Near Earth Small Meteoroids
|
|
|
- Wilfrid Weaver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Near Earth Small Meteoroids (CPS: Center for Planetary Science) 2007/07/03
2 Source of Meteoroids Stream Meteoroids Sporadic Meteoroids Source of Sporadic Interplanetary dusts;,, ( dust) Interstellar dust; 72km/s, dust 40μm?, flux? It is evident that sporadic meteors exhibit diurnal and seasonal variations in their activity. Sporadic radiants were initially distributed isotropicly, but appear to be concentrated about the apex of the Earth because of the Earth s orbital motion. The seasonal variation of sporadic meteors in the strength of the apparent maxima of the helion and antihelion sources shows asymmetric features during certain periods.
3 Source; planet-approaching comets : Halley Type Comets high speed; > 25 km/s strong annual activity outbursts : Jupiter Family Comets low speed; > 25 km/s weak annual activity outbursts Δ<0.1 AU the contribution from JFCs is an increasing function of heliocentric distance roughly similar numbers of HTCs at the three planets two hat trick comets: 1P/Halley and 45P/Honda-Mrkos-Pajdusáková Beech, MNRAS, 1998, Christou & Beurle, P&SS, 1999, Treiman & Treiman 2000, Larson, AJ, 2001, Christou, Icarus, 2004, Selsis et al, A&A, 2004
4 Apex( ) 15-28% Halley-type comets Long-period comets Source: 15 Apex sources V 45-72km/s, Vmean=62km/s Antihelion( ) Helion( ) 30-40% Jupiter-family comets Appolo-type asteroids Source: ±70 from the Apex V 11-45km/s, Vmean=20km/s daily motion 1 /day Ecliptic showers(, Zodiac) : HR 15/hr in fall, HR 5/hr in spring N-S-Troidal 3-6% N-S Source: ±67 latitude a 1.0AU, e 0.3, Variations of Sporadic Meteors and Radiant Distribution Vmean 24-42km/s?, JFC? Contours of apparent density of meteor radiants from the combined Harvard (upper plot) and Adelaide (lower plot) radio surveys (Jones and Brown, 1994). H denotes the position of the Sun, AP the Earth s apex and AH the antihelion point.
5 Production rate of cometary meteoroids Comet group % of total Jupiter family 91 Halley family 5 Long period 4 JF / Q<7AU JF
6 Activity of short period cometary meteoroids HRMP: Harvard Radio Meteor Project (Sekanina, 1967, Lindblad, 1987) CMOR: Canadian Meteor Orbit Radar (Campbell-Brown&Jones, 2003) meteoroids
7 Activity of long period cometary meteoroids meteoroids
8 Toroidal source V_mean = 42 km/s V_mean = 24 km/s
9 Distribution of asteroid taxonomy C SV sin i a C; carbonaceous chondrites, outer region S ; ordinary chondrites, inner region V; HED meteorites, around 2.3AU
10
11 Circumsolar ring 20% of 12µm asteroidal dust particles (β=0.37) trapped in resonance(3:4-17:18). Carbonaceous particles are dominant. Asteroidal Dusts S.F. Dermott et al., Nature, 1994 Drag forces Light Pressure Poynting-Robertson Solar Wind
12 Meteor observation from LEO Distance of Horizon at each altitude 1997 Leonids observed by MSX 40 (Jenniskens, et al., 2000) 900 km 150 km 100 km X 3300km 6,378 km MSX image of 1997 Leonids Earth P. Jenniskens et al., 2000 altitude (km) distance (km) Leonid MAC ISS MSX
13
14 1/1000 s high speed camera image of a meteor Hans Stenbaek-Nielsen, 2001 with ablation Ablation without ablation Ian Boyd, EMP 82/83, 2000 The term ablation has the meaning of mass loss of a meteoroid in any form and phase: solid as fragments, fluid as droplets and loss of hot gas, which forms always the final stage and is responsible for the observed meteor phenomenon. Trains with duration up to 3 s are produced by the forbidden auroral line of neutral oxygen at nm. temperature in meteor plasma Fe I, Mg I, Ca I, Na I. Main component ( 4,500 K) Ca II, Mg II, Fe II.. 2 nd component ( 10,000 K) Jiří Borovička (1993) 1999 Leonid Meteor Storm, Leonid MAC, 4,000 hr -1 at 02:02 UT on November 18, Yano, Abe, NHK, NASA
15 1999 Leonid Meteor Spectrum (V=71 km/s) S. Abe et al. Earth Moon & Planets, 82/83, 2000 Meteor light consists mostly of radiation of discrete emission spectral lines belonging for the most part to metals and mainly to iron. More than 90% of the meteor light originates from radiation of single low-excited atoms of meteoroid material (several ev; temperatures 3000 to 5000 K).
16 Interplanetary Dust Models Interplanetary Dust Model, ( ) ; Grün, Zook, Fechtig and Giese (1985) Interplanetary dust complex,, impact data ; Divine (1993) Divine's model ( ) ; Taylor (1995) Taylor(1995) model ; Garret, Drouilhet, Oliver and Evans (1999), Jehn (2000)
17 P. Brown et al. (2002)
18 ISS Revised from Ceplecha et al., (1998) 40km/s, km The interplanetary dust component of the influx is 4 x10^6 kg per year per Earth, about 17% of the influx originates in the interplanetary dust. about 83% in bodies mostly inside a mass range of 10^5 to 10^8 kg (10 to 100 m sizes). Atmospheric penetration of meter and ten meter size bodies can be regularly and globally observed by satellites.
19 ISS HDTV 1999 MSX 1997 (1) Meteor Watcher (2) JAXA DLR ESA (3) (4) ISS 2001 by HDTV( NASDA )
20 JEM-EUSO Extreme Universe Space Observatory -2005; EUSO was originally planed to be deployed by ESA 2005 Original plan was canceled because of changing situation of ESA s budget. 2006; Phase-A (JEM-EUSO WG) collaborating with Italy, France, Switzerland, Germany, Portugal, Spain, Japan, USA, Brazil, I m involved as a meteor analyst ; Phase-A, B We were selected as phase-a ; Phase-C,D 2013; Launch using Japanese transport plane (HTV)
21 Time JEM-EUSO(Japanese Extreme Universe Space Observatory) The purpose is to distinguish the source of extreme high energy particles more than 1.0E20 ev originated probably from AGNs, which relates with cosmology. The technics is to observe the extensive air-shower induced by energetic particle entered the atmosphere. By using EUSO main telescope, 2.5 m in diameter, Evaporated N2 and N2+ by electron shower can be observed as fluorescence, moreover Cerenkov light along the path of shower can also be detected. FOV; ±30 deg from height of 430km Time resolution; 2.5μsec Spacial resolution; 9.75 x 0.75 km(0.1 deg.) Wavelength region; nm Photon counts fluorescence Cerenkov light
22 Advantages from Space Determination of mass distribution especially for bright-end. Between meteoroids and asteroids. Steady monitoring for sporadic meteors. EUSO has 2 view angles, 90 deg for perpendicular- and 45 deg for tilt-mode. Ultraviolet region without absorption. Below 300nm region is absorbed by ozone layer. High-altitude meteors. Higher than 200 km would be detected. Disadvantages from Space CCD noises caused by cosmic ray. Limited data down-link rate, 300 Kbps from ISS. Disturbed by cloud, reflected moon-light and ionospheric emissions.
