Observations of the effects of meteors on the ionospheres of Venus, Earth and Mars
|
|
|
- Russell Clarke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Observations of the effects of meteors on the ionospheres of Venus, Earth and Mars Paul Withers 1, A. A. Christou 2, M. Mendillo 1, M. Pätzold 3, K. Peter 3, S. Tellmann 3, J. Vaubaillon 4 1 Boston University 2 Armagh Observatory 3 Department for Planetary Research, Cologne 4 IMCCE, Observatoire de Paris (withers@bu.edu) Thursday :30-16:50 International Conference on Comparative Planetology: Venus-Earth-Mars, ESLAB 2009 ESTEC, The Netherlands
2 Observations of the effects of meteors on the ionospheres of Venus, Earth Observations Earth Venus Mars Comparison and Mars Some factors that affect metal ion layers Meteor showers Sporadic meteoroids Magnetic fields and winds Status of theoretical simulations Unanswered questions
3 Metal ions on Earth Figure 8.3 of Grebowsky and Aikin (2002)
4 Sporadic E on Earth Figure 2a of Mathews et al. (1997) Ionosonde data from Arecibo Sporadic E = Dense layers of plasma at E-region altitudes that aren t related to normal E layer Plasma persists into night, requires long-lived ions atomic metal ions Formed by wind shear in strong, inclined magnetic field
5 Metal ion layer on Venus VEX PVO Figure 4 of Kliore (1992) Candidate layers seen in 18 VEX VeRa profiles from SZA of 60 o to 90 o Some double layers seen Figure 1 of Pätzold et al. (2009)
6 Metal ion layer on Mars MEX MGS double metal ion layer Figure 4 of Withers et al. (2008) metal ion layer Candidate layers seen in 71 MGS profiles and 75 MEX profiles from SZA of 50 o to 90 o Some double layers seen Withers et al., in prep
7 Comparison of observations for Venus, Earth and Mars Planet Layering N (m -3 ) Height (km) Width (km) Pressure (Pa) Density (kg m -3 ) Scale height (km) Temp (K) Venus Mostly single, some double (radio occ) 1E E Earth Many (rockets), 1E ~ E single (Sporadic E) (XX) (rockets) Mars Mostly single, some double (radio occ) 1E E Venus PV Sounder probe data at 112 km from Seiff et al. (1980) Earth MSISE-90 model at 100 km for mean solar activities, averaged over local time, season, latitude Taken from Mars Viking Lander 1 data at 92 km from Seiff and Kirk (1977)
8 Comets and meteor showers Composite image of comet Wild 2 taken by Stardust Comet West (1975, San Diego) Positions in 2003 of debris ejected from comet 79P/du Toit-Hartley in Orbits and positions of Mars and Jupiter in 2003 shown. (Left) Stardust, NASA (Centre) (Right) Figure 1 of Christou et al. (2007)
9 Effects of meteor showers Predicted, but not yet definitively detected, on Earth Too many other causes of variability If robust repeatable annual variations seen on Venus or Mars, then must discriminate between possible causes seasonal variations in wind shear in magnetic field seasonal variations in sporadic meteoroids meteor showers (insignificant source of mass on Earth) The first possibility should be easy to exclude at Venus, which has no magnetic fields and no seasons Discrimination between variations in meteoroid influx at Venus or Mars due to changes in showers or sporadics is harder Timescales for changes should be shorter for showers If enhanced metal ion layers seen during expected meteor shower, meteor shower is most likely cause
10 Observed distribution of sporadic meteors Figure 8 of Chau et al. (2007)
11 Schematic distribution of sporadic meteors North toroidial North apex Anti-Helion Helion South apex South toroidial
12 Meteors beyond Earth Sporadic meteoroids seen at Earth do not have uniform distribution of radiants Wiegert et al. (2009) showed that sporadic meteoroid distribution at Earth is dominated by debris from Encke and Tempel-Tuttle Do sporadic meteoroids at other planets have a uniform distribution of radiants? Are sporadic meteoroids at other planets predominantly produced by a small number of comets? Which comets? How does ratio of sporadic meteoroid mass flux to shower meteoroid mass flux vary from planet to planet?
13 Magnetic fields and wind shear Important for Sporadic E and metal ion layers on Earth What about Venus (draped solar wind magnetic field) and Mars (localized crustal fields)? Figure 1 of Mathews (1998)
14 Status of theoretical simulations Earth Relatively sophisticated models, but geo-centric designs make transfer to other planets difficult Mars Two groups have published one paper each 1D model, steady-state, inappropriate conditions for comparison with available observations Critical reaction rate estimated, assumed value is 80x smaller than subsequent laboratory measurements Venus Nothing published Several conference abstracts by one group, whose peak electron densities have grown from 10 7 to 10 9 m -3
15 Unanswered questions What are the compositions of metal ion layers on Venus and Mars? How do different magnetic environments affect the formation of metal ion layers? How do fluxes of shower and sporadic meteoroids vary with heliocentric distance? What properties and processes control temporal and spatial variations in the physical characteristics of metal ion layers? Can a single physics-based model successfully simulate metal ion layers on Venus, Earth and Mars?
