field in the running nde gi which has neighburhd Vi with radius di, where i = 1,..., m 1, m 1 m (m 1 is the number f ndes with d d min ). Let Vi cntain N ndes with values d j, j = 1,..., N. We define di as a lcal maximum pint (i.e. a pint in the regin f a lcal maximum f the d-field) in if fr all j V i di d j 1+p, where p. If the parameter p = the abve cnditin reduces t di d j fr all j. Inthiscasedi is an abslute maximum in Vi and crrespnds t the largest empty sphere embedded in the vid. If p>thealgrithm identifies di as a lcal maximum pint nt nly when it is an abslute maximum in Vi but als when it is smaller by less than p 1% than the maximum value f the d-field in Vi. In this case the algrithm describes the LM f the d-field by a larger number f pints than fr p =. Thus, a vid is identified (in the next stages f the prcedure) as a grup f LM pints, i.e. the vid is apprximated by a system f crssing empty spheres. Distance field crss-sectin A 3 d 3 d 1 d2 A 1 A 2 largest cnstituent sphere k cnstituent sphere lcal maximum pint nearest neighbur Fig. 6. A schematic representatin f the multi-sphere methd fr the vid search. A crss-sectin f the distance field defined n a grid with cnstant k is shwn with three lcal maximum pints d 1, d 2, d 3 and their nearest neighburs A 1, A 2, A 3, defining three cnstituent spheres f a vid, ne f which is the largest empty sphere We shall call hereafter the empty spheres cnstituting a vid cnstituent spheres (CS). Fr cnvenience, the methd fr the determinatin f the LM pints by direct cmparisnusing the parameter p will be called p-methd. The secnd methd ptinally used in AVSAS fr the determinatin f the LM pints cnsists f the fllwing. First, we calculate the mean f the d-field in the neighburhd Vi f the running nde gi d i = 1 N N j=1 d j and the standard deviatin σi 1 N = dj 2 1 N N 1 N j=1 d j j=1 2 Then, di is a LM pint in Vi if di d i + νσ i, where ν. Chsing higher r lwer values fr the parameter ν we can tune the search algrithm t select mre r less statistically significant vids. We shall call this methd ν-methd. Applying any f the tw described methds n all d i d min, the search prcedure prduces a set f LM pints (r CS). Part f them lie at the bundaries f the examined space vlume. These peripheral LM pints can ptinally be remved frm further analysis if it is judged that they are f lw significance because f bundary effects r/and sample incmpleteness. In the next stage, the search algrithm grups the LM pints n the basis f criteria fr their mutual psitins. 1/2.
9 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters 331 Each defined grup f LM pints cnstitutes a separate vid in the spatial distributin f the sampled bjects. The prcess f gruping f the LM pints is cmplicated by the perclatin f the neighburing vids, especially when samples f rare tracers f the LSS, such as the rich clusters f galaxies, are used. Often the perclatin is strengthened by the sample incmpleteness. Because f the uncertainty in delimiting neighburing vids the search algrithm allws fr a certain degree f verlap amng them. It ffers a chice between three ptins fr gruping the LM pints: (1) cmpact gruping, (2) medium-cmpact gruping, and (3) lse gruping. Accrding t the first ptin tw LM pints affiliate t the same grup if the distance between their psitins r = k, wherek is the grid cnstant. This ptin leads t cmpact grups f a cmparatively small number f LM pints, and cnsequently a large number f vids with a high degree f perclatin f neighburing vids. The criterin fr the medium-cmpact gruping is r 3 k (i.e. a distance equal t the diagnal f the elementary grid cube). This ptin prduces vids with mre cmplicated cnfiguratins f CS and less verlap with neighburing vids than the first ptin. The criterin fr the third ptin lse gruping, unlike the first tw ptins, des nt depend n k: tw LM pints with values d 1 and d 2 are gruped tgether if r <max(d 1,d 2 ). This criterin assures that the center f at least ne f the tw CS lies within the ther CS. The vids prduced by lse gruping f LM pints may have cmplicated (irregular) shapes and a large number f CS, i.e. large sizes. Hwever, the verlap f neighburing vids is less (relative t vid size) cmpared with the first tw ptins. The vids identified with ptin 1 can be cnsidered as substructures f the vids identified with ptins 2 and 3, and vice versa the vids identified with ptin 3 can be cnsidered as unificatins f the vids identified with ptins 1 and 2. The chice f the gruping ptin frm 1 t 3 acts parallel t the chice f a higher value f the parameter p and a lwer value f the parameter ν, i.e. twards larger vids with mre cmplicated shapes. As is seen frm the abve the vid-search algrithm needs chices f suitable values fr the fllwing free parameters: k, d min, p/ν, and the gruping ptin. The questin arises: given the ther values, what values f p and ν, respectively, are mst suitable fr the vid search? T answer this questin a number f tests f the p- methd and the ν-methd have been carried ut ver tw test samples (AR/L and AR/N, limited t vlume V 2, see Sect. 2.3) using tw values fr k (1 and 2 h 1 Mpc), tw values fr the minimum vid diameter D min =2d min (5 and 8 h 1 Mpc), and tw gruping ptins (mediumcmpact and lse gruping). Then, fr a certain cmbinatin f k, D min, and the gruping ptin we check hw the number f identified vids and CS changes as a functin f p r ν. The values f D min have been chsen t be rughly equal t r larger than the mean separatin f clusters which is 53 h 1 Mpc and 42 h 1 Mpc fr the R 1 and R Abell clusters, respectively (Batuski et al. 1991). With these D min the values f k are chsen t be sufficiently small, s that the LM crrespnding t the smallest identified vids can be determined frm statistics ver at least several dzens f d-field pints. The nly cmbinatin fr which this requirement is nt fulfilled is the ne with D min =5h 1 Mpc, k =2h 1 Mpc. The chice f a sufficiently small value f k is als f imprtance fr the accuracy f the determined vid parameters. Frm elementary cnsideratins fllws that the errr f the psitins f the CS centres due t the discreteness f the d-field can be estimated as 3 4 k.fr the tw chsen values f k (2 and 1 h 1 Mpc) the errr is 8.66 and 4.33 h 1 Mpc, respectively. In the latter case the errr is cmparable t the diameter f Abell clusters (3 h 1 Mpc), and it is less than 1% f the diameter f the smallest identified vids (5 h 1 Mpc). Let us als nte that the backgrund cntaminatin, the large peculiar velcities f the cluster members, and the use f estimated redshifts may lead t psitinal errrs larger than bth chsen values fr k. The results frm the tests are shwn in Fig. 7. Meaningful values f p and ν lie in the ranges p <.2 and ν > 1.. Outside these ranges the search prcedure prduces a t large number f LM pints and this causes difficulties in delimiting neighburing vids because f increased verlap amng them. Fr the case f the medium-cmpact gruping (Fig. 7, left panel) the number f vids increases cntinuusly with increasing p and decreasing ν, while fr the lse gruping (Fig. 7, right panel) the curves shw well defined maxima in the number f vids. Fr values f p andν the search algrithm identifies nly the mst significant vids deep, spherical and well islated regins, apprximated by single empty spheres. The increase f p, respectively the decrease f ν, relaxes the criterin fr the selectin f LM pints, hence the number f vids grws. At the same time, vids enlarge and start t verlap mre due t the increased number f CS. This causes the merging f neighburing vids and cnsequently a decrease f the number f vids. In the case f the lse gruping f the LM pints, fr certain values f the parameters p and ν the prcess f merging vertakes the increase f the number f LM pints, hence the number f vids decreases. If p is left t grw very large r ν t becme very small the number f vids tends t 1: a single, cntinuus, netwrk structure is frmed. Fr the medium-cmpact ptin the prcess f merging is nt strng enugh t stp the grwth f the number f vids with the grwth f p, respectively with the decrease f ν. (This is true fr the case f cmpact gruping f the LM pints, t.)
