drops in motion Frieder Mugele the physics of electrowetting and its applications Physics of Complex Fluids University of Twente
|
|
|
- Samson Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 drops in motion the physics of electrowetting and its applications Frieder Mugele Physics of Complex Fluids niversity of Twente 1
2 electrowetting: the switch on the wettability voltage
3 outline q q q q q introduction electrowetting basics q historic note q origin of the EW effect q electromechanical model q contact angle saturation physical principles and challenges of EW devices FNdamental fluid dynamics with EW q contact angle hysteresis in EW q contact line motion in ambient oil q electrowetting driven drop oscillations and mixing flows q channel-based microfluidic systems with EW functionality conclusion 3
4 the origin 1875: Annales de Chimie et de Physique english translation: in Mugele&Baret J. Phys. Cond. Matt. 17, R705-R774 (005) Gabriel Lippmann ( ) Nobel prize : interferometric color photography
5 Lippmann s experiment on electrocapillarity σ Hg/HSO4 voltage [Daniell] First law the capillaryconstantat the mercury/diluted sulfuricacid interfaceis a function of the electrical differenceat the surface. σ f ( ) 5
6 effective surface tension H SO 4 capillary depression (Jurin): p L σ cosθ R Y ρ g h ph h h h( ) σ σ ( ) σ α 0 Hg build-up of a Debye layer electrostatic energy/area 1 Eel c double layer capacitance: ε c 0 ε λ D total free energy (per unit area): F( ) σ ( ) σ c 0 no dielectric! 6
7 modern electrowetting equation on dielectric basic setup: σ lv σ sl σ sv conductive liquid insulator counter electrode Berge 1993 Electrowetting on dielectric (EWOD) 7 electrowetting equation: cos( θ( )) cosθ Y electrowetting number 1 ε 0ε dσ h lv water in silicone oil low voltage: parabolic behavior high voltage: contact angle saturation advancing receding
8 examples of EW-curves electrowetting equation: cos( θ ( )) cosθ Y 1 ε 0 dσ ε lv cos θ () cos θ().0 0, ,4 0, , , /γ wo (10 5 V m/n) α (V ) water gelatin (%; 40 C) milk SDS (0.7%) Triton-x 100 (0.1%) Triton SDS milk gelatin water σ macro [mj/m ]] Banpurkar et al., Langmuir 008 Teflon AF-coated ITO glass in silicone oil; AC voltage
9 EW as microdrop tensiometer Liquid Interface (Temperature 3 o C) Planar Electrode γ wo (EW drop tensiometer (mn/m) Interdigitated Electrode γ wo (Du Noüy ring) (mn/m) H O/silicone oil (θ Y 169 O ) calibration calibration 38± 0. H O/ mineral oil (168 O ) 48.8± ± ± 0. H O/ air (6 O ) 7.4 ± ±0. 7.6± 0.5 H O/ n-hexadecane (169 O ) 5.9± ± ±0.5 Aqu. Gelatin ( % )/ mineral oil (160 O ) 4.1± ± ± 0.4 Aqu. Gelatin ( %)/silicone oil (167 O ) 0.1± ± ± 0.5 Aqu. SDS (0.7 %)/ silicone oil (165 O ) 7.5± ± ± 0.4 Aqu. CTAB (0.1 %)/mineral oil (164 O ) 6.5± ± ± 0.4 Aqu. Triton X-100 (0.1%)/ silicone oil (163 O ) 4.7± ± ± 0.4 Aqu. Glycerin (50% )/ silicone oil (169 O ) 3.8± ± ± 0.5 Milk / silicone oil (167 O ) 19.4± ± ± 0.1 yeast protein (1% )/ silicone oil (167 O ) 0.0± ± ± Banpurkar et al., Langmuir 008 interfacial tension measurements for nl drops consistent with bulk values
10 origin of EW G i σ i A i E r 1 r r D EdV σ A i i i ε 0ε d r A sl Maxwell stress: p el ε r E( ) 0 r εε 0 σ lv Alv σ sl σ d σ sl eff sv A sl? p σ lv κ ε r E( ) 0 r modified Young equation modified capillary equation 10
11 local equilibrium surface profiles D geometry iterative calculation: initial profile (fixed θ A ) field distribution (FEM) force balance refined profile 1. local force balance p el ( x) 0 r ε! E( ) γ lv r h ( ) r 1 h ( ) p cap r ( ). free energy minimization ~ A η! F cosθ L ds ( ) min ( ) dv φ ε Y sl r B 11
12 numerical results surface profiles curvature / Maxwell stress x 1 liquid air η (0,.,.4,, 1.) log P el η ν -0,4 ε 1: ε : -0,6-0,8 0,4 0,5 0,6 0,7 α / π θ Y / π Buehrle et al. PRL 003 Bienia et al. EuroPhysLett h/d ins q local contact angle Young s angle q divergent curvature near contact line: κ ~ p el ~ h ν ; -1 < ν < 0 q range of surface distortions: d ins no contact angle saturation (in -dim model) log h/d ins
13 experimental verification η 0 η 0.5 η 1 d 10µm d 50µm d 150µm 13 Mugele, Buehrle, J.Phys.Cond.Matt 007
14 relation between local and apparent c.a. D geometry apparent c.a. cos( θ ( )) cosθ η Y local c.a. θ B θ Y 14 apparent c.a. follows EW equation
15 equivalence of force balance & energy minimization S f x, el 0 ρ E dz x εε 0 d x total force: (per unit length) f x T Σ xk n k da Maxwell stress tensor: εε 0 d σ lv η T.B. Jones force / unit length σ lv independent of drop shape! f el σ sl 15 σ sv
16 reconciliation ε 0ε σ i Ai d i r macroscopic picture A sl F i σ E r i A i 1 r r D EdV Maxwell stress: microscopic picture p el ε r E( ) 0 r εε 0 σ lv Alv σ sl σ d σ sl eff sv A sl h>> d electrical force / unit length fel 0 p p σ el ( z) dz modified Young equation modified capillary equation lv ε κ r E( ) 0 r 16 both pictures are equivalent on a scale >> d ins
17 contact angle saturation: the mystery of EW what causes deviations from EW equation at high voltage? advancing receding cos( θ ( )) cosθ Y 1 ε 0ε dσ lv diverging electric fields can cause dielectric breakdown of coating! break down safe operation (Seyrat, Heyes, J. Appl. Phys. 001) 17
18 refined version: local breakdown at contact line potential magnitude of field self-consistent calculation of field and surface configuration local breakdown upon calculated EW curve including saturation exceeding V T (Papathanasiou et al. Appl. Phys. Lett. 005, J. 18Appl. Phys. 008, Langmuir 009)
19 contact line instability d Coulomb explosion: balance of capillary energy and electrostatic energy top view: water-silanized glass ; f 00 Hz 100 µm 19 Berge et al. Eur. Phys. J. B 1999; Mugele, Herminghaus Appl. Phys. Lett. 00
20 AC- vs. DC-EW: frequency-dependence EW equation: cos( θ( )) cosθ Y 1 ε 0ε dσ lv RMS σ 0.7 µs/cm 70V rms f AC khz 0
21 finite-conductivity effects in AC-EW -0,7 5 µs/cm 0 µs/cm 300 µs/cm -0,7-0,7 ( 1mM NaCl) cos θ -0,8-0,8 f 0, 100kHz -0,8-0,9-0,9-0,9-1, , (V ) -1, conducticvity
22 modeling equivalent circuit ~ 0 droplet ~ 0 insulator loc loc << 0 due to Ohmic losses f ( ω) loc σ 0 1 ω 1 R l C d α f cosθ ( ω) (cosθ cosθ Y cosθ Y ε ε σ ) 0 d fσ ( ω) lvd 0 α 1 ω R l 0 C d
