University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 355 Spring Quarter 2005
|
|
|
- Angel Copeland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 55 Spring Quarter 5 Homework Assignment 7: Due no later than 5: pm on 5/14/4 8., 8.6, ) According to text equation 16, after N jumps the probability of a displacement m N! places from the origin is Pm b g. Then the relative probability bn + mg /! bn mg /! of observing after 8 total jumps four displacements from the origin versus two displacements is Pbg 4 8! b8+ g/! b8 g/! P 8+ 4 /! 8 4 /! 8! b g b g b g b g b g b g b g 8+ /! 8 /! 5!! 8+ 4 /! 8 4 /! 6!! 1 8.6) Consider the fact that for spherical molecules the frictional coefficient f is proportional to the radius R (Stokes Law). Consider also that the volume is proportional to the mass and the volume of a sphere is proportional to the radius cubed. Then f is proportional to the cube root of volume and thus is also proportional to the cube root of mass. Take that proportionality (i.e. f proportional to the cube root of mass) and determine how s and D depend on mass when the molecule is spherical. Solution: Suppose the molecule is spherical. The easiest case to study is if the molecule is unhydrated in solution i.e. has no waters of hydration attached. Then the volume of one F 4 mole of spherical molecules is V M V N H G I R K J π where N is Avagadro s number. F MV Then R H G 1 / I N K J. k T RT From the statement D we get 6πηR 6πηNR 1 / RT RT F N 1 D D 1 6 NR 6 N H G I / πη πη MV KJ M 1 / mc1 Vρh M c1 V ρh F N From the statement s s M R N H G I / 6πη 6πη MV KJ 8.1) Calculate the molecular radii for myoglobin and hemoglobin. The ratio of the radii equals the cube root of the ratio of the volumes.
2 k T k T D R 6πηR k T c18. 1 J / Khb9Kg Myoglobin: R 11 6π. 1kg / m s m / s b gc h c18. 1 J / Khb9Kg 11 πb. kg / m sgc. m / sh kt Hemoglobin: R rhb rmb 186. If Hb were a tetramer, its volume would be four times that of Mb: r Hb F VHb VMb H G I K J F 1 / H G 1 / 4 I 1 / K J rmb VMb theoretical ratio V Mb b g 186. nm 5. nm The experimental ratio is close to the ) A base pair DNA may be modeled as a rigid rod that is 6.8x1-8 m in length and has a radius of 1-9 m. a) Calculate the axial ratio and the volume of a base pair DNA molecule. Solution: L L 68 P 4. d R V R L m 68 1 m m π b gc h c h b) Calculate the radius of a sphere which has an equal volume to the rod-shaped DNA in part a. Solution: 1 / 4 F 14 1 m I 9 V πr 14 1 m R 7. 1 m HG KJ c) Assuming the base pair DNA may be modeled as a rigid rod, calculate the frictional coefficient f. Assume the solvent viscosity is.1 gm cm -1 s / / 1 / / b/ g P b/ g P f f 6πηR ln bpg. ln bpg. 1 / / / 4 b6 gb. 1gm / cm sgc. 7 1 cmh b g b g π ln 68. F I HG K J b g g / s g/ s 9.
3 d) Calculate the diffusion coefficient of a base pair DNA. Assume T98K. D k T 16 c18. 1 ergs / Khb9Kg cm / s f g / s ) A base pair fragment of DNA is 68 Angstroms long and Angstroms in diameter. It has a molecular weight of 15, grams/mole. a) Calculate the frictional coefficient of this DNA fragment, assuming it can be treated as a rod of length L68 Angstoms and diameter d Angstroms. Solution: From Lecture 6 a rod-like particle has a length a and radius b. Its volume is given by the formula: Vrod π ab. The axial ratio P is defined as P a. b 1 / / b/ g P the frictional coefficient is defined as f f. ln( P). The term f in the equation above is defined as f 6πη R. R is defined as the radius of a sphere which has a volume equal to the volume of the rod with axial ratio Pa/b. F R is ab ab determined as follows: Vsphere Vrod R ab R R H G 1 / I π K J So Pa/b68/4 Note 1 Angstrom is 1-1 m. Then a68 Ang. And b Ang. Then 1/ / 1/ / ( /) P ( /) P f f ( 6πηR) ln( P). ln( P). 1/ 1 1 6π (.1Pa s) ( 4 1 m)( 1 1 m) 1/ / ( /) ( 4) 1/ (.188Pa s)( 51 1 m ) (.8) ln(68) kg / s g / s b) Calculate the sedimentation coefficient of the DNA assuming the gram specific volume of DNA is.51 ml/gram. Solution: m V M V s f N f ( 1 ρ) ( 1 ρ) ( ) ( 6. 1 / mole)( g / s) ( 15, gm / mole) 1 (.51 ml / gm)( 1 gm / ml) sec 6.66 A S
4 c) For the purpose of calculating the frictional coefficient f, a rod-like, linear polymer can be more accurately treated as a string of N touching beads, each spherical bead has a diameter δ. The rod is therefore of length Nδ. πηn δ For such a polymer the frictional coefficient is f where η is the ln N viscosity of the solvent, assumed here to be water. Calculate the bead diameter and number of beads required to have the same total volume and length as the DNA described in part a. Solution: The length of the string of beads is 68 AngstromsNδ. The volume of the DNA cylinder is 1 9 V aπ b m 1 m.14 1 ( )( )( )( ) m 5 4 Te volume of the string of beads is the volume of the bead δ πδ π times 6 Nπδ the number of beads N or. So we have two unknowns N and d but two 6 equations 1 Nδ 68 1 m Nπδ m 6 1 Nπδ ( Nδ) πδ ( 68 1 m) πδ m ( 6 )(.14 1 m ) 18 9 δ m δ.45 1 m m π ( ) m N m Comment: The rise between adjacent base pairs is about 4 Angstroms in form DNA, so these beads are of dimension much larger than a single base pair.it means that for the purposes of calculating friction coefficients, the minimal unit in DNA is about 5-6 base pairs at least according to this model. d) Calculate the frictional coefficient and the sedimentation coefficient of the DNA described in part c.