10 332 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters NUMBER OF VOIDS Medium-cmpact gruping f LM pints Test sample AR/L k=1, D>5 h -1 Mpc k=2, D>5 k=1, D>8 k=2, D>8 Test sample AR/N k=1, D>5 h -1 Mpc k=2, D>5 k=1, D>8 k=2, D>8 a NUMBER OF VOIDS Lse gruping f LM pints Test sample AR/L k=1, D>5 h -1 Mpc k=2, D>5 k=1, D>8 k=2, D>8 Test sample AR/N k=1, D>5 h -1 Mpc k=2, D>5 k=1, D>8 k=2, D>8 b p p NUMBER OF VOIDS Medium-cmpact gruping f LM pints Test sample AR/L k=1, D>5 h -1 Mpc k=2, D>5 k=1, D>8 k=2, D>8 Test sample AR/N k=1, D>5 h -1 Mpc k=2, D>5 k=1, D>8 k=2, D>8 c NUMBER OF VOIDS Lse gruping f LM pints Test sample AR/L k=1, D>5 h -1 Mpc k=2, D>5 k=1, D>8 k=2, D>8 Test sample AR/N k=1, D>5 h -1 Mpc k=2, D>5 k=1, D>8 k=2, D>8 d ν ν Fig. 7. Number f vids as functins f the parameters p a and b) and ν c and d) fr medium-cmpact (left panel) and lse (right panel) gruping f the lcal maximum pints, fr tw test samples (AR/L and AR/N) and fur cmbinatins f the grid cnstant k and the minimum vid dimensin D min The test curves fr the p-methd, lse gruping (Fig. 7b) shw maxima apprximately fr the same value p m = The ν-methd, hwever, shws tw distinct maxima depending n the value f k: ν m =1.8 fr k =1h 1 Mpc and ν m = frk =2h 1 Mpc. This strnger dependence f the ν-methd n k in cmparisn with the p-methd is well utlined in Fig. 7c. On the ther hand, it is seen frm Figs. 7a d that the ν-methd is less dependent n D min than the p-methd. Figure 7b shws that fr the p-methd the cmbinatin k =2h 1 Mpc, D min =5h 1 Mpc leads t a substantially higher number f vids than all ther cmbinatins. This case differs frm the ther three cmbinatins by its very lw rati D min /k = 2.5. As a result part f the LM pints are defined in neighburhds Vi cntaining a very small number f grid pints. This prbably has the effect f relaxing the criterin fr the selectin f vids, hence increasing the number f vids. The ν-methd is less sensitive t this effect. We cnclude that values f D min /k lwer than 4 5 shuld be avided, especially when the p- methd is used. If we exclude this peculiar case and cmpare the number f vids fr all ther cases at p m (Fig. 7b) with the number f vids at ν m (Fig. 7d) we see that fr bth methds the number f vids is in the same range f abut 2 3 depending slightly n the cmbinatin (k, D min ), i.e. the agreement between the tw methds is gd. In rder t check hw p m and ν m depend n the number density we have used test samples with grwing numbers f bjects in the same vlume. These tests shw that p m decreases slightly with increasing number density, while ν m is almst independent f it. The reasn fr this difference between the tw methds is that the ν- methd is mre efficient than the p-methd at rejecting the smaller vids (near D min ) in the denser regins as insignificant fluctuatins f the d-field. Fr the p-methd the increase f the sample density leads t an increase f the number and the verlap f the CS, hence the number f vids decreases. This effect is cmpensated by a smaller value f p m which tightens the criterin fr selectin f LM pints. The tests f the vid-search prcedure suggest that it can be ptimized by chsing values f p = p m and ν = ν m. That leads t the detectin f the maximum number f vids at a lw degree f verlapping f the neighburing vids in the case f the lse gruping f the LM pints. These values f p and ν can be applied as well in the ther tw ptins cmpact and mediumcmpact gruping, in spite f the fact that the number f detected vids is nt maximized, but fr the sake f
11 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters 333 keeping a lw degree f verlapping f the neighburing vids, hence better delimited vids Determinatin f the vid parameters After vids are identified, AVSAS analyses their prperties and defines the fllwing parameters: (1) Cartesian, equatrial and galactic crdinates f the CS centres and f the vid centre. The latter is defined as the centre f the largest CS f the vid, and alternatively, as the centrid f all CS f the vid. The centrid is determined as the centre f gravity f the system f CS. If a vid is cmpsed f n cs > 1 CS, each ne with vlume V i, i = 1,..., n cs,andweight n cs w i = V i / V j, j=1 then the Cartesian crdinates f the centrid f CS are cmputed frm n cs n cs n cs x c = w i x i, y c = w i y i, z c = w i z i, i=1 i=1 where x i, y i,z i are the Cartesian crdinates f the i-th CS. Fr cnvenience, the centrids are slightly shifted in rder t cincide with the nearest grid nde. The Cartesian crdinates x L,y L in a Lambert equalarea prjectin f the CS centres and f the centrid are cmputed, t, as described in Sect (2) Distances are cmputed t the centres f all CS, as well as t the CS centrid frm the Cartesian crdinates: r i = x 2 i + y2 i + z2 i [h 1 Mpc], and r c = x 2 c + y2 c + z2 c [h 1 Mpc]. (3) Dimensins: (a) Diameters f the CS are cmputed directly frm the values f the d-field as D i =2d i [h 1 Mpc]. (b) Vid dimensins alng x, y, z axes are determined frm the prjected distances between the centres f thse tw CS f the vid, which are the farthest apart alng each axis, plus their radii. Thus, fr the x axis D x = x + d A + d B [h 1 Mpc]. (c) The maximum vid dimensin is determined frm the distance between the centres f the tw mst widely separated CS f the vid plus the radii f these tw CS: D max = max + d A + d B [h 1 Mpc]. (d) The equivalent vid diameter is the diameter f the sphere whse vlume is equal t the ttal vlume V T f the vid (see belw): ( ) 1/3 6 D e = π V T [h 1 Mpc]. i=1 (4) Sphericity s. This parameter is intrduced fr a characterizatin f the vid shape. It is defined as s = D/D max, where D is the diameter f the largest CS f the vid. (5) Vlume: (a) The vlume f each CS is cmputed frm V i = 4 3 πd3 i [h 3 Mpc 3 ]. (b) The ttal vid vlume V T is cmputed numerically because f the cmplicated vid shape (especially when the vid is cmpsed f a large number f CS), by cunting the number f elementary grid cubes n g in the vid (strictly speaking, the cubes whse centres are inside the vid). Then V T = n g k 3 [h 3 Mpc 3 ], where k is the grid cnstant. (6) The bjects surrunding the vid are defined as the nearest neighburs t the centres f the CS f the vid. (See Sect. 6 fr a mre cmplete identificatin f the bjects surrunding a vid.) (7) The neighburing vids f the vid are determined frm a cnditin fr verlapping f at least ne CS f the vid with at least ne CS f the neighburing vid. If d 1 and d 2 are the radii f tw CS belnging t tw different vids, they verlap if r <d 1 + d 2,where r is the distance between the centres f the tw CS. (Nte the difference between this criterin and the criterin fr lse gruping f the LM pints in Sect. 3.1.) 4. Generatin f vid catalgues We have applied AVSAS ver the 8 bservatinal samples described in Sect. 2 (see Table 1) which ccupy the same vlume. The generated vid catalgues cntain the vids whse CS have centres lying in vlume V 2. All catalgues are generated with the same grid cnstant k =1h 1 Mpc (see discussin in Sect. 3.1), prducing grid ndes in vlume V 2, n which the d-field is calculated. The semi-cube cntaining the cnical vlume V 2 has dimensins 85k 85k 43k alng the x, y, z axes, respectively. The vid selectin criterin with which a vid catalgue is generated is a cmbinatin f five cnditins fr (1) the minimum vid diameter D min, (2) the search methd p r ν, (3) the value f the search parameter p r ν, (4) the ptin fr the gruping f the LM pints (cmpact, medium-cmpact, lse), and (5) the treatment f the peripheral LM pints (acceptance r rejectin). Since we are interested in large vidswehavechsen D min =5h 1 Mpc (see discussin in Sect. 3.1). This dimensin is cmparable with the characteristic size f the superclusters f galaxies. We have applied fr each sample bth search methds, setting p = p m and ν = ν m t ptimize the search.
12 334 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters Table 2. Vid catalgues: number f lcal maximum pints and vids in vlumes V 1andV 2 The values f p m r ν m fr each generated catalgue are given in Table 2. All three ptins fr the gruping f the LM pints have been used fr each sample and each methd t generate vid catalgues. Thus, 6 catalgues 3 fr the p-methd and 3 fr the ν-methd have been prduced fr each sample. Hwever, fr further vid analysis in this paper we have chsen nly the vids generated by the medium-cmpact gruping f the LM pints assuming that the cmpact gruping is mre suitable fr the study f vid substructures, while the lse gruping is suitable fr the study f vid superstructures (see Sect. 3.1). All vid catalgues have been generated rejecting the peripheral LM pints. The ttal number f generated vid catalgues is 48. The numbers f vids and LM pints in each catalgue are given in Table 2. Hereafter, we shall designate the vid catalgues fr the medium-cmpact ptin by the crrespnding sample designatin (Table 2, Cl. 2) supplemented by the suffix p r ν fr the methd applied (Table 2, Cl. 3), r we shall simply use the number given in the first clumn f Table 2. Tw f the vid catalgues listed in Table 2 crrespnding t samples AR/L and A/L are presented in Tables 3and 4. They aregenerated with the p-methd and the medium-cmpact gruping f the LM pints. Because f the large number f vid parameters and vid CS the catalgues are given in a cncise frm, with ne r tw lines f data fr each vid: the first line cntains (after Cl. 2) the parameters f the largest CS f the vid, and the secnd line cntains the