23 results α f(ω) (10-4 V - ) 1, 0,8 0,4 µs/cm 5.1 µs/cm 17 µs/cm 300 µs/cm 0, ω / (πσ) (khz m/s) few mm of salt perfect conductivity (up to a few tens of khz) 3
24 summary electrowetting basics contact angle reduction arises from minimization of interfacial and electrostatic energy (maximum of capacitance) equilibrium shape is determined by local balance of Maxwell stress and Laplace pressure q local contact angle Young s angle q diverging curvature near contact line q equivalence of force balance and effective surface tension approach on scales >> d contact angle saturation arises from non-linearities in diverging electric fields at contact line q c.a. saturation can be minimized by use of high quality substrates, AC voltage, ambient oil. 4
Electrowetting based microliter drop tensiometer. Arun G. Banpurkar* Kevin Nichols and Frieder Mugele
 Electrowetting based microliter drop tensiometer Arun G. Banpurkar* Kevin Nichols and Frieder Mugele Physics of Complex Fluids, Faculty of Science and Technology, IMPACT and MESA+ Institute, University
Electrowetting based microliter drop tensiometer Arun G. Banpurkar* Kevin Nichols and Frieder Mugele Physics of Complex Fluids, Faculty of Science and Technology, IMPACT and MESA+ Institute, University
Wetting of complex functional surfaces
 Wetting of complex functional surfaces Frieder Mugele Physics of Complex Fluids University of Twente Twente 2 Twente University the entrepreneurial university founded in 1961 part of 3TU federation of
Wetting of complex functional surfaces Frieder Mugele Physics of Complex Fluids University of Twente Twente 2 Twente University the entrepreneurial university founded in 1961 part of 3TU federation of
Electrowetting. space and ε l the liquid dielectric constant, Eq. (1) can be written as. γ = ε 0ε l 2d V2. (2)
 600 Electrowetting and hence a reduced flow rate in the pressure-drop direction. This reduced flow rate seems to suggest that the liquid have an apparent higher viscosity. The apparent viscosity is called
600 Electrowetting and hence a reduced flow rate in the pressure-drop direction. This reduced flow rate seems to suggest that the liquid have an apparent higher viscosity. The apparent viscosity is called
Analysis and Measurement of Forces in an Electrowetting-Driven Oscillator
 Mater. es. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 15 8 Materials esearch Society 15-DD8-1 Analysis and Measurement of Forces in an Electrowetting-Driven Oscillator Nathan Brad Crane 1, Alex A Volinsky 1, Vivek amadoss
Mater. es. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 15 8 Materials esearch Society 15-DD8-1 Analysis and Measurement of Forces in an Electrowetting-Driven Oscillator Nathan Brad Crane 1, Alex A Volinsky 1, Vivek amadoss
Electrowetting on dielectrics on lubricating fluid based slippery surfaces with negligible hysteresis
 Electrowetting on dielectrics on lubricating fluid based slippery surfaces with negligible hysteresis J. Barman a, A. K. Nagarajan b and K. Khare a* a Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology
Electrowetting on dielectrics on lubricating fluid based slippery surfaces with negligible hysteresis J. Barman a, A. K. Nagarajan b and K. Khare a* a Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology
Dielectrowetting: Statics and Dynamics
 Dielectrowetting: Statics and Dynamics Glen McHale University of Northumbria Carl V. Brown, Nottingham Trent University Naresh Sampara, Gary G. Wells, Michael I. Newton 8 th Intl. Electrowetting Workshop,
Dielectrowetting: Statics and Dynamics Glen McHale University of Northumbria Carl V. Brown, Nottingham Trent University Naresh Sampara, Gary G. Wells, Michael I. Newton 8 th Intl. Electrowetting Workshop,
Frieder Mugele. Physics of Complex Fluids. University of Twente. Jacco Snoeier Physics of Fluids / UT
 coorganizers: Frieder Mugele Physics of Comple Fluids Jacco Snoeier Physics of Fluids / UT University of Twente Anton Darhuber Mesoscopic Transport Phenomena / Tu/e speakers: José Bico (ESPCI Paris) Daniel
coorganizers: Frieder Mugele Physics of Comple Fluids Jacco Snoeier Physics of Fluids / UT University of Twente Anton Darhuber Mesoscopic Transport Phenomena / Tu/e speakers: José Bico (ESPCI Paris) Daniel
Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow
 MT-0.6081 Microfluidics and BioMEMS Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow 28.1.2017 Ville Jokinen Surface tension & Surface energy Work required to create new surface = surface
MT-0.6081 Microfluidics and BioMEMS Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow 28.1.2017 Ville Jokinen Surface tension & Surface energy Work required to create new surface = surface
Resonant Oscillations of Liquid Marbles
 Resonant Oscillations of Liquid Marbles Glen McHale*, Stephen J. Elliott*, Michael I. Newton*, Dale L. Herbertson* and Kadir Esmer $ *School of Science & Technology, Nottingham Trent University, UK $ Department
Resonant Oscillations of Liquid Marbles Glen McHale*, Stephen J. Elliott*, Michael I. Newton*, Dale L. Herbertson* and Kadir Esmer $ *School of Science & Technology, Nottingham Trent University, UK $ Department
Contact angle saturation in electrowetting: Injection of ions into the surrounding media
 December 215 EPL, 112 (215) 561 doi: 1.129/295-575/112/561 www.epljournal.org Contact angle saturation in electrowetting: Injection of ions into the surrounding media Tetsuya Yamamoto 1,2,MasaoDoi 1 and
December 215 EPL, 112 (215) 561 doi: 1.129/295-575/112/561 www.epljournal.org Contact angle saturation in electrowetting: Injection of ions into the surrounding media Tetsuya Yamamoto 1,2,MasaoDoi 1 and
T. B. Jones / University of Rochester 1
 1 T. B. Jones / University of Rochester 1 Electromechanical interpretation of electrowetting & relationship to liquid dielectrophoresis 18 July 2007 T. B. Jones University of Rochester Rochester, NY (USA)
1 T. B. Jones / University of Rochester 1 Electromechanical interpretation of electrowetting & relationship to liquid dielectrophoresis 18 July 2007 T. B. Jones University of Rochester Rochester, NY (USA)
Fundamentals of Droplet Flow in Microfluidics. R.B. Fair Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Duke University Durham, N.C.
