SIMULATION OF THE RESITIVE FORCES ACTING ON THE BUCKET OF WHEEL LOADER BY USE OF DEM
|
|
|
- Roy Johns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SIMULATION OF THE RESITIVE FORCES ACTING ON THE BUCKET OF WHEEL LOADER BY USE OF DEM Hiroshi TAKAHASHI Department of Geoscience and Technology Graduate School of Engineering Tohoku University Sendai , JAPAN ABSTRACT In order to automate the scooping task, it is necessary to obtain the theoretical resistive forces acting on the bucket. The resistive forces strongly depend on the shape changing process of the rock pile due to the bucket movement. In other words, in order to derive the theoretical model on the resistive forces, the shape changing process of the rock pile due to the bucket movement has to be made clear. In this paper, the behavior of particles in the rock pile due to the bucket movement was simulated by use of DEM (Distinct Element Method). Furthermore, the resistive forces acting on the bucket were calculated and compared with the experimental ones. INTRODUCTION Robotics has been receiving considerable attention in many fields, especially in mining and construction field because the working environment in these fields is very severe for workers. Many tasks in these fields have been mechanized and some of them are already carried out automatically [1-4]. However, the scooping task is much more difficult to automate compared to other tasks because the interaction between the bucket and crushed rocks is very complicated and many parameters are necessary to describe the scooping phenomena. In order to automate the scooping task, the resistive forces acting on the bucket of wheel loaders have to be obtained before the scooping task is performed [5]. And the resistive forces strongly depend on the shape changing process of the rock pile due to the bucket movement In this study, the behavior of particles in the rock pile due to the bucket movement is simulated by use of DEM (Distinct Element Method)[6]. Furthermore, the resistive forces acting on the bucket are calculated and compared with the experimental ones obtained in the previous research. PRINCIPLE OF DEM DEM is often used to analyze the behavior of granular materials. In the calculation of DEM, an equation of motion is given in each element to analyze the behavior of elements. In order to derive the equation of motion, it is necessary to estimate the forces acting among elements. Usually, the model as shown in Figure 1 is used. The actual scooping process is three dimensional, but it is sometimes simplified and is analyzed two dimensionally. Therefore, two-dimensional model was assumed in this study. In this case, each element is assumed to be a circular disc, and the radius of the disc defines the size of element. When the two elements contact each other, a spring
2 and a dashpot are introduced between two elements in the normal and tangential direction. The spring and dashpot indicate the effect of elasticity and viscous resistance, respectively. Furthermore, a slider is set in the tangential direction to consider the frictional effect. ϕ Fig. 1 Contact model in DEM ϕ Fig.2 Schematic Diagram of element contact The equation of motion of element is given by Eq.(1). Fx = mx, Fy = my, M = Iϕ Here, (x,y) is the coordinate of central gravity of the element, ϕ is the rotation of the element, F x and F y are total contact forces and body forces acting on the element. Figure 2 shows the schematic diagram of the contact between two elements. The contact between two elements can be judged by the following equations. Ri + Rj Rij 2 2 Rij = ( xj xi ) + ( yj yi ) The normal direction coincides with the line connecting between the center of two elements. Now, let the angle between above mentioned line and x-axis be ij. Then, the next equation can be obtained. ( xj xi) cosα ij = Rij ( yj yi) sinα ij = Rij The increment of relative displacement of the element in the time interval of calculation in the normal and tangential direction are expressed as follows: u = ( x x )cos α ( y y )sinα n j i ij j i ij us = ( x j xi )sinα ij + ( y j yi ) cosα ij Ri ϕ i R j ϕ j Here, t is the time interval of calculation, x and y are the increment of displacement in x and y direction, ϕ is the increment of rotation. The suffix, i and j indicate each element. Normal direction The increment of the force in the normal direction due to the spring, e n and the force due to the viscous dashpot, d n are expressed by the following equations.
3 en = kn un u dn = η n n t Here, k n is the spring constant in the normal direction, n is the viscous coefficient. Tangential direction The increment of the force in the tangential direction due to the spring, e s and the force due to the viscous dashpot, d s are expressed by the following equations. es = ks us u ds = η s s t Here, k s is the spring constant in the tangential direction, and s is the viscous coefficient. e n and e s can be obtained by adding each increment to the values at t=t dt. When the two elements are separated, no force will act on two elements. Therefore, the following condition is necessary. en < 0, en = dn = es = ds = 0 From above equations, the forces acting on two elements in the normal and tangential direction are expressed, respectively as follows: fn = en + dn, fs = es + ds The next condition should be introduced based on the assumption that the frictional force in the frictional direction follows the Coulomb s law. f if fs > µ f, then s n f s = µ f n f s Here, S is the frictional coefficient between two elements. The next step is to obtain the total forces from all elements, which are contacting with the element, i. Total forces acting on the element, i in x and y direction and total moment are expressed, respectively. F = ( f cosα f sin α ) + B xi j nj ij sj ij F = ( f sin α + f cos α ) + B yi j nj ij sj ij yi xi Mi = ri( j fsj) Here, B x and B y are body forces in x and y direction. The acceleration of the element is given by x = Fxi / mi, y = Fyi / mi, ϕ = Mi / Ii Here, m i is the mass of the element and I i is the inertial moment of the element. In the calculation, the above equations are integrated to obtain the displacement in t. Then, the same calculation is repeated by using the obtained displacement as an initial value for the next step of calculation. CALCULATION OF THE FORCES BETWEEN THE BUCKET AND PARTICLES When the bucket is penetrated into the rock pile, it is necessary to estimate the forces between the bucket wall and particles. In the case that the bucket wall contacts