16 Backup
17 Meteors and metals in the atmosphere 1966 Leonids, New Mexico Artificial guide star produced by 589 nm laser Number density of Na measured by lidar at 589 nm (Left) (Centre) (Right) Figure 6 of Butler et al. (2003)
18 Metal ion layers beyond Earth? Meteoroids all planets Dominant short-lived (molecular) ions all planets Magnetic field some planets Problem Available data from radio occultations show electron density, not ion composition. Direct evidence for metal ions impossible
19 Metal chemistry Produce Mg + (used here as representative metal species) Directly during ablation Photoionize neutral Mg Neutral Mg charge-exchanges with short-lived molecular ion to form longer-lived atomic ion Rate of Mg + + e -> Mg + hv is very slow Main pathway for loss of metal ions is Mg + + 2X -> Mg +.X + X Mg +.X + e -> Mg + X Three body reaction with two neutrals is often rate-limiting step, proceeds much faster at lower altitudes, so vertical transport of metal ions will be important Relevant reaction rate coefficients are poorly known Lifetimes ~ days
Comparative meteor science The effects of meteoroids on planetary atmospheres and ionospheres
 Comparative meteor science The effects of meteoroids on planetary atmospheres and ionospheres Paul Withers and Meers Oppenheim Boston University (withers@bu.edu, meerso@bu.edu) Tuesday 2009.06.30 1930-2130
Comparative meteor science The effects of meteoroids on planetary atmospheres and ionospheres Paul Withers and Meers Oppenheim Boston University (withers@bu.edu, meerso@bu.edu) Tuesday 2009.06.30 1930-2130
The Mars Ionosphere: More than a Chapman Layer
 The Mars Ionosphere: More than a Chapman Layer Paul Withers Center for Space Physics Boston University (withers@bu.edu) 2008.02.25 2008.02.29 Armagh Observatory Armagh, UK Acknowledgements Michael Mendillo,
The Mars Ionosphere: More than a Chapman Layer Paul Withers Center for Space Physics Boston University (withers@bu.edu) 2008.02.25 2008.02.29 Armagh Observatory Armagh, UK Acknowledgements Michael Mendillo,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113, A12314, doi: /2008ja013636, 2008
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013636, 2008 Physical characteristics and occurrence rates of meteoric plasma layers detected in the Martian ionosphere
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008ja013636, 2008 Physical characteristics and occurrence rates of meteoric plasma layers detected in the Martian ionosphere
Exploring the ionosphere of Mars
 Exploring the ionosphere of Mars This hazy region contains the atmosphere and ionosphere of Mars Paul Withers Boston University (withers@bu.edu) Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Iowa,
Exploring the ionosphere of Mars This hazy region contains the atmosphere and ionosphere of Mars Paul Withers Boston University (withers@bu.edu) Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Iowa,
Simulations of the Mars ionosphere during a solar flare
 Simulations of the Mars ionosphere during a solar flare Paul Withers, Joei Wroten, Michael Mendillo - Boston University Phil Chamberlin - University of Colorado (withers@bu.edu) SA31B-05 Wednesday 2007.05.23
Simulations of the Mars ionosphere during a solar flare Paul Withers, Joei Wroten, Michael Mendillo - Boston University Phil Chamberlin - University of Colorado (withers@bu.edu) SA31B-05 Wednesday 2007.05.23
The Response of an Ionosphere to changes in the solar F 10.7 flux: Comparison of Venus, Earth and Mars
 The Response of an Ionosphere to changes in the solar F 10.7 flux: Comparison of Venus, Earth and Mars Paul Withers and Michael Mendillo Boston University (withers@bu.edu) Spring AGU 2005, #SA41A-03 New
The Response of an Ionosphere to changes in the solar F 10.7 flux: Comparison of Venus, Earth and Mars Paul Withers and Michael Mendillo Boston University (withers@bu.edu) Spring AGU 2005, #SA41A-03 New
Anomalous Ionospheric Profiles. Association of Anomalous Profiles and Magnetic Fields. The Effects of Solar Flares on Earth and Mars
 Anomalous Ionospheric Profiles Association of Anomalous Profiles and Magnetic Fields The Effects of Solar Flares on Earth and Mars Examples of the Response of the Mars Ionosphere to Solar Flares Implications
Anomalous Ionospheric Profiles Association of Anomalous Profiles and Magnetic Fields The Effects of Solar Flares on Earth and Mars Examples of the Response of the Mars Ionosphere to Solar Flares Implications
J.D. Mathews Penn State
 Metal Ions in Sporadic-E Layers Along with Some Speculation About Analogous Phenomena on Other Planets Iron Meteorite - Meridiani Planum J.D. Mathews Penn State NASA/JPL/Cornell image PIA07269 This is
Metal Ions in Sporadic-E Layers Along with Some Speculation About Analogous Phenomena on Other Planets Iron Meteorite - Meridiani Planum J.D. Mathews Penn State NASA/JPL/Cornell image PIA07269 This is
Simplifying the martian carbon dioxide cycle: An empirical method for predicting surface pressure
 Simplifying the martian carbon dioxide cycle: An empirical method for predicting surface pressure Paul Withers 1, Silvia Tellmann 2 1 - Boston University 2 Rheinisches Institut fur Umweltforschung, Cologne,
Simplifying the martian carbon dioxide cycle: An empirical method for predicting surface pressure Paul Withers 1, Silvia Tellmann 2 1 - Boston University 2 Rheinisches Institut fur Umweltforschung, Cologne,
Ionospheres of the Terrestrial Planets
 Ionospheres of the Terrestrial Planets Stan Solomon High Altitude Observatory National Center for Atmospheric Research stans@ucar.edu Heliophysics Summer School Boulder, Colorado 28 July 2009 1 Outline
Ionospheres of the Terrestrial Planets Stan Solomon High Altitude Observatory National Center for Atmospheric Research stans@ucar.edu Heliophysics Summer School Boulder, Colorado 28 July 2009 1 Outline
Meteor Science and Aeronomy Using the Arecibo VHF and UHF Radars.
