dewetting driving forces dewetting mechanism? dewetting dynamics? final equilibrium state: drops with θ = θ Y
|
|
|
- Corey Harper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 dewetting initial state: continuous film of partially wetting liquid final equilibrium state: drops wit θ = θ Y driving forces dewetting mecanism? dewetting dynamics? 1
2 free energy vs. film tickness water drop on teflon: q Y =10 water film wit tickness small volume: equilibrium configuration = drop wit c.a. q Y if is not too large large volume: equilibrium configuration = tick film stability analysis: film is always stable against perturbations wat is te critical volume (tickness) below wic te film is unstable? ow do unstable films break up?
3 global stability F flat film: 1 Ffilm ( ) = σ sl + σ lv + ρ g A film dry surface: F dry = σ sv A dry eq energy of film + dry patc: F( A dry ) 1 = σ sl + σ lv + ρ g Afilm + σ sv Adry! = min 3 partial wetting: S = σ sv sl lv ( σ + σ ) < = σ lv (cosθy 1) 0 Afilm + Adry = A = const. V = A0 = Afilm = const. = λ (1 cosθ ) = λ sin eq. c Y c Y eigt of a liquid pancake θ /
4 global stability (II) metastable films globally stable films F tangent construction! eq 0 > eq : film is globally stable 4 0 < eq : film is globally unstable against breakup but locally stable against small perturbations metastable
5 a practical experiment 5 nucleation barrier >> k B T: create defect to initiate dewetting
6 nucleated dewetting ole nucleation at defect sites (e.g. due to surface rougness, cem. eterogeneity, ) random distribution of ole locations and time of appearance 6
7 a second dewetting scenario polystyrene films on Si eterogeneous nucleation spinodal dewetting oles appear at random locations and at random times oles appear at regular distances and at te same time allmarks of a linear instability 7 Seemann et al. Pys. Rev. Lett. 001
8 wetting and long-range forces disjoining pressure and effective interface potential (II) r i >> r i : F = σ + σ sl = O(r i ) : F = F( ) = σ + σ + Φ( ) lv sl lv Φ () : effective interface potential 8
9 properties of F() Φ( ) = F( ) ( σ sl + σ lv ) : = 0 : Φ 0 Φ = σ sv ( σ lv + σ sl ) = S O(F) = O(σ) [ mj/m (typical organic liquids)] Φ() : interaction energy / unit area of adjacent interfaces dφ d = Π() force / unit area between interfaces: disjoining pressure example: van der Waals interaction Φ( ) = A 1π A: Hamaker constant A=f(n v,n l,n s,ε v,ε l,ε s ) O(A)=10-0 J (.4k B RT) 9
10 contributions to disjoining pressure van der Waals interaction Φ( ) = A/1π electrostatic interaction ( double layer forces ) structural solvation forces ydrogen bonding forces sort-range cemical forces 10
11 F and macroscopic wetting F long range wetting partial wetting omogeneous film drop + dry substrate pseudo-partial wetting drop + tin film 0 S = σ 1 cosθ lv ( Y ) θ tin film comment on stability: unstable vs stable 11
12 stability of tin wetting films tin film equation: t = 1 3µ d dx 3 ( P) x 3 0 = xx P 3µ small perturbation: ( x, t) = 0 + δ( t) cos qx δ << 0 local pressure: P( x, t) = σ xx + dφ d ( x) dφ d ( x) Φ' ( 0 ) + Φ''( 0 ) δ δ& 3 t) = 3µ ( σ q + Φ' '( )) δ( ) ( 0 q t 0 F > 0: film locally stable for all q F < 0: film locally stable for large q but unstable for small q 1
13 stability of tin wetting films (II) critical wavevector: q c = Φ' '( 0 ) /σ fastest growing mode: maximum of prefactor q * = qc / caracteristic growt time: van der Waals: τ 5 * 0 1µ 3 σ τ* = 4 0q c tin films wit an initial tickness, for wic F <0 are linearly unstable 13
14 interface potential & stability F always stable 0 S = σ 1 cosθ lv ( Y ) unstable 14
15 example of a complex interfacial potential Φ( ) = c 8 8 A air PS SiO 1π 1 1 ( + d) A 1π ( + d) air PS Si sort range cemical force vdw: air-liq.-si vdw: air-liq.-sio air polystyrene SiO Si layered substrates: SiO:Si 15 Seemann et al. J. Pys. Cond. Matt. 13, 495 (001)
16 various dewetting scenarios Seemann, Jacobs, Hermingaus 16
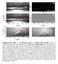
17 dewetting dynamics PDMS (30 µm) on fluorinated Si 17 Redon et al. Pys. Rev. Lett. 1991
18 dewetting dynamics observations: -excess material collects in rim - constant dewetting velocity v - dewetting velocity v ~ q 3 Y 18 Redon et al. Pys. Rev. Lett. 1991
19 model 0 R(t) w(t) B q D < q Y assumptions: - 0 <<w<<r; θ <<1 -rim profile is circular and symmetric -rim volume: V rim = π R 0 A dynamics: 3µ V θ D ln balance of viscous dissipation & imbalanced Young force w a = ( v) dxdz = σ (cosθ cosθ V D = µ ) z Y D σ = V ( θ Y θ D ) σ point A & B: VA = θd ( θy θ ) D 6µ l A V B σ σ 3 = θd (0 θ ) = θ D D 6µ l 6µ l B B 19 θy V A = V B : θ D = = const. V=const. ~θ 3 Y 1+ l / l A B
Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS
 Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS dynamics dynamics freezing dynamics freezing microscopics of capillarity Menu 1. surface tension: thermodynamics & microscopics 2. wetting (statics): thermodynamics & microscopics
Jacco Snoeijer PHYSICS OF FLUIDS dynamics dynamics freezing dynamics freezing microscopics of capillarity Menu 1. surface tension: thermodynamics & microscopics 2. wetting (statics): thermodynamics & microscopics
Lecture 7 Contact angle phenomena and wetting
 Lecture 7 Contact angle phenomena and Contact angle phenomena and wetting Young s equation Drop on the surface complete spreading Establishing finite contact angle γ cosθ = γ γ L S SL γ S γ > 0 partial
Lecture 7 Contact angle phenomena and Contact angle phenomena and wetting Young s equation Drop on the surface complete spreading Establishing finite contact angle γ cosθ = γ γ L S SL γ S γ > 0 partial
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Supplementary Figure 1 Extracting process of wetting ridge profiles. a1-4, An extraction example of a ridge profile for E 16 kpa. An original image (a1) was binarized, as shown in a2, by Canny edge detector
Module 3: "Thin Film Hydrodynamics" Lecture 12: "" The Lecture Contains: Linear Stability Analysis. Some well known instabilities. Objectives_template
 The Lecture Contains: Linear Stability Analysis Some well known instabilities file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture12/12_1.htm[6/16/2012 1:39:16 PM] Linear Stability Analysis This analysis
The Lecture Contains: Linear Stability Analysis Some well known instabilities file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture12/12_1.htm[6/16/2012 1:39:16 PM] Linear Stability Analysis This analysis
DLVO interaction between the spheres
 DLVO interaction between the spheres DL-interaction energy for two spheres: D w ( x) 64c π ktrϕ e λ DL 2 x λ 2 0 0 D DLVO interaction w ( x) 64πkTRϕ e λ DLVO AR /12x 2 x λd 2 0 D Lecture 11 Contact angle
DLVO interaction between the spheres DL-interaction energy for two spheres: D w ( x) 64c π ktrϕ e λ DL 2 x λ 2 0 0 D DLVO interaction w ( x) 64πkTRϕ e λ DLVO AR /12x 2 x λd 2 0 D Lecture 11 Contact angle