4 with the particles, the element with having zero-radius is assumed at the cross section of the bucket wall and the line from the center of element, which is perpendicular to the bucket wall. Physical properties, which are necessary for DEM simulation, are listed in Table 1. Table 1 Physical properties used in the DEM simulation Time Interval sec. Designed Value Number of Particles 374 Designed Value Particle Diameter 12mm Designed Value Slope of the Rock Pile 34 degrees Designed Value Density of Particles 2.5g/cm 3 Measured Value Friction Coefficient between the Bucket and Particles 0.59 Measured Value Friction Coefficient among 0.93 Measured Value Particles Spring Constant g/s 2 Assumed Value Coefficient of Viscosity 8000g/s Assumed Value Air Resistance 100g/s Assumed Value SIMULATION RESULTS Penetration of the bucket into the rock pile Figures 3 and 4 show the particle behavior and trajectories when the bucket penetrates into the rock pile. The penetration speed of the bucket is 5cm/sec in this simulation. The simulation was carried out in the Sun work station and calculation time was about 50 hours. In our previous visualization experiment of the shape change of the rock pile [7], it has been already confirmed that the particle trajectories are divided into three regions, that is, 1)the region which moves horizontally with the bucket movement, 2)the region which moves upward with sliding on the failure plane and 3)the region which does not move. It was confirmed from Figures 3 and 4 that the simulation results show the same tendency as the experimental results. Figure 5 shows the comparison between the simulated resistive forces acting on the bucket and measured resistive forces. The solid line indicates the simulated results and white circles indicate the measured resistive forces. The details about the experiments to measure the resistive forces are described in the reference [7]. Since the simulation is two dimensional, simulated results were multiplied by the bucket width that was used in the experiment, and were compared with the measured resistive forces. The horizontal axis shows the non-dimensional distance (X and L show the penetration distance and bucket bottom length, respectively). The DEM simulation does not consider the frictional force between the bucket side and particles. However, it was already confirmed that the effect of the frictional resistive force is very small. Therefore, simulated results well agree with the experimental results, although the fluctuation of the simulation results is very large. Lifting of the bucket to scoop the rocks Few studies have dealt with the internal change of the rock pile while scooping the rocks because the visualization of the internal shape change of the rock pile is
5 very difficult. However, it is inevitable to know the internal shape change of the rock pile in the theoretical analysis on the resistive forces acting on the bucket of the loading machine. Therefore, the behavior of rocks by lifting the bucket was simulated. 15 Measured Values Simulated Results Force [kgf] X/L [-] Fig.5 Comparison between Simulated Resistive Forces and Measured Ones Fig.6 Schematic Diagram of the Bucket Movement in the Scooping Task Some studies have already been conducted on the planning of the scooping, and it was reported that from the energy consumption of view, the smooth movement of the bucket from the skirts of the rock pile is the best. However, the most effective planning of scooping is not still made clear. Therefore, it was assumed that scooping strategy was as shown in Figure 6 with considering the task by an expert operator, that is, 1) the bucket is penetrated into the rock pile at distance, D, 2) then, the bucket is lifted to scoop the rocks. When the task is finished, it is assumed that the bucket tip is on the surface of the rock pile. Then, the scooped area by the bucket in Figure 6 is expressed by the next equation. sinθ sinα 2 S = D (19) 2(sinθ sinα) The distance D is determined so that the scooped area is equal to the bucket area. Figures 7 and 8 show the particle behavior and trajectories when the bucket is lifted to scoop the rocks. The lifting speed of the bucket is 5cm/sec in this simulation. It was confirmed that the particle trajectories are divided into three regions, that is, 1) the region which moves with the bucket movement, 2) the region which slides down to the bucket bottom and 3) the region which does not move. CONCLUSIONS The behavior of particles in the rock pile due to the bucket movement was simulated by use of DEM. Since the scooping task is usually carried out by two steps, that is, the penetration and lifting of the bucket, the trajectory of the bucket movement was assumed as shown in Figure 6. The shape changing process of the rock pile was made clear from the simulated results. These results will give useful information for the theoretical consideration on the resistive forces acting on the bucket in the scooping task.
6 REFERENCES [1] M.St-Amant et al. : A Simple Robust Vision System for Underground Vehicle Guidance, Proc. of 1st Int. Int. Symposium on Mine Mechanization and Automation, pp.6/1-10, [2] P.H.King et al. : Ultrasonic Rangers for Underground Mine Equipment Navigation, Proc. of 1st Int. Int. Symposium on Mine Mechanization and Automation, pp.6/31-44, [3] M.K.Petty : Autonomous LHD Loading, Proc. of 4th Annual Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice, pp , [4] T.Gocho et al. : Automatic Wheel-Loader in Asphalt Plant, Proc. of 9th Int. Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction, pp , [5] A.Hemami : Force Analysis in the Scooping/Loading Operation of an LHD Loader, Proc. of 2nd Int. Int. Symposium on Mine Mechanization and Automation, pp , [6] P.A.Cundall and O.D.L.Strack : A Discrete Numerical model for Granular Assemblies, Geotechnique, Vol.29, No.1, pp.47-65, [7] H.Takahashi, Y.Tsukamoto and E.Nakano: Fundamental Study on the Resistive Force Acting on the Bucket during Scooping of Piled Rock Fragments, Trans. of Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers, Vol.63, No.609, pp , 1997.
7 Fig.3 Behavior of particles (Penetration process) Fig.4 Trajectory of particles (Penetration process)
8 Fig.7 Behavior of particles (Lifting process) Fig.8 Trajectory of particles (Lifting process)
Vibratory conveyance of granular materials M. Saeki*l and E. Takano*2
 FIFTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION DECEMBER 15-18, 1997 ADELAIDE, SOUTH AUSTRALIA Vibratory conveyance of granular materials M. Saeki*l and E. Takano*2 *1 Department of Mechanical and
FIFTH INTERNATIONAL CONGRESS ON SOUND AND VIBRATION DECEMBER 15-18, 1997 ADELAIDE, SOUTH AUSTRALIA Vibratory conveyance of granular materials M. Saeki*l and E. Takano*2 *1 Department of Mechanical and
Automatic Breaking System of Large Rocks by use of Force Sensors
 Automatic Breaking System of Large Rocks by use of Force Sensors Hiroshi TAKAHASHI and Takashi MONDEN Dept. of Geoscience and Technology, Graduate School of Engineering, Abstract: The automation of breaking
Automatic Breaking System of Large Rocks by use of Force Sensors Hiroshi TAKAHASHI and Takashi MONDEN Dept. of Geoscience and Technology, Graduate School of Engineering, Abstract: The automation of breaking
ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics
 ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Washington Lecture 8 Kinetics of a particle: Work and Energy (Chapter 14) - 14.1-14.3 W. Wang 2 Kinetics
ME 230 Kinematics and Dynamics Wei-Chih Wang Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Washington Lecture 8 Kinetics of a particle: Work and Energy (Chapter 14) - 14.1-14.3 W. Wang 2 Kinetics
Terra-Mechanical Simulation Using Distinct Element Method
 Shinya Kanou Masaharu Amano Yuji Terasaka Norihisa Matsumoto Tatsuo Wada To our company that designs and manufactures equipment for handling soil and rock, analyzing the interaction or contact between
Shinya Kanou Masaharu Amano Yuji Terasaka Norihisa Matsumoto Tatsuo Wada To our company that designs and manufactures equipment for handling soil and rock, analyzing the interaction or contact between
Chapter 4. Motion in Two Dimensions
 Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Kinematics in Two Dimensions Will study the vector nature of position, velocity and acceleration in greater detail Will treat projectile motion and uniform circular motion
Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Kinematics in Two Dimensions Will study the vector nature of position, velocity and acceleration in greater detail Will treat projectile motion and uniform circular motion
Chapter 4. Motion in Two Dimensions. Professor Wa el Salah
 Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Kinematics in Two Dimensions Will study the vector nature of position, velocity and acceleration in greater detail. Will treat projectile motion and uniform circular
Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Kinematics in Two Dimensions Will study the vector nature of position, velocity and acceleration in greater detail. Will treat projectile motion and uniform circular
PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2)
 PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2) We will limit our study of planar kinetics to rigid bodies that are symmetric with respect to a fixed reference plane. As discussed in Chapter 16, when
PLANAR KINETIC EQUATIONS OF MOTION (Section 17.2) We will limit our study of planar kinetics to rigid bodies that are symmetric with respect to a fixed reference plane. As discussed in Chapter 16, when
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK UNIT I - PART-A
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK Sub. Code: CE1151 Sub. Name: Engg. Mechanics UNIT I - PART-A Sem / Year II / I 1.Distinguish the following system of forces with a suitable
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING ENGINEERING MECHANICS QUESTION BANK Sub. Code: CE1151 Sub. Name: Engg. Mechanics UNIT I - PART-A Sem / Year II / I 1.Distinguish the following system of forces with a suitable
Analysis of ball movement for research of grinding mechanism of a stirred ball mill with 3D discrete element method
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 25(3), 585-592 (2008) SHORT COMMUNICATION Analysis of ball movement for research of grinding mechanism of a stirred ball mill with 3D discrete element method Seongsoo Kim and Woo
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 25(3), 585-592 (2008) SHORT COMMUNICATION Analysis of ball movement for research of grinding mechanism of a stirred ball mill with 3D discrete element method Seongsoo Kim and Woo
1 Motion of a single particle - Linear momentum, work and energy principle
 1 Motion of a single particle - Linear momentum, work and energy principle 1.1 In-class problem A block of mass m slides down a frictionless incline (see Fig.). The block is released at height h above
1 Motion of a single particle - Linear momentum, work and energy principle 1.1 In-class problem A block of mass m slides down a frictionless incline (see Fig.). The block is released at height h above
Chapter 4. Motion in Two Dimensions
 Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Kinematics in Two Dimensions Will study the vector nature of position, velocity and acceleration in greater detail Will treat projectile motion and uniform circular motion
Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Kinematics in Two Dimensions Will study the vector nature of position, velocity and acceleration in greater detail Will treat projectile motion and uniform circular motion
Chapter 4. Motion in Two Dimensions. With modifications by Pinkney
 Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions With modifications by Pinkney Kinematics in Two Dimensions covers: the vector nature of position, velocity and acceleration in greater detail projectile motion a special
Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions With modifications by Pinkney Kinematics in Two Dimensions covers: the vector nature of position, velocity and acceleration in greater detail projectile motion a special
3. Kinetics of Particles
 3. Kinetics of Particles 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration 3.3 Impulse and Momentum 3.4 Impact 1 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration We draw two important conclusions from the results of the experiments. First,
3. Kinetics of Particles 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration 3.3 Impulse and Momentum 3.4 Impact 1 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration We draw two important conclusions from the results of the experiments. First,
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems. Kinetic Energy and
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 7 Kinetic Energy and Work Kinetic energy Work Work-energy theorem Gravitational work Work of spring forces Power 1. A single force acts on a 5.0-kg object in such
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 7 Kinetic Energy and Work Kinetic energy Work Work-energy theorem Gravitational work Work of spring forces Power 1. A single force acts on a 5.0-kg object in such
Fluid-soil multiphase flow simulation by an SPH-DEM coupled method
 Fluid-soil multiphase flow simulation by an SPH-DEM coupled method *Kensuke Harasaki 1) and Mitsuteru Asai 2) 1), 2) Department of Civil and Structural Engineering, Kyushu University, 744 Motooka, Nishi-ku,
Fluid-soil multiphase flow simulation by an SPH-DEM coupled method *Kensuke Harasaki 1) and Mitsuteru Asai 2) 1), 2) Department of Civil and Structural Engineering, Kyushu University, 744 Motooka, Nishi-ku,
Chapter 4. Motion in Two Dimensions
 Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Kinematics in Two Dimensions Will study the vector nature of position, velocity and acceleration in greater detail Will treat projectile motion and uniform circular motion
Chapter 4 Motion in Two Dimensions Kinematics in Two Dimensions Will study the vector nature of position, velocity and acceleration in greater detail Will treat projectile motion and uniform circular motion
CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 9: Ch.13, Sec.4-5
 1 / 40 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 9: Ch.13, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa 2 / 40 EQUATIONS OF MOTION:RECTANGULAR COORDINATES
1 / 40 CEE 271: Applied Mechanics II, Dynamics Lecture 9: Ch.13, Sec.4-5 Prof. Albert S. Kim Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Hawaii at Manoa 2 / 40 EQUATIONS OF MOTION:RECTANGULAR COORDINATES
Friction. Modeling, Identification, & Analysis
 Friction Modeling, Identification, & Analysis Objectives Understand the friction phenomenon as it relates to motion systems. Develop a control-oriented model with appropriate simplifying assumptions for
Friction Modeling, Identification, & Analysis Objectives Understand the friction phenomenon as it relates to motion systems. Develop a control-oriented model with appropriate simplifying assumptions for
Performance evaluation of first stage support system of launcher
 Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research Vol. 64, December 005, pp. 949-956 Performance evaluation of first stage support system of launcher A C Pankaj 1, *, Jhankar Basu 1, S N Shome 1, P K Mehta and
Journal of Scientific & Industrial Research Vol. 64, December 005, pp. 949-956 Performance evaluation of first stage support system of launcher A C Pankaj 1, *, Jhankar Basu 1, S N Shome 1, P K Mehta and
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING BRANCH: MECHANICAL YEAR / SEMESTER: I / II UNIT 1 PART- A 1. State Newton's three laws of motion? 2.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING BRANCH: MECHANICAL YEAR / SEMESTER: I / II UNIT 1 PART- A 1. State Newton's three laws of motion? 2.