23 Search for organics through Iron free windows from the space Oparin, 1924 Iron windows
24 S. Abe et al., ApJ 618, L141-L144, Discovery of new UV Bands in Leonid Fireball(-5 mag.) from the ground. Atoms + N + 2 +OH N 2 + was strongest band in UV emission. Atom;4500K N 2+ ;10000K Bow shock neck recompression shock thermochemical non-equilibrium state wake core Mg I + OH N 2 + (2,0) N 2 + (1,0) Shock layer N 2 + (0,1) backward flow N 2 + (0,0)
25 Moon Impact Flush NASA-MSFS The Video plays 7x slow motion. 7th magnitude corresponds diameter of 25 cm and velocity of 38 km/s rocky meteoroid.
26 Sodium Tail enhanced by meteoroids impacts. (Na, K) (Stream)
27 Lunar impact prospects Japanese spacecraft heading for the Moon this year: Table 10c from Jenniskens (2006)
28
Transneptunian objects. Minor bodies in the outer Solar System. Transneptunian objects
 Transneptunian objects Minor bodies in the outer Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Around 1980 it was proposed that the hypothetical disk of small bodies beyond Neptune (called
Transneptunian objects Minor bodies in the outer Solar System Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo Around 1980 it was proposed that the hypothetical disk of small bodies beyond Neptune (called
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM. James Martin. Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC
 OUR SOLAR SYSTEM James Martin Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC It s time for the human race to enter the solar system. -Dan Quayle Structure of the Solar System Our Solar System contains
OUR SOLAR SYSTEM James Martin Facebook.com/groups/AstroLSSC Twitter.com/AstroLSSC It s time for the human race to enter the solar system. -Dan Quayle Structure of the Solar System Our Solar System contains
DIN EN : (E)
 DIN EN 16603-10-04:2015-05 (E) Space engineering - Space environment; English version EN 16603-10-04:2015 Foreword... 12 Introduction... 13 1 Scope... 14 2 Normative references... 15 3 Terms, definitions
DIN EN 16603-10-04:2015-05 (E) Space engineering - Space environment; English version EN 16603-10-04:2015 Foreword... 12 Introduction... 13 1 Scope... 14 2 Normative references... 15 3 Terms, definitions
High resolution radiant distribution and orbits of sporadic radar meteoroids
 Icarus 196 (2008) 144 163 www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus High resolution radiant distribution and orbits of sporadic radar meteoroids M.D. Campbell-Brown Department of Physics and Astronomy, University
Icarus 196 (2008) 144 163 www.elsevier.com/locate/icarus High resolution radiant distribution and orbits of sporadic radar meteoroids M.D. Campbell-Brown Department of Physics and Astronomy, University
Observations of the effects of meteors on the ionospheres of Venus, Earth and Mars
 Observations of the effects of meteors on the ionospheres of Venus, Earth and Mars Paul Withers 1, A. A. Christou 2, M. Mendillo 1, M. Pätzold 3, K. Peter 3, S. Tellmann 3, J. Vaubaillon 4 1 Boston University
Observations of the effects of meteors on the ionospheres of Venus, Earth and Mars Paul Withers 1, A. A. Christou 2, M. Mendillo 1, M. Pätzold 3, K. Peter 3, S. Tellmann 3, J. Vaubaillon 4 1 Boston University
Lecture 39. Asteroids/ Minor Planets In "Gap" between Mars and Jupiter: 20,000 observed small objects, 6000 with known orbits:
 Lecture 39 Interplanetary Matter Asteroids Meteorites Comets Oort Cloud Apr 28, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 39 1 Asteroids/ Minor Planets In "Gap" between Mars and Jupiter: 20,000 observed small objects, 6000
Lecture 39 Interplanetary Matter Asteroids Meteorites Comets Oort Cloud Apr 28, 2006 Astro 100 Lecture 39 1 Asteroids/ Minor Planets In "Gap" between Mars and Jupiter: 20,000 observed small objects, 6000
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 4 - Group Homework Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Density is defined as A) mass times weight. B) mass per unit volume.
Chapter 4 - Group Homework Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Density is defined as A) mass times weight. B) mass per unit volume.
At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion?
 At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion? These small, rocky worlds orbit the sun generally between the orbits of
At this point of its orbit, any solar satellite such as a comet or a planet is farthest away from the sun. What is the aphelion? These small, rocky worlds orbit the sun generally between the orbits of
Artificial Meteor and Chelyabinsk Ablation Test using Arc-heated Wind Tunnel
 Artificial Meteor and Chelyabinsk Ablation Test using Arc-heated Wind Tunnel Shinsuke ABE Nihon University, Dept. Aerospace Engineering Collaborators; K. Araki, T. Iwasaki, K. Toen (Nihon Univ.) Hironori
Artificial Meteor and Chelyabinsk Ablation Test using Arc-heated Wind Tunnel Shinsuke ABE Nihon University, Dept. Aerospace Engineering Collaborators; K. Araki, T. Iwasaki, K. Toen (Nihon Univ.) Hironori
Wed. Aug. 30, 2017 Reading:
 Wed. Aug. 30, 2017 Reading: Reading for Fri.: Wood Ch. 1 (solar system overview) Reading for Wed. Wed. Wood Ch. 6 & 8 (Asteroids & Meteorites, Solar Nebula) Reading for Fri. Sept. 8. Rozel et al. (link
Wed. Aug. 30, 2017 Reading: Reading for Fri.: Wood Ch. 1 (solar system overview) Reading for Wed. Wed. Wood Ch. 6 & 8 (Asteroids & Meteorites, Solar Nebula) Reading for Fri. Sept. 8. Rozel et al. (link
1star 1 star 9 8 planets 63 (major) moons asteroids, comets, meteoroids
 The Solar System 1star 1 star 9 8 planets 63 (major) moons asteroids, comets, meteoroids The distances to planets are known from Kepler s Laws (once calibrated with radar ranging to Venus) How are planet
The Solar System 1star 1 star 9 8 planets 63 (major) moons asteroids, comets, meteoroids The distances to planets are known from Kepler s Laws (once calibrated with radar ranging to Venus) How are planet
Possible Sources of Toroidal Region in Sporadic Meteoroid Complex
 WDS'11 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 13 18, 2011. ISBN 978-80-7378-186-6 MATFYZPRESS Possible Sources of Toroidal Region in Sporadic Meteoroid Complex P. Pokorný Institute of Astronomy,