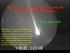 Meteor Science and Aeronomy Using the Arecibo VHF and UHF Radars. Bolide AIDA 1989 Bolide AIDA was in a near-earth asteroidal orbit with V ~15.5 km/sec, a period of ~1.4 yrs, aubritic compositon, ~30 kg
Meteor Science and Aeronomy Using the Arecibo VHF and UHF Radars. Bolide AIDA 1989 Bolide AIDA was in a near-earth asteroidal orbit with V ~15.5 km/sec, a period of ~1.4 yrs, aubritic compositon, ~30 kg
MST radar observations of the Leonid meteor storm during
 Indian Journal of Radio & Space Physics Vol 40 April 2011, pp 67-71 MST radar observations of the Leonid meteor storm during 1996-2007 N Rakesh Chandra 1,$,*, G Yellaiah 2 & S Vijaya Bhaskara Rao 3 1 Nishitha
Indian Journal of Radio & Space Physics Vol 40 April 2011, pp 67-71 MST radar observations of the Leonid meteor storm during 1996-2007 N Rakesh Chandra 1,$,*, G Yellaiah 2 & S Vijaya Bhaskara Rao 3 1 Nishitha
The P/Halley Stream: Meteor Showers on Earth, Venus and Mars
 Earth Moon Planet (2008) 102:125 131 DOI 10.1007/s11038-007-9201-3 The P/Halley Stream: Meteor Showers on Earth, Venus and Mars Apostolos A. Christou Æ Jeremie Vaubaillon Æ Paul Withers Received: 11 July
Earth Moon Planet (2008) 102:125 131 DOI 10.1007/s11038-007-9201-3 The P/Halley Stream: Meteor Showers on Earth, Venus and Mars Apostolos A. Christou Æ Jeremie Vaubaillon Æ Paul Withers Received: 11 July
Paper Reference. Monday 9 June 2008 Morning Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1627/01 Edexcel GCSE Astronomy Paper 01 Monday 9 June 2008 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Calculator Items included with question papers
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1627/01 Edexcel GCSE Astronomy Paper 01 Monday 9 June 2008 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Calculator Items included with question papers
DIN EN : (E)
 DIN EN 16603-10-04:2015-05 (E) Space engineering - Space environment; English version EN 16603-10-04:2015 Foreword... 12 Introduction... 13 1 Scope... 14 2 Normative references... 15 3 Terms, definitions
DIN EN 16603-10-04:2015-05 (E) Space engineering - Space environment; English version EN 16603-10-04:2015 Foreword... 12 Introduction... 13 1 Scope... 14 2 Normative references... 15 3 Terms, definitions
Mars. Professor Withers Boston University Guest lecture in AS105 Alien Worlds. Thursday :00 NASA
 Mars Professor Withers Boston University (withers@bu.edu) Guest lecture in AS105 Alien Worlds Thursday 2014.10.02 14:00 NASA This is Mars One scale Different scale 0.5 x R-Earth 1.5 AU from Sun Same rotation
Mars Professor Withers Boston University (withers@bu.edu) Guest lecture in AS105 Alien Worlds Thursday 2014.10.02 14:00 NASA This is Mars One scale Different scale 0.5 x R-Earth 1.5 AU from Sun Same rotation
Near Earth Small Meteoroids
 Near Earth Small Meteoroids (avell@kobe-u.ac.jp) (CPS: Center for Planetary Science) 2007/07/03 Source of Meteoroids Stream Meteoroids Sporadic Meteoroids Source of Sporadic Interplanetary dusts;,, ( dust)
Near Earth Small Meteoroids (avell@kobe-u.ac.jp) (CPS: Center for Planetary Science) 2007/07/03 Source of Meteoroids Stream Meteoroids Sporadic Meteoroids Source of Sporadic Interplanetary dusts;,, ( dust)
The Martian Upper Atmosphere
 The Martian Upper Atmosphere By Paul Withers, newly graduated from LPL s PhD program Dissertation on Tides in the Martian Atmosphere Lecture given to Roger Yelle s PTYS 544 class 2003.04.08 Plan Summary
The Martian Upper Atmosphere By Paul Withers, newly graduated from LPL s PhD program Dissertation on Tides in the Martian Atmosphere Lecture given to Roger Yelle s PTYS 544 class 2003.04.08 Plan Summary
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 6. Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 6 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 6 The Solar System Units of Chapter 6 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System 6.2 Measuring the Planets 6.3 The Overall Layout
Lecture Outlines Chapter 6 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 6 The Solar System Units of Chapter 6 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System 6.2 Measuring the Planets 6.3 The Overall Layout
Chapter 19: Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets
 Chapter 19: Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Comet Superstition Throughout history, comets have been considered as portants of doom, even until very recently: Appearances of comet Kohoutek (1973), Halley
Chapter 19: Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Comet Superstition Throughout history, comets have been considered as portants of doom, even until very recently: Appearances of comet Kohoutek (1973), Halley
Comparison of Terrestrial and Martian TEC at Dawn and Dusk during Solstices
 Comparison of Terrestrial and Martian TEC at Dawn and Dusk during Solstices Angeline G. Burrell 1 Beatriz Sanchez-Cano 2, Mark Lester 2, Russell Stoneback 1, Olivier Witasse 3, Marco Cartacci 4 1 Center
Comparison of Terrestrial and Martian TEC at Dawn and Dusk during Solstices Angeline G. Burrell 1 Beatriz Sanchez-Cano 2, Mark Lester 2, Russell Stoneback 1, Olivier Witasse 3, Marco Cartacci 4 1 Center
CHAPTER 6. The Solar System
 CHAPTER 6 The Solar System 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System The Greeks knew about 5 planets other than Earth They also knew about two other objects that were not planets or stars: meteors and comets
CHAPTER 6 The Solar System 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System The Greeks knew about 5 planets other than Earth They also knew about two other objects that were not planets or stars: meteors and comets
Solar System Formation/The Sun
 Solar System Formation/The Sun Objective 4 Examine the orbital paths of planets and other astronomical bodies (comets and asteroids). Examine the theories of geocentric and heliocentric models and Kepler
Solar System Formation/The Sun Objective 4 Examine the orbital paths of planets and other astronomical bodies (comets and asteroids). Examine the theories of geocentric and heliocentric models and Kepler
The Solar Nebula Theory. This lecture will help you understand: Conceptual Integrated Science. Chapter 28 THE SOLAR SYSTEM
 This lecture will help you understand: Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 28 THE SOLAR SYSTEM Overview of the Solar System The Nebular Theory The Sun Asteroids, Comets, and
This lecture will help you understand: Hewitt/Lyons/Suchocki/Yeh Conceptual Integrated Science Chapter 28 THE SOLAR SYSTEM Overview of the Solar System The Nebular Theory The Sun Asteroids, Comets, and
Solar System Debris: Comets and Asteroids
 1 Solar System Debris: Comets and Asteroids Primarily found in two zones in the solar system. The Asteroid Belt (rocky, between Jupiter and Mars) The Edgeworth/Kuiper Belt (beyond Neptune) and Oort Cloud
1 Solar System Debris: Comets and Asteroids Primarily found in two zones in the solar system. The Asteroid Belt (rocky, between Jupiter and Mars) The Edgeworth/Kuiper Belt (beyond Neptune) and Oort Cloud
AST Section 2: Test 1
 AST1002 - Section 2: Test 1 Date: 10/06/2009 Name: Equations: c = λ f, λ peak = Question 1: A star with a declination of +40.0 degrees will be 1. east of the vernal equinox. 2. west of the vernal equinox.
AST1002 - Section 2: Test 1 Date: 10/06/2009 Name: Equations: c = λ f, λ peak = Question 1: A star with a declination of +40.0 degrees will be 1. east of the vernal equinox. 2. west of the vernal equinox.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 4 - Group Homework Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Density is defined as A) mass times weight. B) mass per unit volume.