Where, m = slope of line = constant c = Intercept on y axis = effort required to start the machine
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Model Answer: Summer 07 Code: 70 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Model Answer: Summer 07 Code: 70 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
(Refer Slide Time: 01:15)
 Soil Mechanics Prof. B.V.S. Viswanathan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 56 Stability analysis of slopes II Welcome to lecture two on stability analysis of
Soil Mechanics Prof. B.V.S. Viswanathan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 56 Stability analysis of slopes II Welcome to lecture two on stability analysis of
Old Exam. Question Chapter 7 072
 Old Exam. Question Chapter 7 072 Q1.Fig 1 shows a simple pendulum, consisting of a ball of mass M = 0.50 kg, attached to one end of a massless string of length L = 1.5 m. The other end is fixed. If the
Old Exam. Question Chapter 7 072 Q1.Fig 1 shows a simple pendulum, consisting of a ball of mass M = 0.50 kg, attached to one end of a massless string of length L = 1.5 m. The other end is fixed. If the
Announcements. Principle of Work and Energy - Sections Engr222 Spring 2004 Chapter Test Wednesday
 Announcements Test Wednesday Closed book 3 page sheet sheet (on web) Calculator Chap 12.6-10, 13.1-6 Principle of Work and Energy - Sections 14.1-3 Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Calculate
Announcements Test Wednesday Closed book 3 page sheet sheet (on web) Calculator Chap 12.6-10, 13.1-6 Principle of Work and Energy - Sections 14.1-3 Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: a) Calculate
MOTION IN TWO OR THREE DIMENSIONS
 MOTION IN TWO OR THREE DIMENSIONS 3 Sections Covered 3.1 : Position & velocity vectors 3.2 : The acceleration vector 3.3 : Projectile motion 3.4 : Motion in a circle 3.5 : Relative velocity 3.1 Position
MOTION IN TWO OR THREE DIMENSIONS 3 Sections Covered 3.1 : Position & velocity vectors 3.2 : The acceleration vector 3.3 : Projectile motion 3.4 : Motion in a circle 3.5 : Relative velocity 3.1 Position
Improvement of Calculation Stability for Slow Fluid Flow Analysis Using Particle Method *
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 58, No. 3 (2017) pp. 479 to 484 2017 Japan Foundry Engineering Society Improvement of Calculation Stability for Slow Fluid Flow Analysis Using Particle Method * Naoya Hirata
Materials Transactions, Vol. 58, No. 3 (2017) pp. 479 to 484 2017 Japan Foundry Engineering Society Improvement of Calculation Stability for Slow Fluid Flow Analysis Using Particle Method * Naoya Hirata
A B Ax Bx Ay By Az Bz
 Lecture 5.1 Dynamics of Rotation For some time now we have been discussing the laws of classical dynamics. However, for the most part, we only talked about examples of translational motion. On the other
Lecture 5.1 Dynamics of Rotation For some time now we have been discussing the laws of classical dynamics. However, for the most part, we only talked about examples of translational motion. On the other
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are standing in a moving bus, facing forward, and you suddenly fall forward as the
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) You are standing in a moving bus, facing forward, and you suddenly fall forward as the
The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval.
 Distance is the. of a path followed by a particle. Distance is a quantity. The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval. Displacement is a.. quantity. The... of a particle
Distance is the. of a path followed by a particle. Distance is a quantity. The... of a particle is defined as its change in position in some time interval. Displacement is a.. quantity. The... of a particle
Note: Referred equations are from your textbook.
 Note: Referred equations are from your textbook 70 DENTFY: Use energy methods There are changes in both elastic and gravitational potential energy SET UP: K + U + W K U other + Points and in the motion
Note: Referred equations are from your textbook 70 DENTFY: Use energy methods There are changes in both elastic and gravitational potential energy SET UP: K + U + W K U other + Points and in the motion
 Subject : Engineering Mechanics Subject Code : 1704 Page No: 1 / 6 ----------------------------- Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
Subject : Engineering Mechanics Subject Code : 1704 Page No: 1 / 6 ----------------------------- Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word
Projectile Motion. directions simultaneously. deal with is called projectile motion. ! An object may move in both the x and y
 Projectile Motion! An object may move in both the x and y directions simultaneously! The form of two-dimensional motion we will deal with is called projectile motion Assumptions of Projectile Motion! The
Projectile Motion! An object may move in both the x and y directions simultaneously! The form of two-dimensional motion we will deal with is called projectile motion Assumptions of Projectile Motion! The
Physics 20 Practice Problems for Exam 1 Fall 2014
 Physics 20 Practice Problems for Exam 1 Fall 2014 Multiple Choice Short Questions (1 pt ea.) Circle the best answer. 1. An apple falls from a tree and hits the ground 5 meters below. It hits the ground
Physics 20 Practice Problems for Exam 1 Fall 2014 Multiple Choice Short Questions (1 pt ea.) Circle the best answer. 1. An apple falls from a tree and hits the ground 5 meters below. It hits the ground
The Self-Excite Vibrations of Multi-Scoop Digger Machine
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 12, No. 1 (2008) 79 86 c Technical University of Lodz The Self-Excite Vibrations of Multi-Scoop Digger Machine Józef Giergiel Department of Applied Mechanics and
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 12, No. 1 (2008) 79 86 c Technical University of Lodz The Self-Excite Vibrations of Multi-Scoop Digger Machine Józef Giergiel Department of Applied Mechanics and
Normal Force. W = mg cos(θ) Normal force F N = mg cos(θ) F N
 Normal Force W = mg cos(θ) Normal force F N = mg cos(θ) Note there is no weight force parallel/down the include. The car is not pressing on anything causing a force in that direction. If there were a person
Normal Force W = mg cos(θ) Normal force F N = mg cos(θ) Note there is no weight force parallel/down the include. The car is not pressing on anything causing a force in that direction. If there were a person
Chapter 10: Friction A gem cannot be polished without friction, nor an individual perfected without
 Chapter 10: Friction 10-1 Chapter 10 Friction A gem cannot be polished without friction, nor an individual perfected without trials. Lucius Annaeus Seneca (4 BC - 65 AD) 10.1 Overview When two bodies are
Chapter 10: Friction 10-1 Chapter 10 Friction A gem cannot be polished without friction, nor an individual perfected without trials. Lucius Annaeus Seneca (4 BC - 65 AD) 10.1 Overview When two bodies are
 Laws of Motion. A fighter aircraft is looping in a vertical plane. The minimum velocity at the highest point is (Given r = radius of the loop) a) gr b) gr c) gr d) 3gr. In non-inertial frame, the second
Laws of Motion. A fighter aircraft is looping in a vertical plane. The minimum velocity at the highest point is (Given r = radius of the loop) a) gr b) gr c) gr d) 3gr. In non-inertial frame, the second
Find the magnitude of F when t = 2. (9 marks)
 Condensed M2 Paper These questions are all taken from a Mechanics 2 exam paper, but any intermediate steps and diagrams have been removed, leaving enough information to answer the question, but none of
Condensed M2 Paper These questions are all taken from a Mechanics 2 exam paper, but any intermediate steps and diagrams have been removed, leaving enough information to answer the question, but none of
Model Answers Attempt any TEN of the following :
 (ISO/IEC - 70-005 Certified) Model Answer: Winter 7 Sub. Code: 17 Important Instructions to Examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
(ISO/IEC - 70-005 Certified) Model Answer: Winter 7 Sub. Code: 17 Important Instructions to Examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion. Preparation for unit test
 Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
Force, Energy & Periodic Motion Preparation for unit test Summary of assessment standards (Unit assessment standard only) In the unit test you can expect to be asked at least one question on each sub-skill.
WORK, POWER AND ENERGY
 WORK, POWER AND ENERGY Important Points:. Dot Product: a) Scalar product is defined as the product of the magnitudes of two vectors and the cosine of the angle between them. The dot product of two vectors
WORK, POWER AND ENERGY Important Points:. Dot Product: a) Scalar product is defined as the product of the magnitudes of two vectors and the cosine of the angle between them. The dot product of two vectors
q 1 F m d p q 2 Figure 1: An automated crane with the relevant kinematic and dynamic definitions.