parameters f the whle vid. Only ne line appears fr vids cnsisting nly f ne CS. If the vid centre cincides with the centre f the largest CS, the psitinal parameters are given nly in the first line. Vids are rdered by increasing right ascensin f the centre f the largest CS. Tables 3 and 4 have the fllwing cntents: Cl. (1) vid serial number; Cl. (2) number f CS f the vid; Cls. (3) and (4) equatrial crdinates α, δ fr B195. f the centre f the largest CS f the vid (line 1), and α c, δ c f the centrid f all CS (line 2); Cls. (5) and (6) galactic crdinates l, b f the centre f the largest CS (line 1), and l c, b c f the centrid f all CS (line 2); Cls. (7) (9) Cartesian crdinates x, y, z f the centre f the largest CS (line 1), and x c, y c, z c f the centrid f all CS (line 2); Cl. (1) distance r t the centre f the largest CS (line 1), and r c t the centrid f all CS (line 2); Cl. (11) psitin f the centre f the largest CS (line 1) and f the centrid f all CS (line 2) with respect t vlumes V 1andV 2: 1 in vlume V 1, 2 in vlume V 2, utside vlume V 1; Cl. (12) diameter D f the largest CS (line 1), and equivalent vid diameter D e (line 2); Cls. (13) (15) vid dimensins alng axes x, y, z; Cl. (16) largest vid dimensin D max ; Cl. (17) vlumev f the largest CS (line 1), and ttal vlume f the vid V T (line 2); Cl. (18) sphericity s. The vid catalgues listed in Table 2, tw f which are given in Tables 3 and 4, represent the currently mst cmplete mapping f the large vids in the distributin f galaxy clusters in the NGH t a limiting distance f 42 h 1 Mpc. Cmpared t similar wide-angle studies (Batuski & Burns 1985; Tully 1986; Einast et al. 1994) they cntain larger numbers f vids t larger distances. They can be used as identificatin lists f the vids in the NGH, in studies f individual vids, as well as fr statistical investigatins f the vid prperties. The spatial and surface distributins f the vids in Tables 3 and 4 are presented in Figs. 8 1 by different types f visualizatins allwing fr a visual examinatin and cmparisn f the vid catalgues. The spatial
13 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters 335 Table 3. Vids f R 1 A/ACO clusters (sample AR/L, p-methd)
14 336 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters Table 4. Vids f R A/ACO clusters (sample A/L, p-methd)
15 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters 337 Table 4. cntinued distributins (Fig. 8) can be rtated and examined frm an arbitrary view pint n a cmputer screen. The crsssectins f the 3-D vid distributin (Fig. 9) are shwn jintly with the distributin f the crrespnding tracers in slices f a thickness equal t the grid cnstant k = 1 h 1 Mpc. The 3-D distributin f the vids in Fig. 8 (left panel) suggests a vid-filled Universe with clsely packed and intersecting vids. Hwever, the crss-sectins f the 3-D distributin in Fig. 9 shw that the large vids may be separated by large znes f enhanced density f the tracing bjects. Such a zne is best utlined in the y =Mpc crss-sectin f the distributin f the R 1 A/ACO clusters fr z = 2 25 h 1 Mpc (Fig. 9a), but it can be identified in the ther crss-sectins, as well as in the adjacent cuts fr y andx, althugh in the directin alng the y axis (Fig. 9, right panel) it is smaller and nt well utlined. This feature is prbably due t the presence f a large rthgnal structure at this distance similar t the Great Wall (Tully 1986, 1987). 5. Analysis f the vid catalgues 5.1. Autmated cmparisn f the vid catalgues The generatin f a large number f vid catalgues by varying the sample, the search methd, r the vid selectin criterin has evked the necessity fr an easy and bjective way t cmpare the results. AVSAS ffers such a pssibility, applicable als t the cmparisn with vids frm previus investigatins. The cmparisn f tw vid catalgues is based n the cmparisn f the psitins and dimensins f the CS f the vids. The criterin fr cincidence f tw vids frm different catalgues is r <max (d 1,d 2 ), where r is the distance between the centres f the cmpared CS, and d 1, d 2 are their radii. This criterin must be satisfied fr at least ne pair f cinciding CS. A rigrus criterin fr vid cincidence may be chsen by setting r =. The results frm the cmparisn are utput as crss-identificatin tables with the cinciding vids, and
16 338 K.Y. Stavrev: A study f the large vids in the spatial distributin f galaxy clusters 42 z [h -1 Mpc] -4 x [h -1 Mpc] 4-4 Vids f R>1 A/ACO clusters (sample AR/L, p-methd) y [h -1 Mpc] 4 b vid centre cnstituent sphere centre 42 z [h -1 Mpc] -4 x [h -1 Mpc] 4-4 Vids f R> A/ACO clusters (sample A/L, p-methd) y [h -1 Mpc] 4 d vid centre cnstituent sphere centre Fig. 8. Spatial distributin f the vids (left panel) and f the vid and cnstituent sphere centres (right panel) frm the catalgues in Tables 3 and 4: a and b) vids f R 1 A/ACO clusters (catalgue AR/Lp), c and d) vids f R A/ACOclusters (catalgue A/Lp). Crdinate system and view pint are the same as in Fig. 5 as detailed lists f the cinciding CS with the differences in their psitins and dimensins. We have applied bth the rigrus and lse criteria t cmpare the vid catalgues listed in Table 2. Table 5 cntains the results f the cmparisn f the tw catalgues AR/Lp and A/Lp given in Tables 3 and 4, respectively. The numbers in Table 5 marked by an asterisk crrespnd t cases satisfying the rigrus criterin r =.Asitis seen in Table 5 mst f the vids f R 1 clusters (9%) can be identified with vids f R clusters. We have cmpared als ur vid catalgues with vids knwn frm previus investigatins. T d this we have cmpsed a cmpilatin f vids in the NGH, hereafter referred t as VC, cntaining 39 vids f clusters f galaxies frm the fllwing surces: (1) Bahcall & Sneira (1982b) nevidfr 1 Abell clusters; (2) Batuski & Burns (1985) 22 vids f Abell clusters; (3) Einast et al. (1994) 16 vids f A/ACO clusters. We shall use the abbreviatins BS, BB, and E fr surces 1-3, respectively. The cmpilatin VC ccupies a vlume cnsiderably smaller than the vlume ccupied by ur vid catalgues: the vid centres reach a limiting distance f abut 25 h 1 Mpc. The dimensins f the vids f clusters frm VC crrespnd rughly t ur criterin fr vid selectin D min = 5 h 1 Mpc. Befre the cmparisn, the vids frm VC with nnspherical shapes have been reduced t the largest empty spheres which can be nested in them, with the exceptin f the huge BS vid which, because f its extended frm, has been apprximated with 21 nn-verlapping equal spheres with diameters f 6 h 1 Mpc. The results f the cmparisn f the vid catalgues AR/Lp and A/Lp (Tables 3 and 4) with the vids frm the cmpilatin VC are given as identificatin lists in Table 6, where the first clumn cntains the serial numbers (frm Tables 3 and 4) f the vids identified in VC, and the secnd clumn cntains the identificatins frm VC, presented with their riginal numbers frm the crrespnding literature surces, preceded by the surce abbreviatin. The cmparisn shws that abut 7% f the vids f clusters frm VC can be identified in at least ne f the tw vid catalgues. On the ther hand, 35 4% f the vids in these catalgues, mst f them in the nearer subvlume V 1, are identified in VC. The rest > 6% f the vids lie predminantly beynd subvlume V 1, i.e. in regins nt cvered by the cmpilatin VC. We can cnclude that abut 2% f the vids detected by us in vlume V 1 and 9% f the vids utside vlume V 1 are newly discvered vids r vid candidates. The reality f the latter needs t be cnfirmed by future cmplete redshift surveys.
Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis
 Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis } 3.1 Basic Cncepts f Clustering 3.1.1 Cluster Analysis 3.1. Clustering Categries } 3. Partitining Methds 3..1 The principle 3.. K-Means Methd 3..3 K-Medids Methd 3..4 CLARA
Chapter 3: Cluster Analysis } 3.1 Basic Cncepts f Clustering 3.1.1 Cluster Analysis 3.1. Clustering Categries } 3. Partitining Methds 3..1 The principle 3.. K-Means Methd 3..3 K-Medids Methd 3..4 CLARA
Biplots in Practice MICHAEL GREENACRE. Professor of Statistics at the Pompeu Fabra University. Chapter 13 Offprint
 Biplts in Practice MICHAEL GREENACRE Prfessr f Statistics at the Pmpeu Fabra University Chapter 13 Offprint CASE STUDY BIOMEDICINE Cmparing Cancer Types Accrding t Gene Epressin Arrays First published:
Biplts in Practice MICHAEL GREENACRE Prfessr f Statistics at the Pmpeu Fabra University Chapter 13 Offprint CASE STUDY BIOMEDICINE Cmparing Cancer Types Accrding t Gene Epressin Arrays First published:
Cells though to send feedback signals from the medulla back to the lamina o L: Lamina Monopolar cells
 Classificatin Rules (and Exceptins) Name: Cell type fllwed by either a clumn ID (determined by the visual lcatin f the cell) r a numeric identifier t separate ut different examples f a given cell type
Classificatin Rules (and Exceptins) Name: Cell type fllwed by either a clumn ID (determined by the visual lcatin f the cell) r a numeric identifier t separate ut different examples f a given cell type
Module 4: General Formulation of Electric Circuit Theory
 Mdule 4: General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery 4. General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery All electrmagnetic phenmena are described at a fundamental level by Maxwell's equatins and the assciated
Mdule 4: General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery 4. General Frmulatin f Electric Circuit Thery All electrmagnetic phenmena are described at a fundamental level by Maxwell's equatins and the assciated