WDS'11 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 13 18, 2011. ISBN 978-80-7378-186-6 MATFYZPRESS Possible Sources of Toroidal Region in Sporadic Meteoroid Complex P. Pokorný Institute of Astronomy,
HNRS 227 Fall 2006 Chapter 13. What is Pluto? What is a Planet? There are two broad categories of planets: Terrestrial and Jovian
 Key Points of Chapter 13 HNRS 227 Fall 2006 Chapter 13 The Solar System presented by Prof. Geller 24 October 2006 Planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Dwarf Planets Pluto,
Key Points of Chapter 13 HNRS 227 Fall 2006 Chapter 13 The Solar System presented by Prof. Geller 24 October 2006 Planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune Dwarf Planets Pluto,
Chapter 19: Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets
 Chapter 19: Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Comet Superstition Throughout history, comets have been considered as portants of doom, even until very recently: Appearances of comet Kohoutek (1973), Halley
Chapter 19: Meteorites, Asteroids, and Comets Comet Superstition Throughout history, comets have been considered as portants of doom, even until very recently: Appearances of comet Kohoutek (1973), Halley
Solar System revised.notebook October 12, 2016 Solar Nebula Theory
 Solar System revised.notebook The Solar System Solar Nebula Theory Solar Nebula was a rotating disk of dust and gas w/ a dense center dense center eventually becomes the sun start to condense b/c of gravity
Solar System revised.notebook The Solar System Solar Nebula Theory Solar Nebula was a rotating disk of dust and gas w/ a dense center dense center eventually becomes the sun start to condense b/c of gravity
UNIT 3: Chapter 8: The Solar System (pages )
 CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
CORNELL NOTES Directions: You must create a minimum of 5 questions in this column per page (average). Use these to study your notes and prepare for tests and quizzes. Notes will be turned in to your teacher
THE VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION OF METEOROIDS AT THE EARTH AS MEASURED BY THE CANADIAN METEOR ORBIT RADAR (CMOR)
 Earth, Moon, and Planets (2005) Ó Springer 2005 DOI 10.1007/s11038-005-5041-1 THE VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION OF METEOROIDS AT THE EARTH AS MEASURED BY THE CANADIAN METEOR ORBIT RADAR (CMOR) P. BROWN, J. JONES,
Earth, Moon, and Planets (2005) Ó Springer 2005 DOI 10.1007/s11038-005-5041-1 THE VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION OF METEOROIDS AT THE EARTH AS MEASURED BY THE CANADIAN METEOR ORBIT RADAR (CMOR) P. BROWN, J. JONES,
Chapter 4 The Solar System
 Chapter 4 The Solar System Comet Tempel Chapter overview Solar system inhabitants Solar system formation Extrasolar planets Solar system inhabitants Sun Planets Moons Asteroids Comets Meteoroids Kuiper
Chapter 4 The Solar System Comet Tempel Chapter overview Solar system inhabitants Solar system formation Extrasolar planets Solar system inhabitants Sun Planets Moons Asteroids Comets Meteoroids Kuiper
The Northern ω-scorpiid meteoroid stream: orbits and emission spectra
 The Northern ω-scorpiid meteoroid stream: orbits and emission spectra Francisco A. Espartero 1 and José M. Madiedo 2,1 1 Facultad de Ciencias Experimentales, Universidad de Huelva. 21071 Huelva (Spain).
The Northern ω-scorpiid meteoroid stream: orbits and emission spectra Francisco A. Espartero 1 and José M. Madiedo 2,1 1 Facultad de Ciencias Experimentales, Universidad de Huelva. 21071 Huelva (Spain).
Comparative meteor science The effects of meteoroids on planetary atmospheres and ionospheres
 Comparative meteor science The effects of meteoroids on planetary atmospheres and ionospheres Paul Withers and Meers Oppenheim Boston University (withers@bu.edu, meerso@bu.edu) Tuesday 2009.06.30 1930-2130
Comparative meteor science The effects of meteoroids on planetary atmospheres and ionospheres Paul Withers and Meers Oppenheim Boston University (withers@bu.edu, meerso@bu.edu) Tuesday 2009.06.30 1930-2130
LEARNING ABOUT THE OUTER PLANETS. NASA's Cassini spacecraft. Io Above Jupiter s Clouds on New Year's Day, Credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona
 LEARNING ABOUT THE OUTER PLANETS Can see basic features through Earth-based telescopes. Hubble Space Telescope especially useful because of sharp imaging. Distances from Kepler s 3 rd law, diameters from
LEARNING ABOUT THE OUTER PLANETS Can see basic features through Earth-based telescopes. Hubble Space Telescope especially useful because of sharp imaging. Distances from Kepler s 3 rd law, diameters from
Comets, Asteroids, and Meteors. By: Annette Miles
 Comets, Asteroids, and Meteors By: Annette Miles What is a comet? A comet is a small body which scientists sometimes call a planetesimal. They are made out of dust, ice rock, gas, and. They are kind of
Comets, Asteroids, and Meteors By: Annette Miles What is a comet? A comet is a small body which scientists sometimes call a planetesimal. They are made out of dust, ice rock, gas, and. They are kind of
Contents of the Solar System
 The Solar System Contents of the Solar System Sun Planets 9 known (now: 8) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars ( Terrestrials ) Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune ( Jovians ) Pluto (a Kuiper Belt object?) Natural
The Solar System Contents of the Solar System Sun Planets 9 known (now: 8) Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars ( Terrestrials ) Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune ( Jovians ) Pluto (a Kuiper Belt object?) Natural
Smaller Bodies of the Solar System Chapter 2 continued
 Smaller Bodies of the Solar System Chapter 2 continued Small, rocky (sometimes metallic) bodies with no atmospheres. or planetoids 100,000 numbered and 12,000 named 1-1000 km in size most are small ~ 1
Smaller Bodies of the Solar System Chapter 2 continued Small, rocky (sometimes metallic) bodies with no atmospheres. or planetoids 100,000 numbered and 12,000 named 1-1000 km in size most are small ~ 1
