University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 453 Winter Quarter 2005
|
|
|
- April Blake
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture /4/ University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 4 Winter Quarter A. Polymer Properties of DNA When a linear polymer like DNA becomes long enough it can no longer be treated as a prolate ellipsoid. DNA must be viewed as a random-coil polymer. For the purposes of calculating the the frictional coefficient f, a very long random-coil polymer may be treated as a spherical molecule, with radius R H, called the hydrodynamic radius. The hydrodynamic radius is related to the radius of gyration R G by the equation: RH =.66RG (.). The radius of gyration for a very long DNA can be calculated in turn: 8 PN (.4 cm) RG = (.) 6 where N is the number of base pairs and P is a property of a polymer called the persistence length. The persistence length measures the length over which a polymer points in the same direction as its first bond. The persistence length for DNA is P=x -8 8 cm, equivalent to about 4 base pairs. The number.4 cm is the approximate distance between successive base pairs in DNA. Example : Calculate the radius of gyration R G for a DNA which is base pairs in length. Also, calculate the hydrodynamic radius R H. c h b gc hc h PN 4. cm cm. 4 cm : RG = = Then R = 7. cm. R = 66. R = cm. G H G = 7. Example : Treating the base pair DNA as a sphere with radius R H, calculate the frictional coefficient f. Assume the viscosity of the solvent η is. poise. 6 7 Solution: f = 6πη R = g/ cm s cm= 9. 4 g/ s H Example : Using the frictional coefficient calculated above, determine the diffusion coefficient for base pair long DNA at T=9K. kt (.8 J / K)(.9 K) B Solution: D = = = 4.9 m / s f 9.4 kg/ s Example 4: What is the root-mean-squared displacement of a base pair DNA at T=9K after second? Assume properties for DNA from examples -. cm
2 Solution: The root mean squared displacement is defined for a three dimensions as R = R = x + y + z = Dt + Dt + Dt = 6Dt rms 6 Rrms = m / s s =.7 m Note that unlike Newtonian mechanics where the displacement of a particle R moving at constant velocity v is proportional to time, i.e. R = v t, the rms displacement of a particle undergoing diffusive motion goes like the square root of time. B. Integrals of Gaussian functions Here we give general guidelines and rules for handling integrals that involve functions of n x r the form xe where r is a constant and n =,,, The function f ( x) = e xr is called a bell-shaped curve or a Gaussian function. A common form for integrals of importance in this class are: x e dx where n=,,, We also use integrals of the type The integral x e dx. x e dx has standard form, which means you can find it in a table of standard integrals. The answer you get depends upon whether n is an even integer, and odd integer or zero. Case : n=. The integral is e xr dx = Case : n is even. We can guarantee that n is even by making the substitution k x r ( k ) n=k, where k=,, Then we get x e dx = π. The k+ k+ r commonest cases we have used in Chemistry 4 are xr π k= or xe dx=. r 4 4 xr k= or xe dx= π 8r Case : n is odd. We can guarantee that n is even by making the substitution k+ x r k! n=k+, where k=,,, Then we get x e dx =. The k + r commonest cases we have used in Chemistry 4 are xr k= or xe dx =. r k= or xr xe dx= r π r
3 C. Even and Odd Functions In Chemistry 4 we encounter integrals of the form x e dx where n=,, Note the integral differs from the standard forms discussed above in that the limits are from to instead of from to. In such cases the standard forms may or may not be applicable depending on certain properties of the integrand. The property in question is whether the function in the integrand is even or odd. o An even function has the property f ( x) f ( x) =. If you change the sign of the variable the value of the function does not change. Consider the function f ( x) = e xr ( x) r xr. We find f ( x) = e = e = f ( x). Therefore f(x) is even. Similarly m mu /kbt u = uf u du = ue du = π kt B xr x r f x = x e = x e = f x, so all functions of the form k x r x e xr xe o An odd function has the property x k+ x r e k=,,, are odd. is also even. In fact k=,,, are even. f x = f x. Functions of the form D. Integrals of Even and Odd Functions An important type of integral that we encounter in Chemistry 4 is an integral + a over a symmetric interval f ( x) dx. These integrals have the property: + a + a + a + a = + = + ( ) f x dx f x dx f x dx f x dx f x dx. f(x) is even i.e. f ( x) = f ( x). Then + a + a + a + a + a = + = + ( ) = f x dx f x dx f x dx f x dx f x dx f x dx. f(x) is odd i.e. f(x)=-f(-x). Then + a + a + a + a + a + a f x dx = f x dx + f x dx = f x dx + f x dx = f x dx f x dx = The integral of an odd function over a symmetric interval is zero. An application of these principles is the evaluation of integrals of Gaussian functions.
4 k. For even functions of the form x e k=,,, x r k x r k x r x e dx = x e dx. For odd functions of the form x k+ x r e k=,,, k+ x r x e dx = E. Physical Examples: Kinetic Theory of Gases:. For a hypothetical one dimensional gas the velocity distribution function is m mu /kbt f u = e. The average velocity in one dimension is π kt B m mu /kbt u = uf u du = ue du π kt =, a result that is due to the B mu fact that an odd function /k B T ue is being integrated over a symmetric interval. The diffusion equation dc k T d C D d C B = = has the solution dt f dx dx D=.*^(-)m^/s 6 4 Series t= C t=. t= d= to.x^-m C bx, tg= CD t e x / 4 D t, where D is the diffusion coefficient. 4π The plot above is a graph of C (x,t) for a diffusion coefficient of D=.x - m /s. Note C =. The function C(x,t) can be used to calculate the average displacement of a solute particle x rms
5 z z z x xc x t dx xcd t e dx xc Dt e x / 4 Dt x / 4 Dt dx rms = (, ) = = = 4π 4π Average displacement.. x*c(x,t) Series d= -.*^-m This result can be understood if we plot the function xc(x,t) versus x The area under this curve(i.e. the integral of the function xc(x,t) is zero which indicates that the average displacement is zero. That is z xrmx = x C( x, t) dx =. This is reasonable because for a bell-shaped distribution for every molecule that travels a distance +x, another molecule travels x. The average is thus zero. z However, the mean squared displacement is given by x = x C( x, t) = Dt This quantity is clearly non-zero, a fact which is shown by the graph below
6 Root Mean Square Displacement x^*c(x,t) Series 7 9 distance -.x^(-)m Where the area under the curve is the root mean square displacement z / x x x C( x, t) Dt rms = = L N M O Q P =
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 453 Winter Quarter 2008
 Lecture /1/8 University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 45 Winter Quarter 8 A. Analysis of Diffusion Coefficients: Friction Diffusion coefficients can be measured by a variety of methods
Lecture /1/8 University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 45 Winter Quarter 8 A. Analysis of Diffusion Coefficients: Friction Diffusion coefficients can be measured by a variety of methods
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 355 Spring Quarter 2005
 University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 55 Spring Quarter 5 Homework Assignment 7: Due no later than 5: pm on 5/14/4 8., 8.6, 8.1 8.) According to text equation 16, after N jumps the
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 55 Spring Quarter 5 Homework Assignment 7: Due no later than 5: pm on 5/14/4 8., 8.6, 8.1 8.) According to text equation 16, after N jumps the
Measuring the size and shape of macromolecules. Hydrodynamics: study of the objects in water How do the move? Translation Rotation
 Measuring the size and shape of macromolecules Hydrodynamics: study of the objects in water How do the move? Translation Rotation 1) Movement with no external forcefree diffusion 2) Movement under the
Measuring the size and shape of macromolecules Hydrodynamics: study of the objects in water How do the move? Translation Rotation 1) Movement with no external forcefree diffusion 2) Movement under the
There are 6 parts to this exam. Parts 1-3 deal with material covered since the midterm exam. Part 4-6 cover all course material.