, which yields. where z1. and z2
 The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
The Gaussian r Nrmal PDF, Page 1 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin Authr: Jhn M Cimbala, Penn State University Latest revisin: 11 September 13 The Gaussian r Nrmal Prbability Density Functin
Chapter 2 GAUSS LAW Recommended Problems:
 Chapter GAUSS LAW Recmmended Prblems: 1,4,5,6,7,9,11,13,15,18,19,1,7,9,31,35,37,39,41,43,45,47,49,51,55,57,61,6,69. LCTRIC FLUX lectric flux is a measure f the number f electric filed lines penetrating
Chapter GAUSS LAW Recmmended Prblems: 1,4,5,6,7,9,11,13,15,18,19,1,7,9,31,35,37,39,41,43,45,47,49,51,55,57,61,6,69. LCTRIC FLUX lectric flux is a measure f the number f electric filed lines penetrating
MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b
![MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b MODULE 1. e x + c. [You can t separate a demominator, but you can divide a single denominator into each numerator term] a + b a(a + b)+1 = a + b](/thumbs/78/78051685.jpg) . REVIEW OF SOME BASIC ALGEBRA MODULE () Slving Equatins Yu shuld be able t slve fr x: a + b = c a d + e x + c and get x = e(ba +) b(c a) d(ba +) c Cmmn mistakes and strategies:. a b + c a b + a c, but
. REVIEW OF SOME BASIC ALGEBRA MODULE () Slving Equatins Yu shuld be able t slve fr x: a + b = c a d + e x + c and get x = e(ba +) b(c a) d(ba +) c Cmmn mistakes and strategies:. a b + c a b + a c, but
CS 477/677 Analysis of Algorithms Fall 2007 Dr. George Bebis Course Project Due Date: 11/29/2007
 CS 477/677 Analysis f Algrithms Fall 2007 Dr. Gerge Bebis Curse Prject Due Date: 11/29/2007 Part1: Cmparisn f Srting Algrithms (70% f the prject grade) The bjective f the first part f the assignment is
CS 477/677 Analysis f Algrithms Fall 2007 Dr. Gerge Bebis Curse Prject Due Date: 11/29/2007 Part1: Cmparisn f Srting Algrithms (70% f the prject grade) The bjective f the first part f the assignment is
Physics 2010 Motion with Constant Acceleration Experiment 1
 . Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
. Physics 00 Mtin with Cnstant Acceleratin Experiment In this lab, we will study the mtin f a glider as it accelerates dwnhill n a tilted air track. The glider is supprted ver the air track by a cushin
The ultra-high energy cosmic rays image of Virgo A
 The ultra-high energy csmic rays image f Virg A Radmír Šmída Karlsruhe Institute f Technlgy, Germany E-mail: radmir.smida@kit.edu Ralph Engel Karlsruhe Institute f Technlgy, Germany Arrival directins f
The ultra-high energy csmic rays image f Virg A Radmír Šmída Karlsruhe Institute f Technlgy, Germany E-mail: radmir.smida@kit.edu Ralph Engel Karlsruhe Institute f Technlgy, Germany Arrival directins f
Lab 1 The Scientific Method
 INTRODUCTION The fllwing labratry exercise is designed t give yu, the student, an pprtunity t explre unknwn systems, r universes, and hypthesize pssible rules which may gvern the behavir within them. Scientific
INTRODUCTION The fllwing labratry exercise is designed t give yu, the student, an pprtunity t explre unknwn systems, r universes, and hypthesize pssible rules which may gvern the behavir within them. Scientific
5 th grade Common Core Standards
 5 th grade Cmmn Cre Standards In Grade 5, instructinal time shuld fcus n three critical areas: (1) develping fluency with additin and subtractin f fractins, and develping understanding f the multiplicatin
5 th grade Cmmn Cre Standards In Grade 5, instructinal time shuld fcus n three critical areas: (1) develping fluency with additin and subtractin f fractins, and develping understanding f the multiplicatin
Pipetting 101 Developed by BSU CityLab
 Discver the Micrbes Within: The Wlbachia Prject Pipetting 101 Develped by BSU CityLab Clr Cmparisns Pipetting Exercise #1 STUDENT OBJECTIVES Students will be able t: Chse the crrect size micrpipette fr
Discver the Micrbes Within: The Wlbachia Prject Pipetting 101 Develped by BSU CityLab Clr Cmparisns Pipetting Exercise #1 STUDENT OBJECTIVES Students will be able t: Chse the crrect size micrpipette fr
Bootstrap Method > # Purpose: understand how bootstrap method works > obs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(obs) >
 Btstrap Methd > # Purpse: understand hw btstrap methd wrks > bs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(bs) > mean(bs) [1] 21.64625 > # estimate f lambda > lambda = 1/mean(bs);
Btstrap Methd > # Purpse: understand hw btstrap methd wrks > bs=c(11.96, 5.03, 67.40, 16.07, 31.50, 7.73, 11.10, 22.38) > n=length(bs) > mean(bs) [1] 21.64625 > # estimate f lambda > lambda = 1/mean(bs);
Interference is when two (or more) sets of waves meet and combine to produce a new pattern.
 Interference Interference is when tw (r mre) sets f waves meet and cmbine t prduce a new pattern. This pattern can vary depending n the riginal wave directin, wavelength, amplitude, etc. The tw mst extreme
Interference Interference is when tw (r mre) sets f waves meet and cmbine t prduce a new pattern. This pattern can vary depending n the riginal wave directin, wavelength, amplitude, etc. The tw mst extreme
MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR
 Eurpean Schls Office f the Secretary-General Pedaggical Develpment Unit Ref. : 011-01-D-8-en- Orig. : EN MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR 6 perid/week curse APPROVED BY THE JOINT TEACHING COMMITTEE
Eurpean Schls Office f the Secretary-General Pedaggical Develpment Unit Ref. : 011-01-D-8-en- Orig. : EN MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 5th YEAR 6 perid/week curse APPROVED BY THE JOINT TEACHING COMMITTEE
Aerodynamic Separability in Tip Speed Ratio and Separability in Wind Speed- a Comparison
 Jurnal f Physics: Cnference Series OPEN ACCESS Aerdynamic Separability in Tip Speed Rati and Separability in Wind Speed- a Cmparisn T cite this article: M L Gala Sants et al 14 J. Phys.: Cnf. Ser. 555
Jurnal f Physics: Cnference Series OPEN ACCESS Aerdynamic Separability in Tip Speed Rati and Separability in Wind Speed- a Cmparisn T cite this article: M L Gala Sants et al 14 J. Phys.: Cnf. Ser. 555
Sections 15.1 to 15.12, 16.1 and 16.2 of the textbook (Robbins-Miller) cover the materials required for this topic.
 Tpic : AC Fundamentals, Sinusidal Wavefrm, and Phasrs Sectins 5. t 5., 6. and 6. f the textbk (Rbbins-Miller) cver the materials required fr this tpic.. Wavefrms in electrical systems are current r vltage
Tpic : AC Fundamentals, Sinusidal Wavefrm, and Phasrs Sectins 5. t 5., 6. and 6. f the textbk (Rbbins-Miller) cver the materials required fr this tpic.. Wavefrms in electrical systems are current r vltage
AP Statistics Notes Unit Two: The Normal Distributions
 AP Statistics Ntes Unit Tw: The Nrmal Distributins Syllabus Objectives: 1.5 The student will summarize distributins f data measuring the psitin using quartiles, percentiles, and standardized scres (z-scres).
AP Statistics Ntes Unit Tw: The Nrmal Distributins Syllabus Objectives: 1.5 The student will summarize distributins f data measuring the psitin using quartiles, percentiles, and standardized scres (z-scres).
Phys. 344 Ch 7 Lecture 8 Fri., April. 10 th,
 Phys. 344 Ch 7 Lecture 8 Fri., April. 0 th, 009 Fri. 4/0 8. Ising Mdel f Ferrmagnets HW30 66, 74 Mn. 4/3 Review Sat. 4/8 3pm Exam 3 HW Mnday: Review fr est 3. See n-line practice test lecture-prep is t
Phys. 344 Ch 7 Lecture 8 Fri., April. 0 th, 009 Fri. 4/0 8. Ising Mdel f Ferrmagnets HW30 66, 74 Mn. 4/3 Review Sat. 4/8 3pm Exam 3 HW Mnday: Review fr est 3. See n-line practice test lecture-prep is t
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical model for microarray data analysis
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical mdel fr micrarray data analysis David Rssell Department f Bistatistics M.D. Andersn Cancer Center, Hustn, TX 77030, USA rsselldavid@gmail.cm
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL GaGa: a simple and flexible hierarchical mdel fr micrarray data analysis David Rssell Department f Bistatistics M.D. Andersn Cancer Center, Hustn, TX 77030, USA rsselldavid@gmail.cm
Homology groups of disks with holes
 Hmlgy grups f disks with hles THEOREM. Let p 1,, p k } be a sequence f distinct pints in the interir unit disk D n where n 2, and suppse that fr all j the sets E j Int D n are clsed, pairwise disjint subdisks.
Hmlgy grups f disks with hles THEOREM. Let p 1,, p k } be a sequence f distinct pints in the interir unit disk D n where n 2, and suppse that fr all j the sets E j Int D n are clsed, pairwise disjint subdisks.
Differentiation Applications 1: Related Rates
 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates 151 Differentiatin Applicatins 1: Related Rates Mdel 1: Sliding Ladder 10 ladder y 10 ladder 10 ladder A 10 ft ladder is leaning against a wall when the bttm
Kinetic Model Completeness
 5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Lecture Ntes Tuesday April 15, 2003 Kinetic Mdel Cmpleteness We say a chemical kinetic mdel is cmplete fr a particular reactin cnditin when it cntains all the species and reactins
5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Lecture Ntes Tuesday April 15, 2003 Kinetic Mdel Cmpleteness We say a chemical kinetic mdel is cmplete fr a particular reactin cnditin when it cntains all the species and reactins
How do scientists measure trees? What is DBH?