 Robotics II March 7, 018 Exercise 1 An automated crane can be seen as a mechanical system with two degrees of freedom that moves along a horizontal rail subject to the actuation force F, and that transports
Robotics II March 7, 018 Exercise 1 An automated crane can be seen as a mechanical system with two degrees of freedom that moves along a horizontal rail subject to the actuation force F, and that transports
Faculty of Engineering and Department of Physics Engineering Physics 131 Midterm Examination Monday February 24, 2014; 7:00 pm 8:30 pm
 Faculty of Engineering and Department of Physics Engineering Physics 131 Midterm Examination Monday February 4, 014; 7:00 pm 8:30 pm 1. No notes or textbooks allowed.. Formula sheets are included (may
Faculty of Engineering and Department of Physics Engineering Physics 131 Midterm Examination Monday February 4, 014; 7:00 pm 8:30 pm 1. No notes or textbooks allowed.. Formula sheets are included (may
Mechanics Answers to Examples B (Momentum) - 1 David Apsley
 TOPIC B: MOMENTUM ANSWERS SPRING 2019 (Full worked answers follow on later pages) Q1. (a) 2.26 m s 2 (b) 5.89 m s 2 Q2. 8.41 m s 2 and 4.20 m s 2 ; 841 N Q3. (a) 1.70 m s 1 (b) 1.86 s Q4. (a) 1 s (b) 1.5
TOPIC B: MOMENTUM ANSWERS SPRING 2019 (Full worked answers follow on later pages) Q1. (a) 2.26 m s 2 (b) 5.89 m s 2 Q2. 8.41 m s 2 and 4.20 m s 2 ; 841 N Q3. (a) 1.70 m s 1 (b) 1.86 s Q4. (a) 1 s (b) 1.5
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium
 Chapter Static Equilibrium. Analysis Model: Rigid Body in Equilibrium. More on the Center of Gravity. Examples of Rigid Objects in Static Equilibrium CHAPTER : STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY.) The Conditions
Chapter Static Equilibrium. Analysis Model: Rigid Body in Equilibrium. More on the Center of Gravity. Examples of Rigid Objects in Static Equilibrium CHAPTER : STATIC EQUILIBRIUM AND ELASTICITY.) The Conditions
Everybody remains in a state of rest or continues to move in a uniform motion, in a straight line, unless acting on by an external force.
 NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION Newton s First Law Everybody remains in a state of rest or continues to move in a uniform motion, in a straight line, unless acting on by an external force. Inertia (Newton s 1
NEWTON S LAWS OF MOTION Newton s First Law Everybody remains in a state of rest or continues to move in a uniform motion, in a straight line, unless acting on by an external force. Inertia (Newton s 1
Jurong Junior College 2014 J1 H1 Physics (8866) Tutorial 3: Forces (Solutions)
 Jurong Junior College 2014 J1 H1 Physics (8866) Tutorial 3: Forces (Solutions) Take g = 9.81 m s -2, P atm = 1.0 x 10 5 Pa unless otherwise stated Learning Outcomes (a) Sub-Topic recall and apply Hooke
Jurong Junior College 2014 J1 H1 Physics (8866) Tutorial 3: Forces (Solutions) Take g = 9.81 m s -2, P atm = 1.0 x 10 5 Pa unless otherwise stated Learning Outcomes (a) Sub-Topic recall and apply Hooke
2. a) Explain the equilibrium of i) Concurrent force system, and ii) General force system.
 Code No: R21031 R10 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 2013 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Com to ME, AE, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions
Code No: R21031 R10 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 2013 ENGINEERING MECHANICS (Com to ME, AE, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics IC_W05D1 ConcepTests
 Reading Question MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 IC_W05D1 ConcepTests Two objects are pushed on a frictionless surface from a starting line to a finish line with
Reading Question MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01 IC_W05D1 ConcepTests Two objects are pushed on a frictionless surface from a starting line to a finish line with
24/06/13 Forces ( F.Robilliard) 1
 R Fr F W 24/06/13 Forces ( F.Robilliard) 1 Mass: So far, in our studies of mechanics, we have considered the motion of idealised particles moving geometrically through space. Why a particular particle
R Fr F W 24/06/13 Forces ( F.Robilliard) 1 Mass: So far, in our studies of mechanics, we have considered the motion of idealised particles moving geometrically through space. Why a particular particle
Proceedings oh the 18th IAHR International Symposium on Ice (2006) DISCRETE ELEMENT SIMULATION OF ICE PILE-UP AGAINST AN INCLINED STRUCTURE
 DISCRETE ELEMENT SIMULATION OF ICE PILE-UP AGAINST AN INCLINED STRUCTURE Jani Paavilainen, Jukka Tuhkuri and Arttu Polojärvi Helsinki University of Technology, Laboratory for Mechanics of Materials, Finland
DISCRETE ELEMENT SIMULATION OF ICE PILE-UP AGAINST AN INCLINED STRUCTURE Jani Paavilainen, Jukka Tuhkuri and Arttu Polojärvi Helsinki University of Technology, Laboratory for Mechanics of Materials, Finland
l1, l2, l3, ln l1 + l2 + l3 + ln
 Work done by a constant force: Consider an object undergoes a displacement S along a straight line while acted on a force F that makes an angle θ with S as shown The work done W by the agent is the product
Work done by a constant force: Consider an object undergoes a displacement S along a straight line while acted on a force F that makes an angle θ with S as shown The work done W by the agent is the product
R.SUNDARAVADIVELU Professor IIT Madras,Chennai - 36.