 Chemistry 453 March 9, 03 Enter answers in a lue ook Final Examination Key There are 6 parts to this exam. Parts -3 deal with material covered since the midterm exam. Part 4-6 cover all course material.
Chemistry 453 March 9, 03 Enter answers in a lue ook Final Examination Key There are 6 parts to this exam. Parts -3 deal with material covered since the midterm exam. Part 4-6 cover all course material.
University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 453 Winter Quarter 2013
 Lecture 1 3/13/13 University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 53 Winter Quarter 013 A. Definition of Viscosity Viscosity refers to the resistance of fluids to flow. Consider a flowing liquid
Lecture 1 3/13/13 University of Washington Department of Chemistry Chemistry 53 Winter Quarter 013 A. Definition of Viscosity Viscosity refers to the resistance of fluids to flow. Consider a flowing liquid
Hydrodynamics: Viscosity and Diffusion Hydrodynamics is the study of mechanics in a liquid, where the frictional drag of the liquid cannot be ignored
 Hydrodynamics: Viscosity and Diffusion Hydrodynamics is the study of mechanics in a liquid, where the frictional drag of the liquid cannot be ignored First let s just consider fluid flow, where the fluid
Hydrodynamics: Viscosity and Diffusion Hydrodynamics is the study of mechanics in a liquid, where the frictional drag of the liquid cannot be ignored First let s just consider fluid flow, where the fluid
Viscometry. - neglect Brownian motion. CHEM 305
 Viscometry When a macromolecule moves in solution (e.g. of water), it induces net motions of the individual solvent molecules, i.e. the solvent molecules will feel a force. - neglect Brownian motion. To
Viscometry When a macromolecule moves in solution (e.g. of water), it induces net motions of the individual solvent molecules, i.e. the solvent molecules will feel a force. - neglect Brownian motion. To
TRANSPORT PHENOMENON FICK S LAW OF DIFFUSION ATP-POWERED PUMPS -II-
 TRANSPORT PHENOMENON FICK S LAW OF DIFFUSION ATP-POWERED PUMPS -II- Yalçın İŞLER, PhD Izmir Katip Celebi University Department of Biomedical Engineering islerya@yahoo.com DIFFUSION Diffusion describes
TRANSPORT PHENOMENON FICK S LAW OF DIFFUSION ATP-POWERED PUMPS -II- Yalçın İŞLER, PhD Izmir Katip Celebi University Department of Biomedical Engineering islerya@yahoo.com DIFFUSION Diffusion describes
Polymer Dynamics and Rheology
 Polymer Dynamics and Rheology 1 Polymer Dynamics and Rheology Brownian motion Harmonic Oscillator Damped harmonic oscillator Elastic dumbbell model Boltzmann superposition principle Rubber elasticity and
Polymer Dynamics and Rheology 1 Polymer Dynamics and Rheology Brownian motion Harmonic Oscillator Damped harmonic oscillator Elastic dumbbell model Boltzmann superposition principle Rubber elasticity and
2. Molecules in Motion
 2. Molecules in Motion Kinetic Theory of Gases (microscopic viewpoint) assumptions (1) particles of mass m and diameter d; ceaseless random motion (2) dilute gas: d λ, λ = mean free path = average distance
2. Molecules in Motion Kinetic Theory of Gases (microscopic viewpoint) assumptions (1) particles of mass m and diameter d; ceaseless random motion (2) dilute gas: d λ, λ = mean free path = average distance
Light scattering Small and large particles
 Scattering by macromolecules E B Incident light Scattered Light particle Oscillating E field from light makes electronic cloud oscillate surrounding the particle Intensity: I E Accelerating charges means
Scattering by macromolecules E B Incident light Scattered Light particle Oscillating E field from light makes electronic cloud oscillate surrounding the particle Intensity: I E Accelerating charges means
Measuring S using an analytical ultracentrifuge. Moving boundary
 Measuring S using an analytical ultracentrifuge Moving boundary [C] t = 0 t 1 t 2 0 top r bottom 1 dr b r b (t) r b ω 2 = S ln = ω 2 S (t-t dt r b (t o ) o ) r b = boundary position velocity = dr b dt
Measuring S using an analytical ultracentrifuge Moving boundary [C] t = 0 t 1 t 2 0 top r bottom 1 dr b r b (t) r b ω 2 = S ln = ω 2 S (t-t dt r b (t o ) o ) r b = boundary position velocity = dr b dt
Chemical Engineering 160/260 Polymer Science and Engineering. Lecture 14: Amorphous State February 14, 2001
 Chemical Engineering 160/260 Polymer Science and Engineering Lecture 14: Amorphous State February 14, 2001 Objectives! To provide guidance toward understanding why an amorphous polymer glass may be considered
Chemical Engineering 160/260 Polymer Science and Engineering Lecture 14: Amorphous State February 14, 2001 Objectives! To provide guidance toward understanding why an amorphous polymer glass may be considered
Polymer dynamics. Course M6 Lecture 5 26/1/2004 (JAE) 5.1 Introduction. Diffusion of polymers in melts and dilute solution.