Chapter 4 - Group Homework Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Density is defined as A) mass times weight. B) mass per unit volume.
Observations of the nightside ionosphere of Mars by the Mars Express Radio Science Experiment (MaRS)
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012ja018185, 2012 Observations of the nightside ionosphere of Mars by the Mars Express Radio Science Experiment (MaRS) Paul Withers, 1 M. O. Fillingim,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012ja018185, 2012 Observations of the nightside ionosphere of Mars by the Mars Express Radio Science Experiment (MaRS) Paul Withers, 1 M. O. Fillingim,
2. The distance between the Sun and the next closest star, Proxima Centuari, is MOST accurately measured in
 Name: Date: 1. Some scientists study the revolution of the Moon very closely and have recently suggested that the Moon is gradually moving away from Earth. Which statement below would be a prediction of
Name: Date: 1. Some scientists study the revolution of the Moon very closely and have recently suggested that the Moon is gradually moving away from Earth. Which statement below would be a prediction of
Solar System revised.notebook October 12, 2016 Solar Nebula Theory
 Solar System revised.notebook The Solar System Solar Nebula Theory Solar Nebula was a rotating disk of dust and gas w/ a dense center dense center eventually becomes the sun start to condense b/c of gravity
Solar System revised.notebook The Solar System Solar Nebula Theory Solar Nebula was a rotating disk of dust and gas w/ a dense center dense center eventually becomes the sun start to condense b/c of gravity
Planetary magnetospheres
 Planetary magnetospheres Text-book chapter 19 Solar system planets Terrestrial planets: Mercury Venus Earth Mars Pluto is no more a planet! Interiors of terrestrial planets are different very different
Planetary magnetospheres Text-book chapter 19 Solar system planets Terrestrial planets: Mercury Venus Earth Mars Pluto is no more a planet! Interiors of terrestrial planets are different very different
Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of the normal stars.
 Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of
Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths of
Leibniz Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Schlossstr. 6, Kühlungsborn, Germany b)
 Neutral air density variations during strong planetary wave activity in the mesopause region derived from meteor radar observations G. Stober a), C. Jacobi b), V. Matthias a), P. Hoffmann a), M. Gerding
Neutral air density variations during strong planetary wave activity in the mesopause region derived from meteor radar observations G. Stober a), C. Jacobi b), V. Matthias a), P. Hoffmann a), M. Gerding
A Crucial Space Weather Effect: Meteors and Meteoroids
 A Crucial Space Weather Effect: Meteors and Meteoroids Lars Dyrud, Sigrid Close, Diego Janches, Meers Oppenheim, John Plane, John Mathews, Julio Urbina, Mihaly Horanyi, Jorge Chau, Jonathan Fentzke, Mike
A Crucial Space Weather Effect: Meteors and Meteoroids Lars Dyrud, Sigrid Close, Diego Janches, Meers Oppenheim, John Plane, John Mathews, Julio Urbina, Mihaly Horanyi, Jorge Chau, Jonathan Fentzke, Mike
On the sources of day-to-day variability in the occurrence of equatorial plasma bubbles: An analysis using the TIEGCM
 On the sources of day-to-day variability in the occurrence of equatorial plasma bubbles: An analysis using the TIEGCM Brett A. Carter, RMIT University, Australia, www.rmit.edu.au/space Institute for Scientific
On the sources of day-to-day variability in the occurrence of equatorial plasma bubbles: An analysis using the TIEGCM Brett A. Carter, RMIT University, Australia, www.rmit.edu.au/space Institute for Scientific
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 14. Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 14 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 14 Solar System Debris Units of Chapter 14 14.1 Asteroids What Killed the Dinosaurs? 14.2 Comets 14.3 Beyond Neptune 14.4
Lecture Outlines Chapter 14 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 14 Solar System Debris Units of Chapter 14 14.1 Asteroids What Killed the Dinosaurs? 14.2 Comets 14.3 Beyond Neptune 14.4
Assessment Vocabulary Instructional Strategies
 Inner Planets and the similarities for each of the inner planets? (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars - such as Size, atmosphere, moons/rings, ) What are the unique characteristics and details of each of
Inner Planets and the similarities for each of the inner planets? (Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars - such as Size, atmosphere, moons/rings, ) What are the unique characteristics and details of each of
Universe: everything that exists, including all matter and energy everywhere
 WHAT DO YOU KNOW? Universe: everything that exists, including all matter and energy everywhere The study of what is beyond Earth Many years ago, skywatchers took note of patterns in the stars and there
WHAT DO YOU KNOW? Universe: everything that exists, including all matter and energy everywhere The study of what is beyond Earth Many years ago, skywatchers took note of patterns in the stars and there
HST Observations of Planetary Atmospheres
 HST Observations of Planetary Atmospheres John T. Clarke Boston University Hubble Science Legacy 3 April 2002 Venus - Near-UV images reveal cloud motions and winds - UV spectra track SO 2 composition,
HST Observations of Planetary Atmospheres John T. Clarke Boston University Hubble Science Legacy 3 April 2002 Venus - Near-UV images reveal cloud motions and winds - UV spectra track SO 2 composition,
Venus Express Radio Science Experiment VeRa
 Venus Express Radio Science Experiment VeRa Bernd Häusler (1), Martin Pätzold (2) and the VeRa Team Venus Express Legacy Session (1) Universität der Bundeswehr München, (2) Institute for Planetary Research,
Venus Express Radio Science Experiment VeRa Bernd Häusler (1), Martin Pätzold (2) and the VeRa Team Venus Express Legacy Session (1) Universität der Bundeswehr München, (2) Institute for Planetary Research,
Paper Reference. Tuesday 14 June 2005 Morning Time: 2 hours
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1627/01 Edexcel GCSE Astronomy Paper 01 Tuesday 14 June 2005 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Items included with question papers