 Hw d scientists measure trees? What is DBH? Purpse Students develp an understanding f tree size and hw scientists measure trees. Students bserve and measure tree ckies and explre the relatinship between
Hw d scientists measure trees? What is DBH? Purpse Students develp an understanding f tree size and hw scientists measure trees. Students bserve and measure tree ckies and explre the relatinship between
Resampling Methods. Chapter 5. Chapter 5 1 / 52
 Resampling Methds Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 / 52 1 51 Validatin set apprach 2 52 Crss validatin 3 53 Btstrap Chapter 5 2 / 52 Abut Resampling An imprtant statistical tl Pretending the data as ppulatin and
Resampling Methds Chapter 5 Chapter 5 1 / 52 1 51 Validatin set apprach 2 52 Crss validatin 3 53 Btstrap Chapter 5 2 / 52 Abut Resampling An imprtant statistical tl Pretending the data as ppulatin and
CESAR Science Case The differential rotation of the Sun and its Chromosphere. Introduction. Material that is necessary during the laboratory
 Teacher s guide CESAR Science Case The differential rtatin f the Sun and its Chrmsphere Material that is necessary during the labratry CESAR Astrnmical wrd list CESAR Bklet CESAR Frmula sheet CESAR Student
Teacher s guide CESAR Science Case The differential rtatin f the Sun and its Chrmsphere Material that is necessary during the labratry CESAR Astrnmical wrd list CESAR Bklet CESAR Frmula sheet CESAR Student
FIELD QUALITY IN ACCELERATOR MAGNETS
 FIELD QUALITY IN ACCELERATOR MAGNETS S. Russenschuck CERN, 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Abstract The field quality in the supercnducting magnets is expressed in terms f the cefficients f the Furier series
FIELD QUALITY IN ACCELERATOR MAGNETS S. Russenschuck CERN, 1211 Geneva 23, Switzerland Abstract The field quality in the supercnducting magnets is expressed in terms f the cefficients f the Furier series
Subject description processes
 Subject representatin 6.1.2. Subject descriptin prcesses Overview Fur majr prcesses r areas f practice fr representing subjects are classificatin, subject catalging, indexing, and abstracting. The prcesses
Subject representatin 6.1.2. Subject descriptin prcesses Overview Fur majr prcesses r areas f practice fr representing subjects are classificatin, subject catalging, indexing, and abstracting. The prcesses
22.54 Neutron Interactions and Applications (Spring 2004) Chapter 11 (3/11/04) Neutron Diffusion
 .54 Neutrn Interactins and Applicatins (Spring 004) Chapter (3//04) Neutrn Diffusin References -- J. R. Lamarsh, Intrductin t Nuclear Reactr Thery (Addisn-Wesley, Reading, 966) T study neutrn diffusin
.54 Neutrn Interactins and Applicatins (Spring 004) Chapter (3//04) Neutrn Diffusin References -- J. R. Lamarsh, Intrductin t Nuclear Reactr Thery (Addisn-Wesley, Reading, 966) T study neutrn diffusin
Study Group Report: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technology
 Study Grup Reprt: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technlgy The prblem under study cncerned the apparent discrepancy between a series f experiments using a plate fin heat exchanger and the classical thery
Study Grup Reprt: Plate-fin Heat Exchangers: AEA Technlgy The prblem under study cncerned the apparent discrepancy between a series f experiments using a plate fin heat exchanger and the classical thery
Chemistry 20 Lesson 11 Electronegativity, Polarity and Shapes
 Chemistry 20 Lessn 11 Electrnegativity, Plarity and Shapes In ur previus wrk we learned why atms frm cvalent bnds and hw t draw the resulting rganizatin f atms. In this lessn we will learn (a) hw the cmbinatin
Chemistry 20 Lessn 11 Electrnegativity, Plarity and Shapes In ur previus wrk we learned why atms frm cvalent bnds and hw t draw the resulting rganizatin f atms. In this lessn we will learn (a) hw the cmbinatin
Pattern Recognition 2014 Support Vector Machines
 Pattern Recgnitin 2014 Supprt Vectr Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recgnitin 1 / 55 Overview 1 Separable Case 2 Kernel Functins 3 Allwing Errrs (Sft
Pattern Recgnitin 2014 Supprt Vectr Machines Ad Feelders Universiteit Utrecht Ad Feelders ( Universiteit Utrecht ) Pattern Recgnitin 1 / 55 Overview 1 Separable Case 2 Kernel Functins 3 Allwing Errrs (Sft
GAUSS' LAW E. A. surface
 Prf. Dr. I. M. A. Nasser GAUSS' LAW 08.11.017 GAUSS' LAW Intrductin: The electric field f a given charge distributin can in principle be calculated using Culmb's law. The examples discussed in electric
Prf. Dr. I. M. A. Nasser GAUSS' LAW 08.11.017 GAUSS' LAW Intrductin: The electric field f a given charge distributin can in principle be calculated using Culmb's law. The examples discussed in electric
Computational modeling techniques
 Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 4: Mdel checing fr ODE mdels In Petre Department f IT, Åb Aademi http://www.users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent Stichimetric matrix Calculating the mass cnservatin relatins
Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 4: Mdel checing fr ODE mdels In Petre Department f IT, Åb Aademi http://www.users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent Stichimetric matrix Calculating the mass cnservatin relatins
ENSC Discrete Time Systems. Project Outline. Semester
 ENSC 49 - iscrete Time Systems Prject Outline Semester 006-1. Objectives The gal f the prject is t design a channel fading simulatr. Upn successful cmpletin f the prject, yu will reinfrce yur understanding
ENSC 49 - iscrete Time Systems Prject Outline Semester 006-1. Objectives The gal f the prject is t design a channel fading simulatr. Upn successful cmpletin f the prject, yu will reinfrce yur understanding
Preparation work for A2 Mathematics [2017]
![Preparation work for A2 Mathematics [2017] Preparation work for A2 Mathematics [2017]](/thumbs/95/123024115.jpg) Preparatin wrk fr A2 Mathematics [2017] The wrk studied in Y12 after the return frm study leave is frm the Cre 3 mdule f the A2 Mathematics curse. This wrk will nly be reviewed during Year 13, it will
Preparatin wrk fr A2 Mathematics [2017] The wrk studied in Y12 after the return frm study leave is frm the Cre 3 mdule f the A2 Mathematics curse. This wrk will nly be reviewed during Year 13, it will
and the Doppler frequency rate f R , can be related to the coefficients of this polynomial. The relationships are:
 Algrithm fr Estimating R and R - (David Sandwell, SIO, August 4, 2006) Azimith cmpressin invlves the alignment f successive eches t be fcused n a pint target Let s be the slw time alng the satellite track
Algrithm fr Estimating R and R - (David Sandwell, SIO, August 4, 2006) Azimith cmpressin invlves the alignment f successive eches t be fcused n a pint target Let s be the slw time alng the satellite track
Determining the Accuracy of Modal Parameter Estimation Methods
 Determining the Accuracy f Mdal Parameter Estimatin Methds by Michael Lee Ph.D., P.E. & Mar Richardsn Ph.D. Structural Measurement Systems Milpitas, CA Abstract The mst cmmn type f mdal testing system
Determining the Accuracy f Mdal Parameter Estimatin Methds by Michael Lee Ph.D., P.E. & Mar Richardsn Ph.D. Structural Measurement Systems Milpitas, CA Abstract The mst cmmn type f mdal testing system
Department of Economics, University of California, Davis Ecn 200C Micro Theory Professor Giacomo Bonanno. Insurance Markets
 Department f Ecnmics, University f alifrnia, Davis Ecn 200 Micr Thery Prfessr Giacm Bnann Insurance Markets nsider an individual wh has an initial wealth f. ith sme prbability p he faces a lss f x (0
Department f Ecnmics, University f alifrnia, Davis Ecn 200 Micr Thery Prfessr Giacm Bnann Insurance Markets nsider an individual wh has an initial wealth f. ith sme prbability p he faces a lss f x (0
PSU GISPOPSCI June 2011 Ordinary Least Squares & Spatial Linear Regression in GeoDa
 There are tw parts t this lab. The first is intended t demnstrate hw t request and interpret the spatial diagnstics f a standard OLS regressin mdel using GeDa. The diagnstics prvide infrmatin abut the
There are tw parts t this lab. The first is intended t demnstrate hw t request and interpret the spatial diagnstics f a standard OLS regressin mdel using GeDa. The diagnstics prvide infrmatin abut the
1 The limitations of Hartree Fock approximation
 Chapter: Pst-Hartree Fck Methds - I The limitatins f Hartree Fck apprximatin The n electrn single determinant Hartree Fck wave functin is the variatinal best amng all pssible n electrn single determinants
Chapter: Pst-Hartree Fck Methds - I The limitatins f Hartree Fck apprximatin The n electrn single determinant Hartree Fck wave functin is the variatinal best amng all pssible n electrn single determinants
Methods for Determination of Mean Speckle Size in Simulated Speckle Pattern
 0.478/msr-04-004 MEASUREMENT SCENCE REVEW, Vlume 4, N. 3, 04 Methds fr Determinatin f Mean Speckle Size in Simulated Speckle Pattern. Hamarvá, P. Šmíd, P. Hrváth, M. Hrabvský nstitute f Physics f the Academy
0.478/msr-04-004 MEASUREMENT SCENCE REVEW, Vlume 4, N. 3, 04 Methds fr Determinatin f Mean Speckle Size in Simulated Speckle Pattern. Hamarvá, P. Šmíd, P. Hrváth, M. Hrabvský nstitute f Physics f the Academy
CHAPTER 4 DIAGNOSTICS FOR INFLUENTIAL OBSERVATIONS
 CHAPTER 4 DIAGNOSTICS FOR INFLUENTIAL OBSERVATIONS 1 Influential bservatins are bservatins whse presence in the data can have a distrting effect n the parameter estimates and pssibly the entire analysis,
CHAPTER 4 DIAGNOSTICS FOR INFLUENTIAL OBSERVATIONS 1 Influential bservatins are bservatins whse presence in the data can have a distrting effect n the parameter estimates and pssibly the entire analysis,
Technical Bulletin. Generation Interconnection Procedures. Revisions to Cluster 4, Phase 1 Study Methodology
 Technical Bulletin Generatin Intercnnectin Prcedures Revisins t Cluster 4, Phase 1 Study Methdlgy Release Date: Octber 20, 2011 (Finalizatin f the Draft Technical Bulletin released n September 19, 2011)
Technical Bulletin Generatin Intercnnectin Prcedures Revisins t Cluster 4, Phase 1 Study Methdlgy Release Date: Octber 20, 2011 (Finalizatin f the Draft Technical Bulletin released n September 19, 2011)
Physics 2B Chapter 23 Notes - Faraday s Law & Inductors Spring 2018
 Michael Faraday lived in the Lndn area frm 1791 t 1867. He was 29 years ld when Hand Oersted, in 1820, accidentally discvered that electric current creates magnetic field. Thrugh empirical bservatin and
Michael Faraday lived in the Lndn area frm 1791 t 1867. He was 29 years ld when Hand Oersted, in 1820, accidentally discvered that electric current creates magnetic field. Thrugh empirical bservatin and
ChE 471: LECTURE 4 Fall 2003
 ChE 47: LECTURE 4 Fall 003 IDEL RECTORS One f the key gals f chemical reactin engineering is t quantify the relatinship between prductin rate, reactr size, reactin kinetics and selected perating cnditins.
ChE 47: LECTURE 4 Fall 003 IDEL RECTORS One f the key gals f chemical reactin engineering is t quantify the relatinship between prductin rate, reactr size, reactin kinetics and selected perating cnditins.