5 1 ( )(.14)(.1Pa s)( 8)( m) πηnδ f ln N ln ( 8) kg / s. e) kg / s / ) Chromatin is the complex of DNA and proteins (mostly histones) found in all eukaryotic cells. The fundamental repeating unit of chromatin is the nucleosome particle. The properties of the DNA and the protein in nucleosome particles were determined using a combination of velocity sedimentation, dynamic light scattering, and gel electrophoresis. Dynamic light scattering studies determined the diffusion coefficient of the nucleosome particle in solution at 9K to be 4.7x1-7 cm /s. In the same solution velocity sedimentation performed at 18,1 revolutions per minute, obtained the following data: g s Time (minutes) oundary Position r (cm) Gel electrophoresis showed that the DNA molecule associated with a single nucleosome protein complex is base pairs in length. a) What is the molecular weight of the nucleosome particle? Assume the solution has a density of 1.g/cm and the specific volume of the nucleosome particle is.66cm /g. mc1 V D M V D s ρ h c1 ρh kt N A kt Obtain s from a plot of lnr versus time
6 Nucleosome Sedimentation Data Time (sec) Ln(R) Series1 The slope is 6 1 c57. 1 sec hb6sec/ ming sω sec s sec 158. S 1 π 18, 1 min Then M sk T N A c1 VρhD c6. 1 mole hc18. 1 ergs / Khc sechb9kg c1 b. 66gb1. ghc cm / sh c h g / mole b) Assuming the nucleosome particle is spherical, calculate its Stokes radius. Assume the viscosity of the solution is.1 gm cm -1 s -1. c hb g 16 k T k T ergs / K 9K D R cm 6πηR 6πb1. g / cm sgc47. 1 cm / sh c) Assuming each base pair in DNA is separated from the adjacent base pairs by about.4x1-1 m, approximately how long is a piece of DNA base pairs in length? ased on this result, and the result from part b, comment on how tightly packed the DNA is in the nucleosome. b gc h 8 Length of DNA base pairs. 4 1 cm / base pair 68 1 cm ecause the length of the DNA is much greater than the diameter of the nucleosome particle we assume the DNA must be tightly folded in the nucleosome. d) Other evidence suggests that the protein component of the nucleosome is composed of a complex of eight protein molecules. Assuming that a single DNA base pair weighs 66g/mole, estimate the total weight of the protein in the nucleosome and the weight of each component protein.
7 Weight Protein Complex Weight Nucleosome Weight DNA7,g/mole- (66g/mole)()18,g/mole Weight Protein Monomer18,/817,5g/mole e) How are the proteins and DNA packed in the nucleosome? To answer this question, assume the eight proteins form a unhydrated, spherical complex with specific volume.74 cm /g. Calculate the radius of this hypothetical protein sphere. Assume the base pair DNA behaves as a random coil polymer. Calculate the root mean square (rms) end-to-end distance. Comparing the protein sphere radius with the rms end-toend distance for the DNA, is most of the DNA packed outside or inside the protein core of the nucleosome? Explain. R protein F MV g moleof complex cc g H G 1 / I F I N A K J H G b, / gb. / g 1 c6. 1 mole h K 4 1 / c. hbg R N cm cm DNA J 5. 1 Note because RDNA >> Rprotein, the DNA occupies a larger volume than the protein and is thus largely located outside the protein core particle. cm
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 453 Winter Quarter 2008
 Lecture /1/8 University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 45 Winter Quarter 8 A. Analysis of Diffusion Coefficients: Friction Diffusion coefficients can be measured by a variety of methods
Lecture /1/8 University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 45 Winter Quarter 8 A. Analysis of Diffusion Coefficients: Friction Diffusion coefficients can be measured by a variety of methods
There are 6 parts to this exam. Parts 1-3 deal with material covered since the midterm exam. Part 4-6 cover all course material.
 Chemistry 453 March 9, 03 Enter answers in a lue ook Final Examination Key There are 6 parts to this exam. Parts -3 deal with material covered since the midterm exam. Part 4-6 cover all course material.
Chemistry 453 March 9, 03 Enter answers in a lue ook Final Examination Key There are 6 parts to this exam. Parts -3 deal with material covered since the midterm exam. Part 4-6 cover all course material.
Measuring the size and shape of macromolecules. Hydrodynamics: study of the objects in water How do the move? Translation Rotation
 Measuring the size and shape of macromolecules Hydrodynamics: study of the objects in water How do the move? Translation Rotation 1) Movement with no external forcefree diffusion 2) Movement under the
Measuring the size and shape of macromolecules Hydrodynamics: study of the objects in water How do the move? Translation Rotation 1) Movement with no external forcefree diffusion 2) Movement under the
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 453 Winter Quarter 2005
 Lecture /4/ University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 4 Winter Quarter A. Polymer Properties of DNA When a linear polymer like DNA becomes long enough it can no longer be treated as a
Lecture /4/ University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 4 Winter Quarter A. Polymer Properties of DNA When a linear polymer like DNA becomes long enough it can no longer be treated as a
Measuring S using an analytical ultracentrifuge. Moving boundary
 Measuring S using an analytical ultracentrifuge Moving boundary [C] t = 0 t 1 t 2 0 top r bottom 1 dr b r b (t) r b ω 2 = S ln = ω 2 S (t-t dt r b (t o ) o ) r b = boundary position velocity = dr b dt
Measuring S using an analytical ultracentrifuge Moving boundary [C] t = 0 t 1 t 2 0 top r bottom 1 dr b r b (t) r b ω 2 = S ln = ω 2 S (t-t dt r b (t o ) o ) r b = boundary position velocity = dr b dt
Viscometry. - neglect Brownian motion. CHEM 305
 Viscometry When a macromolecule moves in solution (e.g. of water), it induces net motions of the individual solvent molecules, i.e. the solvent molecules will feel a force. - neglect Brownian motion. To
Viscometry When a macromolecule moves in solution (e.g. of water), it induces net motions of the individual solvent molecules, i.e. the solvent molecules will feel a force. - neglect Brownian motion. To
Chem 406 Biophysical Chemistry Lecture 1 Transport Processes, Sedimentation & Diffusion
 Chem 406 Biophysical Chemistry Lecture 1 Transport Processes, Sedimentation & Diusion I. Introduction A. There are a group o biophysical techniques that are based on transport processes. 1. Transport processes
Chem 406 Biophysical Chemistry Lecture 1 Transport Processes, Sedimentation & Diusion I. Introduction A. There are a group o biophysical techniques that are based on transport processes. 1. Transport processes
Phys 450 Spring 2011 Solution set 6. A bimolecular reaction in which A and B combine to form the product P may be written as:
 Problem Phys 45 Spring Solution set 6 A bimolecular reaction in which A and combine to form the product P may be written as: k d A + A P k d k a where k d is a diffusion-limited, bimolecular rate constant
Problem Phys 45 Spring Solution set 6 A bimolecular reaction in which A and combine to form the product P may be written as: k d A + A P k d k a where k d is a diffusion-limited, bimolecular rate constant