 Course M6 Lecture 5 6//004 Polymer dynamics Diffusion of polymers in melts and dilute solution Dr James Elliott 5. Introduction So far, we have considered the static configurations and morphologies of
Course M6 Lecture 5 6//004 Polymer dynamics Diffusion of polymers in melts and dilute solution Dr James Elliott 5. Introduction So far, we have considered the static configurations and morphologies of
Transport Properties
 EDR = Engel, Drobny, Reid, Physical Chemistry for the Life Sciences text Transport Properties EDR Chapter 24 "I have said that the Brownian movement is explained...by the incessant movement of the molecules
EDR = Engel, Drobny, Reid, Physical Chemistry for the Life Sciences text Transport Properties EDR Chapter 24 "I have said that the Brownian movement is explained...by the incessant movement of the molecules
Final Morphology of Complex Materials
 120314 Final Morphology of Complex Materials 1) Proteins are the prototypical model for hierarchy. a) Give the generic chemical structure for an amino acid and a protein molecule (a tripeptide). b) Label
120314 Final Morphology of Complex Materials 1) Proteins are the prototypical model for hierarchy. a) Give the generic chemical structure for an amino acid and a protein molecule (a tripeptide). b) Label
t = no of steps of length s
 s t = no of steps of length s Figure : Schematic of the path of a diffusing molecule, for example, one in a gas or a liquid. The particle is moving in steps of length s. For a molecule in a liquid the
s t = no of steps of length s Figure : Schematic of the path of a diffusing molecule, for example, one in a gas or a liquid. The particle is moving in steps of length s. For a molecule in a liquid the
Created by T. Madas CALCULUS KINEMATICS. Created by T. Madas
 CALCULUS KINEMATICS CALCULUS KINEMATICS IN SCALAR FORM Question (**) A particle P is moving on the x axis and its acceleration a ms, t seconds after a given instant, is given by a = 6t 8, t 0. The particle
CALCULUS KINEMATICS CALCULUS KINEMATICS IN SCALAR FORM Question (**) A particle P is moving on the x axis and its acceleration a ms, t seconds after a given instant, is given by a = 6t 8, t 0. The particle
AP CALCULUS AB 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B)
 AP CALCULUS AB 27 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 2 A particle moves along the x-axis so that its velocity v at time 2 t is given by vt () = sin ( t ). The graph of v is shown above for t 5 π. The
AP CALCULUS AB 27 SCORING GUIDELINES (Form B) Question 2 A particle moves along the x-axis so that its velocity v at time 2 t is given by vt () = sin ( t ). The graph of v is shown above for t 5 π. The
Part III. Polymer Dynamics molecular models
 Part III. Polymer Dynamics molecular models I. Unentangled polymer dynamics I.1 Diffusion of a small colloidal particle I.2 Diffusion of an unentangled polymer chain II. Entangled polymer dynamics II.1.
Part III. Polymer Dynamics molecular models I. Unentangled polymer dynamics I.1 Diffusion of a small colloidal particle I.2 Diffusion of an unentangled polymer chain II. Entangled polymer dynamics II.1.
Biomolecular hydrodynamics
 Biomolecular hydrodynamics Chem 341, Fall, 2014 1 Frictional coefficients Consider a particle moving with velocity v under the influence of some external force F (say a graviational or electrostatic external
Biomolecular hydrodynamics Chem 341, Fall, 2014 1 Frictional coefficients Consider a particle moving with velocity v under the influence of some external force F (say a graviational or electrostatic external
Calculus with Algebra and Trigonometry II Lecture 21 Probability applications
 Calculus with Algebra and Trigonometry II Lecture 21 Probability applications Apr 16, 215 Calculus with Algebra and Trigonometry II Lecture 21Probability Apr applications 16, 215 1 / 1 Histograms The distribution
Calculus with Algebra and Trigonometry II Lecture 21 Probability applications Apr 16, 215 Calculus with Algebra and Trigonometry II Lecture 21Probability Apr applications 16, 215 1 / 1 Histograms The distribution
Minimal encounter time and separation determine ligand-receptor binding in cell adhesion SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Minimal encounter time and separation determine ligand-receptor binding in cell adhesion SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Philippe Robert Alice Nicolas Said Aranda-Espinoza Pierre Bongrand Laurent Limozin Molecular
Minimal encounter time and separation determine ligand-receptor binding in cell adhesion SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Philippe Robert Alice Nicolas Said Aranda-Espinoza Pierre Bongrand Laurent Limozin Molecular
Transport Properties: Momentum Transport, Viscosity
 Transport Properties: Momentum Transport, Viscosity 13th February 2011 1 Introduction Much as mass(material) is transported within luids (gases and liquids), linear momentum is also associated with transport,
Transport Properties: Momentum Transport, Viscosity 13th February 2011 1 Introduction Much as mass(material) is transported within luids (gases and liquids), linear momentum is also associated with transport,
QuickCheck. Collisions between molecules. Collisions between molecules
 Collisions between molecules We model molecules as rigid spheres of radius r as shown at the right. The mean free path of a molecule is the average distance it travels between collisions. The average time
Collisions between molecules We model molecules as rigid spheres of radius r as shown at the right. The mean free path of a molecule is the average distance it travels between collisions. The average time
Added topics: depend on time/rate - Skipped
 VIa- 1 Added topics: depend on time/rate - Skipped - 2012 a) diffusion rate material moves in medium faster motion more friction affect equilibrium separations like electrophoresis HPLC pharmacological
VIa- 1 Added topics: depend on time/rate - Skipped - 2012 a) diffusion rate material moves in medium faster motion more friction affect equilibrium separations like electrophoresis HPLC pharmacological
Collisions between molecules
 Collisions between molecules We model molecules as rigid spheres of radius r as shown at the right. The mean free path of a molecule is the average distance it travels between collisions. The average time
Collisions between molecules We model molecules as rigid spheres of radius r as shown at the right. The mean free path of a molecule is the average distance it travels between collisions. The average time
HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS MATH 1910 Sections 6.4, 6.5, 7.1 Fall 2016
 HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS MATH 9 Sections 6.4, 6.5, 7. Fall 6 Problem 6.4. Sketch the region enclosed by x = 4 y +, x = 4y, and y =. Use the Shell Method to calculate the volume of rotation about the x-axis SOLUTION.
HOMEWORK SOLUTIONS MATH 9 Sections 6.4, 6.5, 7. Fall 6 Problem 6.4. Sketch the region enclosed by x = 4 y +, x = 4y, and y =. Use the Shell Method to calculate the volume of rotation about the x-axis SOLUTION.
Entanglements. M < M e. M > M e. Rouse. Zero-shear viscosity vs. M (note change of slope) Edwards degennes Doi. Berry + Fox, slope 3.4.