Astr 1050 Wed., March. 22, 2017
 Astr 1050 Wed., March. 22, 2017 Today: Chapter 12, Pluto and Debris March 24: Exam #2, Ch. 5-12 (9:00-9:50) March 27: Mastering Astronomy HW Chapter 11 & 12 1 Chapter 12: Meteorites, Asteroids, Comets
Astr 1050 Wed., March. 22, 2017 Today: Chapter 12, Pluto and Debris March 24: Exam #2, Ch. 5-12 (9:00-9:50) March 27: Mastering Astronomy HW Chapter 11 & 12 1 Chapter 12: Meteorites, Asteroids, Comets
Pluto is not alone out there
 Reading: Chapter 13, Sect. 13.1-13.4, Chapter 14, Sect. 14.1-14.2 Homework 9 - See course webpage later this week Exam 2 - Tuesday November 2 - in class - Physics 3 and 5 Practice exam, review sheets posted
Reading: Chapter 13, Sect. 13.1-13.4, Chapter 14, Sect. 14.1-14.2 Homework 9 - See course webpage later this week Exam 2 - Tuesday November 2 - in class - Physics 3 and 5 Practice exam, review sheets posted
Estimating the number of impact flashes visible on the Moon from an orbiting camera
 Meteoritics & Planetary Science 44, Nr 12, 1871 1875 (2009) Abstract available online at http://meteoritics.org Estimating the number of impact flashes visible on the Moon from an orbiting camera Detlef
Meteoritics & Planetary Science 44, Nr 12, 1871 1875 (2009) Abstract available online at http://meteoritics.org Estimating the number of impact flashes visible on the Moon from an orbiting camera Detlef
MST radar observations of the Leonid meteor storm during
 Indian Journal of Radio & Space Physics Vol 40 April 2011, pp 67-71 MST radar observations of the Leonid meteor storm during 1996-2007 N Rakesh Chandra 1,$,*, G Yellaiah 2 & S Vijaya Bhaskara Rao 3 1 Nishitha
Indian Journal of Radio & Space Physics Vol 40 April 2011, pp 67-71 MST radar observations of the Leonid meteor storm during 1996-2007 N Rakesh Chandra 1,$,*, G Yellaiah 2 & S Vijaya Bhaskara Rao 3 1 Nishitha
ESA s activities related to the meteoroid environment
 ESA s activities related to the meteoroid environment G. Drolshagen, D. Koschny ESA/ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands Engineering flux models In-situ impacts Fireball database as part of SSA Sep 2010,
ESA s activities related to the meteoroid environment G. Drolshagen, D. Koschny ESA/ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands Engineering flux models In-situ impacts Fireball database as part of SSA Sep 2010,
Unit 2 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Unit 2 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Florida Benchmarks SC.5.E.5.2 Recognize the major common characteristics of all planets and compare/contrast the properties of inner and outer
Unit 2 Lesson 1 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Florida Benchmarks SC.5.E.5.2 Recognize the major common characteristics of all planets and compare/contrast the properties of inner and outer
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens 23.1 The Solar System The Planets: An Overview The terrestrial planets are planets that are small and rocky Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The Jovian planets
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens 23.1 The Solar System The Planets: An Overview The terrestrial planets are planets that are small and rocky Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The Jovian planets
CHAPTER 6. The Solar System
 CHAPTER 6 The Solar System 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System The Greeks knew about 5 planets other than Earth They also knew about two other objects that were not planets or stars: meteors and comets
CHAPTER 6 The Solar System 6.1 An Inventory of the Solar System The Greeks knew about 5 planets other than Earth They also knew about two other objects that were not planets or stars: meteors and comets
J.D. Mathews Penn State
 Metal Ions in Sporadic-E Layers Along with Some Speculation About Analogous Phenomena on Other Planets Iron Meteorite - Meridiani Planum J.D. Mathews Penn State NASA/JPL/Cornell image PIA07269 This is
Metal Ions in Sporadic-E Layers Along with Some Speculation About Analogous Phenomena on Other Planets Iron Meteorite - Meridiani Planum J.D. Mathews Penn State NASA/JPL/Cornell image PIA07269 This is
Astronomy 3. Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets
 Astronomy 3 Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets Earth s Movements Orbit- the path in which an object travels around another object in space Revolution the
Astronomy 3 Earth Movements Seasons The Moon Eclipses Tides Planets Asteroids, Meteors, Comets Earth s Movements Orbit- the path in which an object travels around another object in space Revolution the
(Astro)Physics 343 Lecture # 5: Sun, Stars, and Planets; Fourier Transforms
 (Astro)Physics 343 Lecture # 5: Sun, Stars, and Planets; Fourier Transforms Schedule for the next week Office hours: Mon 5:00 6:20pm = Baker; Thu 3:20 4:40 = Lindner + Sections A, B, F = Baker; Sections
(Astro)Physics 343 Lecture # 5: Sun, Stars, and Planets; Fourier Transforms Schedule for the next week Office hours: Mon 5:00 6:20pm = Baker; Thu 3:20 4:40 = Lindner + Sections A, B, F = Baker; Sections
1 Solar System Debris and Formation
 1 Solar System Debris and Formation Chapters 14 and 15 of your textbook Exercises: Do all Review and Discussion and all Conceptual Self-Test 1.1 Solar System Debris Asteroids small rocky bodies Most under
1 Solar System Debris and Formation Chapters 14 and 15 of your textbook Exercises: Do all Review and Discussion and all Conceptual Self-Test 1.1 Solar System Debris Asteroids small rocky bodies Most under
Extrasolar Planets: Molecules and Disks
 Extrasolar Planets: Molecules and Disks The basic question: Is our solar system typical of what we should affect around other stars (inhabited or not), or is it an unusual freak? One approach is to look
Extrasolar Planets: Molecules and Disks The basic question: Is our solar system typical of what we should affect around other stars (inhabited or not), or is it an unusual freak? One approach is to look
Starting from closest to the Sun, name the orbiting planets in order.