 Behaviour of Berthing Structure under Changing Slope in Seismic Condition - A Case Study K.MUTHUKKUMARAN Research Scholar Department of Ocean Engineering, R.SUNDARAVADIVELU Professor IIT Madras,Chennai
Behaviour of Berthing Structure under Changing Slope in Seismic Condition - A Case Study K.MUTHUKKUMARAN Research Scholar Department of Ocean Engineering, R.SUNDARAVADIVELU Professor IIT Madras,Chennai
Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics. UCVTS AIT Physics
 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics UCVTS AIT Physics Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin Angular Position,
Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics UCVTS AIT Physics Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin Angular Position,
STATICS. FE Review. Statics, Fourteenth Edition R.C. Hibbeler. Copyright 2016 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 STATICS FE Review 1. Resultants of force systems VECTOR OPERATIONS (Section 2.2) Scalar Multiplication and Division VECTOR ADDITION USING EITHER THE PARALLELOGRAM LAW OR TRIANGLE Parallelogram Law: Triangle
STATICS FE Review 1. Resultants of force systems VECTOR OPERATIONS (Section 2.2) Scalar Multiplication and Division VECTOR ADDITION USING EITHER THE PARALLELOGRAM LAW OR TRIANGLE Parallelogram Law: Triangle
Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particle: Work & Energy
 Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particle: Work & Energy Dr. Khairul Salleh Basaruddin Applied Mechanics Division School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) khsalleh@unimap.edu.my THE WORK
Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particle: Work & Energy Dr. Khairul Salleh Basaruddin Applied Mechanics Division School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) khsalleh@unimap.edu.my THE WORK
1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? 20cm T =? 20kg
 1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? F2 5cm 20cm F1 (a) 3 N (b) 5 N (c) 4N (d) None of the above 2. The stress in a wire of diameter 2 mm, if a load of 100 gram is applied
1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? F2 5cm 20cm F1 (a) 3 N (b) 5 N (c) 4N (d) None of the above 2. The stress in a wire of diameter 2 mm, if a load of 100 gram is applied
4) Vector = and vector = What is vector = +? A) B) C) D) E)
 1) Suppose that an object is moving with constant nonzero acceleration. Which of the following is an accurate statement concerning its motion? A) In equal times its speed changes by equal amounts. B) In
1) Suppose that an object is moving with constant nonzero acceleration. Which of the following is an accurate statement concerning its motion? A) In equal times its speed changes by equal amounts. B) In
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
Common Quiz Mistakes / Practice for Final Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) A ball is thrown directly upward and experiences
Energy Conservation AP
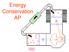 Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
Energy Conservation AP Manicouagan Reservoir seen from space shuttle; formed almost 1 million years ago when a large meteorite hit Earth Earth did work on meteorite to change its kinetic energy energy
DEM Simulation of Soil Loosening Process Caused by a Vibrating Subsoiler
 1 DEM Simulation of Soil Loosening Process Caused by a Vibrating Subsoiler Hiroaki Tanaka 1,*, Akira Oida 2, Masamichi Daikoku 1, Koji Inooku 3, Osamu Sumikawa 4, Yuji Nagasaki 1 and Masahiro Miyazaki
1 DEM Simulation of Soil Loosening Process Caused by a Vibrating Subsoiler Hiroaki Tanaka 1,*, Akira Oida 2, Masamichi Daikoku 1, Koji Inooku 3, Osamu Sumikawa 4, Yuji Nagasaki 1 and Masahiro Miyazaki
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions
 PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
PHYS 1303 Final Exam Example Questions 1.Which quantity can be converted from the English system to the metric system by the conversion factor 5280 mi f 12 f in 2.54 cm 1 in 1 m 100 cm 1 3600 h? s a. feet
SOLUTION T 1 + U 1-2 = T C(31.5)(2.5)A10 6 B(0.2)D = 1 2 (7)(v 2) 2. v 2 = 2121 m>s = 2.12 km>s. Ans. (approx.
 4 5. When a 7-kg projectile is fired from a cannon barrel that has a length of 2 m, the explosive force exerted on the projectile, while it is in the barrel, varies in the manner shown. Determine the approximate
4 5. When a 7-kg projectile is fired from a cannon barrel that has a length of 2 m, the explosive force exerted on the projectile, while it is in the barrel, varies in the manner shown. Determine the approximate
Chapter 6. Circular Motion and Other Applications of Newton s Laws
 Chapter 6 Circular Motion and Other Applications of Newton s Laws Circular Motion Two analysis models using Newton s Laws of Motion have been developed. The models have been applied to linear motion. Newton
Chapter 6 Circular Motion and Other Applications of Newton s Laws Circular Motion Two analysis models using Newton s Laws of Motion have been developed. The models have been applied to linear motion. Newton
18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007
 MIT OpenourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable alculus Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.02 Lecture 21. Test for
MIT OpenourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable alculus Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 18.02 Lecture 21. Test for
Q2. A machine carries a 4.0 kg package from an initial position of d ˆ. = (2.0 m)j at t = 0 to a final position of d ˆ ˆ
 Coordinator: Dr. S. Kunwar Monday, March 25, 2019 Page: 1 Q1. An object moves in a horizontal circle at constant speed. The work done by the centripetal force is zero because: A) the centripetal force
Coordinator: Dr. S. Kunwar Monday, March 25, 2019 Page: 1 Q1. An object moves in a horizontal circle at constant speed. The work done by the centripetal force is zero because: A) the centripetal force
Antiderivatives. Definition A function, F, is said to be an antiderivative of a function, f, on an interval, I, if. F x f x for all x I.
 Antiderivatives Definition A function, F, is said to be an antiderivative of a function, f, on an interval, I, if F x f x for all x I. Theorem If F is an antiderivative of f on I, then every function of
Antiderivatives Definition A function, F, is said to be an antiderivative of a function, f, on an interval, I, if F x f x for all x I. Theorem If F is an antiderivative of f on I, then every function of
Phys101 First Major-111 Zero Version Monday, October 17, 2011 Page: 1
 Monday, October 17, 011 Page: 1 Q1. 1 b The speed-time relation of a moving particle is given by: v = at +, where v is the speed, t t + c is the time and a, b, c are constants. The dimensional formulae
Monday, October 17, 011 Page: 1 Q1. 1 b The speed-time relation of a moving particle is given by: v = at +, where v is the speed, t t + c is the time and a, b, c are constants. The dimensional formulae
N - W = 0. + F = m a ; N = W. Fs = 0.7W r. Ans. r = 9.32 m
 91962_05_R1_p0479-0512 6/5/09 3:53 PM Page 479 R1 1. The ball is thrown horizontally with a speed of 8 m>s. Find the equation of the path, y = f(x), and then determine the ball s velocity and the normal
91962_05_R1_p0479-0512 6/5/09 3:53 PM Page 479 R1 1. The ball is thrown horizontally with a speed of 8 m>s. Find the equation of the path, y = f(x), and then determine the ball s velocity and the normal
Newton s Laws.
 Newton s Laws http://mathsforeurope.digibel.be/images Forces and Equilibrium If the net force on a body is zero, it is in equilibrium. dynamic equilibrium: moving relative to us static equilibrium: appears
Newton s Laws http://mathsforeurope.digibel.be/images Forces and Equilibrium If the net force on a body is zero, it is in equilibrium. dynamic equilibrium: moving relative to us static equilibrium: appears
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar Torres. Chapter 2 Motion Cengage Learning
 James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar Torres Chapter 2 Motion Defining Motion Motion is a continuous change in position can be described by measuring the rate of change of position
James T. Shipman Jerry D. Wilson Charles A. Higgins, Jr. Omar Torres Chapter 2 Motion Defining Motion Motion is a continuous change in position can be described by measuring the rate of change of position
KINEMATICS OF A PARTICLE. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 KINEMATICS OF A PARTICLE Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Particle has a mass but negligible size and shape. bodies of finite size, such as rockets, projectiles, or vehicles. objects can be considered
KINEMATICS OF A PARTICLE Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Particle has a mass but negligible size and shape. bodies of finite size, such as rockets, projectiles, or vehicles. objects can be considered
Analysis of Damage of Asphalt Pavement due to Dynamic Load of Heavy Vehicles Caused by Surface Roughness
 Analysis of Damage of Asphalt Pavement due to Dynamic Load of Heavy Vehicles Caused by Surface Roughness T. Kanai, K. Tomisawa and T. Endoh Technical Research Institute, Kajima road Co., Ltd., Chofu, Tokyo,
Analysis of Damage of Asphalt Pavement due to Dynamic Load of Heavy Vehicles Caused by Surface Roughness T. Kanai, K. Tomisawa and T. Endoh Technical Research Institute, Kajima road Co., Ltd., Chofu, Tokyo,
4.0 m s 2. 2 A submarine descends vertically at constant velocity. The three forces acting on the submarine are viscous drag, upthrust and weight.