contact line dynamics
 contact line dynamics Jacco Snoeijer Physics of Fluids - University of Twente sliding drops flow near contact line static contact line Ingbrigtsen & Toxvaerd (2007) γ γ sv θ e γ sl molecular scales macroscopic
contact line dynamics Jacco Snoeijer Physics of Fluids - University of Twente sliding drops flow near contact line static contact line Ingbrigtsen & Toxvaerd (2007) γ γ sv θ e γ sl molecular scales macroscopic
On the breakup of fluid films of finite and infinite extent
 PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 19, 072107 2007 On the breakup of fluid films of finite and infinite extent Javier A. Diez a Instituto de Física Arroyo Seco, Universidad Nacional del Centro de la Provincia de Buenos
PHYSICS OF FLUIDS 19, 072107 2007 On the breakup of fluid films of finite and infinite extent Javier A. Diez a Instituto de Física Arroyo Seco, Universidad Nacional del Centro de la Provincia de Buenos
Module17: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles. Lecture 23: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles
 Module17: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles Lecture 23: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles 1 We now try to understand the nature of spontaneous instability in a confined
Module17: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles Lecture 23: Intermolecular Force between Surfaces and Particles 1 We now try to understand the nature of spontaneous instability in a confined
Interfaces and interfacial energy
 Interfaces and interfacial energy 1/14 kinds: l/g }{{ l/l } mobile s/g s/l s/s Example. Estimate the percetage of water molecules on the surface of a fog droplet of diameter (i) 0.1 mm (naked eye visibility
Interfaces and interfacial energy 1/14 kinds: l/g }{{ l/l } mobile s/g s/l s/s Example. Estimate the percetage of water molecules on the surface of a fog droplet of diameter (i) 0.1 mm (naked eye visibility
Instability and Patterning of Thin Polymer Films Prof. R. Mukherjee Department Of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Kharagpur
 Instability and Patterning of Thin Polymer Films Prof. R. Mukherjee Department Of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 36 Spontaneous Instability & Dewetting of
Instability and Patterning of Thin Polymer Films Prof. R. Mukherjee Department Of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 36 Spontaneous Instability & Dewetting of
On the Breakup of Patterned Nanoscale Copper. Rings into Nanoparticles: Competing Instability and. Transport Mechanisms
 On the Breakup of Patterned Nanoscale Copper Rings into Nanoparticles: Competing Instability and Transport Mechanisms Yueying Wu, Jason D. Fowlkes, Philip D. Rack,, Javier A. Diez, and Lou Kondic Department
On the Breakup of Patterned Nanoscale Copper Rings into Nanoparticles: Competing Instability and Transport Mechanisms Yueying Wu, Jason D. Fowlkes, Philip D. Rack,, Javier A. Diez, and Lou Kondic Department
Spinodal Dewetting of Thin Films with Large Interfacial Slip: Implications from the Dispersion Relation
 12290 Langmuir 2008, 24, 12290-12294 Spinodal Dewetting of Thin Films with Large Interfacial Slip: Implications from the Dispersion Relation Markus Rauscher,*,, Ralf Blossey, Andreas Münch, and Barbara
12290 Langmuir 2008, 24, 12290-12294 Spinodal Dewetting of Thin Films with Large Interfacial Slip: Implications from the Dispersion Relation Markus Rauscher,*,, Ralf Blossey, Andreas Münch, and Barbara
Surface and Interfacial Tensions. Lecture 1
 Surface and Interfacial Tensions Lecture 1 Surface tension is a pull Surfaces and Interfaces 1 Thermodynamics for Interfacial Systems Work must be done to increase surface area just as work must be done
Surface and Interfacial Tensions Lecture 1 Surface tension is a pull Surfaces and Interfaces 1 Thermodynamics for Interfacial Systems Work must be done to increase surface area just as work must be done
Dynamics and structure formation in thin polymer melt films
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICSPUBLISHING J.Phys.: Condens. Matter 17 (2005) S267 S290 JOURNAL OFPHYSICS: CONDENSED MATTER doi:10.1088/0953-8984/17/9/001 Dynamics and structure formation in thin polymer melt films
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICSPUBLISHING J.Phys.: Condens. Matter 17 (2005) S267 S290 JOURNAL OFPHYSICS: CONDENSED MATTER doi:10.1088/0953-8984/17/9/001 Dynamics and structure formation in thin polymer melt films
Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context
 Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context Top-down method Bottom-up method Classical lithography techniques Fast processes Size limitations it ti E-beam techniques Small sizes Slow processes
Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context Top-down method Bottom-up method Classical lithography techniques Fast processes Size limitations it ti E-beam techniques Small sizes Slow processes
VIII. Phase Transformations. Lecture 38: Nucleation and Spinodal Decomposition
 VIII. Phase Transformations Lecture 38: Nucleation and Spinodal Decomposition MIT Student In this lecture we will study the onset of phase transformation for phases that differ only in their equilibrium
VIII. Phase Transformations Lecture 38: Nucleation and Spinodal Decomposition MIT Student In this lecture we will study the onset of phase transformation for phases that differ only in their equilibrium
emulsions, and foams March 21 22, 2009
 Wetting and adhesion Dispersions in liquids: suspensions, emulsions, and foams ACS National Meeting March 21 22, 2009 Salt Lake City Ian Morrison 2009 Ian Morrison 2009 Lecure 2 - Wetting and adhesion
Wetting and adhesion Dispersions in liquids: suspensions, emulsions, and foams ACS National Meeting March 21 22, 2009 Salt Lake City Ian Morrison 2009 Ian Morrison 2009 Lecure 2 - Wetting and adhesion
Frieder Mugele. Physics of Complex Fluids. University of Twente. Jacco Snoeier Physics of Fluids / UT
 coorganizers: Frieder Mugele Physics of Comple Fluids Jacco Snoeier Physics of Fluids / UT University of Twente Anton Darhuber Mesoscopic Transport Phenomena / Tu/e speakers: José Bico (ESPCI Paris) Daniel
coorganizers: Frieder Mugele Physics of Comple Fluids Jacco Snoeier Physics of Fluids / UT University of Twente Anton Darhuber Mesoscopic Transport Phenomena / Tu/e speakers: José Bico (ESPCI Paris) Daniel
Solutions to the Multivariable Calculus and Linear Algebra problems on the Comprehensive Examination of January 31, 2014
 Solutions to te Multivariable Calculus and Linear Algebra problems on te Compreensive Examination of January 3, 24 Tere are 9 problems ( points eac, totaling 9 points) on tis portion of te examination.