 Fundamentals of Droplet Flow in Microfluidics R.B. Fair Computer Engineering Duke University Durham, N.C., USA Outline of Presentation Review of droplet actuation mechanisms Thermocapillarity SAW Electrostatic
Fundamentals of Droplet Flow in Microfluidics R.B. Fair Computer Engineering Duke University Durham, N.C., USA Outline of Presentation Review of droplet actuation mechanisms Thermocapillarity SAW Electrostatic
ON-CHIP DOUBLE EMULSION DROPLET ASSEMBLY USING ELECTROWETTING-ON-DIELECTRIC AND DIELECTROPHORESIS
 ON-CHIP DOUBLE EMULSION DROPLET ASSEMBLY USING ELECTROWETTING-ON-DIELECTRIC AND DIELECTROPHORESIS W. WANG, a T. B. JONES, a * and D. R. HARDING b a University of Rochester, Department of Electrical and
ON-CHIP DOUBLE EMULSION DROPLET ASSEMBLY USING ELECTROWETTING-ON-DIELECTRIC AND DIELECTROPHORESIS W. WANG, a T. B. JONES, a * and D. R. HARDING b a University of Rochester, Department of Electrical and
Effects and applications of surface tension for fluidic MEMS components
 Effects and applications of surface tension for fluidic MEMS components Ryan T. Marinis and Ryszard J. Pryputniewicz NEST NanoEngineering, Science and Technology CHSLT Center for Holographic Studies and
Effects and applications of surface tension for fluidic MEMS components Ryan T. Marinis and Ryszard J. Pryputniewicz NEST NanoEngineering, Science and Technology CHSLT Center for Holographic Studies and
How Electrostatic Fields Change Contact Angle in Electrowetting
 038 Langmuir 2002, 8, 038-0322 How Electrostatic Fields Change Contact Angle in Electrowetting Kwan Hyoung Kang* Department of Mechanical Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology, San 3,
038 Langmuir 2002, 8, 038-0322 How Electrostatic Fields Change Contact Angle in Electrowetting Kwan Hyoung Kang* Department of Mechanical Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology, San 3,
Smart lens: tunable liquid lens for laser tracking
 Smart lens: tunable liquid lens for laser tracking Fan-Yi Lin a, Li-Yu Chu b, Yu-Shan Juan a, Sih-Ting Pan b, Shih-Kang Fan* b a Institute of Photonics Technologies, Department of Electrical Engineering,
Smart lens: tunable liquid lens for laser tracking Fan-Yi Lin a, Li-Yu Chu b, Yu-Shan Juan a, Sih-Ting Pan b, Shih-Kang Fan* b a Institute of Photonics Technologies, Department of Electrical Engineering,
Liquid lens based on electrowetting: a new adaptive component for imaging applications in consumer electronics
 Liquid lens based on electrowetting: a new adaptive component for imaging applications in consumer electronics Jerome CRASSOUS **, Claude GABAY **, Gaetan LIOGIER *, Bruno BERGE *,** * Varioptic, 8B rue
Liquid lens based on electrowetting: a new adaptive component for imaging applications in consumer electronics Jerome CRASSOUS **, Claude GABAY **, Gaetan LIOGIER *, Bruno BERGE *,** * Varioptic, 8B rue
Electrowetting on a semiconductor
 Electrowetting on a semiconductor Steve Arscott (a) and Matthieu Gaudet Institut d Electronique, de Microélectronique et de Nanotechnologie (IEMN), CNRS UMR8520, The University of Lille, Cité Scientifique,
Electrowetting on a semiconductor Steve Arscott (a) and Matthieu Gaudet Institut d Electronique, de Microélectronique et de Nanotechnologie (IEMN), CNRS UMR8520, The University of Lille, Cité Scientifique,
STATIC AND SPONTANEOUS ELECTROWETTING
 Brief Review Modern Physics Letters B, Vol. 19, No. 12 (2005) 549 569 c World Scientific Publishing Company STATIC AND SPONTANEOUS ELECTROWETTING LESLIE Y. YEO and HSUEH-CHIA CHANG Department of Chemical
Brief Review Modern Physics Letters B, Vol. 19, No. 12 (2005) 549 569 c World Scientific Publishing Company STATIC AND SPONTANEOUS ELECTROWETTING LESLIE Y. YEO and HSUEH-CHIA CHANG Department of Chemical
emulsions, and foams March 21 22, 2009
 Wetting and adhesion Dispersions in liquids: suspensions, emulsions, and foams ACS National Meeting March 21 22, 2009 Salt Lake City Ian Morrison 2009 Ian Morrison 2009 Lecure 2 - Wetting and adhesion
Wetting and adhesion Dispersions in liquids: suspensions, emulsions, and foams ACS National Meeting March 21 22, 2009 Salt Lake City Ian Morrison 2009 Ian Morrison 2009 Lecure 2 - Wetting and adhesion
Lecture 7 Contact angle phenomena and wetting
 Lecture 7 Contact angle phenomena and Contact angle phenomena and wetting Young s equation Drop on the surface complete spreading Establishing finite contact angle γ cosθ = γ γ L S SL γ S γ > 0 partial
Lecture 7 Contact angle phenomena and Contact angle phenomena and wetting Young s equation Drop on the surface complete spreading Establishing finite contact angle γ cosθ = γ γ L S SL γ S γ > 0 partial
Electrocoalescence a multi-disiplinary arena
 Electrocoalescence a multi-disiplinary arena Electrical Engineering SINTEF Chemistry ELECTRO- COALESCENCE Physics NTNU CNRS Fluid Dynamics 1 Electrocoalescence project Need for smaller working equipment
Electrocoalescence a multi-disiplinary arena Electrical Engineering SINTEF Chemistry ELECTRO- COALESCENCE Physics NTNU CNRS Fluid Dynamics 1 Electrocoalescence project Need for smaller working equipment
Surface and Interfacial Tensions. Lecture 1
 Surface and Interfacial Tensions Lecture 1 Surface tension is a pull Surfaces and Interfaces 1 Thermodynamics for Interfacial Systems Work must be done to increase surface area just as work must be done
Surface and Interfacial Tensions Lecture 1 Surface tension is a pull Surfaces and Interfaces 1 Thermodynamics for Interfacial Systems Work must be done to increase surface area just as work must be done
Droplet-based DEP microfluidics - High speed liquid actuation on planar substrates and factors influencing picolitre droplet formation
 Droplet-based DEP microfluidics - High speed liquid actuation on planar substrates and factors influencing picolitre droplet formation Thirukumaran T.K., Thomas B. Jones *, Karan V.I.S. Kaler Department
Droplet-based DEP microfluidics - High speed liquid actuation on planar substrates and factors influencing picolitre droplet formation Thirukumaran T.K., Thomas B. Jones *, Karan V.I.S. Kaler Department
Experimental Validation of the Invariance of Electrowetting Contact Angle Saturation
 J. Adhesion Sci. Technol. (2011) DOI:10.1163/156856111X599580 brill.nl/jast Experimental Validation of the Invariance of Electrowetting Contact Angle Saturation Stéphanie Chevalliot a,b, Stein Kuiper c
J. Adhesion Sci. Technol. (2011) DOI:10.1163/156856111X599580 brill.nl/jast Experimental Validation of the Invariance of Electrowetting Contact Angle Saturation Stéphanie Chevalliot a,b, Stein Kuiper c
Equilibrium behavior of sessile drops under surface tension, applied external fields, and material variations
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 93, NUMBER 9 1 MAY 2003 Equilibrium behavior of sessile drops under surface tension, applied external fields, and material variations Benjamin Shapiro a) Aerospace Engineering