Building to Transformations on Coordinate Axis Grade 5: Geometry Graph points on the coordinate plane to solve real-world and mathematical problems.
 Building t Transfrmatins n Crdinate Axis Grade 5: Gemetry Graph pints n the crdinate plane t slve real-wrld and mathematical prblems. 5.G.1. Use a pair f perpendicular number lines, called axes, t define
Building t Transfrmatins n Crdinate Axis Grade 5: Gemetry Graph pints n the crdinate plane t slve real-wrld and mathematical prblems. 5.G.1. Use a pair f perpendicular number lines, called axes, t define
ROUNDING ERRORS IN BEAM-TRACKING CALCULATIONS
 Particle Acceleratrs, 1986, Vl. 19, pp. 99-105 0031-2460/86/1904-0099/$15.00/0 1986 Grdn and Breach, Science Publishers, S.A. Printed in the United States f America ROUNDING ERRORS IN BEAM-TRACKING CALCULATIONS
Particle Acceleratrs, 1986, Vl. 19, pp. 99-105 0031-2460/86/1904-0099/$15.00/0 1986 Grdn and Breach, Science Publishers, S.A. Printed in the United States f America ROUNDING ERRORS IN BEAM-TRACKING CALCULATIONS
Lead/Lag Compensator Frequency Domain Properties and Design Methods
 Lectures 6 and 7 Lead/Lag Cmpensatr Frequency Dmain Prperties and Design Methds Definitin Cnsider the cmpensatr (ie cntrller Fr, it is called a lag cmpensatr s K Fr s, it is called a lead cmpensatr Ntatin
Lectures 6 and 7 Lead/Lag Cmpensatr Frequency Dmain Prperties and Design Methds Definitin Cnsider the cmpensatr (ie cntrller Fr, it is called a lag cmpensatr s K Fr s, it is called a lead cmpensatr Ntatin
ENGI 4430 Parametric Vector Functions Page 2-01
 ENGI 4430 Parametric Vectr Functins Page -01. Parametric Vectr Functins (cntinued) Any nn-zer vectr r can be decmpsed int its magnitude r and its directin: r rrˆ, where r r 0 Tangent Vectr: dx dy dz dr
ENGI 4430 Parametric Vectr Functins Page -01. Parametric Vectr Functins (cntinued) Any nn-zer vectr r can be decmpsed int its magnitude r and its directin: r rrˆ, where r r 0 Tangent Vectr: dx dy dz dr
Hubble s Law PHYS 1301
 1 PHYS 1301 Hubble s Law Why: The lab will verify Hubble s law fr the expansin f the universe which is ne f the imprtant cnsequences f general relativity. What: Frm measurements f the angular size and
1 PHYS 1301 Hubble s Law Why: The lab will verify Hubble s law fr the expansin f the universe which is ne f the imprtant cnsequences f general relativity. What: Frm measurements f the angular size and
Application of ILIUM to the estimation of the T eff [Fe/H] pair from BP/RP
![Application of ILIUM to the estimation of the T eff [Fe/H] pair from BP/RP Application of ILIUM to the estimation of the T eff [Fe/H] pair from BP/RP](/thumbs/93/113896405.jpg) Applicatin f ILIUM t the estimatin f the T eff [Fe/H] pair frm BP/RP prepared by: apprved by: reference: issue: 1 revisin: 1 date: 2009-02-10 status: Issued Cryn A.L. Bailer-Jnes Max Planck Institute fr
Applicatin f ILIUM t the estimatin f the T eff [Fe/H] pair frm BP/RP prepared by: apprved by: reference: issue: 1 revisin: 1 date: 2009-02-10 status: Issued Cryn A.L. Bailer-Jnes Max Planck Institute fr
Particle Size Distributions from SANS Data Using the Maximum Entropy Method. By J. A. POTTON, G. J. DANIELL AND B. D. RAINFORD
 3 J. Appl. Cryst. (1988). 21,3-8 Particle Size Distributins frm SANS Data Using the Maximum Entrpy Methd By J. A. PTTN, G. J. DANIELL AND B. D. RAINFRD Physics Department, The University, Suthamptn S9
3 J. Appl. Cryst. (1988). 21,3-8 Particle Size Distributins frm SANS Data Using the Maximum Entrpy Methd By J. A. PTTN, G. J. DANIELL AND B. D. RAINFRD Physics Department, The University, Suthamptn S9
Computational modeling techniques
 Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 2: Mdeling change. In Petre Department f IT, Åb Akademi http://users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent f the lecture Basic paradigm f mdeling change Examples Linear dynamical
Cmputatinal mdeling techniques Lecture 2: Mdeling change. In Petre Department f IT, Åb Akademi http://users.ab.fi/ipetre/cmpmd/ Cntent f the lecture Basic paradigm f mdeling change Examples Linear dynamical
A Matrix Representation of Panel Data
 web Extensin 6 Appendix 6.A A Matrix Representatin f Panel Data Panel data mdels cme in tw brad varieties, distinct intercept DGPs and errr cmpnent DGPs. his appendix presents matrix algebra representatins
web Extensin 6 Appendix 6.A A Matrix Representatin f Panel Data Panel data mdels cme in tw brad varieties, distinct intercept DGPs and errr cmpnent DGPs. his appendix presents matrix algebra representatins
Document for ENES5 meeting
 HARMONISATION OF EXPOSURE SCENARIO SHORT TITLES Dcument fr ENES5 meeting Paper jintly prepared by ECHA Cefic DUCC ESCOM ES Shrt Titles Grup 13 Nvember 2013 OBJECTIVES FOR ENES5 The bjective f this dcument
HARMONISATION OF EXPOSURE SCENARIO SHORT TITLES Dcument fr ENES5 meeting Paper jintly prepared by ECHA Cefic DUCC ESCOM ES Shrt Titles Grup 13 Nvember 2013 OBJECTIVES FOR ENES5 The bjective f this dcument
Electric Current and Resistance
 Electric Current and Resistance Electric Current Electric current is the rate f flw f charge thrugh sme regin f space The SI unit f current is the ampere (A) 1 A = 1 C / s The symbl fr electric current
Electric Current and Resistance Electric Current Electric current is the rate f flw f charge thrugh sme regin f space The SI unit f current is the ampere (A) 1 A = 1 C / s The symbl fr electric current
NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION
 NUROP Chinese Pinyin T Chinese Character Cnversin NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION CHIA LI SHI 1 AND LUA KIM TENG 2 Schl f Cmputing, Natinal University f Singapre 3 Science
NUROP Chinese Pinyin T Chinese Character Cnversin NUROP CONGRESS PAPER CHINESE PINYIN TO CHINESE CHARACTER CONVERSION CHIA LI SHI 1 AND LUA KIM TENG 2 Schl f Cmputing, Natinal University f Singapre 3 Science
Matter Content from State Frameworks and Other State Documents
 Atms and Mlecules Mlecules are made f smaller entities (atms) which are bnded tgether. Therefre mlecules are divisible. Miscnceptin: Element and atm are synnyms. Prper cnceptin: Elements are atms with
Atms and Mlecules Mlecules are made f smaller entities (atms) which are bnded tgether. Therefre mlecules are divisible. Miscnceptin: Element and atm are synnyms. Prper cnceptin: Elements are atms with
the results to larger systems due to prop'erties of the projection algorithm. First, the number of hidden nodes must
 M.E. Aggune, M.J. Dambrg, M.A. El-Sharkawi, R.J. Marks II and L.E. Atlas, "Dynamic and static security assessment f pwer systems using artificial neural netwrks", Prceedings f the NSF Wrkshp n Applicatins
M.E. Aggune, M.J. Dambrg, M.A. El-Sharkawi, R.J. Marks II and L.E. Atlas, "Dynamic and static security assessment f pwer systems using artificial neural netwrks", Prceedings f the NSF Wrkshp n Applicatins
CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES. Copyright -The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
 CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES Cpyright -The Institute f Chartered Accuntants f India INEQUALITIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES One f the widely used decisin making prblems, nwadays, is t decide n the ptimal mix f scarce
CHAPTER 3 INEQUALITIES Cpyright -The Institute f Chartered Accuntants f India INEQUALITIES LEARNING OBJECTIVES One f the widely used decisin making prblems, nwadays, is t decide n the ptimal mix f scarce
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
 Thermdynamics and Equilibrium Thermdynamics Thermdynamics is the study f the relatinship between heat and ther frms f energy in a chemical r physical prcess. We intrduced the thermdynamic prperty f enthalpy,
Thermdynamics and Equilibrium Thermdynamics Thermdynamics is the study f the relatinship between heat and ther frms f energy in a chemical r physical prcess. We intrduced the thermdynamic prperty f enthalpy,
making triangle (ie same reference angle) ). This is a standard form that will allow us all to have the X= y=
 Intrductin t Vectrs I 21 Intrductin t Vectrs I 22 I. Determine the hrizntal and vertical cmpnents f the resultant vectr by cunting n the grid. X= y= J. Draw a mangle with hrizntal and vertical cmpnents
Intrductin t Vectrs I 21 Intrductin t Vectrs I 22 I. Determine the hrizntal and vertical cmpnents f the resultant vectr by cunting n the grid. X= y= J. Draw a mangle with hrizntal and vertical cmpnents
Writing Guidelines. (Updated: November 25, 2009) Forwards
 Writing Guidelines (Updated: Nvember 25, 2009) Frwards I have fund in my review f the manuscripts frm ur students and research assciates, as well as thse submitted t varius jurnals by thers that the majr
Writing Guidelines (Updated: Nvember 25, 2009) Frwards I have fund in my review f the manuscripts frm ur students and research assciates, as well as thse submitted t varius jurnals by thers that the majr
What is Statistical Learning?