Chem/Biochem 471 Exam 2 11/14/07 Page 1 of 7 Name:
 Page 1 of 7 Please leave the exam pages stapled together. The formulas are on a separate sheet. This exam has 5 questions. You must answer at least 4 of the questions. You may answer all 5 questions if
Page 1 of 7 Please leave the exam pages stapled together. The formulas are on a separate sheet. This exam has 5 questions. You must answer at least 4 of the questions. You may answer all 5 questions if
8.6 Drag Forces in Fluids
 86 Drag Forces in Fluids When a solid object moves through a fluid it will experience a resistive force, called the drag force, opposing its motion The fluid may be a liquid or a gas This force is a very
86 Drag Forces in Fluids When a solid object moves through a fluid it will experience a resistive force, called the drag force, opposing its motion The fluid may be a liquid or a gas This force is a very
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 453 Winter Quarter 2013
 Lecture 1 3/13/13 University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 53 Winter Quarter 013 A. Definition of Viscosity Viscosity refers to the resistance of fluids to flow. Consider a flowing liquid
Lecture 1 3/13/13 University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 53 Winter Quarter 013 A. Definition of Viscosity Viscosity refers to the resistance of fluids to flow. Consider a flowing liquid
Physics 231 Topic 12: Temperature, Thermal Expansion, and Ideal Gases Alex Brown Nov
 Physics 231 Topic 12: Temperature, Thermal Expansion, and Ideal Gases Alex Brown Nov 18-23 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 homework 3 rd midterm final Thursday 8-10 pm makeup Friday final 9-11 am MSU
Physics 231 Topic 12: Temperature, Thermal Expansion, and Ideal Gases Alex Brown Nov 18-23 2015 MSU Physics 231 Fall 2015 1 homework 3 rd midterm final Thursday 8-10 pm makeup Friday final 9-11 am MSU
Pressure drop due to viscosity in a round pipe of radius R is given by the Poiseuille equation: P L. = 8η v R 2
 PHY 302 K. Solutions for Problem set # 12. Textbook problem 10.55: Pressure drop due to viscosity in a round pipe of radius R is given by the Poiseuille equation: P L 8η v R 2 8ηF πr 4 (1) where η is viscosity
PHY 302 K. Solutions for Problem set # 12. Textbook problem 10.55: Pressure drop due to viscosity in a round pipe of radius R is given by the Poiseuille equation: P L 8η v R 2 8ηF πr 4 (1) where η is viscosity
What s important: viscosity Poiseuille's law Stokes' law Demo: dissipation in flow through a tube
 PHYS 101 Lecture 29x - Viscosity 29x - 1 Lecture 29x Viscosity (extended version) What s important: viscosity Poiseuille's law Stokes' law Demo: dissipation in flow through a tube Viscosity We introduced
PHYS 101 Lecture 29x - Viscosity 29x - 1 Lecture 29x Viscosity (extended version) What s important: viscosity Poiseuille's law Stokes' law Demo: dissipation in flow through a tube Viscosity We introduced
Answers to test yourself questions
 Answers to test yourself questions Option B B Rotational dynamics ( ω + ω )t Use 0 ( +.).0 θ to get θ 46. 46 rad. Use ω ω0 + αθ to get ω.0 +. 4 and so ω 7.8 7 rad s. Use ω ω0 + αθ to get.4. + α 0 π. Hence
Answers to test yourself questions Option B B Rotational dynamics ( ω + ω )t Use 0 ( +.).0 θ to get θ 46. 46 rad. Use ω ω0 + αθ to get ω.0 +. 4 and so ω 7.8 7 rad s. Use ω ω0 + αθ to get.4. + α 0 π. Hence
Physics 231 Lecture 32 Problem and review
 Physics 231 Lecture 32 Problem and review Checking Understanding: Pressure and Forces The two identical cylinders contain samples of gas. Each cylinder has a lightweight piston on top that is free to move,
Physics 231 Lecture 32 Problem and review Checking Understanding: Pressure and Forces The two identical cylinders contain samples of gas. Each cylinder has a lightweight piston on top that is free to move,
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 355 Spring Quarter 2003
 University o Washington Department o Chemistry Chemistry 355 Spring Quarter 3 Homework Assignment : Due no later than 5 pm on 4/14 Text Problems:.4,.8,.1,.11,.17.4) Carbohydrate: Select sucrose C1 HO11
University o Washington Department o Chemistry Chemistry 355 Spring Quarter 3 Homework Assignment : Due no later than 5 pm on 4/14 Text Problems:.4,.8,.1,.11,.17.4) Carbohydrate: Select sucrose C1 HO11
SEC MALLs and AUC. 2. Conformation and flexibility Viscometry,
 1. Molecular weight distribution analysis SEC MALLs and AUC 2. Conformation and flexibility Viscometry, AUC, Light scattering Lecture 4. Analytical l Ultracentrifugation t ti I: Molecular weight and conformation
1. Molecular weight distribution analysis SEC MALLs and AUC 2. Conformation and flexibility Viscometry, AUC, Light scattering Lecture 4. Analytical l Ultracentrifugation t ti I: Molecular weight and conformation
Homework: 13, 14, 18, 20, 24 (p )
 Homework: 13, 14, 18, 0, 4 (p. 531-53) 13. A sample of an ideal gas is taken through the cyclic process abca shown in the figure below; at point a, T=00 K. (a) How many moles of gas are in the sample?
Homework: 13, 14, 18, 0, 4 (p. 531-53) 13. A sample of an ideal gas is taken through the cyclic process abca shown in the figure below; at point a, T=00 K. (a) How many moles of gas are in the sample?
Multimedia : Fibronectin and Titin unfolding simulation movies.
 I LECTURE 21: SINGLE CHAIN ELASTICITY OF BIOMACROMOLECULES: THE GIANT PROTEIN TITIN AND DNA Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #2 : EXTENSIBLE FJC AND WLC... 2 STRUCTURE OF MUSCLE AND TITIN... 3 SINGLE MOLECULE
I LECTURE 21: SINGLE CHAIN ELASTICITY OF BIOMACROMOLECULES: THE GIANT PROTEIN TITIN AND DNA Outline : REVIEW LECTURE #2 : EXTENSIBLE FJC AND WLC... 2 STRUCTURE OF MUSCLE AND TITIN... 3 SINGLE MOLECULE
Polymer Dynamics and Rheology
 Polymer Dynamics and Rheology 1 Polymer Dynamics and Rheology Brownian motion Harmonic Oscillator Damped harmonic oscillator Elastic dumbbell model Boltzmann superposition principle Rubber elasticity and
Polymer Dynamics and Rheology 1 Polymer Dynamics and Rheology Brownian motion Harmonic Oscillator Damped harmonic oscillator Elastic dumbbell model Boltzmann superposition principle Rubber elasticity and
Delhi Public School, Jammu Question Bank ( )
 Class : XI Delhi Public School, Jammu Question Bank (2017 18) Subject : Physics 1. When real gases obey the ideal gas equation pv = RT? Ans. a) Low pressure b) High temperature 2. Give reason: Though earth
Class : XI Delhi Public School, Jammu Question Bank (2017 18) Subject : Physics 1. When real gases obey the ideal gas equation pv = RT? Ans. a) Low pressure b) High temperature 2. Give reason: Though earth
Lecture 26: More on Gel Filtration Chromatography and the Trypsin Resurrection Experiment
 Biological Chemistry Laboratory Biology 3515/Chemistry 3515 Spring 2018 Lecture 26: More on Gel Filtration Chromatography and the Trypsin Resurrection Experiment 12 April 2018 c David P. Goldenberg University
Biological Chemistry Laboratory Biology 3515/Chemistry 3515 Spring 2018 Lecture 26: More on Gel Filtration Chromatography and the Trypsin Resurrection Experiment 12 April 2018 c David P. Goldenberg University
Chem 112 Exam 1 Version A Spring /16/ :00am/Odago, M. O.