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 93, NUMBER 9 1 MAY 2003 Equilibrium behavior of sessile drops under surface tension, applied external fields, and material variations Benjamin Shapiro a) Aerospace Engineering
A phase field model for the coupling between Navier-Stokes and e
 A phase field model for the coupling between Navier-Stokes and electrokinetic equations Instituto de Matemáticas, CSIC Collaborators: C. Eck, G. Grün, F. Klingbeil (Erlangen Univertsität), O. Vantzos (Bonn)
A phase field model for the coupling between Navier-Stokes and electrokinetic equations Instituto de Matemáticas, CSIC Collaborators: C. Eck, G. Grün, F. Klingbeil (Erlangen Univertsität), O. Vantzos (Bonn)
Introduction to Micro/Nanofluidics. Date: 2015/03/13. Dr. Yi-Chung Tung. Outline
 Introduction to Micro/Nanofluidics Date: 2015/03/13 Dr. Yi-Chung Tung Outline Introduction to Microfluidics Basic Fluid Mechanics Concepts Equivalent Fluidic Circuit Model Conclusion What is Microfluidics
Introduction to Micro/Nanofluidics Date: 2015/03/13 Dr. Yi-Chung Tung Outline Introduction to Microfluidics Basic Fluid Mechanics Concepts Equivalent Fluidic Circuit Model Conclusion What is Microfluidics
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/10/e1600964/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Constructing 3D heterogeneous hydrogels from electrically manipulated prepolymer droplets and crosslinked microgels
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/10/e1600964/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Constructing 3D heterogeneous hydrogels from electrically manipulated prepolymer droplets and crosslinked microgels
University of Central Florida. Roxana Shabani University of Central Florida. Doctoral Dissertation (Open Access) Electronic Theses and Dissertations
 University of Central Florida Electronic Theses and Dissertations Doctoral Dissertation (Open Access) Three-phase Contact Line Phenomena In Droplets On Solid And Liquid Surfaces: Electrocapillary, Pinning,
University of Central Florida Electronic Theses and Dissertations Doctoral Dissertation (Open Access) Three-phase Contact Line Phenomena In Droplets On Solid And Liquid Surfaces: Electrocapillary, Pinning,
Frequency-Dependent Electromechanics of Aqueous Liquids: Electrowetting and Dielectrophoresis
 Langmuir 2004, 20, 2813-2818 2813 Frequency-Dependent Electromechanics of Aqueous Liquids: Electrowetting and Dielectrophoresis T. B. Jones* and K.-L. Wang Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering,
Langmuir 2004, 20, 2813-2818 2813 Frequency-Dependent Electromechanics of Aqueous Liquids: Electrowetting and Dielectrophoresis T. B. Jones* and K.-L. Wang Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering,
Characterization of electrowetting systems for microfluidic applications
 University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2009 Characterization of electrowetting systems for microfluidic applications Pradeep K. Mishra University
University of South Florida Scholar Commons Graduate Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2009 Characterization of electrowetting systems for microfluidic applications Pradeep K. Mishra University
Instabilities in the Flow of Thin Liquid Films
 Instabilities in the Flow of Thin Liquid Films Lou Kondic Department of Mathematical Sciences Center for Applied Mathematics and Statistics New Jersey Institute of Technology Presented at Annual Meeting
Instabilities in the Flow of Thin Liquid Films Lou Kondic Department of Mathematical Sciences Center for Applied Mathematics and Statistics New Jersey Institute of Technology Presented at Annual Meeting
films in low voltage electrowetting
 Superior performance of multilayered fluoropolymer films in low voltage electrowetting Dimitrios P. Papageorgiou 1, Angeliki Tserepi 2, Andreas G. Boudouvis 1, Athanasios G. Papathanasiou 1* 1 School of
Superior performance of multilayered fluoropolymer films in low voltage electrowetting Dimitrios P. Papageorgiou 1, Angeliki Tserepi 2, Andreas G. Boudouvis 1, Athanasios G. Papathanasiou 1* 1 School of
Forces and movement of small water droplets in oil due to applied electric field
 Nordic Insulation Symposium Tampere, June 3, 23 Forces and movement of small water droplets in oil due to applied electric field A. Pedersen E. Ildstad A. Nysveen Norwegian University of Norwegian University
Nordic Insulation Symposium Tampere, June 3, 23 Forces and movement of small water droplets in oil due to applied electric field A. Pedersen E. Ildstad A. Nysveen Norwegian University of Norwegian University
Numerical Modeling of 3D Electrowetting Droplet Actuation and Cooling of a Hotspot
 Numerical Modeling of 3D Electrowetting Droplet Actuation and Cooling of a Hotspot Mun Mun Nahar, Govindraj Shreyas Bindiganavale, Jagath Nikapitiya and Hyejin Moon University of Texas at Arlington 10/20/2015
Numerical Modeling of 3D Electrowetting Droplet Actuation and Cooling of a Hotspot Mun Mun Nahar, Govindraj Shreyas Bindiganavale, Jagath Nikapitiya and Hyejin Moon University of Texas at Arlington 10/20/2015
An OpenFOAM-based electro-hydrodynamical model
 An OpenFOAM-based electro-hydrodynamical model Ivo Roghair, Dirk van den Ende, Frieder Mugele Department of Science and Technology, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands Keywords: modelling,
An OpenFOAM-based electro-hydrodynamical model Ivo Roghair, Dirk van den Ende, Frieder Mugele Department of Science and Technology, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands Keywords: modelling,
Electrokinetic assembly and manipulation II Lecture by Chung, Jae-Hyun
 Electrokinetic assembly and manipulation II Lecture by Chung, Jae-Hyun Chung, Jae-Hyun, Mechanical Engineering, University of Washington Liu, Wing Kam, Mechanical Engineering, Northwestern University Liu,
Electrokinetic assembly and manipulation II Lecture by Chung, Jae-Hyun Chung, Jae-Hyun, Mechanical Engineering, University of Washington Liu, Wing Kam, Mechanical Engineering, Northwestern University Liu,
Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS
 Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS dynamics dynamics freezing dynamics freezing microscopics of capillarity Menu 1. surface tension: thermodynamics & microscopics 2. wetting (statics): thermodynamics & microscopics
Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS dynamics dynamics freezing dynamics freezing microscopics of capillarity Menu 1. surface tension: thermodynamics & microscopics 2. wetting (statics): thermodynamics & microscopics
Low Voltage Reversible Electrowetting Exploiting Lubricated Polymer. Honeycomb Substrates. Published: Applied Physics Letters 104 (2014)
 Low Voltage Reversible Electrowetting Exploiting Lubricated Polymer Honeycomb Substrates Published: Applied Physics Letters 104 (2014) 171601. Edward Bormashenko 1, Roman Pogreb, Yelena Bormashenko 1,