 Chapter 9 Section 1: Our Solar System Solar System: The solar system includes the sun, planets and many smaller structures. A planet and its moon(s) make up smaller systems in the solar system. Scientist
Chapter 9 Section 1: Our Solar System Solar System: The solar system includes the sun, planets and many smaller structures. A planet and its moon(s) make up smaller systems in the solar system. Scientist
The Magnetic Sun. CESAR s Booklet
 The Magnetic Sun CESAR s Booklet 1 Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium Most of the planets in our Solar system are enclosed by huge magnetic structures, named magnetospheres
The Magnetic Sun CESAR s Booklet 1 Introduction to planetary magnetospheres and the interplanetary medium Most of the planets in our Solar system are enclosed by huge magnetic structures, named magnetospheres
The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS. Scientific Language. Name Test Date Hour
 Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
Chapter 8 Geospace 1
 Chapter 8 Geospace 1 Previously Sources of the Earth's magnetic field. 2 Content Basic concepts The Sun and solar wind Near-Earth space About other planets 3 Basic concepts 4 Plasma The molecules of an
Chapter 8 Geospace 1 Previously Sources of the Earth's magnetic field. 2 Content Basic concepts The Sun and solar wind Near-Earth space About other planets 3 Basic concepts 4 Plasma The molecules of an
Exam# 2 Review. Exam #2 is Wednesday November 8th at 10:40 AM in room FLG-280
 Exam# 2 Review Exam #2 is Wednesday November 8th at 10:40 AM in room FLG-280 Bring Gator 1 ID card Bring pencil #2 with eraser No use of calculator or any electronic device during the exam We provide the
Exam# 2 Review Exam #2 is Wednesday November 8th at 10:40 AM in room FLG-280 Bring Gator 1 ID card Bring pencil #2 with eraser No use of calculator or any electronic device during the exam We provide the
Vagabonds of the Solar System
 Vagabonds of the Solar System Guiding Questions 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
Vagabonds of the Solar System Guiding Questions 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
12/3/14. Guiding Questions. Vagabonds of the Solar System. A search for a planet between Mars and Jupiter led to the discovery of asteroids
 Guiding Questions Vagabonds of the Solar System 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
Guiding Questions Vagabonds of the Solar System 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
1 of 5 5/2/2015 5:50 PM
 1 of 5 5/2/2015 5:50 PM 1. A comet that has a semi-major axis of 100 AU must have a period of about 10 years. 20 years. 100 years. 1000 years. 2. Astronomers believe chondrite meteorites are about 4.6
1 of 5 5/2/2015 5:50 PM 1. A comet that has a semi-major axis of 100 AU must have a period of about 10 years. 20 years. 100 years. 1000 years. 2. Astronomers believe chondrite meteorites are about 4.6
Human Understanding of both Earth and Space has Changed Over Time. Unit E: Topic One
 Human Understanding of both Earth and Space has Changed Over Time Unit E: Topic One 1.4 Our Solar Neighbourhood Nebular Hypothesis The theory of how solar systems are formed Evolution of solar system
Human Understanding of both Earth and Space has Changed Over Time Unit E: Topic One 1.4 Our Solar Neighbourhood Nebular Hypothesis The theory of how solar systems are formed Evolution of solar system
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System The Planets: An Overview The terrestrial planets are planets that are small and rocky Mercury, Venus,
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 23 Touring Our Solar System 23.1 The Solar System The Planets: An Overview The terrestrial planets are planets that are small and rocky Mercury, Venus,
Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes
 Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes The Planets in order from the Sun are: Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune To help us remember, we use the sentence: My Very Excited Mother Just Served
Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes The Planets in order from the Sun are: Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune To help us remember, we use the sentence: My Very Excited Mother Just Served
INCIDENCE OF LOW DENSITY METEOROIDS OF THE POLONNARUWA-TYPE
 INCIDENCE OF LOW DENSITY METEOROIDS OF THE POLONNARUWA-TYPE N. C. Wickramasinghe* 1, J. Wallis 2, D.H. Wallis 1, M.K. Wallis 1, N. Miyake 1, S.G. Coulson 1, Carl H. Gibson 4, J.T. Wickramasinghe 1, A.
INCIDENCE OF LOW DENSITY METEOROIDS OF THE POLONNARUWA-TYPE N. C. Wickramasinghe* 1, J. Wallis 2, D.H. Wallis 1, M.K. Wallis 1, N. Miyake 1, S.G. Coulson 1, Carl H. Gibson 4, J.T. Wickramasinghe 1, A.
6. (11.2) What shape are typical asteroids and how do we know? Why does Ceres not have this shape?
 SUMMARY Our Solar System contains numerous small bodies: dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. They are important astronomically because they give us information about the time of formation,
SUMMARY Our Solar System contains numerous small bodies: dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. They are important astronomically because they give us information about the time of formation,
23.1 The Solar System. Orbits of the Planets. Planetary Data The Solar System. Scale of the Planets The Solar System
 23.1 The Solar System Orbits of the Planets The Planets: An Overview The terrestrial planets are planets that are small and rocky Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The Jovian planets are the huge gas giants
23.1 The Solar System Orbits of the Planets The Planets: An Overview The terrestrial planets are planets that are small and rocky Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The Jovian planets are the huge gas giants
Survey of the Solar System. The Sun Giant Planets Terrestrial Planets Minor Planets Satellite/Ring Systems
 Survey of the Solar System The Sun Giant Planets Terrestrial Planets Minor Planets Satellite/Ring Systems The Sun Mass, M ~ 2 x 10 30 kg Radius, R ~ 7 x 10 8 m Surface Temperature ~ 5800 K Density ~ 1.4
Survey of the Solar System The Sun Giant Planets Terrestrial Planets Minor Planets Satellite/Ring Systems The Sun Mass, M ~ 2 x 10 30 kg Radius, R ~ 7 x 10 8 m Surface Temperature ~ 5800 K Density ~ 1.4
Astronomy 103: First Exam
 Name: Astronomy 103: First Exam Stephen Lepp October 27, 2010 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. 1 Short Answer A. What is the largest of the terrestrial
Name: Astronomy 103: First Exam Stephen Lepp October 27, 2010 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. 1 Short Answer A. What is the largest of the terrestrial
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest).
 Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Solar Noon The point at which the Sun is highest in the sky (and when shadows are shortest). Rotation The movement of one object as it turns or spins around a central point or axis. Revolution The movement
Mapping Document. GCSE (9-1) Astronomy. Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Astronomy (1AS0)
 Mapping Document GCSE (9-1) Astronomy Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Astronomy (1AS0) GCSE (9-1) Astronomy Mapping document This document is designed to help you compare the existing 2011
Mapping Document GCSE (9-1) Astronomy Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Astronomy (1AS0) GCSE (9-1) Astronomy Mapping document This document is designed to help you compare the existing 2011
The Solar System. Name Test Date Hour
 Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
Name Test Date Hour Astronomy#3 - Notebook The Solar System LEARNING TARGETS I can describe the objects that make up our solar system. I can identify the inner and outer planets. I can explain the difference
Meteor Science and Aeronomy Using the Arecibo VHF and UHF Radars.