Solutions to te Multivariable Calculus and Linear Algebra problems on te Compreensive Examination of January 3, 24 Tere are 9 problems ( points eac, totaling 9 points) on tis portion of te examination.
drops in motion Frieder Mugele the physics of electrowetting and its applications Physics of Complex Fluids University of Twente
 drops in motion the physics of electrowetting and its applications Frieder Mugele Physics of Complex Fluids niversity of Twente 1 electrowetting: the switch on the wettability voltage outline q q q q q
drops in motion the physics of electrowetting and its applications Frieder Mugele Physics of Complex Fluids niversity of Twente 1 electrowetting: the switch on the wettability voltage outline q q q q q
Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena
 ? Pierre-Gilles de Gennes Frangoise Brochard-Wyart David Quere Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena Drops, Bubbles, Pearls, Waves Translated by Axel Reisinger With 177 Figures Springer Springer New York Berlin
? Pierre-Gilles de Gennes Frangoise Brochard-Wyart David Quere Capillarity and Wetting Phenomena Drops, Bubbles, Pearls, Waves Translated by Axel Reisinger With 177 Figures Springer Springer New York Berlin
Nano-domains formation on photoalignment thin film by self-organized dewetting
 Nano-domains formation on photoalignment thin film by self-organized dewetting Chung-Yung Lee (SID Member) Yuet-Wing Li (SID Member) Man-Chun Tseng (SID Student Member) Vladimir G. Chigrinov (SID Fellow)
Nano-domains formation on photoalignment thin film by self-organized dewetting Chung-Yung Lee (SID Member) Yuet-Wing Li (SID Member) Man-Chun Tseng (SID Student Member) Vladimir G. Chigrinov (SID Fellow)
Instabilities in Thin Polymer Films: From Pattern Formation to Rupture
 Instabilities in Thin Polymer Films: From Pattern Formation to Rupture John R. Dutcher*, Kari Dalnoki-Veress Η, Bernie G. Nickel and Connie B. Roth Department of Physics, University of Guelph, Guelph,
Instabilities in Thin Polymer Films: From Pattern Formation to Rupture John R. Dutcher*, Kari Dalnoki-Veress Η, Bernie G. Nickel and Connie B. Roth Department of Physics, University of Guelph, Guelph,
Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces
 Hans Jürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces Second, Revised and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XI 1 Introduction
Hans Jürgen Butt, Karlheinz Graf, and Michael Kappl Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces Second, Revised and Enlarged Edition WILEY- VCH WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XI 1 Introduction
VAN DER WAALS AND STRUCTURAL FORCES: STABILITY OF THIN LIQUID-CRYSTALLINE FILMS. Andreja [arlah 1
 VAN DER WAALS AND STRUCTURAL FORCES: STABILITY OF THIN LIQUID-CRYSTALLINE FILMS Andreja [arlah 1 Primo` Ziherl, 2,3 and Slobodan @umer 1,3 1. Department of Physics, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics,
VAN DER WAALS AND STRUCTURAL FORCES: STABILITY OF THIN LIQUID-CRYSTALLINE FILMS Andreja [arlah 1 Primo` Ziherl, 2,3 and Slobodan @umer 1,3 1. Department of Physics, Faculty of Mathematics and Physics,
Module 3: "Thin Film Hydrodynamics" Lecture 11: "" The Lecture Contains: Micro and Nano Scale Hydrodynamics with and without Free Surfaces
 The Lecture Contains: Micro and Nano Scale Hydrodynamics with and without Free Surfaces Order of Magnitude Analysis file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture11/11_1.htm[6/16/2012 1:39:56 PM]
The Lecture Contains: Micro and Nano Scale Hydrodynamics with and without Free Surfaces Order of Magnitude Analysis file:///e /courses/colloid_interface_science/lecture11/11_1.htm[6/16/2012 1:39:56 PM]
Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow
 MT-0.6081 Microfluidics and BioMEMS Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow 28.1.2017 Ville Jokinen Surface tension & Surface energy Work required to create new surface = surface
MT-0.6081 Microfluidics and BioMEMS Microfluidics 2 Surface tension, contact angle, capillary flow 28.1.2017 Ville Jokinen Surface tension & Surface energy Work required to create new surface = surface
Early stages of dewetting of microscopically thin polymer films: A molecular dynamics study
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 109, NUMBER 19 15 NOVEMBER 1998 Early stages of dewetting of microscopically thin polymer films: A molecular dynamics study Hong Liu Department of Physics, Kansas State
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 109, NUMBER 19 15 NOVEMBER 1998 Early stages of dewetting of microscopically thin polymer films: A molecular dynamics study Hong Liu Department of Physics, Kansas State
Solid-State Dewetting: From Flat to Curved Substrates
 Solid-State Dewetting: From Flat to Curved Substrates Yan Wang with Prof. Weizhu Bao, Prof. David J. Srolovitz, Prof. Wei Jiang and Dr. Quan Zhao IMS, 2 May, 2018 Wang Yan (CSRC) Solid-State Dewetting
Solid-State Dewetting: From Flat to Curved Substrates Yan Wang with Prof. Weizhu Bao, Prof. David J. Srolovitz, Prof. Wei Jiang and Dr. Quan Zhao IMS, 2 May, 2018 Wang Yan (CSRC) Solid-State Dewetting
THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL E. Modelling thin-film dewetting on structured substrates and templates: Bifurcation analysis and numerical simulations
 ur. Pys. J., 7 (3) DOI./epje/i3-9- TH UROPAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL Modelling tin-film dewetting on structured substrates and templates: Bifurcation analysis and numerical simulations U. Tiele,a,L.Brusc,M.Besteorn,andM.Bär