Low Voltage Reversible Electrowetting Exploiting Lubricated Polymer Honeycomb Substrates Published: Applied Physics Letters 104 (2014) 171601. Edward Bormashenko 1, Roman Pogreb, Yelena Bormashenko 1,
WELL-DESIGNED MEMS devices take advantage of the
 986 JOURNAL OF MICROELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEMS, VOL. 15, NO. 4, AUGUST 2006 Modeling the Fluid Dynamics of Electrowetting on Dielectric (EWOD) Shawn W. Walker and Benjamin Shapiro, Member, IEEE Abstract
986 JOURNAL OF MICROELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEMS, VOL. 15, NO. 4, AUGUST 2006 Modeling the Fluid Dynamics of Electrowetting on Dielectric (EWOD) Shawn W. Walker and Benjamin Shapiro, Member, IEEE Abstract
Experimental Studies of Liquid Marbles and Superhydrophobic Surfaces
 Experimental Studies of Liquid Marbles and Superhydrophobic Surfaces Stephen James Elliott A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements of Nottingham Trent University for the degree of
Experimental Studies of Liquid Marbles and Superhydrophobic Surfaces Stephen James Elliott A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements of Nottingham Trent University for the degree of
Contents. 2. Fluids. 1. Introduction
 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Fluids 3. Physics of Microfluidic Systems 4. Microfabrication Technologies 5. Flow Control 6. Micropumps 7. Sensors 8. Ink-Jet Technology 9. Liquid Handling 10.Microarrays 11.Microreactors
Contents 1. Introduction 2. Fluids 3. Physics of Microfluidic Systems 4. Microfabrication Technologies 5. Flow Control 6. Micropumps 7. Sensors 8. Ink-Jet Technology 9. Liquid Handling 10.Microarrays 11.Microreactors
Capillary force actuation
 J. Micro-Nano Mech. 9 5:57 68 DOI.7/s3-9-3-4 RESEARCH PAPER Capillary force actuation Carl R. Knospe & Seyed Ali Nezamoddini Received: 3 June 9 / Accepted: 4 December 9 / Published online: 6 January #
J. Micro-Nano Mech. 9 5:57 68 DOI.7/s3-9-3-4 RESEARCH PAPER Capillary force actuation Carl R. Knospe & Seyed Ali Nezamoddini Received: 3 June 9 / Accepted: 4 December 9 / Published online: 6 January #
Dr. Todd Satogata (ODU/Jefferson Lab) Wednesday, February
 University Physics 227N/232N Capacitors, Field Energy, Current and Ohm s Law Lab deferred to Fri Feb 28 QUIZ this Friday! (Feb 21) Fred lectures Monday! (Feb 24) Dr. Todd Satogata (ODU/Jefferson Lab) satogata@jlab.org
University Physics 227N/232N Capacitors, Field Energy, Current and Ohm s Law Lab deferred to Fri Feb 28 QUIZ this Friday! (Feb 21) Fred lectures Monday! (Feb 24) Dr. Todd Satogata (ODU/Jefferson Lab) satogata@jlab.org
Changes of polymer material wettability by surface discharge
 Changes of polymer material wettability by surface discharge Surface discharge and material treatment Surface treatment of materials in low temperature plasma belongs to the modern and very perspective
Changes of polymer material wettability by surface discharge Surface discharge and material treatment Surface treatment of materials in low temperature plasma belongs to the modern and very perspective
Non-Faradaic Impedance Characterization of an
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Non-Faradaic Impedance Characterization of an Evaporating Droplet
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Non-Faradaic Impedance Characterization of an Evaporating Droplet
The Shape of a Rain Drop as determined from the Navier-Stokes equation John Caleb Speirs Classical Mechanics PHGN 505 December 12th, 2011
 The Shape of a Rain Drop as determined from the Navier-Stokes equation John Caleb Speirs Classical Mechanics PHGN 505 December 12th, 2011 Derivation of Navier-Stokes Equation 1 The total stress tensor
The Shape of a Rain Drop as determined from the Navier-Stokes equation John Caleb Speirs Classical Mechanics PHGN 505 December 12th, 2011 Derivation of Navier-Stokes Equation 1 The total stress tensor
dewetting driving forces dewetting mechanism? dewetting dynamics? final equilibrium state: drops with θ = θ Y
 dewetting initial state: continuous film of partially wetting liquid final equilibrium state: drops wit θ = θ Y driving forces dewetting mecanism? dewetting dynamics? 1 free energy vs. film tickness water
dewetting initial state: continuous film of partially wetting liquid final equilibrium state: drops wit θ = θ Y driving forces dewetting mecanism? dewetting dynamics? 1 free energy vs. film tickness water
Four-phase merging in sessile compound drops
 J. Fluid Mech. (00), vol. 45, pp. 4 40. c 00 Cambridge University Press DOI: 0.07/S000000708 Printed in the United Kingdom 4 Four-phase merging in sessile compound drops By L. M A H A D E V A N, M. A D
J. Fluid Mech. (00), vol. 45, pp. 4 40. c 00 Cambridge University Press DOI: 0.07/S000000708 Printed in the United Kingdom 4 Four-phase merging in sessile compound drops By L. M A H A D E V A N, M. A D
JOURNAL OF MICROELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEMS 1
 JOURNAL OF MICROELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEMS 1 Interrogation of Droplet Configuration During Electrowetting via Impedance Spectroscopy Xiaoyu Hu, Marcel Mibus, Giovanni Zangari, Carl Knospe, Senior Member,
JOURNAL OF MICROELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEMS 1 Interrogation of Droplet Configuration During Electrowetting via Impedance Spectroscopy Xiaoyu Hu, Marcel Mibus, Giovanni Zangari, Carl Knospe, Senior Member,
Experimental and Theoretical Study of Motion of Drops on Horizontal Solid Surfaces with a Wettability Gradient Nadjoua Moumen
 Experimental and Theoretical Study of Motion of Drops on Horizontal Solid Surfaces with a Wettability Gradient Nadjoua Moumen Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkson University Outline
Experimental and Theoretical Study of Motion of Drops on Horizontal Solid Surfaces with a Wettability Gradient Nadjoua Moumen Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkson University Outline
Single cell impedance spectroscopy label free analysis of cells
 Single cell impedance spectroscopy label free analysis of cells The Coulter counter Each cell that passes through the aperture reduces the current gives a spike. Cell behaves like an insulating sphere.
Single cell impedance spectroscopy label free analysis of cells The Coulter counter Each cell that passes through the aperture reduces the current gives a spike. Cell behaves like an insulating sphere.
Dynamiczna kontrola separacji ładunków elektrostatycznych w układach miękkiej materii
 Dynamiczna kontrola separacji ładunków elektrostatycznych w układach miękkiej materii Tomasz Szymborski, Natalia Ziębacz, Piotr Korczyk, Jan Tobiś, Olgierd Cybulski, Stefan Wieczorek, Andrzej Żywocioski,
Dynamiczna kontrola separacji ładunków elektrostatycznych w układach miękkiej materii Tomasz Szymborski, Natalia Ziębacz, Piotr Korczyk, Jan Tobiś, Olgierd Cybulski, Stefan Wieczorek, Andrzej Żywocioski,
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa.