 Chem 112 Exam 1 Version A Spring 2011 02/16/2011 10:00am/Odago, M. O. 1. The pressure of a certain gas is measured to be 25.1 mmhg. What is this pressure expressed in units of pascals? (1 atm=1.0125 x10
Chem 112 Exam 1 Version A Spring 2011 02/16/2011 10:00am/Odago, M. O. 1. The pressure of a certain gas is measured to be 25.1 mmhg. What is this pressure expressed in units of pascals? (1 atm=1.0125 x10
Chapter 14. The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory
 Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number The atomic number of an element is the # of protons in its nucleus. Isotopes of an element have different
Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number The atomic number of an element is the # of protons in its nucleus. Isotopes of an element have different
Physics 202 Exam 1. May 1, 2013
 Name: Physics 202 Exam 1 May 1, 2013 Word Problems Show all your work and circle your final answer. (Ten points each.) 1. If 2.4 m 3 of a gas initially at STP is compressed to 1.6 m 3 and its temperature
Name: Physics 202 Exam 1 May 1, 2013 Word Problems Show all your work and circle your final answer. (Ten points each.) 1. If 2.4 m 3 of a gas initially at STP is compressed to 1.6 m 3 and its temperature
Physics 101: Lecture 17 Fluids
 Exam III Physics 101: Lecture 17 Fluids Exam 2 is Mon Nov. 4, 7pm Extra office hours on Fri. (see webpage!) Physics 101: Lecture 17, Pg 1 Homework 9 Help A block of mass M 1 = 3 kg rests on a table with
Exam III Physics 101: Lecture 17 Fluids Exam 2 is Mon Nov. 4, 7pm Extra office hours on Fri. (see webpage!) Physics 101: Lecture 17, Pg 1 Homework 9 Help A block of mass M 1 = 3 kg rests on a table with
Chemistry Section Review 2.2
 Chemistry Section Review 2.2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Standards of measurement are chosen because they a. can be related to everyday
Chemistry Section Review 2.2 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Standards of measurement are chosen because they a. can be related to everyday
Diffusion. Spring Quarter 2004 Instructor: Richard Roberts. Reading Assignment: Ch 6: Tinoco; Ch 16: Levine; Ch 15: Eisenberg&Crothers
 Chemistry 24b Spring Quarter 2004 Instructor: Richard Roberts Lecture 2 RWR Reading Assignment: Ch 6: Tinoco; Ch 16: Leine; Ch 15: Eisenberg&Crothers Diffusion Real processes, such as those that go on
Chemistry 24b Spring Quarter 2004 Instructor: Richard Roberts Lecture 2 RWR Reading Assignment: Ch 6: Tinoco; Ch 16: Leine; Ch 15: Eisenberg&Crothers Diffusion Real processes, such as those that go on
SPRING 2011 Phys 450 Solution set 2
 SPRING 011 Phys 450 Solution set Problem 1 (a) Estimate the diameter of a ater molecule from its self-diffusion coefficient, and using the Stokes-Einstein relation, assuming that it is a spherical molecule.
SPRING 011 Phys 450 Solution set Problem 1 (a) Estimate the diameter of a ater molecule from its self-diffusion coefficient, and using the Stokes-Einstein relation, assuming that it is a spherical molecule.
Name : Applied Physics II Exam One Winter Multiple Choice ( 7 Points ):
 Name : e-mail: Applied Physics II Exam One Winter 2006-2007 Multiple Choice ( 7 Points ): 1. Pure nitrogen gas is contained in a sealed tank containing a movable piston. The initial volume, pressure and
Name : e-mail: Applied Physics II Exam One Winter 2006-2007 Multiple Choice ( 7 Points ): 1. Pure nitrogen gas is contained in a sealed tank containing a movable piston. The initial volume, pressure and
Biomolecular hydrodynamics
 Biomolecular hydrodynamics David Case Rutgers, Spring, 2009 February 1, 2009 Why study hydrodynamical methods? The methods we study in this section are low resolution ones one studies diffusional motion
Biomolecular hydrodynamics David Case Rutgers, Spring, 2009 February 1, 2009 Why study hydrodynamical methods? The methods we study in this section are low resolution ones one studies diffusional motion
Entanglements. M < M e. M > M e. Rouse. Zero-shear viscosity vs. M (note change of slope) Edwards degennes Doi. Berry + Fox, slope 3.4.
 Entanglements Zero-shear viscosity vs. M (note change of slope) M < M e Rouse slope 3.4 M > M e Edwards degennes Doi slope 1 Berry + Fox, 1968 Question: Which factors affect the Me: T, P, M, flexibility,
Entanglements Zero-shear viscosity vs. M (note change of slope) M < M e Rouse slope 3.4 M > M e Edwards degennes Doi slope 1 Berry + Fox, 1968 Question: Which factors affect the Me: T, P, M, flexibility,
τ = (Force)(lever arm) #
 EXPERIMENT: MOMENT OF INERTIA OBJECTIVES : 1) To familiarize yourself with the concept of the moment of inertia, I, which plays the same role in the description of the rotation of the rigid body as the
EXPERIMENT: MOMENT OF INERTIA OBJECTIVES : 1) To familiarize yourself with the concept of the moment of inertia, I, which plays the same role in the description of the rotation of the rigid body as the
Q1. A) 46 m/s B) 21 m/s C) 17 m/s D) 52 m/s E) 82 m/s. Ans: v = ( ( 9 8) ( 98)
 Coordinator: Dr. Kunwar S. Wednesday, May 24, 207 Page: Q. A hot-air balloon is ascending (going up) at the rate of 4 m/s and when the balloon is 98 m above the ground a package is dropped from it, vertically
Coordinator: Dr. Kunwar S. Wednesday, May 24, 207 Page: Q. A hot-air balloon is ascending (going up) at the rate of 4 m/s and when the balloon is 98 m above the ground a package is dropped from it, vertically
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 452/456 Summer Quarter 2005
 University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 45/456 Summer Quarter 005 Homework Assignment #5: Due at 500 pm Friday 9 July, Drobny Mailbox #10. 1) Here are some assorted phase equilibrium
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 45/456 Summer Quarter 005 Homework Assignment #5: Due at 500 pm Friday 9 July, Drobny Mailbox #10. 1) Here are some assorted phase equilibrium
CONNECTED RATE OF CHANGE PACK
 C4 CONNECTED RATE OF CHANGE PACK 1. A vase with a circular cross-section is shown in. Water is flowing into the vase. When the depth of the water is h cm, the volume of water V cm 3 is given by V = 4 πh(h
C4 CONNECTED RATE OF CHANGE PACK 1. A vase with a circular cross-section is shown in. Water is flowing into the vase. When the depth of the water is h cm, the volume of water V cm 3 is given by V = 4 πh(h
ε tran ε tran = nrt = 2 3 N ε tran = 2 3 nn A ε tran nn A nr ε tran = 2 N A i.e. T = R ε tran = 2
 F1 (a) Since the ideal gas equation of state is PV = nrt, we can equate the right-hand sides of both these equations (i.e. with PV = 2 3 N ε tran )and write: nrt = 2 3 N ε tran = 2 3 nn A ε tran i.e. T
F1 (a) Since the ideal gas equation of state is PV = nrt, we can equate the right-hand sides of both these equations (i.e. with PV = 2 3 N ε tran )and write: nrt = 2 3 N ε tran = 2 3 nn A ε tran i.e. T
Statistical Mechanics
 Statistical Mechanics Newton's laws in principle tell us how anything works But in a system with many particles, the actual computations can become complicated. We will therefore be happy to get some 'average'
Statistical Mechanics Newton's laws in principle tell us how anything works But in a system with many particles, the actual computations can become complicated. We will therefore be happy to get some 'average'
Separation Sciences. 1. Introduction: Fundamentals of Distribution Equilibrium. 2. Gas Chromatography (Chapter 2 & 3)
 Separation Sciences 1. Introduction: Fundamentals of Distribution Equilibrium 2. Gas Chromatography (Chapter 2 & 3) 3. Liquid Chromatography (Chapter 4 & 5) 4. Other Analytical Separations (Chapter 6-8)
Separation Sciences 1. Introduction: Fundamentals of Distribution Equilibrium 2. Gas Chromatography (Chapter 2 & 3) 3. Liquid Chromatography (Chapter 4 & 5) 4. Other Analytical Separations (Chapter 6-8)
Department of Physics
 Department of Physics PHYS101-051 FINAL EXAM Test Code: 100 Tuesday, 4 January 006 in Building 54 Exam Duration: 3 hrs (from 1:30pm to 3:30pm) Name: Student Number: Section Number: Page 1 1. A car starts
Department of Physics PHYS101-051 FINAL EXAM Test Code: 100 Tuesday, 4 January 006 in Building 54 Exam Duration: 3 hrs (from 1:30pm to 3:30pm) Name: Student Number: Section Number: Page 1 1. A car starts
PHYSICS DEPARTMENT, PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PHYSICS 301 FINAL EXAMINATION. January 13, 2005, 7:30 10:30pm, Jadwin A10 SOLUTIONS
 PHYSICS DEPARTMENT, PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PHYSICS 301 FINAL EXAMINATION January 13, 2005, 7:30 10:30pm, Jadwin A10 SOLUTIONS This exam contains five problems. Work any three of the five problems. All problems
PHYSICS DEPARTMENT, PRINCETON UNIVERSITY PHYSICS 301 FINAL EXAMINATION January 13, 2005, 7:30 10:30pm, Jadwin A10 SOLUTIONS This exam contains five problems. Work any three of the five problems. All problems
Physics H7A, Fall 2011 Homework 6 Solutions
 Physics H7A, Fall 2011 Homework 6 Solutions 1. (Hooke s law) (a) What are the dimensions (in terms of M, L, and T ) of the spring constant k in Hooke s law? (b) If it takes 4.00 J of work to stretch a
Physics H7A, Fall 2011 Homework 6 Solutions 1. (Hooke s law) (a) What are the dimensions (in terms of M, L, and T ) of the spring constant k in Hooke s law? (b) If it takes 4.00 J of work to stretch a
PHYSICS 111 SPRING FINAL EXAM: April 30, 2018; 4:30pm - 6:30pm. Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section #
 PHYSICS 111 SPRING 2018 FINAL EXAM: April 30, 2018; 4:30pm - 6:30pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 30 multiple-choice question, each worth 3 points, for
PHYSICS 111 SPRING 2018 FINAL EXAM: April 30, 2018; 4:30pm - 6:30pm Name (printed): Recitation Instructor: Section # INSTRUCTIONS: This exam contains 30 multiple-choice question, each worth 3 points, for
Sem /2007. Fisika Polimer Ariadne L. Juwono
 Chapter 8. Measurement of molecular weight and size 8.. End-group analysis 8.. Colligative property measurement 8.3. Osmometry 8.4. Gel-permeation chromatography 8.5. Ultracentrifugation 8.6. Light-scattering
Chapter 8. Measurement of molecular weight and size 8.. End-group analysis 8.. Colligative property measurement 8.3. Osmometry 8.4. Gel-permeation chromatography 8.5. Ultracentrifugation 8.6. Light-scattering
Physics 53 Exam 3 November 3, 2010 Dr. Alward
 1. When the speed of a rear-drive car (a car that's driven forward by the rear wheels alone) is increasing on a horizontal road the direction of the frictional force on the tires is: A) forward for all
1. When the speed of a rear-drive car (a car that's driven forward by the rear wheels alone) is increasing on a horizontal road the direction of the frictional force on the tires is: A) forward for all
Unit 1 - Introduction
 Unit 1 - Introduction Units and Measurements In Physics, we are constantly measuring PHYSICAL QUANTITIES using MEASURING INSTRUMENTS. When we measure something we need to pay attention to the following:
Unit 1 - Introduction Units and Measurements In Physics, we are constantly measuring PHYSICAL QUANTITIES using MEASURING INSTRUMENTS. When we measure something we need to pay attention to the following:
Biomolecular hydrodynamics
 Biomolecular hydrodynamics David Case Rutgers, Spring, 2014 January 29, 2014 Why study hydrodynamical methods? The methods we study in this section are low resolution ones one studies diffusional motion
Biomolecular hydrodynamics David Case Rutgers, Spring, 2014 January 29, 2014 Why study hydrodynamical methods? The methods we study in this section are low resolution ones one studies diffusional motion
Unit-2. Properties of Matter. Solutions 2.2 Solids page V sphere. =V cylinder. π.r 2.h= 4 3.π.r 3. h= 4r 3 =4.6 =8 cm
 page - 74 V sphere =V cylinder 1. The radius of a sphere and a cylinder are 6 cm. If their volumes are the same, what is the SA/V ratio of the cylinder? π.r 2.h= 4 3.π.r 3 h= 4r 3 =4.6 =8 cm 3 SA V =2
page - 74 V sphere =V cylinder 1. The radius of a sphere and a cylinder are 6 cm. If their volumes are the same, what is the SA/V ratio of the cylinder? π.r 2.h= 4 3.π.r 3 h= 4r 3 =4.6 =8 cm 3 SA V =2
Lecture 4: Classical Illustrations of Macroscopic Thermal Effects
 Lecture 4: Classical Illustrations of Macroscopic Thermal Effects Heat capacity of solids & liquids Thermal conductivity Irreversibility References for this Lecture: Elements Ch 3,4A-C Reference for Lecture
Lecture 4: Classical Illustrations of Macroscopic Thermal Effects Heat capacity of solids & liquids Thermal conductivity Irreversibility References for this Lecture: Elements Ch 3,4A-C Reference for Lecture
askiitians Class: 11 Subject: Chemistry Topic: Kinetic theory of gases No. of Questions: The unit of universal gas constant in S.I.
 Class: 11 Subject: Chemistry Topic: Kinetic theory of gases No. of Questions: 33 1. The unit of universal gas constant in S.I.unit is A. calorie per degree Celsius B. joule per mole C. joule/k mole C 2.
Class: 11 Subject: Chemistry Topic: Kinetic theory of gases No. of Questions: 33 1. The unit of universal gas constant in S.I.unit is A. calorie per degree Celsius B. joule per mole C. joule/k mole C 2.
Polymer dynamics. Course M6 Lecture 5 26/1/2004 (JAE) 5.1 Introduction. Diffusion of polymers in melts and dilute solution.
 Course M6 Lecture 5 6//004 Polymer dynamics Diffusion of polymers in melts and dilute solution Dr James Elliott 5. Introduction So far, we have considered the static configurations and morphologies of
Course M6 Lecture 5 6//004 Polymer dynamics Diffusion of polymers in melts and dilute solution Dr James Elliott 5. Introduction So far, we have considered the static configurations and morphologies of
Experiment 3: Centripetal Force
 012-05293F Complete Rotational System Experiment 3: Centripetal Force EQUIPMENT NEEDED - Centripetal Force Accessory (ME-8952) - Rotating Platform (ME-8951) - Stopwatch - Balance - Graph paper (2 sheets)
012-05293F Complete Rotational System Experiment 3: Centripetal Force EQUIPMENT NEEDED - Centripetal Force Accessory (ME-8952) - Rotating Platform (ME-8951) - Stopwatch - Balance - Graph paper (2 sheets)
Analytical Ultracentrifugation. by: Andrew Rouff and Andrew Gioe
 Analytical Ultracentrifugation by: Andrew Rouff and Andrew Gioe Partial Specific Volume (v) Partial Specific Volume is defined as the specific volume of the solute, which is related to volume increase
Analytical Ultracentrifugation by: Andrew Rouff and Andrew Gioe Partial Specific Volume (v) Partial Specific Volume is defined as the specific volume of the solute, which is related to volume increase
Chapter 10 Gases Characteristics of Gases Elements that exist as gases: Noble gases, O 2, N 2,H 2, F 2 and Cl 2. (For compounds see table 10.
 Chapter 10 Gases 10.1 Characteristics of Gases Elements that exist as gases: Noble gases, O 2, N 2,H 2, F 2 and Cl 2. (For compounds see table 10.1) Unlike liquids and solids, gases expand to fill their
Chapter 10 Gases 10.1 Characteristics of Gases Elements that exist as gases: Noble gases, O 2, N 2,H 2, F 2 and Cl 2. (For compounds see table 10.1) Unlike liquids and solids, gases expand to fill their
DO NOW LABEL LEFT AND RIGHT PAGES PROPERTIES OF MATTER: DENSITY
 DO NOW LABEL LEFT AND RIGHT PAGES PROPERTIES OF MATTER: DENSITY LAB DEBRIEF What was the independent (test) variable? What was the dependent (outcome) variable? Which trial was solid, liquid, gas? Explain.
DO NOW LABEL LEFT AND RIGHT PAGES PROPERTIES OF MATTER: DENSITY LAB DEBRIEF What was the independent (test) variable? What was the dependent (outcome) variable? Which trial was solid, liquid, gas? Explain.
Physics. TOPIC : Rotational motion. 1. A shell (at rest) explodes in to smalll fragment. The C.M. of mass of fragment will move with:
 TOPIC : Rotational motion Date : Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr 1. A shell (at rest) explodes in to smalll fragment. The C.M. of mass of fragment will move with: a) zero velocity b) constantt velocity c)
TOPIC : Rotational motion Date : Marks : 120 mks Time : ½ hr 1. A shell (at rest) explodes in to smalll fragment. The C.M. of mass of fragment will move with: a) zero velocity b) constantt velocity c)
a) 1.3 x 10 3 atm b) 2.44 atm c) 8.35 atm d) 4.21 x 10-3 atm e) 86.5 atm
 1. (6 pts) A sample of gas with a volume of 750 ml exerts a pressure of 756 mm Hg at 30.0 0 C. What pressure (atm) will the sample exert when it is compressed to 250 ml and cooled to -25.0 0 C? a) 1.3
1. (6 pts) A sample of gas with a volume of 750 ml exerts a pressure of 756 mm Hg at 30.0 0 C. What pressure (atm) will the sample exert when it is compressed to 250 ml and cooled to -25.0 0 C? a) 1.3
b) (6) What is the volume of the iron cube, in m 3?
 General Physics I Exam 4 - Chs. 10,11,12 - Fluids, Waves, Sound Nov. 14, 2012 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential steps, and results
General Physics I Exam 4 - Chs. 10,11,12 - Fluids, Waves, Sound Nov. 14, 2012 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential steps, and results
Transport Properties: Momentum Transport, Viscosity
 Transport Properties: Momentum Transport, Viscosity 13th February 2011 1 Introduction Much as mass(material) is transported within luids (gases and liquids), linear momentum is also associated with transport,
Transport Properties: Momentum Transport, Viscosity 13th February 2011 1 Introduction Much as mass(material) is transported within luids (gases and liquids), linear momentum is also associated with transport,
L = I ω = const. I = 2 3 MR2. When the balloon shrinks (because the air inside it cools down), the moment of inertia decreases, R = 1. L = I ω = I ω.
 PHY 30 K. Solutions for mid-term test #3. Problem 1: Out in space, there are no forces acting on the balloon except gravity and hence no torques (with respect to an axis through the center of mass). Consequently,
PHY 30 K. Solutions for mid-term test #3. Problem 1: Out in space, there are no forces acting on the balloon except gravity and hence no torques (with respect to an axis through the center of mass). Consequently,
Pre-AP Physics Review Problems
 Pre-AP Physics Review Problems SECTION ONE: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (50x2=100 points) 1. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t =
Pre-AP Physics Review Problems SECTION ONE: MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (50x2=100 points) 1. The graph above shows the velocity versus time for an object moving in a straight line. At what time after t =
Light scattering Small and large particles
 Scattering by macromolecules E B Incident light Scattered Light particle Oscillating E field from light makes electronic cloud oscillate surrounding the particle Intensity: I E Accelerating charges means
Scattering by macromolecules E B Incident light Scattered Light particle Oscillating E field from light makes electronic cloud oscillate surrounding the particle Intensity: I E Accelerating charges means
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2011 EXAM #2 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER 2, 2011
 PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
PHYSICS 1, FALL 011 EXAM SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, NOVEMBER, 011 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively. In this
Hydrodynamics: Viscosity and Diffusion Hydrodynamics is the study of mechanics in a liquid, where the frictional drag of the liquid cannot be ignored
 Hydrodynamics: Viscosity and Diffusion Hydrodynamics is the study of mechanics in a liquid, where the frictional drag of the liquid cannot be ignored First let s just consider fluid flow, where the fluid
Hydrodynamics: Viscosity and Diffusion Hydrodynamics is the study of mechanics in a liquid, where the frictional drag of the liquid cannot be ignored First let s just consider fluid flow, where the fluid
Measurement Stations. Length, Mass, Volume, Density, Temperature, and Time
 Measurement Stations Length, Mass, Volume, Density, Temperature, and Time Length Length measures the distance from end to end on an object; height and width are variations on length. Standard (S.I.) Unit:
Measurement Stations Length, Mass, Volume, Density, Temperature, and Time Length Length measures the distance from end to end on an object; height and width are variations on length. Standard (S.I.) Unit:
FIITJEE PET III (EXTENDED)
 FIITJEE PET III (EXTENDED) MAINS DATE: 9.07.017 Time: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 360 INSTRUCTIONS: Instructions to the Candidates 1. This Test Booklet consists of 90 questions. Use Blue/Black ball Point Pen
FIITJEE PET III (EXTENDED) MAINS DATE: 9.07.017 Time: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 360 INSTRUCTIONS: Instructions to the Candidates 1. This Test Booklet consists of 90 questions. Use Blue/Black ball Point Pen
1. (a) The charge that passes through any cross section is the product of the current and time. Since t = 4.0 min = (4.0 min)(60 s/min) = 240 s,
 Chapter 6 1 (a) The charge that passes through any cross section is the product of the current and time Since t = 4 min = (4 min)(6 s/min) = 4 s, q = it = (5 A)(4 s) = 1 1 3 C (b) The number of electrons
Chapter 6 1 (a) The charge that passes through any cross section is the product of the current and time Since t = 4 min = (4 min)(6 s/min) = 4 s, q = it = (5 A)(4 s) = 1 1 3 C (b) The number of electrons
BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems
 BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems Estimation of diffusion Coefficient Dr. Zifei Liu Diffusion mass transfer Diffusion mass transfer refers to mass in transit due to a species concentration
BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems Estimation of diffusion Coefficient Dr. Zifei Liu Diffusion mass transfer Diffusion mass transfer refers to mass in transit due to a species concentration
Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.)
 Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.) Heat and temperature Gases & Kinetic theory http://candidchatter.files.wordpress.com/2009/02/hell.jpg Specific Heat Specific Heat: heat capacity per unit
Lecture 25 Thermodynamics, Heat and Temp (cont.) Heat and temperature Gases & Kinetic theory http://candidchatter.files.wordpress.com/2009/02/hell.jpg Specific Heat Specific Heat: heat capacity per unit
Chemistry 25 (Spring term 2016) Final Examination for NON-SENIORS GOOD LUCK AND HAVE A GREAT SUMMER!!!
 Name ANSWER KEY Distributed Thursday, June 2 Due Chemistry 25 (Spring term 2016) Final Examination for NON-SENIORS GOOD LUCK AND HAVE A GREAT SUMMER!!! by Thursday, June 2 at 1 pm to 362 Broad a drop box
Name ANSWER KEY Distributed Thursday, June 2 Due Chemistry 25 (Spring term 2016) Final Examination for NON-SENIORS GOOD LUCK AND HAVE A GREAT SUMMER!!! by Thursday, June 2 at 1 pm to 362 Broad a drop box
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Characterizing the Effect of Salt and Surfactant Concentration on the Counter-ion Atmosphere around Surfactant Stabilized SWCNTs using Analytical Ultracentrifugation Stephanie Lam
Supporting Information Characterizing the Effect of Salt and Surfactant Concentration on the Counter-ion Atmosphere around Surfactant Stabilized SWCNTs using Analytical Ultracentrifugation Stephanie Lam
Compiled and rearranged by Sajit Chandra Shakya
 1 (a) (i) The kinetic theory of gases leads to the equation m = kt. (b) Explain the significance of the quantity m... the equation to suggest what is meant by the absolute zero of temperature...
1 (a) (i) The kinetic theory of gases leads to the equation m = kt. (b) Explain the significance of the quantity m... the equation to suggest what is meant by the absolute zero of temperature...
A) 1 gm 2 /s. B) 3 gm 2 /s. C) 6 gm 2 /s. D) 9 gm 2 /s. E) 10 gm 2 /s. A) 0.1 kg. B) 1 kg. C) 2 kg. D) 5 kg. E) 10 kg A) 2:5 B) 4:5 C) 1:1 D) 5:4
 1. A 4 kg object moves in a circle of radius 8 m at a constant speed of 2 m/s. What is the angular momentum of the object with respect to an axis perpendicular to the circle and through its center? A)
1. A 4 kg object moves in a circle of radius 8 m at a constant speed of 2 m/s. What is the angular momentum of the object with respect to an axis perpendicular to the circle and through its center? A)
Particle Nature of Matter. Solutions of Selected Problems
 Chapter 4 Particle Nature of Matter. Solutions of Selected Problems 4. Problem 4.5 In the text book A Thomson-type experiment with relativistic electmns. One of the earliest experiments to show that p
Chapter 4 Particle Nature of Matter. Solutions of Selected Problems 4. Problem 4.5 In the text book A Thomson-type experiment with relativistic electmns. One of the earliest experiments to show that p
Homework #4 Physics 498Bio Spring 2012 Prof. Paul Selvin
 Assigned Wednesday Feb. 22, 2012: Due Wednesday February 29, 10:30am. Hand in at start of class. Late homework is not accepted. (Solution sets will be posted shortly after deadline.) Note: Marco will give
Assigned Wednesday Feb. 22, 2012: Due Wednesday February 29, 10:30am. Hand in at start of class. Late homework is not accepted. (Solution sets will be posted shortly after deadline.) Note: Marco will give
Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion. Torque and angular momentum
 Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion Torque and angular momentum In Figure, in order to turn a rod about a fixed hinge at one end, a force F is applied at a
Handout 7: Torque, angular momentum, rotational kinetic energy and rolling motion Torque and angular momentum In Figure, in order to turn a rod about a fixed hinge at one end, a force F is applied at a
Chapter 5. Methods for the Separation and Characterization of Macromolecules
 Chapter 5 Methods for the Separation and Characterization of Macromolecules 1 5.1 General Principles Diversity, Complexity and Dynamics of macromolecular structure 1. Protein exit, under physiological
Chapter 5 Methods for the Separation and Characterization of Macromolecules 1 5.1 General Principles Diversity, Complexity and Dynamics of macromolecular structure 1. Protein exit, under physiological
EXAM 1 PHYS 103 FALL 2011 A NAME: SECTION
 EXAM 1 PHYS 103 FALL 2011 A NAME: SECTION As a student at NJIT I, will conduct myself in a professional manner and will comply with the provisions of the NJIT Academic Honor Code. I also understand that
EXAM 1 PHYS 103 FALL 2011 A NAME: SECTION As a student at NJIT I, will conduct myself in a professional manner and will comply with the provisions of the NJIT Academic Honor Code. I also understand that
Chemistry 471 Final exam 12/18/06 Page 1 of 6 Name:
 Chemistry 47 Final exam /8/6 Page of 6 Please leave the exam pages stapled together. The formulas are on a separate sheet. This exam has 5 questions. You must answer at least 4 of the questions. You may
Chemistry 47 Final exam /8/6 Page of 6 Please leave the exam pages stapled together. The formulas are on a separate sheet. This exam has 5 questions. You must answer at least 4 of the questions. You may
Chapter 14. The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory
 Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number To facilitate comparison of the mass of one atom with another, a mass scale know as the atomic mass
Chapter 14 The Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory 14.1 Molecular Mass, the Mole, and Avogadro s Number To facilitate comparison of the mass of one atom with another, a mass scale know as the atomic mass
Physics 351, Spring 2017, Homework #2. Due at start of class, Friday, January 27, 2017
 Physics 351, Spring 2017, Homework #2. Due at start of class, Friday, January 27, 2017 Course info is at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p351 When you finish this homework, remember to visit the feedback page at
Physics 351, Spring 2017, Homework #2. Due at start of class, Friday, January 27, 2017 Course info is at positron.hep.upenn.edu/p351 When you finish this homework, remember to visit the feedback page at
Mt. Douglas Secondary
 Foundations of Math Section.5 Volume of Similar Figures 47.5 Volume of Similar Figures The cubes shown below are similar. The corresponding sides are in a ratio of :. What is the ratio of the volumes?