ur. Pys. J., 7 (3) DOI./epje/i3-9- TH UROPAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL Modelling tin-film dewetting on structured substrates and templates: Bifurcation analysis and numerical simulations U. Tiele,a,L.Brusc,M.Besteorn,andM.Bär
THE MODIFIED YOUNG S EQUATION FOR THE CONTACT ANGLE OF A SMALL SESSILE DROP FROM AN INTERFACE DISPLACEMENT MODEL
 International Journal of Modern Physics B, Vol. 13, No. 7 (1999) 355 359 c World Scientific Publishing Company THE MODIFIED YOUNG S EQUATION FOR THE CONTACT ANGLE OF A SMALL SESSILE DROP FROM AN INTERFACE
International Journal of Modern Physics B, Vol. 13, No. 7 (1999) 355 359 c World Scientific Publishing Company THE MODIFIED YOUNG S EQUATION FOR THE CONTACT ANGLE OF A SMALL SESSILE DROP FROM AN INTERFACE
Phase Equilibria and Molecular Solutions Jan G. Korvink and Evgenii Rudnyi IMTEK Albert Ludwig University Freiburg, Germany
 Phase Equilibria and Molecular Solutions Jan G. Korvink and Evgenii Rudnyi IMTEK Albert Ludwig University Freiburg, Germany Preliminaries Learning Goals Phase Equilibria Phase diagrams and classical thermodynamics
Phase Equilibria and Molecular Solutions Jan G. Korvink and Evgenii Rudnyi IMTEK Albert Ludwig University Freiburg, Germany Preliminaries Learning Goals Phase Equilibria Phase diagrams and classical thermodynamics
J. Bico, C. Tordeux and D. Quéré Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée, URA 792 du CNRS Collège de France Paris Cedex 05, France
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 July 2001 Europhys. Lett., 55 (2), pp. 214 220 (2001) Rough wetting J. Bico, C. Tordeux and D. Quéré Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée, URA 792 du CNRS Collège de France
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS 15 July 2001 Europhys. Lett., 55 (2), pp. 214 220 (2001) Rough wetting J. Bico, C. Tordeux and D. Quéré Laboratoire de Physique de la Matière Condensée, URA 792 du CNRS Collège de France
Chapter 2. Block copolymers. a b c
 Chapter 2 Block copolymers In this thesis, the lamellar orientation in thin films of a symmetric diblock copolymer polystyrene-polymethylmethacylate P(S-b-MMA) under competing effects of surface interactions
Chapter 2 Block copolymers In this thesis, the lamellar orientation in thin films of a symmetric diblock copolymer polystyrene-polymethylmethacylate P(S-b-MMA) under competing effects of surface interactions
On the importance of nucleation solutions for the rupture of thin liquid films
 Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 206 (2002) 135 155 www.elsevier.com/locate/colsurfa On the importance of nucleation solutions for the rupture of thin liquid films Uwe Thiele
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 206 (2002) 135 155 www.elsevier.com/locate/colsurfa On the importance of nucleation solutions for the rupture of thin liquid films Uwe Thiele
Lecture 7: quick review
 Lecture 7: quick review We discussed the meaning of the critical r* and ΔG*: since it s unstable, if we can form a drop with r > r*, the system will keep going falling down the energy curve, trying to
Lecture 7: quick review We discussed the meaning of the critical r* and ΔG*: since it s unstable, if we can form a drop with r > r*, the system will keep going falling down the energy curve, trying to
Coarsening: transient and self-similar dynamics in 1-D
 Coarsening: transient and self-similar dynamics in 1-D ½ 1 5 1 4 h ln(t) Ú ¼º N 1 3 N t 2/5 1 2 1 5 1 15 x ¼ 1 ¼ ¼º ½ 1 1 4 1 8 1 12 1 16 Ü t Michael Gratton (Northwestern) and Thomas Witelsi (Due) Cahn-Hilliard
Coarsening: transient and self-similar dynamics in 1-D ½ 1 5 1 4 h ln(t) Ú ¼º N 1 3 N t 2/5 1 2 1 5 1 15 x ¼ 1 ¼ ¼º ½ 1 1 4 1 8 1 12 1 16 Ü t Michael Gratton (Northwestern) and Thomas Witelsi (Due) Cahn-Hilliard
Dewetting of polymer films by ion implantation
 Eur. Phys. J. E 28, 273 278 (2009) DOI 10.1140/epje/i2008-10430-4 Regular Article THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL E Dewetting of polymer films by ion implantation Z.J. Han a and B.K. Tay Nanoelectronics
Eur. Phys. J. E 28, 273 278 (2009) DOI 10.1140/epje/i2008-10430-4 Regular Article THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL E Dewetting of polymer films by ion implantation Z.J. Han a and B.K. Tay Nanoelectronics
3.10. Capillary Condensation and Adsorption Hysteresis
 3.10. Capillary Condensation and Adsorption Hysteresis We shall restrict our attention to the adsorption behavior of porous solids. Hysteresis: two quantities of adsorbed material for each equilibrium
3.10. Capillary Condensation and Adsorption Hysteresis We shall restrict our attention to the adsorption behavior of porous solids. Hysteresis: two quantities of adsorbed material for each equilibrium
Dewetting of Thin Viscoelastic Polymer Films on Slippery Substrates
 Dewetting of Thin Viscoelastic Polymer Films on Slippery Substrates Elie Raphael, Thomas Vilmin To cite this version: Elie Raphael, Thomas Vilmin. Dewetting of Thin Viscoelastic Polymer Films on Slippery
Dewetting of Thin Viscoelastic Polymer Films on Slippery Substrates Elie Raphael, Thomas Vilmin To cite this version: Elie Raphael, Thomas Vilmin. Dewetting of Thin Viscoelastic Polymer Films on Slippery
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Micro and nano-textured boiling surfaces. (a) A schematic of the textured boiling surfaces. (b) An isometric view of the square array of square micropillars.
Supplementary Figures 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Micro and nano-textured boiling surfaces. (a) A schematic of the textured boiling surfaces. (b) An isometric view of the square array of square micropillars.
Contact Angle Hysteresis on a Heterogeneous Surface: Solution in the Limit of a Weakly Distorted Contact Line.
 EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 28 (6), pp. 415-420 (1994) 20 November 1994 Contact Angle Hysteresis on a Heterogeneous Surface: Solution in the Limit of a Weakly Distorted Contact Line. J. CRASSOUS
EUROPHYSICS LETTERS Europhys. Lett., 28 (6), pp. 415-420 (1994) 20 November 1994 Contact Angle Hysteresis on a Heterogeneous Surface: Solution in the Limit of a Weakly Distorted Contact Line. J. CRASSOUS
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 S1 Transition from WZ to ZB by addition of Zinc. By p-doping with zinc, the WZ fraction in the wires changes dramatically at a partial pressure of DEZn around 4.610-5 mbar. At high dopant levels fewer
S1 Transition from WZ to ZB by addition of Zinc. By p-doping with zinc, the WZ fraction in the wires changes dramatically at a partial pressure of DEZn around 4.610-5 mbar. At high dopant levels fewer
Ultrathin liquid films under alternating intermolecular potential fields and capillary force
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 117, NUMBER 13 1 OCTOBER 2002 Ultrathin liquid films under alternating intermolecular potential fields and capillary force Kahp Y. Suh and Hong H. Lee a) School of Chemical
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 117, NUMBER 13 1 OCTOBER 2002 Ultrathin liquid films under alternating intermolecular potential fields and capillary force Kahp Y. Suh and Hong H. Lee a) School of Chemical
Contents. Preface XI Symbols and Abbreviations XIII. 1 Introduction 1
 V Contents Preface XI Symbols and Abbreviations XIII 1 Introduction 1 2 Van der Waals Forces 5 2.1 Van der Waals Forces Between Molecules 5 2.1.1 Coulomb Interaction 5 2.1.2 Monopole Dipole Interaction
V Contents Preface XI Symbols and Abbreviations XIII 1 Introduction 1 2 Van der Waals Forces 5 2.1 Van der Waals Forces Between Molecules 5 2.1.1 Coulomb Interaction 5 2.1.2 Monopole Dipole Interaction
Sliding drops on an inclined plane
 Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 206 (2002) 87 104 www.elsevier.com/locate/colsurfa Sliding drops on an inclined plane Uwe Thiele a, *, Kai Neuffer a,b, Michael Bestehorn
Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 206 (2002) 87 104 www.elsevier.com/locate/colsurfa Sliding drops on an inclined plane Uwe Thiele a, *, Kai Neuffer a,b, Michael Bestehorn
PH 222-3A Spring 2007
 PH -3A Spring 7 ELECTRIC FIELDS Lectures,3 Chapter (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter Electric Fields In this chapter we will introduce the concept of an electric
PH -3A Spring 7 ELECTRIC FIELDS Lectures,3 Chapter (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter Electric Fields In this chapter we will introduce the concept of an electric
Section A 01. (12 M) (s 2 s 3 ) = 313 s 2 = s 1, h 3 = h 4 (s 1 s 3 ) = kj/kgk. = kj/kgk. 313 (s 3 s 4f ) = ln
 0. (a) Sol: Section A A refrigerator macine uses R- as te working fluid. Te temperature of R- in te evaporator coil is 5C, and te gas leaves te compressor as dry saturated at a temperature of 40C. Te mean
0. (a) Sol: Section A A refrigerator macine uses R- as te working fluid. Te temperature of R- in te evaporator coil is 5C, and te gas leaves te compressor as dry saturated at a temperature of 40C. Te mean
Film rupture in the diffuse interface model coupled to hydrodynamics
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E, VOLUME 64, 031602 Film rupture in the diffuse interface model coupled to hydrodynamics Uwe Thiele and Manuel G. Velarde Instituto Pluridisciplinar, Universidad Complutense, Paseo Juan
PHYSICAL REVIEW E, VOLUME 64, 031602 Film rupture in the diffuse interface model coupled to hydrodynamics Uwe Thiele and Manuel G. Velarde Instituto Pluridisciplinar, Universidad Complutense, Paseo Juan
INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES
 INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES SECOND EDITION JACOB N. ISRAELACHVILI Department of Chemical & Nuclear Engineering and Materials Department University of California, Santa Barbara California, USA ACADEMIC
INTERMOLECULAR AND SURFACE FORCES SECOND EDITION JACOB N. ISRAELACHVILI Department of Chemical & Nuclear Engineering and Materials Department University of California, Santa Barbara California, USA ACADEMIC
Supratelechelics: thermoreversible bonding in difunctional polymer blends
 Supratelechelics: thermoreversible bonding in difunctional polymer blends Richard Elliott Won Bo Lee Glenn Fredrickson Complex Fluids Design Consortium Annual Meeting MRL, UCSB 02/02/09 Supramolecular
Supratelechelics: thermoreversible bonding in difunctional polymer blends Richard Elliott Won Bo Lee Glenn Fredrickson Complex Fluids Design Consortium Annual Meeting MRL, UCSB 02/02/09 Supramolecular
of Nebraska - Lincoln
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Xiao Cheng Zeng Publications Published Research - Department of Chemistry 10-1-2006 Homogeneous nucleation at high supersaturation
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Xiao Cheng Zeng Publications Published Research - Department of Chemistry 10-1-2006 Homogeneous nucleation at high supersaturation
Solvability condition for the moving contact line
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 78, 564 28 Solvability condition for the moving contact line L. M. Pismen 1 and Jens Eggers 2 1 Department of Chemical Engineering and Minerva Center for Nonlinear Physics of Complex
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 78, 564 28 Solvability condition for the moving contact line L. M. Pismen 1 and Jens Eggers 2 1 Department of Chemical Engineering and Minerva Center for Nonlinear Physics of Complex
MPIKG Public Access Author Manuscript
 MPIKG Public Access Author Manuscript Max Planck Institute of of Colloids and Interfaces Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Stocco, A., & Möhwald, H. (2015). The influence of long-range
MPIKG Public Access Author Manuscript Max Planck Institute of of Colloids and Interfaces Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Stocco, A., & Möhwald, H. (2015). The influence of long-range
Modelling and analysis for contact angle hysteresis on rough surfaces
 Modelling and analysis for contact angle hysteresis on rough surfaces Xianmin Xu Institute of Computational Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Collaborators: Xiaoping Wang(HKUST) Workshop on Modeling
Modelling and analysis for contact angle hysteresis on rough surfaces Xianmin Xu Institute of Computational Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Collaborators: Xiaoping Wang(HKUST) Workshop on Modeling
Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces. Levente Novák István Bányai
 Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces. Levente Novák István Bányai Surfaces and Interfaces Defining of interfacial region Types of interfaces: surface vs interface Surface
Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces. Levente Novák István Bányai Surfaces and Interfaces Defining of interfacial region Types of interfaces: surface vs interface Surface
Exam in Fluid Mechanics SG2214
 Exam in Fluid Mecanics G2214 Final exam for te course G2214 23/10 2008 Examiner: Anders Dalkild Te point value of eac question is given in parentesis and you need more tan 20 points to pass te course including
Exam in Fluid Mecanics G2214 Final exam for te course G2214 23/10 2008 Examiner: Anders Dalkild Te point value of eac question is given in parentesis and you need more tan 20 points to pass te course including
Instability & Patterning of Thin Polymer Films Prof. R. Mukherjee Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Kharagpur
 Instability & Patterning of Thin Polymer Films Prof. R. Mukherjee Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 33 Spontaneous Instability & Dewetting of Thin
Instability & Patterning of Thin Polymer Films Prof. R. Mukherjee Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute Of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No. # 33 Spontaneous Instability & Dewetting of Thin