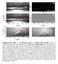 Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
The evaporation of sessile droplets onto solid surfaces : experiments and simulations of the contact line pinning-depinning
 The evaporation of sessile droplets onto solid surfaces : experiments and simulations of the contact line pinning-depinning L.Kabeya-Mukeba, N.Vandewalle and S.Dorbolo GRASP, Institut de Physique B5a,
The evaporation of sessile droplets onto solid surfaces : experiments and simulations of the contact line pinning-depinning L.Kabeya-Mukeba, N.Vandewalle and S.Dorbolo GRASP, Institut de Physique B5a,
Thin Solid Films. Reliable and low-voltage electrowetting on thin parylene films. Manjeet Dhindsa a,b,1, Stein Kuiper b,2, Jason Heikenfeld a,
 Thin Solid Films 519 (2011) 3346 3351 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Thin Solid Films journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/tsf Reliable and low-voltage electrowetting on thin parylene films
Thin Solid Films 519 (2011) 3346 3351 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Thin Solid Films journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/tsf Reliable and low-voltage electrowetting on thin parylene films
High-Mobility n-channel Organic Field Effect Transistors based on Epitaxially Grown C 60 Films
 High-Mobility n-channel Organic Field Effect Transistors based on Epitaxially Grown C 60 Films Th. B. Singh, N. Marjanović, G. J. Matt, S. Günes and N. S. Sariciftci Linz Institute for Organic Solar Cells
High-Mobility n-channel Organic Field Effect Transistors based on Epitaxially Grown C 60 Films Th. B. Singh, N. Marjanović, G. J. Matt, S. Günes and N. S. Sariciftci Linz Institute for Organic Solar Cells
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 4 May 2018
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 4 May 2018 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.soft] 4 May 2018](/thumbs/78/77865312.jpg) Solvation effects and contact angle saturation in electrowetting Nicolas Rivas 1, and Jens Harting 1,2 1 Helmholtz Institute Erlangen-Nürnberg for Renewable Energy (IEK-11), Forschungszentrum Jülich, Fürther
Solvation effects and contact angle saturation in electrowetting Nicolas Rivas 1, and Jens Harting 1,2 1 Helmholtz Institute Erlangen-Nürnberg for Renewable Energy (IEK-11), Forschungszentrum Jülich, Fürther
Fast Biofluid Transport of High Conductive Liquids Using AC Electrothermal Phenomenon, A Study on Substrate Characteristics
 Fast Biofluid Transport of High Conductive Liquids Using AC Electrothermal Phenomenon, A Study on Substrate Characteristics A. Salari, C. Dalton Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University
Fast Biofluid Transport of High Conductive Liquids Using AC Electrothermal Phenomenon, A Study on Substrate Characteristics A. Salari, C. Dalton Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University
contact line dynamics
 contact line dynamics Jacco Snoeijer Physics of Fluids - University of Twente sliding drops flow near contact line static contact line Ingbrigtsen & Toxvaerd (2007) γ γ sv θ e γ sl molecular scales macroscopic
contact line dynamics Jacco Snoeijer Physics of Fluids - University of Twente sliding drops flow near contact line static contact line Ingbrigtsen & Toxvaerd (2007) γ γ sv θ e γ sl molecular scales macroscopic
Absorption of gas by a falling liquid film
 Absorption of gas by a falling liquid film Christoph Albert Dieter Bothe Mathematical Modeling and Analysis Center of Smart Interfaces/ IRTG 1529 Darmstadt University of Technology 4th Japanese-German
Absorption of gas by a falling liquid film Christoph Albert Dieter Bothe Mathematical Modeling and Analysis Center of Smart Interfaces/ IRTG 1529 Darmstadt University of Technology 4th Japanese-German
The Wilhelmy balance. How can we measure surface tension? Surface tension, contact angles and wettability. Measuring surface tension.
 ow can we measure surface tension? Surface tension, contact angles and wettability www.wikihow.com/measure-surface-tension Measuring surface tension The Wilhelmy balance F Some methods: Wilhelmy plate
ow can we measure surface tension? Surface tension, contact angles and wettability www.wikihow.com/measure-surface-tension Measuring surface tension The Wilhelmy balance F Some methods: Wilhelmy plate
Electrohydromechanical analysis based on conductivity gradient in microchannel
 Vol 17 No 12, December 2008 c 2008 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1674-1056/2008/17(12)/4541-06 Chinese Physics B and IOP Publishing Ltd Electrohydromechanical analysis based on conductivity gradient in microchannel
Vol 17 No 12, December 2008 c 2008 Chin. Phys. Soc. 1674-1056/2008/17(12)/4541-06 Chinese Physics B and IOP Publishing Ltd Electrohydromechanical analysis based on conductivity gradient in microchannel
Unique Fluid Ensemble including Silicone Oil for the Application Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2008, Vol. 29, No Articles
 Unique Fluid Ensemble including Silicone Oil for the Application Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2008, Vol. 29, No. 4 731 Articles Unique Fluid Ensemble including Silicone Oil for the Application of Optical Liquid
Unique Fluid Ensemble including Silicone Oil for the Application Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2008, Vol. 29, No. 4 731 Articles Unique Fluid Ensemble including Silicone Oil for the Application of Optical Liquid
Outline. 4 Mechanical Sensors Introduction General Mechanical properties Piezoresistivity Piezoresistive Sensors Capacitive sensors Applications
 Sensor devices Outline 4 Mechanical Sensors Introduction General Mechanical properties Piezoresistivity Piezoresistive Sensors Capacitive sensors Applications Introduction Two Major classes of mechanical
Sensor devices Outline 4 Mechanical Sensors Introduction General Mechanical properties Piezoresistivity Piezoresistive Sensors Capacitive sensors Applications Introduction Two Major classes of mechanical
Simulation of Evaporating Droplets on AFM-Cantilevers
 Simulation of Evaporating Droplets on AFM-Cantilevers Thomas Haschke 1, Daniel Lautenschlager 1, Wolfgang Wiechert 1, Elmar Bonaccurso 2, Hans- Jürgen Butt 2 1 University of Siegen, Faculty 11, Department
Simulation of Evaporating Droplets on AFM-Cantilevers Thomas Haschke 1, Daniel Lautenschlager 1, Wolfgang Wiechert 1, Elmar Bonaccurso 2, Hans- Jürgen Butt 2 1 University of Siegen, Faculty 11, Department
MPIKG Public Access Author Manuscript
 MPIKG Public Access Author Manuscript Max Planck Institute of of Colloids and Interfaces Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Stocco, A., & Möhwald, H. (2015). The influence of long-range
MPIKG Public Access Author Manuscript Max Planck Institute of of Colloids and Interfaces Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Stocco, A., & Möhwald, H. (2015). The influence of long-range
Modeling the combined effect of surface roughness and shear rate on slip flow of simple fluids
 Modeling the combined effect of surface roughness and shear rate on slip flow of simple fluids Anoosheh Niavarani and Nikolai Priezjev www.egr.msu.edu/~niavaran November 2009 A. Niavarani and N.V. Priezjev,
Modeling the combined effect of surface roughness and shear rate on slip flow of simple fluids Anoosheh Niavarani and Nikolai Priezjev www.egr.msu.edu/~niavaran November 2009 A. Niavarani and N.V. Priezjev,
8.2 Surface phenomenon of liquid. Out-class reading: Levine p Curved interfaces