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 1627/01 Edexcel GCSE Astronomy Paper 01 Tuesday 14 June 2005 Morning Time: 2 hours Materials required for examination Nil Items included with question papers
Ring Rain and Other Drivers Luke Moore, Marina Galand, Arv Kliore, Andy Nagy, James O Donoghue
 Ring Rain and Other Drivers Luke Moore, Marina Galand, Arv Kliore, Andy Nagy, James O Donoghue Outline Introduction to Saturn s ionosphere Basic properties and theory Observations: what do we know? Radio
Ring Rain and Other Drivers Luke Moore, Marina Galand, Arv Kliore, Andy Nagy, James O Donoghue Outline Introduction to Saturn s ionosphere Basic properties and theory Observations: what do we know? Radio
Earth Science 11 Learning Guide Unit Complete the following table with information about the sun:
 Earth Science 11 Learning Guide Unit 2 Name: 2-1 The sun 1. Complete the following table with information about the sun: a. Mass compare to the Earth: b. Temperature of the gases: c. The light and heat
Earth Science 11 Learning Guide Unit 2 Name: 2-1 The sun 1. Complete the following table with information about the sun: a. Mass compare to the Earth: b. Temperature of the gases: c. The light and heat
Roosevelt Elementary Planet Tour. Prepared by Mr. Dabb Roosevelt Elementary
 Roosevelt Elementary Planet Tour Prepared by Mr. Dabb Roosevelt Elementary Relative Size of the Planets This graphic thanks to http://www.bautforum.c om/showthread.php?t= 14356 Tour of the Planets This
Roosevelt Elementary Planet Tour Prepared by Mr. Dabb Roosevelt Elementary Relative Size of the Planets This graphic thanks to http://www.bautforum.c om/showthread.php?t= 14356 Tour of the Planets This
Absorption of MARSIS radar signals: Solar energetic particles and the daytime ionosphere
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L09101, doi:10.1029/2006gl028829, 2007 Absorption of MARSIS radar signals: Solar energetic particles and the daytime ionosphere Jared
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 34, L09101, doi:10.1029/2006gl028829, 2007 Absorption of MARSIS radar signals: Solar energetic particles and the daytime ionosphere Jared
Asteroids, Comets and NEOs. (Answers) Solar System Impacts. Author: Sarah Roberts
 Asteroids, Comets and NEOs (Answers) Author: Sarah Roberts Asteroids, Comets and NEOs - Impact craters on the Earth 1. Using the data given below for real impact craters on the Earth, investigate the effect
Asteroids, Comets and NEOs (Answers) Author: Sarah Roberts Asteroids, Comets and NEOs - Impact craters on the Earth 1. Using the data given below for real impact craters on the Earth, investigate the effect
Chapter 23. Our Solar System
 Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System 1 Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths
Chapter 23 Our Solar System Our Solar System 1 Historical Astronomy Wandering Stars Greeks watched the stars move across the sky and noticed five stars that wandered around and did not follow the paths
Space Test Review. Unit Test on Thursday April 17
 Space Test Review Unit Test on Thursday April 17 True/False 1. A(n) asteroid is a massive collection of gases in space that emits large amounts of energy. 2. A(n) moon is a large, round celestial object
Space Test Review Unit Test on Thursday April 17 True/False 1. A(n) asteroid is a massive collection of gases in space that emits large amounts of energy. 2. A(n) moon is a large, round celestial object
What is the Solar System?
 What is the Solar System? Our Solar System is one of many planetary systems. It consists of: The Sun Eight planets with their natural satellites Five dwarf planets Billions of asteroids, comets and meteors
What is the Solar System? Our Solar System is one of many planetary systems. It consists of: The Sun Eight planets with their natural satellites Five dwarf planets Billions of asteroids, comets and meteors
MODELING THE METEOROID INPUT FUNCTION AT MID-LATITUDE USING METEOR OBSERVATIONS BY THE MU RADAR. David Nesvorny 5
 https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?r=20120014292 2018-11-27T20:47:31+00:00Z MODELING THE METEOROID INPUT FUNCTION AT MID-LATITUDE USING METEOR OBSERVATIONS BY THE MU RADAR Steven Pifko 1, Diego Janches 2,
https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?r=20120014292 2018-11-27T20:47:31+00:00Z MODELING THE METEOROID INPUT FUNCTION AT MID-LATITUDE USING METEOR OBSERVATIONS BY THE MU RADAR Steven Pifko 1, Diego Janches 2,
At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion?
 At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion? These small, rocky worlds orbit the sun generally between the orbits of
At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion? These small, rocky worlds orbit the sun generally between the orbits of
Chapter Outline. Earth and Other Planets. The Formation of the Solar System. Clue #1: Planetary Orbits. Clues to the Origin of the Solar System
 Chapter Outline Earth and Other Planets The Formation of the Solar System Exploring the Solar System Chapter 16 Great Idea: Earth, one of the planets that orbit the Sun, formed 4.5 billion years ago from
Chapter Outline Earth and Other Planets The Formation of the Solar System Exploring the Solar System Chapter 16 Great Idea: Earth, one of the planets that orbit the Sun, formed 4.5 billion years ago from
Gravity: Motivation An initial theory describing the nature of the gravitational force by Newton is a product of the resolution of the
 Gravity: Motivation An initial theory describing the nature of the gravitational force by Newton is a product of the resolution of the Geocentric-Heliocentric debate (Brahe s data and Kepler s analysis)
Gravity: Motivation An initial theory describing the nature of the gravitational force by Newton is a product of the resolution of the Geocentric-Heliocentric debate (Brahe s data and Kepler s analysis)
Lecture 3: The Earth, Magnetosphere and Ionosphere.
 Lecture 3: The Earth, Magnetosphere and Ionosphere. Sun Earth system Magnetospheric Physics Heliophysics Ionospheric Physics Spacecraft Heating of Solar Corona Convection cells Charged particles are moving
Lecture 3: The Earth, Magnetosphere and Ionosphere. Sun Earth system Magnetospheric Physics Heliophysics Ionospheric Physics Spacecraft Heating of Solar Corona Convection cells Charged particles are moving