Morphological evolution of single-crystal ultrathin solid films
 Western Kentucky University From the SelectedWorks of Mikhail Khenner March 29, 2010 Morphological evolution of single-crystal ultrathin solid films Mikhail Khenner, Western Kentucky University Available
Western Kentucky University From the SelectedWorks of Mikhail Khenner March 29, 2010 Morphological evolution of single-crystal ultrathin solid films Mikhail Khenner, Western Kentucky University Available
arxiv: v2 [physics.flu-dyn] 24 Oct 2013
![arxiv: v2 [physics.flu-dyn] 24 Oct 2013 arxiv: v2 [physics.flu-dyn] 24 Oct 2013](/thumbs/73/68817731.jpg) Supporting Information: Short and long time drop dynamics on lubricated substrates Andreas Carlson1,3,4,, Pilnam Kim2,4, Gustav Amberg3, and Howard A. Stone4, arxiv:1309.6339v2 [physics.flu-dyn] 24 Oct
Supporting Information: Short and long time drop dynamics on lubricated substrates Andreas Carlson1,3,4,, Pilnam Kim2,4, Gustav Amberg3, and Howard A. Stone4, arxiv:1309.6339v2 [physics.flu-dyn] 24 Oct
Thin films in partial wetting: stability, dewetting and coarsening
 Thin films in partial wetting: stability, dewetting and coarsening The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published
Thin films in partial wetting: stability, dewetting and coarsening The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published
SYNTHESIS OF INORGANIC MATERIALS AND NANOMATERIALS. Pr. Charles Kappenstein LACCO, Laboratoire de Catalyse en Chimie Organique, Poitiers, France
 SYNTHESIS OF INORGANIC MATERIALS AND NANOMATERIALS Pr. Charles Kappenstein LACCO, Laboratoire de Catalyse en Chimie Organique, Poitiers, France Outline IV - FORMATION OF SOLIDS FROM SOLUTIONS 1) Glass
SYNTHESIS OF INORGANIC MATERIALS AND NANOMATERIALS Pr. Charles Kappenstein LACCO, Laboratoire de Catalyse en Chimie Organique, Poitiers, France Outline IV - FORMATION OF SOLIDS FROM SOLUTIONS 1) Glass
A shallow water type model to describe the dynamic. of thin partially wetting films
 A shallow water type model to describe the dynamic of thin partially wetting films J. LALLEMENT a, P. VILLEDIEU a, P. TRONTIN a, C. LAURENT a a. Onera - The French Aerospace Lab Toulouse) - ONERA - F-31055
A shallow water type model to describe the dynamic of thin partially wetting films J. LALLEMENT a, P. VILLEDIEU a, P. TRONTIN a, C. LAURENT a a. Onera - The French Aerospace Lab Toulouse) - ONERA - F-31055
Parameter passing between molecular dynamics and continuum models for droplets on solid substrates: The static case
 Parameter passing between molecular dynamics and continuum models for droplets on solid substrates: The static case Nikita Tretyakov, Marcus Müller, Desislava Todorova, and Uwe Thiele Citation: J. Chem.
Parameter passing between molecular dynamics and continuum models for droplets on solid substrates: The static case Nikita Tretyakov, Marcus Müller, Desislava Todorova, and Uwe Thiele Citation: J. Chem.
Lecture 12: Biomaterials Characterization in Aqueous Environments
 3.051J/20.340J 1 Lecture 12: Biomaterials Characterization in Aqueous Environments High vacuum techniques are important tools for characterizing surface composition, but do not yield information on surface
3.051J/20.340J 1 Lecture 12: Biomaterials Characterization in Aqueous Environments High vacuum techniques are important tools for characterizing surface composition, but do not yield information on surface
Prediction of Coating Thickness
 Prediction of Coating Tickness Jon D. Wind Surface Penomena CE 385M 4 May 1 Introduction Tis project involves te modeling of te coating of metal plates wit a viscous liquid by pulling te plate vertically
Prediction of Coating Tickness Jon D. Wind Surface Penomena CE 385M 4 May 1 Introduction Tis project involves te modeling of te coating of metal plates wit a viscous liquid by pulling te plate vertically
Line Tension Effect upon Static Wetting
 Line Tension Effect upon Static Wetting Pierre SEPPECHER Université de Toulon et du Var, BP 132 La Garde Cedex seppecher@univ tln.fr Abstract. Adding simply, in the classical capillary model, a constant
Line Tension Effect upon Static Wetting Pierre SEPPECHER Université de Toulon et du Var, BP 132 La Garde Cedex seppecher@univ tln.fr Abstract. Adding simply, in the classical capillary model, a constant
Effects of Size, Humidity, and Aging on Particle Removal
 LEVITRONIX Ultrapure Fluid Handling and Wafer Cleaning Conference 2009 February 10, 2009 Effects of Size, Humidity, and Aging on Particle Removal Jin-Goo Park Feb. 10, 2009 Department t of Materials Engineering,
LEVITRONIX Ultrapure Fluid Handling and Wafer Cleaning Conference 2009 February 10, 2009 Effects of Size, Humidity, and Aging on Particle Removal Jin-Goo Park Feb. 10, 2009 Department t of Materials Engineering,
A thin-film equation for viscoelastic liquids of Jeffreys type
 Eur. Pys. J. E 7, 373 379 5) DOI.4/epje/i5-6-8 THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL E A tin-film equation for viscoelastic liquids of Jeffreys type M. Rauscer,, A. Münc 3, B. Wagner 4, and R. Blossey 5,a Max-Planck-Institut
Eur. Pys. J. E 7, 373 379 5) DOI.4/epje/i5-6-8 THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL E A tin-film equation for viscoelastic liquids of Jeffreys type M. Rauscer,, A. Münc 3, B. Wagner 4, and R. Blossey 5,a Max-Planck-Institut
spreading of drops on soft surfaces
 Supplementary Material on Electrically modulated dynamic spreading of drops on soft surfaces Ranabir Dey 1, Ashish Daga 1, Sunando DasGupta 2,3, Suman Chakraborty 1,3 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Supplementary Material on Electrically modulated dynamic spreading of drops on soft surfaces Ranabir Dey 1, Ashish Daga 1, Sunando DasGupta 2,3, Suman Chakraborty 1,3 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering,
The Wilhelmy balance. How can we measure surface tension? Surface tension, contact angles and wettability. Measuring surface tension.
 ow can we measure surface tension? Surface tension, contact angles and wettability www.wikihow.com/measure-surface-tension Measuring surface tension The Wilhelmy balance F Some methods: Wilhelmy plate
ow can we measure surface tension? Surface tension, contact angles and wettability www.wikihow.com/measure-surface-tension Measuring surface tension The Wilhelmy balance F Some methods: Wilhelmy plate
hal , version 1-29 Jan 2008
 ENERGY OF INTERACTION BETWEEN SOLID SURFACES AND LIQUIDS Henri GOUIN L. M. M. T. Box 3, University of Aix-Marseille Avenue Escadrille Normandie-Niemen, 3397 Marseille Cedex 0 France E-mail: enri.gouin@univ-cezanne.fr
ENERGY OF INTERACTION BETWEEN SOLID SURFACES AND LIQUIDS Henri GOUIN L. M. M. T. Box 3, University of Aix-Marseille Avenue Escadrille Normandie-Niemen, 3397 Marseille Cedex 0 France E-mail: enri.gouin@univ-cezanne.fr
2. Exploiting wetting phenomena to tailor 1D nano- and microstructures
 2. Exploiting wetting phenomena to tailor 1D nano- and microstructures 2.1 Wetting on a macroscopic scale As a large part of the work in this thesis deals with wetting of porous materials, the phenomena
2. Exploiting wetting phenomena to tailor 1D nano- and microstructures 2.1 Wetting on a macroscopic scale As a large part of the work in this thesis deals with wetting of porous materials, the phenomena
Derivation of continuum models for the moving contact line problem based on thermodynamic principles. Abstract
 Derivation of continuum models for the moving contact line problem based on thermodynamic principles Weiqing Ren Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, New York, NY 002, USA Weinan
Derivation of continuum models for the moving contact line problem based on thermodynamic principles Weiqing Ren Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University, New York, NY 002, USA Weinan
MAY THE FORCE BE WITH YOU, YOUNG JEDIS!!!