 Out-class reading: Levine p. 387-390 13.2 Curved interfaces https://news.cnblogs.com/n/559867/ 8.2.1 Some interesting phenomena 8.2.1 Some interesting phenomena Provided by Prof. Yu-Peng GUO of Jilin
Out-class reading: Levine p. 387-390 13.2 Curved interfaces https://news.cnblogs.com/n/559867/ 8.2.1 Some interesting phenomena 8.2.1 Some interesting phenomena Provided by Prof. Yu-Peng GUO of Jilin
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DIT UNIVERSITY HIGH VOLTAGE ENGINEERING
 UNIT 1: BREAKDOWN IN SOLIDS 1.) Introduction: The solid dielectric materials are used in all kinds of electrical apparatus and devices to insulate current carrying part from another when they operate at
UNIT 1: BREAKDOWN IN SOLIDS 1.) Introduction: The solid dielectric materials are used in all kinds of electrical apparatus and devices to insulate current carrying part from another when they operate at
ESS 5855 Surface Engineering for. MicroElectroMechanicalechanical Systems. Fall 2010
 ESS 5855 Surface Engineering for Microelectromechanical Systems Fall 2010 MicroElectroMechanicalechanical Systems Miniaturized systems with integrated electrical and mechanical components for actuation
ESS 5855 Surface Engineering for Microelectromechanical Systems Fall 2010 MicroElectroMechanicalechanical Systems Miniaturized systems with integrated electrical and mechanical components for actuation
Numerical simulation for a droplet fission process of electrowetting on dielectric device
 Numerical simulation for a droplet fission process of electrowetting on dielectric device Dongdong He a, Huaxiong Huang b,, Yongji Tan a a Department of Mathematical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai,
Numerical simulation for a droplet fission process of electrowetting on dielectric device Dongdong He a, Huaxiong Huang b,, Yongji Tan a a Department of Mathematical Sciences, Fudan University, Shanghai,
Laplace Barriers for Electrowetting Thresholding and Virtual Fluid Confinement
 pubs.acs.org/langmuir XXXX American Chemical Society Laplace Barriers for Electrowetting Thresholding and Virtual Fluid Confinement E. Kreit, M. Dhindsa, S. Yang, M. Hagedon, K. Zhou, I. Papautsky, and
pubs.acs.org/langmuir XXXX American Chemical Society Laplace Barriers for Electrowetting Thresholding and Virtual Fluid Confinement E. Kreit, M. Dhindsa, S. Yang, M. Hagedon, K. Zhou, I. Papautsky, and
Supplementary table I. Table of contact angles of the different solutions on the surfaces used here. Supplementary Notes
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Sketch of the experimental setup (not to scale) : it consists of a thin mylar sheet (0, 02 4 3cm 3 ) held fixed vertically. The spacing y 0 between the glass plate and the upper
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Sketch of the experimental setup (not to scale) : it consists of a thin mylar sheet (0, 02 4 3cm 3 ) held fixed vertically. The spacing y 0 between the glass plate and the upper
Derivation of continuum models for the moving contact line problem based on thermodynamic principles. Abstract
 Derivation of continuum models for the moving contact line problem based on thermodynamic principles Weiqing Ren Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, New York, NY 002, USA Weinan
Derivation of continuum models for the moving contact line problem based on thermodynamic principles Weiqing Ren Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, New York, NY 002, USA Weinan
Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces.
 Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces. Levente Novák & István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://kolloid.unideb.hu/~kolloid/
Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces. Levente Novák & István Bányai, University of Debrecen Dept of Colloid and Environmental Chemistry http://kolloid.unideb.hu/~kolloid/
PRINCIPLES OF PLASMA DISCHARGES AND MATERIALS PROCESSING
 PRINCIPLES OF PLASMA DISCHARGES AND MATERIALS PROCESSING Second Edition MICHAEL A. LIEBERMAN ALLAN J, LICHTENBERG WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC PUBLICATION CONTENTS PREFACE xrrii PREFACE
PRINCIPLES OF PLASMA DISCHARGES AND MATERIALS PROCESSING Second Edition MICHAEL A. LIEBERMAN ALLAN J, LICHTENBERG WILEY- INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC PUBLICATION CONTENTS PREFACE xrrii PREFACE
ECE185 LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAYS
 ECE185 LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAYS Objective: To study characteristics of liquid crystal modulators and to construct a simple liquid crystal modulator in lab and measure its characteristics. References: B.
ECE185 LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAYS Objective: To study characteristics of liquid crystal modulators and to construct a simple liquid crystal modulator in lab and measure its characteristics. References: B.
Lab 1: Numerical Solution of Laplace s Equation
 Lab 1: Numerical Solution of Laplace s Equation ELEC 3105 last modified August 27, 2012 1 Before You Start This lab and all relevant files can be found at the course website. You will need to obtain an
Lab 1: Numerical Solution of Laplace s Equation ELEC 3105 last modified August 27, 2012 1 Before You Start This lab and all relevant files can be found at the course website. You will need to obtain an
ENERGY HARVESTING TRANSDUCERS - ELECTROSTATIC (ICT-ENERGY SUMMER SCHOOL 2016)
 ENERGY HARVESTING TRANSDUCERS - ELECTROSTATIC (ICT-ENERGY SUMMER SCHOOL 2016) Shad Roundy, PhD Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Utah shad.roundy@utah.edu Three Types of Electromechanical
ENERGY HARVESTING TRANSDUCERS - ELECTROSTATIC (ICT-ENERGY SUMMER SCHOOL 2016) Shad Roundy, PhD Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Utah shad.roundy@utah.edu Three Types of Electromechanical
Reaction at the Interfaces
 Reaction at the Interfaces Lecture 1 On the course Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces by HansJürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl Wiley VCH; 2nd edition (2006) http://homes.nano.aau.dk/lg/surface2009.htm
Reaction at the Interfaces Lecture 1 On the course Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces by HansJürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl Wiley VCH; 2nd edition (2006) http://homes.nano.aau.dk/lg/surface2009.htm
Bursting Drops in Solids Caused by High Voltages
 Supplementary Information for Bursting Drops in Solids Caused by High Voltages Qiming Wang 1, Zhigang Suo 2 and Xuanhe Zhao 1 * 1 Soft Active Materials Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering
Supplementary Information for Bursting Drops in Solids Caused by High Voltages Qiming Wang 1, Zhigang Suo 2 and Xuanhe Zhao 1 * 1 Soft Active Materials Laboratory, Department of Mechanical Engineering
Modelling and analysis for contact angle hysteresis on rough surfaces
 Modelling and analysis for contact angle hysteresis on rough surfaces Xianmin Xu Institute of Computational Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Collaborators: Xiaoping Wang(HKUST) Workshop on Modeling
Modelling and analysis for contact angle hysteresis on rough surfaces Xianmin Xu Institute of Computational Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Collaborators: Xiaoping Wang(HKUST) Workshop on Modeling
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Dispensing nano-pico droplets and liquid patterning by pyroelectrodynamic shooting P. Ferraro, S. Coppola, S. Grilli, M. Paturzo and V. Vespini Theoretical simulation of temperature