3. The diagram below shows the Moon at four positions in its orbit around Earth as viewed from above the North Pole.
 1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
1. Which object orbits Earth in both the Earth-centered (geocentric) and Sun-centered (heliocentric) models of our solar system? (1) Polaris (3) the Sun (2) Venus (4) the Moon 2. A cycle of Moon phases
Tides are Important EAS 4803/ CP 7:1
 Tides are Important Roche Limit - The closer a moon is to a planet, the stronger the tidal forces it will feel (I.e. the stronger the differential gravity will be between the surface nearest the planet
Tides are Important Roche Limit - The closer a moon is to a planet, the stronger the tidal forces it will feel (I.e. the stronger the differential gravity will be between the surface nearest the planet
Wed. Aug. 30, 2017 Reading:
 Wed. Aug. 30, 2017 Reading: Reading for Fri.: Wood Ch. 1 (solar system overview) Reading for Wed. Wed. Wood Ch. 6 & 8 (Asteroids & Meteorites, Solar Nebula) Reading for Fri. Sept. 8. Rozel et al. (link
Wed. Aug. 30, 2017 Reading: Reading for Fri.: Wood Ch. 1 (solar system overview) Reading for Wed. Wed. Wood Ch. 6 & 8 (Asteroids & Meteorites, Solar Nebula) Reading for Fri. Sept. 8. Rozel et al. (link
Chapter 4 The Solar System
 Chapter 4 The Solar System Comet Tempel Chapter overview Solar system inhabitants Solar system formation Extrasolar planets Solar system inhabitants Sun Planets Moons Asteroids Comets Meteoroids Kuiper
Chapter 4 The Solar System Comet Tempel Chapter overview Solar system inhabitants Solar system formation Extrasolar planets Solar system inhabitants Sun Planets Moons Asteroids Comets Meteoroids Kuiper
4 A(n) is a small, rocky object that orbits the sun; many of these objects are located in a band between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
 Name Vocabulary Fill in the blank with the term that best completes the sentence., 6.11B 1 is the process in which energy is released as the nuclei of small atoms combine to form a larger nucleus., 6.11B
Name Vocabulary Fill in the blank with the term that best completes the sentence., 6.11B 1 is the process in which energy is released as the nuclei of small atoms combine to form a larger nucleus., 6.11B
Simulating the Ionosphere, one electron at a time.
 Simulating the Ionosphere, one electron at a time. Meers Oppenheim CEDAR June 2016 Research supported by NSF, NASA, AFRL, and DOE Grants What? Plasma Physics Particle-in-Cell Simulations Two Examples:
Simulating the Ionosphere, one electron at a time. Meers Oppenheim CEDAR June 2016 Research supported by NSF, NASA, AFRL, and DOE Grants What? Plasma Physics Particle-in-Cell Simulations Two Examples:
Name Class Date. Chapter 29. The Solar System. Review Choose the best response. Write the letter of that choice in the space provided.
 The Solar System Review Choose the best response. Write the letter of that choice in the space provided. 1. Ptolemy modified Aristotle s model of the universe to include a. Oort clouds. b. retrograde motion.
The Solar System Review Choose the best response. Write the letter of that choice in the space provided. 1. Ptolemy modified Aristotle s model of the universe to include a. Oort clouds. b. retrograde motion.
Chapter 23: Touring Our Solar System
 Chapter 23: Touring Our Solar System The Sun The is the center of our solar system. The Sun makes up of all the mass of our solar system. The Sun s force holds the planets in their orbits around the Sun.
Chapter 23: Touring Our Solar System The Sun The is the center of our solar system. The Sun makes up of all the mass of our solar system. The Sun s force holds the planets in their orbits around the Sun.
Starting from closest to the Sun, name the orbiting planets in order.
 Chapter 9 Section 1: Our Solar System Solar System: The solar system includes the sun, planets and many smaller structures. A planet and its moon(s) make up smaller systems in the solar system. Scientist
Chapter 9 Section 1: Our Solar System Solar System: The solar system includes the sun, planets and many smaller structures. A planet and its moon(s) make up smaller systems in the solar system. Scientist
Ch 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System 23.2 The Terrestrial Planet 23.3 The Outer Planets 23.4 Minor Members of the Solar System
 Ch 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System 23.2 The Terrestrial Planet 23.3 The Outer Planets 23.4 Minor Members of the Solar System Ch 23.1 The Solar System Terrestrial planets- Small Rocky
Ch 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System 23.2 The Terrestrial Planet 23.3 The Outer Planets 23.4 Minor Members of the Solar System Ch 23.1 The Solar System Terrestrial planets- Small Rocky
Astronomy Ch. 6 The Solar System: Comparative Planetology
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 6 The Solar System: Comparative Planetology MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The largest asteroid,
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 6 The Solar System: Comparative Planetology MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The largest asteroid,
~15 GA. (Giga Annum: Billion Years) today
 ~15 GA (Giga Annum: Billion Years) today ~ 300,000 years after the Big Bang The first map of the Universe. Not homogeneous. Cosmic microwave background (CMB) anisotropy. First detected by the COBE DMR
~15 GA (Giga Annum: Billion Years) today ~ 300,000 years after the Big Bang The first map of the Universe. Not homogeneous. Cosmic microwave background (CMB) anisotropy. First detected by the COBE DMR
Tides in the Martian Upper Atmosphere - And Other Topics
 Tides in the Martian Upper Atmosphere - And Other Topics Paul Withers Centre for Space Physics Boston University CSP Seminar 2003.10.02 The aim of this talk is to get YOU excited about having ME as a colleague
Tides in the Martian Upper Atmosphere - And Other Topics Paul Withers Centre for Space Physics Boston University CSP Seminar 2003.10.02 The aim of this talk is to get YOU excited about having ME as a colleague
Chapter 15: The Origin of the Solar System
 Chapter 15: The Origin of the Solar System The Solar Nebula Hypothesis Basis of modern theory of planet formation: Planets form at the same time from the same cloud as the star. Planet formation sites
Chapter 15: The Origin of the Solar System The Solar Nebula Hypothesis Basis of modern theory of planet formation: Planets form at the same time from the same cloud as the star. Planet formation sites
Life in the Solar System
 Life in the Solar System Basic Requirements for Life 1. Chemical elements to make biological molecules. On Earth these are mostly C, H, O and N 2. Source of energy for metabolism. This can come from a
Life in the Solar System Basic Requirements for Life 1. Chemical elements to make biological molecules. On Earth these are mostly C, H, O and N 2. Source of energy for metabolism. This can come from a
Sol o ar a r S yste t m e F o F r o m r at a i t on o The Ne N b e u b l u a a Hypothesis
 Solar System Solar system- the sun and all objects that orbit the sun due to its gravity Solar System Formation The Nebula Hypothesis Parts of the Solar System Planet- a celestial body that is in orbit
Solar System Solar system- the sun and all objects that orbit the sun due to its gravity Solar System Formation The Nebula Hypothesis Parts of the Solar System Planet- a celestial body that is in orbit