 Final Exam Math 222 Spring 2011 May 11, 2011 Name: Recitation Instructor s Initials: You may not use any type of calculator whatsoever. (Cell phones off and away!) You are not allowed to have any other
Final Exam Math 222 Spring 2011 May 11, 2011 Name: Recitation Instructor s Initials: You may not use any type of calculator whatsoever. (Cell phones off and away!) You are not allowed to have any other
Changes of polymer material wettability by surface discharge
 Changes of polymer material wettability by surface discharge Surface discharge and material treatment Surface treatment of materials in low temperature plasma belongs to the modern and very perspective
Changes of polymer material wettability by surface discharge Surface discharge and material treatment Surface treatment of materials in low temperature plasma belongs to the modern and very perspective
Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces. Levente Novák István Bányai Zoltán Nagy Department of Physical Chemistry
 Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces. Levente Novák István Bányai Zoltán Nagy Department of Physical Chemistry Surfaces and Interfaces Defining of interfacial region Types
Surface chemistry. Liquid-gas, solid-gas and solid-liquid surfaces. Levente Novák István Bányai Zoltán Nagy Department of Physical Chemistry Surfaces and Interfaces Defining of interfacial region Types
Experimental and Theoretical Study of Motion of Drops on Horizontal Solid Surfaces with a Wettability Gradient Nadjoua Moumen
 Experimental and Theoretical Study of Motion of Drops on Horizontal Solid Surfaces with a Wettability Gradient Nadjoua Moumen Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkson University Outline
Experimental and Theoretical Study of Motion of Drops on Horizontal Solid Surfaces with a Wettability Gradient Nadjoua Moumen Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkson University Outline
Instability of a transverse liquid rivulet on an inclined plane
 Instability of a transverse liquid rivulet on an inclined plane Javier A. Diez, Alejandro G. González Instituto de Física Arroyo Seco, Universidad Nacional del Centro de la Provincia de Buenos Aires, Pinto
Instability of a transverse liquid rivulet on an inclined plane Javier A. Diez, Alejandro G. González Instituto de Física Arroyo Seco, Universidad Nacional del Centro de la Provincia de Buenos Aires, Pinto
Nonlinear Dynamics of Wrinkle Growth and
 Nonlinear Dynamics of Wrinkle Growth and Pattern Formation in Stressed Elastic Thin Films Se Hyuk Im and Rui Huang Center for Mechanics of Solids, Structures and Materials Department of Aerospace Engineering
Nonlinear Dynamics of Wrinkle Growth and Pattern Formation in Stressed Elastic Thin Films Se Hyuk Im and Rui Huang Center for Mechanics of Solids, Structures and Materials Department of Aerospace Engineering
= h. Geometrically this quantity represents the slope of the secant line connecting the points
 Section 3.7: Rates of Cange in te Natural and Social Sciences Recall: Average rate of cange: y y y ) ) ), ere Geometrically tis quantity represents te slope of te secant line connecting te points, f (
Section 3.7: Rates of Cange in te Natural and Social Sciences Recall: Average rate of cange: y y y ) ) ), ere Geometrically tis quantity represents te slope of te secant line connecting te points, f (
PARTICLE ADHESION AND REMOVAL IN POST-CMP APPLICATIONS
 PARTICLE ADHESION AND REMOVAL IN POST-CMP APPLICATIONS George Adams, Ahmed A. Busnaina and Sinan Muftu the oratory Mechanical, Industrial, and Manufacturing Eng. Department Northeastern University, Boston,
PARTICLE ADHESION AND REMOVAL IN POST-CMP APPLICATIONS George Adams, Ahmed A. Busnaina and Sinan Muftu the oratory Mechanical, Industrial, and Manufacturing Eng. Department Northeastern University, Boston,
Ultrafast water harvesting and transport in hierarchical microchannels
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-018-0171-9 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ultrafast water harvesting and transport in hierarchical microchannels Huawei
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-018-0171-9 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ultrafast water harvesting and transport in hierarchical microchannels Huawei
Surface forces action in a vicinity of three phase contact line and other current problems in kinetics of wetting and spreading
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Surface forces action in a vicinity of three phase contact line and other current problems in kinetics of wetting and spreading This item was submitted
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Surface forces action in a vicinity of three phase contact line and other current problems in kinetics of wetting and spreading This item was submitted
Thermal Bending of Circular Plates for Non-axisymmetrical Problems
 Copyrigt 2 Tec Science Press SL, vol.4, no.2, pp.5-2, 2 Termal Bending of Circular Plates for Non-axisymmetrical Problems Dong Zengzu Peng Weiong and Li Suncai Abstract: Due to te complexity of termal
Copyrigt 2 Tec Science Press SL, vol.4, no.2, pp.5-2, 2 Termal Bending of Circular Plates for Non-axisymmetrical Problems Dong Zengzu Peng Weiong and Li Suncai Abstract: Due to te complexity of termal
Spreading Dynamics of Polydimethylsiloxane Drops: Crossover from Laplace to Van der Waals Spreading
 Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 234, 178 193 (2001) doi:10.1006/jcis.2000.7292, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Spreading Dynamics of Polydimethylsiloxane Drops: Crossover from
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 234, 178 193 (2001) doi:10.1006/jcis.2000.7292, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Spreading Dynamics of Polydimethylsiloxane Drops: Crossover from
Desalination by vacuum membrane distillation: sensitivity analysis
 Separation and Purification Tecnology 33 (2003) 75/87 www.elsevier.com/locate/seppur Desalination by vacuum membrane distillation: sensitivity analysis Fawzi Banat *, Fami Abu Al-Rub, Kalid Bani-Melem
Separation and Purification Tecnology 33 (2003) 75/87 www.elsevier.com/locate/seppur Desalination by vacuum membrane distillation: sensitivity analysis Fawzi Banat *, Fami Abu Al-Rub, Kalid Bani-Melem
*blood and bones contain colloids. *milk is a good example of a colloidal dispersion.