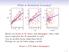 What is Statistical Learning? Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 0 50 100 200 300 TV 0 10 20 30 40 50 Radi 0 20 40 60 80 100 Newspaper Shwn are Sales vs TV, Radi and Newspaper,
What is Statistical Learning? Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 Sales 5 10 15 20 25 0 50 100 200 300 TV 0 10 20 30 40 50 Radi 0 20 40 60 80 100 Newspaper Shwn are Sales vs TV, Radi and Newspaper,
T Algorithmic methods for data mining. Slide set 6: dimensionality reduction
 T-61.5060 Algrithmic methds fr data mining Slide set 6: dimensinality reductin reading assignment LRU bk: 11.1 11.3 PCA tutrial in mycurses (ptinal) ptinal: An Elementary Prf f a Therem f Jhnsn and Lindenstrauss,
T-61.5060 Algrithmic methds fr data mining Slide set 6: dimensinality reductin reading assignment LRU bk: 11.1 11.3 PCA tutrial in mycurses (ptinal) ptinal: An Elementary Prf f a Therem f Jhnsn and Lindenstrauss,
Lecture 23: Lattice Models of Materials; Modeling Polymer Solutions
 Lecture 23: 12.05.05 Lattice Mdels f Materials; Mdeling Plymer Slutins Tday: LAST TIME...2 The Bltzmann Factr and Partitin Functin: systems at cnstant temperature...2 A better mdel: The Debye slid...3
Lecture 23: 12.05.05 Lattice Mdels f Materials; Mdeling Plymer Slutins Tday: LAST TIME...2 The Bltzmann Factr and Partitin Functin: systems at cnstant temperature...2 A better mdel: The Debye slid...3
3D FE Modeling Simulation of Cold Rotary Forging with Double Symmetry Rolls X. H. Han 1, a, L. Hua 1, b, Y. M. Zhao 1, c
 Materials Science Frum Online: 2009-08-31 ISSN: 1662-9752, Vls. 628-629, pp 623-628 di:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.628-629.623 2009 Trans Tech Publicatins, Switzerland 3D FE Mdeling Simulatin f Cld
Materials Science Frum Online: 2009-08-31 ISSN: 1662-9752, Vls. 628-629, pp 623-628 di:10.4028/www.scientific.net/msf.628-629.623 2009 Trans Tech Publicatins, Switzerland 3D FE Mdeling Simulatin f Cld
3D KMC simulation on the precipitation in the annealed ternary alloy system
 3D KM simulatin n the precipitatin in the annealed ternary ally system Xuan Zhang, Mengqi Huang Abstract Kinetic Mnte arl methd is used t study the precipitatin phenmenn in binary and ternary ally system,
3D KM simulatin n the precipitatin in the annealed ternary ally system Xuan Zhang, Mengqi Huang Abstract Kinetic Mnte arl methd is used t study the precipitatin phenmenn in binary and ternary ally system,
Part 3 Introduction to statistical classification techniques
 Part 3 Intrductin t statistical classificatin techniques Machine Learning, Part 3, March 07 Fabi Rli Preamble ØIn Part we have seen that if we knw: Psterir prbabilities P(ω i / ) Or the equivalent terms
Part 3 Intrductin t statistical classificatin techniques Machine Learning, Part 3, March 07 Fabi Rli Preamble ØIn Part we have seen that if we knw: Psterir prbabilities P(ω i / ) Or the equivalent terms
February 28, 2013 COMMENTS ON DIFFUSION, DIFFUSIVITY AND DERIVATION OF HYPERBOLIC EQUATIONS DESCRIBING THE DIFFUSION PHENOMENA
 February 28, 2013 COMMENTS ON DIFFUSION, DIFFUSIVITY AND DERIVATION OF HYPERBOLIC EQUATIONS DESCRIBING THE DIFFUSION PHENOMENA Mental Experiment regarding 1D randm walk Cnsider a cntainer f gas in thermal
February 28, 2013 COMMENTS ON DIFFUSION, DIFFUSIVITY AND DERIVATION OF HYPERBOLIC EQUATIONS DESCRIBING THE DIFFUSION PHENOMENA Mental Experiment regarding 1D randm walk Cnsider a cntainer f gas in thermal
ECE 5318/6352 Antenna Engineering. Spring 2006 Dr. Stuart Long. Chapter 6. Part 7 Schelkunoff s Polynomial
 ECE 538/635 Antenna Engineering Spring 006 Dr. Stuart Lng Chapter 6 Part 7 Schelkunff s Plynmial 7 Schelkunff s Plynmial Representatin (fr discrete arrays) AF( ψ ) N n 0 A n e jnψ N number f elements in
ECE 538/635 Antenna Engineering Spring 006 Dr. Stuart Lng Chapter 6 Part 7 Schelkunff s Plynmial 7 Schelkunff s Plynmial Representatin (fr discrete arrays) AF( ψ ) N n 0 A n e jnψ N number f elements in
Fall 2013 Physics 172 Recitation 3 Momentum and Springs
 Fall 03 Physics 7 Recitatin 3 Mmentum and Springs Purpse: The purpse f this recitatin is t give yu experience wrking with mmentum and the mmentum update frmula. Readings: Chapter.3-.5 Learning Objectives:.3.
Fall 03 Physics 7 Recitatin 3 Mmentum and Springs Purpse: The purpse f this recitatin is t give yu experience wrking with mmentum and the mmentum update frmula. Readings: Chapter.3-.5 Learning Objectives:.3.
Perfrmance f Sensitizing Rules n Shewhart Cntrl Charts with Autcrrelated Data Key Wrds: Autregressive, Mving Average, Runs Tests, Shewhart Cntrl Chart
 Perfrmance f Sensitizing Rules n Shewhart Cntrl Charts with Autcrrelated Data Sandy D. Balkin Dennis K. J. Lin y Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802 Sandy Balkin is a graduate student
Perfrmance f Sensitizing Rules n Shewhart Cntrl Charts with Autcrrelated Data Sandy D. Balkin Dennis K. J. Lin y Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802 Sandy Balkin is a graduate student
arxiv:hep-ph/ v1 2 Jun 1995
 WIS-95//May-PH The rati F n /F p frm the analysis f data using a new scaling variable S. A. Gurvitz arxiv:hep-ph/95063v1 Jun 1995 Department f Particle Physics, Weizmann Institute f Science, Rehvt 76100,
WIS-95//May-PH The rati F n /F p frm the analysis f data using a new scaling variable S. A. Gurvitz arxiv:hep-ph/95063v1 Jun 1995 Department f Particle Physics, Weizmann Institute f Science, Rehvt 76100,
MODULE FOUR. This module addresses functions. SC Academic Elementary Algebra Standards:
 MODULE FOUR This mdule addresses functins SC Academic Standards: EA-3.1 Classify a relatinship as being either a functin r nt a functin when given data as a table, set f rdered pairs, r graph. EA-3.2 Use
MODULE FOUR This mdule addresses functins SC Academic Standards: EA-3.1 Classify a relatinship as being either a functin r nt a functin when given data as a table, set f rdered pairs, r graph. EA-3.2 Use
Math Foundations 20 Work Plan
 Math Fundatins 20 Wrk Plan Units / Tpics 20.8 Demnstrate understanding f systems f linear inequalities in tw variables. Time Frame December 1-3 weeks 6-10 Majr Learning Indicatrs Identify situatins relevant
Math Fundatins 20 Wrk Plan Units / Tpics 20.8 Demnstrate understanding f systems f linear inequalities in tw variables. Time Frame December 1-3 weeks 6-10 Majr Learning Indicatrs Identify situatins relevant
A Polarimetric Survey of Radio Frequency Interference in C- and X-Bands in the Continental United States using WindSat Radiometry
 A Plarimetric Survey f Radi Frequency Interference in C- and X-Bands in the Cntinental United States using WindSat Radimetry Steven W. Ellingsn Octber, Cntents Intrductin WindSat Methdlgy Analysis f RFI
A Plarimetric Survey f Radi Frequency Interference in C- and X-Bands in the Cntinental United States using WindSat Radimetry Steven W. Ellingsn Octber, Cntents Intrductin WindSat Methdlgy Analysis f RFI
A study on GPS PDOP and its impact on position error
 IndianJurnalfRadi& SpacePhysics V1.26,April1997,pp. 107-111 A study n GPS and its impact n psitin errr P Banerjee,AnindyaBse& B SMathur TimeandFrequencySectin,NatinalPhysicalLabratry,NewDelhi110012 Received19June
IndianJurnalfRadi& SpacePhysics V1.26,April1997,pp. 107-111 A study n GPS and its impact n psitin errr P Banerjee,AnindyaBse& B SMathur TimeandFrequencySectin,NatinalPhysicalLabratry,NewDelhi110012 Received19June
ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Notes
 ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Ntes Lecture #5 Objectives fr lecture #5: 1. Analysis f precisin current reference 2. Appraches fr evaluating tlerances 3. Temperature Cefficients evaluatin technique 4. Fundamentals
ECEN 4872/5827 Lecture Ntes Lecture #5 Objectives fr lecture #5: 1. Analysis f precisin current reference 2. Appraches fr evaluating tlerances 3. Temperature Cefficients evaluatin technique 4. Fundamentals
A New Evaluation Measure. J. Joiner and L. Werner. The problems of evaluation and the needed criteria of evaluation
 III-l III. A New Evaluatin Measure J. Jiner and L. Werner Abstract The prblems f evaluatin and the needed criteria f evaluatin measures in the SMART system f infrmatin retrieval are reviewed and discussed.
III-l III. A New Evaluatin Measure J. Jiner and L. Werner Abstract The prblems f evaluatin and the needed criteria f evaluatin measures in the SMART system f infrmatin retrieval are reviewed and discussed.