Structure of the Venus neutral atmosphere as observed by the Radio Science experiment VeRa on Venus Express
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008je003204, 2009 Structure of the Venus neutral atmosphere as observed by the Radio Science experiment VeRa on Venus Express Silvia Tellmann, 1
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2008je003204, 2009 Structure of the Venus neutral atmosphere as observed by the Radio Science experiment VeRa on Venus Express Silvia Tellmann, 1
Solar wind is the name for the radiation that is emitted from the sun - even though it is just energy, it is strong enough to 'push' objects
 I can explain and demonstrate that the Sun and stars are the sources of light in our universe and that the Moon, planets, their moons, comets and asteroids are seen by reflecting that light. Emit vs. Reflect
I can explain and demonstrate that the Sun and stars are the sources of light in our universe and that the Moon, planets, their moons, comets and asteroids are seen by reflecting that light. Emit vs. Reflect
Astronomy Ch. 6 The Solar System. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 6 The Solar System MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The largest asteroid, and probably the only
Name: Period: Date: Astronomy Ch. 6 The Solar System MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The largest asteroid, and probably the only
Contents of the Solar System
 The Solar System Contents of the Solar System Sun Planets 9 known (now: 8) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars ( Terrestrials ) Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune ( Jovians ) Pluto (a Kuiper Belt object?) Natural
The Solar System Contents of the Solar System Sun Planets 9 known (now: 8) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars ( Terrestrials ) Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune ( Jovians ) Pluto (a Kuiper Belt object?) Natural
Asteroids, Comets and Meteorites. What is an Asteroid? Asteroids discovered. Asteroid facts. Example Asteroids
 Asteroids, Comets and Meteorites Perseid meteor shower courtesy NASA Eros: courtesy NASA What is an Asteroid? View from 50 km ~1.5 1.5 km Comet McNaught in 2007 by Aberdeen Astronomical Society member
Asteroids, Comets and Meteorites Perseid meteor shower courtesy NASA Eros: courtesy NASA What is an Asteroid? View from 50 km ~1.5 1.5 km Comet McNaught in 2007 by Aberdeen Astronomical Society member
Asteroids, Comets and Meteorites
 Asteroids, Comets and Meteorites Perseid meteor shower courtesy NASA Eros: courtesy NASA Comet McNaught in 2007 by Aberdeen Astronomical Society member Phil Hart, in Melbourne What is an Asteroid? View
Asteroids, Comets and Meteorites Perseid meteor shower courtesy NASA Eros: courtesy NASA Comet McNaught in 2007 by Aberdeen Astronomical Society member Phil Hart, in Melbourne What is an Asteroid? View
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM. James Martin. Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC
 OUR SOLAR SYSTEM James Martin Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC It s time for the human race to enter the solar system. -Dan Quayle Structure of the Solar System Our Solar System contains
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM James Martin Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC It s time for the human race to enter the solar system. -Dan Quayle Structure of the Solar System Our Solar System contains
Interactive Minds Solar System Review
 Interactive Minds Solar System Review Solar System Use the Solar System App and your class notes to complete this study guide and prepare for your upcoming Science Test! 1. Earth s solar system is in what
Interactive Minds Solar System Review Solar System Use the Solar System App and your class notes to complete this study guide and prepare for your upcoming Science Test! 1. Earth s solar system is in what
RETHINKING GRAVITY. The gravitational force produced by the mass of the atom is determined by the number of electrons that are bound to it.
 RETHINKING GRAVITY. What causes gravity? The mass of an atom is the source of gravity. The gravitational force produced by the mass of the atom is determined by the number of electrons that are bound to
RETHINKING GRAVITY. What causes gravity? The mass of an atom is the source of gravity. The gravitational force produced by the mass of the atom is determined by the number of electrons that are bound to
AST111, Lecture 1b. Measurements of bodies in the solar system (overview continued) Orbital elements
 AST111, Lecture 1b Measurements of bodies in the solar system (overview continued) Orbital elements Planetary properties (continued): Measuring Mass The orbital period of a moon about a planet depends
AST111, Lecture 1b Measurements of bodies in the solar system (overview continued) Orbital elements Planetary properties (continued): Measuring Mass The orbital period of a moon about a planet depends
What s in our solar system?
 What s in our solar system? *Sun *Planets Terrestrial Jovian Dwarf Smaller objects *Meteoroids *Comets Dust http://www.techastronomy.com/userfiles/2007/7/22/solar_system4(1).jpg *Sun a. Most of mass (>99%)
What s in our solar system? *Sun *Planets Terrestrial Jovian Dwarf Smaller objects *Meteoroids *Comets Dust http://www.techastronomy.com/userfiles/2007/7/22/solar_system4(1).jpg *Sun a. Most of mass (>99%)
Galaxies: enormous collections of gases, dust and stars held together by gravity Our galaxy is called the milky way
 Celestial bodies are all of the natural objects in space ex. stars moons, planets, comets etc. Star: celestial body of hot gas that gives off light and heat the closest star to earth is the sun Planet:
Celestial bodies are all of the natural objects in space ex. stars moons, planets, comets etc. Star: celestial body of hot gas that gives off light and heat the closest star to earth is the sun Planet:
Plasma collisions and conductivity
 e ion conductivity Plasma collisions and conductivity Collisions in weakly and fully ionized plasmas Electric conductivity in non-magnetized and magnetized plasmas Collision frequencies In weakly ionized
e ion conductivity Plasma collisions and conductivity Collisions in weakly and fully ionized plasmas Electric conductivity in non-magnetized and magnetized plasmas Collision frequencies In weakly ionized
1star 1 star 9 8 planets 63 (major) moons asteroids, comets, meteoroids
 The Solar System 1star 1 star 9 8 planets 63 (major) moons asteroids, comets, meteoroids The distances to planets are known from Kepler s Laws (once calibrated with radar ranging to Venus) How are planet
The Solar System 1star 1 star 9 8 planets 63 (major) moons asteroids, comets, meteoroids The distances to planets are known from Kepler s Laws (once calibrated with radar ranging to Venus) How are planet
Intro to Earth Science Chapter 23 Study Guide
 Name _ Date _ Period _ Intro to Earth Science Chapter 23 Study Guide 1. is the planet that cannot be classified as either a terrestrial or a Jovian planet. 2. The densities of the planets are about five
Name _ Date _ Period _ Intro to Earth Science Chapter 23 Study Guide 1. is the planet that cannot be classified as either a terrestrial or a Jovian planet. 2. The densities of the planets are about five
Today. The Little Things. Comets. Dwarf Planets. Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then.