 Entanglements Zero-shear viscosity vs. M (note change of slope) M < M e Rouse slope 3.4 M > M e Edwards degennes Doi slope 1 Berry + Fox, 1968 Question: Which factors affect the Me: T, P, M, flexibility,
Entanglements Zero-shear viscosity vs. M (note change of slope) M < M e Rouse slope 3.4 M > M e Edwards degennes Doi slope 1 Berry + Fox, 1968 Question: Which factors affect the Me: T, P, M, flexibility,
From Random Numbers to Monte Carlo. Random Numbers, Random Walks, Diffusion, Monte Carlo integration, and all that
 From Random Numbers to Monte Carlo Random Numbers, Random Walks, Diffusion, Monte Carlo integration, and all that Random Walk Through Life Random Walk Through Life If you flip the coin 5 times you will
From Random Numbers to Monte Carlo Random Numbers, Random Walks, Diffusion, Monte Carlo integration, and all that Random Walk Through Life Random Walk Through Life If you flip the coin 5 times you will
Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Physics 131
 Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Energy Chemical bonding Intermolecular Interactions 1 Physics 131 Quiz 11 60 50 Q 1.1 11 40 30 20 10 0 A B C D 2 18 Q 1.2
Physics 131- Fundamentals of Physics for Biologists I Professor: Arpita Upadhyaya Energy Chemical bonding Intermolecular Interactions 1 Physics 131 Quiz 11 60 50 Q 1.1 11 40 30 20 10 0 A B C D 2 18 Q 1.2
Lecture 10: Brownian Motion, Random Walk & Diffusion Side Chains of Amino Acids
 Lecture 10: Brownian Motion, Random Walk & Diffusion Side Chains of Amino Acids Lecturer: Prof. Brigita Urbanc (brigita@drexel.edu) PHYS 461 & 561, Fall 2009-2010 1 Stochastic Processes: Brownian Motion
Lecture 10: Brownian Motion, Random Walk & Diffusion Side Chains of Amino Acids Lecturer: Prof. Brigita Urbanc (brigita@drexel.edu) PHYS 461 & 561, Fall 2009-2010 1 Stochastic Processes: Brownian Motion
6. Transport phenomena. Basel, 2008
 6. Transport phenomena Basel, 2008 6. Transport phenomena 1. Introduction 2. Phenomenological equations for transport properties 3. Transport properties of a perfect gas 4. Diffusion in a fluid 5. Measurement
6. Transport phenomena Basel, 2008 6. Transport phenomena 1. Introduction 2. Phenomenological equations for transport properties 3. Transport properties of a perfect gas 4. Diffusion in a fluid 5. Measurement
A Model for Non-Newtonian Flow in Porous Media at Different Flow Regimes
 A Model for Non-Newtonian Flow in Porous Media at Different Flow Regimes Quick introduction to polymer flooding Outline of talk Polymer behaviour in bulk versus porous medium Mathematical modeling of polymer
A Model for Non-Newtonian Flow in Porous Media at Different Flow Regimes Quick introduction to polymer flooding Outline of talk Polymer behaviour in bulk versus porous medium Mathematical modeling of polymer
Practice Exam 1 Solutions
 Practice Exam 1 Solutions 1a. Let S be the region bounded by y = x 3, y = 1, and x. Find the area of S. What is the volume of the solid obtained by rotating S about the line y = 1? Area A = Volume 1 1
Practice Exam 1 Solutions 1a. Let S be the region bounded by y = x 3, y = 1, and x. Find the area of S. What is the volume of the solid obtained by rotating S about the line y = 1? Area A = Volume 1 1
PHYSICS PAPER 1. (THEORY) (Three hours)
 PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEY) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) All questions are compulsory. Question number
PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEY) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) All questions are compulsory. Question number
This is a Gaussian probability centered around m = 0 (the most probable and mean position is the origin) and the mean square displacement m 2 = n,or
 Physics 7b: Statistical Mechanics Brownian Motion Brownian motion is the motion of a particle due to the buffeting by the molecules in a gas or liquid. The particle must be small enough that the effects
Physics 7b: Statistical Mechanics Brownian Motion Brownian motion is the motion of a particle due to the buffeting by the molecules in a gas or liquid. The particle must be small enough that the effects
Organization of NAMD Tutorial Files
 Organization of NAMD Tutorial Files .1.1. RMSD for individual residues Objective: Find the average RMSD over time of each residue in the protein using VMD. Display the protein with the residues colored
Organization of NAMD Tutorial Files .1.1. RMSD for individual residues Objective: Find the average RMSD over time of each residue in the protein using VMD. Display the protein with the residues colored
Lecture 5: Macromolecules, polymers and DNA
 1, polymers and DNA Introduction In this lecture, we focus on a subfield of soft matter: macromolecules and more particularly on polymers. As for the previous chapter about surfactants and electro kinetics,
1, polymers and DNA Introduction In this lecture, we focus on a subfield of soft matter: macromolecules and more particularly on polymers. As for the previous chapter about surfactants and electro kinetics,
d. Determine the power output of the boy required to sustain this velocity.
 AP Physics C Dynamics Free Response Problems 1. A 45 kg boy stands on 30 kg platform suspended by a rope passing over a stationary pulley that is free to rotate. The other end of the rope is held by the
AP Physics C Dynamics Free Response Problems 1. A 45 kg boy stands on 30 kg platform suspended by a rope passing over a stationary pulley that is free to rotate. The other end of the rope is held by the
Chem728 Spr. 12 page 1 2/29/12. Assignment 2 Estimates of Hydrodynamic Radii from Dynamic Light Scattering Data. ANSWERS
 Chem728 Spr. 12 page 1 2/29/12 Assignment 2 Estimates of Hydrodynamic Radii from Dynamic Light Scattering Data. ANSWERS Objective: Analyze experimental correlation functions of scattered light to determine
Chem728 Spr. 12 page 1 2/29/12 Assignment 2 Estimates of Hydrodynamic Radii from Dynamic Light Scattering Data. ANSWERS Objective: Analyze experimental correlation functions of scattered light to determine
Lecture 6 Examples and Problems
 Lecture 6 Examples and Problems Heat capacity of solids & liquids Thermal diffusion Thermal conductivity Irreversibility Hot Cold Random Walk and Particle Diffusion Counting and Probability Microstates
Lecture 6 Examples and Problems Heat capacity of solids & liquids Thermal diffusion Thermal conductivity Irreversibility Hot Cold Random Walk and Particle Diffusion Counting and Probability Microstates
Lecture 6 Molecular motion and Transport p roperties properties
 Lecture 6 Molecular motion and Transport properties Molecular motion The Aim: Describe the migration of properties through the matter using simple random motion picture Within this lecture: Transport properties
Lecture 6 Molecular motion and Transport properties Molecular motion The Aim: Describe the migration of properties through the matter using simple random motion picture Within this lecture: Transport properties
19-9 Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas
 19-9 Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas Learning Objectives 19.44 On a p-v diagram, sketch an adiabatic expansion (or contraction) and identify that there is no heat exchange Q with the environment. 19.45
19-9 Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas Learning Objectives 19.44 On a p-v diagram, sketch an adiabatic expansion (or contraction) and identify that there is no heat exchange Q with the environment. 19.45
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
 KINETIC THEORY OF GASES VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS ( MARK). Write two condition when real gases obey the ideal gas equation ( nrt). n number of mole.. If the number of molecule in a container is
KINETIC THEORY OF GASES VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS ( MARK). Write two condition when real gases obey the ideal gas equation ( nrt). n number of mole.. If the number of molecule in a container is
Quiz 3 for Physics 176: Answers. Professor Greenside
 Quiz 3 for Physics 176: Answers Professor Greenside True or False Questions ( points each) For each of the following statements, please circle T or F to indicate respectively whether a given statement
Quiz 3 for Physics 176: Answers Professor Greenside True or False Questions ( points each) For each of the following statements, please circle T or F to indicate respectively whether a given statement
A. B. C. D. E. v x. ΣF x
 Q4.3 The graph to the right shows the velocity of an object as a function of time. Which of the graphs below best shows the net force versus time for this object? 0 v x t ΣF x ΣF x ΣF x ΣF x ΣF x 0 t 0
Q4.3 The graph to the right shows the velocity of an object as a function of time. Which of the graphs below best shows the net force versus time for this object? 0 v x t ΣF x ΣF x ΣF x ΣF x ΣF x 0 t 0
How DLS Works: Interference of Light
 Static light scattering vs. Dynamic light scattering Static light scattering measures time-average intensities (mean square fluctuations) molecular weight radius of gyration second virial coefficient Dynamic
Static light scattering vs. Dynamic light scattering Static light scattering measures time-average intensities (mean square fluctuations) molecular weight radius of gyration second virial coefficient Dynamic
Statistical and hydrodynamic properties of topological polymers for various graphs showing enhanced short-range correlation
 arxiv:1607.08726v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Jul 2016 Statistical and hydrodynamic properties of topological polymers for various graphs showing enhanced short-range correlation Erica Uehara and Tetsuo Deguchi
arxiv:1607.08726v1 [cond-mat.soft] 29 Jul 2016 Statistical and hydrodynamic properties of topological polymers for various graphs showing enhanced short-range correlation Erica Uehara and Tetsuo Deguchi
Module 5: Rise and Fall of the Clockwork Universe. You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of:
 OCR B Physics H557 Module 5: Rise and Fall of the Clockwork Universe You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of: 5.2: Matter Particle model: A gas consists of many very small, rapidly
OCR B Physics H557 Module 5: Rise and Fall of the Clockwork Universe You should be able to demonstrate and show your understanding of: 5.2: Matter Particle model: A gas consists of many very small, rapidly
Mechanical properties of polymers: an overview. Suryasarathi Bose Dept. of Materials Engineering, IISc, Bangalore
 Mechanical properties of polymers: an overview Suryasarathi Bose Dept. of Materials Engineering, IISc, Bangalore UGC-NRCM Summer School on Mechanical Property Characterization- June 2012 Overview of polymer
Mechanical properties of polymers: an overview Suryasarathi Bose Dept. of Materials Engineering, IISc, Bangalore UGC-NRCM Summer School on Mechanical Property Characterization- June 2012 Overview of polymer
A( x) B( x) C( x) y( x) 0, A( x) 0
 3.1 Lexicon Revisited The nonhomogeneous nd Order ODE has the form: d y dy A( x) B( x) C( x) y( x) F( x), A( x) dx dx The homogeneous nd Order ODE has the form: d y dy A( x) B( x) C( x) y( x), A( x) dx
3.1 Lexicon Revisited The nonhomogeneous nd Order ODE has the form: d y dy A( x) B( x) C( x) y( x) F( x), A( x) dx dx The homogeneous nd Order ODE has the form: d y dy A( x) B( x) C( x) y( x), A( x) dx
MD Thermodynamics. Lecture 12 3/26/18. Harvard SEAS AP 275 Atomistic Modeling of Materials Boris Kozinsky
 MD Thermodynamics Lecture 1 3/6/18 1 Molecular dynamics The force depends on positions only (not velocities) Total energy is conserved (micro canonical evolution) Newton s equations of motion (second order
MD Thermodynamics Lecture 1 3/6/18 1 Molecular dynamics The force depends on positions only (not velocities) Total energy is conserved (micro canonical evolution) Newton s equations of motion (second order
Chem/Biochem 471 Exam 2 11/14/07 Page 1 of 7 Name:
 Page 1 of 7 Please leave the exam pages stapled together. The formulas are on a separate sheet. This exam has 5 questions. You must answer at least 4 of the questions. You may answer all 5 questions if
Page 1 of 7 Please leave the exam pages stapled together. The formulas are on a separate sheet. This exam has 5 questions. You must answer at least 4 of the questions. You may answer all 5 questions if
BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems
 BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems Estimation of diffusion Coefficient Dr. Zifei Liu Diffusion mass transfer Diffusion mass transfer refers to mass in transit due to a species concentration
BAE 820 Physical Principles of Environmental Systems Estimation of diffusion Coefficient Dr. Zifei Liu Diffusion mass transfer Diffusion mass transfer refers to mass in transit due to a species concentration
Limits at Infinity. Horizontal Asymptotes. Definition (Limits at Infinity) Horizontal Asymptotes
 Limits at Infinity If a function f has a domain that is unbounded, that is, one of the endpoints of its domain is ±, we can determine the long term behavior of the function using a it at infinity. Definition
Limits at Infinity If a function f has a domain that is unbounded, that is, one of the endpoints of its domain is ±, we can determine the long term behavior of the function using a it at infinity. Definition
Show your work on the problems Box in answers No Naked Numbers!
 AP Physics C! name 100pt TAKE HOME TEST - Chap 7 Work & Kinetic Energy 12/7/12 Show your work on the problems Box in answers No Naked Numbers! [ Yes! ] means that you get a card to help you on the test
AP Physics C! name 100pt TAKE HOME TEST - Chap 7 Work & Kinetic Energy 12/7/12 Show your work on the problems Box in answers No Naked Numbers! [ Yes! ] means that you get a card to help you on the test
Chem 406 Biophysical Chemistry Lecture 1 Transport Processes, Sedimentation & Diffusion
 Chem 406 Biophysical Chemistry Lecture 1 Transport Processes, Sedimentation & Diusion I. Introduction A. There are a group o biophysical techniques that are based on transport processes. 1. Transport processes
Chem 406 Biophysical Chemistry Lecture 1 Transport Processes, Sedimentation & Diusion I. Introduction A. There are a group o biophysical techniques that are based on transport processes. 1. Transport processes
Afternoon Section. Physics 1210 Exam 2 November 8, ! v = d! r dt. a avg. = v2. ) T 2! w = m g! f s. = v at v 2 1.
 Name Physics 1210 Exam 2 November 8, 2012 Afternoon Section Please write directly on the exam and attach other sheets of work if necessary. Calculators are allowed. No notes or books may be used. Multiple-choice
Name Physics 1210 Exam 2 November 8, 2012 Afternoon Section Please write directly on the exam and attach other sheets of work if necessary. Calculators are allowed. No notes or books may be used. Multiple-choice
A101 ASSESSMENT Quadratics, Discriminant, Inequalities 1
 Do the questions as a test circle questions you cannot answer Red (1) Solve a) 7x = x 2-30 b) 4x 2-29x + 7 = 0 (2) Solve the equation x 2 6x 2 = 0, giving your answers in simplified surd form [3] (3) a)
Do the questions as a test circle questions you cannot answer Red (1) Solve a) 7x = x 2-30 b) 4x 2-29x + 7 = 0 (2) Solve the equation x 2 6x 2 = 0, giving your answers in simplified surd form [3] (3) a)
Exercise: concepts from chapter 3
 Reading:, Ch 3 1) The natural representation of a curve, c = c(s), satisfies the condition dc/ds = 1, where s is the natural parameter for the curve. a) Describe in words and a sketch what this condition
Reading:, Ch 3 1) The natural representation of a curve, c = c(s), satisfies the condition dc/ds = 1, where s is the natural parameter for the curve. a) Describe in words and a sketch what this condition
Physics of biological membranes, diffusion, osmosis Dr. László Nagy
 Physics of biological membranes, diffusion, osmosis Dr. László Nagy -Metabolic processes and transport processes. - Macrotransport : transport of large amount of material : through vessel systems : in
Physics of biological membranes, diffusion, osmosis Dr. László Nagy -Metabolic processes and transport processes. - Macrotransport : transport of large amount of material : through vessel systems : in
Lycka till!
 Avd. Matematisk statistik TENTAMEN I SF294 SANNOLIKHETSTEORI/EXAM IN SF294 PROBABILITY THE- ORY MONDAY THE 14 T H OF JANUARY 28 14. p.m. 19. p.m. Examinator : Timo Koski, tel. 79 71 34, e-post: timo@math.kth.se
Avd. Matematisk statistik TENTAMEN I SF294 SANNOLIKHETSTEORI/EXAM IN SF294 PROBABILITY THE- ORY MONDAY THE 14 T H OF JANUARY 28 14. p.m. 19. p.m. Examinator : Timo Koski, tel. 79 71 34, e-post: timo@math.kth.se
Math 241 Final Exam Spring 2013
 Name: Math 241 Final Exam Spring 213 1 Instructor (circle one): Epstein Hynd Wong Please turn off and put away all electronic devices. You may use both sides of a 3 5 card for handwritten notes while you
Name: Math 241 Final Exam Spring 213 1 Instructor (circle one): Epstein Hynd Wong Please turn off and put away all electronic devices. You may use both sides of a 3 5 card for handwritten notes while you
Perfect Gases Transport Phenomena
 Perfect Gases Transport Phenomena We have been able to relate quite a few macroscopic properties of gasses such as P, V, T to molecular behaviour on microscale. We saw how macroscopic pressure is related
Perfect Gases Transport Phenomena We have been able to relate quite a few macroscopic properties of gasses such as P, V, T to molecular behaviour on microscale. We saw how macroscopic pressure is related
Thermodynamics and Statistical Physics Exam
 Thermodynamics and Statistical Physics Exam You may use your textbook (Thermal Physics by Schroeder) and a calculator. 1. Short questions. No calculation needed. (a) Two rooms A and B in a building are
Thermodynamics and Statistical Physics Exam You may use your textbook (Thermal Physics by Schroeder) and a calculator. 1. Short questions. No calculation needed. (a) Two rooms A and B in a building are
Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions
 Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions 1. What forces act on a single colloidal particle suspended in a flowing fluid? Discuss the dependence of these forces on particle radius. 2. What
Colloidal Suspension Rheology Chapter 1 Study Questions 1. What forces act on a single colloidal particle suspended in a flowing fluid? Discuss the dependence of these forces on particle radius. 2. What
(a) x cos 3x dx We apply integration by parts. Take u = x, so that dv = cos 3x dx, v = 1 sin 3x, du = dx. Thus
 Math 128 Midterm Examination 2 October 21, 28 Name 6 problems, 112 (oops) points. Instructions: Show all work partial credit will be given, and Answers without work are worth credit without points. You
Math 128 Midterm Examination 2 October 21, 28 Name 6 problems, 112 (oops) points. Instructions: Show all work partial credit will be given, and Answers without work are worth credit without points. You
Final exam. Please write your name on the exam and keep an ID card ready. You may use a calculator (but no computer or smart phone) and a dictionary.
 Biophysics of Macromolecules Prof. D. Braun and Prof. J. Lipfert SS 2015 Final exam Final exam Name: Student number ( Matrikelnummer ): Please write your name on the exam and keep an ID card ready. You
Biophysics of Macromolecules Prof. D. Braun and Prof. J. Lipfert SS 2015 Final exam Final exam Name: Student number ( Matrikelnummer ): Please write your name on the exam and keep an ID card ready. You
Practice Final Solutions
 Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
Practice Final Solutions Math 1, Fall 17 Problem 1. Find a parameterization for the given curve, including bounds on the parameter t. Part a) The ellipse in R whose major axis has endpoints, ) and 6, )
10.0 Reaction Diffusion Model: Review
 EE65R: Reliability Physics of anoelectronic Devices Lecture 1: egative Bias Temperature Instability: AC Degradation Date: Oct 6 Prepared by: Dhanoop Varghese Reviewed by: Ahmad Ehtesham Islam 1. Reaction
EE65R: Reliability Physics of anoelectronic Devices Lecture 1: egative Bias Temperature Instability: AC Degradation Date: Oct 6 Prepared by: Dhanoop Varghese Reviewed by: Ahmad Ehtesham Islam 1. Reaction
GEM4 Summer School OpenCourseWare
 GEM4 Summer School OpenCourseWare http://gem4.educommons.net/ http://www.gem4.org/ Lecture: Polymer Chains by Ju Li. Given August 16, 2006 during the GEM4 session at MIT in Cambridge, MA. Please use the
GEM4 Summer School OpenCourseWare http://gem4.educommons.net/ http://www.gem4.org/ Lecture: Polymer Chains by Ju Li. Given August 16, 2006 during the GEM4 session at MIT in Cambridge, MA. Please use the
2011 Mathematics Extension 1 HSC Examination Sample Answers
 0 Mathematics Extension HSC Examination Sample Answers When examination committees develop questions for the examination, they may write sample answers or, in the case of some questions, answers could
0 Mathematics Extension HSC Examination Sample Answers When examination committees develop questions for the examination, they may write sample answers or, in the case of some questions, answers could
7.1 Describing Circular and Rotational Motion.notebook November 03, 2017
 Describing Circular and Rotational Motion Rotational motion is the motion of objects that spin about an axis. Section 7.1 Describing Circular and Rotational Motion We use the angle θ from the positive
Describing Circular and Rotational Motion Rotational motion is the motion of objects that spin about an axis. Section 7.1 Describing Circular and Rotational Motion We use the angle θ from the positive
Prelim 1 Solutions V2 Math 1120
 Feb., Prelim Solutions V Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 9 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck! Problem ) ( Points) Calculate the following: x a)
Feb., Prelim Solutions V Math Please show your reasoning and all your work. This is a 9 minute exam. Calculators are not needed or permitted. Good luck! Problem ) ( Points) Calculate the following: x a)
ENGI 9420 Engineering Analysis Solutions to Additional Exercises
 ENGI 940 Engineering Analsis Solutions to Additional Exercises 0 Fall [Partial differential equations; Chapter 8] The function ux (, ) satisfies u u u + = 0, subject to the x x u x,0 = u x, =. Classif
ENGI 940 Engineering Analsis Solutions to Additional Exercises 0 Fall [Partial differential equations; Chapter 8] The function ux (, ) satisfies u u u + = 0, subject to the x x u x,0 = u x, =. Classif
STRUCTURE OF MATTER, VIBRATIONS AND WAVES, AND QUANTUM PHYSICS
 Imperial College London BSc/MSci EXAMINATION June 2008 This paper is also taken for the relevant Examination for the Associateship STRUCTURE OF MATTER, VIBRATIONS AND WAVES, AND QUANTUM PHYSICS For 1st-Year
Imperial College London BSc/MSci EXAMINATION June 2008 This paper is also taken for the relevant Examination for the Associateship STRUCTURE OF MATTER, VIBRATIONS AND WAVES, AND QUANTUM PHYSICS For 1st-Year
A population is modeled by the differential equation
 Math 2, Winter 2016 Weekly Homework #8 Solutions 9.1.9. A population is modeled by the differential equation dt = 1.2 P 1 P ). 4200 a) For what values of P is the population increasing? P is increasing
Math 2, Winter 2016 Weekly Homework #8 Solutions 9.1.9. A population is modeled by the differential equation dt = 1.2 P 1 P ). 4200 a) For what values of P is the population increasing? P is increasing
Work and Kinetic Energy
 Chapter 6 Work and Kinetic Energy PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Copyright 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing
Chapter 6 Work and Kinetic Energy PowerPoint Lectures for University Physics, Twelfth Edition Hugh D. Young and Roger A. Freedman Lectures by James Pazun Copyright 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing
8.6 Drag Forces in Fluids
 86 Drag Forces in Fluids When a solid object moves through a fluid it will experience a resistive force, called the drag force, opposing its motion The fluid may be a liquid or a gas This force is a very
86 Drag Forces in Fluids When a solid object moves through a fluid it will experience a resistive force, called the drag force, opposing its motion The fluid may be a liquid or a gas This force is a very
HW4 : Bivariate Distributions (1) Solutions
 STAT/MATH 395 A - PROBABILITY II UW Winter Quarter 7 Néhémy Lim HW4 : Bivariate Distributions () Solutions Problem. The joint probability mass function of X and Y is given by the following table : X Y
STAT/MATH 395 A - PROBABILITY II UW Winter Quarter 7 Néhémy Lim HW4 : Bivariate Distributions () Solutions Problem. The joint probability mass function of X and Y is given by the following table : X Y
Calculus I Practice Final Exam A
 Calculus I Practice Final Exam A This practice exam emphasizes conceptual connections and understanding to a greater degree than the exams that are usually administered in introductory single-variable
Calculus I Practice Final Exam A This practice exam emphasizes conceptual connections and understanding to a greater degree than the exams that are usually administered in introductory single-variable
f (x) = x 2 Chapter 2 Polynomial Functions Section 4 Polynomial and Rational Functions Shapes of Polynomials Graphs of Polynomials the form n
 Chapter 2 Functions and Graphs Section 4 Polynomial and Rational Functions Polynomial Functions A polynomial function is a function that can be written in the form a n n 1 n x + an 1x + + a1x + a0 for
Chapter 2 Functions and Graphs Section 4 Polynomial and Rational Functions Polynomial Functions A polynomial function is a function that can be written in the form a n n 1 n x + an 1x + + a1x + a0 for
8.3 Partial Fraction Decomposition
 8.3 partial fraction decomposition 575 8.3 Partial Fraction Decomposition Rational functions (polynomials divided by polynomials) and their integrals play important roles in mathematics and applications,
8.3 partial fraction decomposition 575 8.3 Partial Fraction Decomposition Rational functions (polynomials divided by polynomials) and their integrals play important roles in mathematics and applications,
Background and Definitions...2. Legendre s Equation, Functions and Polynomials...4 Legendre s Associated Equation and Functions...
 Legendre Polynomials and Functions Reading Problems Outline Background and Definitions...2 Definitions...3 Theory...4 Legendre s Equation, Functions and Polynomials...4 Legendre s Associated Equation and
Legendre Polynomials and Functions Reading Problems Outline Background and Definitions...2 Definitions...3 Theory...4 Legendre s Equation, Functions and Polynomials...4 Legendre s Associated Equation and
Introduction To Materials Science FOR ENGINEERS, Ch. 5. Diffusion. MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5
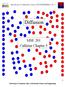 Diffusion MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5 1 Goals: Diffusion - how do atoms move through solids? Fundamental concepts and language Diffusion mechanisms Vacancy diffusion Interstitial diffusion Impurities Diffusion
Diffusion MSE 201 Callister Chapter 5 1 Goals: Diffusion - how do atoms move through solids? Fundamental concepts and language Diffusion mechanisms Vacancy diffusion Interstitial diffusion Impurities Diffusion
ENGI Partial Differentiation Page y f x
 ENGI 344 4 Partial Differentiation Page 4-0 4. Partial Differentiation For functions of one variable, be found unambiguously by differentiation: y f x, the rate of change of the dependent variable can
ENGI 344 4 Partial Differentiation Page 4-0 4. Partial Differentiation For functions of one variable, be found unambiguously by differentiation: y f x, the rate of change of the dependent variable can
Action Principles in Mechanics, and the Transition to Quantum Mechanics
 Physics 5K Lecture 2 - Friday April 13, 2012 Action Principles in Mechanics, and the Transition to Quantum Mechanics Joel Primack Physics Department UCSC This lecture is about how the laws of classical
Physics 5K Lecture 2 - Friday April 13, 2012 Action Principles in Mechanics, and the Transition to Quantum Mechanics Joel Primack Physics Department UCSC This lecture is about how the laws of classical
PDF Created with deskpdf PDF Writer - Trial ::
 y 3 5 Graph of f ' x 76. The graph of f ', the derivative f, is shown above for x 5. n what intervals is f increasing? (A) [, ] only (B) [, 3] (C) [3, 5] only (D) [0,.5] and [3, 5] (E) [, ], [, ], and
y 3 5 Graph of f ' x 76. The graph of f ', the derivative f, is shown above for x 5. n what intervals is f increasing? (A) [, ] only (B) [, 3] (C) [3, 5] only (D) [0,.5] and [3, 5] (E) [, ], [, ], and
Investigating the Relationship Between the Rheological Properties of Hyaluronic Acid and its Molecular Weight and Structure using Multidetector
 Investigating the Relationship Between the Rheological Properties of Hyaluronic Acid and its Molecular Weight and Structure using Multidetector SEC and SEC-MALS Presented by Bassem Sabagh, PhD Technical
Investigating the Relationship Between the Rheological Properties of Hyaluronic Acid and its Molecular Weight and Structure using Multidetector SEC and SEC-MALS Presented by Bassem Sabagh, PhD Technical
Chapter 4 Integration
 Chapter 4 Integration SECTION 4.1 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration Calculus: Chapter 4 Section 4.1 Antiderivative A function F is an antiderivative of f on an interval I if F '( x) f ( x) for
Chapter 4 Integration SECTION 4.1 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integration Calculus: Chapter 4 Section 4.1 Antiderivative A function F is an antiderivative of f on an interval I if F '( x) f ( x) for
AP Calculus AB. Review for Test: Applications of Integration
 Name Review for Test: Applications of Integration AP Calculus AB Test Topics: Mean Value Theorem for Integrals (section 4.4) Average Value of a Function (manipulation of MVT for Integrals) (section 4.4)
Name Review for Test: Applications of Integration AP Calculus AB Test Topics: Mean Value Theorem for Integrals (section 4.4) Average Value of a Function (manipulation of MVT for Integrals) (section 4.4)
Chapter 14 Kinetic Theory
 Chapter 14 Kinetic Theory Kinetic Theory of Gases A remarkable triumph of molecular theory was showing that the macroscopic properties of an ideal gas are related to the molecular properties. This is the
Chapter 14 Kinetic Theory Kinetic Theory of Gases A remarkable triumph of molecular theory was showing that the macroscopic properties of an ideal gas are related to the molecular properties. This is the
16.4. Power Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Power Series 6.4 Introduction In this section we consider power series. These are examples of infinite series where each term contains a variable, x, raised to a positive integer power. We use the ratio
Power Series 6.4 Introduction In this section we consider power series. These are examples of infinite series where each term contains a variable, x, raised to a positive integer power. We use the ratio
Mathematics (Course B) Lent Term 2005 Examples Sheet 2
 N12d Natural Sciences, Part IA Dr M. G. Worster Mathematics (Course B) Lent Term 2005 Examples Sheet 2 Please communicate any errors in this sheet to Dr Worster at M.G.Worster@damtp.cam.ac.uk. Note that
N12d Natural Sciences, Part IA Dr M. G. Worster Mathematics (Course B) Lent Term 2005 Examples Sheet 2 Please communicate any errors in this sheet to Dr Worster at M.G.Worster@damtp.cam.ac.uk. Note that
FORMULA SHEET. General formulas:
 FORMULA SHEET You may use this formula sheet during the Advanced Transport Phenomena course and it should contain all formulas you need during this course. Note that the weeks are numbered from 1.1 to
FORMULA SHEET You may use this formula sheet during the Advanced Transport Phenomena course and it should contain all formulas you need during this course. Note that the weeks are numbered from 1.1 to
Lecture 1 Notes: 06 / 27. The first part of this class will primarily cover oscillating systems (harmonic oscillators and waves).
 Lecture 1 Notes: 06 / 27 The first part of this class will primarily cover oscillating systems (harmonic oscillators and waves). These systems are very common in nature - a system displaced from equilibrium
Lecture 1 Notes: 06 / 27 The first part of this class will primarily cover oscillating systems (harmonic oscillators and waves). These systems are very common in nature - a system displaced from equilibrium
CHAPTER 9 Statistical Physics
 CHAPTER 9 Statistical Physics 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 Historical Overview Maxwell Velocity Distribution Equipartition Theorem Maxwell Speed Distribution Classical and Quantum Statistics Fermi-Dirac
CHAPTER 9 Statistical Physics 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 Historical Overview Maxwell Velocity Distribution Equipartition Theorem Maxwell Speed Distribution Classical and Quantum Statistics Fermi-Dirac
6.1 Polynomial Functions
 6.1 Polynomial Functions Definition. A polynomial function is any function p(x) of the form p(x) = p n x n + p n 1 x n 1 + + p 2 x 2 + p 1 x + p 0 where all of the exponents are non-negative integers and
6.1 Polynomial Functions Definition. A polynomial function is any function p(x) of the form p(x) = p n x n + p n 1 x n 1 + + p 2 x 2 + p 1 x + p 0 where all of the exponents are non-negative integers and
Part 8. Special Topic: Light Scattering
 Part 8. Special Topic: Light Scattering Light scattering occurs when polarizable particles in a sample are placed in the oscillating electric field of a beam of light. The varying field induces oscillating
Part 8. Special Topic: Light Scattering Light scattering occurs when polarizable particles in a sample are placed in the oscillating electric field of a beam of light. The varying field induces oscillating