 1 1 wooden block of mass 0.60 kg is on a rough horizontal surface. force of 12 N is applied to the block and it accelerates at 4.0 m s 2. wooden block 4.0 m s 2 12 N hat is the magnitude of the frictional
1 1 wooden block of mass 0.60 kg is on a rough horizontal surface. force of 12 N is applied to the block and it accelerates at 4.0 m s 2. wooden block 4.0 m s 2 12 N hat is the magnitude of the frictional
N mg N Mg N Figure : Forces acting on particle m and inclined plane M. (b) The equations of motion are obtained by applying the momentum principles to
 .004 MDEING DNMIS ND NTR I I Spring 00 Solutions for Problem Set 5 Problem. Particle slides down movable inclined plane. The inclined plane of mass M is constrained to move parallel to the -axis, and the
.004 MDEING DNMIS ND NTR I I Spring 00 Solutions for Problem Set 5 Problem. Particle slides down movable inclined plane. The inclined plane of mass M is constrained to move parallel to the -axis, and the
6-1. Conservation law of mechanical energy
 6-1. Conservation law of mechanical energy 1. Purpose Investigate the mechanical energy conservation law and energy loss, by studying the kinetic and rotational energy of a marble wheel that is moving
6-1. Conservation law of mechanical energy 1. Purpose Investigate the mechanical energy conservation law and energy loss, by studying the kinetic and rotational energy of a marble wheel that is moving
STICK-SLIP MOTION IN PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS DRIVEN BY METER-OUT CIRCUIT
 STICK-SLIP MOTION IN PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS DRIVEN BY METER-OUT CIRCUIT Toshinori FUJITA*, Luis R. TOKASHIKI*, Toshiharu KAGAWA* * Tokyo Institute of Technology Precision and Intelligence Laboratory 4259,
STICK-SLIP MOTION IN PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS DRIVEN BY METER-OUT CIRCUIT Toshinori FUJITA*, Luis R. TOKASHIKI*, Toshiharu KAGAWA* * Tokyo Institute of Technology Precision and Intelligence Laboratory 4259,
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2009 EXAM #1 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 30, 2009
 PHYSICS 221, FALL 2009 EXAM #1 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 30, 2009 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively.
PHYSICS 221, FALL 2009 EXAM #1 SOLUTIONS WEDNESDAY, SEPTEMBER 30, 2009 Note: The unit vectors in the +x, +y, and +z directions of a right-handed Cartesian coordinate system are î, ĵ, and ˆk, respectively.
2.003 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set 6 with solution
 .00 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set 6 with solution Problem : A slender uniform rod of mass m is attached to a cart of mass m at a frictionless pivot located at point A. The cart is connected to a fixed
.00 Engineering Dynamics Problem Set 6 with solution Problem : A slender uniform rod of mass m is attached to a cart of mass m at a frictionless pivot located at point A. The cart is connected to a fixed
Other Examples of Energy Transfer
 Chapter 7 Work and Energy Overview energy. Study work as defined in physics. Relate work to kinetic energy. Consider work done by a variable force. Study potential energy. Understand energy conservation.
Chapter 7 Work and Energy Overview energy. Study work as defined in physics. Relate work to kinetic energy. Consider work done by a variable force. Study potential energy. Understand energy conservation.
Figure 5.28 (a) Spring-restrained cylinder, (b) Kinematic variables, (c) Free-body diagram
 Lecture 30. MORE GENERAL-MOTION/ROLLING- WITHOUT-SLIPPING EXAMPLES A Cylinder, Restrained by a Spring and Rolling on a Plane Figure 5.28 (a) Spring-restrained cylinder, (b) Kinematic variables, (c) Free-body
Lecture 30. MORE GENERAL-MOTION/ROLLING- WITHOUT-SLIPPING EXAMPLES A Cylinder, Restrained by a Spring and Rolling on a Plane Figure 5.28 (a) Spring-restrained cylinder, (b) Kinematic variables, (c) Free-body
Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy. 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall Lecture 10. Home Page. Title Page. Page 1 of 37.
 Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall 2015 Lecture 10 Page 1 of 37 Midterm I summary 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 39 43 56 28 11 5 3 0 1 Average: 82.00 Page
Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall 2015 Lecture 10 Page 1 of 37 Midterm I summary 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 39 43 56 28 11 5 3 0 1 Average: 82.00 Page
Physics 1A. Lecture 3B
 Physics 1A Lecture 3B Review of Last Lecture For constant acceleration, motion along different axes act independently from each other (independent kinematic equations) One is free to choose a coordinate
Physics 1A Lecture 3B Review of Last Lecture For constant acceleration, motion along different axes act independently from each other (independent kinematic equations) One is free to choose a coordinate
POTENTIAL ENERGY AND ENERGY CONSERVATION
 7 POTENTIAL ENERGY AND ENERGY CONSERVATION 7.. IDENTIFY: U grav = mgy so ΔU grav = mg( y y ) SET UP: + y is upward. EXECUTE: (a) ΔU = (75 kg)(9.8 m/s )(4 m 5 m) = +6.6 5 J (b) ΔU = (75 kg)(9.8 m/s )(35
7 POTENTIAL ENERGY AND ENERGY CONSERVATION 7.. IDENTIFY: U grav = mgy so ΔU grav = mg( y y ) SET UP: + y is upward. EXECUTE: (a) ΔU = (75 kg)(9.8 m/s )(4 m 5 m) = +6.6 5 J (b) ΔU = (75 kg)(9.8 m/s )(35
Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction
 Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng. Professor Graduate School of Engineering Hiroshima University Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Chapter 1 : Introduction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng.
Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng. Professor Graduate School of Engineering Hiroshima University Dynamic Soil Structure Interaction Chapter 1 : Introduction Kenji MIURA, Dr. Eng.