 Today The Little Things Comets Dwarf Planets Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then. 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Comets Fig 9.5 FROST LINE
Today The Little Things Comets Dwarf Planets Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then. 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Comets Fig 9.5 FROST LINE
Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM
 Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM THE NATURE OF THE SUN At the center of our solar system is the Sun which is a typical medium sized star. Composed mainly of Hydrogen (73% by mass), 23% helium and the rest is
Lesson 3 THE SOLAR SYSTEM THE NATURE OF THE SUN At the center of our solar system is the Sun which is a typical medium sized star. Composed mainly of Hydrogen (73% by mass), 23% helium and the rest is
Pluto is not alone out there
 Reading: Chapter 13, Sect. 13.1-13.4, Chapter 14, Sect. 14.1-14.2 Homework 9 - See course webpage later this week Exam 2 - Tuesday November 2 - in class - Physics 3 and 5 Practice exam, review sheets posted
Reading: Chapter 13, Sect. 13.1-13.4, Chapter 14, Sect. 14.1-14.2 Homework 9 - See course webpage later this week Exam 2 - Tuesday November 2 - in class - Physics 3 and 5 Practice exam, review sheets posted
Introduction to the Solar System
 Introduction to the Solar System Sep. 11, 2002 1) Introduction 2) Angular Momentum 3) Formation of the Solar System 4) Cowboy Astronomer Review Kepler s Laws empirical description of planetary motion Newton
Introduction to the Solar System Sep. 11, 2002 1) Introduction 2) Angular Momentum 3) Formation of the Solar System 4) Cowboy Astronomer Review Kepler s Laws empirical description of planetary motion Newton
UNIT 3: Chapter 8: The Solar System (pages )
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
ESS 7 Lectures 21 and 22 November 21 and 24, The Planets
 ESS 7 Lectures 21 and 22 November 21 and 24, 2008 The Planets Exploration Initiative Moon in 2015 Stepping Stone to Mars What will we do on the Moon? Heliophysics Science of the Moon investigating fundamental
ESS 7 Lectures 21 and 22 November 21 and 24, 2008 The Planets Exploration Initiative Moon in 2015 Stepping Stone to Mars What will we do on the Moon? Heliophysics Science of the Moon investigating fundamental
A better way of modeling ionospheric electrodynamics
 A better way of modeling ionospheric electrodynamics Paul Withers Boston University (withers@bu.edu) Center for Space Physics Journal Club Tuesday (Monday) 2008.02.9 Not all magnetic fields are like Earth
A better way of modeling ionospheric electrodynamics Paul Withers Boston University (withers@bu.edu) Center for Space Physics Journal Club Tuesday (Monday) 2008.02.9 Not all magnetic fields are like Earth
ESA s Juice: Mission Summary and Fact Sheet
 ESA s Juice: Mission Summary and Fact Sheet JUICE - JUpiter ICy moons Explorer - is the first large-class mission in ESA's Cosmic Vision 2015-2025 programme. Planned for launch in 2022 and arrival at Jupiter
ESA s Juice: Mission Summary and Fact Sheet JUICE - JUpiter ICy moons Explorer - is the first large-class mission in ESA's Cosmic Vision 2015-2025 programme. Planned for launch in 2022 and arrival at Jupiter
Modeling Mars ionosphere with constraints from same day observations by Mars Global Surveyor and Mars Express
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011ja016865, 2011 Modeling Mars ionosphere with constraints from same day observations by Mars Global Surveyor and Mars Express Michael Mendillo,
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011ja016865, 2011 Modeling Mars ionosphere with constraints from same day observations by Mars Global Surveyor and Mars Express Michael Mendillo,
MEASURING THE METEOROID ENVIRONMENTS OF THE PLANETS WITH METEOR DETECTORS ON EARTH. Submitted to AJ
 Draft version October 4, 218 Typeset using LATEX default style in AASTeX61 MEASURING THE METEOROID ENVIRONMENTS OF THE PLANETS WITH METEOR DETECTORS ON EARTH Paul Wiegert, 1,2 Peter Brown, 1,2 Petr Pokorny,
Draft version October 4, 218 Typeset using LATEX default style in AASTeX61 MEASURING THE METEOROID ENVIRONMENTS OF THE PLANETS WITH METEOR DETECTORS ON EARTH Paul Wiegert, 1,2 Peter Brown, 1,2 Petr Pokorny,
The Science and Technology of Non-Agency Space Missions. A Special Session on Space Technology. at the
 The Science and Technology of Non-Agency Space Missions A at the 5 th European Conference on Intelligent Systems and Technologies The study of the atmosphere and ionosphere of planet Venus by employing
The Science and Technology of Non-Agency Space Missions A at the 5 th European Conference on Intelligent Systems and Technologies The study of the atmosphere and ionosphere of planet Venus by employing
Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n)
 When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n) - ellipse - circle - axis - rotation Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? - Venus, Mars, Saturn and Pluto - Jupiter,
When a planets orbit around the Sun looks like an oval, it s called a(n) - ellipse - circle - axis - rotation Which of the following planets are all made up of gas? - Venus, Mars, Saturn and Pluto - Jupiter,
Motion of the planets
 Our Solar system Motion of the planets Our solar system is made up of the sun and the 9 planets that revolve around the sun Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune & Pluto (maybe?)
Our Solar system Motion of the planets Our solar system is made up of the sun and the 9 planets that revolve around the sun Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune & Pluto (maybe?)
Chapters 7&8. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 21: Solar System [3/12/07] Announcements.
![Chapters 7&8. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 21: Solar System [3/12/07] Announcements. Chapters 7&8. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 21: Solar System [3/12/07] Announcements.](/thumbs/81/83429897.jpg) ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 21: Solar System [3/12/07] Announcements The Solar System Comparative
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 21: Solar System [3/12/07] Announcements The Solar System Comparative
Low Cost Planetary Missions Conference Picture: Etna lava flow, with Catania in the background
 Low Cost Planetary Missions Conference 2013 Picture: Etna lava flow, with Catania in the background Venus Express: a low cost mission Mars Express Venus Express Astrium, ESA Astrium, ESA 2001: Call for
Low Cost Planetary Missions Conference 2013 Picture: Etna lava flow, with Catania in the background Venus Express: a low cost mission Mars Express Venus Express Astrium, ESA Astrium, ESA 2001: Call for