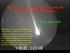 Meteor Science and Aeronomy Using the Arecibo VHF and UHF Radars. Bolide AIDA 1989 Bolide AIDA was in a near-earth asteroidal orbit with V ~15.5 km/sec, a period of ~1.4 yrs, aubritic compositon, ~30 kg
Meteor Science and Aeronomy Using the Arecibo VHF and UHF Radars. Bolide AIDA 1989 Bolide AIDA was in a near-earth asteroidal orbit with V ~15.5 km/sec, a period of ~1.4 yrs, aubritic compositon, ~30 kg
Fundamentals of meteor science
 WGN, the Journal of the IMO 34:3 (2006) 71 Fundamentals of meteor science Visual Sporadic Meteor Rates Jürgen Rendtel 1 Activity from the antihelion region can be regarded as a series of ecliptical showers
WGN, the Journal of the IMO 34:3 (2006) 71 Fundamentals of meteor science Visual Sporadic Meteor Rates Jürgen Rendtel 1 Activity from the antihelion region can be regarded as a series of ecliptical showers
Astronomy 241: Foundations of Astrophysics I. The Solar System
 Astronomy 241: Foundations of Astrophysics I. The Solar System Astronomy 241 is the first part of a year-long introduction to astrophysics. It uses basic classical mechanics and thermodynamics to analyze
Astronomy 241: Foundations of Astrophysics I. The Solar System Astronomy 241 is the first part of a year-long introduction to astrophysics. It uses basic classical mechanics and thermodynamics to analyze
Eos 74(44) (1993):
 Anticipation of the Ulysses Interstellar Dust Findings Paul A. LaViolette, The Starburst Foundation, 1176 Hedgewood Lane, Schenectady, NY 12309 Eos 74(44) (1993): 510-11 It has long been thought that dust
Anticipation of the Ulysses Interstellar Dust Findings Paul A. LaViolette, The Starburst Foundation, 1176 Hedgewood Lane, Schenectady, NY 12309 Eos 74(44) (1993): 510-11 It has long been thought that dust
Predictions for Dusty Mass Loss from Asteroids during Close Encounters with Solar Probe Plus
 Predictions for Dusty Mass Loss from Asteroids during Close Encounters with Solar Probe Plus Steven R. Cranmer University of Colorado Boulder, LASP Paper: http://arxiv.org/abs/1606.01785 Introduction
Predictions for Dusty Mass Loss from Asteroids during Close Encounters with Solar Probe Plus Steven R. Cranmer University of Colorado Boulder, LASP Paper: http://arxiv.org/abs/1606.01785 Introduction
10-20 billion years old
 Universe : 10-20 billion years old Big Bang Theory * the universe started at a single point * that point was extremely dense * it became unstable and expanded outward * The universe is still expanding
Universe : 10-20 billion years old Big Bang Theory * the universe started at a single point * that point was extremely dense * it became unstable and expanded outward * The universe is still expanding
Modeling Meteors. Summer School of Science. Project report. Chloe Udressy Marcell Dorian Kovacs Nensi Komljenovic. Project leader: Dusan Pavlovic
 Modeling Meteors Summer School of Science Project report Chloe Udressy Marcell Dorian Kovacs Nensi Komljenovic Project leader: Dusan Pavlovic 2017. 07. 29-08. 07. Contents 1 Abstract 2 2 Introduction 2
Modeling Meteors Summer School of Science Project report Chloe Udressy Marcell Dorian Kovacs Nensi Komljenovic Project leader: Dusan Pavlovic 2017. 07. 29-08. 07. Contents 1 Abstract 2 2 Introduction 2
Space weather. Introduction to lectures by Dr John S. Reid. Image courtesy:
 Space weather Introduction to lectures by Dr John S. Reid Image courtesy: http://www.astro-photography.com/ss9393.htm Sunspot 9393 First pass from late March to early April, 2001 See: Storms from the Sun
Space weather Introduction to lectures by Dr John S. Reid Image courtesy: http://www.astro-photography.com/ss9393.htm Sunspot 9393 First pass from late March to early April, 2001 See: Storms from the Sun
12a. Jupiter. Jupiter Data (Table 12-1) Jupiter Data: Numbers
 12a. Jupiter Jupiter & Saturn data Jupiter & Saturn seen from the Earth Jupiter & Saturn rotation & structure Jupiter & Saturn clouds Jupiter & Saturn atmospheric motions Jupiter & Saturn rocky cores Jupiter
12a. Jupiter Jupiter & Saturn data Jupiter & Saturn seen from the Earth Jupiter & Saturn rotation & structure Jupiter & Saturn clouds Jupiter & Saturn atmospheric motions Jupiter & Saturn rocky cores Jupiter
Solar System Debris: Comets and Asteroids
 1 Solar System Debris: Comets and Asteroids Primarily found in two zones in the solar system. The Asteroid Belt (rocky, between Jupiter and Mars) The Edgeworth/Kuiper Belt (beyond Neptune) and Oort Cloud
1 Solar System Debris: Comets and Asteroids Primarily found in two zones in the solar system. The Asteroid Belt (rocky, between Jupiter and Mars) The Edgeworth/Kuiper Belt (beyond Neptune) and Oort Cloud
Chapter 23 Earth Science 11
 Chapter 23 Earth Science 11 Inner planets: Closest planets to the sun A.k.a. terrestrial planets All have a rocky crust, dense mantle layer, and a very dense core Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars Outer
Chapter 23 Earth Science 11 Inner planets: Closest planets to the sun A.k.a. terrestrial planets All have a rocky crust, dense mantle layer, and a very dense core Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars Outer
MASS INDEX AND MASS OF THE GEMINID METEOROID STREAM AS FOUND WITH RADAR, OPTICAL, AND LUNAR IMPACT DATA
 MASS INDEX AND MASS OF THE GEMINID METEOROID STREAM AS FOUND WITH RADAR, OPTICAL, AND LUNAR IMPACT DATA June 6, 2016 Rhiannon Blaauw NASA Meteoroid Environments Office/ APL Jacobs ESSSA Outline In 2015,
MASS INDEX AND MASS OF THE GEMINID METEOROID STREAM AS FOUND WITH RADAR, OPTICAL, AND LUNAR IMPACT DATA June 6, 2016 Rhiannon Blaauw NASA Meteoroid Environments Office/ APL Jacobs ESSSA Outline In 2015,
MEASURING THE METEOROID ENVIRONMENTS OF THE PLANETS WITH METEOR DETECTORS ON EARTH. Submitted to AJ
 Draft version October 4, 218 Typeset using LATEX default style in AASTeX61 MEASURING THE METEOROID ENVIRONMENTS OF THE PLANETS WITH METEOR DETECTORS ON EARTH Paul Wiegert, 1,2 Peter Brown, 1,2 Petr Pokorny,
Draft version October 4, 218 Typeset using LATEX default style in AASTeX61 MEASURING THE METEOROID ENVIRONMENTS OF THE PLANETS WITH METEOR DETECTORS ON EARTH Paul Wiegert, 1,2 Peter Brown, 1,2 Petr Pokorny,
The Origin of Near Earth Asteroids
 The Origin of Near Earth Asteroids Judit Györgyey Ries Priors, Quaternions and Residuals, Oh My! September 24, 2004 Austin, Texas Outline Why are we interested in Near Earth Asteroids? How does an asteroid
The Origin of Near Earth Asteroids Judit Györgyey Ries Priors, Quaternions and Residuals, Oh My! September 24, 2004 Austin, Texas Outline Why are we interested in Near Earth Asteroids? How does an asteroid
Zach Meeks. Office: Ford ES&T Phone: (918) Please let me know if you have any questions!