THE WORK OF A FORCE, THE PRINCIPLE OF WORK AND ENERGY & SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES
 THE WORK OF A FORCE, THE PRINCIPLE OF WORK AND ENERGY & SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Calculate the work of a force. 2. Apply the principle of work and energy to
THE WORK OF A FORCE, THE PRINCIPLE OF WORK AND ENERGY & SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES Today s Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Calculate the work of a force. 2. Apply the principle of work and energy to
ONLINE: MATHEMATICS EXTENSION 2 Topic 6 MECHANICS 6.6 MOTION IN A CIRCLE
 ONLINE: MAHEMAICS EXENSION opic 6 MECHANICS 6.6 MOION IN A CICLE When a particle moes along a circular path (or cured path) its elocity must change een if its speed is constant, hence the particle must
ONLINE: MAHEMAICS EXENSION opic 6 MECHANICS 6.6 MOION IN A CICLE When a particle moes along a circular path (or cured path) its elocity must change een if its speed is constant, hence the particle must
Lesson 7: Thermal and Mechanical Element Math Models in Control Systems. 1 lesson7et438a.pptx. After this presentation you will be able to:
 Lesson 7: Thermal and Mechanical Element Math Models in Control Systems ET 438a Automatic Control Systems Technology Learning Objectives After this presentation you will be able to: Explain how heat flows
Lesson 7: Thermal and Mechanical Element Math Models in Control Systems ET 438a Automatic Control Systems Technology Learning Objectives After this presentation you will be able to: Explain how heat flows
Practice Test for Midterm Exam
 A.P. Physics Practice Test for Midterm Exam Kinematics 1. Which of the following statements are about uniformly accelerated motion? Select two answers. a) If an object s acceleration is constant then it
A.P. Physics Practice Test for Midterm Exam Kinematics 1. Which of the following statements are about uniformly accelerated motion? Select two answers. a) If an object s acceleration is constant then it
Review of Engineering Dynamics
 Review of Engineering Dynamics Part 1: Kinematics of Particles and Rigid Bodies by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Overview... 4.0 Basic Introductory Concepts... 4.1 Introduction... 4.1.1 Vectors
Review of Engineering Dynamics Part 1: Kinematics of Particles and Rigid Bodies by James Doane, PhD, PE Contents 1.0 Course Overview... 4.0 Basic Introductory Concepts... 4.1 Introduction... 4.1.1 Vectors
Chapter 3 HW Solution
 Chapter 3 HW Solution Problem 3.6: I placed an xy coordinate system at a convenient point (origin doesn t really matter). y 173 x The positions of both planes are given by r B = v B ti + 173j mi (1) r
Chapter 3 HW Solution Problem 3.6: I placed an xy coordinate system at a convenient point (origin doesn t really matter). y 173 x The positions of both planes are given by r B = v B ti + 173j mi (1) r
1. A sphere with a radius of 1.7 cm has a volume of: A) m 3 B) m 3 C) m 3 D) 0.11 m 3 E) 21 m 3
 1. A sphere with a radius of 1.7 cm has a volume of: A) 2.1 10 5 m 3 B) 9.1 10 4 m 3 C) 3.6 10 3 m 3 D) 0.11 m 3 E) 21 m 3 2. A 25-N crate slides down a frictionless incline that is 25 above the horizontal.
1. A sphere with a radius of 1.7 cm has a volume of: A) 2.1 10 5 m 3 B) 9.1 10 4 m 3 C) 3.6 10 3 m 3 D) 0.11 m 3 E) 21 m 3 2. A 25-N crate slides down a frictionless incline that is 25 above the horizontal.
Earthquake response analysis of rock-fall models by discontinuous deformation analysis
 c Earthquake response analysis of rock-fall models by discontinuous deformation analysis T. Sasaki, I. Hagiwara & K. Sasaki Rock Engineering Lab., Suncoh Consultants Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan R. Yoshinaka
c Earthquake response analysis of rock-fall models by discontinuous deformation analysis T. Sasaki, I. Hagiwara & K. Sasaki Rock Engineering Lab., Suncoh Consultants Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan R. Yoshinaka
SECTION A. 8 kn/m. C 3 m 3m
 SECTION Question 1 150 m 40 kn 5 kn 8 kn/m C 3 m 3m D 50 ll dimensions in mm 15 15 Figure Q1(a) Figure Q1(b) The horizontal beam CD shown in Figure Q1(a) has a uniform cross-section as shown in Figure
SECTION Question 1 150 m 40 kn 5 kn 8 kn/m C 3 m 3m D 50 ll dimensions in mm 15 15 Figure Q1(a) Figure Q1(b) The horizontal beam CD shown in Figure Q1(a) has a uniform cross-section as shown in Figure
AP Calculus AB Chapter 2 Test Review #1
 AP Calculus AB Chapter Test Review # Open-Ended Practice Problems:. Nicole just loves drinking chocolate milk out of her special cone cup which has a radius of inches and a height of 8 inches. Nicole pours
AP Calculus AB Chapter Test Review # Open-Ended Practice Problems:. Nicole just loves drinking chocolate milk out of her special cone cup which has a radius of inches and a height of 8 inches. Nicole pours
7. The gyroscope. 7.1 Introduction. 7.2 Theory. a) The gyroscope
 K 7. The gyroscope 7.1 Introduction This experiment concerns a special type of motion of a gyroscope, called precession. From the angular frequency of the precession, the moment of inertia of the spinning
K 7. The gyroscope 7.1 Introduction This experiment concerns a special type of motion of a gyroscope, called precession. From the angular frequency of the precession, the moment of inertia of the spinning
Advanced Higher Mathematics of Mechanics
 Advanced Higher Mathematics of Mechanics Course Outline (2016-2017) Block 1: Change of timetable to summer holiday Assessment Standard Assessment 1 Applying skills to motion in a straight line (Linear
Advanced Higher Mathematics of Mechanics Course Outline (2016-2017) Block 1: Change of timetable to summer holiday Assessment Standard Assessment 1 Applying skills to motion in a straight line (Linear
Computational Simulation of the Hydraulic Fracturing Process
 Computational Simulation of the Hydraulic Fracturing Process Sergio Andrés Galindo Torrres Jose Daniel Muñoz Castaño Simulation of Physical Systems Group Universidad Nacional de Colombia sagalindot@unal.edu.co
Computational Simulation of the Hydraulic Fracturing Process Sergio Andrés Galindo Torrres Jose Daniel Muñoz Castaño Simulation of Physical Systems Group Universidad Nacional de Colombia sagalindot@unal.edu.co
Chapter 10. Rotation of a Rigid Object about a Fixed Axis
 Chapter 10 Rotation of a Rigid Object about a Fixed Axis Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line. Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin. A small
Chapter 10 Rotation of a Rigid Object about a Fixed Axis Angular Position Axis of rotation is the center of the disc Choose a fixed reference line. Point P is at a fixed distance r from the origin. A small
Foundation Analysis LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE
 Foundation Analysis LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE INTRODUCTION Vertical or near-vertical slopes of soil are supported by retaining walls, cantilever sheet-pile walls, sheet-pile bulkheads, braced cuts, and other
Foundation Analysis LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE INTRODUCTION Vertical or near-vertical slopes of soil are supported by retaining walls, cantilever sheet-pile walls, sheet-pile bulkheads, braced cuts, and other