 Chap. 3. Colloids 3.1. Introduction - Simple definition of a colloid: a macroscopically heterogeneous system where one component has dimensions in between molecules and macroscopic particles like sand
Chap. 3. Colloids 3.1. Introduction - Simple definition of a colloid: a macroscopically heterogeneous system where one component has dimensions in between molecules and macroscopic particles like sand
Supplementary table I. Table of contact angles of the different solutions on the surfaces used here. Supplementary Notes
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Sketch of the experimental setup (not to scale) : it consists of a thin mylar sheet (0, 02 4 3cm 3 ) held fixed vertically. The spacing y 0 between the glass plate and the upper
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Sketch of the experimental setup (not to scale) : it consists of a thin mylar sheet (0, 02 4 3cm 3 ) held fixed vertically. The spacing y 0 between the glass plate and the upper
Wetting Transitions at Fluid Interfaces and Related Topics
 Wetting Transitions at Fluid Interfaces and Related Topics Kenichiro Koga Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Okayama University Tsushima-Naka 3-1-1, Okayama 7-853, Japan Received April 3, 21
Wetting Transitions at Fluid Interfaces and Related Topics Kenichiro Koga Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Okayama University Tsushima-Naka 3-1-1, Okayama 7-853, Japan Received April 3, 21
Topography driven spreading. School of Biomedical & Natural Sciences, Nottingham Trent University. Clifton Lane, Nottingham NG11 8NS, UK.
 Postprint Version G. McHale, N. J. Shirtcliffe, S. Aqil, C. C. Perry and M. I. Newton, Topography driven spreading, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, Art. No. 036102 (2004); DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.036102. The
Postprint Version G. McHale, N. J. Shirtcliffe, S. Aqil, C. C. Perry and M. I. Newton, Topography driven spreading, Phys. Rev. Lett. 93, Art. No. 036102 (2004); DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.036102. The
INTRODUCTION DEFINITION OF FLUID. U p F FLUID IS A SUBSTANCE THAT CAN NOT SUPPORT SHEAR FORCES OF ANY MAGNITUDE WITHOUT CONTINUOUS DEFORMATION
 INTRODUCTION DEFINITION OF FLUID plate solid F at t = 0 t > 0 = F/A plate U p F fluid t 0 t 1 t 2 t 3 FLUID IS A SUBSTANCE THAT CAN NOT SUPPORT SHEAR FORCES OF ANY MAGNITUDE WITHOUT CONTINUOUS DEFORMATION
INTRODUCTION DEFINITION OF FLUID plate solid F at t = 0 t > 0 = F/A plate U p F fluid t 0 t 1 t 2 t 3 FLUID IS A SUBSTANCE THAT CAN NOT SUPPORT SHEAR FORCES OF ANY MAGNITUDE WITHOUT CONTINUOUS DEFORMATION
Thermodynamics of a symmetric toroidal section and break up of a fluid torus
 Thermodynamics of a symmetric toroidal section and break up of a fluid torus Philip Lee March 1, 2016 1 Coordinate systems, and notation The toroidal section makes contact angle θ with the substrate, the
Thermodynamics of a symmetric toroidal section and break up of a fluid torus Philip Lee March 1, 2016 1 Coordinate systems, and notation The toroidal section makes contact angle θ with the substrate, the
EPJ E. Soft Matter and Biological Physics. EPJ.org. Thin viscoelastic dewetting films of Jeffreys type subjected to gravity and substrate interactions
 EPJ E Soft Matter and Biological Pysics EPJ.org your pysics journal Eur. Pys. J. E (9) : DOI./epje/i9-77- Tin viscoelastic dewetting films of Jeffreys type subjected to gravity and substrate interactions
EPJ E Soft Matter and Biological Pysics EPJ.org your pysics journal Eur. Pys. J. E (9) : DOI./epje/i9-77- Tin viscoelastic dewetting films of Jeffreys type subjected to gravity and substrate interactions
2. Derive ideal mixing and the Flory-Huggins models from the van der Waals mixture partition function.
 Lecture #5 1 Lecture 5 Objectives: 1. Identify athermal and residual terms from the van der Waals mixture partition function.. Derive ideal mixing and the Flory-Huggins models from the van der Waals mixture
Lecture #5 1 Lecture 5 Objectives: 1. Identify athermal and residual terms from the van der Waals mixture partition function.. Derive ideal mixing and the Flory-Huggins models from the van der Waals mixture
Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
 Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector Finding rates of cange in different directions Recall tat wen we first started considering derivatives of functions of more tan one variable,
Section 15.6 Directional Derivatives and te Gradient Vector Finding rates of cange in different directions Recall tat wen we first started considering derivatives of functions of more tan one variable,
contact line dynamics
 contact line dynamics part 2: hydrodynamics dynamic contact angle? lubrication: Cox-Voinov theory maximum speed for instability corner shape? dimensional analysis: speed U position r viscosity η pressure
contact line dynamics part 2: hydrodynamics dynamic contact angle? lubrication: Cox-Voinov theory maximum speed for instability corner shape? dimensional analysis: speed U position r viscosity η pressure
Superhydrophobic surfaces. José Bico PMMH-ESPCI, Paris
 Superhydrophobic surfaces José Bico PMMH-ESPCI, Paris Superhydrophobic surfaces José Bico PMMH-ESPCI, Paris? Rain droplet on a window film pinning tear 180? mercury calefaction Leidenfrost point, T = 150
Superhydrophobic surfaces José Bico PMMH-ESPCI, Paris Superhydrophobic surfaces José Bico PMMH-ESPCI, Paris? Rain droplet on a window film pinning tear 180? mercury calefaction Leidenfrost point, T = 150
5.2 Surface Tension Capillary Pressure: The Young-Laplace Equation. Figure 5.1 Origin of surface tension at liquid-vapor interface.
 5.2.1 Capillary Pressure: The Young-Laplace Equation Vapor Fo Fs Fs Fi Figure 5.1 Origin of surface tension at liquid-vapor interface. Liquid 1 5.2.1 Capillary Pressure: The Young-Laplace Equation Figure
5.2.1 Capillary Pressure: The Young-Laplace Equation Vapor Fo Fs Fs Fi Figure 5.1 Origin of surface tension at liquid-vapor interface. Liquid 1 5.2.1 Capillary Pressure: The Young-Laplace Equation Figure
Test 2 Review. 1. Find the determinant of the matrix below using (a) cofactor expansion and (b) row reduction. A = 3 2 =
 Test Review Find te determinant of te matrix below using (a cofactor expansion and (b row reduction Answer: (a det + = (b Observe R R R R R R R R R Ten det B = (((det Hence det Use Cramer s rule to solve:
Test Review Find te determinant of te matrix below using (a cofactor expansion and (b row reduction Answer: (a det + = (b Observe R R R R R R R R R Ten det B = (((det Hence det Use Cramer s rule to solve:
