METODE ZA PREDVIDEVANJE (NAPOVEDOVANJE) VODOTOPNOSTI (topnosti spojin v vodi)
|
|
|
- Maximillian Warren Wells
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 METODE ZA PREDVIDEVANJE (NAPOVEDOVANJE) VODOTOPNOSTI (topnosti spojin v vodi) Delitev metod (metode temeljijo na): 1. Prispevki posameznih skupin v molekuli k aktivnostnemu koeficientu spojine v vodi. Eksperimentalno določene fizikalno kemijske lastnosti; npr. P, k (HPLC), temperatura vrelišča, molekularni volumen 3. Lastnosti, ki jih ne moremo eksperimentalno določiti; ocenimo jih iz molekularne strukture: molekularna površina, molekularna povezanost ( molecular connectivity ) idr. 4. Kombinacije med dvema in (ali) več eksperimentalno določenimi oziroma izračunanimi parametri: topnostni parametri, linearnost energije solvatacije solvatokromni parametri, različne statistične metode. Teoretične predpostavke uporaba (izpeljava) empirična.
2 Prispevki posameznih skupin v molekuli k topnosti Homologne vrste: metilenska skupina prispeva konstantno zmanjšanje topnosti (uvedba ene skupine CH zmanjša topnost za faktor 4 4,5). 4,0 < logs w (S (S w ) ) w = A n < n+ 1 4,5 + B n n = št. metilenskih skupin v alifatski verigi; A,B konstanti B ~ 0,6; neodvisen od narave funkcionalne skupine v molekuli A karakterističen za funkcionalne skupine, neodvisen od dolžine verige Uvajanje korekcijskih faktorjev v enačbo (za razvejene spojine, aromate ipd.) Primerno za tekoče topljence. Potrebna je obširna podatkovna baza za vrednotenje posameznih skupin.
3 Temperatura vrelišča Običajno ni primerna metoda. Topljenec ne sme tvoriti H vezi. Primer za serijo aromatskih ogljikovodikov: log S w = BP 0.76 n = 3, r = 0.07 (Pearsonov koeficient korelacije) BP boiling point Tudi za klorbenzene, heterocikle... Enačbe veljajo le za tisti tip spojin, iz katerih je enačba izpeljana. Obstajati mora povezava med aktivnostnim koeficientom spojine v vodi in vreliščem.
4 Molekularni volumen Pomemben koncept tvorbe prostora pri raztapljanju. Izračunamo ga iz van der Waalsovih radijev; ne moremo meriti direktno. log S w = A V vdw + B A, B konst., določeni empirično za posamezne skupine molekul Metoda temelji na: proces raztapljanja odvisen le od energetskih sprememb, ki so posledice t.i. cavity formation (tvorba prostora, v katerega se molekula topljenca vgradi). Vplivi polarnih skupin niso upoštevani; kot tudi ne interakcije z molekulami vode.
5 Površina molekul Stopnja interakcij topilo topljenec direktno odvisna od molekularnih površin... log S w = B TSA + c g B, c g konst., TSA celotna površina molekule TSA lahko razdelimo na površino polarnih in nepolarnih delov molekule. log S w = ΣB g SA g SA g površina določene funkcionalne skupine B g ustrezen pripadajoči koeficient, določen z regresijo
6 Molekularna povezanost (molecular connectivity) Topološki indeks v molekuli (Randič 1975) povezanost merilo velikosti in kompaktnosti molekule x = 1 Γ i Γ j x indeks povezanosti prvega reda Γ i, Γ j št. C atomov, povezanih z vsakim C atomom v vezi C C Tudi kompleksnejši primeri kasneje dvojne, trojne vezi, aromati, hetero atomi... Korelacije uporabne le v ozkem podatkovnem območju (le za določene skupine spojin).
7 Figure 1: Molecular volume of HCN
8 Figure : Overlap of nonlinear molecules.
9 Figure 3: Cross sectional view of (a) the van der Waals surface, (b) the solvent accessible surface using the center of the solvent molecule, and (c) the periphery of the solvent molecule. (a) (b) (c)
10 Linearna energija solvatacije - solvatokromni parametri: log S w = a 1 + a V + a 3 Π + a 4 β + a 5 (MP 5)... V molarni volumen, a 1, a, a 3... konst. Π merilo polarnosti Β sposobnost spojine, da tvori H vez MP temperatura tališča (ºC) Določanje teh vrednosti: v različnih topilih; e - donorski, akceptorski faktor, spektrofotometrično.
11 Topnostni parameter Van der Waalsove sile med molekulami sledijo geometrijskemu pravilu za topilo in topljenec: w w11w 1 = Zato: ln γ = [(w 11 ) 1 (w ) 1 ] VΦ RT 1 = ( δ 1 δ ) VΦ RT 1 Določitev topnostnih parametrov (σ) [ v prvi aproksimaciji: Φ 1 ~1 (razredčene razt.)] δ izraža kohezijo med podobnomi molekulami; podobno v podobnem
12 Izračun δ: Iz entalpije uparjanja, notranjega pritiska, površinske napetosti idr. ΔHf T0 T V Φ = + 1 log x δ1 δ,303rt T0,303RT δ = du dv ΔHv RT V1 T 1 ; iz notranjega pritiska ( ) notranji pritisk (intermolekularne interakcije privlak, odboj) Porazdelitveni koeficient in predvidevanje vodotopnosti Ravnotežje: x 0 γ 0 = x w γ w (a 0 = a w ) P = x 0 /x w = γ w /γ 0
13 Predpostavka: Neelektroliti, šibki elektroliti (večina zdravilnih učinkovin) idealno za raztapljanje v oktanolu: γ 0 = 1 logγ w logp t Enačba za topnost: ΔHf Tm T log x = log γ,303r Tm T log x w = ΔSf,303RT (T m 98,15K) log P 0,94 T = 5ºC 0,94 = n log n 0 = w 6,35 55,5
14 ΔSf logs = (Tm 98,15K) log P + w,303rt 0,80 log n w (55,5) = 1,74 Yalkowsky preizkus gornje enačbe: logs ΔS = 1,00log P 1,11 (Tm 98,15),303RT f + w 0,54 n = 167, R = 0,994 Toge molekule: ΔS f = 56,7 J/molK (geometrijska entropija) log S w = 1,05 logp 0,01 MP + 0,87 MP temperatura tališča v ºC
15 Figure 4: Entropy of fusion considerations for spherical, rigid and flexible molecules.
16 (1) The solubility of nonpolar and semipolar solutes in octanol is approximately equal to the ideal solubility, γ 0 = 1. Because P = γ W /γ 0, it follows that logγ w logp. () The ideal solubility can be estimated from T m and ΔS f of the solute. (3) The ΔS f of the solute is constant for rigid molecules. (4) The ratio S 0 /S w is equivalent to P, that is, S w is equal to S 0 divided by P.
TOPLJENEC ASOCIIRA LE V VODNI FAZI
 TOPLJENEC ASOCIIRA LE V VODNI FAZI V primeru asociacij molekul topljenca v vodni ali organski fazi eksperimentalno določeni navidezni porazdelitveni koeficient (P n ) v odvisnosti od koncentracije ni konstanten.
TOPLJENEC ASOCIIRA LE V VODNI FAZI V primeru asociacij molekul topljenca v vodni ali organski fazi eksperimentalno določeni navidezni porazdelitveni koeficient (P n ) v odvisnosti od koncentracije ni konstanten.
ENAČBA STANJA VODE IN VODNE PARE
 ENAČBA STANJA VODE IN VODNE PARE SEMINARSKA NALOGA PRI PREDMETU JEDRSKA TEHNIKA IN ENERGETIKA TAMARA STOJANOV MENTOR: IZRED. PROF. DR. IZTOK TISELJ NOVEMBER 2011 Enačba stanja idealni plin: pv = RT p tlak,
ENAČBA STANJA VODE IN VODNE PARE SEMINARSKA NALOGA PRI PREDMETU JEDRSKA TEHNIKA IN ENERGETIKA TAMARA STOJANOV MENTOR: IZRED. PROF. DR. IZTOK TISELJ NOVEMBER 2011 Enačba stanja idealni plin: pv = RT p tlak,
Introduction of Branching Degrees of Octane Isomers
 DOI: 10.17344/acsi.2016.2361 Acta Chim. Slov. 2016, 63, 411 415 411 Short communication Introduction of Branching Degrees of Octane Isomers Anton Perdih Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Technology, University
DOI: 10.17344/acsi.2016.2361 Acta Chim. Slov. 2016, 63, 411 415 411 Short communication Introduction of Branching Degrees of Octane Isomers Anton Perdih Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical Technology, University
Makroekonomija 1: 4. vaje. Igor Feketija
 Makroekonomija 1: 4. vaje Igor Feketija Teorija agregatnega povpraševanja AD = C + I + G + nx padajoča krivulja AD (v modelu AS-AD) učinek ponudbe denarja premiki vzdolž krivulje in premiki krivulje mikro
Makroekonomija 1: 4. vaje Igor Feketija Teorija agregatnega povpraševanja AD = C + I + G + nx padajoča krivulja AD (v modelu AS-AD) učinek ponudbe denarja premiki vzdolž krivulje in premiki krivulje mikro
GRADNIKI VESOLJA. Atomi molekula KAKO MODELIRATI.
 Molekulska strast GRADNIKI VESOLJA. Atomi so gradbene enote vesolja. Pri povezovanju dveh ali več atomov nastane molekula. Molekule se med seboj zelo razlikujejo v velikosti, obliki in funkciji. Naučili
Molekulska strast GRADNIKI VESOLJA. Atomi so gradbene enote vesolja. Pri povezovanju dveh ali več atomov nastane molekula. Molekule se med seboj zelo razlikujejo v velikosti, obliki in funkciji. Naučili
ija 3 m Kislost-bazi - čnost Hammettove konstante ska ke acevt Farm Izr. prof. dr Izr. prof. dr. Marko Anderluh. Marko Anderluh 23 oktober.
 acevts ska kem mija 3 Farm Kislost-bazičnost Hammettove konstante Izr. prof. dr. Marko Anderluh 23. oktober 2012 Vpliv kislinsko bazičnih lastnosti Vezava na tarčno mesto farmakodinamsko delovanje Topnost/sproščanje
acevts ska kem mija 3 Farm Kislost-bazičnost Hammettove konstante Izr. prof. dr. Marko Anderluh 23. oktober 2012 Vpliv kislinsko bazičnih lastnosti Vezava na tarčno mesto farmakodinamsko delovanje Topnost/sproščanje
Electrons and Molecular Forces
 Electrons and Molecular Forces Chemistry 30 Ms. Hayduk Electron Configuration Atomic Structure Atomic Number Number of protons in the nucleus Defines the element Used to organize the periodic table 1 Bohr
Electrons and Molecular Forces Chemistry 30 Ms. Hayduk Electron Configuration Atomic Structure Atomic Number Number of protons in the nucleus Defines the element Used to organize the periodic table 1 Bohr
2A skupina zemeljskoalkalijske kovine
 1. NALOGA: V ČEM SE RAZLIKUJETA BeO IN MgO? 1. NALOGA: ODGOVOR Elementi 2. periode (od Li do F) se po fizikalnih in kemijskih lastnostih (diagonalne lastnosti) znatno razlikujejo od elementov, ki so v
1. NALOGA: V ČEM SE RAZLIKUJETA BeO IN MgO? 1. NALOGA: ODGOVOR Elementi 2. periode (od Li do F) se po fizikalnih in kemijskih lastnostih (diagonalne lastnosti) znatno razlikujejo od elementov, ki so v
Acta Chim. Slov. 2003, 50,
 771 IMPACT OF STRUCTURED PACKING ON BUBBE COUMN MASS TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS EVAUATION. Part 3. Sensitivity of ADM Volumetric Mass Transfer Coefficient evaluation Ana akota Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical
771 IMPACT OF STRUCTURED PACKING ON BUBBE COUMN MASS TRANSFER CHARACTERISTICS EVAUATION. Part 3. Sensitivity of ADM Volumetric Mass Transfer Coefficient evaluation Ana akota Faculty of Chemistry and Chemical
Chem 112 Dr. Kevin Moore
 Chem 112 Dr. Kevin Moore Gas Liquid Solid Polar Covalent Bond Partial Separation of Charge Electronegativity: H 2.1 Cl 3.0 H Cl δ + δ - Dipole Moment measure of the net polarity in a molecule Q Q magnitude
Chem 112 Dr. Kevin Moore Gas Liquid Solid Polar Covalent Bond Partial Separation of Charge Electronegativity: H 2.1 Cl 3.0 H Cl δ + δ - Dipole Moment measure of the net polarity in a molecule Q Q magnitude
ija 3 m Interakcije spojina makromolekula ska ke acevt Farm doc.dr. Marko Anderluh 11 oktober. 2011
 acevts ska kem mija 3 Farm Interakcije spojina makromolekula doc.dr. Marko Anderluh 11. oktober 2011 Interakcije spojina-makromolekula Vezavne regije Spojina Vezavne skupine Medmolekulske vezi Vezavno
acevts ska kem mija 3 Farm Interakcije spojina makromolekula doc.dr. Marko Anderluh 11. oktober 2011 Interakcije spojina-makromolekula Vezavne regije Spojina Vezavne skupine Medmolekulske vezi Vezavno
Multipla korelacija in regresija. Multipla regresija, multipla korelacija, statistično zaključevanje o multiplem R
 Multipla koelacia in egesia Multipla egesia, multipla koelacia, statistično zaklučevane o multiplem Multipla egesia osnovni model in ačunane paametov Z multiplo egesio napoveduemo vednost kiteia (odvisne
Multipla koelacia in egesia Multipla egesia, multipla koelacia, statistično zaklučevane o multiplem Multipla egesia osnovni model in ačunane paametov Z multiplo egesio napoveduemo vednost kiteia (odvisne
Intermolecular Forces I
 I How does the arrangement of atoms differ in the 3 phases of matter (solid, liquid, gas)? Why doesn t ice just evaporate into a gas? Why does liquid water exist at all? There must be some force between
I How does the arrangement of atoms differ in the 3 phases of matter (solid, liquid, gas)? Why doesn t ice just evaporate into a gas? Why does liquid water exist at all? There must be some force between
Fundamentals of Distribution Separations (III)
 Fundamentals of Distribution Separations (III) (01/16/15) K = exp -Δμ 0 ext i - Δμ i RT distribution coefficient C i = exp -Δμ 0 RT - - Δμ i = ΔH i TΔS i 0 0 0 solubility q A---B A + B 0 0 0 ΔH i = ΔH
Fundamentals of Distribution Separations (III) (01/16/15) K = exp -Δμ 0 ext i - Δμ i RT distribution coefficient C i = exp -Δμ 0 RT - - Δμ i = ΔH i TΔS i 0 0 0 solubility q A---B A + B 0 0 0 ΔH i = ΔH
ENERGY AND MASS SPECTROSCOPY OF IONS AND NEUTRALS IN COLD PLASMA
 UDK621.3:(53+54+621 +66), ISSN0352-9045 Informaclje MIDEM 3~(~UU8)4, Ljubljana ENERGY AND MASS SPECTROSCOPY OF IONS AND NEUTRALS IN COLD PLASMA Marijan Macek 1,2* Miha Cekada 2 1 University of Ljubljana,
UDK621.3:(53+54+621 +66), ISSN0352-9045 Informaclje MIDEM 3~(~UU8)4, Ljubljana ENERGY AND MASS SPECTROSCOPY OF IONS AND NEUTRALS IN COLD PLASMA Marijan Macek 1,2* Miha Cekada 2 1 University of Ljubljana,
Termodinamika. FIZIKA PSS-GRAD 29. studenog Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Termodinamika FIZIKA PSS-GRAD 29. studenog 2017. 15.1 Thermodynamic Systems and Their Surroundings Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that is built upon the fundamental laws that heat and work obey.
Termodinamika FIZIKA PSS-GRAD 29. studenog 2017. 15.1 Thermodynamic Systems and Their Surroundings Thermodynamics is the branch of physics that is built upon the fundamental laws that heat and work obey.
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 11. Liquids and Intermolecular Forces. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 11 Liquids and Intermolecular Forces John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Properties of Gases, Liquids, and Solids State Volume Shape of State Density
Lecture Presentation Chapter 11 Liquids and Intermolecular Forces John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Properties of Gases, Liquids, and Solids State Volume Shape of State Density
APPLICATION OF THOMAS-FERMI MODEL TO FULLERENE MOLECULE AND NANOTUBE UDC 547. Yuri Kornyushin
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Series: Physics, Chemistry and Technology Vol. 5, N o 1, 2007, pp. 11-18 DOI: 10.2298/FUPCT0701011K APPLICATION OF THOMAS-FERMI MODEL TO FULLERENE MOLECULE AND NANOTUBE UDC 547 Yuri
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Series: Physics, Chemistry and Technology Vol. 5, N o 1, 2007, pp. 11-18 DOI: 10.2298/FUPCT0701011K APPLICATION OF THOMAS-FERMI MODEL TO FULLERENE MOLECULE AND NANOTUBE UDC 547 Yuri
Chapter 10. Dipole Moments. Intermolecular Forces (IMF) Polar Bonds and Polar Molecules. Polar or Nonpolar Molecules?
 Polar Bonds and Polar Molecules Chapter 10 Liquids, Solids, and Phase Changes Draw Lewis Structures for CCl 4 and CH 3 Cl. What s the same? What s different? 1 Polar Covalent Bonds and Dipole Moments Bonds
Polar Bonds and Polar Molecules Chapter 10 Liquids, Solids, and Phase Changes Draw Lewis Structures for CCl 4 and CH 3 Cl. What s the same? What s different? 1 Polar Covalent Bonds and Dipole Moments Bonds
IZRAČUN MEMBRANSKE RAZTEZNE POSODE - "MRP" za HLADNOVODNE SISTEME (DIN 4807/2)
 IZPIS IZRAČUN MEMBRANSKE RAZTEZNE POSODE - "MRP" za HLADNOVODNE SISTEME Izhodiščni podatki: Objkt : Vrtc Kamnitnik Projkt : PZI Uporaba MRP : Črpalna vrtina Datum : 30.8.2017 Obdlal : Zupan Skupna hladilna
IZPIS IZRAČUN MEMBRANSKE RAZTEZNE POSODE - "MRP" za HLADNOVODNE SISTEME Izhodiščni podatki: Objkt : Vrtc Kamnitnik Projkt : PZI Uporaba MRP : Črpalna vrtina Datum : 30.8.2017 Obdlal : Zupan Skupna hladilna
Dipole-Dipole Interactions https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cerb1d6j4-m London Dispersion Forces https://www.youtube.com/watch?
 CATALYST Lesson Plan GLE Physical Science 22. Predict the kind of bond that will form between two elements based on electronic structure and electronegativity of the elements (e.g., ionic, polar, nonpolar)
CATALYST Lesson Plan GLE Physical Science 22. Predict the kind of bond that will form between two elements based on electronic structure and electronegativity of the elements (e.g., ionic, polar, nonpolar)
LISREL. Mels, G. (2006). LISREL for Windows: Getting Started Guide. Lincolnwood, IL: Scientific Software International, Inc.
 LISREL Mels, G. (2006). LISREL for Windows: Getting Started Guide. Lincolnwood, IL: Scientific Software International, Inc. LISREL: Structural Equation Modeling, Multilevel Structural Equation Modeling,
LISREL Mels, G. (2006). LISREL for Windows: Getting Started Guide. Lincolnwood, IL: Scientific Software International, Inc. LISREL: Structural Equation Modeling, Multilevel Structural Equation Modeling,
Liquid. T > Tm Liquid has. Solid T < Tm Solid has. the lower free energy T. Demo. the lower free energy. Solutions.
 Just to be clear about Free Energy Super Cooled or Super Heated G = H - TS straight line assumes that H and S are independent of temperature Slope is given by S Liquid has a larger entropy and therefore
Just to be clear about Free Energy Super Cooled or Super Heated G = H - TS straight line assumes that H and S are independent of temperature Slope is given by S Liquid has a larger entropy and therefore
Organic Chemistry. Introduction to Organic Molecules and Functional Groups
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Introduction to Organic Molecules and Functional Groups by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Organic Chemistry Introduction to Organic Molecules and Functional Groups by Dr. Seema Zareen & Dr. Izan Izwan Misnon Faculty Industrial Science
Some properties of water
 Some properties of water Hydrogen bond network Solvation under the microscope 1 Water solutions Oil and water does not mix at equilibrium essentially due to entropy Substances that does not mix with water
Some properties of water Hydrogen bond network Solvation under the microscope 1 Water solutions Oil and water does not mix at equilibrium essentially due to entropy Substances that does not mix with water
TERMODINAMIKA, BIOENERGETIKA
 TERMODINAMIKA, BIOENERGETIKA Osnovni termodinamski koncepti Fizikalni pomen termodinamskih količin ph in standardni pogoji Sklopljeni procesi Energijsko bogate biomolekule Osnovni termodinamski koncepti
TERMODINAMIKA, BIOENERGETIKA Osnovni termodinamski koncepti Fizikalni pomen termodinamskih količin ph in standardni pogoji Sklopljeni procesi Energijsko bogate biomolekule Osnovni termodinamski koncepti
CHM 2046 Final Exam Review: Chapters 11 18
 Chapter 11 1. Which of the following has the lowest boiling point? a. NH 3 b. CH 3 Cl c. NaCl d. CO 2 e. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 2. Which of the following has the lowest vapor pressure? a. CH 3 F b. CH
Chapter 11 1. Which of the following has the lowest boiling point? a. NH 3 b. CH 3 Cl c. NaCl d. CO 2 e. CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 2. Which of the following has the lowest vapor pressure? a. CH 3 F b. CH
CHAPTER ELEVEN KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS
 CHAPTER ELEVEN AND LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Differences between condensed states and gases? KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Phase Homogeneous part
CHAPTER ELEVEN AND LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Differences between condensed states and gases? KINETIC MOLECULAR THEORY OF LIQUIDS AND SOLIDS Phase Homogeneous part
Gibbs Free Energy. Evaluating spontaneity
 Gibbs Free Energy Evaluating spontaneity Predicting Spontaneity An increase in entropy; Changing from a more structured to less structured physical state: Solid to liquid Liquid to gas Increase in temperature
Gibbs Free Energy Evaluating spontaneity Predicting Spontaneity An increase in entropy; Changing from a more structured to less structured physical state: Solid to liquid Liquid to gas Increase in temperature
TOPILO IZSTOPNI VENTIL CILINDER KOLONA DUŠILEC
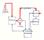 TOPILO VSTOPNI VENTIL CILINDER BAT IZSTOPNI VENTIL KOLONA DUŠILEC HPLC: 1. PORAZDELITVENA ( liquid-liquid ) 2. IONSKA 3. IZKLJUČITVENA oziroma GELSKA 4. ADSORPCIJSKA oziroma LIQUID-SOLID majhni delci (
TOPILO VSTOPNI VENTIL CILINDER BAT IZSTOPNI VENTIL KOLONA DUŠILEC HPLC: 1. PORAZDELITVENA ( liquid-liquid ) 2. IONSKA 3. IZKLJUČITVENA oziroma GELSKA 4. ADSORPCIJSKA oziroma LIQUID-SOLID majhni delci (
Lecture C2 Microscopic to Macroscopic, Part 2: Intermolecular Interactions. Let's get together.
 Lecture C2 Microscopic to Macroscopic, Part 2: Intermolecular Interactions Let's get together. Most gases are NOT ideal except at very low pressures: Z=1 for ideal gases Intermolecular interactions come
Lecture C2 Microscopic to Macroscopic, Part 2: Intermolecular Interactions Let's get together. Most gases are NOT ideal except at very low pressures: Z=1 for ideal gases Intermolecular interactions come
Variable Connectivity Model for Determination of pk a
 Acta Chim. Slov. 2007, 54, 605 610 605 Scientific paper Variable Connectivity Model for Determination of Values for Selected Organic Acids Matev` Pompe*,1 and Milan Randi} 2 1 Faculty of Chemistry and
Acta Chim. Slov. 2007, 54, 605 610 605 Scientific paper Variable Connectivity Model for Determination of Values for Selected Organic Acids Matev` Pompe*,1 and Milan Randi} 2 1 Faculty of Chemistry and
Ch. 9 Liquids and Solids
 Intermolecular Forces I. A note about gases, liquids and gases. A. Gases: very disordered, particles move fast and are far apart. B. Liquid: disordered, particles are close together but can still move.
Intermolecular Forces I. A note about gases, liquids and gases. A. Gases: very disordered, particles move fast and are far apart. B. Liquid: disordered, particles are close together but can still move.
4.1 LAWS OF MECHANICS - Review
 4.1 LAWS OF MECHANICS - Review Ch4 9 SYSTEM System: Moving Fluid Definitions: System is defined as an arbitrary quantity of mass of fixed identity. Surrounding is everything external to this system. Boundary
4.1 LAWS OF MECHANICS - Review Ch4 9 SYSTEM System: Moving Fluid Definitions: System is defined as an arbitrary quantity of mass of fixed identity. Surrounding is everything external to this system. Boundary
Simulation of multilayer coating growth in an industrial magnetron sputtering system
 RMZ Materials and Geoenvironment, Vol. 57, No. 3, pp. 317 330, 2010 317 Simulation of multilayer coating growth in an industrial magnetron sputtering system Simulacija rasti večplastnih prevlek v industrijski
RMZ Materials and Geoenvironment, Vol. 57, No. 3, pp. 317 330, 2010 317 Simulation of multilayer coating growth in an industrial magnetron sputtering system Simulacija rasti večplastnih prevlek v industrijski
ZDRAVLJENJE BOLNICE S VON WILLEBRANDOVO BOLEZNIJO TIPA 3 IN INHIBITORJI
 ZDRAVLJENJE BOLNICE S VON WILLEBRANDOVO BOLEZNIJO TIPA 3 IN INHIBITORJI B. Faganel Kotnik, L. Kitanovski, J. Jazbec, K. Strandberg, M. Debeljak, Bakija, M. Benedik Dolničar A. Trampuš Laško, 9. april 2016
ZDRAVLJENJE BOLNICE S VON WILLEBRANDOVO BOLEZNIJO TIPA 3 IN INHIBITORJI B. Faganel Kotnik, L. Kitanovski, J. Jazbec, K. Strandberg, M. Debeljak, Bakija, M. Benedik Dolničar A. Trampuš Laško, 9. april 2016
Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015,
 Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015, Course,Informa5on, BIOC%530% GraduateAlevel,discussion,of,the,structure,,func5on,,and,chemistry,of,proteins,and, nucleic,acids,,control,of,enzyma5c,reac5ons.,please,see,the,course,syllabus,and,
Biochemistry,530:,, Introduc5on,to,Structural,Biology, Autumn,Quarter,2015, Course,Informa5on, BIOC%530% GraduateAlevel,discussion,of,the,structure,,func5on,,and,chemistry,of,proteins,and, nucleic,acids,,control,of,enzyma5c,reac5ons.,please,see,the,course,syllabus,and,
Organic Chemistry. Review Information for Unit 1. Atomic Structure MO Theory Chemical Bonds
 Organic Chemistry Review Information for Unit 1 Atomic Structure MO Theory Chemical Bonds Atomic Structure Atoms are the smallest representative particle of an element. Three subatomic particles: protons
Organic Chemistry Review Information for Unit 1 Atomic Structure MO Theory Chemical Bonds Atomic Structure Atoms are the smallest representative particle of an element. Three subatomic particles: protons
CHEMISTRY REVIEW FOR AP BIOLOGY Answer Key
 CHEMISTRY REVIEW FOR AP BIOLOGY Answer Key Complete the following and be knowledgeable of the concepts on the first day of school. A. KINETICS = involves factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
CHEMISTRY REVIEW FOR AP BIOLOGY Answer Key Complete the following and be knowledgeable of the concepts on the first day of school. A. KINETICS = involves factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction.
Apparent Molar Volumes and Viscosity B-Coefficients of Glycine in Aqueous Silver Sulphate Solutions at T = (298.15, , 318.
 Acta Chim. Slov. 21, 57, 651 659 651 Scientific paper Apparent Molar Volumes and Viscosity B-Coefficients of Glycine in Aqueous Silver Sulphate Solutions at T = (298.15, 38.15, 318.15) K Biswajit Sinha,*
Acta Chim. Slov. 21, 57, 651 659 651 Scientific paper Apparent Molar Volumes and Viscosity B-Coefficients of Glycine in Aqueous Silver Sulphate Solutions at T = (298.15, 38.15, 318.15) K Biswajit Sinha,*
Attempt to prepare seasonal weather outlook for Slovenia
 Attempt to prepare seasonal weather outlook for Slovenia Main available sources (ECMWF, EUROSIP, IRI, CPC.NCEP.NOAA,..) Two parameters (T and RR anomally) Textual information ( Met Office like ) Issued
Attempt to prepare seasonal weather outlook for Slovenia Main available sources (ECMWF, EUROSIP, IRI, CPC.NCEP.NOAA,..) Two parameters (T and RR anomally) Textual information ( Met Office like ) Issued
Intermolecular Forces and Physical Properties
 Intermolecular Forces and Physical Properties Attractive Forces Particles are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces. The strength of the attractive forces depends on the kind(s) of particles.
Intermolecular Forces and Physical Properties Attractive Forces Particles are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces. The strength of the attractive forces depends on the kind(s) of particles.
Atomic Structure and Bonding. Chapter 1 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry
 Atomic Structure and Bonding Chapter 1 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Common Elements Groups First row Second row In most organic molecules carbon is combined with relatively few elements
Atomic Structure and Bonding Chapter 1 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Common Elements Groups First row Second row In most organic molecules carbon is combined with relatively few elements
Representative Questions Exam 3
 Representative Questions Exam 3 1. The kinetic-molecular theory of gases assumes which of the following? a. gas samples are mostly empty space b. the average kinetic energy is proportional to the Kelvin
Representative Questions Exam 3 1. The kinetic-molecular theory of gases assumes which of the following? a. gas samples are mostly empty space b. the average kinetic energy is proportional to the Kelvin
Lecture 2-3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability
 Lecture 2-3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability Part I. Review of forces Covalent bonds Non-covalent Interactions Van der Waals Interactions
Lecture 2-3: Review of forces (ctd.) and elementary statistical mechanics. Contributions to protein stability Part I. Review of forces Covalent bonds Non-covalent Interactions Van der Waals Interactions
AIR CURTAINS VAZDU[NE ZAVESE V H
 AIR CURTAINS V 15.000 H 21.000 KLIMA Co. 2 KLIMA Co. Flow and system stress should be known factors in air flow. The flow is gas quantity flowing through the system during given time unit and is measured
AIR CURTAINS V 15.000 H 21.000 KLIMA Co. 2 KLIMA Co. Flow and system stress should be known factors in air flow. The flow is gas quantity flowing through the system during given time unit and is measured
Chemistry 163B Absolute Entropies and Entropy of Mixing
 Chemistry 163B Absolute Entropies and Entropy of Mixing 1 APPENDIX A: H f, G f, BUT S (no Δ, no sub f ) Hº f Gº f Sº 2 Third Law of Thermodynamics The entropy of any perfect crystalline substance approaches
Chemistry 163B Absolute Entropies and Entropy of Mixing 1 APPENDIX A: H f, G f, BUT S (no Δ, no sub f ) Hº f Gº f Sº 2 Third Law of Thermodynamics The entropy of any perfect crystalline substance approaches
CfE Higher Chemistry. Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure. Intermolecular forces
 CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure Intermolecular forces 05/09/2017 Van der Waal s Forces and London Dispersion Forces 05/09/2017 Learning Outcomes : I can explain the difference
CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure Intermolecular forces 05/09/2017 Van der Waal s Forces and London Dispersion Forces 05/09/2017 Learning Outcomes : I can explain the difference
CHEMISTRY. Chapter 11 Intermolecular Forces Liquids and Solids
 CHEMISTRY The Central Science 8 th Edition Chapter 11 Liquids and Solids Kozet YAPSAKLI States of Matter difference between states of matter is the distance between particles. In the solid and liquid states
CHEMISTRY The Central Science 8 th Edition Chapter 11 Liquids and Solids Kozet YAPSAKLI States of Matter difference between states of matter is the distance between particles. In the solid and liquid states
Chemical Bonding Basic Concepts
 Chemical Bonding Basic Concepts Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence electrons are the electrons that particpate in chemical bonding. Group e - configuration # of valence
Chemical Bonding Basic Concepts Valence electrons are the outer shell electrons of an atom. The valence electrons are the electrons that particpate in chemical bonding. Group e - configuration # of valence
Van der Waals Fluid Deriving the Fundamental Relation. How do we integrate the differential above to get the fundamental relation?
 Van der Waals Fluid Deriving the Fundamental Relation How do we integrate the differential above to get the fundamental relation? Pitfalls of Integration of Functions of Multiple Variables ds = cr u +
Van der Waals Fluid Deriving the Fundamental Relation How do we integrate the differential above to get the fundamental relation? Pitfalls of Integration of Functions of Multiple Variables ds = cr u +
LECTURE 2 STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF ORGANIC MOLECULES
 LECTURE 2 STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 1. Atomic wave functions and orbitals. LCAO. The important thing to know is that atomic orbitals are represented by wave functions, and they have
LECTURE 2 STRUCTURE AND PROPERTIES OF ORGANIC MOLECULES 1. Atomic wave functions and orbitals. LCAO. The important thing to know is that atomic orbitals are represented by wave functions, and they have
Liquids and Solids The Condensed States of Matter
 Liquids and Solids The Condensed States of Matter AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky Where We Have Been And Where We Are Going In the last few chapters, we saw that atoms can form stable units called molecules by
Liquids and Solids The Condensed States of Matter AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky Where We Have Been And Where We Are Going In the last few chapters, we saw that atoms can form stable units called molecules by
Chemical bonding is the combining of elements to form new substances.
 Name Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature: Unit Objective Study Guide Class Period Date Due 1. Define chemical bonding. What is chemical bonding? Chemical bonding is the combining of elements to form new
Name Covalent Bonding and Nomenclature: Unit Objective Study Guide Class Period Date Due 1. Define chemical bonding. What is chemical bonding? Chemical bonding is the combining of elements to form new
Chapter Eighteen. Thermodynamics
 Chapter Eighteen Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Study of energy changes during observed processes Purpose: To predict spontaneity of a process Spontaneity: Will process go without assistance? Depends
Chapter Eighteen Thermodynamics 1 Thermodynamics Study of energy changes during observed processes Purpose: To predict spontaneity of a process Spontaneity: Will process go without assistance? Depends
Chem 75 February, 2017 Practice Exam 2
 As before, here is last year s Exam 2 in two forms: just the questions, and then the questions followed by their solutions. 1. (2 + 6 + 8 points) At high temperature, aluminum nitride, AlN(s), decomposes
As before, here is last year s Exam 2 in two forms: just the questions, and then the questions followed by their solutions. 1. (2 + 6 + 8 points) At high temperature, aluminum nitride, AlN(s), decomposes
Temperature C. Heat Added (Joules)
 Now let s apply the heat stuff to real-world stuff like phase changes and the energy or cost it takes to carry it out. A heating curve...a plot of temperature of a substance vs heat added to a substance.
Now let s apply the heat stuff to real-world stuff like phase changes and the energy or cost it takes to carry it out. A heating curve...a plot of temperature of a substance vs heat added to a substance.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF INTEMOLECULAR FORCES INTERMOLECULAR FORCES
 DIFFERENT TYPES OF INTEMOLECULAR FORCES Do all the exercises in your studyguide COMPARISON OF THE THREE PHASES OF MATTER. Matter is anything that occupy space and has mass. There are three states of matter:
DIFFERENT TYPES OF INTEMOLECULAR FORCES Do all the exercises in your studyguide COMPARISON OF THE THREE PHASES OF MATTER. Matter is anything that occupy space and has mass. There are three states of matter:
Električne lastnosti organskih molekul
 Tomaž Požar Ledina 3 5230 Bovec tel: 04-386-59 e-mail: tpozar@hotmail.com Ljubljana, 9. maj 2004 Električne lastnosti organskih molekul Pisna prezentacija za predmet seminar II Avtor: Tomaž Požar Mentor:
Tomaž Požar Ledina 3 5230 Bovec tel: 04-386-59 e-mail: tpozar@hotmail.com Ljubljana, 9. maj 2004 Električne lastnosti organskih molekul Pisna prezentacija za predmet seminar II Avtor: Tomaž Požar Mentor:
Electonegativity, Polar Bonds, and Polar Molecules
 Electonegativity, Polar Bonds, and Polar Molecules Some Definitions Electronegativity: the ability of an atom to attract bonding electrons to itself. Intramolecular forces: the attractive force between
Electonegativity, Polar Bonds, and Polar Molecules Some Definitions Electronegativity: the ability of an atom to attract bonding electrons to itself. Intramolecular forces: the attractive force between
PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS SCH4U1
 PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS SCH4U1 Intra vs. Intermolecular Bonds The properties of a substance are influenced by the force of attraction within and between the molecules. Intra vs. Intermolecular Bonds Intramolecular
PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS SCH4U1 Intra vs. Intermolecular Bonds The properties of a substance are influenced by the force of attraction within and between the molecules. Intra vs. Intermolecular Bonds Intramolecular
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Chapter 7 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Three Types of Chemical Bonding (1) Ionic: formed by electron transfer (2) Covalent: formed by electron sharing (3) Metallic: attraction between metal
Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 12 - Solutions Second & Third Laws of Thermodynamics Balancing Redox Equations
 Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 12 - Solutions Second & Third Laws of Thermodynamics Balancing Redox Equations Key Questions 1. Does the entropy of the system increase or decrease for the following changes?
Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 12 - Solutions Second & Third Laws of Thermodynamics Balancing Redox Equations Key Questions 1. Does the entropy of the system increase or decrease for the following changes?
MICROWAVE PLASMAS AT ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE: NEW THEORETICAL DEVELOPMENTS AND APPLICATIONS IN SURFACE SCIENCE
 UDK621.3:(53+54+621 +66), ISSN0352-9045 Informacije MIDEM 38(2008)4, Ljubljana MICROWAVE PLASMAS AT ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE: NEW THEORETICAL DEVELOPMENTS AND APPLICATIONS IN SURFACE SCIENCE T. 8elmonte*,
UDK621.3:(53+54+621 +66), ISSN0352-9045 Informacije MIDEM 38(2008)4, Ljubljana MICROWAVE PLASMAS AT ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE: NEW THEORETICAL DEVELOPMENTS AND APPLICATIONS IN SURFACE SCIENCE T. 8elmonte*,
Name Date Class MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS. Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides
 8.1 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Section Review Objectives Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides Vocabulary covalent bond molecule diatomic molecule
8.1 MOLECULAR COMPOUNDS Section Review Objectives Distinguish molecular compounds from ionic compounds Identify the information a molecular formula provides Vocabulary covalent bond molecule diatomic molecule
Physics 4230 Final Examination 10 May 2007
 Physics 43 Final Examination May 7 In each problem, be sure to give the reasoning for your answer and define any variables you create. If you use a general formula, state that formula clearly before manipulating
Physics 43 Final Examination May 7 In each problem, be sure to give the reasoning for your answer and define any variables you create. If you use a general formula, state that formula clearly before manipulating
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
 Thermodynamics and Equilibrium College of Western Idaho ABSTRACT The purpose of this experiment was to measure how the solubility product constant (Ksp) changes with temperature and to use this information
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium College of Western Idaho ABSTRACT The purpose of this experiment was to measure how the solubility product constant (Ksp) changes with temperature and to use this information
Problem: Calculate the entropy change that results from mixing 54.0 g of water at 280 K with 27.0 g of water at 360 K in a vessel whose walls are
 Problem: Calculate the entropy change that results from mixing 54.0 g of water at 280 K with 27.0 g of water at 360 K in a vessel whose walls are perfectly insulated from the surroundings. Is this a spontaneous
Problem: Calculate the entropy change that results from mixing 54.0 g of water at 280 K with 27.0 g of water at 360 K in a vessel whose walls are perfectly insulated from the surroundings. Is this a spontaneous
1 What is energy?
 http://www.intothecool.com/ 1 What is energy? the capacity to do work? (Greek: en-, in; + ergon, work) the capacity to cause change to produce an effect? a certain quantity that does not change in the
http://www.intothecool.com/ 1 What is energy? the capacity to do work? (Greek: en-, in; + ergon, work) the capacity to cause change to produce an effect? a certain quantity that does not change in the
CH352 Assignment 3: Due Thursday, 27 April 2017
 CH352 Assignment 3: Due Thursday, 27 April 2017 Prof. David Coker Thursday, 20 April 2017 Q1 Adiabatic quasi-static volume and temperature changes in ideal gases In the last assignment you showed that
CH352 Assignment 3: Due Thursday, 27 April 2017 Prof. David Coker Thursday, 20 April 2017 Q1 Adiabatic quasi-static volume and temperature changes in ideal gases In the last assignment you showed that
Unit 12. Thermochemistry
 Unit 12 Thermochemistry A reaction is spontaneous if it will occur without a continuous input of energy However, it may require an initial input of energy to get it started (activation energy) For Thermochemistry
Unit 12 Thermochemistry A reaction is spontaneous if it will occur without a continuous input of energy However, it may require an initial input of energy to get it started (activation energy) For Thermochemistry
Stopnja protolize(disociacije) - merilo za jakost elektrolita. = c d /c
 Stopnja protolize(disociacije) - merilo za jakost elektrolita = N/N 0 = n/n 0 = c d /c = stopnja protolize (disociacije) N = število disociiranih molekul (HCl) oz. formulskih enot (NaCl) N 0 = število
Stopnja protolize(disociacije) - merilo za jakost elektrolita = N/N 0 = n/n 0 = c d /c = stopnja protolize (disociacije) N = število disociiranih molekul (HCl) oz. formulskih enot (NaCl) N 0 = število
Chemistry 112 Spring 2007 Prof. Metz Practice Exam 1 Solutions
 Chemistry 112 Spring 2007 Prof. Metz Practice Exam 1 Solutions 1. The intermolecular attractive forces would be greatest in which of the following molecules: CH 4, CH 2 Cl 2 and CO 2. (A) CH 4 (B) CH 2
Chemistry 112 Spring 2007 Prof. Metz Practice Exam 1 Solutions 1. The intermolecular attractive forces would be greatest in which of the following molecules: CH 4, CH 2 Cl 2 and CO 2. (A) CH 4 (B) CH 2
Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules
 Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules 1. Ionic bonds 2. Covalent bonds (also co-ordinate covalent bonds) 3. Metallic bonds 4. Van der Waals forces
Unit 1 Module 1 Forces of Attraction page 1 of 10 Various forces of attraction between molecules 1. Ionic bonds 2. Covalent bonds (also co-ordinate covalent bonds) 3. Metallic bonds 4. Van der Waals forces
Atoms have the ability to do two things in order to become isoelectronic with a Noble Gas.
 CHEMICAL BONDING Atoms have the ability to do two things in order to become isoelectronic with a Noble Gas. 1.Electrons can be from one atom to another forming. Positive ions (cations) are formed when
CHEMICAL BONDING Atoms have the ability to do two things in order to become isoelectronic with a Noble Gas. 1.Electrons can be from one atom to another forming. Positive ions (cations) are formed when
Property of liquid and Phase Diagram for EN 2017
 Property of Liquid and Phase Diagram by Assist.Prof.Dr.Choosak Poonsawat choosak@kku.ac.th FB: เคม อ ช ศ กด You should know - Intermolecular forces - Properties of Liquids - Phase Diagram Properties of
Property of Liquid and Phase Diagram by Assist.Prof.Dr.Choosak Poonsawat choosak@kku.ac.th FB: เคม อ ช ศ กด You should know - Intermolecular forces - Properties of Liquids - Phase Diagram Properties of
Gases. T boil, K. 11 gaseous elements. Rare gases. He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn Diatomic gaseous elements H 2, N 2, O 2, F 2, Cl 2
 Gases Gas T boil, K Rare gases 11 gaseous elements He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn 165 Rn 211 N 2 O 2 77 F 2 90 85 Diatomic gaseous elements Cl 2 238 H 2, N 2, O 2, F 2, Cl 2 H 2 He Ne Ar Kr Xe 20 4.4 27 87 120
Gases Gas T boil, K Rare gases 11 gaseous elements He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn 165 Rn 211 N 2 O 2 77 F 2 90 85 Diatomic gaseous elements Cl 2 238 H 2, N 2, O 2, F 2, Cl 2 H 2 He Ne Ar Kr Xe 20 4.4 27 87 120
Sinteza homologov paracetamola
 Katedra za farmacevtsko kemijo Sinteza homologov paracetamola Vaje iz Farmacevtske kemije 3 1 Sinteza N-(4-hidroksifenil)dekanamida Vaje iz Farmacevtske kemije 3 2 Vprašanja: 1. Zakaj uporabimo zmes voda/dioksan?
Katedra za farmacevtsko kemijo Sinteza homologov paracetamola Vaje iz Farmacevtske kemije 3 1 Sinteza N-(4-hidroksifenil)dekanamida Vaje iz Farmacevtske kemije 3 2 Vprašanja: 1. Zakaj uporabimo zmes voda/dioksan?
Chapter #3 Chemical Bonding
 Chapter #3 Chemical Bonding Valence Electrons electrons in the last energy level of an atom. Lewis dot symbols Consists of the symbol of an element and one dot for each valence electron in the atom of
Chapter #3 Chemical Bonding Valence Electrons electrons in the last energy level of an atom. Lewis dot symbols Consists of the symbol of an element and one dot for each valence electron in the atom of
States of matter. Chapter 11. Kinetic Molecular Theory of Liquids and Solids. Kinetic Molecular Theory of Solids Intermolecular Forces
 States of matter Chapter 11 Intermolecular Forces Liquids and Solids By changing the T and P, any matter can exist as solid, liquid or gas. Forces of attraction determine physical state Phase homogeneous
States of matter Chapter 11 Intermolecular Forces Liquids and Solids By changing the T and P, any matter can exist as solid, liquid or gas. Forces of attraction determine physical state Phase homogeneous
Dinamika fluidov. Laminarni in turbulentni tok Viskoznost tekočin Faktor trenja h f
 inamika luidov Laminarni in turbulentni tok Viskoznost tekočin Faktor trenja h 1 Energijska bilanca: Celokupna energijska bilanca procesa: W 1 + U 1 + K 1 = W + U + K F + M + T Bernoulijeva enačba Enačba
inamika luidov Laminarni in turbulentni tok Viskoznost tekočin Faktor trenja h 1 Energijska bilanca: Celokupna energijska bilanca procesa: W 1 + U 1 + K 1 = W + U + K F + M + T Bernoulijeva enačba Enačba
Bonding Test pg 1 of 4 Name: Pd. Date:
 Bonding Test pg 1 of 4 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) How many electrons are shared in a single covalent bond? 1. A) 2 B) 3 C)
Bonding Test pg 1 of 4 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) How many electrons are shared in a single covalent bond? 1. A) 2 B) 3 C)
Other Cells. Hormones. Viruses. Toxins. Cell. Bacteria
 Other Cells Hormones Viruses Toxins Cell Bacteria ΔH < 0 reaction is exothermic, tells us nothing about the spontaneity of the reaction Δ H > 0 reaction is endothermic, tells us nothing about the spontaneity
Other Cells Hormones Viruses Toxins Cell Bacteria ΔH < 0 reaction is exothermic, tells us nothing about the spontaneity of the reaction Δ H > 0 reaction is endothermic, tells us nothing about the spontaneity
of its physical and chemical properties.
 8.4 Molecular Shapes VSEPR Model The shape of a molecule determines many of its physical and chemical properties. Molecular l geometry (shape) can be determined with the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
8.4 Molecular Shapes VSEPR Model The shape of a molecule determines many of its physical and chemical properties. Molecular l geometry (shape) can be determined with the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
StudyHub: AP Chemistry
 StudyHub+ 1 StudyHub: AP Chemistry Solution Composition and Energies, Boiling Point, Freezing Point, and Vapor Pressure StudyHub+ 2 Solution Composition: Mole Fraction: Formula: Mole Fraction of Component
StudyHub+ 1 StudyHub: AP Chemistry Solution Composition and Energies, Boiling Point, Freezing Point, and Vapor Pressure StudyHub+ 2 Solution Composition: Mole Fraction: Formula: Mole Fraction of Component
1. When two pure substances are mixed to form a solution, then always
 Name: Date: 1. When two pure substances are mixed to form a solution, then always A) there is an increase in entropy. B) there is a decrease in entropy. C) entropy is conserved. D) heat is released. E)
Name: Date: 1. When two pure substances are mixed to form a solution, then always A) there is an increase in entropy. B) there is a decrease in entropy. C) entropy is conserved. D) heat is released. E)
Nestor S. Valera Ateneo de Manila. Chapter 12 - Intermolecular Forces
 Nestor S. Valera Ateneo de Manila Chapter 12 - Intermolecular Forces 1 A phase is a region that differs in structure and/or composition from another region. 2 Phases Solid phase - ice Liquid phase - water
Nestor S. Valera Ateneo de Manila Chapter 12 - Intermolecular Forces 1 A phase is a region that differs in structure and/or composition from another region. 2 Phases Solid phase - ice Liquid phase - water
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Very Low Temperature Membrane Free Desalination. by Directional Solvent Extraction
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Very Low Temperature Membrane Free Desalination by Directional Solvent Extraction Anurag Bajpayee, Tengfei Luo, Andrew J. Muto, and Gang Chen Department of Mechanical Engineering,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Very Low Temperature Membrane Free Desalination by Directional Solvent Extraction Anurag Bajpayee, Tengfei Luo, Andrew J. Muto, and Gang Chen Department of Mechanical Engineering,
1. A Covalent bonding B Polar covalent bonding C Metallic bonding D Hydrogen bonding E Ionic bonding F London dispersion forces
 Higher (National 6) Unit 1: Chemical changes and structure 1c Bonding and structure Problem sheets 1. A Covalent bonding B Polar covalent bonding C Metallic bonding D Hydrogen bonding E Ionic bonding F
Higher (National 6) Unit 1: Chemical changes and structure 1c Bonding and structure Problem sheets 1. A Covalent bonding B Polar covalent bonding C Metallic bonding D Hydrogen bonding E Ionic bonding F
OA07 ANNEX 4: SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION IN CALIBRATION
 OA07 ANNEX 4: SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION IN CALIBRATION Table of contents 1 TECHNICAL FIELDS... 2 2 PRESENTING THE SCOPE OF A CALIBRATION LABOORATORY... 2 3 CONSIDERING CHANGES TO SCOPES... 6 4 CHANGES WITH
OA07 ANNEX 4: SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION IN CALIBRATION Table of contents 1 TECHNICAL FIELDS... 2 2 PRESENTING THE SCOPE OF A CALIBRATION LABOORATORY... 2 3 CONSIDERING CHANGES TO SCOPES... 6 4 CHANGES WITH
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO FACULTY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TERM TEST 2 17 MARCH First Year APS 104S
 UNIERSIY OF ORONO Please mark X to indicate your tutorial section. Failure to do so will result in a deduction of 3 marks. U 0 U 0 FACULY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING ERM ES 7 MARCH 05 U 03 U 04
UNIERSIY OF ORONO Please mark X to indicate your tutorial section. Failure to do so will result in a deduction of 3 marks. U 0 U 0 FACULY OF APPLIED SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING ERM ES 7 MARCH 05 U 03 U 04
CHEMISTRY - TRO 4E CH.11 - LIQUIDS, SOLIDS & INTERMOLECULAR FORCES
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INTERMOLECULAR FORCES When looking at a molecular substance such as H 2 O you will discover two types of electrostatic forces at work: forces exist within a molecule and
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: INTERMOLECULAR FORCES When looking at a molecular substance such as H 2 O you will discover two types of electrostatic forces at work: forces exist within a molecule and
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Spontaneous Processes Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics The Molecular Interpretation of Entropy Entropy Changes in Chemical Reactions Gibbs Free Energy Free
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Spontaneous Processes Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics The Molecular Interpretation of Entropy Entropy Changes in Chemical Reactions Gibbs Free Energy Free
Topic 04 Bonding 4.3 Intermolecular Forces. IB Chemistry T04D05
 Topic 04 Bonding 4.3 Intermolecular orces IB Chemistry T04D05 Intermolecular orces 2 hrs 4.3.1 Describe the types of intermolecular forces (attractions between molecules that have temporary dipoles, permanent
Topic 04 Bonding 4.3 Intermolecular orces IB Chemistry T04D05 Intermolecular orces 2 hrs 4.3.1 Describe the types of intermolecular forces (attractions between molecules that have temporary dipoles, permanent
PREDICTION OF SUPERCONDUCTING TRANSITION TEMPERATURE USING A MACHINE-LEARNING METHOD
 UDK 620:538.945.91 ISSN 1580-2949 Original scientific article/izvirni znanstveni ~lanek MTAEC9, 52(5)639(2018) Y. LIU et al.: PREDICTION OF SUPERCONDUCTING TRANSITION TEMPERATURE USING A MACHINE-LEARNING
UDK 620:538.945.91 ISSN 1580-2949 Original scientific article/izvirni znanstveni ~lanek MTAEC9, 52(5)639(2018) Y. LIU et al.: PREDICTION OF SUPERCONDUCTING TRANSITION TEMPERATURE USING A MACHINE-LEARNING
8. Relax and do well.
 CHEM 15 Exam II John II. Gelder March 4, 1999 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 7 different pages. The last two pages includes a periodic table, a solubility
CHEM 15 Exam II John II. Gelder March 4, 1999 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 7 different pages. The last two pages includes a periodic table, a solubility
VAJE IZ BIOFARMACIJE S FARMAKOKINETIKO
 FAKULTETA ZA FARMACIJO KATEDRA ZA BIOFARMACIJO IN FARMAKOKINETIKO VAJE IZ BIOFARMACIJE S FARMAKOKINETIKO DNEVNIKI Ime in priimek: Turnus: Ljubljana, 2001 KAZALO 1. vaja: PORAZDELITVENI KOEFICIENT... 2
FAKULTETA ZA FARMACIJO KATEDRA ZA BIOFARMACIJO IN FARMAKOKINETIKO VAJE IZ BIOFARMACIJE S FARMAKOKINETIKO DNEVNIKI Ime in priimek: Turnus: Ljubljana, 2001 KAZALO 1. vaja: PORAZDELITVENI KOEFICIENT... 2
Chemistry. Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations. NC State University
 Chemistry Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations NC State University Thermodynamic state functions expressed in differential form We have seen that the internal energy is conserved and depends on mechanical (dw)
Chemistry Lecture 10 Maxwell Relations NC State University Thermodynamic state functions expressed in differential form We have seen that the internal energy is conserved and depends on mechanical (dw)
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy
 Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy Learning goals and key skills: Explain and apply the terms spontaneous process, reversible process, irreversible process, and isothermal process.
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy Learning goals and key skills: Explain and apply the terms spontaneous process, reversible process, irreversible process, and isothermal process.
Alkenes. Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents
 Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