 Zach Meeks Office: Ford ES&T 2114 Email: zachary.meeks@gatech.edu Phone: (918) 515-0052 Please let me know if you have any questions! The scope of space physics Solar-Terrestrial Relations Solar-Terrestrial
Zach Meeks Office: Ford ES&T 2114 Email: zachary.meeks@gatech.edu Phone: (918) 515-0052 Please let me know if you have any questions! The scope of space physics Solar-Terrestrial Relations Solar-Terrestrial
Space Notes 2. Covers Objectives 3, 4, and 8
 Space Notes 2 Covers Objectives 3, 4, and 8 Sun Average Size Star Sun 101 Sun s Mass almost 100 times the mass of all the planets combined. Most of the mass is hydrogen gas Thermonuclear Reaction Thermonuclear
Space Notes 2 Covers Objectives 3, 4, and 8 Sun Average Size Star Sun 101 Sun s Mass almost 100 times the mass of all the planets combined. Most of the mass is hydrogen gas Thermonuclear Reaction Thermonuclear
The solar system pt 2 MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 The solar system pt 2 MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Dwarf planets Following the discovery of multiple objects similar to Pluto (and one that was even bigger than Pluto) a new classification for planets
The solar system pt 2 MR. BANKS 8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Dwarf planets Following the discovery of multiple objects similar to Pluto (and one that was even bigger than Pluto) a new classification for planets
Physics 343 Lecture # 5: Sun, Stars, and Planets; Bayesian analysis
 Physics 343 Lecture # 5: Sun, Stars, and Planets; Bayesian analysis Schedule for the next week Office hours: Thu 5:00 6:20pm = Deshpande; Fri 10:20 11:40 = Baker + on call Sections A, C = Baker; Sections
Physics 343 Lecture # 5: Sun, Stars, and Planets; Bayesian analysis Schedule for the next week Office hours: Thu 5:00 6:20pm = Deshpande; Fri 10:20 11:40 = Baker + on call Sections A, C = Baker; Sections
1UNIT. The Universe. What do you remember? Key language. Content objectives
 1UNIT The Universe What do you remember? What are the points of light in this photo? What is the difference between a star and a planet? a moon and a comet? Content objectives In this unit, you will Learn
1UNIT The Universe What do you remember? What are the points of light in this photo? What is the difference between a star and a planet? a moon and a comet? Content objectives In this unit, you will Learn
This asteroid was visited by the NEAR Shoemaker probe, which orbited it, taking extensive photographs of its
 Chapter 9 Part 1 Asteroids and Comets Why is there an asteroid belt? This asteroid was visited by the NEAR Shoemaker probe, which orbited it, taking extensive photographs of its surface, and, on February
Chapter 9 Part 1 Asteroids and Comets Why is there an asteroid belt? This asteroid was visited by the NEAR Shoemaker probe, which orbited it, taking extensive photographs of its surface, and, on February
Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium. Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium. Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium
 Test 04 Chapters 15-20 Limited Copies Are available Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium June 4 th from 8:00 pm - 10:00 pm Covering ALL Tests Slide 1 Slide 2 Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin
Test 04 Chapters 15-20 Limited Copies Are available Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin Planetarium June 4 th from 8:00 pm - 10:00 pm Covering ALL Tests Slide 1 Slide 2 Griffith Observatory Samuel Oschin
Chapter 29. The Solar System. The Solar System. Section 29.1 Models of the Solar System notes Models of the Solar System
 The Solar System Chapter 29 The Solar System Section 29.1 Models of the Solar System 29.1 notes Models of the Solar System Geocentric: : Earth-centered model of the solar system. (Everything revolves around
The Solar System Chapter 29 The Solar System Section 29.1 Models of the Solar System 29.1 notes Models of the Solar System Geocentric: : Earth-centered model of the solar system. (Everything revolves around
IX. Dwarf Planets A. A planet is defined to be an object that is large enough to coalesce into a sphere and to have cleared its orbit of other
 7/1 VII. VIII. Uranus A. Gas Giant 1. Rings but not visible 2. HUGE axial tilt 97! 3. Mostly hydrogen and helium 4. Medium rotation rate 5. Cold 55 K at the cloud tops B. Physical characteristics 1. Mass:
7/1 VII. VIII. Uranus A. Gas Giant 1. Rings but not visible 2. HUGE axial tilt 97! 3. Mostly hydrogen and helium 4. Medium rotation rate 5. Cold 55 K at the cloud tops B. Physical characteristics 1. Mass:
Origin of the Solar System
 Origin of the Solar System and Solar System Debris 1 Debris comets meteoroids asteroids gas dust 2 Asteroids irregular, rocky hunks small in mass and size Ceres - largest, 1000 km in diameter (1/3 Moon)
Origin of the Solar System and Solar System Debris 1 Debris comets meteoroids asteroids gas dust 2 Asteroids irregular, rocky hunks small in mass and size Ceres - largest, 1000 km in diameter (1/3 Moon)
What Objects Are Part of the Solar System?
 What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Lesson 1 Quiz Josleen divided some of the planets into two main groups. The table below shows how she grouped them. Paul created a poster showing the solar system.
What Objects Are Part of the Solar System? Lesson 1 Quiz Josleen divided some of the planets into two main groups. The table below shows how she grouped them. Paul created a poster showing the solar system.
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe (29:50) Professor C.C. Lang Exam #1 - Fall 2010 Wednesday, September 22 nd FORM B - SOLUTIONS
 Stars, Galaxies & the Universe (29:50) Professor C.C. Lang Exam #1 - Fall 2010 Wednesday, September 22 nd FORM B - SOLUTIONS Questions 1-6 are True/False questions (worth 4 pts each): 1. The Sun is a Red
Stars, Galaxies & the Universe (29:50) Professor C.C. Lang Exam #1 - Fall 2010 Wednesday, September 22 nd FORM B - SOLUTIONS Questions 1-6 are True/False questions (worth 4 pts each): 1. The Sun is a Red
Intro to Earth Science Chapter 23 Study Guide
 Name _ Date _ Period _ Intro to Earth Science Chapter 23 Study Guide 1. is the planet that cannot be classified as either a terrestrial or a Jovian planet. 2. The densities of the planets are about five
Name _ Date _ Period _ Intro to Earth Science Chapter 23 Study Guide 1. is the planet that cannot be classified as either a terrestrial or a Jovian planet. 2. The densities of the planets are about five
Chapter 19 Exploring Space. I. Fill in the blank
 Chapter 19 Exploring Space 1. All radiation is classified by wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum. 2. Two types of telescopes that collect visible light are refractors and reflectors. 3. An uncrewed
Chapter 19 Exploring Space 1. All radiation is classified by wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum. 2. Two types of telescopes that collect visible light are refractors and reflectors. 3. An uncrewed
Jovian Planet Properties
 The Outer Planets Jovian Planet Properties Jovian Planet Properties Compared to the terrestrial planets, the Jovians: are much larger & more massive are composed mostly of Hydrogen, Helium, & Hydrogen