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Dispensing nano-pico droplets and liquid patterning by pyroelectrodynamic shooting P. Ferraro, S. Coppola, S. Grilli, M. Paturzo and V. Vespini Theoretical simulation of temperature
A Simulation Model of Fluid Flow and Streamlines Induced by Non-Uniform Electric Field
 Proceedings of the 4th International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON ), Cairo University, Egypt, December 9-,, Paper ID 8. A Simulation Model of Fluid Flow and Streamlines Induced by Non-Uniform
Proceedings of the 4th International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON ), Cairo University, Egypt, December 9-,, Paper ID 8. A Simulation Model of Fluid Flow and Streamlines Induced by Non-Uniform
Wetting & Adhesion on Soft Surfaces Young s Law is dead long live Young s Law. Eric Dufresne
 Wetting & Adhesion on Soft Surfaces Young s Law is dead long live Young s Law Eric Dufresne KITP 2014 Wetting Adhesion 3mm 30 um Young s Law relates contact line geometry and material properties in equilibrium
Wetting & Adhesion on Soft Surfaces Young s Law is dead long live Young s Law Eric Dufresne KITP 2014 Wetting Adhesion 3mm 30 um Young s Law relates contact line geometry and material properties in equilibrium
Electrowetting: from basics to applications
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICSPUBLISHING J.Phys.: Condens. Matter 17 (2005) R705 R774 JOURNAL OFPHYSICS: CONDENSED MATTER doi:10.1088/0953-8984/17/28/r01 TOPICAL REVIEW Electrowetting: from basics to applications
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICSPUBLISHING J.Phys.: Condens. Matter 17 (2005) R705 R774 JOURNAL OFPHYSICS: CONDENSED MATTER doi:10.1088/0953-8984/17/28/r01 TOPICAL REVIEW Electrowetting: from basics to applications
DLVO interaction between the spheres
 DLVO interaction between the spheres DL-interaction energy for two spheres: D w ( x) 64c π ktrϕ e λ DL 2 x λ 2 0 0 D DLVO interaction w ( x) 64πkTRϕ e λ DLVO AR /12x 2 x λd 2 0 D Lecture 11 Contact angle
DLVO interaction between the spheres DL-interaction energy for two spheres: D w ( x) 64c π ktrϕ e λ DL 2 x λ 2 0 0 D DLVO interaction w ( x) 64πkTRϕ e λ DLVO AR /12x 2 x λd 2 0 D Lecture 11 Contact angle
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF ELECTROWETTING USING ELECTRIC BODY FORCE DENSITY AND SURFACE TENSION
 Tan Il SUNG NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF ELECTROWETTING USING ELECTRIC BODY FORCE DENSITY AND SURFACE TENSION ABSTRACT The electrowetting is a phenomenon in which the shape of a droplet is deformed by external
Tan Il SUNG NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF ELECTROWETTING USING ELECTRIC BODY FORCE DENSITY AND SURFACE TENSION ABSTRACT The electrowetting is a phenomenon in which the shape of a droplet is deformed by external
Wetting and Adhesion: Manipulating Topography and Surface Free Energy
 Wetting and Adhesion: Manipulating Topography and Surface Free Energy Professor Glen McHale School of Science & Technology Abhesion Meeting, Society for Adhesion and Adhesives, London, UK 23 rd April 2009
Wetting and Adhesion: Manipulating Topography and Surface Free Energy Professor Glen McHale School of Science & Technology Abhesion Meeting, Society for Adhesion and Adhesives, London, UK 23 rd April 2009
ALCT Measurement Principles
 Current-based Measurements At a basic electronics level, a liquid crystal sample cell may be modeled as a combination dynamic capacitor and resistor in parallel. As such, the majority of ALCT measurements
Current-based Measurements At a basic electronics level, a liquid crystal sample cell may be modeled as a combination dynamic capacitor and resistor in parallel. As such, the majority of ALCT measurements
J. Bico, C. Tordeux and D. Quéré Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée, URA 792 du CNRS Collège de France Paris Cedex 05, France
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 July 2001 Europhys. Lett., 55 (2), pp. 214 220 (2001) Rough wetting J. Bico, C. Tordeux and D. Quéré Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée, URA 792 du CNRS Collège de France
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 July 2001 Europhys. Lett., 55 (2), pp. 214 220 (2001) Rough wetting J. Bico, C. Tordeux and D. Quéré Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée, URA 792 du CNRS Collège de France
Piezo Theory: Chapter 1 - Physics & Design
 Piezoelectric effect inverse piezoelectric effect The result of external forces to a piezoelectric material is positive and negative electrical charges at the surface of the material. If electrodes are
Piezoelectric effect inverse piezoelectric effect The result of external forces to a piezoelectric material is positive and negative electrical charges at the surface of the material. If electrodes are
Direct Oil Recovery from Saturated Carbon Nanotube Sponges
 Supporting Information Direct Oil Recovery from Saturated Carbon Nanotube Sponges Xiying Li 1, Yahui Xue 1, Mingchu Zou 2, Dongxiao Zhang 3, Anyuan Cao 2,* 1, 4,*, and Huiling Duan 1 State Key Laboratory
Supporting Information Direct Oil Recovery from Saturated Carbon Nanotube Sponges Xiying Li 1, Yahui Xue 1, Mingchu Zou 2, Dongxiao Zhang 3, Anyuan Cao 2,* 1, 4,*, and Huiling Duan 1 State Key Laboratory
Supplementary Information on Thermally Enhanced Self-Propelled Droplet Motion on Gradient Surfaces
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information on Thermally Enhanced Self-Propelled Droplet Motion on Gradient Surfaces
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information on Thermally Enhanced Self-Propelled Droplet Motion on Gradient Surfaces
Capacitance. PHY2049: Chapter 25 1
 apacitance PHY049: hapter 5 1 oulomb s law Electric fields Equilibrium Gauss law What You Know: Electric Fields Electric fields for several charge configurations Point Dipole (along axes) Line Plane (nonconducting)
apacitance PHY049: hapter 5 1 oulomb s law Electric fields Equilibrium Gauss law What You Know: Electric Fields Electric fields for several charge configurations Point Dipole (along axes) Line Plane (nonconducting)
Particle-stabilized foams
 Particle-stabilized foams Brent S. Murray, Bernie P. Binks*, Eric Dickinson, Zhiping Du, Rammile Ettelaie & Thomas Kostakis Food Colloids Group Procter Department of Food Science, University of Leeds,
Particle-stabilized foams Brent S. Murray, Bernie P. Binks*, Eric Dickinson, Zhiping Du, Rammile Ettelaie & Thomas Kostakis Food Colloids Group Procter Department of Food Science, University of Leeds,
Electrowetting with Contact Line Pinning: Computational Modeling and Comparisons with Experiments
 APS/123-QED Electrowetting with Contact Line Pinning: Computational Modeling and Comparisons with Experiments Shawn W. Walker New York University, Department of Mathematics, Courant Institute Benjamin
APS/123-QED Electrowetting with Contact Line Pinning: Computational Modeling and Comparisons with Experiments Shawn W. Walker New York University, Department of Mathematics, Courant Institute Benjamin
Formation of Droplets and Bubbles in a Microfluidic T-junction. Scaling and Mechanism of Break-Up. Supplementary Information
 Formation of Droplets and Bubbles in a Microfluidic T-junction Scaling and Mechanism of Break-Up Supplementary Information Piotr Garstecki 1,2 *, Michael J. Fuerstman 1, Howard A. Stone 3 and George M.
Formation of Droplets and Bubbles in a Microfluidic T-junction Scaling and Mechanism of Break-Up Supplementary Information Piotr Garstecki 1,2 *, Michael J. Fuerstman 1, Howard A. Stone 3 and George M.