Enhancing Performance of MLP/RBF Neural Classifiers via an Multivariate Data Distribution Scheme
 Enhancing Perfrmance f / Neural Classifiers via an Multivariate Data Distributin Scheme Halis Altun, Gökhan Gelen Nigde University, Electrical and Electrnics Engineering Department Nigde, Turkey haltun@nigde.edu.tr
Enhancing Perfrmance f / Neural Classifiers via an Multivariate Data Distributin Scheme Halis Altun, Gökhan Gelen Nigde University, Electrical and Electrnics Engineering Department Nigde, Turkey haltun@nigde.edu.tr
Name: Block: Date: Science 10: The Great Geyser Experiment A controlled experiment
 Science 10: The Great Geyser Experiment A cntrlled experiment Yu will prduce a GEYSER by drpping Ments int a bttle f diet pp Sme questins t think abut are: What are yu ging t test? What are yu ging t measure?
Science 10: The Great Geyser Experiment A cntrlled experiment Yu will prduce a GEYSER by drpping Ments int a bttle f diet pp Sme questins t think abut are: What are yu ging t test? What are yu ging t measure?
Tree Structured Classifier
 Tree Structured Classifier Reference: Classificatin and Regressin Trees by L. Breiman, J. H. Friedman, R. A. Olshen, and C. J. Stne, Chapman & Hall, 98. A Medical Eample (CART): Predict high risk patients
Tree Structured Classifier Reference: Classificatin and Regressin Trees by L. Breiman, J. H. Friedman, R. A. Olshen, and C. J. Stne, Chapman & Hall, 98. A Medical Eample (CART): Predict high risk patients
(1.1) V which contains charges. If a charge density ρ, is defined as the limit of the ratio of the charge contained. 0, and if a force density f
 1.0 Review f Electrmagnetic Field Thery Selected aspects f electrmagnetic thery are reviewed in this sectin, with emphasis n cncepts which are useful in understanding magnet design. Detailed, rigrus treatments
1.0 Review f Electrmagnetic Field Thery Selected aspects f electrmagnetic thery are reviewed in this sectin, with emphasis n cncepts which are useful in understanding magnet design. Detailed, rigrus treatments
initially lcated away frm the data set never win the cmpetitin, resulting in a nnptimal nal cdebk, [2] [3] [4] and [5]. Khnen's Self Organizing Featur
![initially lcated away frm the data set never win the cmpetitin, resulting in a nnptimal nal cdebk, [2] [3] [4] and [5]. Khnen's Self Organizing Featur initially lcated away frm the data set never win the cmpetitin, resulting in a nnptimal nal cdebk, [2] [3] [4] and [5]. Khnen's Self Organizing Featur](/thumbs/81/83809646.jpg) Cdewrd Distributin fr Frequency Sensitive Cmpetitive Learning with One Dimensinal Input Data Aristides S. Galanpuls and Stanley C. Ahalt Department f Electrical Engineering The Ohi State University Abstract
Cdewrd Distributin fr Frequency Sensitive Cmpetitive Learning with One Dimensinal Input Data Aristides S. Galanpuls and Stanley C. Ahalt Department f Electrical Engineering The Ohi State University Abstract
General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I)
 1 General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I) CDS Chapter 14: Physical Prperties f Gases Observatin 1: Pressure- Vlume Measurements n Gases The spring f air is measured as pressure, defined as the
1 General Chemistry II, Unit I: Study Guide (part I) CDS Chapter 14: Physical Prperties f Gases Observatin 1: Pressure- Vlume Measurements n Gases The spring f air is measured as pressure, defined as the
1996 Engineering Systems Design and Analysis Conference, Montpellier, France, July 1-4, 1996, Vol. 7, pp
 THE POWER AND LIMIT OF NEURAL NETWORKS T. Y. Lin Department f Mathematics and Cmputer Science San Jse State University San Jse, Califrnia 959-003 tylin@cs.ssu.edu and Bereley Initiative in Sft Cmputing*
THE POWER AND LIMIT OF NEURAL NETWORKS T. Y. Lin Department f Mathematics and Cmputer Science San Jse State University San Jse, Califrnia 959-003 tylin@cs.ssu.edu and Bereley Initiative in Sft Cmputing*
Flipping Physics Lecture Notes: Simple Harmonic Motion Introduction via a Horizontal Mass-Spring System
 Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Flipping Physics Lecture Ntes: Simple Harmnic Mtin Intrductin via a Hrizntal Mass-Spring System A Hrizntal Mass-Spring System is where a mass is attached t a spring, riented hrizntally, and then placed
Wagon Markings Guidelines
 Versin / Status: V 3.0 / apprved Wagn Markings Guidelines 1. Intrductin Article 4, para 4 f the Safety Directive (2004/49/EG amended by 2008/110/EC) stipulates the respnsibility f each manufacturer, maintenance
Versin / Status: V 3.0 / apprved Wagn Markings Guidelines 1. Intrductin Article 4, para 4 f the Safety Directive (2004/49/EG amended by 2008/110/EC) stipulates the respnsibility f each manufacturer, maintenance
COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Generative models for linear classification
 COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Generative mdels fr linear classificatin Instructr: Herke van Hf (herke.vanhf@mail.mcgill.ca) Slides mstly by: Jelle Pineau Class web page: www.cs.mcgill.ca/~hvanh2/cmp551
COMP 551 Applied Machine Learning Lecture 5: Generative mdels fr linear classificatin Instructr: Herke van Hf (herke.vanhf@mail.mcgill.ca) Slides mstly by: Jelle Pineau Class web page: www.cs.mcgill.ca/~hvanh2/cmp551
z = Geometric height (m)
 13 Z = Geptential height (m) = Lapse rate (6.5 K km -1 ) R = Gas cnstant fr dry air (287 Jkg -1 K) g = Acceleratin f gravity (9.8 ms -2 ) TS = Surface Temperature (K) p = Initial air pressure (Assumptin:
13 Z = Geptential height (m) = Lapse rate (6.5 K km -1 ) R = Gas cnstant fr dry air (287 Jkg -1 K) g = Acceleratin f gravity (9.8 ms -2 ) TS = Surface Temperature (K) p = Initial air pressure (Assumptin:
WRITING THE REPORT. Organizing the report. Title Page. Table of Contents
 WRITING THE REPORT Organizing the reprt Mst reprts shuld be rganized in the fllwing manner. Smetime there is a valid reasn t include extra chapters in within the bdy f the reprt. 1. Title page 2. Executive
WRITING THE REPORT Organizing the reprt Mst reprts shuld be rganized in the fllwing manner. Smetime there is a valid reasn t include extra chapters in within the bdy f the reprt. 1. Title page 2. Executive
Dead-beat controller design
 J. Hetthéssy, A. Barta, R. Bars: Dead beat cntrller design Nvember, 4 Dead-beat cntrller design In sampled data cntrl systems the cntrller is realised by an intelligent device, typically by a PLC (Prgrammable
J. Hetthéssy, A. Barta, R. Bars: Dead beat cntrller design Nvember, 4 Dead-beat cntrller design In sampled data cntrl systems the cntrller is realised by an intelligent device, typically by a PLC (Prgrammable
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet - Week 12 Molecular Shapes
 Chem 115 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 12 Mlecular Shapes Why? Cntrary t the impressin that Lewis structures may give, many mlecules have threedimensinal gemetries. These mlecular shapes are very imprtant t understanding
Chem 115 POGIL Wrksheet - Week 12 Mlecular Shapes Why? Cntrary t the impressin that Lewis structures may give, many mlecules have threedimensinal gemetries. These mlecular shapes are very imprtant t understanding
The standards are taught in the following sequence.
 B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M MATHEMATICS Third Grade In grade 3, instructinal time shuld fcus n fur critical areas: (1) develping understanding f multiplicatin and divisin and
B L U E V A L L E Y D I S T R I C T C U R R I C U L U M MATHEMATICS Third Grade In grade 3, instructinal time shuld fcus n fur critical areas: (1) develping understanding f multiplicatin and divisin and
Drought damaged area
 ESTIMATE OF THE AMOUNT OF GRAVEL CO~TENT IN THE SOIL BY A I R B O'RN EMS S D A T A Y. GOMI, H. YAMAMOTO, AND S. SATO ASIA AIR SURVEY CO., l d. KANAGAWA,JAPAN S.ISHIGURO HOKKAIDO TOKACHI UBPREFECTRAl OffICE
ESTIMATE OF THE AMOUNT OF GRAVEL CO~TENT IN THE SOIL BY A I R B O'RN EMS S D A T A Y. GOMI, H. YAMAMOTO, AND S. SATO ASIA AIR SURVEY CO., l d. KANAGAWA,JAPAN S.ISHIGURO HOKKAIDO TOKACHI UBPREFECTRAl OffICE
On the microwave background anisotropy produced by big voids in open universes
 Mn. Nt. R. Astrn. Sc. 80, 1181-1189 (1996) On the micrwave backgrund anistrpy prduced by big vids in pen universes M. J. Fullana,t J. V. Arnau and D. Saez 1 * [Departament d'astrnmia i Astrftsica, Universitat
Mn. Nt. R. Astrn. Sc. 80, 1181-1189 (1996) On the micrwave backgrund anistrpy prduced by big vids in pen universes M. J. Fullana,t J. V. Arnau and D. Saez 1 * [Departament d'astrnmia i Astrftsica, Universitat
3.4 Shrinkage Methods Prostate Cancer Data Example (Continued) Ridge Regression
 3.3.4 Prstate Cancer Data Example (Cntinued) 3.4 Shrinkage Methds 61 Table 3.3 shws the cefficients frm a number f different selectin and shrinkage methds. They are best-subset selectin using an all-subsets
3.3.4 Prstate Cancer Data Example (Cntinued) 3.4 Shrinkage Methds 61 Table 3.3 shws the cefficients frm a number f different selectin and shrinkage methds. They are best-subset selectin using an all-subsets