The Outer Planets Jovian Planet Properties Jovian Planet Properties Compared to the terrestrial planets, the Jovians: are much larger & more massive are composed mostly of Hydrogen, Helium, & Hydrogen
ES - Astronomy Part 2 Post-Test
 ES - Astronomy Part 2 Post-Test True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Compared to the human eye, telescopes can collect light over longer periods of time. 2. The inner planets
ES - Astronomy Part 2 Post-Test True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Compared to the human eye, telescopes can collect light over longer periods of time. 2. The inner planets
Ch. 6: Smaller Bodies in the Solar System
 Ch. 6: Smaller Bodies in the Solar System FIGURE 9-1 (Discovering the Universe) Different Classifications of Solar System Objects Some of the definitions of the different types of objects in the solar
Ch. 6: Smaller Bodies in the Solar System FIGURE 9-1 (Discovering the Universe) Different Classifications of Solar System Objects Some of the definitions of the different types of objects in the solar
Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 3
 Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 3 Chapter 6 1. Which of the following statements is false? a) Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one medium to another. b) Mirrors
Astro 1010 Planetary Astronomy Sample Questions for Exam 3 Chapter 6 1. Which of the following statements is false? a) Refraction is the bending of light when it passes from one medium to another. b) Mirrors
Observing Habitable Environments Light & Radiation
 Homework 1 Due Thurs 1/14 Observing Habitable Environments Light & Radiation Given what we know about the origin of life on Earth, how would you recognize life on another world? Would this require a physical
Homework 1 Due Thurs 1/14 Observing Habitable Environments Light & Radiation Given what we know about the origin of life on Earth, how would you recognize life on another world? Would this require a physical
a. 1/3 AU b. 3 AU 5. Meteor showers occur
 1 AST104 Sp. 2006: WELCOME TO EXAM 3 Multiple Choice Questions: Mark the best answer choice on the answer form. Read all answer choices before making selection. CHECK YOUR WORK CAREFULLY BEFORE HANDING
1 AST104 Sp. 2006: WELCOME TO EXAM 3 Multiple Choice Questions: Mark the best answer choice on the answer form. Read all answer choices before making selection. CHECK YOUR WORK CAREFULLY BEFORE HANDING
1. The Sun is the largest and brightest object in the universe. 2. The period that the Earth takes to revolve once around the Sun is approximately a
 PLEASE ANSWER YOUR QUESTIONS ON THIS PROVIDED QUESTION PAPER. EACH QUESTION IS FOLLOWED BY ANSWERS MARKED A AND B, OR A, B, C AND D. ONLY ONE ANSWER IS CORRECT. CHOOSE THE MOST CORRECT ANSWER AND CIRCLE
PLEASE ANSWER YOUR QUESTIONS ON THIS PROVIDED QUESTION PAPER. EACH QUESTION IS FOLLOWED BY ANSWERS MARKED A AND B, OR A, B, C AND D. ONLY ONE ANSWER IS CORRECT. CHOOSE THE MOST CORRECT ANSWER AND CIRCLE
THE PLANETARY SCIENTIST'S COMPANION
 THE PLANETARY SCIENTIST'S COMPANION Katharina Lodders Bruce Fegley, Jr. New York Oxford Oxford University Press 1998 Contents 1 Technical data Table 1.1 The Greek alphabet 1 Table 1.2 Prefixes used with
THE PLANETARY SCIENTIST'S COMPANION Katharina Lodders Bruce Fegley, Jr. New York Oxford Oxford University Press 1998 Contents 1 Technical data Table 1.1 The Greek alphabet 1 Table 1.2 Prefixes used with
Doppler Studies of Near-Antapex UHF Radar Micrometeors
 Icarus 143, 347 353 (2000) doi:10.1006/icar.1999.6257, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Doppler Studies of Near-Antapex UHF Radar Micrometeors D. Janches and J. D. Mathews Communication
Icarus 143, 347 353 (2000) doi:10.1006/icar.1999.6257, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Doppler Studies of Near-Antapex UHF Radar Micrometeors D. Janches and J. D. Mathews Communication
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 1 Mar 2001
 Zodiacal Infrared Foreground Prediction for Space Based Infrared Interferometer Missions arxiv:astro-ph/0103005v1 1 Mar 2001 M.Landgraf (markus.landgraf@esa.int) and R.Jehn (ruediger.jehn@esa.int) European
Zodiacal Infrared Foreground Prediction for Space Based Infrared Interferometer Missions arxiv:astro-ph/0103005v1 1 Mar 2001 M.Landgraf (markus.landgraf@esa.int) and R.Jehn (ruediger.jehn@esa.int) European
The Solar System 6/23
 6/23 The Solar System I. Earth A. Earth is the prototype terrestrial planet 1. Only planet in the solar system (we know of so far) with life 2. Temperature 290 K B. Physical Characteristics 1. Mass: 6
6/23 The Solar System I. Earth A. Earth is the prototype terrestrial planet 1. Only planet in the solar system (we know of so far) with life 2. Temperature 290 K B. Physical Characteristics 1. Mass: 6
Today. The Little Things. Comets. Dwarf Planets. Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then.
 Today The Little Things Comets Dwarf Planets Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then. 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Comets Fig 9.5 FROST LINE
Today The Little Things Comets Dwarf Planets Last Exam in last class, Thursday Dec. 7. Homework also due then. 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Comets Fig 9.5 FROST LINE
Geant4 in JAXA. Masanobu Ozaki (JAXA/ISAS)
 Geant4 in JAXA Masanobu Ozaki (JAXA/ISAS) Japanese Space Science Missions In Japan, most of fundamental researches relating to the on-orbit radiation environment are carried out for non-commercial (i.e.,
Geant4 in JAXA Masanobu Ozaki (JAXA/ISAS) Japanese Space Science Missions In Japan, most of fundamental researches relating to the on-orbit radiation environment are carried out for non-commercial (i.e.,
Astronomy Study Guide Answer Key
 Astronomy Study Guide Answer Key Section 1: The Universe 1. Cosmology is the study of how the universe is arranged. 2. Identify the type of cosmology a. The sun is the center of the Universe Heliocentric
Astronomy Study Guide Answer Key Section 1: The Universe 1. Cosmology is the study of how the universe is arranged. 2. Identify the type of cosmology a. The sun is the center of the Universe Heliocentric
CHAPTER 11. We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration
 CHAPTER 11 We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration Section 11.1 The Sun page 390 -Average sized star -Millions of km away -300,000 more massive then Earth, 99% of all
CHAPTER 11 We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration Section 11.1 The Sun page 390 -Average sized star -Millions of km away -300,000 more massive then Earth, 99% of all
Chapter Outline. Earth and Other Planets. The Formation of the Solar System. Clue #1: Planetary Orbits. Clues to the Origin of the Solar System
 Chapter Outline Earth and Other Planets The Formation of the Solar System Exploring the Solar System Chapter 16 Great Idea: Earth, one of the planets that orbit the Sun, formed 4.5 billion years ago from
Chapter Outline Earth and Other Planets The Formation of the Solar System Exploring the Solar System Chapter 16 Great Idea: Earth, one of the planets that orbit the Sun, formed 4.5 billion years ago from