Foundations of Math Section.5 Volume of Similar Figures 47.5 Volume of Similar Figures The cubes shown below are similar. The corresponding sides are in a ratio of :. What is the ratio of the volumes?
Lecture 24. Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory
 Lecture 4 Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory Today s Topics: Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory of Gases Phase equilibria and phase diagrams Ideal Gas Law An ideal gas is an idealized model for real gases that
Lecture 4 Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory Today s Topics: Ideal Gas Law Kinetic Theory of Gases Phase equilibria and phase diagrams Ideal Gas Law An ideal gas is an idealized model for real gases that
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 2 (*) (1)
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. (a) pressure (*) Pa or N m volume m (*) (*) (not allow kpa) number of moles mol (or none) molar gas constant J K 1 mol 1 (mol 1 implies molar) temperature K 4 (b) (i) W(=
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. (a) pressure (*) Pa or N m volume m (*) (*) (not allow kpa) number of moles mol (or none) molar gas constant J K 1 mol 1 (mol 1 implies molar) temperature K 4 (b) (i) W(=
States of Matter. The Solid State. Particles are tightly packed, very close together (strong cohesive forces) Low kinetic energy (energy of motion)
 States of Matter The Solid State Particles are tightly packed, very close together (strong cohesive forces) Low kinetic energy (energy of motion) Fixed shape and volume Crystalline or amorphous structure
States of Matter The Solid State Particles are tightly packed, very close together (strong cohesive forces) Low kinetic energy (energy of motion) Fixed shape and volume Crystalline or amorphous structure
Dilute-solution properties of biomacromolecules as indicators of macromolecular structure and interactions
 Dilute-solution properties of biomacromolecules as indicators of macromolecular structure and interactions José García de la Torre, Departament of Physical Chemistry University of Murcia, Spain jgt@um.es
Dilute-solution properties of biomacromolecules as indicators of macromolecular structure and interactions José García de la Torre, Departament of Physical Chemistry University of Murcia, Spain jgt@um.es
Solution structure and dynamics of biopolymers
 Solution structure and dynamics of biopolymers Atomic-detail vs. low resolution structure Information available at different scales Mobility of macromolecules in solution Brownian motion, random walk,
Solution structure and dynamics of biopolymers Atomic-detail vs. low resolution structure Information available at different scales Mobility of macromolecules in solution Brownian motion, random walk,
Fluorescence Spectroscopy
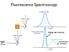 Fluorescence Spectroscopy Raleigh light scattering light all freqs Fluorescence emission Raleigh Scattering 10 nm Raleigh light scattering Fluorescence emission 400 nm Scattering - TWO particle 10 nm Particle
Fluorescence Spectroscopy Raleigh light scattering light all freqs Fluorescence emission Raleigh Scattering 10 nm Raleigh light scattering Fluorescence emission 400 nm Scattering - TWO particle 10 nm Particle
Version 001 circular and gravitation holland (2383) 1
 Version 00 circular and gravitation holland (383) This print-out should have 9 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. AP B 993 MC
Version 00 circular and gravitation holland (383) This print-out should have 9 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. AP B 993 MC
Physical Biochemistry. Kwan Hee Lee, Ph.D. Handong Global University
 Physical Biochemistry Kwan Hee Lee, Ph.D. Handong Global University Week 9 CHAPTER 4 Physical Equilibria Basic Concepts Biological organisms are highly inhomogeneous. Different regions of each cell have
Physical Biochemistry Kwan Hee Lee, Ph.D. Handong Global University Week 9 CHAPTER 4 Physical Equilibria Basic Concepts Biological organisms are highly inhomogeneous. Different regions of each cell have
Transport Properties
 EDR = Engel, Drobny, Reid, Physical Chemistry for the Life Sciences text Transport Properties EDR Chapter 24 "I have said that the Brownian movement is explained...by the incessant movement of the molecules
EDR = Engel, Drobny, Reid, Physical Chemistry for the Life Sciences text Transport Properties EDR Chapter 24 "I have said that the Brownian movement is explained...by the incessant movement of the molecules
Rotation. PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 10 Rotation Rotational kinematics Rotational inertia (moment of inertia) Kinetic energy Torque Newton s 2 nd law Work, power & energy conservation 1. Assume that
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 10 Rotation Rotational kinematics Rotational inertia (moment of inertia) Kinetic energy Torque Newton s 2 nd law Work, power & energy conservation 1. Assume that
PHYSICS PAPER 1. (THEORY) (Three hours)
 PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEY) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) All questions are compulsory. Question number
PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEY) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) All questions are compulsory. Question number
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #3 January 24, 2008 Time: 90 minutes NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN Department of Physics and Engineering Physics Physics 111.6 MIDTERM TEST #3 January 24, 2008 Time: 90 minutes NAME: (Last) Please Print (Given) STUDENT NO.: LECTURE SECTION (please
Polymers Reactions and Polymers Production (3 rd cycle)
 EQ, Q, DEQuim, DQuim nd semester 017/018, IST-UL Science and Technology of Polymers ( nd cycle) Polymers Reactions and Polymers Production (3 rd cycle) Lecture 5 Viscosity easurements of the viscosity
EQ, Q, DEQuim, DQuim nd semester 017/018, IST-UL Science and Technology of Polymers ( nd cycle) Polymers Reactions and Polymers Production (3 rd cycle) Lecture 5 Viscosity easurements of the viscosity
MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS 4764
 OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS Advanced Subsidiary General Certificate of Education Advanced General Certificate of Education MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS 6 Mechanics Wednesday JUNE 6 Afternoon hour
OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS Advanced Subsidiary General Certificate of Education Advanced General Certificate of Education MEI STRUCTURED MATHEMATICS 6 Mechanics Wednesday JUNE 6 Afternoon hour
Pure Liquid with solute. Pure Liquid
 Colligative properties are physical properties of solutions that arise because of the number of solute molecules dissolved in solution and not on the kind of solute particles dissolved in solution. Pure
Colligative properties are physical properties of solutions that arise because of the number of solute molecules dissolved in solution and not on the kind of solute particles dissolved in solution. Pure
This is start of the single grain view
 SOIL TEXTURE, PARTICLE SIZE DISTRIBUTION, SPECIFIC SURFACE AND CLAY MINERALS We will assess the physical realm of soil science in a piecewise fashion starting with the physical phases of soil, -- a single
SOIL TEXTURE, PARTICLE SIZE DISTRIBUTION, SPECIFIC SURFACE AND CLAY MINERALS We will assess the physical realm of soil science in a piecewise fashion starting with the physical phases of soil, -- a single
PHYSICS 1 Simple Harmonic Motion
 Advanced Placement PHYSICS 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Student 014-015 What I Absolutely Have to Know to Survive the AP* Exam Whenever the acceleration of an object is proportional to its displacement and
Advanced Placement PHYSICS 1 Simple Harmonic Motion Student 014-015 What I Absolutely Have to Know to Survive the AP* Exam Whenever the acceleration of an object is proportional to its displacement and
